Page 1
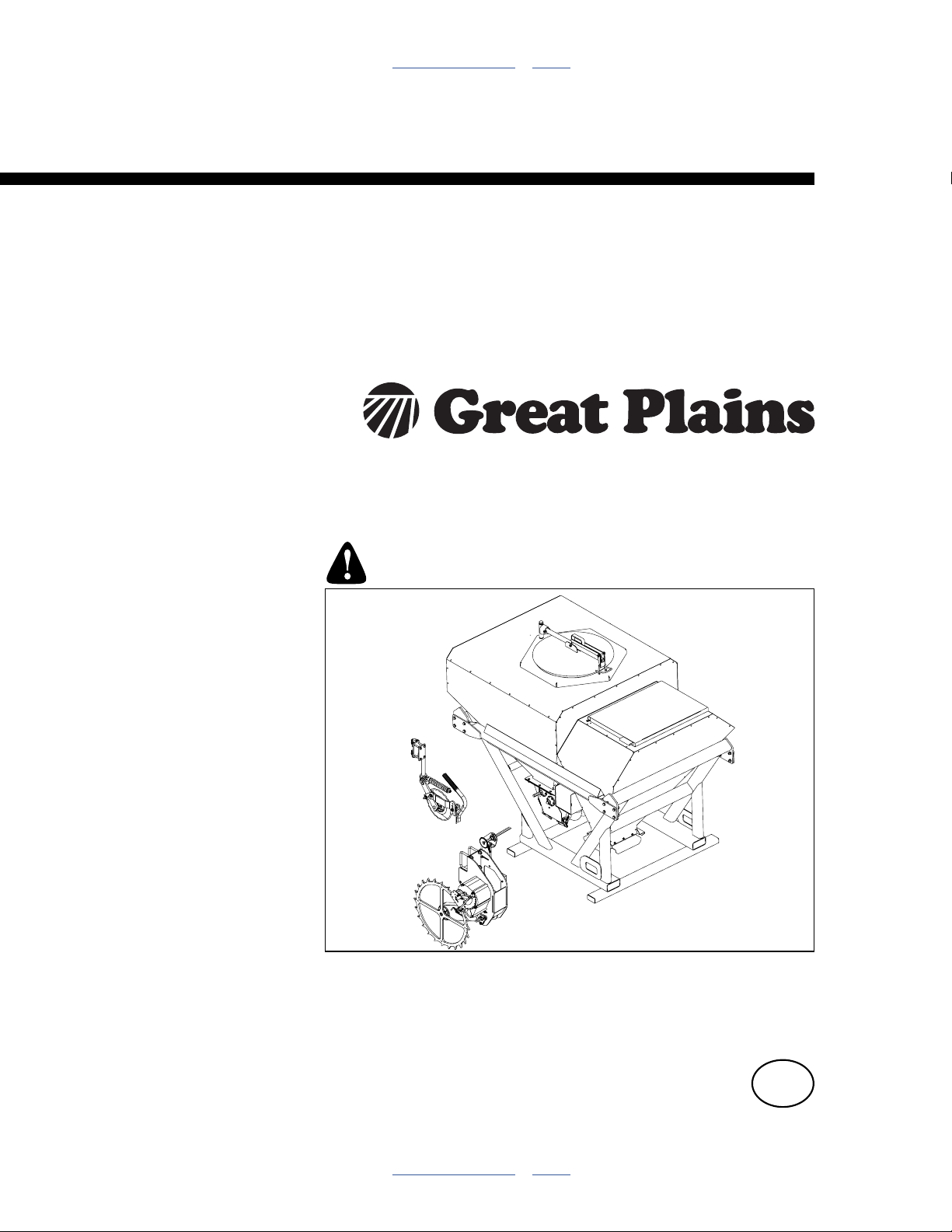
Table of Contents Index
Feature Supplement Manual
YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670
YP2425F and YP4025F Dry Fertilizer/Seeder
Manufacturing, Inc.
www.greatplainsmfg.com
Read the operator manual entirely. When you see this symbol, the
subsequent instructions and warnings are serious - follow without
exception. Your life and the lives of others depend on it!
31088
Illustrations may show optional equipment not supplied with standard unit or may
depict similar models where a topic is identical.
ORIGINAL INSTRUCTIONS
© Copyright 2013 Printed 2013-03-25 403-362M
Table of Contents Index
EN
Page 2

Table of Contents Index
Table of Contents Index
Page 3

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Cover Index iii
Table of Contents
Important Safety Information ......................................1
Safety Decals .................................................................4
Introduction ..................................................................6
Description of Unit ..........................................................6
Intended Usage ..........................................................6
Models Covered .............................................................6
Document Family........................................................7
Using This Manual..........................................................7
Definitions................................................................... 7
Preparation and Setup .................................................8
Initial Setup.....................................................................8
Post-Delivery/Seasonal Setup........................................8
Hitching and Leveling .....................................................8
Operating Instructions.................................................9
Pre-Start Checklist .........................................................9
Planter Folding and Raising ...........................................9
Transport ......................................................................10
Typical YP2425F Weights ........................................ 10
Typical YP4025F Weights ........................................ 10
Loading Materials .........................................................11
Loading Seed ...........................................................11
Loading Fertilizer......................................................12
Changing Seed Box or Hopper ....................................13
Air Systems Operation .................................................14
Seeding System Overview .......................................15
Fertilizer System Overview....................................... 17
Fan Circuit Operation ...........................................18
Fan General Operating Information......................19
Butterfly Valves.....................................................19
Butterfly Valve Operation:.....................................19
Symptoms of Insufficient Air Flow ........................19
Symptoms of Excessive Air Flow .........................19
Monitor Operation.........................................................20
Marker Operation .........................................................20
Field Set-Up Checklists ................................................21
Field Operation.............................................................21
Short-Term Parking ......................................................21
Long-Term Storage ......................................................21
Adjustments................................................................22
Setting Material Rates ..................................................23
Setting Seed Rate ....................................................23
Setting Dry Fertilizer Rate ........................................23
Seed Meter Final Drive Range ................................. 23
Setting Variable Rate Gearbox ................................ 24
Meter Calibration......................................................25
Revolutions for Sample Size ................................ 25
Calibration Procedure .......................................... 25
Initial Calibration Steps ........................................ 25
Row Sample Calibration....................................... 26
Meter Sample Calibration..................................... 27
Calibration Adjustment ............................................. 28
Calibration: Rate Calculation................................ 28
Calibration: Gearbox Adjustment .........................28
Coulter Adjustment ...................................................... 29
Coulter Height Adjustment ....................................... 29
Coulter Applicator Adjustment.................................. 29
Frame-Mounted Coulter Force................................. 30
Troubleshooting......................................................... 31
Maintenance ............................................................... 34
Maintenance ................................................................ 34
No-Change Maintenance Items ................................... 34
Material Clean-Out....................................................... 35
Seeding System Clean-Out...................................... 35
Fertilizer System Clean-Out ..................................... 35
Meter Flute Replacement......................................... 36
Problem Fertilizer Clean-Outs.................................. 36
Removing Meter Box............................................ 37
Hopper Entry ............................................................ 37
Chain Maintenance ...................................................... 39
Fertilizer Meter Drive Chain ..................................... 39
Maintenance Schedule ................................................ 40
Seed Lubricants ....................................................... 45
Options ....................................................................... 46
Compatible Options ..................................................... 46
Options Not Recommended......................................... 46
Incompatible Options ................................................... 46
Appendix A - Reference Information........................ 47
Specifications and Capacities YP4025F ...................... 47
Tire Inflation Chart ....................................................... 47
Specifications and Capacities YP2425F ...................... 48
Torque Values Chart.................................................... 49
Hydraulic Diagrams...................................................... 49
Chain Routing YP2425F .............................................. 50
Chain Routing YP4025F .............................................. 51
Appendix B - Monitor Setup...................................... 53
Seed Monitor Console Setup ....................................... 53
Pre-Programming Preparation: ................................ 53
© Copyright 2012, 2013 All rights Reserved
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. provides this publication “as is” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied. While every precaution has been
taken in the preparation of this manual, Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for
damages resulting from the use of the information contained herein. Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. reserves the right to revise and improve its products as
it sees fit. This publication describes the state of this product at the time of its publication, and may not reflect the product in the future.
2013-03-25 Cover Index 403-362M
Trademarks of Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. include: Singulator Plus, Swath Command, Terra-Tine.
Registered Trademarks of Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. include:
Air-Pro, Clear-Shot, Discovator, Great Plains, Land Pride, MeterCone, Nutri-Pro, Seed-Lok, Solid Stand,
Terra-Guard, Turbo-Chisel, Turbo-Chopper, Turbo Max, Turbo-Till, Ultra-Till, Ver ti-Till, Whirlfilter, Yield-Pro.
Brand and Product Names that appear and are owned by others are trademarks of their respective owners.
Printed in the United States of America
Page 4

iv YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Change User Level to Dealer Level ......................... 53
Auto Configuration ................................................... 54
To Run Auto Config:............................................. 54
Row Status/Row Width Setup.................................. 54
Material Configuration Setup
(Controlled Hydraulic Drive) ............................. 55
Planter Control Channel Setup ................................ 56
Valve Calibration...................................................... 57
Row Monitor Setup .................................................. 57
Speed Set Calibration Setup.................................... 58
Accessory Sensor Setup.......................................... 59
Hopper Assignment.............................................. 59
RPM Assignment ................................................. 59
Clutch Folding Module (CFM) Setup ........................60
Clutch Folding Module Operation .............................60
5 Revolution Test......................................................60
Summary Screen ......................................................61
Appendix C - Fertilizer Rate Charts ..........................62
Reading the Fertilizer Rate Chart .................................62
Fertilizer Rates .............................................................63
Fertilizer Rates, 70cm Row Spacing.........................64
Fertilizer Rates, 30 inch Row Spacing......................65
Density Adjustment.......................................................66
Index ............................................................................67
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 5

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index 1
Important Safety Information
Look for Safety Symbol
The SAFETY ALERT SYMBOL indicates there is a
potential hazard to personal safety involved and extra
safety precaution must be taken. When you see this
symbol, be alert and carefully read the message that
follows it. In addition to design and configuration of
equipment, hazard control and accident prevention are
dependent upon the awareness, concern, prudence and
proper training of personnel involved in the operation,
transport, maintenance and storage of equipment.
Be Aware of Signal Words
Signal words designate a degree or level of hazard
seriousness.
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
This signal word is limited to the most extreme situations,
typically for machine components that, for functional
purposes, cannot be guarded.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious
injury, and includes hazards that are exposed when
guards are removed. It may also be used to alert against
unsafe practices.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate
injury. It may also be used to alert against unsafe
practices.
Prepare for Emergencies
▲ Be prepared if a fire starts.
▲ Keep a first aid kit and fire extinguisher handy.
▲ Keep emergency numbers for doctor, ambulance, hospital
and fire department near phone.
Be Familiar with Safety Decals
▲ Read and understand “Safety Decals” on page 4,
thoroughly.
▲ Read all instructions noted on the decals.
▲ Keep decals clean. Replace damaged, faded and illegible
decals.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 6

2 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Wear Protective Equipment
Great Plains advises use of the following personal safety
equipment.
▲ Hearing protection, such as earmuffs or earplugs, for
making planter adjustments with the hydraulic fan
running.Prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause
hearing impairment or loss.
Avoid wearing entertainment headphones while operating
machinery. Operating equipment safely requires the full
attention of the operator.
▲ Face shield, goggles or full face respirator when handling
treated seed, seed lubricants or seed treatment.
▲ Gloves for working near sharp objects, and for handing
lubricants or treatments.
Handle Chemicals Properly
Agricultural chemicals can be dangerous. Improper use
can seriously injure persons, animals, plants, soil and
property.
▲ Read and follow chemical supplier instructions.
▲ Wear protective clothing.
▲ Handle all chemicals with care.
▲ Agricultural chemicals can be dangerous. Improper use can
seriously injure persons, animals, plants, soil and property.
▲ Inhaling smoke from any type of chemical fire is a serious
health hazard.
▲ Store or dispose of unused chemicals as specified by the
chemical manufacturer.
▲ If chemical is swallowed, carefully follow the chemical
manufacturer’s recommendations and consult with a doctor.
▲ If persons are exposed to a chemical in a way that could
affect their health, consult a doctor immediately with the
chemical label or container in hand. Any delay could cause
serious illness or death.
▲ Dispose of empty chemical containers properly. By law
rinsing of the used chemical container must be repeated
three times. Puncture the container to prevent future use. An
alternative is to jet-rinse or pressure rinse the container.
▲ Wash hands and face before eating after working with
chemicals. Shower as soon as application is completed for
the day.
▲ Apply only with acceptable wind conditions. Wind speed
must be below 8 kph (5 mph). Make sure wind drift of
chemicals will not affect any surrounding land, people or
animals.
▲ Never wash out a hopper within 30m (100 feet) of any
freshwater source or in a car wash.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 7
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Important Safety Information 3
Confined Space
With materials loaded, or once used for hazardous
fertilizers, or seeds with hazardous treatments, your
fertilizer hopper may become a
“permit-required confined space”
under applicable statutes, regulations, insurance rules or
business policy. The vent tube structure in the hopper
has features to assist escape, and is not for routine entry.
▲ A hopper that is full or merely appears full can be an
entrapment hazard. You can sink entirely into the material,
or into an oxygen-deficient void, and suffocate in a matter of
seconds. Fertilizer bridges and crusts are especially
dangerous.
▲ When hazardous fumes are present, you can be quickly
overcome even with the hopper lid open.
▲ Do not enter a hopper for material loading, material
unloading, hopper cleaning or meter maintenance.
▲ Clean hopper by power washing from outside hopper top.
▲ Perform meter maintenance by removing meter from bottom
of empty hopper.
▲ If obstruction removal or repair requires hopper entry, have
the work performed by a team trained in confined space
procedures. See “Hopper Entry” on page 37.
Practice Safe Maintenance
▲ Understand procedure before doing work. Use proper
tools and equipment. Refer to this manual for additional
information.
▲ Work in a clean, dry area.
▲ Lower the planter, put tractor in park, turn off engine, and
remove key before performing maintenance.
▲ Make sure all moving parts have stopped and all system
pressure is relieved.
▲ Allow planter to cool completely.
▲ Disconnect battery ground cable (-) before servicing or
adjusting electrical systems or before welding on planter.
▲ Inspect all parts. Make sure parts are in good condition
and installed properly.
▲ Remove buildup of grease, oil or debris.
▲ Remove all tools and unused parts from planter before
operation.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 8
4 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Safety At All Times
Thoroughly read and understand the instructions in this
manual before operation. Read all instructions noted on
the safety decals.
▲ Be familiar with all planter functions.
▲ Operate machinery from the driver’s seat only.
▲ Do not leave planter unattended with tractor engine
running.
▲ Do not stand between the tractor and planter during
hitching.
▲ Keep hands, feet and clothing away from power-driven
parts.
▲ Wear snug-fitting clothing to avoid entanglement with
moving parts.
▲ Watch out for wires, trees, etc., when folding and raising
planter. Make sure all persons are clear of working area.
Safety Reflectors and Decals
Your YP2425F and YP4025F Dry Fertilizer/Seeder
comes equipped with decals in place. They were
designed to help you safely operate your implement.
▲ Read and follow decal directions.
▲ Keep all safety decals clean and legible.
▲ Replace all damaged or missing decals. Order new decals
from your Great Plains dealer. Refer to this section for
proper decal placement.
▲ When ordering new parts or components, also request
corresponding safety decals.
To install new decals:
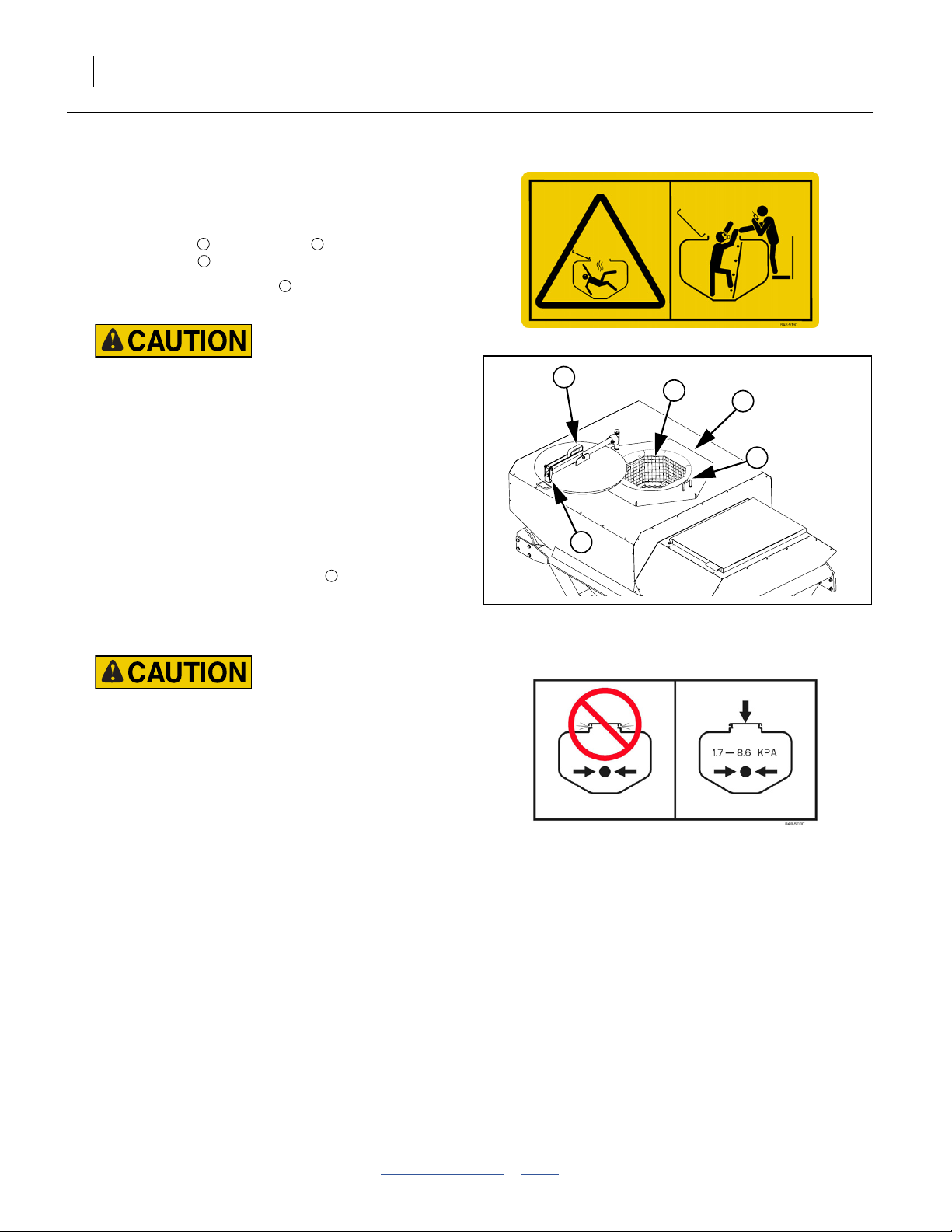
848-519C
Warning: Confined Space Hazard
On upper left facet of fertilizer hopper;
1 total
See page 12 and page 35 through page 37 for further
information.
Safety Decals
1. Clean the area on which the decal is to be placed.
2. Peel backing from decal. Press firmly on surface,
being careful not to cause air bubbles under decal.
Note: This page describes only the option decals. See
your planter Operator manual for additional
decals.
31165
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 9
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Important Safety Information 5
31165
848-509C Caution: Entanglement and Crushing
On left end of fertilizer air inlet manifold;
1 total
.eps
100%
848-510C Caution: Wear Eye Protection
On upper left facet of fertilizer and seed hoppers;
2 total
See page 11 for further information.
848-520C Caution: Possible Chemical Hazard
On upper left facet of fertilizer and seed hoppers;
2 total
See page 11 for further information.
31164
31165
848-522C Caution: Entanglement and Crushing
On right face of seed hopper near final range gears;
1 total
See page 23 for further information.
31166
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 10

6 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Introduction
This feature operator manual (403-362M) is a
supplement to your planter Operator manual (401-406M:
YP2425F) or (401-571M: YP4025F), and covers only the
additional information required to setup, operate and
maintain a YP24 or YP40 planter equipped with the dry
fertilizer/seeder.
Your planter relies on these material rate references:
Pages
62 to 66
Manual
401-406B
Manual
401-571B
Dry Fertilizer Rate
Only the fertilizer rates of this manual
(403-362M) apply to the YP2425F-2470,
YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670. Use of
the granular system for seeding is not
recommended.
YP2425 Seed Rate
Only the seed rates of manual 401-406B
usually apply to the YP2425F-2470.
Fertilizer rates in manual 401-406B apply
only if the YP24F is also equipped for liquid
fertilizer application.
YP4025 Seed Rate
Only the seed rates of manual 401-571B
usually apply to the YP4025-1670F or
YP4025F-1630. Fertilizer rates in manual
401-571B apply only if the YP40F is also
equipped for liquid fertilizer application.
5
2
3
4
Figure 1
YP2425 and YP4025 DF Seeder
1
6
U
F
L
R
B
D
31088
Description of Unit
Refer to Figure 1
The YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670
Planter is a dry fertilizer/seeder version of the YP2425 or
YP4025. The standard seed-only hopper or bulk-box
capability is replaced by a dual-function hopper (one for
the YP4025F and two for the YP2425F).
• The dry fertilizer function includes:
a 1440 liter (41 bu) hopper compartment with
1
integrated volumetric meter;
2
ground drive;
3
gear box; and,
4
frame-mounted fertilizer zone counters.
5
Fertilizer is applied whenever the planter is lowered
and in forward motion. Rate is controlled by range
gears and a crank adjuster on the gearbox.
• The seeder function is a:
670 liter (19 bu) compartment
6
that delivers seed to the standard YP24/YP40 airbox
and row unit seed meters (not shown).
Seed rate is controlled by the standard DICKEY-john
IntelliAg® seed monitor and hydraulic meter drive.
Intended Usage
Use the YP2425F and YP4025F Dry Fertilizer/Seeder
only to apply dry granular fertilizer and/or plant seeds
compatible with Singulator Plus®or finger pickup meters.
Do not modify the planter for use with attachments other
than Great Plains options and accessories specified for
use with the YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and
YP4025F-1670.
Models Covered
This feature operator manual (403-362M) applies only to
these specific planter models equipped with the dry
fertilizer/seeder features:
YP2425F-2470 25-Series, Dry Fertilizer, 24-row, 70cm
YP4025F-1630 25-Series, Dry Fertilizer, 16-row, 30in
YP4025F-1670 25-Series, Dry Fertilizer, 16-row, 70cm
®
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 11
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Introduction 7
Document Family
403-362M Feature Supplement Manual (this manual)
YP2425F:
401-406M Planter Operator Manual
401-406P Planter Parts Manual
401-406B Planter Seed Rate manual
YP4025F:
401-571M Planter Operator Manual
401-571P Planter Parts Manual
401-571B Planter Seed Rate manual
DICKEY-john® manuals:
110011508 Seed Monitor Manual Level 1
110011501 Seed Monitor Manual Level 2 and 3
Using This Manual
This manual will familiarize you with
safety, assembly, operation,
adjustments, troubleshooting, and
maintenance. Read this manual and
follow the recommendations to help
ensure safe and efficient operation.
The information in this manual is current at printing.
Some parts may change to assure top performance.
Definitions
The following terms are used throughout this manual.
A crucial point of information related to the preceding topic.
Read and follow the directions to remain safe, avoid serious
damage to equipment and ensure desired field results.
Note: Useful information related to the preceding topic.
Right-hand and left-hand as used in
this manual are determined by facing
the direction the machine will travel
while in use unless otherwise stated.
An orientation rose in some line art
illustrations shows the directions of:
Up, Back, Left, Down, Front, Right.
R
F
U
B
L
D
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 12

8 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Preparation and Setup
This section helps you prepare the dry fertilizer feature of
your YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670
planter for use, and covers tasks that need to be done
seasonally, or when the tractor/planter configuration
changes.
Before using the planter in the field, you must hitch it to a
suitable tractor, inspect systems and level the planter,
per the instructions in the 401-406M (YP2425) or
401-571M (YP4025) Operator manual. Before using the
planter for the first time, and periodically thereafter,
certain adjustments and calibrations are required. See
the Operator manual for these procedures.
Initial Setup
See the Operator manual, Appendix B, for pre-delivery
and first-time setup items for the basic planter.
First-time/infrequent setup tasks for the
YP24/YP40 DF/seeder feature include:
• Verify monitor setup (page 53 in this manual).
Post-Delivery/Seasonal Setup
On initial delivery, use with a new tractor, and seasonally,
check and as necessary, complete these items before
continuing to the routine setup items:
• Inspect fertilizer meter door seals for leaks or wear.
• Inspect fertilizer meter flutes for damage or wear.
Hitching and Leveling
The YP24/YP40 DF/seeder feature causes no changes
to the hitching procedures described in the planter
Operator manual.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 13
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index 9
Operating Instructions
This section covers general operating procedures.
Experience, machine familiarity, and the following
information will lead to efficient operation and good
working habits. Always operate farm machinery with
safety in mind.
Pre-Start Checklist
Perform the planter pre-start checklist, and the following
steps before transporting the YP24/YP40 DF/seeder
planter to the field. Add this item:
❑ Check for air system leaks at the fertilizer hopper lid,
meter, inlet and outlet manifolds.
Planter Folding and Raising
The YP24/YP40 DF/seeder feature does not affect
raising/lowering, folding/unfolding or tongue operations.
Material Loss Risk
The fertilizer ground drive operates whenever the planter is
lowered and in forward motion. If fertilizer application is not
desired (for example, during speed calibration or row unit
adjustment testing), take any of these steps to prevent fertilizer
metering:
▲ Tie ground drive wheel up out of ground contact.
▲ Remove a chain in the ground drive.
▲ Set meter gearbox adjuster to zero. Do this only on a
temporary basis, such as speed calibration.
▲ Defer loading of fertilizer until after speed calibration or
other non-application lowered movement.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 14
10 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Transport
Loss of Control Hazard:
Ensure that the towing vehicle is adequate for the task. Using
an inadequate tow vehicle is extremely unsafe, and can result
in loss of control, serious injury and death.
21
The planter can weigh over 15 000 kg (33,500 pounds),
depending on configuration and material load. The tractor
unit MUST be rated for the load. If the tractor is not rated for
at least 15 000 kg, calculate or obtain a scale weight of the
planter.
Do not tow if planter exceeds the load rating of the vehicle.
Braking and Loss of Control Hazard:
Do not exceed 20 mph (32 kph).
5
Reduction of Control Risk:
Material loaded prior to travel increases stopping distance,
and increases the need for caution in turns and braking.
Typical YP2425F Weights
Configuration YP2425-2470
Standard¹ Model, Empty
Std. Model, Full Hoppers 13000 kg
Maximum² Configuration, Full
¹ Includes: Markers and Frame-Mounted Coulters
² Adds: Unit-Mounted Coulters & Dual Row Cleaners
9200 kg
13900 kg
Typical YP4025F Weights
YP4025F-
Configuration -1670 -1630
Standard¹ Model, Empty
Std. Model, Full Hoppers 14700 kg 32300 lbs
Maximum² Configuration, Full
¹ Includes: Markers and Frame-Mounted Coulters
² Adds: Unit-Mounted Coulters & Dual Row Cleaners
Other than considerations of planter weight, the
YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670
requires no changes to transport compared to the
standard YP24/YP40. See the 401-406M or 401-571M
Operator manual for transport instructions.
12800 kg 28200 lbs
15200 kg 33500 lbs
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 15
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Operating Instructions 11
Loading Materials
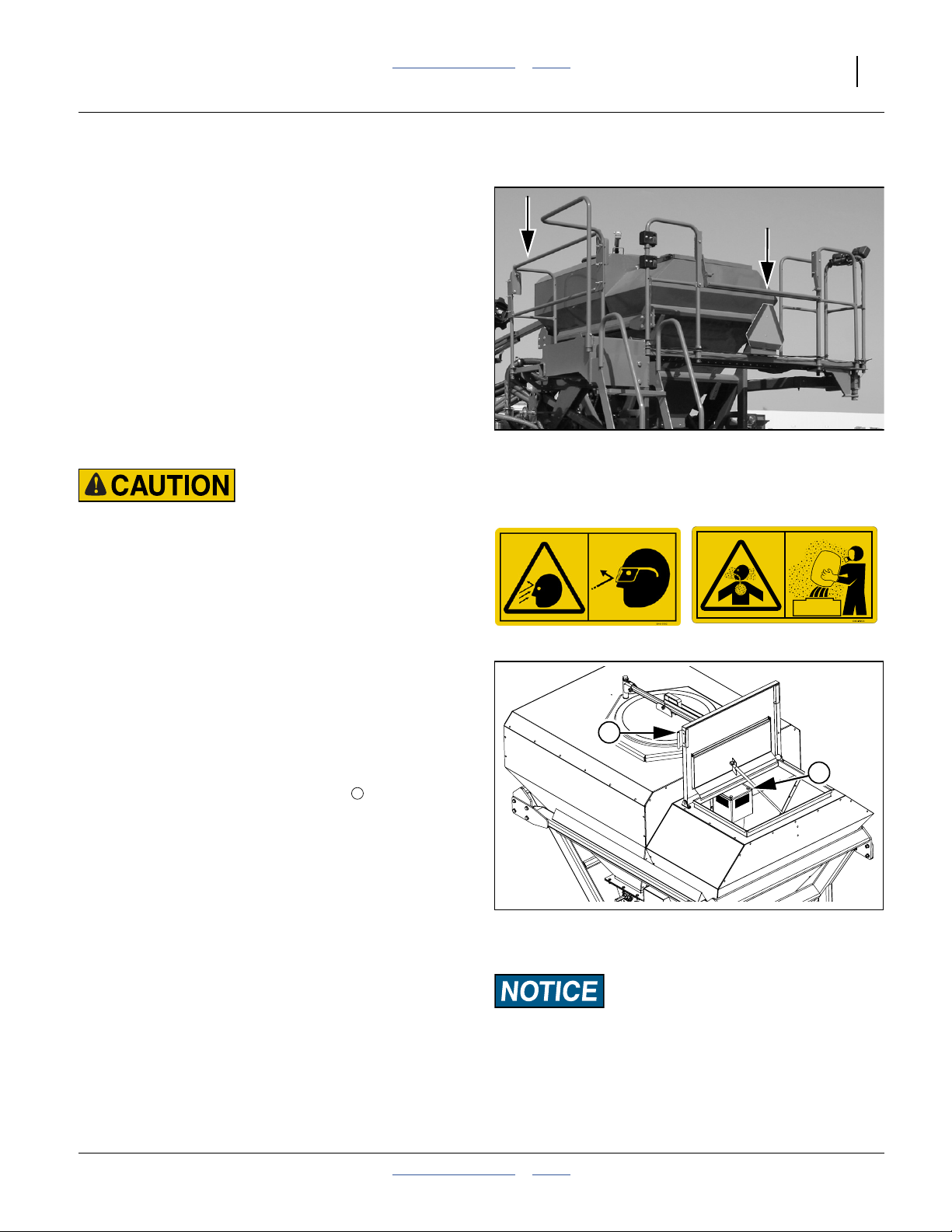
Seed and fertilizer may be loaded manually or via auger.
Walkboard/ladder details, and auger height requirements
are shown in the Operator manual. Before ascending the
ladder for loading or auger outlet control:
• Check that the walkboard is closed and latched.
Although the YP40F walkboard has a side extension,
the latching is identical to the standard walkboard.
• Swing down and latch the lower ladder section.
Refer to Figure 2
(depicting the side railing closed, and rear railing open)
If loading via auger, the side and rear top railings may be
swung down for clearance.
• Shut off hydraulic fan. Both hopper bins are
pressurized when the fan is running.
Figure 2
Walkboard Railings
31092
Blowing Debris and Possible Chemical Hazards:
Do not open hopper lids with fan running. Hopper contents
may blow into your face, possibly causing eye injury, and
exposing you to dust and possible chemical hazards.
Dust and Possible Chemical Hazards:
Seed may present a dust inhalation hazard. Treated seed may
present a chemical exposure hazard. Wear eye protection.
Wear a dust mask or respirator. Wear other protective
equipment specified by the seed and treatment suppliers.
Loading Seed
The seed hopper is the smaller rear hopper.
1. Close the slide gate at the base of the seed hopper.
Refer to Figure 3
2. To open the lid, lift up on the handle . The handle is
also a spring-loaded latch, and tilts up to release.
3. Inspect the hopper for leftover seed and debris.
Clean out anything other than the seed to be
planted. See “Material Clean-Out” on page 35
4. At first use, and seasonally, add seed lubricant to the
empty hopper, and then add a seed/lubricant mix to
the empty hopper per the Operator manual. Mix
lubricant with remaining seed per Operator manual.
5. See Caution at right. Load seed and seed lubricant
no higher than the top cap of the vent structure.
6. Close lid. Check that the latch snaps to horizontal
and is holding lid closed.
7. Swing up and latch railing if lowered for auger
operations.
1
1
Figure 3
Seed Hopper Lid
Sudden Lid Motion:
Open rear (seed) lid carefully. It is supported by a
spring-loaded piston, and may swing up rapidly.
2
31091
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 16
12 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Loading Fertilizer
Check that calibration and clean-out doors are closed at
meter (page 35).
Refer to Figure 4
1. Lift the handle until the hook releases from the
U-bolt shackle .
2. Inspect the strainer basket for debris. Remove and
clean as necessary.
3 4
5
6
Confined Space Hazards:
Leave strainer in place for all routine operations. Do not
enter hopper for routine operations. Risk of entrapment
and rapid suffocation. See “Material Clean-Out” on
page 35 for further information.
3. Inspect the hopper for leftover fertilizer and debris.
Clean out anything other than the fertilizer to be
applied. See “Material Clean-Out” on page 35.
4. Re-install strainer.
5. Inspect the seal under the lid. It must make air-tight
seal against the hopper top plate when the lid is
closed and latched. Replace seal if crushed, worn or
missing.
6. Load fertilizer through strainer.
Dust and Possible Chemical Hazards:
Dry fertilizer may present a dust inhalation hazard and
may present a chemical exposure hazard. Wear eye
protection. Wear a dust mask or respirator. Wear any
other protective equipment specified by the material
supplier.
7
3
6
7
5
4
Figure 4
Fertilizer Hopper Lid
31090
7. Swing lid closed. Lift handle. Engage shackle with
hook. Close handle.
8. Swing up and latch railing if lowered for auger
operations.
Close lid handle for operations or short-term parking. For
long-term storage, do not engage hook or latch handle,
to avoid deforming the seal.
For storage, particularly unlatched, a padlock through
both U-bolts deters unauthorized entry by persons
unaware of possible confined space risks, and prevents
entry of pests, debris and precipitation.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 17

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Operating Instructions 13
Changing Seed Box or Hopper
This topic in the Operator manual does not generally
apply to the YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and
YP4025F-1670. Using a standard 82bu hopper requires
substantial disassembly of the planter seed cart
structure, and modifications to the air system. Using a
150bu hopper or dual 200 gallon liquid fertilizer system
further requires removal of the entire fertilizer ground
drive. Such conversions are not documented or
recommended.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 18
14 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Air Systems Operation
U
R
B
5
F
L
D
6
8
1
2
7
9
3
10
4
11
12
13
14
15
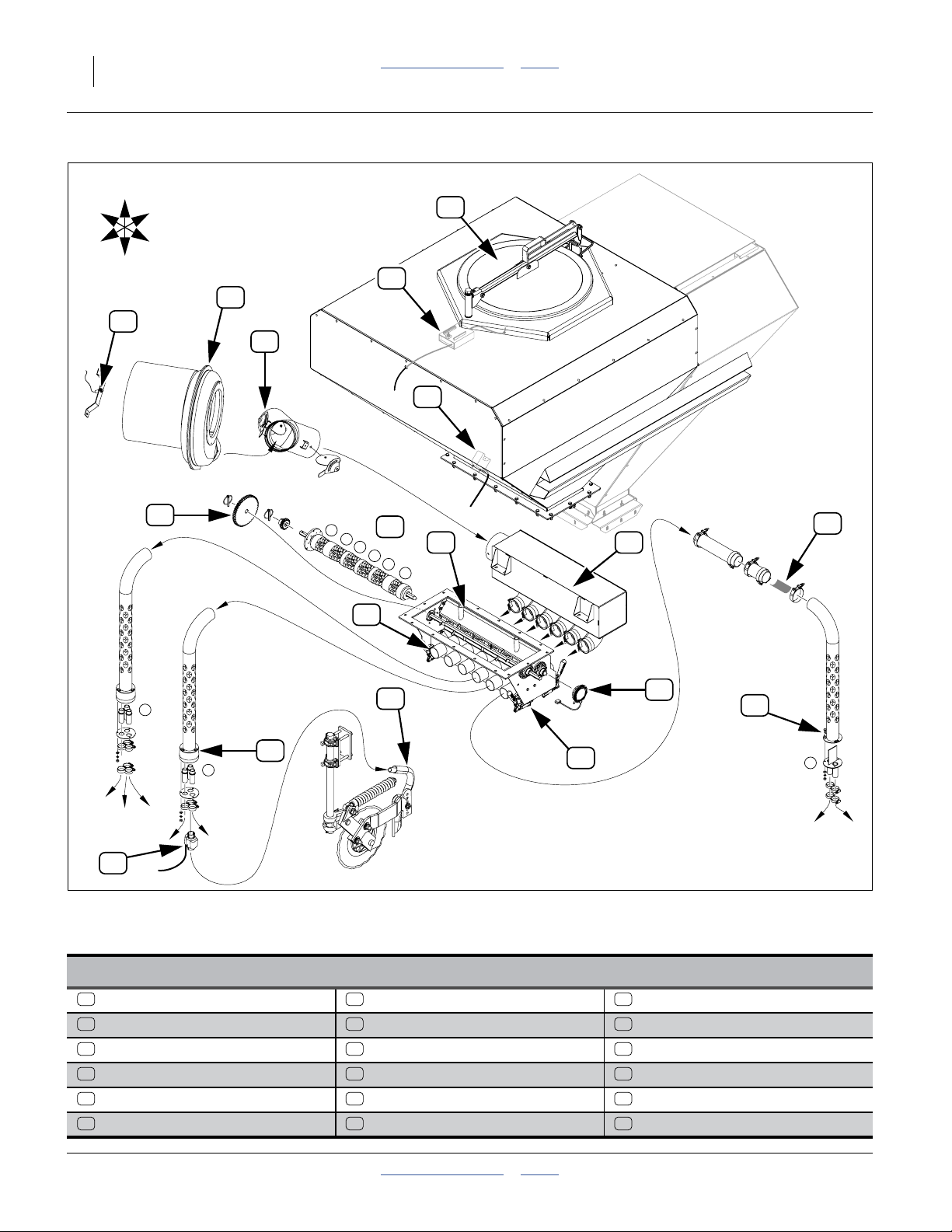
Figure 5
Planter Air System for Seed Metering
Seeding System Elements (Excluding Drive)
1 6 11
Hydraulic Fan Slide Gate Meter Inlet Vent
2 7 12
Fan RPM Sensor Air Box Seed Inlet Seed Meter
3 8 13
Butterfly Valve (Seed Leg) Seed Level Sensor Meter Drive
4 9 14
Manifold Air Inlet Air Box Manifold Outlet Seed Tube
5 10 15
Seed Hopper Seed Delivery Hose Seed Sensor
31094
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 19

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Operating Instructions 15
Seeding System Overview
Refer to Figure 5 on page 14
1. Hydraulic Fan:
The hydraulic fan supplies air for both seed and
fertilizer delivery. Fan rpm is operator-adjusted via
the tractor circuit’s hydraulic flow control.
2. Fan RPM Sensor:
Fan rpm is measured by a sensor mounted inside
the fan cage, and reported on the seed monitor
console.
3. Butterfly Valve (Seed Leg):
Manually-adjusted butterfly valves are provided on
the splitter at the fan outlet. The valve on the left leg
controls air for the seeding system. See page 19 for
valve adjustment.
4. Air Box Air Inlet:
Fan air enters the air box at the manifold inlet and is
mixed with seed.
5. Seed Hopper:
The rear hopper is the seed hopper. See “Loading
Seed” on page 11. The hopper contains a
pressure-balancing system (not shown) to help
prevent seed bridging.
6. Slide Gate:
There is a slide gate at the base of the seed hopper,
used to shut off seed flow during transport,
maintenance and storage.
7. Air Box Seed Inlet:
Seed enters the air box manifold at the top.
8. Seed Level Sensor:
The inlet contains a level sensor. When this sensor is
exposed (seed level below sensor), there may be
less than a hectare of seed remaining.
9. Seed Manifold Outlets:
The fan airflow entrains seed inside the air box, and
exits at the manifold outlets. On this model planter,
there is one outlet port per row.
10. Seed Hoses:
Seed hoses deliver seed to the rows. On this model
planter, there is one hose per row, and no Y-tube
splitters.
11. Air Release Vents:
The meter inlets contain a venting system to exhaust
the delivery air. When seed backs up above the vent,
seed flow to that row stops until the meter has
consumed enough seed to re-expose the vent.
12. Seed Meter:
The Singulator Plus®or finger pickup meter contains
a seed wheel or finger-set that capture seeds at a
precise rate.
13. Seed Meter Drive:
Meter rotation is coupled to the drive system, which
is powered by a hydraulic motor (not shown) under
control of the seed monitor. Clutches control drive
shafts for entire planter sections. See planter
Operator manual for clutch operation.
Note: Seeding rate is independent of air system
operation, if the air system is set to provide
enough bulk seed flow to keep the meters full, but
not so much flow that system plugging occurs.
See page 19 for fan operation.
Note: A coupler at the meter may be disengaged to shut
off seeding at that row. See planter Operator
manual for row shut off. Fertilizer application
cannot be shut off at individual rows.
14. Seed Tube:
The seed wheel or finger set deposits seed in the
row’s seed tube, for delivery to the furrow.
15. Seed Sensor:
In the seed tube, the seed sensor detects passage of
seeds. Medium size and large seeds are counted
individually. With smaller seeds, most are detected,
allowing the monitor to detect stoppages.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 20
16 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
U
R
B
5
F
L
D
6
1
2
3
7
11
2
12
3
3
3
3
8
}
2
4
16
13
3
18
10
15
14
3
9
2
17
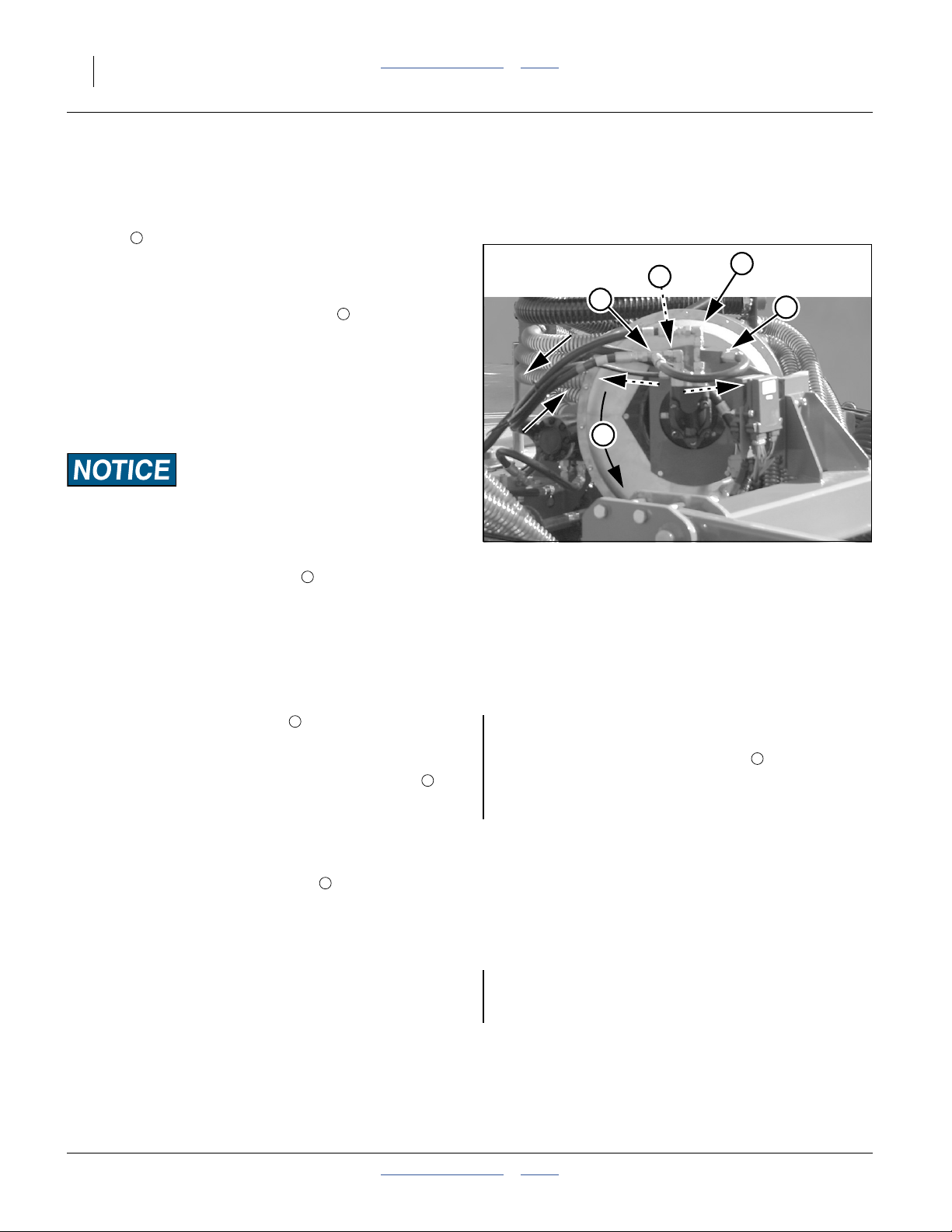
Figure 6
Planter Air System for Fertilizer Metering
Fertilizer System Elements (Excluding Drive)
1 7 13
Hydraulic Fan Level Sensor Manifold Outlets and Hoses
2 8 14
Fan RPM Sensor Fertilizer Meter 3-Way Tower
3 9 15
Butterfly Valve (Fertilizer Leg) Calibration/Clean-Out Doors 2-Way Tower
4 10 16
Air Inlet Manifold Meter Shaft RPM Sensor 2-Way Air Vent
5 12 17
Seed Hopper Flute Stars Blockage Detector
6 11 18
Pressure Sensor Range Gears Coulter Applicator
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
31093
Page 21

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Operating Instructions 17
Fertilizer System Overview
Refer to Figure 6 on page 16
1. Hydraulic Fan:
The fan supplies air for both fertilizer and seed
delivery. Fan rpm is operator-adjusted via the tractor
circuit’s hydraulic flow control.
2. Fan RPM Sensor:
Fan rpm is measured by a sensor mounted inside
the fan cage, and reported on the seed monitor
console.
3. Butterfly Valve (Fertilizer Leg):
Manually-adjusted butterfly valves are provided on
the splitter at the fan outlet. The valve on the right leg
controls air for the fertilizer system. See page 19 for
valve adjustment.
4. Fertilizer Air Inlet Manifold:
Fan air is divided into six equal flows at the inlet
manifold.
5. Fertilizer Hopper:
The front hopper is the fertilizer hopper. See
“Loading Fertilizer” on page 12. The hopper
contains a ladder-style pressure-balancing system
(not shown) to help prevent fertilizer bridging.
6. Pressure Sensor:
A sensor in the fertilizer hopper reports air pressure
to the seed monitor, and is reported on the console.
7. Fertilizer Level Sensor:
The fertilizer hopper contains a level sensor. When
this sensor is exposed (fertilizer level below sensor),
approximately 78 liters (2.2 bu) of fertilizer remains.
8. Fertilizer Meter:
The fertilizer meter is at base of the fertilizer hopper.
There is no slide gate. The meter is always open to
the fertilizer hopper.
9. Meter Doors:
The meter box has doors at the bottom for clean-out
(front) and calibration (rear). See page 27 or
page 35. These doors are closed for field operations.
10. Fertilizer RPM Sensor (shaft monitor):
A sensor on the meter flute shaft reports shaft rate to
the seed monitor. The seed monitor does not report
material rate from this data, but can generate alarms
on shaft stoppages or rpm out-of-limits.
11. Range Gears:
Interchangeable Final Range Gears set the coarse
rate of the flute shaft. The meter system is powered
by a ground drive (not shown), which has a variable
rate gearbox for fine adjustment. See page 23.
Fertilizer metering occurs whenever the planter is
lowered and in forward motion.
12. Flute Stars:
Fertilizer is metered into the manifold air stream by
flutes on the final shaft. The four inside
compartments have three flutes (six halves) and feed
3-way towers. The two outside compartments have
two flutes and feed 2-way towers.
Material Mis-Application Risk:
If it is ever necessary to disconnect delivery hoses at the
manifold, it is essential that the hoses to the wing-end
(2-way) towers be connected to the outside ports
(#1 and #6) at the manifold.
13. Fertilizer Manifold Outlets:
The fan airflow from the inlet manifold entrains
metered fertilizer in the chambers below the flutes,
and exits at the manifold outlets. Each outlet serves
a single hose to a single distribution tower, and
multiple rows.
The center four outlets serve 3-way towers.
The outside two outlets serve 2-way towers.
14. 3-way Tower:
Four of the six towers divide the air/fertilizer flow
3ways.
15. 2-Way Tower:
Two of the six towers (the two serving wing end
rows) divide the air/fertilizer flow 2 ways.
16. Vent for 2-Way Towers:
To balance the airflow at all manifold ports, the 2-way
towers vent some of the air at the tower inlet. See
page 43 for maintenance.
17. Blockage Detectors:
Each tower divider outlet is equipped with a material
sensor, connected to the seed monitor and
configured for “Blockage” mode. These report any
flow failure at the rows. See page 54.
18. Coulter Applicators:
Coulters are factory configured for side-dress
fertilizer application, at 5cm (2in) off-row, and a
depth of 5cm (2in), “zone” application. The coulter
has adjustments for depth and the height of the
applicator exit tube.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 22
18 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Fan Circuit Operation
Refer to Figure 7
Three hydraulic hoses serve the fan, and must be
properly connected for the fan to operate in the correct
direction , at recommended speeds, and without
damage. See “Hydraulic Hose Hookup” in the
401-406M (YP24) or 401-571M (YP40) Operator
manual.
1. Always connect the case drain line first.
1
3
2
2
4
5
This line protects the outer shaft seal of the hydraulic
motor. The case drain is a small line to the hitch,
provisioned with a specialized low-seep flat-face
case drain Quick Disconnect. Pressure spikes during
motor operation, and pressure cycles due to
temperature change are bled off by the case drain.
1
Motor Seal Damage Hazard
Do not apply pressure to the case drain line. Do not change the
special QD connector. A restricted or sealed case drain line
will promptly result in motor seal damage.
2. Connect the motor return line second, to sump.
3
Figure 7
Hydraulics at Fan
31095
The planter includes a 11⁄16in low back-pressure QD
coupler set. Install the receptacle on a tractor sump
port, and not at a normal remote return port. The
unusual size aids in ensuring correct connection, so
that the motor return line handles high volume at low
back-pressure, ensuring full motor performance.
3. Connect the motor inlet line to a tractor remote
4
capable of 95 liters per minute (25 gpm). If a priority
remote is available, use it for the fan.
4. The fan hydraulic circuit includes a check valve ,
5
which provides a relief path for oil at motor shutoff.
If the fan is connected in reverse, flow through this
valve results in low fan rpm, providing strong
indication reversed connection.
Correct fan direction is shown at . If reversed fan is
1
suspected, observe it during shutoff, as the direction
of motion is easier to see at lower rpms as it slows to
a stop (initial startup is virtually instantaneous,
making observation at start difficult).
Fan speed is controlled by the tractor circuit and butterfly
valves (and not the seed monitor).
You may stop the fan by setting the circuit to neutral or
float. The check valve slows the blades to a stop by
locally recirculating the oil.
If the fan is connected in reverse, it may not run at all
(due to no oil source at the return connection). If oil is
present, oil bypass at the check valve prevents the
5
fan from reaching high rpm. A reversed fan may send
some air to the delivery systems, but is incapable of
providing reliable air flow for planting.
Fan speed can change as oil heats to operating
temperature. Re-check fan rpm and hopper pressure
more often during early operations.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 23
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Operating Instructions 19
Fan General Operating Information
Adjust the fan rpm and butterfly valves to provide
sufficient air flow for consistent transport of seed and dry
fertilizer. Suggested values are shown at right.
Fan rpm is controlled by the tractor circuit, and reported
by the seed monitor. Always start the fan with a low flow
setting. Gradually bring fan up to the target rpm.
Fan air pressure is measured by a sensor in the fertilizer
hopper, and reported by the seed monitor. Air pressure is
controlled by fan rpm, butterfly valve settings, material
density and rates. System settings may vary with
material mix, material density and rates.
Recommend initial butterfly valve setting is 0° (wide
open) at both valves (assuming material application from
both hoppers). If one hopper is unused, set the valve for
that hopper to 30° to simulate the normal back-pressure
of material flow from that hopper.
Butterfly Valves
Use tractor remote hydraulic valve flow control to set fan
speed and butterfly valves to balance flow. Precise
technique depends on tractor capabilities:
• For any setup adjustment, operate the tractor engine
at typical field rpms, and not at idle.
• Preset the butterfly valves. Use any settings that you
previously developed for the material mix and rates,
otherwise:
70°
45°
2
20°
If the tractor has fine control of remote flow rates, and
consistent flow at varying tractor engine rpm, initially
set the butterfly valves to 0°.
If the tractor has only coarse control of flow, initially set
the butterfly valves to 45°.
• Set the fan circuit flow to bring the pressure sensor to
near the recommended value.
• If the tractor has marginal flow available, or the list
circuit has priority, you may need to experiment with
combinations of fan flow and butterfly valve settings.
At excessive rpm, too much air flow can cause:
Symptoms of Insufficient Air Flow
• Excessive skips (low seed population) at seed meters.
• Blockage reported at fertilizer applicators.
• Plugging of delivery hoses at low spots.
Symptoms of Excessive Air Flow
• Blockage reported at openers or coulters.
• Plugging of delivery hoses near air boxes.
• oil heating
• slow lift times
1
Figure 8
Fan Butterfly Valve Handle
Butterfly Valve Operation:
To adjust, loosen bolt and rotate the handle .
Re-tighten bolt.
0° is wide open - maximum air flow.
90° is closed - minimum air flow.
The valve provides the most effect at settings between
20° and 70°.
Starting at 30° reduces the fan workload.
Starting at 45° provides the most adjustment range up or
Note: If desired pressure cannot be reached, or requires
unusually high oil flow at low butterfly valve
settings, chances are the fan is running
backwards. Reverse the inlet/return lines at the
hitch.
1 2
25137
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 24

20 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Monitor Operation
The YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670
includes the standard DICKEY-john
operating in Planter/Drill Control mode. There are setup
differences vs. other YP40 planters, generally:
• Row delivery tubes are equipped with blockage
sensors. These rows are treated as “seed” rows
numbered from
®
IntelliAg® monitor,
YP24 YP40
25 (actual seed row 1) to 17 (actual seed row 1) to
48 (actual seed row 24) 32 (actual seed row 16)
• Seed tubes are monitored in Population mode.
Fertilizer applicators are monitored in Blockage mode.
Note: Fertilizer is not set up as a separate Material or
Channel. The monitor’s “GRAN FERT” air drill
mode is not used. The seed monitor is not
engaged for fertilizer calibration, and no
“CAL CONST” is required.
• There are two hopper level sensors in use:
1. Seed air box
2. Fertilizer hopper level
Note: There is no optional level sensor for the seed
hopper.
• There is one air pressure sensor in use, installed in
the fertilizer hopper.
• There is a second
end of the fertilizer meter shaft. Although the seed
monitor can report the rpm, the main use is as a shaft
monitor.
Set upper and lower rpm limits based on the fertilizer
rate chart, and your planned field speed. The chart
shows expected meter rpm for various gearbox
settings, in High and Low range, at 9.7 kph (6 mph). If
using a different field speed, adjust the expected rpm
proportionately.
a
rpm sensor, installed on the left
Marker Operation
The YP24/YP40 DF/seeder feature does not affect
marker operations.
a. The first rpm sensor is on the hydraulic motor for the seed meters.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 25

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Operating Instructions 21
Field Set-Up Checklists
Add the following items to the basic planter checklists, or
any customer checklist you have developed.
Mechanical Checklist (Hitching) Page
No changes
Electrical Checklist Page
No changes
Hydraulic System Checklist Page
No changes
Mechanical Checklist (post-Hitching) Page
No changes
Planter Meter Drive Checklist Page
Check fertilizer ground drive and gearbox
output chain lubrication and slack
Check final Range gears set for desired
High or Low range
Check setting of variable rate gear box
against chart or calibrated rate.
No changes for seeding
Air System Checklist Page
Fan butterfly valves set for fertilizer 19
Fertilizer loaded. Lid closed. 12
No air leaks in fertilizer system
Hoses and tubing - no sags, no pinches
Hoses fully connected to applicators
Row Units Checklist Page
Check frame-mounted coulter:
offset
angle
depth
Check applicator height. 29
39
23
24
29
Field Operation
The YP24 DF/seeder feature requires no changes to the
checklists in the 401-406M Operator manual, the YP40
DF/seeder requires no changes to the checklists in the
401-571M Operator manual.
When the fan is running, and the planter is lowered and
in forward motion, material is applied from the fertilizer
hopper at the currently set rate.
Consult seed monitor for blockage alarms.
When reloading fertilizer, check consumption against
anticipated use to that point.
Short-Term Parking
The YP24 or YP40 DF/seeder feature requires no
changes to the Parking steps in the 401-406M or
401-571M Operator manual.
Long-Term Storage
The YP24 or YP40 DF/seeder feature adds the following
steps to the storage recommendations of the 401-406M
or 401-571M Operator manual:
• Perform a seeding system clean-out (page 35)
• Close the lid of the seed hopper firmly, making sure it
is fully latched (page 11).
• Clean-out the fertilizer air system and hopper
(page 35).
• Tie the clean-out and calibration doors partly open
(page 35).
• Close, but do not tightly seal the fertilizer hopper lid
(page 12).
Equipment Damage Risk:
Perform a fertilizer clean-out when the planter is left unused
for more than 36 hours. Fertilizer is generally very corrosive.
If fertilizer or residue is allowed to remain in the hopper or
meter, exposed metal surfaces will be attacked. See “Material
Clean-Out” on page 35.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 26

22 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Adjustments
This table provides a cross-reference to all adjustment
items unique to the YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and
YP4025F-1670 planter.
For adjustments not listed, see the 401-406M (YP24) or
401-571M (YP40) Operator manual.
Adjustment Page The Adjustment Affects
Air Systems 14
Fan Speed 19 Optimal seed distribution
Butterfly Valve (Seed Leg) 19 Consistent seed flow and disk singulation
Butterfly Valve (Fertilizer Leg) 19
Material Rates
Seed Rate
Seed Rate
Fertilizer Rate 62
Monitor Adjustments
Alarms 20
Restore factory settings 53
Frame-Mounted Coulter Adjustments
Coulter Depth 29
Applicator Depth 29
401-406B
401-571B
(Same as for standard YP24 planters.
Refer to that Seed Rate manual.)
(Same as for standard YP40 planters.
Refer to that Seed Rate manual.)
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 27

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Adjustments 23
Setting Material Rates
Setting Seed Rate
Seed rate setting for the YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630
and YP4025F-1670 planter is identical to the standard
YP24 or YP40 planter. Refer to the Operator and Seed
Rate manuals for details:
YP2425F-2470 401-406M Operator manual
401-406B Seed Rate manual
YP4025F-1630 or
YP4025F-1670
401-571M Operator manual
401-571B Seed Rate manual
Setting Dry Fertilizer Rate
There are three steps to obtaining the target fertilizer
kilograms per hectare (or pounds per acre):
1. Set Final Drive Range on fertilizer meter (below)
2. Set Variable Rate Gearbox (page 24)
3. Calibrate (page 25).
2
DRIVING
3
Seed Meter Final Drive Range
Refer to Figure 9
The meter flute shaft is driven by the agitator shaft
through a pair of interchangeable gears , . The
positioning of these gears creates two final drive ranges.
The rate chart has two page columns, each based on a
specific Final Drive Range. The Ranges are:
• “High” range, which is used for higher fertilizer rates
• “Low” range, which is used for lower fertilizer rates
The two meter shafts are labeled “DRIVING” and
“DRIVEN”.
The “DRIVING” shaft is the upper shaft.
The “DRIVEN” shaft is the lower shaft.
Refer to the Fertilizer Rate chart (page 63), the table at
right, and Figure 9 for setting the meter final drive range.
1. Remove the lynch pins from the ends of both shafts.
2. Remove and position the gears as shown in the table
above.
3. Secure with lynch pins.
1 2
3 4
DRIVEN
1
Figure 9
High Final Drive Range
FINAL DRIVE
RANGE
LOW RANGE 17 Tooth Small 54 Tooth Large
HIGH RANGE 54 Tooth Large 17 Tooth Small
DRIVING DRIVEN
4
91097
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 28

24 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
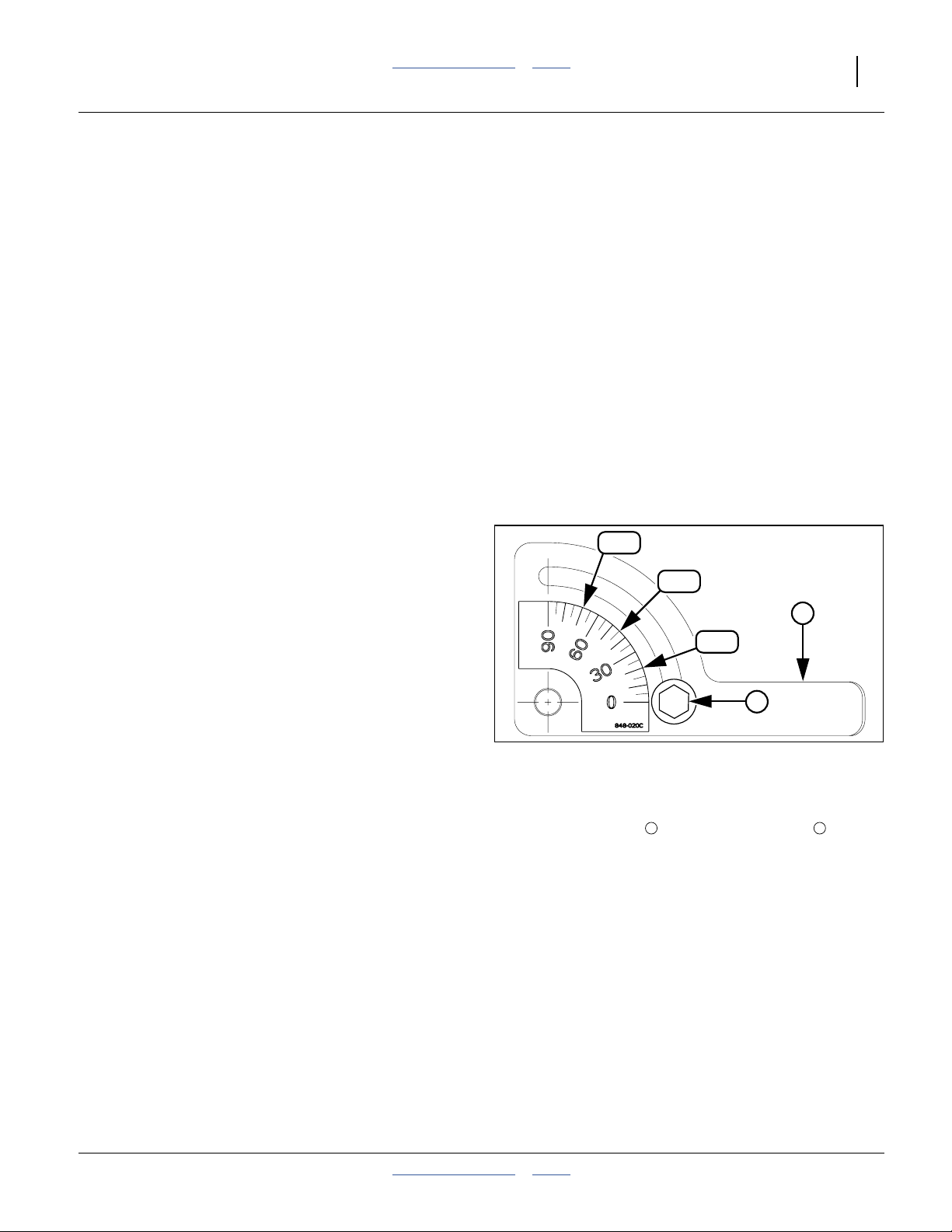
Setting Variable Rate Gearbox
The variable rate gearbox allows an infinitely variable
meter drive speed to attain a wide range of application
rates. The ratio of gearbox input speed to output speed is
controlled by the position of a gearbox control arm. The
control arm has an indicator that points to a scale
marked in degrees. The Fertilizer Rate chart shows the
rate for each five degrees of arm rotation.
Refer to the rate chart and set the variable rate gearbox
control arm to its scale setting for the target fertilizer rate
To adjust the Variable Rate Gearbox:
Refer to Figure 10
1. Remove the hairpin cotter securing the gearbox
adjustment crank .
2. Rotate crank until the control arm indicator
points to the scale setting that matches the rate from
the rate chart or as determined by calibration.
3. Reinsert the hairpin cotter.
Note: The variable rate gearbox operates optimally
between 30 and 70. If the target fertilizer rate
appears on both the Low and High Range charts,
the most consistent results are obtained when the
gearbox control arm is set between 30 and 70.
Settings below 20 degrees are not recommended.
When the control arm is set above 70 degrees,
large movements of the arm result in small
changes in seeding rate.
2
2 3
1
1
3
2
Figure 10
Variable Rate Gearbox
31099
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 29

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Adjustments 25
Meter Calibration
The fertilizer rate charts are based on a representative
11-52-0 dry granular fertilizer. Many factors affect meter
rates including fertilizer density, granularity, texture,
adhesion, humidity and field conditions.
Great Plains recommends calibrating for the exact
material being applied. Calibration determines the kg/ha
(or lbs/ac) of the meter at the current variable rate
gearbox setting for your particular fertilizer.
Calibration Procedure
Calibration consists of:
• metering material for a simulated distance (area), by
manually cranking the ground drive system,
• measuring the sample weight generated, computing
the rate, and, if not the rate desired,
• adjusting the gearbox setting to produce a rate closer
to the target rate, then;
• re-sampling to verify the adjustment.
There are two ways to collect the sample:
a. Fan On / Row Sample (page 26)
Place collection containers under each fertilizer row
applicator (calibration door closed).
b. Fan Off / Meter Sample (page 27)
Place a tarp under the fertilizer meter with the
calibration door open.
Either method relies on manual operation of the fertilizer
ground drive system and meter. You may operate the
drive by turning the ground drive wheel itself, or use the
supplied 403-414H crank to turn the jackshaft at the
ground drive arm pivot.
Initial Calibration Steps
1. Set the final gear Range and variable rate gearbox
adjuster (from the charts on page 64 or 65, or
previous calibrations of similar material).
2. Hitch planter to tractor capable of operating the
planter. (See 401-406M or 401-571M Operator
manual.)
3. Close the slide gate on the seed hopper (page 14).
4. Raise the planter. Install transport locks. (See
401-406M or 401-571M Operator manual.)
5. Load enough fertilizer for at least1⁄10hectare (or
1
⁄10acre) plus an extra 35 to 45 kg (75 to 100 lbs)
(page 12).
Refer to Figure 11
6. Attach the 403-414H calibration crank to the left
1
end of the fertilizer ground drive arm pivot. You can
use the hairpin cotter from the gearbox adjuster
2
crank to secure the calibration crank to the shaft.
Sampling Error Risk:
Do not leave fertilizer hopper lid open. Low pressure above
fertilizer skews results. Perform calibration with lid tightly
closed, as for normal field operations.
Revolutions for Sample Size
Sample Revolutions of:
Size Crank Wheel
1/10th Hectare 4.52 5.24
1/10th Acre 11.16 12.95
1 Hectare 45.2 52.4
1 Acre 111.6 129.5
Note: A cranking speed of 1 revolution per second
(60 rpm) simulates a field speed of 9 kph.
Note: For a more accurate calibration, crank for a full
hectare or acre. Make sure there is enough
material in the hopper.
Material Rate Risk:
Check consumption rates in the field. One variable factor that
calibration cannot compensate for is the effective rolling
radius of the ground wheel in unusually soft or hard ground.
2
Figure 11
Calibration Cranking
1
31000
31104
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 30

26 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Row Sample Calibration
This method requires 16 or 24 containers each with a
capacity of about 1% of a hectare or acre, and a scale
capable of precisely weighing the heaviest empty
container plus the sample size (or all the containers at
once).
7. Turn on the seed monitor system. Although not used
for calibration, you need the monitor to display fan
rpm.
8. Weigh the empty sample containers (the “tare”).
Refer to Figure 12
9. Place the collection containers under each coulter
applicator.
Refer to Figure 13
10. Start the hydraulic fan. Adjust the rpm to normal field
Figure 12
Row Sample Collection
31102
values.
Machine Damage Risk:
Do NOT turn the crank clockwise, or the gearbox may be
damaged. Turn the crank only counter-clockwise (as seen from
planter left, facing planter right).
11. Turn the crank counter-clockwise until material is
consistently appearing in the collection containers.
Stop cranking.
12. Empty the collection containers.
13. Turn the crank for the number of revolutions
necessary to simulate the area to sample, as shown
in chart on page 25.
14. Calculate the material rate per the instructions and
examples on page 28.
15. If the results differ from your target by more than a
few percent, adjust the gearbox setting per the
instructions on page 28.
Then measure another sample starting at step 13.
Row Sample Close-Out
16. Pin the gearbox adjuster in position
3
17. Remove the calibration crank.
3
Figure 13
Calibration Crank (Row)
31000
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 31

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Adjustments 27
Meter Sample Calibration
18. Weigh any container(s) required to hold the sample
on the scale.
Refer to Figure 14
19. Place a tarp under the fertilizer meter. Support the
corners or edges so that no material can spill.
Refer to Figure 15
20. Open the meter calibration door. The calibration door
is the rear door, furthest from the DRIVING gear.
Material Loss Risk:
Do not open the (forward) door under the DRIVING gear.
This is the clean-out door. Opening this door drains the
hopper. Once the clean-out door is open it is difficult to stop
Figure 14
Meter Sample Collection
31105
seed flow until the hopper is empty.
21. Wipe all material off the flanges around the meter
door.
Machine Damage Risk:
Do NOT turn the crank clockwise, or the gearbox may be
damaged. Turn the crank only counter-clockwise (as seen from
planter left, facing planter right).
Refer to Figure 16
22. Turn the crank counter-clockwise until material is
consistently appearing in the collection containers.
Stop cranking.
23. Empty the tarp and return it to the collection position.
24. Turn the crank for the number of revolutions
necessary to simulate the area to sample, as shown
in chart on page 25.
25. Weigh the collected sample. Subtract the weight of
any container required at the scale.
26. Calculate the material rate per the instructions and
examples on page 28.
27. If the results differ from your target by more than a
few percent, adjust the gearbox setting per the
instructions on page 27.
Then measure another sample starting at step 23.
Meter Sample Close-Out
28. Pin the gearbox adjuster in position
3
29. Remove the calibration crank.
Figure 15
Calibration Door Handles
3
Figure 16
Calibration Crank (Meter)
31101
31000
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 32

28 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Calibration Adjustment
Once a sample has been taken, two steps remain:
a. Calculate the current rate.
b. If needed, calculate and apply an adjustment to the
gearbox setting.
Calibration: Rate Calculation
30. If not already done, weigh the metered sample. This
is the gross weight.
31. Subtract the weight of the empty containers (the
tare) from the gross weight.
Net_Weight Gross_Weight Tare–=
If your sample size was based on cranking for a full
hectare or acre, no further rate calculation is necessary.
The net weight is the per-hectare or per-acre rate. Skip
to step 33.
32. If the sample size was1⁄
rate for the full area.
th
ha (or ac), calculate the
10
Area_Rate Net_Weight 10×=
Calibration: Gearbox Adjustment
33. If the calculated rate is within about 2% of your
target, there may be no benefit in attempting further
calibration. Resume at “Row Sample Close-Out”on
page 26 or “Meter Sample Close-Out” on page 27.
34. Calculate a gearbox scale adjustment. Divide the
targeta rate by the sampled rate.
Factor
Target_Rate
---------------------------- -
=
Area_Rate
Example based on YP4025-1670:
The example in this column is based on a target rate:
120 kg/ha
a gearbox setting of:
80
and a row sample, using 16 containers.
When empty the collection of 16 containers weighs:
1.1 kg
Example:
The sample and all containers weighs a total of:
12.6 kg
The net weight of the sample is:
12.6 - 1.1, or:
11.5 kg
Example:
Area rate for the sample is:
11.5 x 10, or:
115 kg/ha
This is just approximately 4% under the desired rate,
and is probably worth adjusting for.
Example:
120 ÷ 115 is:
1.043 or 104.3%
35. Use this factor to determine the next gearbox setting.
Next_Setting Previous_Setting Factor×=
36. Reset the gearbox adjuster to the “Next_Setting”
value.
For corrections of 5% or more, re-calibration is
recommended.
If a Low range correction puts the “Next_Setting” above
90, start settings development over in High range.
If a High Range correction puts the “Next_Setting” below
20, start settings development over in Low range.
a. Use the desired field application rate. Do not use any “adjusted” rate used to determine the initial gearbox setting.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Example:
80 x 1.043 is:
83.5
Note: The gearbox adjustment has a near-linear effect
on rates only near mid-scale or for small
adjustment changes. For corrections of 10% or
more, or near the ends of the scale, recalibration
is essential, as further adjustment is likely.
Page 33

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Adjustments 29
Coulter Adjustment
The frame-mounted coulters standard on the
YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670 are
configured for “zone” application: 5cm offset from seed
furrow, and
5cm depth, or “2x2”in.
As blades wear, or under unusual field conditions, you
may need to adjust the coulter depth. If the depth is
adjusted, the applicator needs to be adjusted as well.
Coulter Height Adjustment
Refer to Figure 17
1. Raise the planter. Install transport locks.
2. Move the planter to a flat level surface. A paved area
is ideal.
3. At each coulter, measure the raised tool bar height
(“Bar_Height”) .
4. For a 2.5cm (2in) coulter depth, compute the ideal
raised height of the disk edge.
1
2
1
4
Metric:
Edge_Height Bar_Height 66– 5–=
Inch:
Edge_Height Bar_Height 26– 2.5–=
5. Reset the coulter shank to the new “Edge_Height”.
Coulter Applicator Adjustment
Normally, the coulter tine tip is set to exactly ground
level, although you may set it higher or lower for unusual
conditions. To change the height, loosen the mounting
bolt and move the applicator weldment up or down.
4
If you are adjusting the tine height, to ground level, with
the planter raised, use:
Metric (cm):
3
Tine_Height Edge_Height 5+=
or, U.S. customary (inches):
Tine_Height Edge_Height 2.5+=
2
Figure 17
Dry Fertilizer Coulter
3
31109
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 34

30 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Frame-Mounted Coulter Force
In normal operation at target running depth, the spring is
at full extension or only slightly compressed. It
compresses briefly as obstructions and denser soil are
encountered.
Coulter springs are set to 181 kg (400 lbs). In normal
operation at target running depth, the spring is at full
extension. It compresses briefly as obstructions are
encountered.
• In heavy no-till conditions, you may observe the
springs in compression most of the time. This means
that the blades are not reaching the desired coulter
depth. If implement weight is sufficient, you can
increase the spring down-force to compensate.
• In light but rocky conditions, the factory spring setting
may be higher than needed. You can extend blade life
by reducing the force at which the blades ride up over
obstructions.
To adjust the coulter spring:
Refer to Figure 18
1. Raise the planter and install transport locks.
2. Determine the new spring length desired. See the
1
table at right.
3. Measure the current length of the spring(s) to be
changed. If already shorter than 24.8cm (9
longer than 26cm (10
1
⁄
in), do not further adjust
4
3
⁄
4
in), or
them.
4. Loosen the jam nut .
5. Rotate the adjuster nut until the spring is at the
2
3
new length. Tighten the jam nut.
Note: If all springs are continuously in compression, the
coulters can lift the wing frames off the ground (at
the gauge wheels), resulting in uneven coulter
depth and/or uneven seed depth. If the planter is
already operating at maximum down-pressure,
reduce coulter depth.
Figure 18
Frame-Mounted Coulter Spring
Spring Length Force at Blade
1
26.0 cm (10.25 in) 136 kg (300 lbs)
25.4 cm (10.00 in) 181 kg (400 lbs)
24.8 cm (9.75 in) 238 kg (525 lbs)
Machine Damage Risk:
Do not use spring lengths shorter than 24.8 cm (9.75 in). It
may contribute to premature parts failure which will not be
covered by warranty.
27139
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 35

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index 31
Troubleshooting
The tables of this section cover possible issues specific
to the YP24/YP40 DF/seeder feature.
See also the Troubleshooting section of the 401-406M or
401-571M Operator manual.
Dry Fertilizer Troubleshooting
Problem Cause Solution
Delivery Hoses
Plugging
No Fertilizer Flow
(all rows)
No Fertilizer Flow
(some rows)
Insufficient airflow to operate both
fertilizer and seed delivery systems.
Fan circuit running in reverse Check and re-connect circuit hoses (see
Fan won’t run fast enough at
maximum tractor circuit setting
Fan speed low on capable tractor.
Hydraulic fan check valve is installed
backwards
Air leaks Check:
False-positive blockage detection.
Some fine materials and/or low rates,
may cause the monitor to report
blockage.
Gearbox set to zero Set and calibrate gearbox (page 24).
Gearbox at zero, even though not set
to zero.
Drive chain broken or skipping Check chain condition and slack (page 39).
Material run-out. Re-load fertilizer. Re-check rate setting and
Bridging in fertilizer hopper due to air
leak
Bridging in fertilizer hopper due to
material consistency
Meter box completely plugged. Clean-out hopper and meter. See page 36.
Butterfly valve closed at fertilizer leg Check setting of valve. Tighten bolt.
Blockage inside tower. Remove cap. Clear blockage.
Increase fan speed (page 19).
If already at 3800 rpm, open fertilizer-leg
butterfly valve (page 19).
401-406M or 401-571M Operator manual).
Check butterfly valves. Notes that tractor must
be able to supply 18 gallons/minute at 200 psi.
Reverse installation of check valve (see
401-406M or 401-571M Operator manual).
hopper lid,
hopper base to airbox seal,
clean-out and calibration door seals and
delivery hoses.
Shut off monitoring for fertilizer rows.
Check that gearbox indicator arm is pinned to
adjuster shaft.
level sensor function if run-out was
unexpected.
Inspect seal under lid. Replace as necessary.
Check that hook and shackle have not become
mis-adjusted.
Clean-out and replace material. See page 35.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 36

32 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Dry Fertilizer Troubleshooting
Problem Cause Solution
No Fertilizer Flow
(single row)
Application Rate Low
(all rows)
Application Rate Low
(some rows)
Application Rate Low
(single row)
Bridging at inlet of applicator tube Remove hose. Clear bridge. Check material for
oversize content. Also check meter flutes for
damage. Generally, anything that passes an
undamaged flute will also pass all
down-stream constrictions.
Bridging at or near tip of applicator
tube
Final drive gears are in Low range
when High is required
Incorrect meter setting Check basic setting against chart (page 63).
Excessive field speed Chart was developed at 9.7 kph. Fan and
Density adjustment and/or calibration
not performed
Excessive gaps between passes.
Area actually covered is less than
intended.
Ground drive arm spring has failed or
gotten out of adjustment.
Hose connection incorrect at
manifold outlets. Outside two outlets
serve only wing end towers and not
inner towers
Meter flutes worn or broken Inspect and replace flutes (page 36).
Foreign matter blocking flow at flute
compartment
Airbox outlet plugged. Clean-out hopper (page 35).
Clean out tube. Inspect fertilizer for clumping,
oversize particles and foreign matter.
Exchange gears (page 23).
Review calibration steps (page 25).
meter performance may not scale to higher
speeds.
Adjust density (page 66) before selecting initial
rate settings. Calibrate (page 25).
Check that pass gap is one row space.
Adjust marker extension if necessary.
Check spring. Reset
Reconnect inside towers to inside manifold
ports (page 17).
Clean-out hopper (page 35).
Inspect and clean above flutes.
Inspect manifold outlet area.
Application Rate High
(all rows)
Application Rate High
(some rows)
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Final drive gears are in High range
when Low is required
Density adjustment and/or calibration
not performed
Overlap between passes. Area
actually covered is greater than
intended.
Hose connection incorrect at
manifold outlets. Center four outlets
serve only inside towers and not wing
end towers
Meter flutes worn or broken Inspect and replace flutes (page 36).
Exchange gears (page 23).
Adjust density (page 66) before selecting initial
rate settings. Calibrate (page 25).
Check that pass gap is one row space.
Adjust marker extension if necessary.
Reconnect wing end towers to outside manifold
ports (page 17).
Page 37

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Troubleshooting 33
This table covers possible issues specific to the
YP24/YP40 DF/seeder feature.
See also the Troubleshooting section of the 401-406M or
401-571M Operator manual.
Seeding Troubleshooting
Problem Cause Solution
Seed Hoses Plugging
No Seed Flow (all rows)
Planting Rate Low
(single row)
Insufficient airflow to operate both
fertilizer and seed delivery systems.
Air leaks Check:
Fan circuit running in reverse Check and re-connect circuit hoses (see
Fan won’t run fast enough at
maximum tractor circuit setting
Fan speed low on capable tractor.
Hydraulic fan check valve is installed
backwards
Material run-out. Re-load seed. Re-check rate setting and level
Bridging in seed hopper due to
material consistency
Butterfly valve closed at seed leg Check setting of valve. Tighten bolt.
Airbox outlet plugged. Clean-out hopper (page 35).
Increase fan speed (page 19).
If already at 3800 rpm, open seed-leg butterfly
valve (page 19).
hopper lid,
hopper base to airbox seal,
clean-out door seal and
delivery hoses.
401-406M or 401-571M Operator manual).
Check butterfly valves. Notes that tractor must
be able to supply 18 gallons/minute at 200 psi.
Reverse installation of check valve (see
401-406M or 401-571M Operator manual).
sensor function if run-out was unexpected.
Clean-out and replace material. See page 35.
Inspect manifold outlet area.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 38

34 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Maintenance
Maintenance
Proper servicing and maintenance is the key to long
implement life. With careful and systematic inspection,
you can avoid costly maintenance, downtime, and repair.
Always turn off and remove the tractor key before making
any adjustments or performing any maintenance.
Crushing Hazard:
Always have transport locks in place when working on
implement. You may be severely injured or killed by being
crushed under a falling implement.
1. After using your planter for several hours, check all
bolts to be sure they are tight.
2. Remove excess slack from chains. Clean and use
chain lube on all roller chains as needed.
3. Lubricate areas listed under “Maintenance
Schedule” on page 40.
4. Replace any worn, damaged, or illegible safety
labels by obtaining new labels from your Great
Plains dealer.
No-Change Maintenance Items
This section of the 403-362M manual covers planter
elements that introduce changes to maintenance,
compared to a standard YP24 or YP40.
Topics unchanged from the standard YP24 or YP40 are:
• Hydraulic Maintenance
• Marker Maintenance
• Leveling and Alignment
• Seed Meter Maintenance
• Seed Flap Maintenance
• Liquid Fertilizer Maintenance
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 39

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Maintenance 35
Material Clean-Out
When planting is completed, it is commonly the case that
some fertilizer and seed remains. There may be seed in
the hoppers, hose lines, and meters.
The clean-out procedures are different for the fertilizer
and seeding systems.
Seeding System Clean-Out
Refer to the 401-406M or 401-571M Operator manual.
Seeding system clean-out is the same as for the
standard YP24 or YP40 planter, with two minor
differences:
• The seed hopper is smaller and cannot be entered for
problem clean-outs.
• There are no Y-tubes in the seed delivery system.
Figure 19 shows the location of the seed airbox
clean-out door handles.
Fertilizer System Clean-Out
1. When planting is completed, raise the planter, but
leave the fan running for 30 seconds to empty the
base of the meter, delivery hoses, and applicators.
2. Unless a tarp will be used to collect the remaining
fertilizer, move the planter to an area with a flat clear
surface. Comply with fertilizer supplier instructions
for suitable areas at which to cover fertilizer.
3. Install transport locks on the raised planter. Shut off
the tractor. Mount a collection tarp if only a small
amount of fertilizer remains.
Refer to Figure 20
4. Open the calibration door (rear door). If the air
system is empty, no material may fall.
5. Open the clean-out door (forward door). Expect
material to flow in significant volume until the hopper
is empty.
6. Turn the ground drive wheel several revolutions to
empty the meter flutes.
If a second person is available, open the hopper lid
and inspect the meter flutes while turning the wheel.
7. Recover the fertilizer.
8. With the clean-out and calibration doors open,
power-wash the fertilizer hopper from above. Rotate
the ground drive to expose all meter flutes to the
water. Wipe doors, seals and meter flanges.
9. Use a wire to tie the doors partly open during drying
and storage. This allows condensation to drain while
preventing pest entry. See page 12 for lid operations
prior to storage.
1
2
Possible Dust and Chemical Residue and Fume Hazards:
Wear a respirator, and any other protective equipment
specified by the seed supplier and/or seed treatment supplier.
Expect chemical residue, dust and fumes during clean-out.
Figure 19
Seed Airbox Clean-Out Door
2
Equipment Damage Risk:
Do not leave fertilizer in the hopper for extended periods.
Fertilizer is generally corrosive, and will attack expose metal
surfaces.
1
Figure 20
Meter Door Handles
1
31107
2
31101
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 40

36 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Meter Flute Replacement
Fertilizer meter flute stars wear over time, and can be
chipped or fractured by hard foreign matter, such as
rocks or ice. Inspect flutes periodically. Replace as
needed.
To remove the flute shaft:
Refer to Figure 21
1. Perform a hopper clean-out (page 35).
2. Dismount the rpm sensor (not shown) from the left
end of the shaft . Dismount the Driven Range
gear at the right end.
2
3. Remove the six1⁄4-20 self-tapping screws from
the outside of the flange at the shaft right end.
4. Pry the flange loose from the meter housing (the
flange is sealed to the housing with silicone).
5. Remove the meter shaft.
6. When replacing stars (each of which is two
817-018C halves), be sure to match the irregular
arrangement of stars and spacers as shown in the
Parts manual.
7. Clean any residual silicone sealant from the shaft
flange and meter box housing. Apply fresh sealant.
8. Re-insert the shaft.
9. Secure the flange to the box housing.
1
3
3
1
4
2
4
Figure 21
Remove Meter Flutes
31016
Carefully re-insert the screws. Avoid cross-threading.
Do not exceed 7 N-m (5 ft-lbs) of torque.
10. Re-mount the rpm sensor on the shaft left end, and
the Range gear at the right end.
Problem Fertilizer Clean-Outs
For normal unloading of residual materials at completion
of planting, see “Material Clean-Out” on page 35.
If, however, parking and storage recommendations have
not been followed, it is possible to have hard-to-remove
material present.
If the material fails to pass through the fertilizer meter
clean-out door, take the following steps to remove it. Do
not consider entering the hopper until first completing
these tasks.
Open the clean-out door (page 35).
Remove the strainer (page 12) and evaluate the
problem.
For small amounts of residual materials, poking with a
long pole may suffice to push it through the clean-out.
If poking doesn’t produce satisfactory results, and you
intend to try wash-out, at least poke one hole down to the
meter clean-out, so that water can flow out.
For example:
• If the problem is a single moveable large object, such
as a dead animal, fishing out from above may be the
solution.
• If the problem is congealed materials, scoop out a
sample from above and see if the mass dissolves in
water. If so, and there is a small amount of the material
involved, rinsing, or rinsing and pumping the hopper
from above may be the solution.
If wash-out is contemplated, start by introducing a small
amount of water, and make sure that it appears at the
clean-out within 15 minutes. If not, you will just be adding
water to the problem. The hopper is not designed to hold
water at full capacity. Add no more water, remove meter
box instead, and clean out from below.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 41

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Maintenance 37
Removing Meter Box
Removing the meter box and inlet manifold exposes a
67x27cm (26x10.7in) hole through which stubborn
material may be extracted.
Refer to Figure 22
1. Not shown: Loosen the gearbox-to-meter chain idler
and remove the chain. Disconnect inlet and outlet
hoses. Disconnect or remove the rpm sensor.
2. Loosen all the nuts securing the meter box to the
hopper bottom plate. Unscrew the nuts to the bolt
ends, but do not completely remove the nuts.
3. The meter box has a bead of silicone sealant
between it and the bottom plate. Use a pry tool to
free the meter box from the hopper bottom plate.
4. Once hanging entirely on the loose bolts, remove the
nuts and lower the meter box from the hopper.
When re-mounting the meter box, scrape off the old
silicone sealant and replace it with fresh sealant.
Hopper Entry
Normal use of the fertilizer hopper and routine
maintenance do not require entry. The hopper vent tube
structure includes features to aid emergency egress. It is
not intended for routine entry. However, do not remove
the vent tube structure, as it is required for
pressure-balancing the space above the material.
▲ A hopper that is full or merely appears full can be an
entrapment hazard. You can sink entirely into the material,
or into a void, and suffocate in a matter of seconds. Bridges
and crusts are especially dangerous.
▲ You can be overcome by hazardous fumes very quickly even
in an empty hopper with the lid open.
▲ A partially full hopper, even with no bridging present, is a
suffocation risk.
Oxygen levels may be insufficient and/or
dust levels may be too high for breathing.
▲ Do not enter a hopper for loading material.
▲ Do not enter a hopper for unloading material.
▲ Do not enter a hopper for routine cleaning.
▲ Do not enter a hopper for any meter maintenance.
▲ Never enter a hopper without at least one trained and
equipped attendant present.
▲ Never enter a hopper for any reason unless you fully comply
with applicable laws, regulations, rules, agreements, and
the instructions in this section. Where applicable laws,
regulations, rules, agreements contradict an instruction
below, do not follow that instruction.
Figure 22
29718
Remove Meter for Cleaning
Rapid Suffocation Hazard:
Encrusted grain may be loose and flowing beneath the crust.
Any hollow spaces are highly likely to have insufficient oxygen
and/or toxic gases from microbial action. Falling through a
crust in either case can result in death in a matter of seconds.
Never enter a hopper to dislodge a crust or bridge.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 42

38 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Depending on their use, the YP2425F-2470,
YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670 fertilizer hopper may
be or become a
“permit-required confined space”
under U.S. OSHA regulations (29 CFR 1910.146) and
similar regulations, statutes, insurance agreements and
local business policy. A written policy and permitting
process may be required for any hopper entry.
Hopper entry may be necessary in some unusual
circumstances, such as:
• hopper level or pressure sensor replacement; or,
• removal of obstructions too difficult to pull out with the
meter box removed and not susceptible to fishing or
pumping out from the open lid.
Should such a situation arise, observe the following
precautions:
1. Evaluate the hazards
Review the material safety data sheets (MSDS) for
any treatments and/or fertilizers used in the hopper
since it was last thoroughly cleaned, and the most
recent materials even if the hopper was
subsequently cleaned. Retain the MSDS information
for any medical treatment that might be required.
2. Designate or engage a team
Hopper entry is never a single-person activity. At
least one attendant/observer is necessary. Give
priority to individuals already trained in confined
space operations. Designate a leader (who will not
be the entrant) with authority to terminate the activity.
3. Protect the team
Obtain the necessary safety equipment specified for
confined space exposure to those materials, paying
particular attention to respiratory support and
protection. This may include contaminant detection
equipment and positive ventilation to refresh air in
the hopper.
4. Equip the team
At least one attendant must be equipped with
communications capability, to summon outside aid in
the event that the hopper worker is overcome. Equip
the entrant with a safety harness and safety line.
5. Train the team
Review the hazards. Review the procedures.
Understand the use of the protective equipment.
Know the steps to take in emergencies. Practice
them. Train the observer to summon aid, and not
attempt hopper entry if the entrant is overcome.
6. Secure the planter
Lower the planter or block the wheels to prevent
movement.
7. Disrupt crusting or bridging
From outside the hopper, break up any hard
surfacing on top of the material, or forming layers
within the material. Such layers are extremely
dangerous to stand on.
8. Empty the hopper
Follow the steps at “Material Clean-Out” on page
35. If a blockage makes this impossible, use an
external pump line to remove as much material as
possible without performing a hopper entry. Pump
until at least some material is exiting the clean-out
door. Leave the clean-out door open.
9. Clean the hopper
From the outside at the walkboard, power-wash the
inside of the hopper. Use a mild detergent sprayer.
Rinse thoroughly.
10. Air the hopper
Leave the hopper lid and clean-out door open, and
do not commence work until the rinse water has
completely evaporated.
11. Plan the work. Work the plan.
Postpone the work if any team members, equipment
or other resources are missing, or weather/lighting
conditions are not favorable. Terminate and evacuate
if any unexpected situations arise.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 43

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Maintenance 39
Chain Maintenance
Inspect and lubricate chains regularly. The slack of new
chains tends to increase during the first few hours of
operation due to seating.
See also “Chain Routing YP4025F” on page 51.
1
Chain Slack
Check slack at fixed idlers within the first 8 hours of
operation and tighten idlers as necessary. Check slack at
spring-operated idlers seasonally.
Refer to Figure 23, which, for clarity, greatly exaggerates
slack, and omits the idlers.
1. Measure the span for allowable slack:
Locate the longest span of each chain (usually the
span which does not run through the idlers).
2. Determine the ideal slack:
Long chains (over 36in/91cm):
Vertical short chains:1⁄4in per foot (2.1cm/m)
Horizontal short chains:1⁄2in per foot (4.2cm/m).
3. Measure the current slack :
Acting at a right angle to the chain span at the center
of the span, deflect the chain in both directions. The
slack is the distance of the movement.
4. Adjust the idlers for ideal slack.
1
1
⁄4in per foot
2
Chain Clips
Whenever mounting a chain, make sure the clip at the
removable link is oriented to minimize snags.
Refer to Figure 24 (arrow shows chain direction)
Install clip with open end facing away from direction of
chain travel (shown by gray or striped arrows in chain
routing diagrams).
2
Figure 23
Measuring Chain Slack
Figure 24
Chain Clip Orientation
27264
26482
Fertilizer Meter Drive Chain
There are four (4) chains in the fertilizer ground drive
system. See page 51 and page 52 for locations.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 44

40 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Maintenance Schedule
Intervals
Multi-purpose
spray lubricant
This section of the 403-362M manual covers planter
elements that introduce changes to lubrication and
scheduled maintenance, compared to a standard YP24
or YP40. For all other planter lubrication points, see the
401-406M or 401-571M Operator manual.
Multi-purpose
grease lubricant
Multi-purpose
oil lubricant
Inspection
34208
(operating hours)
50
at which service
is required
Chain: Ground Drive
As Required
1 chain total
Type of Lubrication: Chain Lube
Quantity: Coat Thoroughly
Note: Lubricate chains any time there is a chance of
moisture, and when being stored at the end of the
planting season.
Chains: Ground Drive Transmission
As Required
3 chains total
Type of Lubrication: Chain Lube
Quantity: Coat Thoroughly
Note: Lubricate chains any time there is a chance of
moisture, and when being stored at the end of the
planting season.
29749
29767
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 45

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Maintenance 41
Coulter Pivots
20
one zerk per pivot;
16 total
Type of Lubrication: Grease
Quantity: Until grease emerges
31015
Coulter Hubs
20
one zerk per hub;
16 total
Type of Lubrication: Grease
Quantity: Until resistance is felt
Ground Drive Wheel Arm Pivot
20
2 zerks total
Type of Lubrication: Grease
Quantity: Until grease emerges
31015
29749
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 46

42 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Ground Drive Wheel Hub
50
one zerk per hub;
1 total
Type of Lubrication: Grease
Quantity: Until resistance is felt
29749
Ground Drive Wheel Bearings
Two races per hub,
1 hubs;
2 races total
Type of Lubrication: Grease
Quantity: Repack
Coulter Hub Bearings
Two races per hub,
16 hubs;
32 races total
Type of Lubrication: Grease
Quantity: Repack
Seasonal
29749
Seasonal
31015
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 47

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Maintenance 43
Air Release Tube
Seasonal
1 tube each wing end fertilizer delivery hose;
2 tubes per planter
Inspect. Clean any build-up on screen. Replace if
damaged. Re-install with opening facing down.
Note: Although depicted in exploded view, the tube is a
weldment and the screen cannot be removed.
29723
Meter Box Door Seals
Seasonal
2 seals per planter
Inspect and replace if leaks are detected or appear
imminent.
Meter Flutes
Seasonal
1 flute shaft per planter,
2 sets of 2 stars (4 stars),
4 sets of 3 stars (12 stars);
16 stars total (each star is two halves)
Inspect from above with hopper empty. Shaft rotation is
required to expose all surfaces. Replace any broken or
visibly worn stars.
31016
31016
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 48

44 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Gearbox Oil
Seasonal
1 port per gearbox; 2 total
Type of Lubrication: High Quality SAE 5W-30 oil
Quantity: 6.5 pints (3.1 liters)
34394
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 49

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Maintenance 45
Seed Lubricants
Note: Seed only - fertilizer does not use lubricants.
29248
Singulator Plus Meters (all seeds)
Ezee Glide Plus Talc-Graphite Mix
821-069C bucket, 5 gallon (19 liter)
Ezee Glide Plus Lubricant
To maximize performance of Great Plains metering
systems, it is imperative to use only “Ezee Glide Plus”
lubricant. “Ezee Glide Plus” Talc-Graphite lubricant is
mandatory for all seeds, especially treated or inoculated
seed. Thorough mixing of seed and added lubricant is
required.
Recommended usage:
For clean seeds other than milo and cotton sprinkle
one cup of Ezee Glide Plus Talc per 4 bushels or units
(170 ml per 100 liters) of seed.
For milo and cotton double the application to
one cup (or more) per 2 bu or units (335 ml per 100
liters) of seed.
Adjust this rate as necessary so all seeds become
coated while avoiding an accumulation of lubricant in the
bottom of the hopper.
For seed with excessive treatment, or for humid planting
environments, increase the rate as needed for smooth
meter operation.
25477
Finger Pickup Meters
EZ-Slide Graphite Powder
821-042C bottle, 1 pound (450 grams)
821-060C jug, 5 pound (2.3 kg)
For Finger Pick Up Meters Only
Use only approved Graphite Powder available from Great
Plains Mfg. Inc. or Precision Planting to ensure proper
lubrication of finger pickup corn seed meters.
Recommended usage:
For finger pickup meters, add one tablespoon (15 ml) of
graphite for each unit of seed corn (80,000 kernels).
In high humidity conditions, or seeds with heavy seed
treatments, increase the application to two tbsp (30ml).
If delivery of seed from the hopper to the finger meter is
an issue, add “Ezee Glide Plus” talc and graphite blend
at a rate of one cup (237ml) per 4 units of seed. Adjust
until issue is resolved.
Irritation and Chronic Exposure Hazard:
Wear gloves. DO NOT use hands or any part of your body to
mix seed lubricant. Wear a respirator when transferring and
mixing. Avoid breathing lubricant dust. Not an acute hazard.
May cause mechanical eye or skin irritation in high
concentrations. As with all mineral spills, minimize dusting
during clean-up. Prolonged inhalation may cause lung injury.
Irritation and Chronic Exposure Hazard:
Wear gloves. DO NOT use hands or any part of your body to
mix seed lubricant. Wear a respirator when transferring and
mixing. Avoid breathing lubricant dust. Not an acute hazard.
May cause mechanical eye or skin irritation in high
concentrations. As with all mineral spills, minimize dusting
during clean-up. Prolonged inhalation may cause lung injury.
Product can become slippery when wet.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 50

46 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Options
The YP2425F and YP4025F Dry Fertilizer/Seeder
subsystem occupies planter spaces that are used by
other subsystems on standard models. Refer to the
Options topic in the 401-406M or 401-571M Operator
manual for option details and ordering information.
Compatible Options
• Hydraulic Tongue
• Markers
• Trailer Hitch
(although all of the Liquid Fertilizer options are not
recommended or incompatible)
• Seed Lubricants
• Gauge Wheel Scrapers
• Inside and Outside Disk Scrapers
• Seed Meters and Wheels
• Seed Firmers
• Row Unit Press Wheels
Options Not Recommended
• Swath Command
(there is no provision for shutting off fertilizer flow to
idled rows)
• Lock-Up Pins
(there is no provision for shutting off fertilizer flow to
unused rows)
• Liquid Fertilizer Carts
• Ground Drive Liquid Fertilizer Pump
• High Rate Dribblers
Incompatible Options
• Frame-Mounted Options
(the standard dry fertilizer frame-mounted
coulter/applicators occupy the mounting points)
• Liquid Fertilizer Tanks
(the dry fertilizer walkboard and ground drive occupy
the same space)
• Liquid Fertilizer Booms
(these may interfere with dry fertilizer delivery hoses)
• Unit-Mounted Coulters
(the frame-mounted dry fertilizer coulters occupy the
same space)
• Unit-Mounted Row Cleaners
(the frame-mounted dry fertilizer coulters occupy the
same space)
• 82bu and 150bu Seed Hoppers
(the dry fertilizer hoppers occupy the same space, and
the fan is plumbed to feed two manifolds, not one)
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 51

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index 47
Appendix A - Reference Information
Specifications and Capacities YP4025F
YP4025F-1670 YP4025F-1630
Number of Openers 16
Row Spacing 70 cm (27.6 inches) 30.0 inches (76 cm)
Swath 1120 cm (440.9in) 480.0in (1219 cm)
Span (width between end rows) 1050 cm (413.4in) 450.0in (1143 cm)
Seed Hopper Capacity 670 liters (19 bu)
Fertilizer Hopper Capacity 1,440 liters (41 bu)
Tractor Power Required 119 to 134 kW (160 to 180 hp)
Hydraulic Circuits 4 Closed Center, 155 bar (2,250 psi), 95 liters/min (25 gpm)
Transport Width 4.5 m (14ft 10in)
Transport Height 3.6 m (11ft 9in)
Transport Length¹
Transport Clearance 56 cm (22in)
Auger Height, Fertilizer 2.7 m (9ft 0in)
Auger Height, Seed 2.6 m (8ft 6in)
Unfolded Width 12.1 m (39ft 7in)
Working Length¹
Hitch to Opener Distance²
Wing Flex 20° up or down
Weight, Empty, Base Configuration 12770 kg (28200 lbs)
Weight, Full, Maximum Configuration 15210 kg (33500 lbs)
Hitch Load 540 kg (1,200 lbs)
Opener Travel 25 cm (10in)
Opener Depth Range 0 to 10 cm (0 to 4in)
Opener Down Pressure 156 to 249 kg (345 to 550 lbs)
Tire Size 395/55B16.5 NHS Skid Steer
¹ Assumes no optional rear hitch weldment
² Assumes 3-point hitch
12.8 m (42ft 0in)
10.4 m (34ft 2in)
612 cm (241in)
Tire Inflation Chart
Tire data is unchanged from standard YP2425 or YP4025.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 52

48 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Specifications and Capacities YP2425F
YP2425F-2470
Number of Openers 24
Row Spacing 70 cm (27.6 inches)
Swath 1680 cm (661.4in)
Span (width between end rows) 1610 cm (633.9in)
Seed Hopper Capacity 670×2 liters (19×2 bu.)
Fertilizer Hopper Capacity 1,440×2 liters (41×2 bu.)
Tractor Power Required 164 to 134 kW (220 to 180 hp)
Hydraulic Circuits 4 Closed Center, 197 bar (2,850 psi), 203 liters/min (54 gpm)
Transport Width 4.5 m (14ft 10in)
Transport Height (without markers) 3.6 m (11ft 9in)
Transport Length¹
Transport Clearance 53 cm (21in)
Auger Height, Fertilizer 2.7 m (9ft 0in)
Auger Height, Seed 2.6 m (8ft 6in)
Field Width 12.1 m (39ft 7in)
Working Length¹
Hitch to Opener Distance²
Wing Flex 20° up or down
Weight, Empty, Base Configuration 9170 kg (20200 lbs)
Weight, Full, Maximum Configuration 13770 kg (30400 lbs)
Hitch Load 540 kg (1,200 lbs)
Opener Travel 25 cm (10in)
Opener Depth Range 0 to 10 cm (0 to 4in)
Opener Down Pressure 156 to 249 kg (345 to 550 lbs)
Tire Size 15-19.5 NHS 12 Ply
¹ Assumes no optional rear hitch weldment
² Assumes 3-point hitch
14.9 m (49ft 0in)
11.3 m (37ft 2in)
833 cm (328in)
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 53

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix A - Reference Information 49
Torque Values Chart
Bolt
Size
in-tpi
1
⁄4-20
1
⁄4-28
5
⁄16-18
5
⁄16-24
3
⁄8-16
3
⁄8-24
7
⁄16-14
7
⁄16-20
1
⁄2-13
1
⁄2-20
9
⁄16-12
9
⁄16-18
5
⁄8-11
5
⁄8-18
3
⁄4-10
3
⁄4-16
7
⁄8-9
7
⁄8-14
1-8
1-12
1
⁄8-7
1
1
1
⁄8-12
1
1
⁄4-7
1
1
⁄4-12
3
⁄8-6
1
3
1
⁄8-12
1
1
⁄2-6
1
1
⁄2-12
Bolt Head Identification
Grade 2 Grade 5 Grade 8 Class 5.8 Class 8.8 Class 10.9
a
b
d
N-m
ft-lb
7.4 11 16
8.5 13 18
15 24 33
17 26 37
27 42 59
31 47 67
43 67 95
49 75 105
66 105 145
75 115 165
95 150 210
105 165 235
130 205 285
150 230 325
235 360 510
260 405 570
225 585 820
250 640 905
340 875 1230
370 955 1350
480 1080 1750
540 1210 1960
680 1520 2460
750 1680 2730
890 1990 3230
1010 2270 3680
1180 2640 4290
1330 2970 4820
N-m N-m
5.6 8 12
61014 5 811
11 17 25 12 19 27
13 19 27 13 21 29
20 31 44 24 39 53
22 35 49 29 45 62
32 49 70 42 67 93
36 55 78 44 70 97
49 76 105 66 77 105
55 85 120 68 105 150
70 110 155 73 115 160
79 120 170 105 165 230
97 150 210 115 180 245
110 170 240 145 230 300
170 265 375 165 260 355
190 295 420 205 325 450
165 430 605 230 480 665
185 475 670 355 560 780
250 645 910 390 610 845
275 705 995 705 1120 1550
355 795 1290 785 1240 1710
395 890 1440 1270 1950 2700
500 1120 1820 1380 2190 3220
555 1240 2010
655 1470 2380
745 1670 2710
870 1950 3160
980 2190 3560
Bolt Head Identification
Bolt
Size
ft-lb ft-lb ft-lb ft-lb ft-lb
mm x pitch
M 5 X 0.8
M 6 X 1
M 8 X 1.25
M 8 X 1
M10 X 1.5
M10 X 0.75
M12 X 1.75
M12 X 1.5
M12 X 1
M14 X 2
M14 X 1.5
M16 X 2
M16 X 1.5
M18 X 2.5
M18 X 1.5
M20 X 2.5
M20 X 1.5
M24 X 3
M24 X 2
M30 X 3.5
M30 X 2
M36 X 3.5
M36 X 2
a. in-tpi = nominal thread diameter in inches-threads per inch
b. N· m = newton-meters
c. mm x pitch = nominal thread diameter in mm x thread pitch
d. ft-lb = foot pounds
c
5.8 8.8 10.9
N-m N-m N-m
357
71115
17 26 36
18 28 39
33 52 72
39 61 85
58 91 125
60 95 130
90 105 145
92 145 200
99 155 215
145 225 315
155 240 335
195 310 405
220 350 485
280 440 610
310 650 900
480 760 1050
525 830 1150
960 1510 2100
1060 1680 2320
1730 2650 3660
1880 2960 4100
946
Torque tolerance + 0%, -15% of torquing values. Unless otherwise specified use torque values listed above.
25199m
25199
Hydraulic Diagrams
Hydraulics are identical to standard YP2425 or YP4025.
Fan mounting hardware is slightly different.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 54

50 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Chain Routing YP2425F
See also “Chain Maintenance” on page 39.
Ground Drive Chain
U
R
F
B
L
D
17T
161
Legend:
34T
56P
Sprocket or idler Tooth count
Chain Pitch count
Direction of chain in motion
29T
25T
140
34737
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 55

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix A - Reference Information 51
Chain Routing YP4025F
See also “Chain Maintenance” on page 39.
Ground Drive Arm Chain
140
Legend:
34T
56P
Sprocket or idler Tooth count
Chain Pitch count
Direction of chain in motion
29T
25T
R
F
U
D
B
L
25T
29749
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 56

52 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Ground Drive Transmission Chains YP4025F
Note: Gearbox reverses chain direction.
72P
25T
30T
29T
125
25T
R
F
U
B
L
D
82P
25T
29767
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 57

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index 53
Appendix B - Monitor Setup
Seed Monitor Console Setup
Refer to Appendix B of the Operator manual for
DICKEY-john®IntelliAg® console installation. This
information below describes the factory settings for the
YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and YP4025F-1670
monitor configuration.
This setup information assumes the Virtual Terminal,
Master Switch, Working Set Master Module, Working Set
Member Module, and all sensors have been connected
and properly installed. Reference Operator’s manual for
installation instructions.
Pre-Programming Preparation:
1. Power on vehicle via ignition switch to activate
Virtual Terminal (VT). Main menu displays
pre-programmed default settings.
2. If errors are detected (e.g., failed sensors, incorrect
configuration) an alarm and code displays. Alarms
are silenced by pressing the Alarm Cancel
button . Refer to Operator’s manual for
troubleshooting assistance.
The system has three User Levels. The system loads in
User Level 1 (operator level) at every power cycle. A
password is required to change to User Level 2 and 3
screens to access setup constants (system
configuration).
Note: The master switch is only required for hydraulic
control systems. Reference the manual for
instructions to assign a master switch as an
auxiliary input.
Change User Level to Dealer Level
To change the User Level, a 6-digit password is required.
Password includes the five-digit serial number found on
the label of the Working Set Master or Information
screen.
3. On the IntelliAg Main Work screen, press the
Diagnostics button .
4. At the Diagnostics screen, press the Information
button .
5. At the Information screen, record serial number of
WSMT.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
6. Press the Password button .
7. On the Password screen, enter the 6-digit password
as follows: enter the first digit as 2 (for User Level 2).
For the next five digits, enter the Working Set Master
serial number taken from the WSMT or Information
screen.
8. Press the OK button . “Dealer screens on”
appears at the bottom of screen confirming the
password and dealer screens are activated.
9. Press the Work Screen button to return to the
Main Work screen.
Page 58

54 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Auto Configuration
(Identifies sensors connected to each module)
Auto config is performed at the factory, but may need to
be done in the field as changes are made to the system
or if options are added to the base planter.
Verify Auto Config results are correct. Check that the
correct number of rows are assigned to the correct
module and number of hopper sensors are assigned
accurately.
To Run Auto Config:
10. Press the Next Page button until the Module
Configuration button appears.
11. Press the Module Configuration button .
12. Press the AUTO CONFIG button .
13. Hour glass indicates system is detecting the
presence of seed or hopper sensors connected to
each module and automatically assigning them to
the appropriate module.
14. When Auto Config completes, press the Row Assign
button to display the Row Assignment screen to
verify correct Row # is assigned to the correct
module based on serial number.
15. Enter # of rows assigned to each module.
Module Configuration Screen
MODULE
ADDR.
(Optional)
(Optional)
SERIAL
NUMBER
10001
10002
10001
10001
10002
10003
10001
MODULE
TYPE
WSMB-POM
WSMB-POM
WSMB-18R
WSMT-GY
WSMB-18R
WSMB-POM
WSMB-CFM
Seed Sensor Configuration Screen
ADDR.
1
2
3
MODULE
TYPE
WSMB-18R
WSMT- GY
WSMB-18R
# OF
ROWS
5
6
5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ROW
#’s
1- 5
6-11
12-16
Row Status/Row Width Setup
16. At the Row Assignment screen, press the Row I/O
button .
17. Begin entering desired values using Table as
reference.
18. Press the Work Screen button when Row
Status/Row Width configurations are complete to
return to the Main Work screen.
Row
Width
Auto
Update
Width
On/Off
Pattern
Pop/Blo
Row Status/Row Width Setup
Default Value or
Value to Enter
YP2425F-2470:
70cm or 27.56in
YP4025F-1670:
70cm or 27.56in
YP4025F-1630
30in or 76.2cm
Disabled
Every Row On
Rows
Instructions/Definitio
ns
Enter row width distance
in inches to calculate
seed rate correctly.
Manually enter
implement width at
Table data entry.
On/Off Pattern indicates
specific row patterns to
be on or off. Select
pre-defined planter All
Row On pattern. For
other pre-defined planter
patterns or individual
row settings, see PDC
Operator manual.
Determines which
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 59

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix B - Monitor Setup 55
Material Configuration Setup
(Controlled Hydraulic Drive)
16 different materials can be configured for use as
planter controls. Reference the System Configuration
section in the PDC Operator manual for additional
information.
19. At the Main Menu screen, press the Control Setup
button .
20. Select and press one of the Material buttons
(Material 1-16).
21. Enter desired values from Table .
22. Press the Control Setup button to return to the
Control Setup screen.
23. Repeat steps 2-4 for additional materials.
24. Press the Channel Setup button to proceed to
channel setup screen.
Matrl
Label
Type
Units
Preset
Metho
d
Seeds
per
Rev
Disc
Low
Limit
Disc
High
Limit
High
Pop
Alarm
Material Setup
Default Value
or Value to
Enter
Matrl 1
Planter Control
Ks/Ha or Ks/Ac
S/Sec
Enable
See Manual
5 (Singulator
Plus)
40 (finger
pickup)
40 (Singulator
Plus)
85 (finger
pickup)
15%
Controlled Hydraulic
Drive
Instructions/Definitions
Material Name can be
customized to accurately
define the material’s type.
Creating a name allows for
quick identification at the
Control Setup screen.
Desired type of application
control channel being used
for a specific material. The
Material Type must correctly
match the Control Type to be
able to select Material from
the Material Summary screen
and operate properly.
Automatically changes with
the type of material
application selected.
Changes units for target
application.
Enabled Preset Method
allows 10 user-defined target
rates to be adjusted from the
Main Work screen using Inc
or Dec buttons. A Disabled
Preset Method
increases/decreases the
target rate based on the %
values set at the Material
Setup screen.
Set to number of seeds per 1
disc revolution.
Set to desired min seed disc
RPM.
Set to desired max seed disc
RPM.
This is the percentage above
the target population of the
planter channel if rows are
assigned to the planter
channel. If rows are not
assigned to a planter, this is
the percentage above
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 60

56 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Planter Control Channel Setup
(Controlled Hydraulic Drive)
25. At the Control Setup screen, press the Channel
Setup button .
26. Select Channel 1 and verify that the channel is set to
Planter Control.
27. Enter desired values using Table as reference.
28. After planter control setup, calibrate hydraulic valve
by pressing the Valve Cal button .
29. Ensure implement is raised. With brakes locked and
transmission in PARK position, start engine.
30. Engage hydraulics and run engine at normal speed
until hydraulic fluid is at operating temperature.
31. Verify point row clutches are turned ON.
Equipment Damage Risk:
Do NOT perform the next step unless meters are installed in all
locations across planter row units or drive damage may occur.
32. Press the START button . Turn the master switch
to the ON position.
33. The valve calibration starts immediately. Keep the
hydraulics engaged until the calibration completes.
34. When the screen indicates calibration is complete,
press the Channel Setup button to return to
Channel 1 home screen.
35. Turn the master switch OFF.
36. To set up additional control channels (planter or
fertilizer control), press the Next Channel button .
37. Press the Work Screen button when channel
configurations are complete to return to the Main
Work screen.
Once a control channel has been established as Planter
Control, any new materials established as Planter
Control on the Material Setup screen are automatically
added as optional materials for Planter Control channels
on the Control Setup screen.
Planter Control Setup
Default
Value or
Value to
Enter
Type Planter
Control
Material
Name
Control
Mode
AUTO
Drive
Type PWM
Drive
Frequen
cy
Input
Filter 50
Gear
Ratio
Sensor
Constan
t
# of
Seed
Rows
100 Hz
1.900
360
Instructions/Definitions
Set desired Channel Type as
Planter Control.
Displays only materials that
have been configured for the
channel type.
Auto is used in normal
operating conditions
calculating the rate of how the
system is running. Manual
mode acts as an override if
application rate sensors are
inoperable allowing the use of
increase/decrease buttons to
set the fl ow rate for the
control. Refer to System
Configuration section of PDC
Operator manual for additional
information.
A hydraulic valve varies the oil
flow to the motor proportioned
to the electric current supplied.
If not using a DICKEY-john
supplied valve, see the
manufacturer’s specifications
for drive frequency.
Feedback frequency filter for
the control channel. DO NOT
CHANGE.
Specifies the actual ratio from
the feedback sensor to the
seed meter shaft RPM.
Number of revolutions the
feedback sensor turns in
relation to one revolution the
seed meter turns.
Sensor Constant establishes
the number of pulses for one
revolution of the feedback
sensor. If a DICKEY-john
application rate sensor is
used, the value should be set
to 360.0.
Entry of a specific number of
seed rows for the control
channel. Row assignment is
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 61

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix B - Monitor Setup 57
Valve Calibration
A valve calibration is required for each control channel
that is enabled. If no additional channels are enabled
other than one channel, this step can be skipped.
Channels must be turned ON for valve calibration to
operate.
38. Press the Control Setup button .
39. Press the Channel Setup button .
40. Press the Valve Calibration button .
41. Ensure implement is raised. With brakes locked and
transmission in PARK position, start engine.
42. Engage hydraulics and run engine at normal speed
until hydraulic fluid is at operating temperature.
Equipment Damage Risk:
Do NOT perform the next step unless meters are installed in all
locations across planter row units or drive damage may occur.
43. Press the START button . Turn the master switch
to the ON position. The valve calibration starts
immediately. Keep the hydraulics engaged until the
calibration completes.
44. Repeat for each configured channel.
Row Monitor Setup
45. At the Main Work screen, press the Row Monitor
button .
46. Enter desired values using Table as reference.
47. Press the Work Screen button to return to the
Main Work screen.
Material
Name
High
Alarm
Delay
Low
Alarm
Delay
Populati
on
Row Monitor Setup
Default
Value or
Value to
Enter
See
Instructions
5
5
Instructions/Definitions
Material Name only appears on
the Row Monitor Setup screen
when all control channels are
disabled and material is set for
Monitor Only. This is only used
for ground drive/non-hydraulic
applications to monitor
population with high and low
alarms. A material must be
configured and selected to
activate alarms.
Desired number of seconds
that high population can be
above high alarm point before
alarm will sound.
Desired number of seconds
that low population can be
below low alarm point before
alarm will sound.
Enter a % to allow for seed
sensor population inaccuracies
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 62

58 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Speed Set Calibration Setup
48. At the Main Work screen, press the Speed Set
button .
49. Enter desired values using Table as reference.
50. Press the Work Screen button when ground
speed calibration configurations are complete to
return to the Main Work screen.
Source
Gspd
Consta
nt
Shutoff
Speed
Minimu
m
Overrid
e
Master
Sw
Timeo
ut
Gspd
Fail
Alarm
Delay
Precha
rge
Groun
Default
Value
or
Value to
Enter
Digital
Frequenc
y
10000
(@100
m)
12192
(@400 ft)
0.8 kph
0.5 mph
3.2 kph
2.0 mph
10
5
Speed Set
Instructions/Definitions
Select CAN Ground if radar is
connected to ISO tractor cab
harness. Select Digital Frequency if
radar or hall-effect is connected to
WSMT actuator harness.
Input based on pulse count
produced by the ground speed
sensor over 100m or 400ft course.
See PDC Operator manual for
calibration instructions.
Set desired minimum ground speed
allowed before the system shuts off.
Set to operate when actual ground
speed falls below the designated
value. Control will operate at this
speed until actual ground speed
rises above minimum override
speed or actual speed drops below
shutoff.
Set to desired number of seconds
system shuts off if the master
switch is turned on and there is no
ground speed. Toggle master
switch to restart the system and
turn off alarm.
Set to desired number of seconds
alarm sounds after the ground
speed is zero and seed flow
continues. (Monitor only).
Set to the desired speed the system
will use when a precharge time has
been enabled for a control channel.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 63

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix B - Monitor Setup 59
Accessory Sensor Setup
Hopper Assignment
51. At the Main Work screen, press the Next Page
button .
52. Press the Module Configuration button to display
the Module Configuration screen.
53. At the Module Configuration screen, press the
Hopper Assign button .
54. Press Hopper Set button .
55. Enter desired values using Table as reference.
RPM Assignment
56. At the Module Configuration screen, press the
Accessory Assignment button .
57. Press the RPM Setup button .
Note: There must be at least 1 RPM sensor configured
before the RPM Setup button appears on the
screen.
58. Enter desired values using Table as reference.
Hopper Setup
# of
Hoppers
Logic
Level
Alarm
Delay
Channel Assigns hopper sensor to
RPM Setup
High
Alarm
(fan
speed)
Low
Alarm
(fan
speed)
High
Alarm
Delay 10 sec
Low
Alarm
Delay 10 sec
Accessory Setup
Default
Valueor
Value to
Enter
# of hopper sensors connected to
2
(base unit
)
2 more
(optional)
Active Lo
5 sec
4200 rpm
2900 rpm
each module (4 sensors
maximum). # of hopper data
items for each listed module and
the Hopper #’s value will
automatically populate if Auto
Config is used to configure
installed sensors.
Sets the active state to low
signifying that an alarm is
generated if the sensor’s output is
in a low state. Use this setting if
the connected sensor outputs a
low condition when empty similar
to the DICKEY-john hopper
sensor.
Controls the delay time between
the detection of a high/low
hopper alarm condition and the
generation of the resulting alarm.
The value is entered in seconds.
channel.
Sets the RPM value at which a
high RPM warning error is
generated.
Sets the RPM value at which a
low RPM warning error is
generated.
Establishes the delay between
the detection of a high RPM
alarm condition and the resulting
alarm display. The value is
entered in seconds.
Establishes the delay between
the detection of a low RPM alarm
condition and the resulting alarm
display. The value is entered in
seconds.
Instructions/Definitions
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 64

60 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Clutch Folding Module (CFM) Setup
The CFM is installed in the cab to control row clutches,
marker, fold, fertilizer on/off, lift and hitch.
59. At the Main Work screen, press the Clutch CFG
button to access the Clutch Configuration screen
and verify that the correct # of clutches are
configured for the system.
Note: The Clutch CFG button only appears as a top level
button when a planter output module and clutch
folding module are installed.
YP4025F
# of Clutches 3
# of Clutches
# OF
Output
OUTPUT
LEFT
Left 5 1-5
CENTER
Center 6 6-11
RIGHT
Right 5 12-16
# OF
ROWS
5
6
5
ROWS
3
ROW
ROW
#’s
#’s
1-5
6-11
12-16
Clutch Folding Module Operation
Refer to Figure 25
60. The planter section “CLUTCH” controls turn the
left, center, and right seeding clutch controls on and
off. Dry fertilizer application is unaffected.
61. The master switch must be in the ON position to
activate any planter section. When a clutch control is
ON, a green light illuminates.
62. Marker/Fold Switch should be in the UP (Marker)
position during planting. In the DOWN (Fold)
position, the switch controls the fold of the main
frame.
63. The fertilizer pump switch usually has no function
on a YP2425F-2470, YP4025F-1630 and
YP4025F-1670 planter. Leave this switch in the
DOWN position (OFF).
64. If the planter has the optional hydraulic tongue, the
Lift/Hitch switch should be in the UP (Lift) position
during normal operation (circuit controls implement
lift).
In the “Hitch” position (DOWN), the hydraulic circuit
controls the telescoping tongue in preparation of
folding the implement for transport.
2
3
4
5
1
5 Revolution Test
65. Press the Control Setup button .
66. Press the Channel Setup button .
67. Press the Next Page button .
68. Ensure implement is raised before starting
5 Rev Test.
69. With brakes locked and transmission in PARK
position, start tractor engine.
70. Engage hydraulics and run engine at normal speed
until hydraulic fluid is at operating temperature.
71. Press the 5 Rev button .
Note: Test Ground Speed and Row data must be entered
to perform test.
72. Press and hold remote test button to initiate 5 Rev Test.
Left 9 1-9
YP2425F
2
Equipment Damage Risk (Hydraulic Tongue Only):
Lift/Hitch switch MUST be in the hitch position and hydraulic
circuit in FLOAT when transporting planter equipped with
hydraulic-operated tongue hitch.
Note: Lift/Hitch switch has no function if planter has
standard 3-point hitch operated tongue hitch.
Center 6 10-15
Right 9 16-24
3
{
1
Figure 25
Clutch-Folding Module
4
5
29718
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 65

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix B - Monitor Setup 61
Summary Screen
The Summary screen provides an overview of setup
constants for active control channels.
73. At the Main Work screen, press the Next Page
button .
74. Press the Summary button
75. To view specific control channel configurations,
press the respective control channel box 1-4.
76. Press inside a yellow highlighted box to open a
specific screen for editing.
77. Press the Work Screen button to return to the
Main Work screen.
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 66

62 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
n
Spacing
P
p
p
page 26).
n
Appendix C - Fertilizer Rate Charts
Reading the Fertilizer Rate Chart
1. Locate the chart for your planter model.
2. Find your target rate in the chart.
Note that each chart is actually two charts, a
Low Range and a High Range. The upper rates of
the Low Range overlap with the lower rates of the
High Range.
3. Determine the Final Range gearing required.
The gear tooth counts are shown on the top of
page 63. The gear change procedure is described
on page 23.
4. Note the reference Material Density used to develop
the chart, shown at the top of page 63.
If your material density is substantially different, or
you are planning to apply without calibration, perform
a density adjustment (page 66) prior to step 5.
0cm Row Spacing
aR hgiH )mc07( 0761-F5304PYegnaR woL )mc07( 07
Gearbox Meter RPM Material Rate Gearbox
egnaR hgiH )mc07( 0761-F5304PYegnaR woL )
earbox Meter RPM Material Rate Gearbox Meter R
etting at 9.7 kph kg/ha lbs/ac Setting at 9.7 k
00 00 00
5 - N/R* N/R* 5 -
10 - N/R* N/R* 10 -
15 - N/R* N/R* 15 -
20 0.45 17 15 20 4.4
25 0.80 30 26 25 7.8
30 1.1 42 38 30 11
terial density
lication (see
Charts are based on factory standard ground drive system sprockets, with Range determined by final gears:
Low Range: 17T Driving, 54T Driven
High Range: 54T Driving, 17T Driven.
See page 24 for gear setting.
“Meter RPM” is based on a field speed of 9.7 kph
Charts are based on:
11-52-0 fertilizer with a density of:
0.96 kg/liter (60 pounds per cubic foot).
If your material has a significantly different density, see
“Density Adjustment” on page 64
5. Find your target fertilizer rate (which is
kilograms-per-hectare or pounds-per-acre).
6. Set the Variable Rate Gearbox control arm as
specified in the “Gearbox Setting” column. See
page 24 for setting procedure.
Note: Charts begin at setting 20 and end at 90.
Settings below 20 and above 90 are not
recommended (N/R), other than zero (0), which
may be used to temporarily shut off flow from the
meter.
ox Meter RPM Material Rate Gearbox Meter RPM
g at 9.7 kph kg/ha lbs/ac Setting at 9.7 kph
00000
- N/R* N/R* 5 -
- N/R* N/R* 10 -
- N/R* N/R* 15 -
0.45 17 15 20 4.4
0.80 30 26 25 7.8
1.1 42 38 30 11
egnaR hgiH )mc07( 0761-F5304PYegnaR w
7. Calibrate for your material (unless applying a
material for which you already have calibrated).
8. For the final gearbox and range, note the
Meter RPM. Set low and high rpm limits for the shaft
sensor. If using a different field speed, scale the
chart rpm by the speed ratios:
ratio = (actual ÷ chart).
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
ox Meter RPM Material Rate Gearbox Meter RPM
g at 9.7 kph kg/ha lbs/ac Setting at 9.7 kph
00000
- N/R* N/R* 5 -
- N/R* N/R* 10 -
- N/R* N/R* 15 -
0.45 17 15 20 4.4
0.80 30 26 25 7.8
egnaR hgiH )mc07( 0761-F5304PYegnaR
Page 67

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix C - Fertilizer Rate Charts 63
Fertilizer Rates
Rates are approximate, and vary with material density
and granularity. Calibrate for accurate application (see
page 25).
Charts are based on:
11-52-0 fertilizer with a density of:
0.96 kg/liter (60 pounds per cubic foot).
If your material has a significantly different density, see
“Density Adjustment” on page 66
Charts are based on factory standard ground drive
system sprockets, with Range determined by final gears:
Low Range: 17T Driving, 54T Driven
High Range: 54T Driving, 17T Driven.
See page 23 for gear setting.
“Meter RPM” is based on a field speed of 9.7 kph
(6 mph). If using a different field speed, scale RPM
proportionately. Set meter rpm limits (for shaft monitor
alarm) to ±25% of this value (or as desired).
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 68

64 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Fertilizer Rates, 70cm Row Spacing
YP2425F-2470 or YP4025F-1670 (70cm) Low Range YP2425F-2470 or YP4025F-1670 (70cm) High Range
Material Rate Gearbox Meter RPM Material Rate Gearbox Meter RPM
kg/ha lbs/ac Setting at 9.7 kph kg/ha lbs/ac Setting at 9.7 kph
0000 0000
N/R* N/R* 5 - N/R* N/R* 5 -
N/R* N/R* 10 - N/R* N/R* 10 -
N/R* N/R* 15 - N/R* N/R* 15 -
1.7 1.5 20 0.45 17 15 20 4.4
3.0 2.7 25 0.80 30 26 25 7.8
4.3 3.9 30 1.1 42 38 30 11
6.2 5.6 35 1.7 61 54 35 16
8.1 7.3 40 2.2 80 71 40 21
10 9 45 2.8 102 91 45 27
13 11 50 3.4 124 110 50 33
16 14 55 4.1 153 137 55 40
19 17 60 4.9 182 163 60 48
22 20 65 5.9 217 194 65 57
26 23 70 6.8 252 225 70 67
30 26 75 7.8 289 258 75 76
33 30 80 8.8 325 290 80 86
37 33 85 9.9 366 327 85 97
42 37 90 11.0 407 364 90 108
N/R* N/R* 95 - N/R* N/R* 95 -
N/R* N/R* 100 - N/R* N/R* 100 -
* Not Recommended. * Not Recommended.
31096m
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 69

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Appendix C - Fertilizer Rate Charts 65
Fertilizer Rates, 30 inch Row Spacing
YP4025F-1630 (30in) Low Range YP4025F-1630 (30in) High Range
Material Rate Gearbox Meter RPM Material Rate Gearbox Meter RPM
kg/ha lbs/ac Setting at 6 mph kg/ha lbs/ac Setting at 6 mph
0000 0000
N/R* N/R* 5 - N/R* N/R* 5 -
N/R* N/R* 10 - N/R* N/R* 10 -
N/R* N/R* 15 - N/R* N/R* 15 -
1.6 1.4 20 0.45 15 14 20 4.4
2.8 2.5 25 0.80 27 24 25 7.8
4.0 3.5 30 1.1 39 35 30 11
5.7 5.1 35 1.7 56 50 35 16
7.5 6.7 40 2.2 73 65 40 21
9.6 8.5 45 2.8 93 83 45 27
11.6 10.4 50 3.4 114 101 50 33
14 12.8 55 4.1 141 126 55 40
17 15 60 4.9 167 150 60 48
20 18 65 5.9 200 178 65 57
24 21 70 6.8 232 207 70 67
27 24 75 7.8 265 237 75 76
31 27 80 8.8 299 267 80 86
34 31 85 9.9 337 301 85 97
38 34 90 11.0 374 334 90 108
N/R* N/R* 95 - N/R* N/R* 95 -
N/R* N/R* 100 - N/R* N/R* 100 -
* Not Recommended. * Not Recommended.
31096u
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 70

66 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Density Adjustment
If your material (seed or fertilizer) has a density that is
materially different from the reference material listed at
the top of each chart, you can compensate for it.
Density variance is only one of many factors that can
cause an actual rate to vary from a chart rate.
Compensating your initial target rate helps reduce the
error, but rely on calibration for the most accurate field
results.
In this example, the target fertilizer application rate is 120
kilograms per hectare.
Example:
Target fertilizer rate is 120 kilograms per hectare
1. Weigh a known volume of your material, and
compute the density in the same units used in the
table, kilograms per liter (pounds per bushel or
pounds per cubic foot). Be sure to subtract out the
container weight.
2. Divide the reference material density by the
measured actual material density, to obtain a
correction factor.
ReferenceMaterialDensity
Factor
-----------------------------------------------------------------
=
MeasuredMaterialDensity
3. Multiply the target field rate by the factor to yield an
adjusted chart rate.
AdjustedRate FieldRate Factor×=
4. Look up the adjusted rate in the chart, and use the
settings for it.
Note: If the adjusted chart rate would correspond to an
apparent variable rate gearbox setting below 20,
use another chart (Low Range chart or lower Flute
Stars chart).
Example:
10 liters of your material weighs 14 kg.
Your material density is: 14 ÷ 10
which is: 1.4 kg per liter
The chart was based on 0.96 kg/l reference material that
is 134% heavier. If the chart value for “120” (a variable
rate gearbox setting of 45,) is used, too much material
will be applied.
Example:
reference material: 0.96 kg/l
factor: 0.96 ÷ 1.4
which is: 68.6%
Example:
if the target field rate is 120 kilograms per hectare, the
adjusted chart rate is:
120 x .686
which is an adjusted target rate of:
82 kilograms per hectare
Example:
Look up 82.
Closest chart value is 90
Use those settings:
High Range
Gearbox 40
Be sure to calibrate (page 25), to verify the adjustment
and setting.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 71

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index 67
Index
A
adhesion ............................................ 25
agitator shaft ...................................... 23
air pressure ........................................ 17
air release .......................................... 15
air release vent................................... 14
air system .................................... 14,16
airbox manifold ................................... 14
airbox seed inlet ................................. 14
Alarm Cancel ..................................... 53
applicator ..............................16,17, 29
auger ........................................... 11,12
Auto Config ........................................ 54
Auto Update Width ............................. 54
B
bar ...................................................... 19
basket ................................................ 12
blade .................................................. 29
Blockage ............................................ 20
blockage detection ............................. 31
blockage sensor ....................16,17, 20
bridge .......................................... 37, 38
bridges .......................................... 3,37
bridging ....................................... 31,32
bulk-box................................................ 6
butterfly valve ........................17,19, 31
fertilizer .................................. 16,17
seed ...................................... 14
,15
C
CAL CONST ...................................... 20
calibration ........................................... 25
calibration door .............. 16, 17,27,35
capacities .................................... 47,48
case drain .......................................... 18
CAUTION, defined ............................... 1
center of gravity.................................. 10
chain
meter drive ................................... 39
chain clip ............................................ 39
chain maintenance ............................. 39
chain routing YP2425F ...................... 50
chain routing YP4025F ...................... 51
Channel Setup ............... 55
check valve, fan .................................. 18
checklists
air system ..................................... 21
electrical ....................................... 21
field ............................................... 21
hydraulic system .......................... 21
mechanical ................................... 21
meter drive ................................... 21
pre-start .......................................... 9
row units ....................................... 21
chemical ............................................... 5
chemicals ............................................. 2
clean-out ............................................ 35
clean-out door .......................16
clean-out, problem ............................. 36
,56,57, 60
,17,35
clip, chain ........................................... 39
Clutch CFG ........................................ 60
cm H2O ............................................. 19
confined space ......................... 3
congealed materials .......................... 36
console
seed monitor ................................ 53
container, sample .............................. 26
Control Setup ........................ 55
corrosive ............................................ 21
cotton ................................................. 45
coulter ................................... 16, 17, 29
coulter tine ......................................... 29
coupler ............................................... 15
covered models ................................... 6
crank ..................................... 25, 26, 27
cranking speed .................................. 25
crusts ......................................3,37, 38
,4,12
,57,60
D
DANGER, defined................................ 1
decal replacement ............................... 4
decals
caution
chemical hazard ....................... 5
entangle/crush.......................... 5
eye protection........................... 5
warning
confined space ......................... 4
decal, safety......................................... 4
definitions ............................................ 7
density ........................... 25
detector blockage .............................. 16
Diagnostics ........................................ 53
DICKEY-john® ........................ 6,20,53
directions ............................................. 7
disposal, chemical ............................... 2
door
calibration...............................17, 27
clean-out ...................................... 17
door, calibration ................................. 16
door, clean-out ................................... 16
drive
meter ............................................ 14
DRIVEN ............................................. 23
DRIVING ......................................23
dust .................................................... 37
,32,62, 66
,27
E
earmuff ................................................ 2
entanglement ....................................... 5
entrapment ....................................3,37
entry, hopper...................................... 37
equipment, safety ................................ 2
example
calibration..................................... 28
density.......................................... 66
excessive rpm .................................... 19
eye protection ...................................... 5
Ezee Glide Plus ................................. 45
F
face shield ............................................2
fan ........................... 14,15,16, 17, 19
fan hoses ............................................18
fan operation ...................................... 18
fan rpm ...............................................18
fan rpm sensor ............................ 14,16
fan speed..................................... 18,31
fertilizer butterfly valve ........................ 16
fertilizer hopper............................ 16,17
fertilizer level sensor...........................16
fertilizer meter.............................. 16,17
fertilizer rate..........................................6
fertilizer shut-off ....................................9
field conditions ................................... 25
field operation .....................................21
finger pickup .......................................15
fire ........................................................ 1
flute shaft ............................................36
flute stars .............................. 16,17, 36
FMC Force ......................................... 30
force, coulter.......................................30
Force, FMC ........................................ 30
fumes ............................................ 3,37
G
gear range .......................................... 23
gearbox .............................................. 24
gears .................................................... 5
gears, range ................................ 16,17
gloves ................................................... 2
goggles .................................................2
gpm, fan ............................................. 18
GRAN FERT.......................................20
granular system ....................................6
granularity...........................................25
graphite powder..................................45
H
hard ground ........................................ 25
headphones ......................................... 2
hearing ................................................. 2
High Range ................................. 23,62
hitching ................................................. 8
hopper ..................................................3
fertilizer ..................................16,17
seed ..............................................14
hopper entry .................................. 3
hopper level sensor ............................38
hopper pressure .................................18
Hopper Set .........................................59
hopper, seed ...................................... 11
hose
seed ..............................................14
hose, fan.............................................18
humidity ....................................... 25
hydraulic diagram ...............................49
hydraulic fan .....................2,14, 15,16
hydraulic flow......................................19
hydraulic hose ....................................18
,38
,45
2013-03-25 Table of Contents 403-362M
Page 72

68 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
I
in H2O ................................................ 19
Information ......................................... 53
inhalation hazard......................... 11,12
IntelliAg® ................................6,20,53
intended usage .................................... 6
K
kPa ..................................................... 19
L
ladder .......................................... 11,17
latch ................................................... 11
leak .................................................... 31
left-hand, defined ................................. 7
level sensor ................................. 15,20
fertilizer......................................... 16
seed ............................................. 14
level sensor, hopper ........................... 38
lid, fertilizer ......................................... 12
lid, seed.............................................. 11
Lift/Hitch ............................................. 60
limits, rpm .......................................... 20
liquid fertilizer ..................................... 13
loading materials ................................ 11
Low Range .................................. 23
lubricant, seed ................................... 45
,62
M
maintenance ...................................... 34
maintenance safety .............................. 3
manifold ................................15,16, 17
fertilizer air.................................... 16
seed ............................................. 14
manifold, airbox.................................. 14
marker operation ................................ 20
Marker/Fold ........................................ 60
master switch .............................. 53
Material .............................................. 55
material clean-out .............................. 35
material rate .................................. 6,23
material safety data sheets ................ 38
meter
fertilizer......................................... 17
seed ............................................. 14
meter box, removing .......................... 37
meter chain ........................................ 39
meter drive ......................................... 14
meter rpm .......................................... 62
meter sample .............................. 25
meter, fertilizer ................................... 16
meter, seed ........................................ 15
milo .................................................... 45
Module Configuration .................. 54,59
moment arm ....................................... 10
motor seals ........................................ 18
MSDS................................................. 38
,60
,27
N
Next Channel ..................................... 56
Next Page ...................... 54,59,60, 61
Note, defined........................................ 7
NOTICE, defined.................................. 7
no-till .................................................. 30
O
obstructions ........................................38
OK ......................................................53
On/Off Pattern ....................................54
operation
marker...........................................20
options ................................................46
orientation rose .....................................7
OSHA .................................................38
oxygen ................................................37
P
parking ................................................21
Password ............................................53
password ............................................53
permit-required confined space .....3, 38
personal safety equipment ...................2
pests ...................................................12
piston ..................................................11
Population...........................................20
Pop/Block Pattern ...............................54
pressure..............................................19
pressure sensor .................... 16,17,20
protection, hearing ................................2
protective equipment ............................2
psi .......................................................19
Q
QD coupler .........................................18
QD (Quick Disconnect) .......................18
Quick Disconnect................................18
R
railing ...........................................11, 12
range gears .......................... 16,17, 23
rate chart ............................................62
rate, material.......................................23
reflectors, safety ...................................4
remove meter box...............................37
respirator ..............................................2
return line, fan.....................................18
reverse fan ..........................................18
reversed fan ........................................18
reverse, fan .........................................31
revolutions ..........................................25
right-hand, defined ...............................7
rocky conditions ..................................30
rose, orientation ....................................7
Row Assign.........................................54
Row I/O...............................................54
Row Monitor .......................................57
row number.........................................20
row sample ..................................25,26
rpm .............................................. 15,17
rpm limits ............................................20
rpm sensor ........................... 16,17, 20
fan .......................................... 14,16
RPM Setup .........................................59
rpm, engine ........................................19
rpm, excessive....................................19
S
safety decal ..........................................4
safety equipment ..................................2
safety information .................................1
hopper entry..................................37
safety symbol ....................................... 1
scale, gearbox .................................... 24
seal, lid ...............................................12
seed butterfly valve ..................... 14
seed hopper ..........................11,14,15
seed hose...........................................14
seed inlet, airbox ................................14
seed level sensor ............................... 14
seed lubricant ................................ 2,45
seed meter .................................. 14,15
seed monitor ........................................ 6
seed monitor console .........................53
Seed Monitor Manual Level 1............... 7
Seed Monitor Manual Level 2 and 3..... 7
seed sensor................................. 14, 15
seed treatment ..................................... 2
seed tube .................................... 14,15
sensor
fan ......................................... 14,16
fertilizer level ................................ 16
pressure ....................................... 17
rpm ............................................... 17
seed ..............................................14
seed level ..................................... 14
sensor, blockage ................................ 16
sensor, hopper level ...........................38
sensor, pressure................................. 16
sensor, rpm ........................................ 16
sensor, seed.......................................15
sensor, seed level...............................15
setup .................................................... 8
initial ............................................... 8
seasonal .........................................8
shackle ...............................................12
shaft monitor ............................... 17
shaft rate ............................................ 17
shaft, flute...........................................36
shut-off, fertilizer...................................9
silicone sealant...................................37
Singulator Plus® ................................ 15
slack, chain ........................................ 39
slide gate ..................................... 14,15
soft ground ......................................... 25
specifications............................... 47, 48
speed limit
forward ......................................... 10
Speed Set .......................................... 58
speed to crank....................................25
springs, coulter ................................... 30
stars ......................................16
START ......................................... 56,57
storage ..................................12,21,35
strainer ........................................ 12,36
stubborn material ............................... 37
suffocation ..................................... 3,37
Summary ............................................ 61
sump return ........................................18
symbol, safety ...................................... 1
,15
,20
,17,36
T
tables
adjustments ..................................22
document family ............................. 7
FMC spring ................................... 30
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 73

Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc. Table of Contents Index Index 69
models covered .............................. 6
torque values ................................ 49
troubleshooting
general............................. 31
weights ......................................... 10
talc-graphite lubricant ......................... 45
tare .............................................. 26
tarp ..................................................... 27
texture ................................................ 25
tine ..................................................... 29
tool bar height .................................... 29
torque
fastener ........................................ 49
tower ........................................... 16
towing vehicle capability.....................10
toxic gases ......................................... 37
trailer operations ................................ 14
transport ............................................. 10
treated seed ......................................... 2
troubleshooting................................... 31
tube
seed ............................................. 14
,33
,28
,17
U
User Level .......................................... 53
V
Valve Cal ............................................ 56
Valve Calibration ................................ 57
variable rate gearbox ......................... 24
vent ....................................... 15
meter inlet .................................... 14
vent structure ..................................... 11
vent tube structure ............................... 3
void ................................................3
VT ...................................................... 53
,16,17
,37
W
walkboard .......................................... 11
WARNING, defined.............................. 1
warranty ............................................. 30
wash .................................................... 2
wash-out ............................................ 36
welding ................................................ 3
wind ..................................................... 2
Work Screen ..... 53,54,56, 57, 58,61
WSMT ................................................ 53
Y
YP2425F weights............................... 10
YP2425F-2470 ................ 6,23,54, 56
YP4025F weights............................... 10
YP4025F-1630 ..........6, 23,54,56, 65
YP4025F-1670 ..........6, 23,54,56, 64
Y-tube ...........................................15, 35
Z
zero setting .......................................... 9
zone ............................................. 17,29
Numerics
110011508, manual..............................7
110011512, manual..............................7
11-52-0 ........................................ 25,63
150bu hopper .....................................13
2-way ..................................................17
20 mph ............................................... 10
29 CFR 1910.146 ............................... 38
3-way ..................................................17
401-406B, manual .................. 7, 22,23
401-406M, manual . 6,7, 8,18,22, 23
401-406P, manual ................................. 7
401-571B, manual .........................7,23
401-571M, manual 6
401-571P, manual ................................. 7
403-362M, manual .......................... 6
403-414H, crank .................................25
5 Rev Test .......................................... 60
82bu hopper .......................................13
821-042C, graphite.............................45
821-060C, graphite.............................45
821-069C, graphite+talc ..................... 45
848-509C, decal ................................... 5
848-510C, decal ................................... 5
848-519C, decal ................................... 4
848-520C, decal ................................... 5
848-522C, decal ................................... 5
,7,10, 18,22,23
,7
2013-03-25 Table of Contents Index 403-362M
Page 74

70 YP2425F/YP4025F Table of Contents Index Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
403-362M Table of Contents Index 2013-03-25
Page 75

Table of Contents Index
Table of Contents Index
Page 76

Table of Contents Index
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
Corporate Office: P.O. Box 5060
Salina, Kansas 67402-5060 USA
 Loading...
Loading...