Page 1

Grandstream Networks, Inc.
SIP Device Provisioning Guide
www.grandstream.com
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SIP DEVICE PROVISIONING GUIDE
OVERVIEW ......................................................................................................................................................... 3
PROVISIONING FLOW ......................................................................................................................................... 3
CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS ......................................................................................................................... 4
GENERATE CONFIGURATION FILES...................................................................................................................... 4
TFTP OR HTTP/HTTPS FOR CONFIGURATION FILE ................................................................................................ 4
CONFIGURATION FILE ENCRYPTION .................................................................................................................... 4
FIRMWARE AND CONFIGURATION FILE PREFIX AND POSTFIX ............................................................................. 4
FIRMWARE SERVER AND CONFIGURATION FILE SERVER ..................................................................................... 5
MANAGING FIRMWARE AND CONFIGURATION FILE DOWNLOAD ....................................................................... 5
PRE-CONFIGURATION AND CONFIGURATION REDIRECTION ................................................................................ 6
AUTOMATIC PROVISIONING WITHIN LAN ........................................................................................................... 6
XML PROVISIONING SCHEMA AND EXAMPLE FILE............................................................................................... 7
XML FILE ENCRYPTION ....................................................................................................................................... 8
SECURE PROVISIONING ...................................................................................................................................... 9
TABLE OF FIGURES
SIP DEVICE PROVISIONING GUIDE
FIGURE 1: PROVISIONING FLOW. ................................................................................................................................ 3
FIGURE 2: USING WEB UI TO DEFINE THE XML CONFIGURATION FILE PASSWORD ................................................................... 8
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 2 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
Page 3
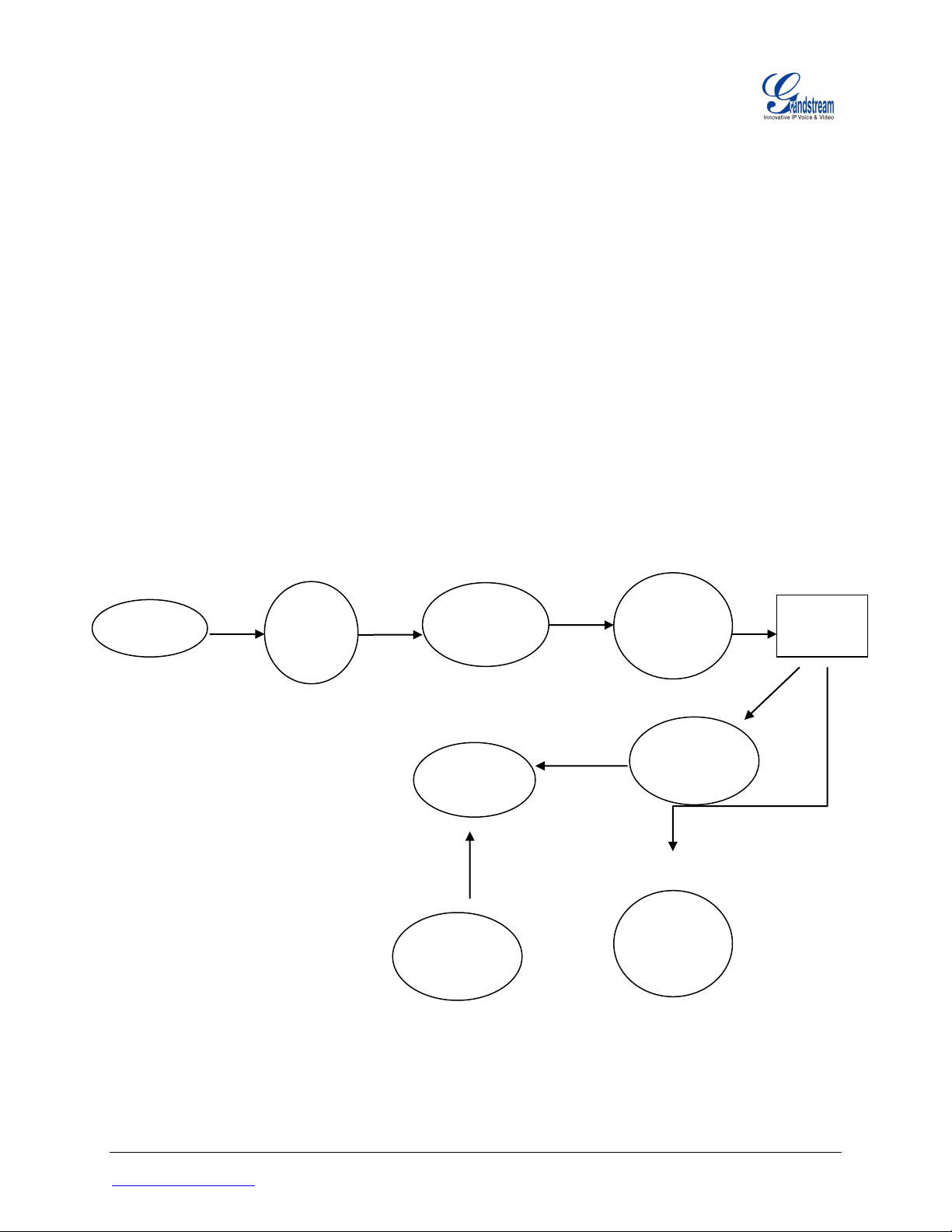
OVERVIEW
Start
provisioning
Request
legacy
config file
cfgMAC
Parse and
apply new
configurations
Parse and
apply new
configurations
Request XML
config file
cfgMAC.xml
Done
cfgMAC.xml
download
successful?
Request XML
config file
cfg.xml
Parse and
apply new
configurations
No
Yes
Grandstream SIP Devices can be configured via Web Interface as well as via Configuration File
through TFTP or HTTP/HTTPS download. All Grandstream SIP devices support a proprietary
binary format configuration file. Product families such as GXP21xx/14xx/11xx, GXV31xx,
HT50x, HT70x, GXW40xx and DP71x accept configuration files in XML format in addition to
the legacy proprietary binary format. The XML provisioning implementation also allow generic
XML configuration file on top of the MAC based configuration file.
When Grandstream device boots up or reboots, it issues a request for a configuration file named
“cfgMAC”, where “MAC” is the MAC address of the device, for example “cfg000b820102ab”. The
configuration file name should be in lower case. The file “cfgMAC” is a proprietary binary format
configuration file that must be generated by Grandstream configuration tools. For devices that
support XML provisioning, they will also issue a request for a XML configuration file
“cfgMAC.xml”.
PROVISIONING FLOW
Figure 1: Provisioning Flow.
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 3 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
Page 4

Note that the provision program will apply and reload the settings after downloading the legacy
binary cfgMAC config file. This means that a provision/re-direction server can redirect the
device to a XML provision server without reboot. It can also be used to send the XML
encryption password.
If the download of cfgMAC.xml file is not successful, the provision program will download the
generic cfg.xml file. This approach can be used to design a two-phase provision process. One
example for such process is a user self-provision system using PIN codes. The provision server
will first hand out a generic XML configuration file that allows the device to make calls to the
automated provision center. After the user enters the number and PIN code, the actual per device
configuration file is generated.
CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS
A configuration parameter is associated with each particular field in the web configuration page.
A parameter consists of a Capital letter P and 2 to 3 (Could be extended to 4 in the future) digit
numeric numbers. i.e., P2 is associated with “Admin Password” in the Advanced Page. For a
detailed parameter list, please refer to the corresponding firmware release configuration
template.
GENERATE CONFIGURATION FILES
Grandstream offers free Configuration File generator software in both Linux/Unix and Windows
platform. Both Configuration File Generators can be downloaded from Grandstream official web
site at http://www.grandstream.com/support/tools .
TFTP OR HTTP/HTTPS FOR CONFIGURATION FILE
Traditionally, TFTP is used for Configuration File download. However, it is more popular today
with HTTP/HTTPS, which is more reliable and has NO NAT issue.
CONFIGURATION FILE ENCRYPTION
Grandstream Configuration Generator allows user to ENCRYPTE the generated Configuration
File with AES 128 bit encryption. Windows version allows user to choose not to encrypt the
Configuration File, but it is recommended to use Encryption for security purpose.
FIRMWARE AND CONFIGURATION FILE PREFIX AND POSTFIX
Prefix and postfix for both firmware and configuration files are supported.
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 4 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
Page 5

Parameter P232 and P233 are for Prefix and Postfix for Firmware, respectively.
firmware.grandstream.com/HT502/1.0.7.6
provisioning.grandstream.com/HT502
Parameter P234 and P235 are for Prefix and Postfix for Configuration File, respectively.
Firmware Prefix and Postfix allows device to download the firmware name with the matching
Prefix and Postfix.
In addition, when Parameter P238 (Check New Firmware only when F/W pre/suffix changes) is
set to 1, the device will only issue the Firmware Upgrade request if there are changes in the
firmware Prefix or Postfix.
Following are the firmware BASIC NAMES related to BT100: “boot.bin”, “bt-110.bin”,
“html110.bin”, “vocbt.bin”, “vp.bin”.
Service provider can use “gs_” as prefix, and “_1.0.7.5” as postfix, the above files will be
changed to: “gs_boot.bin_1.0.7.5”, “gs_bt-110.bin_1.0.7.5”, “gs_html110.bin_1.0.7.5”,
“gs_vocbt.bin_1.0.7.5”, “gs_vp.bin_1.0.7.5”
The purpose for this is that now, ALL of the firmware with different version can be stored in one
single directory, and they can be differentiated by using prefix or postfix, i.e., all files with a
postfix of “_1.0.7.5” belong to the firmware version 1.0.7.5.
Same rule applies to configuration files, i.e., for configuration file named “cfg000b82000001”,
there can be 3 versions: “gs_cfg000b82000001_cfg001”, “gs_cfg000b82000001_cfg002”, and
“gs_cfg000b82000001_cfg003”. Here, the BASIC NAME of the configuration file is
“cfg000b82000001”, but there are 3 different versions, the one that will be accepted is the one
with matching prefix and postfix specified in the current configuration.
FIRMWARE SERVER AND CONFIGURATION FILE SERVER
In addition to the Prefix and Postfix for firmware and configuration files, different server paths
for firmware upgrade or Configuration File Server can be specified in different FQDN, i.e.:
Firmware Server Path:
Config Server Path:
The parameters are P192 and P237 for Firmware and Config Server respectively.
MANAGING FIRMWARE AND CONFIGURATION FILE DOWNLOAD
When parameter P194 (Auto Upgrade) is set to 1, Service Provider can use P193 (Auto Check
Interval) to have the devices periodically check with either Firmware Server or Config Server,
whenever they are defined. This allows the device periodically check if there are any new
changes need to be taken on a scheduled time. By defining different intervals in P193 for
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 5 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
Page 6

different devices, Service Provider can distribute the Firmware or Configuration File download
schedule to reduce the Firmware or Provisioning Server load at any given time.
PRE-CONFIGURATION AND CONFIGURATION REDIRECTION
For mass deployment, Grandstream provides TFTP/HTTP redirection service. This service is
free. Here is how redirection works. By default all Grandstream products point to our
provisioning system. When a unit is powered up, it will automatically contact our provisioning
server. Our provisioning server will then redirect the unit to customer’s TFTP/HTTP/HTTPS
server. The unit will reboot and send further provisioning request asking for configuration file
(or firmware file) from customer’s TFTP/HTTP/HTTPS server.
Below is the information we need from service providers for TFTP/HTTP redirection:
1. MAC address range, this should be printed on the carton box
2. Your TFTP/HTTP server IP address
3. Your company name and address
Here is what service providers should do:
1. Create configuration files for all the devices and put them on your TFTP/HTTP server
2. Download the latest official release from http://www.grandstream.com/support/firmware
and put them on your TFTP/HTTP server (same directory as above)
3. After we inform you that the devices have been entered into our central provisioning
database, please take out a few devices to test. Upon powering up, they should contact
our provisioning server fm.grandstream.com/gs first, and then get redirected to your
TFTP/HTTP server and pull out the firmware files and the configuration files. They will
be upgraded to the latest firmware with your configurations.
Grandstream also offers pre-configuration of our devices in factory, but this will incur an extra
cost to the product ordered.
AUTOMATIC PROVISIONING WITHIN LAN
Grandstream products support DHCP Option 66 or 43 for automatic provisioning within a Local
Area Network. The provisioning server URL is embedded inside standard option 66 or 43 of
DHCP responses. All Grandstream product families support DHCP Option 66 while the new
product series GXP21xx/14xx/11xx
support both DHCP Option 66 and 43.
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 6 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
Page 7

Grandstream SIP devices send out DHCP DISCOVER with the following information:
DHCP Server can be configured to send the following information in its DHCP OFFER. Please
notice that in this example, an HTTP://URL is provided in the Option 66 “TFTP Server Name”
field. Device will then issue HTTP requests instead of the traditional TFTP requests to the server.
This design allows more flexibility in device provisioning. While all Grandstream SIP devices
support DHCP Option 66, only new product series GXP21xx/14xx, GXV31xx, HT50x and
GXW40xx support this additional flexibility.
XML PROVISIONING SCHEMA AND EXAMPLE FILE
The general XML syntax consists of a list of name-value pairs. P-Value is the element and the
value of the element is represents the value for that particular configuration that the
corresponding P-Value represents. For the complete P-value list, please refer to the legacy
configuration templates at
http://www.grandstream.com/support/tools
Example XML configuration file (cfgxxxxxxxxxxxx.xml):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<gs_provision version="1">
<mac>000b82123456</mac>
<config version="1">
<P271>0</P271>
<P270>Account name</P270>
</config>
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 7 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
Page 8

</gs_provision>
The mac element is not mandatory. It is designed this way because not all provision systems
support MAC address. If it is present, the provision program will validate the mac element with
the actual MAC address on the device.
XML FILE ENCRYPTION
The XML configuration file may be encrypted using AES-256-CBC algorithm. The encryption
password is defined in P1359 (XML Config File Password) of the configuration file. The
encryption may use salt to enhance security. The algorithm to derive the key and IV from a
password is the same as the one used by OpenSSL:
The OpenSSL command-line to encrypt the file is as follows:
Openssl enc –e –aes-256-cbc –k password –in config.xml –out cfgxxxxxxxxxxxx.xml
Alternatively, users can also set the XML Config File Password in the web UI of the phone.
Figure 2: Using web UI to define the XML Configuration File Password
When the XML configuration file is encrypted using this method, the phone would only be able
to decrypt and parse the file if user set the XML Config File Password in P1349 of binary
configuration file or in the web UI.
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 8 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
Page 9

SECURE PROVISIONING
Although the XML configuration file can be encrypted and the encryption algorithm itself is
regarded as safe and strong by using AES with 256-bit key length, it remains a question on how
to bootstrap and provision the initial XML encryption password. There are several methods to
provide solutions to this:
1. Use legacy binary configuration file to set the initial XML encryption password. The
legacy binary file is encrypted and it generally regarded safe.
2. Use HTTPS and use client side authentication. This is the industry standard approach and
has the strongest safety.
Grandstream Networks, Inc. SIP Device Provisioning Guide Page 9 of 9
www.grandstream.com Last Updated: 9/2012
 Loading...
Loading...