Page 1
8900NET (Net Card)
NETWORK INTERFACE MODULE
Instruction Manual
Software Version 4.4.0
071061207
AUGUST 2011
Page 2

CERTIFICATE
Certificate Number: 510040.001
The Quality System of:
Grass Valley USA, LLC and its Grass Valley Affiliates
Headquarters:
400 Providence Mine Road
Nevada City, CA 95945
United States
15655 SW Greystone Ct.
Beaverton, OR 97006
United States
Brunnenweg 9
D-64331 Weiterstadt
Germany
Kapittelweg 10
4827 HG Breda
The Nederlands
2300 So. Decker Lake Blvd.
Salt Lake City, UT 84119
United States
Including its implementation, meets the requirements of the standard:
ISO 9001:2008
Scope:
The design, manufacture and support of video and audio hardware and software products and related
systems.
This Certificate is valid until: June 14, 2012
This Certificate is valid as of: December 23, 2010
Certified for the first time: June 14, 2000
H. Pierre Sallé
President
KEMA-Registered Quality
The method of operation for quality certification is defined in the KEMA General Terms And Conditions For
Quality And Environmental Management Systems Certifications. Integral publication of this certificate is allowed.
KEMA-Registered Quality, Inc.
4377 County Line Road
Chalfont, PA 18914
Ph: (215)997-4519
Fax: (215)997-3809
CRT 001 042108
ccredited By:
ANAB
A
Page 3

8900NET (Net Card)
NETWORK INTERFACE MODULE
Instruction Manual
Software Version 4.4.0
071061207
AUGUST 2011
Page 4
Contacting Grass Valley
International
Support Centers
Local Support
Centers
(available
during normal
business hours)
France
24 x 7
Australia and New Zealand: +61 1300 721 495 Central/South America: +55 11 5509 3443
Middle East: +971 4 299 64 40 Near East and Africa: +800 8080 2020 or +33 1 48 25 20 20
Europe
+800 8080 2020 or +33 1 48 25 20 20
Hong Kong, Taiwan, Korea, Macau: +852 2531 3058 Indian Subcontinent: +91 22 24933476
Asia
Southeast Asia/Malaysia: +603 7805 3884 Southeast Asia/Singapore: +65 6379 1313
China: +861 0660 159 450 Japan: +81 3 5484 6868
Belarus, Russia, Tadzikistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan: +7 095 2580924 225 Switzerland: +41 1 487 80 02
S. Europe/Italy-Roma: +39 06 87 20 35 28 -Milan: +39 02 48 41 46 58 S. Europe/Spain: +34 91 512 03 50
Benelux/Belgium: +32 (0) 2 334 90 30 Benelux/Netherlands: +31 (0) 35 62 38 42 1 N. Europe: +45 45 96 88 70
Germany, Austria, Eastern Europe: +49 6150 104 444 UK, Ireland, Israel: +44 118 923 0499
Copyright © Grass Valley USA, LLC. All rights reserved.
This product may be covered by one or more U.S. and foreign patents.
United States/Canada
24 x 7
+1 800 547 8949 or +1 530 478 4148
Grass Valley Web Site
The www.grassvalley.com web site offers the following:
Online User Documentation — Current versions of product catalogs, brochures,
data sheets, ordering guides, planning guides, manuals, and release notes
in .pdf format can be downloaded.
FAQ Database — Solutions to problems and troubleshooting efforts can be
found by searching our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) database.
Software Downloads — Download software updates, drivers, and patches.
4 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 5

Contents
Preface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
8900NET Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Remote Control Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Basic Network Design. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
8900NET Module Alarm DIP Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Module Placement in the Gecko 8900 and GeckoFlex Frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
RS-232 Communication Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Ethernet Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Power Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
8900NET Module Indicator LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Establishing Frame Network Identity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
NetConfig Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Good Networking Practices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Setting Frame Network Identity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Network Configuration Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Web Browser Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Web Browser Notes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Addressing the Frame URL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Default MAC (machine) Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Status Monitoring and Reporting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
External Frame Alarm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Module Health Bus Reporting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
LED Status Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Web Browser Status Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
SNMP Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Using the 8900NET GUI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8900 Frame GUI Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Frame Status Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Older 8900 Module Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Frame Configuration Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Frame Connections Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Frame Alarm Reporting Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
LED Reporting Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
SNMP Reporting Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Power Supply/Demand Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Frame Power Supply Web Pages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
8900NET Module Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
8900NET Module Status Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
8900NET Module Configuration Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
8900NET Network Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Media Module Slot Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 5
Page 6

Contents
Upgrading 8900NET Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
8900NET Software to Part Number Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Acquiring Module Software Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Troubleshooting GUI Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
LogPrint Procedure From Gecko/GeckoFlex Frame. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Temperature Sensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
ROM and RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Ethernet Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
RS-232 Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Module Health Bus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Frame Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Module Present Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Fan Speed Control and Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
On-board Regulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Compatibility Matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Control and Monitoring Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Control and Monitoring Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
8900–FLOAD–CBL Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
8900NET Software Update From FTP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
FTP Method Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
FTP Software Update Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Password Protection for Software Upgrades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Upgrading Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Unsupported Software Updates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
6 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 7

Preface
About This Manual
This manual describes the features of a specific 8900 module as part of the
Gecko and GeckoFlex Signal Processing System families As part of this
module family, it is subject to Safety and Regulatory Compliance described
in the Gecko 8900 Frames Instruction Manual and the GeckoFlex Frames
8900FX/FF/FFN Signal Processing System Instruction Manual.
These manuals can be found on-line in PDF format at this link:
www.grassvalley.com/docs/modular
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 7
Page 8

Preface
8 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 9

8900NET (Net Card) Network Interface Module
Introduction
The 8900NET (Net Card) Network Interface module provides control and
monitor access to the Gecko 8900 and GeckoFlex frames and the
audio/video media modules in the frames through a web browser graph
ical user interface (GUI), the Newton Control Panel, and SNMP management applications.
Note Version 4.4.0 8900NET software can only run on printed circuit boards with
part numbers 771-0121-00/-01/-02 and -03. For older 8900NET modules
with part numbers 671-4852-00/-01 use software version 4.3.0.
8900NET Features
-
The 8900NET module features:
• 10 Base-T Ethernet interface,
• Fan front cover power and control,
• Support for the following:
• Software update downloading
• Newton Modular Control system control panels
• Frame Alarm connector on rear of module
• Asset Tag identification
• HTML protocol
• Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) monitoring
• NetConfig Networking Configuration application
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 9
Page 10
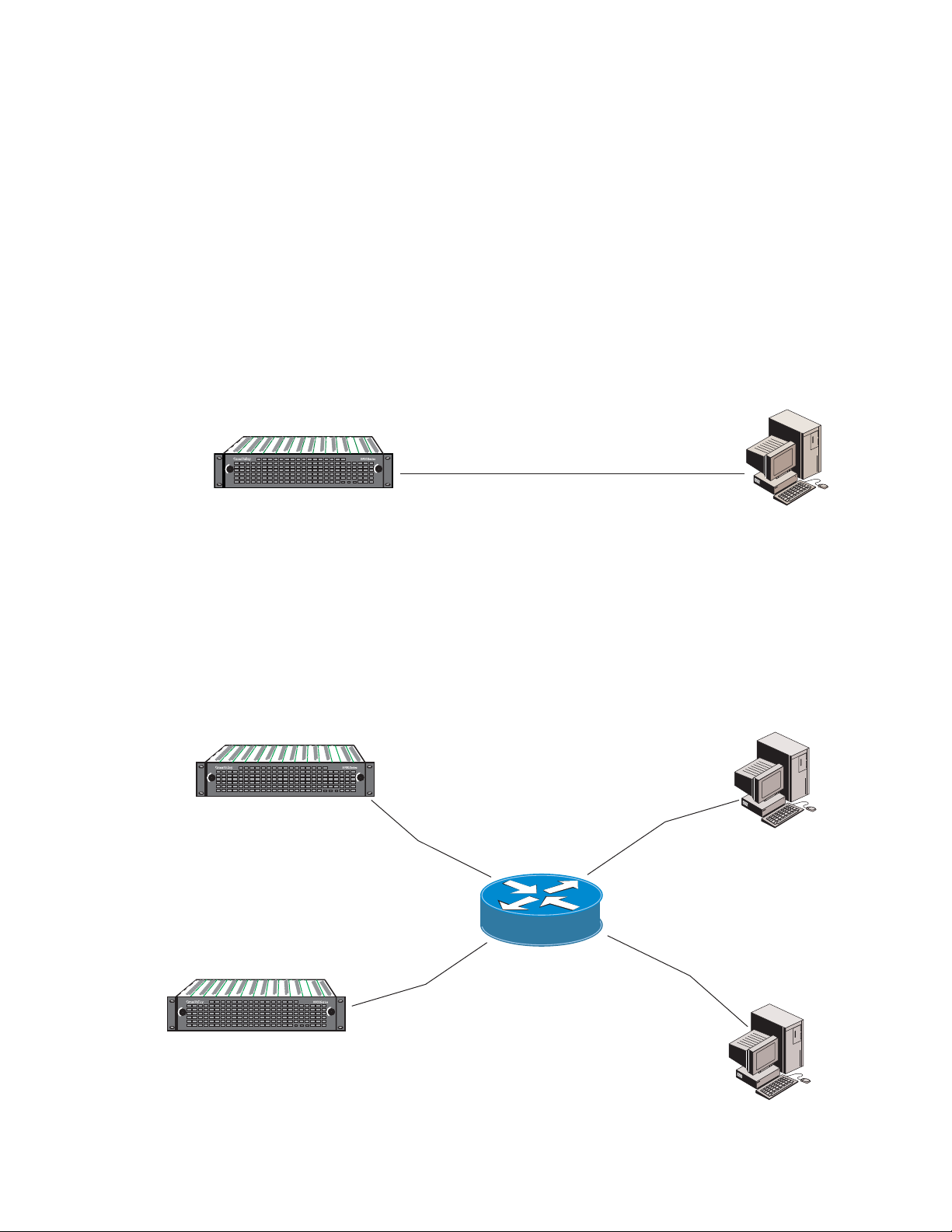
Introduction
0612-07r1
LAN Ethernet Hub
8900 frame with
Network In ter face Module
PS 1 PS 2
LOCK
LOCK
FAULT
8900 frame with
Network In ter face Module
PS 1 PS 2
LOCK
LOCK
FAULT
Ethernet cable: Category 5
PC runnin g:
Windows 2000/XP OS,
Un ix, or Macin tos h OS
Ethernet
Web brows er :
In ternet Explor e r,
version 6.0 or later
or an y compatible
web brows e r
Remote Control Panels
Basic Network Design
The 8900NET module with version 3.2.0 or later software allows the frame
to be remotely controlled by the Newton Control Panel via the Ethernet
port. Refer to the Newton Control Panel documentation for details.
The 8900NET module can be employed in either a point-to-point or local
area network (LAN) control/monitoring configuration.
Figure 1 illustrates
a point-to-point configuration.
Figure 1. Point-to-point Configuration
0612-08r1
LOCK
8900 frame with
Network In ter face Module
Figure 2 illustrates a typical LAN configuration.
Figure 2. Basic Network Configuration
LOCK
PS 1 PS 2
FAULT
Ethernet cable, Category 5 Crossover
PC runnin g:
Windows 2000/XP OS,
Un ix, or Macin tos h OS
Ethernet
Web brows er :
In ternet Explor e r,
version 6.0 or later
or an y compatible
web brows e r
10 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 11
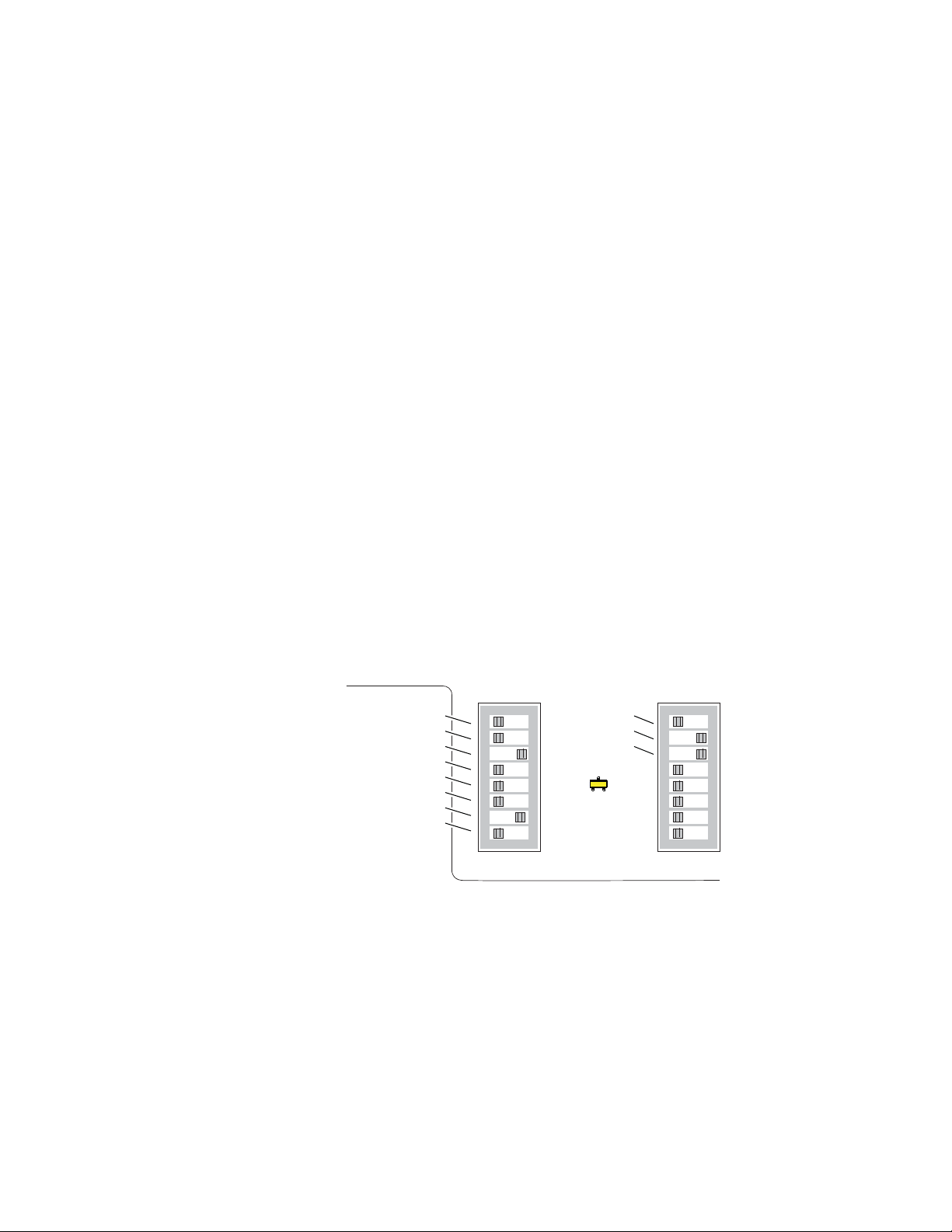
Installation
8900NET Module Alarm DIP Switches
Installation
This section describes placing the module in Gecko 8900 and GeckoFlex
frames and cabling the communications ports for all frame types. Proce
dures for DIP switch settings, installation, and cabling of the module are
described in this section.
An 8900NET module will come installed in Gecko 8900TF/TFN and
GeckoFlex 8900FF/FFN frames. Note that there are two DIP switches
described below that will affect reporting to the 8900NET module, the
external RS-232 Frame Alarm, and the SNMP reporting system.
Note The GeckoFlex frame requires an 8900NET module running 4.0.0 or later
software. See 8900NET Software to Part Number Guide on page 66.
There are two eight-position DIP switches (S1 and S2) on the 8900NET
module for enabling or disabling the overall status reporting of the frame
and modules.
Figure 3 illustrates the DIP switches set with the factory
defaults and Tab le 1 on page 12 gives the function of each DIP switch set-
ting. You may enable or disable reporting functions from this point.
Note Some web page and frame alarm and SNMP reporting functions must be
enabled on the DIP switches to be functional.
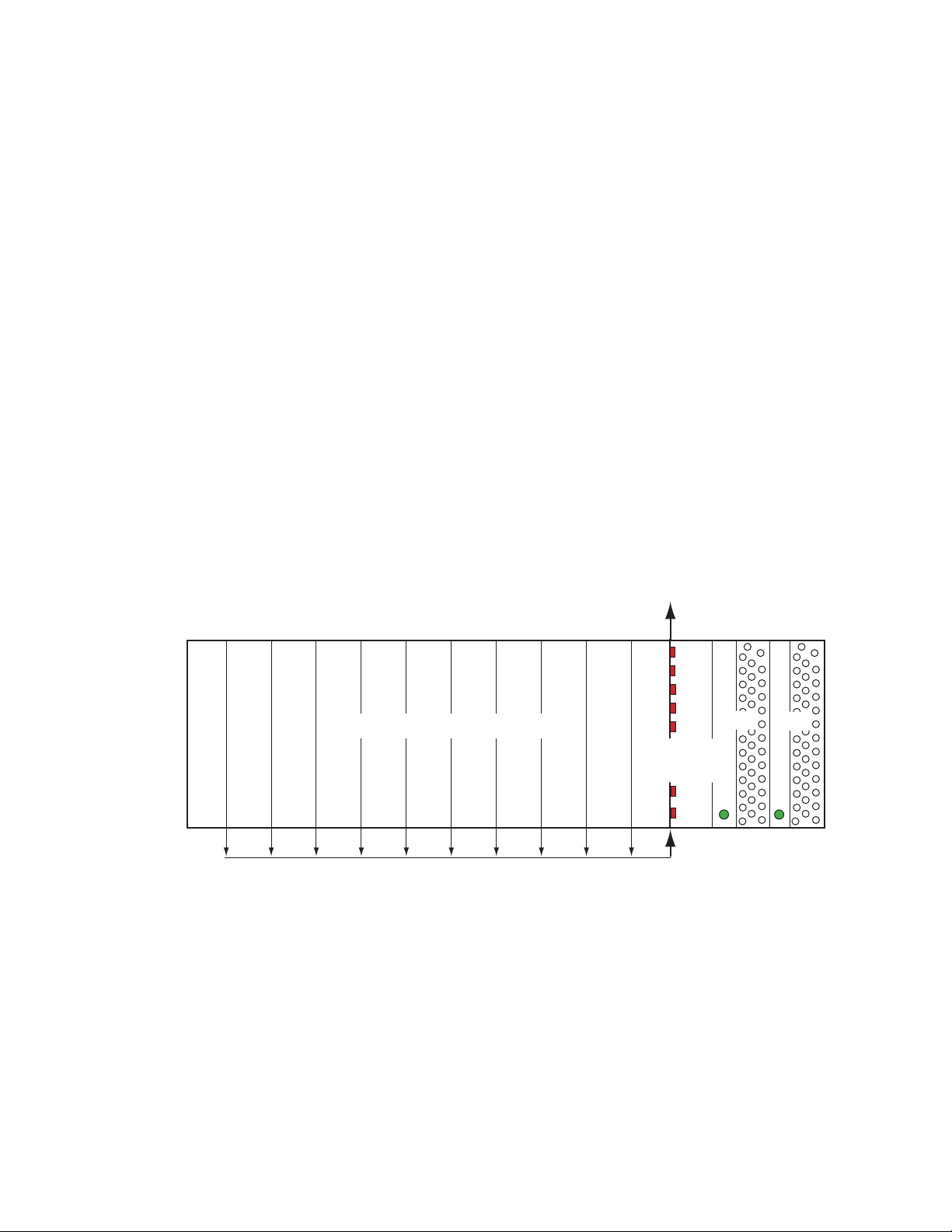
Figure 3. Alarm Reporting DIP Switches (Defaults Shown)
S2S1
Power Supply #1
Power Supply #2
Temperature (not used)
Fan
Module
Frame Bus
Fan Speed
NM Control
12345678
Status
IP Address
Frame Control
Remote
Override
LED
8900NET
12345678
0612_28r2
The current status of the DIP switch settings is always reported on the
8900NET Status (
page 56), Frame Alarm Reporting (page 42), LED
Reporting (page 49), and SNMP Reporting (page 48) frame web pages. You
may check DIP switch status on these web pages instead of pulling out the
module.
Refer to Figure 12 on page 20 for the location of S1 and S2 on the 8900NET
module and Tab le 2 on page 21 for the possible settings. A settings table is
also silk-screened on the bottom of the module. Disabling (or filtering) of
fault reports can sometimes be useful in isolating problems in the frame.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 11
Page 12
Installation
Table 1. 8900NET Module DIP Switches
S1
Segment
1 PS1 Fault Reporting Enabled PS1 Fault Reporting Disabled
2 PS2 Fault Reporting Enabled PS2 Fault Reporting Disabled
3 (Not used) Over Temp reporting is always enabled locally and through SNMP
4 Fan Fault Reporting Enabled Fan Fault Reporting Disabled
5 Module Fault Reporting Enabled Module Fault Reporting Disabled
6 Frame Bus Error Reporting Enabled Frame Bus Error Reporting Disabled
7 Fan Speed Controlled by Temperature Fan Speed Fixed at Maximum
8
S2
Segment
1 Status Enabled (enabled alarms are reported over SNMP) SNMP Reporting is disabled except for Over Temp alarm
2 IP Address (not currently supported)
3 Frame Control Enabled (remote control via GUI is enabled) GUI for the frame and all modules within is placed in read only mode
4 – 8 (Currently Not Used)
Network Module Control Enabled (remote control via GUI is
enabled)
Left Position (Enabled) Right Position (Disabled)
Network Module GUI is placed in read only mode
Left Position (open) Right Position (closed)
Note Disabled faults are still detected by the network GUI but LEDs will be inactive.
Refer to Status Monitoring and Reporting on page 27, for an overview of
overall status reporting from the Gecko and GeckoFlex frames, 8900NET,
power supplies, and media modules in the frame.
Module Placement in the Gecko 8900 and GeckoFlex Frame
There are ten cell locations in the frame to accommodate media modules.
These are the left ten locations. Refer to
with no cover).
The two cells on the right are allocated for the power supplies. For additional information concerning the Power Supply modules, refer to the 8900
Frames Instruction Manual and the GeckoFlex Frames Instruction Manual.
Note Gecko and GeckoFlex frames do not use the same power supply. Refer to
Power Supply/Demand Web Page on page 52.
The third cell from the right is allocated for the 8900NET Network Interface
or Frame Monitor module (GeckoFlex 8900FF and Gecko 8900TF-V/A). For
additional information concerning the Frame Monitor module, refer to the
8900 Frames Instruction Manual or the GeckoFlex Frames Instruction Manual.
Figure 4 (Gecko 8900 frame shown
12 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 13
Installation
Frame Monitor
or 8900NET Network
Interface Module (only)
Any 8900 Module
Power
Supplies
(only)
0612_04r1
0612 -16r0
S1
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
432
1
Configuration DIP switches
Component side
Figure 4. Gecko 8900 Series Frame
Note The 8900NET module can be plugged in and removed from an 8900 frame
with power on. When power is applied to the module, LED indicators reflect
the initialization process (see Power Up on page 20).
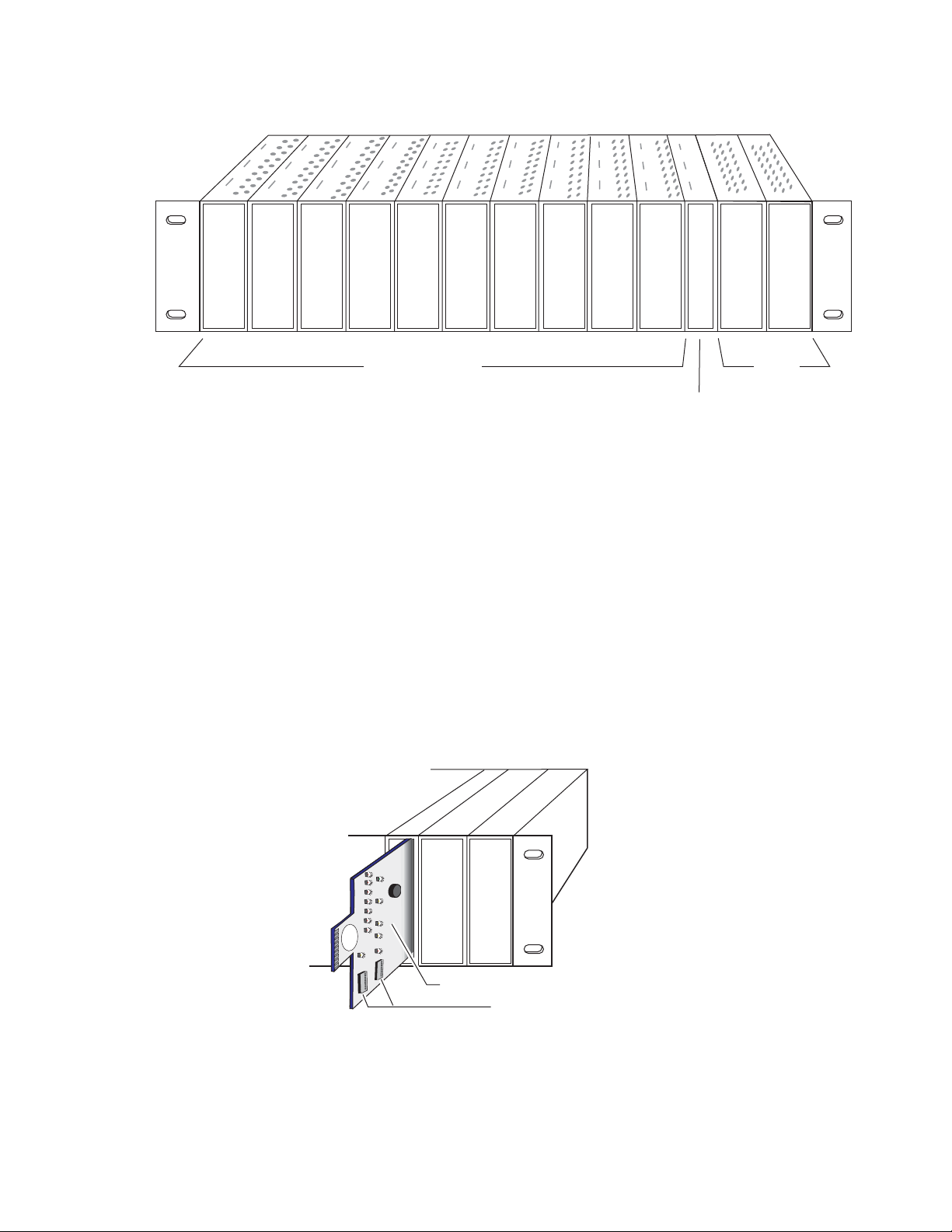
To install the 8900NET module in the frame:
1. Insert the module, connector end first (see Figure 5), with the
component side of the module facing to the right side of the frame.
Instead of an ejector tab, the 8900NET module has a connector tab with
a circular finger-hole for pulling the module.
2. Verify that the module connector seats properly and securely against
the backplane.
Figure 5. Module/Frame Orientation
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 13
Page 14
Installation
Cabling
This section describes physical connections, the connectors and cables,
used for network communications. Setup procedures for each type of con
nection are described in Using the 8900NET GUI on page 34.
An example of control and monitoring connectors on the frame rear are
illustrated in
Figure 6 for the Gecko 8900 frame and Figure 7 for the
GeckoFlex frame.
Note There are variations for the AC rears in the Gecko 8900 and GeckoFlex Series.
Refer to the manual for you specific frame if the information is not covered
here.
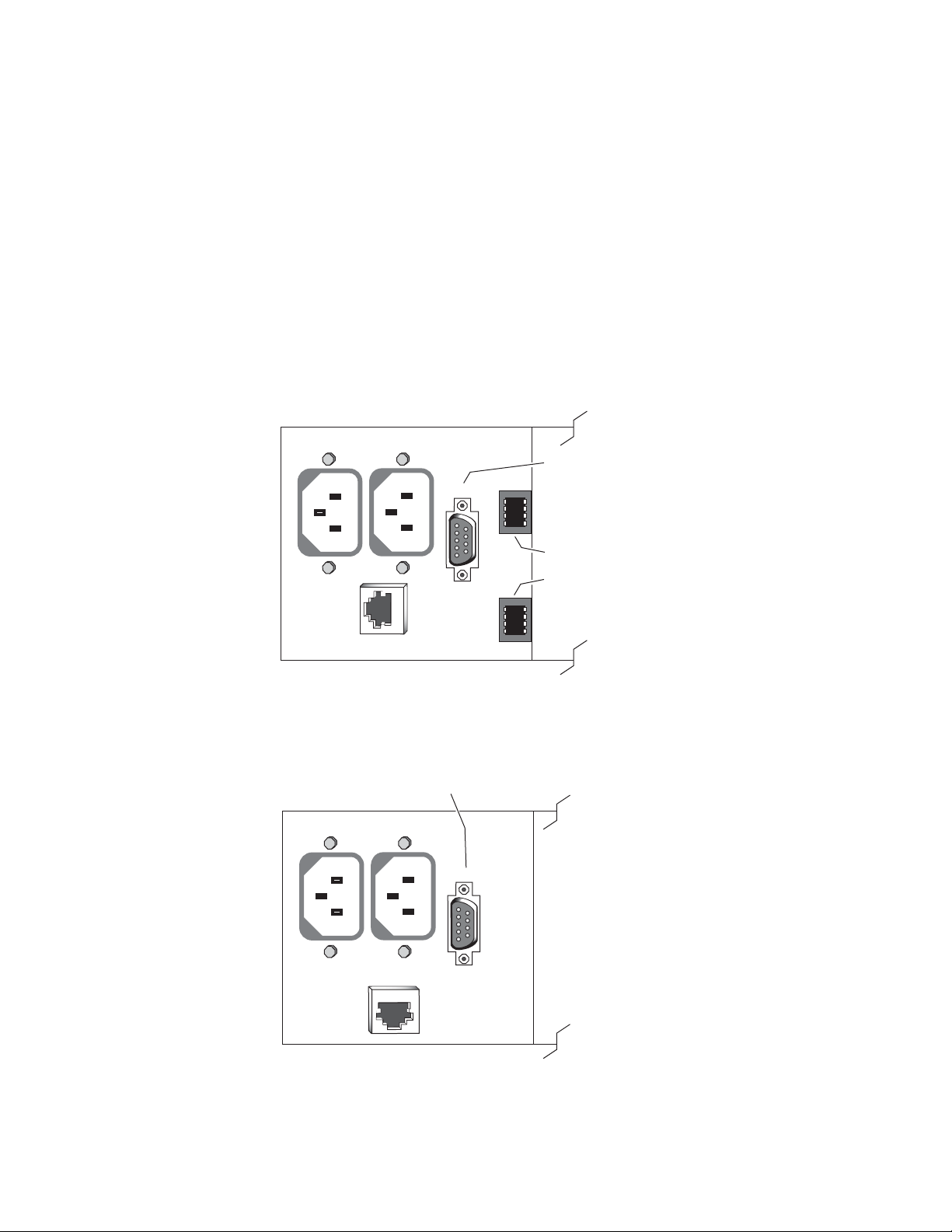
Figure 6. 8900NET Input/Output Connectors on 8900TFN -V/-A Frame
Frame Alarm
RS232
(Video Frame – J102 pins 8 and 9)
(Audio Frame – J7 pins 8 and 9)
-
J1 J2
Network configuration storage
Frame ID
(Frame MAC address storage)
ETHERNET
Figure 7. 8900NET Input/Output Connectors on GeckoFlex Frames
Frame Alarm - J102 pins 8 and 9
RS232
J102
J1 J2
0612_31r1
ETHERNET J103
0612_32r1
14 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 15

RS-232 Communication Port
The RS-232 port on the rear of 8900 frames is used for two purposes: an
output for an external Frame Alarm and to set initial frame communication
parameters. Both of these uses are described below.
Note Earlier version 8900 frames used a BNC connector labeled SMPTE ALARM to
access the frame alarm connection. For information concerning the SMPTE
Alarm bus cable, refer to the 8900 Frames Instruction Manual.
Frame Alarm
The Frame Alarm can be accessed through pins 8 and 9 of the RS-232 connector. The Frame Alarm outputs a continuous or pulsing voltage level to
indicate alarm status. The type of voltage output is selected on the Frame
Alarm Reporting web page. This voltage output is connected to an external
device that responds to a voltage level for displaying Frame component
(PS1, PS2, Fans) and status and Module Health bus status. Details for con
necting an external customer-supplied alarm are given in the 8900 Frames
Instruction Manual and the GeckoFlex Frames Instruction Manual.
Installation
-
The Frame Alarm responds to conditions enabled on the 8900NET
Network Interface module with DIP switches S1 and S2 as given in
on page 21 and settings made on the Frame Alarm Reporting web page
(Frame Alarm Reporting Web Page on page 42).
Tab le 2
Setup of Frame Communication Parameters
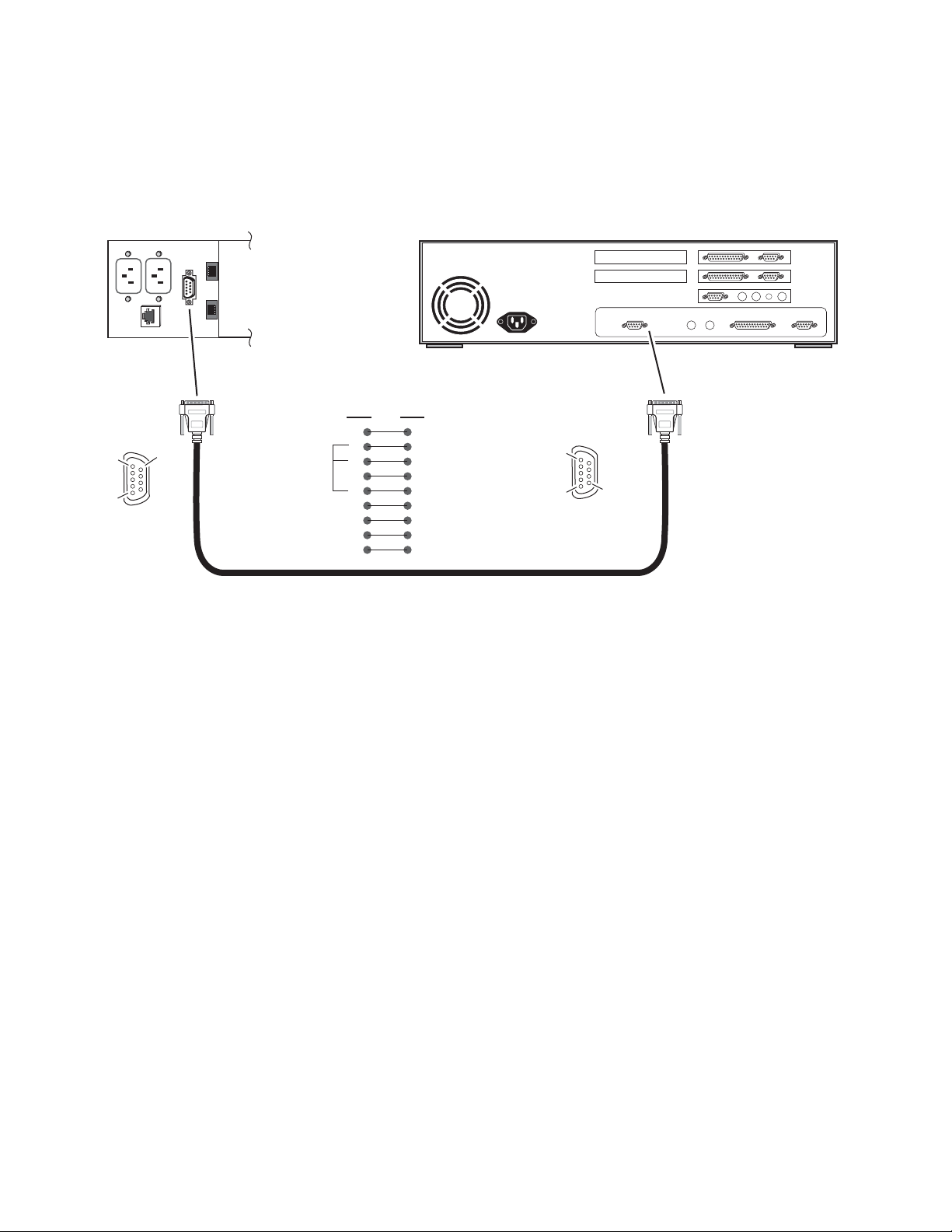
The nine-pin RS-232 connector is also used to connect the frame to a PC to
initially set the frame’s network communication parameters. After network
communication is established, subsequent changes to these parameters can
be made using the network GUI.
CAUTION The RS-232 cable should be removed after completing the initial frame setup.
Leaving a long serial cable connected to the frame without a connection at the
other end may freeze the 8900NET module startup routine.
Note The cable used for this connection is a DB-9F to DB-9M, straight-through
cable available from Grass Valley as part of cable kit model 8900CAB
(10 ft./3 m length).
The communication parameters for the RS-232 connection are:
• Baud rate: 9600
• Data bits: 8
• Parity: none
• Stop bits: 1
• Flow control: none
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 15
Page 16
Installation
8900 Frame
The male end connects to the RS-232 connector on the 8900 frame (see
Figure 8) and the female end connects to either Com1 or Com2 on the PC,
depending upon the configuration of the computer’s I/O ports.
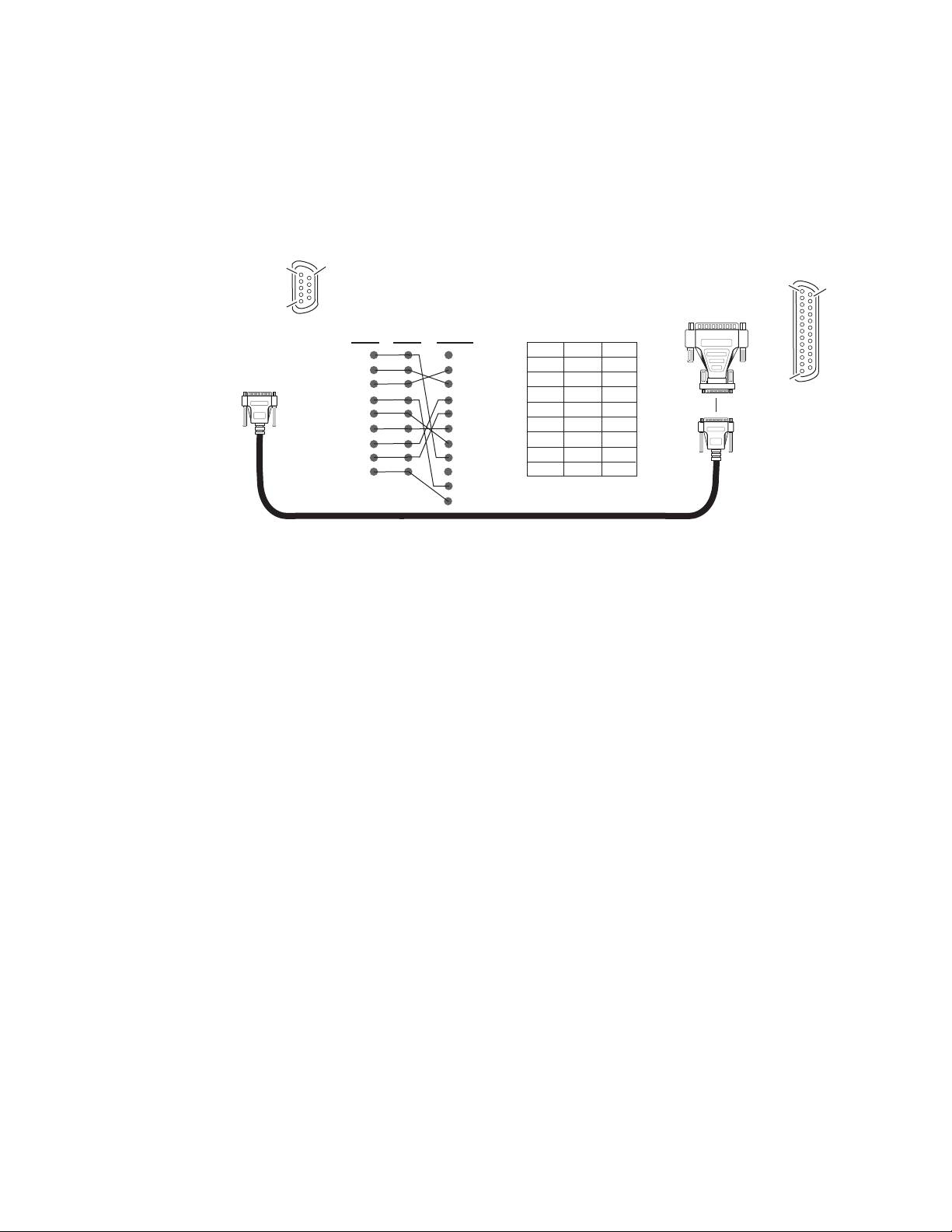
Figure 8. RS-232 to Initialization PC Cable and Pinout
PC running HyperTerminal Emulation
Pin 5
Pin 1
DB-9
Male
Pinout
RS-232
Pin 9
DB-9
Male
Only pins
2,3, & 5
are required
Comm. Parameters: 9600 baud, 8 bits, parity-none, 1 stop, flow-none
Pin Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DB-9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Pin 1
Pin 5
Female
DB-9
Female
Pinout
Com1 or
Com2 port
Pin 9
0612 -09r2
16 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 17
Pin 5
Pin 1
DB-9
Male
Installation
If the PC uses a 25-pin RS-232 connector, use a cable adapter as shown in
Figure 9.
Note The 25-pin adaptor is available from Grass Valley as part of cable kit model
8900CAB.
Figure 9. DB-9 Cable and DB-25 Cable Adaptor Pinout
Pin 9
Pin 1
Pin 13
DB-9
Female
DB-9
Male
Pinout
Tx 2
Rx 3
9-pin
1
4
5
6
7
8
9
25-pin 25-pin9-pin 9-pin9-pin
1
2 Tx
3 Rx
4
5
6
7
8
9
20
22
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DB-25
Female
1
8
2
3
3
2
4
20
5
7
6
6
7
4
8
5
9
22
Pin 14
DB-25
Female
Pinout
0612 -11r0
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 17
Page 18
Installation
8900 Frame
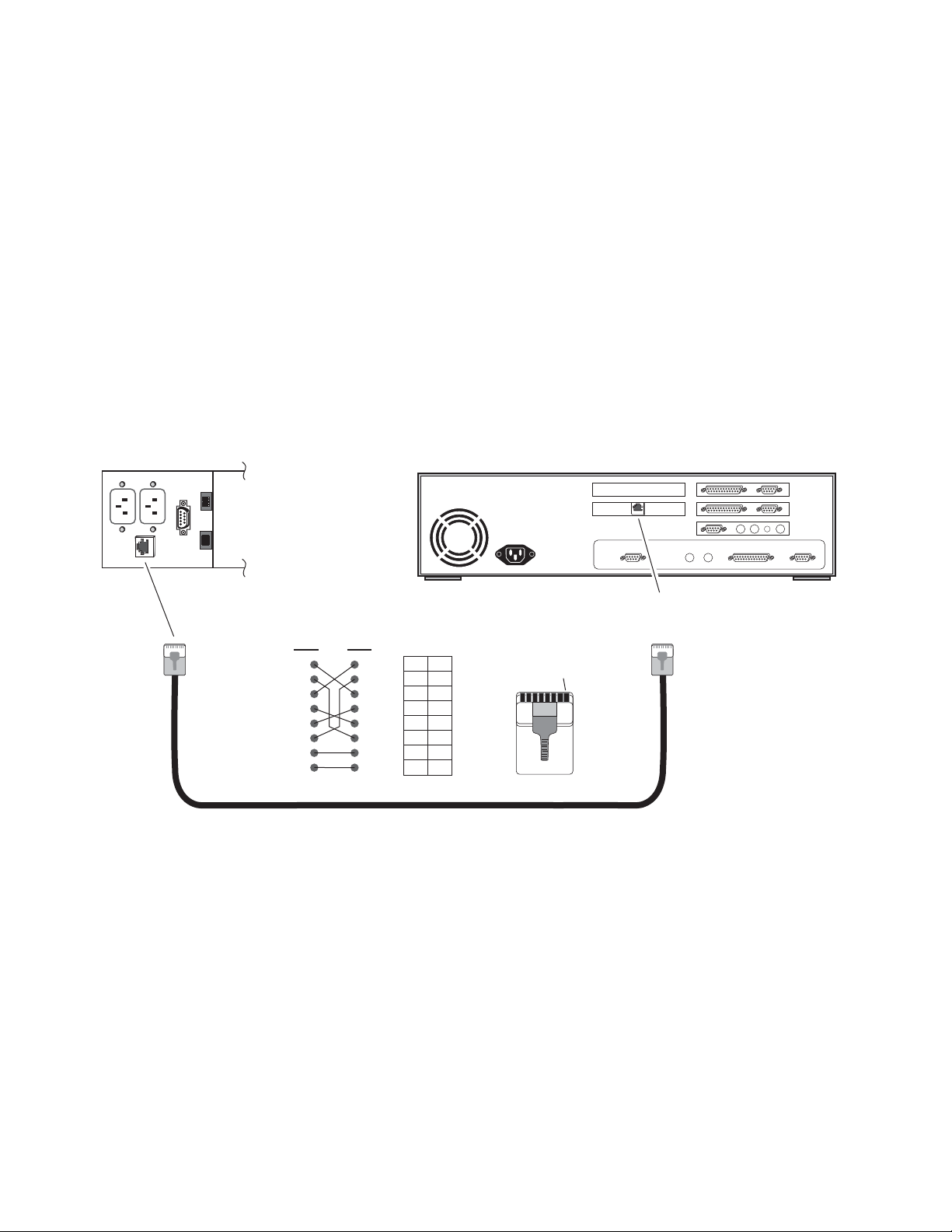
Ethernet Cable
The 8900NET module enables the frame’s RJ-45 Ethernet connector.
Through this port the Gecko frame can connect to:
• A single PC with a network card (point-to-point), or
• A local area network (LAN) through a network hub.
Point-to-Point Connection
Figure 10 illustrates the crossover cable connection and pinout for a
point-to-point connection to the controlling PC.
Note This Category 5, UTP Crossover Cable is available from Grass Valley as part
of cable kit model 8900CAB (10 ft./3 m length).
Figure 10. Point-to-Point RJ-45 Connection and Cable Pinout
PC with network card and net browser software
Ethernet
RJ-45
connector
Pin Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Category 5, UTP Crossover Cable
PinPin
3
1
6
2
1
3
5
4
4
5
2
6
8
7
7
8
Pin 1
To PC network card
RJ-45 connector
RJ-45
connector
0612 -10r1
18 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 19
Installation
8900 Frame
RJ-45
connector
RJ-45
connector
Pin Pin
PinPin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
To network hub
RJ-45 connector
Ethernet
Pin 1
Network Ethernet Hub (typical)
0612 -15r1
Category 5, UTP Cable
8 7
10 BaseT
6 5 4 3 2 1
hp
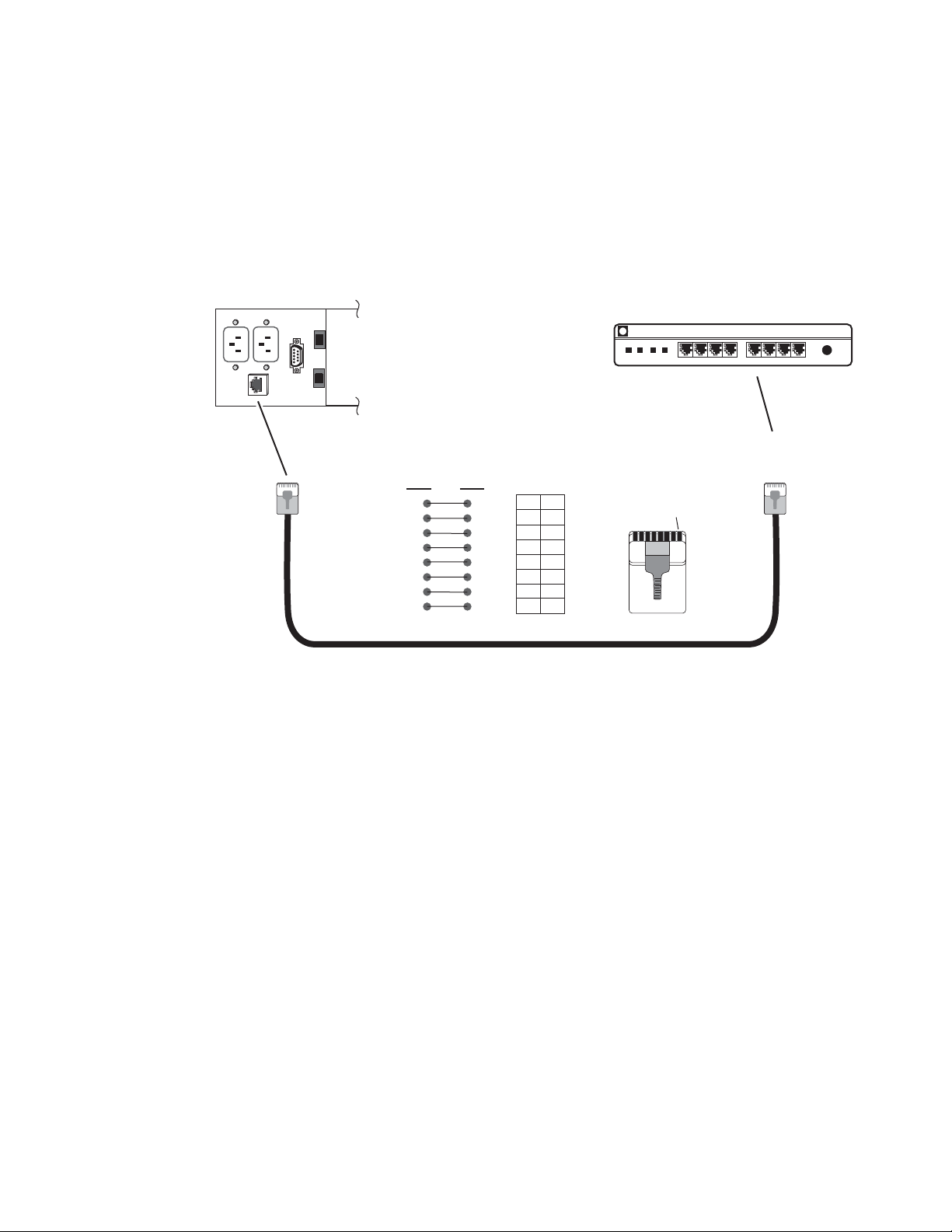
Local Area Network (LAN) Connection
Figure 11 illustrates the cable connection for a LAN connection to a
network hub.
Note Because of varying length requirements and ready availability from network
equipment suppliers, this cable is not supplied by Grass Valley.
Figure 11. LAN RJ-45 Connection and Cable
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 19
Page 20
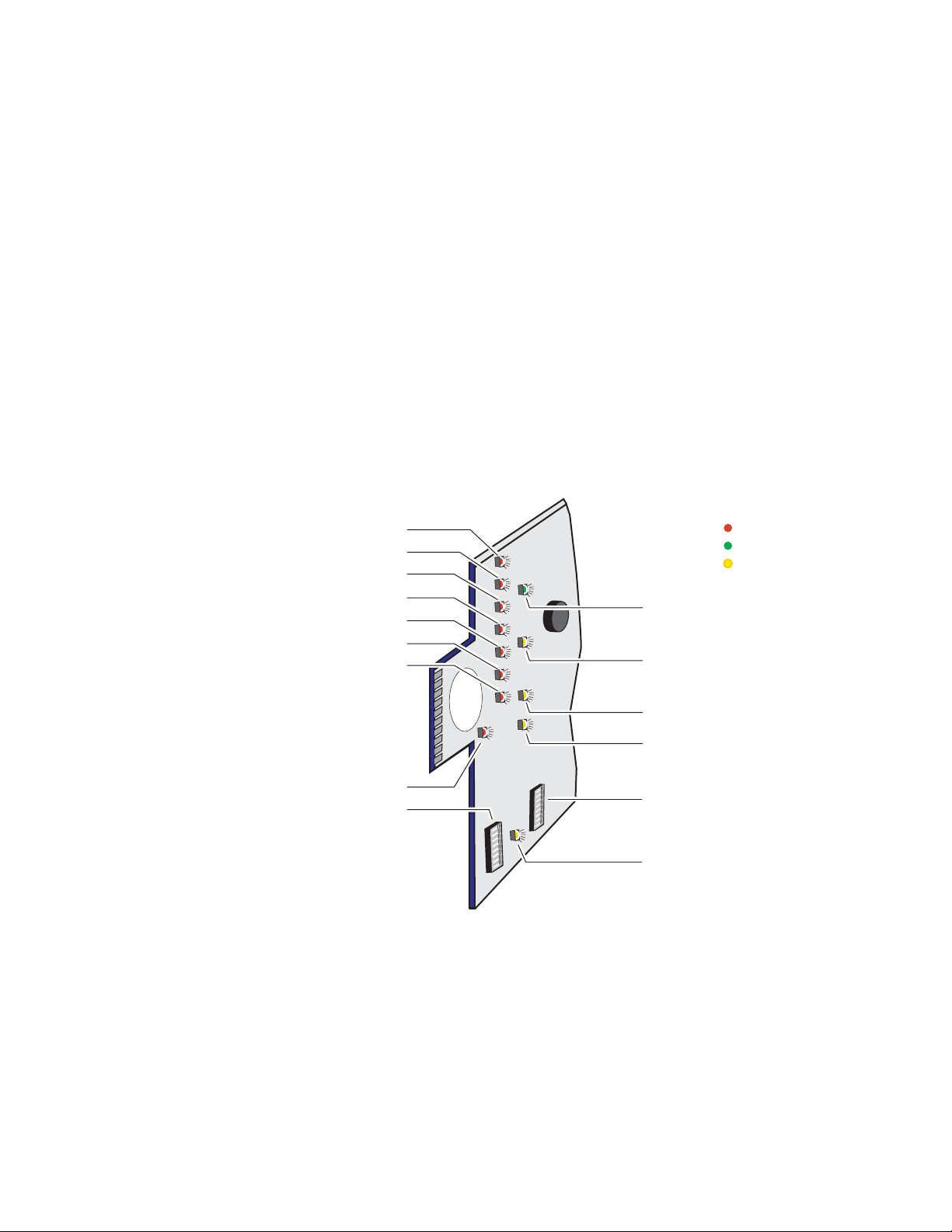
Power Up
Power Up
The various front LED indicators and configuration switches on the
8900NET module are illustrated in
should light for the duration of the initialization process. The frame is
powered up when either of the AC mains connections are made on the rear
of the frame (
Figure 6 on page 14 for Gecko frame and Figure 7 on page 14
for GeckoFlex frame).
After initialization the Power LED will be on and the red Network Module
LED (labeled NM) should be off. All other LEDs report detected fault con
ditions within the frame and the installed modules. If the NM LED does not
go off, the board needs servicing.
Note When a media module is first plugged into an 8900 frame, the 8900NET
module may report a momentary fault. This will clear once the media module
has booted up.
Figure 12. LEDs and Configuration Switches on the 8900NET Module
TEMP - Temperature (red)
PS2 - Power Supply 2 (red)
PS1 - Power Supply 1 (red)
FAN (red)
MOD - Module Health Bus (red)
FB - Frame Bus (red)
NM - Network Interface Module (red)
Figure 12. Upon power-up, all LEDs
LED Color Key
Red = Fault
Green = OK
Yellow = Active
PWR - Power (green)
INHIB - Module Health Inhibited
(yellow)
-
S1
COMM - Communication (yellow)
ETHER - Ethernet communiction
(yellow)
FAULT - Frame Fault (red)
Configuration DIP switch S1
1
2
3
4
65
87
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Configuration DIP switch S2
REM OVR - Remote Override
(yellow)
LEDs on the 8900NET module primarily indicate status items from the
frame and the modules in the frame. Some functions specific to the
8900NET module are also reported (PWR, ETHER, COMM). LED reporting
for each specific LED on the front of the 8900NET module can be disabled
if desired on the LED Reporting web page (
LED Reporting Web Page on
page 48).
Ta bl e 2 on page 21 describes all the module’s LEDs and the conditions indi-
cated.
0612 -06r1
20 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 21
8900NET Module Indicator LEDs
The possible LED status and conditions indicated are shown in Tab le 2.
Table 2. Indicator LEDs and Conditions Indicated
LED LED State Condition
TEMP
(red)
POWER
(green)
PS2
(red)
PS1
(red)
FAN
(red)
MOD
(red)
Long continuous flashing One or more modules is reporting a configuration error
FB
(red)
NM
(red)
INHIB
(yellow)
FAULT
(red)
COMM
(yellow)
ETHER
(yellow)
REM OVR
(yellow)
Off Frame temperature is within specified parameters
On continuously Over-temperature condition detected in frame
Off 8900NET module power is off or on-board regulator has failed
On continuously 8900NET module is powered
Off (Power supply 2 in Slot 13) Normal operation or alarm disabled
On continuously Power supply 2 is present and reporting an alarm condition
Off (Power Supply 1 in Slot 12) Normal operation or alarm disabled
On continuously Power supply 1 is present and reporting an alarm condition
Off (Front cover fans) Normal operation or alarm disabled
On continuously One or more fans in the front cover assembly is not rotating
Off Normal operation or alarm disabled
On continuously Module health bus is not disabled and one or more modules is reporting an internal fault
Off 8900NET module is communicating with modules on the internal frame bus
On Internal frame bus communication failure
Off No fault detected on the 8900NET module
On Fault detected, refer to Frame and module web pages for fault reporting
Off Normal operation or alarm disabled
On continuously A non-compliant module in the frame has disabled the module health bus
Off Normal operation
On continuously One of the on-board fault LEDs on a media module in the frame is illuminated or flashing
Flashing Indicates the MOD (module health LED) is flashing
On Indicates 8900NET module is polling the devices on the internal frame communication bus
On Indicates active communication detected from the 8900NET module on the Ethernet bus
Off All fault reporting is controlled by onboard configuration switches
On Software overrides onboard configuration switches
Power Up
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 21
Page 22

Establishing Frame Network Identity
Establishing Frame Network Identity
The initial configuration of the 8900NET module, using the RS-232 port
(refer to
enable the operation of the Web-based GUI. A PC running a terminal emulation application is used to set the initial parameters for network communication. Once initial identity is established, the GUI can be used to make
subsequent changes to the networking parameters. Parameters established
include:
• Local IP Address,
• Gateway IP Address,
• Subnet Mask, and
•Default Route.
Note If the Gecko frame is to be connected point-to-point to a single PC worksta-
Figure 8 on page 16), establishes the frame’s network identity to
tion, both the frame and the PC must be on the same Subnet.
NetConfig Application
With software release 3.2.0 and later, 8900 frames can interface with NetConfig (Network Configuration Application). NetConfig is a PC software
tool for configuring and setting up NetConfig-enabled Grass Valley
devices. Refer to the NetConfig Instruction Manual or the 8900NET Network
Interface Module Release Notes for current information on using this tool.
Good Networking Practices
The Local IP Address form of a URL can be used within an intranet to
address the 8900 frame’s web page. An intranet is set up and maintained
within your facility and is isolated from the Internet.
Access from outside, through the Internet, may require the use of a Domain
Name and a firewall, depending upon your network architecture. Domain
Name Addressing requires a Domain Name Server located within the
intranet that maps the Domain Name to the frame’s IP Address. The Gecko
frame has no knowledge of its assigned Domain Name. Network traffic
through a Domain Name Server can delay 8900NET response time.
Remote workstations are also subject to network traffic delays. Local PC
workstations should be used for real-time operation of the 8900NET.
The most direct and timely access to the frame is achieved by using a PC
workstation that is assigned to the same Subnet (see
A workstation in a different Subnet, even when located on the same router,
will be subject to processing of the IP Gateway.
22 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Figure 13 on page 23).
Page 23
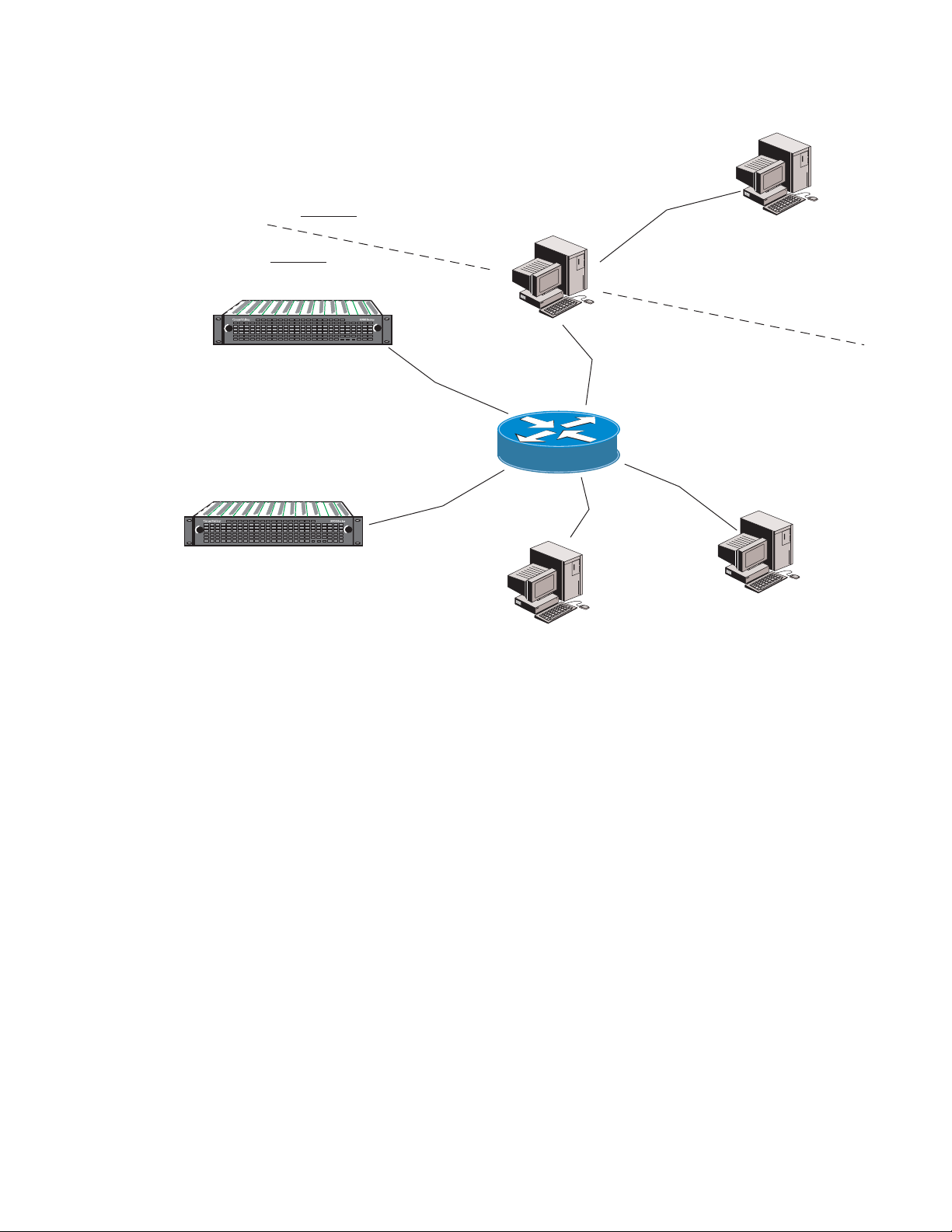
Figure 13. Local IP and Subnet Addressing
0612-17r1
Remote PC
182.1.2.2
IP Gateway
Su b n et 2
182.1.2.1
127.1.2.1
Local PC
127.1.2.5
Router
8900 frame 127.1.2.3
8900 frame 127.1.2.4
FTP Server
127.1.2.6
PS 1 PS 2
LOCK
LOCK
FAULT
PS 1 PS 2
LOCK
LOCK
FAULT
Su b n et 1
Establishing Frame Network Identity
Setting Frame Network Identity
After you have connected the PC to the RS-232 port (refer to Setup of Frame
Communication Parameters on page 15) and established communication
using the terminal emulation application, press the enter/return key
several times to see the active prompt.
At the prompt enter:
setup
You will see:
-> setup
Here are the current parameters and their values:
Local IP Address: 192.168.0.105
Gateway IP Address: 192.168.0.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
If a change is made, it is necessary to reboot
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 23
Page 24

Establishing Frame Network Identity
this machine. This will occur automatically when
you have completed making changes.
Do you wish to change any of the values? y/n (n): y
For each parameter, you will be given the name of the
parameter and its current value in parenthesis. To
change it, just type in the new value. If you don't
wish to change it, just hit the Enter key.
If you make a mistake on a previous value, continue
with the remaining parameters; you will be given an
opportunity to modify the value again.
Please ensure that you change from Factory defaults
to your network parameters.
The local Ip Address is the Internet address of this
machine. It consists of four numbers separated by pe
riods ('.'). Each number can be in the range of 0 to
255. For example: 192.168.0.105
There must an IP address.
-
IP Address (192.168.0.105):
The Default Route is the Internet address of the machine which routes network packets outside of the local network. It consists of four numbers separated by
periods ('.').
Each number can be in the range of 0 to 255.
For example: 192.168.0.1
If you respond with a single period (.),a default
route will not be assigned.
Default Route (192.168.0.1):
The Subnet Mask is used in the routing algorithm.
The Net Card will use the mask to determine if a address is in local net or to send the message to the
default. It consists of four numbers separated by pe
riods ('.').
Each number can be in the range of 0 to 255.
For example: 255.255.255.0
-
If you respond with a single period (.),
a Subnet Mask will not be assigned.
Subnet Mask (255.255.255.0):
24 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 25
Network Configuration Storage
8900NET software version 3.2.0 and later enables storage of the IP
addresses (network configuration) on the frame backplane on frames that
are equipped with storage capability (see
versions of software and frame types with no storage capacity, the IP
addresses are stored on the 8900NET module and stay with the module
when it is moved to another frame.
There are a number of ways to determine what type of frame you have.
Ta bl e 3 lists all available frame types and how they can be identified. The
assembly number of the frame is identified on a label located inside the
frame inside the chassis.
Table 3. Gecko 8900 Frames Types IP Storage Capability
Model Number Backplane Assembly Number
8900TFN-A Audio backplane with 1 IC 610-0960-00 8900NET module
8900TFN-V Video backplane with 1 IC 630-0063-00 8900NET module
8900TFN-A Audio backplane with 2 ICs 610-0960-01 Frame backplane
8900TFN-V Video backplane with 2 ICs 610-0984-00 Frame backplane
8900FFN Frame AC Rear with 2 ICs – Frame backplane
Web Browser Setup
Figure 6 on page 14). In earlier
Network Config
Storage
Web Browser Setup
To determine what frame model you have and where IP addresses are
stored, you may also access the Frame Status page with the web browser
Figure 31 on page 56). All frames with 8900NET cards with software
(see
version 3.2.0 and later will report a Network Config status message as one of
the following:
• Network configuration stored on 8900NET module, or
• Network configuration stored on frame.
The recommended Windows operating systems currently supported for
the web browser interface are Windows 2000, 2007, and XP. The web
browser for use with the 8900NET Control and Monitoring System is any
standard web browser with the same functionality as the ones listed below:
• Netscape Navigator 6.x or later, or
• Internet Explorer 6.x or later.
Versions 5.x or earlier of these browsers may cause undesirable results in
the presentation of HTML frames.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 25
Page 26

Web Browser Setup
Web Browser Notes
Addressing the Frame URL
• If applicable, configure the browser for direct HTTP requests to the
frame rather than addressing a Proxy Web Server. The Modular Frame
Web Server will typically be installed inside the firewall.
• For older Netscape browsers, the Cache should be configured to always
refresh.
To address an 8900 frame from an internet browser, enter the frame’s
default URL into the URL line of the browser (“Location” in Netscape Nav
igator, “Address” in Internet Explorer). The URL will be the IP Address
given to the frame during initial setup (see
page 23), or a Domain name that has been mapped to the IP Address in
your Domain Name Server tables. The URL should look like this:
http://{Frame’s IP Address}/
Setting Frame Network Identity on
-
Example:
http://127.123.234.2/
Or:
http://{Frame’s Domain Name}/
Example:
http://frame1.xyz.com/
The correctly entered URL will call up the Gecko frame’s default first
page—Frame Status.
Default MAC (machine) Address
Each 8900 frame has a unique ethernet physical level MAC address that is
stored in the frame ID memory chip (see
memory is missing, the 8900NET module will substitute a default MAC
address: 08-00-11-09-CD-AB. If more than one 8900 frame in your network
is assigned the default MAC address, network conflicts will occur. To verify
the frame has a unique MAC address refer to
on page 62.
Figure 6 on page 14). If this
8900NET Network Web Page
26 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 27

Status Monitoring and Reporting
This section provides a complete summary of frame and module status
monitoring and reporting in a Gecko or GeckoFlex system with an
8900NET module installed in the frame. It summarizes what status items
are reported and how to enable/disable reporting of each item.
There are a number of ways to monitor status of frame power supplies,
fans, modules in the frame, and other status items depending on the
method of monitoring being used including a voltage level on the external
Frame Alarm from the Module Health bus, module front edge LEDs, web
browser indicators, and SNMP reporting.
Status reporting methods include the following:
• External frame alarm output on the rear of the 8900 frame from the
Module Health Bus and other frame status alarm reporting,
• LEDs on the Frame, 8900NET module, and individual frame media
modules,
• Web browser status reporting for each frame component, and
Status Monitoring and Reporting
• SNMP traps, captured by Grass Valley’s NetCentral or another SNMP
Manager Application.
Note SNMP trap information is only available when an SNMP Agent has been
installed and configured.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 27
Page 28
Status Monitoring and Reporting
External Frame Alarm
The Frame Alarm outputs a voltage level indicating there is an alarm condition on the Module Health Bus or one of the other frame components
reported to the Frame Monitor module in a Gecko 8900TF or GeckoFlex
8900FF frame or the 8900NET module in an 8900TFN and GeckoFlex
8900FFN frame. The type of pulse on the external Frame Alarm can be set
for
Alarm Reporting Web Page on page 42). Refer also to Frame Alarm on page 15
for more details on using this connector.
Module Health Bus Reporting
The Module Health bus (Figure 14) is a separate line on the motherboard
that provides a means for older or less capable modules (such as DAs with
no microprocessor) that cannot communicate over the Frame (serial) bus to
report alarm conditions to the Frame Monitor or 8900NET module. All
media modules in frame slots 1-10 report to this line, unless otherwise
noted.
Continuous or Pulsing on the Frame Alarm Reporting web page (Frame
Figure 14. Module Health Bus
Module Health Bus and other frame component reporting to
External Frame Alarm RS-232 from 8900NET or Frame Monitor Module
Temp
PS2
PS1
Slots 1-10 8900 Front Media Modules
Module Health Bus Line
FAN
MOD
8900NET or
Frame Monitor
FB
Fault
PS1
PS2
The reporting is done using a voltage level sent by the front media module
on the Module Health Bus line to the 8900NET module or Frame Monitor
module. When a problem exists on a front media module, it will send a
voltage level signal to the Module Health bus line indicating that a problem
exists on the module but will not indicate what the problem is. The
8900NET or Frame Monitor module reports this voltage level to the
external Frame Alarm connector on the rear of the frame. The red MOD
LED on the 8900NET or Frame Monitor module will also light (
Figure 14).
0612_33r1
28 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 29

Status Monitoring and Reporting
The following warning and fault conditions on a media module will trigger
a voltage level signal on the Module Health Bus line:
• Internal module state (and state of submodule or options enabled)
including configuration errors (warning) and internal faults.
• Signal input states including monitored signal not present or invalid
(warning).
• Reference input states including locked, not locked/invalid (warning).
• Signal output states with reporting functionality (reference output).
For 8900TFN and GeckoFlex 8900FFN frames with an 8900NET module,
you may determine what is causing the warning condition on the module
by first viewing the Frame Status web page (see
page 34). The status of each module will be reported by color. If a module
is shown in yellow (Warning) or red (Fault), click on the module in the
frame graphic to link to the module Status web page where warning and
fault information will be reported for the that module.
When three or more modules are indicating a warning condition, this may
be reported to the 8900NET module as a Fault condition. This will be
reported on the Frame Status web page (
reporting can be enabled or disabled using the Internal Healthbus control on
the Frame Alarm Reporting web page (
page 42). Disabling this reporting does not disable the actual Module
Health Bus reporting to the Frame Alarm, only status reporting to the
Frame Status web page.
Figure 15 on page 36). This status
Frame Alarm Reporting Web Page on
Frame Status Page on
The Module Health Bus may be completely disabled by:
• Setting DIP switch S1, segment 5 to Disabled (Tab le 1 on p age 12 ), or
• (8900NET module) Unchecking the Module Health Reporting selection
on the Frame Reporting web page (page 42) or the LED Reporting web
page (page 48).
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 29
Page 30

Status Monitoring and Reporting
LED Status Reporting
LEDs on the 8900NET module, media modules in the frame, and on the
front cover of the Gecko (8900TF/TFN-V/-A) and GeckoFlex
(8900FF/FFN) frames indicate fault status of the frame and the installed
power supplies, fans in the front covers, and front media modules.
When the red FAULT LED is lit on an 8900NET module the fault will also
be reported on the frame front cover. The LEDs on the front of the 8900NET
module can then be read to determine the following frame and module
fault conditions:
• Power Supply 1 and 2 health,
• Fan rotation status,
• Frame over-temperature condition,
• Frame Bus fault (8900NET only), and
• Module health Bus status.
In general, LED colors used on the frame and modules indicate:
• Green – normal operation, (Pass) or signal present, module locked.
• Red – On continuously = fault condition, flashing = configuration error.
• Yellow – On continuously = active condition (configuration mode or
communication), flashing in sequence = module locator function.
Status LEDs for the 8900NET module are shown in Figure 12 on page 20
and described in Tab le 2 on page 21. LEDs for the Frame Monitor module
that comes in the 8900TF-V/TF-A or 8900FF frames are described in the
Gecko 8900 Frames Instruction Manual or the GeckoFlex Frames Instruction
Manual.
Status reporting to the LEDs on the front of the 8900NET card can be disabled if desired on the LED Reporting web page. Refer to the LED Reporting
Web Page on page 48 for complete details.
30 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 31

Web Browser Status Reporting
When the 8900NET module is installed in the frame, a web browser GUI
can indicate frame and module status on the following web pages:
• Frame Status web page – reports overall frame and module status in
graphical and text formats. Refer to Frame Status Page on page 34 for
complete details.
• Module Status web page – shows specific input and reference signal
status to the module along with enabled options and module versions.
• A Status LED icon is present on each web page to report communica-
tion status for the frame slot and acts as a link to the Status web page
where warnings and faults are displayed (8900NET version 3.0 or later).
In general, web page graphics and text colors used indicate the following:
• Green = Pass – signal or reference present, no problems detected.
• Red = Fault – fault condition.
• Yellow = Warning – signal is absent, has errors, or is mis-configured.
Status Monitoring and Reporting
• Gray = Not monitored (older 8900 module).
• White = Not present.
Status reporting for the frame is enabled or disabled with the 8900NET
module configuration DIP switches (see
Switches on page 11). Some module status reporting items can also be
enabled or disabled on individual configuration web pages.
8900NET Module Alarm DIP
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 31
Page 32

Status Monitoring and Reporting
SNMP Monitoring
The Grass Valley Modular Control and Monitoring System uses the Simple
Network Monitoring Protocol (SNMP) internet standard for reporting
status information to remote monitoring stations. The SNMP reporting
from the 8900NET module provides status reports (traps) for various frame
and module faults and warnings as described in
Status reports (traps) are unsolicited reports sent from the SNMP Agent to
one or more SNMP Managers such as Grass Valley’s NetCentral. Once an
SNMP agent has been installed, the Gecko frame and each module slot can
be configured to enable or disable these reports through the Frame SNMP
Reporting web page (see
Note Two of the DIP switches described in Table 2 on page 21 must be enabled for
SNMP Trap severity can be one of three degrees:
• Warning – a limitation in the module’s intended performance,
Ta bl e 4 on page 33.
LED Reporting Web Page on page 48).
corresponding SNMP reporting of the system components (S1 segment 5
and S2 segment 1).
• Alarm – a failure in communication with the module, or
• Informational – a configuration change such as a switch setting.
The enabled SNMP traps will be reported to any SNMP manager that is
identified as an SNMP Report Destination in 8900NET configuration (see
8900NET Module Configuration Web Page on page 57. Trap severity is
read-only hard-coded information that is interpreted and responded to by
the SNMP Manager software configuration.
The SNMP traps available on the Gecko frames and modules are outlined
in
Tab le 4 on page 33. The SNMP trap reports available and their severity
are configured on the Gecko Frame SNMP Reporting web page for all
media modules, the 8900NET module, Power Supply 1 and 2, the Frame
Bus Status, and Module Health status (8900TFN Video and GeckoFlex
frames only).
32 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 33

Status Monitoring and Reporting
Table 4. Gecko Frame and Module SNMP Reporting Summary
SNMP Trap Report Trap Severity
Gecko Frame
Frame Bus Status Alarm
Cover Status Warning
Fan Status Alarm
Module Health
Power Supply Fault Alarm
Power Supply Removed Warning
Net Card Status Alarm
Hardware Switch Warning
Slot Fault Alarm
Module Removed Warning
Signal Loss Warning
Reference Loss Warning
Config Error Warning
1
Module Health is not reported on older 8900TFN Audio frames.
1
Frame Power Supply 1 and 2
8900NET Module
Media Modules
Alarm
For the latest MIB (Management Information Base) files for the modular
control system, go to the Grass Valley public ftp site at:
ftp://ftp.grassvalley.com/modular/MIB
Some GeckoFlex modules have additional SNMP controls with the
8900NET version 4.2.0 release. The version 2.0.0 MIB must be used in con
junction with this 8900NET release for the additional.
Details for using these additional controls are included in the specific
module instruction manual.
-
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 33
Page 34

Using the 8900NET GUI
Using the 8900NET GUI
Once the frame’s first web page—Frame Status—has been accessed (see
Figure 15 on page 36), navigation can be done using the hypertext Link List
in the left column. The Link List is a two-tier list with the frame’s devices
at the highest tier and sub-pages for each device in a secondary tier
(sub-list) below the parent device.
To navigate from device to device, click on a device link. This will open the
device’s Status web page and open the sub-list of device web pages. You
can also click on the slot icon in the content display to access a particular
module’s Status web page.
To navigate to one of the device’s web pages click on any of the device’s
sub-list of links. This will update the content display to the right.
Note To update status, web pages must be manually refreshed by clicking on the
Refresh button (to the right of the page title and shown at left). Changes
made at the frame or from other browsers or when a module has been
removed and reinstalled, will not be displayed until the page is refreshed.
8900 Frame GUI Interface
This section describes the web browser interface for the Gecko and
GeckoFlex frames.
Frame Status Page
The Frame Status web page (Figure 15 on page 36) displays an overall
status for the frame.
The top section reports the following for the frame:
• Model Number,
• Description,
• Frame Location is defined on Frame Configuration web page on
page 39,
• Temperature Status (Pass or Fault),
• Frame Health Alarm status (Pass, Warn, or Alarm),
• Power Status indicates the power demand status from the Power
Supply/Demand web page (page 52),
• Front Cover status (Cover Installed or No Cover), and
• Fan Status (On or Fault)
34 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 35

Using the 8900NET GUI
The graphical content frame display shows:
• Module slot status and media module status,
• Power supplies installed (and empty slots),
• Presence of the 8900NET module (Net Card), and
• A clickable link to each device’s status page.
Module Slot Status
Module Slot Status icons report one of the following (Tab le 5):
Table 5. Module Status Indicators
Icon
Color
White None Empty No module detected in slot.
Gray No Comm No Comm Slot contains a legacy module which was not designed to support Frame Bus
Green Pass Module Slot contains a fully Frame Bus capable module.
Yellow Warning Module 8900NET has detected a warning condition in module due to lack of input sig-
Red Fault Module 8900NET has detected a fault condition in module. Fault may have been com-
Module
Status
Icon Text Indication
communications with an 8900NET module.
nal or incomplete support for remote monitoring and control. Ability of module
to perform intended operation is limited.
municated over the Frame Bus, or may indicate a failure of the module to
respond over the Frame Bus.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 35
Page 36

Using the 8900NET GUI
0612-12r5
The Links section lists the frame and its current modules. The selected link's Status
page is first displayed and the sub-list of links for the selection is opened. The sub-list
allows you to select a particular information page for the selected device.
Content display section dis
plays the information page
for the selected frame or module (frame slot icons are also
active links).
Refresh button for manual
refresh of page
Figure 15. 8900NET GUI for Frame Control
During initial polling, modules that do not respond immediately may transition to a WARNING, MODULE NOT RESPONDING status. In this case, this is a temporary status until a maximum number of sequential attempts fail and a
Fault is reported.
Note The first release of 8960DEC module code causes a Fault condition because
it never responds on the Frame Bus. There is no way for the 8900NET module
to tell the difference between a fully functional early release of 8960DEC and
a module whose Frame Bus Interface has failed.
Note Early releases of the 8960ENC, 8950DAC, 8950ADC, 8920DAC, 8920ADC,
and the 8916 signal a warning condition due to limited capability over the
Frame Bus. All of these, except the 8916, can be upgraded by the user with
fully capable Frame Bus software.
36 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 37

Frame Properties
The Properties section on the Frame Status page reports:
•Vendor name,
• Number of media module slots,
• Software version (installed on the 8900NET module),
• Network Config (whether the network configuration is stored on the
8900NET module or on the frame backplane, depending on frame
model). Refer to Network Configuration Storage on page 25.
Older 8900 Module Support
8900 and other module type (8500/8800) Grass Valley modules that can
reside in 8900 frames are supported to different degrees by the 8900NET
module. A compatibility matrix describing the hardware versions, software
update methods required, and remote control features of the various
modules supported by the 8900 frames and 8900NET module is located in
the
Compatibility Matrix on page 85.
Using the 8900NET GUI
Note When the 8900NET is first installed or when many modules are installed
simultaneously, it may take some time for the 8900NET to poll, update status
and build the HTML pages, especially if there are modules that do not
respond as expected, such as 8500/8800 modules. During these periods the
Frame Status Page may fall behind temporarily until the 8900NET board can
catch up and present a true current status. This process of background web
page loading can be disabled with the control discussed on page 57.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 37
Page 38

Using the 8900NET GUI
Pin 10 Pin 50
0612-18r0
Pin 2
Top of Module
Pin 50
Removed
Typical
8500/8800 Module Support
Installation of 8500 and 8800 modules shipped prior to November 15, 1999
will cause interruption of the Gecko and GeckoFlex frame communication
bus. Modules shipped after this date have pins removed in the rear con
nector to provide compatibility. Compatible modules can be identified by
the absence of connector pins 10 and 50 (see
Figure 16). Incompatible
legacy modules can be returned to Grass Valley for upgrade to the new connector.
Note If an unmodified legacy module is installed in the frame, the frame commu-
nication bus will be interrupted and all module icons in the frame status
display will be red. This problem occurs with legacy modules only and does
not occur with other 8900 Series modules.
Figure 16. Modified Legacy Module Connector
-
38 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 39

Frame Configuration Web Page
Use
this
link
Use the Frame Configuration web page shown in Figure 17 on page 40 to
do the following for the frame:
Locate Frame – Select the Flash radio button in the Locate Frame function to
•
flash the front cover FAULT Indicator LED on the 8900NET module on
and off with a 50 ms duty cycle to help locate the 8900 frame.
Note This function can also be performed using the NetConfig application. For Net-
Config, right click on the frame name in the menu tree on the left side of the
NetConfig screen and select Identify Device.
• Save/Load Frame Configuration File – save a frame configuration to a file by
clicking on the
default file (FrameConfigData.mcm) and the name cannot currently be
changed. Follow the file download instructions for saving the file. This
file can be recalled on this or any other networked 8900 frame to create
a duplicate configuration.
Save To button. A frame configuration is saved to a
Using the 8900NET GUI
Use the
a path and file name into the display. Select the
Browse button to locate a saved frame configuration file or enter
Load button to load the
selected configuration to the frame.
Frame Identification – enter any name, an index number (for SNMP
•
reporting), and a location name to identify a frame. You may also use
the factory default frame name or location by selecting either
button.
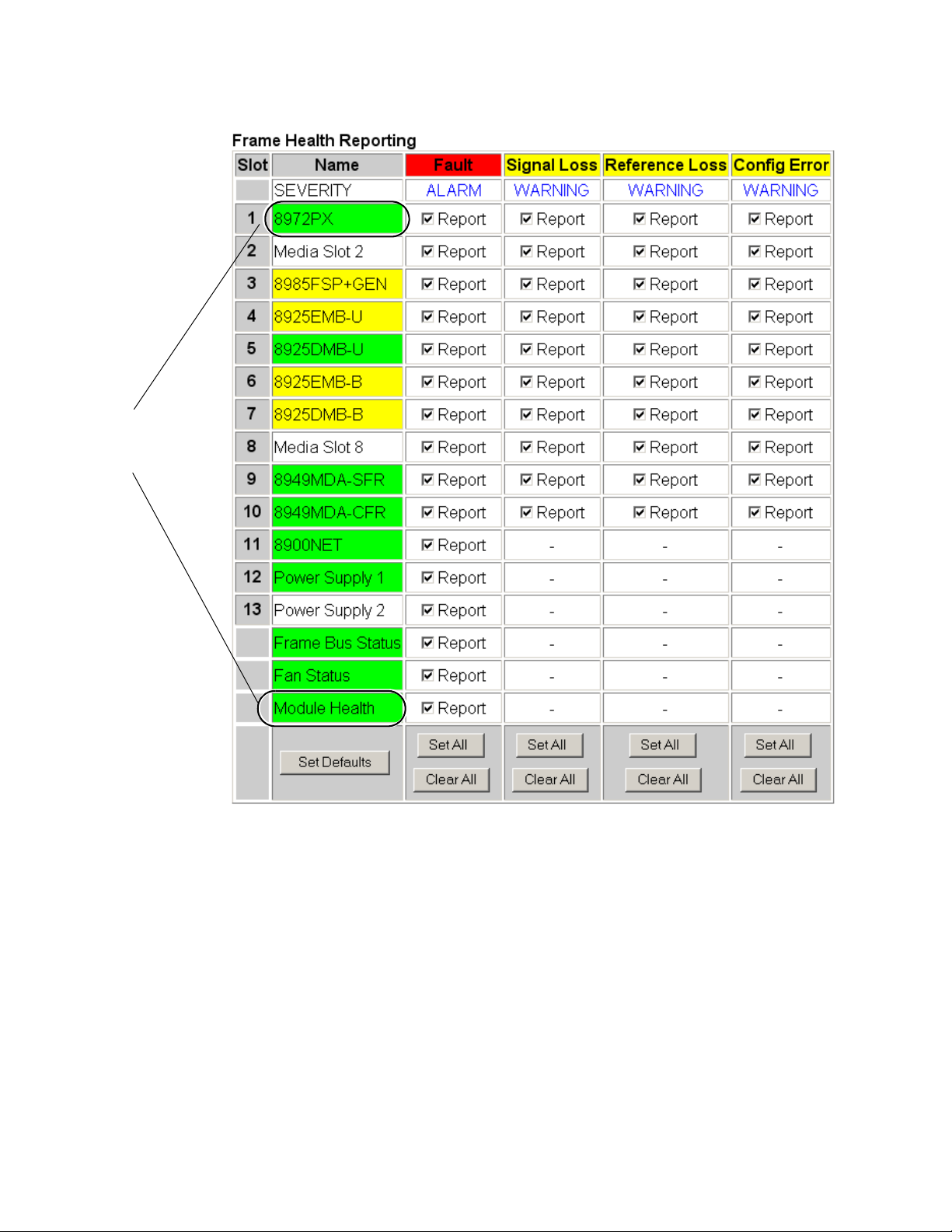
Frame Health Reports – A link is provided to the Frame Alarm Reporting
•
web page for (see Frame Alarm Reporting Web Page on page 42).
LED Reports – a link is provided to the LED Reporting web page for (see
•
LED Reporting Web Page on page 48).
•
Frame SNMP Trap Reports – a link is provided to the SNMP Reporting web
page (see Frame SNMP Trap Reports – a link is provided to the SNMP
Reporting web page (see ). on page 39).
Default
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 39
Page 40

Using the 8900NET GUI
Figure 17. GeckoFlex Frame Configuration Web Page
40 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 41

Frame Connections Web Page
Use
this
link
Selecting the Connections link will bring up the Connections web page.
This page provides a summary of the type and IP Address of any Newton
oftware or hardware panel or other control panel communicating with
s
any module in the frame. The example in Figure 18 shows an 8900TFN-V
frame connected to two Newton control panels.
Figure 18. Frame Connections Web Page – 8900TFN-V Frame
Using the 8900NET GUI
When no control panels are communicating with modules in the frame, the
display will report
Figure 19. No Frame Connections – 8900FFN Frame
No Connections as shown in Figure 19.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 41
Page 42

Using the 8900NET GUI
Use
this
link
Frame Alarm Reporting Web Page
Selecting the Frame Alarm Reports link on any Frame or 8900NET web
page will bring up the Frame Alarm Reporting
Figure 20 on page 43. This page provides a summary of the various alarms
and warning reports that can be enabled and
ponents for reporting status to the Fram
and the SNMP traps.
Hardware Switch Status – the Hardware Switch Status section of this web
•
page displays the current settings of the DIP switches, S1 and S2, on the
8900NET circuit board as described in 8900NET Module Alarm DIP
Switches on page 11.
Module Health Report status – under the Hardware Switch Status table is a
•
message in blue text giving the current status of the Module Health
Report checkbox in the Frame Health Reporting list. When the Module
Health selection is enabled in the Frame Health Reporting table
(Figure 20 on page 43), the message will read:
e Alarm on the rear of the frame
web page shown in
disabled for the frame com-
If the Module Health Report checkbox is unchecked in the Frame
Health Reporting
Note This message does not reflect the setting made on the Internal Module
Healthbus control explained later in this section.
• Output Format for Warnings – set the Frame Alarm output on the RS-232
connector to output a pulse or a continuous voltage level when a
warning condition is detected from the Module Health bus. For more
information on the voltage level from the Module Health Bus, refer to
External Frame Alarm on page 28.
Internal Module Healthbus – this control is provided to enable or disable
•
Module Health Bus
and the Frame Health Reporting table.
When a fault condition is occurring on the Module Health Bus (caused
y 3 or more modules reporting a Warning or Configuration error con-
b
dition and/or a single module reporting a fault) and the
Healthbus
Status web page (Figure 20 on page 43) and in the Frame Health
Reporting table (Figure 22 on page 44).
control is set for Enable, the fault will be reported on the Frame
list, the message will read:
FAULT status reporting to the Frame Status web page
Internal Module
42 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 43

Reports status of
Enable (Report checked)
or disable (unchecked)
Module Health line to
external Frame Alarm.
Module Health Report
checkbox in Frame
Health Reporting table.
Status is reported in
blue text above.
Disable or Enable
Module Health Fault
reporting to Frame
Status web page and
Frame Heath Reporting.
Using the 8900NET GUI
Figure 20. Frame Alarm Reporting Web Page
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 43
Page 44

Using the 8900NET GUI
Figure 21. Frame Status Web Page with Internal Module Healthbus Enabled
Figure 22. Frame Health Reporting Table with Internal Module Healthbus Enabled
44 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 45

Using the 8900NET GUI
Setting the Internal Module Healthbus control to Disable turns off the Module
Health bus fault reporting to the Frame Status web page, and changes the
reporting of the module with a fault and the Module Health selection in the
Frame Health Reporting table to green.
As shown in Figure 23, the Fault message on the Frame Status web page
will no longer be present. The Frame graphic will still report the module
fault in red and the modules with warning or configuration errors in
yellow.
The Module Health Selection in the Frame Alarm Reporting table will be
now green as shown in
This control feature is designed to allow the user to turn off Module Health
bus fault reporting if desired. Faults and warning and configuration errors
occurring on a module will always be reported for each module in the
frame graphic on the Frame Status web page. The user can find the specific
fault or errors on the module by clicking on the module graphic to take
them to the individual media module Status web pages.
As explained earlier, setting the Internal Module Healthbus to Disable does
not disable the Module Health bus reporting to the Frame Alarm on the
frame rear.
Figure 24 on page 46.
Figure 23. Frame Status Web Page with Internal Module Healthbus Disabled
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 45
Page 46
Using the 8900NET GUI
Fault reporting (Red)
has been disabled and
set for Pass (green).
Figure 24. Frame Health Reporting Table with Internal Module Healthbus Disabled
46 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 47

Using the 8900NET GUI
• Frame Health Reporting – the Frame Health Reporting table (Figure 24 on
page 46) listing each of the frame components is provided for enabling
or disabling the report status of the following frame functions to the
Frame Alarm on the rear of the frame and the SNMP traps:
• Media module (Slots 1-10) fault alarms, and loss of signal, loss of
reference, and configuration error warnings (as specified for each
specific module),
• 8900NET module fault reporting,
• Power supply 1 and 2 fault reporting,
• Frame Bus status fault reporting,
• Fan (in front cover) Status fault reporting, and
• Module Health bus reporting.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 47
Page 48

Using the 8900NET GUI
Use
this
link
LED Reporting Web Page
Selecting the LED Reporting link on any frame or 8900NET web page will
bring up the web page shown in Figure 25 on page 49. This web page
allows enabling and disabling of LED r
components in the frame to the LEDs on the front of the 8900NET module.
Hardware Switch Status – the Hardware Switch Status section of this web
•
page displays the current settings of the DIP switches, S1 and S2, on the
8900NET circuit board as described in 8900NET Module Alarm DIP
Switches on page 11. These switches allow enabling and disabling of
what status reporting information is provided to the Frame Alarm and
SNMP traps.
Module Health Report status – under the Hardware Switch Status table is a
•
message in blue text giving the current status of the Module Health
Report checkbox in either the LED Reporting list and the Frame Alarm
Reporting list. When the Module Health selection is enabled in both
tables, the message will read:
eporting from modules and other
If the Module Health checkbox i
Reporting or the Frame Health Reporting list, the message will read:
Disabling this reporting disables the reporting of the Module Health
Bus to the rear Frame Alarm. See Module Health Bus on page 82.
LED Reporting – enable or disable Alarm and Warning reporting for the
•
following functions or devices in the frame:
• Media module (Slots 1-10) fault alarms, and loss of signal, loss of
reference, and configuration error warnings (as specified for each
specific module),
• 8900NET module fault reporting,
• Power supply 1 and 2 fault reporting,
• Frame Bus status fault reporting,
• Fan (in front cover) Status fault reporting, and
• Module health fault reporting and when unchecked, disables
Module Health Bus reporting to rear Frame Alarm via the 8900NET
module.
s unchecked in either the LED
48 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 49

Figure 25. LED Reporting Web Page
Using the 8900NET GUI
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 49
Page 50

Using the 8900NET GUI
Use
this
link
SNMP Reporting Web Page
Selecting the SNMP Reporting web page link from any frame or 8900NET
web page will bring up the web page shown in Figure 26 on page 51. When
an SNMP Managers such as Grass Valley’s Ne
trap reporting from the frame and modules can be configured using these
controls.
Trap Destinations – selecting the Trap Destinations link from this web page
•
will bring up the 8900NET Configuration web page explained and
shown in Figure 34 on page 61.
•
Hardware Switch Status – the Hardware Switch Status section of this web
page displays the current settings of the DIP switches, S1 and S2, on the
8900NET circuit board as described in 8900NET Module Alarm DIP
Switches on page 11. These switches allow enabling and disabling of
what status reporting information is provided to the Frame Alarm and
SNMP traps.
SNMP Trap Reporting – enable or disable SNMP Trap Alarm and Warning
•
reporting for the following functions in the frame:
tCentral is installed, SNMP
• Media module (Slots 1-10) fault alarms, and removed, loss of signal,
loss of reference, and configuration error warnings (as specified for
each specific module),
• 8900NET module fault reporting,
• Power supply 1 and 2 fault reporting,
• Frame Bus status fault reporting,
• Fan (in front cover) Status fault reporting, and
• Module health fault reporting.
50 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 51
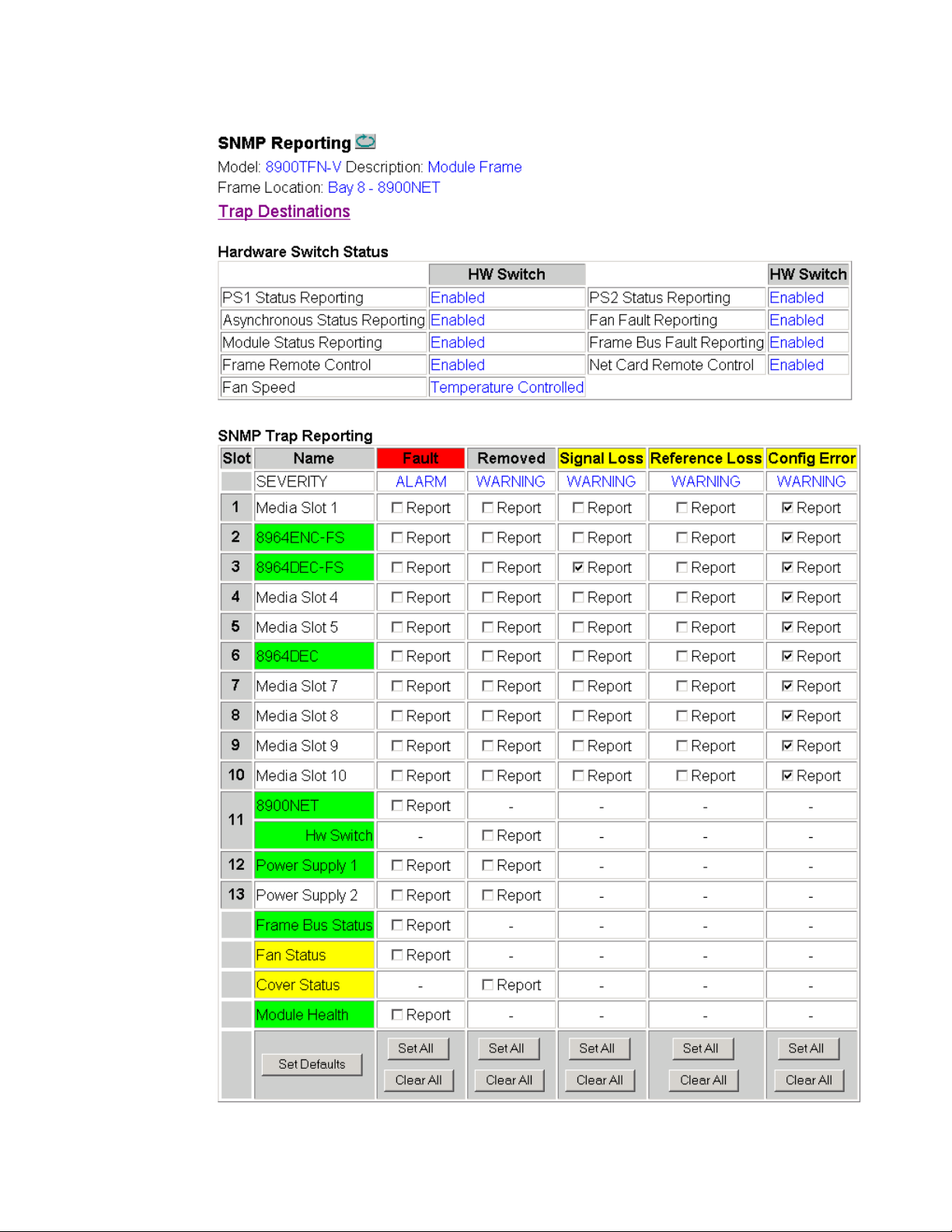
Figure 26. SNMP Reporting Web Page
Using the 8900NET GUI
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 51
Page 52

Using the 8900NET GUI
Use
this
link
Power Supply/Demand Web Page
The Power Supply/Demand web page (Figure 28 on page 53 for GeckoFlex
frame and Figure 29 on page 54 for Gecko frame) provides the following
for the 8900 power supplies installed:
Installed Power Supply – for GeckoFlex frames only, an Installed Power Supply
•
setting is provided to identify to the frame what wattage power supplies are installed in the frame. The GeckoFlex frame currently ships
with 125W power supplies and the
125W at the factory.
Older GeckoFlex frames shipped with 100 Watt GeckoFlex power supplies installed. If you change a power supply from 125 Watt to 100 Wat t,
you will need to
supply is installed. This setting is not auto-sensing by the frame and
must be set by the user. Using a 100W and a 125W supply in the same
GeckoFlex frame will provide 100W of power for the frame.
CAUTION Do not swap power supplies between Gecko and GeckoFlex frames. Power
supplies from a Gecko Frame are not swappable with the GeckoFlex frame
power supply. Gecko power supplies are longer and do not fit in a GeckoFlex
frame.
select the 100W setting to tell the frame what power
Installed Power Supply setting is set for
There are currently three types of power supplies available as listed
below:
• Gecko Frame Power Supply (100W) – part number 119-6055-60
(used only
• GeckoFlex Frame Power Supply (100W) – part number 711000120
(used in older GeckoFlex frames)
• GeckoFlex Frame Power Supply (125W) – part number 711017800
(used in currently shipping GeckoFlex frames)
To identify a power supply, note the part number on the large label on
the s
ide of the supply (Figure 27).
Figure 27. Power Supply Part Number Location
in Gecko Frames)
52 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 53

Using the 8900NET GUI
• Power Status – gives the status of the power capacity for the frame. This
is also reported on the Frame Status page.
Power – a Power table lists each of the media modules, the 8900NET
•
module, and the power supplies present in the frame and their power
demand. The total amount of power demand is totaled at the bottom of
the display.
Figure 28. GeckoFlex Frame – Power Supply/Demand Web Page
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 53
Page 54

Using the 8900NET GUI
Figure 29. Gecko Frame – Power Supply/Demand Web Page
54 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 55

Frame Power Supply Web Pages
Use
this
link
The frame Power Supply 1 or Power Supply 2 status web pages provide:
• Power Slot Status – pass/fail status of the supply and fan in the power
supply sled
• A Frame Health Reports link is given to the Frame Health Reporting
web page (page 42) where a fault report in the power supply can be
enabled or disabled as an alarm to the Frame Alarm connector on the
rear of the frame.
• An LED Reports link is given to the LED Reporting web page (page 48)
where the power supply status reporting to the PS1 and/or PS2 LED on
the front of the 8900NET module can be disabled if desired.
• When an SNMP manager is installed on the 8900NET module, an
SNMP Trap Reports link will be present. This will link to the SNMP
Reporting web page (page 48) where power supply fault and removal
can be configured for reporting to the SNMP manager.
Figure 30. Power Supply Slot Status Page
(see Figure 30).
Using the 8900NET GUI
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 55
Page 56

Using the 8900NET GUI
Use
this
link
8900NET Module Interface
8900NET Module Status Web Page
This section describes the web browser interface for the 8900NET module.
The Status web page illustrated in Figure 31 displays 8900NET:
• Module identity, location and internal
Pass/Fail /Warning, status,
• Hardware and software properties,
• Asset Tag identifier (set on 8900NET Configuration web page), and
• Status of on-board hardware configuration switches (set as described in
8900NET Module Alarm DIP Switches on page 11).
A Status LED icon on each module page changes color to r
network interface, frame bus, and internal diagnostics:
• Green indicates a Pass condition,
Red indicates a Fail condition, and
•
• Yellow indicates a Warning condition.
Figure 31. 8900NET Module Network Status Page
Net Card diagnostic
eport status of
56 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 57

8900NET Module Configuration Web Page
Use
this
link
The 8900NET Configuration web page (Figure 32 on page 58) provides the
following for configuring the 8900NET module:
Reboot Module – reboot the 8900NET module by selecting the reboot
•
button at the top of the page. A reboot can also be done on the Network
web page.
•
Install SNMP Agent – to use an SNMP Manager, an SNMP Agent software
must be installed on the 8900NET module. The Configuration web page
shown in Figure 32 on page 58 is displayed if the agent software has not
already been installed.
Using the 8900NET GUI
To install an SNMP Agent, refer to Install SNMP Agent on
When the SNMP Agent has been installed,
an SNMP Trap Reports link
page 59.
will be present on the Configuration web page (Figure 34 on page 61).
•
Asset Tag Assignment – the 8900NET module can be assigned as asset tag
identifier by entering numbers or text in the Asset Tag field. This information will appear on the 8900NET Status web page and in the module
inventory when using the NetConfig Network Configuration application.
Always Slot Refresh – the 8900NET module automatically polls and
•
refreshes all media modules installed in each frame slot about every 50
minutes for a fully stuffed frame. The
Always Slot Refresh checkbox,
which is enabled by default, can be unchecked to disable the 8900NET
module from doing the automatic refresh in conjunction with
Upon Install
function on each media module Slot Config web page
(Figure 36 on page 65).
If
Always Slot Refresh is checked, every slot is refreshed, regardless of any
Restore upon Install settings. If Always Slot Refresh is unchecked, only media
module slots that have the
Restore upon Install setting checked are
refreshed.
•
Disable Background Web Page Loading – when the frame is powered up or
the 8900NET module is rebooted, the 8900NET module will automatically load every web page for every module in the frame. This is the
default condition (
Disable Background Web Page Loading unchecked).
Restore
Disable Background Web Page Loading checkbox can be selected to
The
disable the background loading of all web pages. The web pages will
only be loaded when selected by the user. This will slow down the page
response slightly the first time each web page is selected.
Frame Health Reporting – a Frame Health Reports link to the Frame Alarm
•
Reporting web page is provided. Refer to Frame Alarm Reporting Web
Page on page 42.
LED Reporting – an LED Reports link to the LED Reporting web page is
•
provided. Refer to LED Reporting Web Page on page 48.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 57
Page 58

Using the 8900NET GUI
Figure 32. 8900NET Module Configuration Web Page (SNMP Installed)
58 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 59

Using the 8900NET GUI
Install SNMP Agent
When SNMP Agent software is installed on the 8900NET module, enabled
status reports are sent to an SNMP Manager such as the Grass Valley’s Net
Central application. Refer to Establishing Frame Network Identity on page 22
for more information.
To install an SNMP Agent, click on the Install SNMP Agent button (Figure 32
on page 58) to view the license agreement.
After reading the agreement, click on Accept to finish installing the SNMP
Agent (
installation and return you to the Configuration web page.
Figure 33. SNMP Agent Installation Agreement
Figure 33). Clicking the Decline button will abort the SNMP Agent
-
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 59
Page 60

Using the 8900NET GUI
When the SNMP Agent is successfully installed, the Configuration web
page will contain the additional items listed below and shown in
Figure 34
on page 61.
• SNMP Trap Reports Link – when the SNMP Agent is installed an SNMP
Trap Reports link will be present on the Configuration web page (and
other web pages) to link to the SNMP Reporting web page (page 51).
The following SNMP trap reports are provided for the 8900NET
module:
• Net Card Status (Alarm)
• Hardware Switch (Informational)
•
SNMP Report Activation Modes – each report destination has an activation
control that can select one of the following modes of operation:
CREATE – GO creates a new report destination that becomes active
•
after the next module reboot.
CREATE – WAIT creates a new report destination that remains out of
•
service until the user selects active and then reboots the module.
•
ACTIVE changes a NOT IN SERVICE report destination to active after the
next module reboot.
NOT IN SERVICE changes an active report destination to inactive after
•
the next module reboot.
DELETE removes the report destination entry. If the entry was active
•
it remains active until the next module reboot.
Note Report destination status does not change until the 8900NET module is
rebooted.
The status column to the left of the activation operation pull-down
window provides one of the following status reports:
• <BLANK> – No entry has been applied.
ACTIVE – All new status reports will be sent to this destination.
•
NOT IN SERVICE – The destination has a valid definition but the user
•
has not activated it.
ACTIVE PENDING REBOOT – This entry indicates the report destination
•
will become active upon the next module reboot.
NOT IN SERVICE PENDING REBOOT – This entry indicates the report des-
•
tination will become inactive upon the next module reboot.
NOT READY – The destination entry is invalid. The IP Address may
•
not be properly defined or there is no IP Address or Community
entry.
60 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 61
Using the 8900NET GUI
Figure 34. 8900NET Configuration Web Page (SNMP Agent Installed)
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 61
Page 62

Using the 8900NET GUI
Use
this
link
8900NET Network Web Page
To view or change the module identity and currently assigned network
addresses for the 8900NET
trated in Figure 35.
Note Depending on the type of frame this module is installed in, this network con-
figuration is saved on either the 8900NET module or on the frame backplane.
Refer to Network Configuration Storage on page 25 for details.
Figure 35. 8900NET Module Network Identification Page
module access the Network web page illus-
After initial frame network addressing is done using the RS-232 port, subsequent address changes may be made using the
Note SubNet Mask and Gateway IP Address are required.
web page shown above.
Rebooting the NET Module
Reboot the module for changes to take effect. You can reboot the 8900NET
module from the Network page by clicking the
button can also be found on the Configuration page.
reboot button. A reboot
62 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 63

Media Module Slot Configuration
Use
this
link
The 8900NET module also provides the functions for the Slot Config web
page for each media module in the frame (Figure 36 on page 65). Media
module slots may be named to reflect specific functions for that
module within the facility. The configuration for the module can also be
saved to slot memory on the 8900NET module. Setting made on this page
affect the 8900NET (Net Card) module’s actions.
Note Both frame and module names and configuration information can be saved
to file and recalled as necessary. This allows quick and easy reconfiguration
of the 8900NET module if it must be replaced or moved to another frame (see
Frame Configuration Web Page on page 39).
• Slot Identification – the module may be identified by typing a specific
name in the
module and travels with the 8900NET module if it is moved to another
frame. Select
Name field. The assigned name is stored on the 8900NET
Default to enter the factory default module name.
Using the 8900NET GUI
slot or
The module may also be assigned an asse
or numbers into the
Asset Tag field. A maximum of 23 characters is rec-
t tag identifier by entering text
ommended for the identifier to appear completely on the media
ule Status web page.
mod
Note Asset tag functionality is not available on all media modules.
• Locate Module – when enabled by selecting the Flash pulldown, the Locate
Module
function flashes the yellow COMM and CONF LEDs on the front
of the module to make it easy to locate in the frame.
Note This function is not available on all modules and may operate differently on
some modules (only the COMM LED will flash).
• Slot Memory – the slot configuration for each media module is automati-
cally polled and refreshed periodically (about every 50 minutes) by the
8900NET module when the
Configuration web page (page 57) and/or the
Always Slot Refresh checkbox on the 8900NET
Restore upon Install
checkbox on any media module Slot Config web page (page 63) is
selected.
When the
Restore upon Install checkbox on any media module Slot Config
web page has been selected, the current configuration from that
module is saved in slot memory on the 8900NET module. This allows
the current module to be removed and when another module of the
same type, part number, and software version is installed, the configuration saved to the 8900NET module
module. The
Restore upon Install checkbox must be selected before the
will be downloaded to the new
current module with the saved configuration is removed.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 63
Page 64

Using the 8900NET GUI
Note Make sure all modules of the same type are running the same software
version and have the same part number silk-screened on the printed circuit
board. Downloading a configuration to a module with a different software
version or part number can produce unexpected results.
If a different type of module is installed in this slot, a warning message
will state that the original module type has been replaced with another
module type. In this case, a
clear the stored configuration from the previous module.
You may also select the Learn Module Config button at any time to save the
current configuration for this slot. The configuration is saved on the
8900NET module. If the 8900NET module is removed or powered
down, the stored configurations are not saved.
When no Restore upon Install checkboxes on any of the media module Slot
Config web pages are selected and the
the 8900NET Configuration web page is unchecked, the slot refresh
polling function on the 8900NET module will be disabled. See the
Always Slot Refresh checkbox description on page 57 for more details.
•A Frame Health Reports link is provided to the Frame Alarm Reporting
web page for setting up frame health reporting for this media module
(see the Frame Alarm Reporting Web Page on page 42).
Clear button will appear allowing you to
Always Slot Refresh checkbox on
•An
•An
LED Reports link is provided to the LED Reporting web page for
setting up LED reporting to the 8900NET module for this media
module (see the LED Reporting Web Page on page 48).
SNMP Trap Reports link is provided to the SNMP Reporting web page
for setting up SNMP Trap Reporting for this media module (see the
SNMP Reporting Web Page on page 50).
64 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 65

Figure 36. Media Module Slot Configuration Page
Using the 8900NET GUI
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 65
Page 66

Using the 8900NET GUI
Upgrading 8900NET Software
Software updating procedures for 8900 Gecko and GeckoFlex products are
provided in the release notes that accompany the specific software release.
Refer to the latest 8900NET version release notes for full updating instruc
tions. These release notes are normally posted on the Modular documentation area of the Grass Valley web site at this URL:
www.grassvalley.com/docs/modular/
There are currently two ways of updating software on 8900NET modules
as described below:
• 8900NET (version 3.2.0 and later) and some applicable 8900 modules
should be updated using the NetConfig Networking Application
(latest version 2.0.12 as of this printing) available free of charge from the
Grass Valley ftp site:
ftp://ftp.grassvalley.com/router/NetConfig/Version%202.0.12/
• Older version (2.1.2 and earlier) 8900NET modules must be updated
using the FTP download method described in 8900NET Software Update
From FTP Server on page 88.
-
8900NET Software to Part Number Guide
The latest version of 8900NET software, version 4.4.0, has limitations on
what printed circuit boards it can be used on. This is due to changes made
for RoHS compliant and obsolete parts used on the 771- circuit boards.
Functionality is the same for both software versions 4.3.0 and 4.4.0. The
release of the latest 8900NET software 4.4.0 was necessary to meet the
requirements for the 771-0121-XX circuit board updates.
Refer to Tab le 6 for an overview of what software can be installed on different 8900NET module part numbers.
Table 6. 8900NET Software Usage Table
Software Version
Module Part Number 4.3.0 4.4.0
671-4852-00 Yes No
671-4852-01 Yes No
771-0121-00 Yes Yes
771-0121-01 Yes Yes
771-0121-02 Yes Yes
771-0121-03 No Yes
Note For optimal operation of 8900 Gecko and GeckoFlex modules, 8900NET
modules should be running either 4.3.0 or 4.4.0 software.
66 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 67

Acquiring Module Software Updates
Software field upgrade packages for modules are available from the Grass
Valley Customer Service FAQ site and the public ftp site. For an overview
of software updating capabilities, refer to the
page 85.
You may connect to the Grass Valley FAQ site to access the latest module
and free NetConfig software and subscribe to software updates automati
cally at the following URL:
http://www.grassvalley.com/downloads
This link will direct you to the Customer Service FAQ database where all
software downloads are distributed. The information provided here is the
most up-to-date. Using this link is recommended so that when new ver
sions of software are released, you are notified by E-mail. It also provides
information on module software updating, including a list of the modules
that do not support remote upgrades and require the cable kit.
You may also connect directly to the Grass Valley FTP server at this location:
Using the 8900NET GUI
Compatibility Matrix on
-
-
ftp://ftp.grassvalley.com/modular/8900/
For earlier version 8900NET modules with
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 67
Page 68

Service
Service
The 8900NET modules make extensive use of surface-mount technology
and programmed parts to achieve compact size and adherence to
demanding technical specifications. Circuit modules should not be ser
viced in the field.
If your module is not operating correctly, proceed as follows:
• Check frame and module power and signal present LEDs.
• Check network connections at the frame and network routing devices.
• Verify that all ethernet devices have a unique MAC and IP Address/
Domain Name.
• Reboot the 8900NET module (see Rebooting the NET Module on page 62).
Refer to Figure 12 on page 20 for the location of PWR LED and Tab le 2 on
page 21 for proper LED indications.
If the module is still not operating correctly, replace it with a known good
spare and return the faulty module to a designated Grass Valley repair
depot. Call your Grass Valley representative for depot location.
-
Refer to Contacting Grass Valley on page 4 at the front of this document for
the Grass Valley Customer Service Information number.
68 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 69

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
The following is a list of possible 8900NET GUI and network problems and
logical steps for troubleshooting them.
Cannot Open Any of the Frame’s Web Pages
1. Check power to the frame.
a. Is at least one of the power supplies operating?
b. Is the 8900NET module’s PWR LED on?
2. Check that the frame is physically connected to the network.
a. Is a cable plugged into the RJ45 connector of the frame?
b. Is that cable also connected to a 10Base-T Ethernet hub?
c. Does the 8900NET module’s ETHER LED indicate network
activity?
d. Does the Ethernet hub have any indication that a link is established
to the frame?
Troubleshooting GUI Operation
3. Is the correct IP Address/URL being used to address the frame?
If a Domain Name is being used to address the frame, try to connect
using the frame IP Address instead.
The Domain Name may not be properly assigned in the local Domain
Name Server or in the workstation’s host file.
The Domain Name Server may not be available to the workstation.
Check that the 8900NET module has been properly configured.
a. Is the correct IP Address or URL being addressed in the web
browser?
b. Was the 8900NET module configured over the serial connection
with the
c. Has the 8900NET module been assigned the correct IP Address in
SETUP (re-run setup over the serial connection)?
d. Is the workstation in the same subnet as the frame? If not:
Has the 8900NET module been assigned the correct Default
Routing Address?
Has the 8900NET module been assigned the correct Subnet Mask?
e. Has the 8900NET module been rebooted since new IP Address,
Default Routing, or Subnet Mask were assigned or changed?
SETUP command?
4. Check if the frame web pages can be opened from a different
workstation on the network.
5. Is the subject workstation physically connected to the network?
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 69
Page 70

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
6. Check that the workstation and browser have been properly
7. Check that network traffic can be routed between the workstation and
configured.
a. Can the frame be opened from a different workstation?
b. Has the workstation been assigned a proper IP Address?
c. Has the workstation been assigned a Gateway Address?
d. Is the browser configured to connect to the correct port?
Is it attempting to connect through a modem when it should be connecting through a network interface module?
Some laptop have two separate network ports, one for stand-alone
operation, and the other for operation with a docking station. Is the
correct port being used?
the frame.
a. If the workstation supports a network ping, ping the frame. For
example:
Open a command prompt (DOS window)
In the DOS window, enter:
C:\> ping frame’s ip address
The results will indicate if the ping reached the frame.
b. If the workstation does not support a network ping, ping the
workstation for the frame serial interface:
In the frame serial command window, enter:
->ping “workstation’s IP address”
The workstation’s IP address must be inside the double quotes. The
results will indicate if the ping reached the workstation.
c. If the network ping failed, there may be a network problem
between the frame and the workstation. To ensure it is not the
frame, check the frame with a point-to-point connection:
Using a crossover Ethernet cable, connect the frame directly to a
workstation. The workstation should be assigned an IP Address on
the same Subnet as the frame. Attempt to load the frame’s web page
from a Browser on this workstation.
8. If the point-to-point connection attempt fails call Customer Service. If
the point-to-point connection attempt succeeds, the problem is
somewhere in the network between the original workstation and the
frame.
a. Check the connectivity to the frame from different locations in the
network to attempt to isolate physical disconnect problems.
70 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 71

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
b. Check the connectivity to the frame from inside and outside the
frame’s subnet to isolate IP Gateway routing problems.
c. Check for possible Ethernet MAC Address collisions.
If the Frame ID Memory chip installed on the rear of the frame is
missing or has failed, the frame adopts the default Ethernet MAC
Address.
If more than one frame in the Network adopts the default Ethernet
MAC Address, there could be address resolution problems. Upon
power up the frame will indicate in the serial port console window,
either:
“MAC address is unique!” – The Frame has successfully
retrieved a unique Ethernet MAC Address from the Frame ID
Memory chip
or
“MAC address is default!” - The Frame is using the default
Ethernet MAC Address. The Frame ID Memory chip is missing
or has failed. Call Grass valley Group Customer Service
Cannot modify parameters on Web Page
1. Check if parameters can be set for other modules.
If so, the module may be in a remote lockout state.
a. Check if the LOC/REM – LOCAL jumper on the module is set for
local control only. (Refer to that specific module’s manual for help.)
b. In version 2.0 and later of the 8900NET module software, the web
pages for a module in the remote lockout state will indicate that
module remote control is disabled and the module’s controls on the
web pages will be in read-only mode.
If other modules are not controllable, the entire frame may be in a
remote lockout state. In this state, software updates to the modules and
the 8900NET module are also locked out.
c. Check The 8900NET module’s status page if the frame remote
control is disabled.
If so, flip Switch 3 on the S2 DIP switch block (FRAME CNTRL) to
the enabled setting.
2. If it is only a specific parameter that is read-only, the module may be in
a mode assigning read-only operation to that parameter. Refer to the
module’s instruction manual.
3. If only the 8900NET module is read-only, the 8900NET module may be
in remote lockout mode.
a. Check the 8900NET module’s status page to see if the NET CARD
REMOTE CONTROL
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 71
status is disabled.
Page 72

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
Cannot Connect to the Frame From a VTECS1 VideoFrame Control Panel
1. Check that the frame is powered and configured with a 8900NET
2. Check that the 8900NET module in the frame is loaded with software
3. Check that the control panel has been properly configured with IP
4. Check that the frame’s correct IP Address has been configured in the
5. Check that the control panel is physically connected to the network.
b. If so, flip Switch 8 on the S1 DIP switch block (NM CNTRL) to the
enabled setting.
module on the network.
version 2 or later.
Version 1 software does not support the control panel connection.
Address, Gateway IP Address, and Subnet Mask. (Refer to the control
panel’s help feature or instruction manual.)
control panel’s frame address.
a. Check that the control panel is connected to a port on an Ethernet
hub.
b. Check if the L LED (L for link) on the back of the control panel is on.
If the LED indicates no link (off), try a different hub port connection.
If the LED still indicates no link, change the cable.
If the LED still indicates no link, contact VideoFrame.
6. Check that the frame is addressable by the control panel.
a. Check if the T LED (T for transmit) on the back of the control panel
flashes upon the attempt to connect to the frame.
If T does not flash, contact VideoFrame.
b. Check if the R LED (R for receive) on the back of the control panel
flashes upon the attempt to connect to the frame.
If R does not flash, there may be a problem in the network path
between the frame and the control panel.
7. Check that the frame is addressable on the network from a Web
browser, refer to the steps on page 69.
a. Attempt to connect to a different frame.
If successful the problem may be with the original frame or the path
between the control panel and the original frame.
b. Check from a workstation connected to the same Ethernet hub as
the control panel. If unsuccessful, there may be a problem with the
network path between the frame and this hub.
72 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 73

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
Event Messages From the Frame Are Not Being Displayed by NetCentral or
Another SNMP Manager Application
1. Check that the frame is powered on and configured with an 8900NET
module on the Network.
2. Check that the 8900NET module in the frame is loaded with software
version 2.1 or later.
Earlier versions of software do not support SNMP.
3. Check that the SNMP Agent has been installed and configured on the
8900NET module.
View the 8900NET module CONFIGURATION page and note the event con-
figuration parameters, the NET CARD EVENT REPORTS form and REPORT
DESTINATIONS
If these are not visible, install the SNMP Agent per the instructions in
the manual.
4. Check that the IP Address and Community Name for the SNMP
Manager has been assigned in the
Active.
table.
REPORT DESTINATIONS table and is
• If there is no entry for the SNMP Manager in the Table, the SNMP
manager’s IP Address and Community name must be entered (see
8900NET Module Configuration Web Page on page 57).
• If the entry for the SNMP Manager is incorrect, it must be corrected,
activated, and the 8900NET module must be rebooted.
• If the entry has been entered and the Status of the entry is reported
NOT IN SERVICE, the Active operation for that entry must be selected,
applied and the 8900NET module must be rebooted.
• If the entry has been entered and the Status of the entry is
the entry must be corrected, activated and the 8900NET module
must be rebooted.
• If the entry has been entered and the Status of the entry is
–PENDING REBOOT
, the 8900NET module must be rebooted.
NOT READY,
ACTIVE
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 73
Page 74

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
5. Check that the particular event has been enabled in the frame.
• For all events, check that the STATUS switch (Switch 1) on the S2
DIP switch block of the 8900NET module is Enabled.
• For Module Failure-Fixed events:
Check that the MODULE switch (Switch 5) on the S1 DIP switch
block of the 8900NET module is Enabled, and
Check that the SLOT STATUS REPORTING parameter on the slot’s SLOT
CONFIG
• For Power Supply Failure-Fixed events:
Check that the PS1 or PS2 switch (Switch 1 or 2) on the S1 DIP
switch block of the 8900NET module is Enabled, and
Check that the POWER SUPPLY STATUS REPORTING parameter on the
power supply’s
• For 8900NET module Failure-Fixed events, check that the NET CARD
STATUS REPORTING
TION
page is Enabled.
CONFIGURATION page is Enabled.
parameter on the 8900NET module’s CONFIGURA-
page is Enabled.
• For Hardware Switch change events, check that the
SWITCH REPORTING
TION
page is Enabled.
• For Frame Bus Failure-Fixed events:
Check that the FRAME BUS switch (Switch 6) on the S1 DIP switch
block of the 8900NET module is Enabled, and
Check that the FRAME BUS STATUS REPORTING parameter on the
frame’s
• For Front Cover Removed -Installed events, check that the COVER
STATUS REPORTING
Enabled.
• For Frame Bus Failure-Fixed events:
Check that the FRAME BUS switch (Switch 6) on the S1 DIP switch
block of the 8900NET module is Enabled, and
Check that the FRAME BUS STATUS REPORTING parameter on the
frame’s
• For Cooling Fan Failure-Fixed events:
Check that the FAN switch (Switch 4) on the S1 DIP switch block of
the 8900NET module is Enabled, and
CONFIGURATION page is Enabled.
CONFIGURATION page is Enabled.
parameter on the 8900NET module’s CONFIGURA-
parameter on the frame’s CONFIGURATION page is
HARDWARE
Check that the FAN STATUS REPORTING parameter on the frame’s CON-
FIGURATION page is Enabled.
• For Module Health Failure-Fixed events,
Check that the MODULE switch (Switch 5) on the S1 DIP switch
74 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 75

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
block of the 8900NET module is Enabled, and
Check that the MODULE HEALTH REPORTING parameter on the frame’s
CONFIGURATION page is Enabled.
• Check that the SNMP Manager is properly configured to receive the
Event Messages.
Check that the SNMP Manager has been assigned the same community name as in the frame’s configuration.
6. Check the network connectivity between the SNMP Manager and the
frame as described in the steps on page 69.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 75
Page 76
Troubleshooting GUI Operation
LogPrint Procedure From Gecko/GeckoFlex Frame
You may use the logging function of the 8900NET module to troubleshoot
errors from modules in the Gecko or GeckoFlex frame. The log will report
the last 300 commands received by the Gecko frame. It will contain all com
mands from changes made through the web interface or control panel.
To access a LogPrint from an 8900 frame do the following:
1. Access HyperTerminal by pressing the Start button. Select
Figure 37. Find HyperTerminal
-
Programs/Accessories/Communications/HyperTerminal as shown in
Figure 37.
2. Click on the HyperTerminal accessory. HyperTerminal will open and
bring up the
page 77.
3. Typ e telnet into the Name field and select OK.
Connection Description window shown in Figure 38 on
76 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 77

Figure 38. Connection ‘Description Window
Troubleshooting GUI Operation
This will bring up the Connect To window shown in Figure 39.
4. In the Connect To window, select TCP/IP (Winsock) selection in the
Connect Using pulldown.
Figure 39. Connect To Window
This will bring up the telnet window shown in Figure 40 on page 78.
5. In the Host address field that appears, type the IP address of the frame
you wish to connect to and press
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 77
OK.
Page 78

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
Figure 40. Enter Host Address
This will bring up the telnet-HyperTerminal screen shown in Figure 41.
Figure 41. Telnet Screen
6. To save the log to a .txt file while it is running, select the Transfer
pulldown in HyperTerminal and select
log (Figure 42 on page 79).
Capture Text before running the
78 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 79

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
Figure 42. Capture Text Pulldown
7. In the Capture Text window, browse to a location to save the text file as
shown in Figure 43. Select the
until you indicate it to stop.
Figure 43. Capture Text
Start button. This will capture the text
8. On the HyperTerminal screen, Press the Enter key several times to verify
the connection, then enter the
Figure 44. LogPrint Prompt
9. Press the Enter key to run the log.
10. Once the log has stopped, you may also stop the text capture by
selecting
(Figure 45).
The text file will now contain a record of the last 300 commands
received by the frame.
Capture Text in the Transfer pulldown again and select Stop
LogPrint command shown in Figure 44.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 79
Page 80

Troubleshooting GUI Operation
Figure 45. Stop Text Capture
The log will also appear in the HyperText window as shown in Figure 46.
Figure 46. Log Print
80 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 81
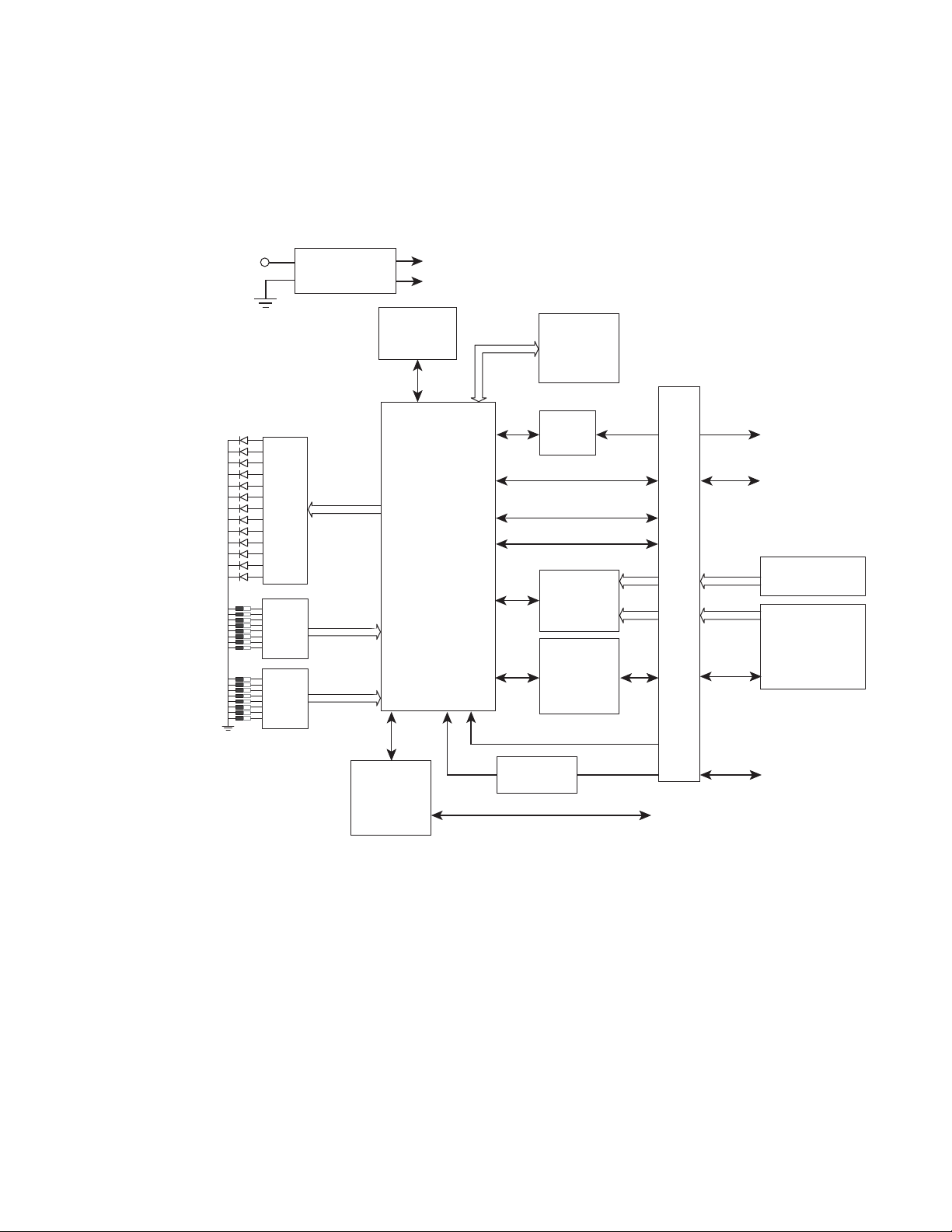
Functional Description
Refer to the block diagram in Figure 47 while reading the following functional description.
Figure 47. 8900NET Block Diagram
Functional Description
+12 V
LEDs
User
Setup
Sw.
User
Setup
Sw.
On-board
Regulator
+5 V
+3.3 V
Temperature
Sensing
Microprocessor
Boot ROM
SDRAM
NVRAM
RS-232
Driver
10BaseT Ethernet
Module Health Bus
Frame Bus
Module
Present
Detection
SMPTE
Alarm
Signal
Processing
Ethernet/MAC Address
Alarm
Bus
RS-232 (9-pin D)
Ethernet (RJ-45)
M
o
t
h
e
r
b
o
a
r
d
Power Supply
Cells
Module Cells
Fan Speed
Control and
Rotation
Sensing
SMPTE
Relay
To Fan Assembly
Frame Alarm
(BNC)
Temperature Sensing
Two temperature sensors on the module report to the microprocessor when
they detect:
• External ambient temperature above 50° C, or
• Internal frame temperature above 70° C.
The microprocessor will then report a temperature fault.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 81
0612_01r1
Page 82

Functional Description
ROM and RAM
Ethernet Port
RS-232 Serial Port
Software updates can be made to the 8900NET ROM through the
Web-based interface. Non-volatile RAM is provided to store key setup
values when power is cycled.
The 10Base-T Ethernet port provides configuration and monitoring access
to the frame, frame modules and the 8900NET module using a web
browser.
The RS-232 port is used to initialize the module with critical network
parameters including a static assigned IP Address. Ethernet MAC address
is stored on a serial EPROM on the frame. (The frame needs both MAC and
IP Addresses.)
Module Health Bus
The Module Health bus connects all the audio/video module cells to the
microprocessor. It is used to report module faults or data errors. Refer to
Module Health Bus Reporting on page 28.
Frame Bus
The Frame Bus provides serial communication to each of the audio/video
modules for remote configuration and monitoring over a network.
Module Present Detection
Module Present lines from cells 1 through 10 and Present/Health lines
from cells 12 and 13 are monitored by the microprocessor using the Module
Present Detection circuitry. For cells 1 through 10, this circuit reports to the
processor whether a module is present and if it supports frame bus com
munications (control and monitoring). For cells 12 and 13, this circuit
reports if the power supply is present and if it is working properly.
-
82 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 83

Fan Speed Control and Monitor
The fan speed circuit controls the speed of the fans based upon the ambient
temperature in the area in which the frame is located. If the temperature is
30° C or lower, the fans are set to minimum speed. For temperatures above
30° C, the fan speed is set higher as the temperature increases. The fan
speed is set to maximum for ambient temperatures above 40° C.
The fans are set for maximum speed at the factory to accommodate HD
modules and other higher power modules such as the 8995UDX which
require a dual rear slot in the GeckoFlex frame. This setting is made on the
8900NET module switch S1 segment 7 (refer to
Switches on page 11).
On-board Regulator
+12 V supply voltage is regulated on-board to provide +5 V and +3.3 V to
the module
Functional Description
8900NET Module Alarm DIP
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 83
Page 84

Specifications
Specifications
Table 7. 8900NET Specifications
Parameter Value
Recommended Software
Web browser Netscape 6.x, Internet Explorer 6.x or later, or any compatible web browser
Recommended PC operating system Windows 2000, XP, and Windows 7
Terminal emulation Hyperterminal
Environmental
Frame temperature range 0 to 45° C
Operating humidity range 0 to 90% non-condensing
Non-operating temperature 0 to 45° C
Mechanical
Frame type Gecko 8900 (all versions) and GeckoFlex Series
RS-232 connector DB-9 Female
Ethernet connector RJ-45
Frame alarm connector DB-9 Female or BNC (depending on frame model)
Power Requirements
Supply voltage ± 12 V
Power consumption < 6 W
84 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 85
Appendix
Compatibility Matrix
The compatibility matrix in Tab le 8 lists the software compatibility for 8900
modules, features that are supported, and how software updates are handled.
For the latest Release Notes and Instruction Manuals for all Modular products in PDF format, go to this link:
www.grassvalley.com/docs/modular
Table 8. 8900 Software Compatibility Matrix
Control &
Model #
8910ADA-ST full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8916
8920DAC full c&m
8920ADC
8920ADT full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8920DMX full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8920MUX full c&m – 8900-FLOAD_CBL
8921ADT full c&m – ftp download
8921DAC full c&m – 8900-FLOAD_CBL
8925DMB-B/-U full c&m – NetConfig or microSD
8925EMB-B/-U full c&m – NetConfig or microSD
8931 no comm – N/A
8935CF full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8935FC full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8936 no comm – n/a
8937/8937D full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8939FCA/FCB monitoring Requires 8900NET 4.3.0 No software /passive device
8941 no comm – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
Monitoring
Support
basic status Id defect, faults not reported Not upgradeable
full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
basic status
full c&m –
Control & Monitoring Notes
1
Id defect, faults not reported
Faults not reported
Id defect, faults not reported
Faults not reported
–
2
Software
Update
8900-FLOAD-CBL
8900-FLOAD-CBL
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 85
Page 86

Appendix
Table 8. 8900 Software Compatibility Matrix - (continued)
Control &
Model #
8943CF full c&m Requires 8900NET 4.3.0 NetConfig
8943FC full c&m Requires 8900NET 4.3.0 NetConfig
8943RDA/-D/-DFR full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.3.0 NetConfig
8945EDA full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8945EDA-D full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8947RDA-D full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8947RDA-FR full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8949MDA-CFR full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8949MDA-SFR full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.0.2 NetConfig
8949MDA-CXF full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.3.0 NetConfig
8949MDA-SXF full c&m Requires 8900NET v4.3.0 NetConfig
8950DAC
8950ADC
8960DEC
8960ENC full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8964DEC full c&m Requires 8900NET v3.2.0 NetConfig
8964ENC full c&m Requires 8900NET v3.2.0 NetConfig
8964FS full c&m Requires 8900NET v3.2.2 NetConfig
8964MON full c&m Requires 8900NET v3.2.0 NetConfig
8972PX full c&m Requires 8900NET 4.2.0 NetConfig or microSD
8977-AP-4B/-4U full c&m Requires 8900NET 4.0.2 NetConfig or microSD
8981FS full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8981NR full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8985FS/FSP/PRC full c&m Requires 8900NET 4.3.0 NetConfig
8990ARC full c&m – 8900-FLOAD-CBL
8995UPC/DNC/UDX full c&m Requires 8900NET 4.3.0 NetConfig and microSD
8500 Series – – –
8800 Series – – –
1
See Control and Monitoring Support on page 87 for definitions
2
See Control and Monitoring Notes on page 87 for definitions
3
See 8900–FLOAD–CBL Assembly on page 87 for information
Monitoring
Support
basic status faults not reported
full c&m –
basic status faults not reported
full c&m –
no comm misleading status reported
full c&m –
Control & Monitoring Notes
1
2
Software
Update
8900-FLOAD-CBL
8900-FLOAD-CBL
8900-FLOAD-CBL
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
86 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 87

Control and Monitoring Support
The following abbreviations are used to indicate the features supported or
not supported by the modules listed in
• No comm — The module does not support any remote control or monitoring functions.
• Basic status — The module responds to only low-level probe from the
Network module and only returns model number and description.
Fault and signal presence are not reported. No control is supported.
• Full C&M — The module fully supports the control and monitoring
system. The module reports status of all settings. The module can be
configured remotely.
Control and Monitoring Notes
The following abbreviations are used in Tab le A-8 to indicate performance
limitations for the listed legacy modules:
Compatibility Matrix
Tab le 8:
• Comm problem — The module shorts out the frame communication
bus. When the problem module is installed, the NET module cannot
communicate with any of the modules in slots 1 through 10.
• ID defects — The module is susceptible to ESD (electro-static discharge)
damage of the module ID lines. If this damage occurs, the module will
be reported as faulted on the frame status page and software download
will not work.
• Faults not reported — The module may not report an error to the NET
module even though its fault LED is on. The LED gives the correct fault
status.
• Misleading status reported — The module does not support control
and monitoring but indicates through a motherboard connection that it
does. This module will show up as red on the frame status page even if
it is working correctly.
8900–FLOAD–CBL Assembly
Some modules require a cable assembly and software loading application
for the software update process. This cable assembly and CD–ROM con
taining update software files can be ordered from Grass Valley. Contact
your Grass Valley sales or service representative about ordering the
8900-FLOAD–CBL assembly.
-
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 87
Page 88

Appendix
8900NET Software Update From FTP Server
If you are updating an 8900NET module with a software version earlier
than version 3.2.0, you must use the following procedure.
FTP Method Overview
The Modular Remote Monitoring and Control System is an extension of the
Grass Valley Signal Management System (SMS) routing system and uses
the same File Transfer Protocol (FTP) technique to download software.
Note This procedure assumes your Local FTP Server computer is a 32-bit
Windows host running Win95, 98, NT or later.
If you do not have an FTP server, Grass Valley provides a free FTP server
package that is easy to install and operate. This procedure assumes you will
use the Xitami FTPD provided. If you already have an FTPD available, you
can skip steps 3 through 5.
The software update process consists of the following steps:
1. Acquire the software update files and, if needed, the FTP Server
package.
2. Place the module software update files into an FTPD modular directory.
3. Extract the FTP Daemon (Xitami FTPD).
4. Run the Xitami installation program.
5. Modify the FTPD configuration files to the Xitami directory.
6. Start the FTPD.
7. Use the 8900 GUI to initiate software updates.
Note When updating numerous Gecko 8900 modules, it is a good idea to dedicate
one frame for the update process to avoid interrupting communication with
active modules.
8. Verify the software update results.
88 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 89

FTP Software Update Procedure
1. Acquire the software update files from Grass Valley (refer to Acquiring
Module Software Updates on page 66).
a. Create a temporary download directory on your PC:
c:\temp\
b. Using the web browser, select the desired .fld zipped file.
c. Click to download the .bin (8900NET only), .fld (8900 media
modules) or zipped file. You are queried to either
SAVE AS. Select the SAVE AS option and set the path to the temporary
directory on your computer.
This process will trigger the download of the file to your computer.
Note If you have access to an existing FTP Server’s directory, the module update
files can be downloaded directly into that directory.
2. Move or extract the module update files into an FTPD modular
directory.
8900NET Software Update From FTP Server
OPEN the file or
The module software update files must reside in a directory that the
FTPD can access. The Grass Valley supplied FTPD is configured to
access a directory designated:
\modular\8900
The new software for the 8900NET module (version 3.2.0 and later) will
be a binary file (.bin extension) or a field update files (.fld extension).
a. Open Windows Explorer on the local server computer.
b. If one does not already exist, create a directory on the C drive:
c:\modular\8900
c. Double-click the module software.exe file (in the temporary
directory) and save it to the appropriate directory. The resulting file
will be a .bin or .fld:
c:\modular\8900\8900net_sw400a_fw1.bin
Note The file name shown indicates: 8900NET, software version 4.00, firmware
version 1.0.
3. Extract the FTPD (Xitami FTP Server) files.
Note This section is for facilities that do not already have an FTP Daemon (FTPD),
also known as a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Server, installed on the Gecko
8900 frame’s network. For those facilities that already have an FTPD or other
FTP Service available in their network, go to step 6.
Grass Valley provides a free FTP server for those facilities that do not
have a local FTP service. The FTP server package is the same Xitami
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 89
Page 90

Appendix
Web Server-FTP package that is provided with the Grass Valley SMS
router upgrade package. The version of the Xitami Web-FTP server dis
tributed with module software upgrades is for a 32-bit Windows host.
The FTP Daemon in the temporary directory is a self-extracting file
(ftpd.exe). To extract the files:
a. Open Windows Explorer and find the ftpd.exe file.
b. Double click on the .exe file and extract the files to C:\temp.
These files will be extracted:
• xic3223c.exe – the Xitami installation file,
• defaults.cfg – an FTPD configuration file that has been modified
specifically for Grass Valley software downloads, and
• ftpusers.sms – the FTPD’s admin file specifying user names and
passwords network access to files in the ftp server directories.
4. Run the Xitami installation program.
a. Double Click on xic3223c.exe. You will see the Xitami Welcome
(Figure 48). Click on
Next >.
-
Figure 48. Xitami Web Server Welcome
b. You will see the Xitami Installation Notes (not shown). Click on
Next >.
c. You will see Select Destination Directory (Figure 49). Do not change
the default settings. Click on
90 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Next >
Page 91

Figure 49. Select Destination Directory
8900NET Software Update From FTP Server
d. You will see the Select Program Group screen (Figure 50). Do not
change the default settings. Click on
Figure 50. Select Program Group
Next >.
e. You will see the Automatic Startup Query screen (Figure 51). Select
No. Click on Next >.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 91
Page 92
Appendix
Figure 51. Automatic Startup Query
f. You will see the Administration Password screen (Figure 52). Do
not enter anything in these fields. Click on
Figure 52. FTPD Server Administration Password
Next >.
g. You will see the Choose Server Profile screen (Figure 53). Select
Tiny - never block another task. Click on Next >.
92 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 93

Figure 53. Choose Server Profile
8900NET Software Update From FTP Server
h. You will see the Ready To Install screen (Figure 54). Click on Next >
to begin installation.
Figure 54. Ready to Install
i. An installation meter box will appear as shown in Figure 55.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 93
Page 94

Appendix
Figure 55. Installation Meter Box
j. Upon completion, you will see the Installation Complete! screen
(Figure 56). Click on
Figure 56. Installation Complete
Finish.
An Icon (see Figure 57) will have been created in the Program
Group window that was selected during installation (see Figure 50
on page 91).
94 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 95

8900NET Software Update From FTP Server
Figure 57. FTPD Icon in Program Group Window
5. Move the FTP Daemon Start-up Configuration Files.
The FTP Daemon has now been installed and requires configuration files
be placed in the Xitami directory.
a. Open Windows Explorer.
b. From the Explorer window, return to the FTPD directory and move
the extracted defaults.cfg and ftpusers.sms files to the directory at:
c:\Program Files\Xitami
The defaults.cfg and the ftpusers.sms files contain default configuration instructions that the FTPD application reads at start-up.
6. Start the FTPD.
If the Xitami Web Server (FTPD) is not already running, start it.
a. Click on the Start popup window on the PC.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 95
Page 96

Appendix
b. Select PROGRAMS, then INTERNET TOOLS, and click on Xitami Web Server
– 32 bit console
The Xitami Console will open as a DOS window. There will be a log
of events, at least one of which will indicate it is accepting connec
tions (see Figure 58).
Figure 58. Typical FTPD Console Screen
(Figure 57 on page 95).
-
The IP Address line should actually indicate the IP address of the
PC you are using for the FTP server. This is the IP Address that will
be used to initiate the software update.
The line that verifies that the FTPD is running reads:
ready for FTP connections on port 21
96 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 97

8900NET Software Update From FTP Server
Password Protection for Software Upgrades
The FTPD distributed for software downloads provides user name and
password protection for software updates. User name and password entry
is required in the Software Update web pages.
The assignment of user names and passwords for a given FTP root directory is administered by editing the ftpuser.sms file included in the FTPD
distribution (see Step
default user name and password (user name: moduser, password:
moduser) for access to the modular root directory and instructions for
setting up an account.
The contents of the file are shown in Figure 59. (The file also includes the
SMS7000 account for customers with Grass Valley SMS routers.)
Figure 59. User Name and Password File ftpuser.sms
3 of this procedure). This file initially contains the
Note The FTPD configuration files should be installed in a password protected
directory.
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 97
Page 98

Appendix
Upgrading Software
With the FTPD running, use the 8900 GUI to initiate software updates. Use
the web-browser to:
• Access the appropriate Software Update page for a given module,
• Enter the required data into the HTML Form on that page, and
• Submit the form.
The 8900 frame uses the data in the form to contact the FTPD on the
server, download the update file, and reprogram the targeted module.
Note Prior to attempting update of software, refer to the target module’s manual
and confirm that the Remote/Local Only jumper is in the Remote position.
Note To monitor the progress of the download, you may use the serial port con-
nection (see Figure 60 on page 99) with a computer running a terminal emulation application.
98 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
Page 99

8900NET Software Update From FTP Server
Serial Connection for console interface
Comm. Parameters: 9600 baud, 8 bits,
parity-none, 1 stop, flow-none
Comm 1 or
Comm 2 port
RS-232
PC running Hyperterm Terminal Emulation
PC running web browser GUI
8900TFN Frame
0612 -29r1
Ethernet
8900TFN Frame
RJ-45
connector
To PC network card
RJ-45 connector
Ethernet Hub
Figure 60. Serial Port Console and PC Network Connections
8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual 99
Page 100

Appendix
Use
this
link
a. Open a web browser on a PC that is connected over the network to
the Gecko 8900 frame.
b. Enter the URL of the frame where the module to be updated resides.
The frame’s main status page will appear.
c. Click on the module’s link and then click on Software Update (the
8900NET module link is shown at left).
Note This link and web page appears only when the 8900NET module in the frame
is running software v3.2.2 and earlier. 8900NET modules running v4.0.0 software no longer have this web page and must be updated with NetConfig as
described in Upgrading 8900NET Software on page 66.
The module’s Software Update web page will appear as shown in
Figure 61. This form is the same for all 8900 modules that support a
network software update.
Figure 61. 8900NET Module Software Update Page
d. In the FTP Server Address field, enter the IP Address of the PC that
has the FTPD installed and running.
e. You can enter the Host Name of the PC that has the FTPD running
into the FTP Server Name field. This is an optional step and can be
omitted.
f. Click on Apply to set the FTP Address.
The web page will refresh and the new FTP address should be displayed as the current setting.
100 8900NET (Net Card) — Instruction Manual
 Loading...
Loading...