Page 1

®
PN 458294
Model Proximity (Backshelf)
Kitchen Hoods
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
Please read and save these instructions. Read carefully before attempting to assemble, install, operate or maintain the
product described. Protect yourself and others by observing all safety information. Failure to comply with instructions
could result in personal injury and/or property damage! Retain instructions for future reference.
Please record the Serial, Model #, and Mark for the hood and other equipment for future reference.
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________ Mark: _________________
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________ Mark: _________________
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________ Mark: _________________
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________ Mark: _________________
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________ Mark: _________________
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________ Mark: _________________
Serial #: _______________________ Model #: ______________________ Mark: _________________
Proximity Hood
1
Mark: _________________
Page 2

®
Table of Contents
Receiving and Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Hood Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Hood Installation Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Filler Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Hood Hanging Height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Continuous Capture Plenum. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Ductwork . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Electrical Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
External Supply Plenum Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
External Supply Plenums Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Back Supply Plenum Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Hanging the Hood . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Enclosure Panel Installation Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 - 12
Backsplash Panel Installation Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Duct Collar Installation Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Exhaust Air Balancing Baffle (EABB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Balancing the Kitchen Exhaust. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Baffle Filters (GH Series)
High Velocity Cartridge Filters (Gk Series)
High Efficiency Filters (GX Series)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 - 19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 - 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Fire Suppression Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 - 25
Overall Wiring Plan View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Wiring for Switch Panels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Grease Grabber™ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29 - 31
Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 - 34
Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Proximity Hood
2
Page 3
®
Receiving and Handling
Upon receiving the equipment, check for both obvious and hidden damage. If damage is found, record all
necessary information on the bill of lading and file a claim with the final carrier. Check to be sure that all parts of
the shipment, including accessories, are accounted for.
STORAGE
If a kitchen hood must be stored prior to installation it must be protected from dirt and moisture. Indoor storage
is recommended. For outdoor storage, cover the hood with a tarp to keep it clean, dry, and protected from UV
(Ultra Violet) Radiation damage.
Improper storage which results in damage to the unit will void the warranty.
Hood Weights
Hood weight is determined using a simple formula. Select the figures provided in columns A and B (see tables)
from the three respective categories—Hood Width, Filter Type and Hood Height—based on the hood received.
Total the three numbers in column A and the three numbers in column B. Place the sum for column A and the
sum for column B in the Hood Weight equation where shown and solve for the total Hood Weight.
IMPERIAL A B
Category 1: Hood Width (in.)
23 - 25 1.3 28
26 - 28 1.35 30
29 - 32 1.4 31.5
33 - 36 1.45 33.5
Category 2: Filter Type
Baffle 0.3 0
GX or Cartridge 0.4 0
Grease Grabber™ 1 0
Category 3:
Hood Height (in.)
24 - 27 0 0
28 - 33 0.08 5
34 - 38 0.16 10
39 - 42 0.24 15
Example: A B
Category 1: Hood Width 23 - 25 1.3 28
Category 2: Filter Type Baffle 0.3 0
Category 3: Hood Height 24 - 27 0 0
Total: 1.6 28
Hood Weight Equation (lb.)
A x Length (in.) + B = Weight (lb.)
1.6 x 48 + 28 = 104.8 lb.
METRIC A B
Category 1: Hood Width (cm)
58.42 - 63.50 0.232 12.68
66.04 - 71.12 0.241 13.59
73.66 - 81.28 0.250 14.27
83.82 - 91.44 0.259 15.18
Category 2: Filter Type
Example: A B
Category 1: Hood Width 58.42 - 63.50 0.232 12.68
Category 2: Filter Type Baffle 0.054 0
Category 3: Hood Height 60.96 - 68.58 0 0
Total: 1.6 28
Baffle 0.054 0
GX or Cartridge 0.071 0
Grease Grabber™ 0.178 0
Category 3: Hood Height (cm)
60.96 - 68.58 0.000 0
71.12 - 83.82 0.014 2.27
86.36 - 96.52 0.029 4.53
Hood Weight Equation (kg.)
A x Length (cm.) + B = Weight (kg.)
0.286 x 121.92 + 12.68 = 47.5 kg.
99.06 - 106.68 0.043 6.80
Proximity Hood
3
Page 4
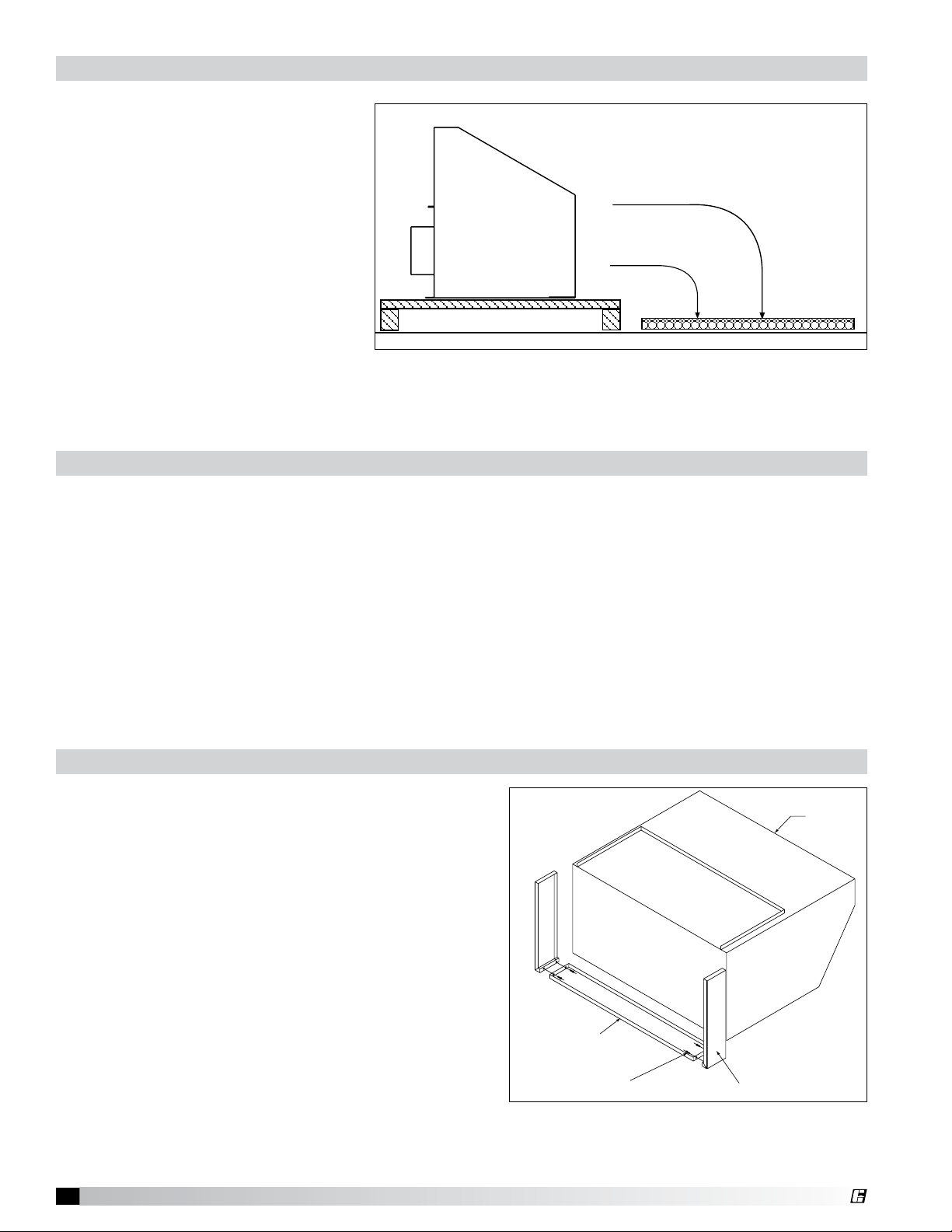
®
Hood Top
Hood Back
Backshelf
Bottom Filler Panel
5/16 x 3/4 in. (8 x 19 mm)
Bolts with Washers and Nuts
Hood Front
Hood Front
Installation
NOTE: If you have a Back Supply
Plenum, this must be installed before
Fig. 1
the hood. Please see page 8 now.
Prior to installation, check with local
authorities having jurisdiction on
clearances to combustible surfaces.
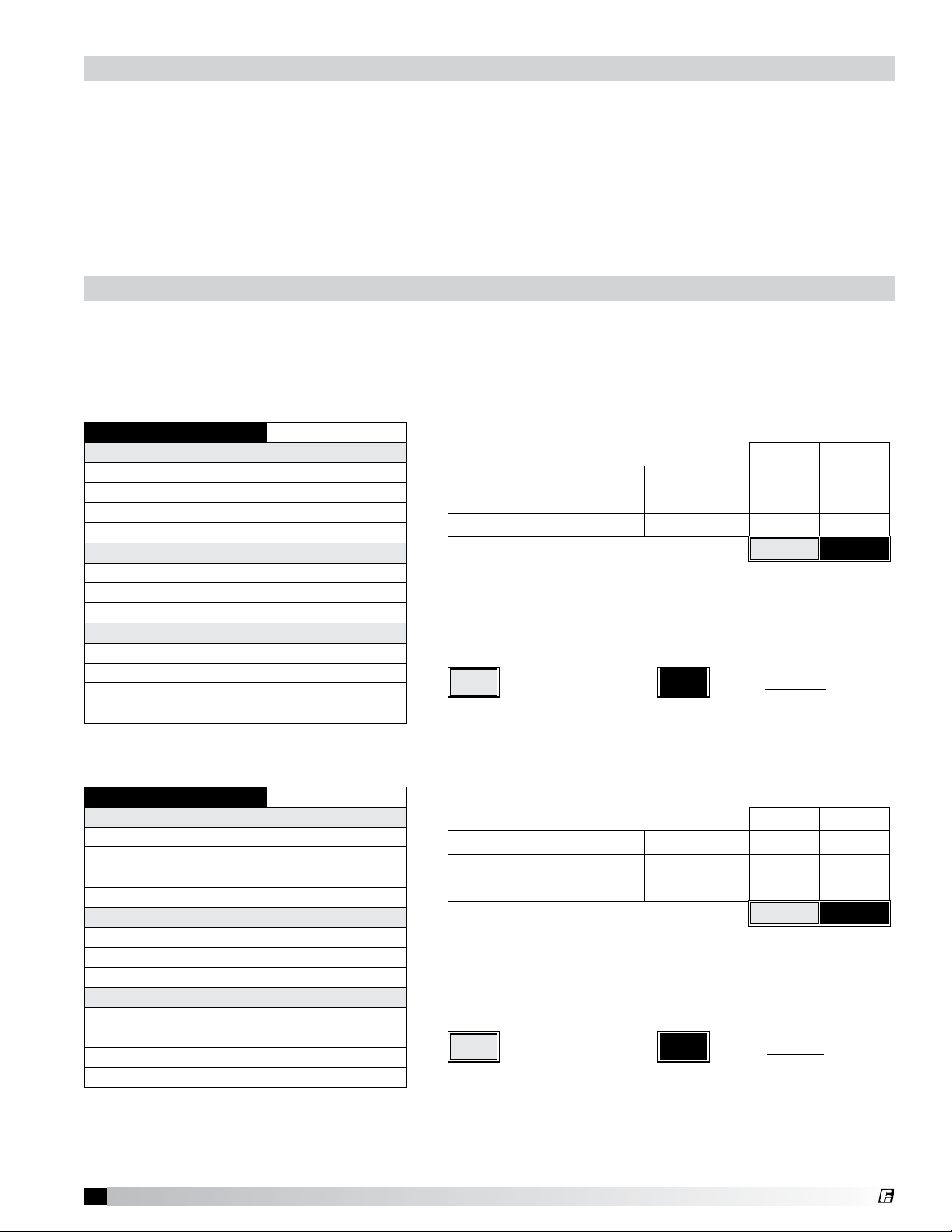
With the hood still inside its packing
crate, position the unit beneath its
installation location.
Carefully remove the packing crate.
Place some protective material on
the floor next to the crate to avoid
damaging the hood as it is tipped on its side (Fig. 1). Tip the hood carefully onto the protective
material. If you have filler panels, see Fig. 2 below. If you have integral filler panels, no additional
installation is needed.
Hood Installation Overview
If a Back Supply Plenum is provided, install first. Before raising hood, insert 1/2 in. (12.7 mm) diameter
threaded rod (by others) into hanger brackets on hood top. Check the engineering drawings or UL
label located on the inside of the hood for proper hood height above finished floor. Install filler panels
if needed. Raise and hang hood from adequate roof or ceiling supports and secure mounting flange
to the wall using lag bolts, or fasten to the Back Supply Plenum if provided. All hanger brackets must
be used and the hood must be properly supported while lifting to prevent damage or distortion to the
hood. The hood must be hung level to operate properly. After hood is secured, make the exhaust duct
connections. The fire system distributer must be contacted at this time. After the fire system has been
installed, mount the enclosures, then the supply plenums. If a Horizontal Supply Plenum is provided, it
should be installed according to the external supply plenum installation section found on page 7. The
hood and accessories are now installed. Finally, make the electrical connections from switches to fans
and complete the fire system circuits as required by the job specification.
Rear Filler Panel Installation Instructions
Rear filler panels may be shipped loose for field
installaton or are integral to the hood. If fillers are
integral to hood, skip this section.
1. Uncrate the hood and lay it on the floor with
protective material between the hood and the floor.
2. Bolt the filler panels together with 5/16 in. bolts
from the hardware package.
3. Position the filler panels on the hood, and tackweld them to the hood back.
4. To allow for ease of cleaning, caulk the external
seams with NSF Approved silicone caulk
(GE SCS1009, or its equivalent). The caulk is
not provided.
Proximity Hood
4
Fig. 2
Page 5
®
UL Vertical Distance
Above Cooking Surface
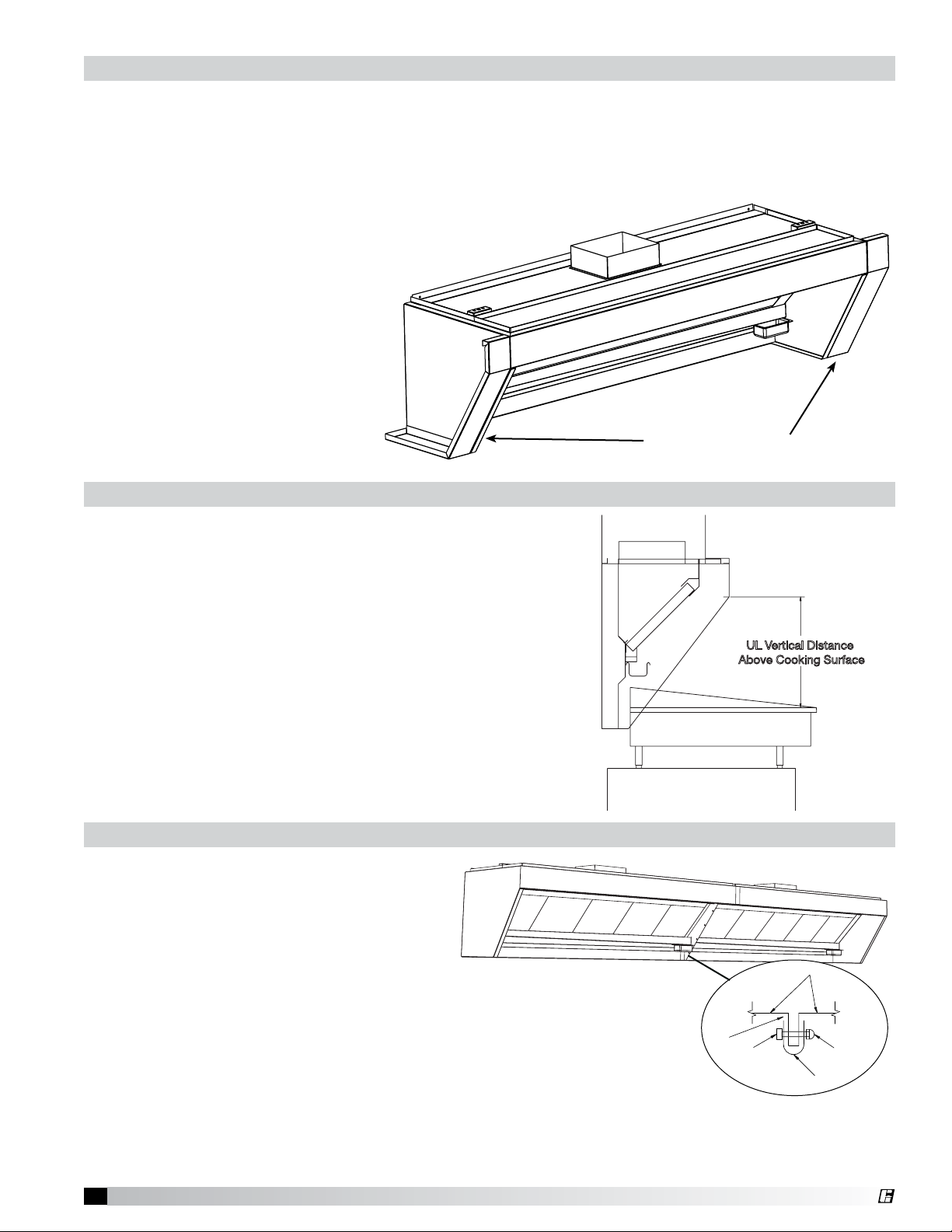
End Filler Panel Installation Instructions
H
OOD
ACO
RN N
UT
BOL
T
U-CLIP
CAULK
End filler panels may be shipped loose for field installaton or are facory mounted to the hood. If fillers
are factory mounted to hood, skip this section.
1. Uncrate the hood and lay it on the floor with protective material between the hood and the floor.
2. Bolt the filler panels together with 5/16 in. bolts from the hardware package.
3. Position the filler panels on the
hood and tack-weld them to the
appropriate side of the hood.
4. To allow for ease of cleaning,
caulk the external seams with
NSF Approved silicone caulk
(GE SCS1009, or its equivalent).
The caulk is not provided.
Note: Hood may be furnished with
finished end fillers when mounting
against a partial wall.
End Filler Panels
Fig. 3
Hood Hanging Height
The hood hanging height is critical, hanging the hood at the
incorrect height may significantly reduce the ability for the
hood to function properly and may be in violation of codes.
The hood hanging height is given on the UL label located
on the inside of the hood on the end panel. The distance
given is from the front lip of the hood (shown in Fig. 4) to
the surface of the cooking equipment.
Continuous Capture Plenum Hoods
Use the installation procedure described on
page 4 for single island hoods; install and
level both hoods. After leveling, secure the
hoods together. Fasten the hoods together
using u-clips and bolts. (Fig. 6) Caulk this
joint with NSF Approved silicone caulk (GE
SCS1009 or its equivalent). The caulk is not
provided.
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
5
Proximity Hood
Fig. 6
Page 6
®
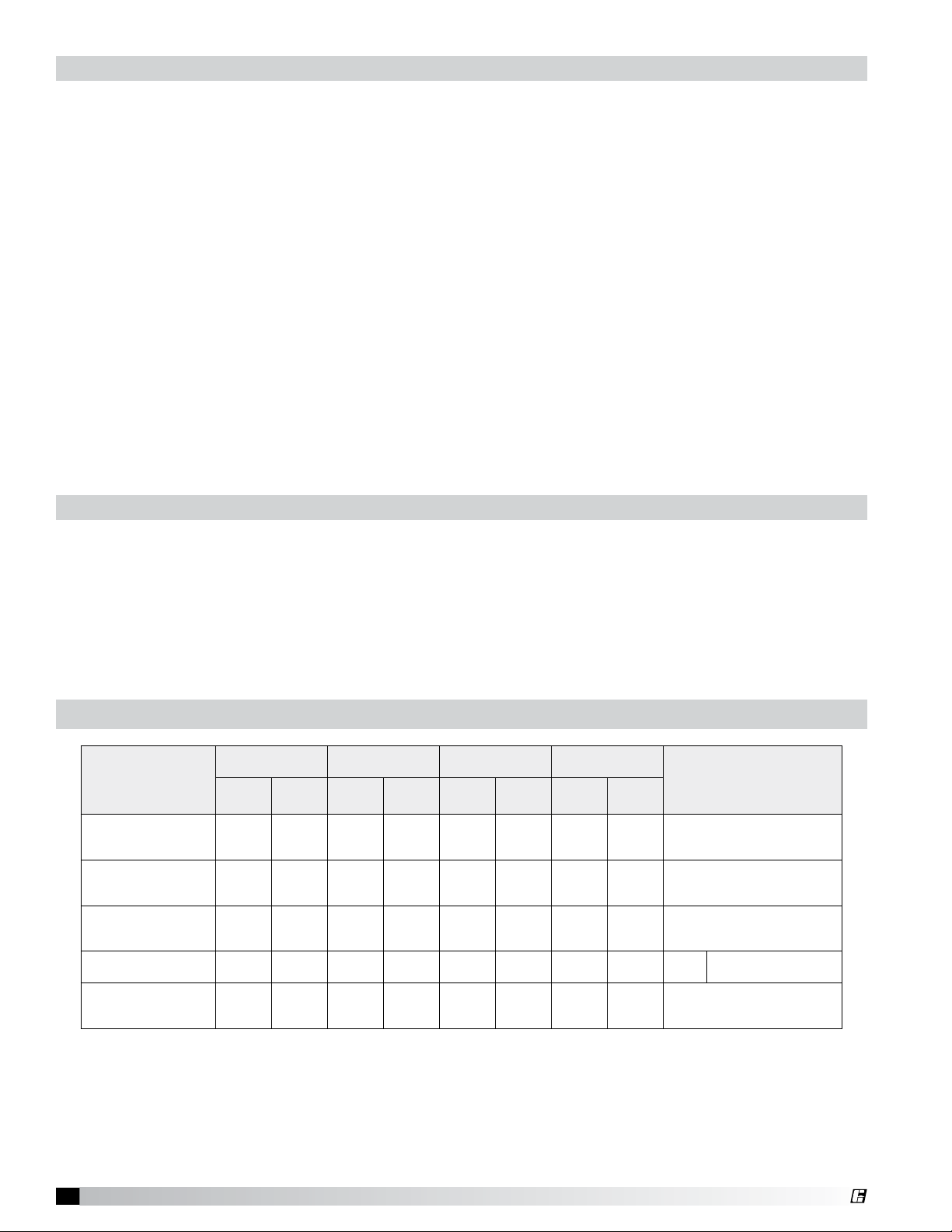
Ductwork
Exhaust
As specified in NFPA 96, Ch. 7.5 (latest edition), exhaust duct systems must be constructed in the
following manner:
Materials. Ducts shall be constructed of and supported by carbon steel not less than 1.37 mm
(0.054 in.) (No. 16 MSG) in thickness or stainless steel not less than 1.09 mm (0.043 in.) (No. 18 MSG) in
thickness.
Installation. All seams, joints, penetrations, and duct-to-hood collar connections shall have a
liquid-tight continuous external weld.
Supply
Supply ductwork (where applicable) should be connected to the hood in a manner approved by the
local code authorities.
Note: For hoods with fire dampers in the exhaust and supply duct collars, an access panel for cleaning
and inspection shall be provided in the duct. This panel shall be as close to the hood as possible but
should not exceed 18 in. (45.72 cm).
For proper installation of duct collars when they are shipped unattached, see page 14
Electrical Connections
Access for wiring the hood control panel (when applicable) is provided by a junction box located on
top of the hood when the control panel is mounted in the hood, or by the switch junction box when the
control panel is mounted in the fire protection cabinet. The box is labeled “Control Voltage Wiring to
Roof Top Fan Package”. Use minimum 14 AWG copper wire.
Standard light switches for remote mounting are rated for 15 amps and shall not have more than 14
lights connected to them. Higher amperage switches are available upon special request.
External Supply Plenum Weights, Dimensions, and Supply Rates
Length per
section
.91 to
4.88
.91 to
4.88
.91 to
4.88
.91 to
4.88
.91 to
4.88
Recommended
Supply Rate
145 cfm/ft
(246.36 m3/hr)
110 cfm/ft
(186.89 m3/hr)
145 cfm/ft
(246.36 m3/hr)
face
(135.92 -271.84 m3/hr)
150 cfm/ft
(254.85 m3/hr)
80-160 cfm/ft
External Supply
Plenum Type
Back Supply
Air CurtainSupply
• 14 inch
Air Curtain Supply
• 24 inch
Variable Supply
Horizontal Supply
Weight Width Height
(lbs/ft) (kg/ft) (in) (mm) (in) (mm) (ft) (m)
35.0 15.878 6 152.4 Variable Variable 3 to 16
9.5 4.31 14 355.6 10 254 3 to 16
12.5 5.67 24 609.6 10 254 3 to 16
16.0 7.26 12 304.8 18 457.20 3 to 16
14.0 6.35 12 304.8 18 457.20 3 to 16
Proximity Hood
6
Page 7
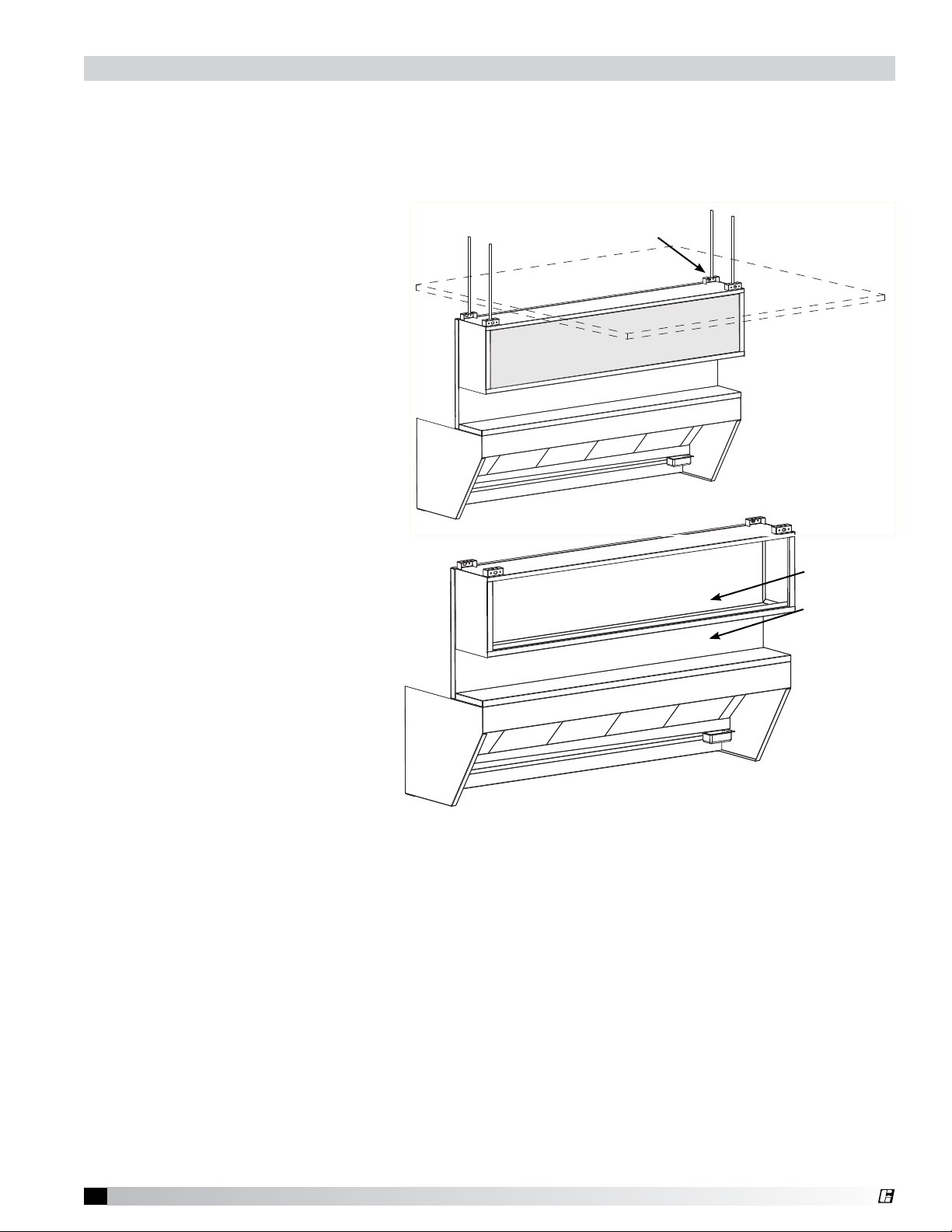
®
External Supply Plenum Installation
The purpose of the external supply plenum is to provide make-up air to an exhaust hood to maintain
the air balance in the space. The external supply plenum must be hung independent of the hood.
Follow the instructions for hanging the following supply plenums: Horizontal, Air Curtain and Variable.
See page 8 for Back Supply Plenum. If an external supply plenum is not provided, skip this section.
Installation Instructions
1. If duct collar(s) is shipped loose,
place the duct collar(s) over the
opening, fastening with tackwelds at 1 to 2 in. (2.54 to 5.08 cm)
intervals, or sheet metal screws
at 3 to 6 in. (7.62 to 15.24 cm)
intervals.
2. Insert 1/2 in. (12.7 mm) diameter
threaded rod (by others) into all
of the hanger brackets on the
supply plenum top. Raise external
supply plenum and hang level from
adequate roof or ceiling supports.
(Horizontal Supply Plenum shown
in Fig. 7, must be below finished
ceiling. Air Curtain Supply Plenum
may be fit into drop ceiling.)
3. Remove perforated panel from
plenum and bolt to enclosures
through back of plenum (Fig. 8).
This will draw plenum tight to the
enclosures. Fasteners are not
intended to support the plenum;
for alignment purposes only.
Support plenum from all
hangers provided
Fig. 7
Bolt back of
plenum to
enclosures
Fig. 8
4. Caulk mating joints with
NSF Approved silicone caulk
(GE SCS1009, or its equivalent).
The caulk is not provided.
Proximity Hood
7
Page 8
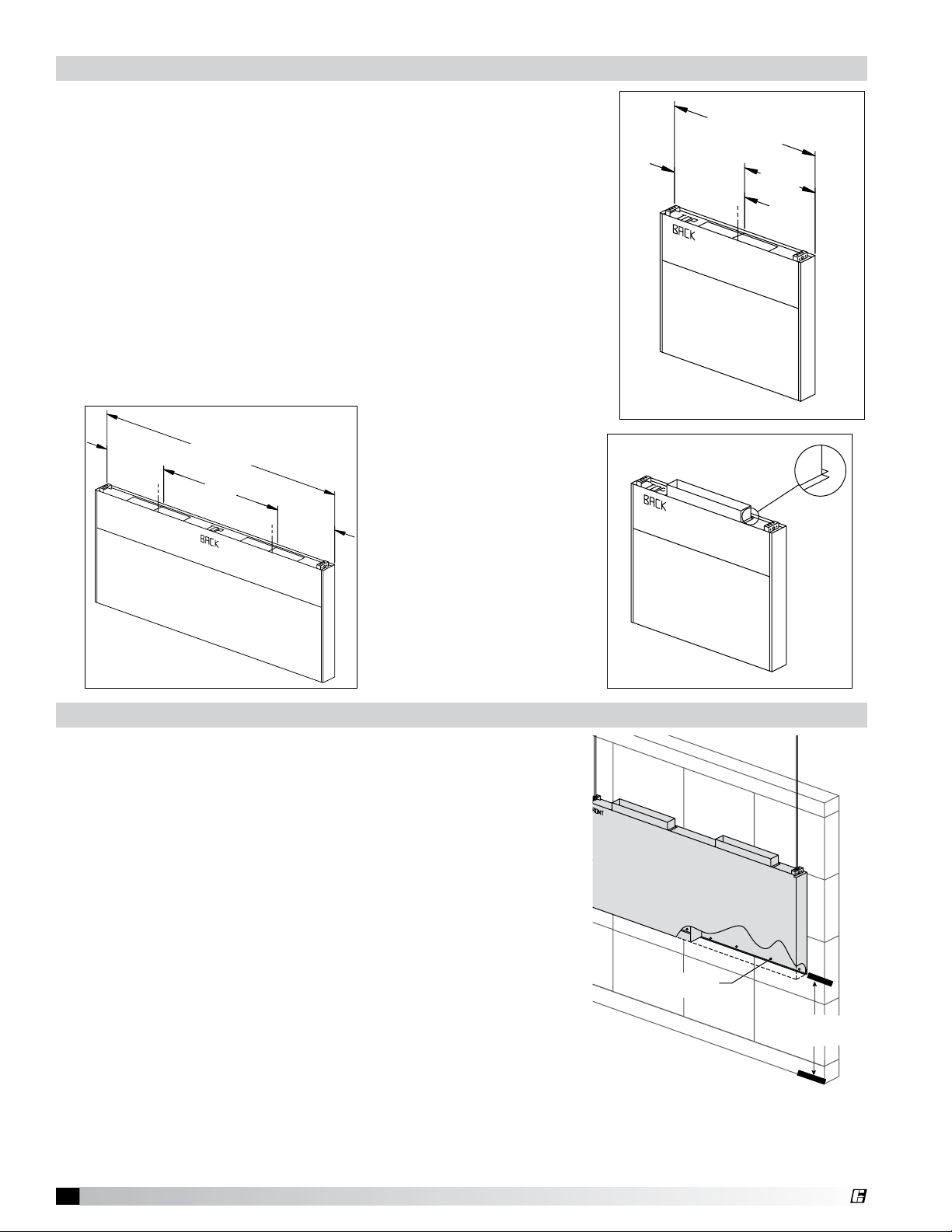
®
FASTENERS HOLDING THE
BACK SUPPLY TO THE WALL
32 in. (813 mm)
CRITICAL
DIMENSION
HANGER BRACKET
DETAIL
0.500 in. THREADED ROD
0.500 in. THREADED NUTS
(FURNISHED BY OTHERS)
FURNISHED BY
OTHERS
STEP 2
L (MODULE WIDTH)
L/2
L/4
L/2
STEP 1
(IF MODULE > 6 ft.)
4 in. TO 6 in.
FASTEN WITH SCREWS, OR TACK WELDS EVERY
PLACE THE DUCT COLLAR OVER THE OPENING,
STEP 2
L (MODULE WIDTH)
L/2
L/2
L/2
L (MODULE WIDTH)
L/4
L/2
STEP 1
(IF MODULE > 6 ft.)
(IF MODULE < 6 ft.)
STEP 1
4 in. TO 6 in.
FASTEN WITH SCREWS, OR TACK WELDS EVERY
PLACE THE DUCT COLLAR OVER THE OPENING,
STEP 2
Installing the Back Supply Plenum
Installing the Supply Duct Collar
1. Find the center of the Back Supply Plenum.
2. If the Back Supply Plenum is less than 9 ft. 10 in. (299.72 cm) long,
cut opening at the suggested location, centering the opening over
the center of the Back Supply Plenum. (Fig. 9)
3. If the Back Supply Plenum is greater than 9 ft. 10 in. (299.72 cm)
long, divide the length of the back supply by four. This will give you
the center of each half. Cut openings at the suggested location,
centering the duct collar over the center measurement of each
half. (Fig. 10)
4. Place the duct collar(s) over the opening, fastening with screws or
tack-welds every 4 to 6 in. (10.16 to 15.24 cm). (Fig. 11)
• The 4 in. (10.16 cm)
high duct collar is to be
attached to the back
supply.
Fig. 9
Fig. 10
Hanging the Back Supply Plenum
5. Hang the Back Supply Plenum from the ceiling.
The Back Supply Plenum needs to be mounted 31.25 in.
(79.375 cm) above the finished floor. This is measured
from the lowest rear edge of the Back Supply Plenum to
the finished floor.
6. Fasten the Back Supply to the wall, going through the
lower Back Supply wall. (Fig. 12)
• These fasteners are to help maintain the location of
the Back Supply and are not intended to hold the
weight of the Back Supply Unit.
• The fasteners should not interfere with the removable
air diffusers.
Fig. 11
Fig. 12
Proximity Hood
8
Page 9
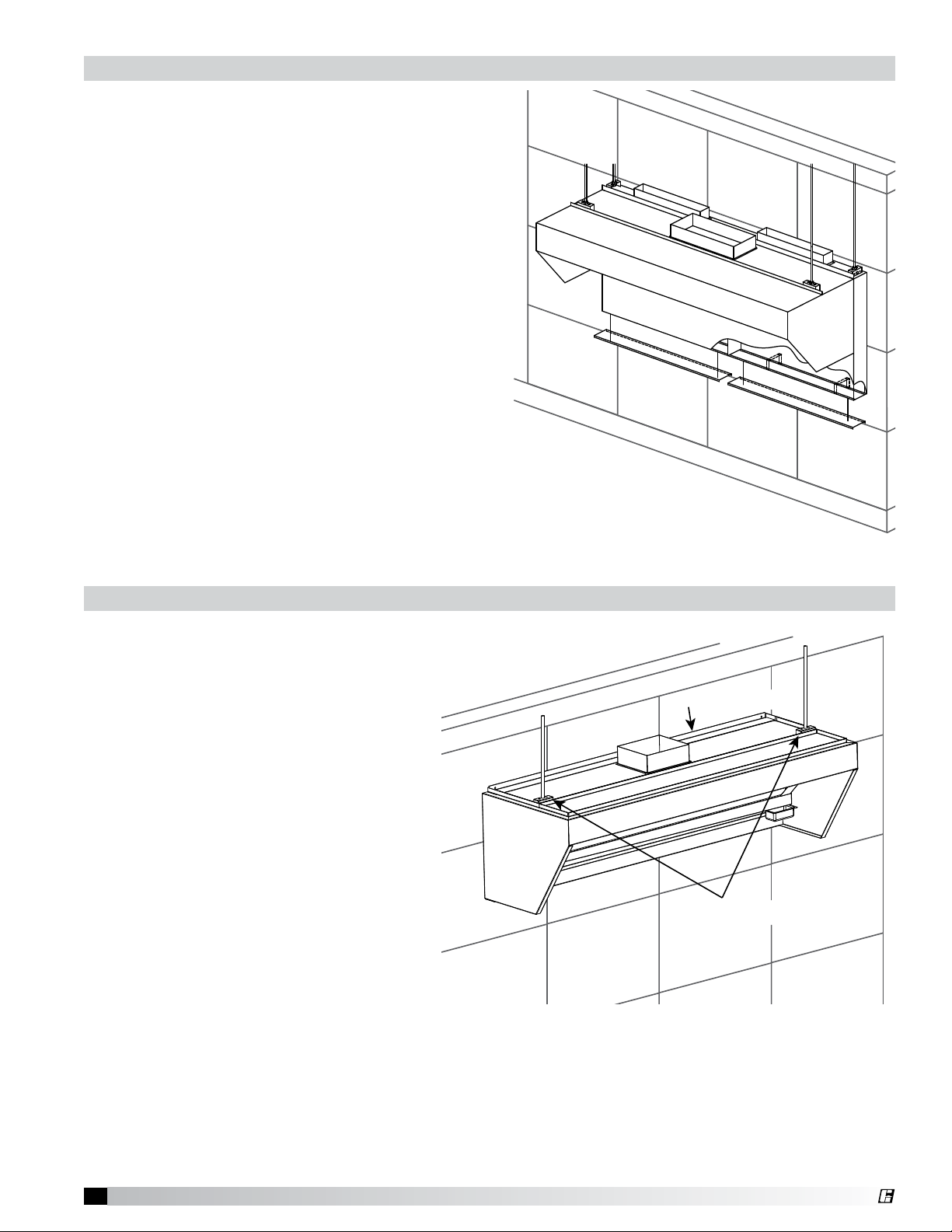
®
Hanging the Hood with Back Supply Plenum
Hanger Brackets
Mounting Flange
Before hanging the hood according to the hood
installation instructions, please check the following:
1. Make sure the back supply unit is properly
secured, as described in steps 5 and 6, page 8.
2. Any filler panels should be attached to the hood
before the hood installation.
To hang the hood:
1. Lift the hood and position it so the top of the
hood is even with the back supply (Fig. 13). This
height should correspond to the UL hanging
height of the hood.
2. After the hood is hung from the ceiling, a hood
mounting flange may be fastened to the back
supply using sheet metal screws (by others).
Pilot holes are recommended.
3. Connect the remaining ductwork for the back
supply and the hood. Caulk all mating seams
and surfaces of the back supply, the hood, and
the wall.
Fig. 13
Hood Mounting Instructions
Fig. 14 shows the locations where the
hood must be fastened. If a Back Supply
Plenum is part of the hood system,
please see pages 8-9, Back Supply
Plenum/Hood Installation.
To hang the hood:
1) Locate the studs in the wall.
2) Drill 1/2 in. (13 mm) diameter holes in
the hood mouting flange. Be sure to
align to wall studs.
3) Lift hood into a level position and
lag bolt hood to wall (fasteners by
others).
4) Bolt 1/2 in. (13 mm) threaded rod into
the hanger brackets.
5) Fasten threaded rod to ceiling
supports then level the hood.
Fig. 14
Note: The installation of the hoods shall be in accordance with NFPA 96 (latest edition), Standard for
Ventilation Control and Fire Protection of Commercial Cooking Operations.
Proximity Hood
9
Page 10
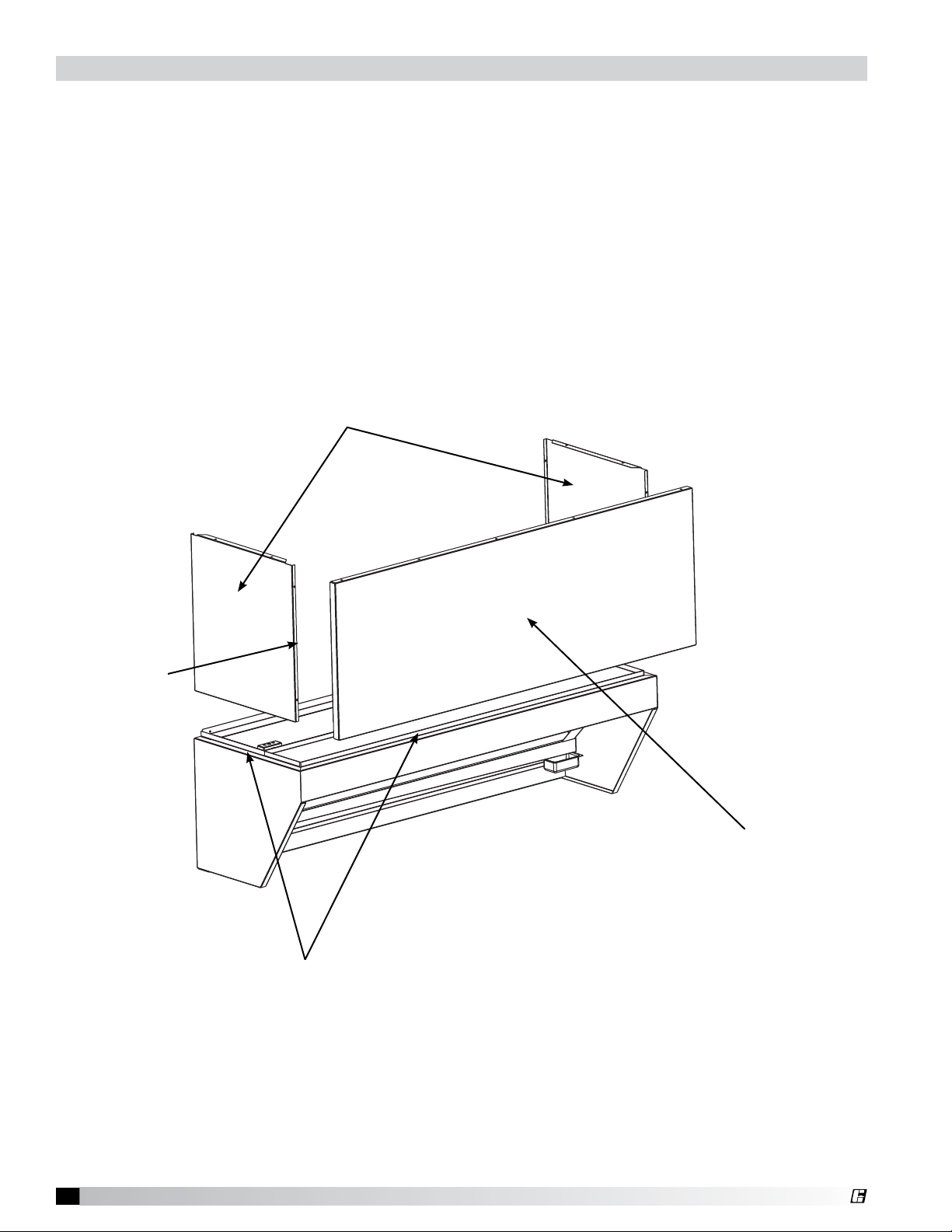
®
Full Enclosure Panels
Before installing the enclosure panels, make sure the hood is hung in position with all the ductwork
attached and fire system connections completed.
1. Tack-weld or clamp end enclosure panels onto standing seam (clamps provided).
2. Attach the end enclosure panels to the wall (fasteners by others).
3. Position the front enclosure panel(s) on the hood and bolt to the end enclosure panels with the
5/16 in. bolts provided.
4. Tack-weld or clamp the front enclosure panel(s) to the standing seam. If clamps are used, they
must be positioned 4 in. (100 mm) from the ends and in the center of the front enclosure panel.
5. To allow for ease of cleaning, caulk the external seams with NSF Approved silicone caulk.
(GE SCS1009, or its equivalent). The caulk is not provided.
6. Installation instructions may not be applicable for concrete ceilings.
End Enclosures
Bolt Here
Standing Seams
Front Enclosure(s)
Fig. 15
Proximity Hood
10
Page 11
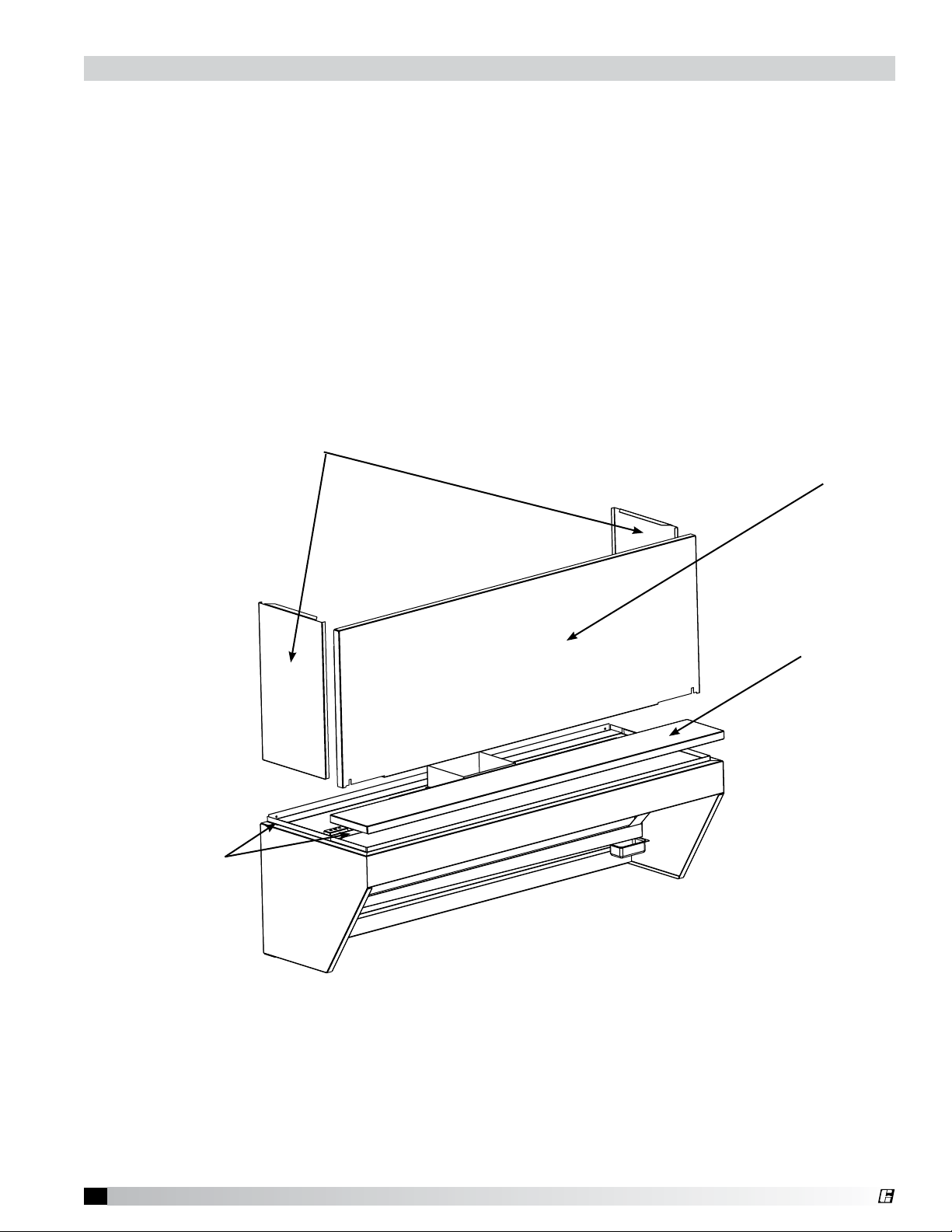
®
Plate Shelf with Duct Enclosure Panels
Before installing the enclosure panels, make sure the hood is hung in position with all the ductwork
attached and the fire system connections completed. Plate shelf will be factory mounted to hood
(shown loose).
1. Tack-weld or clamp end enclosure panels into place (clamps provided).
2. Attach the end enclosure panels to the wall (fasteners are not provided).
3. Position the front enclosure panel(s) on the hood and bolt to the end enclosure panels with the
5/16 in. bolts provided.
4. Tack-weld or clamp the front enclosure panel(s) to the hood. If clamps are used, they must be
positioned 4 in. (100 mm) from the ends and in the center of the front enclosure panel.
5. To allow for ease of cleaning, caulk the external seams with NSF Approved silicone caulk.
(GE SCS1009, or its equivalent). The caulk is not provided.
6. Installation instructions may not be applicable for concrete ceilings.
End Enclosures
Front Enclosure(s)
Standing Seams
Plate Shelf
Fig. 16
Proximity Hood
11
Page 12

®
Passover Shelf with Duct Enclosure Panels
Before installing the enclosure panels, make sure the hood is hung in position with all the ductwork
attached and fire system connections completed.
1. Attach mounting channels to the wall in the correct location.
2. Fasten end and front enclosure panels to Passover shelf with fasteners provided.
3. Bolt front and end enclosure panels together with the 5/16 in. bolts provided in the hardware
package.
4. Place enclosure assembly on hood top, tack-weld shelf to hood in rear corners.
5. Attach the end enclosure panels to mounting channels (fasteners provided).
6. To allow for ease of cleaning, caulk the external seams with NSF Approved silicone caulk.
(GE SCS1009, or its equivalent). The caulk is not provided.
7. Installation instructions may not be applicable for concrete ceilings.
End Enclosures
Mounting Channels
Front Enclosure
Passover Shelf
Fig. 17
Proximity Hood
12
Page 13

®
MATERIAL GAUGE — STAINLESS
FLAT BACKSPLASH PANEL
WALL
NOTE: PANELS UP TO 48 IN. (1219.2 MM) WIDE SHIP IN ONE PIECE; OVER 48 IN. (1219.2 MM) IN MULTIPLE PIECES.
HEIGHT
LENGTH
Backsplash Panel Installation Instructions
MATERIAL GAUGE — STAINLESS
MATERIAL GAUGE — STAINLESS
INSULATION — 1 IN. (25.4 MM)
FLAT BACKSPLASH PANEL
INSULATED BACKSPLASH PANEL
WALL
WALL
NOTE: PANELS UP TO 46 IN. (1168.4 MM) WIDE SHIP IN ONE PIECE; OVER 46 IN. (1168.4 MM) IN MULTIPLE PIECES.
NOTE: PANELS UP TO 48 IN. (1219.2 MM) WIDE SHIP IN ONE PIECE; OVER 48 IN. (1219.2 MM) IN MULTIPLE PIECES.
LENGTH
1 IN. (25.4 MM)
HEIGHT
LENGTH
HEIGHT
1. Layout backsplash panels
according to Fig. 18
Note offset in panel for overlap.
If the backsplash panel length
is greater than 46 in. (1168.4
mm), it will be shipped in
multiple pieces. Be sure offsets
match up to other panels.
LENGTH
Inches Millimeters
<= 48 <= 1219.2 1
>48<=94 >1219.2<=2387.6 2
>94<=141 >2387.6<=3581.4 3
>141<=188 >3581.4<=4775.2 4
>188<=235 >4775.2<=5969 5
QTY
2. Insulated Panels extend
1 inch from the wall
(Fig. 19). Bottom edge of
hood must mount tight to
top of panel. Check hood
mounting height before
panel installation.
3. After the backsplash
panel has been
positioned, drill holes
in the panel and fasten
Fig. 18
to the wall. (fasteners
provided by others).
4. Caulk the joints between
the hood and the
backsplash panel with
NSF Approved silicone
caulk. (GE SCS1009,
or its equivalent). The
caulk is not provided.
When multiple panels
are required, caulk
the joint between the
LENGTH
Inches Millimeters
<= 46 <= 1168.4 1
>46<=91 >1168.4<=2311.4 2
>91<=136 >2311.4<=3454.4 3
>136<=181 >3454.4<=4597.4 4
>181<=226 >4597.4<=5740.4 5
QTY
backsplash panels with
NSF approved silicone
caulk (GE SCS1009, or its
equivalent). The caulk is
not provided.
Fig. 19
Proximity Hood
13
Page 14

®
FRONT OF HOOD
HANGER BRACKET
EXHAUST PLENUM
DUCT CUT OUT AREA
x
y
Duct Collar Installation
Exhaust Ducts
1. If the exhaust duct has been factory mounted, skip this section.
2. The exhaust duct must be located within the shaded region of Fig. 20. Note dimensions.
Dimension Y assumes a 3 in. (76.2 mm) integral airspace on the hood back. When no 3 in.
(76.2 mm) integral airspace is present, Y=0 in. (0 mm).
3. Cut out appropriate size hole to match the duct collar provided.
4. The exhaust duct connection is to be a continuous liquid-tight weld.
X= 12 in. (304.8 mm)
Fig. 20
Y= 3 in. (76.2 mm)
Supply Ducts
Proximity hoods do not have integral supply plenums. Reference External Supply Plenums (Page 7).
Fire System Installation
The final fire system hook-up must be completed at this time. Unobstructed access is required for the
fire system installer to make plumbing connections to various locations on the hood top. Do not install
any enclosures until the fire system installation is complete.
Proximity Hood
14
Page 15

®
Maximum Increase in Static Pressure for Exhaust Air Balancing Baffle
(Fully Closed)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500
Duct Velocity FPM
Increase in Collar Staitc Pressure
Exhaust Air Balancing Baffles (EABB)
This is a guide to assist in determining if multiple hoods on one fan can be balanced to have equal
static pressure. For multiple hoods on one fan to achieve their designed exhaust flow, all of the hoods
must have equal static pressure at their designed exhaust flow.
The laws of physics force the static pressure for each branch of a duct system on one fan to always be
equal. This will happen by the flow rate increasing in low static branches and decreasing in high static
branches until the static pressure is equal in all branches.
Checking for Balance
Every hood with Exhaust Air Balancing Baffles (EABB) has a range for its static pressure. The low
number in this range is given by the standard calculation for hood static. (Static that is printed with
the CAPS submittal). The maximum increase above the low number can be calculated from the duct
velocity at the low static, (also given on CAPS submittal). This is then added to the low number to get
the highest static pressure possible with an EABB.
The maximum potential increase in static is given in the graph, or can be calculated from:
Max. Increase = 0.00000036 x (Duct velocity)
2
After the range for each hood is calculated, it
should be compared to the hood with the highest
static pressure. If the highest hood falls inside of
the range, then the hoods can be balanced with
the EABB. If it is higher than the range, the hoods
cannot be balanced.
Example 1:
Hood 1: Ps = 0.58 in. wg
Duct Velocity = 1900 FPM
Hood 2: Ps = 0.44 in. wg.
Duct Velocity = 1800 FPM
Hood 2 has the lower Ps, at 1800 FPM the maximum increase in Ps is 1.17. The range for Hood 2 is
0.44 to 1.61. Hood 1 is less than 1.61 so these hoods can be balanced.
Example 2:
Hood 3: Ps = 2.00 in. wg
Duct Velocity = 2000 FPM
Hood 4: Ps = 0.44 in. wg
Duct Velocity = 1500 FPM
Hood 4 has the lower Ps, at 1500 FPM the maximum increase in Ps is .81. The range for Hood 4 is 0.44
to 1.25. Hood 3 is higher than 1.25 so these hoods cannot be balanced.
Note 1: For many systems, an EABB may not be needed on the hood that has the highest static pressure. The
exception to this is if the individual ductwork has uneven static pressures.
Note 2: When sizing the fan, use the static pressure from the highest hood and sum the CFM from all the hoods.
Proximity Hood
15
Page 16

®
x
x
x
x
x
Rotating Vane Anemometer
Airflow
2
H/4
H/2
H/4
H
Balancing the Kitchen Exhaust System
A. To determine the proper dining room air balance:
1. Refer to engineering drawings to determine total exhaust CFM from dining areas.
(Exhaust fans, heating and air conditioning units, restrooms, etc.)
2. Determine the total CFM of make-up air supplied to dining area.
3. Subtract #1 from #2 above. If the result is a negative number, a negative pressure is present
in the dining area. In this case, kitchen exhaust odors could be drawn from the kitchen to the
dining area. Therefore, exhaust or supply air should be adjusted to provide a slight positive
pressure in the dining area.
B. To determine proper kitchen air balance:
1. Refer to engineering drawings to determine total exhaust from the kitchen area.
(Exhaust hoods, dishwasher hoods, etc.)
2. Determine total CFM of make-up air supplied to kitchen area.
(Make-up air hoods, heating and air conditioning units, etc.)
3. Subtract #1 from #2 above. The result should be a negative number. If the result is a positive
number, a positive pressure is present in the kitchen area. Kitchen odors could be forced into
the dining area. Also, a positively balanced kitchen area can adversely affect the performance
of the exhaust hood.
Caution: According to NFPA 96, Ch. 8-3 Replacement Air: Replacement air quantity shall be adequate
to prevent negative pressures in the commercial cooking area(s) from exceeding 4.98 kPa (0.02 in.
water column).
Testing Hood Air Volume
Baffle Filter Style Hoods
A. Exhaust:
With all the filters in place, determine the
total hood exhaust volume with a rotating
vane anemometer as follows:
1. All cooking equipment should be on.
2. Measure the velocities
Velocity measurements should be
taken at five locations per filter. These
must be over a filter slot as in Fig. 21.
Fig. 21
Proximity Hood
16
Page 17

®
Measure the velocity of each location.
2 in.
Airflow
Rotating Vane Anemometer
255
(4663.44 m/h)
248
(4535.42 m/h)
256
(4681.73 m/h)
240
(4389.12 m/h)
250
(4572 m/h)
A digital 2.75 in. (70 mm) rotating
vane anemometer or equivalent
is suggested. The center of the
anemometer should be held 2 in.
(50 mm) from the face of the filters
as shown in Fig. 22. It is helpful
to make a bracket to keep the
anemometer at the 2 in. (50 mm)
distance and parallel to the filter.
Fig. 22
Both squareness and distance are
very important for accuracy.
Calculate the average velocity for the filter.
3. Determine the filter’s conversion factor from the table.
3
4. Calculate the filter’s volume in CFM (m
/hr) by multiplying the average velocity by the
conversion factor.
5. Calculate the hood’s volume by repeating the process for the remaining filters and summing the
individual filter volumes.
Nominal Filter Size (H x L)
Inches Millimeters
Imperial
Conversion Factor
Metric
Conversion Factor
16 x 16 400 x 400 1.63 .157
16 x 20 500 x 400 2.13 .198
20 x 16 400 x 500 1.90 .177
20 x 20 500 x 500 2.48 .230
Example: Exhaust Only Hood with three 20 x 16 Filters
Measured velocities in fpm for one 20 x 16 Filter
Average Velocity =
(Imperial)
(Metric)
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
255 + 250 + 256 + 248 + 240
=
5
4663 + 4572 + 4681 + 4535 + 4389
=
5
= 249.8 fpm
= 4568 m/hr
For a nominal filter size of 20 x 16, the conversion factor is 1.90 Imperial (.177 Metric)
Volume for one filter = Conversion Factor x Average Velocity
= 1.90 x 249.8 fpm = 474.6 cfm
= .177 x 4568 m/hr = 809 m3/hr
Total hood volume = (Filter 1 Volume) + (Filter 2 Volume) + (Filter 3 Volume)
Proximity Hood
17
= 474.6 + 455.4 + 470.1 = 1400.1 cfm
= 809 + 880 + 799 = 2488 m3/hr
Page 18

®
B. Supply (If Applicable):
Example for Perforated Face Supply
1. Hood set up
If the make-up air unit has a temperature control, it should be used to keep the supply air at the
desired room discharge air temperature.
2. Measure Velocities
Divide the perforated face panel into a grid of equal areas, each approximately 4 in. (100 mm)
square.
Measure the velocity at the center of each grid area. A digital 2.75 in. (70 mm) rotating vane
anemometer or equivalent is suggested. The center of the anemometer should be held tight to
the face of the panel, and parallel to the filter. Both squareness and distance are important for
accuracy. Calculate the average velocity of the panel.
3. Measure the length, height, and width of the perforated face panel.
4. Calculate the perforated face panel volume in CFM by using the following formula:
Volume = Avg. Velocity
Volume = Avg. Velocity
5. Calculate the system’s volume by repeating the process for the remaining panels and adding
the individual panel volumes together.
Length (in.) * Height (in.) * 0.005
*
Length (m) * Height (m) * 0.72
*
Filter Readings (fpm)
260 250 255 260 250 255 265
270 275 270 280 265 265 270
290 285 280 280 275 290 295
285 275 280 260 270 265 260
4755 4572 4663 4755 4572 4663 4846
4938 5029 4938 5121 4846 4846 4938
5304 5212 5121 5121 5029 5304 5395
5212 5029 5121 4755 4938 4846 4755
Filter Readings (m/hr)
Example: Face Supply Hood with three 28 in. (.711 m) Perforated Panels
Measured velocities in FPM for one perforated panel
Average Velocity =
(Imperial)
(Metric)
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
260 + 250 + … + 265 + 260
=
28
4755 + 4572 + … + 4846 + 4755
=
28
= 270.7 fpm
= 4951 m/hr
Measure Length and Height = 28 in. (.711 m) long perforated panels x 16 in. (.406 m) high
Volume for one panel =
Conversion
Factor
x
Average
Velocity
x Length x Height
= 0.005 x 270.7 fpm x 28 x 16 = 606.4 cfm
= 0.72 x 4951 m/hr x .711 x .406 = 1029 m3/hr
Total system volume = (Panel 1 Volume) + (Panel 2 Volume) + (Panel 3 Volume)
= 606.4 + 614.3 + 593.8 = 1814.5 cfm
= 1029 + 1044 + 1009 = 3082 m3/hr
Proximity Hood
18
Page 19

®
Testing Hood Air Volume
Baffle Filters Style Hoods with the Shortridge Meter
A. Exhaust
With all the filters in place, determine the total hood exhaust
volume with a shortridge meter as follows:
1. All cooking equipment should be on. If the hood has
internal short circuit make-up air, it should be turned off.
2. Measuring Velocities
• Set up the shortridge meter.
• For 20 in. (500 mm) wide filters, position the grid as
shown in Fig. 24 and 25. Average two measurements.
• For 16 in. (400 mm) wide filters position the grid as
shown in Fig. 26.
• Take velocity readings for each filter.
3. *Calculate each filter’s volumetric flow rate by summing
the flow rate of each individual filter in the hood.
4. *Calculate the total hood’s volumetric flow rate by
summing the flow rate of each individual filter in the hood.
*Note: For best accuracy multiply the velocity of each filter by its
conversion factor and sum the flow rates Averaging the velocity
measured for all filters may cause error.
Fig. 23
Nominal Filter Size (H x L)
Inches Millimeters
16 x 16 400 x 400 1.66 .154
16 x 20 400 x 500 2.10 .195
20 x 16 500 x 400 1.96 .182
20 x 20 500 x 500 2.40 .223
Imperial
Conversion Factor
Conversion Factor
Example: Measured velocities for 20 x 20 filter = 185 and 189 fpm
Average Velocity =
(Imperial)
(Metric)
Flow rate for one filter =
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
185 + 189
=
2
3383 + 3456
=
2
Conversion
Factor
= 187.0 fpm
=
3420 m/hr
Average
x
Velocity
= 2.40 x 187.0 fpm = 448.8 cfm
= .223 x 3420 m/hr = 763 m3/hr
Metric
Fig. 24
Fig. 25
14 in.
2.75 in.
17.25 in.
14 in.
2.75 in.
10 in.
6 in.
10 in.
Total hood flow rate =
(Filter 1
Flow Rate)
+ … +
(Filter X
Flow Rate)
10 in.
= 448.8 + 457.8 + 437.5 + 444.8 = 1788.9 cfm
= 763 + 778 + 743 + 756 = 3040 m3/hr
Proximity Hood
19
Fig. 26
Page 20

®
High Velocity Cartridge Filters
Rotating V ane
Anemometer
2 in.
1/4 Width
1/4 Width
1/2 Width
1/2 Height
Inlet Height
A. Exhaust
With all the filters in place, determine the total hood exhaust
volume with a rotating vane anemometer as follows:
1. All cooking equipment should be on. If the hood has
internal short circuit make-up air, it should be turned off.
2. Measuring Velocities
• Velocity measurement should be taken at three locations per filter.
These must be over the inlet opening as shown in Fig. 27.
• Measure the velocity of each location. A digital 2.75 in. (70 mm)
rotating vane anemometer or its equivalent is suggested. The center
of the anemometer should be held 2 in. (50 mm) from the face of
the filters as in Fig. 28. It is helpful to make brackets to keep the
anemometer at the 2 in. (50 mm) distance and parallel to the filter.
Both squareness and distance are important for accuracy.
3. Calculate the average slot velocity.
4. Calculate the CFM per linear foot by dividing the average velocity by a
conversion factor listed in the following table.
5. Calculate the hood’s exhaust volume by multiplying the CFM per linear
foot by the length of hood.
Fig. 27
Fig. 28
Cartridge Filter Size
16 in. (400 mm) high with 4 in. (100 mm) high inlet
20 in. (500 mm) high with 4 in. (100 mm) high inlet
16 in. (400 mm) high with 7 in. (120 mm) high inlet
20 in. (500 mm) high with 7 in. (120 mm) high inlet
Imperial
Conversion Factor
1.63 1/ft
2.15 1/ft
1.24 1/ft
1.58 1/ft
3
3
3
3
Metric
Conversion Factor
5.35 1/m
7.05 1/m
4.07 1/m
5.18 1/m
3
3
3
3
Example:
Measure the slot velocities in fpm for a 9 ft. (2.74 m) hood with four 20 x 20 in. (500 x 500 mm)
filters with standard opening, three readings per filter.
Filter Readings (fpm)
470 440 425
482 430 453
455 431 441
399 439 465
Filter Readings (m/hr)
8595 8047 7772
8815 7864 8284
8321 7882 8065
7297 8028 8504
Average slot velocity =
(Imperial)
(Metric)
CFM per linear foot =
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
5330
=
=
12
97474
12
= 444.2 fpm
= 8123 m/hr
Average Slot Velocity
Conversion Factor
444.2 fpm
=
=
2.15
8123 m/hr
7.05
= 206.6 cfm/linear foot
=
1152 m3/hr
Hood exhaust volume = CFM/linear foot (or m3/hr / m) x Hood Length
= 206.6 x 9 ft. = 1859.4 cfm
= 1152 x 2.74 m = 3156 m3/hr
Proximity Hood
20
Page 21

®
High Velocity Cartridge Filters
A. Exhaust
With all the filters in place, determine the total hood exhaust
volume with a shortridge meter as follows:
1. All cooking equipment should be on. If the hood has
internal short circuit make-up air, it should be turned off.
2. Measuring Velocities
• Set up the shortridge meter. Leave all holes of
Velgrid open. Do NOT tape over holes that are not
over openings. The conversion factor takes this into
account.
• Position the grid over each filter as shown.
• Take velocity readings for each filter.
3. *Calculate each filter’s volumetric flow rate by summing
the flow rate of each individual filter in the hood.
4. *Calculate the total hood’s volumetric flow rate by
summing the flow rate of each individual filter in the hood.
*Note: For best accuracy multiply the velocity of each filter by
its conversion factor and sum the flow rates. Averaging the velocity
measured for all filters may cause error.
Fig. 29
Nominal Filter Size (H x L)
Inches Millimeters
16 x 16 400 x 400
16 x 20 400 x 500
20 x 16 500 x 400
20 x 20 500 x 500
Imperial
Conversion Factor
2
1.22 ft
2
1.67 ft
2
1.21 ft
2
1.50 ft
Metric
Conversion Factor
.113 m
.155 m
.112 m
.139 m
2
2
2
2
Example: Measured velocities for 20 x 20 filter = 282 fpm (5157 m/hr)
Flow rate for one filter =
(Imperial)
(Metric)
Conversion
Factor
= 1.50 x 282 fpm = 423.0 cfm
= .139 x 5157 m/hr = 717 m3/hr
x
Average
Velocity
Total hood flow rate = (Filter 1 Flow Rate) + … + (Filter X Flow Rate)
= 423.0 + 421.8 + 420.7 + 418.2 = 1683.7 cfm
= 717 + 717 + 715 + 711 = 2860 m3/hr
1/2 width
1/2 height
Fig. 30
Proximity Hood
21
Page 22

®
2 in.
Rotating Vane
Anemometer
Grease-X-Tractor™ High Efficiency Filters or Grease Grabber™ Multi-Filtration System
2 in.
Rotating Vane
Anemometer
1/2 Width
1/4 Width
1/4 Width
1/2 Height
A. Exhaust
With all the filters in place, determine the total hood exhaust
volume with a rotating vane anemometer as follows:
1. All cooking equipment should be off. If the hood has internal
short circuit make-up air, it should be turned off.
2. Measuring Velocities
• Measurement should be taken at six locations per filter.
They must be over the inlet opening as shown in Fig. 31.
• Measure the velocity of each location. A digital 2.75 in.
(70 mm) rotating vane anemometer or its equivalent is
suggested. The center of the anemometer should be held
2 in. (50 mm) from the face of the filters as in Fig. 32. It is helpful to make brackets to keep the
anemometer at the 2 in. (50 mm) distance and parallel to the filter. Both squareness and distance
are important for accuracy.
3. Calculate the average velocity for the filter.
4. Determine the filter’s conversion factor from the table.
5. Calculate each filters volume in CFM by multiplying the average velocity
by the conversion factor.
Fig. 31
Example: (Imperial)
Hood Length = 7 feet 0 inches with four 20 x 20 filters.
Measure the velocities in fpm for each 20 x 20 filter
(six readings per filter)
Average slot velocity for Filter 1 =
(repeat for each filter)
For a nominal filter size of 20 x 20, the conversion factor is 1.65
Volume for Filter 1 = Conversion Factor x Average Velocity
Total hood volume
=
= 346.0 + 377.6 + 386.9 + 378.1 = 1488.6 cfm
Nominal Filter Size (H x L)
Inches Millimeters
16 x 16 400 x 400
16 x 20 400 x 500
20 x 16 500 x 400
20 x 20 500 x 500
Filter 1
Filter 2
Filter 3
Filter 4
Filter 1
Volume
+
225 201 187
210 238 197
228 222 226
237 240 220
230 245 240
250 223 219
225 265 219
245 221 200
= 1.65 ft
= 346.0 cfm (repeat for each filter)
Filter 2
Volume
+
Volume
Filter 3
+
Conversion Factor
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
1258
=
2
Filter 4
Volume
= 209.7 fpm
6
x 209.7 ft./min.
Imperial
1.31 ft
1.65 ft
1.23 ft
1.65 ft
Metric
Conversion Factor
2
2
2
2
Example: (Metric)
Hood Length = 2.13 meters, with four 500 x 500 mm filters.
Measure the velocities in m/hr for each 500 x 500 mm filter
(six readings per filter)
Filter 1
Filter 2
Filter 3
Filter 4
Average slot velocity for Filter 1 =
(repeat for each filter)
For a nominal filter size of 500 x 500, the conversion factor is .153
Volume for Filter 1 = Conversion Factor x Average Velocity
.122 m
.153 m
.114 m
.153 m
Total hood volume
Filter 1
=
Volume
= 587 + 642 + 657 + 642 = 2528 m3/hr
Filter 2
+
Volume
2
2
2
2
4114.80 3675.88 3419.86
3840.48 4352.54 3602.74
4169.66 4059.94 4133.08
4334.26 4389.21 4023.36
4420.12 4480.56 4389.12
4572.00 4078.22 4005.07
4114.80 4846.52 4005.07
4480.56 4041.65 3657.60
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
23006
=
6
+
Volume
2
Filter 4
x 3834 m/hr
= .153 m
= 586.7 m3/hr (repeat for each filter)
Filter 3
+
Volume
= 3834 m/hr
Fig. 32
Proximity Hood
22
Page 23

®
Grease-X-Tractor™ High Efficiency Filters or Grease Grabber™ Multi-Filtration System
A. Exhaust
With all the filters in place, determine the total hood exhaust
volume with a shortridge meter as follows:
1. All cooking equipment should be on. If the hood has
internal short circuit make-up air, it should be turned off.
2. Measuring Velocities
• Set up the shortridge meter. Leave all holes of
Velgrid open. Do NOT tape over holes that are not
over openings. The conversion factor takes this into
account.
• For 20 in. (500 mm) high filters, position the grid
as shown in Fig. 34 and 35. Average the two
measurements.
• For 16 in. (400 mm) high filters position the grid as
shown in Fig. 36.
• For 20 in. (500 mm) wide filters, position the grid over
the left and right side of the filter. Average the two
measurements.
• Take velocity readings for each filter.
3. *Calculate each filter’s volumetric flow rate by summing the
flow rate of each individual filter in the hood.
4. *Calculate the total hood’s volumetric flow rate by summing
the flow rate of each individual filter in the hood.
*Note: For best accuracy multiply the velocity of each filter by its
conversion factor and sum the flow rates. Averaging the velocity
measured for all filters may cause error.
Fig. 33
Nominal Filter Size (H x L)
Inches Millimeters
16 x 16 400 x 400
16 x 20 400 x 500
20 x 16 500 x 400
20 x 20 500 x 500
Example:
Measured velocities for 20 x 20 in. (500 x 500 mm) filter.
Average slot velocity =
(Imperial) =
(Metric)
Flow rate for one filter = Conversion Factor x Average Velocity
= 3.0 x 201.5 fpm = 604.5 cfm
= .279 x 3385 m/hr = 944 m3/hr
Total hood flow rate =
Filter 1
Flow Rate
= 604.5 + 600.3 + 592.4 +
944 + 1020 1006 +
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
198 + 205
2
3021 + 3749
=
2
+ … +
Imperial
Conversion Factor
1.53 ft
2.00 ft
2.25 ft
3.00 ft
= 201.5 fpm
= 3385 m/hr
Filter X
Flow Rate
2
2
2
2
613.3 =
1042 =
Metric
Conversion Factor
.142 m
.185 m
.209 m
.279 m
2410.5 cfm
4012 m3/hr
2
2
2
2
Fig. 34
Fig. 35
Fig. 36
2.5 in.
3.25 in.
14.75 in.
14.25 in.
2.75 in.
14.25 in.
2.75 in.
2.75 in.
2.75 in.
Proximity Hood
23
Page 24

®
POWER SOURCE
MANUAL RESET RELAY
MICROSWITCH
MICROSWITCH
ELECTRIC GAS VALVE
INSTALLER PROVIDED JUNCTION BOXES
PRM
BASIC WIRING DIAGRAM
RED (COMMON)
POWER SOURCE
MANUAL RESET RELAY
YELLOW (N.O)
BLACK (N.C.)
GAS VALVE
MICROSWITCH
BASIC WIRING DIAGRAM
RED (COMMON)
MANUAL RESET RELAY
YELLOW (N.O)
BLACK (N.C.)
GAS VALVE
SEE NOTE 3
NOTE: DO NOT USE YELLOW WIRE ON MICROSWITCH IN NORMAL
INSTALLATION. THE YELLOW WIRE IS TO BE USED ONLY FOR
EXTINGUISHER ALARM, LIGHTS, CIRCUITS, ETC.
L1
L2
PUSHBUTTON SWITCH
120V/60HZ
K1
Ka
K1b
CURRENT DRAW MAX:
8A RESISTIVE
8A INDUCTIVE
120VAC
NOTES:
1. DENOTES FIELD INSTALLATION
2. DENOTES FACTORY INSTALLATION
3. GAS VALVE: UL LISTED ELECTRICALLY-OPERATED SAFETY VALVE FOR NATURAL OR LP GAS AS NEEDED OF
APPROPRIATE PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE RATING, 110V/60HZ OR AMEREX GAS VALVES, PN 12870, 12871,
12872, 12873, 12874, 12875 and 12876.
4. K1a and K1b ARE N.0. WHEN K1 IS DE-ENERGIZED.
Amerex Wiring Plan View
Fig. 37
Proximity Hood
24
Page 25

®
Field Wiring for the Ansul Snap-Action Switch
Option A
Relay Part No. 14702
* K1a and K1b are N.O. when K1 is de-energized
Manual Reset Relay
Part No. 14702
K1*
N.O.
K1a
K1b
N.O.
Push Button
Switch
Gas Valve
See Note 3
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
L1
110V/60HZ
Black
Red
Brown
L2
Snap-Action Switch
Part No. 423878
Option B
Relay Part No. 426151
Ansul Snap-Action Switch
(Switch contacts shown with Ansul
Automan in the cocked position)
Snap-Action Switch
Part No. 423878
Black
Red
Brown
L2 Neutral
L1 Hot
110 VAC/60HZ
5
4
3
2
1
GND
Screw
Power
Indicator
Reset
A B
Relay Coil
Manual Reset Relay
(Part No. 426151)
Electrical Rating
1/3 HP, 10 AMP, 120 VAC
1/2 HP, 10 AMP, 240 VAC
13 AMP, 28 VDC
Gas Valve
See Note 3
6
9
3
4
7
1
2 Snap-Action Switches provided by Greenheck
may be wired as shown.
Four typical examples shown
Power to cooking
equipment
Shunt Trip Breaker
120 VAC
N
Input
NO
NC
Electric gas valve - If reset relay is
used, see option A or B at right.
Mechanical gas shut off valve does not
require electrical connection.
NO
NC
NO
Input
NC
Voltage Free
Contacts for
Building Alarm(s)
Power to
Fan(s)
Fan
Starter
Terminal strip in
Waterwash Control Panel
NO
NC
3
4
5
6
NO
NC
120 VAC
N
Input
Power to
fan(s)
Fan Starter
Manual Switch
If prohibited by local codes, do not shut down
exhaust fans with this method of wiring.
Note:
1. Denotes field installation.
2. Denotes factory installation.
3. Gas Valves: “UL Listed electrically-operated safety valve for natural or LP gas
as needed of appropriate pressure and temperature rating, 110V/60HZ”
or Ansul gas valves.
4. Do not use black wire on snap-action switch in normal installation. Black
wire may only be used for extraneous alarm, light circuits, etc.
Equipment
Alarms
Waterwash
Fans
Ansul Wiring Plan View
Proximity Hood
25
Fig. 38
Page 26

®
HOOD-1BHOOD-1A
BASIC WIRING DIAGRAM (WIRING BY OTHERS)
FROM MAKE-UP AIR
STARTER #3
TO CUBE FAN
DISCONNECT SWITCH
WIRED THROUGH
BREATHER TUBE ONLY
FROM MAKE-UP AIR
STARTER #2
TO CUBE FAN
DISCONNECT SWITCH
WIRED THROUGH
BREATHER TUBE ONLY
EXHAUST FAN-1A
EXHAUST FAN-1B
POWER
PANEL
SUPPLY POWER TO
JUNCTION BOX
ON HOOD FOR HOOD LIGHTS
JUNCTION BOX ON
TOP OF HOOD FOR
FIELD CONNECTION
OF SUPPLY POWER
TWO (2) CONTROL WIRES FROM
ANSUL SNAP ACTION SWITCH TO
MOTOR CONTROLS AREA.
ELECTRICAL CONTRACTOR TO
PROVIDE HANDIBOX ON SIDE
OF AUTOMAN.
ANSUL AUTOMAN IS NOT AN
ELECTRICAL RATED BOX.
NO CONNECTIONS INSIDE.
FIVE (5) CONTROL WIRES
FROM SWITCH JUNCTION
BOX ON HOOD TO MAKE-UP
AIR CONTROL CENTER
CONTROL CENTER
MAKE-UP AIR UNIT
FIELD WIRING
SUPPLY POWER
TO MAKE-UP AIR
CONTROL CENTER
Overall Wiring Plan View
Fig. 39
Proximity Hood
26
Page 27

®
EXHAUST FAN CONTACT
SUPPLY FAN CONTACT
EXHAUST FAN CONTACT
SUPPLY FAN CONTACT
SEPARATE EXHAUST & SUPPLY SWITCHING
COMBINED EXHAUST & SUPPLY SWITCHING
THE SUPPLY FAN WILL BE TURNED OFF IF THE FIRE SYSTEM IS ACTIVATED, AND
ALLOW THE EXHAUST FAN TO CONTINUE TO OPERATE.
CONTROL PANEL TO A FIRE SUPPRESSION CONTACT (FSC1). WHEN WIRED PROPERLY,
THE DIAGRAM BELOW SHOWS HOW TO WIRE THE EXHAUST AND SUPPLY FANS WITH A
SUPPRESSION SYSTEM AND IS NORMALLY MOUNTED IN THE FIRE SYSTEM CONTROL BOX.
THE FIRE SUPPRESSION CONTACT (FSC1) IS PROVIDED AS PART OF THE FIRE
OL
OL
ON TOP OF HOOD
LIGHTS
SUPPLY POWER
HOOD
WHITE
JUNCTION BOX
FOR FIELD
CONNECTION OF
120 VOLT
FSC1
CONTROL
VOLTAGE
N
H
EXH
FAN
STR CTRLSTR
SUP
FAN HTR
SUP
OL
ON TOP OF HOOD
LIGHTS
HOOD
SUPPLY POWER
JUNCTION BOX
FOR FIELD
CONNECTION OF
120 VOLT
FAN
SUP
STR
CONTROL
115VOLT
N
H
STR
FAN
EXH
CTRL
SUP
HTR
SUP FAN
OPTIONAL
OL
FSC1
LIGHT
SWITCH
EXHAUST & SUPPLY
SWITCH
HEATER
SWITCH
LIGHT
SWITCH
EXHAUST
SWITCH
SUPPLY
SWITCH
HEATER
SWITCH
HOOD SWITCH
PANEL DETAIL
THE DIAGRAMS BELOW SHOW A TYPICAL HOOD SWITCH PANEL REMOTE MOUNTED.
FOR HOOD MOUNTED SWITCHES REFER TO THE WIRING CONNECTION DECAL ON THE
COVER OF THE JUNCTION BOX ON THE HOOD TOP.
Wiring for Switch Panels
The diagrams below show a typical hood switch panel remote mounted. For hood mounted switches
refer to the wiring connection decal on the cover of the junction box on the hood top.
The diagram below shows how to wire the exhaust and supply fans with a control panel to a fire
suppression contact (FSC1). When wired properly, the suppy fan will be turned off if the fire system is
activated and allow the exhaust fan to continue to operate.
The fire suppression contact (FSC1) is provided as part of the fire suppression system and is normally
mounted in the fire system control box.
Fig. 40
Proximity Hood
27
Page 28

®
Maintenance
Daily Maintenance
1. Wipe grease from exposed metal surfaces on the hood interior using a clean, dry cloth.
2. Visually inspect the filters for grease accumulation. Wash as needed.
3. Remove grease cup, empty contents, and replace cup.
Weekly Maintenance
1. Remove the grease filters and wash in dishwasher or pot sink.
Note: Filters installed over heavy grease producing equipment may require more frequent cleaning.
2. Before replacing filters, clean the interior plenum surfaces of any residual grease accumulations.
Periodic Maintenance
Stainless steel hood exterior surfaces should be cleaned with a mild detergent and then polished with
a good grade stainless steel polish to preserve the original luster.
Note: Never use abrasive cleaners or chemicals on hood surfaces. Never use chlorine based cleaners
or iron wool pads to clean the hood. They may scratch or mar the material and promote corrosion.
Always rub with the grain of the stainless.
Proximity Hood
28
Page 29

®
Grease Grabber™ Multi-Stage Filtration System
For use in Model GG__ Canopy Hoods Only
Installation
Note: Never install the Second Stage filter in the front filter channel. The Second Stage filter
must be installed behind a UL Classified Grease-X-Tractor™ primary filter Model HE or GX.
1. Slide the top edge of the Second Stage filter into the top rear filter channel; Fig. 41.
2. Lifting the lower edge of the filter past the grease trough, continue to push the top of the filter into
the channel.
3. When the filter is even with the bottom rear filter channel, set the filter into the channel; Fig. 42.
4. Slide the filter to one end of the hood and repeat until all the filters are installed. Make sure the
filters are placed tightly together with no visible gaps.
5. Latch filters together by connecting hooks to handle on next filte; Fig. 43.
6. Install the Grease-X-Tractor™ primary filters in the same manner using the front filter channel.
Fig. 41 Fig. 42 Fig. 43
Proximity Hood
29
Page 30

®
Grease Grabber™ Filter Cleaning
Step 1 Remove the front
GX filters: (1A) Remove middle filters first, (1B) slide ends toward middle and remove.
GX Filters, first row of filters
1A 1B
GG Filters, second row of filters
1C
Step 2 Release the hooks that hold the filters together. Slide the top hook upward and the bottom hook downward until the
hook releases. Do this to all filters.
Slide
hooks
2A 2B
2C
Step 3 Remove the GG filters, starting in the middle of the hood: (3A) Grab the handles on either side and lift the filter up,
(3B) Pull the bottom of the filter toward yourself, (3C) Lower the filter out of the hood. Repeat this process for each
filter. The filters that are on the ends will have to be slid toward the middle and then lifted out.
Pull filter down
3C
Step 4
Slide
filter up
Frequent Maintenance:
Pull bottom of
filter towards yourself
3A 3B
Note: Required washing frequency is dependent on type of cooking and quantity of food cooked.
- Remove filters from hood and place each filter in a whirlpool sink or dishwasher.
- If using a whirlpool sink, cycle for 10 minutes. Use standard dishwash soap. (4A)
- If using a dishwasher, cycle it three times to ensure all grease is removed. (4B)
- If using standard sink, cover with hot water and degreaser and soak for two hours. Rinse after soaking.
Note: For hoods with large quantities of filters, it is acceptable to wash 3 to 4 filters each day, cycling all of the filters in three days.
Note: The beads will discolor. Standard cooking will turn the beads yellow in color. Open flame cooking will cause the beads to
blacken. Neither affects the performance of the filters.
Periodic Inspection:
- Each filter may be soaked in hot soapy water for two hours once a month prior to washing if grease build-up is found.
- Inspect the filters by holding it up to a light. Light shining through more than six holes in a group indicates filter
damage.
- For filter replacement, call 1-800-337-7400
4A 4B
Step 5 Replace GG filters in hood. Do Step 3 in reverse order. (3C, then 3B, then 3A)
Step 6 Latch filters together by connecting the hooks to the handle on the next filter. Slide hook on from the top and bottom
of the handle. Do not try to snap the hooks into place. Do Step 2 in reverse.
Step 7 Replace the front GX filters. Do Step 1 in reverse. Be sure to install filters in the ends of the hood first, then install the
filters in the middle of the hood (1B, then 1A)
Caution: To prevent damage to filter media, do not wash second stage filters in detergents that contain
hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide.
Proximity Hood
30
Page 31

®
Filter Washing Frequency Guide
NOTE: Standard cooking will turn the beads yellow in color. Open flame cooking will cause the beads to
blacken. Neither affects the performance of the beads.
Caution: To prevent damage to filter media, do not wash second stage filters in detergents that contain
hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide.
Preference
1
Best
2
3
4
5
Washing Equipment
Type Temp
Commercial
Grade Dish
Washer
Low Temp.
Dish Washer
(Chemical
Sanitizer)
Power
Wash Sink
(Whirlpool)
with Heater
Power
Wash Sink
(Whirlpool)
no Heater
Pot Sink
with Heater
(rinse with
sprayer after
soaking)
180º F
Min
140º F
180º F
Min
140º F
180º F
Cooking
Equipment
Griddle
Fryer Weekly 2 Cycles
Charbroiler Daily 2 Cycles
Wok Daily 2 Cycles
Griddle
Fryer Weekly 3 Cycles
Charbroiler Daily 4 Cycles
Wok Daily 4 Cycles
Griddle
Fryer Weekly 10 Minutes
Charbroiler Daily 15 Minutes
Wok Daily 15 Minutes
Griddle
Fryer Weekly 15 Minutes
Charbroiler Daily 25 Minutes
Wok Daily 25 Minutes
Griddle
Fryer Every 2 days 1 Hour
Charbroiler Daily 2 Hours
Wok Daily 2 Hours
Chemical
Dish
Washer
Detergent
Dish
Washer
Detergent
Pot & Pan
Detergent
Pot & Pan
Detergent
Pot & Pan
Detergent
and/or
Degreaser
Frequency
Required
Every 3 days 2 Cycles
Every 3 days 3 Cycles
Every 3 days 10 Minutes
Every 3 days 15 Minutes
Every 2 days 1 Hour
Time
or
Cycles
Baffle Filter or
Grease-X-Tractor™
Wash Frequency
Every 3 days
2 Cycles
Twice a week
1 Cycle
Daily
2 Cycles
Daily
2 Cycles
Every 3 days
2 Cycles
Twice a week
2 Cycles
Daily
2 Cycles
Daily
2 Cycles
Every 3 days
5 minutes
Twice a week
5 minutes
Daily
5 minutes
Daily
5 minutes
Daily
5 minutes
Twice a week
5 minutes
Daily
10 minutes
Daily
10 minutes
Daily
Soak 10 min., then scrub with
scour pad and bottle brush
Daily
Soak 5 min., then scrub with
scour pad and bottle brush
Daily
Soak 10 min., then scrub with
scour pad and bottle brush
Griddle
Pot Sink
6
Worst
Proximity Hood
31
no Heater
(rinse with
sprayer after
soaking)
140º F
Fryer Every 2 days
Charbroiler Not Recommended
Wok Not Recommended
Commercial
Grade
Kitchen
Degreaser
Daily
2 Hours
Change hot water
every 30 minutes
2 Hours
Change hot water
every 30 minutes
Soak 10 minutes then scrub
Daily
with scour pad & bottle brush
Page 32

®
Troubleshooting
Problem: Exhaust fan is not operating or is not operating at design levels.
Is the fan receiving power? Replace fuses, reset circuit breakers, check disconnect.
Is the belt loose or broken? Replace or tighten belt.
Is the fan rotating in correct direction? Have the electrician correctly wire the fan.
Is the make-up air operating?
Does the airflow need to be increased? Adjust or replace pulleys to increase fan RPM, install a larger motor.
Does the fan vibrate?
Problem: Hood is full of smoke. There is smoke coming out of the edges of the hood.
Is the fan operating at design levels? See exhaust fan troubleshooting section.
Is the fan correctly sized?
Are the filters in good condition? Clean filters, replace damaged filters, properly position filters.
Is there sufficient make-up air?
(Kitchen should be in a slight negative
but not excessive. Check to see if there
is a strong draft through an open door).
Does the current cooking equipment
match the original design?
Are there multiple hoods on one fan?
Are there closed dampers in the duct? Open dampers.
Is the ductwork complex or to small? Change to a higher static fan, modify the ductwork.
Is the ductwork obstructed? Clear obstruction.
Is this a short circuit hood? Turn off or reduce the amount of air supplied to short circuit.
Problems with make-up air may interfere with the exhaust fan check the manufacturers installation manual.
Clean the fan wheel/blade, replace fan wheel if damaged, check for
loose bolts, check for broken or damaged components, check for
rags and other foreign objects.
Refer to test and balance report, design specifications and fan
curves; have an electrician check the motor amperage; try removing
the filter temporarily to see if capture improves. (Make sure to
replace filter to prevent risk of fire!); switch to different filters with
lower static pressure.
Check make-up air unit, increase make-up air, make-up air should be
evenly distributed throughout the kitchen.
Adjust or replace fan to match the cooking equipment load.
One hood may be over exhausting and the other hood not drawing
enough. Restrict second hood to help problem hood.
Problem: Smoke blows away before reaching the bottom of the hood.
Are there cooling fans directed at the
hood or cooking equipment?
Are there ceiling diffusers directing air at
the hood?
Are there open windows or doors? Close windows and doors.
Are there cross drafts or other drafts in
the kitchen?
Is the hood near a main walkway?
Proximity Hood
32
Turn off or redirect fans.
Move diffusers to more neutral area or replace with a diffuser that
directs air away from the hood.
Find source of the draft and eliminate, add side skirts to hood (test
with cardboard – use stainless for permanent side skirts); increase
the amount of overhang on the spillage side; add a 6 in. lip around
the base of the hood (test with cardboard – use stainless for
permanent side skirts); make-up air should be spread out evenly
through the kitchen.
Add side skirts to hood (test with cardboard first); increase the
amount of overhang on spillage side.
Page 33

®
Troubleshooting
Problem: Smoke blows away before reaching the bottom of the hood.
Are there pass-thru windows near
the hood?
Adjust amount and locations of make-up air to eliminate drafts
through the pass-thru windows.
Is this an air curtain hood? Turn off or reduce the amount of make-up air.
Is the make-up air part of the hood
or an attached plenum?
Try turning off or reducing the amount of make-up air; block off
portions of the supply to direct air away from the problem area (test
with cardboard).
Problem: Pilot lights are being blown out or cooking equipment is being cooled by make-up air.
Try turning off or reducing the amount of make-up air; block off
Are there drafts from make-up air?
portions of the supply to direct air away from the problem area (test
with cardboard first); remove any obstructions in front of supply that
directs air toward cooking equipment.
Problem: Cold air can be felt by the cook at the hood.
Is this a short circuit hood? Turn off or reduce the amount of air supplied to short circuit.
Is this an air curtain hood?
Is the make-up air part of the hood
or an attached plenum?
Turn off or reduce the amount of air supplied to the air curtain; heat
the supply air.
Try turning off or reducing the amount of make-up air; heat the
supply air.
Problem: The kitchen gets hot.
Is the hood capturing?
Hood is not drawing enough air, see sections above on fan
performance and hood capture.
Is this an air curtain hood? Turn off or reduce the amount of air supplied to the air curtain.
Is the make-up air part of the hood
or an attached plenum?
Try turning off or reducing the amount of make-up air; cool the
supply air.
Problem: Cooking odors in the dining area.
Is the hood capturing?
Is there a draft through doors between
the kitchen and dining area?
Hood is not drawing enough air, see sections above on fan
performance and hood capture.
Decrease make-up air in the kitchen; increase exhaust air through
hood.
Problem: Grease is running off the hood.
Is there grease on top of the hood? Exhaust duct is not correctly welded.
Is the caulk missing or damaged? Clean problem area and re-caulk.
Is the grease cup inserted properly? Put grease cup back in place.
Problem: Hood is noisy.
Is the fan running in the correct direction? See exhaust fan troubleshooting section.
Are the filters in place? Replace missing filters.
Is the hood over exhausting? Slow down fan (see exhaust fan troubleshooting section)
Proximity Hood
33
Page 34

®
Before calling your manufacturers representative to report a problem, have the following
information available:
1. Review / summary of troubleshooting section in installation operation manual.
2. Hood model and serial number.
3. Current cooking equipment line-up.
4. Size of hood (length, width and height).
5. Island or wall configuration.
6. Multiple hoods on one fan.
7. Nature of spillage (one end; all around the edges).
8. Does the smoke make it to the hood?
9. Height hood is mounted above finished floor.
10. How make-up air is brought into the kitchen (hood, ceiling diffusers, separate plenum).
11. Is exhaust system controlled by a variable volume system?
12. Is the fan noisy?
REPLACEMENT PARTS
GREENHECK
PART NUMBER
457627 16X16 SS Baffle Filters
457629 16x20 SS Baffle Filters
851656 16x16 High Velocity Cartridge Filters
851657 16x20 High Velocity Cartridge Filters
851709 16x16 Grease-X-Tractor™ Filters
851710 16x20 Grease-X-Tractor™ Filters
852388 16x16 Grease Grabber™ Filters
852389 16x20 Grease Grabber™ Filters
850551 Lights Only
851776 Fans Only
851777 Lights and Fan (2 switches)
851778 Fan and Heat (2 switches)
851779 Exhaust and Supply Fan (2 switches)
851780 Light, Fan and Heat (3 switches)
851781 Light, Exhaust, Supply separate switch (3 switches)
851782 Exhaust, Supply, and Heat separate switch (3 switches)
851783 Light, Exhaust, Supply, Heat separate switch (4 switches)
851784 Fan and Temper (3 positions) (2 switches)
851510 Light, Fan and Temper (3 positions) (3 switches)
851511 Exhaust, Supply, and Temper (3 positions) (3 switches)
851512 Light, Exhaust, Supply and Temper (3 positions) (4 switches)
851618 Automatic Fire Damper Test Switch
451131 Grease Cup
470674 Replacement Filters Handles
FILTER DESCRIPTION
(HEIGHT x WIDTH x DEPTH)
Proximity Hood
34
Page 35

®
Maintenance Log
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Date __________________ Time _____________ AM/PM
Notes:___________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Proximity Hood
35
Page 36

®
Warranty
Greenheck warrants this equipment to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of one year from
the purchase date. Any units or parts which prove defective during the warranty period will be replaced at our option
when returned to our factory, transportation prepaid. Motors are warranted by the motor manufacturer for a period of
one year. Should motors furnished by Greenheck prove defective during this period, they should be returned to the
nearest authorized motor service station. Greenheck will not be responsible for any removal or installation costs.
As a result of our commitment to continuous improvement, Greenheck reserves the right to change specifications
without notice.
Contact Greenheck Fan Corporation:
Phone: (715) 359-6171 • Fax: (715) 355-2399 • E-mail: gfcinfo@greenheck.com • Website: www.greenheck.com
458294 • Proximity Hood, Rev. 3, March 2008 Copyright 2008 © Greenheck Fan Corp.
36
 Loading...
Loading...