Page 1
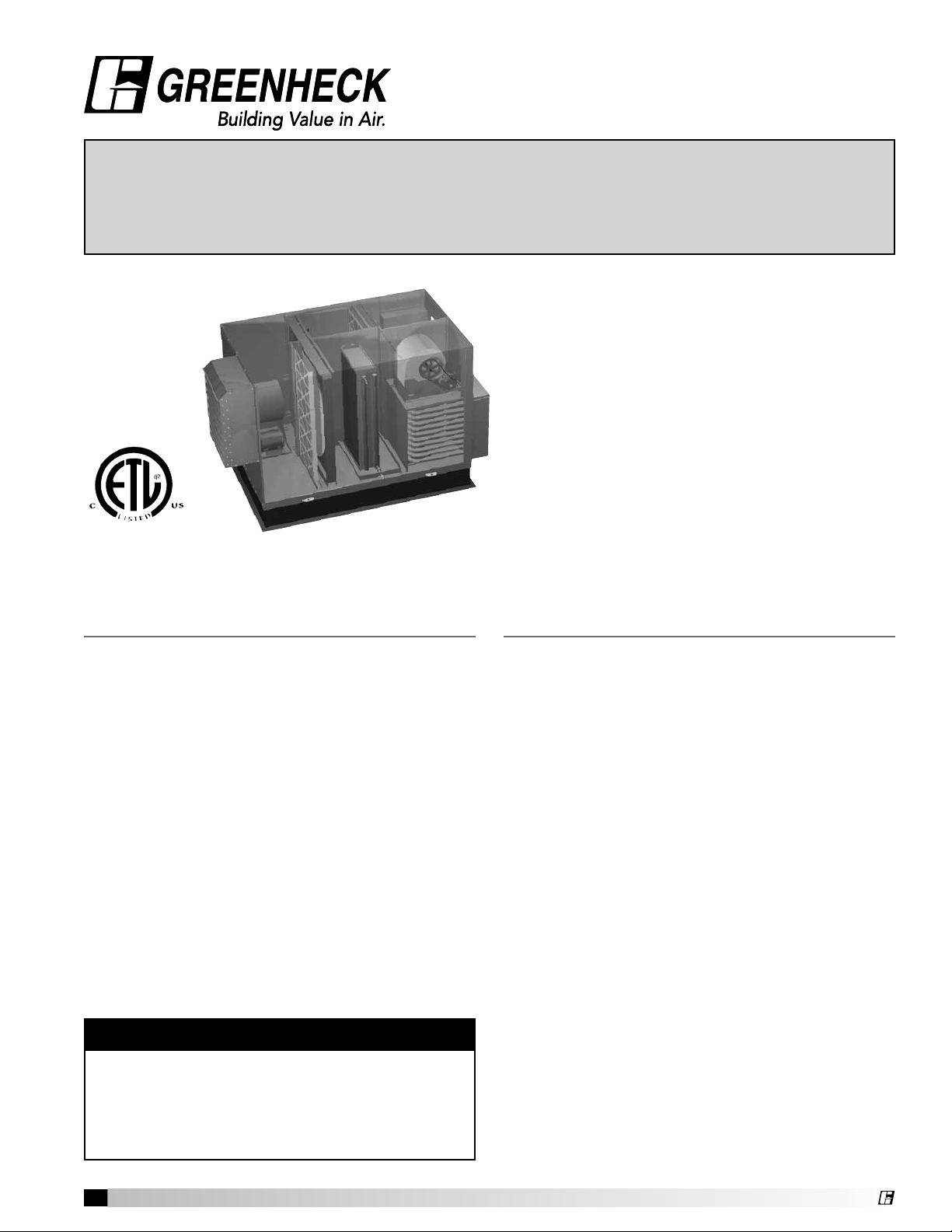
Part #461006
®
®
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
Please read and save these instructions. Read carefully before attempting to assemble, install, operate or maintain the
Please read and save these instructions. Read carefully before attempting to assemble, install, operate or maintain the
product described. Protect yourself and others by observing all safety information. Failure to comply with instructions
product described. Protect yourself and others by observing all safety information. Failure to comply with instructions
could result in personal injury and/or property damage! Retain instructions for future reference.
could result in personal injury and/or property damage! Retain instructions for future reference.
Indirect Gas-Fired Furnaces
Model PVF
General Safety Information
Model PVF Indirect Gas Furnace, available in Energy
Recovery models ERH, ERCH, HRE and VersiVent.
For unit specific information, refer to the respective
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual.
Units are listed for installation in the United States and
Canada.
• Installation of gas-fired duct furnaces must
conform with local building codes. In the absence
of local codes, installation must conform to
the National Fuel Gas code, ANSI Z223.1 or in
Canada, CAN/CGA-B149 installation does.
• All electrical wiring must be in accordance with
the regualtion of the National Electric Code, ANSI/
NFPA 70.
• Unit is approved for installation downstream from
refrigeration units. In these conditions, condensate
could form in the duct furnace and provision must
be made to dispose of the condensate.
WARNING
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service
or maintenance can cause property damage,
injury or death. Read the installation, operating
and maintenance instructions thoroughly before
installing or servicing this equipment.
Table of Contents
Installation
Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Venting for Outdoor Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Venting for Indoor Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Standard Indoor Venting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Furnace Connection Locations . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Concentric Venting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
Two Pipe Venting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-9
Electrical Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Furnace Control Center Layout. . . . . . . . . . .10
Gas Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Start-Up Operation
Start-Up, General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Furnace Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-13
Sequence of Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Performance Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Routine Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
1
®
®
Page 2

This page is intentionally blank.
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
2
®
Page 3
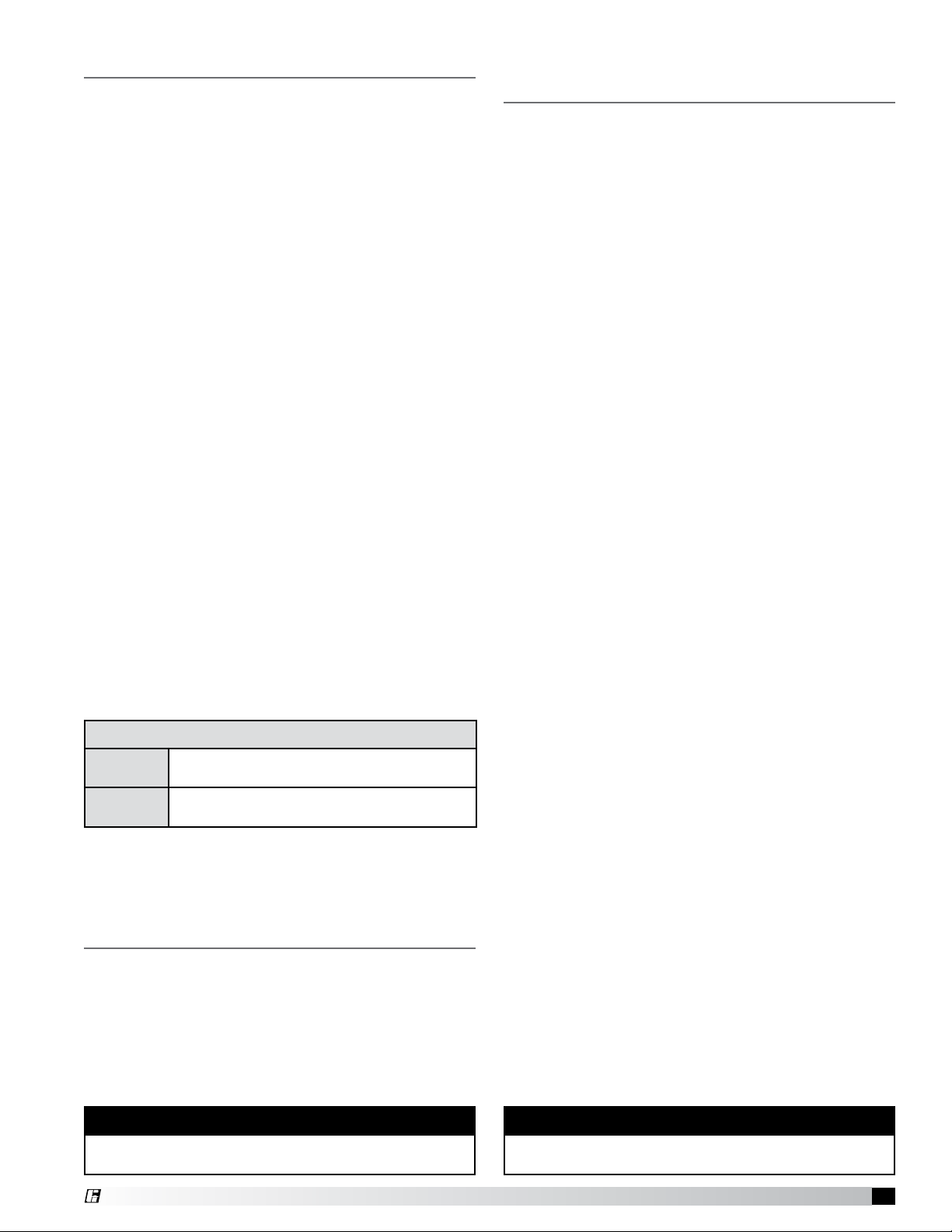
Installation – Location
1. Do not install units in locations where flue
products can be drawn into adjacent building
openings such as windows, fresh air intakes, etc.
Distance from vent terminal to adjacent public
walkways, adjacent buildings, operable windows,
and building openings shall conform with the local
codes. In the absence of local codes, installation
shall conform with the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1, or the CAN/CGA B-149 Installation
Codes.
2. Building materials that will be affected by flue
gases should be protected.
3. Avoid locating in an area where deep snow is
likely to accumulate. During the winter months,
keep snow clear on the access side of the unit to
prevent any blockage of combustion air inlet or
flue exhaust openings.
4. Maintain minimum horizontal clearance of 4 feet
from electric meters, gas meters, regulators,
and relief equipment. In Canada, the minimum
clearance is 6 feet.
5. Local codes may supercede any of the above
provisions.
6. Be sure that the minimum clearances to
combustible materials are maintained.
7. To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, do
not locate units where chlorinated, halogenated,
or acid vapors are present.
8. Units must not be installed in a potentially
explosive, flammable, or corrosive atmosphere.
For additional information on installation of the energy
recovery unit, refer to the respective units Installation,
Operation, and Maintenance (IOM) manuals:
Unit Clearances to Combustible Materials
Outdoor
Indoor
Combustion blower discharge must be located
42 inches from any cmobustible materials
Clearances are determined by the National Fuel
Gas Code and/or other local codes.
Installation of Venting for Outdoor
Units
1. Do not modify or obstruct the combustion air inlet
cover or the combustion blower weatherhood.
2. During the winter months, periodically clear snow
from access side of unit to prevent blockage of
the inlet and exhaust openings.
3. Do not add any vents other than those supplied by
the manufacturer.
Installation of Venting for Indoor
Units
There are three venting methods for indoor mounted
units. For each method, the units can be vented
horizontally through an exterior wall or vertically
through the roof. Specific venting instructions are
provided for each method and shown in the following
pages. Construct the vent system as shown in these
instructions. Refer to your unit specific submittal to
determine the applicable venting option.
The venting method options are:
Standard Indoor Venting
• uses building air for combustion
• vents exhaust to outdoors
• one exterior roof or wall penetration
Separated Combustion Concentric Venting
• uses outside air for combustion
• vents exhaust to outdoors
• one exterior roof or wall penetration
Separated Combustion 2-Pipe Venting
• uses outside air for combustion
• vents exhaust to outdoors
• two exterior roof or wall penetrations
The following guidelines must be adhered to for all
indoor units:
1. Venting installation must conform with local
building codes. In the absence of local codes,
installation must conform with the National Fuel
Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 or in Canada, CAN/
CGA-B149 installation codes.
2. For Standard Indoor Venting, use exhaust pipe
approved for a category III appliance or single
wall, 26 gauge or heavier galvanized vent pipe.
The piping is required to be gas tight by ANSI.
3. For Separated Combustion venting, sealed singlewall galvanized air pipe is recommended.
4. The joints must be sealed with a metallic tape or
silastic suitable for temperatures up to 350ºF.
5. A minimum of 12 inches of straight vent pipe is
recommended after the exhaust connection and
before any elbows.
6. Vertical combustion air pipes should be fitted with
a tee, drip leg, and clean-out cap to prevent any
moisture in the combustion air pipe from entering
the unit. The drip leg should be cleaned out
periodically during the heating season.
7. To reduce condensation, insulate any vent runs
greater than 5 feet.
8. All vent pipe connections should be made with at
least three corrosion resistant sheet metal screws.
9. Refer to the National Fuel Gas Code for additional
piping guidelines.
NOTE
Vent piping is supplied by others, not Greenheck.
®
NOTE
Vent piping is supplied by others, not Greenheck.
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
3
Page 4
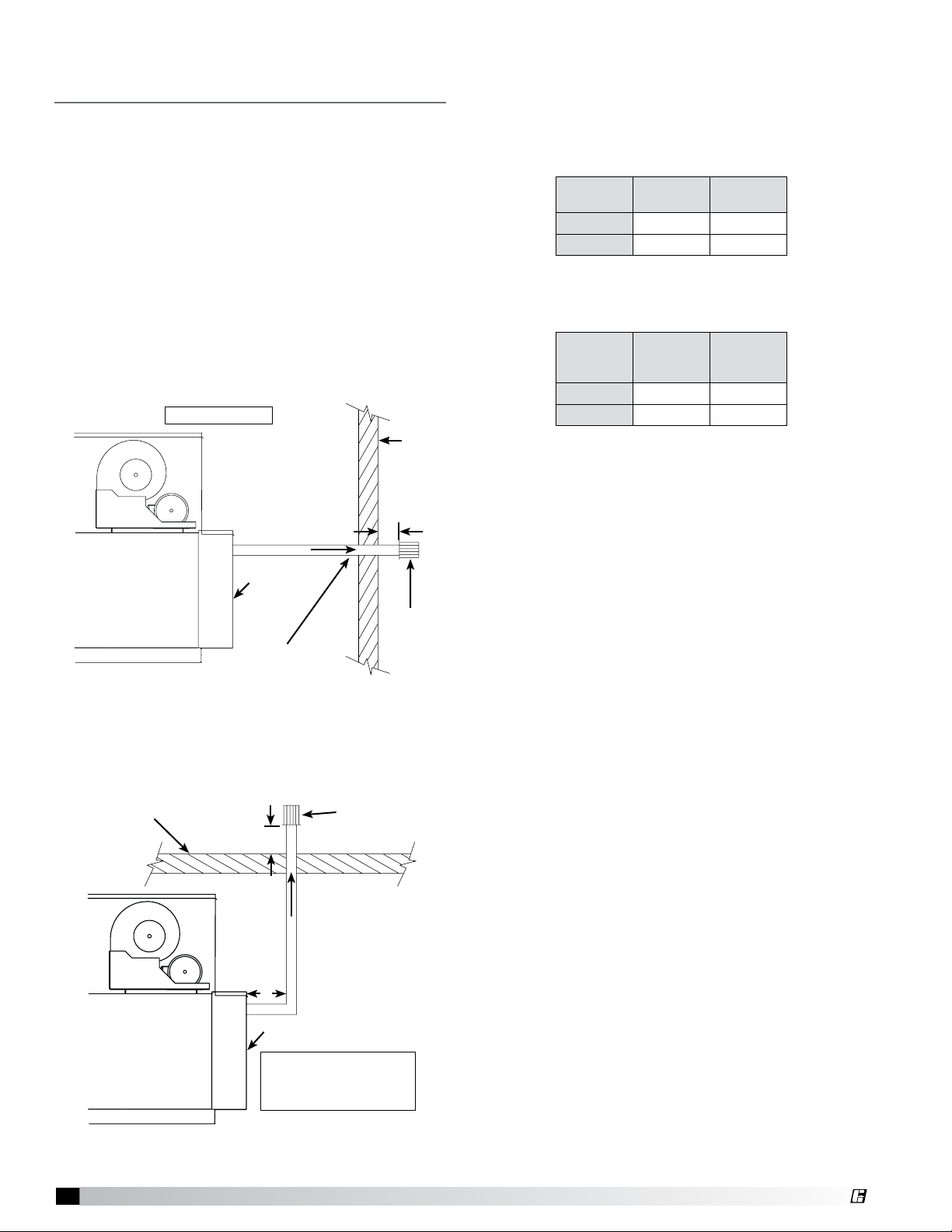
Installation of Standard Indoor
Venting
Standard Indoor Venting uses one penetration through
an exterior wall or roof for venting the flue exhaust.
The combustion air is scavenged from the air inside
the building (no piping required). When units are
installed in tightly sealed buildings, provisions should
be made to supply an adequate amount of infiltration
air from the outside. The rule of thumb is that an
opening of one square inch should be provided for
every 1000 BTUs per hour of input rating.
Vent terminals must be used (one vent terminal
included with each furnace). Construct the vent
system as shown in the Horizontal and Vertical
drawings below and reference the Vent Pipe Diameter
table for the correct vent pipe diameters.
A = 12 in. minimum
Exterior
Wall
A
EXHAUST
Air Inlet
Exhaust
Vent
Terminal
Pitch vent pipe
downward from
furnace
1/4 inch per foot
Vent Length Limitations
Refer to table for minimum and maximum vent
lengths. The total equivalent vent length must include
elbows. The equivalent length of a 4 inch elbow is
6 feet and the equivalent length of a 6 inch elbow is
10 feet.
Vent
Length
Horizontal 5 70
Vertical 10 70
Minimum
(feet)
Maximum
(feet)
Vent Pipe Diameter
Select the vent pipe diameter. Use only the specified
pipe size.
Furnace
Size
(MBH)
100 - 150 4 6
200 - 400 6 8
Exhaust
(inches)
Combustion
(inches)
Installing Exhaust Vent Pipe
Install the vent pipe with a minimum downward slope
(from the unit) of 1/4-inch per foot (horizontal venting
only). Securely suspend the pipe from overhead
structures at points no greater than 3 feet apart.
Attach the vent terminal to the end of the exhaust
pipe.
Seal Opening
Using an appropriate method, seal the wall/roof
opening around the exhaust pipe.
Standard Indoor Venting - Horizontal
Roof Line
B
EXHAUST
A
Air Inlet
A = 12 inch minimum
B = 12 inch minimum but
should size according to
expected snow depth
Exhaust Vent
Terminal
Standard Indoor Venting - Vertical
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
4
®
Page 5
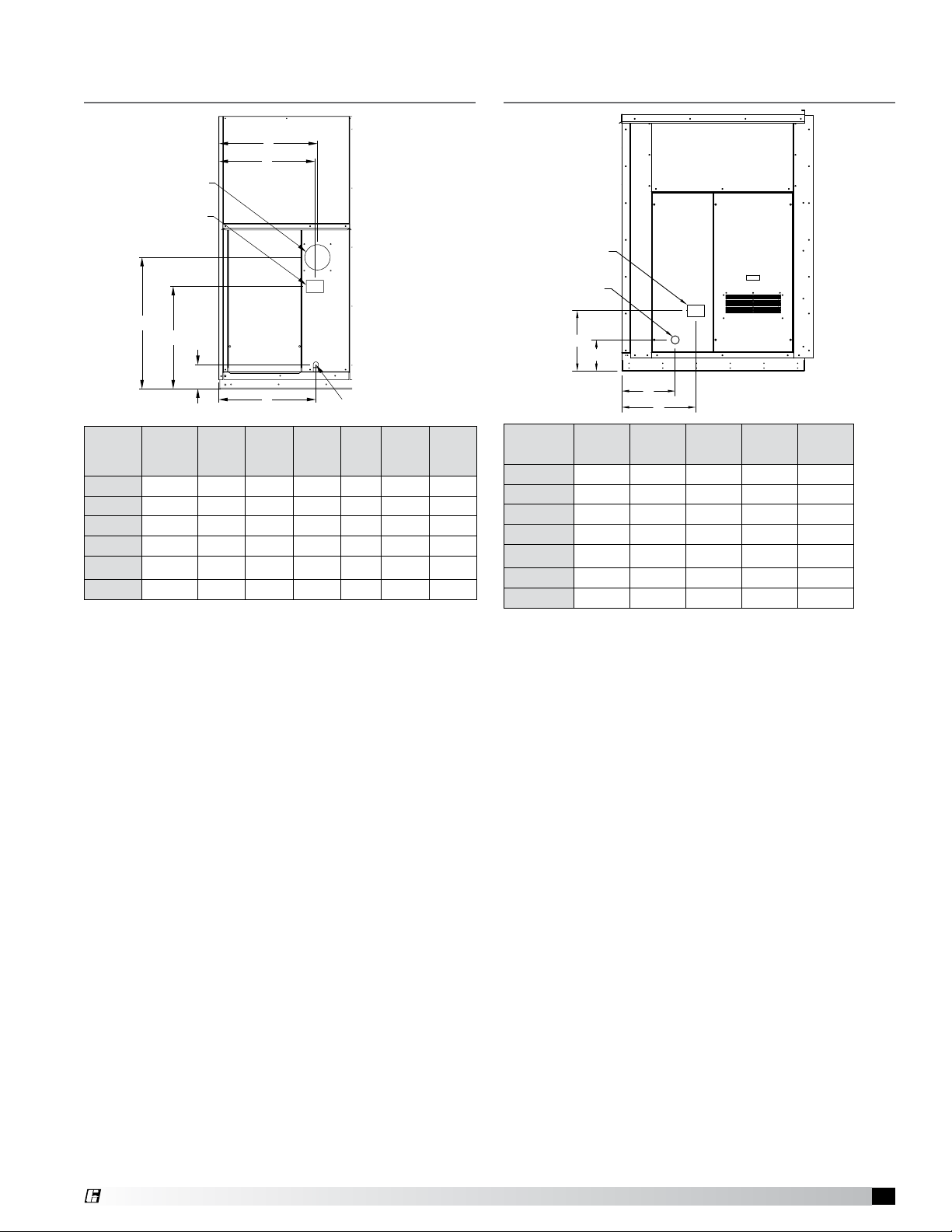
Furnace Connection Locations
Model ERH, ERCH, HRE
C
B
Combustion Air Inlet
Exhaust Outlet
F
E
D
A
3/4 inch
Gas Connection
Furnace Connection Locations
Model VersiVent
Exhaust Outlet
3/4 inch
Gas Connection
C
A
B
D
ERH
ERCH
HRE
20
45
45
55
55
90
Furnace
(MBH)
100-150 23.75 24.438 24.438 3.75 10.50 16.625
100-150 23.75 24.50 24.50 6.00 12.75 18.875
200-250 23.75 23.50 24.125 6.00 25.125 32.25
150 26.63 27.25 27.25 6.00 12.75 18.875
200-300 26.63 26.38 27.00 6.00 22.50 29.63
300-400 37.63 37.38 38.00 6.00 25.00 32.125
A B C D E F
VersiVent
45
45, 65
45, 65
45, 65, 90
45, 65, 90
45, 65, 90
45, 65, 90
Furnace
(MBH)
75 19.587 14.372 15.638 18.083
100 19.587 14.372 15.638 18.083
150 8.092 13.872 12.838 19.208
200 8.092 13.872 12.838 19.208
250 8.092 13.872 15.686 19.208
300 8.092 13.872 17.709 19.208
350-400 8.092 13.372 21.838 19.208
A B C D
®
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
5
Page 6

Installation of Concentric Venting
ÿ4.00 COLLAR WITH
CRIMPED END
(ÿ3 7/8 +/- 1/16
ÿ6 COLLAR WITH CRIMPED
END (ÿ5 7/8+/- 1/16 AFTER
CRIMPING)
ÿ6 COLLAR WITH CRIMPED
END (ÿ5 7/8+/- 1/16 AFTER
CRIMPING)
(General)
Concentric venting allows the exhaust pipe and
combustion air pipe to pass through a single hole in
the roof or wall of the building. A concentric venting
adapter (CVA) is required for concentric venting.
Depending upon whether the furnace was ordered for
Horizontal or Vertical concentric venting, each indirect
gas furnace will ship with the following items:
Horizontal
Venting
Vertical
Venting
The concentric venting adapter is designed for
indoor installations and should never be installed
on the exterior of the building. The exhaust pipe
must terminate with the vent terminal. For horizontal
venting, the combustion air pipe must terminate with
the inlet guard. For vertical venting, the combustion air
pipe must terminate with the inlet terminal.
a. Exhaust Pipe Vent Terminal
b. Concentric Venting Adapter
c. Inlet Guard
a. Exhaust Pipe Vent Terminal
b. Concentric Venting Adapter
c. Inlet Terminal
Horizontal Venting
Refer to the diagram below for venting on horizontal
concentric systems. Maintain at least 12 inches from
the combustion air inlet guard to the exhaust vent
terminal (Dim. B). To prevent water from running
into the combustion air pipe and to allow for easy
installation of the combustion air inlet guard, the
combustion air pipe must terminate at least 2 inches
from the exterior surface of the outside wall (Dim. A).
A = 2 inch minimum
B =
12 inch minimum
Mounting
Bracket
COMBUSTION AIR
EXHAUST
Mounting
Bracket
Pitch vent pipe downward from
furnace 1/4 inch per foot
Exterior
Wall
B
A
Exhaust
Vent
Terminal
Combustion
Air Inlet
Guard
CVA-4
4-inch Concentric
Venting Adapter
Combustion Air Connection
Concentric Side
6-inch Concentric
Venting Adapter
Exhaust Connection
Concentric Side
CVA
CVA-6
Vertical Venting
Refer to the diagram below for venting on vertical
concentric systems. Maintain at least 12 inches
between the top of the combustion air inlet terminal
and the bottom of the exhaust vent terminal (Dim. B).
The bottom of the combustion air inlet terminal must
terminate above the snow line, or at least 12 inches
above the roof, which ever is greater (Dim. A). A tee
with cleanout must be provided on the combustion air
and exhaust pipe to prevent debris from entering the
heat exchanger.
A = 12 inch minimum but
should size according to
expected snow depth
B = 12 inch minimum
C = 12 inch minimum
Roofline
Mounting
Bracket
C
B
A
COMBUSTION AIR
Exhaust Vent Terminal
Combustion Air
Inlet Terminal
Mounting
Bracket
EXHAUST
Combustion Air Connection
Non-Concentric Side
Top View
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
6
Exhaust Connection
Non-Concentric Side
Tee with drip leg
C
and cleanout cap
®
Page 7

Concentric Vent Connection Diameter
Vent terminals must be used (one vent terminal
included with each furnace). Construct the vent
system as shown in the Horizontal and Vertical
drawings on
previous page and
reference the table
for the correct
vent connection
diameters.
Furnace
Size
(MBH)
100 - 150 4 6
200 - 400 6 8
Exhaust
(inches)
Combustion
(inches)
Vent Length
Refer to table for minimum and maximum vent
lengths. The total equivalent vent length must
include elbows. The
equivalent length
of a 4 inch elbow
is 6 feet and the
equivalent length of
a 6 inch elbow
Vent
Length
Horizontal 5 70
Vertical 10 70
Minimum
(feet)
Maximum
(feet)
is 10feet.
1. Determine Venting Location
Determine the location of the concentric venting
adapter (CVA) based on any clearances that must
be maintained (follow all codes referenced in these
instructions).
2. Attach Mounting Brackets
Attach field supplied, corrosion resistant, mounting
brackets to the CVA using corrosion resistant sheet
metal screws.
5. Install CVA Assembly
Place the CVA assembly through the wall/roof and
verify that all minimum clearance requirements as
specified in these instructions are met. Secure the
CVA assembly to the wall/ceiling with mounting
brackets and corrosion resistant sheet metal screws.
6. Attach CVA Assembly to Unit
Attach the exhaust pipe to the unit’s combustion
exhaust. Using an additional combustion air pipe,
connect the unit’s combustion air supply intake to the
combustion air connection on the CVA. For vertical
venting, include the required tees with drip legs and
clean outs.
Combustion Air
Connection
IG
Furnace
Control
Center
Access
Exhaust
Connection
3. Install Exhaust Pipe
Slide the exhaust pipe through the CVA. Provide
enough exhaust piping to pass through the wall (or
floor) and provide the minimum clearance of 12inches
between the exhaust pipe termination and the
combustion air intake. With all required clearances
satisfied, attach the exhaust pipe to the CVA.
4. Install Combustion Air Pipe
Attach a field supplied combustion air pipe to the
concentric side of the CVA.
For horizontal venting, provide enough combustion
air piping to pass through the wall and provide
the minimum clearance of 2 inches between the
combustion air intake and the exterior surface of the
outside wall.
For vertical venting, provide enough combustion
air piping to pass through the roof and provide
the minimum clearance of 12 inches between the
combustion air intake and the exterior surface of the
roof. This clearance may need to be increased to allow
for snow accumulation.
Be sure to maintain the minimum clearance of
12inches between the exhaust pipe termination and
the combustion air intake.
7. Install Combustion Air Inlet Guard/
Terminal and Exhaust Vent Terminal
Slide the combustion air inlet guard (for horizontal
venting) or the inlet terminal (for vertical venting) over
the exhaust pipe and fasten it to the combustion
air pipe. Attach the exhaust vent terminal to the
discharge end of the exhaust piping.
8. Seal Opening
Seal the opening between the wall/floor and the air
intake pipe using an appropriate method.
®
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
7
Page 8

Installation of Two Pipe Venting
Horizontal Venting
Refer to the diagram below for venting on horizontal
two pipe systems. Maintain at least 12 inches of
clearance between the exhaust pipe termination and
the exterior surface of the outside wall (Dim. A). The
combustion air pipe must be a minimum of 12 inches
below the exhaust pipe (Dim. C) and 12 inches from
the exhaust pipe vent terminal (Dim. B). A minimum
of 1 inch and a maximum of 48 inches of building wall
thickness is required for separated combustion vent
pipe.
A = 2 inch minimum
B =
12 inch minimum
C =
12 inch minimum
EXHAUST
Pitch vent pipe
downward from
furnace
1/4 inch per foot
Two (2) Field
Supplied Support
Brackets
COMBUSTION AIR
Vertical Venting
Refer to the diagram below for venting on vertical two
pipe systems. The combustion air pipe must terminate
at least 12 inches above the roof. This clearance
may need to be increased to accommodate for snow
accumulation (Dim. A). The exhaust must terminate
at least 12 inches above (Dim. B) and 12 inches
horizontally (Dim. C) from the combustion air inlet.
Exterior
Wall
Exhaust
Vent
Terminal
B
A
Combustion
Air Inlet
Terminal
Two Pipe Vent Connection Diameter
Vent terminals must be used (two vent terminals
included with each furnace). Construct the vent
system as shown in the Horizontal and Vertical
drawings on this
page and reference
the table at the
right for the correct
vent connection
diameters.
Furnace
Size
(MBH)
100 - 150 4 6
200 - 400 6 8
Exhaust
(inches)
Vent Length
Refer to the table for minimum and maximum vent
lengths. The total equivalent vent length must
include elbows. The
equivalent length
of a 4 inch elbow
is 6 feet and the
equivalent length
of a 6 inch elbow is
Vent
Length
Horizontal 5 70
Vertical 10 70
Minimum
(feet)
10feet.
1. Install Combustion Air Pipe
C
Run a combustion air pipe from the unit’s combustion
air intake through the exterior wall/roof to the
outdoors.
For horizontal venting, the combustion air pipe must
terminate at least 12 inches from the exhaust pipe
vent terminal. Attach the combustion air inlet terminal
to the end of the combustion air pipe. Using field
supplied mounting brackets, support the combustion
air pipe as needed.
For vertical venting, the combustion air pipe must
terminate at least 12 inches above the roof. This
clearance may need to be increased to accommodate
snow accumulation.
Combustion
(inches)
Maximum
(feet)
Combustion Air
Inlet Terminal
Roofline
A
D
A = 12 inch minimum but should size
B = 12 inch minimum
C = 12 inch minimum
D = 12 inch minimum
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
8
Exhaust Vent
B
EXHAUST
COMBUSTION AIR
D
according to expected snow depth
Terminal
Tee with drip leg
and cleanout cap
Combustion Air
Connection
IG
Furnace
Control
Center
Access
®
Page 9

2. Install Exhaust Pipe
Run an exhaust pipe from the unit’s combustion
exhaust through the exterior wall/roof to the outdoors.
For horizontal venting, the exhaust pipe must
terminate at least 12 inches from the exterior surface
of the outside wall and at least 12 inches above the
combustion air pipe. Attach exhaust vent terminal
to the end of the exhaust pipe. Using field supplied
mounting brackets, support the exhaust pipe as
needed.
For vertical venting, maintain at least 12 inches
between the bottom of the exhaust vent terminal and
the top of the combustion air inlet terminal. Maintain
at least 12 inches horizontally between the exhaust
vent and the combustion air inlet. Attach exhaust vent
terminal to the end of the exhaust pipe.
3. Seal Openings
Using an appropriate method, seal the wall/roof
openings around the piping.
®
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
9
Page 10

Installation of Electric Wiring Furnace Control Center Layout
WARNING
Disconnect power supply before making wiring
connections to prevent electrical shock and
equipment damage.
WARNING
All appliances must be wired strictly in accordance
with wiring diagram furnished with the unit. Any
wiring different from the diagram could result in a
hazard to persons and property.
WARNING
Any original factory wiring that requires replacement
must be replaced with wiring material having a
temperature rating of at least 105°C
1. Installation of wiring must conform with local
building codes. In the absence of local codes,
installation must conform to the National Electric
Code ANSI/NFPA 70-Latest Edition. Unit must be
electrically grounded in conformance with this
code. In Canada, wiring must comply with CSA
C22.1, Canadian Electrical Code.
2. All furnaces are provided with a wiring diagram
located on the inside of the access panel. Refer to
this wiring diagram for all wiring connections.
3. The combustion blower motor will not run unless
the furnace is turned on and the gas controls are
calling for heat.
9
1
2
3
4
6
5
7
8
1. Two-stage temperature controls - Controls
the furnace stages based on the unit discharge
temperature.
2. Combustion blower - Exhausts the products of
combustion from the furnace tubes.
3. Ignition controller - Continually monitors,
analyzes, and controls the proper operation of the
gas burner.
4. Manifold pressure test port (1/4-inch pipe thread)
- Used for checking the manifold gas pressure.
5. Time delay relay - Allows burner to stay at high
fire for 10 seconds upon being lit.
6. Air pressure switch - Tests to ensure the
combustion blower is operating.
7. Two-stage gas valve - Contains main pressure
regulator, safety shut-off valves, and manual shut
off knob. It controls the furnace to 50% or 100%
fire.
8. Ignitor - Provides spark for burner ignition.
9. Flame sensor - Ensures that each burner has
ignited.
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
10
®
Page 11

Installation of Gas Piping
TSU-1 - 56.5"
-
+
1.5"
TSU-2 - 61.5"
-
+
1.5"
TSU-3 - 67.5"
-
+
1.5"
C
L
of Supply Duct
TSU Gas
Connection
Gas Section Door
Direct Gas
Nameplate
Gas Pressure Requirements
Natural:
*Falling below minimum gas pressure requirements will
reduce the MBH output. In turn, the unit will not be
able to fully condition the space on peak heating days.
If gas pressure is simply too low for requirements, we
recommend the local gas company be contacted to
determine if a booster pump would be feasible.
From
Gas
Gas Cock
6 in. Trap
Recommended Piping to Controls
1. Furnaces (input 100 to 400 MBH) have a single
3/4inch, female pipe thread connection.
*6 to 14 in. wg
LP:
*11 to 14 in. wg
Ground Joint Union
1/8 in. Plugged
To Controls
2. When connecting the gas supply, the length of the
run must be considered in determining the pipe
size to avoid excessive pressure drop. Refer to a
Gas Engineer’s Handbook for gas pipe capacities.
3. A 6-inch drip leg should be installed in the pipe
run to the unit.
4. Install an easily accessible ground joint union
and a manual shut off valve (these are required
by some local codes) for emergency shut off and
easy servicing of the controls.
5. A 1/8 inch NPT plugged tap shall be installed
immediately ahead of the gas supply connection
to the furnace.
6. After gas piping is completed, carefully check
all piping connections for gas leaks. Use soap
solution or equivalent for testing. DO NOT use a
flame or other source of ignition to check for gas
leaks.
7. When leak testing pressures above 14 in. wg
(1/2 psi), close the field installed shutoff valve,
disconnect the furnace and its gas train from the
gas supply line, and plug the supply line before
testing.
8. When leak testing at pressures equal to or less
than 14 in. wg (1/2 psi) close the field-installed
shutoff valve to isolate the unit from the gas
supply line before testing.
®
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
11
Page 12

Start-Up
1. Turn off power to the unit at the disconnect
switch. Close all manual gas valves.
2. Check that all gas and electrical connections are
weatherized.
3. Make sure that the combustion air inlet and the
combustion blower discharge are free from
obstructions.
4. Inspect the unit to make sure that no damage has
occurred during installation.
5. With the furnace control center access panel
removed, connect a U tube manometer to the
manifold pressure test port (refer to the Control
Center Layout under Installation). This will be used
for checking the manifold gas pressure.
6. Set the thermostat or discharge temperature
controls to lowest setting.
7. Open all manual gas valves including the
combination gas valve and turn power on.
8. Call for heat with the thermostat or discharge
temperature controls and allow the burner to
light. Greenheck duct furnaces are equipped
with an automatic spark ignition system which
automatically lights the burner. DO NOT attempt to
light the burners manually.
9. After the burner is lit, check to make sure that the
supply blower is operating.
10. Verify that the gas controls sequence properly (see
Sequence of Operation).
11. Check the manifold gas pressure (see Burner
Adjustments on following pages).
Furnace Controls
Staged Temperature Controls
For Energy Recovery Units without Temperature
Control Package
The furnace stage controls are located in the furnace
control center. One control is provided for each stage
of heating. The discharge
temperature setting is located
on the control furthest to the
left. The offset and differential
settings for each stage
are preset at the factory;
however, field-adjustments
may be made to get the best
control for your application.
See the literature provided
with the controls for further
information.
Staged Temperature
Controls
For Energy Recovery Units with Temperature Control
Package
If two-stage control is ordered with a Temperature
Control Package, the controller in the unit’s main
control center will control the stages of heating.
The temperature set point may be adjusted on the
controller (See Temperature Controller IOM).
Turndown Modulation
Two Stage 2 : 1 50%, 100%
Electronic Modulation 2 : 1 50% - 100%
Staged Burner Adjustments
Setting Manifold Pressure for Two Stage Gas Control
1. Set the unit to high fire by setting the discharge
temperature control or thermostat to its maximum
setting. If the ambient temperature is warm, the
unit may not stay at high fire.
2. Measure the burner manifold pressure at the
manifold pressure test port (see Control Center
Layout on page 10) using a “U” tube manometer.
The pressure on high fire should be 3.5 in. wg for
natural gas and 10 in. wg for LP gas. To change
the pressure, adjust the regulator adjustment
screw on the combination gas valve. Clockwise
rotation will decrease the gas pressure and
counter clockwise rotation will increase the gas
pressure.
3. Set the unit to low fire by removing the wire from
the high fire terminal on the combination gas
valve. Clockwise rotation will decrease the gas
pressure and counter clockwise rotation will
increase the gas pressure.
4. The manifold pressure on low fire for natural gas
should be 0.88 in. wg and 2.5 in. wg for LP gas. To
change the pressure, use the low fire adjustment
screw on the combination gas valve.
Solenoid
High Fire Adjustment
Low Fire Adjustment
High Fire
Terminal
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
12
Combination Gas Valve
®
Page 13

Electronic Modulation Temperature
Controls
B
Combination Gas Valve
High fire adjustment
Low Fire Operation
3. Remove the wire from terminal 3 on the amplifier
and isolate it from touching anything. Set the
discharge temperature selector to the highest
setting. If there is a room override thermostat, turn
the dial to the highest setting.
4. Measure the manifold pressure on low fire, it
should be 0.88 in. wg for natural gas and 2.5 in.
wg for LP gas.
5. To adjust the low fire, remove the bypass cap (A)
and turn screw (B) as shown in diagram. Adjust
the screw indicated on the modulating valve.
Clockwise rotation will decrease gas pressure
and counterclockwise rotation will increase gas
pressure.
6. Reconnect wire to terminal 3.
7. Remove jumper and place all wires back to where
they were and plug the manifold pressure port.
Modulating Valve
Low fire adjustment
A
Electronic Modulation Valves
For Energy Recovery Units without Temperature
Control Package
A Discharge Temperature Dial is used for temperature
control for electronic modulation. The temperature dial
will be located in the furnace control center.
For Energy Recovery Units with Temperature Control
Package
The Temperature Controller in the unit’s main control
center will provide the electronic modulation control.
High and Low Fire Settings for Electronic
Modulation
Check the high and low gas pressures on initial start
up per the instructions below. These settings are
preset at the factory, but should be adjusted in the
field if necessary. Set the high fire first and the low fire
second. The low fire must always be checked if the
high fire is changed.
High Fire Operation
1. Place a jumper between terminals 7 and 8 on the
Maxitrol amplifier.
2. Measure the burner manifold pressure at each
furnace at the pressure test port (see Control
Center Layout under Installation) using a high
quality manometer that can measure low gas
pressures. The pressure at high fire should be
3.5in. wg for natural gas and 10.0 in. wg for LP
gas. To change the pressure, adjust the high fire
screw (under cap screw) on the combination
gas valve. Clockwise rotation will decrease the
gas pressure and counter clockwise rotation will
increase gas pressure.
Manifold Pressure (inches wg)
Natural Gas LP
Low High Low High
2 : 1 Electronic Modulation 3.5 0.88 10 2.5
®
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
13
Page 14

Sequence of Operation
Power-up/Standby
After power is supplied to the unit:
1. The ignition control will reset and perform a selfcheck routine.
2. The diagnostic LED will flash for up to four
seconds.
3. The ignition control will begin scanning the
thermostats.
Heat Mode
When the thermostat or discharge temperature
controls call for heat:
1. The ignition control will check that the pressure
switch for the combustion blower is open.
2. The combustion blower will be energized and the
15-second pre-purge begins.
3. The gas valve is energized and the ignitor will
spark for up to 10 seconds.
Natural Gas – If a flame is not sensed during
the trial for ignition, two additional trials will be
attempted before going into lockout for one hour.
LP Gas – If a flame is not sensed during the trial
for ignition, the control will go into lockout for one
hour.
4. When a flame is sensed, sparking stops
immediately. The gas valve and combustion
blower remain energized.
5a. Two-stage control – The burner will light at
100% fire and remain there for 10 seconds. The
thermostat will then operate the burners at high or
low fire, depending on the demand for heat.
5b. Electronic Modulation – The burner will light at
100% fire and remain there for 10 seconds. The
main burner gas valve will then modulate from
100% down to 50% as needed. If the burner
remains on low fire for an extended period of time,
the burner will shut off and re-light as necessary.
6. The ignition control constantly monitors the
thermostat, pressure switch, and burner flame to
assure proper operation.
7. When the thermostat or discharge temperature
controls are satisfied, the main valve is deenergized and the combustion blower shuts off
following a 30-second post-purge period.
Recovery from Lockout
The ignition control will automatically reset after one
hour if the thermostat is still calling for heat. Prior
to one hour, a manual reset (cycle power to unit) is
required. The thermostat may be reset or the power
interrupted for a period of 5 seconds. See page 7 for
Ignition Control Diagnostics.
Performance Data
Model
Number
PVF 100 100 80 3704 2963 2469 2116 1852 1646 1481 1347 1235 1140 1058 988 926 871 823 780 741
PVF 150 150 120 5556 4444 3704 3175 2778 2469 2222 2020 1852 1709 1587 1481 1389 1307 1235 1170 1111
PVF 200 200 160 7407 5926 4938 4233 3704 3292 2963 2694 2469 2279 2116 1975 1852 1743 1646 1559 1481
PVF 250 250 200 9259 7407 6173 5291 4630 4115 3704 3367 3086 2849 2646 2469 2315 2179 2058 1949 1852
PVF 300 300 240 11111 8889 7407 6349 5556 4938 4444 4040 3704 3419 3175 2963 2778 2614 2469 2339 2222
PVF 350 350 280 12963 10370 8642 7407 6481 5761 5185 4714 4321 3989 3704 3457 3241 3050 2881 2729 2593
PVF 400 400 320 14815 11852 9877 8466 7407 6584 5926 5387 4938 4558 4233 3951 3704 3486 3292 3119 2963
Input
(MBH)
Output
(MBH)
20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Ratings shown are for elevations up to 2000 ft. For higher elevations, the input should be reduced by 4% per
1000 ft. of elevation above sea level. In Canada, from 2000 to 4500 ft in elevation, the unit must be derated to
90% of the input listed above. The unit shall also be used in accordance with standard CGA 2.17.
Air Temperature Rise Through Unit (°F)
CFM
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
14
®
Page 15

Troubleshooting
LED Indication Error Mode
Steady On Internal control failure
1 flash Airflow fault
2 flashes Flame with no call for heat
3 flashes Ignition lockout
Ignition Control Diagnostic LED
During normal operation, the LED is shut off. The
LED will be on or flashing during a fault condition. If
a fault condition is occurring, turn the unit off and on
again. If the LED is still flashing, refer to the following
troubleshooting section.
Airflow Fault (1 Flash)
An airflow fault may occur for the following reasons:
• An airflow switch continually monitors the
combustion airflow during an ignition sequence.
During the initial call for heat, if the pressure
switch contacts are in the closed position for
30seconds without an output to the combustion
blower, an airflow fault will be declared. The
control will remain in this mode with the
combustion blower off.
• After the combustion blower output (L1 and IND)
is energized and the airflow switch remains open
for more than 30 seconds, an airflow fault will be
declared. The control will stay in this mode with
the combustion blower on, waiting for the airflow
switch to close.
• If the airflow signal is lost while the burner is firing,
the control will immediately de-energize the gas
valve and the combustion blower will remain on.
If the call for heat remains, the control will wait
for proper airflow to return. If proper airflow is not
detected after 30 seconds, an airflow fault will be
declared. If proper airflow is detected at any time,
a normal ignition sequence will begin.
Once proper airflow is detected, the normal
Sequence of Operation for ignition will follow (see
page 14).
Flame Fault (2 Flashes)
If the main valve fails to close completely and
maintains a flame, the full-time flame sense circuit will
detect it and energize the combustion blower. Should
the main valve later close completely and remove
the flame signal, the combustion blower will be deenergized.
Ignition Lockout (3 Flashes)
Possible Cause Solution
Manual gas valve not open Open manual valve
Air in the gas line Bleed gas line
Supply gas pressure too high or too
low
Loose wire connections Check for tight wire connections
No spark…
a. Tranformer failure
b. Spark electrode
c. Spark cable shorted to ground Replace spark cable
d. Ignition controller not grounded Check unit airflow and manifold pressure
High limit control tripper Check unit airflow and manifold pressure
Faulty combination gas valve
Faulty ignition control
Check that supply pressure is between 6 and 14 in. wg for natural gas
and between 11 and 14 in. wg for LP
Check primary and secondary voltages of transformer. Replace if
necessary
Ensure spark gap is 1/8 inch and ceramic insulator is not cracked.
Replace if necessary. Electrode is NOT field adjustable.
If 24 volts is measured between terminals MV and common, but valve
remains closed, replace valve
Check diagnostic LED for steady on and for voltage between V1 and V2.
If no voltage is present, replace ignition control.
®
Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace
15
Page 16

Routine Maintenance
WARNING
Turn off all gas and electrical power to the unit
before performing any maintenance or service
operations to this unit.
Combustion Blower Motor
Motor maintenance is generally limited to cleaning.
Cleaning should be limited to exterior surfaces only.
Removing dust and grease build-up on the motor
housing assures proper motor cooling. Use caution
and do not allow water or solvents to enter the motor
or bearings. Under no circumstances should motors
or bearings be sprayed with steam, water or solvents.
The motor bearings are pre-lubricated and sealed,
requiring no further lubrication.
Burners and Orifices
Before each heating season, examine the burners and
gas orifices to make sure they are clear of any debris
such as spider webs, etc. Clean burner as follows:
• Turn off both electrical and gas supplies to the
unit.
• Disconnect union between manifold and gas
valve.
• Remove manifold and burner assembly.
• Inspect and clean orifices and burners as
necessary. Avoid using any hard or sharp
instruments which could cause damage to the
orifices or burners.
a. Remove any soot deposits from the burner
with a wire brush.
b. Clean the ports with an aerosol degreaser or
compressed air.
c. Wipe the inside of the burner clean. Cleaning
the burner with a degreaser will slow the future
buildup of dirt.
• Before reinstalling the burner assembly, look down
the heat exchanger tubes to make sure they are
clear of any debris.
• Reinstall manifold and burner assembly, reconnect
wire leads, and gas supply piping.
• Turn on the electrical power and gas supply.
• Follow the start-up procedure to light the burners
and verify proper operation.
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger should be checked annually for
cracks and discoloration of the tubes. If a crack is
detected, the heat exchanger should be replaced
before the unit is put back into operation. If the tubes
are dark gray, airflow across the heat exchanger
should be checked to make sure the blower is
operating properly.
Flue Collector Box
The flue passageway and flue collector box should be
inspected prior to each heating season and cleared of
any debris.
Electrical Wiring
The electrical wiring should be checked annually for
loose connections or wiring deterioration.
Gas Train
The gas train connections, joints and valves should be
checked annually for tightness.
Replacement Parts
When ordering replacement parts, include the
complete unit model number and serial number listed
on the unit rating plate.
Warranty
Greenheck warrants this equipment to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of one year from
the shipment date. Any units or parts which prove defective during the warranty period will be replaced at our option
when returned to our factory, transportation prepaid. Motors are warranted by the motor manufacturer for a period of
one year. Should motors furnished by Greenheck prove defective during this period, they should be returned to the
nearest authorized motor service station. Greenheck will not be responsible for any removal or installation costs.
As a result of our commitment to continuous improvement, Greenheck reserves the right to change specifications
without notice.
®
Phone: (715) 359-6171 • Fax: (715) 355-2399 • E-mail: gfcinfo@greenheck.com • Website: www.greenheck.com
461006 • Model PVF Indirect Gas-Fired Furnace, Rev. 4, September 2008 Copyright 2008 © Greenheck Fan Corporation
16
 Loading...
Loading...