Page 1

User Manual
BudgeTone - 200 Series
IP Phone
For Firmware Version 1.1.0.16
Grandstream Networks, Inc.
www.grandstream.com
1
Page 2

Table of Contents
1 WELCOME……………………………………………………………. 4
2 INSTALLATION……………………………………………………… 5
2.1 W
2.2 C
2.3 S
2.4 W
HAT IS INCLUDED IN THE PACKAGE…………………………………5
ONNECTING YOUR PHONE…………………………………………...5
AFETY COMPLIANCES………………………………………………..6
ARRANTY…………………………………………………………...6
3 PRODUCT OVERVIEW……………………………………………… 8
3.1 K
3.2 H
EY FEATURES………………………………………………………. 9
ARDWARE SPECIFICATION………………………………………….10
4 USING BUDGETONE-200 IP PHONE……………………………... 12
4.1 G
4.2 G
4.3 M
ETTING FAMILIAR WITH LCD……………………………………... 12
ETTING FAMILIAR WITH KEYPAD…………………………………. 14
AKING AND ANSWERING PHONE CALLS…………………………... 16
4.3.1 Handset, Speakerphone and Headset Mode……………………. 16
4.3.2 Making Calls……………………………………………………….. 16
4.3.3 Making Calls using IP Address………………………………….. 17
4.3.4 Receiving Calls…………………………………………………….. 17
4.3.5 Call Hold…………………………………………………………… 18
4.3.6 Call Waiting and Switch between Calls………………………… 18
4.3.7 Call Transfer……………………………………………………….. 18
4.3.8 3-Way Conferencing………………………………………………. 19
4.3.9 Checking Message and Message Waiting Indication………… 20
4.3.10 Mute and Delete……………………………………………………. 20
4.4 C
ALL FEATURES……………………………………………………. 20
5 CONFIGURATION GUIDE………………………………………... 22
5.1 C
5.2 C
ONFIGURATION WITH KEYPAD……………………………………. 22
ONFIGURATION WITH WEB BROWSER……………………………... 25
5.2.1 Access the Web Configuration Menu…………………………… 25
5.2.2 End User Configuration………………………………………….. 25
5.2.3 Advanced User Configuration…………………………………… 30
5.2.4 Saving the Configuration Changes……………………………… 43
5.2.5 Rebooting the Phone from Remote……………………………… 43
5.3 C
ONFIGURATION THROUGH CENTRAL PROVISIONING SERVER……... 44
6 FIRMWARE UPGRADE……………………………………………. 45
6.1 U
PGRADE THROUGH HTTP…………………………………………. 45
2
Page 3

6.2 U
PGRADE THROUGH TFTP………………………………………….. 45
7 RESTORE FACTORY DEFAULT SETTING……………………47
APPENDIX I GLOSSARY OF TERMS………………………………...48
3
Page 4
1 Welcome
Thank you for purchasing Grandstream BudgeTone-200 IP Phone. You
made an excellent choice and we hope you will enjoy all its capabilities.
Grandstream's BudgeTone-200 SIP IP phone is the innovative IP telephone
that offers a rich set of functionality and superb sound quality. They are
fully compatible with SIP industry standard and can interoperate with many
other SIP compliant devices and software on the market.
This document is subject to changes without notice. The latest electronic
version of this user manual is available for download from the following
location:
http://www.grandstream.com/user_manuals/BudgeTone200.pdf
4
Page 5

2 Installation
2.1 What is Included in the Package
The BudgeTone-200 phone package contains:
1. One BudgeTone -200 Main Case
2. One Handset
3. One Phone Cord
4. One Universal Power Adapter
5. One Ethernet Cable
2.2 Connecting Your Phone
Following is a backside picture of BudgeTone-200, each connection port is
labeled with the name in the following table:-
LAN port
PC Port
POWER
HEADSET
5
Page 6

The table below describes the connectors on the BudgeTone-200 phone:
LAN
PC 10/100 Switch port for connecting PC
POWER 5V power port
HEADSET 2.5mm Headset port
10/100 Switch LAN port for connecting to
Ethernet.
2.3 Safety Compliances
The BudgeTone-200 phone is compliant with various safety standards
including FCC/CE. Its power adaptor is compliant with UL standard. The
phone should only be operated with the universal power adaptor provided
with the package. Damages to the phone caused by using other unsupported
power adaptors are not covered by the manufacturer’s warranty.
2.4 Warranty
Grandstream has a reseller agreement with our reseller customer. End user
should contact the company from whom you purchased the product for
replacement, repair or refund.
If you purchased the product directly from Grandstream, contact your
Grandstream Sales and Service Representative for a RMA (Return Materials
Authorization) number.
Grandstream reserves the right to remedy warranty policy without prior
notification.
6
Page 7

Warning: Please do not attempt to use a different power adaptor. Using other power
adaptor may damage the BudgeTone-200 and will void the manufacturer warranty.
Caution: Changes or modifications to this product not expressly approved
by Grandstream, or operation of this product in any way other than as
detailed by this User Manual, could void your manufacturer warranty.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose without
the express written permission of Grandstream Networks, Inc..
7
Page 8

3 Product Overview
The following photo illustrates the appearance of a BudgeTone-200 IP
phone.
Front View
Side View
8
Page 9

3.1 Key Features
Grandstream BudgeTone-200 IP Phone is a next generation IP telephone based on
industry open standard SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). Built on innovative technology,
Grandstream IP Phone features market leading superb sound quality and rich
functionalities at mass-affordable price.
Software Features:
• Support SIP 2.0, TCP/UDP/IP, PPPoE, RTP/RTCP, HTTP, ARP/RARP, ICMP,
DNS, DHCP, NTP/SNTP, TFTP.
• Support multiparty conferencing
• Supports Quick IP Call Mode.
• Support NAT traversal using IETF STUN and Symmetric RTP
• Advanced Digital Signal Processing (DSP) technology to ensure superior hi-
fidelity audio quality, interoperable with various 3rd party SIP end user device,
Proxy/Registrar/Server and Gateway products
• Advanced and patent pending adaptive jitter buffer control, packet delay and loss
concealment technology
• Support popular codecs including G711 (a-law and u-law), G.723.1 (6.3K),
G.729A/B and GSM. Dynamic negotiation of codec and voice payload length
• Support standard voice features such as Caller ID Display or Block, Call Waiting,
Call Waiting Caller ID, Call Hold, Call Transfer (attended/blind), Do-Not-Disturb,
Call Forwarding, in-band and out-of-band DTMF(RFC2833), SIP INFO, Dial
Plans, Off-Hook Auto Dial, Auto Answer, Early Dial and Speed Dial, etc.
• Full duplex hands-free speakerphone, redial, call log, volume control, voice mail
with indicator, downloadable ring tone, etc.
• Support Silence Suppression, VAD (Voice Activity Detection), CNG (Comfort
Noise Generation), Line Echo Cancellation (G.168) and AGC (Automatic Gain
Control)
• Support Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) with Acoustic Gain Control (AGC)
for speakerphone mode
• Support sidetone
• Support DIGEST authentication and encryption using MD5 and MD5-sess
• Provide easy configuration through manual operation (phone keypad), Web
interface or automated provisioning by downloading encrypted configuration file
via HTTP/TFTP for mass deployment
• Support for Layer 2 (802.1Q VLAN, 802.1p) and Layer 3 QoS (ToS, DiffServ,
MPLS)
• Support firmware upgrade via TFTP or HTTP.
• Support DNS SRV Look up and SIP Server Fail Over
• Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) with Acoustic Gain Control (AGC) for
speakerphone mode
• Support for Authenticating configuration file before accepting changes
9
Page 10

• allow user to specify different URL for configuration file and firmware files
Hardware Features:
• Support Headset which will auto switch to Headset when plugged in
• Support 10/100 Full/Half Duplex Ethernet Switch with LAN and PC port,
Ethernet polarity can be auto detected, thus either straight through or twist cable
can be used.
• Support Message Waiting Indication LED
10
Page 11

3.2 Hardware Specification
The table below describes the hardware specification of BudgeTone-200:
Model
LAN interface 2xRJ45 10/100Base-T
Headset Jack 2.5mm Headset port
LED 1 LED in RED color
Phone Case 25-button keypad
Universal Switching
Power Adaptor
Dimension 18cm (W)
Weight 0.9kg (2lbs)
Temperature 40 - 130oF
Humidity 10% - 90%
Compliance FCC / CE / C-Tick
BudgeTone-200
12-digit caller ID LCD
Input: 100-240VAC 50-60 Hz
Output: +5VDC, 1200mA,
UL certified
22cm (D)
6.5cm (H)
5 – 45oC
(non-condensing)
11
Page 12
4 Using BudgeTone-200 IP Phone
A
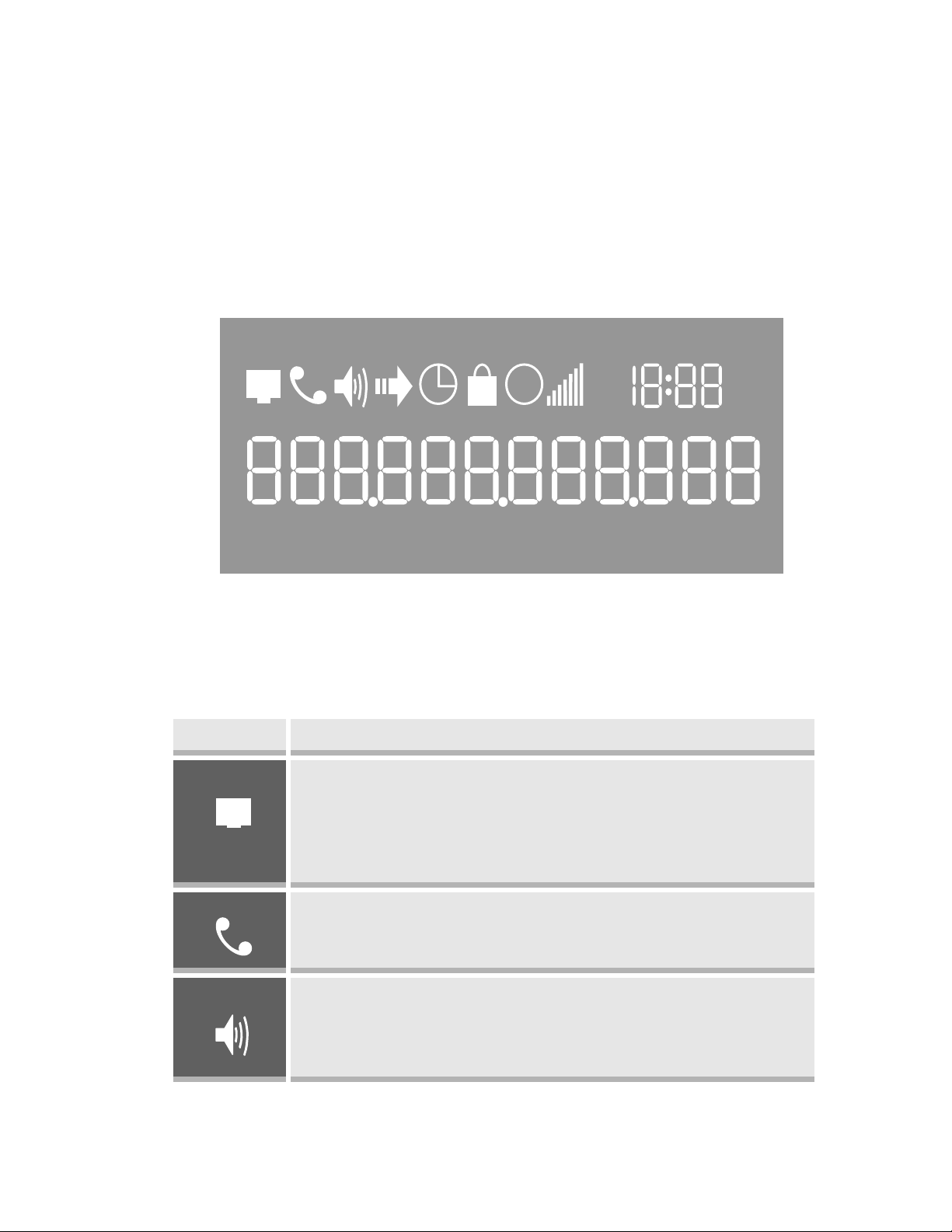
4.1 Getting Familiar with LCD / LED
BudgeTone-200 phone has a numeric LCD of 64mmx24mm size with backlight. This
model has a small red LED status reminder. Here is the display when all segments
illuminate:
010
下午
M 上午
PM
When the phone is in the normal idle state, the backlight is off. Whenever an event (call)
occurs, the backlight will turn on automatically to bring the user’s attention. In addition,
if Voice Mail configured and there is a VM waiting, the red LED will be blinking to
remind user there is a Voice Mail in the Voice Mail server.
Icon LCD Icon Definitions
Network Status Icon:
FLASH in the case of Ethernet link failure or the phone
is not registered properly.
OFF if IP address or SIP server is not found
ON if IP address and SIP server are located
Phone Status Icon:
OFF when the handset is on-hook
ON when the handset is off-hook
Speakerphone/Headset Status Icon:
FLASH when phone rings
OFF when the speakerphone/headset is off
ON when the speakerphone/headset is on
12
Page 13

A
Handset and Speakerphone/Headset Volume Icons:
0-7 scales to adjust handset / speakerphone volume
Real-time Clock:
Synchronized to Internet time server
Time zone configurable via web browser
Call Logs:
01-10 for CALLED history (dialed number)
01-10 for CALLERS history (Incoming caller ID)
M
PM
Time Icon:
AM for the morning
PM for the afternoon
IP Address Separator Icons:
Numerical Numbers and Characters:
0 - 9
* = └
# = ┘
A, b, C, c, d, E, F, G, g, H, h, I, L, n, O, o, P, q, r, S, t,
U, u, Y
13
Page 14

4.2 Getting Familiar with Keypad
Callers
Up/Down
Keys
Called
Numbers
Menu
Button
Message
Hold
Transfer
Conference
Flash
Speakerphone
Send/Dial
Mute/Delete
14
Page 15

Key Button Key Button Definitions
0 - 9, *, #
↓
↑
MENU
Digit, star and pound keys are usually used to make
phone calls
1) Reduce handset, speakerphone/headset volume after
off hook the phone via handset or speaker
2) Reduce ring tone volume when phone in IDLE and off
hook to confirm the changed ring tone volume
3) Next menu item browsing when phone is in IDLE
mode after MENU key pressed, off hook to interrupt and
exit
1) Increase handset, speakerphone/headset volume after
off hook the phone via handset or speaker
2) Increase ring tone volume when phone in IDLE and
off hook to confirm the changed ring tone volume
3) Previous menu item browsing when phone is in IDLE
mode after MENU key pressed, off hook to interrupt and
exit
Enter keypad MENU mode when phone is in IDLE
mode.
It is also the ENTER key once entering MENU
CALLED
CALLERS
MESSAGE
HOLD
TRANSFER
CONFERENCE
FLASH
MUTE/DEL
After off hook, press to display the dialed numbers.
When number displayed, press the SEND key can make
call using that displayed number
After off hook, press to display the incoming Caller IDs.
When number displayed, press the SEND key can make
call using that displayed number
Enter to retrieve voice mails from Voice Mail Portal or
Server
Temporarily hold the active call
Transfer the active call to another party
Establish 3-way conferencing call
Flash event to switch between two lines
Mute an active call; or Delete a key entry, call log etc
Also used to ‘REJECT’ incoming call.
15
Page 16

SEND/(RE)DIAL
Dial a new number inputted or Redial the number last
dialed. After entering the phone number, pressing this
key would force a call to go out immediately before
timeout
SPEAKERPHONE
4.3 Making and Answering Phone Calls
Enter hands-free mode
4.3.1 Handset, Speakerphone and Headset Mode
The regular Handset mode can be switched with either the Speaker mode (Hand free) or
the Headset mode, however, whenever the Headset is plugged in, Speaker mode will be
switched to the Headset mode automatically.
Handset mode and Speakerphone/Headset mode cannot be enabled at the same time.
Pressing the hook-switch or Speakerphone button would toggle the phone between these
two modes.
To Switch between Handset and Speaker/Headset, simply press the Hook Flash in the
Handset cradle or the Speaker button.
4.3.2 Make Calls using Numbers
There are FIVE ways to make phone calls:
• Pick up handset or press SPEAKERPHONE button, and then enter the phone
numbers
• Press the SEND button directly to redial the number last called.
• Once pressed, the last dialed number will be displayed on the LCD as the
corresponding DTMF tones are played out and an outgoing call is sent.
• Browse the CALLED/CALLER history and press the SEND/REDIAL button.
• Pick up the handset or press the speakerphone button, then press the
“CALLED/CALLERS” button to browse thru the last 10 numbers dialed out.
Once the desired number is identified and displayed on the LCD screen, press the
SEND button and a new call to that displayed number will be sent out
immediately.
Examples:
16
Page 17

• To dial another extension on the same proxy, such as 1008, simply pick up
handset or press speakerphone, dial 1008 and then press the “SEND” button.
• To dial a PSTN number such as 6266667890, you might need to enter in some
prefix number followed by the phone number. Please check with your VoIP
service provider to get the information. If you phone is assigned with a PSTN-like
number such as 6265556789, most likely you just follow the rule to dial
16266667890 as if you were calling from a regular analog phone, followed by
pressing the “SEND” button.
4.3.3 Make Calls using IP Address
Direct IP calling allows two parties, that is, a BudgeTone phone and another VoIP
Device, to talk to each other in an ad hoc fashion without a SIP proxy. This kind of VoIP
calls can be made between two parties if:
• Both BudgeTone phone and other VoIP Device(i.e., another IP Phone or
BudgeTone SIP phone or other VoIP unit) have public IP addresses, or
• Both BudgeTone phone and other VoIP Device are on the same LAN using
private or public IP addresses, or
• Both BudgeTone phone and other VoIP Device can be connected through a router
using public or private IP addresses (with necessary port forwarding or DMZ).
This model has the ability to dial an IP address under the same LAN segment by simply
pressing the last octet in the IP address.
In the Advanced Settings page there is an option "Use Quick IP-call mode", by default it
is set to No. When this option is set to YES, and #XXX is dialed, where X is 0-9 and
XXX <=255, phone will make direct IP call to aaa.bbb.ccc.XXX where aaa.bbb.ccc
comes from the local IP address REGARDLESS of subnet mask.
#XX or #X are also valid so leading 0 is not required (but OK).
eg.
192.168.0.2 calling 192.168.0.3 just dial #3 follow by SEND or #
192.168.0.2 calling 192.168.0.23 just dial #23 follow by SEND or #
192.168.0.2 calling 192.168.0.123 just dial #123 follow by SEND or #
192.168.0.2 dial #3 and #03 and #003 has same effect --> call 192.168.0.3
Note:- If you have a SIP Server configured, Direct IP-IP call will still work. However, if
you are using STUN, Direct IP-IP call will also use STUN.
OR
17
Page 18

To make a direct IP to IP call, first off hook, then press “MENU” key, then enter a 12-
digit target IP address to make the call. If port is not default 5060, destination ports can
be specified by using “*4” (encoding for “:”) followed by the port number.
Examples:
• If the target IP address is 192.168.0.10, the dialing convention is
MENU_key 192 168 000 010
followed by pressing the “SEND” key or wait for seconds in the No Key Entry
Timeout.
• If the target IP address/port is 192.168.1.20:5062, then the dialing convention
would be:
MENU_key 192168001020*45062
followed by pressing the “SEND” key wait for seconds in the No Key Entry
Timeout.
4.3.4 Answer an Incoming Call
There are two ways to answer an incoming call:
1. Pick up the handset to answer the call normally using handset, or
2. Press the SPEAKERPHONE button to answer in speakerphone or headset mode
4.3.5 Call Hold
While in conversation, pressing the “Hold” button will put the remote end on hold.
Pressing the “Hold” button again will release the previously Hold state and resume the bidirectional media.
4.3.6 Call Waiting and Call Flashing
If call waiting feature is enabled, while the user is in a conversation, he will hear a
special stutter tone if there is another incoming call. User then can press FLASH button
to put the current call party on hold automatically and switch to the other call. Pressing
flash button toggles between two active calls.
4.3.7 Call Transfer
Two transfer operations are supported.
18
Page 19

4.3.7.1 Blind Transfer
User can transfer an active call to a third party without announcement.
User presses the “TRANSFER” button and if the other voice channel is available
(i.e., there is no other active conversation besides the current one), user will hear a
dial tone. User can then dial the third party’s phone number followed by pressing
SEND button.
NOTE:
• “Enable Call Feature” has to be configured to “Yes” in web configuration page
in order to make the features to work.
A can hold on to the phone and wait for one of the three following behaviors:
• A quick confirmation tone (temporarily using the call waiting indication tone)
follows by a dial tone. This indicates the transfer has been successful. At this
point, the user can either hang up or make another call.
• A quick busy tone followed by a restored call (On supported platforms
only). This means the transfer has failed due to the failed response sent from
server and the phone will try to recover the call. The busy tone is just to indicate
to the transferor that the transfer has failed.
• Busy tone keeps playing. This means the phone has failed to receive the final
response and decide to time out. Be advised that this does not indicate the
transfer has been successful, nor does it indicate the transfer has failed.
4.3.7.2 Attended Transfer
User can transfer an active call to a third party with announcement.
User presses the “FLASH” button and hears a dial tone, then dial the third party’s
phone number followed by pressing “SEND” button. If the call is answered, press
“TRANSFER” to complete the transfer operation and hand up, if the call is not
answered, pressing “FLASH” button to resume the original call.
NOTE:
• When Attended Transfer failed, if A hangs up, the BudgeTone phone will ring user
A back again to remind A that B is still on the call. A can pick up the phone to
restore conversation with B.
4.3.8 Conference Call
BudgeTone 200 phone supports 3-way conference.
19
Page 20

Assuming that call party A and B are in conversation. A wants to bring C in a conference:
1. A presses the “CONFERENCE” button to get a dial tone and put B on hold
2. A dials C’s number then “SEND” key to make the call
3. If C answers the call, then A presses “CONFERENCE” button to bring B, C in
the conference.
4. If C does not answer the call, A can press FLASH back to talk to B.
NOTE:
• During the conference, if B or C drops the call, the remaining two parties
can still talk. However, if A the conference initiator hangs up, all calls will
be terminated.
4.3.9 Checking Message and Message Waiting Indication
When BudgeTone-200 is on-hook, pressing the MESSAGE button will trigger the phone
to call the VM Server (VMS) configured for the Account.
The MWI (Message Waiting Indicator) LED will flash in red color in three quarters of a
second when voicemail server sends message waiting information to BudgeTone-200.
4.3.10 Mute and Delete
When in conversation with an ACTIVE LINE, pressing “MUTE/DEL” will mute the
conversation, that is, you can hear the other party but the other party cannot hear you.
Pressing the button again will resume the conversation.
When dialing a number, press “MUTE/DEL” will delete the last entered digit.
When receiving incoming call, press “MUTE/DEL” will Reject the call and forward to
voice mail.
4.4 Call Features
BudgeTone-200 series phone supports a list of call features: Caller ID Block (or
Anonymous Call), Disable/Enable Call Waiting, Call Forward on Busy, Delay, or
Unconditional, etc.
Following table shows the call features of BudgeTone-200 series phone.
20
Page 21

Key Call Features
*30 Block Caller ID (for all subsequent calls)
*31 Send Caller ID (for all subsequent calls)
*67 Block Caller ID (per call)
*82 Send Caller ID (per call)
*70 Disable Call Waiting. (Per Call)
*71 Enable Call Waiting (Per Call)
*72 Unconditional Call Forward
To use this feature, dial “*72” and get the dial tone. Dial the forward
number and “#” for a dial tone, then hang up.
*73 Cancel Unconditional Call Forward
To cancel “Unconditional Call Forward”, dial “*73” and get the dial
tone, then hang up.
*90 Busy Call Forward
To use this feature, dial “*90” and get the dial tone. Dial the forward
number and “#” for a dial tone, then hang up.
*91 Cancel Busy Call Forward
To cancel “Busy Call Forward”, dial “*91” and get the dial tone, then
hang up.
*92 Delayed Call Forward
To use this feature, dial “*92” and get the dial tone. Dial the forward
number and “#” for a dial tone, then hang up.
*93 Cancel Delayed Call Forward
To cancel this Forward, dial “*93” and get the dial tone, then hang up.
21
Page 22

5 Configuration Guide
5.1 Configuration with Keypad
When the phone is IDLE or On Hook, press the MENU button to enter key pad menu
state. When the phone goes off-hook or a call comes in, the phone automatically exits the
key pad menu state and prepare for the call. It also exits the key pad menu state if left idle
for 20 seconds.
Here are the key pad menu options supported:
Menu Item Menu Functions
Display “[1] dhcP On ”
or “[1] dhcP oFF” for the current selection
1
Press MENU key to enter edit mode
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to toggle the selection
Press MENU to save and exit
Must recycle power to take effective!!!
2
3
4
Display “[2] IP Addr ”
Press MENU to display the current IP address
Enter new IP address if DHCP is OFF
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to exit
Press MENU to (save and) exit
Must recycle power to take effective!!!
Display “[3] SubNet ”
Press MENU to display the Subnet mask
Enter new Subnet mask if DHCP is OFF
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to exit
Press MENU to (save and) exit
Must recycle power to take effective!!!
Display “[4] routEr ”
Press MENU to display the Router/Gateway address
Enter new Router/Gateway address if DHCP is OFF
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to exit
Press MENU to (save and) exit
Must recycle power to take effective!!!
22
Page 23

Menu Item Menu Functions
Display “[5] dnS ”
Press MENU to display the DNS address
5
6
7
Enter new DNS address if DHCP is OFF
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to exit
Press MENU to (save and) exit
Must recycle power to take effective!!!
Display “[6] tFtP ”
Press MENU to display the TFTP address
Enter new TFTP server IP address
Press MENU to save
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to exit
Display “[7] G-711u 2”
Press MENU to select new codec
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to browse a list of available codecs
line 2 “ - G-711A 2”
3 “ - G-723 1”
4 “ - G-729 2”
5 “ - GS 1”
Press 1 to 9 to indicate number of frames per TX packet
Press MENU to save and exit
Must recycle power to take effective!!!
8
9
Display “[8] SIP SP-1”
Reserve for future products.
Display “[9] codE rEL”
Press Menu to display the code releases
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to browse
line 1 “b 2006-03-14” – date: boot code
2 “ 1. 1. 0. 1” – version: boot code
3 “P 2006-04-28” – date: phone code
4 “ 1. 1. 0. 16 – version: phone code
5 “1r 2004-05-12” – date: 1st ring tone
6 “ 0. 0. 0. 0” – version: ring tone
7 “2r 2004-05-12” – date: 2nd ring tone
8 “ 0. 0. 0. 0” – version: ring tone
9 “3r 0000-00-00” – date: 3rd ring tone
10 “ 0. 0. 0. 0” – version: ring tone
(all zeroes means unavailable or unsupported)
Press MENU to exit
23
Page 24

Menu Item Menu Functions
Display “[10] Phy Addr”
10
11
Others
Press MENU to display the physical / MAC address
Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to exit
Display “[11] ring 0”
Press MENU to hear the selected ring tone, press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to select the
stored ring tones. Now only 3 are available, ring 0 (default), ring 1 and ring
2. ring 3 is unavailable or unsupported.
Press MENU to select and exit
Display “ -- rESEt --”, please be very CAREFUL here
• Key in the physical / MAC address on back of the phone, Press
MENU, phone will be reset to FACTORY DEFAULT setting, and
all your setting will be erased.
• Press MENU key without key in anything, phone will function the
same as power cycle or reboot
When phone is powered on and time is displayed
• Press ‘↓’ or ’↑’, Display “ ring [4] ”, press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ again to hear
and adjust the ring tone volume, from 0 (off) to 7 (maximum), off
and on hook to set
• Press “SPEAKERPHONE” button, or off hook and pick up
handset, press ‘↓’ or ’↑’ to adjust the speakerphone/headset or
handset volume
24
Page 25

5.2 Configuration with Web Browser
BudgeTone 200 series IP phone has an embedded Web server that will respond to HTTP
GET/POST requests. It also has embedded HTML pages that allow a user to configure
the IP phone through a Web browser such as Microsoft’s IE.
5.2.1 Access the Web Configuration Menu
The IP Phone Web Configuration Menu can be accessed by the following URI:
http://Phone-IP-Address
where the Phone-IP-Address is the IP address of the phone.
When the phone is on-hook, press Menu button and then select the Status item to see “IP:
IP Address”
NOTE:
• To type IP address into browser to get into the configuration page, please strip
out the leading “0” as the browser will parse in octet. e.g.: if the IP address is:
192.168.001.014, please type in: 192.168.1.14.
5.2.2 End User Configuration
Once this HTTP request is entered and sent from a Web browser, the BudgeTone 200
will respond with the following login screen:
Grandstream Device Configuration
Password
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004
Login
25
Page 26

The password is case sensitive with maximum length of 25 characters and the factory
default password for End User is “123”.
After a correct password is entered in the login screen, the embedded Web server inside
the BudgeTone 200 will respond with the Configuration page which is explained in
details below.
Grandstream Device Configuration
STATUS
End User
Password:
IP Address:
BASIC
SETTINGS
ADVANCED
SETTINGS
ACCOUNT
(purposely not displayed for security protection)
dynamically assigned via DHCP (default) or PPPoE
(will attempt PPPoE if DHCP fails and following is non-blank)
PPPoE account ID:
PPPoE password:
Host name
(Option 12):
Domain name
(Option 15):
Vendor Class ID
(Option 60):
Preferred DNS server: . . .
Time Zone:
Daylight
statically configured as:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Default Router:
DNS Server 1:
DNS Server 2:
GMT-7:00 (US Mountain Time, Denver)
192.168 .0
0
.
0
.
0
.
0
.
0
0
0
0
0
.
0
.
0
.
0
.
160
.
.
.
.
.
0
0
0
0
Allow DHCP Option 2 to override Time Zone setting:
No Yes
No Yes (if set to Yes, display time will be 1 hour ahead of
26
Page 27

Savings
Time:
normal time)
Date
Display
Year-Month-Day
Month-Day-Year
Format:
Day-Month-Year
System Device Mode
Device
Mode:
Switch (default) NAT/Router
NAT/Router Configuration
WAN side
http access:
No Yes (WAN side access to http server will be rejected if set
to No)
Reply to
ICMP on
WAN port:
No Yes (Unit will not respond to PING from WAN side if set to
No)
Cloned
WAN MAC
(in hex format)
Addr:
LAN Subnet
Mask:
LAN DHCP
Base IP:
DHCP IP
Lease Time:
DMZ IP:
Port
Forwarding:
255.255.255.0
192.168.2.1
120
(in units of hours, default is 120 hours or 5 days)
(default is 255.255.255.0)
(base IP for the LAN port, default is 192.168.2.1)
WAN port LAN IP LAN port Protocol
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
UDP Only
UDP Only
UDP Only
UDP Only
UDP Only
UDP Only
UDP Only
UDP Only
27
Page 28

Update
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004, 2005
End User
Password
IP Address
Time Zone
Daylight Savings Time
This contains the password to access the Web Configuration Menu.
This field is case sensitive with a maximum length of 25 characters.
There are two modes under which the BudgeTone 200 can operate:
• If DHCP mode is enabled, then all the field values for the Static
IP mode are not used (even though they are still saved in the
Flash memory.) The BudgeTone 200 will acquire its IP address
from the first DHCP server it discovers from the LAN it is
connected.
• To use the PPPoE feature the PPPoE account settings need to
be set. The BudgeTone 200 will attempt to establish a PPPoE
session if any of the PPPoE fields is set.
• If Static IP mode is enabled, then the IP address, Subnet Mask,
Default Router IP address, DNS Server 1 (primary), DNS
Server 2 (secondary) fields will need to be configured. These
fields are set to zero by default.
This parameter controls how the date/time is displayed according to the
specified time zone.
This parameter controls whether the time will be displayed in daylight
savings time or not. If set to “Yes”, then the displayed time will be 1
hour ahead of normal time.
Date Display Format
Device Mode
WAN side http access
Reply to ICMP on WAN port
Allow user to choose among the following three formats:
Year-Month-Day
Month-Day-Year
Day-Month-Year
This parameter controls whether the device is working in NAT router
mode or Bridge mode. Need save the setting and reboot the device
before the setting start to work.
If set to “Yes”, user can access the configuration page through the
WAN port, instead of connecting PC and BT200 through the “PC” port
to do the configuration. On the other hand, it exposes the BT200 to
others, and may cause some security issues for users. Default is No.
If set to “Yes”, The BT200 will respond to the PING command from
other computers for testing, but it also is vulnerable to the DOS attack.
Default is No.
28
Page 29

Cloned WAN MAC Addr
Allow the user to set a specific MAC address. Set in Hex format.
LAN Subnet Mask
LAN DHCP Base IP
DHCP IP Lease Time
DMZ IP
Port Forwarding
In addition to the Basic Settings configuration page, end user also has access to the
device Status page. The following is a screen shot of the device Status page. Details are
explained next.
Sets the LAN subnet mask. Default value is 255.255.255.0
Base IP for the LAN port, which function as a Gateway for the subnet.
Default value is 192.168.2.1.
Value is set in units of hours. Default value is 120hr (5 Days.) The
time IP address is assigned to the LAN clients.
Forward all WAN IP traffic to a specific IP address if no matching port
is used by HandyTone-486 itself or in the defined port forwarding.
Allow the user to forward a matching (TCP/UDP) port to a specific
LAN IP address with a specific (TCP/UDP) port.
Grandstream Device Configuration
STATUS BASIC SETTINGS ADVANCED SETTINGS ACCOUNT
MAC Address:
IP Address:
Product Model:
Software Version:
System Up Time:
Registered:
PPPoE Link Up:
detected NAT type is full cone
00.0B.82.08.3D.6E
192.168.1.113
BT200
Program-- 1.1.0.16 Bootloader-- 1.1.0.1
0 day(s) 7 hour(s) 7 minute(s)
Account : Yes
disabled
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004, 2005
29
Page 30

MAC Address
The device ID, in HEX format. This is a very important ID for ISP
troubleshooting.
IP Address
Product Model
Software Version
System Up Time
Registered
PPPoE Link Up
Detected NAT
Type
This field shows LAN IP address of BudgeTone 200
This field contains the product model info.
• Program: This is the main software release, its number is always used for
firmware upgrade.
• Bootloader: This is normally not changed.
This field shows system up time since the last reboot.
This field indicates whether the device is registered to the SIP server(s).
This field shows whether the PPPoE connection is up if connected to DSL
modem.
This field shows what kind NAT the BudgeTone 200 is connected to via its LAN
port. It is based on STUN protocol.
5.2.3 Advanced User Configuration
To login to the Advanced User Configuration page, please follow the instructions in
section 5.2.1 to get to the following login page. The password is case sensitive with a
maximum length of 25 characters and the factory default password for Advanced User is
“admin”.
Grandstream Device Configuration
Password
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004
Login
30
Page 31

Advanced User configuration includes not only the end user configuration, but also
advanced configuration such as SIP configuration, Codec selection, NAT Traversal
Setting and other miscellaneous configuration. Following is a screen shot of the
advanced configuration page:
Grandstream Device Configuration
STATUS BASIC SETTINGS ADVANCED SETTINGS ACCOUNT
Admin Password:
Silence Suppression:
Voice Frames per TX:
Layer 3 QoS:
Layer 2 QoS:
No Key Entry Timeout:
Use # as Dial Key:
local RTP port:
Use random port:
keep-alive interval:
(purposely not displayed for security
protection)
No Yes
2
(up to 10/20/32/64 for G711/G726/G723/other codecs
respectively)
48
802.1Q/VLAN Tag
(Diff-Serv or Precedence value)
0
4
(in seconds, default is 4 seconds)
802.1p priority value
0
(0-7)
No Yes (if set to Yes, "#" will function as the "(Re)Dial" key)
5004
(1024-65535, default 5004)
No Yes
20
(in seconds, default 20 seconds)
Use NAT IP
STUN server:
Firmware Upgrade and
Provisioning:
(if specified, this will be used in SIP/SDP
message)
(URI or IP:port)
Upgrade Via TFTP HTTP
Firmware Server Path:
Config Server Path:
fm.grandstream.com/gs
fm.grandstream.com/gs
Firmware File Prefix: Firmware File Postfix:
Config File Prefix: Config File
Postfix:
31
Page 32

0
Allow DHCP Option 66 to override server:
No Yes
Automatic Upgrade:
No Yes, check for upgrade every
1008
minutes (default
7 days)
Always Check for New Firmware
Check New Firmware only when F/W pre/suffix changes
Authenticate Conf File:
DTMF Payload Type:
Syslog Server:
Syslog Level:
NTP Server:
Distinctive Ring Tone:
Disable Call-Waiting:
Use Quick IP-call mode:
No Yes (cfg file would be authenticated before
acceptance if set to Yes)
101
NONE
time.nist.gov
(URI or IP address)
Allow DHCP Option 42 to override NTP server:
No Yes
Custom ring tone 1, used if incoming caller ID is
Custom ring tone 2, used if incoming caller ID is
Custom ring tone 3, used if incoming caller ID is
No Yes
No Yes
Lock keypad update:
No Yes (configuration update via keypad is disabled if
set to Yes)
Update
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004, 2005
32
Page 33

Admin
Password
Administrator password. Only administrator can configure the “Advanced
Settings” page. Password field is purposely left blank for security reason
after clicking update and saved. The maximum password length is 25
characters.
Silence
Suppression
Voice Frames
per TX
This controls the silence suppression/VAD feature of G723 and G729. If set
to “Yes”, when a silence is detected, small quantity of VAD packets (instead
of audio packets) will be sent during the period of no talking. If set to “No”,
this feature is disabled.
This field contains the number of voice frames to be transmitted in a single
packet. When setting this value, the user should be aware of the requested
packet time (used in SDP message) as a result of configuring this parameter.
This parameter is associated with the first vocoder in the above vocoder
Preference List or the actual used payload type negotiated between the 2
conversation parties at run time.
e.g., if the first vocoder is configured as G723 and the “Voice Frames per
TX” is set to be 2, then the “ptime” value in the SDP message of an INVITE
request will be 60ms because each G723 voice frame contains 30ms of
audio. Similarly, if this field is set to be 2 and if the first vocoder chosen is
G729 or G711 or G726, then the “ptime” value in the SDP message of an
INVITE request will be 20ms.
If the configured voice frames per TX exceeds the maximum allowed value,
the BudgeTone 200 will use and save the maximum allowed value for the
corresponding first vocoder choice. The maximum value for PCM is
10(x10ms) frames; for G726, it is 20 (x10ms) frames; for G723, it is 32
(x30ms) frames; for G729/G728, 64 (x10ms) and 64 (x2.5ms) frames
respectively.
Layer 3 QoS
Layer 2 QoS
No Key Entry
Timeout
Use # as
Send Key
This field defines the layer 3 QoS parameter which can be the value used for
IP Precedence or Diff-Serv or MPLS. Default value is 48.
This contains the value used for layer 2 VLAN tag. Default setting is
blank.
Default is 4 seconds.
This parameter allows users to configure the “#” key to be used as the
“Send” (or “Dial”) key. If set to “Yes”, pressing this key will immediately
trigger the sending of dialed string collected so far. In this case, this key is
essentially equivalent to the “(Re)Dial” key. If set to “No”, this “#” key will
then be included as part of the dial string to be sent out.
33
Page 34

Local RTP
port
This parameter defines the local RTP-RTCP port pair the BudgeTone 200
will listen and transmit. It is the base RTP port for channel 0. When
configured, channel 0 will use this port _value for RTP and the port_value+1
for its RTCP; channel 1 will use port_value+2 for RTP and port_value+3 for
its RTCP. The default value is 5004.
Use Random
Port
Keep-alive
interval
Use NAT IP
STUN Server
Firmware
Upgrade and
provisioning
Via TFTP
Server
This parameter, when set to Yes, will force random generation of both the
local SIP and RTP ports. This is usually necessary when multiple
BudgeTone 200s are behind the same NAT.
This parameter specifies how often the BudgeTone 200 sends a blank UDP
packet to the SIP server in order to keep the “hole” on the NAT open.
Default is 20 seconds.
NAT IP address used in SIP/SDP message. Default is blank.
IP address or Domain name of the STUN server.
This radio button will enable BudgeTone 200 to download firmware or
configuration file through either TFTP or HTTP.
This is the IP address of the configured TFTP server. If selected and it is
non-zero or not blank, the BudgeTone 200 will attempt to retrieve new
configuration file or new code image from the specified TFTP server at boot
time. It will make up to 3 attempts before timeout and then it will start the
boot process using the existing code image in the Flash memory. If a TFTP
server is configured and a new code image is retrieved, the new downloaded
image will be verified and then saved into the Flash memory.
Note: Please do NOT interrupt the TFTP upgrade process (especially the
power supply) as this will damage the device. Depending on the network
environment this process can take up to 15 or 20 minutes.
Via HTTP
Server
Allow DHCP
Option 66 to
override
server
The URL for the HTTP server used for firmware upgrade and configuration
via HTTP. For example,
http://provisioning.mycompany.com:6688/Grandstream/1.0.5.16
Here “:6688” is the specific TCP port that the HTTP server is listening at, it
can be omitted if using default port 80.
Note: If Auto Upgrade is set to No, BudgeTone 200 will only do HTTP
download once at boot up.
DHCP Option 66 is used to identify a TFTP server when the 'sname' field in
the DHCP header has been used for DHCP options. If you choose yes,
BT200 will use the TFTP server resolved from DHCP, instead of the one you
specified in the "TFTP Server" option above.
34
Page 35

Automatic
Upgrade
Choose Yes to enable automatic upgrade and provisioning.
In “Check for new firmware every” field, enter the number of days to enable
BudgeTone 200 to check the server for firmware upgrade or configuration in
the defined period of days.
When set to No, BudgeTone 200 will only do upgrade once at boot up.
“Always check for New Firmware”
“Check New Firmware only when F/W pre/suffix changes”
Authenticate
Conf File
DTMF
Payload Type
Syslog Server
Syslog Level
if set to Yes, cfg file would be authenticated before acceptance. This
mechanism is useful for the protection of configuration on the device from
unauthorized change.
This parameter sets the payload type for DTMF using RFC2833.
The IP address or URL of System log server. This feature is especially useful
for ITSP (Internet Telephone Service Provider)
Select the ATA to report the log level. Default is NONE. The level is one of
DEBUG, INFO, WARNING or ERROR. Syslog messages are sent based on
the following events:
• product model/version on boot up (INFO level)
• NAT related info (INFO level)
• sent or received SIP message (DEBUG level)
• SIP message summary (INFO level)
• inbound and outbound calls (INFO level)
• registration status change (INFO level)
• negotiated codec (INFO level)
• Ethernet link up (INFO level)
• SLIC chip exception (WARNING and ERROR levels)
• memory exception (ERROR level)
NTP server
The Syslog uses USER facility. In addition to standard Syslog payload, it
contains the following components:
GS_LOG: [device MAC address][error code] error message
Here is an example: May 19 02:40:38 192.168.1.14 GS_LOG:
[00:0b:82:00:a1:be][000] Ethernet link is up
URI or IP address of the NTP (Network Time Protocol) server, which will be
used by the phone to synchronize the date and time.
35
Page 36

Allow DHCP
Option 42 to
override NTP
server
DHCP Option 42 specifies a list of IP addresses for Network Time Protocol
(NTP) servers available to the client. If you choose yes, BT200 will use the
NTP servers resolved from DHCP, instead of the one you specified in the
"NTP Server" option above.
Distinctive
Ring Tone
Disable Call
Waiting
Quick IP Call
Mode
Customer Ring Tone 1 to 3 with associate Caller ID: when selected, if Caller
ID is configured, then the device will ONLY sound this ring tone when the
incoming call is from the Caller ID, device will use System Ring Tone for all
other calls.
When selected but no Caller ID is configured, the selected ring tone will be
used for all incoming calls.
Default is No.
This model has the ability to dial an IP address under the same LAN segment
by simply pressing the last octet in the IP address.
In the Advanced Settings page there is an option "Use Quick IP-call mode",
by default it is set to No. When this option is set to YES, and #XXX is
dialed, where X is 0-9 and XXX <=255, phone will make direct IP call to
aaa.bbb.ccc.XXX where aaa.bbb.ccc comes from the local IP address
REGARDLESS of subnet mask.
#XX or #X are also valid so leading 0 is not required (but OK).
eg.
192.168.0.2 calling 192.168.0.3 just dial #3 follow by SEND or #
192.168.0.2 calling 192.168.0.23 just dial #23 follow by SEND or #
192.168.0.2 calling 192.168.0.123 just dial #123 follow by SEND or #
192.168.0.2 dial #3 and #03 and #003 has same effect --> call 192.168.0.3
Note:- If you have a SIP Server configured, Direct IP-IP call will still work.
However, if you are using STUN, Direct IP-IP call will also use STUN.
Lock keypad
update
If this parameter is set to “Yes”, the configuration updates via keypad for
Menu Item 7, 9, 12 are disabled.
36
Page 37

Following is the screenshot of the Account Configuration Page:-
R
Grandstream Device Configuration
STATUS BASIC SETTINGS ADVANCED SETTINGS ACCOUNT
Account Active:
Account Name:
SIP Server:
Outbound Proxy:
SIP User ID:
Authenticate ID:
Authenticate Password:
Name:
Use DNS SRV:
No Yes
MyCom pany
sip.mycompany.com
(e.g., MyCompany)
(e.g., sip.mycompany.com, or IP address)
(e.g., proxy.myprovider.com, or IP
address, if any)
123
123
(the user part of an SIP address)
(can be identical to or different from SIP
User ID)
(purposely not displayed for security
protection)
John Doe
(optional, e.g., John Doe)
No Yes
User ID is phone number:
SIP Registration:
Unregister On Reboot:
egister Expiration:
local SIP port:
SIP T1 Timeout:
SIP T2 Interval:
NAT Traversal (STUN):
SUBSCRIBE for MWI:
Proxy-Require:
Voice Mail UserID:
No Yes
No Yes
No Yes
60
(in minutes. default 1 hour, max 45 days)
5060
(default 5060)
1 sec
4 sec
No No, but send keep-alive Yes
No Yes
(User ID/extension for 3rd party voice
37
Page 38

mail system)
I
Send DTMF:
Early Dial:
Dial Plan Prefix:
Enable Call Features:
Session Expiration:
Min-SE:
Caller Request Timer:
Callee Request Timer:
Force Timer:
in-audio via RTP (RFC2833) via SIP INFO
No Yes (use "Yes" only if proxy supports 484
response)
(this prefix string is added to each dialed number)
No Yes (if Yes, Call Forwarding & Call-WaitingDisable are supported locally)
180
(in seconds. default 180 seconds)
90
(in seconds. default and minimum 90 seconds)
No Yes (Request for timer when making outbound
calls)
No Yes (When caller supports timer but did not
request one)
No Yes (Use timer even when remote party does not
support)
UAC Specify Refresher:
UAS Specify Refresher:
Force INVITE:
Enable 100rel:
Account Ring Tone:
Send Anonymous:
Auto Answer:
Allow Auto Answer by Call-
nfo:
UAC UAS Omit (Recommended)
UAC UAS (When UAC did not specify refresher tag)
No Yes (Always refresh with INVITE instead of
UPDATE)
No Yes
system ring tone
custom ring tone 1
custom ring tone 2
custom ring tone 3
No Yes (caller ID will be blocked if set to Yes)
No Yes
No Yes
38
Page 39

Turn off speaker on remote
disconnect:
No Yes
Preferred Vocoder:
(in listed order)
Special Feature:
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004, 2005
Individual Account Settings
Account Active
Account Name
This field indicates whether the account is active or not.
A name to identify an account which will be displayed in LCD.
choice 1:
choice 2:
choice 3:
choice 4:
Standard
Update
G.723.1
PCMU
PCMA
G.729A/B
choice 5:
choice 6:
choice 7:
choice 8:
GSM
PCMU
PCMA
G.729A/B
SIP Server
Outbound Proxy
SIP User ID
Authenticate ID
Authenticate
Password
Name
SIP Server’s IP address or Domain name provided by VoIP service
provider.
IP address or Domain name of Outbound Proxy, or Media Gateway, or
Session Border Controller. Used by BudgeTone 200 for firewall or
NAT penetration in different network environment. If symmetric NAT
is detected, STUN will not work and ONLY outbound proxy can
provide solution for it.
User account information, provided by VoIP service provider (ITSP),
usually has the form of digit similar to phone number or actually a
phone number.
SIP service subscriber’s Authenticate ID used for authentication. Can be
identical to or different from SIP User ID.
SIP service subscriber’s account password for BudgeTone 200 to
register to (SIP) servers of ITSP.
SIP service subscriber’s name which will be used for Caller ID display.
39
Page 40

Use DNS SRV:
Default is No. If set to Yes the client will use DNS SRV to look up
server.
User ID is Phone
Number
SIP Registration
Unregister on
Reboot
Register Expiration
Local SIP port
SIP T1 Timeout
If the BudgeTone 200 has an assigned PSTN telephone number, this
field should be set to “Yes”. Otherwise, set it to “No”. If “Yes” is set, a
“user=phone” parameter will be attached to the “From” header in SIP
request
This parameter controls whether the BudgeTone 200 needs to send
REGISTER messages to the proxy server. The default setting is “Yes”.
Default is No. If set to yes, the SIP user’s registration information will
be cleared on reboot.
This parameter allows user to specify the time frequency (in minutes)
that BudgeTone 200 refreshes its registration with the specified
registrar. The default interval is 60 minutes (or 1 hour). The maximum
interval is 65535 minutes (about 45 days).
This parameter defines the local SIP port the BudgeTone 200 will listen
and transmit. The default value for Account 1 is 5060. It is 5062, 5064,
5066 for Account 2, Account 3 and Account 4 respectively.
T1 is an estimate of the round-trip time (RTT) between the client and
server transactions. If the network latency is high, select bigger value
for reliable usage.
SIP T2 Interval
NAT Traversal
Subscribe for
MWI:
This element sets the value of the SIP protocol T2 timer, in seconds.
Timer T2 defines the retransmit interval for INVITE responses and nonINVITE requests. The SIP protocol default value is 4 seconds.
This parameter defines whether the BudgeTone 200 NAT traversal
mechanism will be activated or not. If activated (by choosing “Yes”)
and a STUN server is also specified, then the BudgeTone 200 will
behave according to the STUN client specification. Under this mode,
the embedded STUN client inside the BudgeTone 200 will attempt to
detect if and what type of firewall/NAT it is sitting behind through
communication with the specified STUN server. If the detected NAT is
a Full Cone, Restricted Cone, or a Port-Restricted Cone, the BudgeTone
200 will attempt to use its mapped public IP address and port in all of
its SIP and SDP messages. If the NAT Traversal field is set to “Yes”
with no specified STUN server, the BudgeTone 200 will periodically
(every 20 seconds or so) send a blank UDP packet (with no payload
data) to the SIP server to keep the “hole” on the NAT open.
Default is No. When set to “Yes” a SUBSCRIBE for Message Waiting
Indication will be sent periodically.
40
Page 41

Proxy-Require
SIP Extension to notify SIP server that the unit is behind the
NAT/Firewall.
Voice Mail User ID
Send DTMF
Early Dial
Dial Plan Prefix
Enable Call
Features
Disable Missed-Call
Session Expiration
When configured, user will be able to dial voice mail server by pressing
“MSG” button.
This parameter specifies the mechanism to transmit DTMF digit. There
are 3 modes supported: in audio which means DTMF is combined in
audio signal (not very reliable with low-bit-rate codec), via RTP
(RFC2833), or via SIP INFO.
Default is No. Use only if proxy supports 484 response.
Sets the prefix added to each dialed number.
Default is No. If set to Yes, Call transfer, Call Forwarding & Do-NotDisturb are supported locally.
Default is No. If set to Yes, missed calls will not be recorded for your
review.
Grandstream implemented SIP Session Timer. The session timer
extension enables SIP sessions to be periodically “refreshed” via a SIP
request (UPDATE, or re-INVITE. Once the session interval expires, if
there is no refresh via a UPDATE or re-INVITE message, the session
will be terminated.
Session Expiration is the time (in seconds) at which the session is
considered timed out, if no successful session refresh transaction occurs
beforehand. The default value is 180 seconds.
Min-SE
Caller Request
Timer
Callee Request
Timer
Force Timer
UAC Specify
Refresher
The minimum session expiration (in seconds). The default value is 90
seconds.
If selecting “Yes” the phone will use session timer when it makes
outbound calls if remote party supports session timer.
If selecting “Yes” the phone will use session timer when it receives
inbound calls with session timer request.
If selecting “Yes” the phone will use session timer even if the remote
party does not support this feature. Selecting “No” will allow the phone
to enable session timer only when the remote party support this feature.
To turn off Session Timer, select “No” for Caller Request Timer, Callee
Request Timer, and Force Timer.
As a Caller, select UAC to use the phone as the refresher, or UAS to use
the Callee or proxy server as the refresher.
41
Page 42

UAS Specify
Refresher
As a Callee, select UAC to use caller or proxy server as the refresher, or
UAS to use the phone as the refresher.
Force INVITE
Enable 100rel
Account Ring Tone
Send Anonymous
Session Timer can be refreshed using INVITE method or UPDATE
method. Select “Yes” to use INVITE method to refresh the session
timer.
The use of the PRACK (Provisional Acknowledgment) method enables
reliability to be offered to SIP provisional responses (1xx series). This
is very important if PSTN internetworking is to be supported. A user’s
wish to use reliable provisional responses is invoked by the 100rel tag
which is appended to the value of the required header of initial
signalling messages.
There are 4 different ring tone that are defined:
• System Ring Tone: when selected, all calls will ring with
system ring tone.
• Customer Ring Tone 1 to 3: when selected, BudgeTone 200 will
ONLY play this ring tone for all the incoming calls for this
account.
If this parameter is set to “Yes”, the “From” header in outgoing INVITE
message will be set to anonymous, essentially blocking the Caller ID
from displaying.
Auto Answer
Allow Auto Answer
by Call-Info
Turn off speaker on
remote disconnect
Preferred Vocoder
Special Feature
When set to “Yes”, BudgeTone 200 will automatically switch to
speaker when there is an incoming call.
Default is No. If set to Yes, auto answer depends on the Call-Info in the
SIP message. This feature needs the support of IP-PBX.
Default is No. If set to Yes, the speaker will turn off, and the phone will
go back to idle status, after the other party of the call hands up.
The BudgeTone 200 supports up to 5 different Vocoder types including
G.711 A-/U-law, GSM, G.723.1, G.729A/B.
User can configure Vocoders in a preference list that will be included
with the same preference order in SDP message. The first Vocoder in
this list can be entered by choosing the appropriate option in “Choice
1”. Similarly, the last Vocoder in this list can be entered by choosing
the appropriate option in “Choice 8”.
Default is Standard. Choose the selection to meet some special
requirements from Soft Switch vendors like Nortel, Broadsoft, etc.
42
Page 43

5.2.4 Saving the Configuration Changes
Once a change is made, the user should press the “Update” button in the Configuration
Menu. The IP phone will then display the following screen to confirm that the changes
have been saved:
Grandstream Device Configuration
STATUS BASIC SETTINGS ADVANCED SETTINGS ACCOUNT
Your configuration changes have been saved.
They will take effect on next reboot.
User is recommended to power cycle the IP phone after seeing the above message.
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004
5.2.5 Rebooting the Phone from Remote
The administrator of the phone can remotely reboot the phone by pressing the “Reboot”
button at the bottom of the configuration menu. Once done, the following screen will be
displayed to indicate that rebooting is underway.
Grandstream Device Configuration
The device is rebooting now...
You may relogin by clicking on the link below in 30 seconds.
Click to relogin
At this point, user can relogin to the phone after waiting for about 30 seconds.
All Rights Reserved Grandstream Networks, Inc. 2004
43
Page 44

5.3 Configuration through Central Provisioning Server
Grandstream BudgeTone 200 can be automatically configured from a central
provisioning system.
When BudgeTone 200 boots up, it will send TFTP or HTTP request to download
configuration files, there are two configuration files, one is “cfg.txt” and the other is
“cfg000b82xxxxxx”, where “000b82xxxxxx” is the MAC address of the BudgeTone 200.
The configuration files can be downloaded via TFTP or HTTP from the central server. A
service provider or an enterprise with large deployment of BudgeTone 200 can easily
manage the configuration and service provisioning of individual devices remotely from a
central server.
Grandstream provides a licensed provisioning system called GAPS that can be used to
support automated configuration of BudgeTone 200. GAPS (Grandstream Automated
Provisioning System) uses enhanced (NAT friendly) TFTP or HTTP (thus no NAT
issues) and other communication protocols to communicate with each individual
BudgeTone 200 for firmware upgrade, remote reboot, etc.
Grandstream provide GAPS (Grandstream Automated Provisioning System) service to
VoIP service providers. It could be either simple redirection or with certain special
provisioning settings. Initially upon booting up, Grandstream devices by default point to
Grandstream provisioning server GAPS, based on the unique MAC address of each
device, GAPS provision the devices with redirection settings so that they will be
redirected to customer’s TFTP or http server for further provisioning.
Grandstream also provide GAPSLite software package which contains our NAT friendly
TFTP server and a configuration tool to facilitate the task of generating device
configuration files.
The GAPSLite configuration tool is now free to end users. The tool and configuration
templates can be downloaded from
http://www.grandstream.com/DOWNLOAD/Configuration_Tool/.
For details on how GAPS works, please refer to the documentation of GAPS product.
44
Page 45

6 Firmware Upgrade
6.1 Upgrade through HTTP
To upgrade software, BudgeTone 200 can be configured with an HTTP server where the
new code image file is located. For example, following URL in the HTTP Upgrade
Server:
http://firmware.mycompany.com:6688/Grandstream/1.0.1.12
Where firmware.mycompany.com is the FQDN of the HTTP server, “:6688” is the TCP
port the HTTP server listening to, “/Grandstream/1.0.0.4” is the RELATIVE directory to
the root dir in HTTP server. Thus, you can put different firmware into different directory
as well.
NOTE:
• If “Auto Upgrade” field is set to “No”, HTTP upgrade will be performed only
once during boot up. If it is set to “Yes”, the device will check the HTTP server
in the number of days that is defined in “Check for new firmware every” field.
6.2 Upgrade through TFTP
To upgrade software, BudgeTone 200 can be configured with a TFTP server where the
new code image is located. It is recommended to set the TFTP server address in either a
public IP address or on the same LAN with the BudgeTone 200.
There are two ways to set up the TFTP server to upgrade the firmware, namely through
voice menu prompt or via the BudgeTone 200’s Web configuration interface. To
configure the TFTP server via voice prompt, please refer to section 5.1 with option 06,
once set up the TFTP IP address, power cycle the device, the firmware will be fetched
once the device boots up.
To configure the TFTP server via the Web configuration interface, open up your browser
to point at the IP address of the BudgeTone 200. Input the admin password to enter the
configuration screen. From there, enter the TFTP server address in the designated field
towards the bottom of the configuration screen. Once the TFTP server is set, user needs
to update the change by clicking the “Update” button. Then “Reboot” or power cycle the
phone, the firmware files will be fetched upon booting up.
TFTP checking is only performed during the initial power up. If the configured TFTP
server is found and a new code image is available, the BudgeTone 200 will attempt to
45
Page 46

retrieve the new image files by downloading them into the BudgeTone 200’s SRAM.
During this stage, the BudgeTone 200’s LEDs will blink until the checking/downloading
process is completed. Upon verification of checksum, the new code image will then be
saved into the Flash. If TFTP fails for any reason (e.g., TFTP server is not responding,
there are no code image files available for upgrade, or checksum test fails, etc), the
BudgeTone 200 will stop the TFTP process and simply boot using the existing code
image in the flash.
TFTP process may take as long as 1 to 2 minutes over the Internet, or just 20+ seconds if
it is performed on a LAN. Users are recommended to conduct TFTP upgrade in a
controlled LAN environment if possible. For those who do not have a local TFTP server,
Grandstream provides a NAT-friendly TFTP server on the public Internet for firmware
upgrade. Please check the Services section of Grandstream’s Web site to obtain this
TFTP server’s IP address.
NOTE:
• When BudgeTone 200 boots up, it will send TFTP or HTTP request to download
configuration files, there are two configuration files, one is “cfg.txt” and the
other is “cfg000b82xxxxxx”, where “000b82xxxxxx” is the MAC address of the
BudgeTone 200. These two files are for initial automatically provisioning
purpose only, for normal TFTP or HTTP firmware upgrade, the following error
messages in a TFTP or HTTP server log can be ignored.
TFTP Error from [IP ADRESS] requesting cfg000b82023dd4 : File
does not exist
TFTP Error from [IP ADRESS] requesting cfg.txt : File does not
exist
46
Page 47

7 Restore Factory Default Setting
Warning !!!
Restore the Factory Default Setting will DELETE all configuration information of the
device. Please backup or print out all the settings before you approach to following
steps. Grandstream will not take any responsibility if you lose all the parameters of
setting and cannot connect to your service provider.
Please disconnect network cable and power cycle the unit before trying to reset the unit to
factory default. The steps are as follows:
Step 1:
Find the MAC address of the device. It is a 12 digits HEX number located on the bottom
of the unit.
Step 2:
Encode the MAC address. Please use the following mapping:
0-9: 0-9
A: 22 (when pressed 2 twice, the “A” letter will show on the LCD)
B: 222
C: 2222
D: 33
E: 333
F: 3333
For example, if the MAC address is 000b8200e395, it should be encoded as
“0002228200333395”.
Step 3:
To perform factory reset:
a. Press the MENU button for Key Pad Menu options.
b. Press the Up or Down button to see “reset”.
c. Enter the encoded MAC address.
d. Press the MENU button again
e. Wait for phone reboot and the LCD backlight finish flashing.
47
Page 48

8 Appendix I Glossary of Terms
ADSL
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line: Modems attached to twisted pair copper
wiring that transmit from 1.5 Mbps to 9 Mbps downstream (to the subscriber) and
from 16 kbps to 800 kbps upstream, depending on line distance.
AGC
Automatic Gain Control, is an electronic system found in many types of devices.
Its purpose is to control the gain of a system in order to maintain some measure of
performance over a changing range of real world conditions.
ARP
Address Resolution Protocol is a protocol used by the Internet Protocol (IP)
[RFC826], pecifically IPv4, to map IP network addresses to the hardware
addresses used by a data link protocol. The protocol operates below the network
layer as a part of the interface between the OSI network and OSI link layer. It is
used when IPv4 is used over Ethernet
ATA
Analogue Telephone Adapter. Covert analogue telephone to be used in data
network for VoIP, like Grandstream HT series products.
CODEC
Abbreviation for Coder-Decoder. It's an analog-to-digital (A/D) and digital-toanalog (D/A) converter for translating the signals from the outside world to
digital, and back again.
CNG
Comfort Noise Generator, geneate artificial background noise used in radio and
wireless communications to fill the silent time in a transmission resulting from
voice activity detection.
DATAGRAM
A data packet carrying its own address information so it can be independently
routed from its source to the destination computer
DECIMATE
To discard portions of a signal in order to reduce the amount of information to be
encoded or compressed. Lossy compression algorithms ordinarily decimate while
subsampling.
DECT
Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications: A standard developed by the
European Telecommunication Standard Institute from 1988, governing pan-
48
Page 49

DNS
DID
European digital mobile telephony. DECT covers wireless PBXs, telepoint,
residential cordless telephones, wireless access to the public switched telephone
network, Closed User Groups (CUGs), Local Area Networks, and wireless local
loop. The DECT Common Interface radio standard is a multicarrier time division
multiple access, time division duplex (MC-TDMA-TDD) radio transmission
technique using ten radio frequency channels from 1880 to 1930 MHz, each
divided into 24 time slots of 10ms, and twelve full-duplex accesses per carrier, for
a total of 120 possible combinations. A DECT base station (an RFP, Radio Fixed
Part) can transmit all 12 possible accesses (time slots) simultaneously by using
different frequencies or using only one frequency. All signaling information is
transmitted from the RFP within a multiframe (16 frames). Voice signals are
digitally encoded into a 32 kbit/s signal using Adaptive Differential Pulse Code
Modulation.
Short for Domain Name System (or Service or Server), an Internet service that
translates domain names into IP addresses
Direct Inward Dialing
Direct Inward Dialing. The ability for an outside caller to dial to a PBX extension
without going through an attendant or auto-attendant.
DSP
Digital Signal Processing. Using computers to process signals such as sound,
video, and other analog signals which have been converted to digital form.
Digital Signal Processor. A specialized CPU used for digital signal processing.
Grandstream products all have DSP chips built inside.
DTMF
Dual Tone Multi Frequency
The standard tone-pairs used on telephone terminals for dialing using in-band
signaling. The standards define 16 tone-pairs (0-9, #, * and A-F) although most
terminals support only 12 of them (0-9, * and #).
FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name
49
Page 50

FXO
FXS
A FQDN consists of a host and domain name, including top-level domain. For
example, www.grandstream.com is a fully qualified domain name. www is the
host, grandstream is the second-level domain, and.com is the top level domain.
Foreign eXchange Office
An FXO device can be an analog phone, answering machine, fax, or anything that
handles a call from the telephone company like AT&T. They should also operate
the same way when connected to an FXS interface.
An FXO interface will accept calls from FXS or PSTN interfaces. All countries
and regions have their own standards.
FXO is complimentary to FXS (and the PSTN).
Foreign eXchange Station
An FXS device has hardware to generate the ring signal to the FXO extension
(usually an analog phone).
An FXS device will allow any FXO device to operate as if it were connected to
the phone company. This makes your PBX the POTS+PSTN for the phone.
The FXS Interface connects to FXO devices (by an FXO interface, of course).
DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an Internet protocol for
automating the configuration of computers that use TCP/IP. DHCP can be used to
automatically assign IP addresses, to deliver TCP/IP stack configuration
parameters such as the subnet mask and default router, and to provide other
configuration information such as the addresses for printer, time and news
servers.
ECHO CANCELLATION
Echo Cancellation is used in telephony to describe the process of removing echo
from a voice communication in order to improve voice quality on a telephone call.
In addition to improving quality, this process improves bandwidth savings
achieved through silence suppression by preventing echo from traveling across a
network.
50
Page 51

There are two types of echo of relevance in telephony: acoustic echo and hybrid
echo. Speech compression techniques and digital processing delay often
contribute to echo generation in telephone networks.
H.323
A suite of standards for multimedia conferences on traditional packet-switched
networks.
HTTP
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol; the World Wide Web protocol that performs the
request and retrieve functions of a server
IP
Internet Protocol. A packet-based protocol for delivering data across networks.
IP-PBX
IP-based Private Branch Exchange
IP Telephony
(Internet Protocol telephony, also known as Voice over IP Telephony) A general
term for the technologies that use the Internet Protocol's packet-switched
connections to exchange voice, fax, and other forms of information that have
traditionally been carried over the dedicated circuit-switched connections of the
public switched telephone network (PSTN). The basic steps involved in
originating an IP Telephony call are conversion of the analog voice signal to
digital format and compression/translation of the signal into Internet protocol (IP)
packets for transmission over the Internet or other packet-switched networks; the
process is reversed at the receiving end. The terms IP Telephony and Internet
Telephony are often used to mean the same; however, they are not 100 per cent
interchangeable, since Internet is only a subcase of packet-switched networks. For
users who have free or fixed-price Internet access, IP Telephony software
essentially provides free telephone calls anywhere in the world. However, the
challenge of IP Telephony is maintaining the quality of service expected by
subscribers. Session border controllers resolve this issue by providing quality
assurance comparable to legacy telephone systems.
IVR
IVR is a software application that accepts a combination of voice telephone input
and touch-tone keypad selection and provides appropriate responses in the form
of voice, fax, callback, e-mail and perhaps other media.
MTU
A Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is the largest size packet
specified in octet
network such as the Internet. The maximum for Ethernet is 1500 byte.
or frame,
s (eight-bit bytes), that can be sent in a packet- or frame-based
51
Page 52

NAT
Network Address Translation
NTP
Network Time Protocol, a protocol to exchange and synchronize time over
networks
The port used is UDP 123
Grandstream products using NTP to get time from Internet
OBP/SBC
Outbound Proxy or another name Session Border Controller. A device used in
VoIP networks. OBP/SBCs are put into the signaling and media path between
calling and called party. The OBP/SBC acts as if it was the called VoIP phone and
places a second call to the called party. The effect of this behaviour is that not
only the signaling traffic, but also the media traffic (voice, video etc) crosses the
OBP/SBC. Without an OBP/SBC, the media traffic travels directly between the
VoIP phones. Private OBP/SBCs are used along with firewalls to enable VoIP
calls to and from a protected enterprise network. Public VoIP service providers
use OBP/SBCs to allow the use of VoIP protocols from private networks with
internet connections using NAT.
PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet, is a network protocol for encapsulating
PPP frames in Ethernet frames. It is used mainly with cable modem and DSL
services.
PSTN
RTCP
RTP
Public Switched Telephone Network
i.e. the phone service we use for every ordinary phone call, or called POT (Plain
Old Telephone), or circuit switched network.
Real-time Transport Control Protocol, defined in RFC 3550
the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP), It partners RTP in the delivery and
packaging of multimedia data, but does not transport any data itself. It is used
periodically to transmit control packets to participants in a streaming multimedia
session. The primary function of RTCP is to provide feedback on the quality of
service being provided by RTP.
, a sister protocol of
52
Page 53

SDP
SIP
STUN
TCP
TFTP
UDP
VAD
Real-time Transport Protocol defines a standardized packet format for delivering
audio and video over the Internet. It was developed by the Audio-Video Transport
Working Group of the IETF and first published in 1996 as RFC 1889
Session Description Protocol, is a format for describing streaming media
initialization parameters. It has been published by the IETF as RFC 2327.
Session Initiation Protocol, An IP telephony signaling protocol developed by the
IETF (RFC3261). SIP is a text-based protocol suitable for integrated voice-data
applications. SIP is designed for voice transmission and uses fewer resources and
is considerably less complex than H.323.
All Grandstream products are SIP based
Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs, is a network protocol allowing clients
behind NAT (or multiple NATs) to find out its public address, the type of NAT it
is behind and the internet side port associated by the NAT with a particular local
port. This information is used to set up UDP communication between two hosts
that are both behind NAT routers. The protocol is defined in RFC 3489. STUN
will usually work good with non-symmetric NAT routers.
Transmission Control Protocol, is one of the core protocols of the Internet
protocol suite
connections to one another, over which they can exchange data or packets. The
protocol guarantees reliable and in-order delivery of sender to receiver data.
Trivial File Transfer Protocol, is a very simple file transfer protocol, with the
functionality of a very basic form of FTP; It uses UDP (port 69) as its transport
protocol
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core protocols of the
.
protocol suite
messages known as datagrams to one another. UDP does not provide the
reliability and ordering guarantees that
order or go missing without notice. However, as a result, UDP is faster and more
efficient for many lightweight or time-sensitive purposes.
. Using TCP, applications on networked hosts can create
Internet
. Using UDP, programs on networked computers can send short
TCP does; datagrams may arrive out of
53
Page 54

VLAN
VoIP
Voice Activity Detection or Voice Activity Detector is an algorithm used in
speech processing wherein, the presence or absence of human speech is
detected from the audio samples.
A virtual LAN, known as a VLAN, is a logically-independent network. Several
VLANs can co-exist on a single physical switch. It is usually refer to the IEEE
802.1Q tagging protocol.
Voice over IP
VoIP encompasses many protocols. All the protocols do some form of signalling
of call capabilities and transport of voice data from one point to another. e.g: SIP,
H.323, etc.
54
 Loading...
Loading...