
L
o
L
User Manual for P/N 140-71xx-XX0
gii
o
g
Broadband Cellular Router
c--
c
5
5
0
0
0
0
0
0
September 2011 Firmware Version 3.2.2

Table of C
1.
PREFACE .............................................................................................. 3
ontents
1.1. Copyright Notice ............................................................................... 3
1.2. Modem Use...................................................................................... 3
1.3. Interference Issues ........................................................................... 3
1.4. FCC Notification ................................................................................ 4
2. PRODUCT OVERVIEW........................................................................... 5
2.1. Device Identification.......................................................................... 5
2.2. General Description........................................................................... 5
2.3. Features .......................................................................................... 5
2.4. Part Number Breakdown .................................................................... 6
2.5. External Interfaces............................................................................ 7
2.6. RJ-45 Ethernet Port........................................................................... 9
2.7. Power Cable Connections ................................................................... 9
2.8. Antenna Options ............................................................................... 9
3. Networking Basics ............................................................................. 13
3.1. General Networking Definitions ..........................................................13
4. Getting Started .................................................................................. 15
4.1. Package Contents ............................................................................15
4.2. Setup Requirements.........................................................................15
4.3. Quick Start .....................................................................................15
4.4. Configuring Local PC.........................................................................16
4.5. Logic-5000 Radio Modem Setup .........................................................16
4.6. Provisioning the Logic-5000 Radio Modem ...........................................17
5. Logic-5000 Configuration................................................................... 21
5.1. General Instructions.........................................................................21
5.2. Home Page Parameters.....................................................................21
5.3. Cellular WAN Parameters ..................................................................24
5.4. LAN Settings ...................................................................................29
5.5. WiFi (WLAN) ...................................................................................32
5.6. Router Settings ...............................................................................36
5.7. Advanced Settings ...........................................................................38
5.8. SNMP .............................................................................................46
5.9. GPS ...............................................................................................47
5.10. Serial Port Settings .......................................................................51
5.11. I/O Settings.................................................................................53
5.12. System Upgrade...........................................................................56
6. Carrier Specific Information............................................................... 57
6.1. Verizon Wireless ..............................................................................57
6.2. Bell Mobility ....................................................................................57
6.3. Sprint PCS ......................................................................................58
7. Service and Support........................................................................... 59
7.1. Product Warranty, RMA and Contact Information ..................................59
7.2. RMA Request...................................................................................59
7.3. Product Documentation.....................................................................59
7.4. Technical Support ............................................................................59

1. PREFACE
1.1. Copyright Notice
©2010 GPS Logic LLC. All Rights Reserved.
This manual covers the operation of the GPS Logic Logic-5000 CDMA Cellular Modem.
Specifications described are typical only and are subject to normal manufacturing and
service tolerances.
GPS Logic LLC reserves the right to modify the equipment, its specifications or this manual
without prior notice, in the interest of improving performance, reliability, or servicing. At the
time of publication all data is correct for the operation of the equipment at the voltage
and/or temperature referred to. Performance data indicates typical values related to the
particular product.
No part of this documentation or information supplied may be divulged to any third party
without the express written consent of GPS Logic LLC.
Products offered may contain software which is proprietary to GPS Logic LLC or partner
companies. The offer or supply of these products and services does not include or infer any
transfer of ownership.
1.2. Modem Use
The GPS Logic Logic-5000 cellular modem is designed and intended for use in fixed,
nomadic, or mobile applications. “Fixed” assumes the device is physically secured at one
location and not easily moved to another location. “Mobile” assumes the modem is
physically secured in a vehicle and is operated when the vehicle is moving. “Nomadic”
assumes the modem is installed in a vehicle but is operated when the vehicle is stationary.
Please keep the cellular antenna of the Logic-5000 radio modem at a safe distance from
your head and body while the modem is in use (see below).
Caution: Maintain a distance of at least 20 cm (8 inches) between the transmitter antennas
and any person while in use. This modem is designed for use in applications that observe
the 20 cm separation distance.
1.3. Interference Issues
Avoid possible radio frequency (RF) interference by following these guidelines:
The use of cellular telephones or devices in aircraft is illegal. Use in aircraft may
endanger operation and disrupt the cellular network. Failure to observe this
restriction may result in suspension or denial of cellular services to the offender,
legal action or both.
Page 3 of
59

Page 4 of 59
Do not operate in the vicinity of gasoline or diesel-fuel pumps unless use has been approved
and authorized.
Do not operate in locations where medical equipment that the device could interfere with
may be in use.
Do not operate in fuel depots, chemical plants, or blasting areas unless use has been
approved and authorized.
Use care if operating in the vicinity of protected personal medical devices, i.e., hearing aids
and pacemakers.
Operation in the presence of other electronic equipment may cause interference if
equipment is incorrectly protected. Follow recommendations for installation from equipment
manufacturers.
1.4. FCC Notification
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user
is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.

2. PRODUCT OVERVIEW
2.1. Device Identification
2.1.1. Label Information
The label contains the part number, serial number, MAC ID, FCC ID and the IMEI numbers
in both Hex and decimal format.
2.2. General Description
The Logic-5000 Modem from GPS Logic is the ideal solution for a wide range of Internet
Access, Corporate Network and wireless IP connectivity requirements.
The Logic-5000 product features high-speed wireless wide-area-network access to IP
networks over 3G cellular networks. The Logic-5000 cellular radio modem advanced router
features full Ethernet routing, DHCP Server, and NAT support. The embedded GPS makes it
an ideal fit for mobile applications requiring position information and Internet connectivity.
The optional built-in 802.11 WiFi tether allows you to step away from your vehicle and
remain connected at all time. Alternatively, the client mode forwards all traffic via the WiFi
interface instead of the cellular interface.
The Logic-5000 is often referred to by its former name, the Vanguard 3G. Occasional
references to the Vanguard 3G may be encountered in various instances.
2.3. Features
EVDO Rev A with data transfer rates up to 3.1 Mbps downlink, 1.8 Mbps uplink
Embedded Linux (with support for custom applications) on ARM 9 processor
Built-in DHCP server and NAT support
Browser-based management
Embedded GPS
Local and remote configuration
10/100 Ethernet interface
WiFi IEEE 802.11b/g 2.4GHz (optional)
Built-in WiFi client and access point (AD HOC mode)
RSSI indicator
I/O capability
MAC pairing
Page 5 of
59

Page 6 of 59
2.4. Part Number Breakdown
140-71CC-LST
140-71 = Logic-5000 model identifier
CC = 00-99 Carrier/Technology/Cell Module Number
00 = None
01 = Verizon Wireless (CDMA - MC5727)
02 = AT&T (GSM - MC8790)
03 = Sprint (CDMA - MC5727)
05 = Bell Mobility (CDMA - MC5727)
06 = T-Mobile/Rogers Communication (GSM - MC8790)
07 = Telstra (Australia) (GSM - MC8790)
09 = Telus (CDMA - MC5727)
L = LAN Communication Options
0 = Wired LAN
1 = WiFi + Wired LAN
S = Sensor Options
1 = GPS & I/Os
T = TBD options
Reserved for future Options (0=Standard)

2.5. External Interfaces
2.5.1. Front Panel Connections
Figure 1 - Logic-5000 (formerly Vanguard 3G) radio modem's front panel
The Logic-5000 radio modem's front panel connections include:
GPS: SMA female, GPS antenna connector. This input requires a 3.3V, GPS antenna with an
SMA connection. For best coverage, use an active GPS antenna with a gain of >25dBm.
PWR: 9-28 VDC; the mating connector is a Molex 43025-0400 4 position connector.
LAN: Input for standard or crossover Ethernet cable.
USB: Connection for USB Client port. USB is not supported at this time.
COM: Standard RS-232 port for debugging and maintenance only.
ANT: TNC female, primary antenna connection. See section “Antenna options” for more
information.
RX DIV: SMA female, receive diversity antenna. See section “Antenna options” for more
information.
WiFi: RP-SMA jack, WiFi antenna. See section “Antenna options” for more information.
Page 7 of
59

2.5.2. LEDs
There are five LEDs on the front panel of the Logic-5000 unit. Each can display three colors:
Red, Green, and Amber. The definition for each LED is as follows:
LED OFF GREEN FLASHING
GREEN
RED FLASHING
RED
AMBER
WiFi
No power
or Interface
Disabled
Interface
Enabled
Tx/Rx
Activity
N/A N/A N/A
PWR (Power)
No Power Power On N/A N/A Power Timer
Activated
Power Up,
Ignition
Sense Off
STAT
(Status)
No Power Status OK N/A N/A N/A Medium or
Low RSSI
NET
(Network
Connectivity)
No Power Network
Connected
Tx/Rx
Activity
No
Coverage
N/A N/A
GPS
No Power Position Fix
Acquired
N/A No
Satellites in
View
Fault
Detected
Acquiring
Satellites,
no fix yet
2.5.3. Back Panel Connections
The Logic-5000 radio modem's back panel connections include:
Reset: Hard reset button
1
I/O: I/O interface connector
Figure 2 - Logic-5000 radio modem's back panel
1
Hard reset does not default parameter configuration
Page 8 of
59
2.6. RJ-45 Ethernet Port
The Logic-5000 radio modem can accept either a standard or cross over ethernet cable.
2.7. Power Cable Connections
If using the provided power cable to connect to a DC supply (car battery) use the following
diagrams and table to connect the unit.
Ensure the ignition sense line is connected to the vehicle's ignition. This line will initiate the
shutdown timer following ignition deactivation (if enabled).
Note: Both ignition sense and DC power are required to start up a Logic-5000.
Caution: Connect the red power wire to a CONSTANT hot source. To prevent corruption of
the Logic-5000 firmware, only use the ignition source to power off the unit.
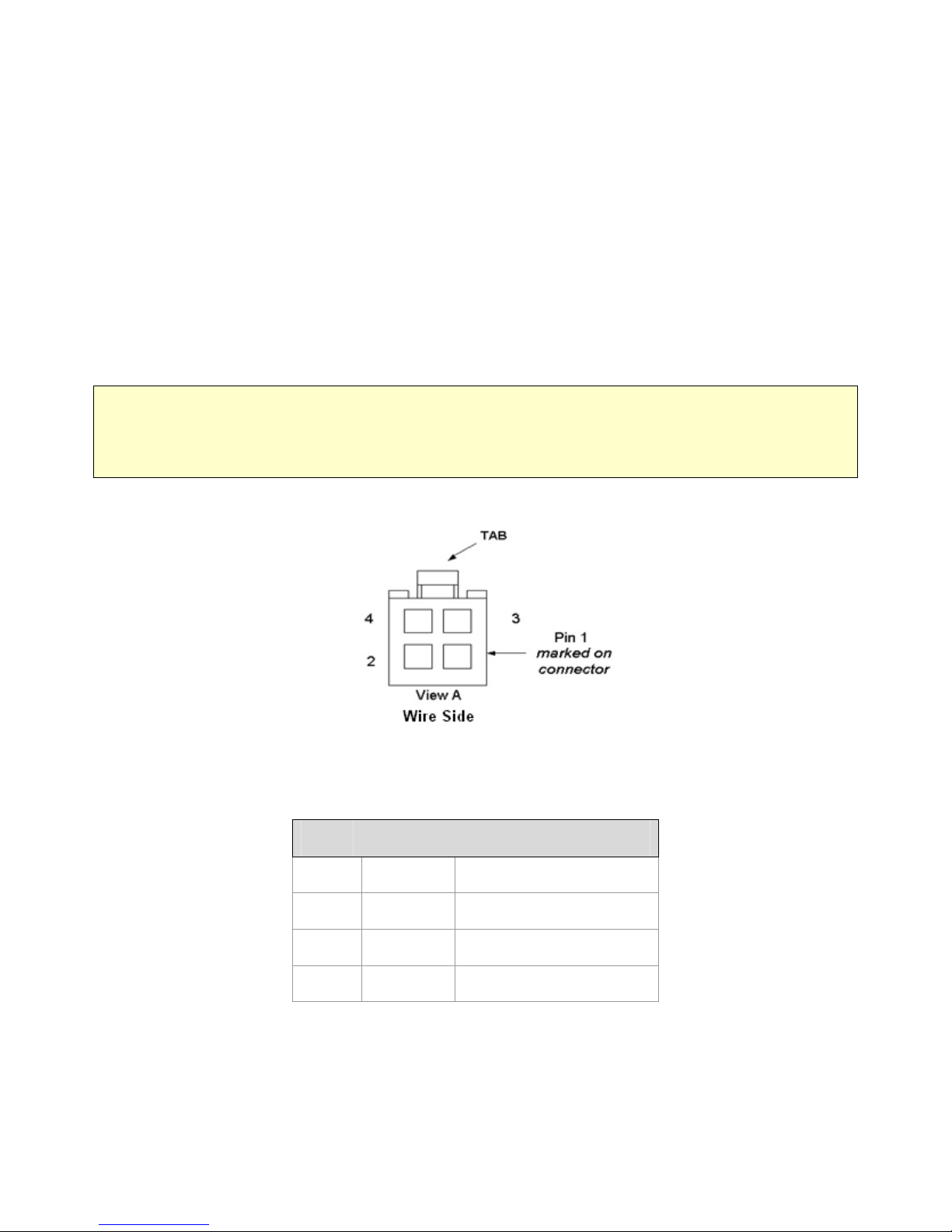
Figure 3 - Logic-5000 power cable connections
Pin Color Description
1
Red DC Power, 9 to 28V DC
2
Blue Ground
3
White Ignition Sense
4
NA Not Connected
2.8. Antenna Options
Antennas are available for Logic-5000 radio modems installations from GPS Logic.
Page 9 of
59

2.8.1. Primary Cellular Antenna
The Logic-5000 product requires a multi-band cellular antenna for operation in the 800 MHz
band, the 1900 MHz band, and the 2100 MHz band. The primary antenna connection on the
Logic-5000 unit is a TNC female connector; therefore you must purchase an antenna with a
TNC male connector. Do not select a TNC antenna with “reverse polarity” or RP-Male.
Mounting options and cable lengths are the user’s choice and application specific.
Caution: To comply with FCC approval for this device, do not use a cellular antenna with a
gain greater than 5 dBi in the cellular (800MHz) band, or 4 dBi in the 1900MHz band.
2.8.2. RX Diversity Cellular Antenna
The Logic-5000 radio modem RX Diversity antenna has the same requirements as the
primary antenna with the exception of the connection. The RX Diversity antenna connection
on the Logic-5000 product is an SMA female connector; therefore an antenna with an SMA
Male connection is required. Mounting options and cable lengths are the user’s choice and
application specific. For best performance, separation between the Primary and Diversity
antenna should be at least 5/8 wavelength (=8 inches or 20 cm for 915 MHz).
Caution: To comply with FCC approval for this device, do not use a cellular antenna with a
gain greater than 5 dBi in the cellular (800MHz) band, or 4 dBi in the 1900MHz band.
2.8.3. GPS Antenna
The Logic-5000 radio modem’s GPS connector requires an external 3.3V GPS antenna. The
GPS antenna connection on the Logic-5000 product is a female SMA connector; therefore an
antenna with an SMA male connector is required. For best coverage, use an active antenna
with a gain >25dB. Mounting options and cable lengths are user’s choice and application
specific.
2.8.4. WiFi Antenna
The WiFi antenna connection on the Logic-5000 product is an RP-SMA jack; therefore an
antenna with an RP-SMA plug is required. Mounting options and cable lengths are user’s
choice and application specific.
2.8.5. Antenna Spacing
Referring to Figure 4 for illustration, the Logic-5000 radio modem commonly uses four
separate antennas:
“T” - Main transceiver - Constraints are the limit of 20 cm and omni-directional
factors
“R” - Auxiliary receiver – Constraints are the receiver spacing of at least 5/8 λ
(wavelength) from transceiver antenna and omni-directional requirements
Page 10 of
59
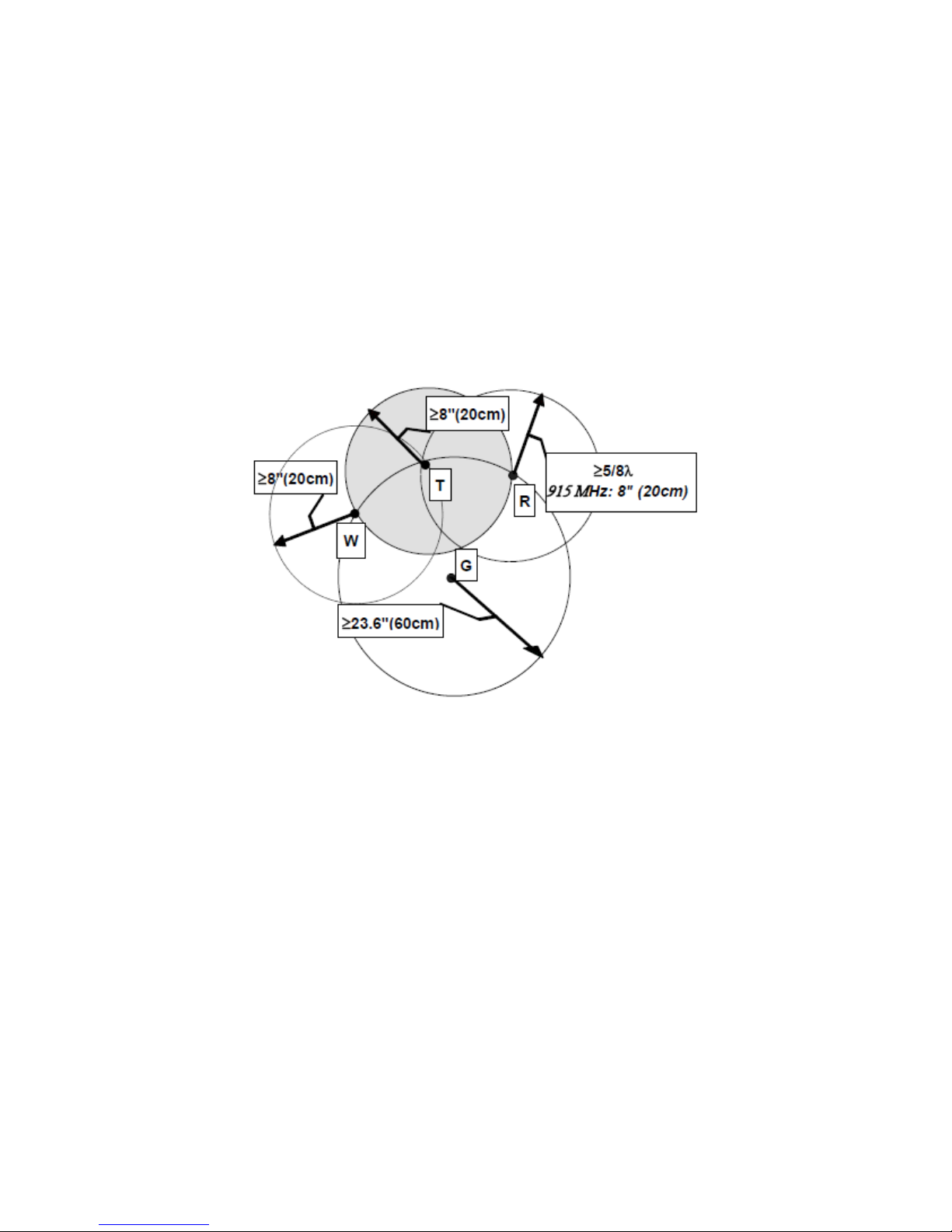
“G”
- Global Positioning System (GPS) - Constraints are TX spacing of at least
60cm/23.62 inch from all transmitting antennas and a clear view of the sky.
“W” – WiFi antenna - Constraints are TX spacing of at least 8 inches or 20 cm from
all transmitting antennas
Note: For units utilizing diversity cellular antennas, best overall operation is achieved
utilizing antennas with equal gains.
WARNING: As per FCC rules, all Logic-5000 transmitting antennas (T & W) should be at a
minimum of eight (8) inches (approximately 20 centimeters) from all persons.
Figure 4 - Antenna Spacing (T: primary antenna, R: diversity antenna, W: WiFi antenna, G:
GPS antenna)
For installation of ground-plane dependent antennas (main cellular and WiFi antennas), the
center of the metal surface used for mounting is preferable for best omni-directional
pattern. For ground-plane independent antennas (diversity and GPS antennas), installation
may be close to the edges of the surface.
For vehicular installations GPS Logic recommends the following antenna positions:
Most preferred for all antennas: centerline of roof. For transmitter antenna, it is the
ONLY acceptable position.
Less preferred for receiver antenna: trunk lid, providing distance to transmitting
antenna is respected whether lid is opened or closed.
Much less preferred, but permissible for receiver antenna: left or right rear fenders,
just in back of rear window
Page 11 of
59

Page 12 of 59
Least preferred, but permissible for receiver antenna: left or right front fenders,
ahead of windshield
3. Networking Basics
3.1. General Networking Definitions
The Logic-5000 cellular modem is based on Ethernet connectivity and follows general IP
networking guidelines and terminology. Below are definitions of some basic network
terminology as they pertain to the Logic-5000 environment.
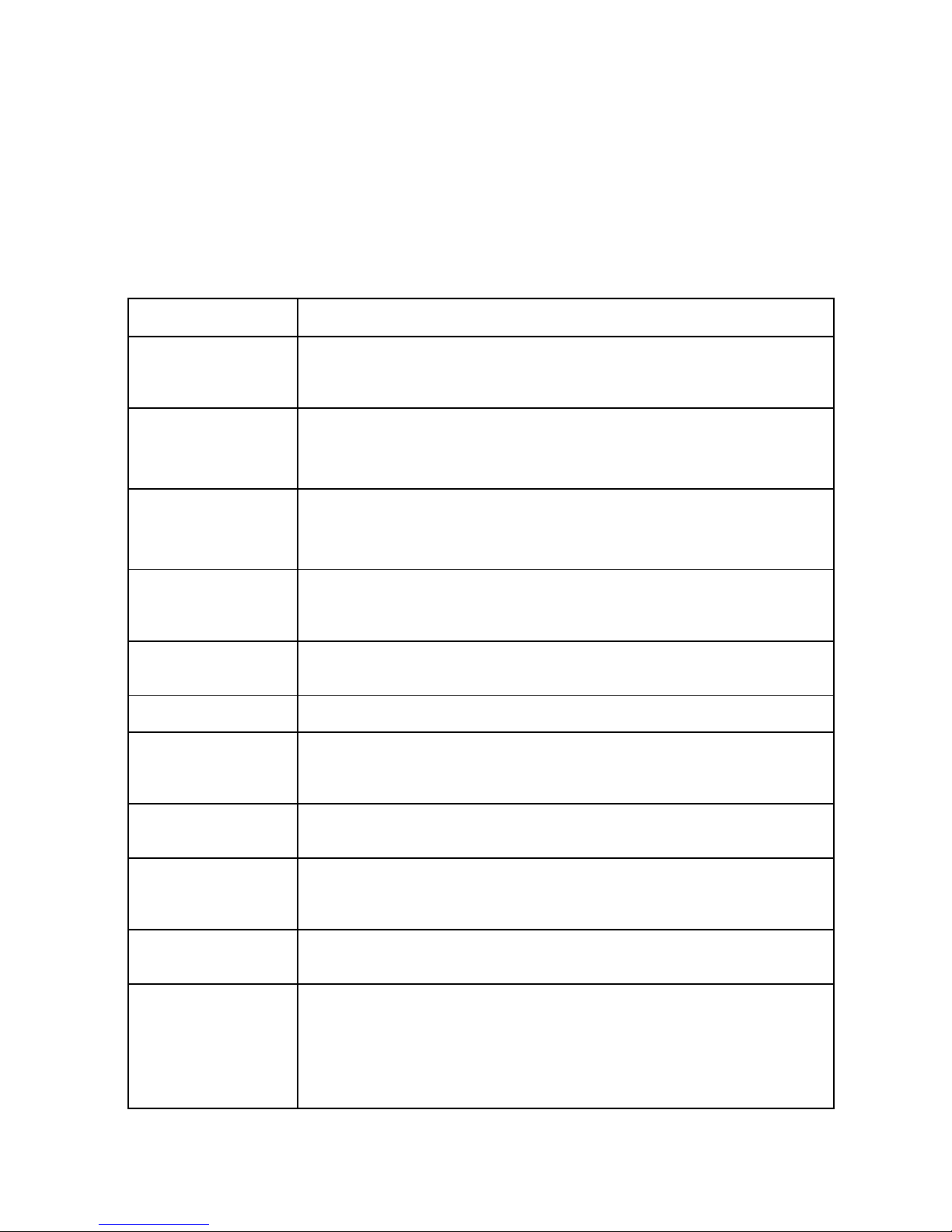
Term Definition
Circuit Switched Data Circuit Switched Data is the original form of a cellular connection where a
radio channel is dedicated to an active phone and the connection is drop ped
when not in use.
DNS Domain Name System: operates like a phone book to translate domain
names (i.e., google.com) to IP addresses (70.212.19.1).
The Logic-5000 unit functions as the DNS Server in the network.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol: the DHCP server assigns IP
addresses, gateway and subnet masks to all clients on the network.
The Logic-5000 unit functions as a DHCP Server.
Dynamic/Static IP A device with Dynamic IP selected may have a different IP address every
time it connects to the network. A device with a Static IP will always connect
with the same IP address.
Gateway A (node) device enabling data transfer between different networks (i.e., from
a private LAN to a public WAN).
LAN Local Area Network. A private network.
NAT Network Address Transl ation: A technology that allows hosts on the LAN with
private IP addresses to communicate with public IP addresses on the WAN.
This is an essential function of a network router.
Packet Data Packet Data is used by 3G cellular standards. On a packet data network,
users share a channel and the connection is always on.
Port A special number present in the header of a data packet in the data transfer
process. Ports are typically used to map data to a particular process running
on a computer.
PPP Point-to-point Protocol: creating a direct link between two nodes in network
communication.
Private IP address Private IP addresses are addresses that will not be routed on external
networks. Any device on an internal LAN should be assigned a private IP
address to avoid contention. The suggested private address ranges are
Class A: 10.x.x.x
Class B: 172.16.x.x through 172.31.x.x
Page 13 of
59
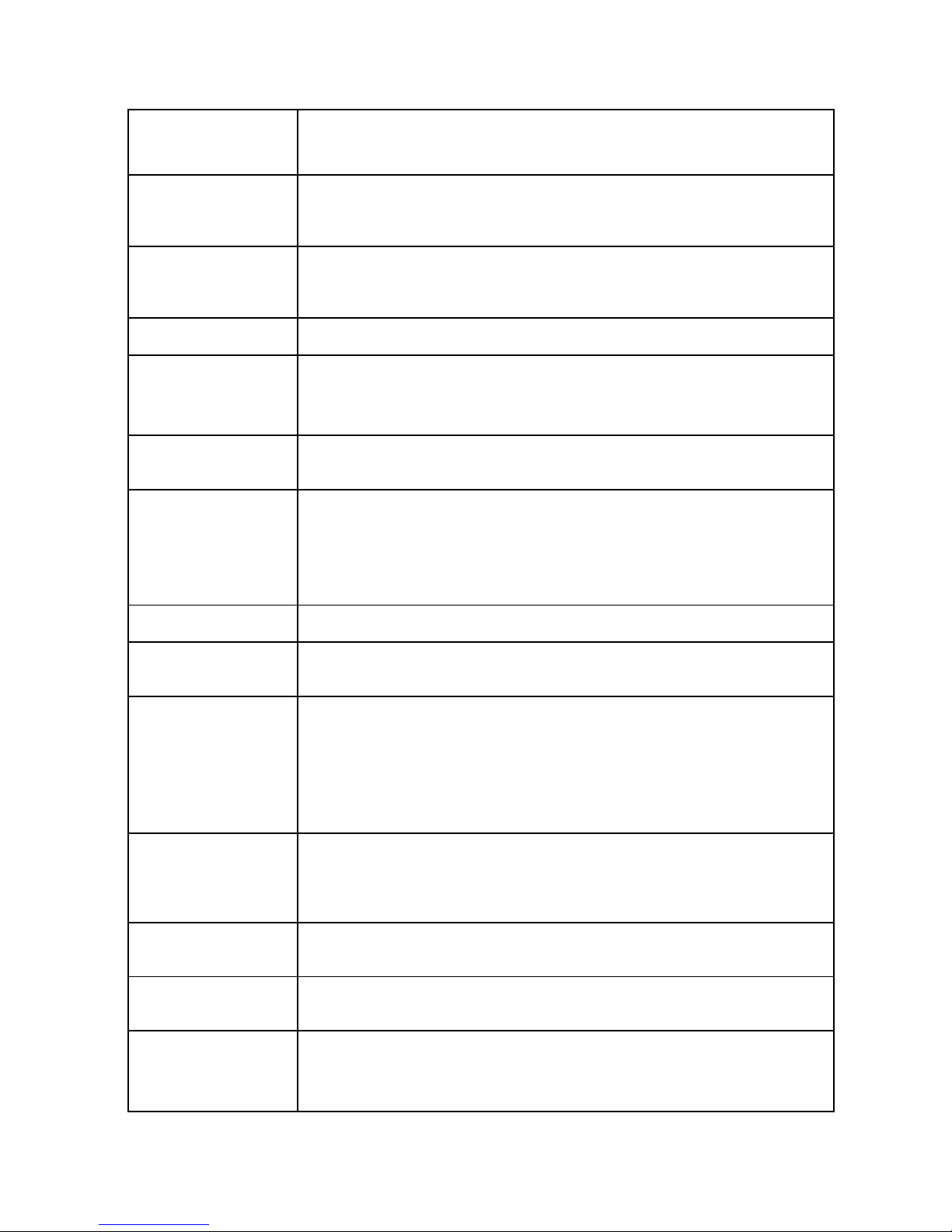
Cla
ss C: 192.168.x.x
By default the Logic-5000 radio modem uses the 192.168.1.x address range.
Provisioning The process of activating a unit for the first time on a cellular carrier’s
network. You must have a service contract in place with the carrier prior to
provisioning your device.
RIP Routing Information Protocol, protocol that helps routers dynamically adapt to
changes of network connections by communicating information about which
networks each router can reach and how far away those networks are.
SSID Service Set Identifier. This is a name used to identify a WiFi wireless network.
Subnet A range of addresses assigned to a LAN.
All devices connected in a Logic-5000 network must be on the same subnet
as the Logic-5000 radio modems.
Subnet Mask Binary string that separates the subnet portion of an IP address and the host
portion.
TKIP/AES “Temporal Key Integrity Protocol” is an encryption method used by the WiFi
interface when operating in WPA mode. TKIP was designed to solve security
issues in WEP (it is considered stronger then WEP).
"Advanced Encryption Standard" is the encryption protocol used by the WiFi
interface when it operates in WPA2 mode.
WAN Wide Area Network, a public network. The Internet is an example of a WAN.
WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy. This is an IEEE security protocol for wireless
802.11 networks. It is an encryption method used by the WiFi interface.
WiFi
(802.11b, 802.11g)
Wireless Fidelity is an IEEE 802.11 standard for wireless LANs
802.11b is a standard for operating at 2.4 GHz frequency with
data rates up to 11 Mbps
802.11g is a standard for operating at 2.4 GHz frequency with
data rates up to 54 Mbps
WiFi Access Point
(802.11 Ad-Hoc mode)
A Logic-5000 unit can operate in 802.11 Ad-Hoc mode. It can communicate
with other devices operating in 802.11 Ad-Hoc mode. Although it is not a true
WiFi access point, we call it one because it serves as the gateway to the
WAN for the other wireless devices operating in Ad-Hoc mode.
WiFi Client (802.11
Infrastructure mode)
A Logic-5000 unit can operate in 802.11 Infrastructure mode. In this mode it is
a WiFi client and will try to connect to a WiFi access point.
WLAN Wireless Lo cal Area Network, a private netwo rk. Refers to the network
covered by the WiFi interface.
WPA/WPA2 WiFi Protected Access" is a subset of 802.11i (security mechanisms for
wireless networks).
"WiFi Protected Access 2" is the complete version of 802.11i.
Page 14 of
59

4. Getting Started
4.1. Package Contents
Logic-5000 cellular modem
Power cable and Fuse
User Manual and Quick Start Guide
Mounting Bracket and Screws
4.2. Setup Requirements
Logic-5000 cellular modem
Computer running any operating system
9 to 28 Volt power supply
Ethernet cable*
Active cellular data account
Cellular antenna with male TNC connector*
Cellular Diversity Antenna (SMA Male) *
GPS Antenna (SMA Male) *
WiFi Antenna (RP-SMA Plug) * ( if applicable)
*These accessories are available from GPS Logic.
4.3. Quick Start
4.3.1. Hardware Setup
1. Connect the primary cellular antenna to the ANT connector on the front of the unit.
For units utilizing diversity, install RX Diversity antenna on SMA connector. Connect
the GPS antenna to the GPS connector. For units utilizing WiFi, connect the WiFi
antenna to the WiFi connector.
2. Connect an Ethernet cable from the LAN connector of the Logic-5000 unit to the PC.
If multiple PCs are being used, connect the Logic-5000 unit to an Ethernet switch or
hub connected to the PCs.
3. Connect a power supply cable to the PWR connector of the Logic-5000 unit. Do not
power the unit on yet.
Page 15 of
59

4.4. Configuring Local PC
1. Verify network settings on local PC are set to automatically detect IP and DNS
server. The path to network settings varies with the version of Windows you are
using.
Windows XP: Start-> Control Panel -> Network Connections
Windows 2000: Start -> Settings -> Network and dial up connections
2. Select the appropriate network connection, typically the Local Area Connection ->
right click on the connection and select “Properties”
3. Select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)" properties.
4. Verify that "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS Server address
automatically" are selected.
4.5. Logic-5000 Radio Modem Setup
1. Power on the Logic-5000 radio modem with 9-28VDC 15-Watt supply.
2. In an Internet browser, enter http://192.168.1.50. This will bring up the Logic-5000
product login page (Note: It may take 30 seconds from initial power-up for the
homepage to be available.)
3. Login to the device
Default Values:
User logon: admin
password: password
4. This brings up the Logic-5000 product homepage. Status and configuration
parameters are viewed from this screen. The configuration options are further
explained later in this document.
Page 16 of
59

Figure 5 - Logic-5000 radio modem Home page
4.6. Provisioning the Logic-5000 Radio Modem
IMPORTANT NOTE:
The Logic-5000 cellular radio modem requires an active cellular data service
contract for provisioning. Verify that your cellular service contract is a data
service contract with packet data NOT circuit switched technology. If you do not
have an active data contract, contact your service provider.
Note:
The Logic-5000 radio modems are carrier specific. You must activate your unit
with the carrier specified when the product was ordered. The unit must be
activated in the carrier’s home area.
Depending on your carrier, the Logic-5000 radio modem can be activated manually (see
Figure 6) or using OTASP (Over-The-Air Service Programming) or IOTA (Internet Over-TheAir) (see Figure 6). In either case, the carrier will require
you to provide them with the ESN
(electronic serial number) that is assigned to the cellular modem at the factory. You can see
Page 17 of
59
y
our ESN by selecting the Cellular (WAN) page -> “Status” tab or on the label on the
bottom of your Logic-5000 unit.
For manual activation, you will also need the following specific information from the
provider:
Mobile Directory number (MDN)
Mobile Station ID (MSID or MIN). In many cases, this number will be the same as
the MDN.
Unlock Code (if required)-provided by most carriers when activating a contract.
Figure 6 - Cellular (WAN) page, Activation
4.6.1. Provisioning with Verizon Wireless
1. On the left side of the screen, select the Cellular (WAN) page. Select “Activation”
tab.
2. In the “OTASP/IOTA Activation” portion of the screen (Figure 9), select “OTASP”.
C
lick Submit.
Note: “Command (OTASP Only)” is a carrier specific command used for OTASP. The
default value is *22899 (Verizon OTA command).
3. After a few moments you will receive a message saying the OTA was successful.
Once OTA is complete, the unit will reset.
4. Once the module is activated, browse to an Internet web page to confirm
connectivity.
Page 18 of
59

Note: S
hould you experience problems connecting to the web page, reset the Logic-5000
unit by clicking RESET on the top right of the screen and try reconnecting to the web page.
4.6.2. Provisioning with Sprint
Logic-5000 cellular routers with a Sprint modem are configured to activate by default
without user intervention. However, a manual activation may be initiated by performing the
following steps.
1. On the left side of the screen, select the Cellular (WAN) page. Select “Activation”
tab.
2. In the “Manual initiation of OMA-DM Provisioning” portion of the screen (Figure 7),
select “OMA
-DM”.
3. After a few moments you will receive a message saying the OMA-DM was successful.
Once OMA-DM is complete, the unit will reset.
4. Once the module is activated, browse to an Internet web page to confirm
connectivity.
Note: Should you experience problems connecting to the web page, reset the Logic5000 unit by clicking RESET on the top right of the screen and try reconnecting to
the web page.
Figure 7 - Cellular (WAN) page, manual activation and auto activation for Sprint
4.6.3. Provisioning with Bell Mobility
1. On the left side of the screen, select the Cellular (WAN) page. Select “Activation”
tab.
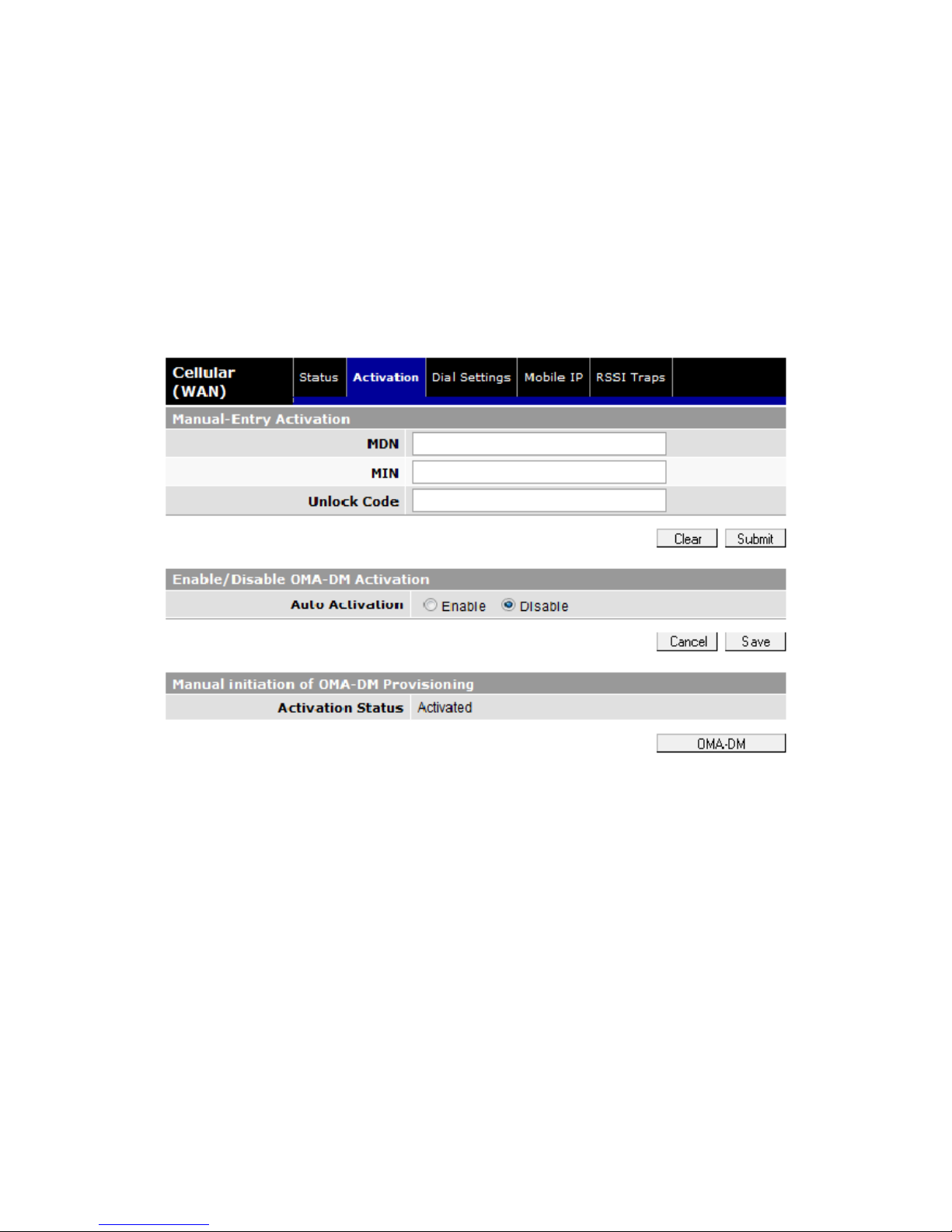
2. In the “Manual-Entry Activation” portion of the screen (Figure 8), enter MDN, MIN,
an
d Unlock code as provided by Bell Mobility. Click Submit. Provisioning will occur
automatically after the parameters are loaded.
3. After a few moments you will receive a message saying the activation was
successful. Once activation is complete, the unit will reset.
4. Once the module is activated, browse to an Internet web page to confirm
connectivity.
Page 19 of
59

Page 20 of 59
Figure 8 - Cellular (WAN) page, Manual-Entry Activation
Figure 9 - Cellular (WAN) page, OTASP/IOTA Activation

5. Logic-5000 Configuration
This section explains status information and configuration options available on all HTML
pages.
5.1. General Instructions
The following instructions are common to all HTML pages
The Help, Home and Reset links are located at the top right of all HTML pages.
Help: Select this link on any of the devices configuration pages to bring up the help text for
that screen.
Home: Select this link to return to the home page of the modem.
Reset: Select this link to command the unit to reboot. This process will take about 40
seconds. The software will ask you to confirm this command prior to re-booting.
Save: Most changes to a configuration parameter require the user to click save before the
change will take effect.
Clear/Cancel: Most configuration menus also have a “Clear/Cancel” option. Selecting this
button will restore all fields in a section to their last saved value. Note: This does not return
them to their factory defaults.
5.2. Home Page Parameters
The Logic-5000 cellular modem home page lists the unit’s primary operating parameters
and status. Configuration changes cannot be made from this page.
Page 21 of
59

Figure 10 - Home Page
5.2.1. Home Page Parameter Descriptions
System Information
Unit ID: Unit identification number (configured under Basic Settings).
System Up Time: System Up Time displays a counter that starts when the unit is powered
on and resets when the unit is powered down or hardware reset.
Page 22 of
59

Note: T
his counter does NOT indicate how long the WAN connection has been up.
Software Version: This reflects the version of application software loaded on the unit.
Phone Module Version: This is the version of the cellular module installed in the device.
This may be required by tech support but is not required for any user applications.
Serial Number: This is assigned at the factory. This may be required by tech support but is
not required for any user applications.
Default Route: Network route used by the Logic-5000 cellular radio modem when no other
known route exists for a given IP packet's destination address.
The default route points to the Cellular interface when WAN is up. The only exception to this
rule is if the WiFi interface is configured in wireless client mode and is connected to a WiFi
access point (WiFi Status=Up). In that case, the default route will point to the WiFi
interface.
Note: When the connection to the WiFi access point is down the default route is set back to
the Cellular interface.
Ethernet (LAN)
IP Addres
s: IP Lists the LAN IP address of the Logic-5000 unit. This IP becomes the
gateway and DNS server for all PCs and devices connected on the LAN. This value is
configured on the LAN Settings Page.
Subnet Mask: The Subnet mask is used in conjunction with the network address to
partition the IP address into the network (subnet) portion and the host portion. In most
cases, this value will be automatically set by the software based on the class of IP address
used for the Ethernet IP. This value can be modified on the LAN Settings page.
MAC Address: Media Access Control Address, this is configured at the factory and cannot
be changed by the user.
WiFi (WLAN)
Stat
us: Indicates if the WiFi interface is “UP” or “DOWN”
IP Address: IP address assigned to the WiFi interface of this device. When the WiFi
interface is set to operate in WiFi Client mode, the WiFi Access Point must have a DHCP
server running to assign an IP address to its WiFi clients.
Subnet Mask: Subnet Mask assigned to the WiFi interface of this device.
MAC Address: Media Access Control Address of the WiFi interface.
Cellular (WAN)
Stat
us: indicates if the device has an established connection to the WAN. Status is UP or
DOWN
IP Address: WAN IP address of the Logic-5000 unit. Remote access for the device requires
entering this address into a browser. The PPP IP Address is assigned by the cellular carrier
and will be dynamic unless a static address is specifically requested
Page 23 of
59

Warn
ing: Be aware of the dynamic nature of the WAN IP Address as it can affect related
applications.
Subnet Mask: This subnet mask is assigned by the carrier and is not configurable by the
user.
P-t-P: WAN IP address of the network access point of the cellular carrier
CDMA Connection
Ser
vice Type: Service Type indicates the type of service connection. The Logic-5000 radio
modem will automatically connect to the most advanced service available and will fall back
to other networks (such as 1xRTT) when EV-DO Rev A is not available.
Roaming Status: Roaming Status indicates the unit roaming status. Status is ROAMING or
NOT ROAMING
ESN: Electronic Serial Number is assigned to the cellular modem at the factory. This
number must be provided to the carrier to activate the module.
Signal Strength: Receive Signal Strength Indication indicates the strength of the network
signal with both a numerical value and a good/medium/poor message.
Call End Reason: Code indicating the reason for a call ending.
5.3. Cellular WAN Parameters
This page contains the provisioning information and the carrier activation settings. For more
information on the procedure for carrier activation, see “Provisioning the Logic-5000 Radio
Modem”.
5.3.1. Status
WAN Status information available (Figure 11):
ESN: Electronic Serial Number is assigned to the cellular modem at the factory. This
number must be provided to the carrier to activate the module.
MDN/MTN: The Mobile Directory Number; assigned by the carrier when the module is
activated.
MIN/MSI: Mobile Identification Number, in most cases, this is the same as the MDN.
PRL: Preferred Roaming List; a database that declares the priority of other carriers while
roaming. This file should be updated periodically to ensure proper connectivity while
roaming. The PRL file can be updated by performing an OTA or IOTA operation (see
provisioning section).
SID: System ID, this is status only and is assigned by the carrier when connecting to the
network.
NID: Network ID; this is status only and is assigned by the carrier when connecting to the
network.
Page 24 of
59

Channel: S
tatus only, indicates the channel assigned by the carrier when connecting to the
network.
Frequency: Status only, indicates the frequency band on which the unit is communicating.
If the unit is being used in North America, it will indicate either 800 MHz or 1900 MHz.
Signal Strength: Receive Signal Strength Indication indicates the strength of the network
signal with both a numerical value and a good/medium/poor message
Figure 11 - Cellular (WAN) Page
5.3.2. Activation
Provisioning information (see section 4.6)
5.3.3. Dial Settings
The Dial Settings page allows the user to Disable auto-connect. This page also contains
information on the reconnect timers in the note under the “Connect” selection. These
reconnect timers are defined per carriers certification requirements; they cannot be
changed.
By default, the auto-connect feature (labeled “Connect”) is enabled. When this feature is
enabled, the Logic-5000 radio modem will automatically connect to the network on power
up. If the auto-connect is disabled, you must re-enable the auto-connect, then cycle power
or perform a hardware reset to connect to the network. If you want to keep the autoconnection function disabled, you will have to disable it before powering down again.
This page also contains dial number, user and password information. This information
should only be entered if required by your carrier.
Note: When establishing a connection to a provider’s network, there are two ways your
Logic-5000 modem can authenticate and receive its IP address: Mobile IP (MIP) or Simple
Page 25 of
59

IP
(SIP). Most providers can allow a MIP-only account, a SIP-only account, or a MIP with SIP
fallback account.
On a Mobile IP network, the Logic-5000 will maintain the same IP address over any
geographical region, while on the SIP network IP addresses may change depending on the
geographical location. If you are using a SIP account, the carrier must provide you with a
username and password that should be entered under Cellular (WAN) -> Dial Settings. If
the entries are left blank, the Logic-5000 modem will consider itself working with a MIP
account.
Figure 12 - Cellular (WAN) page, Dial Settings
Note: In order to access the Mobile IP tab, auto-connect must be disabled.
Page 26 of
59

5.3.4. Mobile IP Settings
By default the Mobile IP settings are automatically configured by the cellular carrier
following provisioning. In cases where Mobile IP settings must be modified, the Mobile IP
page is available.
NOTE: The mobile IP settings page is only accessible when the modem is offline. Prior to
configuration, ensure auto-connect (labeled Connect) is disabled from the Dial Settings
page.
Mobile IP: Disabled – Permits Simple IP only. Using this setting may require PPP
authentication parameters to be configured on the Dial Settings page.
Preferred – During the initial registration, mobile IP will be selected if supported by the
network. If mobile IP is not available, the modem will revert to Simple IP.
Required – Allows only a mobile IP connection. If the modem hands off to a network that
does not support mobile IP, the connection will be dropped and stay offline until a mobile IP
network becomes available.
Reverse Tunneling: Enabled - the mobile node tunnels all transmissions back to the home
agent for transmission back to the internet rather than sending datagrams directly.
Disabled – When the mobile node is on a foreign network, transmissions to the internet will
be done directly rather than via a tunnel to the home agent.
NAI (Network Access Identifier): Identifier used by the AAA server to identify clients.
This should be formatted in the form of an e-mail address, for example:
8884770911@sprintpcs.com.
HA SPI (Home Agent Security Parameter Index): Security parameter index required to
authenticate on the primary and secondary home agents. Supported values: 0 to
4294967295.
HA (Home Agent) Shared Secret: Shared secret password for registration with the Home
Agent. Once the HA Shared Secret is set, its value cannot be obtained from the modem.
Thus, this field will always appear blank even after setting a value. To remove the
password, check the Clear checkbox.
AAA SPI: Security parameter index required to authenticate on the AAA server. Supported
values: 0 to 4294967295.
AAA Shared Secret: Shared secret password for registration with the AAA server.
Primary HA IP: IP Address of the primary home agent.
Secondary HA IP: IP Address of the secondary home agent.
Home HA IP: Primary HA address of the mobile node.
Page 27 of
59

Note: When the HA Shared Secret or AAA Shared Secret fields are left blank, all other fields
on the Mobile IP settings page will be updated except these. To change the HA or AAA
shared secret, simply enter a value in the respective field.
Figure 13 - Cellular (WAN), Mobile IP Settings Page
Page 28 of
59

5.4. LAN Settings
Figure 14 - LAN Settings Page
The LAN Settings page contains the basic configuration information required to customize
your LAN with the Logic-5000 radio modem as the network connection point. User
configuration will primarily occur on this page.
5.4.1. IP Settings
5.4.1.1. IP Configuration
Ethernet IP address: LAN IP of the LOGIC-5000 radio modem. This address is entered
into a browser on a local PC when logging into the Logic-5000 radio modem home page. To
decrease the chances of unwanted access, this value should be changed from its default
prior to use.
IMPORTAT NOTE:
Changing this value will cause you to lose connection to the Logic-5000 unit.
Enter the new address in the browser to reconnect. If you forget an address or
make a mistake entering the new value, it may be difficult to reconnect to the
device.
Ethernet Subnet Mask: The Subnet mask is used in conjunction with the Ethernet IP
address to partition the address into the network (subnet) portion and the host portion.
Page 29 of
59

Thi
s value will be entered automatically by the software based on the class of IP address
entered. It is not necessary to change the default value once the Ethernet IP is entered.
5.4.1.2. DNS Masquerade
See the definition for DNS in Network Basics in section 3.1 above.
DNS Auto: This command enables / disables the Logic-5000 DNS server. Except in special
cases, this should always be enabled.
5.4.1.3. DHCP Server Configuration
DHCP Server: (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) A protocol used by client devices that
are connected to the LAN port of this device to automatically obtain an IP address assigned
by this server/router. Selecting Enable will configure this device to assign IP addresses to
client devices taken from a pool specified by the values entered in DHCP start range and
DHCP end range. If DHCP is disabled, the information must be entered manually on all PCs.
DHCP Start IP Address/End IP Address: Sets the range of IP addresses assigned to the
PCs. The user can limit the number of devices allowed on the network by limiting the range
of IP addresses.
DHCP Lease Time: Number that dictates the length of time a device on the LAN can hold
an IP address. In most cases, this should be set to the maximum (default value) of 86400.
If this value is set too low, it can cause network connectivity problems.
Domain Name Suffix: The DNS suffix to be assigned by the DHCP server.
Preferred DNS Server: IP address of the preferred DNS server. This value is
automatically set when DNS Auto is enabled.
Alternate DNS Server: IP address of the alternate DNS server. This value is automatically
set when DNS Auto is enabled.
5.4.1.4. Disabling DHCP Server
When DHCP server is enabled, any PC with physical access to the Logic-5000 Ethernet port
will be assigned an IP address and have access to browse the Internet. This may cause
security problems. Disabling DHCP server will allow the user to control which PCs have the
ability to connect through the Logic-5000 radio modem. If changes are made to the network
settings, be sure to keep a record of the changes for future use.
Disabling DHCP server is performed on the LAN settings page. Under the DHCP
section, select Disable, the click Save.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
This also disables DNS Masquerading. Disabling DHCP server will remove all
values in the DHCP and DNS sections. Record all values in these fields prior to
disabling in case you are required to go back to the original configuration.
On the network setting page of each PC, set the IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway.
Page 30 of
59

5.4.1.5. Static IP Setup
If your network requires each PC to have a statically set LAN IP addresses, follow the
previous procedure for all PCs on the network. If the network requires a mix of static and
dynamically assigned IP addresses, assign static IPs outside the DHCP address range for
PCs that require static IP addresses and allow the Logic-5000 radio modem DHCP to assign
the remaining PC IP addresses.
5.4.2. MAC Pairing
For enhanced security, the user can pair a Host PC to the Logic-5000 unit by specifying the
Host’s Ethernet MAC address.
This ensures that only this particular host PC can send and receive traffic to and from the
WAN interface of the Logic-5000 unit. Connections that do not have the matching source
MAC address will be blocked.
Note: Access to the Logic-5000 unit itself is always available regardless of the Ethernet MAC
address and will not be blocked.
Status:
Logic-5000 is unpaired: No host PC is paired with the Logic-5000 unit. Any host
PC on the LAN can send and receive traffic to and from the WAN interface
Logic-5000 is paired: A host PC is paired with the Logic-5000 unit. Only the paired
host PC can pass data to and from the WAN interface.
Current Address: The current Ethernet MAC address of the paired host PC.
Note: to change the paired host PC, the user must specify the current Ethernet MAC
address of the last paired host PC.
New Address: Ethernet MAC address of the host PC to be paired with the Logic-5000.
Confirm New Address: Confirm the new Ethernet MAC address of the host PC to be paired
with the Logic-5000.
Figure 15 - MAC Pairing
Page 31 of
59

5.5. WiFi (WLAN)
A Logic-5000 unit can operate in an access point mode (Ad-Hoc) and in a client mode.
In access point mode, the Logic-5000 radio modem offers wireless tether. It forwards local
WiFi traffic to application servers over the cellular network and works in parallel with
Ethernet connection, providing for simultaneous WiFi and Ethernet connections.
In client mode the Logic-5000 unit can automatically switch between cellular and WiFi
connections providing for seamless handover when coupled with modern applications.
5.5.1. WiFi (WLAN) - Main
WiFi settings provide user configuration for optional WiFi interface operation.
Figure 16 - WiFi (WLAN) -> Status
5.5.1.1. Configuration
Wireless Mode
Disable: The WiFi interface is disabled
Client: The WiFi interface operates in Client mode
Access Point: The WiFi interface operates in Access Point mode (Ad-Hoc)
5.5.1.2. Status
IP Address: IP address assigned to the WiFi interface
Subnet Mask: IP Subnet Mask assigned to the WiFi interface
SSID: Name of the wireless local area network
Authentication: Authentication method currently used (Example: Open, Shared,
Page 32 of
59

WPANONE, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK)
Encryption
: Encryption method currently used
Channel: Channel currently used (Auto or 1-11)
State: Current state of the WiFi interface (Disabled, Ready if in Access point Mode, or Not
Connected, Scanning, and Connected if in Client Mode)
RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indicator (displayed in Client Mode only)
5.5.2. WiFi (WLAN) - Wireless Settings (Client)
The Logic-5000 can be configured for up to 20 access points.
Note: All access points must run a DHCP server.
In wireless client mode, the Logic-5000 unit will try to connect to the Access Point with the
strongest signal on the list. When the Logic-5000 unit connects to an access point, it starts
a DHCP client service. The DHCP server running on the access point must provide an IP
address, netmask, and gateway to the Logic-5000 unit. When the WiFi client is connected to
a WiFi access point, the default route is set to point to the gateway address obtained by the
DHCP client.
Figure 17 - WiFi (WLAN) -> Wireless Settings (Client)
5.5.2.1. Wireless Settings
Access Point Number: Access point number (automatically assigned)
SSID: Service Set Identifier. This is the name of the wireless local area network.
Channel: RF channel number (Auto or 1 to 11)
Authentication: Authentication method to be used (Example: Open, Shared, WPANONE,
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK)
Page 33 of
59

Encryption
: None, WEP, TKIP, or AES
WEP Key Length: Bit key length
WEP Key Type: Type of WEP security
WEP Key Index: Index of WEP Key (1 to 4)
Key: Encryption key
Note: For a 64-bit key, keys are 5 character strings long if WEP Key Type is set to ASCII
and 10 hexadecimal digits long if WEP Key Type is set to HEX.
For a 128-bit key, keys are 13 character strings long if WEP Key Type is set to ASCII and 26
hexadecimal digits long if WEP Key Type is set to HEX.
5.5.3. WiFi (WLAN) – Wireless Settings (Access Point)
Figure 18 - WiFi (WLAN) -> Wireless Settings (Access Point)
5.5.3.1. IP Settings
IP Address: IP address of the WiFi interface
Subnet Mask: The network mask of the WiFi interface
Page 34 of
59

5.5.3.2. DNS Masquerade
DNS Auto: Enables or disables the Logic-5000 DNS server on the WiFi interface
5.5.3.3. DHCP Server
DHCP Server: Enables or disables DHCP server on the WiFi interface
Start IP Address: Starting IP address (defines the pool of addresses allocated for DHCP
purpose)
End IP Address: Ending IP address (defines the pool of addresses allocated for DHCP
purpose)
Lease Time: The period over which the IP address allocated to a DHCP client is referred to
as a “lease”. Lease duration is the amount entered in seconds.
Domain Name Suffix: DNS suffix to be assigned by the DHCP server
Preferred DNS Suffix: IP address of the preferred DNS server
Alternate DNS Suffix: IP address of the alternate DNS server
5.5.3.4. Wireless Settings
SSID: Service Set Identifier. This is the name of the wireless local area network.
Channel: Channel number to use (Auto or 1-11)
Authentication: Authentication method to be used (Example: Open, Shared, WPANONE,
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK)
Encryption: Encryption method currently used
WEP Key Length: the bit key length
WEP Key Type: type of WEP security
WEP Key Index: 1-4
Key: The encryption key
Note: For a 64-bit key, keys are 5 character strings long if WEP Key Type is set to ASCII
and 10 hexadecimal digits long if WEP Key Type is set to HEX.
For a 128-bit key, keys are 13 character strings long if WEP Key Type is set to ASCII and 26
hexadecimal digits long if WEP Key Type is set to HEX.
5.5.4. WiFi (WLAN) – Stats
Figure 19 - WiFi (WLAN) -> Wireless Settings (Stats)
Page 35 of
59

5.5.4.1. Transmit
TX Packets: Number of packets sent by the Logic-5000 over the WiFi interface
TX Bytes: Number of bytes sent by the Logic-5000 over the WiFi interface
5.5.4.2. Receive
RX Packets: Number of packets received by the Logic-5000 over the WiFi interface
RX Bytes: Number of bytes received by the Logic-5000 over the WiFi interface
5.5.5. WiFi (WLAN) – Site Survey
Figure 20 - WiFi (WLAN) -> Wireless Settings (Site Survey)
When the WiFi interface of the Logic-5000 unit operates in Client mode, this screen shows
the WiFi Access Point detected during last wireless scan.
The list is empty when the Logic-5000 unit is operating in Access Point mode.
5.6. Router Settings
Figure 21 - Router Settings Screen
Page 36 of
59

5.6.1. RIP Routing
RIP Enable: Enables the Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
5.6.2. Static Routes
The Logic-5000 will automatically set up routing to all devices on the same subnet. In some
cases however, the Logic-5000 unit may need to communicate with a previously existing
subnet other than its own. This route cannot automatically be generated; it must be
manually entered as a static route by the user. The static route gives the Logic-5000 its
“next hop” instructions.
Route no: A generic number assigned to the route. Multiple static routes can be assigned
as long as they have distinct route numbers.
Route Name: Nickname assigned to the route by the user.
Destination IP Address: This is the destination IP address that is delivered to the Logic-
5000 radio modem. Since this IP address will not be on the same subnet, the Logic-5000
will not have a defined route, and will not know where to send it by default. Setting up the
static route will inform the Logic-5000 where to send the data.
IP Subnet Mask: The subnet mask is defined by the subnet mask of the destination
address
Gateway IP Address: This is the address that the data packet will be routed to.
Note:
The device at this address must be a router that is either on the same subnet as
the Destination IP or one with its own statically setup route to the destination
address. If this is not the case, the packet data will be dropped.
Metric: This sets the priority of the routes compared to other static routes defined. The
lower the number, the higher priority the route.
Click on “Add” when all necessary information has been entered. The route will be shown on
the bottom of the screen (under Static Routing Table). Additional routes can be added
provided they have a unique Route no, name and metric. Routes can be deleted by clicking
the Delete Entry option of the desired entry.
Note:
Routing Table (found under “Table” tab) shows all routes, while Static Table
(found under “Settings” tab) shows manually entered routes only.
5.6.3. Routing Table
The table in Figure 22 shows a list of all routes (static and dynamic).
Page 37 of
59

Figure 22 - Routing Table
5.7. Advanced Settings
5.7.1. Advanced Settings – NAT and Port Forwarding (Mapping)
When NAT is enabled, the LAN (Ethernet) is considered private, the WAN is considered
public. Any IP packets leaving the Logic-5000 unit through the WAN interface will have its
source IP address changed to that of the WAN interface.
Any data transfer must be initiated from the private side of the network toward the public
side.
Port Forwarding is used to provide remote access to third party devices on the LAN, such as
Web Cameras or printers. Port Forwarding routes incoming requests from the WAN, with a
specific port to a local device with a static IP.
Figure 23 – Port Forwarding & NAT Screen
Page 38 of
59

NAT: Network Address Translation (NAT) o
n the WAN interface of the Logic-5000 unit.
When NAT is enabled, the LAN (Ethernet) is considered private, the WAN is considered
public. Any IP packets leaving the Logic-5000 unit through the WAN interface will have its
source IP address changed to that of the WAN interface.
Port Forwarding: Enable - The Logic-5000 unit performs port forwarding. The "IP Mapping
Table" contains the rules used to perform port forwarding. Disable - The Logic-5000 unit
does not perform port forwarding on the WAN interface.
Mapping Number: User selected generic number assigned for this route.
Protocol: TCP, UDP, or both - driven by the protocol used by the third party device
Source IP Address: Enter the IP address of the remote PC connecting to the third party
device. (This should only be done if a single PC with a STATIC IP is accessing the device and
you want to limit access to the device.) If you will be accessing the third party device from
multiple PCs, or from a PC that has a dynamically assigned WAN IP, enter 0.0.0.0 (wildcard)
to allow all remote PCs to access the third party device.
Incoming Port: Enter the port of incoming request. This can be any non-conflicting port
(can be the same as the destination port). This value must be entered following the Logic5000 IP address into a browser on a remote PC to access the third party device.
Destination IP Address: IP address of third party device; must be on the same subnet as
the Logic-5000.
Destination Port: Enter the port of the third party device. This will be assigned to the
device by the third party manufacturer and should be in the user manual of the third party
device.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
The password protection on the Logic-5000 product does not protect logging into a third
party device. The third party device must provide its own password protection (confirm if
password protection is required).
Click Add when route configuration is complete. The route will be displayed at the bottom of
the page. Additional routes may be added but require a unique mapping number and port
number. Routes can be deleted (cleared) if no longer needed.
Once the route of the third party device is added you can enter the following on a remote
PC to access the third party device.
5.7.2. Advanced Settings – Dynamic DNS (NO-IP Configuration)
Dynamic DNS is an option for remote monitoring if a static WAN IP address is not available
or not yet assigned. When Dynamic DNS is activated, the Logic-5000 radio modem will
register its dynamically assigned IP address with NO-IP’s application, allowing the user to
login to the device remotely without knowing the IP address of the Logic-5000 radio
modem.
Page 39 of
59

A n
umber of providers offer services to track dynamic IP addresses and map them to
constant domain names. The Logic-5000 product supports connection with NO-IP.com, one
provider of this service.
NOTE:
As it is more reliable GPS Logic recommends the use of a static IP whenever
possible.
Figure 24 – Dynamic DNS (NO-IP Configuration) Setup Screen
NO-IP: Enable / Disable (disabled by default)
User at NO-IP.com: User name setup at NO-IP.com. This information is required when
logging into your account.
NOIP Password: Password used when logging into your account at NO-IP.
Hostname: This is unique domain name setup on your NO-IP account. This is the domain
name entered into a browser to remotely login to the Logic-5000 radio modem. You may
have multiple host names registered on the same account. See section below for
instructions to set up NO IP account and host name.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Do not assign more than one Logic-5000 unit the same domain name.
Update Interval: This setting determines how often the device will update its IP
information at NO-IP. The IP addresses assigned by the carrier are dynamic; therefore it is
necessary to update the registered IP periodically. Setting a high value in this field may
cause extended periods of no connection but will reduce the number of times the Logic5000 registers, decreasing the amount data used on the contract. Setting a low value
minimizes the chance of lost network connection but will increase the total amount of data
used on the contract.
The Logic-5000 radio modem will always register when first powered up or upon hardware
reset.
5.7.2.1. Instructions for NO IP Setup
1. Setup up an account at NO-IP.com http://www.no-ip.com/. You will need to setup a
user name and password on your account
Page 40 of
59

2. On No-I
P, create a host account for each device you want to remotely monitor. The
domain name you set up here will be used to remotely login to the device.
3. On the Logic-5000 radio modem, click “Dynamic DNS” on the left side of the web
Browser.
4. Enable NO-IP
5. Enter your NO-IP username, password and hostname for this device (do not assign
the same host name to multiple devices.)
6. Set the update interval (30 minutes is the default).
7. After registration is complete, you can login into the unit or use the port forwarding
feature by entering the hostname into a web browser followed by the port number.
(Example http://Logic-5000_user.no-ip.biz:8080
)
5.7.3. Advanced Settings – IP Filter
IP Filtering provides certain Internet firewall protection. The user can enter up to 20 IP
filters. Each IP filter is identified by a unique number (from 1 to 20). When IP filtering is
enabled, any custom IP filters entered by the user as well as predefined IP filters will be
taken into account when processing IP packets.
An IP packet passes through the filtering logic when IP filtering is enabled:
1) An IP packet is received on one of the interface and is destined to the Logic5000 unit
OR
2) An IP packet is sent by the Logic-5000 unit
OR
3) An IP packet is forwarded by the Logic-5000 unit.
5.7.3.1. Predefined IP Filters
Figure 25 – Advanced Settings -> IP Filters, Predefined IP Filters section
Drop Remote Pings: If enabled, any ICMP echo request coming from the WAN interface
will not be replied to. This prevents remote hosts from detecting your IP address on the
WAN.
Drop Remote IP Fragments: If IP filtering is enabled, any fragmented IP packets coming
from the WAN interface will be dropped.
Page 41 of
59

Dro
p Invalid Packets: If IP filtering is enabled, any invalid IP packets received by the unit
will be silently dropped. An invalid IP packet is one that cannot be identified for some
reason.
5.7.3.2. Add Custom IP Filters
Fill in the parameters described below and click “Add …”. Your entry should appear in the
Custom IP Filters table on the bottom of the page.
Figure 26 – Advanced Settings -> IP Filter, Add Custom IP Filter section
Note: Criteria are for inclusion by default. Select “exclude” if your criterion is for exclusion.
Filter Number: Each IP filter is identified by a unique number from 1 to 20.
Source IP Address:
Any: Any source IP address will satisfy these criteria
Specific: A specific Host IP address
Range: A range of IP addresses
Page 42 of
59

Destin
ation IP Address:
Any: Any destination IP address will satisfy these criteria
Specific: A specific Host IP address
Range: A range of IP addresses
Protocol:
Any: Any protocol number
ICMP: The ICMP protocol (1)
TCP: The TCP protocol (6)
UDP: The UDP protocol (17)
Other: Any other IP protocol (specify number a number between 1 and 255)
Source Port:
Any: Any source port number
Specific: A specific source port range
Range: A range of source port numbers
Destination Port:
Any: Any destination port number
Specific: A specific destination port number
Range: A range of destination port numbers
Direction: The direction corresponds to the path taken by the IP packet inside the Logic5000 unit.
Action:
Keep: If IP filtering is enabled and an IP packet matches all criteria in the IP filter,
keep the IP packet (continue normal processing of the packet).
Drop: If IP filtering is enabled and an IP packet matches all the criteria in the IP
filter, drop the packet.
Page 43 of
59

5.7.3.3. Delete Custom IP Filters
Figure 27 – Advanced Settings -> IP Filters, Custom IP Filters table
Click the Del link to delete the corresponding filter entry.
5.7.4. Advanced Settings – IPsec
5.7.4.1. IPsec Support
Selecting Enable will launch the IPSEC process and start all the enabled set tunnels.
Selecting Disable will stop all tunnels and shutdown the main process. By after, all the
enabled tunnels will be launched automatically when the unit connects to the cellular
carrier.
5.7.4.2. IPsec Configuration
Figure 28 – Advanced Settings -> IPsec, IPsec Configuration section
Tunnel no: Tunnel number, start at 1 and increment for each new tunnel. If you want to
modify an existing tunnel, use its number from the table below. The Enabled checkbox will
enable autostart directly after you saved the tunnel.
Label: This is a convenience label used to differentiate tunnels easily.
Remote IP Address: The Logic-5000 is considered the left local side, the remote IP is the
address of the right remote side where the unit will connect to establish a tunnel.
Remote Subnet: If you tick the Enabled checkbox, enter the IP netmask protected on the
remote side, for instance 10.0.0.0/24. If checkbox is not ticked, no subnet will be used and
encryption is possible when the destination IP is the VPN gateway itself (Remote IP address
above), it is useful if you use port forwarding from your VPN gateway to servers.
Page 44 of
59

Loca
l Subnet: If the Enabled checkbox is checked, the ETH0 subnet will be used for
encryption based source IP address. If not checked, no local subnet will be used and
encryption will be done when packets with source IP of the Logic-5000’s occur. This is
useful for AAVL reports that get out directly from the Logic-5000.
Encryption: This is to determine the use of AES-128 or AES-256 encryption.
Pre-shared Key: Matching key residing on the remote server.
5.7.4.3. Tunnel Table
This is the table of configured tunnels. To delete an entry, click the corresponding Delete
Entry link.
Figure 29 – Advanced Settings -> IPsec, Tunnel Table section
5.7.5. Advanced Settings – Remote Admin
Figure 30 – Advanced Settings -> Remote Admin page
Remote Configure: Selecting Enable will allow remote access to the modem’s
configuration screens through the cellular network connection. Selecting Disable will shut off
the ability to remotely access the modem’s configuration screens.
Incoming Port: Change the port of incoming requests. It is not necessary to change this
parameter unless it conflicts with other devices on the network.
Admin Password: Set the password for BOTH remote login and local login. The password
must be entered twice for the password to change.
Page 45 of
59

5.7.6. Advanced Settings – Power Management
Figure 31 – Advanced Settings -> Power Management section
The LOGIC-5000 unit is designed to stay ON even if the ignition is turned OFF. You can
configure your Logic-5000 unit to automatically shut down 1, 5, 30, 60, or 240 minutes
after ignition is turned off or when the supply voltage drops to a certain level.
Shutdown Method: Disabled by default (unit always ON after ignition is turned OFF).
Select “Power Off” to enable power management.
After ignition line off: Select between the following time intervals: 1 minute, 5 minutes,
30 minutes, 60 minutes or 240 minutes.
When Voltage Drops to: Enter desired voltage. Enter “0” to disable. (Note: A value of 11V
would be usually entered here as a precaution in order to ensure the vehicle battery does
not drain.)
5.8. SNMP
SNMP is currently reserved for systems integrators. Contact GPS Logic for further support
on this functionality.
Page 46 of
59

5.9. GPS
The GPS page allows the user to see the GPS status and configure remote or local delivery
of GPS position reports. Viewing the GPS data from a local or remote PC requires a UDP port
listener program be installed on the PC. Any UDP listener will work provided you can set an
appropriate port value for the program.
5.9.1. GPS Status
Figure 32 – GPS Status section
Condition: Indicates No Fix, Standard GPS Fix, Differential GPS Fix, or Estimated / Last
Known Position
Number of Satellites: Indicates the number of satellites the GPS has locked on to. A
minimum of 3 is required to establish a position. Generally, the more satellites the GPS has
locked, the more accurate the position reporting will be.
UTC: Time of day in Universal Coordinated Time
Position: Device position reported in degrees and minutes
Altitude: Altitude from Mean Sea Level reported in meters.
True Course: Heading, reported in degrees (0 – 360)
Ground Speed: Reported in km/hr
Page 47 of
59

5.9.2. AAVL Settings (Local and Remote Delivery)
Figure 33 - GPS Local and Remote Delivery
Page 48 of
59

TAIP Vehi
cle ID: User assigned number to identify the vehicle or Logic-5000 unit that
each GPS report belongs to. This will be reported in the GPS messages if TAIP with ID is
selected for TCP Server Format and/or UDP Host format. Configured under Basic Settings
Page.
Differential Correction: Differential GPS corrects various inaccuracies in the GPS system
to yield measurements accurate to a couple of meters when the mobile is moving and even
better when stationary.
Ignition Pinning: When enabled, the vehicle’s reported location becomes locked to the
current position when the vehicle ignition is turned off. The reported vehicle location will
not change until the ignition is turned back on, even if the vehicle moves. This feature is
useful for overcoming the inherent drift issues found in GPS location data.
5.9.2.1. Local Delivery
The GPS data can be delivered to up to two local PCs with UDP viewer programs can provide
data through a TCP connection, e.g. telnet. GPS data will be delivered once per second to all
local PCs.
TCP Server Format: Select one of the following options for the format of the GPS
messages
TAIP no ID: Trimble ASCII Interface Protocol, a Trimble specified digital
communication interface. When this option is selected, the TAIP vehicle ID is not
included in the GPS messages.
TAIP with ID: Same as above except the Vehicle ID is reported.
NMEA: National Marine Electronics Association interface specification for electronic
equipment. The NMEA GPS message set includes several message types, each
containing specific GPS information. See message descriptions below. TAIP Vehicle
ID is not reported when NMEA is selected.
NMEA GLL: Position in LAT/LONG coordinates and time of day in UTC coordinates.
NMEA GGA: Position in LAT/LONG coordinates, time of day in UTC coordinates, fix
quality, number of satellites and altitude.
NMEA RMC: Position in LAT/LONG coordinates, time of day in UTC coordinates,
ground speed in knots, heading in degrees and date.
NMEA VTG: Ground speed in kilometers per hour and knots, heading in degrees.
UDP Host Format:
Disabled: Position reports are not sent on the local subnet.
TAIP, No ID: Trimble ASCII Interface Protocol without the ID field. When selected,
several checked boxes will appear beneath the drop down to give an option for each
TAIP sentence. Ensure at least one checkbox is selected.
TAIP with ID: Same as above except with the Vehicle ID reported.
Page 49 of
59

NMEA: NMEA 0183
Protocol. When selected, a checkbox appears for selecting the
following sentence formats: GLL, GGA, RMC, VTG.
UDP Host Address: IP address of local PC that GPS data will be delivered to. This address
must be on the same subnet as the Logic-5000 LAN IP. To broadcast addresses across the
entire subnet, enter the IP address in the form 192.168.1.255.
UDP Host Port: Port assigned to UDP program. This must match the port assigned in the
chosen UDP Port Listener Program.
5.9.2.2. Remote Delivery
The GPS data can be delivered to up to three remote hosts.
Report every: GPS can be programmed to report position after a specified time has
elapsed or the unit has moved a specified distance since its last report. This field indicates
the maximum length of time or distance that can elapse between position reports.
But no less than: This feature prevents a fast moving vehicle from reporting too frequently
if its “Report every ….. meters” setting is sufficiently low by setting a minimum amount of
time, in seconds, between GPS reports.
The remaining fields are the same as what’s listed in Section 5.9.2.1.
Page 50 of
59

5.10. Serial Port Settings
The following settings allow local or remote GPS reports to be sent out to the user COM
port.
Figure 34 – Serial Port Settings
Page 51 of
59

5.10.1. USB Port
Currently the USB port is reserved for use by GPS Logic.
5.10.2. Serial Port
5.10.2.1. GPS Configuration
The serial port settings are disabled by default. To enable GPS reports to be sent out to the
user COM port, select “GPS”. The GPS reports could be sent over the serial port “Always” or
only “On Loss of Cellular Signal”.
Note that the following delays apply if the latter is selected:
On power-up: Reports are delayed for 90 seconds to allow time for cellular connectivity to
be established.
During Operation: Reports are delayed for 30 seconds after loss of cellular connectivity is
detected.
Select “Local (1 sec)” if every GPS report is required or “Remote (aavl)” for GPS reports to
be sent out based on the AAVL settings (see AAVL settings).
Note: GPS Report format is set in the “TCP Server Format” pick lists on the GPS web page.
5.10.2.2. Garmin Messaging
Enables transfer of navigation and messaging functions to an attached Garmin navigation
device for automated dispatch and messaging. Requires subscription to GPS Logic Fleet
Management System.
5.10.2.3. Road Safety RS-3000
Allows transmission of Road Safety data using the cellular data network. When selected,
ensure the Logic-5000 COM port is connected to COM4 on the RS-3000 black box.
NOTE: When using the Logic-5000 in conjunction with the Road Safety RS-3000, a static IP
address is highly recommended.
5.10.2.4. Serial Over TCP/UDP
Reserved for future use.
5.10.3. PAD Settings
When Serial Over TCP/UDP is selected, enter the remote IP address and port for the server
that will be receiving the Logic-5000 data.
Page 52 of
59

5.11. I/O Settings
The Logic-5000 supports the following I/Os:
Logic 5000 Input Status: Ignition sense, main voltage, and modem temperature
Four general purpose external analog input lines (AIN1 … AIN4)
Four general purpose external digital input lines (DIN1 … DIN4)
Four general purpose external digital outputs (relay-driven contact closures).
Implemented as four sets of SPST contacts (normally open) (NO1a … NO4b)
See Figure 35 for pin output diagram.
Figure 35 - Logic-5000 Pin-output. View looking into device.
Digital inputs are internally biased high. To trigger a digital input, connect the pin to
ground.
When digital outputs are triggered, the a and b pins are connected via an internal relay.
The internal relays are rated for 1A @ 30V, or .3A @ 125VAC.
Pin # Description Wiring Harness Color
Pin 1 Analog Input 4 (AIN4) Not populated*
Pin 2 Analog Input 2 (AIN2) Not populated*
Pin 3 Analog Ground Not populated*
Pin 4 Digital Output 4b (NO4b) Red/White
Pin 5 Digital Output 4a (NO4a) Red
Pin 6 Digital Output 2b (NO2b) Purple/White
Pin 7 Digital Output 2a (NO2a) Purple
Pin 8 Not used Not populated*
Pin 9 Digital Ground Black
Pin 10 Digital Input 4 (DIN4) Brown
Pin 11 Digital Input 2 (DIN2) Orange
Page 53 of
59

Pin 12
Analog Input 3 (AIN3) Not populated*
Pin 13 Analog Input 1 (AIN1) Not populated*
Pin 14 Analog Ground Not populated*
Pin 15 Digital Output 3b (NO3b) Blue/White
Pin 16 Digital Output 3a (NO3a) Blue
Pin 17 Digital Output 1b (NO1b) Green/White
Pin 18 Digital Output 1a (NO1a) Green
Pin 19 Not used Not populated*
Pin 20 Digital Ground Not populated*
Pin 21 Digital Input 3 (DIN3) Gray
Pin 22 Digital Input 1 (DIN1) Yellow
* Pigtail leads are available from GPS Logic for populating unfilled slots in the I/O connector.
Digital Outputs 4a and 4b are reserved for controlling the power of a connected Garmin
navigation device. Pins 4 and 5 will be connected whenever the vehicle ignition is activated,
or a Garmin message is received. To use these, connect Digital Output 4a to a constant hot
source via a 3A fuse. Connect Digital Output 4b to the red wire on the Garmin FMI 40 data
cable.
5.11.1. I/O Signal Specifications
The following values are acceptable ranges for digital inputs and outputs:
Input Type Label Specification
Analog Input AIN1 … AIN4 Input voltage: 0 to +28V
Digital Input DIN1 … DIN4 Schmitt-trigger inputs:
Positive threshold: 2.2V max
Negative threshold: 0.6V min
Maximum input: 5.5V
Digital Output NO1a … NO4b Nominal switching capacity (resistive load):
1A, 30VDC
0.3A, 125VAC
The default power up state for the digital outputs is normally open (a and b pins
disconnected).
Page 54 of
59

Page 55 of 59
5.11.2. Debouncing
All analog and digital input signals are debounced for 500ms. Thus pins must maintain the
same input condition for 500ms continuously before the pin state is changed.
5.11.3. I/O Configuration
The Logic-5000 I/O subsystem is configured via the Logic-5000 web pages. Status
monitoring is provided either by the GPS Logic Fleet Management System using the LM
Direct protocol, or by an NMEA-based protocol. The Logic-5000 I/O subsystem operates
according to a manager/agent module. The PC-hosted manager sends requests to the
Logic-5000 I/O agent, which performs the required actions. The Logic-5000 agent reports
alarms and indications to the PC-hosted manager.

5.12. System Upgrade
GPS Logic periodically releases firmware updates for bug fixes and enhanced functionality.
Typically firmware is automatically managed by the GPS Logic modem maintenance server.
Customers also have the option of manually updating devices by uploading a firmware file
using a locally attached PC. To initiate a local firmware update, click the browse button to
select the GPS Logic firmware update file. Click the Save button to begin the upgrade
process. When the update is complete, the Logic-5000 will automatically restart.
5.12.1. Configuration File
The Logic-5000 configuration can be saved and uploaded into multiple units allowing
customers to create and save a master configuration file for deployment to multiple devices.
To save the configuration for the current modem, select the Save Config button.
Conversely, a configuration file can be uploaded into the device by selecting the Browse
button corresponding to the Upload File field. Once the config.tar.gz file is selected, click
the Upload button to apply the new settings.
Warning: Do not attempt to perform a modem update from a remote connection.
Page 56 of
59

6. Carrier Specific Information
Each cellular provider uses a different PRI file that needs to be programmed into the modem
for the modem to register properly on their cellular network and connect. These PRI files are
typically programmed into the modem by the manufacturer of the RF module. The following
sections list different carriers and the requirements for activating modems on their
networks. Cellular providers will (where applicable) supply username and password formats
for making EVDO calls. GPS Logic modems support the service provisioning features called
Over-the-Air Service Provisioning (OTASP) and Over-the-Air Parameter Administration
(OTAPA). OTASP occurs when a user initiates a call to the service provider. No further
commands are (typically) required to provision the modem. For example, a user with a new
modem/phone without service programming data can call the service provider's special
OTASP number to have the device programmed without physically taking it to the service
provider. OTAPA occurs when the network initiates a call to the modem and programs it
without any user intervention. OTAPA is typically used when the service provider decides to
update information on many cellular devices at the same time.
Note:
Logic-5000 radio modems are carrier specific, you must specify the carrier you
will be using when ordering. A unit purchased for one carrier cannot be activated
on any other carrier.
Note:
Generally, you will not be able to provision a device if you are not in your home
network area. You will also need to make sure that you have sufficient signal
strength to perform provisioning.
6.1. Verizon Wireless
Note:
Before starting the OTA process, ensure that you have a strong enough signal for
cellular communication
When you activate a contract with Verizon, Verizon will assign a 10 digit MDN/MIN number
to your module’s ESN. When this is done, you are ready to OTA the module. Verizon
activation is done by submitting an OTA command of *22899 to the Verizon network. This
command is entered by default into the OTA command box on the “WAN Cellular Page”. It
should not be necessary to modify this command, simply select OTASP, click “Submit” and
allow the activation to complete. This process may take several minutes. This command is
also used to update the PRL file. When the OTA is complete, the MDN provided by Verizon
should be displayed on the home page.
6.2. Bell Mobility
Activation on the Bell mobility network requires manual entry of the MDN, MIN and Unlock
code. Bell will provide these numbers when you initiate your data contract with them. In
most cases, the MDN and MIN will be the same number. On the WAN Cellular page, enter
the MDN, MIN and Unlock code and click “Submit”. The activation process will occur
automatically once the parameters are entered. This process may take a few minutes and
you may need to reset the device to have full network access.
Page 57 of
59

Page 58 of 59
6.3. Sprint PCS
6.3.1. IOTA Provisioning
The 3GPD parameters are easily configured using Over The Air Provisioning. Sprint PCS uses
IOTA (IP-based Over The Air) for their OTA provisioning system. IOTA uses packet data calls
to transfer the configuration data to the modem. These IOTA data sessions can be network
initiated or Client initiated. Network Initiated IOTA is the preferred method. An automatic
network initiated IOTA session occurs when the module first registers onto the Sprint
network. This IOTA session is queued when Sprint originally sets up and 'activates' the
account. In their current implementation, Sprint imposes a 72 hour expiration timer for this
queued IOTA session. An IOTA session has a device time out of 15 minutes. If unsuccessful
after 15 minutes, the status changes to fail and the module stops trying. A normal IOTA
session takes from 1 to 3 minutes. To register on the network, the module needs a
sufficient signal and requires manual provisioning with the MDN and MSID. The IOTA
session will occur and populate the 3GPD parameters. If it is the first IOTA session, it is
called a Network Initiated Initial Provisioning (NIIP.)
NOTE:
An IOTA session MUST occur while the device has sufficient signal and is
registered on the Sprint PCS Network. A session will not be successful if the
device is out of coverage or not properly registered on the Sprint PCS network.

7. Service and Support
7.1. Product Warranty, RMA and Contact Information
GPS Logic LLC guarantees that every Logic-5000 Cellular Modem will be free from physical
defects in material and workmanship for one (1) year from the date of purchase when used
within the limits set forth in the Specifications section of this manual. Extended warranty
plans are available.
If the product proves defective during the warranty period, contact GPS Logic Customer
Service to obtain a Return Material Authorization (RMA).
7.2. RMA Request
Contact Customer Service:
GPS Logic LLC
23461 South Pointe Dr, Suite 115
Laguna Hills, CA 92653
Phone: (888) GPS-0911
BE SURE TO HAVE THE EQUIPMENT MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER, AND BILLING AND
SHIPPING ADDRESSES ON HAND WHEN CALLING.
When returning a product, mark the RMA clearly on the outside of the package. Include a
complete description of the problem and the name and telephone number of a contact
person. RETURN REQUESTS WILL NOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT THIS INFORMATION.
For units in warranty, customers are responsible for shipping charges to GPS Logic LLC. For
units returned out of warranty, customers are responsible for all shipping charges. Return
shipping instructions are the responsibility of the customer.
7.3. Product Documentation
GPS Logic LLC reserves the right to update its products, software, or documentation without
obligation to notify any individual or entity. Product updates may result in differences
between the information provided in this manual and the product shipped. For the most
current product documentation, visit www.gpslogic.com for spec sheets.
7.4. Technical Support
Technical support hours: Monday to Friday 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM, Pacific Time
GPS Logic LLC, 23461 South Pointe Dr, Suite 115, Laguna Hills, CA 92653
Phone: 888.GPS.0911
support@gpslogic.com
Page 59 of
59
 Loading...
Loading...