Page 1
8921ADT
4-CH AUDIO A-D CONVERTER w/DELAY TRACK
Instruction Manual
SOFTWARE VERSION 1.0.0
071820400
OCTOBER 2003
Page 2

Contacting Grass Valley
Region Voice Fax Address Web Site
North America (800) 547-8949
Support: 530-478-4148
Pacific Operations +852-2585-6688
Support: 852-2585-6579
U.K., Europe, Asia, Middle East +44 1753 218 777 +44 1753 218 757
France +33 1 45 29 73 00
Germany +49 221 1791 234 +49 221 1791 235
Copyright © Thomson Broadcast and Media Solutions All rights reserved.
Grass Valley Web Site
Sales: (530) 478-3347
Support: (530) 478-3181
+852-2802-2996
Grass Valley
P.O. Box 599000
Nevada City, CA 959597900 USA
www.thomsongrassvalley.com
The www
Online User Documentation
.thomsongrassvalley.com web site offers the following:
— Current versions of product catalogs, brochures,
data sheets, ordering guides, planning guides, manuals, and release notes
in .pdf format can be downloaded.
FAQ Database
— Solutions to problems and troubleshooting efforts can be
found by searching our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) database.
Software Downloads
— Software updates, drivers, and patches can be down-
loaded.
2 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 3

Contents
Preface
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
8921ADT 4-Channel Audio A-D Converter with Delay
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Module On-board Jumper Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Frame Capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Module Placement in the Gecko 8900-A Audio Frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Analog Audio Inputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Digital AES Audio Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Tracking Input/Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Reference Loop-through Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Power Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Operation Indicator LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuration Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Analog Audio Inputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Audio Channel Pairing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Audio Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Audio Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Auto Tracking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Reference Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Recalling Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Local Onboard Module Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Configuration Switches and Controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
8921ADT Module Onboard Configuration Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Remote Configuration and Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
8921ADT Links and Web Pages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Status Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
I/O Config Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Functional View Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Module Configuration Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
E-MEM Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Slot Config Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Software Update Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Control Panel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Status Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
8921ADT Instruction Manual 3
Page 4

Contents
Frame Alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Web Browser Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
SNMP Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
4 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 5

Preface
About This Manual
This manual describes the features of a specific module of the Gecko 8900
Signal Processing System. As part of this module family, it is subject to
Safety and Regulatory Compliance described in the Gecko 8900 Series
frame and power supply documentation (see the
Frames Instruction Manual
8900TX/8900TF/8900TFN
).
8921ADT Instruction Manual 5
Page 6

Preface
6 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 7

8921ADT 4-Channel Audio A-D Converter with Delay
Introduction
The 8921ADT module offers four independent, audio A-D conversions on
a single module. Four channels of analog audio are converted to two digital
audio streams. Two forms of delay are provided—a fixed delay and a variable delay based on a signal from a video decoder with a frame synchronizer or from a frame sync card.
The 8921ADT features:
• 24-bit ADC A-to-D conversion,
• >105 dB A weighted signal-to-noise ratio,
• The four channels of audio analog to digital conversion has independent controls for:
•Channel pairing,
• Level adjustment,
•Output swapping, summation, phase inversion,
•Delay up to 5 seconds for each channel or channel pair, and
• 400 Hz, 1 k Hz, and 1 kHz channel ID test tones.
•Auto-tracking delay of video frame synchronizers (8900FSS and
8981FS),
• Four inputs, two pairs of balanced High Z analog audio inputs,
• Looping reference input supports NTSC/PAL analog color black,
48 kHz AES Word Clock, and 48 kHz AES3-id DARS.
•Optional 8900-A-CBL package of four breakout cables, to convert 3-pin
balanced AES audio to dual 75
Ω BNCs, unbalanced AES audio, and
•Remote control and SNMP alarms with the 8900NET module.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 7
Page 8
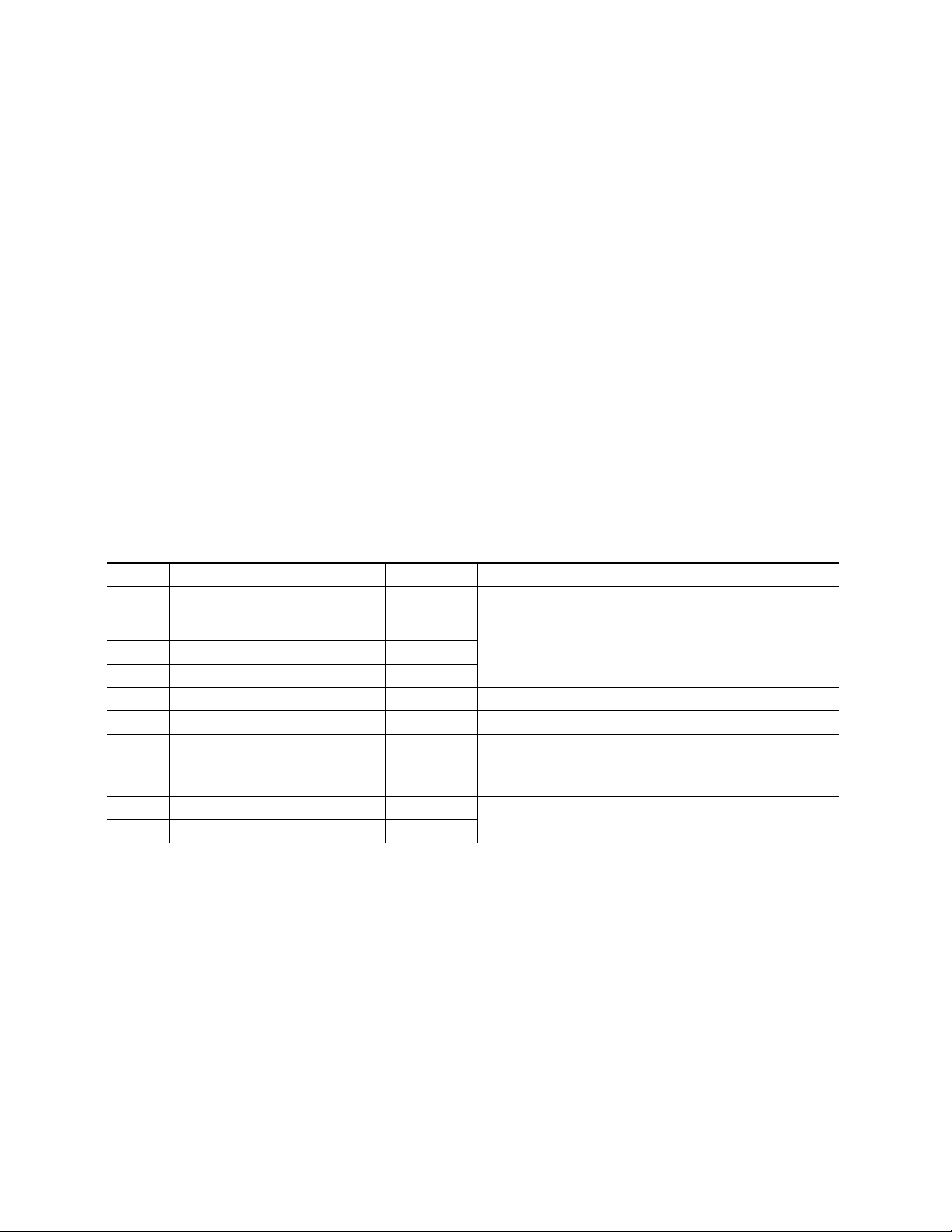
Installation
Installation
Module On-board Jumper Settings
1.
2.
3.
Installation of the 8921ADT module is a process of:
The 8921ADT module can be plugged in and removed from a Gecko 8900
audio frame with power on. When power is applied to the module, LED
indicators reflect the initialization process (see Power Up on page 14).
A number of jumpers must be set on the module to determine module formatting before installing it in the frame. Refer to Table 1 for a summary of
each jumper and Figure 1 on page 9 for jumper locations on the module
circuit board.
Setting on-board jumpers for desired output formats,
Placing the module in the proper audio frame slot, and
Cabling and terminating signal ports.
Table 1. 8921ADT Jumper Settings
Jumper Function Pins 1-2 Pins 2-3 Notes
J2 AES 1&2 Out 1
J3 AES 1&2 Out 2 BAL UN
J4 AES 1&2 Out 3 BAL UN
J5 BNC J11 AES 1 TRK IN Assign BNC function as Tracking In or AES 1 output (unbalanced)
J6 BNC J12 AES 2 TRK OUT Assign BNC function as Tracking Out or AES 2 output (unbalanced)
J11 Local/Remote LOCAL REMOTE
J12 Sample Rate – 48 kHZ Sample rate default is set to 48 KHz for this release.
J13 AES 1 Output Resolution 20 BITS 24 BITS
J14 AES 2 Output Resolution 20 BITS 24 BITS
BAL
(Balanced
110
Ω )
UN
(Unbalanced
75 Ω ) Set AES outputs to balanced or unbalanced (unbalanced setting requires
cable adapter).
Move jumper to Local to lock out remote control if desired. Shipped
from factory with Remote setting.
Set output resolution for AES outputs. These settings can be overridden
remotely on the Audio Proc web page or with a control panel.
8 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 9
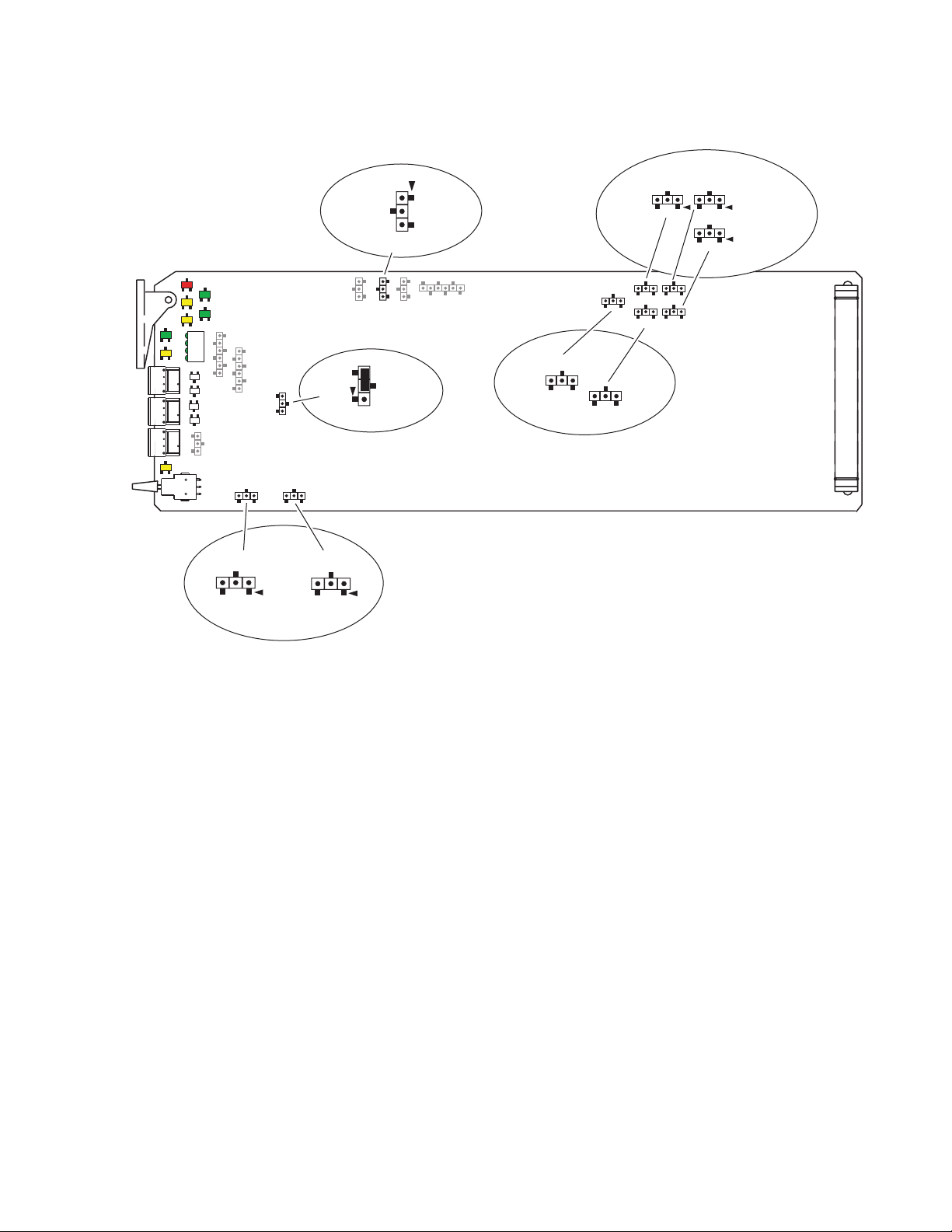
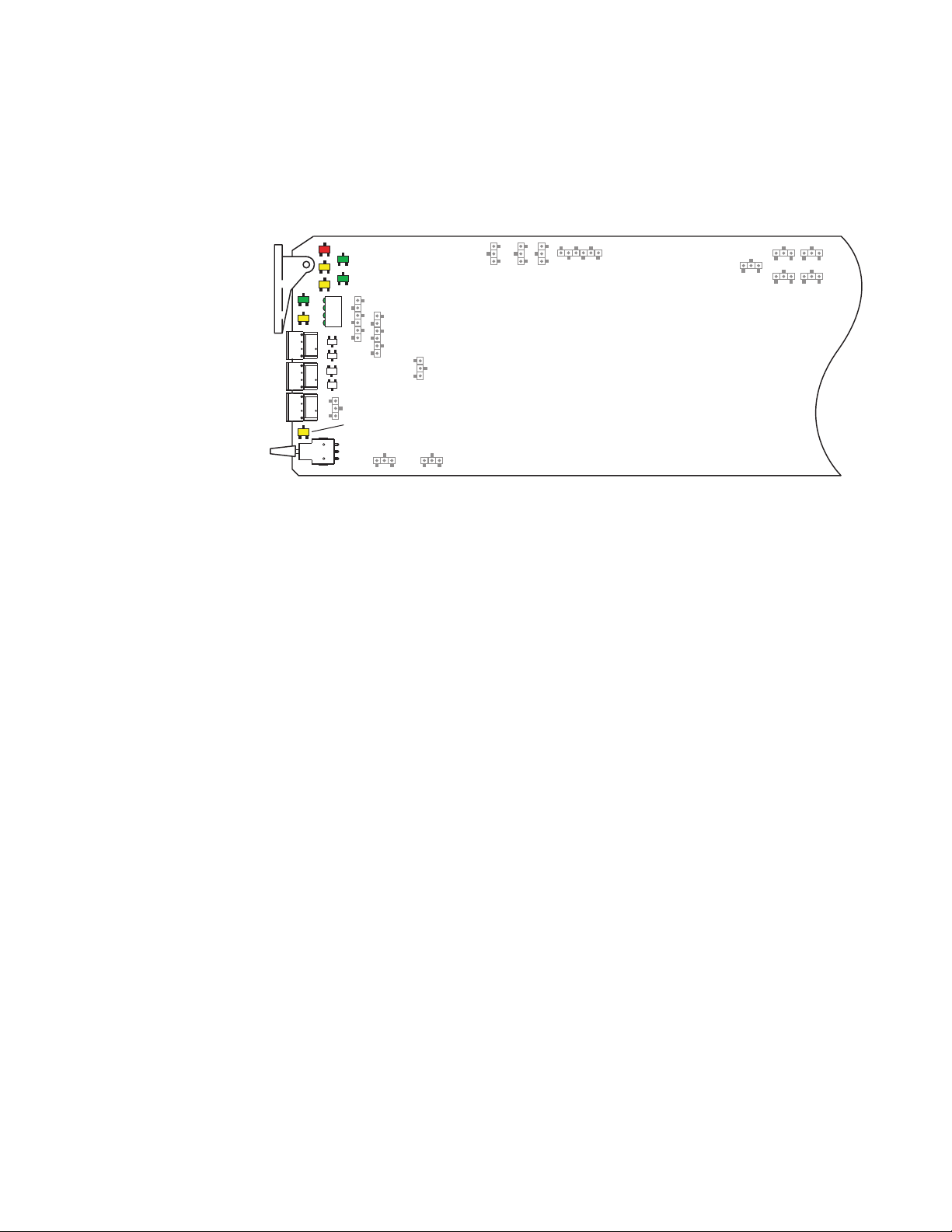
Figure 1. On-Board Jumper Locations
Set jumper J11 to
LOC (1-2) local only, remote lockout
or LOC/REM (2-3) local and remote.
LOC
J11
LOC/REM
J11
Set jumpers J2, J3, and J4
to BAL (1-2) balanced or
UN (2-3) unbalanced to
match output format.
AES 1&2 0UT3
UN
J4
J6
J4
J5
BAL
J2
J3
AES 1&2 0UT1
UNUNBAL
J2
BAL
J3
AES 1&2 0UT2
Installation
J14
J14
AES2
24BITS 20 BITS
SAMPLE RATE
J12
J13
AES1
J13
24BITS 20 BITS
48kHz
J12
96kHz
TRK
Leave jumper J12
set for sample rate
of 48kHz (2-3).
Set jumpers J13 (AES1) and J14 (AES2)
for an output resolution of
20 BITS (pins 1-2) or
24 BITS (pins 2-3).
OUT
AES2
J6
TRK IN
J5
AES1
Set jumper J5 for AES1 (1-2)
or TRK IN (2-3) for BNC J11.
Set jumper J6 to AES2 (1-2)
or TRK OUT (2-3) for BNC J12.
8204_04
8921ADT Instruction Manual 9
Page 10
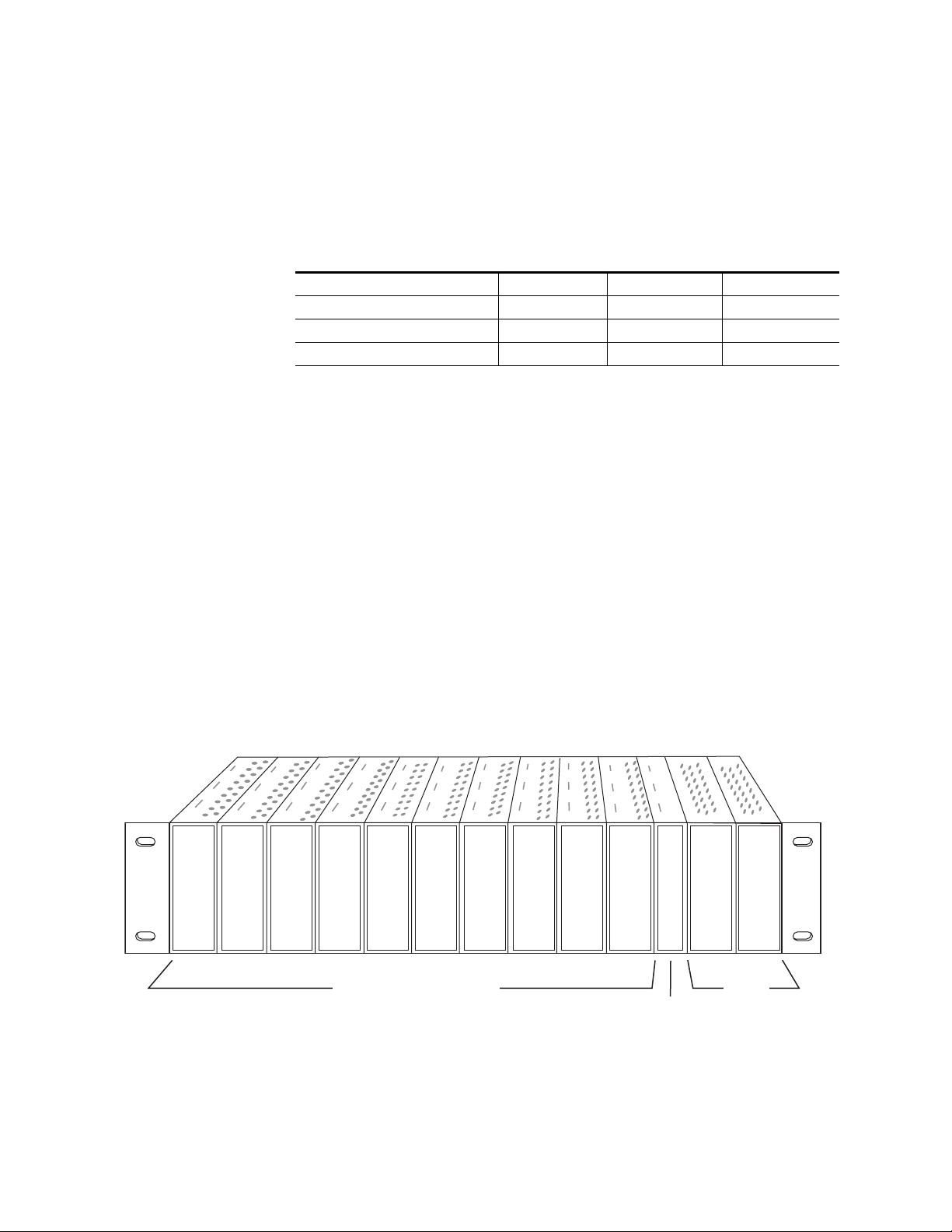
Installation
Frame Capacity
The 8921ADT module can be installed in all Gecko 8900-A audio frames
but with varying maximum quantities determined by frame cooling
capacity. Table 2 provides the power capacity, cooling capacity, and
maximum module count for each frame type.
Table 2. Video Frame Power Capacity
Capacity Calculated 8900TX Frame 8900TF Frame 8900TFN Frame
Power (W) 100 100 100
Recommended Module Cooling (W) 30 90 90
8921ADT Modules 10 10 10
Note
Module capacity figures assume no other modules are in the frame.
X = Not recommended without forced air cooling.
Module Placement in the Gecko 8900-A Audio Frame
There are ten cell locations in the audio frame to accommodate audio modules. These are the left ten locations. Refer to Figure 2.
The two cells on the right are allocated for the power supplies. For additional information concerning the Power Supply module, refer to the 8900
Power Supply manual.
The third cell from the right is allocated for the Frame Monitor or 8900NET
Network Interface module. These modules provide health monitoring and
control options.
Figure 2. Gecko 8900 Series Frame
8157_04r1
8900 Audio Media Modules
Frame Monitor or
8900NET Network
Interface Module
10 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Power
Supplies
(only)
Page 11
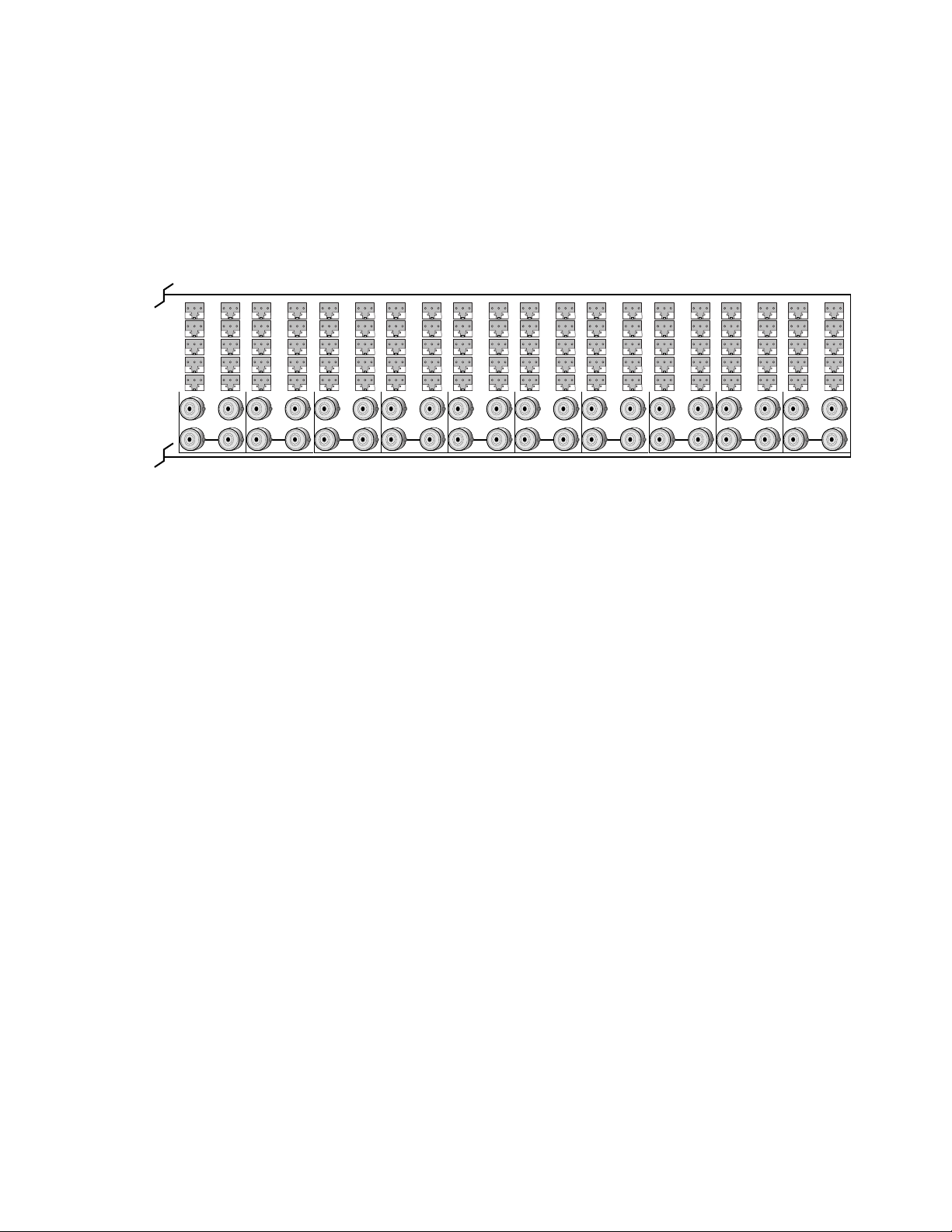
1.
3.
Installation
8900 module slots are interchangeable within the frame. There are audio
connectors and BNCs in each slot’s I/O group. The functional assignment
of each connector in a group is determined by the module that is placed in
that slot. The maximum number of modules a Gecko 8900 audio frame can
accept is ten. Figure 3 illustrates the rear connector plate for a Gecko 8900
audio frame. A detail of the audio connector is given in Figure 4 on page 13.
Figure 3. Gecko 8900 Series Audio Frame Rear Connector
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
10
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
9
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
8
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
7
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
6
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
5
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
4
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
3
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
J14
IN
2
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J11
J12
J13
0636 -17
J14
IN
1
To install a module in the frame:
Insert the module, connector end first, with the component side of the
module facing to the right and the ejector tab to the top.
2.
Verify that the module connector seats properly against the backplane.
Press in the ejector tab to seat the module.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 11
Page 12

Installation
Cabling
Cabling to and from the module is done at the back of the Gecko 8900 audio
frame as described below. A number of jumpers on the module circuit
board must first be set to assign connectors for the desired outputs (see
Module On-board Jumper Settings on page 8).
Analog Audio Inputs
Four balanced analog audio inputs are provided at 3-pin mini-terminal
strip audio connectors J7, J8, J9 and J10. Plastic strain reliefs are provided
for connecting balanced audio connections. Refer to Figure 4 on page 13.
Note
Inputs can be routed to any of the four output streams in configuration.
Refer to
Operation with unbalanced analog audio requires single-ended audio with the
negative side and shield tied together with a signal level of < +30 dBu.
Audio Channel Pairing
Digital AES Audio Outputs
The digital AES audio outputs can be balanced or unbalanced. Each audio
pair must be jumpered on the circuit board for the correct output format.
An optional cable kit is available with four 3-terminal to dual BNC cables
to allow conversion of one balanced output to two unbalanced BNC outputs. Another unbalanced output for each channel can also be accessed on
BNCs J11 (AES 1) and J12 (AES 2) by jumpering the module as explained in
Unbalanced Outputs
Balanced Outputs
Three balanced 110
mini-terminal strip connectors for each AES output stream. Balanced
AES 1&2 Out 1 are available at rear connectors J1/J2, AES 1&2 Out 2 at
J3/J4, and AES 1&2 Out 3 at J5/J6. Plastic strain reliefs are provided for
connecting balanced audio connections. See Figure 4 on page 13.
on page 17.
below.
Ω
AES outputs are available with standard 3-pin
For a balanced output (the factory default), set the following jumpers to
balanced (
• J2 (AES 1&2 Out 1)
• J3 (AES 1&2 Out 2)
• J4 (AES 1&2 Out 3)
BAL
, pins 1-2) as shown in Figure 1 on page 9:
Unbalanced Outputs
Each balanced audio output pair can be converted to unbalanced by connecting an optional 3-terminal to dual-BNC breakout cable (8900-A-CBL)
to the balanced connector and setting the jumpers described in Table 1 on
page 8 to unbalanced (
12 8921ADT Instruction Manual
,
pins 2-3).
UN
Page 13
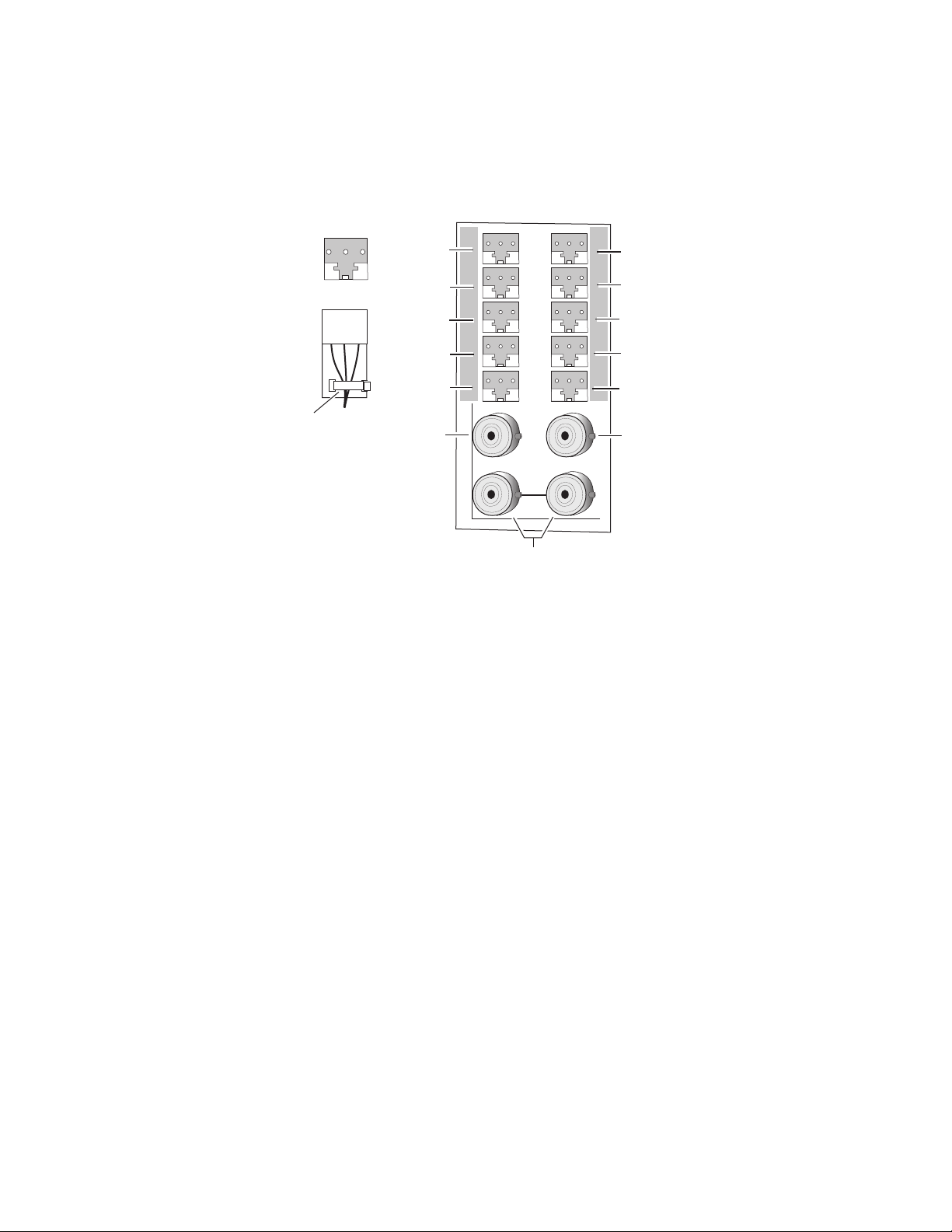
Installation
To use J11 and J12 as unbalanced audio outputs if a tracking input or output
is not required, jumper J5 to pins 1-2 (AES1) and J6 to pins 1-2 (AES2). Refer
to Figure 1 on page 9 and Tracking Input/Output on page 13.
Figure 4. 8921ADT Rear Input/Output Connectors
+ - G
Strain relief
+ - G
Secure with
cable tie
AES 1-1
AES 1-2
AES 1-3
Audio In 1
Audio In 3
Tracking Input
(J5 set to 2-3)
or
AES 1 Out
(J5 set to 1-2)
J11
J13
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
J10
J12
J14
IN
AES 2-1 (Set jumper J2 for BAL or UN outputs
on both AES 1-1 and AES 2-1)
J2
AES 2-2 (Set jumper J3 for BAL or UN output
on both AES 1-2 and AES 2-2)
AES 2-3 (Set jumper J4 for BAL or UN output
on both AES 1-3 and AES 2-3)
Audio In 2
Audio In 4
Tracking Output
(J6 set to 2-3)
or
AES 2 Out
(J6 set to 1-2)
Tracking Input/Output
A Tracking Input is provided at BNC J11. Connect an RS-232 level auto
tracking signal from a video frame synchronizer (such as an 8900FSS or
8981FS) to this BNC and set jumper J5 (Figure 1 on page 9) to TRK IN
(pins 2-3).
If you need to loop the tracking input signal to another destination, a buffered looping output is available at BNC J12. To make this Tracking Output
available, jumper J6 (Figure 1 on page 9) to pins 2-3 (TRK OUT).
If no input and/or output audio tracking is needed, these BNCs can be
jumpered to provide additional unbalanced AES 1 and AES 2 BNC outputs
as described in
Digital AES Audio Outputs
Reference Loop-through Input
Connect an NTSC/PAL analog color black reference, AES 48 kHz Word
Clock signal, or 48 KHz AES3-id DARS signal to one of the loop-through
reference connectors, J13 or J14. Terminate the unused connector into 75
if the signal is not looped to other equipment.
Looping
Reference Input
on page 12.
8204_03
Ω
8921ADT Instruction Manual 13
Page 14
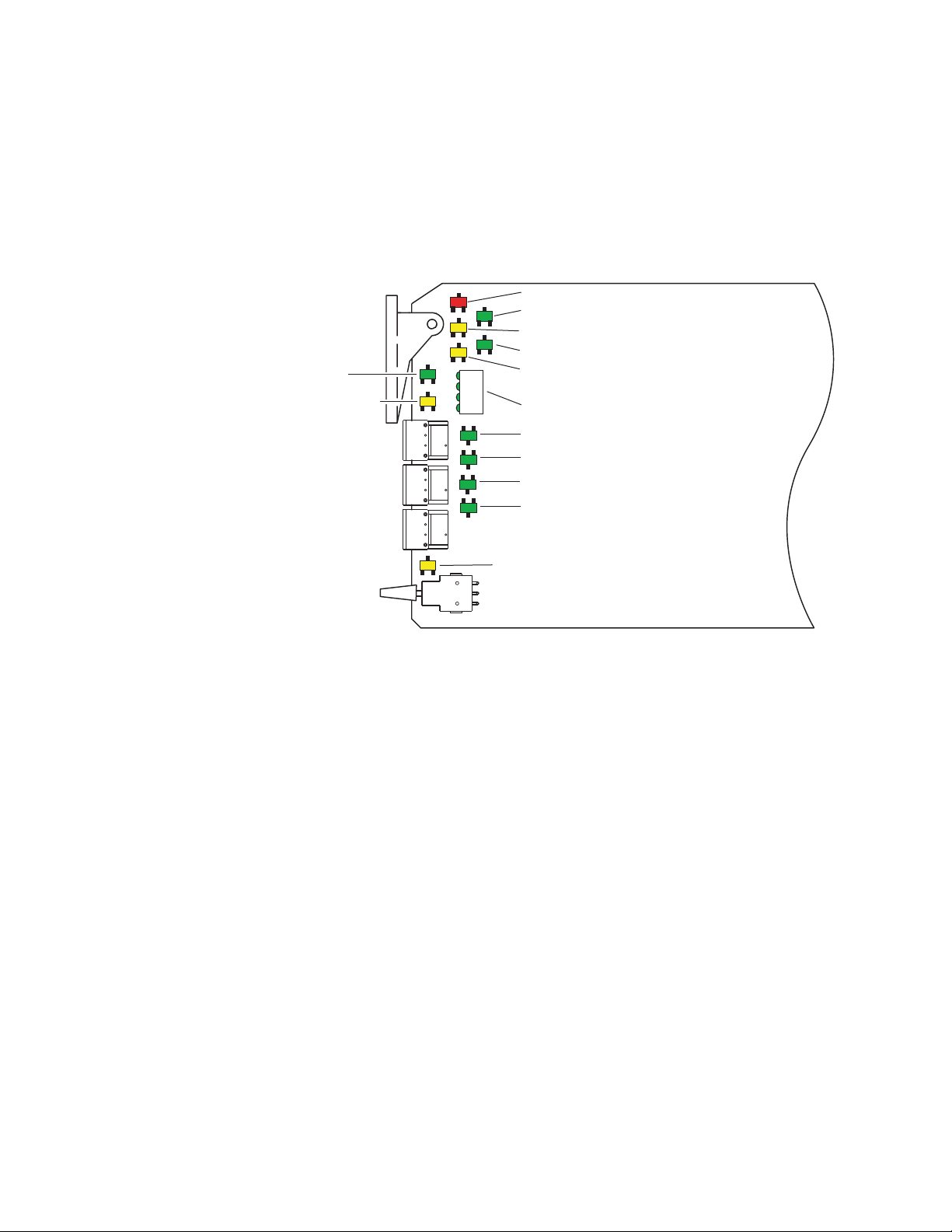
Power Up
Power Up
The front LED indicators and configuration switches are illustrated in
Figure 5. Upon power-up, the green PWR LED should light and the yellow
CONF LED should illuminate for a few seconds for the duration of module
initialization.
Figure 5. LEDs and Configuration Switches
FAULT (red)
TRK ON (green)
COMM (yellow)
LOCKED (green)
PWR (green)
REM OVR (yellow)
1
2
3
4
CONFIG (yellow)
INPUT SELECT (green)
CH1
CH2
> -40 dBFS/CLIP LEDS
CH3
CH4
(green or red)
BANK 2 (yellow)
8204_06
14 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 15
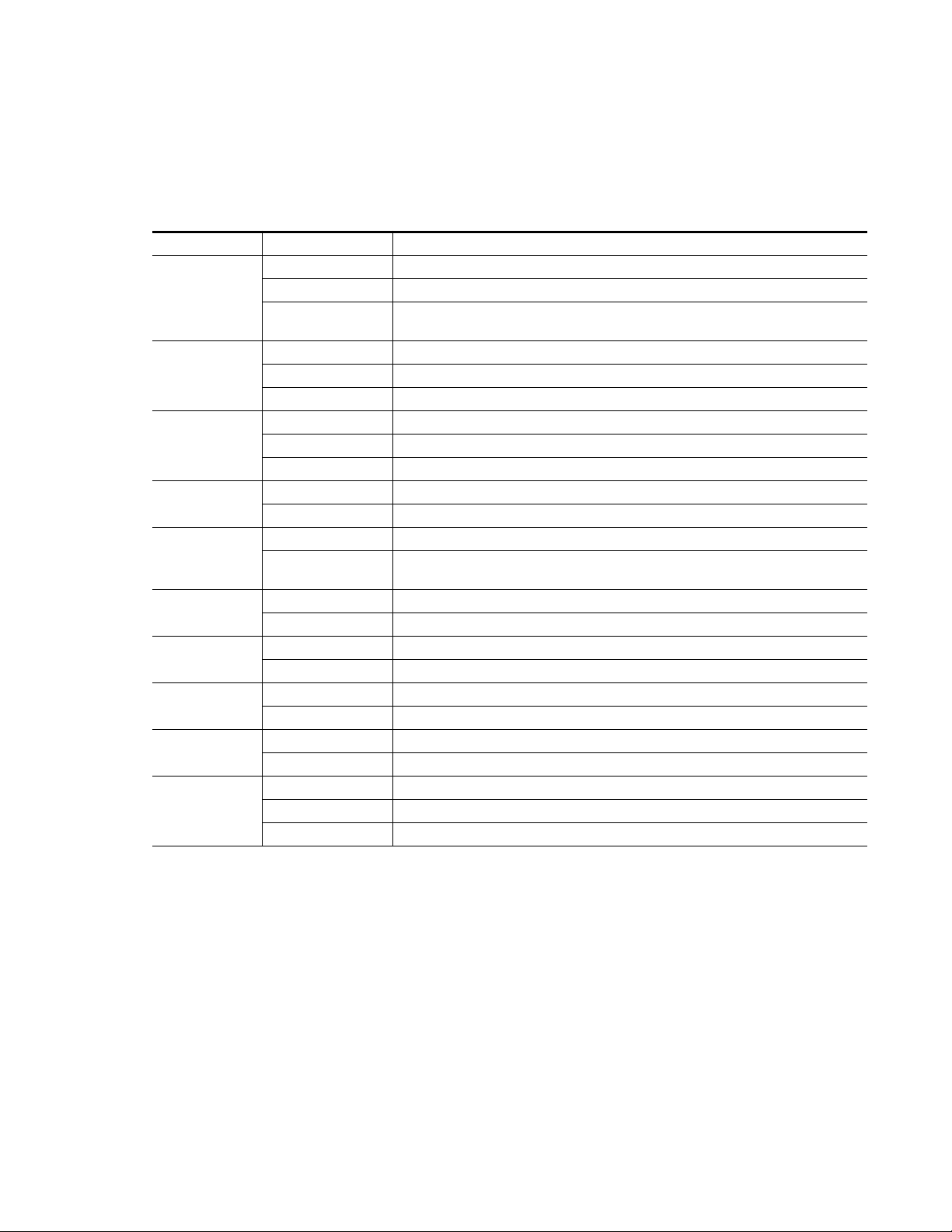
Operation Indicator LEDs
Refer to Figure 5 and Table 3 for the name and meaning of each of the board
edge operating indicators on the module circuit board.
Table 3. Board Edge LED Names and Meaning
LED Indication Condition
Off Normal operation.
FAULT
(red)
COMM
(yellow)
CONFIG
(yellow)
PWR
(green)
REM OVR
(yellow)
TRK ON
(green)
LOCKED
(green)
BANK 2
(yellow)
INPUT 1-4
(green)
> –40 dBFS/CLIP
CH 1-4
(green/red)
On continuously Module has detected an internal fault. (Refer to Functional Description on page 48.)
Long Flash
Off No activity on frame communication bus.
3 Quick Pulses Locate Module command received by the module from a remote control system.
Short flash Activity present on the frame communication bus.
Off Module is in normal operating mode.
On continuously Module is initializing, changing operating modes or programming hardware.
3 Quick Pulses Locate Module command received by the module from a remote control system.
Off No power to module or module’s DC/DC converter failed.
On continuously Normal operation, module is powered.
Off Parameter settings match those set on module switches and jumpers.
On
Off No delay tracking. Tracking signal not received.
On Auto delay is receiving a tracking delay input.
Off No reference is present or reference is present but not locked.
On Module is timed to the reference input.
Off Bank 1 of Control rotary switch is active.
On Bank 2 of Control rotary switch is active.
Off Indicated input is not selected for AES output channel selected with CONTROL rotary switch.
On Indicated input is selected for AES output channel selected with CONTROL rotary switch.
Off Input level is less than –40dBFS and not clipping.
Green Input level is greater than –40dBFS and not clipping.
Red Input level is greater than –40dBFS and clipping.
User configuration problems. Reference input missing or not locked. Processor failed to
load/configure or diagnostics failed on one or more devices.
A setting on the module circuit board switches or jumpers is being overridden by remote control
system.
Power Up
8921ADT Instruction Manual 15
Page 16

Configuration
Configuration
The 8921ADT can be configured locally using onboard switches or
remotely using the 8900NET network interface GUI or a networked control
panel. Operation of these control types is explained in detail in their respective sections of this manual.
Refer to the following sections for configuration instructions:
•Configuration Summary (page 16)
• Local Onboard Module Configuration (page 25)
•Remote Control and Monitoring (page 28)
•Control Panel Configuration (page 45)
Configuration Summary
This section provides a summary of all parameters that can be configured
on the 8921ADT module. Use this section in conjunction with the specific
configuration method instructions for each configuration type. Table 4 on
page 22 provides a summary in table format of all parameters and their
ranges, default values, and remote, local, and control panel function names
and locations for setting each value.
For a functional block diagram and an overview of the module stages, refer
to the
Analog Audio Inputs
The maximum signal level of the analog inputs (before clipping and distortion occur) should be set for full-scale digital outputs (0 dBFS). This level
can be adjusted from 0 to +30 dBu. Each input can be adjusted individually
or locked together in two groups, Inputs 1 and 2, and Inputs 3 and 4. When
locked together, any gain offsets are preserved between channels.
It is helpful before making any input level adjustments to have the module
set up for factory default audio values. This will assure that no summing,
phase inversion, or channel swapping is occurring on the outputs and will
set the module with the following factory defaults:
Functional Description
on page 48.
•Maximum input levels to + 24 dBu = 0 dBFS.
•Output gains to 0 dB
•Delay to 0 sec
• Input mapping to Inputs 1, 2 = AES 1 A, B, Inputs 3, 4 to AES 2 C, D
To quickly access these defaults, select position F on the front panel Control
rotary switch on Bank 2 then activate the paddle switch in the up direction.
16 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 17

If you know the maximum signal level of your audio inputs, you can enter
the value directly into the web page level adjustment fields. Refer to
Audio Inputs Page
For local control (no 8900NET module), you can adjust maximum input
levels by metering the corresponding output with a digital audio meter. To
correctly adjust the input levels for your digital application, use one of the
methods below:
•Apply a signal at – 1 dB below your maximum signal level to the analog
input and monitor the corresponding AES output with a meter that
indicates digital level in dBFS. Adjust each output until the meter indicates – 1 dBFS.
•Apply an input audio level that is -20 dB below the maximum level,
(+4 dBu for the default, +24 dBu -20 dB = +4 dBu) and adjust the level
as indicated on a digital audio meter to -20 dBFS.
Audio Channel Pairing
The four analog input channels can be routed to any of the left and right
channel outputs of AES 1 and AES 2.
Configuration
Analog
on page 35.
Audio Delay
The audio outputs can be delayed manually or synchronized to an external
auto-tracking input signal such as an input from an 8960DEC with 8900FSS
or 8981FS.
Each output channel can be delayed individually or locked together in two
groups, AES 1 Ch A and B, and AES 2 Ch C and D.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 17
Page 18

Configuration
Audio Processing
Audio processing can be performed on the outputs of AES 1 and AES 2 to
set the output processing mode, the output resolution, gain of each output
stream, and the output sample rate with the Audio Proc controls.
Output Processing Modes
The AES 1 output can be set to one of the following output modes:
•A, B (Pass) – the inputs selected for A and B appear at the AES output
unmodified.
•– A, – B (both phase inverted) – the inputs selected for A and B are both
inverted at the AES output.
•– A, B (A Phase Inverted) – the input selected for the A channel is
inverted while the B channel is non-inverted at the AES output.
•A, – B (B Phase Inverted) – the input selected for the A channel is not
inverted while the B channel is inverted at the AES output.
•A + B, (monaural sum) – the inputs selected for the A and B channels
are reduced in level by 6 dB, summed together, and output on both
channels at the AES output.
•A + B, A–B (MD D/E) – will be a – 6 dB mono sum to A and – 6 dB difference decode/encode to B.
•– (A + B) (A + B to Both and Phase Invert) – the inputs selected for the
A and B channels are reduced in level by 6 dB, summed together,
inverted, and output on both channels at the AES output.
•1 kHz (Tone) – a 1 kHz tone is put on both channels at the AES output
with a – 20 dBFS level.
• 400 Hz (Tone) – a 400 Hz tone is put on both channels at the AES output
with a – 20 dBFS level.
• Silence – digital silence is placed on both channels at the AES output.
•A + B, C – the two channels chosen for AES 1 A and B are reduced in
level by 6 dB, summed and sent to the A output. The Ch C audio from
AES 2 will be put on both sides of the Ch B output. In this mode, AES 2
will pass its inputs for C and D as selected with the output processing
control for AES 2.
•A + B, D – the two channels chosen for AES 1 A and B are reduced in
level by 6 dB, summed and sent to the A output. The Ch D audio from
AES 2 will be put on both sides of the Ch B output. In this mode, AES 2
will pass its inputs for C and D as selected with the output processing
control for AES 2.
•A/B ID – A/B identification tone. A 1 kHz continuous tone with a
– 20 dBFS level for 1 second on Ch A followed by a 3 second continuous
tone on the Ch B (keeps repeating).
18 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 19

Configuration
The AES 2 output can be set to one of the following output modes:
•C, D (Pass) – the inputs selected for C and D appear at the AES output
unmodified.
•– C, – D (both phase inverted) – the inputs selected for C and D are both
inverted at the AES output.
•– C, D (C Phase Inverted) – the input selected for the C channel is
inverted while the D channel is non-inverted at the AES output.
•C, – D (D Phase Inverted) – the input selected for the C channel is not
inverted while the D channel is inverted at the AES output.
•C + D, (monaural sum) – the inputs selected for the C and D channels
are reduced in level by 6 dB, summed together, and output on both
channels at the AES output.
•C + D, C–D (MD D/E) – will be a – 6 dB mono sum to C and – 6 dB dif-
ference decode/encode to D.
•– (C + D) (C + D to Both and Phase Invert) – the inputs selected for the
C and D channels are reduced in level by 6 dB, summed together,
inverted, and output on both channels at the AES output.
•1 kHz (Tone) – a 1 kHz tone is put on both channels at the AES output
with a – 20 dBFS level.
• 400 Hz (Tone) – a 400 Hz tone is put on both channels at the AES output
with a – 20 dBFS level.
• Silence – digital silence is put on both channels at the AES output.
•C/D ID – C/D identification tone. A 1 kHz continuous tone with a
– 20 dBFS level for 1 second on Ch C followed by a 3 second continuous
tone on the Ch D (keeps repeating).
8921ADT Instruction Manual 19
Page 20

Configuration
Gain Adjustments
Once the output mode for each AES output has been selected, the gain of
the outputs can be adjusted from – 40 to + 6 dB in the audio processor as
required. Each output can be adjusted individually or locked together in
two groups, AES 1 A and B, and AES 2 C and D.
AES Output Resolution
The output resolution for AES 1and AES 2 can be set to either 20 or 24 bits.
This is set locally during installation with on-board jumpers J13 (AES 1)
and J14 (AES 2). The jumper settings can be overridden with the remote
controls.
Output Sample Rate
The output sample rate for both AES 1and AES 2 will always default to
48 kHz for this release.
Auto Tracking
If an external tracking signal is connected to the module, the TRK IN BNC,
J11, must be jumpered on the module as an input with jumper J5 (see
Module On-board Jumper Settings on page 8). Auto tracking must also be
enabled with local or remote controls.
20 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 21

Reference Source
The module can lock to an external reference or free run. The reference
source can be selected with local or remote controls. If a reference signal is
connected to the loop-through input, the reference source should be set to
Reference In. If no external reference is used, or you don not wish to have the
module lock to its reference input, set the module to
Recalling Factory Defaults
When the factory defaults are recalled with either the local controls or the
remote control from the web page, the module will revert to the following
values:
•Maximum input levels to + 24 dBu
•Output gains to 0 dB
•Delay to 0 sec
• Input mapping to Inputs 1, 2 = AES 1 A, B, Inputs 3, 4 to AES 2 C, D
The following controls will default to the current on-board jumper and
rotary switch settings on the module:
Configuration
Free Run.
• Sample Rate – jumper J12 is set for 48 kHz, the current default for this
release.
•Output Resolution – will default to the jumper setting for 20 or 24 bit
word length on jumper J13 for AES 1 and jumper J14 for AES 2.
•Output processing mode – will default to the rotary switch setting on
rotary switch SW1 for AES 1 and SW2 for AES 2.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 21
Page 22
Configuration
Table 4 provides a complete summary of the 8921ADT functions and a
comparison of the functionality available with each control type along with
the ranges and default values for each parameter.
Table 4. Summary of 8921ADT Configuration Functions
Function
Type
Analog input levels and routing
Inputs 1 and 2
Inputs 3 and 4
Input 1
Input 2
Input 3
Input 4
Input to AES 1 A output Audio In 1 Audio In 1-4
Input to AES 1 B output Audio In 2 Audio In 1-4
Input to AES 2 A output Audio In 3 Audio In 1-4
Input to AES 2 B output Audio In 4 Audio In 1-4
Adjust AES output delay
Delay AES 1 A
Delay AES 1 B
Delay AES 2 A
Delay AES 2 B
Delay AES 1 (A & B)
Delay AES 2 (A & B)
Default
+ 24 dBu
0 sec
Range/Choices
Resolution
0 – + 30 dBu
(0.1 dB steps)
0 – 5 sec
(2 ms steps)
Web Page/
Function Name
Analog Audio Inputs/
Max Input Levels 1&2
Select
Locked checkbox
Analog Audio Inputs/
Max Input Levels 3&4
Select
Locked checkbox
Analog Audio Inputs/
Max Input Level 1
Analog Audio Inputs/
Max Input Level 2
Analog Audio Inputs/
Max Input Level 3
Analog Audio Inputs/
Max Input Level 4
Audio Channel Pairing/
Assign AES 1 ChA
Audio Channel Pairing/
Assign AES 1 ChB
Audio Channel Pairing/
Assign AES 2 ChA
Audio Channel Pairing/
Assign AES 2 ChB
Audio Delay/
AES 1 A Delay (ms)
Audio Delay/
AES 1 B Delay (ms)
Audio Delay/
AES 2 A Delay (ms)
Audio Delay/
AES 2 B Delay (ms)
Audio Delay/
AES 1 A or B Delay (ms)
Select
Locked checkbox
Audio Delay/
AES 2 A or B Delay (ms)
Select
Locked checkbox
Jumper or
Rotary Switch
Bank/Setting
1:1
1:2
1:3
1:4
1:5
1:6
1:7 Ch1A Sel
1:8 Ch1B Sel
1:9 Ch2C Sel
1:A Ch2D Sel
2:7 Ch1ADly
2:8 Ch1BDly
2:9 Ch2CDly
2:A Ch2DDly
2:B
2:C
Newton
Panel
Mnemonic
N/A
N/A
N/A
Notes/
Conditions
Preserves gain offsets
between channels.
Locked boxes must
be unchecked on web
pages.
Route analog input to
AES output
Locked boxes must
be unchecked on web
pages.
Locked boxes must
be checked on web
pages.
22 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 23
Table 4. Summary of 8921ADT Configuration Functions
Function
Type
Auto-tracking AES 1 Disable Disable or Enable
Auto-tracking AES 2 Disable Disable or Enable
Select reference source
Adjust AES output gain
AES 1 (A & B) Gain
AES 2 (A & B) gain
AES 1 A gain
AES 1 B gain
AES 2 A gain
AES 2 B gain
Set AES output resolution
AES 1 output
AES 2 output
Default
Reference InReference In or
0 dB
Jumper
J13 value
Jumper
J14 value
Range/Choices
Resolution
Free Run
– 40 – +6 dB
(0.1 dB steps)
20 or 24 bit
Web Page/
Function Name
Audio Delay/AES 1
Enable Auto Track On button
Audio Delay/AES 2
Enable Auto Track On button
Reference Source radio button
I/O Config/
Audio Proc/
AES 1 A or B Gain (dB)
Select
Locked checkbox
Audio Proc/
AES 2 A or B Gain (dB)
Select
Locked checkbox
Audio Proc/
AES 1 A (dB)
Audio Proc/
AES 1 B (dB)
Audio Proc/
AES 2 A (dB)
Audio Proc/
AES 2 B (dB)
Audio Proc/
AES output resolution
20 bit or 24 bit radio button
Audio Proc/
AES Output Resolution
20 bit or 24 bit radio button
Jumper or
Rotary Switch
Bank/Setting
1:C
(both AES 1 and
AES 2)
1:B N/A
2:1
2:2
2:3 Ch1AGain
2:4 Ch1BGain
2:5 Ch2CGain
2:6 Ch2DGain
Jumper J13
(see Figure 6 on
page 25)
Jumper J14
(see Figure 6 on
page 25)
Newton
Panel
Mnemonic
N/A
N/A
N/A
Configuration
Notes/
Conditions
Independent control
of auto-tracking in
remote control only.
Locked boxes must
be checked on web
pages.
Locked boxes must
be unchecked on web
pages.
Remote control can
override on-board
jumper settings.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 23
Page 24

Configuration
Function
Type
User settings N/A
Recall factory defaults N/A
Set output processing
AES 1 processing A, B
AES 2 processing
Default
C, D C, D
Table 4. Summary of 8921ADT Configuration Functions
Range/Choices
Resolution
Recall or Learn
(Save)
See Default
column
A, B
– A, – B – A, – B
– A, B – A, B
A, – B A, – B
A + B A + B
A+B, A-B A+B, A-B
– (A + B) – (A + B)
1 kHz 1 kHz
400 Hz 400 Hz
Silence Silence
A + B, C A + B, C
A + B, D A + B, D
A/B ID A/B ID
– C, – D – C, – D
– C, D – C, D
C, – D C, – D
C + D C + D
C+D, C-D C+D, C-D
– (C + D) – (C + D)
1 kHz 1 kHz
400 Hz 400 Hz
Silence Silence
C/D ID C/D ID
Web Page/
Function Name
E-MEM/
Recall or Learn buttons
E-MEM/
Recall factory settings button
Audio Proc/
AES 1 Processing pulldown
Audio Proc/
AES 2 Processing pulldown
Jumper or
Rotary Switch
Bank/Setting
1:E N/A
1:F N/A
AES 1 Mode
Rotary Switch
S1
(see Table 6 on
page 27)
AES 2 Mode
Rotary Switch
S2
(see Table 6 on
page 27)
Newton
Panel
Mnemonic
A, B
C, D
Notes/
Conditions
24 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 25
Local Onboard Module Configuration
The 8921ADT module can be configured and operated locally using the
rotary and paddle switches on the front edge of the module (Figure 6).
Figure 6. Module Jumpers and Switches for Local Configuration
AES 1 Mode Switch
AES 2 Mode Switch
CONTROL Switch
BANK 2 LED
Paddle Switch
Configuration
8204_05
Configuration Switches and Controls
The switches available for local configuration are described below. Refer to
Figure 6 for the following descriptions:
• MODE and CONTROL (rotary) switches — Three rotary hex switches
are present on the front edge of the module, AES 1 MODE,
AES 2 MODE, and CONTROL.
The AES 1and AES 2 MODE rotary switches select the output mode for
each AES channel from 1 of 16 possible settings. Local settings for each
output mode are given in Table 6 on page 27.
The CONTROL switch is used to set input/output gain, delay, save and
recall user settings, and for input selection in conjunction with the
CONTROL paddle switch. It addresses two banks of functions; each
bank has 16 possible positions (0 through 9 and A through F). Not all
positions are used. The next bank of functions is accessed each time the
CONTROL switch makes a complete revolution past zero (or back
through F): While in Bank 1, a complete revolution past zero accesses
Bank 2; while in Bank 2, a complete revolution past zero accesses Bank
1 again. The yellow BANK 2 LED indicates which bank is currently
being accessed.
CAUTION The CONTROL rotary switch should be kept in position 0 in any bank (parked)
when not in use to avoid any inadvertent change in configuration. Position 0
in each bank is inactive.
•BANK 2 (second Function) yellow LED – when off, indicates that the
rotary switch is addressing the first bank of functions. When on, indicates that the rotary switch is addressing the second bank of functions.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 25
Page 26

Configuration
• CONTROL (paddle) switch – actuates or selects the desired setting for
the selected function when the switch is held momentarily in either the
up or down position.
• CONF (configuring) yellow LED – when on, indicates the module is
programming hardware.
8921ADT Module Onboard Configuration Settings
To make a configuration setting:
1. Rotate the CONTROL rotary switch to Bank 1 (BANK 2 LED off) or
Bank 2 BANK 2 LED on) and to the desired function within that bank.
2. Move the paddle switch to the up or down position and hold
momentarily to set the desired function (refer to Table 5).
Note Holding the paddle switch in the up or down position for more than a half
second will automatically accelerate through the value range for parameters
with 256 or more values. The full range can be accessed in about 10 seconds.
Table 5. CONTROL Rotary and Paddle Switch Functions
Rotary
Switch
Setting
Bank 1 (BANK 2 LED off)
0– –Default position for normal operation (paddle has no effect).
1 Increase Decrease Adjust maximum input level for inputs 1 and 2 together.
2 Increase Decrease Adjust maximum input level for inputs 3 and 4 together.
3 Increase Decrease Adjust maximum input level for input 1 separately.
4 Increase Decrease Adjust maximum input level for input 2 separately.
5 Increase Decrease Adjust maximum input level for input 3 separately.
6 Increase Decrease Adjust maximum input level for input 4 separately.
7 Increment input # Decrement input # Select input channel to be used for Ch A (L) on AES 1 output.
8 Increment input # Decrement input # Select input channel to be used for Ch B (R) on AES 1 output.
9 Increment input # Decrement input # Select input channel to be used for Ch C (L) on AES 2 output.
A Increment input # Decrement input # Select input channel to be used for Ch D (R) on AES 2 output.
B Reference In Free Run Select the reference source input to lock or free run.
Bank 1 (BANK 2 LED off)
C Enable Disable Auto tracking enable or disable.
D- –Not used
E Recall Save Save and recall current user settings.
F Recall –
Switch Up
Paddle
Paddle
Switch Down
Function Description
1
1
Recall the following factory defaults:
Maximum input levels to + 24 dBu
Output gains to 0 dB
Delay to 0 sec
Input mapping to Inputs 1, 2 = AES 1 A, B, Inputs 3, 4 to AES 2 C, D
26 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 27

Table 5. CONTROL Rotary and Paddle Switch Functions
Configuration
Rotary
Switch
Setting
Bank 2 (BANK 2 LED on)
0– –Default position for normal operation (paddle has no effect).
1 Increase Decrease Adjust output gain of both Ch A and Ch B of AES 1 together.
2 Increase Decrease Adjust output gain of both Ch C and Ch D of AES 2 together.
3 Increase Decrease Adjust output gain of Ch A of AES 1.
4 Increase Decrease Adjust output gain of Ch B of AES 1.
5 Increase Decrease Adjust output gain of Ch C of AES 2.
6 Increase Decrease Adjust output gain of Ch D of AES 2.
7 Increase Decrease Delay Ch A output of AES 1 separately.
8 Increase Decrease Delay Ch B output of AES 1 separately.
9 Increase Decrease Delay Ch C output of AES 2 separately
Bank 2 (BANK 2 LED on)
A Increase Decrease Delay Ch D output of AES 2 separately.
B Increase Decrease Delay both channels of AES 1 output together.
C Increase Decrease Delay both channels of AES 2 output together.
D-E – – Not used.
F Recall – Recall defaults as given in Bank 1, position F.
1
Preserves gain offsets between channels.
Paddle
Switch Up
Paddle
Switch Down
Function Description
1
1
Set Output Processing Modes
Two rotary switches are provided on the front edge of the module for
setting the desired output mode for AES 1 (SW1) and AES 2 (SW2). Refer to
Output Processing Modes on page 18 for an overview of each mode.
Table 6. AES 1 and AES Modes Switch Settings
Position AES 1 Processing Mode AES 2 Processing Mode
0 A, B (Pass) C, D (Pass)
1– A, – B – C, – D
2– A, B – C, D
3 A, – B C, – D
4A + B (– 6 dB) C + D (– 6 dB)
5A + B, A–B (MS D/E) C + D, C–D (MS D/E)
6– (A + B) – (C + D)
71 kHz 1 kHz
8 400 Hz 400 Hz
9 Silence Silence
AA + B, C C, D (Pass)
BA + B, D C, D (Pass)
C-D A, B Pass C, D (Pass)
E A/B ID C/D ID
F A, B (Pass) C, D (Pass)
8921ADT Instruction Manual 27
Page 28

Configuration
Remote Configuration and Monitoring
8921ADT configuration and monitoring can be performed using a web
browser GUI interface when the 8900NET Network Interface module is
present in the audio frame (Gecko 8900TFN-A frame). This section
describes the GUI access to the module configuration functions.
For remote access, make sure the jumper block on the module is set for both
Local and Remote access (Figure 6 on page 25).
Refer to the 8900NET Network Interface Module Instruction Manual for information on the 8900NET Network Interface module and setting up and
operating the Gecko 8900 frame network.
Note For optimal performance and access to the latest features, it is recommended
that the 8900NET module be updated to the latest software release. Check the
Grass Valley web site for the current 8900NET software.
Refer to the Frame Status page shown in Figure 7 on page 29. The 8900
audio modules can be addressed by clicking either on a specific module
icon in the frame status display or on a module name or slot number in the
link list on the left.
Note The physical appearance of the menu displays on the web pages shown in
this manual represent the use of a particular platform, browser and version
of 8900NET module software. They are provided for reference only. Displays
will differ depending on the type of platform and browser you are using and
the version of the 8900NET software installed in your system.
Use the Refresh button to update the display (available with 8900NET software version 3.0 and later).
The
Online Manual Link button can be set up to link to the documentation in
pdf format. Link configuration is done on the Frame Configuration page.
For information on status and fault monitoring and reporting shown on the
Status page, refer to Status Monitoring on page 51.
28 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 29

Figure 7. Frame Status Page
8204_08
The Links section lists the frame and its current modules. The selected link's Status
page is first displayed and the sub-list of links for the selection is opened. The sub-list
allows you to select a particular information page for the selected device.
Content display section displays the information page
for the selected frame or module (frame slot icons are also
active links).
Online Manual Link
Refresh button for manual
update of page
Configuration
8921ADT Instruction Manual 29
Page 30

Configuration
8921ADT Links and Web Pages
The 8900 GUI provides the following links and web pages for the 8921ADT
module (Figure 8):
• Status – reports input and reference signal status and module information (page 31),
• I/O Config – shows a graphic representation of inputs and outputs to
the module and allows naming of each input (page 32),
• Functional View – shows a block diagram of the module with links to
each configuration page (page 33),
•Module Configuration pages for setting up the module (page 34),
• E-MEM – provides Learn and Recall functions for local operations as
well as
(page 39),
• Slot Config – provides a Locate Module function and Slot Memory
(page 42), and
• Software Update – allows updating of software from a CD-ROM or the
web site (page 44).
Save to and Load from file operations for current and user settings
Figure 8. 8921ADT Web Page Links
30 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 31

Use
this
link
Configuration
Status Page
The Status page (Figure 9) shows the signal status of the audio, reference,
and AES 1 or Tracking inputs and the AES 1 and AES 2 and Tracking outputs. Color coding of the display indicates the signal status. Refer to Status
Monitoring on page 51 for an explanation of the color coding.
Information about the module, such as part number, serial number, hardware revision and software and firmware versions are given in a read-only
section at the bottom of the display. Enabled options are also reported.
The Asset Tag field is for future 8900NET capability.
Clicking on the underlined links to the audio inputs and outputs will take
you to the I/O Config page.
Clicking on the model number in the center box will take you to the Functional View page illustrating a block diagram overview of the module with
links to each of the configuration pages.
Figure 9. 8921ADT Status Page
8921ADT Instruction Manual 31
Page 32
Configuration
Use
this
link
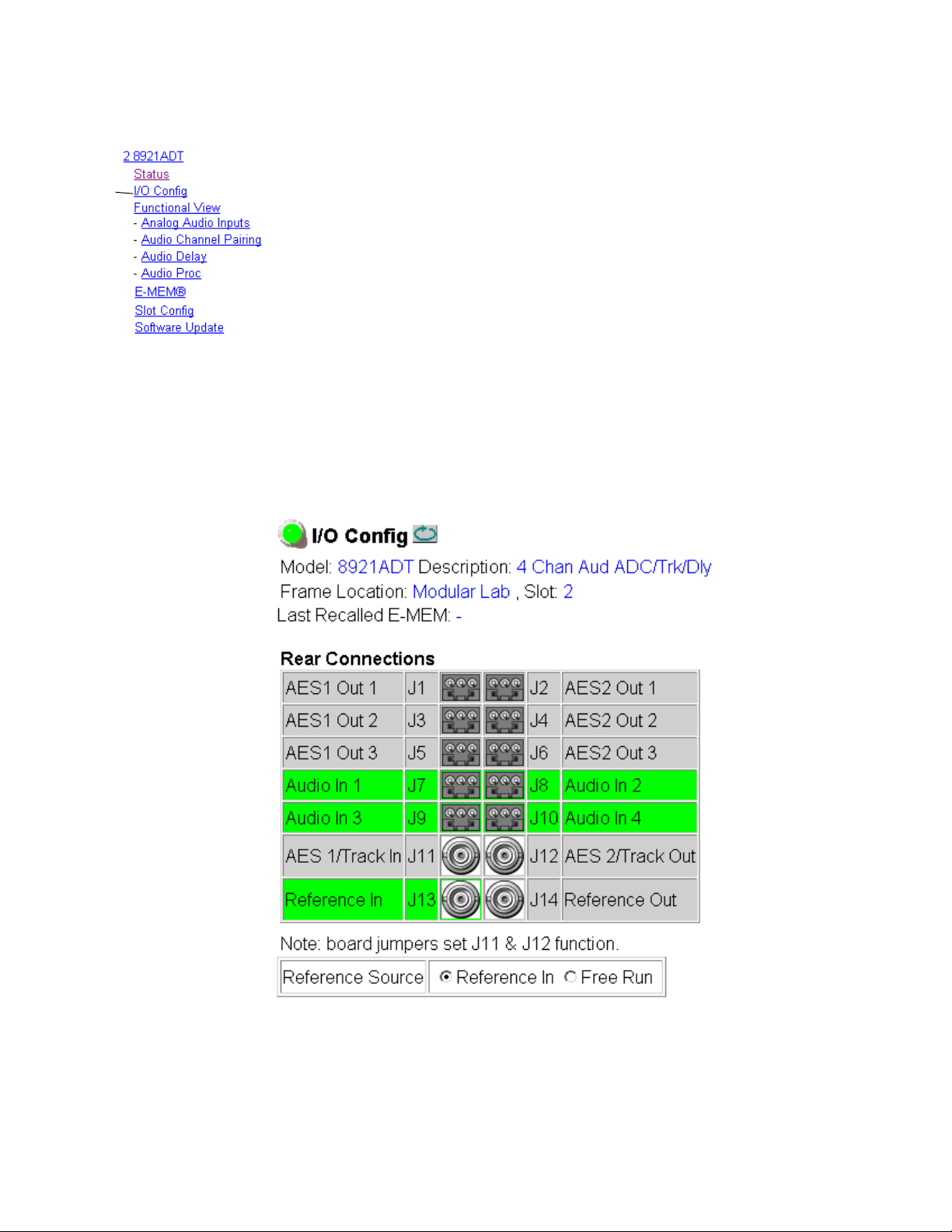
I/O Config Page
The I/O Config page (Figure 10) shows the rear input and output connections to the module. Audio input and Reference In status is reported by the
color-coding of the corresponding blocks. Grayed components are inactive
due to hardware and/or software constraints. Refer to Web Browser Interface
on page 52 for a complete explanation of status reporting.
Note Output status is not reported in this application.
Use this page to do the following:
• Set the Reference Source to either
ence when present) or
module to free run and not lock to an input reference).
Rear BNC functionality for BNCs J11 and J12 is defined by jumper settings
on the module. Refer to Module On-board Jumper Settings on page 8 for more
information.
Figure 10. 8921ADT I/O Config Page
Free Run (no reference input present or to force
Reference In (to lock to an input refer-
32 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 33
Use
this
link
Configuration
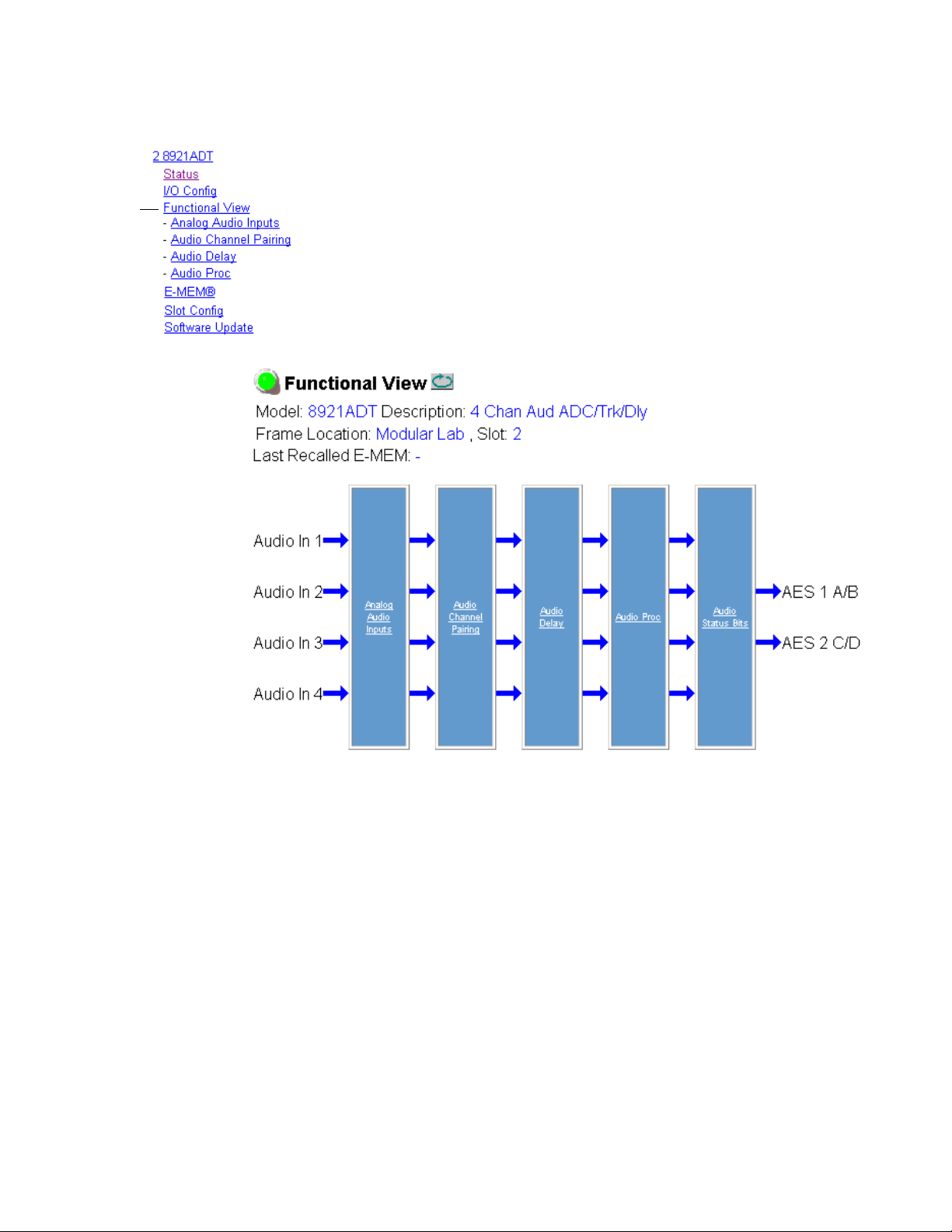
Functional View Page
The Functional View page (Figure 11) illustrates a block diagram of the
8921ADT module showing module functions and signal paths that are
active or inactive in the current configuration. It can be used as a link map
for configuring module functions. Underlined module functions are links
to the web page for that function.
Use the Functional View to configure the 8921ADT module in the order of
the signal flow. Refer to each of the module configuration web pages given
in the next section.
Figure 11. 8921ADT Functional View Page
8921ADT Instruction Manual 33
Page 34

Configuration
Module Configuration Pages
Module configuration is provided for the following functions with the GUI
interface:
•Analog Audio Inputs (page 35)
•Audio Channel Pairing (page 36)
•Audio Delay (page 37)
•Audio Proc (page 38)
Read-only information about the module is given on the top of each page
including model name and description, frame and slot location and last
E-MEM function recalled (E-MEM, File, or Defaults).
Note If the module is power cycled, the Last E-MEM Recalled field will indicate a
dash (–) instead of the last E-MEM function name recalled. The last recalled
function information will be retained by the module, but the function name
will not be remembered.
After making a parameter value change, click on Apply to activate settings
in each selection.
Select the
use the links on the left of the web page.
Click on the
play.
Back, Functional View, or Next link to navigate to the next function or
Refresh button at the top of the display to update the entire dis-
34 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 35

Configuration
Analog Audio Inputs Page
The Analog Audio Inputs page (Figure 12) reports the following for each of
the analog audio inputs:
Use
this
link
•Presence of input signal (True = > – 40 DBFS)
•Clip status of input signal (True = > – 0.5 dBFS).
Set the maximum input level of each of the analog audio inputs from
0 to + 30 dBu with the Max Input Levels controls. Input levels can also be
adjusted in pairs (J7 and J8, J9, and J10) by selecting the corresponding
Locked checkbox and adjusting either level control in the pair.
Figure 12. 8921ADT Analog Audio Inputs Page
8921ADT Instruction Manual 35
Page 36
Configuration
Use
this
link
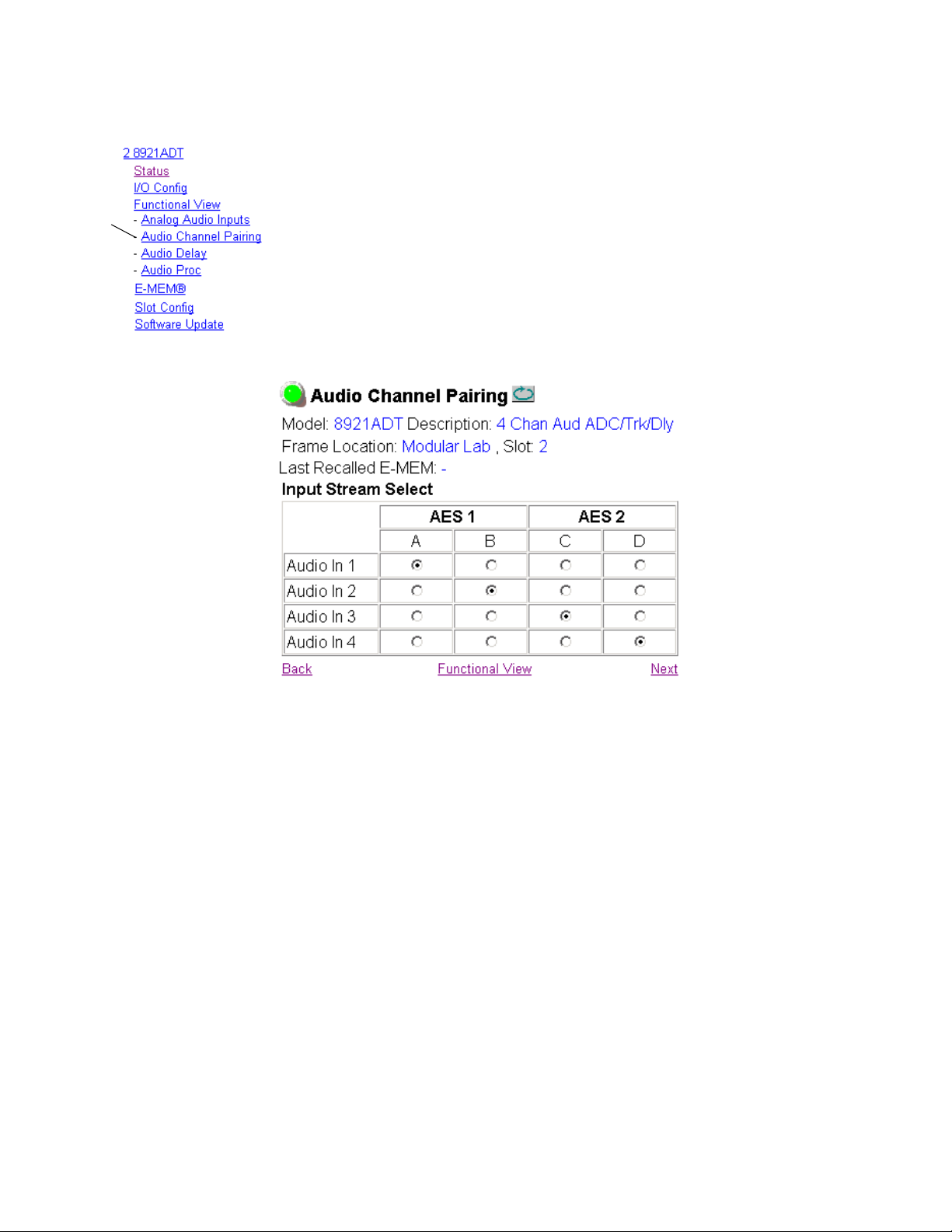
Audio Channel Pairing Page
The Audio Channel Pairing page (Figure 13) allows routing the four audio
input streams to be output on any of the four output channels AES 1 A and
B, AES 2 C and D.
Assign each input audio stream from the list on the left to AES 1 A or B or
AES 2 C or D by clicking on the corresponding radio button under the AES
output. The default routing (Input 1 to AES 1 Ch A, Input 2 to AES Ch 2,
Input 3 to AES 2 Ch C and Input 4 to AES 2 Ch D) is shown in the example.
Figure 13. 8921ADT Audio Channel Pairing Page
36 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 37
Use
this
link
Configuration
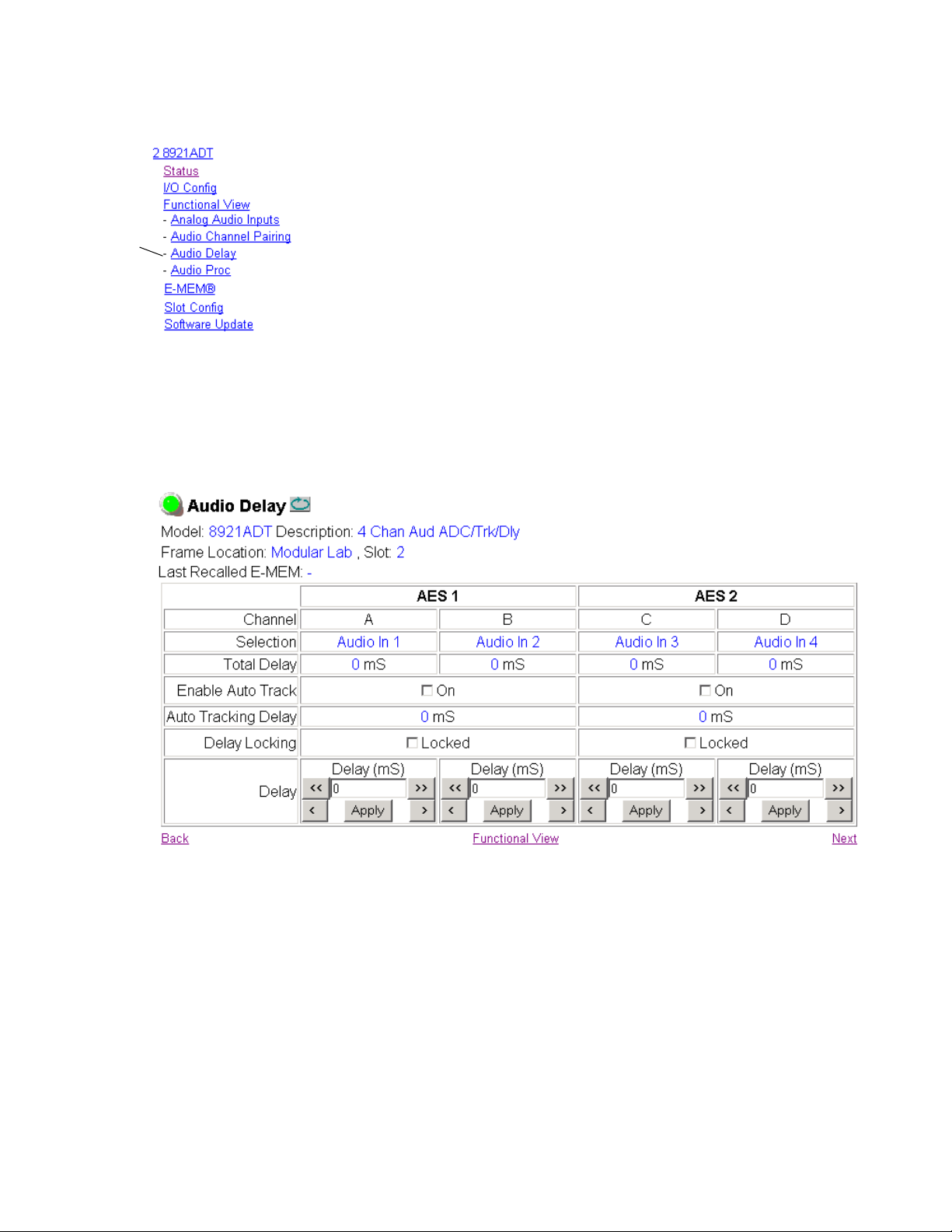
Audio Delay Page
The Audio Delay page (Figure 14) provides delay controls for the AES 1
and AES 2 outputs. Use this page to do the following:
• Enable auto tracking to an external tracking signal from an 8900FSS or
8981FS module input. Select the
either channel.
The amount of auto tracking delay in ms will be shown in the Auto
Tracking Delay boxes for both channels.
• Set manual delay for each output channel with the Delay controls at the
bottom of the page. AES 1 A and B and AES 2 C and D can also be
adjusted together by selecting the corresponding
Delay Locking areas for each channel.
The total amount of delay for each channel is reported in the Total
Delay boxes.
Figure 14. 8921ADT Audio Delay Page
On checkbox to enable auto-tracking for
Locked checkbox in the
8921ADT Instruction Manual 37
Page 38

Configuration
Audio Proc Page
The Audio Proc page (Figure 15) reports the following for each AES output
channel:
•Presence of audio input signal (True = > – 40 dBFS)
Use
this
link
•Clip status of audio input signal (True = > – 0.5 dBFS)
Use the Audio Proc page to make the following adjustments:
•Processing – set the output processing mode for AES 1 and AES 2 from
the corresponding Processing pulldown. Refer to Output Processing
Modes on page 18 for an overview of each output processing mode.
Note Also set the on-board AES1 and AES2 Mode rotary switches on the front of
the module to match your settings. Refer to Set Output Processing Modes on
page 27. If defaults are recalled, the module will default to the local settings.
•AES Output Resolution – set the output resolution to 20 or 24 bit for
AES 1 and AES 2. This setting will override the on-board settings made
at jumpers J13 and J14 (Table 1 on page 8 and Figure 1 on page 9).
•Gain – adjust the output gain in dB for each channel with the corresponding
Output gains can also be adjusted in pairs (AES 1 A and B, AES 2 C and
D) by selecting the corresponding
area and adjusting either
•Output Sample Rate – the default output sample rate for AES 1 and
AES 2 of
Gain controls.
Locked checkbox in the Gain Locking
Gain control in the pair.
48kHz will be reported (read only).
Figure 15. 8921ADT Audio Proc Page
38 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 39

E-MEM Page
The E-MEM page (Figure 16) provides local operations for learning and
recalling the current user configuration. File operations are also available
for saving or loading the saved files to and from a hard disk or other accessible media. Defaults can also be recalled from this page.
Configuration
Use
this
link
Local Operations
To save the current module configuration to the E-MEM register stored on
the module, select the
Local Operations E-MEM register by selecting the
Recalled E-MEM field will report E-MEM as shown in Figure 16.
Figure 16. 8921ADT E-MEM Page
Learn button. Recall a configuration stored in the
Recall button. The Last
File Operations
Current module configurations and the E-MEM configuration can also be
saved and recalled to/from a file for storage in another location outside of
the frame.
To save the current configuration or E-MEM to a file:
1. Select the Save to... button under the Current or E-MEM row.
2. This will bring up a File Download screen (Figure 17 on page 40).
3. Follow the prompts and select the Save this file to disk button and OK.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 39
Page 40

Configuration
Figure 17. E-MEM Save to Operation
4. In the resulting Save As dialog box, the default file name can be
changed to an identifying name for the file, such as Audio_Studio_1.
Browse to the folder where you want to save the configuration and
select
Save. The file saves as a .mcm file type.
40 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 41

Configuration
To load a saved file from a location outside of the frame:
1. Select the Load from ... button under File Operations in the Current or
E-MEM row.
This will bring up the Load Current Config page (Figure 18) or the Load
E-MEM page (not shown).
2. Browse to the location of the file you wish to load and select the file.
Select the
the Enter filename box.
3. Once the correct path and filename is loaded, select the Load button on
the Load Current Config or Load E-MEM page.
4. This will place the recalled configuration from the file into the module.
The
Figure 18. Load Current Config Page
Open button to load the file or enter the filename and path in
Last Recalled E-MEM field will report File.
Recall Defaults
Default settings for the module can be recalled by selecting the Recall
Defaults
tings given in the Default column in Table 4 on page 22. The
E-MEM
Note Default settings for Sample Rate, AES Output Resolution, and Output Pro-
button on the main E-MEM page. The defaults will revert to the set-
Last Recalled
field will report Default.
cessing Mode will match the hardware jumper settings made in Module
On-board Jumper Settings on page 8 during installation. Default settings for
the AES 1 and AES 2 output processing modes will match the setting on the
AES 1 and AES 2 rotary switches on the front of the module.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 41
Page 42

Configuration
Use
this
link
Slot Config Page
Use the Slot Config page (Figure 19 on page 43) to perform the following
functions on the 8921ADT module:
•
Locate Module – selecting the On pulldown flashes the yellow COMM
and CONF LEDs on the front of the module so it can be located in the
frame.
•
Slot Identification – You may identify the module by typing a specific
name in the
module and travels with the 8900NET module if it is moved to another
frame. Select
•
Slot Memory – the slot configuration for each media module is automati-
cally saved periodically (once an hour) to the 8900NET module in that
frame. You may also select the
save the current configuration for this slot. The configuration is saved
on the 8900NET module. If the 8900NET module is removed or
powered down, the stored configurations are not saved.
Name field. The assigned name is stored on the 8900NET
Default to enter the factory default module name.
Learn Module Config button at any time to
When the
ration saved to this slot is saved as slot memory. When the current
module is removed and another module of the same type is installed,
the configuration saved to the 8900NET module will be downloaded to
the new module. The box must be checked before the current module
with the saved configuration is removed.
•
Hardware Switch Controls – a read-only status report of 8900NET module
switch settings for Module Status Reporting and Asynchronous Status
Reporting. These functions must be enabled for the following Slot
SNMP Trap Reports to function.
•
Slot SNMP Trap Reports – displayed only when the SNMP Agent software
has been installed on the 8900NET module. Slot SNMP traps can be
enabled only when the hardware switches for Module Fault reporting
and Asynchronous Status reporting are in enabled on the 8900NET
module (dipswitch S1 segment 7 and dipswitch S2 segment 1).
The enabled SNMP traps will be reported to any SNMP manager that
is identified as an SNMP Report Destination in 8900NET configuration.
Trap severity is read-only hard-coded information that is interpreted
and responded to by the SNMP Manager software configuration.
SNMP reporting can be also be disabled for individual signal inputs on
the I/O Config and Video Composite In web pages.
Restore upon Install box has been checked, the current configu-
42 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 43

Figure 19. 8921ADT Slot Config Page
Configuration
8921ADT Instruction Manual 43
Page 44

Configuration
Use
this
link
Software Update Page
The Software update page (Figure 20) allows updating of software from
remote locations such as a CD-ROM or the Grass Valley web site. For
instructions on updating to the latest software, refer first to the 8921ADT
Release Notes that accompany the software update for compete details.
Updating with this method requires the use of an ftp server application
available from the Grass Valley web site. Refer to the 8900NET Network
Interface Instruction Manual for instructions for installing and using the ftp
server application.
Software updates may also be performed using the NetConfig application
available from Grass Valley. Refer to the NetConfig Instruction Manual for
more information.
Figure 20. 8921ADT Software Update Page
44 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 45

Control Panel Configuration
An external control panel is available to interface over the network to the
8921ADT module. The configuration functions available with the Grass
Valley Newton Control System are summarized in Table 4 on page 22. In
addition, the Control Panel mnemonics that will appear with each available function are given in the table.
Note Not all configuration parameters may be available with the Control Panel.
Installation, configuration, and operation of the Newton Modular Control
System is provided in a separate manual provided with option.
Configuration
8921ADT Instruction Manual 45
Page 46

Specifications
Specifications
Table 7. 8921ADT Specifications
Parameter Value
Reference Input
Number of inputs 1 loop-through
Impedance 75 Ω
Connector type BNC loop-through
Input return loss > 40 dB 10 kHz to 10 MHz @ 75 Ω
Common mode input voltage ± 1 V maximum
Differential DC ± 0.25 V maximum
Common mode rejection ratio > 35 dB @ 50/60 Hz
Free run frequency accuracy ± 20 ppm of selected sampling frequency
Reference input types:
48 kHz sample rate
AES3ID or Word Clock
Video (NTSC/PAL)
Tracking I/O (jumper J5 set for Trk In and J6 set for Trk Out)
Number of inputs/outputs 1 input and 1 output
Input/output type Conforms to RS-232 levels and impedance
Analog Input s
Number of inputs 4 balanced
Impedance > 22 k Ω
Common mode input voltage 20 V maximum
Differential DC ± 0.25 V maximum
Common mode rejection ratio > 72 dB, 20 Hz to 20 kHz
Connector type 3-pin mini-terminal strip
Digital Outputs
Balanced (jumpers J2, J3, and J4 set to Bal)
Number of outputs 3 balanced for AES1 and 3 balanced for AES 2 outputs
Signal type AES3-1992
Output voltage level 3 V p-p ± 0.2 V @ 110 Ω
Output impedance 110 Ω
Output return loss > 25 dB (100 kHz to 6 MHz)
Output rise/fall time 5 ns to 30 ns with 110 Ω load
Connector type 3-pin mini-terminal strip
AES3ID level = 1V p-p nominal, 200 mV to 2 V p-p
Word clock level = 2.5 V p-p nominal, 200 mV to 5 V p-p
Capture range = ± 100 ppm (48 kHz ± 4.8 Hz)
Locks to video within ± 50 ppm of the nominal video rate for
SMPTE170M/NTSC and CCIR624?PAL. NTSC can use SMPTE318M-1999 signal on line 15 to sync AES blocks. (Downstream equipment may not be able to
lock to this wide of range.)
Level = 1 V p-p nominal
46 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 47

Specifications
Table 7. 8921ADT Specifications
Parameter Value
Unbalanced (jumpers J2, J3, and J4 set to Un)
Number of outputs
Signal type AES3id-2001
Output voltage level 1 V p-p ± 0.2 V @ 75 Ω
Output impedance 75 Ω
Output return loss > 15 dB (100 kHz to 6 MHz)
Output rise/fall time 37 ns ± 7 ns @ 75 Ω
Connector type BNC with 8900-A-CBL option (package of four 3 terminal to dual BNC cables)
Bit Resolution 20 or 24 bit
Sample rate 48 kHz
Delay, minimum and maximum and
resolution
A/D Audio Performance
Signal/Noise ratio
THD+noise, swept 20 Hz - 20 kHz < - 75 dB, 20 to 20 kHz @ + 28 dBu
Interchannel crosstalk < - 95 dB, 20 Hz to 20 kHz
Intermodulation distortion < - 100 dB, CCIF 2-tone test, 19 and 20 kHz tones
Frequency response ± 0.1 dB, relative to 1 kHz, 20 Hz to 20 kHz
Interchannel gain mismatch 1 dB, (correctable to 0.1 dB)
DC offset ± 1 mV
Emphasis Not supported
Static withstand 5 kV (330 Ω, 150 pF) for any input or output
Output resolution 24 bits
Environmental
Frame temperature range 0 to 45 degrees C
Operating humidity range 0 to 90% non-condensing
Non-operating temperature - 10 to 70 degrees C
Mechanical
Frame type Gecko 8900 Audio
Power
Power consumption < 4.7 W
6 unbalanced (with cable adapter) plus 1 additional AES3id output for each AES
stream if tracking input and output BNCs not used.
Minimum = 530 µs
Maximum = 5 sec @ 48 kHz sample rate
Step size = 2 ms
> 107 dB. 20 Hz to 20 KHz
> 110 dB A weighted
8921ADT Instruction Manual 47
Page 48

Functional Description
Functional Description
Refer to the block diagram in Figure 21 for the following functional
description.
The 8921ADT receives four channels of balanced analog audio differentially to reduce common mode interference. The audio inputs are converted into single-ended signals that feed a gain amplifier where the
maximum input levels can be adjusted to just below the clip point for the
analog to digital converter.
Figure 21. 8921ADT Functional Block Diagram
Maximum Input
Level Adjust
Balanced Analog
Audio Inputs
Channel
Pairing
Delay Adjust
Output
Processing
AES 1/ 2
Gain
Status Bits
Audio
In 1
Audio
In 2
Audio
In 3
Audio
In 4
Reference
In
Frame
Bus
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
Gain Amplifiers
Sync Separator
Microcontroller
Fault
Pwr Comm
LEDs
A-D Convertion
Conf
Deserializers
Generator
Genlock Timing
Ovr
Silence Tone
Input
Timing
to Module
Level Detection
Multiplexer (4 x 4 Router)
> -40 dBFS/Clip 1-4
Ch 1/2
Delay Adjust
Ch 3/4
1 kHz/400 Hz
Ton e Gen
Input
Control
to Module
Control and Status Registers
Input 1-4 LEDs
Trk O n
Locked
LEDs
Output Drivers
Gain and AES Output
Output Drivers
RS232
Tracking
Data I/O
AES 1 Mode
Control
Bank 2 LED
Switch
Bal/Unbal
Trk In
Switch
Bal/Unbal
Trk Out
AES 2 Mode
Control Paddle
AES 1
Out
AES 2
Out
8204_01
48 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 49

Functional Description
The outputs from the gain amplifiers are converted back to a differential
signal before being applied to the A-D converter inputs. The output of the
A-D converter is a serial bit stream which is deserialized into two 24-bit
parallel words in the deserializer block.
A level detection circuit reports when the output is above – 40 dBFS and
near or above clipping on the front panel controls and the web pages.
The multiplexer acts as a 4 x 4 router. Each channel can be routed to any one
of the four channels in the output AES streams with the channel pairing
control.
The output channels from the routing multiplexer are then stored in delay
memory where user-selected delay can be added in increments of 2 mseconds.
The channels then enter the gain and AES output section where the audio
processing controls can be used to set the desired output mode such as
inversion, summing etc. The AES 1 and AES 2 gain can be adjusted after
processing has been defined. The channels are serialized and formatted
into an AES stream then sent on to the output drivers.
The output drivers drive either balanced 110 ohm cables or 75 ohm coaxial
cable depending on the selected output format. If no tracking input or
output is required, two unbalanced AES outputs are available on the TRK
IN/AES 1and TRK OUT/AES 2 BNCS.
The reference input uses loop-through BNCs. The AES or AES word clock
and sync from the reference input signal are stripped and the signal is sent
to a genlock circuit that locks 27 MHz to the input. This clock is then used
to generate all internal and AES timing signals.
The microcontroller handles communications with the frame bus and contains the program for controlling and monitoring the module. Switch settings and read and write registers are read by the microcontroller to
perform user adjustments and report status to the user.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 49
Page 50

Service
Service
The 8921ADT modules make extensive use of surface-mount technology
and programmed parts to achieve compact size and adherence to
demanding technical specifications. Circuit modules should not be serviced in the field unless directed otherwise by Customer Service.
If your module is not operating correctly, proceed as follows:
•Check frame and module power and signal present LEDs.
•Verify power at the voltage testpoints (see Figure 22) and check fuse if
no voltage is detected.
•Check for presence and quality of input signals.
•Verify that source equipment is operating correctly.
•Check cable connections.
•Check output connections for correct I/O mapping (correct input connector is used for the corresponding channel output).
Refer to Figure 5 for the location of PWR LED and Table 3 on page 15 for
proper LED indications.
If the module is still not operating correctly, replace it with a known good
spare and return the faulty module to a designated Grass Valley repair
depot. Call your Grass Valley representative for depot location.
Refer to the Contacting Grass Valley at the front of this document for the
Grass Valley Customer Service Information number.
Figure 22. 8921ADT Fuse and Voltage Testpoint Locations
F1
Fuses: 2 A Slow
125 V
F2
8204_07
50 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 51

Status Monitoring
This section provides a summary of status monitoring and reporting for a
Gecko 8900 Series system. It also summarizes what status items are
reported and how to enable/disable reporting of each item. There are a
number of ways to monitor status of modules, power supplies, fans and
other status items depending on the method of monitoring being used.
8900 Frame status will report the following items:
• Power supply health,
• Status of fans in the frame front cover,
•Temperature,
•Module health, and
• Frame bus status.
Module health status will report the following items:
• Internal module state (and state of submodule or options enabled)
Status Monitoring
including configuration errors (warning), internal faults, and normal
operation (Pass).
• Signal input states including valid/present (pass), not present or
invalid (warning), not monitored, and not available (no signal inputs).
•Reference input states including locked/valid (pass), not
locked/invalid (warning), and not monitored.
• Signal output states with reporting functionality (reference output).
LEDs
LEDs on modules in the frame and on the front of the 8900TF/TFN frames
indicate status of the frame and the installed power supplies, fans in the
front covers, and modules. (The 8900TX-V/A frames have no LED indicators on the front cover.)
When a red FAULT LED is lit on a frame front cover, the fault will also be
reported on the 8900NET or Frame Monitor module. The LEDs on the front
of these modules can then be read to determine the following fault conditions:
• Power Supply 1 and 2 health,
• Fan rotation status,
• Frame over-temperature condition,
• Frame Bus fault (8900NET only), and
•Module health bus.
8921ADT Instruction Manual 51
Page 52

Status Monitoring
Frame Alarm
In general, LED colors used on the frame and modules indicate:
•Green = normal operation, (Pass) or signal present, module locked.
•Red – On continuously = fault condition, flashing = configuration error.
•Yellow – On continuously = active condition (configuration mode or
communication), flashing in sequence = module locator function.
Status LEDs for this module are described in Operation Indicator LEDs on
page 15. LEDs for the 8900NET module are described in the 8900NET
Network Interface Instruction Manual.
A Frame Alarm connection is available on pins 8 and 9 of the RS-232 connector on the rear of the 8900 frame (Frame Monitor or 8900NET Network
Interface module required). This will report any of the status items enabled
with the 8900NET or Frame Monitor module configuration DIP switch.
Connection and use of the Frame Alarm is covered in detail in the 8900NET
Network Interface Instruction Manual.
Web Browser Interface
When the 8900NET module is installed in the frame, a web browser GUI
can indicate frame and module status on the following web pages:
• Frame Status page – reports overall frame and module status in graphical and text formats.
•Module Status page – shows specific input and reference signal status
to the module along with enabled options and module versions.
•A Status LED icon on each web page to report communication status
for the frame slot and acts as a link to the Status page where warnings
and faults are displayed (8900NET version 3.0 or later).
In general, graphics and text colors used indicate the following:
•Green = Pass – signal or reference present, no problems detected.
•Red = Fault – fault condition.
•Yellow = Warning – signal is absent, has errors, or is mis-configured.
•Gray = Not monitored (older 8900 module).
•White = Not present.
Status reporting for the frame is enabled or disabled with the configuration
DIP switches on the 8900NET module. Most module status reporting items
can be enabled or disabled on individual configuration web pages.
52 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 53

SNMP Reporting
The Gecko 8900 Series system uses the Simple Network Monitoring Protocol (SNMP) internet standard for reporting status information to remote
monitoring stations. When SNMP Agent software is installed on the
8900NET module, enabled status reports are sent to an SNMP Manager
such as the Grass Valley’s NetCentral application.
There are both hardware and software report enable switches for each
report. Both must be enabled for the report to be sent. Software report
switches are set on the 8900NET Configuration page for the Frame, the
8900NET module, and each module slot. Refer to the 8900NET Network
Interface Instruction Manual for installation instructions.
Status Monitoring
8921ADT Instruction Manual 53
Page 54

Status Monitoring
54 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 55

Index
Symbols
>-40 dBFS/CLIP LEDs 15
Numerics
8900 frame
frame alarm
module capacity 10
status reporting 51
8900-A-CBL option 7
8900NET module
installation
8921ADT
block diagram
features 7
specifications 46
A
AES audio outputs
balanced
jumper settings
gain adjustments
configuration summary
local controls 27
overview 20
remote controls 38
output resolution
jumper setting
unbalanced 12
jumper settings 8
AES outputs
specification
analog audio inputs
cabling
configuration summary 22
setting maximum levels
local controls
remote controls 35
specification 46
Analog Audio Inputs web page 35
audio channel pairing
52
10
48
8
8
46
12
26
23
configuration summary
local controls 26
overview 17
remote controls 36
Audio Channel Pairing web page 36
audio delay
configuration summary
local controls 27
overview 17
remote controls 37
Audio Delay web page 37
Audio Proc web page 38
auto tracking
cabling
configuration summary 23
enabling
overview 20
13
local controls
remote controls 37
26
22
22
B
backplane 11
BANK 2 LED 15, 25
C
COMM LED 15
CONF LED 15, 26
configuration
Local, onboard
overview 16
Remote, GUI 28
summary table 22
connectors 11
control panel
configuration
mneumonics 22
Control rotary switch
accessing banks
controller module 10
25
45
25
8921ADT Instruction Manual 55
Page 56

Index
D
documentation online 28
web site 2
E
E-MEM
description
load from file 41
web page 39
enable SNMP 53
environmental 47
39
F
factory defaults
overview
recall factory defaults
configuration summary
local control 26
remote controls 41
summary table 22
FAQ database 2
FAULT LED
states
troubleshooting 51
Frame Controller module 10
Frame Status page 52
frequently asked questions 2
functional description 48
Functional View web page 33
fuse 50
21
24
15
G
Gecko frame 10, 47
graphical user interface (GUI) 30
Grass Valley
website
2
I
I/O Config web page 32
INPUT 1-4 LEDs 15
installation 8
J
jumpers, on-board 8
L
LEDs
front edge
Names and Meanings table 15
locate module 42
loop-through 13
15
M
module
controller
installation 10
power supply 10
slots 11
module health status 51
Module Status web page 52
10
N
NetConfig
software updating
Newton Control Panel
configuration summary
overview 45
44
22
O
online documentation
Online Manual Link
web site 2
Online Manual Link 28
options 7
output processing
configuration summary
factory default 21, 38
local controls 27
overview 18
remote controls 38
output resolution
configuration summary
factory default 21
local controls 8
overview 20
28
24
23
56 8921ADT Instruction Manual
Page 57

Index
remote controls 38
output sample rate
factory default
onboard jumper 8
overview 20
remote controls 38
P
power 47
power supply 10
power up 14
PWR LED 15
R
rear connectors 11
reference source
cabling
configuration summary 23
local controls 26
overview 21
remote controls 32
Refresh button 28
REM OVR LED 15
repair depot 50
report enable switches 53
13
21
testpoints 50
Tracking input
cabling
on-board jumper 8
Tracking output
cabling
on-board jumper 8
TRK ON LED 15
troubleshooting 50
13
13
U
user settings
configuration summary
local controls 26
remote controls 39
V
voltage tespoints 50
W
web site
documentation
FAQ database 2
Grass Valley 2
software download 2
2
24
S
Slot Config web page 42
slot memory 42
SNMP reporting
enabling
overview 53
software download from web 2
Software Update web page 44
specifications 46
status monitoring 51
Status web page 31
switches
onboard control
42
25
T
termination 13
8921ADT Instruction Manual 57
Page 58

Index
58 8921ADT Instruction Manual
 Loading...
Loading...