Page 1

GREAT-150iM-II
For Milling Machine
& Machining Center
User Manual
Page 2

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
INDEX
CHAPTER I PREFACE................................................................................................................................................ 1
CHAPTER II TECHNICAL FEATURE............................................................................................................................2
2.1 SYSTEM CONSTRUCTIONS ...................................................................................................................................... 2
2.2 SYSTEM TECHNICAL PARAMETER....................................................................................................................... 2
2.3 SYSTEM FUNCTION.................................................................................................................................................... 2
2.3.1 AUTO-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION:...................................................................................................................................... 2
2.3.2 COMPENSATION FUNCTION: ........................................................................................................................................2
2.3.3 ABUNDANT INSTRUCTION SYSTEM:............................................................................................................................. 3
2.3.4 CHINESE/ENGLISH MENU, FULL SCREEN EDITION:....................................................................................................... 3
2.3.5 ABUNDANT DEBUGGING FUNCTIONS:.......................................................................................................................... 3
2.3.6 PROGRAM EXCHANGE BETWEEN CNC SYSTEM AND IBM/PC SERIES COMPATIBLE COMPUTER................................... 3
2.4 SYSTEM OPERATION CONDITION......................................................................................................................... 3
2.4.1 POWER SUPPLY:........................................................................................................................................................... 3
2.4.2 CLIMATE CONDITION................................................................................................................................................... 3
2.4.3 OPERATION ENVIRONMENT:........................................................................................................................................ 3
CHAPTER III OPERATION...............................................................................................................................................4
3.1 PANEL L AYOUT AND SWITCH................................................................................................................................. 4
3.2 OPERATION INTERFACE .......................................................................................................................................... 6
3.3 PARAMETER................................................................................................................................................................. 9
3.4 PARAMETER EXPLANATION................................................................................................................................. 10
3.4.1 USER PARAMETER..................................................................................................................................................... 10
3.4.2 SPEED ....................................................................................................................................................................... 14
3.4.3 COORDINATE SYSTEM ............................................................................................................................................... 19
3.4.4 MACRO VARIABLE PARAMETER ................................................................................................................................ 20
3.4.5 AXIS PARAMETER...................................................................................................................................................... 20
3.4.6 COMPREHENSIVE PARAMETER .................................................................................................................................. 31
3.4.7 PASSWORD ................................................................................................................................................................ 39
3.4.7.1 Access authority setting .................................................................................................................................... 40
3.5 DIAGNOSE................................................................................................................................................................... 43
3.5.1 I/O REAL-TIME MONITOR ..........................................................................................................................................43
3.5.2 LADDER REAL-TIME MONITOR .................................................................................................................................. 44
3.5.3 CONFIGURATION OF INPUT/OUTPUT AND SELF-DEFINED ALARM................................................................................ 44
3.5.4 CLEAR ALARM ACCIDENT OF FEED SERVO DRIVER..................................................................................................... 45
3.5.5 EDIT LADDER DIAGRAM............................................................................................................................................ 45
3.5.6 ALARM DISPLAY........................................................................................................................................................ 46
3.6 PITCH ERROR COMPENSATION........................................................................................................................... 46
3.7 TOOL............................................................................................................................................................................. 49
3.8 PROGRAM................................................................................................................................................................... 52
1
Page 3

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
3.8.1 NEW/SEK.................................................................................................................................................................. 52
3.8.2 COPY ........................................................................................................................................................................ 53
3.8.3 RENAME ...................................................................................................................................................................53
3.8.4 DELETE..................................................................................................................................................................... 54
3.8.5 INFORMATION ........................................................................................................................................................... 54
3.8.6 COPY PROGRAM APPLY USB-DISK ............................................................................................................................ 54
3.8.7 PROGRAM TRANSMITTED BY SERIAL PORT ................................................................................................................ 57
3.8.8 EDIT.......................................................................................................................................................................... 59
3.8.9 SELECT PROCESSING PROGRAM ................................................................................................................................ 63
3.8.10 SHIFT PROGRAM FILES PATH.................................................................................................................................... 63
3.9 MANUAL ......................................................................................................................................................................63
3.9.1 CONTINUOUS MODE.................................................................................................................................................. 63
3.9.2 INCREMENT............................................................................................................................................................... 64
3.9.3 MPG MODE............................................................................................................................................................... 64
3.9.4 REFERENCE RETURNING............................................................................................................................................ 64
3.9.5 AUTOMATIC MIDPOINT IDENTIFICATION FUNCTION ................................................................................................... 65
3.9.6 RETURN TO THE ZERO POINT OF G17 PLANE OF WORK COORDINATE SYSTEM ............................................................ 67
3.9.7 OTHER OPERATION IN MANUAL MODE:...................................................................................................................... 68
3.10 AUTO........................................................................................................................................................................... 70
3.10.1 COORDINATES......................................................................................................................................................... 70
3.10.2 GRAPHIC................................................................................................................................................................. 70
3.10.3 CONTINUAL ............................................................................................................................................................ 71
3.10.4 STEP...................................................................................................................................................................... 71
3.10.5 SIMULATION............................................................................................................................................................ 71
3.10.6 FEEDING HOLD........................................................................................................................................................ 71
3.10.7 MPG WHEEL TRIGGER IN AUTO RUNNING............................................................................................................... 71
3.10.8 DNC FUNCTION ...................................................................................................................................................... 72
3.11 MDI MODE................................................................................................................................................................. 73
3.12 RUN PROGRAM FROM A REAL LINE................................................................................................................. 73
3.13 RUN PROGRAM FROM A CERTAIN MARKED LINE....................................................................................... 73
3.14 RUN PROGRAM FROM A CERTAIN TOOL NUMBER...................................................................................... 74
3.15 SET COORDINATES/CHOOSE COORDINATES................................................................................................ 74
3.16 MASS PROGRAM FOR MOULD PROCESSING................................................................................................. 75
3.17 TOOL EXCHANGE AND T OOL SETTING ........................................................................................................... 75
3.17.1 TOOL MAGAZINE OPERATION...................................................................................................................................75
3.17.2 TOOL EXCHANGE .................................................................................................................................................... 76
3.17.3 TOOL SETTING......................................................................................................................................................... 76
3.18 EXIT SYSTEM........................................................................................................................................................... 77
CHAPTER IV PROGRAMING........................................................................................................................................ 78
4.1 BASIC CONCEPTS......................................................................................................................................................78
4.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PROGRAM............................................................................................................ 79
2
Page 4

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
4.3 PROGRAM INSTRUCTION...................................................................................................................................... 79
4.3.1 FUNCTION AND MEANING OF ADDRESS SYMBOL, DATA RANGE LIST........................................................................... 79
4.3.2 G, M FUNCTION INSTRUCTION DATA LIST .................................................................................................................. 80
4.3.3 F FUNCTION:............................................................................................................................................................. 83
4.3.4 T/H/D FUNCTION ...................................................................................................................................................... 84
4.3.5 S FUNCTION .............................................................................................................................................................. 84
4.4 PREPARATION FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................................................... 85
4.4.1 COORDINATE SYSTEM SETTING (G92)....................................................................................................................... 85
4.4.2 CHOOSE COORDINATE SYSTE M (G53/G54/G55/G56/G57/G58/G59)........................................................................ 85
4.4.3 LOCAL COORDINATE SYSTEM (G52).......................................................................................................................... 86
4.4.4 PROGRAMMING METHODS (G90/G91) ......................................................................................................................87
4.4.5 SELECT PLANE (G17/G18/G19)................................................................................................................................ 87
4.4.6 RAPID POSITIONING (G00)........................................................................................................................................ 88
4.4.7 LINEAR INTERPOLATION (G01) ................................................................................................................................. 88
4.4.8 CIRCULAR/ARC INTERPOLATION (G02/G03) ............................................................................................................. 88
4.4.9 HELICAL INTERPOLATION (G02/G03) ....................................................................................................................... 90
4.4.10 DWELL (G04)..........................................................................................................................................................90
4.4.11 MIRROR INSTRUCTION (G11/G12).......................................................................................................................... 91
4.4.12 SCALING (G36/G37)............................................................................................................................................... 92
4.4.13 COORDINATE SYSTEM ROTATE (G68/G69) .............................................................................................................. 93
4.4.14 REFERENCE POINT (G28/G281/ G282/ G283/ G30/ G301/ G302/ G303)................................................................ 95
4.4.15 TOOL LENGTH COMPENSATION (G43/G44/G49)...................................................................................................... 96
4.4.16 TOOL RADIUS INCREASING OR DECREASING (G45/G46/G47/G48).......................................................................... 97
4.4.17 TOOL RADIUS COMPENSATION (G40/G41/G42)....................................................................................................... 98
4.4.18 PROGRAM RECYCLE INSTRUCTION (G22--G800)..................................................................................................... 99
4.4.19 ACCURATE POSITIONING/CONTINUAL PATH WORKING (G60/G64) ......................................................................... 100
4.4.20 CANNED CYCLE OF MACRO DEFINITION (G73,G74,G76,G80~G89).................................................................... 101
4.4.20.1 High speed deep hole drilling (G73) ............................................................................................................ 102
4.4.20.2 CCW peck deep hole tapping cycle (G74) .................................................................................................... 103
4.4.20.3 Finished boring cycle (G76)......................................................................................................................... 105
4.4.20. 4 Drilling cycle, point drilling cycle (G81) .................................................................................................... 106
4.4.20.5 Drilling cycle, countersink boring cycle (G82) ............................................................................................ 106
4.4.20.6 Chip removal drilling cycle (G83)................................................................................................................ 107
4.4.20.7 CW peck deep hole tapping cycle (G84)....................................................................................................... 108
4.4.20.8 Boring cycle (G85) ........................................................................................................................................110
4.4.20.9 Boring cycle (G86) ........................................................................................................................................110
4.4.20.10 Boring cycle, counter boring cycle (G87)....................................................................................................111
4.4.20.11Boring cycle (G89)........................................................................................................................................112
4.4.20.12 Cancel cycle instruction (G80)....................................................................................................................11 3
4.4.21 POLAR COORDINATE (G15/G16)........................................................................................................................... 114
4.4.22 METRIC AND INCH SYSTEM (G20/G21)................................................................................................................. 115
4.4.23 THREADING(G33)................................................................................................................................................. 116
4.4.24 RETURN TO PROGRAM ORIGINAL POINT (G26/ G261/G262/G263)........................................................................ 117
4.4.25 SPINDLE POSITIONING (SP)................................................................................................................................... 117
4.4.26 WAITING FOR AUX-RELAY M1XXX IS VALID, WAITING FOR AUX-RELAY M2XXX INVALID...................................... 117
4.4.27 MAKE AUX-RELAY M3XXX VALID, MAKE AUX-RELAY M4XXX INVALID................................................................ 117
3
Page 5

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
4.4.28 EDIT THE OUTPUT FUNCTION OF OUTPUT POINT AND AUX-RELAY IN CNC PROGRAM DIRECTLY ............................ 118
4.4.29 CONDITIONAL SKIP FUNCTION ............................................................................................................................... 118
4.4.30 AUXILIARY FUNCTION........................................................................................................................................... 118
4.5 PROGRAM CONVENTION................................................................................................................................ 120
4.5.1 MULTI-COMMANDS CAN BE ONE BLOCK TOGETHER ................................................................................................120
4.5.2 THE COMMANDS AND PARAMETER CAN BE LOCATED ARBITRARILY IN PROGRAM BLOCK......................................... 120
4.5.3 REPEATABLE COMMANDS ISN’T ALLOWED IN THE PROGRAM BLOCK ....................................................................... 121
4.5.4 THE OPERATION THAT IRRELA TIVE T O THE COMMANDS ISN’T ALLOWED IN PROGRAM BLOCK.................................. 121
4.5.5 SEMICOLON CAN BE APPLIED AT THE END OF PROGRAM BLOCK, REMARK FOLLOWED SEMICOLON .......................... 121
4.5.6 THE FIRST CHARACTER OF PROGRAM BLOCK IS “%”,“O”,“(”,MEANS THIS BLOCK IS REMARK LINE......................... 121
4.5.7 SPACE IS AVAILABLE BETWEEN COMMANDS IN PROGRAM BLOCK ............................................................................ 121
4.5.8 THE CODES G00, G01, G02, G03, M02 CAN BE WRITTEN TO BE G0, G1, G2, G3, M2............................................. 121
4.5.9 GLOBAL VARIABLE AND SYSTEM VARIABLE CAN BE ADOPTED INTO PROGRAM........................................................ 121
4.5.10 ARITHMETIC EXPRESSION CAN BE ADOPTED INTO PROGRAM ................................................................................. 121
4.5.11 MDI FUNCTION EXPLANATION .............................................................................................................................. 122
4.6 THE INTRODUCTION FOR TOOL RADIUS COMPENSATION C.................................................................. 122
4.6.1 INSIDE AND OUTSIDE .............................................................................................................................................. 122
4.6.2 ESTABLISH TOOL RADIUS COMPENSATION ...............................................................................................................122
4.6.2.1 The tool moving along inside of the corner (
4.6.2.2 The tool moving along outside of the corner for obtuse angle (90
4.6.2.3 The tool moving along outside of the corner for acute angle (α<90)............................................................. 123
4.6.3 THE TOOL MOVING OF TOOL OFFSET MODE.............................................................................................................. 123
4.6.3.1The tool moving along inside of the corner (180
4.6.3.2 The tool moving along outside of the corner for obtuse angle (90
4.6.3.3 The tool moving along outside of the corner for acute angle (α<90)............................................................. 124
4.6.4 THE TOOL MOVING IN THE MODE OF TOOL OFFSET CANCELING ............................................................................... 125
4.6.4.1 The tool moving along inside of the corner (
4.6.4.2 The tool moving along outside of the corner for obtuse angle (90
4.6.4.3 The tool moving along outside of the corner for acute angle (α<90)............................................................. 126
4.7 PROGRAM EXAMPLE.............................................................................................................................................126
4.8 USER MACRO PROGRAM..................................................................................................................................... 128
CHAPTER V PLC FUNCTION...................................................................................................................................... 143
5.1 GENERAL................................................................................................................................................................... 143
α≥
180)................................................................................... 122
≤α
<180) ............................................... 122
≤α
).................................................................................... 123
≤α
<180) ............................................... 124
α≤
180)................................................................................... 125
≤α
<180) ............................................... 125
5.2 CELLS INTRODUCTION......................................................................................................................................... 143
5.2.1 CELL AND CELL NUMBER......................................................................................................................................... 143
5.2.2 CELL TABLE ............................................................................................................................................................ 143
5.2.3 CELL INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................................................................. 143
5.2.3.1 Input relay ( X )............................................................................................................................................... 143
5.2.3.2 Output relay (Y) .............................................................................................................................................. 144
5.2.3.3 Interior relay (M)............................................................................................................................................ 144
5.2.3.4 Timer (T) ......................................................................................................................................................... 144
5.2.3.5 Counter (C)..................................................................................................................................................... 145
5.3 BASIC CELL SIGN IN LADDER DIAGRAM........................................................................................................ 146
4
Page 6

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
5.4 BASIC LOGIC COMMANDS IN INSTRUCTION LIST...................................................................................... 146
5.4.1 LD, LDI, OUT COMMANDS .................................................................................................................................... 146
5.4.2 AND, ANI COMMANDS........................................................................................................................................... 147
5.4.3 OR, ORI COMMANDS.............................................................................................................................................. 147
5.4.4 ORB COMMAND ..................................................................................................................................................... 147
5.4.5 ANB COMMAND ..................................................................................................................................................... 147
5.4.6 MPS, MRD, MPP MEMORIZER AND MULTIPLE OUTPUT COMMANDS....................................................................... 147
5.4.7 SET AND RST COMMANDS ..................................................................................................................................... 147
5.4.8 NOP AND END COMMANDS.................................................................................................................................... 147
5.5 PLC PROGRAM EDITING...................................................................................................................................... 147
5.5.1 EDIT PLC PROGRAM ON PC.................................................................................................................................... 147
5.5.1.1 Edit software installation and running environment....................................................................................... 147
5.5.1.2 Basic operation of software editing................................................................................................................ 148
5.5.1.3 Edit PLC Ladder............................................................................................................................................. 149
5.5.1.4 Generate instruction list file ........................................................................................................................... 151
5.5.1.5 Logic testing ................................................................................................................................................... 152
5.5.2 EDIT PLC PROGRAM ON THE PANEL OF THE CONTROLLER....................................................................................... 153
5.5.2.1 Basic operation in editing interface................................................................................................................ 153
5.5.2.2 Edit PLC ladder.............................................................................................................................................. 154
5.6 PLC FILE TRANSMISSION..................................................................................................................................... 156
5.6.1 TRANSMIT PLC FILE BY RS232 .............................................................................................................................. 156
5.6.1.1 Transmit PLC file (PLC.lad, PLC.plc) to controller....................................................................................... 156
5.6.1.2 Transmit PLC file (PLC.plc, PLC.plc) to PC from controller......................................................................... 158
5.6.2 TRANSMIT PLC FILE BY USB PORT ......................................................................................................................... 159
5.6.2.1 Restore PLC file to controller from U disk ..................................................................................................... 159
5.6.2.2 Backup PLC file into U disk ........................................................................................................................... 160
5.7 THE DEFINITION OF INTERI OR AUXILIARY RELAY....................................................................................161
5.8 PROGRAMMABLE I/O DIAGRAM IN SYSTEM.................................................................................................165
5.8.1 GENERAL I/O BOARD..............................................................................................................................................165
5.8.1.1 General I/O board (GREAT-GEN-IO) ............................................................................................................ 165
5.8.1.2 General I/O board (GREAT-GEN-IO-A) ........................................................................................................ 166
5.8.2 MOVEMENT CONTROL BOARD................................................................................................................................. 167
5.8.3 SUBPANEL............................................................................................................................................................... 167
5.8.4 MANUAL PULSE GENERATOR................................................................................................................................... 169
5.9 EXAMPLE AND EXPLANATION OF PLC PROGRAMMING...........................................................................169
5.10 EDIT REPLY NAME................................................................................................................................................ 172
5.10.1 EDIT RELAY NAME ON PANEL................................................................................................................................. 172
5.10.2 EDIT RELAY NAME ON PC...................................................................................................................................... 173
5.10.3 EXAMPLES TO SELF-DEFINED ALARM USAGE OF INTERIOR RELAYS M80---M95.................................................... 174
5.11 PROGRAMMABLE I/O PRESET FUNCTION DEFINITION........................................................................... 176
5.11.1 MOVEMENT CONTROL BOARD............................................................................................................................... 176
5.11.2 SUBPANEL ............................................................................................................................................................. 177
5
Page 7

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
5.11.3 MANUAL PULSE GENERATOR................................................................................................................................. 178
5.11.4 GENERAL I/O BOARD ............................................................................................................................................ 178
5.12 THE DEFINITION OF PLC, INSTRUCTION AND PARAMETER FOR MACHINE MATCH WITH
TOOL MAGAZINE..........................................................................................................................................................
181
5.12.1 SPECIFICATION OF MACHINING CENTRE WITH UMBRELLA TOOL MAGAZINE........................................................... 181
5.12.2 SPECIFICATION OF MACHINING CENTRE WITH ATC TOOL MAGAZINE..................................................................... 183
CHAPTER VI. CONNECTION& INSTALLATION.................................................................................................... 186
6.1 GENERAL................................................................................................................................................................... 186
6.2 SYSTERM CONFIGURATION................................................................................................................................ 186
6.2.1 SYSTEM ASSEMBLIES AND FUNCTION ...................................................................................................................... 186
6.3 SYSTEM CONNECTION DIAGRAM..................................................................................................................... 189
6.3.1 THE CONNECTION DIAGRAM MATCH WITH A TYPE SUBP ANEL..................................................................................189
6.3.2 CONNECTION DIAGRAM MATCH WITH B TYPE SUBPANEL ........................................................................................190
6.4 DIMENSION............................................................................................................................................................... 190
6.4.1 MAIN PANEL DIMENSION......................................................................................................................................... 190
6.4.2 SUBPANEL DIMENSION (A TYPE AND B TYPE IS SAME)............................................................................................. 191
6.4.3 GENERAL I/O BOARD DIMENSION ........................................................................................................................... 192
6.4.4 DIMENSION OF MOVEMENT CONTROL BOARD ......................................................................................................... 193
6.4.5 THE INSTALLATION DIMENSION OF I/O POWER MODULE (DC24V/ 3A)................................................................... 193
6.5 SYSTEM INSTALLATION ENVIRONMENT........................................................................................................ 193
6.5.1 POWER CAPACITY ................................................................................................................................................... 194
6.5.2 POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION AND CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................194
6.5.2.1 Power supply connection diagram ................................................................................................................. 194
6.5.2.2 I/O power supply setting................................................................................................................................. 194
6.5.3 CNC POWER TURN ON/ OFF SEQUENCE ................................................................................................................... 195
6.6 SYSTEM CONNECTED WITH SURROUNDING EQUIPMENT....................................................................... 195
6.6.1 CONNECTION WITH COMMUNICATION BOARD ......................................................................................................... 196
6.6.1.1 connection with communication board ........................................................................................................... 196
6.6.1.2 Interface connection ....................................................................................................................................... 196
6.6.2 CONNECTED WITH SPINDLE ENCODER ..................................................................................................................... 197
6.6.2.1 Connected with spindle encoder..................................................................................................................... 197
6.6.2.2 Interface with spindle encoder........................................................................................................................ 197
6.6.3 CONNECTED WITH MPG (MANUAL PULSE GENERATOR).......................................................................................... 197
6.6.3.1 Connected with MPG...................................................................................................................................... 197
6.6.3.2 The interface connected with MPG................................................................................................................. 198
6.6.3.3 MPG internal connection diagram................................................................................................................. 198
6.6.4 CONNECTED WITH SUBPANEL.................................................................................................................................. 199
6.6.4.1 Connected with subpanel................................................................................................................................ 199
6.6.4.2 Connected with subpanel................................................................................................................................ 200
6.6.5 CONNECTED WITH GENERAL I/O BOARD ................................................................................................................. 202
6.6.5.1 Connected with general I/O board.................................................................................................................. 202
6.6.5.2 Interface connected with general I/O board ................................................................................................... 202
6
Page 8

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
6.6.6 CONNECTED WITH MOVEMENT CONTROL BOARD.................................................................................................... 204
6.6.6.1 Connection with movement control board ...................................................................................................... 204
6.6.6.2 Interface connected with movement control board ......................................................................................... 204
6.7 CNC CONTROLS CONNECTED WITH SPINDLE DRIVER............................................................................. 207
6.7.1 CNC CONTROLS CONNECTED WITH FREQUENCY INVERTER..................................................................................... 207
6.7.2 CNC CONTROLS CONNECTED WITH SPINDLE SERVO DRIVE ..................................................................................... 207
6.7.2.1 Connection diagram of CNC controls connected with GTB-GA spindle servo drive ..................................... 207
6.7.2.2 Connection diagram of CNC controls connected with MODROL spindle servo drive................................... 208
6.8 CNC CONTROL CONNECTED WITH FEED SERVO DRIVE...........................................................................209
6.9 MACHINE ELECTRIC INSTALLATION PRINCIPLE....................................................................................... 210
6.9.1 DIRECT-CURRENT POWER SUPPLY............................................................................................................................ 210
6.9.2 I/O PORTS................................................................................................................................................................ 211
6.9.2.1 I/O port classification and distribution............................................................................................................211
6.9.2.2 General I/O input port principle which is available by "IPE".........................................................................211
6.9.2.3 General I/O input port principle which is available by "+24V ".....................................................................211
6.9.2.4 Sub-panel input port principle which is available by " GND "....................................................................... 212
6.9.2.5 Sub-panel output port principle which is availability by "+5V ".................................................................... 212
6.9.2.6 General, movement control I/O output port principle which is availability by "IPE".................................... 212
6.9.2.7 Reference points connection principle............................................................................................................ 213
6.9.2.8 Limit signal connection principle ................................................................................................................... 214
7
Page 9

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
CHAPTER I PREFACE
GTCNC-150IM-II is one middle grade flush type CNC control system that has been designed by
Chengdu Great Industrial Co., Ltd, aiming specially at milling machine & machining center.
Based on modern computer technology, system move control core & PLC program running technology,
and stable unique real time control engine subsystem RTAI, this system ensures the stabilization of
operation. The use of high performance, low power consumption industrial grade ARM microprocessor
as core of hardware, large scale FPGA integrate circuit, multiple layer (4,6) printed circuit, 32MB flash
memory, 8.4 inch real color LCD which provides friendly human-machine dialogue interface makes this
system work to its best.
DEFINITION OF CAUTION, WARNING, AND NOTE
1. WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of user being injured or user being injured and equipment is damaged.
2. CAUTION
Reminds operator must be caution
damage the equipment.
3. NOTE
in the relative operation, otherwise lead this operation failure or
APPLIED TO INDICATE SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION AND EXPLANATION.
NOTE
This system has function to backup parameters. After debugging machine, it can backup all parameters
of machine & system and PLC documents to computer. It is convenient not only for mass debugging, but
also for machine recovery to normal after changing system. (refer to Chapter 3.6)
NOTE
WHEN USE THIS SYSTEM AT THE FIRST TIME, PLEASE READ CAREFULLY ALL
THE DETAILS OF EACH CHAPTER SO AS TO MAKE IT WORK MORE EFFICIENTLY.
1
Page 10

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
CHAPTER II TECHNICAL FEATURE
2.1 System constructions
● 32 bits high performance, low power consumption industrial grade ARM microprocessor
● 64MB memory
● 32MB user store room
● 640x480 8.4 inch real color LCD displayer
● Touch screen main and sub panel
● High anti-jamming switch power
● USB-disk interface
● RS232 interface
● Programmable I/O 118X46
● Spindle servo speed control/spindle frequency conversion speed control
● Manual pulse generator
2.2 System technical parameter
● controllable axes: X, Y, Z, A, B five axes
● simultaneous axes: Arc 2-3 axes, liner 2-5 axes.
● pulse equivalent: X, Y, Z, A, B axes: 0.001mm
● max speed: X, Y, Z, A, B: 60000mm/min
● cutting speed: 1-20000mm/min
● min input unit: 0.001mm
● program size range: ± 99999.999
● 99 tools management
● umbrella type and turn-plate type tool magazines are available
● program code: ISO-840 international standard
● program coordinate system definition: ISO-841
● mean time between failure(MTBF): more than 5000 hours
● cabinet protection complies with regulation of IP54
2.3 System function
2.3.1 Auto-diagnosis function:
All around diagnosis of CPU, memory, LCD, I/O interface, parameter status, coordinates, machining
program etc. shall execute when the system starts or resets. In operation, it makes real time diagnosis
for power supply, spindle, limit and all I/O interface.
2.3.2 Compensation function:
● automatic backlash compensation
● tool length automatic compensation
● tool radius automatic compensation
● tool radius automatic offset and sharp angle transition
● leading screw pitch error automatic compensation
2
Page 11

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
2.3.3 Abundant instruction system:
● scaling up/down instruction
● mirror machining instruction
● multiple tool offset instruction
● program cycle, jump, call and different program ending
● multiple positioning instruction: starting point, setting fixed point, etc.
● linear, circular, spiral line interpolation instruction
● program management instructions: program cycle, call, transfer and different
program ending method, etc.
● 6 work coordinate system and 4 reference points
2.3.4 Chinese/English menu, full screen edition:
Easy operation, convenient viewing
2.3.5 Abundant debugging functions:
it can point out clearly what errors of operation are and guide to correct them.
2.3.6 Program exchange between CNC system and IBM/PC series compatible computer
Apply CAD/CAM/CAPP auxiliary programming by using PC series compatible computer's abundant
software resources, then transfer the CNC program into CNC system through (USB-disc port, RS232
port. Likewise it also can transfer the program from system to PC through communication port.
2.4 System operation condition
2.4.1 Power supply:
AC 220V(+10% /-15%), Frequency 50Hz±2%. Power: ≤ 200W.
NOTE: It must apply isolation transformer to supply power, primary input: 380V
2.4.2 Climate condition
z operation condition: temperature 0~45 ,relative moisture ℃ 30-95%
z storage & transportation condition temperature: -40~55 ,relative moisture<93℃ %(40 )℃
z atmosphere pressure: 86-106kpa
2.4.3 Operation environment:
No excessive dust, acid, alkali corrosive gas and explosive gas, no strong electromagnetic interference
3
Page 12
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
CHAPTER III OPERATION
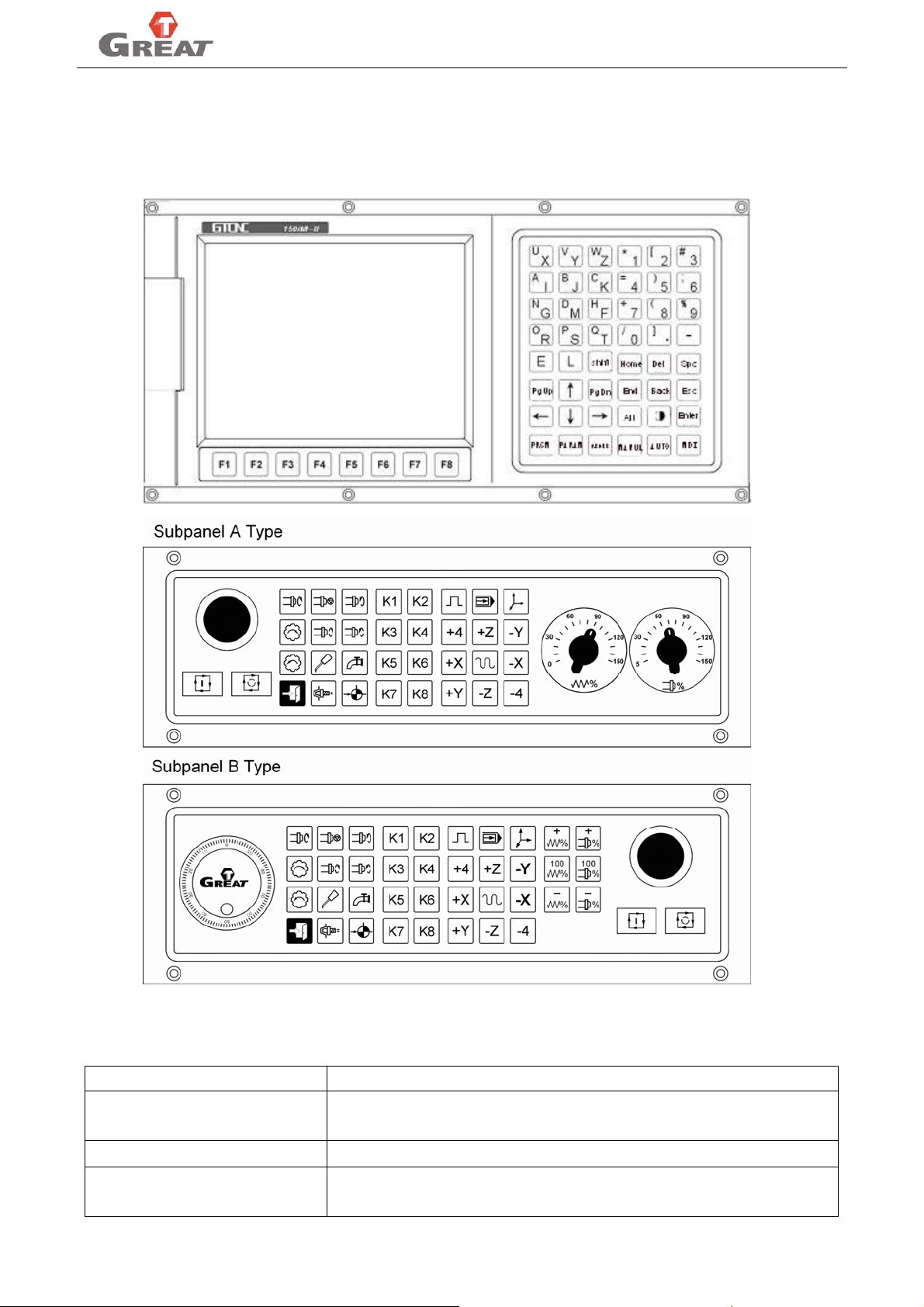
3.1 Panel layout and switch
Switch introduction:
Chart 1: Switch introduction
Emergency stop (yellow/red)
Program run (green) Execute the auto-machining program, meanwhile light turns on
Program end (red)
4
Fig 3.1 panel layout
Switch Functions
Driver and motor stop immediately, turns off the spindle, coolant,
waits for the release E-stop button, and initializes values
In automatic continual run, press once to pause, twice to end
immediately; in manual mode run, press once to end.
Page 13
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Spindle override switch In the process of spindle running, adjusts the speed accordingly.
Feed axes override switch
Chart 2: buttons introduction:
Keyboards Functions
Letter key
Number key
CHRTAXYZLIJKSFMGDPN0123456789.-: used for editing program
instructions, parameters; number keys are used for inputting data and selecting
sub-menu.
↑, ↓, →, ←: move cursor, input data or select menu. etc
Del: delete one character behind the cursor
PgUp, PgDn: page up, page down
Alt: shift key , shift coordinate system in manual or auto mode
Edit key
Back: delete one character before the cursor
Home: move the cursor to the beginning of line in programming editing status; move
cursor to the first parameter place in parameter menu
End: move the cursor to the end of line in programming editing status; move cursor
to the last parameter place in parameter menu
“Esc” returning to upper level or stop a operation
“Enter” selecting sub-menu and changing a new line
“Shift” top key input
“program” shift to program edition interface
“para” shift to parameter setting interface
“dgnos” shift to diagnosis function interface
Function key
“manual” shift to manual status interface
“auto” shift to automatic status interface
“ M D I ” shift to MDI function interface
” adjust manual increment or handwheel override
“
“
” shift auto-coordinates/graphic machining mode
“
” shift between single block/continuous mode
“
“ work with “PgUp” or ”PgDn”: set the brightness of the screen.
“
“
” coolant on/off
When program runs or in manual state, it can make a real-time
adjustment of feed speed
” spindle cw, stop, ccw, jog cw, jog ccw
” axis reference returning
“
“ ” spindle tool tighten / release
Control key
“
“
“
“
“
” tool magazine rotate CW, CCW
” lubrication on/off
” adjust federate
” adjust spindle rotating speed
” exit system safely
Feed key +X +Y +Z +4 –X –Y –Z -4 For X, Y, Z, A axes feed
5
Page 14

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Rapid key
Used for rapid moving axis in manual mode
Self-definition key K1, K2, . . . K8 Self definition control
Soft key F1, F2, ……F8 Menu shift, function selection
3.2 Operation interface
Whole system adopts multi-leveled menu full screen operation, user-friendly interface, providing
comprehensive information. It enters into the main interface as followed as booting.
Fig3.2 operation panel
Definition of each display area (fig 3.2) in the system main screen as below:
1. title bar: the top column shows company’s logo and current time
2. program display area: show the program which will execute or being running “/tmp/NC/”is default path
or program and “89” is program name.
3. G code display area: show the G status of current executing program or the coordinate system in
non-auto mode. For example: G53 means machine coordinate system.
4. program display area: show the program content which being executed or running and the progress
(show through scroll bar)
5. feed speed display area: show the speed, rate, real speed and speed ratio of feed axis. “F5000” in the
column means the speed is 5000mm/min; “F0” means real running speed is 0mm/min; percentage
means the rate switch gear level is 100%.proportional band shows the proportion between real running
speed and the max speed setting in the parameter. The green part means the real running speed is less
than 60% of the max running speed, it is safety area; yellow part means the real running speed is
60%-100% of the max speed, it is warning area; red part means the real running speed is more than
100% of the max running speed. It is dangerous area.
6. spindle revolution display area: show speed, rate, real running speed and speed ratio of spindle under
present code. “S2000” in the column means the speed is 2000r/min; “S0” followed means the real
running speed is 0r/min; percentage means the rate switch gear level is 100%. proportional band shows
the proportion between real running speed and the max speed setting in the parameter. the green part
means the real running speed is less than 60% of the max running speed, it is safe area; yellow part
means the real running speed is 60%-100% of the max speed, it is warning area; red part means the real
running speed is higher than 100% of the max running speed. It is dangerous area.
7. manual or auto mode display area: show the display mode in manual or auto and continuous,
increment, MPG status etc and relevant information in the manual mode.
6
Page 15

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
8. M code display area: show the validity of M code. Green light means valid and red-light means invalid.
9. tool status display area: show relevant information, as show in fig3.2 from left to right, the first T01
means the current tool number on the spindle; H0 means the current tool edge H (length compensation
number); D0 means the current tool edge D (radius compensation number) 01 means current cutter seat
number, cutter seat number at tool exchange position; T00 means tool number on the current cutter seat.
10. machine coordinates display area: show the coordinates value of machine coordinates (G53)
11. coordinates display area: dynamic coordinates display, showing present coordinates (machine
coordinate system or work coordinate system).the circle behind coordinates sign (X, Y, Z, A)means
indicator light, which shows the status of reference returning for each coordinate, green light means the
coordinates has returned machine refer zero, otherwise not. Make sure all zero returning indicator are
green during running or before auto running.
NOTE: If servo driver alarm or other phenomenon after zero returning, the green light will go off.
12. machining time display area: show the executed time for present program.
13. workpiece number display area: show the cycle times for present program, quantity of machined
workpieces
14. program block display area: show the exact program block for present program.
15. information display area: show the relevant information of system and machine. such as alarm, soft
limit and so on.
16. program running status display area: show the auto running status of the program .such as step,
continual, real machining, simulation, stop, run etc.
17. menu display area: used for display function menu. Press corresponding softkey (F) to shift.
System menu structure:
Whole system adopts multi-leveled menu as followed:
7
Page 16
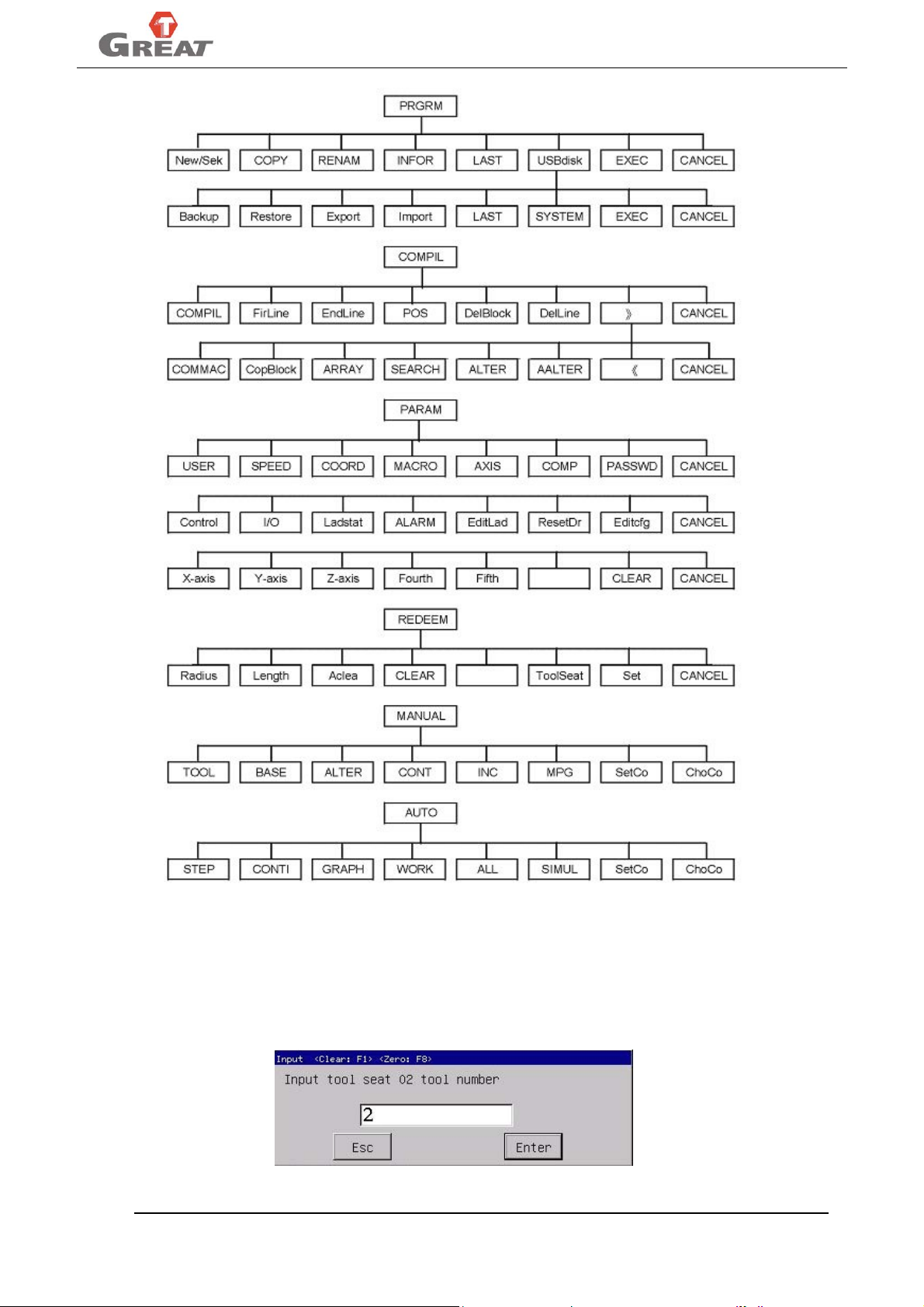
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Above menus in fig3.3 can be viewed by press the function softkeys of “PRGRM”, “PARAM”, “REDEEM”,
“MANUAL”, “AUTO” on the panel, press “ESC” will return to main menu.
Input data into the dialogue box:
The whole system adopts dialogue data input. Replace the data directly when input data in the dialogue
box and confirm by pressing “Enter” key or cancel by pressing “Esc” key.
NOTE: There are words like“<-Clear:F1> <-Zero:F8>” on the top of dialogue box, means you can clear
8
Fig 3.3 menu array
Fig3.4 dialogue box for data input
Page 17
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
the data in the dialogue box by pressing “F1”, set the data as 0 by pressing “F8”.
3.3 Parameter
Shift to parameter setting menu by pressing “PARAM” on the main panel, press “PARAM” once will shift
to parameter interface, including “USER”, “SPEED”, “COORD”, “MACRO”, “AXIS”, “COMP”, “PASSWD”,
“CANCEL”; press twice will shift to diagnosis interface, including “Contrl”, “I/O”, “LadStat”, “ALARM”,
“EditLad”, “ResetDr”, “Editcfg”, “CANCEL”; press three times will shift to pitch error compensation
interface, including “X-axis”, “Y-axis”, “Z-axis”, “Fourth”, “Fifth”, “CLEAR”, “CANCEL”; shift to the
parameter setting interface by pressing corresponding key, press “CANCEL” or “Esc” will return to main
interface.
NOTE
Repeat press “PARAM” will shift among “PARAM”, “Diagnosis”, and “PITCH”.
The 1st screen parameter
The 2nd screen diagnosis
rd
The 3
screen pitch compensation
Fig3.5 parameter interface
First interface: Parameter
“USER” system basic function parameter, user maybe set these parameters as machining.
“SPEED” the parameters related to speed of each axis.
“COORD” set the coordinates value of work coordinate systems from G54 to G59 in the machine
coordinate system.
“MACRO” set macro variable value from No.30 to No.190.
“AXIS” set parameters related to each axis such as compensation, limit, function parameters.
“COMP” set the parameters except for above menus.
“PASSWD” set the parameters related to system operation limit.
Second interface: diagnosis
“Contrl” set the program type of tool exchanging.
“I/O” display of input and output.
“LadStat” status display of PLC ladder.
“ALARM” display the current alarm and history records of 10 alarms.
“EditLad” set embedded PLC ladder online.
“ResetDr” reset servo driver.
“Editcfg” edit the current configuration.
Third interface: pitch error compensation
“X-axis”, “Y-axis”, “Z-axis”, “Fourth”, “Fifth” used for setting the parameter related to pitch error
compensation of X-axis, Y-axis, Z-axis, fourth axis and fifth axis.
“CLEAR” clear the current pitch error compensation.
9
Page 18
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
3.4 Parameter Explanation
For convenient search for parameters, parameters are classified to be “user parameter”, ”speed
parameter”, “coordinate system”, “macro variable parameter”, “axis parameter” and “comprehensive
parameter”.
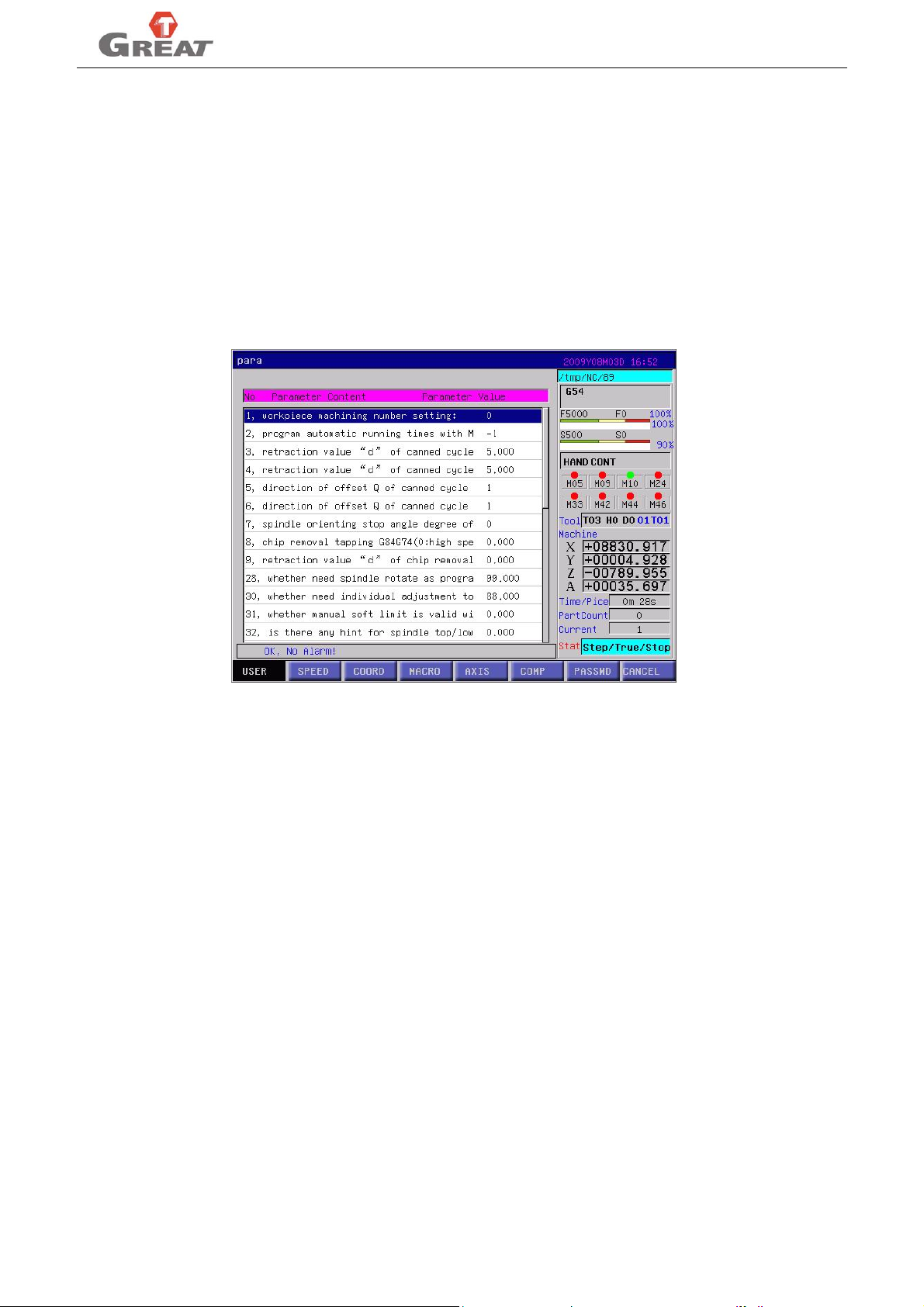
3.4.1 User parameter
User parameter composed by basic function parameter, which are frequent applied in the system.
Under the main interface, press ”USER”(F1) softkey, will shift to user parameter setting interface, refer to
fig 3.6
Fig 3.6 User parameter
User parameter list:
1. workpiece machining number setting
2. program automatic running times with M20
3. retraction value "d" of canned cycle G73(mm)
4. retraction value "d" of canned cycle G83(mm)
5. direction of offset Q of canned cycle G76
6. direction of offset Q of canned cycle G87
7. spindle orienting stop degree of boring canned cycle(0.1degree)
8. chip removal tapping G84G74(0:high speed, 8:normal)
9. retraction value “d” of chip removal tapping G84G74 (mm)
28. whether need spindle rotate as program running(0: yes, 90: no)
30. whether need individual adjustment to G00 override(88:yes, 0: no)
31. whether manual soft limit is valid without zero returning (88:yes, 0: no)
32. is there any hint for spindle top/low gear(88:yes, 0: no)
33. whether apply intervention switch(88:yes, 0: no)
34. make soft limit invalid(X4,Z16,Y8,A32,B64)
35. system default coordinate system(54-59 corresponding G54-G59,other G53)
36. can G92 modify G54-G59 (800:yes, 0: no)
37. are lubrication and cooling keys valid in auto mode(1:yes, 0: no)
38. does spindle rotation and tool unclamp interlock (1:yes, 0: no)
39. request for zero return as booting and program running(1: no need, 0: hint, 8:force, 9:super force )
10
Page 19
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
40. checking input point of G31 (valid+300, invalid+400)
41. G31_X
42, G31_Y
43. G31_Z
44, G31_A
45. G31_B
51. edit increment value of program sequence number
100. set LCD brightness
101. set system time(Y-M-D-H-M)
102. restore factory para setting
User parameter explanation:
No.1 workpiece machining number setting
To set the work count showing on the screen for current machining, after set this parameter, the
“PartCount” will display the refreshed number, and the this value will be increased according to the
machined parts increasing.
Fig3.7
NO.2 program automatic running times with M20
Set times of cycle programming using M20 command. if the value is set to be minus, means limitless
recycle.
NO.3 retraction value "d" of canned cycle G73 (mm)
Set the dimension of retraction value “d” of high speed deep hole drill cycle G73. unit:mm.
NO.4 retraction value "d" of canned cycle G83 (mm)
Set the dimension of retraction value “d” of chip removal drill cycle G83. unit: mm.
NO. 5 direction of offset Q of canned cycle G76
To set G76 Circle code’s offset (Q) direction of precision boring cycle. The coordinates and directions are
some differences to same value in different plane, refer to following tables:
Plane NO.5 parameter setting NO. 5 direction of offset Q of canned cycle G76
1 +X
G17
2 -X
3 +Y
4 -Y
1 +Z
G18
2 -Z
3 +X
4 -X
1 +Y
G19
2 -Y
3 +Z
4 -Z
NO.6 direction of offset Q of canned cycle G87
To set G87 Circle code’s offset (Q) direction of back boring cycle. The coordinates and direction are
11
Page 20
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
different to same value in different plane, please refer to following tables:
Plane NO.6 parameter setting NO.6 direction of offset Q of canned cycle G87
1 +X
G17
2 -X
3 +Y
4 -Y
1 +Z
G18
2 -Z
3 +X
4 -X
1 +Y
G19
2 -Y
3 +Z
4 -Z
NO.7 spindle orienting stop degree of boring canned cycle (0.1degree)
Used for set the spindle stop angel degree after boring job when execute boring canned cycle, ensure the
workpiece not be scratched by tools. Unit: 0.1 degree, set range: 0-3600.
NO.8 chip removal tapping G84G74 (0: high speed, 8: normal)
As chip removal tapping G84G74; this value is set to be 0 means removal chip high speed, set to be 8
means normal removal chip.
NO.9 retraction value “d” of chip removal tapping G84G74 (mm)
Set the retraction value “d” of chip removal tapping G84G74. unit: mm
NO.28 whether need spindle rotate as program running (0: yes, 90: no)
Set the spindle rotate interlock with program running, set to be 0, program running need spindle rotating;
set to be 90 means no need detect spindle rotate as program running.
NO.30 whether need individual adjustment to G00 override (88: yes, 0: no)
Set the G00 override. Set to be 88 means individual adjustment, means G00 override is set by PgUp and
PgDn; set to be 0 means machining speed override is adjusted by feed override.
NO.31 whether manual soft limit is valid without zero returning (88: yes, 0: no)
Set the relationship between reference returning status and soft limit. Set to be 88 means the soft limit
function is valid although without reference returning; set to be 0 means the soft limit function is invalid
before reference returning.
CAUTION
This parameter’s setting depends on using situation, but may lead to accident because of improper
setting or operation, please pay attention!
NO.32 is there any hint for spindle top/low gear (88: yes, 0: no)
Set whether automatic hint when shift spindle gear. Set to be 88 means there is hint automatically if the
speed is not suitable for the gear as automatic gear shifting; set to be 0 means system does not check
whether speed is suitable for the gear.
NO.33 whether apply intervention switch (88: yes, 0: no)
This value set to be 88 means apply intervention switch, set to be 0 means not apply intervention switch.
NO.34 make soft limit invalid (X4, Z16, Y8, A32, B64)
This parameter is used for setting whether soft limit function valid. When set this value is 0 means soft
limit is valid; set to be 4 means X-axis soft limit function is invalid; set to be 16 means Z-axis soft limit
12
Page 21

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
function is invalid; set to be 8 means Y-axis soft limit function is invalid; set to be 32 means A-axis soft
limit function is invalid; set to be 64 means B-axis soft limit function is invalid;
NOTE
1. Set two or more axes soft limit function is invalid, just add the corresponding axes parameter value. i.e.
set X and Z axes soft limit function is invalid, the parameter is set to be 20(4+16).
2. This parameter setting depends on user’s need, normally we suggest this value set to be valid, to
prevent equipment is damaged from excess of stroke. Please attention, to realize soft limit function,
besides set this parameter, you have to set the each axis’ limit stroke in the “USER” parameter.
CAUTION
This parameter’s setting depends on using situation, but may lead to accident because of improper
setting or operation, please pay attention!
NO.35 system default coordinate system (54-59 corresponding G54-G59, other G53)
Applied to set the system default coordinate system, value 54-59 corresponding to G54-G59, other value
is G53.
i.e.: this parameter is set to be 54 means system default coordinate system is G54.
NO.36 can G92 modify G54-G59 (800: yes, 0: no)
As this parameter set to be 800, G92 will modify the current work coordinate system as program running,
set to be 0 will not modify the current work coordinate system.
37. are lubrication and cooling keys valid in auto mode(1:yes, 0: no)
Set whether the lubrication and cooling keys valid in the “AUTO” mode. As this parameter set to be 0
means invalid; set to be 1 means valid.
This parameter setting related to operation mode, as this parameter set to be valid, operator can control
the valid status of lubrication and cooling to satisfy the condition of manufacturing process.
NO.38 does spindle rotation and tool unclamp interlock (1:yes, 0: no)
Set whether spindle rotation and tool unclamp interlock, as this parameter set to be 0 means spindle
tighten/release tool is not related to spindle rotation; as this parameter set to be 1 means that spindle
tighten/release tool is interlocked with spindle rotation, that means spindle can be rotated only in the
status of tool tightened.
This parameter setting is related to machine tools configuration and user applied request, for the sake of
safety, strongly recommend set this parameter to be 1 and make it interlock.
NO.39 request for zero return as booting and program running (1: no need, 0: hint, 8:force,
9:super force)
To set the treatment mode of reference returning as system booting, there are 4 kinds of treatment mode
as below:
Set to be 1: there is no remind or limit to reference returning after system booting.
Set to be 0 is remind mode: there is a dialogue box remind operator to execute reference returning
after system booting every time, there is no limit after then.
Set to be 8 is force mode: there is a dialogue box reminds operator to execute reference returning
every time after system booting and run system, system will reminds “feed axes have not returned to
reference” and won’t execute program if not execute reference returning before running in the “AUTO”
mode.
Set to be 9 is super forcing mode: there is a dialogue box reminds operator to execute reference
returning every time after system booting and feed axes moving, system will reminds “feed axes have
not returned to reference” and won’t execute moving if not execute reference returning.
CAUTION
13
Page 22

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
This parameter setting is related to machine tools configuration, set to be other value if no reference
point switch on the machine, if there is reference point switch on the machine, suggest set this parameter
to be 8 or 9, to prevent equipment failure from without reference returning.
NO.40 checking input point of G31 (valid+300, invalid+400)
As this parameter set to be 300, will check the input signal of skip function; as this value set to be 400,
won’t check the input signal of skip function.
NO.41 G31_X
NO.42 G31_Y
NO.43 G31_Z
NO.44 G31_A
NO.45 G31_B
NO.41~NO.45 parameters are skip block function.
NO.51 edit increment value of program sequence number
This parameter is applied to set increment value of program sequence number.
NO.100 set LCD brightness
Set the brightness of LCD display. In the parameter dialogue box: PgUp means increasing brightness,
PgDn means decrease brightness, Home means back to default.
NO.101 set system time(Y-M-D-H-M)
Applied to modify system date and rime, system will base on this time after setting, will time according to
inner clock, and display on the top right corner.
Set methods as below:
Select NO.101 under the interface of “USER”, press “enter” and pop up dialogue as Fig3.8, input year,
month, day, hour, minute to set, press “Enter” after setting: for example: August, 04, 2008. 09:50, will input
2008-8-4-09-50 and then press “Enter”.
Fig3.8
NO.102 restore factory para setting
Set factory parameter to be current parameter. If there is parameter confused in the process of
debugging, apply this parameter to set the factory parameter to be current parameter.
NOTE
After executing restore factory parameter, the existing parameter will be covered.
3.4.2 Speed
in order to make sure feed axis motor(machine work table) run in the safe scope and guaranty operation
characteristic, this system supply some parameter setting related to speed and acceleration.
In the parameter interface, press “SPEED” soft key will shift to speed parameter setting menu. Select the
parameter needs to be modified, then press “Enter” will pop up a dialogue box, then input value. Refer to
fig3.9.
14
Page 23
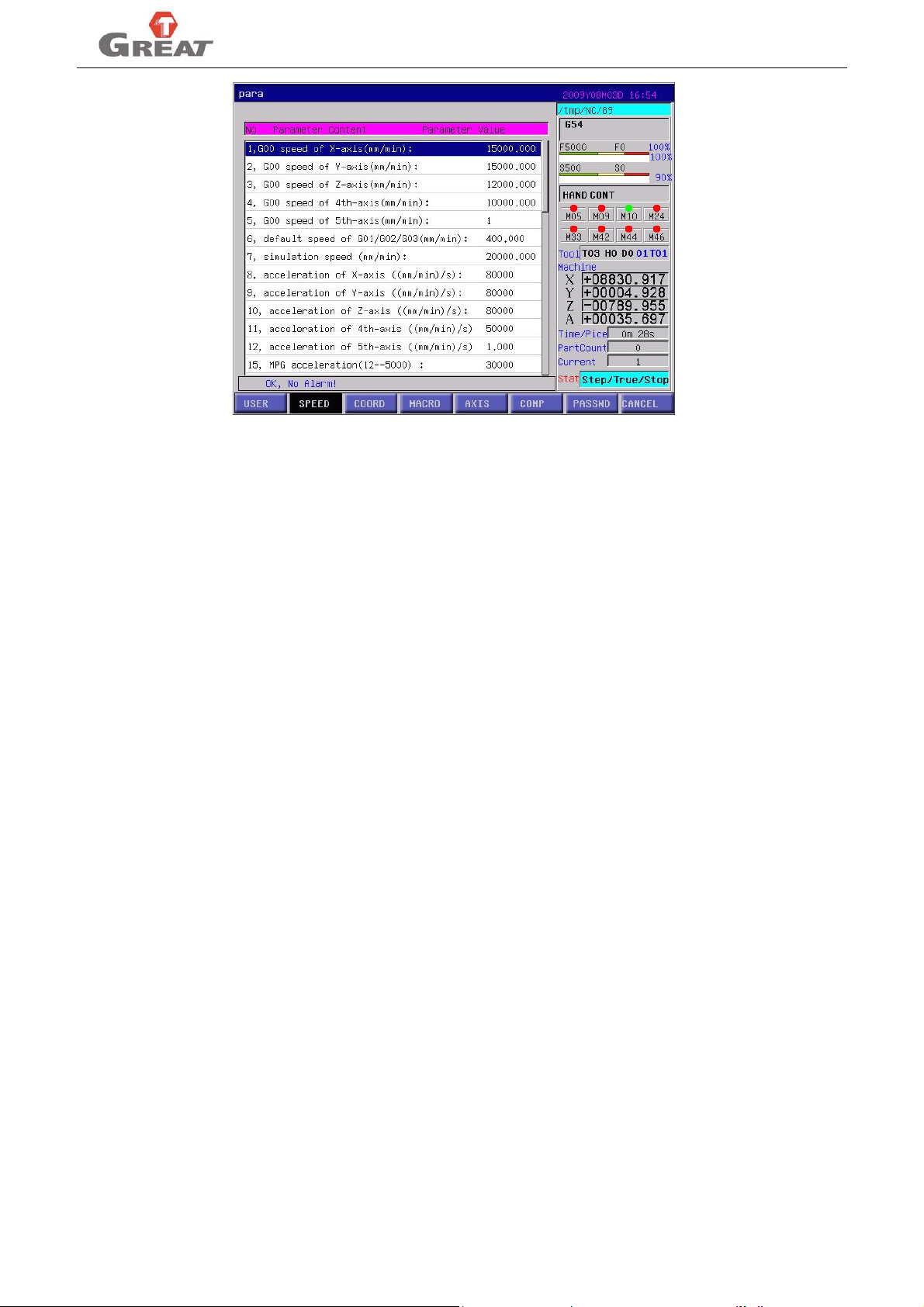
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
fig3.9 speed parameter setting
Speed parameter list:
1. G00 speed of X-axis(mm/min)
2. G00 speed of Y-axis(mm/min)
3. G00 speed of Z-axis(mm/min)
4. G00 speed of 4th-axis(mm/min)
5. G00 speed of 5th-axis(mm/min)
6. default speed of G01/G02/G03(mm/min)
7. simulation speed (mm/min)
8. acceleration of X-axis ((mm/min)/s)
9. acceleration of Y-axis ((mm/min)/s)
10. acceleration of Z-axis ((mm/min)/s)
11. acceleration of 4th-axis ((mm/min)/s)
12. acceleration of 5th-axis ((mm/min)/s)
15. MPG acceleration(12--5000)
16. speed up/down in auto running mode(500-32000)
17. positive speed of X-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
18. positive speed of Y-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
19. positive speed of Z-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
20. positive speed of 4th-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
21. positive speed of 5th-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
22. reverse speed of X-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
23. reverse speed of Y-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
24. reverse speed of Z-axis as reference returning
25. reverse speed of 4th-axis as reference returning
26. reverse speed when 5th-axis as reference returning (mm/min)
27. max speed as rapidly stop feed axis (mm/min)
28. max feed speed in manual mode (mm/min)
29. max feed speed in auto mode (mm/min)
30. max MPG speed of Z-axis (mm/min)
31. max MPG speed of X,Y(C), 4th-axis (mm/min)
32. initial speed as feed axis running(mm/min)
33. speed skip variable of continuous track(mm/min)
15
Page 24

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
34. end speed of reverse deceleration in program running(mm/min)
35. whether enable speed treating function (76: yes, 0: no)
36. manual feed axis speed (mm/min)
100. spindle manual revolution (rpm)
101. max spindle revolution at top gear(rpm)
102. max spindle revolution at low gear (2nd gear) (rpm)
103. max spindle revolution at 3rd gear (rpm)
104. max spindle speed at 4th gear (rpm)
105. max revolution of 2nd spindle (rpm)
106. acceleration of spindle pulse control((mm/min)/s)
120. serial communication speed of RS232
Speed parameter explanation:
NO.1 G00 speed of X-axis, unit: mm/min
X axis running at the rapid traverse rate in auto mode (G00 called speed). initial value: 10000, Max
value:30000.
NO.2 G00 speed of Y-axis, unit: mm/min
Y axis running at the rapid traverse rate in auto mode (G00 called speed). initial value: 10000, Max
value:30000.
NO.3 G00 speed of Z-axis, unit: mm/min
Z axis running at the rapid traverse rate in auto mode (G00 called speed). initial value: 10000, Max
value:30000.
NO.4 G00 speed of 4th-axis, unit: mm/min or deg/min
th
The 4
axis running at the rapid traverse rate in auto mode (G00 called speed). initial value: 10000, Max
value:30000.
NO.5 G00 speed of 5th-axis, unit: mm/min or deg/min
th
The 5
axis running at the rapid traverse rate in auto mode (G00 called speed). initial value: 10000, Max
value:30000.
NO.6 default speed of G01/G02/G03, unit: mm/min
As no given speed for the first interpolation command (G01/G02/G03) in the program, the command
called default speed in the auto mode. Initial value: 2000, max value: 5000.
NO.7 simulation speed, unit: mm/min
Running speed in simulation mode. initial value: 20000, Max:30000
NO.8 acceleration of X-axis, unit: (mm/min)/s
The acceleration time constant for X-axis, the more the value the faster the speed. initial value: 50000,
value range: 1-99999
NO.9 acceleration of Y-axis, unit: (mm/min)/s
The acceleration time constant for Y-axis, the more the value the faster the speed. initial value: 50000,
value range: 1-99999
NO.10 acceleration of Z-axis, unit: (mm/min)/s
The acceleration time constant for Z-axis, the more the value the faster the speed. initial value: 50000,
value range: 1-99999
th
NO.11 acceleration of 4
The acceleration time constant for 4
-axis, unit: (mm/min)/s
th
-axis, the more the value the faster the speed. initial value: 50000,
value range: 1-99999
th
NO.12 acceleration of 5
The acceleration time constant for 5
-axis, unit: (mm/min)/s
th
-axis, the more the value the faster the speed. initial value: 50000,
16
Page 25

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
value range: 1-99999
NOTE: The value of acceleration is related to equipment configuration. usually, the heavier the load the
smaller the value.
NO.15 MPG acceleration(12--5000)
To set the acceleration time constant as apply MPG, setting range is 12-5000, the bigger the value, the
bigger the acceleration.
NO.16 speed up/down in auto running mode (500-32000)
To set acceleration constant in the auto mode, value range: 500-32000. as this parameter value set
within the range of 500-32000, speed will depends on this parameter in auto mode, otherwise, will
depends on each axis’ acceleration value in user parameter.
This parameter is mainly used to distinguish acceleration in manual mode and auto mode; Set this
parameter only there is much difference of acceleration in the two modes; otherwise, usually set as
invalid.
NO.17 positive speed of X-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
The running speed of X-axis meets reference switch moving towards positive direction as returning
reference point. Initial speed: 5000, value range: less than G00 speed of X-axis.
NO.18 positive speed of Y-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
The running speed of Y-axis meets reference switch moving towards positive direction as returning
reference point. Initial speed: 5000, value range: less than G00 speed of Y-axis.
NO.19 positive speed of Z-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
The running speed of Z-axis meets reference switch moving towards positive direction as returning
reference point. Initial speed: 5000, value range: less than G00 speed of Z-axis.
NO.20 positive speed of 4th-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
The running speed of 4th-axis meets reference switch moving towards positive direction as returning
reference point. Initial speed: 5000, value range: less than G00 speed of 4th-axis.
NO.21 positive speed of 5th-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
The running speed of 5th-axis meets reference switch moving towards positive direction as returning
reference point. Initial speed: 5000, value range: less than G00 speed of 5th-axis.
NO.22 reverse speed of X-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
As X-axis returning reference point, the running speed of checking encoder zero position after leaving
reference switch. Initial value: 250, value range:20-500.
NO.23 reverse speed of Y-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
As Y-axis returning reference point, the running speed of checking encoder zero position after leaving
reference switch. Initial value: 250, value range:20-500.
NO.24 reverse speed of Z-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
As Z-axis returning reference point, the running speed of checking encoder zero position after leaving
reference switch. Initial value: 250, value range:20-500.
NO.25 reverse speed of 4th-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
As 4th-axis returning reference point, the running speed of checking encoder zero position after leaving
reference switch. Initial value: 250, value range:20-500.
NO.26 reverse speed of 5th-axis as reference returning, unit: mm/min
As 5th-axis returning reference point, the running speed of checking encoder zero position after leaving
reference switch. Initial value: 250, value range:20-500.
NOTE
1. “return to reference point” also named as “return to machine zero point”
2. the revere speed parameter value affects precision of reference returning, the smaller the value the
higher the precision, do not change the value after setting, otherwise will affect reference point position.
17
Page 26

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
NO.27 max speed as rapid stop feed axis, unit: mm/min
Set the stop mode limit in running. No deceleration as the speed is higher than this parameter value,
otherwise these is deceleration as the speed is lower than this parameter value.
As one axis running speed is higher than this parameter value, system will stop the current running axis
directly if meets E-top or other failure (i.e.: limit), that means the speed of current axis will become zero
from current value directly (pay attention: now the machine zero will be lost, demand returning reference
point again); contrarily, as axis running speed is lower than this parameter value, system will control
running axis’ speed decelerated to zero according to normal.
NO.28 max feed speed in manual mode, unit: mm/min
The max running speed limitation to feed axis in manual mode.
NO.29 max feed speed in auto mode, unit: mm/min
The max speed of each axis in auto mode. Initial value: 12000, max value: 30000.
NO.30 max MPG speed of Z-axis, unit: mm/min
Set the max MPG speed of Z-axis in manual mode, unit: mm/min. setting range100—max manual speed.
This parameter setting related to load of equipment, recommend this value is not more than 2000.
NOTE: It is valid as setting value is more than 100, otherwise, will no limit to max speed.
NO.31 max MPG speed of X, Y, (C), 4th-axis, unit: mm/min
Set the max MPG speed of X, Y, (C), 4th-axis in manual mode, unit: mm/min. setting range 100—max
manual speed. If the setting value is less than 100, will no limit to max speed.
This parameter setting related to load of equipment, recommend this value is not more than 3000.
NO.32 initial speed as feed axis running, unit: mm/min
Set the initial speed as feed axis speed up, also is the end speed as axis speed down. It means, as the
feed speed lower than this value will arrival without speed up/down, as running speed is more than this
value, speed up began from this value.
The parameter value setting depends on drive type and loading, initial value is 500.
NO.33 speed skip variable of continuous track, unit: mm/min
Applied as speed is changed when multiple axes continuous track interpolation, make sure the max
mutational increment of each axis as interpolating speed, it means there will be speed up/down as the
speed increment is more than this value, if less than this value will arrival directly.
Mainly used for increasing coherence as multi-axes continuous track interpolation.
For example: as this value is 200 and X-axis speed changed from F1000 to F2000 in multi-axes
continuous track interpolation, the change process is Z-axis speed is changed from F1000 to 12000 at
first, then accelerated to F2000 by the No.8 value in “SPEED” parameter.
NO.34 end speed of reverse deceleration in program running, unit: mm/min
Set the start speed of speed up/down of each axis reverse moving in auto mode. Unit: mm/min.
This parameter is different with NO.32 (initial speed as feed axis running) in “SPEED”, NO.32 is normal
start speed of speed up/down, but this parameter is applied in reverse moving in auto mode, generally
this parameter is a little less than NO.32.
NO.35 whether enable speed treating function (76: yes, 0: no)
Whether enable speed smooth treating function in auto mode, as set to be 0 means not enable, set as 76
means enable.
Speed smooth treating function is applied in continuous high speed short line segment interpolation, it
preview and pre-treatment to the speed, to get the smooth transition speed in reverse or corner, to
increase surface finish of workpiece.
NOTE
18
Page 27

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Normally this parameter is set as “not enable”, it will increase calculation cost of CPU, may decrease the
running efficiency of system.
NO.36 manual feed axis speed, unit: mm/min
Set feed axis speed in manual mode. Initial value: 5000, value range: less than the max speed in the
manual mode (the value of NO.28 in “SPEED”).
NOTE:
The two parameters above is changed depends on manual setting, that means system will refresh this
parameter as modify the speed in the manual mode.
NO.100 spindle manual revolution, unit: rpm
Set the max rotate speed of spindle in manual mode. Initial value: 2000, value range: less than the max
speed of spindle.
NO.101 max spindle revolution at top gear (rpm)
Set the max rotate speed of spindle. Unit: r/min
This parameter is the top gear or first gear speed if there is top/low gears or multi-gears function.
NO.102 max spindle revolution at low gear (2nd gear) , unit: rpm
nd
Set the max speed of low gear/2
gear of spindle. Unit: r/min
NO.103 max spindle revolution at 3rd gear, unit: rpm
rd
For multi-gears function, this parameter is applied to set the max speed of the 3
gear. Unit: r/min.
NO.104 max spindle speed at 4th gear, unit: rpm
For multi-gears function, this parameter is applied to set the max speed of the 4th gear. Unit: r/min.
NO.105 max revolution of 2nd spindle, unit: rpm
nd
For double spindles, this parameter is applied to set the max speed of the 2
spindle. Unit: r/min.
NO.106 acceleration of spindle pulse control, unit: (mm/min)/s
Set the speed up/down time constant(acceleration) as spindle is pulse control mode, the more the value,
the higher the speed, contrarily, the speed is lower.
Initial value:8000, value range: 1—99999.
NO.120 serial communication speed of RS232
Set the baud rate of RS232 serial communication. the corresponding baud rate table as below:
NO.120 parameter
value setting
serial communication
rate(unit: bps)
NO.120 parameter
value setting
serial communication
rate(unit: bps)
0 7200 4 38400
1 9600 5 57600
2 14400 6 115200
3 19200
3.4.3 Coordinate system
The coordinate system in this parameter is work coordinate system and one machine coordinate
systemG53. The coordinate system applied for machining is named as work coordinate system and preset
by CNC. One or more work coordinate systems are allowed in one work program, the work coordinate
system can be changed by moving its zero point. That means, the coordinates value is the coordinates of
its own zero point in the machine coordinate system.
It’s allowable to set 6 work coordinates from G54 to G59, can modify the coordinates value of zero point of
6 work coordinate systems in the machine coordinate system.
amend their zero point value standing on the machine. refer to Fig3.12
19
Page 28
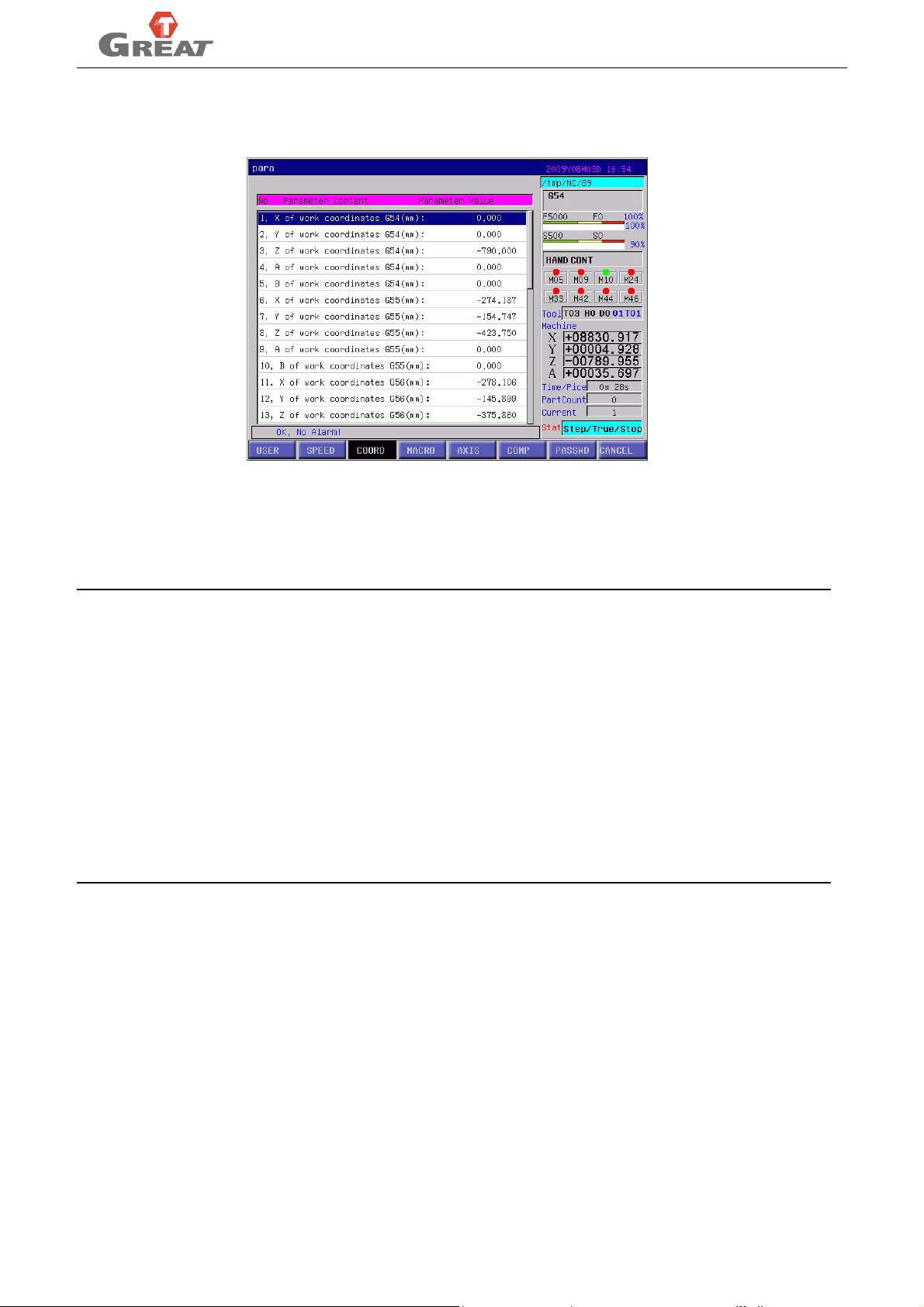
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
G54 : work coordinate system 1 G55 : work coordinate system 2
G56 : work coordinate system 3 G57 : work coordinate system 4
G58 : work coordinate system 5 G59 : work coordinate system 6
Fig3.10 work coordinate system setting
Press “↑”, “↓”softkey to select the work coordinate system which you want to modify, then press ”Enter” and
input the value into the dialogue box.
The six work coordinate systems can be set by users and calling by G54, G55, G56, G57, G58, G59.
NOTE
1. the machine coordinate system G53 in this parameter, is established according to the machine
reference point, can modify the offset of machine coordinate system G53 from original status, can be
applied to adjust tool setting error. If want to return to original status, only set the offset of G53 to be 0.
this offset is cleared after system reboot or return to zero; all the work coordinates will offset
correspondingly after this parameter is set.
2. generally, work coordinate system is established in the manual mode at first time and modify it under
“PARAM” menu if some offset when machining. For example: tool moves to certain point and select
corresponding coordinate system, and input your intent value, system will automatically calculate the
coordinates value of original point of current coordinate system in the machine coordinate system,
and save in the parameter. If there is deviation after machining, modify the coordinate value of
corresponding coordinate system in “PARAM”
3.4.4 Macro Variable parameter
In this system, there are 161 macro variables parameters "#30-#190”, macro variables “#30-#100” are
intermediate type, they are not saved after power off, so must assign them before using in macro
program; macro variables “#101-#190” are retainable type, they will be saved after power off.
Press “MACRO” softkey in the interface of “PARAM” will shift to macro variable setting interface. Select
the parameter by up/down key, then input value after press “Enter”.
Detailed explanation for macro variables, please refer to "User macro program"
3.4.5 Axis parameter
Axis parameter applied to set the parameter which is related to compensation, limit, function setting and
so on.
20
Page 29
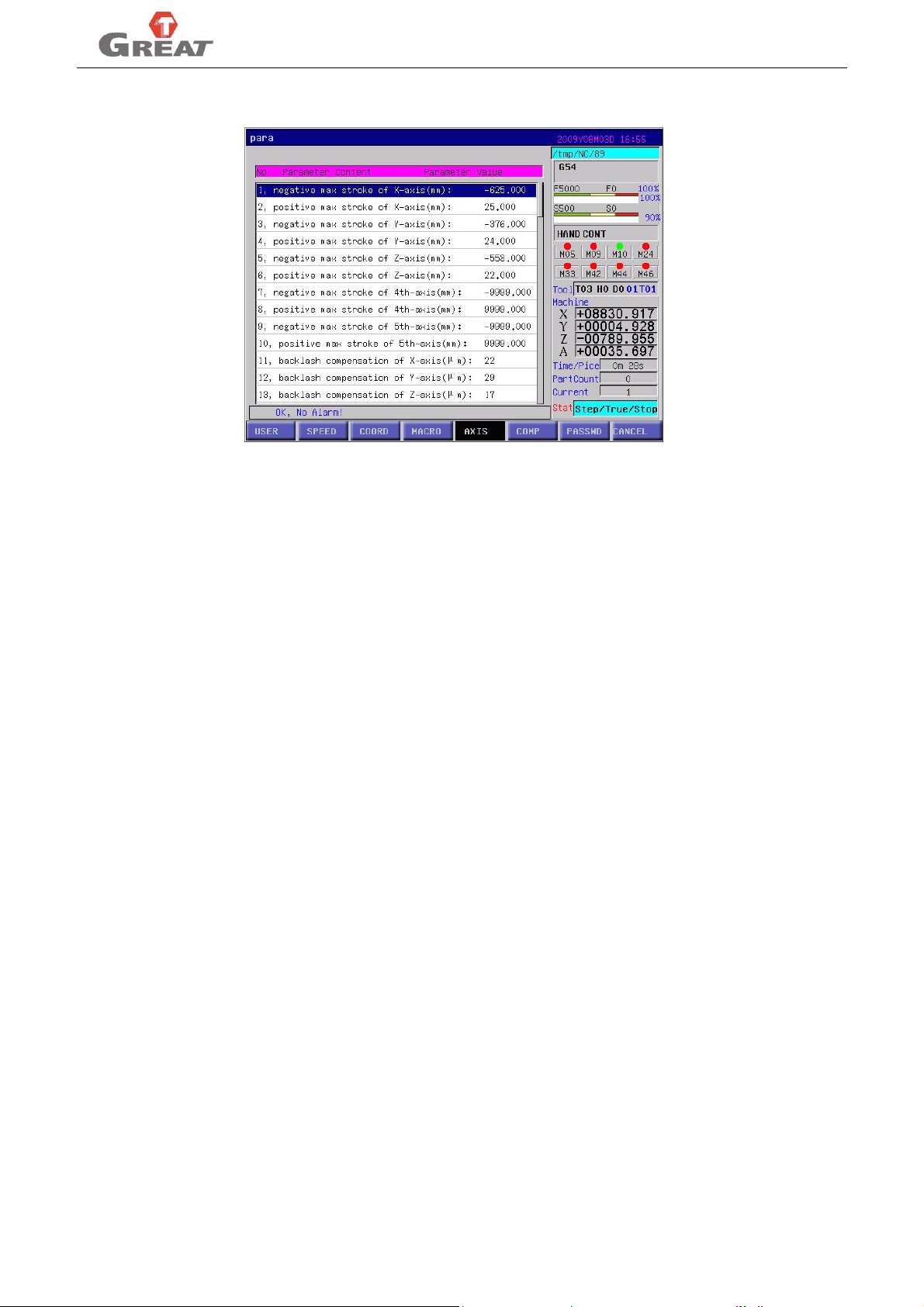
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
In the interface of “PARAM”, press “AXIS” soft key, will shift to “AXIS” parameter setting interface, select
parameter need to be modified by up/ down key and input value by press “Enter”. Refer to fig 3.11.
Fig 3.11 axis parameter setting
Axis parameter list
1. negative max stroke of X-axis(mm)
2. positive max stroke of X-axis(mm)
3. negative max stroke of Y-axis(mm)
4. positive max stroke of Y-axis(mm)
5. negative max stroke of Z-axis(mm)
6. positive max stroke of Z-axis(mm)
7. negative max stroke of 4th-axis(mm)
8. positive max stroke of 4th-axis(mm)
9. negative max stroke of 5th-axis(mm)
10. positive max stroke of 5th-axis(mm)
11. backlash compensation of X-axis(um)
12. backlash compensation of Y-axis(um)
13. backlash compensation of Z-axis(um)
14. backlash compensation of 4th-axis(um)
15. backlash compensation of 5th-axis(um)
16. whether apply electronic gear for feed axis (0: yes, 1: no)
17. numerator of X-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
18. denominator of X-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
19. numerator of Y-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
20. denominator of Y-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
21. numerator of Z-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
22. denominator of Z-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
23. numerator of 4th-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
24. denominator of 4th-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
25. numerator of 5th-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
26. denominator of 5th-axis’s electronic gear(1-32767)
27. direction signal of X-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
28. direction signal of Y-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
29. direction signal of Z-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
30. direction signal of 4th-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
21
Page 30

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
31. direction signal of 5th-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
32. reference returning method for feed axis
(0-reverse, check 0; 1-REV, no CHE 0; 2-no REV, CHE 0; other-no REV, no CHE 0)
33. switch NC setting of feed axis for reference return (X1,Y2,Z4,A8,B16)
34. reverse of reference returning for feed axis(X4,Y8,Z16,A32,B64)
35. the max length to check zero as X-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
36. the max length to check zero as Y-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
37. the max length to check zero as Z-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
38. the max length to check zero as 4th-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
39. the max length to check zero as 5th-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
40. offset after X-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
41. offset after Y-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
42. offset after Z-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
43. offset after 4th-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
44. offset after 5th-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
46. reverse delay time of feed axis(ms)
47. feed axes follow(AX7,AY8,AZ9,CX17,CY18,CZ19)
48. equivalent treating for XY(C)ZA axis
51. 4th-axis’ function setting (0: rotary axis, 1: linear axis)
52. 5th-axis’ function setting (0: rotary axis, 1: linear axis)
54. regular calculation as the 4th-axis is rotary axis (work coordi: +1; machine coordi: +2)
55. regular calculation as the 5th-axis is rotary axis (work coordi: +1; machine coordi:+2)
56. system inner parameter
58. system inner parameter
59. system inner parameter
100. pulse number per revolution of spindle encoder
101. whether check spindle position feedback(1: yes; 0: no)
102. detecting degree as spindle do orientating
103. degree detecting error as spindle orientating
104. control mode as spindle homing (0:speed control, 1:pulse control, 2: driver control)
105. spindle running before homing(0.1s)
106. threading and spindle positioning control(0:both track; 1:thrd is interp, pos is track; 2:thrd is track, pos
is interp; 3:both interp)
107. delay time for spindle rotate direction abrupt changing(0.1s)
108. servo spindle type(0: MODROL, 1: CTB, 8:DELTA)
109. direction signal of spindle pulse control (0: reverse, 1: normal)
110. whether apply electronic gear for spindle(0: yes; 1: no)
111. numerator of electronic gear as spindle at low gear (1-32767)
112. denominator of electronic gear as spindle at low gear(1-32767)
113. numerator of electronic gear as spindle at top gear(1-32767)
114. denominator of electronic gear as spindle at top gear(1-32767)
115. is there gear control for spindle (1:yes, 0: no)
116. whether close spindle 3rd, 4th gear (1:yes, 0: no)
117. whether start spindle as gear shifting (1:yes, 0: no)
118. duration from stop to swing as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
119. duration from swing to gear-shifting as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
120. swing speed of motor as spindle shifting gear (0.01 rpm)
22
Page 31

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
121. the initial swing direction as spindle shifting gear (0:positive, 1:negative)
122. positive swing duration as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
123. reverse swing duration as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
124. will output signal of spindle gear-shifting be hold (0:no, 1: yes)
130. high speed detection for hard limit of feed axis (0:yes, 1: no)
Axis parameter explanation
NO.1. negative max stroke of X-axis (mm/inch)
To set the max stroke of X axis in the reverse direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.2. positive max stroke of X-axis(mm/inch)
Set the max stroke of X axis in the positive direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.3. negative max stroke of Y-axis(mm/inch)
Set the max stroke of Y axis in the reverse direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.4. positive max stroke of Y-axis(mm/inch)
Set the max stroke of Y axis in the positive direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.5. negative max stroke of Z-axis(mm/inch)
Set the max stroke of Z axis in the reverse direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.6. positive max stroke of Z-axis(mm/inch)
Set the max stroke of Z axis in the positive direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.7. negative max stroke of 4th-axis(mm/inch/deg)
th
Set the max stroke of 4
-axis in the reverse direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.8. positive max stroke of 4th-axis(mm/inch/deg)
th
Set the max stroke of 4
-axis in the positive direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.9. negative max stroke of 5th-axis(mm/inch/deg)
Set the max stroke of 5th-axis in the reverse direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
NO.10. positive max stroke of 5th-axis(mm/inch/deg)
Set the max stroke of 5th-axis in the positive direction, unit: mm/inch, range:-99999~+99999.
CAUTION
Value setting for soft limit is related to equipment stroke and the usage of user. While the max value can’t
be more than the value which the hard limit detection switch show on the machine coordinates,
otherwise, machine accident may occur.
NO.11. backlash compensation of X-axis(um)
To set backlash compensation value as X-axis reverse moving. As this axis move to reverse direction,
system will call this value and execute compensation automatically to eliminate errors.
NO.12. backlash compensation of Y-axis(um)
To set backlash compensation value as Y-axis reverse moving. As this axis move to reverse direction,
system will call this value and execute compensation automatically to eliminate errors.
NO.13. backlash compensation of Z-axis(um)
To set backlash compensation value as Z-axis reverse moving. As this axis move to reverse direction,
system will call this value and execute compensation automatically to eliminate errors.
NO.14. backlash compensation of 4th-axis(um)
To set backlash compensation value as 4th-axis reverse moving. As this axis move to reverse direction,
system will call this value and execute compensation automatically to eliminate errors.
NO.15. backlash compensation of 5th-axis(um)
To set backlash compensation value as 5th-axis reverse moving. As this axis move to reverse direction,
system will call this value and execute compensation automatically to eliminate errors.
23
Page 32

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
NO.16. whether apply electronic gear for feed axis (0: yes, 1: no)
To set whether apply electric gear for feed axis, ”0” means use electric gear "1" means not use.
NO.17. numerator of X-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set X-axis’ electronic gear numerator, value range: 1--32767
NO.18. denominator of X-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set X-axis’ electronic gear denominator, value range: 1--32767
NO.19. numerator of Y-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set Y-axis’ electronic gear numerator, value range: 1--32767
NO.20. denominator of Y-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set Y-axis’ electronic gear denominator, value range: 1--32767
NO.21. numerator of Z-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set Z-axis’ electronic gear numerator, value range: 1--32767
NO.22. denominator of Z-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set Z-axis’ electronic gear denominator, value range: 1--32767
NO.23. numerator of 4th-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set 4th-axis’ electronic gear numerator, value range: 1--32767
NO.24. denominator of 4th-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set 4th-axis’ electronic gear denominator, value range: 1--32767
NO.25. numerator of 5th-axis’ electronic gear(1-32767)
To set 5th-axis’ electronic gear numerator, value range: 1--32767
NO.26. denominator of 5th-axis’s electronic gear(1-32767)
To set 5th-axis’ electronic gear denominator, value range: 1—32767
NOTE
The setting methods of feed axis’ electronic gear (to match with servo motor), refer to following formula:
L: machine displacement as the servo motor rotates one period, unit: mm
P: pulse feedback as the servo motor rotates one period (motor encoder line ×4)
NOTE : We strongly recommend set electronic gear into servo driver to avoid the bad synchronization in
simultaneous control.
NO.27. direction signal of X-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
To change moving direction of X-axis, as this value is “0”, the moving direction of X axis equates to
command direction reverse; as this value is “1”, the moving direction of X axis equates to command
direction.
NO.28. direction signal of Y-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
To change moving direction of Y-axis, as this value is “0”, the moving direction of Y axis equates to
command direction reverse; as this value is “1”, the moving direction of Y axis equates to command
direction.
NO.29. direction signal of Z-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
To change moving direction of Z-axis, as this value is “0”, the moving direction of Z axis equates to
command direction reverse; as this value is “1”, the moving direction of Z axis equates to command
direction.
NO.30. direction signal of 4th-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
To change moving direction of 4th-axis, as this value is “0”, the moving direction of 4th-axis equates to
24
Page 33

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
command direction reverse; as this value is “1”, the moving direction of 4th-axis equates to command
direction.
NO.31. direction signal of 5th-axis(0:reverse, 1:normal )
To change moving direction of 5th-axis, as this value is “0”, the moving direction of 5th-axis equates to
command direction reverse; as this value is “1”, the moving direction of 5th-axis equates to command
direction.
NO.32. reference returning method for feed axis
(0-reverse, check 0; 1-REV, no CHE 0; 2-no REV, CHE 0; other-no REV, no CHE 0)
To set the methods of detecting reference switch and zero pulse signal of motor encoder as axes do
reference returning.
“0”: as reference returning, run in reverse to detect switch after hitting reference switch, then
detect zero pulse signal of motor encoder.
“1”: as reference returning, run reversely to detect switch and free after hitting reference switch.
“2”: as reference returning, running forward to detect switch and free, then detect zero pulse
signal of motor encoder after hitting reference switch.
“3”: as reference returning, running forward to detect switch and free after hitting reference switch.
Please set the methods of Reference returning according to equipment circuit. Normally, we recommend
to set as “0” or “2”, because if not to detect zero pulse signal of motor encoder, the precision will all relay
on reference and the precision will be poorer than detect by motor encoder.
NO.33. switch NC setting of feed axis for reference return (X1,Y2,Z4,A8,B16)
To set the reference switch type of each axis as reference returning is NO or NC. As this parameter is set
to be “0”, means all axes switch as reference returning are NO; set to be “1” means X-axis’ reference
returning switch is NC; set to be “2” means Y-axis’ reference returning switch is NC; set to be “4” means
Z-axis’ reference returning switch is NC; set to be “8” means A-axis’ reference returning switch is NC; set
to be “16” means B-axis’ reference returning switch is NC;
Want to set multiple axes’ reference returning switches to be NC, should plus corresponding axes value
setting.
It is related to the switches of machine.
For example: to set the reference switches of X-axis, Z-axis and A-axis to be NC, set this parameter to
be 13(1+4+8=13).
NO.34. reverse of reference returning for feed axis(X4,Y8,Z16,A32,B64)
To set the direction of feed axis reference point returning. Value “0” means the axis reference point return
to positive direction; as return to reverse direction, please follow the steps below:
Reference point of X axis return to reverse direction: 4;
Reference point of Y axis return to reverse direction: 8;
Reference point of Z axis return to reverse direction: 16;
Reference point of A axis return to reverse direction: 32;
Reference point of B axis return to reverse direction: 64;
To set multiple axes return to reverse direction, should plus corresponding axes value setting.
For example: to set the reference points of X-axis and Z-axis return to reverse direction, this parameter
set to be 20(4+16=20).
NO.35. the max length to check zero as X-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
To set the detection range of zero pulse signal of motor encoder after release from reference switch as
X-axis return to reference, Unit: 0.1mm.
NO.36. the max length to check zero as Y-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
To set the detection range of zero pulse signal of motor encoder after release from reference switch as
25
Page 34

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Y-axis return to reference, Unit: 0.1mm.
NO.37. the max length to check zero as Z-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
To set the detection range of zero pulse signal of motor encoder after release from reference switch as
Z-axis return to reference, Unit: 0.1mm.
NO.38. the max length to check zero as 4th-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
To set the detection range of zero pulse signal of motor encoder after release from reference switch as
4th-axis return to reference, Unit: 0.1mm.
NO.39. the max length to check zero as 5th-axis reference returning (0.1mm)
To set the detection range of zero pulse signal of motor encoder after release from reference switch as
5th-axis return to reference, Unit: 0.1mm.
NOTE
Value setting for parameters N0.52~55 must be less than the distance of the corresponding motor rotate
one period. if match servo driver from Great CNC, please refer to following formula:
L: max length to detect zero as homing
Electronic gear numerator: electronic gear numerator of servo drive, No.12 parameter
Electronic gear denominator: electronic gear denominator of servo drive, No.13 parameter
NO.40. offset after X-axis finished reference return (0.01mm)
As X-axis do reference point returning, after detecting the zero pulse signal of servo motor, to set the offset
distance to complete reference returning function. Unit: 0.01mm. Range:-99999~+99999.
This parameter setting is related to installation position of machine reference switch and machine
coordinate system setting.
NOTE: The offset after reference returning execute G00 speed.
NO.41. offset after Y-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
As Y-axis do reference point returning, after detecting the zero pulse signal of servo motor, to set the offset
distance to complete reference returning function. Unit: 0.01mm. Range:-99999~+99999.
This parameter setting is related to installation position of machine reference switch and machine
coordinate system setting.
NOTE: The offset after reference returning execute G00 speed.
NO.42. offset after Z-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
As Z-axis do reference point returning, after detecting the zero pulse signal of servo motor, to set the offset
distance to complete reference returning function. Unit: 0.01mm. Range:-99999~+99999.
This parameter setting is related to installation position of machine reference switch and machine
coordinate system setting.
NOTE: The offset after reference returning execute G00 speed.
NO.43. offset after 4th-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
As 4th-axis do reference point returning, after detecting the zero pulse signal of servo motor, to set the
offset distance to complete reference returning function. Unit: 0.01mm. Range:-99999~+99999.
This parameter setting is related to installation position of machine reference switch and machine
coordinate system setting.
26
Page 35

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
NOTE: The offset after reference returning execute G00 speed.
NO.44. offset after 5th-axis finished reference return(0.01mm)
As 5th-axis do reference point returning, after detecting the zero pulse signal of servo motor, to set the
offset distance to complete reference returning function. Unit: 0.01mm. Range:-99999~+99999.
This parameter setting is related to installation position of machine reference switch and machine
coordinate system setting.
NOTE :The offset after reference returning execute G00 speed.
NO.46. reverse delay time of feed axis (ms)
To set delay time when the feed axis reverse in auto mode. Value non-“0” means need delay; value “0”
means not delay.
This parameter setting related to machine situation and machining process. Heavy load and frequent
reverse operation will impact much to machine, a delay time will reduce the impact to machine when the
table completely stop and then reverse operation; as continuous high speed small line segment running, if
set to be reverse delay will decrease the roughness.
NO.47. feed axes follow (AX7, AY8, AZ9, CX17, CY18, CZ19)
th
To set following up function for A (4th-axis), C( 5
-axis)
Value “7” means A axis follows up X axis; value “8” means A axis follows up Y axis; value “9” means A
axis follows up Z axis; value”17” means C axis follows up X axis; value”18” means C axis follows up Y
axis; value “19” means C axis follows up Z axis. others means without following up function.
Following up function definition applying for this system:
For example
A axis follows up “X “axis ---means running track of A axis and X axis are absolutely same. As
programming or in manual mode, only operate X-axis, A axis will completely follows up X axis,
For hardware, the pulse quantity from X axis drive output is same with that of from A axis drive output, to
realize following up function.
NOTE
1. Following up function usually applied into situation with high synchronicity requirement. Synchronicity
coordination adjusting for two axes, please adjust parameters like rigidity parameter, etc to up to the best
status.
2. In this system, only realize one axis (A axis or C axis) follow up a certain axis.
NO.48. equivalent treating for XY(C)ZA axis
To set frequency multiple for each axes’ pulse equivalent. This parameter setting will avoid motor over
speed in multi-axes simultaneous and mainly apply into the cases that there is much difference between
reduction ratio of certain axis and other axes.
Setting guide:
Value setting to change equivalent frequency multiply of X axis: 16+ multiple
Value setting to change equivalent frequency multiply of Y axis: 32+ multiple
Value setting to change equivalent frequency multiply of Z axis: 64+ multiple
Value setting to change equivalent frequency multiply of Z axis: 128+ multiple
For example:
1/2 original pulse equivalent of X axis(2 times frequency): 16+2=18;
1/2 original pulse equivalent of Y axis(2 times frequency): 32+2=34;
27
Page 36

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
1/2 original pulse equivalent of Z axis(2 times frequency): 64+2=66;
1/2 original pulse equivalent of A axis(2 times frequency): 128+2=130;
1/3 original pulse equivalent of X axis(3 times frequency): 16+3=19;
1/3 original pulse equivalent of Y axis(3 times frequency): 32+3=35;
1/3 original pulse equivalent of Z axis(3 times frequency): 64+3=67;
1/3 original pulse equivalent of A axis(3 times frequency): 128+3=131;
1/2 original pulse equivalent of XY axis(2 times frequency): 16+32+2=50;
1/2 original pulse equivalent of XYZ axis(2 times frequency): 16+32+64+2=114;
NOTE
1. when multiply frequency to certain axis pulse equivalent ,the corresponding drive electronic gear also
need multiply frequency, then can ensure the moving size of work table is consistent with actual size.
2. when multiply frequency to multi-axes pulse equivalent, the multiply frequency value must be consistent
to each axis.
NO.51. 4th-axis’ function setting (0: rotary axis, 1: linear axis)
th
To set the application of the 4
-axis, including rotary axis and linear axis.
As this parameter is set to be “0” means apply rotary axis mode, as this parameter set to be “1” means
apply linear axis mode. It depends on machine situation.
NO.52. 5th-axis’ function setting (0: rotary axis, 1: linear axis)
th
To set the application of the 5
-axis, including rotary axis and linear axis.
As this parameter is set to be “0” means apply rotary axis mode, as this parameter set to be “1” means
apply linear axis mode. It depends on machine situation.
NO.54. regular calculation as the 4th-axis is rotary axis (work coordi: +1; machine coordi: +2)
To set display mode of work coordinates and machine coordinates display and calculation method, when
the 4th-axis is rotary axis. The calculation method includes regular calculation and irregular calculation.
Regular calculation means within the range from 0 to 360, when the data over 360, divide by 360,
irregular calculation means to increase as same as liner axes.
The input value “+1” means the work coordinates show as regular method; while input value “+2”
means the display and calculation method are regular method. The parameter setting depends on users’
circumstance.
For example
When the parameter is 3(1+2), means the display and calculation of work coordinates and machine
coordinates are regular method.
NOTE
The track calculation of rotary axis function type is unrelated with above parameter, the regular or
irregular of axes track depends on programming method (absolute or increase ). when use G90 code to
do absolute programming, then will calculate in 360 regular method and run to the programming point in
the shortest way; while use G91 code increment programming ,apply irregular method , same as linear
axes.
NO.56. system inner parameter
Applied to set system function, set by CNC company.
NO.58. system inner parameter
Applied to set system function, set by CNC company.
NO.59. system inner parameter
28
Page 37

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Applied to set system function, set by CNC company.
NO.100. pulse number per revolution of spindle encoder
Applied to set the pulse number per revolution of spindle encoder, the values is: encoder line x 4.
NO.101. whether check spindle position feedback (1: yes; 0: no)
To set whether the system detects spindle position feedback signal. Value ”1” means to detect, value “0”
means not.
This parameter is to set function connected with spindle speed, such as real revolution and degree of
spindle and rotate feed, to realize this function, spindle must possess encoder feedback signal.
NO.102. detecting degree as spindle orientating
To detect stopped degree of spindle as tool changing in the auto mode.
NO.103. degree detecting error as spindle orientating
To set position error range as spindle executes positioning function. Unit: 0.01 degree
NO.104. control mode as spindle homing (0:speed control, 1:pulse control, 2: driver control)
To set control mode of spindle zero returning (return stop degree of tool exchange)
Value”0” means spindle homing realized by applying speed control mode and detect encoder’s degree;
value “1” means spindle homing realized by applying pulse control mode and detect encoder’s degree;
value “2“ means spindle homing realized by driver self-controlling.
This parameter setting is related to spindle driver type. Set this parameter to be “2” to improve efficiency if
the spindle drive possesses self-control homing function. Otherwise set this parameter to be “0”, and have
to feedback synchronous encoder signal with spindle.
NO.105. spindle running before homing(0.1s)
Set the running time before spindle homing.
NO.106. threading and spindle positioning control(0:both track; 1:thrd is interp, pos is track; 2:thrd
is track, pos is interp; 3:both interp)
To set spindle control mode when executes threading and spindle positioning. Details as followed:
0—both are tracking;
1—threading is interpolation and positioning is tracking
2—threading is tracking and positioning is interpolation;
3—both are interpolation
Tracking: means the spindle motion depends on feedback signal from spindle encoder
Interpolation: means the spindle motion depends on pulse signal from system
NO.107. delay time for spindle rotate direction abrupt changing (0.1s)
To set the delay time between last commands canceling and the next command starting as the spindle
change direction from CW to CCW or from CCW to CW. Unit: 0.1s
NO.108. servo spindle type (0: MODROL, 1: CTB, 8: DELTA)
To set servo spindle type of machine, to confirm the control mode of the system to servo spindle.
Value”0” means the servo spindle brand is MODRO; value “1” means the servo spindle brand is CTB-GA
or general-purpose frequency inverter. Value “8” means the servo spindle brand is DELTA.
NO.109. direction signal of spindle pulse control (0: reverse, 1: normal)
To change the rotate direction in position (pulse) control mode, value”0” means spindle rotate direction is
same with commands reverse direction, value “1” means spindle rotate direction is same with commands
direction.
NO.110. whether apply electronic gear for spindle(0: yes; 1: no)
To set whether apply electronic gear as spindle is in position control mode. Value ”0” means apply
electronic gear, value”1” means not.
NO.111. numerator of electronic gear as spindle at low gear (1-32767)
29
Page 38

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
To set electronic gear numerator at low grade, the value range : 1—32767
NO.112. denominator of electronic gear as spindle at low gear(1-32767)
To set electronic gear denominator at low grade, the value range : 1—32767
NO.113. numerator of electronic gear as spindle at top gear(1-32767)
To set electronic gear numerator at top grade, the value range : 1—32767
NO.114. denominator of electronic gear as spindle at top gear(1-32767)
To set electronic gear denominator at top grade, the value range : 1—32767
NOTE
Spindle electronic gear setting, please calculate according to following formula:
A: spindle rotation degree when the spindle motor rotates one revolution. unit: degree
P: feedback pulse number when the spindle motor rotates one revolution.(motor encoder line x4 )
NO.115. is there gear control for spindle (1:yes, 0: no)
To set spindle high and low grade function. As machine possesses auto gear shifting function, system
will realize gear shifting between high and low grade, and speed control corresponding to gears
according to the commands.
Value “1” means the machine possesses high and low grade;
Value “0” means the machine no high and low grade.
If set the spindle has high and low grade, the standard setting of “K1”on subpanel is high grade and “K2”
to control low gear grade. M61 is spindle high gear grade and M62 is spindle low gear grade in program.
Auxiliary relay M64, M65 are separately high gear grade and low gear grade control, to realize high or
low gear grade control, please edit PLC ladder to lead corresponding auxiliary relay to output relay Y,
then to control gear shift circuit. M40, M41 separately are high or low gear grade detection, to detect gear
shift in position, please edit PLC ladder and lead corresponding detection signal to the corresponding
auxiliary relay.
Revolution setting at high or low gear grade: set revolution for high or low gear grade through No.101 or
No.102 parameter in “SPEED” menu.
NOTE
If the high or low gear are manual shift mode, please just lead corresponding detection signal to
corresponding auxiliary relay and set right revolution at high or low gears when edit the PLC ladder. No
need enable high or low gear grade function.
NO.116. whether close spindle 3rd, 4th gear (1:yes, 0: no)
rd
Whether close the 3
and 4th gear function of spindle, value “1” means close the 3rd and 4th gear function;
value “0” means not close.
NO.117. whether start spindle as gear shifting (1:yes, 0: no)
This parameter is to confirm whether the spindle swing or not when gear shift, value “1” means swing,
value ”0” means not swing.
To swing or not is connected with the machine structure; usually spindle need swing when change gears.
NO.118. duration from stop to swing as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
To set the delay time from system output stop signal to start shifting gear, change gears as spindle
running, unit: 0.01s.
30
Page 39

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
The setting status is connected with the spindle highest speed, if this value set too small, the gear teeth
may be damaged.
NO.119. duration from swing to gear-shifting as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
Set the swing signal duration before output gear shifting signal. Unit: 0.01s
NO.120. swing speed of motor as spindle shifting gear (0.01 rpm)
Set the spindle motor speed as shifting gear, unit: .0.01r/min.
It is related to the machine structure.
NO.121. the initial swing direction as spindle shifting gear (0: positive, 1:negative)
Set the initial rotate direction of spindle motor as shifting gear. Value “0” means same direction with M03;
value “1” means the opposite direction of M03.
NO.122. positive swing duration as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
Set positive swing duration when shifting gear, unit: 0.01s
Setting status is connected with machine structure of gear shifting unit
NO.123. reverse swing duration as spindle shifting gear (0.01s)
Set reverse swing duration when shifting gear, unit: 0.01s.
Setting status is connected with machine structure of gear unit. Generally, the rotate time is same
between CW and CCW.
NO.124. will output signal of spindle gear-shifting be hold (0:no, 1: yes)
Set whether keep the spindle gear shifting signal after completed shifting (the status of auxiliary relay
M64, M65), value “1” means keep; value ”0” means not keep.
Setting status is connected with machine structure of gear shifting unit. Usually not keep.
NO.130. high speed detection for hard limit of feed axis (0:yes, 1: no)
Value “0” means high speed detecting the hard limit of feed axis, the detecting period is 2ms, value “1”
means not execute high speed detecting.
3.4.6 Comprehensive parameter
Comprehensive parameter is that of not including into above parameters.
Press “COMP” softkey in the parameter interface, will shift to comprehensive parameter setting interface.
Refer to fig 3.12.
Fig3.12 comprehensive parameter
Select current parameter by Up/Down key, press “Enter” will pops up dialog for input data, for example as
below:
31
Page 40

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.13
Comprehensive parameter list:
1. subpanel control(18: all controlled by PLC)
2. inner para(6: auto enter, 8: allow import, reset by inputting “9” and “enter”)
3. language selection(1: 中文, 0: English)
4. tool length/canned cycle/circular backlash type
5. B-type backlash speed of arc (mm/min)
6. subpanel type (A3;B0;C3;D6;E7;F15)
7. whether display self-defined alarm(0:no, 1: yes)
8. whether display feed axis and spindle alarm(0:no, 1: yes)
9. whether display cool/lub alarm(0:no, 1: yes)
10. whether enable tool selection and tool exchanging function(0:no, 1: yes)
11. tool management type
12. tool selection mode/ tool count signal
13. the axis returned to tool exchanging point (3:ZX;4:ZY;5:ZXY;other:Z)
14. which reference point does feed axis return as tool exchanging
15. whether detect spindle orientation and feed axis return to exchange tool point before tool exchanging (0:
no, 1 : yes)
16. whether spindle do orientation as tool exchanging (0: not orientation, 1: orientation)
17. spindle orientation stopping degree as tool exchanging (0.1 deg) negative means no orientation
18. tool magazine type(0: rotary, 1: no magazine or lathe tool post, other: umbrella)
19. special tool magazine(0: standard, 16: special umbrella, 32: servo ,64:special ARM)
20. the lifting height of Z-axis as tool exchanging for umbrella tool magazine (mm)
21. lifting speed of Z-axis as tool exchanging for umbrella tool magazine (mm/min)
22. Z-axis’ rapid lifting distance for umbrella tool magazine mm
23. delay time of tool restoring for umbrella tool magazine(rotary tool seat down/tight)(0.1s)
24. delay time after tool release as exchanging tool(0.1s)
25. does Z-axis’ motion are interlocked with arm seizing tool/umbrella tool magazine (1:yes, 0: no)
26. whether tool magazine forward instruction “M41” check Z-axis’ position(0: yes, 1: no)
27. the max tool No. in fixed tool location zone (initialize tool seat after setting this parameter)
28. axis’ power status as startup (0: auto power up when startup, 1: no power up when startup)
29. delay time between driver power off and reboot(0.1s)
32
Page 41

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
31. setup type of tool radius C compensation (0: A type, 1: B type)
32. cancellation method of tool radius C compensation (0: A type, 1: B type)
33. does M03/M04 instruction check spindle speed up to request(0: yes, 1:no)
34. delay time before spindle speed up to request (0.1s)
100. X of reference point 1(mm)
101. Y of reference point 1(mm)
102. Z of reference point 1(mm)
103. A of reference point 1(mm)
104. X of reference point 2(mm)
105. Y of reference point 2(mm)
106. Z of reference point 2(mm)
107. A of reference point 2(mm)
108. X of reference point 3(mm)
109. Y of reference point 3(mm)
110. Z of reference point 3(mm)
111. A of reference point 3(mm)
112. X of reference point 4(mm)
113. Y of reference point 4(mm)
114. Z of reference point 4(mm)
115. A of reference point 4(mm)
150. whether enable voltage compensation(2:yes, 0:no)
151. voltage compensation point 0.1V
152. voltage compensation point 0.2V
153. voltage compensation point 0.3V
154. voltage compensation point 0.4V
155. voltage compensation point 0.5V
156. voltage compensation point 0.6V
157. voltage compensation point 0.7V
158. voltage compensation point 0.8V
159. voltage compensation point 0.9V
160. voltage compensation point 1V
161. voltage compensation point 2V
162. voltage compensation point 3V
163. voltage compensation point 4V
164. voltage compensation point 5V
165. voltage compensation point 6V
166. voltage compensation point 7V
167. voltage compensation point 8V
168. voltage compensation point 9V
169. voltage compensation point 10V
170. voltage compensation value
200. standby
201. standby
202. whether start PLC program running(0:stop, 1: start)
203. defined current parameter as factory parameter
Explanation for comprehensive parameter
33
Page 42

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
NO.1. subpanel control (18: all controlled by PLC)
Set the control mode for softkey ports of subpanel. Value “18” means the soffkey ports controlled by PLC
program edited by user (except for the softkeys of coordinate system and override switch), ”non 18”
means the softkeys ports will be controlled by preset embedded program in the system.
NO.2. inner para (6: auto enter, 8: allow import, reset by inputting “9” and “enter”)
Set the booting picture of controller, set this parameter to be “6” means auto display the preset booting
picture as controller power up; set to be “8” means allow import booting picture; set to be “9” means delete
the imported picture and reset.
NO.3. language selection(1: 中文, 0: English)
Set the display language of controller is Chinese or English. Value “1” means apply Chinese, value “0”
means apply English.
NO.4. tool length/canned cycle/circular backlash type
(0 digit: length compensation; 1 digit: canned cycle; 3 digit: circular backlash) (0:A; 1:B)
Set tool length compensation/canned cycle/arc pitch compensation mode A and B, this parameter
Input by decimal system transferred from binary system after calculation,
0 digit: set tool length compensation mode, there are two modes A and B.”0” is “A” mode,”1” is B mode
A mode tool length compensation means compensate the difference value along Z axis.
B mode tool length compensation refer to the tool length difference compensation along X,Y,Z axes by
the instruction of G17/G18/G19.
I digit: set canned cycle mode, including two modes A and B. ”0” is “A” mode, ”1” is B mode
A mode means the position plane of canned cycle always is G17 (XY plane);
B mode means the position plane of canned cycle is decided by G17/G18/G19
2 digit: set arc backlash compensation mode. There are two modes A and B. ”0” is “A” mode, ”1” is ”B”
mode.
A mode: means execute backlash compensation together with arc interpolation;
B mode: means stop arc interpolation at first, then execute backlash compensation by the speed of NO.5,
then continue execute are interpolation.
For example:
If select B mode for length compensation, A mode for canned cycle and B mode for arc backlash
compensation; should input “5” (value in binary system: 101).
NO.5. B-type backlash speed of arc (mm/min)
Set the running speed of B mode backlash compensation. Unit: mm/min.
NO.6. subpanel type (A3;B0;C3;D6;E7;F15)
Set the subpanel type. Value 3“ means A type or C type, “0” means B type, “6” means D type, “7” means
E type, “”15” means F type.
NO.7. whether display self-defined alarm (0:no, 1: yes)
Whether display the status of auxiliary relay of self-defined alarm on the information bar real time. Value
“1” means display, “0” means not display.
NO.8. whether display feed axis and spindle alarm(0:no, 1: yes)
Whether display the status of auxiliary relay of feed axis alarm and spindle alarm on the information bar
real time. Value “1” means display, “0” means not display.
NO.9. whether display cool/lub alarm(0:no, 1: yes)
Whether display the status of auxiliary relay of cooling and lubrication on the information bar real time.
Value “1” means display, “0” means not display.
NO.10. whether enable tool selection and tool exchanging function(0:no, 1: yes)
34
Page 43

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Set whether enable select & exchange tool function or not, this parameter setting is connected with
machine equipment configuration (whether possesses tool magazine). Value “0” means the function is not
available; ”1” means enable.
Value “1” means the machine equipment with automatic tool exchange function and can work with
multiple tools. if there is no tool magazine on the machine, should set this parameter to be “0”, but in the
auto mode, after manual change tool, still apply TxxDxxHxx instruction to realize multi-tools control and
radius, length compensation.
NO.11. tool management type
(0: use M06, 1: directly tool exchanging by T instruction)
Set the tool exchanging mode for tool magazine of “rotary type” and “umbrella type”, value “1” means
apply T commands to change tool directly, value “0” means apply M06 commands to change tool.
NO.12. tool selection mode/ tool count signal
(0 digit: 0 means single dir/1 means bi-dir tool select; 1digit: tool count REV)
Set tool selection mode and whether tool count signal is reverse, which denoted by double figure in
binary system. Input in decimal system transferred from binary system calculation.
0 digit: set the rotate direction of cutterhead is uni-direction or bi-direction as selecting tools: “0” means
uni-direction, “1” means bi-direction (select tool from nearer side).
1digit: set whether the tool count signal valid mode is reverse: “0” means the valid mode of tool count
signal is same direction with default mode; “1” means the valid mode of tool count signal is reverse with
default mode.
The tool selection mode is related to tool magazine type, normally set to be bi-direction tool selection; set
whether tool count signal is valid related to debugging, as debugging, if cutterhead rotate CW and CCW
alternately, but the tool seat number in the tool status column on the display doesn’t change accordingly,
need to set the valid mode of tool count signal to be reverse from current mode, normally set as reverse.
NO.13. the axis returned to tool exchanging point (3:ZX;4:ZY;5:ZXY;other:Z)
Set which feed axes need to return to a given reference point (tool exchange point). Value “3” means X, Z
axes return to tool exchange point as auto exchange tool; value “4” means Y, Z return to tool exchange
point as auto exchange tool; “5” means X, Y, Z axes return to tool exchange point as auto exchange tool;
other value except for 3, 4, 5 means only Z axis return to tool exchange point as auto exchange tool.
This parameter setting related to machine type and tool magazine type, normally auto exchange tool for
vertical machining center, only Z axis return to tool exchange point.
NO.14. which reference point does feed axis return as tool exchanging
(1, 2,3, 4 denotes corresponding reference point, other value means no motion)
Set the coordinates value of auto exchange tool applies which reference point, setting range 1—4
st
(corresponding to 1
refer to 4th refer), normally apply the 2nd reference point value as exchange tool
point. Set to be other values expect for 1, 2, 3, 4 means all axes won’t moving as exchanging tool.
NO.15. whether detect spindle orientation and feed axis return to exchange tool point before tool
exchanging (0: no, 1: yes)
Set whether detect spindle orientation finished and feed axes moved to tool exchange point before auto
exchange tool. Set to be “1” means detect the spindle orientation degree and feed axes coordinates to
improve safety; se to be “0 means no need detect spindle orientation degree and feed axes coordinates.
Recommend set this parameter to be “1” as machine possesses auto exchange tools function, to
improve safety of auto exchange tools.
NO.16. whether spindle do orientation as tool exchanging (0: not orientation, 1: orientation)
Set whether system control spindle orientation function automatically and prepare fortool exchange in
automatic tool exchange mode
Value ”0” means the system will not control spindle orientation automatically, apply corresponding
35
Page 44

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
commands to let spindle orientating before exchange tool, ”1” means the system control spindle orientation
automatically.
NO.17. spindle orientation stopping degree as tool exchanging (0.1 deg) negative means no
orientation
Set spindle stop degree in automatic tool exchange mode. Value range: 0-3600, unit: 0.1degree.
Usually spindle stop degree is realized through spindle servo driver in automatic tool exchange status. Set
this parameter to confirm spindle stop degree as auto exchange tool only as parameter NO.104 set to be
“0”.
NO.18. tool magazine type (0: rotary, 1: no magazine or lathe tool post, other: umbrella)
Set tool magazine type of the machine equipment in order to determine the control mode of tool magazine.
Value “0” means to match with “rotary type tool magazine”(cam type with mechanical arm)
Value ”1” means without tool magazine; value “2” means to match “umbrella type tool magazine”
The parameter setting is connected with machine equipment. to control tool magazine beside set this
parameter and also need to edit relative PLC program.
NO.19. special tool magazine (0: standard, 16: special umbrella, 32: servo ,64:special ARM)
Set tool magazine type of the machine equipment in order to determine the control mode of tool magazine.
Set this parameter to be “0” means standard “rotary type” or “umbrella type” tool magazine; “16” means
special umbrella tool magazine; “32” means servo control tool magazine; “64” means special ARM tool
magazine.
The parameter setting is connected with machine equipment. to control tool magazine beside set this
parameter and also need to edit relative PLC program.
NO.20. the lifting height of Z-axis as tool exchanging for umbrella tool magazine (mm)
To set Z axis lift up height as tool release in automatic tool exchange process when match with umbrella
tool magazine .unit: mm
The parameter value must larger than the tool handle length to avoid interference between tool handle and
spindle head as cutterhead rotate or back after tool releasing.
NO.21. lifting speed of Z-axis as tool exchanging for umbrella tool magazine (mm/min)
Set the moving speed of Z axis get to the lift height which set by No.22 as tool releasing in the process of
exchanging tool for umbrella tool magazine. Unit: mm/min.
This parameter value not too large, Otherwise affect the precision of cutterhead rotation or lead to tool
magazine deformation because spindle will hit the cutterhead as departing and approaching; but not too
small to decrease exchange tool efficiency.
NO.22. Z-axis’ rapid lifting distance for umbrella tool magazine mm
Set the rapid lift distance of Z-axis in auto exchange tool process as tool releasing when match umbrella
type tool magazine, unit: mm.
This value must less than the value of NO.20.
NO.23. delay time of tool restoring for umbrella tool magazine(rotary tool seat down/tight)(0.1s)
This parameter is to set delay time for three cases.
1. Umbrella type tool magazine exchange tool: To set delay time to retract cutterhead after
spindle move down to catch the tool handle and tighten the tool;
2. Rotary type tool magazine exchange tool: delay time for manipulator to perform fasten tool
operation after tool down.
3. Rotary type tool magazine exchange tool: delay time for manipulator return to zero after tool
exchange and tighten the tool. Unit: 0.1s
This parameter setting is related to tool magazine type.
NO.24. delay time after tool release as exchanging tool (0.1s)
Set time delay time to execute the next operation of tool exchange after the exact tool release signal is
36
Page 45

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
valid in auto tool exchange mode, which can avoid delay of mechanical parts. Unit: 0.1s
NO.25. does Z-axis’ motion is interlocked with arm seizing tool/umbrella tool magazine (1:yes, 0:
no)
Set whether the motion range of Z-axis is interlocked with cutterhead (umbrella tool magazine ) or
manipulator (rotary tool magazine). That’s to say, whether limit the coordinates of Z axis lower than tool
exchange point value of Z axis when the cutterhead pushed out or the manipulator stay in fastening tool
status.
Value ”1” means to limit to avoid Z axis moving lower than tool exchange point and enhance safety.
Value”0” means not limit.
This parameter setting is connected with usage status. Usually set as “0” as debugging, but should make
sure the position of Z axis not interfere with cutterhead. We recommend to set as”1” for safety in normal
operation.
NO.26. whether tool magazine forward instruction “M41” check Z-axis’ position (0: yes, 1: no)
Whether detect Z-axis position when the tool magazine moves forward in manual and MDI mode.
Value”0” means to detect and the system can move forward only when the tool exchange point of Z axis
is more than +20mm; value”1” mean not to detect.
This parameter is set to be “1” when the machine debugging at the first time; in normal operation, we
recommend set to be “0” for safety sake.
NO.27. the max tool No. in fixed tool location zone (initialize tool seat after setting this parameter)
Set the fixed tool number area zone for rotary tool magazine (tool and toolseat must be one-to-one
correspondence and can’t exchange tools randomly).value range: from No.1 to the max tool number
For example:
Value “5”, means the fixed tool seat zone is from No.1 toolseat to No.5 toolseat, tools status as exchange
tools in this zone are one-to-one correspondence with the initial install tools and can’t exchange tools
random.
This parameter mainly applied into the installation of tools with big diameter. The tool diameter may
bigger than the distance between two toolseats and may create tool collision trouble once change tools
random. So it’s better to place in a fixed tool number area.
NOTE : Must initialize toolseat table after setting this parameter
NO.28. axis’ power status as startup (0: auto power up when startup, 1: no power up when startup)
Set power control status of axes in system control interface after start the system. Value”0” means power
up to each axis automatically after system self checking normal at booting; value "1" Means the system will
not power up to each axis automatically and need to operate manually.
The precondition for setting this parameter is the power supply of each axis driver is controlled by contactor
and etc. there is no significance to set this parameter if the power supplied directly by the machine
equipment.
1. If set as “0”, then light indicator K8 will be lighten when the system starts and the E-STOP button
released. Control outside circuit by editing PLC program to power up each axis.
2. if set as ”1”, need to press K8 keypad and edit PLC program to power up all axes.
NO.29. delay time between driver power off and reboot (0.1s)
As driver power supply controlled by CNC system, the delay time between system cut off the power supply
to driver and re-supply power to driver. Unit: 0.1s
NO.31. setup type of tool radius C compensation (0: A type, 1: B type)
Set establishment patterns of tool radius compensation C, there are two kinds of establishment of tool
radius compensation A and B (please refer to Chapter4.6 for detail)
Value“0” means the establishment type of tool radius compensation is A mode;
37
Page 46

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Value”1” means the establishment type of tool radius compensation is B mode.
NO.32. cancellation method of tool radius C compensation (0: A type, 1: B type)
Set cancellation types of tool radius compensation, there are two methods to cancel tool radius
compensation in this system. (refer to Chapter 4.6 for details)
Value”0” means to select A mode to cancel tool radius compensation C;
Value “1”means to select B mode to cancel tool radius compensation C.
NO.33. does M03/M04 instruction check spindle speed up to request (0: yes, 1:no)
To check spindle speed up to request after executing commands M03/M04 in auto running mode. Value
"0" means detect and value "1" means not to detect.
This parameter setting depends on the configuration of machine equipment and usage. to detect
machine, users need configure spindle revolution adjustment instrument and also edit PLC program to
lead the spindle revolution adjustment instrument signal to system auxiliary relay.
NO.34. delay time before spindle speed up to request (0.1s)
Set the delay time to detect revolution auxiliary relay status after the system send out M03/M04
commands unit: 0.1s
This parameter setting depends on max spindle revolution and spindle inertia. The larger of the
revolution or the larger of the inertia, the more this parameter (the longer the spindle acceleration last)
NO.100----NO.115 reference point parameter (mm)
In this system is available to set four reference points and can modify each reference coordinates value
under reference point setting interface.
The first reference point is named as machine reference point
, which is fixed on the machine and depends
on inspection device. Tool can be easily moved to machine reference point along appointed axis by using
reference returning function (manual or auto mode are both ok). The machine coordinates will be refreshed
to the first reference point coordinates value after finishing reference point returning. Usually the first
reference point is coincident with machine home. Usually the first reference point is coincident with
machine zero and all other reference points are established on base of the first reference point. refer to Fig
3.14
Fig3.14 machine home and the four reference points
Press “COMP” softkey and shift to reference point setting interface under “PARAM” menu. as refer to
Fig3.15
38
Page 47

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig3.15 reference point setting
Press “↑”, “↓” softkey to select right reference point which you want to modify and “Enter” into dialogue box
for value input.
The first reference point is a special position point, usually set by machine manufacturer and never change.
And other three reference points are usually applied as auto tool exchange point or other usage.
NO.150. whether enable voltage compensation(2:yes, 0:no)
NO.170. voltage compensation value
NO.200. standby
NO.201. standby
NO.202. whether start PLC program running (0:stop, 1: start)
Set PLC running mode;”0” means stop running of PLC program.”1” means start PLC program.
CAUTION
All I/O status will out of control by PLC program, once stop running the PLC program, all input will remain
its current status and output will not be detected. But for output control, can shift to “DGNOS”→“I/O”
→“OUTPUT RELAY” interface and move the cursor to select right Output “Yxx”, then press “Alt” to
control output of this signal, as refer to fig3.16. This normally applied in the first time debugging,
otherwise can’t be allowed and accident may happen.
Fig3.16
NO.203. defined current parameter as factory parameter
Define the current parameter to be factory parameter (original parameter). Applied for backup parameter
after debugging, it is convenient for maintenance of machine in the future.
3.4.7 Password
Password interface mainly used for right setting and system program upgrade and backup. ”Enter” into
password setting interface by pressing “PASSWD” soft key, please refer to Fig3.17:
39
Page 48

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.17 password setting
Password parameter setting interface includes items as followed:
1. Is enable CNC Co.’s password?
2. Is enable Machine Co.’s password
3. Is enable User’s password?
4. Modify CNC Co.’s password
5. Modify Machine Co.’s password
6. Modify User’s password
7. Current work time
8. print screen function
9. Current system software version
3.4.7.1 Access authority setting
To avoid parameters being revised unexpectedly, system allows parameters to be set under 3 levels
access authority (“CNC Co.”, “Machine Co.” , “User”).
”CNC Co. ” authority is to set system function, belonging to inner system parameter;
”Machine Co.” authority is to set parameter relative to machine requirement configuration and machine
index or safety.
”User’s Corporation” authority is to set parameters relative to manufacturing process, performance or
machining program.
Once enabled all of these access authority, modify or adjust to corresponding parameter and program,
the system will remind operator to input password to get access.
The initial status of the 3 levels access authority is: “CNC Co.” access authority has been enabled, both
“Machine Co.” and “User” authority have not enabled. To enable the authority function, must input the
initial password to enable access authority function, then set new password.
NOTE
The initial password can be only used once and it will be invalid once you set a new password, so please
keep your new password in mind. The initial “Machine CO.” password is”888888” and “User” password is
“999999”.
Password must be a group data of 6 digits, the data can be number or letters.
40
Page 49
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
“Machine Co.” password setting
The first step is to enable password: move the cursor to No.2 parameter “Is enable Machine Co.’s
password” then press “Enter” into dialogue box.
Fig 3.18 input machine Co.’ original password
Input original password ,then dialogue pop up; input “0” ,then ”Enter” to start the right .
Fig3.19 enable password or not
The second step is to set new password: move the cursor to No.5 parameter” Modify Machine
Co.’s password”, then “Enter” into dialogue box as followed.
Fig3.20 input machine Co.’ new password
Input new password in dialogue box as above shows, then “Enter” to confirm, then the system will remind
password inputting once again. as followed:
Fig 3.21 confirm machine Co.’ new password
Input password again and “Enter” to confirm. System will show password successfully !
Fig3.22 machine Co.’ password modified successful
If you want to modify some parameter after you setting new password successfully, system will ask you
to input new password and then you can modify it after confirmation. As refer to fig3.23
41
Page 50

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig3.23 input machine Co.’ password
“User” password setting:
The first step to enable password: move the cursor to No.3 parameter “Is enable User’s password“,
then “Enter” into dialogue box as followed.
Fig3.24 input user’s original password
Input original password, then a dialogue pop up, you can input “0” or “1”
“0” means to start right for both user parameter and machining program;”1” means only start user
parameter right function, then press ”Enter” to confirm and start the right.
Fig3.25 enable password or not
NOTE
If both user parameter and machining program password is enabled, as operator modify user parameter
and machining program, the system will remind operator to input password at first; if only enable user
parameter password, operator only need input user parameter password and no need input password
when modify machining program. All correct setting depends on the details of user management.
The second step set new password: move the cursor to NO.6”modify user’s password”, then
“Enter” into dialogue as followed:
Fig3.26 input user’s password
Enter new password and “Enter” to confirm, a dialogue pop up and remind input again as followed:
Fig3.27 confirm user‘s new password
Input new password once again and “Enter”, a dialogue pop up say password set successful.
42
Page 51

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig3.28 user’s password modified successful
If you want to modify some parameter after you setting new right password successfully, system will
remind you to input password and then you can modify it after confirmation. As refer to fig3.29
Fig3.29 input user’s password
3.5 Diagnose
Under the main interface, press "PARAM" key to enter the diagnosis interface. Under this interface,
operator can monitor every I/O port and edit every I/O function name and reset of driver error alarm
3.5.1 I/O real-time monitor
Under the diagnose face, press "I/ O" to enters I/O port monitor face, refer to fig 3.30, Through pressing
"PgUP" "PgDn" to shift among "input relay", "subpanel input", "outputs relay", " auxiliary relay 1", "
auxiliary relay 2", monitoring every I/O port status.
Fig 3.30 I/O interface
NOTE :Red indicator means invalid, green indicator means valid.
43
Page 52

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
3.5.2 Ladder real-time monitor
Fig3.31 edit PLC ladder
Shift to ladder detection interface by pressing LADDER function key under DIAGNOSE interface,
through which all can observe the logic relation among I/O, timer, auxiliary relay etc and detect PLC
running status.
NOTE: Red light means the relay off and green light means the relay on.
3.5.3 Configuration of input/output and self-defined alarm
Shift to editing interface by pressing “EditCfg” under DIAGNOSIS interface, where we can edit the
specification for the usage of I/O and auxiliary relay .Please refer to 3.32
Fig 3.32
Editing method: Move the cursor to the cell need to edit by pressing "↑""↓" And "ENTER" and insert
configure explanation in the dialogue box.
44
Page 53

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
3.5.4 Clear alarm accident of feed servo driver
Once driver alarm, user need to clear it by following steps: under parameter interface, press "ResetDr"
Function soft key and "Enter"; system will clear alarm error of feed servo driver according to preset PLC
output signal.
CAUTION: This function is applied to remind to clear alarm information after solved the failure. Only
press “RESET” can not solve the failure.
3.5.5 Edit ladder diagram
After pressing “EditLad” key under DIAGNOSE interface, shift to interface to edit:
Fig 3.33
press “ 》 ” key in menu, shift to the other interface:
Fig 3.34
press“ 《 ” will back to the interface in fig 3.33. In these two interfaces, it can edit PLC ladder diagram
according to system PLC source. Finished editing, press “save” in fig 3.34 to “Enter”, then press
“COMPIL” softkey, it creates or modify PLC documents. “ESC” to quit from “EditLad” interface.
Operation guide for editing ladder, please refer to the chapter of “programmable logic control PLC”.
NOTE: 1. in the status of “LadStat” and ”EditLad” under DIAGNOSE interface, press “S” key and input
45
Page 54

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
the cell wanted to search for, will find the needed cell.
2. After PLC files renewed, must reboot system or shift to “Ladder” in the “PARAM” to press “R”
3.5.6 Alarm display
When machine alarm, view the alarm details by press “ALARM” in the “PARAM” interface, will view the
current alarm information and 10 items of alarm history.
3.6 Pitch error compensation
It is used for pitch error automatic compensation, due to the effect of screw pitch error on machine
transmission accuracy. System adopts store pitch error compensation: when debugging, it measures out
the screw error curve based on the machine zero point as start point, makes out revised curve on the
basis of error curve, then input the value of revised curve into revised parameters table, and
compensates according to this table.
Press “PARAM” on the panel, shift to pitch error compensation interface, as showed in fig3.35, there are
two areas (basic parameter and compensation setting area) in ”PITCH” screen. Press “Å” “Æ” move
cursor and shift between the two areas. The pitch parameters setting or saving are based on the unit of
axes. Press the corresponding F soft keys to shift to corresponding parameters for each axis.
Fig3.35 pitch interface
Shift to basic parameter setting area by pressing “<-“ and select by pressing ”↑””↓”. A dialogue box for
parameter setting of pitch error compensation will pop up, when press ”Enter” as Fig3.36 shows.
46
Page 55

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig3.36 basic parameter setting of pitch
th
Press “->” to shift to pitch error compensation setting. Press X,Y,Z,4
, 5th Axis soft key, will show the
pitch error compensation point and compensation value.
Select required compensation point by pressing ”↑””↓” or PgUp, PgDn; dialogue box of compensation
value will pop up ,when press “Enter”. Please refer to Fig3.37:
Fig3.37 compensation value setting
The number setting of compensation points are free, the max compensation points number of each axis
can be up to 300 points. The basic parameter of pitch error compensation for each axis includes
following aspects:
1. Compensation point No. of reference point: set pitch error compensation points No.
corresponding to reference points of each axis.
2. Compensation No. of furthest end in negative direction: set the furthest end compensation
points No. in negative direction on each axis.
3. Compensation No. of furthest end in positive direction: set compensation No. of furthest end in
the positive direction, the parameter value setting should be bigger than
“compensation No. of furthest end in the negative direction”
4. Compensation ratio: compensation coefficient of each compensation points, usually set as “1”.
5. Compensation interval: distance between two compensation points on each axis. unit: um
Fig3.38 space between compensation points
System automatically calculates each axis pitch error compensation point position according to basic
parameters. Each axis pitch error compensation point is distributed with equal interval; users can input
each point compensation value.
47
Page 56

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
The pitch error compensation points of each axis are evenly distributed. The interval of compensation
points is set on the each axis. The minimum value of pitch error compensation points are limited,
calculated by following formula:
Minimum value of pitch error compensation points = max feed speed (rapid feed speed) /3750.
Unit: minimum value of pitch error compensation points: mm max feed speed mm/min
For example
Example 1: Linear axis: when length of travel is -400mm~+800mm,interval of points 50mm,reference
point compensation NO. is No.40, it can figure out that Com. Point NO. of furthest end in the negative
direction is:
Compensation point No of reference-machine travel in negative direction/compensation point interval
+1=40-400/50+1=33
Com. point No. of the furthest end in the positive direction is :
Compensation point No. of reference + machine travel in positive direction/ compensation point interval =
40+800/50=56.
Machine coordinate and compensation point NO. correspondence is:
Fig 3.39 Correspondence between machine coordinates and compensation points No
Output compensation value at the position of “0”
Parameters set as follows:
z Compensation point NO. of reference point:40
z Com. point NO. of furthest end in negative direction:33
z Com. point NO. of furthest end in positive direction:56
z Compensation percentage:1
z Compensation point interval:50000
Output compensation value at corresponding point:
No
value
33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 … 56
+2 +1 +1 -2 0 -1 0 -1 +2 +1 0 -1 -1 -2 0 +1 … +1
Compensation point and value contrast as showed in Fig3.40
Fig 3.40 Compensation point and value contrast
48
Page 57

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Example 2: rotary axis: when movement per revolution is 360°, interval of points 45°, reference point
compensation NO. is No.60, the Com. Point NO. of furthest end in the negative direction is usually same
with the reference point com. point NO.
Com. point NO.of the furthest end in positive direction is:
Reference compensation point NO.+ movement per revolution/comp point interval=60+ 360/45=68.
Machine coordinate and compensation point NO. correspondence is:
Fig 3.41
EXPLANATION
Input value in small circle. If the total amount from 61 to 68 doesn’t equal 0, accumulated pitch error per
revolution will deviate, so same value shall be input into point 60 and 68. Parameter sets as follows:
z Compensation point NO.of reference point: 60
z Com.point NO.of furthest end in negative direction: 60
z Com.point NO.of furthest end in positive direction: 68
z Compensation percentage:1
z Compensation point interval:45000
Output compensation value at corresponding point:
NO. 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68
VALUE +1 -2 +1 +3 -1 -1 -3 +2 +1
Compensation point and value contrast:
Fig3.42 Compensation point and value
3.7 Tool
Press “REDEEM” on the panel will shift to tool parameter setting interface.
49
Page 58

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
There are six function keys in “REDEEM” menu as” Radius”, “Length”, “ACLEA”, “CLEAR”,
“Toolseat”, “Set”.
“Radius” to set radius compensation value of tool
“Length” to set length compensation value of tool
“ACLEA” clear all the length and radius compensation value
“CLEAR” clear the current length and radius compensation value
“Toolseat” to set or monitor match status between tool and toolseat
“Set” set tool management (at most 99tools)
Radius compensation value setting:
Press “Radius” button to shift to radius compensation interface. There are three groups of compensation
value for each tool as refer to Fig3.43. Move cursor to select the right tool and “Enter” to dialogue box.
Fig 3.43 Radius compensation value setting
As above shows, press “↑”, “↓” to insert value of D1,D2 or D3 in the dialogue box, then press” Enter” to
save all the compensation value or press ”ESC” to cancel it and return.
Length compensation value setting:
Press “Length” button to shift to radius compensation interface, under “Tool” parameter interface. There
are four groups of compensation value for each tool as refer to Fig3.44, move cursor to select the right
tool and “Enter” into dialogue box.
50
Page 59

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.44 Length compensation value setting
As above shows, press“↑”, “↓” to insert value of H1,H2,H3 or H4 in the dialogue box, then press ”Enter” to
save all the compensation value or press ”ESC” to cancel it and return.
NOTE
Length compensation value can be positive or negative, but radius value must be positive.
Tool setting explanation:
Press “BASE” under main interface in manual mode will to set tool setting base, the default tool setting
base point in this system is Z-axis machine coordinates. Press “TOOL” to memorize tool setting
automatically, after tool changing. That’s to say, this system will automatically memorize the difference
between tool setting value and Z-axis machine coordinates and save it.
Toolseat table setting:
Press “Toolseat” softkey to shift to toolseat setting interface, under “Tool” parameter setting interface. all
match status can be checked in the interface. as shows in Fig3.45, the left data is toolseat No and the
right data are Tool No. move “↑”, “↓” to select Tool No and “Enter” to dialogue box.
Fig3.45 Toolseat table setting
”Toolseat 00” means spindle toolseat. Usually, toolseat table is set at the first time tool installation and
should check the status encountering unexpected power off when tool changing or normal operation
(have tool changing action). Based on tool changing characteristic, toolseat and tool always keep fixed
correspondence when controlling ““umbrella” type tool magazine. while toolseat and tool may not follow
fixed correspondence but change time to time according to the process of tool changing when controlling
“manipulator type tool magazine”.
As above shows, there is “INI” softkey in the “Toolseat” interface, which is used to initialize default
correspondence relation between toolseat and tool under “Toolseat” parameter interface (refer to
Fig3.46), the usual steps is to initialize the correspondence between toolseat and tool at the first time
install tools and before setting.
Tool count setting:
Press ”Set” softkey under “REDEEM” to enter tool count parameter setting interface and set controllable
tool count(at most 99tools)as shows Fig3.46
51
Page 60

3.8 Program
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig3.46 Tool count setting
All programs in this system are managed in files and can be saved up to 32MB in NAND FLASH storage.
Program editing can be operated in full screen and protected by insert password.
Press "PRAM" on the panel and shift to program interface, refer to fig3.47.
Fig 3.47 Program choice
As above shows program name and folder are displayed in the middle of the screen, select program by
moving the cursor or press "PgUp" /"PgDn" Keys and "Enter" corresponding files. At the bottom of the
screen is program path and" /tmp/NC" are default storage path in this system .All new files are saved
under this menu. There are 8 function soft keys at the bottom of the screen, named as "New/Sek",
"COPY", "RENAM", "LAST", "INFOR", "LAST", "USBdisk", "EXEC", "CANCEL", press corresponding soft
key to shift to the interface.
3.8.1 New/Sek
Press ”New/Sek” soft key under Program interface, then a dialogue box pop up and ask for input new
file or sought files(refer to fig3.48)
52
Page 61

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.48 New/Sek
In this system, program name can be made up of number, letters (capital letter/lowercase is available) or
other characters(/ \ : * ? “ < > | and space are not allowable) and length is unlimited. Insert file name in
the dialogue box and "Enter", if the file is existed in the system will display the name with reverse color,
otherwise it is the new file of the current program and displayed with reverse color, if need editing, press
“Enter”.
NOTE
To new or seek a folder, insert file name and end with "[" character. If the folder is existed in the system, it
will be displayed with reverse color, if not existed in the system, will new folder and reverse color display.
3.8.2 Copy
"Copy" Means to copy the current program file or folder into another program file or folder. Press
"↑","↓"keys to select program files or folder to do copy operation and "Enter", then a dialogue box pop up
and ask for inserting a new file name or folder name.
Fig3.49 Copy
As fig 3.49 shows, if the inserting file name already exist and another dialogue box like fig3.50 pops up
and remind whether to cover the file. If not the file name, it will be treated as the current program file or
current folder and displayed with reverse color.
Fig 3.50
3.8.3 Rename
Select the file to rename and press "RENAM" Soft key, then a dialogue box (refer to fig3.51) pops up and
ask for inputting new file name or folder name.
Fig 3.51 Rename
53
Page 62

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
As fig 3.52 shows, if the inputted file name already exist and another dialogue box like fig3.52 pops up
and remind whether to cover the file. If not existed, it will be treated as the new file or folder.
Fig 3.52
3.8.4 Delete
Under program interface, move the cursor to select the program file or file box and "Del" it.
CAUTION
Please make sure everything before deleting a file, because the data can not be recovered after deleting.
3.8.5 Information
in the “PRGRM” interface, Move the cursor to select program file and press "INFOR" Soft key to know
relative information of the program file, (refer to fig3.53)
Fig3.53 Information
NOTE
Folder only display the system remaining space.
3.8.6 Copy Program apply USB-disk
In this system, program can be transmitted between CNC controller and PC or other CNC controller with
USB-disk. Most USB-disk is available for this system, and no need driver program, but other USB
memory such as MP3 is not available.
Insert the USB-disk into USB port and press "USBdisk" Soft key under program interface to shift to USB
management interface. Please refer to fig3.54:
54
Page 63

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.54
As fig3.54 shows all files in USB disk displayed in the middle area of the screen (Display area) and at the
bottom of the screen is path display area and "/tmp/USB" is system default path.
Return to program interface by pressing "SYSTEM" Under USB interface.
A dialogue like fig3.55 may pop up and remind unidentified after inserting the USB disk, please reboot
system, if the USB-disk still can’t be found, need to change another USB disk.
Fig 3.55
Import program files from USB disk to the system: Insert USB-disk, press “USBdisk” will display
program file in the USB-disk. Select the file or folder needs to be imported into system by press"↑","↓" key,
then press “Import” key, will pop up a dialogue box, input program folder or folder name and press
“Enter”.
Fig 3.56
If the inputted file name already exist, a dialogue box (Fig3.57) pops up and remind whether to cover it. If
this name is not existed in the system, it will be acted as the current program file or folder and reverse
color display.
Fig 3.57
Export program file or folder from system into USB disk: press "↑","↓"Keys to select program files to
be exported and press "USBdisk"--->"EXPORT"-->insert file name in dialogue box and "Enter" .Refer to
fig3.58
55
Page 64

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig3.58
If the inputted file name already exist, a dialogue box (Fig3.59) pops up and remind whether to cover it. If
this name is not existed in the USB-disk, it will be acted as the current program file or folder and reverse
color display.
Fig 3.59
CAUTION
Return to program display interface before pulling out the USB-disk. Otherwise, the data in the USB-disk
will be lost.
Import or export parameter or system software(used for upgrading, renewing or backup )
Import parameter, software to system with USB-disk (upgrade, renew)
First insert U disk in CNC. Press "PRGM" -> "USBdisk "(F6), will display file in the USB-disk. Select the
file need to be imported and press “Restore”(F2), pops up dialog as below, press “Enter”. restore
succeed, press SYSTEM”, plug out USB-disk and reboot system.
Fig3.60
Export parameter system software with USB-disk(backup)
The operate path is: “PRGM”-Æ”USBdisk”(F6)Æselect file and press “Enter”Æ”Export”, input password
of machine tools builder, press “Enter”Æpop up the dialog as below figure, press “Enter” will export the
parameter file and system software to the USB-disk. Press “SYSTEM”, plug out USB-disk.
Fig3.61
NOTE
1. All files including parameter files, system software or PLC files will automatically exported into
USB disk use USB disk export parameter, meanwhile, all permitted files selected will be imported to
56
Page 65

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
system and cover the original ones.
2. When using USB disk, space character is impermissible in the folder name.
Check the current software version of the system.
Check the system software version No, refer to No.7 parameter under ”PASSWD” interface, details as
followed:
3.8.7 Program transmitted by serial port
Program transmission can be realized not only with USB but also through RS232 port. Press "R" Key to
receive a program and "T" Key to send a program under “PRGM”.
Through RS232 cable connect PC and CNC control system, set the corresponding serial No and
transmit rate before transmission.
Program transmission from PC to system: run system professional communication software on PC
(refer to fig3.62)
Fig 3.62
After setting serial number and transmit rate in the configuration column and press "Transmit CNC
program file" Button--->select the file to transmit and "Open". Now PC is waiting for transmitting software.
Press "R" Button under system "PRGM" Interface, then a dialogue box pops up (refer tofig3.63)
Fig 3.63
Input file name in above dialogue box and “Enter”, then PC will start to transmit program file and the
system start to receive it (refer to fig3.64)
57
Page 66

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.64
Program transmitted from system to PC: press "↑","↓"Keys to select a program file to be transmitted
under "PRGM" Interface and press "T" Button. Refer to fig3.65
Fig 3.65
Run system professional communication software developed by our GREAT CNC company on PC (refer
to fig3.66)
58
Page 67

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.66
Correctly set serial port number and speed rate to connect with PC and press "Receive CNC program
file" button --Æinsert the file name ,--Æ press" Save" Button .system start to transmit program file and PC
will store the file into appointed file path.
NOTE
1. to transmit a program ,must run the system professional communication software developed by our
GREAT CNC company on PC.
2. Keep consistent of transmit rate between PC equipment and the system, otherwise can't be
transmitted successfully.
3. the connecting serial number must keep consistent with setting in system and we strongly
recommend to use communication shield supplied by our company to avoid damage to serial port for
continual insertion, and baud rate of RS232 should be better less than 38.4Kbps.
4. RS232 communication wire length can't be longer than 10 meters.
5. User can use the communication software directly by copying it into PC equipment from CD matched
with this system and no need to install it.
3.8.8 Edit
Move the cursor to select a program under “PRGM” interface, then "Enter" into program editing
status .refer to fig3.67
59
Page 68

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig3.67 Edit
Editing interface mainly edit program, insertion, modify, delete etc. Select the program name and “Enter”
into full screen editing status.
In editing screen, left top area is file name display area and right top area is total program lines and line
number where the cursor stands. All program contents displayed in the middle area. At the bottom of the
screen, there are 8 commands keys in two menus .Named as "COMPIL", "FirLine", "Endline""POS",
"DelBlock", "DelLine", "COMMAC", "CopBlock","ARRAY", "SEARCH", "ALTER", "AALTER" and shift two
menus by pressing "> >"and "< <" keys. Refer to fig3.68
Fig 3.68
Operation method under editing status as follows:
1) Pose the cursor: change the cursor's position
.“↑↓”:up and down between the lines
.“→←”Move Left and right between characters
.“PgUp, PgDn” Goes to last page or next page
.“Enter” Move to the home of next line
Press “POS” Soft key and insert line number can locate directly to the line which you insert in
.press “Home” and “End” To the home / end of the line
.press “home” Key to directly locate to home of the line.
.press “End” Key to directly located to end of the line.
When the located program line surpasses the page, it will automatically change to the next page and
located program line will be contained in the display.
2) Delete: press “Del” key to delete the character behind the cursor.
3) Backspace: press “Back” key to delete the character before the cursor.
4) Space: press “Spc” key to insert a SPACE before the cursor.
5) Upper key: press "Shift" key and press character key to insert the upper character
6) Line delete: press "Deline" soft key to delete the line where the cursor stands.
7) Block operation: includes block copy and block delete function
Block copy: copy one block to the line where the cursor stands. Follow steps below: move the cursor to
correct position under editing status and press "Copblock" Under the second menu, then a dialogue pops
up (fig3.69).
Fig3.69
Insert starting line number in above dialogue box and "Enter" Into another dialogue box as fig3.70 shows:
60
Page 69

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.70
Insert ending line number of the copy block in the dialogue box and "Enter", then the selected block will
be copied to the line behind of the cursor.
NOTE
1, the insert line number must be the real line number rather than line number started by N
2, if copy only one line, just set begin line number and end line number as same line number
Block delete: system will take line where the cursor stands as beginning line number and decide
program block according to inserted line number and delete it from the program, operation method as
followed:
Move the cursor to the beginning line of the block to delete and press "Delblock" Soft key under the first
menu, then a dialogue box pops up (fig3.71).
Fig 3.71
Insert the end line number of the block to delete in above dialogue box and press "Enter", then the
selected block will be deleted.
NOTE
The insert line number must be the real line number rather than line number started by N
8) Compile
Program written using ISO codes (original program) according to ruled programming instruction can't
directly run in the system, but should convert into executable machine codes (object program).
Compiling function actually is the process to translate the original program into machine codes program.
Compile includes "Compile NC" And "Compile MAC": "Compile NC" Means to compile NC processing
program; "Compile MAC" Means to compile macro program.
There is rigorous fault checking function in compile process, if there is error in the program, it is can be
modified in time. If there is no fault, a information box pops up and shows "OK, compile successfully!”,
refer to fig3.72.
61
Page 70

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.72
If there is some fault, system will remind the fault line number and its characteristic, refer to fig3.73
Fig 3.73
NOTE
In Auto mode, system will automatically compile the original program and remind fault information, if
there is any fault in the program.
9) SEARCH: search for appointed character string backwards from the point where the cursor stands.
10) ALTER: replace appointed character string once backwards from the point where the cursor stands.
11) AALTER: to replace appointed character string from the point where the cursor stands to the
end of the program. Operation instruction as followed:
Move the cursor to the start line of the character string to replace and press "AALTER" Soft key, then a
dialogue (fig3.74) box pops up.
Fig 3.74
Insert character replaced in above dialogue box and "Enter", refer to Fig3.75.
Fig 3.75
Input replaced character in above dialog box, press “Enter” all the character string will be replaced from
the current line to the end of the program
NOTE: stop actions of “Seek”, ”ALTER”, ” AALTER” by pressing “Emergency stop” switch
12)Array lines: Array the program line number under edition in the decimal system. there is no strictly
requirement to system line number, it can be numerical value with 1-4 figures and increase on any base
or never use it at all
13)Esc: press "Esc" or "Return" Keys to return to file management menu. System will reminds whether
to save program.
CAUTION
Program file won’t be saved encountering unexpected power off during program edition. If user wants to
62
Page 71

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
save files during edition, just press “COMPIL” key to do compiling operation will save the program.
3.8.9 Select processing Program
Select processing program under “PRGRM” menu before automatic machining. Operation guide: press
"↑","↓" under PRGRM menu to select program and press “EXEC” soft key. Now the program has been
selected (can be checked from the status menu on the right top of screen)
CAUTION
Do follow all steps described above to select machining program, otherwise, system will execute the
program run last time. Thereby, please check program name before running.
3.8.10 Shift Program files path
/tmp/NC is the default path storage for Program files or establishes a new file under this path. To return to
the root, please press “LAST” soft key.
3.9 Manual
Press “MANUAL” soft key on the main panel will shift to manual operation menu. Refer to fig3.76 as
followed:
Fig3.76 manual mode
In manual mode, including manual continuous, manual increment, MPG and override adjustment and etc,
please refer to above fig,
3.9.1 Continuous mode
Press “CONT” soft key in the “MANUAL” menu shift to manual continuous mode. Manual or auto status
display column, please refer to fig3.77
Fig 3.77
63
Page 72

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Axes feed on when press the key and stop when release it. Press “+X, -X, +Y, -Y, +Z,-Z, +4, -4” to realize
the manual continuous accordingly, The feed speed is manual speed set in parameter multiply its ratio.
There are two hard limits in both two directions of the axis, will stop feed when meet the limit and remind
the status. Now only feed reverse.
In manual mode, execute axes simultaneous operation by pressing multi-axes at the same time.
3.9.2 Increment
Press “INC” soft key under manual mode shift to manual increment mode. Manual/auto mode status
display as fig3.78:
Fig3.78
Press “+X, -X, +Y, -Y, +Z,-Z, +4, -4” to feed a increment value to realize manual increment, the feed seep
is manual speed multiply feed rate.
Increment value shift keys
0.01mm-->0.001mm". Meanwhile, users can set any increment value directly by pressing "I" Key in the
increment mode. Refer to fig3.79
and conform to sequence and shift cycle mode: "1.0mm-->0.1mm-->
Fig 3.79 to set increment value
3.9.3 MPG mode
Press “MPG” soft key to shift to MPG operation in the manual mode. MPG status display refer to fig3.80.
Fig 3.80
In MPG mode, select current axis by pressing axis (X, Y, Z, 4th, 5th) on sub-panel and set ratio override
by pressing
select axis and ratio by rotating knob on the pendant MPG. when do level shift operation, please do press
the button at the left side of the MPG generator to confirm, otherwise, not any motion.
keys repeatedly to shift among there levels X1, X10, X100,while use pendant MPG,
3.9.4 Reference returning
Reference return operation make all coordinates axes run to basis switch of the machine equipment in
turn. When coordinates axis detect reference signal and again detect zero pulse as returning, machine
64
Page 73

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
coordinates data will be automatically set as the first reference point,.
In manual mode, press
key then a dialogue box (refer to fig3.81) will pop up and ask for insert axis
which will do reference returning.
Input address X or Y or Z or 4, 5 and press ENTER soft key, then corresponding axis return to reference
point. Press A and ENTER ,then axes do reference returning in sequence Z→X→Y. input S means
spindle return to reference point, input T means tool magazine return to reference point. Axis indicator
will turn green after finishing reference returning, otherwise failed.
Fig 3.81
Running speed, running direction, detection method, offset value set in parameter. Press STOP button to
stop reference returning operation.
NOTE
1. During the process of reference returning, a dialogue may pops up (fig3.82), which reminds zero pulse
detection of motor failed as reference returning. In that case, do reference returning again. If this problem
repeatedly happened, there may be some problem with parameter setting(reverse speed of reference
returning is too rapid) or circuit problem, please check carefully.
2. the precondition of doing spindle reference returning is spindle possesses encoder signal feedback;
the precision of reference returning is related to execution mode and speed, the precision will be higher
as the control mode of spindle is position control, as in speed control mode, the precision will be worser;
meanwhile, the more of the speed of reference returning, the worse of precision.
Fig 3.82
CAUTION
Please do reference returning operation each time after starting the system or cases of unexpected
power off or abnormal switch-off to make sure of machining precision. Otherwise, accident may happen.
3.9.5 Automatic midpoint identification function
This system has automatic midpoint identification function and can identify the midpoint of a line (parallel
the coordinates axes) using two points or identify the center of a circle by three points under G17
coordinates surface. This function mainly used for establishing the zero point of work coordinate system.
Follow the instructions below:
65
Page 74

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Diagram 1 diagram 2
Fig3.83
Identify the midpoint of a line through two points (refer to diagram 1)
Firstly, choose corresponding work coordinate system, move the coordinates to point A and press key E,
then a dialogue box pops up (refer to fig3.84)
Fig 3.84
input 1 and ENTER to specify the coordinates of point P1, then move the coordinates to point B and
press key E .A dialogue box pops up refer to fig3.85 (note ”the point P1 has been set ”)
Fig 3.85
Input 2 and press ENTER to specify the coordinates of point P2, press key E and a dialogue box pops up
refer to fig3.86 (note ”the point P1,P2 has been set ”)
Fig 3.86
Input X(the line is parallel to X axis) and ENTER, system will automatically set the midpoint of the line to
be the zero point of X-axis, the current X-axis coordinates set as an offset value based on the X-axis zero
point of work coordinate system.
Specify the centre of a circle through three points (refer to diagram 2)
Select corresponding work coordinate system and move coordinates to point A, then press key E and a
dialogue box will pop up (refer to fig3.87)
66
Page 75

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.87
Now, input 1 and ENTER to specify the coordinates of point P1 and then move the coordinates to point B,
press key E and a dialogue box will pop up, refer to fig3.88(point P1 has been set already)
Fig 3.88
Now input 2 and ENTER to specify the coordinates of point P2 and then move the coordinates to point
C, press E key and a dialogue box will pop up(refer to fig3.89) please check setting result on the dialogue
box,P1,P2 point S have been set already.
Fig 3.89
Now, input 3 and ENTER to specify the coordinates of point P3 and press key E, then a dialogue box will
pop up(refer to fig3.90)please check setting result on the dialogue box, points P1,P2,P3 have been set
already.
Fig 3.90
Now input R and ENTER, system will automatically set zero point of X, Y axis of current coordinates at
the centre of circle, the current value of X,Y axis will be set as offset value based on zero point of work
coordinate system.
NOTE
1. To cancel the operation of midpoint identification during setting process, please input 0 and ENTER .
2. This operation actually is to set the zero points of X,Y axis' of work coordinate system, thereby can't
operated under machine coordinate system.
3.9.6 Return to the zero point of G17 plane of work coordinate system
For convenient operation, this system supply function of returning to the zero point of current work
coordinates G17 plane (X,Y axis),steps as followed:
Press HOME key under work coordinates in manual mode, then a dialogue box will pop up (refer to
fig3.91)
67
Page 76

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 3.91
X, Y axis will return to zero point of current work coordinate system in turn at G00 speed after pressing
ENTER as show in dialogue box fig 3.91
CAUTION
When executing zero returning by one key, should move Z axis to the safe position where no interference
between spindle and worktable or work piece, otherwise, accident may happen.
3.9.7 Other operation in manual mode:
1)manual spindle status control:
press
press
press
then spindle start by CW rotation and show M03
then spindle start by CCW rotation and show M04
then spindle stop rotation and show M05.Under the status of spindle stopping, press
once , spindle motor powers on ;and press again, spindle motor power off.
press
press
then spindle jog moving by CW rotation and show M03
then spindle jog moving by CCW rotation and show M04
2)manual coolant status control:
key is a repeat key ,shift between off(M09)and on(M08) status
3)Manual clamp control
key is a repeat key ,shift between clamp and unclamp status
4)manual cutter head rotation control
press key to rotate cutter head for selection of tool position in tool seat
5)lubricant switch
key is a repeat key ,shift between off and on status of lubrication.
6) feedrate override control:
feedrate override ratio is controlled by wave band switch or key pressing. Skip one space CW or press"+"
Key, ratio will increase by 10% or skip one space CCW or press"-" Key, ratio will decrease by 10%;the
range is from 5% to 150% and total16 gears. feedrate override ratio value shows in the column of feed
68
Page 77

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
speed as refer to fig3.92
Fig3.92
7) spindle override control:
Spindle override ratio is controlled by wave band switch or key pressing. Skip one space CW or press"+"
Key, ratio will increase by 10% or skip one space CCW or press"-" Key, ratio will decrease by 10%;the
range is from 5% to 150% and total 16 gears. Adjustment value shows in the column of spindle revolution
as refer to fig3.93
Fig3.93
8) press STOP key: stop current manual operation
9)press "F" key and a dialogue box for manual feedrate override will pop up to set running speed
of each axis in manual mode. Refer to fig3.94
Fig 3.94 manual feedrate override
10)press "S" key and a dialogue box for adjusting manual spindle revolution pops up. set spindle
revolution in manual status. Refer to fig3.95:
Fig 3.95 spindle revolution adjustment
11)Press "BASE" key to set tool setting base of tool length compensation. Usually set the first
tool as tool setting. Refer to fig3.96:
Fig3.96 tool base setting for tool length compensation
12)press "TOOL" key, system can automatically calculate tool length compensation value and
save it . Set difference value between length direction and compensation base of each tool. Insert
compensation value into H1-H4 by press "↑", "↓" Keys .refer to fig 3.97
Fig 3.97
69
Page 78
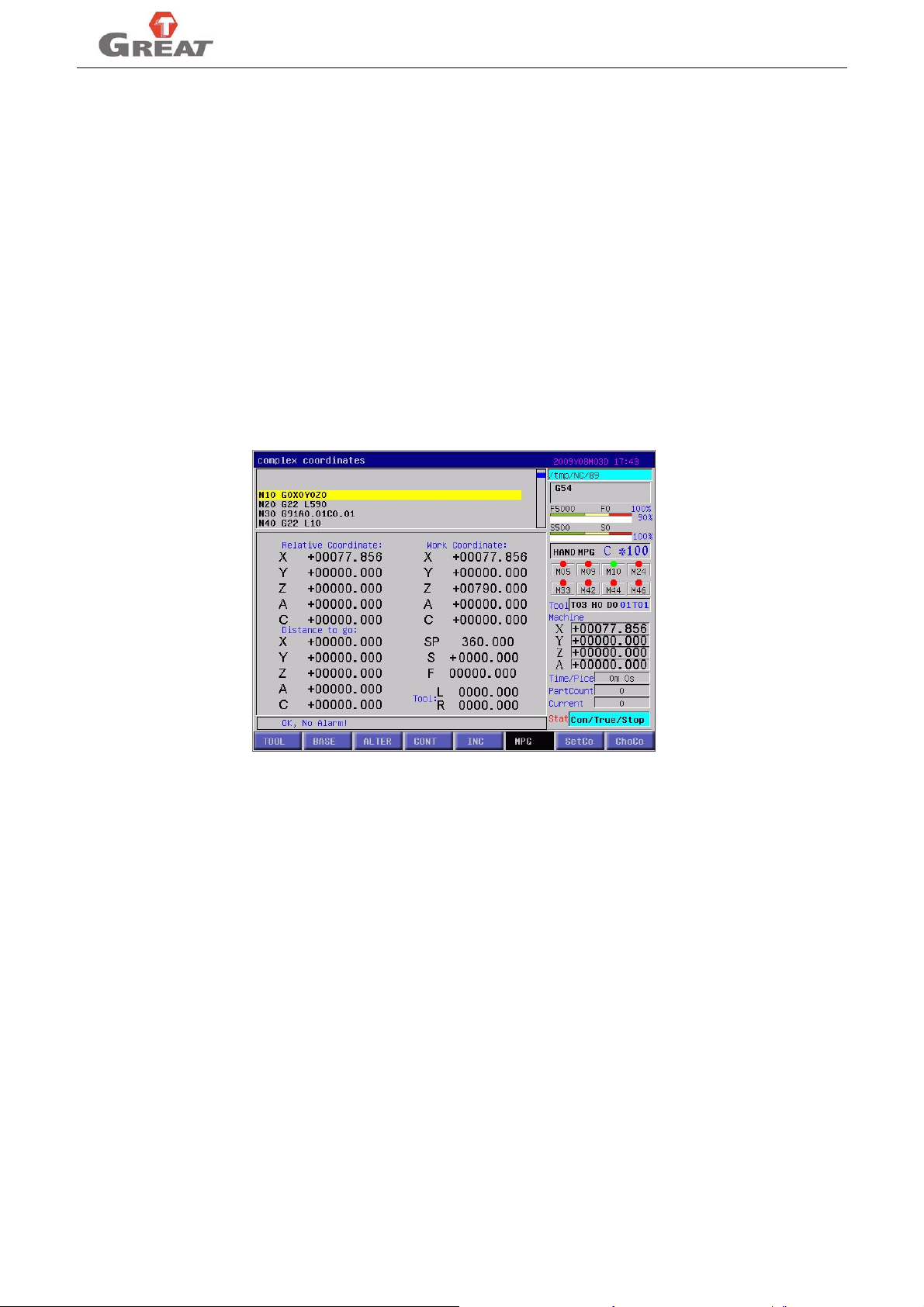
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
3.10 Auto
Press “Auto” on the panel will shift to auto mode. System will compile the current program under auto
mode, will remind error information, if there is error in the program.
Press "RUN" Key: program run
Press "STOP" Key: under status of continual program running, press once to pause and press STOP key
under pause status to stop immediately, continue to run by pressing RUN button. Under step program
running status, press once to stop.
3.10.1 Coordinates
Coordinates running status is to confirm machining path are tracked and showed by coordinate method,
which shows the current position of tool. There are two types of coordinate status: work coordinates and
comprehensive coordinates, which can be shifted by pressing ALTER key. The comprehensive
coordinates, please refer to fig3.98
Fig 3.98 comprehensive coordinates interface
Relative coordinates, work coordinates and rest coordinates are all shown in the comprehensive
interface. besides, value of SP,S,F,L,R are also shown in the interface,
SP: spindle angle
S: real spindle revolution;
F: instruction speed of axes;
L : the current tool length compensation ;
R: the current tool radius compensation.
3.10.2 Graphic
Graphic running status is to confirm the machining path is tracked and shown by graphic. For different
machining program and different starting point of machining, System will automatically calculate out
display effect to fully extent. Operator can parallel move and whirl the drawing by cursor and zoom in and
zoom out by pressing PgUp and PgDn or return to original status by pressing HOME button. Users can
also select showing method on XOY plane, YOZ plane, ZOX plane or 3D graphics by pressing "X, Y, Z,
ALT "keys in turn. The whole path process of tool can be previewed before machining.
Shift between coordinates and graphic can be easily done in the status of program RUN/PAUSE / STOP
70
Page 79

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
by pressing shift key .
3.10.3 Continual
Continual running status means the program will continually execute each block continuously after
pressing RUN button.
3.10.4 STEP
STEP mode means system will run current block and pause to waiting for operation.
Shift between step mode and continual mode can be easily done in the status of program RUN/PAUSE /
STOP by pressing shift key
. or by pressing “STEP” and “CONT”
3.10.5 Simulation
In Auto interface, press “SIMUL” to shift to simulation status, will show the tool center running path
through track graphic or coordinates method. All machinery operation including machine feed or other
assistant function etc will not be executed in simulation mode.
Press Run button, real-time display of real shape of current workpiece automatically and can revolve
randomly, zoom in and zoom out or shift between track graphic and coordinates method
3.10.6 Feeding hold
Under auto continual operation pause status or step operation stop status, Press MANUAL soft key can
shift to manual mode and do operation such as hand continual, MPG, hand increment etc; cancel
MANUAL mode and press RUN button, system will return to holding point at default speed of
G01/G02/G03 which set in SPEED parameter menu and then continue to run. The sequence of returning
of axes is: if Z-axis moves towards positive, will return Z axis at first; if Z axis moves towards negative,
will return Z axis at last; other axes will return in sequence of X->Y->A
3.10.7 MPG wheel trigger in Auto running
Auto running of program in this system can be generated by means of MPG, which mainly used for first
trial machining. The principle is: in the mode of MPG auto run, to judge the program is executed as it
running by viewing whether the MPG wheel rotates, program is executed only the wheel rotates.
Operation method: press DEL key in auto mode, then a dialogue box will pop up to ask whether to
perform MPG auto running mode:
Fig 3.99
Press ENTER key under dialogue box (refer to fig3.99) shift to MPG auto running mode and press RUN
key, running indicator turn on. System waiting for program running, rotate MPG wheel, program will be
71
Page 80

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
executed, if stop MPG wheel, program will pause and wait for MPG wheel rotated again.
To exit MPG auto running mode, press DEL key and ENTER in the dialogue box of fig3.100
Fig 3.100
NOTE
MPG wheel just do trigger function under MPG auto running mode and running speed of axis still
decided by program itself.
3.10.8 DNC function
There is 32MB user storage in this system. Always need DNC machining function encountering large
program or poor rest storage .DNC function can be realized through RS232 and USB port.
RS232-DNC explanation
1, safely connect PC and system with professional communication cable and correctly set corresponding
communication port and speed rate in the system.
2, run system professional communication software on PC and correctly set corresponding
communication port and speed rate. Click "TRANSFER CNC PROGRAM FILE" And select machining
program file and waiting for program transmitting.
3. Press key D to shift to simultaneous machining status under program file content interface and
"RS232--DNC" Show on top right of screen, refer to fig3.101.
Fig 3.101
NOTE
Stop simultaneous function by pressing STOP button.
Guide to cancel simultaneous machining mode: shift to file path and select system program file need to
be executed and press F7 key to cancel simultaneous machining mode
NOTE
1. File transmitting through serial port related to baud rate and environment. For safe sake, we
recommend to use a medium rate less than 38400
2. Communication cable length should be less than 10 meters and communication shield board is
requested.
3. To run system professional communication software on PC to transmit and make sure the transmit
rate setting for PC and system must be same.
4. System professional software goes with CNC package and save it into PC hardware to run without
installation.
USB-DNC explanation
USB-DNC is completed through USB disk. Please open USBdisk under PRGM interface and select
required program, then press EXEC soft key to return to auto mode and press RUN to execute program.
72
Page 81

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
CAUTION
Never pull out USB disk during USB-DNC process, otherwise will lead to machining failure. Please return
to program interface after finished USB-DNC transmission
3.11 MDI mode
A MDI dialogue will pops up when press MDI soft key. Please refer to fig3.102
Fig 3.102
Insert code according to guide and press RUN key, then System will execute the block at once. to pause
it by pressing PAUSE and exit MDI function by pressing ESC key.
NOTE
If there is no code of G53, G54, G55, G56, G57, G58, G59, when using MDI function, which means the
MDI program is executed at work coordinates (G53, G54-G59)
For example
Current coordinates is G55
Insert X50Z67F400 in MDI dialogue box and press RUN keys, then system will move to coordinates
point X50Z67 in the work coordinates G55 at the speed of F400.
3.12 Run program from a real line
This system possesses the function to execute program from a real line. press "-" Key under main
interface, then a dialogue box pops up and insert the line number to execute the program and ENTER to
confirm, press RUN soft key will run from the inserted real line number.
CAUTION
The line number is the real line number of the program rather than the line number N address. System
will run to the home of the appointed line at the default speed of G01/G02/G03, then execute program as
normal.
3.13 Run program from a certain marked line
Press the "M" key under main interface, a dialog box will be popped out, after input marked line number
and ENTER, then press the “RUN” key, CNC will execute program from the input marked line.
CAUTION
The line No. is appointed by N address of program, may be not the real line No. CNC will move to the
home of the marked line at the default speed of G01/G02/G03 at first, then execute the program as
73
Page 82

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
normal.
3.14 Run program from a certain tool number
Pressing the "G" key under main interface, a dialog box will be popped out, after input mark tool number
and ENTER, then press the “run” key, CNC will execute program from the input tool number.
NOTE
The CNC will move to the home of appointed line at the default speed of G01/G02/G03 at first, then
execute the program as normal.
3.15 Set coordinates/choose coordinates
Choose coordinates
After pressing the “Choco” soft key in the interface of MANUL or AUTO mode, then input 53, 54, 55, 56,
57, 58, 59 will choose G53, G54, G55,G56,G57,G58,G59 work coordinate individually. Corresponding
work coordinate status is displaying in the top right interface. refer to fig below
Fig103 coordinate system choice
Fig3.104
Set coordinates
To set value of any work coordinates or relative coordinates. Work coordinates is set under work
coordinate system and relative coordinates is set under comprehensive coordinate system or in the
running process of the program. Press “SetCo” soft key to achieve the operation under corresponding
interface. Refer to fig3.105
Fig 3.105
To set G54 work coordinates value under work coordinates display mode. Press "↑","↓" Keys to decide
which axis to set.
74
Fig 3.106
Page 83

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
To set relative coordinates value under comprehensive coordinates display mode. Press "↑","↓" Keys to
decide which axis to set.
NOTE: Machine coordinates (G53) can not be set
3.16 Mass Program for mould processing
Because this CNC have 32MB flash storage for saving user NC program, so it is no limit for the length of
program. The program which longer than 3000 lines can be used except for the recycle instructions such
as G22, system will preview and pre-treat 1000 lines of program to ensure continuous machining
process.
For the mass program more than 3000 lines, it would be better to execute “Compile” operation by press
“C” under “PRGM” interface.
CAUTION
At most 3000 lines can be displayed on the program file editor in the system. If the program file is more
than 3000 lines, the file can't be compiled and saved in program editing mode and may lead to program
lost
3.17 Tool exchange and tool setting
Tool exchange and tool setting will be required as the machine has tool magazine.
NOTE
Correctly set parameter to confirm tool magazine type and parameters relative to match with machine
before using the tool magazine, such as spindle orientation position, tool exchange point position etc.
3.17.1 Tool magazine operation
Define softkey K regarding to machine match with tool magazine:
K3: set toolseat number of current toolseat
K4: spindle orientation (indicator of K4 turns on as spindle orientation completed)
K5: Z axis return to tool exchange point(indicator of K5 turns on as after returning to tool exchange point)
K8: spindle and feed axis power off (indicator of K8 turns off after spindle and feed axes power off)
Definition of M commands as recording to turn-plate type tool magazine:
Self-defined M codes:
M41 toolseat down
M43 toolseat up
M36 step execution to exchange tools(means: step execute individually the toolseat down, manipulator
seize tool, exchange tools, manipulator return to original point, toolseat up. )
M57 manipulator unconditional rotate one step
WAR NING
1. Conditions not detected as using M57. Be special careful as using it, otherwise accident may happen.
Definition of M codes regarding to umbrella type tool magazine:
M41 tool magazine forward
M43 tool magazine backward
2. Check Z axis position carefully to avoid accident as using M41 to do tool magazine forward operation.
75
Page 84
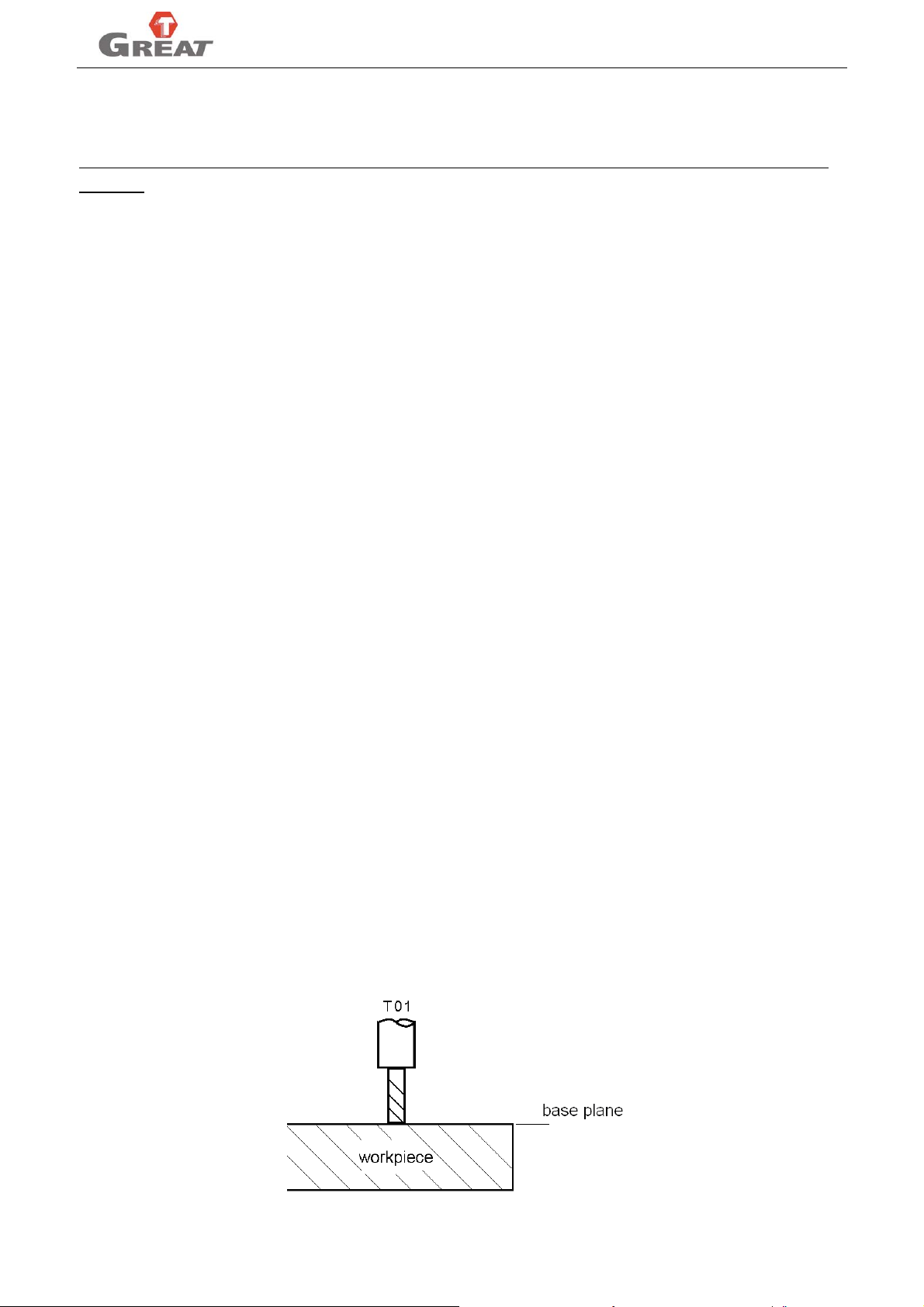
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
3.17.2 Tool exchange
WAR NING
Make sure return to machine base point before executing tool exchange operation, otherwise may arise
accident.
Tool exchange operation regarding to turnplate type tool magazine
M06: change the tool from the current toolseat to the spindle.
M06 Txx: change the tool from the current toolseat to the spindle and rotate the Txx in instruction to the
current tool exchange position to prepare for the tool exchange followed.(exchange tool first and then
select tool)
M16 Txx: rotate the Txx in instruction to the exchange point and change the tool from the current
toolseat to the spindle.(select tool first and then exchange. That's to say exchange the tool Txx in the
instruction to the spindle)
Tool exchange operation for umbrella tool magazine
Txx: change the tool Txx in commands to the spindle (firstly return the tool from spindle to corresponding
toolseat and then change tool Txx to the spindle; if the current tool is T00, then directly exchange it to the
spindle).
3.17.3 Tool setting
As using several tools in one program, execute tool setting is required. Tool setting means to enable the
system automatically establish the length difference between tools(size of z axis)so that to do
compensation as doing auto tool exchange operation.
Explanation to tool setting
In main interface and manual mode, press "BASE" to set base point of tool setting, system will take the
current machine coordinates of Z axis as tool setting base point; after exchange tools, press "TOOL" Soft
key to automatically memories result of tool setting. System will automatically take the difference
between machine coordinates of Z axis and toolsetting base point as its length compensation value and
save in the length compensation parameter list. If toolsetting difference discovered length compensation
parameter will be modified directly.
Example
There are T01, T02, T03 three tools need to be set.
Step1, change tool T01 to the spindle and run spindle. Move Z axis in manual mode to let the tool close
to workpiece surface(suppose the current coordinates value is -150)refer to fig3.107, now, press
"BASE" Soft key to set workpiece surface as tool setting base point(that's to say take coordinates value
-150 as tool setting base point), meanwhile, system will automatically set the length compensation
parameter H1 of tool T1 as "0".
76
Fig 3.107
Page 85

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Step 2, Stop spindle, exchange tool T02, run spindle. In the manual mode to move Z axis to approach
the work piece surface (suppose current coordinates value is -135) like as fig 3.108, press "TOOL" Soft
key and operate according to the guide and realize automatically remember of toolsetting. System will
automatically set the length compensation parameter of tool(T2) Hx as "15"(-135 - -150).
NOTE
Hx means either of H1-H4 and select by pressing "TOOL" Soft key, usually select H1
Fig 3.108
Step3, Stop spindle, change tool T03, run spindle. Move Z-axis in manual mode to make the tool close to
workpiece surface(suppose the current coordinates value is -165)fig3.109, press "TOOL" Soft key and
operate according to the guide and realize automatically remember of tool setting. System will
automatically set the length compensation parameter Hx of tool T03 as "-15"(-165 - -150).
NOTE: Hx means either of H1-H4 and select by pressing "TOOL" Soft key, usually select H1
Fig 3.109
Step 4, tool setting finished
NOTE
System automatically remember length compensation after finishing tool setting, to realize compensation
in the processing, will need some length compensation instructions.
3.18 Exit system
Press " " key -> press "Enter" -> exit CNC system.
CAUTION :If do not accord above method, the current coordinates may lose and accident may occur as
starting system next time.
WAR NING :Do reference returning operation once starting the system every time to ensure of machine
processing precision. Also need to do reference returning encountering unexpected power off or
abnormal system turning-off, otherwise, accident may occur.
77
Page 86
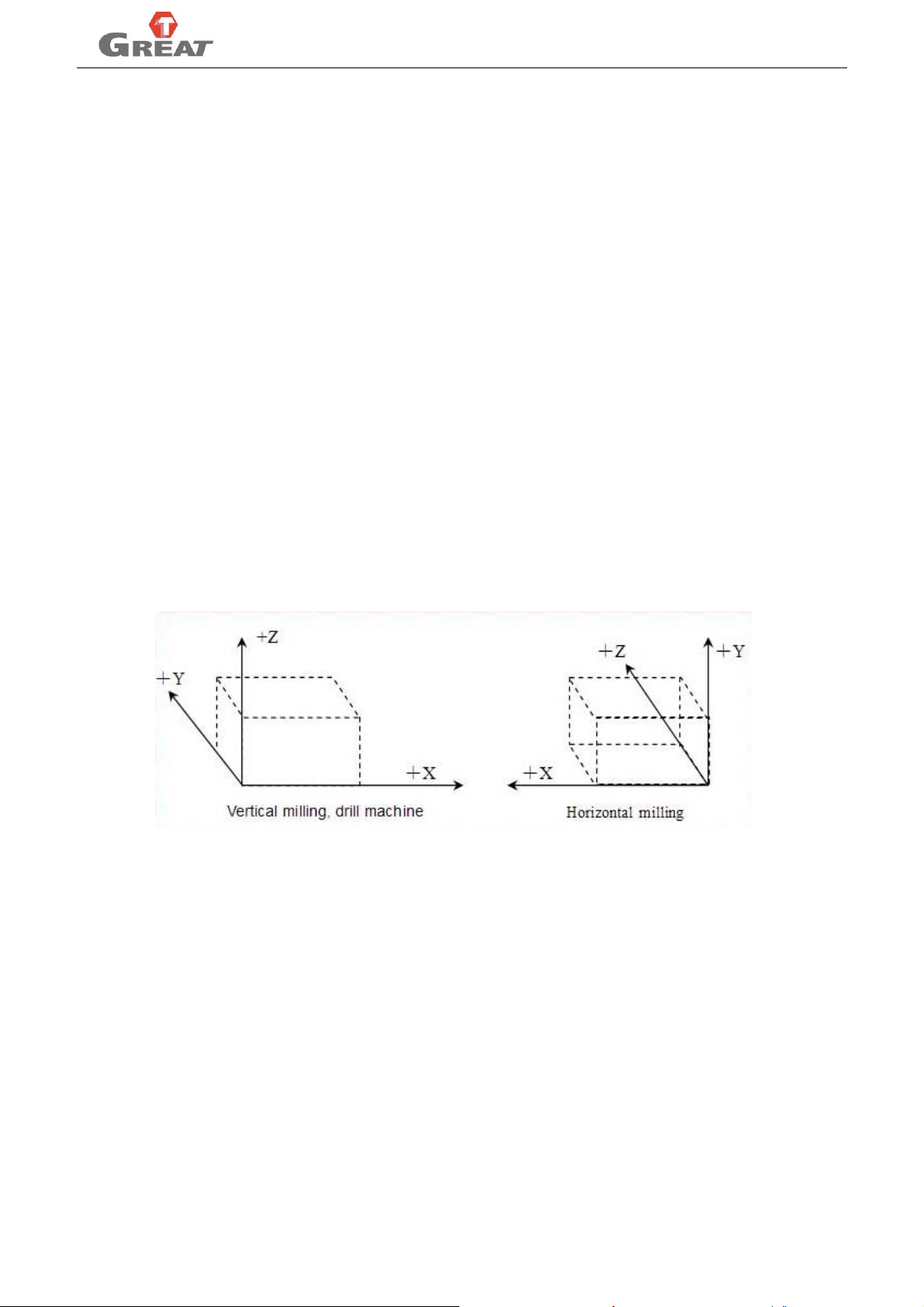
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
CHAPTER IV PROGRAMING
Programming is used to describe machining track and assistant motion with CNC language according to
the blueprint of workpiece and requirement of machining process
4.1 Basic Concepts
Program block (program line):
It is an integrated commands line consisted of instruction block and data block.
Program:
It is a congregation of program block by machining logic structure in order to complete the machining to
workpiece.
Machine Coordinate System:
It is established that machine zero point as the original point. Milling machine coordinate axis and its
direction should comply with "ISO841" standards. The methods as following: make Cartesian
coordinates determined with right hand rules as the standard programming coordinate system, Z axis is
parallel with spindle, X-axis is horizontal, Y-axis is determined by right hand rule. A-axis is rotary axis or
assistant axis parallel with X-axis, B-axis is rotary axis or assistant axis parallel with Y-axis, C-axis is
rotary axis or assistant axis parallel with X-axis, the positive direction of each axis is the direction that
increasing the dimension of workpiece.
When work coordinate isn’t set, make machine coordinate system as work coordinate system.
Fig4.1 machine coordinate axes& direction
Work Coordinate System:
The coordinate system is used for workpiece machining is called work coordinate system, it is preset in
CNC system. The value of work coordinate system can be changed through moving its original point.
Through one of the three methods to set the work coordinate system:
1 Use G92
Use G92 to assign a value to set the work coordinate system in the program running
2 Automatic setup
When reference returning in manual mode, the machine coordinate system set as work coordinate
system automatically.
3 Use G54 to G59
Through the coordinate system in parameter can set 6 work coordinate systems.
When use absolute value instruction, must use above method to establish the work coordinate system
Local coordinate system:
In work coordinate system for easy to programming it may establish the sub- coordinate system, this
sub-coordinate system is called local coordinate system
78
Page 87

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Absolute Programming:
The confirmed coordinate data programming method based on established absolute coordinate system.
It is set with “G90”.
Relative Programming (increment programming):
The distance and direction of moving end point relative to start point. It is set with “G90”.
Mode Instruction:
The instruction remains the function in the program. It works both in the current program and following.
Until replaced by another mode instruction in identical group.
In the same operation, there may be several mode instructions, such as M03 (spindle CW), M04 (spindle
CCW), M05 (spindle stop). They are all mode used to control spindle. The modes of same kinds are
categorized into one mode group. At any time it must be one of them, and must be only one of them. The
original chosen mode instruction is called mode origin. In the above mode group, M05 is such a mode
origin.
Suspending mode (destroying mode):
The instruction which can turn mode instruction into mode origin or destroy the mode, such as M20
(program ending instruction), means the end of operation and return to original status.
Non-Mode instruction:
The instruction cannot remain function, and only works in the current program block.
4.2 General description of program
%04, N04, G02, T02, H02, D02, M02, S04, F04, X-043, Y-043, Z-043, A-043, I-043, J-043, K-043, L04,
P4, R043
Note 1: “-”means this data can be with “-”(“+” is omitted).
Note 2: if “0” in front of data, means this data can be written with only valid digits
Note 3: The digital denotes bits, when it is two, the top digit denotes the maximum figures of integer, and
the low digit denotes the maximum figures after decimal point.
4.3 Program instruction
4.3.1 Function and meaning of address symbol, data range list
Function
File No.
Program block No. N Sequence No. of program block 0000-9999
Preparation function G
Auxiliary function M Auxiliary operation instruction 00-99
Tool selection T Tool No. 01-99
Tool compensation H D
Spindle function S SP
Cutting speed F Specify cutting speed per minute 1-3000mm/min
Address
symbol
%
meaning Data range
File name of workpiece 0-9, A-Z
Specify content and methods of
instructions
No. of the radius compensation
and length compensation
Spindle revolution, spindle
positioning
00-99
1- 4
00-99999
Coordinates character X Y Z A The coordinates value of X, Y, Z 9999.999mm
79
Page 88

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
(B/C/U/ V/W) and 4th axes
center coordinates I J K
increment value of X ,Y and Z
axes center coordinates
9999.999mm
Step length R arc radius 0.001-999.999mm
Delay time P specified delay time 0.001-99.999s
Program entrance P Entrance of calling program name 0000-9999
Repeat times L
Times of cycle or calling times of
subprogram
1-9999
4.3.2 G, M Function instruction data list
Table 1 G Instruction-code and function
G-code groups function
G00 Rapid positioning
G01 Linear interpolation
Circular/helical interpolation CW: the helical interpolation instruction of
G02
01
G03 Circular/helical interpolation CCW
G33
G04 00 Dwell
G15 cancel polar coordinates instruction
17
G16
G17 select Xp-Yp plane
G18 select Zp-Xp plane
02
G19
G20
06
G21
G28/G281/
G282/G283
G30/G301/
G302/G303
G26 ZXY axes return to program original point
00
helical motion can assign 2 other arc interpolation axes simultaneous
moving, which methods is just to add a moving axis that isn’t arc
interpolation.
Threading
Polar coordinates instruction: polar coordinate (radius and angle), the
positive direction of angle is the CCW direction of positive direction of the
first axis in the selected plane, and the negative direction is CW.
Format :
G** G## G16;
G00 IP;
G** : plane selection
G## : G90 (original point of work coordinate system)or G91(Current
position) Assigns original point of polar coordinate.
Xp: X axis or its parallel axis
Yp:Y axis or its parallel axis
select Yp-Z p plane
Zp:Z axis or its parallel axis
Inch input(English system)
Millimeter input(metric system)
return to the first reference point
nd
return to 2
,3rd ,4th reference point
G261 X axis return to program original point
G262 Y axis return to program original point
G263
Z axis return to program original point
G40 07 Cancel tool radius compensation
80
Page 89

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
G41 tool radius compensation, left
G42 tool radius compensation, right
G43 Tool length positive compensation
G44
08
Tool length negative compensation
G45 tool offset value increase
G46 tool offset value decrease
00
G47 Increase by twice of the tool offset value
G48
decrease by twice of the tool offset value
G49 08 Cancel tool length compensation
G37 Cancel scaling
G36
G12 Cancel programmable mirror
G11
11
Enable scaling: format:G36 X_Y_Z_R_
22
Enable programmable mirror: realize symmetric machining.
G52 00 Local coordinate system
G53 Machine coordinate system
G54 work coordinate system 1
G55 work coordinate system 2
G56 work coordinate system 3
14
Note: These six work coordinates are
saved in the CNC, user can select any
one of them.
G57 work coordinate system 4
G58 work coordinate system 5
G59
G60 accurate positioning
15
G64
work coordinate system 6
Continual path working
Coordinate rotation valid. format:
G68
16
G17
G18 G68 a-b- R-; R: Angle displacement
G19
G69
Cancel coordinate rotation
Deep hole drilling cycle: intermittent feed, rapid retract.
format:
G73 X-Y-Z-R-Q-F- L -
G73
09
Z: distance from R to hole bottom
R: distance from original plane to R
Q: cutting depth at one time
F: feed speed
L: repeated times
CCW pecking deep hole tapping cycle: cutting feed, stop tool at the
G74
bottom of hole, CW. format:G74X-Y-Z-R-P-F- L
P: pause time
Finished boring cycle: cutting feed, spindle oriented stops at the bottom
G76
of the hole, rapid retraction. format:G76 X-Y-Z-R-Q-P-F- L -
Q: offset value at the bottom of hole, mode value saved in canned cycle.
G80 Canned cycle cancel/external operated function canceling.
Drilling cycle: cutting feed, boring cycle or external operation function,
G81
rapid retraction
Format: G81 X-Y-Z-R-F- L -
81
Page 90

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Chip removal drilling cycle or counter boring cycle: cutting feed, stop tool
G82
at the bottom of hole, rapid retraction.
Format:G82 X-Y-Z-R-P-F- L -
G83
Chip removal drilling cycle: intermittent feed, rapid retraction.
Format:G83 X-Y-Z-R-Q-F- L -P-
CW peck deep hole tapping cycle: cutting feed, stop tool at the bottom of
G84
hole--reverse, retraction.
Format:G84 X-Y-Z-R-P-F- L -
Note: select standard or rigid tapping through parameter setting
G85
Boring cycle: cutting feed, retraction.
Format: G85 X-Y-Z-R-F- L -
Boring cycle: cutting feed, spindle stops at the bottom of hole, rapid
G86
retraction
Format :G86 X-Y-Z-R-F- L -
boring cycle, counter boring cycle: cutting feed, spindle CW at the bottom
G87
of hole, rapid retraction:
Format:G87 X-Y-Z-R-Q-P-F- L -
boring cycle:
G89
stop tool at the bottom of hole, retraction:
Format:G89 X-Y-Z-R-P-F-L-
G90 Absolute program
G91
03
Increment program
G92 00 Set work coordinates or suppress the max speed of spindle
G94 Feed per minute
G95
05
Feed per revolution
G98 Canned cycle return to original point: apply to final drilling
10
G99
G22 Program cycle command
19
G800
Canned cycle return to R point: apply to hole drilling at the first time
Cancel Program cycle command
G65 Non-mode calling for macro program
G66 Mode calling for macro program
12
G67 Cancel Mode calling for macro program
G180—G189
User self defined macro program
Table 2 M-code and function
M02 Program end, stop auto run (default is M02)
M30 Program end, turn off spindle and cool
M00 Program pause, press “run” to continue run
M20
Program end, repeated executes program according to running times set in
parameter, applied to test CNC
M98 sub-program calling
M99 sub-program end
M97 Program skip
M03 Spindle CW
M04 Spindle CCW
82
Page 91

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
M05 Spindle stop
M06/M16 Exchange tool
M08 Turn on cool
M09 Turn off cool
M10 Tighten tool
M11 Loosen tool
M24 Turn off blowing
M25 Turn on blowing
M32 Turn on lubrication
M33 Turn off lubrication
M41 User self-defined turn on
M42 User self-defined turn off
M43 User self-defined turn on
M44 User self-defined turn off
M45 User self-defined turn on
M46 User self-defined turn off
M47 User self-defined turn on
M48 User self-defined turn off
M49 User self-defined turn on
M50 User self-defined turn off
M51 User self-defined turn on
M52 User self-defined turn off
M53 User self-defined turn on
M54 User self-defined turn off
M55 User self-defined turn on
M56 User self-defined turn off
M57 User self-defined turn on
M58 User self-defined turn off
M61 Spindle top gear shift (the first)
M62 Spindle low gear shift(the second)
M63 Spindle 3rd gear shifting
M64 Spindle 4th gear shifting
M317 Clear X-axis of machine coordinates
M318 Clear Y-axis of machine coordinates
M319 Clear Z-axis of machine coordinates
M320 Clear all axes of machine coordinates including X,Y(C),Z,A,B
4.3.3 F function:
In this CNC system, feed speed use F word. It is mode. The actual feed speed equals the setting speed
multiply speed override.
Feed speed of linear interpolation G01, circular interpolation G02, G03 is determined by the data
followed F code. In the cutting process, program block run continuously, the feed speed is the minimum
feed speed.
Apply 2 methods to specify the feed speed.
1. Feed per minute G94
83
Page 92

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Specify the feed value per minute (mm/min)
2. Feed per revolution G95
Specify the feed value per revolution of spindle (mm/rev)
Directly specify the value of F to define spindle feed value per revolution after specifying feed value per
minute of command G94, G94 is a mode code, it is valid before specified with G95. The default setting is
feed per minute as power on.
Set feed ratio by rotate switches on machine operation panel and override from 5% to 150% count by
10%. Please note override function can't be applied in thread cutting commands.
Fig4.2 feed per minute
Specify the value of F to define spindle feed value per revolution after specifying feed value per
revolution of command G95, G95 is a mode code, it is valid till another feed rate specified to command
G94. Set feed ratio by rotate switches on machine operation panel and override from 5% to 150% count
by 10%. Please note override function can't be applied in thread cutting commands. Feed speed may
fluctuate at low speed level of spindle .The lower of the spindle speed, the more often of the fluctuation of
the feed speed.
Feed per revolution determined by actual spindle speed if the parameter No. 101 in “AXIS” is set to check
spindle path, and set the encoder lines in No.100. Otherwise, feed per revolution determined by spindle
instruction.
Fig4.3 feed per revolution
4.3.4 T/H/D function
The T/H/D function is that of calling tool length and radius compensation, which are mode, called with
number in program.
T01 to T99 are tool number, there are four tool edges for each tool, H1 to H4 are parameter number of
tool length compensation, D1 to D3 are parameter numbers of tool radius compensation.
4.3.5 S function
S function is used to control spindle speed, this function is valid to all the machines which spindle speed
is controlled by transducer. In program, execute stepless speed control with S word. CNC provides
analog voltage between 0~+10V, and S function is mode order. Spindle speed can be maximum
specified 5 digits followed address S(r/min)
84
Page 93

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
4.4 Preparation functions
4.4.1 Coordinate system setting (G92)
It is used to set work coordinate system
Format:G92 X- Y- Z- (it is mode after setting)
Explanation:
G92 command doesn’t generate motion, just apply to set work coordinate system. X, Y, Z means the
coordinates position of the setting coordinate system that the point on the tool located in (e.g.: tool nose ).
If use G92 set coordinate system during tool length offset, the tool radius compensation in the system
which set by non-offset coordinates will be deleted by G92 temporarily
e.g.:
Fig4.4
Example 3 N0000 G92 X65.2 Y100 Z28
Means to establish work coordinate system and current workpiece coordinates position is X=65.2,Y=
100,Z=28
4.4.2 Choose coordinate system (G53/G54/G55/G56/G57/G58/G59)
These instructions are used for selecting work or machine coordinate system.
Format:G53(G54/G55/G56/G57/G58/G59) (Mode)
G53 machine coordinate system
G54 work coordinate system 1
G55 work coordinate system 2
G56 work coordinate system 3
G57 work coordinate system 4
G58 work coordinate system 5
G59 work coordinate system 6
G53 machine coordinate system is determined by machine first reference point (machine zero point).
The default coordinate system is G53.
The offset of work coordinate system G54/G55/G56/G57/G58/G59 in the machine coordinate system set
in parameter.
Example 1:
G01 X34
85
Page 94

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
G54 X78
The first line means move to the point of X34 in G53 machine coordinate system through G01 instruction,
the second line means move to the point of X78 in G54 work coordinate system through G01 instruction.
Example 2:
G01 G56 Y64
G57
G00 Z178
The first line means move to the point of Y64 in G56 work coordinate system through G01 instruction, the
second line means enter G57 work coordinate system, the third line means move to the point of Z178 in
G57 work coordinate system through G00 instruction. E.g.:
Fig4.5
4.4.3 Local coordinate system (G52)
Edit program in work coordinate system, in order to program easily, will set sub-coordinate system of
work coordinate system as local coordinate system.
Use G52 to set local coordinate system in the machine coordinate system(G53) or work coordinate
system(G54~G59). The original point of the local coordinate system set at the position of X- Y- Z-
specified in the machine coordinate system or work coordinate system.
After local coordinate system setting, the followed moving specified by G90 is coordinates in the local
coordinate system. Specify new zero point with G52. can modify the position of local coordinate system.
To cancel local coordinate system and specify coordinates value in the work coordinate system, the zero
point of local coordinate system should be consistent with that of work coordinate system.
The local coordinate system setting does not change work and machine coordinate system. Specify work
coordinate system with G92, if not specify all axes coordinates, the local coordinate system of axis
which coordinates not specified won’t cancel but holding. Specify movement with absolute mode after
G52 program block.
e.g.:
Format: G52 X- Y- Z- ; set.(Mode)
G52 X0 (Y0 Z0); cancel.
86
Page 95

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Fig 4.6
4.4.4 Programming methods (G90/G91)
There are two methods to move tool in program: absolute instruction and increment instruction. In
absolute instruction, the number is coordinate value; but in increment instruction, the number is motion
distance.G90 and G91 are used for point out absolute or increment program.
Format: G90 (Mode, original) ; absolute program.
G91 (Mode) ; increment program.
Example:
Fig 4.7
As above example, the first line G90 means absolute programming, X-axis move to where the absolute
coordinate is 40mm, Y-axis move to where the absolute coordinate is 70mm.
The second line G91 denotes relative programming, means move the distance of 60mm from current
position toward negative of X-axis, 40mm toward positive of Y-axis
4.4.5 Select Plane (G17/G18/G19)
Format: G17 (Mode, Original) ;Set XY Plane
G18 (Mode) ;Set ZX Plane
G19 (Mode) ;Set YZ Plane
87
Page 96
GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Applied to specify arc interpolation plane
Explanation
This instruction doesn’t produce motion
4.4.6 Rapid positioning (G00)
Tool moves to instruction position with rapid speed in parameter in absolute/increment coordinate system.
As absolute method, use section end point coordinate to program;
As increment method, use motion distance to program.
Format:G00 X- Y- Z- A- (Mode, original)
Explanation
X, Y, Z, A means motion axis. The data point out motion distance and direction by absolute or increment
method.
G00 moves to aim point with straight line path.
Moving speed is determined by parameter.
4.4.7 Linear interpolation (G01)
Used for single axis motion or 2, 3, 4 axis interpolation motion.
Format:G01 X- Y- Z- A- F- (Mode)
Explanation:
X, Y, Z, A means motion axes. The data point out feed and direction by absolute or increment method.
Interpolation speed is determined by F word. The F instruction is mode.
The tool will move to the specified position at speed of specified F speed along straight line and the F
speed is valid till be replaced by a new specified F speed, so no need to define F speed in each block.
The feed speed unit of rotary axis is deg/min. Speed of rotary axis: calculate the time required, then convert
the axis feed speed unit into deg/min
4.4.8 Circular/arc interpolation (G02/G03)
In the program plane, these instructions execute G02 CW and G03 CCW arc interpolation.
Format:
G17
⎧
⎨
⎩
G02
G03
⎫
X_Y_
⎬
⎭
⎧
⎨
⎩
I_J_
R_
⎫
Z_F_
⎬
⎭
; XY plane(Mode)
G02
⎫
⎧
G18
⎨
⎩
⎧
G19
⎨
⎩
Explanation:
Arc interpolation must point out interpolation plane, the X, Y, Z word point out the arc end coordinate
value, I, J, K separately is X, Y, Z increment value from original point to center point. In another words,
88
G03
G02
G03
X_Z_
⎬
⎭
⎫
Y_Z_
⎬
⎭
I_K_
⎧
⎨
⎩
J_K_
⎧
⎨
⎩
R_
R_
⎫
Y_F_
⎬
⎭
⎫
X_F_
⎬
⎭
; ZX plane(Mode)
; YZ plane(Mode)
Page 97

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Make the original point as zero point, As center point locate to positive direction of original point the value
will be positive, As center point locate to negative direction of original point the value will be negative. I J
K are used to describe the center point coordinate. Also no need use I,J,K but use R to program, the R is
negative when the angle larger than 180 degree, R isn’t available for whole circular programming.
The direction of arc is set towards negative direction vertical the arc interpolation plane.
The arc track as following:
Fig4.8
The center of arc specified with address I J K, the number after I J K is the vector component looked
along start point to the center of arc, depends on the direction to specify the symbol of I J K is positive or
negative. I J K can be omitted, the end point is identical with the start point as it is omitted, it is whole
circular that the center of arc is specified with I J K
the value is always denoted with increment whether in G90 or G91 as following:
Fig4.9
The arc interpolation speed is determined by F word.
NOTE
I, J, K and R are the non- modality instruction.
e.g.:
1) Absolute programming;
N0000 G92 X200 Y40 Z0; set the absolute coordinates position of start point
N0010 G90 G03 X160 Y40 I-20 J0; CCW arc
N0020 G02 X120 Y40 R20; CW arc
N0030 G02 X120 Y40 R20; whole circular
N0040 G26 M02; return to the start point, ends.
2) Increment programming
N0000 G91 G17 G03 X-40 Y0 R20 F300; CCW arc
N0010 G02 X-40 Y0 R20; CW arc
N0020 G02 X0 Y0 R20; whole circular
N0030 G26 M02; return to the start point, ends
Two methods have the same result.
89
Page 98

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
4.4.9 Helical interpolation (G02/G03)
The helical interpolation instruction of helical motion can assign another axis which synchronous motion
with arc interpolation axes, which method is just to add a moving axis that isn’t arc interpolation. F
instruction defines feed speed along arc. Therefore, the feed speed of linear axis is as following:
Format :
G02
⎫
G18
G19
⎧
⎨
G03
⎩
G02
⎧
⎨
G03
⎩
G02
⎧
⎨
⎩
G03
X_Y_
⎬
⎭
⎫
X_Z_
⎬
⎭
⎫
Y_Z_
⎬
⎭
G17
Tool radius compensation only applied to arc, tool offset and tool length compensation instruction isn’t
available for helical interpolation program.
I_J_
⎧
⎨
R_
⎩
I_K_
⎧
⎨
R_
⎩
J_K_
⎧
⎨
⎩
R_
⎫
Z_F_
⎬
⎭
⎫
Y_F_
⎬
⎭
⎫
X_F_
⎬
⎭
; XY plane(mode)
; ZX plane(mode)
; YZ plane(mode)
Fig 4.10
G90G17G54
G01X20Y0Z0F200
G03X0Y20R20Z15F150
……
4.4.10 Dwell (G04)
In machining process because of requirement of machining technique, delay certain period before
executing another motion.
Format:G04 P-
The unit of data after P is second, means delay time.
Example:
G92X0Y0Z0
M03S600
G90G01G43H01Z20F200
Z-10
G04P5
90
Page 99

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
G49G0Z20
M05M30
4.4.11 Mirror instruction (G11/G12)
Be used for machining symmetric workpiece so as to decrease program codes.
format:
G11 X_ Y_ (Z_ X_ ) (Y_ Z_ ) (mode)
; Feed toward the symmetry direction specified with XYZ
G12 (mode, original) ; Cancel Mirror.
Explanation:
Mirror machining by changing the feed direction of axis to realize symmetric point machining at the axis.
The axes which the direction need to be changed is specified with the address symbol of current
interpolation planes G17 (X_ Y_), G18 (Z_ X_), G19 (Y_ Z_). The numeral values after X_ Y_ Z_ are the
coordinates under the current work coordinate system.
In the mode of programmable mirror method, the instructions of reference point returning G27, G28, G29,
G30 and the instruction of changing coordinate system from G52 to G59, G92 and etc not allowed used.
If need any of those G-codes, must be specified after canceling programmable mirror method.
E.g.:
e.g.:
Sub-program
%9000
G00 G90 X60.0 Y60.0;
G01 X100.0 F100;
G01 Y100.0;
G01 X60.0 Y60.0;
M99;
Fig4.11
91
Page 100

GREAT-150IM-II MANUALS
Main program
N10 G00 G90;
N20 M98 P%9000;
N30 G11 X50.0
N40 M98 P%9000;
N50 G11 X50.0 Y50.0
N60 M98 P%9000;
N70 G11 Y50.0
N80 M98 P%9000;
N90 G12;
4.4.12 Scaling (G36/G37)
In the condition of no changing program, scale down or scale up machined workpiece. Programming
configuration is scaled down or scaled up (scaling), specify scale center with X_, Y_ and Z_. if one axis
isn’t specified, which won’t be executed scaling. The value after X_, Y_, Z_ is the coordinates in current
coordinate system.
format: G36 X_Y_Z_R_ (mode) ;execute proportional scale
G37 (mode, original) ;cancel proportional scale
Explanation:
The data after R is scaling coefficient.
As showed in fig4.12, as P1’P2’P3’P4’ is scaled up to P1P2P3P4, R=P0P4’/ P0P4. as P1P2P3P4 is
scaled down to P1’P2’P3’P4’, R= P0P4/ P0P4’. Means as graphic is scaled up, R<1, as graphic is
scaled down, R>1. The default value is 1.
Fig 4.12
Example:
Example of scaling:
92
Fig4.13
 Loading...
Loading...