Page 1
Instructions - Parts
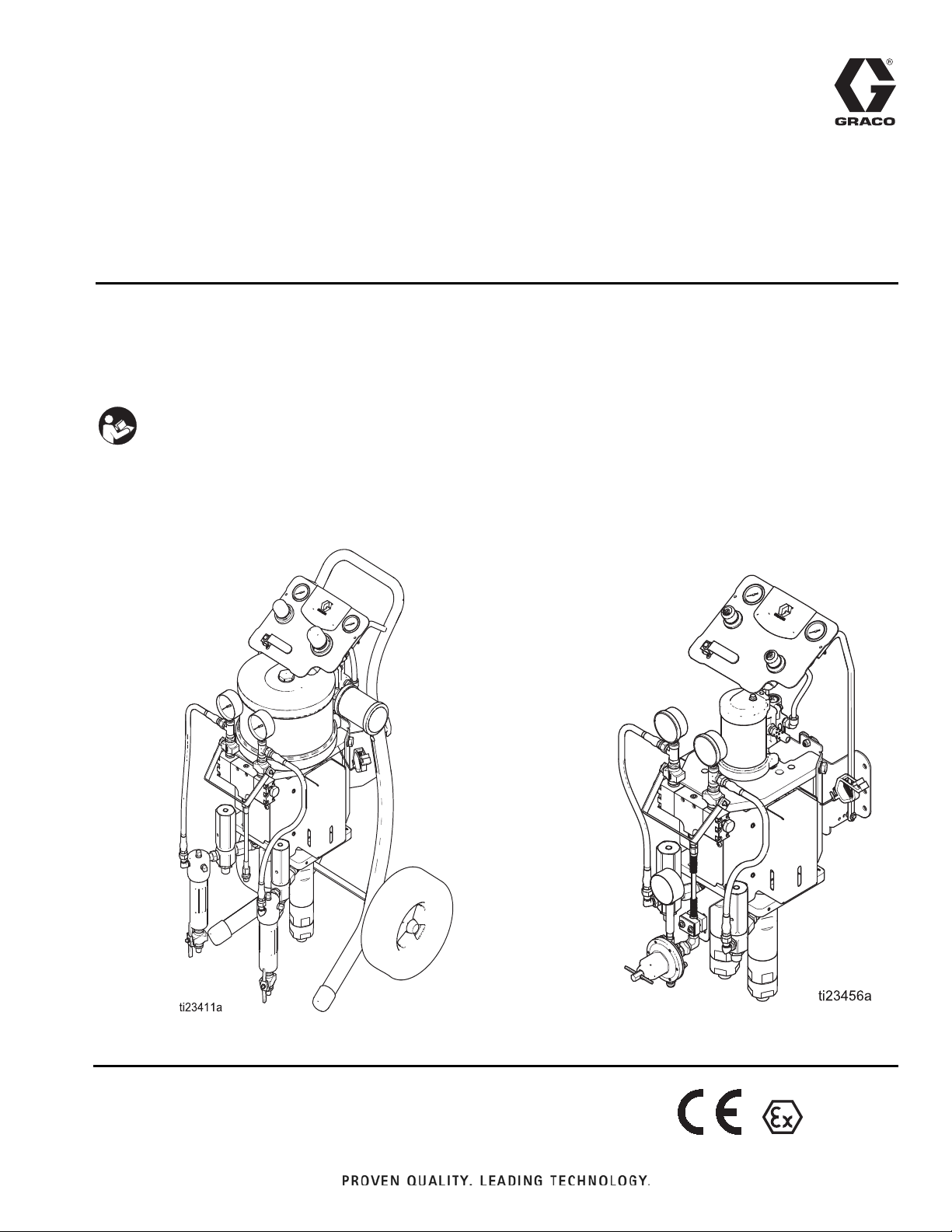
Cart Mount
Wall Mount
II 2 G
M2K Spray Packages
For two-component finishing and coating applications in hazardous and non-hazardous
locations. For professional use only.
Important Safety Instructions
Read all warnings and instructions in this manual.
Save these instructions.
See page 4 for Model Information.
See page 53 for Maximum Working Pressure.
333309E
EN
c IIB T3
Page 2

Contents
Related Manuals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Important Isocyanate (ISO) Information . . . . . . . . 7
Isocyanate Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Keep Components A and B Separate . . . . . . . . . 7
Moisture Sensitivity of Isocyanates . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Changing Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Typical System Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Proportioner Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Model 24W609 (for Polyester applications) . . . . 12
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Prepare the Operator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Prepare the Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Wall Mount Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air Line Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Connect Air Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Feed Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
A and B Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Checking the Mix Ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Flush the Pump Before First Use . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Wet Cup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Pressure Relief Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Prime the Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Load Mix Material to the Gun . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Spray Gun Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Mix Material Flush Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Using the Proportioning Pump System . . . . . . . 26
Monitoring the Proportioner During Operation . 27
Changing ratios . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Care of the Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Preventive Maintenance Schedule . . . . . . . . . . 29
Tighten Threaded Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Flush the Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Wet Cup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Fluid Pressure Relief Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Storage and Extended Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Performance Charts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Cart Mount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Wall Mounting Bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Air Control Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Motor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Lower Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Fluid Inlet Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Fluid Outlet Assembly
(Except Model 24W609) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Fluid Outlet Assembly
(for Polyester Model 24W609) . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Spray Gun and Hose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Wall Bracket Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Technical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Technical Data Matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Graco Standard Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
2 333309E
Page 3

Related Manuals
Manual Description
333309 M2K Spray Packages
334625 M2K Mix Manifolds
3A0732
308652
312796
312792
Merkur
Husky
NXT
Merkur
307273 Fluid Outlet Filter
308547 Pressure Relief Valve
306861 Ball Valves, Check Valves, and Swivels
312414
AirPro
3A0149 G15/G40 Spray Gun
312145
XTR
311254 Silver and Flex Plus Airless Spray Guns
®
ES Spray Packages
™
205 Air-Operated Diaphragm Pumps
®
Air Motor
®
Displacement Pump
™
Pressure Feed Airspray Gun
™
5 and XTR™ 7 Airless Spray Gun
Related Manuals
333309E 3
Page 4
Models
Models
Sprayer
Type
Air Spray
Air Assisted
Air Spray
Airless
Airless - For
Split-Batch
Polyester
Applications
Pump
Ratio
1:1
2:1
3:1
4:1
5:1
6:1
1:1
2:1
3:1
4:1
5:1
6:1
1:1
2:1
3:1
4:1
5:1
6:1
1:1 Cart 24W609
Mounting
Type
Cart 24V868 1/4 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V874 None
Cart 24V869 1/4 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V875 None
Cart 24V870 1/4 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V876 None
Cart 24V871 1/4 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V877 None
Cart 24V872 1/4 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V878 None
Cart 24V873 1/4 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V879 None
Cart 24V880 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V886 None
Cart 24V881 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V887 None
Cart 24V882 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V888 None
Cart 24V883 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V889 None
Cart 24V884 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V890 None
Cart 24V885 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V891 None
Cart 24V892 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V898 None
Cart 24V893 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V899 None
Cart 24V894 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V901 None
Cart 24V895 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V902 None
Cart 24V896 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V903 None
Cart 24V897 3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m)
Wall 24V904 None
Model Fluid/Air Hose Lower A Lower B
Remote Manifold to Airless Gun
3/16 ID Mix Fluid Hose x 25 ft. (7.6 m) +
10 ft. (3 m)
Air
Motor
50cc 50cc
100cc 50cc
75cc 25cc
2.5 in.
100cc 25cc
125cc 25cc
150cc 25cc
50cc 50cc
100cc 50cc
75cc 25cc
7.5 in.
100cc 25cc
125cc 25cc
150cc 25cc
50cc 50cc
100cc 50cc
75cc 25cc
7.5 in.
100cc 25cc
125cc 25cc
150cc 25cc
25cc 25cc 4.5 in.
4 333309E
Page 5
Warnings
WARNINGWARNINGWARNING
WARNING
Warnings
The following warnings are for the setup, use, grounding, maintenance, and repair of this equipment. The exclamation point symbol alerts you to a general warning and the hazard symbols refer to procedure-specific risks. When
these symbols appear in the body of this manual, refer back to these Warnings. Additional, product-specific warnings
may be found throughout the body of this manual where applicable.
FIRE AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
Flammable fumes, such as solvent and paint fumes, in work area can ignite or explode. To help prevent
fire and explosion:
• Use equipment only in well ventilated area.
• Eliminate all ignition sources; such as pilot lights, cigarettes, portable electric lamps, and plastic drop
cloths (potential static arc).
• Keep work area free of debris, including solvent, rags and gasoline.
• Do not plug or unplug power cords, or turn power or light switches on or off when flammable fumes are
present.
• Ground all equipment in the work area. See Grounding instructions.
• Use only grounded hoses.
• Hold gun firmly to side of grounded pail when triggering into pail.
• If there is static sparking or you feel a shock, stop operation immediately. Do not use equipment
until you identify and correct the problem.
• Keep a working fire extinguisher in the work area.
SKIN INJECTION HAZARD
High-pressure fluid from gun, hose leaks, or ruptured components will pierce skin. This may look like just a
cut, but it is a serious injury that can result in amputation. Get immediate surgical treatment.
• Do not spray without tip guard and trigger guard installed.
• Engage trigger lock when not spraying.
• Do not point gun at anyone or at any part of the body.
• Do not put your hand over the spray tip.
• Do not stop or deflect leaks with your hand, body, glove, or rag.
• Follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when you stop spraying and before cleaning, checking, or ser-
vicing equipment.
• Tighten all fluid connections before operating the equipment.
• Check hoses and couplings daily. Replace worn or damaged parts immediately.
333309E 5
Page 6

Warnings
WARNINGWARNINGWARNING
WARNING
EQUIPMENT MISUSE HAZARD
Misuse can cause death or serious injury.
• Do not operate the unit when fatigued or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
• Do not exceed the maximum working pressure or temperature rating of the lowest rated system com-
ponent. See Technical Data in all equipment manuals.
• Use fluids and solvents that are compatible with equipment wetted parts. See Technical Data in all
equipment manuals. Read fluid and solvent manufacturer’s warnings. For complete information about
your material, request MSDS from distributor or retailer.
• Do not leave the work area while equipment is energized or under pressure.
• Turn off all equipment and follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when equipment is not in use.
• Check equipment daily. Repair or replace worn or damaged parts immediately with genuine manufacturer’s replacement parts only.
• Do not alter or modify equipment. Alterations or modifications may void agency approvals and create
safety hazards.
• Make sure all equipment is rated and approved for the environment in which you are using it.
• Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Call your distributor for information.
• Route hoses and cables away from traffic areas, sharp edges, moving parts, and hot surfaces.
• Do not kink or over bend hoses or use hoses to pull equipment.
• Keep children and animals away from work area.
• Comply with all applicable safety regulations.
MOVING PARTS HAZARD
Moving parts can pinch or amputate fingers and other body parts.
• Keep clear of moving parts.
• Do not operate equipment with protective guards or covers removed.
• Pressurized equipment can start without warning. Before checking, moving, or servicing equipment,
follow the Pressure Relief Procedure in this manual. Disconnect power or air supply.
TOXIC FLUID OR FUMES HAZARD
Toxic fluids or fumes can cause serious injury or death if splashed in the eyes or on skin, inhaled, or swallowed.
• Read MSDS’s to know the specific hazards of the fluids you are using.
• Store hazardous fluid in approved containers, and dispose of it according to applicable guidelines.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
You must wear appropriate protective equipment when operating, servicing, or when in the operating area
of the equipment to help protect you from serious injury, including eye injury, inhalation of toxic fumes,
burns, and hearing loss. This equipment includes but is not limited to:
• Protective eyewear
• Clothing and respirator as recommended by the fluid and solvent manufacturer
•Gloves
• Hearing protection
6 333309E
Page 7
Important Isocyanate (ISO) Information
Important Isocyanate (ISO) Information
Isocyanates (ISO) are catalysts used in two component materials.
Isocyanate Conditions
Partially cured ISO will reduce performance and the life
of all wetted parts.
Spraying or dispensing materials containing isocyanates creates potentially harmful mists, vapors, and
atomized particulates.
Read material manufacturer’s warnings and material
MSDS to know specific hazards and precautions
related to isocyanates.
Prevent inhalation of isocyanate mists, vapors, and
atomized particulates by providing sufficient ventilation in the work area. If sufficient ventilation is not
available, a supplied-air respirator is required for
everyone in the work area.
To prevent contact with isocyanates, appropriate personal protective equipment, including chemically
impermeable gloves, boots, aprons, and goggles, is
also required for everyone in the work area.
Keep Components A and B
• Always use a sealed container with a desiccant
dryer in the vent, or a nitrogen atmosphere. Never
store ISO in an open container.
• Keep the ISO pump wet cup or reservoir (if
installed) filled with appropriate lubricant. The lubricant creates a barrier between the ISO and the
atmosphere.
• Use only moisture-proof hoses compatible with
ISO.
• Never use reclaimed solvents, which may contain
moisture. Always keep solvent containers closed
when not in use.
• Always lubricate threaded parts with an appropriate lubricant when reassembling.
NOTE: The amount of film formation and rate of crystallization varies depending on the blend of ISO, the
humidity, and the temperature.
NOTICE
Separate
Cross-contamination can result in cured material in
fluid lines which could cause serious injury or damage
equipment. To prevent cross-contamination:
• Never interchange component A and component
B wetted parts.
• Never use solvent on one side if it has been contaminated from the other side.
Moisture Sensitivity of Isocyanates
Exposure to moisture (such as humidity) will cause ISO
to partially cure; forming small, hard, abrasive crystals,
which become suspended in the fluid. Eventually a film
will form on the surface and the ISO will begin to gel,
increasing in viscosity.
Changing Materials
NOTICE
Changing the material types used in your equipment
requires special attention to avoid equipment damage
and downtime.
• When changing materials, flush the equipment
multiple times to ensure it is thoroughly clean.
• Always clean the fluid inlet strainers after flushing.
• Check with your material manufacturer for chemical
compatibility.
• When changing between epoxies and urethanes or
polyureas, disassemble and clean all fluid components and change hoses. Epoxies often have
amines on the B (hardener) side. Polyureas often
have amines on the B (resin) side
333309E 7
Page 8
Introduction
B Supply
A Supply
Solvent
Solvent Flush Supply Hose
Air Supply
Solvent Pump
Introduction
The Graco M2K spray packages are intended for use
with two-component epoxy, polyurethane, and polyester
split batch (Model 24W609) materials in industrial applications. When maintained and operated properly they
can produce a ±1% ratio accuracy, while simultaneously
reducing material waste and cleanup solvent use, over
hand mixing, and hot potting applications.
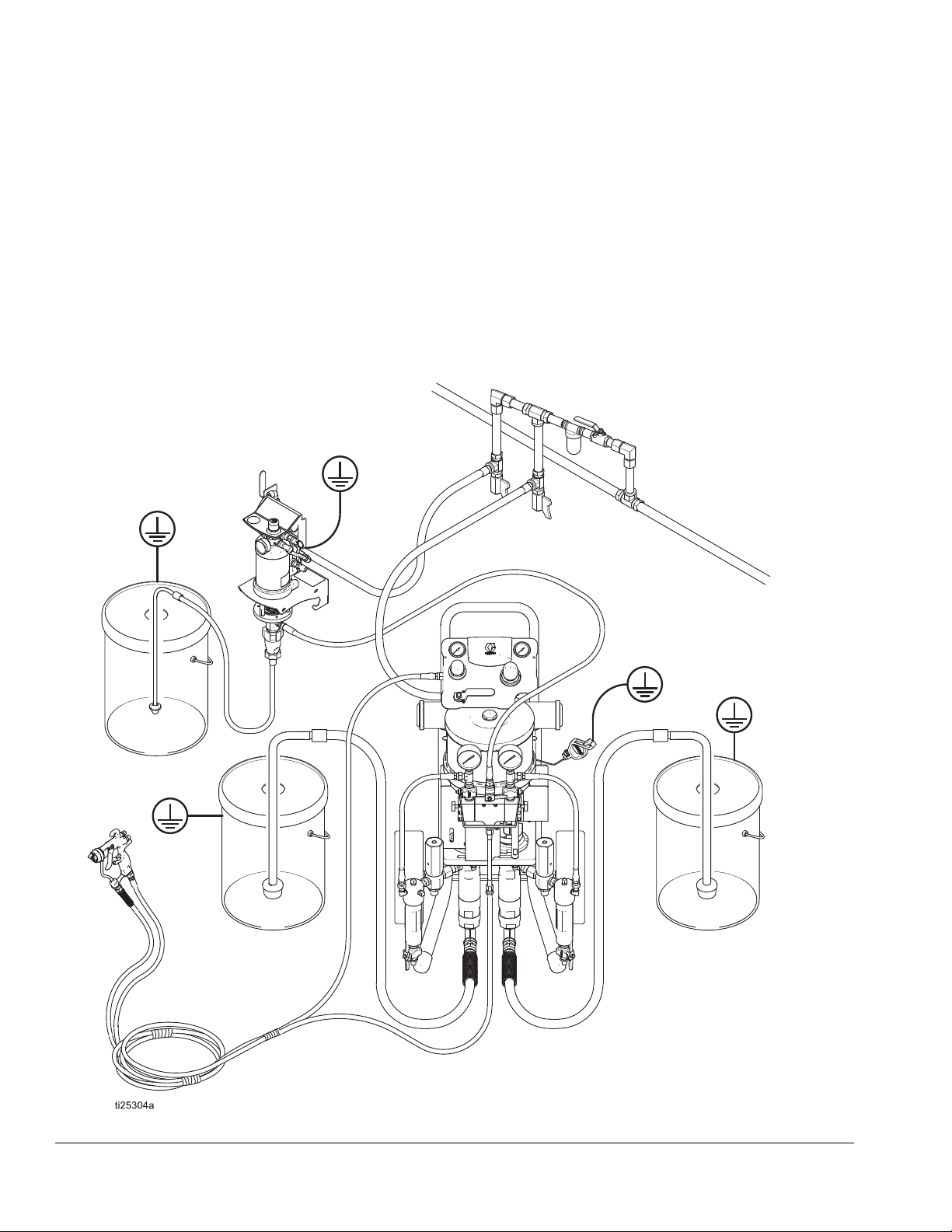
Typical System Installation
FIG. 1 is only a guide for selecting and installing system
components and accessories. Contact your Graco distributor for assistance in designing a system to suit your
particular needs.
Always use Genuine Graco Parts and Accessories,
available from your Graco distributor. If you supply your
own accessories, be sure they are adequately sized and
pressure-rated for your system.
FIG. 1 Typical System Installation
8 333309E
Page 9

Notes
Introduction
333309E 9
Page 10
Introduction
B Supply
A Supply
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
Z
Q
R
S
T
VB
W
X
Y
EE
CC
VA
W
U
U
N
M
PB
PA
DD
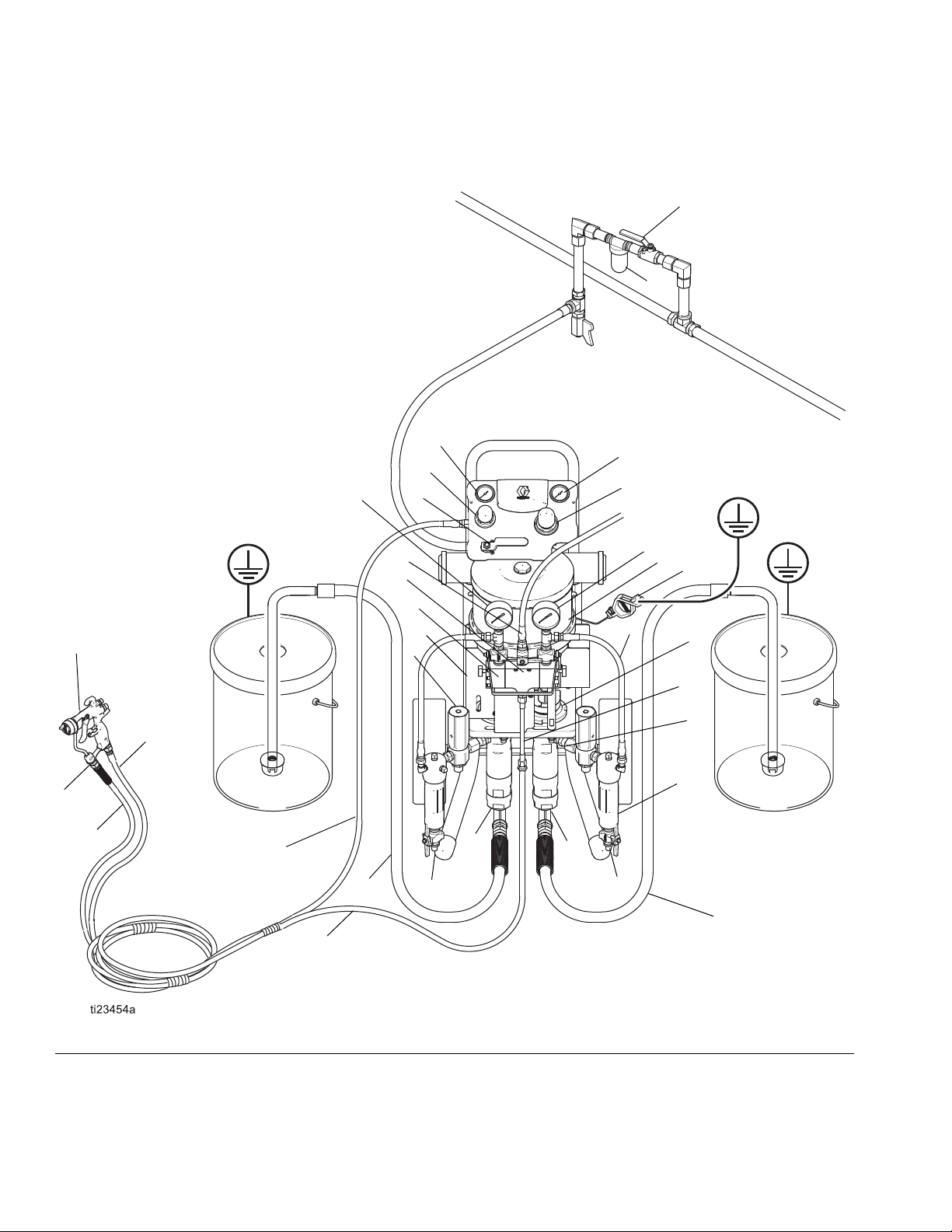
Proportioner Overview
FIG. 2 Typical Installation, Non-Polyester Models
10 333309E
Page 11

Introduction
A Air Shutoff Valve (optional accessory, purchase separately) - Isolates the air line accessories for servicing.
B Air Filter (optional accessory, purchase separately) - Removes harmful dirt and moisture from the com-
pressed air supply.
C Gun Air Pressure Gauge - Displays atomizing air pressure to spray gun.
D Gun Air Pressure Regulator - Adjusts the air pressure to the air spray or air-assisted spray gun (L).
E Bleed Type Master Air Valve - Red-handled valve required to relieve air trapped between it and the air motor
and gun when the valve is closed. Do not block access to the valve.
F Mix Manifold - Combines A and B fluid flows out to mixer.
G Pump Air Pressure Gauge - Displays pump air pressure.
H Pump Air Pressure Regulator - Controls pump speed and outlet pressure by adjusting the air pressure to the
pump.
J Solvent Flush Inlet - On the mix manifold; provides flush point for mixed material.
K Gun Swivel - Allows for easier gun movement and comes attached to the blue hose (AA packages). The airless
gun has a built-in fluid swivel.
L Spray Gun - The air spray, air-assisted, or airless spray gun (L) dispenses the fluid. The gun houses the spray
tip or nozzle (not shown), which is available in a wide range of sizes for different spray patterns and rates of
flow. Refer to gun manual for tip installation. See Related Manuals, page 3.
M Gun Fluid Supply Hose - Blue hose. Provides the gun fluid supply.
N Gun Air Supply Hose - Transparent hose (labeled “Air Hose Only”) provides the gun air supply.
PA Fluid Pressure Gauge A Supply Side - Displays fluid pressure from pump to mix manifold
PB Fluid Pressure Gauge B Supply Side - Displays fluid pressure from pump to mix manifold
Q Pinch Guard - Shield covering all moving parts.
R Pump Fluid Outlet - Outlet port of the pump.
S Grounding Wire - Provides true earth ground for static dissipation.
T Wet-Cup - Maintains consistent lubrication for packings and keeps paint from drying on displacement rod.
U Pump Fluid Inlet - Inlet port of the pump.
VA Suction Hose with Strainer A Supply - Allows the pump to draw fluid from a 5 gallon (19 liter) pail. A fluid hop-
per with screen also is available.
VB Suction Hose with Strainer B Supply - Allows the pump to draw fluid from a 5 gallon (19 liter) pail. A fluid hop-
per with screen also is available.
W Fluid Drain Valve - Relieves fluid pressure in the filter and allows for easier filter removal for cleaning.
X Mixer - Static fluid mixer. Mixes combined flows of A and B from mix manifold.
Y Motor - Powers pump
Z Pressure Relief Valve - Prevents pumps from generating pressures higher than system rated pressure. Do not
cap or restrict the bottom threaded port. Fluid must be allowed to exit the bottom port if an over pressure
occurs. Refer to Relief Valve manual. See Related Manuals, page 3.
CC Pump Outlet Hose - Provides fluid to the mix manifold from the pump.
DD Solvent Flush Supply Hose -
Provides fluid to the mix manifold from solvent pump.
EE Fluid Filter - 60 mesh (250 micron) stainless steel element filters particles from fluid as it leaves the pump.
Air Relief Valve (not shown) - Opens automatically to prevent overpressurization of the air motor.
333309E 11
Page 12
Introduction
B Supply
A Supply
A
B
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
Z
Q
GG
S
T
VB
X
Z
Y
CC
VA
W
U
U
M
PB
PA
DD
C
D
GG
T
HH
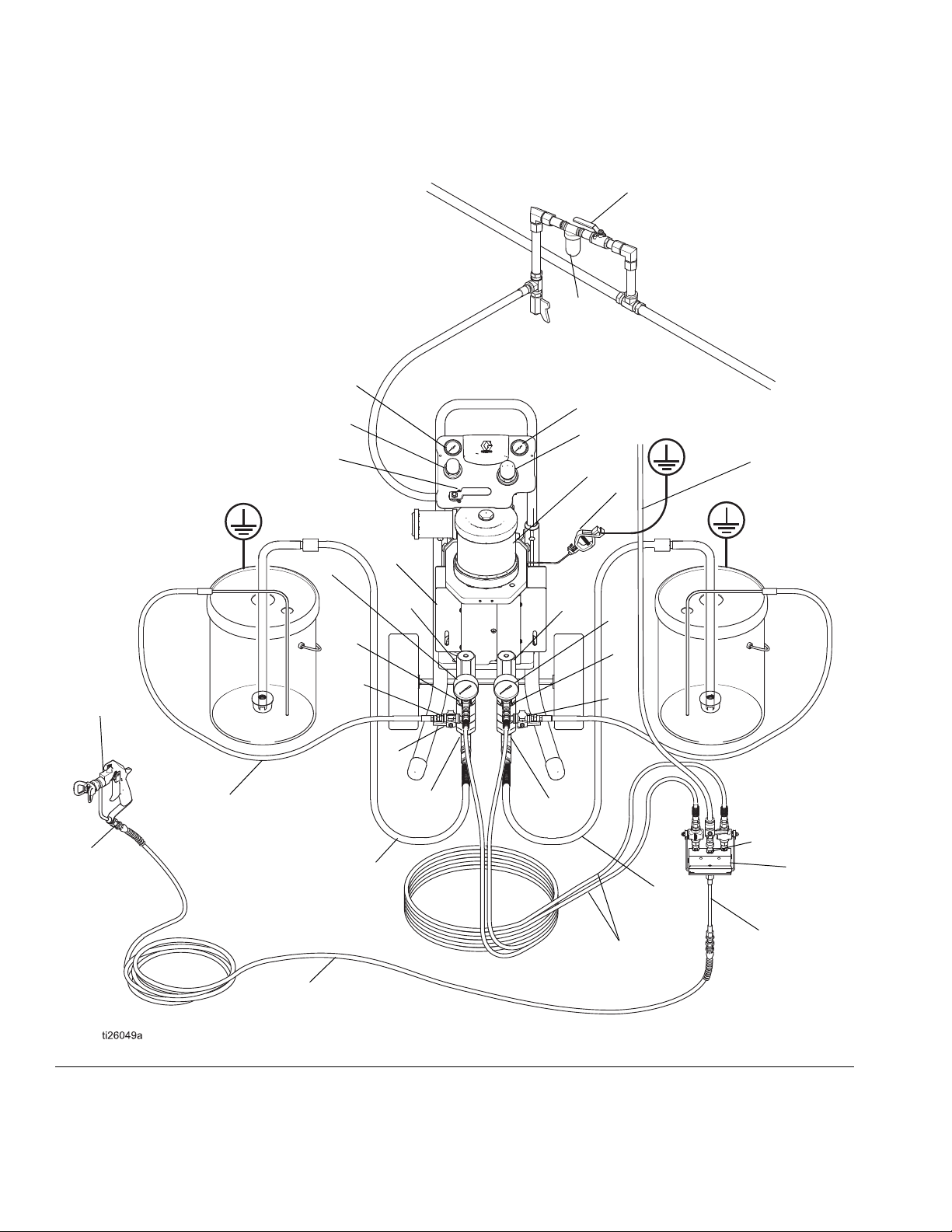
Model 24W609 (for Polyester applications)
FIG. 3 Typical Installation, Polyester Model
12 333309E
Page 13

Introduction
A Air Shutoff Valve (optional accessory, purchase separately) - Isolates the air line accessories for servicing.
B Air Filter (optional accessory, purchase separately) - Removes harmful dirt and moisture from the com-
pressed air supply.
C Gun Air Pressure Gauge - Displays atomizing air pressure to spray gun. Used only if the application requires
an optional air spray or air-assisted spray gun (sold separately).
D Gun Air Pressure Regulator - Adjusts the air pressure to the air spray or air-assisted spray gun (L). Used only
if the application requires an optional air spray or air-assisted spray gun (sold separately).
E Bleed Type Master Air Valve - Red-handled valve required to relieve air trapped between it and the air motor
and gun when the valve is closed. Do not block access to the valve.
F Mix Manifold - Combines A and B fluid flows out to mixer.
G Pump Air Pressure Gauge - Displays pump air pressure.
H Pump Air Pressure Regulator - Controls pump speed and outlet pressure by adjusting the air pressure to the
pump.
J Solvent Flush Inlet - On the mix manifold; provides flush point for mixed material.
K Gun Swivel - Allows for easier gun movement and comes attached to the blue hose (AA packages). The airless
gun has a built-in fluid swivel.
L Spray Gun - The air spray, air-assisted, or airless spray gun (L) dispenses the fluid. The gun houses the spray
tip or nozzle (not shown), which is available in a wide range of sizes for different spray patterns and rates of
flow. Refer to gun manual for tip installation. See Related Manuals, page 3.
M Gun Fluid Supply Hose - Blue hose. Provides the gun fluid supply.
PA Fluid Pressure Gauge A Supply Side - Displays fluid pressure from pump to mix manifold
PB Fluid Pressure Gauge B Supply Side - Displays fluid pressure from pump to mix manifold
Q Pinch Guard - Shield covering all moving parts.
S Grounding Wire - Provides true earth ground for static dissipation.
T Wet-Cup - Maintains consistent lubrication for packings and keeps paint from drying on displacement rod.
U Pump Fluid Inlet - Inlet port of the pump.
VA Suction Hose with Strainer A Supply - Allows the pump to draw fluid from a 5 gallon (19 liter) pail. A fluid hop-
per with screen also is available.
VB Suction Hose with Strainer B Supply - Allows the pump to draw fluid from a 5 gallon (19 liter) pail. A fluid hop-
per with screen also is available.
X Mixer - Static fluid mixer. Mixes combined flows of A and B from mix manifold.
Y Motor - Powers pump
Z Pressure Relief Valve - Prevents pumps from generating pressures higher than system rated pressure. Do not
cap or restrict the bottom threaded port. Fluid must be allowed to exit the bottom port if an over pressure
occurs. Refer to Relief Valve manual. See Related Manuals, page 3.
CC Pump Outlet Hose - Provides fluid to the mix manifold from the pump.
DD Solvent Flush Supply Hose - Provides fluid to the mix manifold from solvent pump.
Air Relief Valve (not shown) - Opens automatically to prevent overpressurization of the air motor.
GG Return Line Valve
HH Return Line Tube/Hose Assembly
333309E 13
Page 14

Installation
Installation
Prepare the Operator
All persons who operate the equipment must be trained
in the operation of all system components as well as the
proper handling of all fluids. All operators must thoroughly read all instruction manuals, tags, and labels
before operating the equipment.
Prepare the Site
Compressed Air
• Ensure that you have an adequate compressed air
supply.
• Bring a compressed air supply line from the air compressor to the pump location.
• Be sure all air hoses are properly sized and pressure-rated for your system. The air hose should
have a 3/8 npt(m) thread and minimum 3/8” (9.5
mm) ID.
• Use only electrically conductive hoses. A quick disconnect coupling may be used.
Work Area
Wall Mount Packages
Before installing a wall mounted package, ensure the
wall can support the weight of the pump, bracket, hoses
and accessories, as well as the stress caused during
operation.
1. Position the wall bracket about 1-1.5 m (3-5 ft)
above the floor. For ease of operation and service,
make sure the pump air inlet, fluid inlet, and fluid
outlet ports are easily accessible.
2. Using the wall bracket as a template, drill 10 mm
(0.4 in.) mounting holes in the wall. Wall mounting
dimensions are shown on page 51.
3. Attach the bracket to the wall. Use 3/8 in. (9 mm)
screws that are long enough to anchor the pump
securely during operation.
NOTE: Be sure the bracket is level.
Air Line Accessories
Install the following accessories in FIG. 1, using adapters as necessary.
• Keep the site clear of any obstacles or debris that
could interfere with the operator's movement.
• Have a grounded, metal pail available for use when
flushing the system.
• An air filter (B) removes harmful dirt and moisture
from the compressed air supply.
• A second bleed-type air shutoff valve (A) isolates
the air line accessories for servicing. Locate
upstream from all other air line accessories.
14 333309E
Page 15
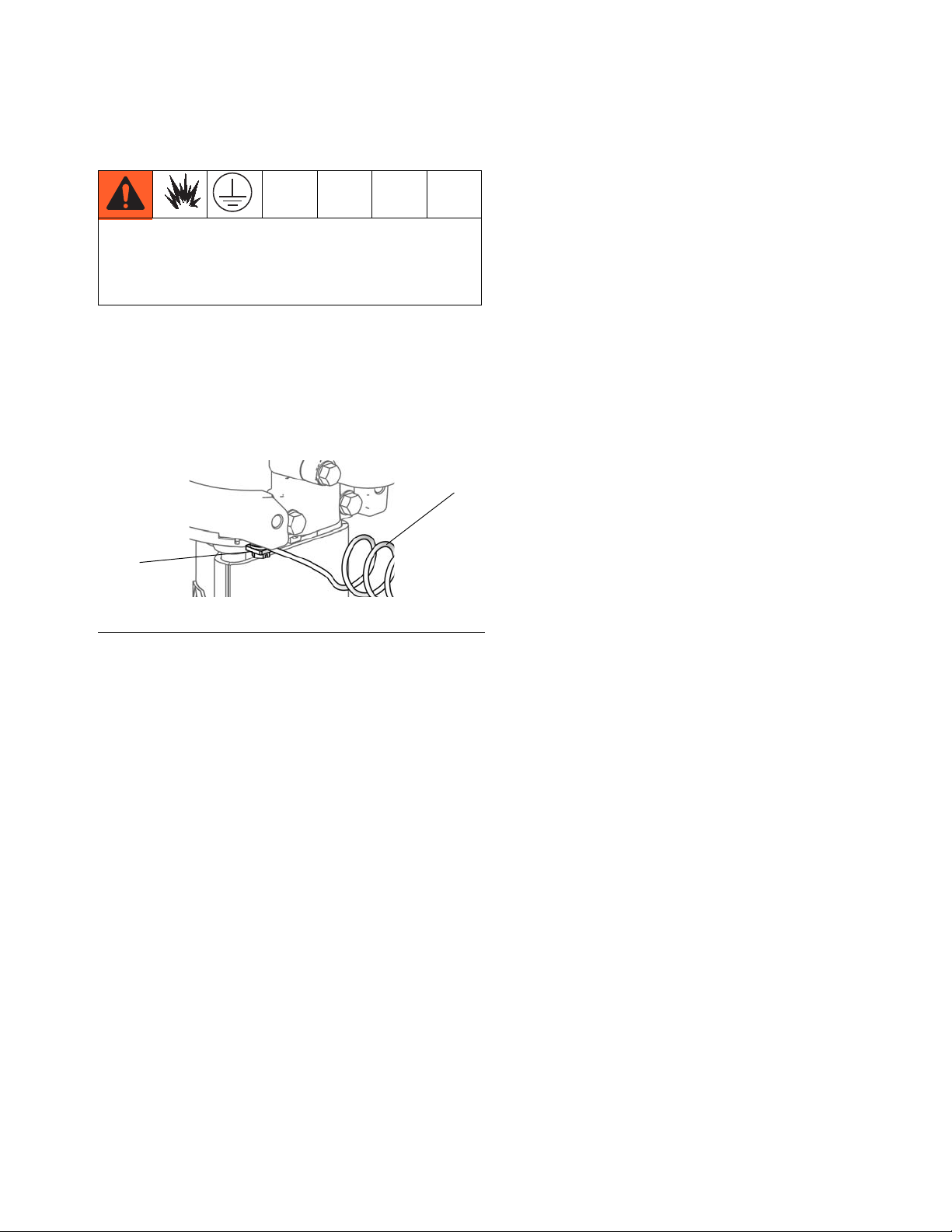
Grounding
S
GS
ti12914a
Installation
3. Air compressor
Follow manufacturer's recommendations.
The equipment must be grounded to reduce the risk
of static sparking. Static sparking can cause fumes to
ignite or explode. Grounding wire provides an escape
path for static electric current.
The following components must be grounded.
1. Pump
See F
IG. 4. Verify that the ground screw (GS) is
attached and tightened securely to the air motor.
Connect the other end of the ground wire (S) to a
true earth ground.
F
IG. 4. Ground screw and wire
2. Pump fluid hoses
Use only electrically conductive fluid hoses. Check
electrical resistance of hoses. If total resistance to
ground exceeds 25 megohms, replace hose
immediately.
4. Spray gun
Ground through connection to a properly grounded
fluid hose and pump.
5. Fluid supply container
Follow your local code.
6. Object being sprayed
Follow your local code.
7. Solvent pails used when flushing
Use only metal pails, which are conductive, placed
on a grounded surface. Do not place the pail on a
non-conductive surface, such as paper or
cardboard, which interrupts the grounding
continuity. All solvent pails used when flushing must
be grounded according to local code.
NOTE: To maintain grounding continuity when flushing
or relieving pressure, hold a metal part of the spray gun
firmly to the side of a grounded metal pail, then trigger
the gun.
333309E 15
Page 16
Setup
Setup
See FIG. 2.
1. Install suction hoses (VA, VB) to the pump fluid
inlets (U). See page 46.
2. Connect solvent supply (DD) to solvent flush inlet
(J).
3. Attach one end of the gun fluid supply hose (M) to
the mixer (X) outlet.
4. Attach one end of the gun air supply hose (N) to gun
air pressure regulator (D) atomizing air port.
5. Attach remaining end of the gun air supply hose (N)
to air inlet at base of gun (L).
6. Connect gun fluid supply hose (M) to the base of the
gun (L) at swivel (K).
7. Clip gun fluid supply hose (M) and gun air supply
hose (N) together with the supplied hose clips (qty.
of 7). Space clips as needed.
8. Apply lens cover to both regulator gauge lenses.
Feed Systems
Ensure your feed systems are designed to supply twice
the volume used by each component. This supply pump
pressure should never exceed 25% of the proportioner
output pressure or 250 psi (16 bar) maximum supply
pressure.
Example: 4:1 proportioner. 2.0 lpm output, 100 bar.
4:1 ratio at 2.0 lpm = 1.6 lpm of “A” component and.4
lpm of component “B”.
• “A” feed pump needs to have a 3.2 lpm capacity at a
max of 250psi (16 bar).
• “B” feed pump needs to be at least.8 lpm at 250 psi
max.
Material supply is critical to proper proportioner operation. Material must fill the proportioner cylinders on their
upstroke totally to eliminate a “diving” of the cylinders on
the top change–over. This “diving” will also be seen as a
pressure drop at the change over. This will cause an off
ratio condition.
9. Verify that suction hose (VA, VB) fittings are tight.
NOTE: Loose suction hose fittings allow air to enter into
the proportioning pump resulting in the fluid ratio to be
altered.
Connect Air Lines
See FIG. 1.
1. Attach fittings to the air control module.
2. Attach the air hose to the fitting on the air control
module.
NOTE: The air supply line to proportioner module has to
be a minimum of 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) ID.
3. Attach air line to solvent pump.
NOTICE
Using more supply pressure than necessary to fully
supply the proportioning cylinder can cause varying
atomization, inconsistent spray pressure, and incorrect fluid ratios.
If materials require heating they can be heated in the
supply feed as well as the outbound side of the pumps.
The maximum fluid temperature of 160°F should not be
exceeded.
Review your feed systems with your Graco Distributor.
16 333309E
Page 17
Setup
A and B Components
Cross-contamination can result in cured material in
fluid lines which could cause serious injury or damage
equipment. To prevent cross-contamination:
• Never interchange component A and component
B wetted parts.
• Never use solvent on one side if it has been contaminated from the other side.
NOTE: Material suppliers can vary in how they refer to
plural component materials.
Be aware that when facing the manifold on the proportioner:
• Component A is on the left side.
• Component B is on the right side.
For all machines:
• The A side is intended for polyols, resins, and
bases.
• If one of the materials being used is moisturesensitive, that material should always be in the B
side.
• The B side is intended for ISO, hardeners, and catalysts.
NOTE: For machines with material volume ratios other
than 1:1, the higher volume side is typically at the A
side.
Polyester Model 24W609: This model is intended for
use with split-batch polyester applications. The A side
will contain polyester, resin, and the promoter. The B
side will contain polyester, resin, and the activator.
Checking the Mix Ratio
The pump must be operating in order to accurately
check the proportioning ratio of the pumps. The outlet
pressures at the pumps must be maintained at a minimum level of 4 times that of the inlet pressures.
When the mix manifold is removed to check the mix
ratio, a flow restrictor will be needed to simulate the
pressure conditions during normal operation. The preferred flow restrictor is a small diameter, 1/16 in. ID, 1/2
in. (13 mm) long steel tube, coupled to the fluid supply
hoses. A needle-type flow control valve could also be
used. Contact your Graco distributor for assistance in
selecting the proper type of flow restrictor for your application.
If the mixed fluid does not cure or harden properly,
check the ratio of part A to part B. To check the ratio:
1. Relieve the pressure, see page 19.
2. Flush the mixed fluid out of the mix manifold, dispensing lines, and equipment.
3. Disconnect the fluid hoses from the mix manifold
inlet, taking note of which hose was connected to
which valve.
4. Place the hose ends into a waste container. Set two
graduated cylinders of the same size next to the
waste container. See F
5. Set the air pressure to the proportioning pumps at
zero pressure. Open the air shut off valves to the
feed pumps and proportioning pump.
IG. 5.
6. Turn up air pressure until fluids are flowing freely, at
exactly the same time, move the hoses over the cylinders – part A hose over one cylinder and part B
hose over the other.
333309E 17
Page 18

Setup
MOVE HOSES AT THE SAME TIME
Fluid
Supply
Hoses
T
T
Q
Q
7. When you have a large enough sample, move both
hoses back into the waste containers, at exactly the
same time. Then shut off the air to all the pumps.
8. Compare part A volume to part B volume. If the ratio
is not correct, refer to the Troubleshooting Chart
on page 31 for further information on how to correct
the ratio.
9. Connect the fluid hoses back to the mix manifold
inlet.
NOTICE
Be sure to connect the hoses back to the same valves
they had originally been connected to. The mix manifold could be damaged by reversing them. See F
IG. 5.
Wet Cup
Check the wet cup (T) daily before starting the pump.
1. To access the wet cups (T) remove the pinch guard
(Q) using a Phillips head screwdriver.
2. Fill the wet cup (T) one-half full with Graco Throat
Seal Liquid (TSL) or compatible solvent. ISO oil may
be used on the “B” side of the proportioner.
FIG. 5 Checking Mix Ratio
Flush the Pump Before First Use
The pump is tested with lightweight oil, which is left in to
protect the pump parts. To avoid contaminating your
fluid with oil, flush the equipment with a compatible solvent before using. See Flush the Pump on page 29.
FIG. 6. Wet Cup
3. Re-install the pinch guard (Q) and screw using a
Phillips head screwdriver.
18 333309E
Page 19

Operation
Operation
Pressure Relief Procedure
Follow the Pressure Relief Procedure whenever
you see this symbol.
This equipment stays pressurized until pressure is
manually relieved. To help prevent serious injury from
pressurized fluid, such as skin injection, splashing
fluid and moving parts, follow the Pressure Relief
Procedure when you stop spraying and before
cleaning, checking, or servicing the equipment.
1. Engage the gun trigger lock, if present.
2. See F
3. Disengage the gun trigger lock, if present.
4. Hold a metal part of the gun firmly to a grounded
IG. 2. Turn off the bleed-type master air valve
(E) and air to supply pumps, if present.
metal waste container. Trigger the gun to relieve
fluid pressure.
7. If you suspect that pressure has not been fully
relieved after following the steps above, check the
following:
a. The spray tip may be completely clogged. Very
slowly loosen the air cap retaining ring to relieve
pressure in the cavity between the ball/seat
shutoff and the plugged tip. Clear the tip orifice.
b. The gun fluid filter or the fluid hose may be com-
pletely clogged. Very slowly loosen the hose
end coupling at the gun and relieve pressure
gradually. Then loosen completely to clear the
obstruction.
c. After following the steps above, if the spray tip
or hose still seems completely clogged, very
slowly loosen the tip guard retaining nut or hose
end coupling and relieve pressure gradually,
then loosen completely. With tip removed, trigger gun into waste container.
Prime the Pump
1. Engage the gun trigger lock. Remove tip guard and
spray tip from gun (L). Refer to gun manual. See
Related Manuals, page 3.
5. Engage the trigger lock, if present.
6. Open all fluid drain valves (W) in the system, having
a waste container ready to catch the drainage.
Leave the drain valve(s) open until you are ready to
spray again.
2. Close gun air pressure regulator (D) and pump air
pressure regulator (H) by turning knobs counterclockwise reducing pressure to zero. Close
bleed-type master air valve (E). Also verify that all
drain valves are closed.
3. Check that all fittings throughout system are tightened securely.
4. Position pail close to pump. Suction hose is 4 ft
(1.2 m) long. Do not stretch hose tight; let it hang to
assist fluid flow into pump.
NOTE: Loose suction hose fittings allow air to enter into
the proportioning pump resulting in the fluid ratio to be
altered.
5. Standard Procedure: Disconnect the fluid hoses
from the mix manifold inlet, taking note of which
hose was connected to which valve.
Procedure for Polyester Model 24W609: Open the
return valves on both A and B pump outlets.
333309E 19
Page 20

Operation
VB
VA
A Supply B Supply
S
S
(A Side)
(B Side)
H
E
D
6. Standard Procedure: Direct A and B pump outlet
hoses (CC) from manifold (F) to a grounded metal
waste pail.
Procedure for Polyester Model 24W609: Direct A
and B return hoses and tubes to a grounded metal
pail.
7. Open bleed-type air valve (E). Slowly turn clockwise
pump air regulator (H) increasing pressure until
pump starts.
8. Cycle pump slowly until all air is pushed out and
pump and hoses are fully primed.
9. Standard Procedure: Reattach A and B pump outlet hoses (CC) to fluid pressure gauges (PA, PB) on
the mix manifold (F).
Procedure for Polyester Model 24W609: Close
the return valves on both A and B pump outlets.
NOTE: For Polyester Model 24W609, continue with
steps 10 to 14.
10. Disengage the gun trigger lock and trigger the spray
gun into a grounded metal waste container.
2. Verify solvent valves (S) on the mix manifold (F) are
closed (both A and B sides). Move mix manifold
handle to the mix position.
3. Verify pump air pressure regulator (H) and the gun
air pressure regulator (D) are in the off (no pressure) setting.
4. Turn on bleed type master air valve (E).
11. Increase the pump air supply pressure until the
pump cycles.
12. Cycle the pumps until mixed material flows from the
spray gun.
13. Engage the trigger lock.
14. Install the spray tip into the spray gun.
15. Disengage the trigger lock, increase the air pressure, and begin to spray.
Load Mix Material to the Gun
1. Insert the A supply suction hose (VA) into a full container of part A supply. Insert the B (VB) supply suction hose into a full container of part B supply.
5.
a. Engage the gun trigger lock.
b. Remove the tip guard, spray tip and/or air cap.
c. Disengage the gun trigger lock.
d. Open the pump air pressure regulator (H).
Increase the air pressure just enough to keep
the pumps running. Trigger the spray gun.
6.
20 333309E
Page 21

Operation
H
D
7. Allow pumps to run until mixed material is flowing
from the front of the gun then release the gun trigger.
8. Engage the gun trigger lock.
9. Install the tip guard, spray tip and/or air cap.
10. Increase pump air pressure regulator (H) and gun
air pressure regulator (D) until desired fluid and air
pressure is achieved.
1. Do not turn on atomizing air supply. Fluid pressure
is controlled by the air pressure supplied to the
pump (pump air pressure regulator). Set fluid pressure at low starting pressure.
• For low viscosity fluids (less than 25 sec, #2
Zahn cup) with lower percent solids (typically
less than 40%), start at 300 psi (2.1 MPa, 21
bar) at pump outlet.
• For fluids with higher viscosity or higher solids
content, start at 600 psi (4.2 MPa, 42 bar).
Refer to the following example.
Example:
Pump
Fluid/Air
Pressure
Ratio
15:1 x 20 (0.14, 1.4) = 300 (2.1, 21)
30:1 x 20 (0.14, 1.4) = 600 (4.2, 42)
2. Hold gun perpendicular and approximately 12
inches (304 mm) from surface.
3. Move gun first, then pull gun trigger to spray onto
test paper.
Pump Air
Regulator Setting
psi (MPa, bar)
Approximate
Fluid Pressure
psig (MPa, bar)
4. Increase fluid pressure in 100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7 bar)
increments, just to the point where a further
increase in fluid pressure does not significantly
11. Disengage the gun trigger lock and spray. See
Spray Gun Adjustment. page 21.
NOTE: The following section is intended as a general
guideline for spray gun operation. Refer to the appropriate spray gun manual for more details.
Spray Gun Adjustment
For AA Spray Guns
Adjust the Atomization
improve fluid atomization. Refer to the following
example.
Example:
Pump
Fluid/Air
Pressure
Ratio
15:1 x 7 (.05, 0.5) = 100 (0.7, 7.0)
30:1 x 3.3 (0.02, 0.2) = 100 (0.7, 7.0)
Pump Air Regulator
Increment
psi (MPa, bar)
Incremental
Fluid Pressure
psi (MPa, bar)
Adjust the Spray Pattern
Packages with Airless Guns
The spray tip orifice and spray angle determine pattern
coverage and size. When you need more coverage, use
a larger spray tip rather than increasing fluid pressure.
Align guard horizontally to spray a horizontal pattern.
Align guard vertically to spray a vertical pattern.
333309E 21
Page 22

Operation
TI6559A
OUT (narrower
pattern)
IN (wider
pattern)
AA
AA
no air
too little air
correct
amount of air
H
E
D
Packages with AA Guns
1. See F
IG. 7. Close off pattern adjustment air by turn-
ing knob (AA) clockwise (in) all the way. This sets
gun for its widest pattern.
F
IG. 7. Pattern Air Knob
2. See F
IG. 8. Set atomizing air pressure at about 5 psi
(0.35 bar, 35 kPa) when triggered. Check spray pattern, then slowly increase air pressure until tails are
completely atomized and pulled into spray pattern.
Do not exceed 100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7 bar) air pressure
to gun.
Mix Material Flush Procedure
Standard procedure for all pumps except
polyester model 24W609
To avoid fire and explosion, always ground
equipment and waste container. To avoid static
sparking and injury from splashing, always flush at
lowest possible pressure.
NOTICE
Before flushing stop the pump at the bottom of its
stroke to keep fluid from drying on the exposed displacement rod and damaging throat packings.
1. Trigger the gun to stop the pump at the bottom of its
stroke.
3. See F
adjustment valve knob (AA) counterclockwise (out).
If pattern is still not narrow enough, increase air
pressure to gun slightly or use different size tip.
IG. 8. Spray Pattern Problems
F
IG. 7. For narrower pattern, turn pattern
2. Shut off air to gun air pressure regulator (D) and the
pump air pressure regulator (H). Close the bleed
type master air valve (E).
3. Relieve the pressure, see page 19.
22 333309E
Page 23

Operation
4. Engage the gun trigger lock.
5. Remove the spray tip and/or air cap.
6. Move mix manifold handle to standby position. Open
B side solvent flush valve.
9. Trigger gun for 3 seconds into a grounded metal
waste pail holding a metal part of gun firmly to the
pail.
10. Close B side solvent flush valve.
7. Open bleed type air valve on the solvent pump to
provide air to flush the pump. Increase air pressure
regulator on solvent pump.
8. Disengage the gun trigger lock.
11. Open A side solvent flush valve.
12. Trigger gun for 3 seconds into a grounded metal
waste pail, holding a metal part of gun firmly to the
333309E 23
Page 24

Operation
pail, until the mixed fluid is purged from the system
and clean solvent is flowing.
13. Close A side solvent flush valve.
15. Trigger gun for 3 seconds into a grounded metal
waste pail holding a metal part of gun firmly to the
pail.
16. Engage trigger lock. Install the spray tip and/or air
cap. Disengage trigger lock and trigger gun to flush
tip and/or air cap with solvent. Engage trigger lock
and remove the spray tip and/or air cap.
14. Open B side solvent flush valve.
17. Close B side solvent flush valve.
24 333309E
Page 25

Operation
18. Turn off air regulator to solvent pump. Close the
bleed type air supply valve to the solvent pump.
19. Disengage the trigger lock and trigger the gun into a
grounded metal waste pail until flow stops and pressure is relieved.
8. Turn off the solvent supply pump.
9. Trigger the gun into a grounded metal waste pail
until flow stops and pressure is relieved.
10. Close the solvent inlet valve (J).
11. Engage the gun trigger lock.
Procedure to Flush Polyester Model
24W609 Pumps
1. Place return line tube and hose assembly (HH) into
a grounded metal waste pail.
2. Open A and B return line valves.
3. Place suction tubes into a clean solvent supply pail.
4. Open the pump air inlet valve.
5. Increase the pump air pressure until the pump
cycles. Run the pump until clean solvent is flowing
from both return tubes.
6. Close the A and B return line valves.
Procedure for Polyester Model 24W609 with
Solvent Flush Pump
1. Move remote mix manifold handle to standby position.
2. Open the solvent inlet valve (J).
3. Turn on the solvent pump and adjust the air pressure.
4. Engage the gun trigger lock.
5. Remove the spray tip from the gun.
6. Disengage the trigger lock and trigger the gun into a
grounded metal waste pail until the mixed fluid is
purged from the system and clean solvent is flowing.
7. Engage trigger lock. Install the spray tip and/or air
cap. Disengage trigger lock and trigger gun to flush
tip and/or air cap with solvent. Engage trigger lock
and remove the spray tip and/or air cap.
7. Engage the gun trigger lock. Remove the spray tip.
8. Disengage the gun trigger lock. Spray the gun into a
grounded metal waste pail until clean solvent is
flowing from the gun.
9. Engage trigger lock. Install the spray tip and/or air
cap. Disengage trigger lock and trigger gun to flush
tip and/or air cap with solvent. Engage trigger lock
and remove the spray tip and/or air cap.
10. Shut off the pump air pressure and close the pump
air inlet valve.
11. Disengage the trigger lock and trigger the gun into a
grounded metal waste pail until flow stops and pressure is relieved.
333309E 25
Page 26

Operation
Using the Proportioning Pump System
To reduce the risk of serious injury, including fluid
injection:
• Do not exceed the maximum air and fluid working
pressure of the lowest rated component in your
system.
• Always close the air supply valve to the pump
before opening the fluid drain valves to relieve
system pressure. This will reduce the risk of
excessive pressure buildup in the opposite
component hose and fittings.
When the system is primed and operating, check the
fluid outlet pressure gauges. Check the gauges frequently while using the system and note the pressures.
These notes will be helpful in analyzing problems that
may occur, as a change in the displacement pump performance will be indicated by a change in the pressure
gauge readings.
NOTE: A pressure drop does occur during pump stroke
changeover.
1. Set the air pressure to the proportioning pump to
obtain the fluid pressure you require.
2. Set the air pressure to the feed pumps at a pressure
that will not give more than 25% of sprayer outlet
pressure at their fluid outlets.
NOTE: Pressures greater than 25% may prevent the
proportioning pump inlet ball checks from seating properly.
3. Point the spray gun into a grounded metal waste
container and trigger the spray gun to purge air out
of the dispensing lines. After all air has been purged
from the lines, release the trigger and engage the
gun trigger lock.
NOTE: The pumps will start and stop as the gun is triggered and released.
26 333309E
Page 27

Operation
Monitoring the Proportioner During Operation
When the spray gun is triggered:
• Both A and B fluid pressure gauges should be
increasing and decreasing in pressure at the same
time.
Changing ratios
Remove Pump Lowers
Remove pump lowers as needed (change only the
pump(s) required to achieve the new ratio)
1. Disconnect the suction tube assembly from the
pump inlet.
2. Disconnect the Fluid filter and safety relief valve
assembly from the pump outlet port.
3. Remove coupler nut (24) from connecting rod (36)
using wrench on coupler nut and flats on the connecting rod. Do not lose keepers (23 Qty. 2)
required.
4. Remove retaining ring (22) using a spanner wrench
or hammer and punch.
5. Remove pump assembly by lowering out the bottom
of the mounting plate.
Install Replacement Lower for New Ratio
• If one pressure or the other increases while the
other decreases the proportioner is not working correctly. The cause should be determined and corrected.
• The most typical time for pressure variations to
occur is right after the top change over. This pressure variation is caused by one of the double acting
piston pumps “A” or “B” cavitating during the up, or
fill stroke, and then not having fluid to pump until it
travels down to the filled level. Cavitation causes
ratio errors and should not be allowed at any time
while spraying.
1. Install pump adapter (29) and new pump. Thread
adapter (29) flush with top threaded upper pump
housing. Secure in position by locking in place with
jam ring on pump assembly. See F
2. Install pump into mounting plate and retain in position with lock ring (22) loose fit.
3. Install coupler nut (24) and keepers (23, qty. 2) on
pump displacement rod. Thread coupler nut (24) to
connector rod (36). Tighten and torque to 75-80 lb-ft
(102-108 N•m). If changing to a 25 cc fluid section,
the pump connecting rod (36), keepers (23, qty 2)
and connector nut (24) need to be replaced with the
25cc parts. For the 25cc lower coupler nut (24)
torque to 25-30 lb-ft (31-35 N•m) See Lower
Assembly, page 44.
4. Position pump outlet port fitting for connection to the
relief valve/ fluid filter.
5. Allow pump assembly to center in mounting plate
vertically under connecting rod center line.
6. Torque locking ring (22) to approximately 50 lb/ft
with spanner wrench or hammer and punch while
ensuring pump remains vertical under the yoke to
prevent throat packing side loading when in operation.
7. Re-connect the safety relief valve, filter, and outlet
hose
IG. 6.
333309E 27
Page 28

Operation
23
29
15
36
44
24
22
32
33
38
14
37
See Detail A
Detail A
32
31
8. Reconnect the suction tube assembly.
Adjust Pump Assembly for Balanced Yoke
Forces
At each ratio setup the pump assembly must be
adjusted to balance the yoke forces. To adjust the pump
assembly:
1. Loosen mounting plate screw (44, 2 locations)
2. Loosen yoke bolts (33, 2 locations).
3. Loosen Tie rod nuts (14, 4 locations)
4. Slide the yoke (32) until the desired ratio marks on
the yoke (32) align with the center line mark on the
connector (31). See Detail A.
5. Remove yoke assembly screws (33, 2 locations),
clean threads and apply medium strength thread
adhesive. Re-install screws (33, 2 locations) and
tighten the yoke assembly screws (33, 2 locations),
while maintaining the mark alignment. Torque to 40
lb-ft (47-54 N•m).
6. Position the fluid assembly vertically under the yoke
and tighten the tie rod nuts (14), ensure washers
(15) are in place. Torque to 45 lb-ft (68-80 N•m).
NOTICE
Verify that fluid pumps are aligned vertically under the
yoke position. If they are not aligned correctly, side
loading of motor and fluid pumps will occur, causing
premature wear to seals and bearings.
7. Re-tighten mounting bracket screws (44) and torque
to 35 lb-ft. (47 N•m)
Cycle the pump slowly and observe up and down stroke
changeover verifying correct operation. If binding is
observed, re-align fluid pumps by repeating step 6.
NOTE: 1:1 and 6:1 ratios have yoke and pump positioned against yoke and plate slot ends. Adjusted full left
or right positions.
28 333309E
Page 29

Maintenance
Maintenance
Care of the Pump
NOTICE
Do not allow the supply containers to run dry of the
fluid being pumped. A dry container allows air to be
pumped into the system and can cause incorrect proportioning. One dry displacement pump can damage
the other displacement pump by causing a pressure
rise in the other pump.
• If a supply container is dry, stop the pump immediately and relieve the pressure. Refill the container,
and prime the system. Be sure to eliminate all of the
air from the system.
• Keep the throat packing reservoirs one-half filled
with TSL.
• Observe the pot life limit. Flush the mixed fluid out of
the mix manifold, dispensing lines and equipment
before it hardens.
• Flush the complete system, when necessary to prevent the fluids from hardening in the equipment and
hoses.
• Check the fluid manufacturer’s instructions for fluid
shelf life, and flush the entire system before this
time is reached.
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
The operating conditions of your particular system
determine how often maintenance is required. Establish
a preventive maintenance schedule by recording when
and what kind of maintenance is needed, and then
determine a regular schedule for checking your system.
Tighten Threaded Connections
Before each use, check all hoses for wear or damage.
Replace as necessary. Check that all threaded connections are tight and leak-free.
Flush the Pump
To avoid fire and explosion, always ground
equipment and waste container. To avoid static
sparking and injury from splashing, always flush at
lowest possible pressure.
When to Flush the Pump:
• Flush the system with a compatible solvent.
• With heavy fluids, flushing solvents could channel
through the fluid, leaving a coating of fluid on the
inside of the hoses. Allow pump to flush at higher
cycle rates to create turbulent flow and better cleaning action. Disconnect the hoses and clean the fluid
out with a rag and wire or a ramrod type cleaner, or
use a solvent and air purge to agitate the solvent,
and flush until the mix manifold, hose, and gun are
clean.
• For daily or long term shutdown stop the pump at
the bottom of the stroke to protect the displacement
rod from dried or cured material.
333309E 29
• Before first use
• When changing colors or fluids
• Before repairing equipment
• Before fluid dries or settles out in a dormant pump
(check the pot life of catalyzed fluids)
• Before storing the pump
Flushing Guidelines
• Flush at the lowest pressure possible.
• Flush with a fluid that is compatible with the fluid you
are pumping and with the wetted parts in your system.
• Check with your fluid manufacturer or supplier for
recommended flushing fluids and flushing frequency.
• If the pump is to be stored for any period of time,
and you are pumping water-based fluid, first flush it
with water, then with mineral spirits to protect the
pump parts.
Page 30

Maintenance
Wet Cup
The wet cup helps to provide consistent lubrication for
the pump packings and to keep exposed rod from being
coated with dried paint. To maintain the wet cup:
1. Fill the wet cup one-half full with Graco Throat Seal
Liquid (TSL).
2. Maintain level daily.
Fluid Pressure Relief Valves
The fluid pressure relief valves are used to prevent
pumps from generating pressures higher than they system rated pressure. If an overpressure situation occurs
the valve will open and discharge fluid from the bottom
relief port. Do not modify, remove, or plug the pressure
relief valve.
Materials that cure when exposed to air may defeat
the ability of the pressure relief valve to relieve an
overpressure condition, resulting in burst
components and serious injury
Storage and Extended Shutdown
NOTICE
Before flushing stop the pump at the bottom of its
stroke to keep fluid from drying on the exposed displacement rod and damaging throat packings.
Water or moist air can cause material residue in ball
checks and packings to cure.
• Never leave the pump filled with water or air.
• After normal flushing, flush the pump again with
mineral spirits or oil-based solvent; relieve the pressure; and leave the mineral spirits in the pump.
Refer to separate relief valve manual for additional
details. See Related Manuals, page 3.
Lubrication
An accessory air line lubricator provides automatic air
motor lubrication. For daily, manual lubrication:
1. Disconnect the regulator
2. Place about 15 drops of light machine oil in the
pump air inlet
3. Reconnect the regulator.
4. Turn on the air supply to blow oil into the motor.
30 333309E
Page 31

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
NOTE: Check all possible problems and causes before
disassembling the pump.
To avoid serious injury, always Relieve the pressure
before checking or servicing the equipment.
Problem Cause Solution
Pump does not cycle Air supply pressure not “on” Verify air supply is on and pressure set high
Air supply pressure set too low
Mix manifold turned to off position Place manifold in mix position
Gun tip is plugged Make sure that the Fluid lines are clear and
Mix manifold or mixed material hose
plugged
Pump does not load material Suction hose is plugged Make sure suction hose and tube are clear
Pump is vapor locked Open a gun or drain valve to allow for air to
Paint viscosity is too high to siphon Make sure paint is thin enough to siphon to
Pump cycles erratically Air supply is too restricted The air supply hose should be a minimum of
Pump packing’s are dry Check TSL level in wet cups. Verify pump is
Pump cavitation
Fluid pressures are low Air supply is too restrictive Use a larger air hose
Pump friction is high Check TSL level in wet cup
Fluid filters plugging Clean fluid filters
Paint not mixed Static mixer is not clean Replace static mixer
Paint not at correct ratio Pump cavitation Suction tube and hose restricted
Ball check in pump is not checking Pump is contaminated with dried paint or
System speeds up or runs
erratically
A and B fluid pressures not
equal
Pump cavitation Suction tube and hose restricted
Pump checks are not checking con-
sistently
Very different viscosities Can be OK. Should not exceed 10% differ-
Mix manifold check valves and ports
restricted by cured paint
enough to cycle pump
open for mixed paint flow
and free of caps or plugged strainers.
escape the system while filling with paint or
solvent.
the pump
3/8” id and a max of 50 ft in length.
loading fully on up stroke
Suction hose and tube fittings are loose
allowing suction of air into pump
foreign materials
Suction hose and tube fittings are loose
allowing suction of air into pump
Pump is contaminated with dried paint or
foreign materials
ential with unit mounted mix manifold.
Remote mounted mix manifold A and B
pressures may have a greater differential,
but greater than 20% can cause ratio errors.
Clean and repair mix manifold
333309E 31
Page 32

Troubleshooting
Problem Cause Solution
A and B fluid pressures not
consistent
Pump cavitation Suction tube and hose restricted
Suction inlet plumbing drawing air Suction hose and tube fittings are loose
allowing suction of air into pump
Ball check in pump is not checking Pump is contaminated with dried paint of
foreign materials
A or B fluid pressure falls off
Pump cavitation Suction tube restricted
after top change over
A or B pressure changes after
mix manifold is closed
External fluid leak Fix hose and fitting leaks
Internal leak of fluid pump seals or
Clean or repair proportioning pump
check valves causing loss of outlet
pressure.
Fluid relief valve opens allowing fluid out of bottom port.
Fluid pressure in line
exceeded system pressure rating
Pump fluid pressure set too high. Reduce air supply pressure to proportioner
Unbalanced load between A and B
fluid pump.
Suction tube and hose restricted
Suction hose and tube fittings are loose
allowing suction of air into pump
Pump is contaminated with dried paint of
foreign materials
Fix hose and fitting leaks
Clean or repair proportioning pump
Filter plugged. Clean filters
Flush pump does not run Air supply to flush pump turned off Turn on air supply
Air supply pressure to flush pump set
Increase air supply pressure
too low
Mix manifold solvent valves not “on” Open flush valves and gun
Gun not triggered Trigger spray gun
Mix Manifold or mixed material hose
plugged
Repair and replace mix manifold and mixed
material hoses
* To determine if the fluid hose or gun is obstructed, relieve the pressure. Disconnect the fluid hose and place a container at the pump fluid outlet to catch any fluid. Turn on the air just enough to start the pump. It the pump starts when
the air is turned on, the obstruction is in the hose or gun.
32 333309E
Page 33

Performance Charts
0 0.2
(0.8)
0.4
(1.5)
0.6
(2.3)
0.8
(3.0)
1.0
(3.8)
815 3038
0
50
(0.3, 3)
100
(0.7, 7)
150
(1.0, 10)
200
(1.4, 14)
250
(1.7, 17)
300
(2.0, 20)
350
(2.4, 24)
1
(0.03)
2
(0.06)
3
(0.08)
4
(0.1)
5
(0.14)
6
(0.17)
7
(0.2)
2320*
B
C
B
C
Cycles per Minute
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
KEY
B
=
65 psi (0.45 MPa, 4.5 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
0 0.32
(1.20)
0.60
(2.25)
0.91
(3.45)
1.20
(4.50)
1.51
(5.70)
815 3038
0
50
(0.3, 3)
100
(0.7, 7)
150
(1.0, 10)
200
(1.4, 14)
250
(1.7, 17)
1
(0.03)
2
(0.06)
3
(0.08)
4
(0.1)
5
(0.14)
6
(0.17)
7
(0.2)
8
(0.23)
9
(0.25)
2320*
A
B
C
A
B
C
Cycles per Minute
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
KEY
A
=
100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7.0 bar)
B
=
70 psi (0.48 MPa, 4.8 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
2.5” Air Motor with 1:1 and 3:1 Lower Pump Ratio
100 cc/cycle
Performance Charts
2.5” Air Motor with 2:1 and 5:1 Lower Pump Ratio
150 cc/cycle
* See Note in Technical Data, page 52.
333309E 33
Page 34

Performance Charts
0 0.25
(1.00)
0.50
(1.87)
0.75
(2.87)
1.00
(3.75)
1.25
(4.75)
815 3038
0
50
(0.3, 3)
100
(0.7, 7)
150
(1.0, 10)
200
(1.4, 14)
250
(1.7, 17)
300
(2.0, 20)
1
(0.03)
2
(0.06)
3
(0.08)
4
(0.1)
5
(0.14)
6
(0.17)
7
(0.2)
8
(0.23)
9
(0.25)
2320*
B
C
B
C
Cycles per Minute
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
KEY
B
=
75 psi (0.52 MPa, 5.2 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
0 0.37
(1.40)
0.69
(2.62)
1.06
(4.02)
1.39
(5.25)
1.76
(6.65)
815233038
0
50
(0.3, 3)
100
(0.7, 7)
150
(1.0, 10)
200
(1.4, 14)
250
(1.7, 17)
1
(0.03)
2
(0.06)
3
(0.08)
4
(0.1)
5
(0.14)
6
(0.17)
7
(0.2)
8
(0.23)
9
(0.25)
20*
A
B
C
A
B
C
Cycles per Minute
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
KEY
A
=
100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7.0 bar)
B
=
70 psi (0.48 MPa, 4.8 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
2.5” Air Motor with 4:1 Lower Pump Ratio
125 cc/cycle
2.5” Air Motor with 6:1 Lower Pump Ratio
175 cc/cycle
* See Note in Technical Data, page 52.
34 333309E
Page 35

4.5” Air Motor with 1:1 Lower Pump Ratio (for Polyester Model 24W609)
Cycles per Minute
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
KEY
A
=
100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7.0 bar)
B
=
70 psi (0.48 MPa, 4.8 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
500
1000
2000
(13.8, 138)
2500
(17.2, 172)
3000
(20.7, 207)
0
0.2
(0.8)
0.4
(1.5)
0.6
(2.3)
0.8
(3.0)
25
(0.71)
20
(0.57)
15
(0.42)
10
(0.28)
5
(0.14)
82338536115 30 45
1500
(10.3, 103)
20*
A
B
C
A
B
C
0 0.2
(0.8)
0.4
(1.5)
0.6
(2.3)
0.8
(3.0)
1.0
(3.8)
815 3038
0
500
(3, 30)
1000
(7, 70)
1500
(10, 100)
2000
(14, 140)
2500
(17, 170)
3000
(21, 210)
3500
(24, 240)
4000
(28, 280)
10
(0.3)
20
(0.6)
30
(0.9)
40
(1.1)
50
(1.4)
60
(1.7)
2320*
Cycles per Minute
0
A
B
C
A
B
C
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
KEY
A
=
95 psi (0.65 MPa, 6.5 bar)
B
=
70 psi (0.48 MPa, 4.8 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
50 cc/cycle
Performance Charts
7.5” Air Motor with 1:1 and 3:1 Lower Pump Ratio
100 cc/cycle
* See Note in Technical Data, page 52.
333309E 35
Page 36

Performance Charts
0
500
(3, 30)
1000
(7, 70)
1500
(10, 100)
2000
(14, 140)
2500
(17, 170)
3000
(21, 210)
0 0.4
(1.5)
0.8
(3.0)
1.2
(4.5)
1.6
(6.0)
10 20* 30 40
10
(0.3)
20
(0.6)
30
(0.9)
40
(1.1)
50
(1.4)
60
(1.7)
A
B
C
A
B
C
Cycles per Minute
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
KEY
A
=
100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7.0 bar)
B
=
70 psi (0.48 MPa, 4.8 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
0 0.5
(1.9)
0.75
(2.8)
0.25
(0.9)
1.0
(3.8)
1.25
(4.7)
15 2210 30 38
0
500
(3, 30)
1000
(7, 70)
1500
(10, 100)
2000
(14, 140)
2500
(17, 170)
3000
(21, 210)
10
(0.3)
20
(0.6)
30
(0.9)
40
(1.1)
50
(1.4)
60
(1.7)
20*
Cycles per Minute
A
B
C
A
B
C
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
KEY
A
=
100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7.0 bar)
B
=
70 psi (0.48 MPa, 4.8 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
7.5” Air Motor with 2:1 and 5:1 Lower Pump Ratio
150 cc/cycle
7.5” Air Motor with 4:1 Lower Pump Ratio
125 cc/cycle
* See Note in Technical Data, page 52.
36 333309E
Page 37

7.5” Air Motor with 6:1 Lower Pump Ratio
0
500
(3, 30)
1000
(7, 70)
1500
(10, 100)
2000
(14, 140)
0 0.46
(1.75)
0.92
(3.5)
1.39
(5.25)
1.85
(7.0)
10 20* 30 40
10
(0.3)
20
(0.6)
30
(0.9)
40
(1.1)
50
(1.4)
60
(1.7)
A
B
C
A
B
C
Cycles per Minute
Fluid Flow gpm (lpm) tested in No. 10 weight oil
Air Flow scfm (m
3
/min)
Fluid Outlet Pressure psi (MPa, bar)
KEY
A
=
100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7.0 bar)
B
=
70 psi (0.48 MPa, 4.8 bar)
C
=
40 psi (0.28 MPa, 2.8 bar)
=
fluid flow
=
air consumption
175 cc/cycle
Performance Charts
* See Note in Technical Data, page 52.
333309E 37
Page 38

Parts
Ref. Part Description Qty.
7 See Air Control Assembly, page 39
9 105332 NUT, lock 2
40 113358 SCREW, cap, hex hd 4
59 277794 INSERT, control panel 1
76◆ ------- CART, frame. small 1
77◆ ------- HANDLE, cart, small P3 1
78◆ ------- SLEEVE, cart handle, SP3 2
79◆ 116630 SCREW, carriage 2
80◆ 115480 KNOB, T-handle 2
81◆ 119451 WHEEL, semi-pneumatic 2
82◆ 119452 CAP, hub 2
83◆ 15C871 CAP, leg 2
84 108788 WASHER, flat 4
◆ Parts included in Cart Mount Kit 289694 (purchase separately).
Parts
Cart Mount Wall Mounting Bracket
Ref. Part Description Qty.
7See Air Control Assembly, page 39
9 105332 NUT, lock 2
40 113358 SCREW, cap, hex hd 4
59 277794 INSERT, control panel 1
76 17C945 BAR, control mounting 1
77 127965 SCREW, cap, hex hd 4
78 110170 WASHER 12
79 15T795 PLATE, wall mount, small 1
38 333309E
80 105332 NUT, lock 4
84 108788 WASHER, flat 4
Page 39

Parts
Air Control Assembly
24W969 - Air Assisted Air Spray
Models 24V880, 24V881, 24V882, 24V883, 24V884, 24V885, 24V886, 24V887, 24V888, 24V889, 24V890, 24V891,
24W609
Ref. Part Description Qty.
101 114362 VALVE, ball 1
102 15T643 SWIVEL, tee, 3/8 npt(m) x 1/2T 1
103◆ -------- TUBE, nylon 1/2 OD, cut to fit 1
104 121212 ELBOW, swivel, 1/2T x 3/8 npt(m) 3
105 15T536 REGULATOR, air, pump, 3/8 npt(m) 1
106 15T937 FITTING, elbow, swivel,
1/4npt(m) x 5/32 npt(m)
107◆ -------- TUBE, nylon, rd, black 1
108 15T498 FITTING, 90, swivel,
5/32T x 1/8 FNPT
109 15T866 FITTING, elbow, swivel,
1/8 npt x 5/32T
110 15T500 GAUGE, pressure 2
333309E 39
Ref. Part Description Qty.
111 113498 VALVE, safety 1
112 164672 ADAPTER 1
113 15T538 PANEL, nut (plastic) (R73) 1
114 114381 SCREW, cap, button HD 2
115 15T539 REGULATOR, air, gun, 3/8 npt 1
116 116514 NUT, regulator mnt 1
1
117 15T555 PANEL, mounting, w/gun, 4.5/6/7.5 1
122 16P423 CLIP, ground, regulator 1
123 16P424 CLIP, ground, regulator 1
2
1
◆ Parts included in Tubing Repair Kit 24D496 (purchase separately).
Page 40

Parts
24W970 - Air Spray
Models 24V868, 24V869, 24V870, 24V871, 24V872, 24V873, 24V874, 24V875, 24V876, 24V877, 24V878, 24V879
Ref. Part Description Qty.
101 114362 VALVE, ball 1
102 15T638 SWIVEL, tee, 3/8 npt(m) x 3/8T 1
103◆ -------- TUBING, nylon round (Air Spray) 1
104 121141 ELBOW, swivel, 3/8T x 1/4 npt(m) 3
105 15T499 REGULATOR, air, pump, 1/4 npt(m) 2
106 15T866 FITTING, elbow, swivel,
1/8npt(m) x 5/32 npt(m)
107◆ -------- TUBE, nylon, rd, black 1
108 15T498 FITTING, 90, swivel,
5/32T x 1/8 FNPT
109 115244 NUT, regulator 2
40 333309E
Ref. Part Description Qty.
110 15T500 GAUGE, pressure 2
111 121150 FITTING, elbow, 1/4 npt(f)x1/8
npt(m)
112 113498 VALVE, safety, 110 psi 1
113 162453 FITTING, 1/4 mpsm 1
114 15T556 PANEL, mounting, w/gun, datatrack
(Air Spray)
115 114381 SCREW, cap, button HD 2
120 16P421 CLIP, ground, regulator 2
2
◆ Parts included in Tubing Repair Kit 24D496 (pur-
chase separately).
1
1
Page 41

Parts
24W971 - Airless Sprayer
Models 24V892, 24V893, 24V894, 24V895, 24V896, 24V897, 24V898, 24V899, 24V901, 24V902, 24V903, 24V904
Ref. Part Description Qty.
101 114362 VALVE, ball 1
102 121210 FITTING, straight, 1/2T x 3/8 npt(m)
103◆ -------- TUBE, nylon 1/2 OD, cut to fit 1
104 121212 ELBOW, swivel, 1/2T x 3/8 npt(m) 3
105 15T536 REGULATOR, air, pump, 3/8 npt(m) 1
106 15T937 FITTING, elbow, swivel,
1/4npt(m) x 5/32 npt(m)
107◆ -------- TUBE, nylon, rd, black 1
108 15T498 FITTING, 90, swivel,
5/32T x 1/8 FNPT
109 15T500 GAUGE, pressure 2
111 113498 VALVE, safety 1
112 15T538 PANEL, nut (plastic) (R73) 1
113 15T557 PANEL, control, no gun, 4.5/6/7.5 1
333309E 41
Ref. Part Description Qty.
114 114381 SCREW, cap, button HD 2
116 116514 NUT, regulator mnt
(Air Assisted)
119 16P424 CLIP, ground, regulator 1
◆ Parts included in Tubing Repair Kit 24D496 (pur-
1
2
chase separately).
1
Page 42

Parts
Motor Assembly
42 333309E
Page 43

Motor Assembly Parts List
Parts
Ref. Part Description Qty.
1MOTOR 1
M02LN0 Low Pressure (Air Spray)
M18LN0 High Pressure (Air Assisted
and Airless, except Polyester
Model 24W609)
Ref. Part Description Qty.
33 127864 SCREW, cap, socket hd 2
34 100731 WASHER 2
35 16Y850 ROD, piston, A Side 1
36 ROD, piston, B Side 1
17A253 Packages with LW025A (25cc)
M07LN0 Polyester Model 24W609 (Air-
less)
2 WASHER 3
127865 Air Spray
16Y850 Packages with any other lower
37 17D754 BASE, motor
41 104541 LOCK NUT
186652 Air Assisted and Airless
3 LOCK WASHER 3
100133 Air Spray
100128 Air Assisted and Airless
4SCREW 3
C20021 Air Spray
42 107541 WASHER, lock, spring 4
43 17B268 SCREW, hex hd, M12 x 25 LG 4
44 111449 WASHER, plain 4
49 15F744 LABEL, pinch hazard (not
123208 Air Assisted and Airless
10 FITTING 1
121141 Air Spray
15V204 Air Assisted and Airless
13 17D759 ROD, tie 4
16 17D751 BRACKET, mounting 1
65 238909 WIRE, grounding assembly 1
69 17D756 GUARD, pinch, left 1
70 17D757 GUARD, pinch, right 1
85 551295 SCREW, mach, pan, hd 1
99 334665 Quick Start Guide (not used
31 CONNECTOR 1
17B290 Air Spray
17D752 Air Assisted and Airless
32 17D753 YOKE 1
lower
Air Spray 4
Air Assisted and Airless 2
1
shown)
1
with polyester model 24W609)
333309E 43
Page 44

Parts
(A Side)
(B Side)
Lower Assembly
44 333309E
Page 45

Lower Assembly Parts List
Parts
Ref. Part Description Qty.
5 COUPLING COLLAR, A Side 2
184128 Used on all models except 24W609
184132 Used on model 24W609
6 COUPLING NUT, A Side 1
15T311 Used on all models except 24W609
P01043 Used on model 24W609
14 127938 NUT, nylon lock, M12 x 1.75 4
15 109570 WASHER, plain 4
20 LOWER (A Side) 1
LW025A 25 cc, used for 1:1 polyester model
24W609
LW050A 50 cc, used for 1:1 ratio pump
(except 24W609)
LW075A 75 cc, used for 3:1 ratio pump
LW100A 100 cc, used for 2:1 and 4:1 ratio
pumps
LW125A 125 cc, used for 5:1 ratio pump
LW150A 150 cc, used for 6:1 ratio pump
21 LOWER (B Side) 1
LW025A 25 cc, used for 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio
pump and 1:1 polyester model
24W609
LW050A 50 cc, used for 1:1 (except 24W609)
and 2:1 ratio pumps
22 24A639 NUT, jam 1
23 COUPLING COLLAR, B Side 2
184128 1:1 (except 24W609) or 2:1 ratio
pumps
184132 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio pumps, and 1:1
ratio polyester model 24W609
24 COUPLING NUT, B Side 1
15T311 1:1 (except 24W609) or 2:1 ratio
pumps
P01043 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio pumps and 1:1
ratio polyester model 24W609
25 JAM NUT 1
24A638 5:1 ratio pump
24A639 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, 6:1 ratio pumps
29 ADAPTOR, A side 1
17D760 25 cc, used on1:1 ratio polyester
model 24W609
17D758 50 cc, used on 1:1 ratio pump
(except 24W609)
17D770 75 cc, used on 3:1 ratio pump
17D761 100 cc, used on 2:1 and 4:1 ratio
pumps
17D771 125 cc, used on 5:1 ratio pump
Ref. Part Description Qty.
30 ADAPTOR, B Side 1
17D758 50 cc, used on 1:1 (except 24W609)
and 2:1 ratio pumps
17D760 25 cc, used on 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio
pumps and 1:1 polyester model
24W609
38 17D755 BASE, lower 1
51 17C891 REGULATOR BRACKET; used on
models 24V868, 24V869, 24V870,
24V871, 24V872, 24V873
54 123724 NIPPLE; used on all models except
24W609
16C633 NIPPLE; used on polyester model
24W609
55 17D762 FILTER, fluid; used on all models
except 24W609
67 TSL RESERVOIR, A Side 1
15K127 25 cc, used on 1:1 polyester model
24W609
15M031 50 cc, used on 1:1 ratio pump
(except 24W609)
15T339 100 cc, used on 2:1 and 4:1 ratio
pump
15K945 75 cc, used on 3:1 ratio pump
15T340 125 cc, used on 5:1 ratio pump
15T341 150 cc, used on 6:1 ratio pump
68 TSL RESERVOIR, B Side 1
15M031 50 cc, used on 1:1 and 2:1 ratio
pumps
15K127 25 cc, used on 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio
pumps
71 RELIEF VALVE 2
237060 Air Spray
237073 Air Assisted and Airless (except
24W609)
237062 Polyester model 24W609 (Airless)
72 BUSHING 1
502265 1/2 x 3/8; used on 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1
ratio pumps
114499 1/2-14 npt; used on 5:1 ratio pump
15U426 3/4 npt(f) x 1/2 npt(m); used on 6:1
ratio pump
73 114499 FITTING, adapter, 1/2-14 npt 2
75 114342 ELBOW, (1/4-18 NPSM); not used on
polyester model 24W609
88 502265 BUSHING, reducer, pipe 1/2 x 3/8 1
2
2
2
333309E 45
Page 46

Parts
(A Side)
(B Side)
Fluid Inlet Assembly
Ref Part Description Qty
45 SUCTION HOSE (A Side) 1
255872 Used on 1:1 (except 24W609),
2:1, 3:1, 4:1 ratio pumps
256377 Used on 1:1 ratio polyester model
24W609
24A232 Used on 5:1 and 6:1 ratio pumps
46 SUCTION HOSE (B Side) 1
255872 Used on 1:1 (except 24W609)
and 2:1 ratio pumps
256377 Used on 1:1 ratio polyester model
24W609
25640 Used on 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio
pumps
47 STRAINER (A Side) 1
187146 Used on 1:1 (except 24W609),
2:1, 3:1, 4:1 ratio pumps
256426 Used on 1:1 ratio polyester model
24W609
187190 Used on 5:1 and 6:1 ratio pumps
48 STRAINER (B Side) 1
187146 Used on 1:1 (except 24W609)
and 2:1 ratio pumps
256426 Used on 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio
pumps and 1:1 ratio polyester
model 24W609
Ref Part Description Qty
52 90° ELBOW (A Side) 1
102325 Used on 1:1 (except 24W609),
2:1, 3:1, 4:1 ratio pumps
500947 Used on 1:1 ratio polyester model
24W609
500251 Used on 5:1 and 6:1 ratio pumps
90 NIPPLE (A Side) 1
190724 3/4 npt, used on 1:1 (except
24W609), 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 ratio
pumps
114373 Used on 1:1 ratio polyester model
24W609
17D153 1 in. npt, used on 5:1 and 6:1
ratio pumps
94 NIPPLE (B Side) 1
190724 Used on 1:1 (except 24W609) and
2:1 ratio pumps
114373 Used on 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio
pumps and 1:1 ratio polyester
model 24W609
95 90° ELBOW (B Side) 1
102325 Used on 1:1 (except 24W609) and
2:1 ratio pumps
500947 Used on 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1 ratio
pumps and 1:1 ratio polyester
model 24W609
46 333309E
Page 47

Fluid Outlet Assembly (Except Model 24W609)
Parts
17 MANIFOLD, mix; see manual
334625
18 GAUGE 2
187876 Air Spray
C06323 Air Assisted and Airless
19 24N345 HOSE, coupled 2
26 STATIC MIXER HOSE 1
16W564 Air Spray
16W563 Air Assisted and Airless
28 214706 REGULATOR (used only with Air
Spray guns)
39 114196 SCREW 2
86 FITTING 1
114504 Air Spray, Wall Mount
127947 Air Spray, Cart Mount
166846 Air Assisted and Airless, Cart
and Wall Mount
333309E 47
1
1
Page 48

Parts
18
54
48
48
91
74
74
89
89
92
92
66
66
17
26
93
93
Fluid Outlet Assembly (for Polyester Model 24W609)
17 24W861 MANIFOLD, remote mix;
see manual 334625
18 C06323 GAUGE 2
26 24N291‘ STATIC MIXER HOSE 1
48 110191 CROSS, pipe 2
54 16C633 NIPPLE, 1/2 x 1/4 2
74 248271 VALVE, ball 2
48 333309E
1
89 166421 NIPPLE, 5/8 hex x 1/1/2 2
91 166866 ELBOW, street 2
92 17D276 HOSE, return, sst 2
93 256377 HOSE, suction, assembly 2
96 166846 ADAPTER, 1/4 npt x 1/4 npsm 2
Page 49

Spray Gun and Hose
Airless Spray Gun
Ref. Part Description Qty.
1 XTR501 GUN, XTR 5 1
2 241812 HOSE, 25 ft. (7.6 m), 3/16 in. ID 1
▲ Hose warning label 15G026 is available at no cost
AA Spray Gun
Ref. Part Description Qty.
1 24C855 GUN, G40 air-assisted high-pressure spray gun 1
2 256390 AIR HOSE 1
3 241812 HOSE, 25 ft. (7.6 m), 3/16 in. ID 1
4 120706 T-CLIP 1
▲ Hose warning label 15G026 is available at no cost
Air Spray Gun
Ref. Part Description Qty.
1 288950 GUN, AirPro, conventional, stainless steel tip 1
2 205406 HOSE, coupled, 25 ft. (7.6 m) 1
3 256390 AIR HOSE 1
▲ Hose warning label 15G026 is available at no cost
1
2
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
Airless Spray Gun and Hose
(for Polyester Model 24W609)
Ref. Part Description Qty.
1 243283 GUN, Silver, RAC 1
2 826210 HOSE, 10 ft. (3 m), 3/16 in. ID, mix material 1
3 241812 HOSE, 25 ft. (7.6 m), 3/16 in. ID, A and B 2
▲ Hose warning label 15G026 is available at no cost
1
2
3
Parts
333309E 49
Page 50

Dimensions
Dimensions
50 333309E
Page 51

Wall Bracket Mounting
4 in.
11 in.
(279 mm)
Four 0.40 in. (10 mm)
mounting holes
(102 mm)
Dimensions
333309E 51
Page 52

Technical Data
Technical Data
M2K Spray Packages
US Metric
Maximum fluid working pressure Refer to Technical Data Matrix, page 53.
Maximum flow rate Refer to Technical Data Matrix, page 53.
Maximum pump air pressure Refer to Technical Data Matrix, page 53.
Maximum spray gun pressure See your gun manual for spray gun pressures.
Pump air consumption
(See gun manual for additional air consumption)
Maximum free-flow delivery
*NOTE: M2K proportioners are rated to 20 cycles per minute related flowrate to prevent cavitation and ensure complete pump loading, necessary to maintain ratio accuracy.
Recommended cycle rate for continuous duty 20 cycles per minute
Maximum viscosity 10,000 cps
Ambient air temperature range 35°–120°F 2°–49°C
Maximum fluid temperature 160°F 71°C
Fluid flow per cycle Refer to Technical Data Matrix, page 53.
Noise (dBa)
Maximum sound pressure
Inlet/Outlet Sizes
Air inlet size
Materials of Construction**
Wetted materials on all models Displacement pump: Stainless steel, tungsten carbide
with 6% nickel, UHMWPE, PTFE, PEEK
Refer to Performance Charts, page 33.
See Technical Data in air motor manual 312796.
1/4 in. npt(f)
Spray gun: See Manual 312414 (Air Spray guns).
3A0149 (AA guns), or Manual 312145 (XTR guns).
Fluid hoses: nylon 303/304 SST
Suction assembly: stainless steel, nylon
Relief valve, 304 SST, graphite-filled PTFE, tungsten
carbide with nickel binder
Fluid filter: See manual 307273.
Drain valve: stainless steel, nylon
Weight
All models Refer to Technical Data Matrix, page 53.
52 333309E
Page 53

Technical Data Matrix
Lower
A B lb kg Gal/Min L/min Psi
50cc 50cc
100cc 50cc
75cc 25cc
100cc 25cc
125cc 25cc
150cc 25cc
50cc 50cc
100cc 50cc
75cc 25cc
100cc 25cc
125cc 25cc
150cc 25cc
50cc 50cc
100cc 50cc
75cc 25cc
100cc 25cc
125cc 25cc
150cc 25cc
Sprayer
Type
Air
Spray
Air
Assisted
Air
Spray
Airless
Pump
Mix
Ratio
1:1
2:1
3:1
4:1
5:1
6:1 24V873
1:1
2:1
3:1
4:1
5:1
6:1
1:1
2:1
3:1
4:1
5:1
6:1
1:1 24W609 25 cc 25 cc 4.5 135 61.2 0.2 0.9 3000
Model
24V868
24V874 122 55.5
24V869
24V875 127 57.9
24V870
24V876 123 56
24V871
24V877 127 57.5
24V872
24V878 129 58.7
24V879 130 59.0
24V880
24V886 145 65.7
24V881
24V887 150 68.1
24V882
24V888 146 66.2
24V883
24V889 149 67.7
24V884
24V890 152 68.9
24V885
24V891 150 68.4
24V892
24V898 142 64.5
24V893
24V899 147 67.0
24V894
24V901 143 65.1
24V895
24V902 147 66.6
24V896
24V903 149 67.8
24V897
24V904 148 67.2
Air
Motor
2.5”
7.5”
7.5”
Weight
153 69.5
158 72.0
154 70.1
158 71.6
160 72.8
161 73.1
176 79.8
181 82.2
177 80.3
180 81.8
183 83.0
181 82.5
173 78.6
178 81.1
174 79.2
178 80.7
180 81.9
179 81.3
Max Fluid
Max Flow Rate
at rated 20 cpm
0.5 1.9
0.8 3.0 2.6:1 100
0.5 1.9 4:1 65
0.7 2.6 3.2:1 75
0.8 3.0 2.7:1 100
0.9 3.4 2.3:1 100
0.5 1.9
0.8 3.0 24:1 100
0.5 1.9 36:1 95
0.7 2.6 29:1 100
0.8 3.0 2900
0.9 3.4 2400
0.5 1.9
0.8 3.0 24:1 100
0.5 1.9 36:1 95
0.7 2.6 29:1 100
0.8 3.0 2900
0.9 3.4 2400
Working
Pressure
Bar
(MPa)
225 15 (1.5)
3000
3000
204
(20.4)
197
(19.7)
163
(16.3)
204
(20.4)
197
(19.7)
163
(16.3)
204
(20.4)
Fluid/Air
Ratio
4:1 65
35:1 95
24:1 100
20:1 100
35:1 95
24:1 100
20:1 100
24:1 100
Technical Data
Max Pump
Air Pressure
Bar
(MPa)
Psi
4.5
(0.45)
7.0
(0.7)
4.5
(0.45)
5.2
(0.52)
7.0
(0.7)
7.0
(0.7)
6.5
(0.65)
7.0
(0.7)
6.5
(0.65)
7.0
(0.7)
7.0
(0.7)
7.0
(0.7)
6.5
(0.65)
7.0
(0.7)
6.5
(0.65)
7.0
(0.7)
7.0
(0.7)
7.0
(0.7)
7.0
(0.7)
333309E 53
Page 54

Graco Standard Warranty
Graco warrants all equipment referenced in this document which is manufactured by Graco and bearing its name to be free from defects in
material and workmanship on the date of sale to the original purchaser for use. With the exception of any special, extended, or limited warranty
published by Graco, Graco will, for a period of twelve months from the date of sale, repair or replace any part of the equipment determined by
Graco to be defective. This warranty applies only when the equipment is installed, operated and maintained in accordance with Graco’s written
recommendations.
This warranty does not cover, and Graco shall not be liable for general wear and tear, or any malfunction, damage or wear caused by faulty
installation, misapplication, abrasion, corrosion, inadequate or improper maintenance, negligence, accident, tampering, or substitution of
non-Graco component parts. Nor shall Graco be liable for malfunction, damage or wear caused by the incompatibility of Graco equipment with
structures, accessories, equipment or materials not supplied by Graco, or the improper design, manufacture, installation, operation or
maintenance of structures, accessories, equipment or materials not supplied by Graco.
This warranty is conditioned upon the prepaid return of the equipment claimed to be defective to an authorized Graco distributor for verification of
the claimed defect. If the claimed defect is verified, Graco will repair or replace free of charge any defective parts. The equipment will be returned
to the original purchaser transportation prepaid. If inspection of the equipment does not disclose any defect in material or workmanship, repairs will
be made at a reasonable charge, which charges may include the costs of parts, labor, and transportation.
THIS WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE, AND IS IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
TO WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Graco’s sole obligation and buyer’s sole remedy for any breach of warranty shall be as set forth above. The buyer agrees that no other remedy
(including, but not limited to, incidental or consequential damages for lost profits, lost sales, injury to person or property, or any other incidental or
consequential loss) shall be available. Any action for breach of warranty must be brought within two (2) years of the date of sale.
GRACO MAKES NO WARRANTY, AND DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, IN CONNECTION WITH ACCESSORIES, EQUIPMENT, MATERIALS OR COMPONENTS SOLD BUT NOT
MANUFACTURED BY GRACO. These items sold, but not manufactured by Graco (such as electric motors, switches, hose, etc.), are subject to
the warranty, if any, of their manufacturer. Graco will provide purchaser with reasonable assistance in making any claim for breach of these
warranties.
In no event will Graco be liable for indirect, incidental, special or consequential damages resulting from Graco supplying equipment hereunder, or
the furnishing, performance, or use of any products or other goods sold hereto, whether due to a breach of contract, breach of warranty, the
negligence of Graco, or otherwise.
FOR GRACO CANADA CUSTOMERS
The Parties acknowledge that they have required that the present document, as well as all documents, notices and legal proceedings entered into,
given or instituted pursuant hereto or relating directly or indirectly hereto, be drawn up in English. Les parties reconnaissent avoir convenu que la
rédaction du présente document sera en Anglais, ainsi que tous documents, avis et procédures judiciaires exécutés, donnés ou intentés, à la suite
de ou en rapport, directement ou indirectement, avec les procédures concernées.
Graco Information
For the latest information about Graco products, visit www.graco.com.
For patent information, see www.graco.com/patents.
TO PLACE AN ORDER, contact your Graco distributor or call to identify the nearest distributor.
Phone: 612-623-6921 or Toll Free: 1-800-328-0211 Fax: 612-378-3505
All written and visual data contained in this document reflects the latest product information available at the time of publication.
GRACO INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES • P.O. BOX 1441 • MINNEAPOLIS MN 55440-1441 • USA
Copyright 2014, Graco Inc. All Graco manufacturing locations are registered to ISO 9001.
Graco reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice.
Original instructions. This manual contains English. MM 333309
Graco Headquarters: Minneapolis
International Offices: Belgium, China, Japan, Korea
www.graco.com
Revision E, April 2015
 Loading...
Loading...