Page 1

Page 2

Pump Safety Tips
Safety Apparel:
• Insulated work gloves when handling hot bearings
or using a bearing heater
• Heavy work gloves when handling parts with sharp
edges, especially impellers
• Safety glasses (with side shields) for eye protection,
especially in machine shop areas
• Steel-toed shoes for foot protection when handling
parts, heavy tools, etc.
• Other personal protective equipment to protect
against hazard/toxic fluids
Coupling Guards:
• Never operate a pump without a V-belt guard
properly installed
Flanged Connections:
• Never force piping to make a connection with a
pump
• Use only fasteners of the proper size and material
• Ensure there are no missing fasteners
• Beware of corroded or loose fasteners
Operation:
• Do not operate below minimum rated flow, or with
discharge valves closed
• Do not open vent or drain valves, or remove plugs
while system is pressurized
Maintenance Safety:
• Always lockout power
• Ensure pump is isolated from system and pressure
is relieved before disassembling pump, removing
plugs, or disconnecting piping
• Use proper lifting and supporting equipment to
prevent serious injury
• Observe proper decontamination procedures
• Know and follow company safety regulations
• Never apply heat to remove impeller
• Observe all cautions and warnings highlighted in
pump instruction manual
Safety Definitions
These pumps have been designed for saf e and reliable operation when properly used and maintained in accordance
with instructions contained in this manual. A pum p is a pressure containing device with rotating parts that can be
hazardous. Operators and maintenance personnel must realize this and follow safety meas ures. Goulds pumps
shall not be liable for physical injury, damage or delays caused by a failure to observe the instructions in this manual.
The following symbols are used to denote special attention:
Electrical Hazard. Particular care must be taken when electrical power source to the equipment is
energized.
Warning. O perating procedure, prac tice etc which, if not c orrect ly followed, could result in personal injury or
loss of life
Caution. Operating procedure, practice etc which if not followed could result in dam age or destruction of
equipment
ATEX. If equipment is to be installed in a potentially explosive atmosphere and these procedures are not
followed, personal injury or equipment damage from an explosion may
Page 3

FOREWORD
When pumping unit is installed in a potentially explosive atmosphere, the instructions after the Ex symbol
please contact a Goulds representative before proceeding.
This manual provides instructions for the Installation, operation, and maintenance of the
Goulds Axial Flow (AF) pump model. This manual covers the standard product. For special
options, supplemental instructions are supplied. This manual must be read and understood
before installation and start-up.
The design, materials and workmanship incorporated in the construction of Goulds pumps
makes them capable of giving long, trouble-free service. The life and satisfactory service of any
mechanical unit, however, is enhanced and extended by correct application, proper installation,
periodic inspection, condition monitoring and careful maintenance. This instruction manual was
prepared to assist operators in understanding the construction and the correct methods of
installing, operating, and maintaining these pumps.
Goulds shall not be liable for physical injury, damage or delays caused by a failure to
observe the instructions for Installation, Operation, and Maintenance contained i n thi s
manual.
Warranty is valid only when genuine Goulds parts are used.
Use of the equipment on a service other than stated in the order will nullify the warranty,
unless written approval is obtained in advance from Goulds Pumps, Inc.
Supervision by an authorized Goulds representative is recommended to assure proper
installation.
Additional manuals can be obtained by contacting your local Goulds representative or by
calling 1-800-446-8537.
THIS MANUAL EXPLAINS
Proper Installation
Start-up Procedures
Operation Procedures
Routine Maintenance
Pump Overhaul
Trouble shooting
Order Spare or Repair Parts
must be followed. Personal injury and/or equipment damage may occur if these instructions are not
followed. If there is any question regarding these requirements or if the equipment is to be modified,
AF (42-66) IOM 3
Page 4
4
General Precautions
potentially explosive environment.
Never apply heat to remove impeller. It may explode due to trapped
liquid
Never use heat to disassemble pump due to risk of explosion from
trapped liquid
Never operate pump without coupling guard correctly installed
Never operate pump beyond the rated conditions to which the pump was
sold
Never start pump without proper prime, or proper liquid level in self
priming pumps
Never run pump below recommended minimum flow or when dry
Always lock out power to the driver before performing pump maintenance
Never operate pump without safety devices installed
Never operate pump with discharge valve closed
Never operate pump with suction valve closed
Do not change conditions of service without approval of an authorized
Goulds representative
Explosion Prevention
In order to reduce the possibility of accidental explosions in atmospheres containing explosive gasses
and/or dust, the instructions under the ATEX symbol must be closely followed. ATEX certification is a
directive enforced in Europe for non-electrical and electrical equipment installed in Europe. ATEX
requirements are not restricted to Europe, and are useful guidelines for equipment installed in any
Special ATEX considera ti ons
All installation and operation instructions in this manual must be strictly adhered to. In addition, care must be taken to
ensure that the equipment is properly maintained. This includes but is not limited to:
1. monitoring the pump frame and liquid end temperature
2. maintining proper bearing lubrication
3. ensuring that the pump is operated in the intended hydraulic range
AF (42-66) IOM
Page 5
ATEX Identification
Temperature in Celsius
Temperature in Celsius
T1
T3
T4
T5
For a pumping unit (pump, seal, coupling, motor and pump accessories) to be certified for use in an ATEX classified
environment, the proper ATEX identification must be present. The ATEX tag will be secured to the pump or the
baseplate on which it is mounted. A typical tag will look like this:
II 2 G/D X
The CE and the Ex designate the ATEX compliance. The code directly below these symbols reads as follows:
II ------------ Group 2
2 ------------- Category 2
G/D ------------ Gas and Dust present
X ------------ Temperature class, can be T1 to T6 (see following table)
Maximum Process Temperature to achieve desired T rating
T Rating per EN 1127-1 Maximum Surface
450 410
T2
300 260
200 165
135 100
100 65
Maximum Process
T6
The code classification marked on the equipment should be in accordance with the specified area where the
equipment will be installed. If it is not, please contact your ITT/Goulds representative before proceeding.
85 50
Intended Use
The ATEX conformance is only applicable when the pump unit is operated within its intended use. All instructions
within this manual must be followed at all times. Operating, installing or maintaining the pump unit in any way that is
not covered in this manual can cause serious personal injury or damage to the equipment. This includes any
modification to the equipment or use of parts not provided by ITT/Goulds. If there is any question regarding the
intended use of the equipment please contact an ITT/Goulds representative before proceeding.
AF (42-66) IOM 5
Page 6

6
THIS PAGE
INTENTIONALLY
LEFT BLANK
AF (42-66) IOM
Page 7
7
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
9
11
15
31
39
45
SAFETY
GENERAL INFORMATION
INSTALLATION
OPERATION
PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
DISASSEMBLY & RE-ASSEMBLY
3
4
5
6
Section
1
2
49
61
AF (42-66) IOM
SPARE PARTS
APPENDIX 1
7
8
Page 8

8
THIS PAGE
INTENTIONALLY
LEFT BLANK
AF (42-66) IOM
Page 9
SAFETY
1
! ! !
!
!
DEFINITIONS ................................................................................................... 9
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS.............................................................................. 9
DEFINITIONS
Axial flow pumps are pressure-containing devices with
rotating parts that can be hazardous. It has been
designed for safe and reliable operation when properly
used and maintained in accordance with instructions
contained in this manual. It is not to be operated at
speeds, working pressures, discharge pressures, or
temperatures higher than, nor used with liquids other
than stated in the original order acknowledgement,
without written permission of ITT Industries, Gould’s
Pumps, Inc. Operators and maintenance personnel
must realize this and follow safety measures. ITT
Industries, Gould’s Pumps, Inc. shall not be liable for
physical injury, damage or delays caused by a failure to
observe the instructions in this manual.
Throughout this manual, the words Warning, Caution,
and Note are used to indicate procedures or situations
which require special operator attention:
WARNING
Warning is used to indicate the presence of a
hazard which can cause severe personal injury,
death or substantial property damage if the warning
is ignored.
CAUTION
Caution is used to indica te the presence of a hazard
which will or can cause minor personal injury or
property damage if the warning is ignored.
NOTE: Operating procedure, condition, etc. that is
essential to observe.
EXAMPLES
WARNING
Pump shall never be operated without V-belt or
coupling guard installed correctly.
CAUTION
Obstructions to flow or pipe fowling may cause
cavitation and pump damage.
NOTE: Proper alignment is essential for long pump
life.
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
Personal injury will result if procedures outli n ed in
this manual are not followed.
• Never apply heat to remove the impeller. It may
explode due to trapped liquid.
• Never use heat to disassemble pump due to risk of
explosion from trapped liquid.
• Never operate pump without V-belt or coupling
guard correctly installed.
• Never operate pump beyond the rated conditions
to which the pump was sold.
• Never start pump without proper prime (sufficient
liquid in pump casing).
• Never run the pump < 75% or > 115% of the Best
Efficiency Point (B.E.P.), AF pumps are unstable in
these regions.
• Always lock out power to the driver before
performing maintenance.
• Never operate pump without safety devices
installed.
• Never operate pump with suction valve closed.
• Never operate pump with discharge valve closed.
• Do not change conditions of service without
approval of an authorized Gould’s representative
AF (42-66) IOM 9
Page 10

THIS PAGE
INTENTIONALLY
LEFT BLANK
AF (42-66) IOM
10
Page 11
2
GENERAL INFORMATION
GENERAL .................................................................................................... 11
PUMP DESCRIPTION .................................................................................. 11
NAME PLATE INFORMATION .................................................................... 12
RECEIVING THE PUMP .............................................................................. 13
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION CHECKLIST ........................................ 13
GENERAL
This instruction manual is intended to assist those
involved with the installation, operation and
maintenance of Gould’s pumps. It is recommended
that this manual be thoroughly reviewed prior to
installing or performing any work on the pump or
motor.
The design, material and workmanship incorporated
into the construction of Gould’s pumps makes them
capable of giving long, trouble-free service. The life
and satisfactory service of any mechanical unit,
however, are enhanced and extended by periodic
inspection and careful maintenance. Keep this
instruction manual handy for reference. Further
information can be obtained by contacting Gould’s
Pumps, Ashland Operations, East Centre St., Ashland,
PA 17921 or your local representative.
Gould’s Pumps will not be liable for any damages or
delay caused by failure to comply with the provisions of
this instruction manual. This pump is not to be
operated at speeds, working pressures, discharge
pressures, or temperatures, nor used on liquids other
than stated in the original order acknowledgment
without written permission of Gould’s Pumps.
PUMP DESCRIPTION
The AF pump generates flow by the thrust or lift
action of the rotating axial vanes of the impeller. It
provides high flow rates and low heads which are
ideal for re-circulation, evaporator, and generator
cooling systems. The AF utilizes an elbow to direct
the flow through the suction and out the discharge
end of the pump. The pump accommodates top or
end suction configurations using either the LMR or
LM bearing arrangement. The LMR is for top
suction and the LM is for end suction.
Arrangements are as follows:
Power Inboard Outboard
End Bearing Bearing
LMR Spherical roller Spherical thrust/spacer/Spherical
roller
LM Spherical roller Spherical roller/spacer/Spherical
thrust
Elbow – AF elbows are fabricated with 150# flat
face suction and discharge flanges. They come
with fabricated feet for mounting to a sub-base or
without feet to be mounted directly in the piping.
The elbows have a built in stuffing box and a rear
flange for mounting the power end to the elbow.
There are also adjusting lugs for aligning the shaft
to the stuffing box.
Casing – The AF comes with a casing or spool piece to
simplify impeller installation and alignment. The casing
bolts to the elbow and shrouds the impeller. It has a gasket
or o-ring seal between it and the elbow. Adjusting lugs on
the elbow center the casing relative to the impeller.
Power End - The power end is made up of the bearing
housing, bearings, locknuts, lock washers, labyrinth oil
seals, shaft, shaft sleeve (w/packing), oil slinger, keys,
shaft, and shaft washer.
Stuffing Box – The stuffing box is integral with the elbow
and provides a mounting surface for a mechanical seal or
cylindrical bore with flush ports and gland face for packing.
The standard packed box includes (5) rings of packing and
(2) lantern rings to seal the shaft area. (2) flush ports are
provided for lubrication. The innermost flush port is used
with process flow and the outermost port for water flush. A
special alternate packing arrangement is available that
includes a throat bushing and additional ring of packing
near the gland (see the attached addendum). A gland is
used for packing adjustment.
AF (42-66) IOM 11
Page 12
Shaft Sleeve – If packing is specified, a
replaceable wear sleeve is provided with the power
end. The sleeve is keyed to prevent rotation. The
stuffing box can also be modified to accept a
mechanical seal if required.
Impeller - The impeller is cast with (4) fixed vanes
at 0 or +5 degrees, CW or CCW rotation, and top
or end suction. The impeller bore is stepped for
easy assembly to the shaft. It is held in place with
a key, shaft washer, and bolts. It has a cover plate
and o-rings to prevent corrosion and allow for easy
impeller replacement. The impeller is dynamically
balanced (two plane) per ISO 1940 to a quality
grade G-16.
Shaft – The shaft is cantilevered into the elbow to
eliminate the need for internal bearings. It is sized
for minimal deflection, high critical speed, and
extreme corrosion resistance. The shafts are
stepped for easy assembly with the impeller. The
shaft comes with a replaceable sleeve when used
with stuffing boxes.
Bearings - The inboard radial bearing absorbs shaft radial
loads and aligns the pump shaft. It is a spherical roller
bearing. The outboard thrust bearing absorbs impeller
thrust loads and comes as either back-to-back angular
contacts or a single taper roller bearing, depending on
pump size. Lubrication is by flood oil or grease, depending
on customer requirements.
Oil-Cooling (Optional ) – An oil-cooling coil is available on
all sizes, it is installed in the bottom of the bearing housing
and circulates water to cool the oil bath. Generally, it is
used when process temperatures cause excessive heat
build up in the bearing housing and/or bearings.
Configurations and Drives – The 42”, 1200mm, 54”, 60”,
and 66”pumps are usually gear driven and come on a
subbase as standard. They can also be pipe mounted with
a drive shaft to a motor on a separate subbase.
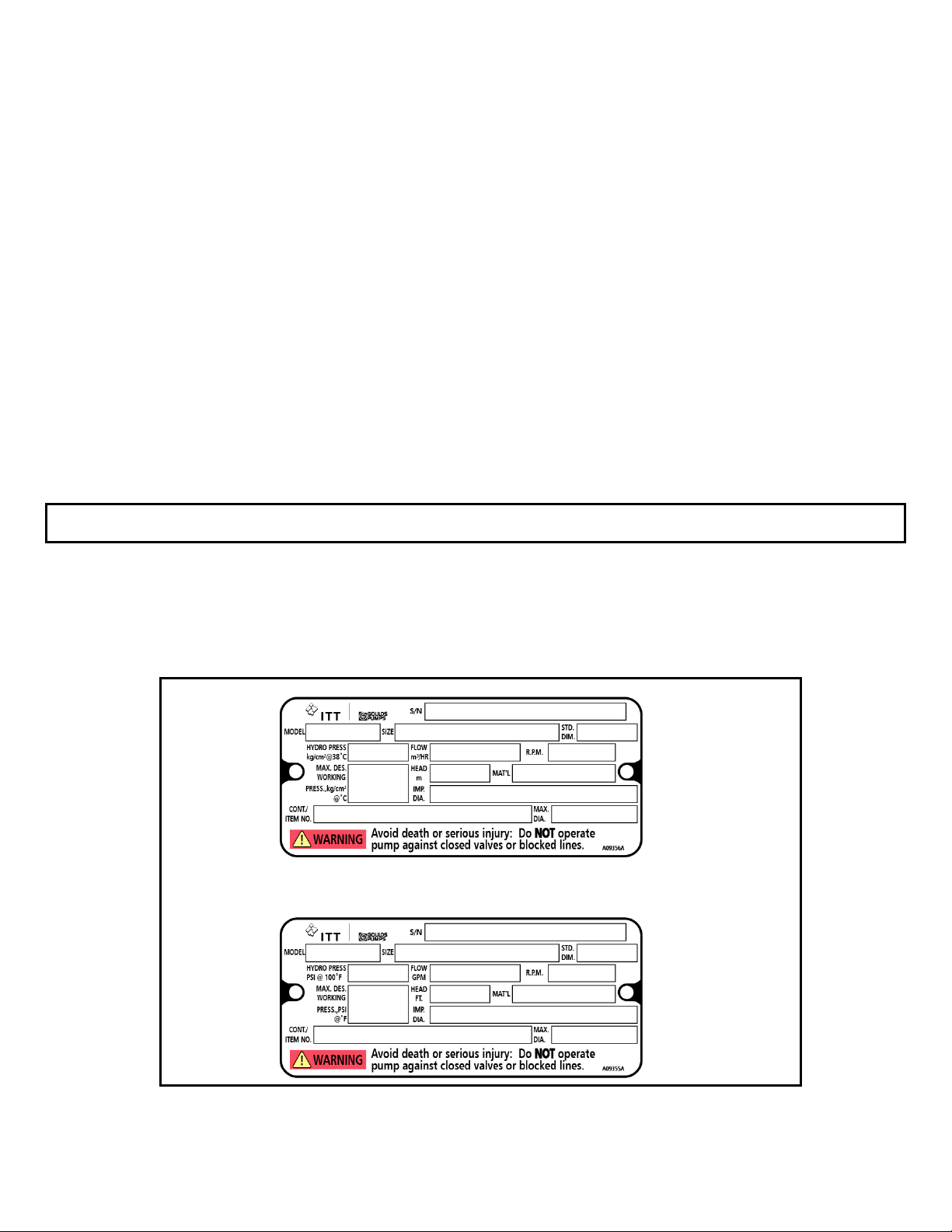
NAMEPLATE INFORMATION
Every Gould’s pump has a nameplate that provides
information about the pump, including hydraulic
characteristics. The nameplate for the AF is located on the
bearing housing. Note the format of the pump size:
Discharge X Suction - Impeller Diameter in inches or
millimeters (Example 42” X 42”-42” or 1200mm X
1200mm-1200mm, see Fig. 1). When ordering spare
parts you will need to identify pump model, size, serial
number, and the item number of required parts.
Information can be found in this manual.
12 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 13
COMPLETE
INITIAL
DESCRIPTION
PAGE NO.
Manual read and understood
1~54
Level foundation
15
Level subbase
16
Check motor rotation ---CW _____ ---CCW _____
28
Component rough alignment complete
21~26
V-belt tension and alignment per drive mfgr.
21,22
Coupling alignment per cplg mfgr.
22
Piping installed and alignment rechecked
19, 20
Mech. seal adjusted per mfgr.
Mfgrs Mnl
Seal flush lines connected
41
Impeller alignment and clearance set ______ Inch/Side
27
Pump shaft-free turning
30
Bearing lubrication
30, 38
V-belt or coupling guards installed
9, 22,30
Motor electrical connections
Mfgrs Man’l
2
!
RECEIVING THE PUMP
Inspect the pump as soon as it is received.
Carefully check that everything is in good order.
Make notes of damaged or missing items on the
receipt and freight bill. File any claims with the
transportation company as soon as possible.
STORAGE REQUIREMENTS
Short Term: (Less than 6 months) Gould’s normal
packaging is via a skid. It is designed to protect
the pump during shipping only. Upon receipt, store
in a covered and dry location.
Long Term: (More than 6 months) Gould’s longterm packaging via crating. Preservative treatment
of bearings and machined surfaces is required.
Rotate the shaft several times every 3 months.
Refer to drive manufacturer's instruction manual
for their long-term storage procedures. Store in a
covered dry location
Note: Long-term storage treatment can be
purchased with initial p u mp order.
UNCRATING/DE-SKIDDING
Care should be taken when uncrating or de-skidding
pumps. If shipment is not delivered in proper order, and in
accordance with the bill of lading, note the damage or
shortage on both the receipt and freight bill. Make any
claims to the transportation company promptly. Instruction
books and sheets are included in the shipment - DO NOT
DISCARD.
LIFTING THE PUMP/SUB-BASE
WARNING
Pump and components are heavy. Failure to properly
lift and support equipment could result in serious
physical injury or damage to pumps.
Use care when moving pumps. Lifting equipment must be
able to adequately support the entire assembly. Lift
assembled unit by the lifting holes found in the sub-base.
If the motor, sheaves, and guard are in place, be sure that
the lifting cable or chain clears these components. If
necessary remove the guard or use a spreader bar to
prevent damage. In case the motor ships separate use the
eyebolts or lifting lugs found on the motor to hoist it into
place on the sub-base.
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION CHECKLIST
AF (42-66) IOM 13
Page 14

THIS PAGE
INTENTIONALLY
LEFT BLANK
14 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 15
Equipment that will operate in a potentially
accordance with the following instructions.
All equipment being installed must be
maintenance purposes.
3
INSTALLATION
PREPARATION FOR INSTALLATION ........................................................ 15
LOCATION/FOUNDATION .......................................................................... 15
SUB-BASE LEVELING ................................................................................ 16
CONNECTION OF PIPI NG .......................................................................... 19
PIPE HUNG INSTALLATION ....................................................................... 21
DRIVE ALIGNMENT PROCEDURES .......................................................... 22
IMPELLER ALIGNMENT ............................................................................. 27
ROTATION CHECK ..................................................................................... 29
PREPARATION FOR INSTALLATION
AF units are usually shipped completely assembled.
Check all bolts and nuts on the entire unit and make
sure they are securely tightened. If necessary, install
and adjust drive components per manufacturer’s
recommendations
explosive environment must be installed in
properly grounded to prevent unexpected
static electric discharge. If not, a static
electric discharge may occur when the pump
is drained and disassembled for
AF pump shall be located in a clean, dry area free from
flooding. The area should provide adequate space for
operation, maintenance, inspection and repair,
considering complete disassembly and handling of
equipment. The pump should have a supply of clean
liquid for packing or mechanical seal lubrication. The
pump should be positioned to provide the most efficient
pipeline system.
The AF pumps covered by these instructions may be
designed to hang in the piping system, furnished with
spring loaded sub-base bolts, or have a sub-base
designed to be anchor bolted and grouted to the
foundation.
The foundation must be substantial enough to absorb
any vibration and form a permanent, rigid support for the
pumping unit to the degree that there shall not be any
adverse movement or settling over a long period of time.
Foundations for anchor bolted and grouted sub-bases
are typically concrete with anchor bolts cast in to secure
the pump.
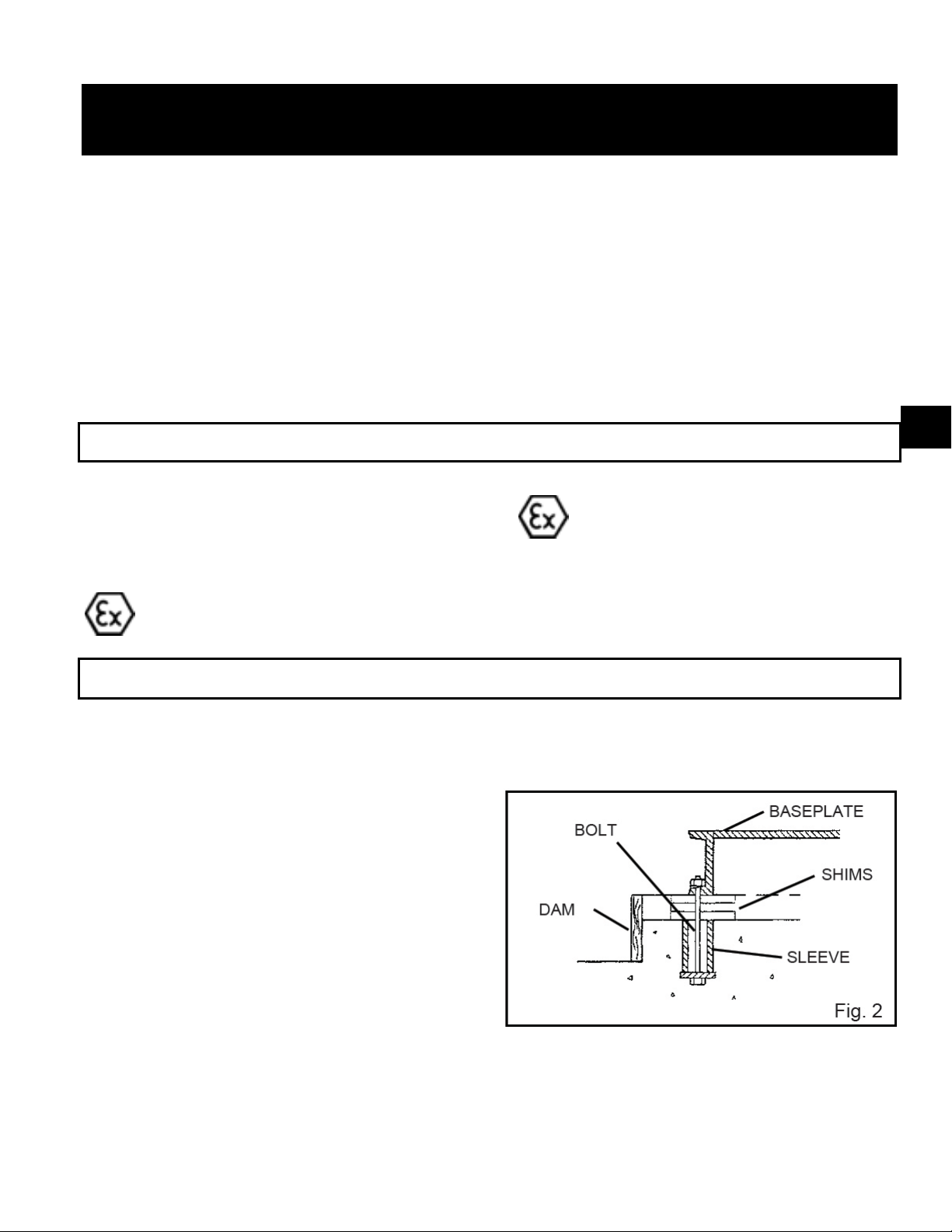
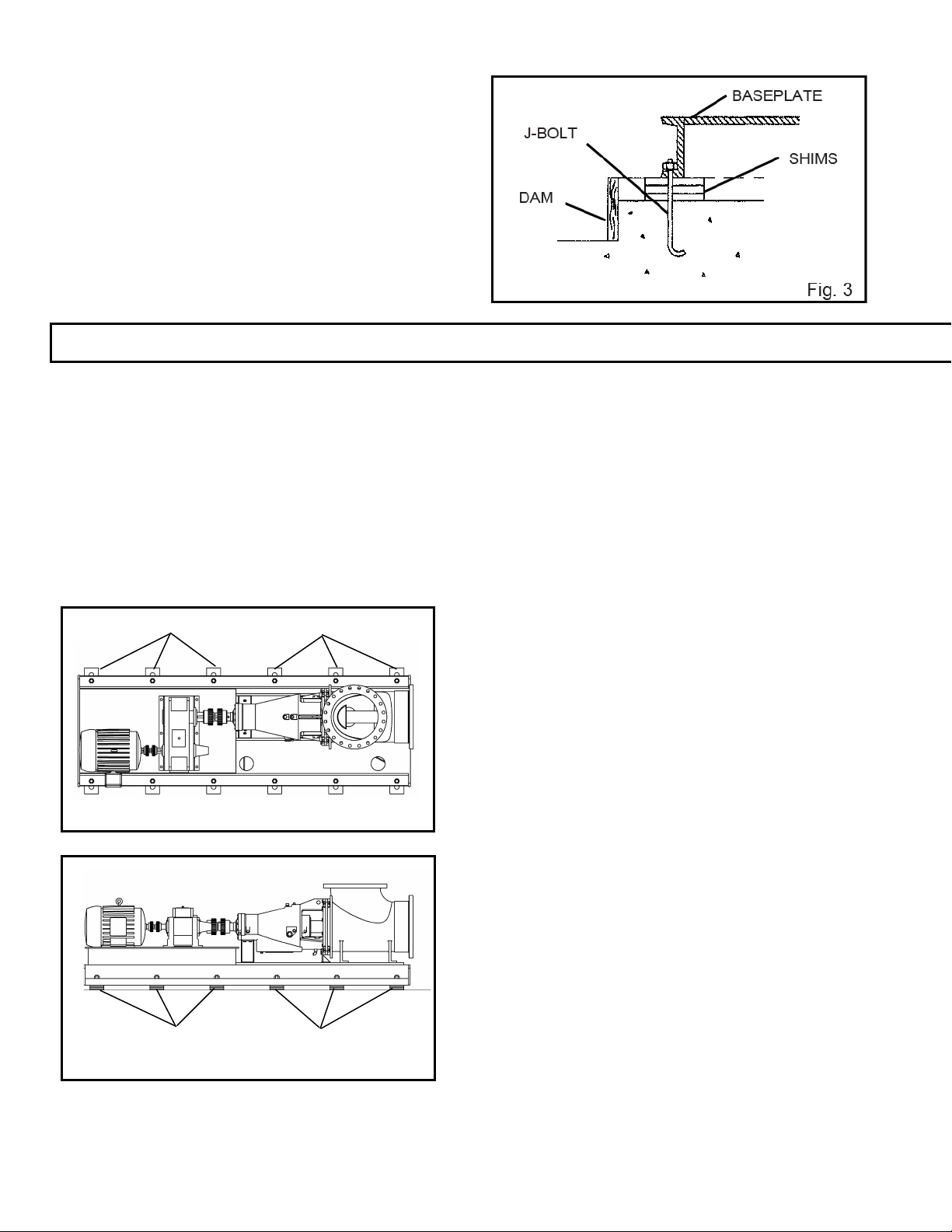
LOCATION/FOUNDATION
The most commonly used foundation bolts are the
sleeve-type (Fig 2 and J type Fig. 3)
AF (42-66) IOM 15
Page 16
SHIMS OR WEDGES
SHIMS OR WEDGES
Both designs permit movement for final bolt
adjustment. Anchor bolts should be located in the
concrete by a template dimensioned from the pump
installation drawing. The top of the sleeve-type bolt
should be temporarily sealed with waste material to
prevent concrete from entering during the concrete
pouring operation. Foundation bolts are located
according to the bolt hole dimensions shown on the
installation drawing. Bolt size is based on hole size,
they should be 1/8” to ¼” under the sub-base hole size.
For information on spring mounted sub-bases, see the
following section under spring mounted bases.
SUB-BASE LEVELING
GROUTED BASE
When the unit is received with the pump and driver
mounted to the sub-base, it should be placed on the
foundation and the coupling halves or V-belts
disconnected (Fig. 4). The coupling should not be
reconnected until all realignment operations have been
completed. A recommended coupling alignment
procedure is included in the following sections.
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
1. The sub-base should be supported on rectangular
metal blocks or on metal wedges having a slight
taper. There should be support blocks or wedges
on both sides of each foundation bolt. A gap of
about 3/4" to 1-1/2' should be allowed between the
sub-base and the foundation for grouting (Fig. 5).
2. Adjust the metal supports or wedges until the
shafts of the pump and driver and sub-base are
level. Check the coupling faces, as well as the
suction and discharge flanges of the pump, for
horizontal and vertical position by means of a level.
Check also for any internal rubbing in the pump.
Correct, if necessary, by adjusting the supports or
wedges under the sub-base as required. In most
cases, factory alignment will be regained by
shimming under the sub-base alone. Provisions
must be made to support the discharge piping
independently from the pump to prevent excessive
loads and maintain pump-driver alignment.
3. The sub-base should be level to within .125 in. (3
mm) over the length of the base and .0875 in. (1.5
mm) over the width of the base. Bases anchored
with conventional foundation bolts use shims on
both sides of the anchor bolts to level the base.
The bolts which secure the pump sub-base to the
foundation should be 1/8” – 1/4” less in diameter
than the holes in the sub-base (hole size is shown
on the certified installation drawing).
4. Clean outside areas of sub-base that will contact
grout. Do not use oil-based cleaners because
grout will not bond to it. Refer to grout
manufacturer's instructions.
5. Build a dam around foundation and thoroughly wet
the foundation (Fig. 6).
16 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 17
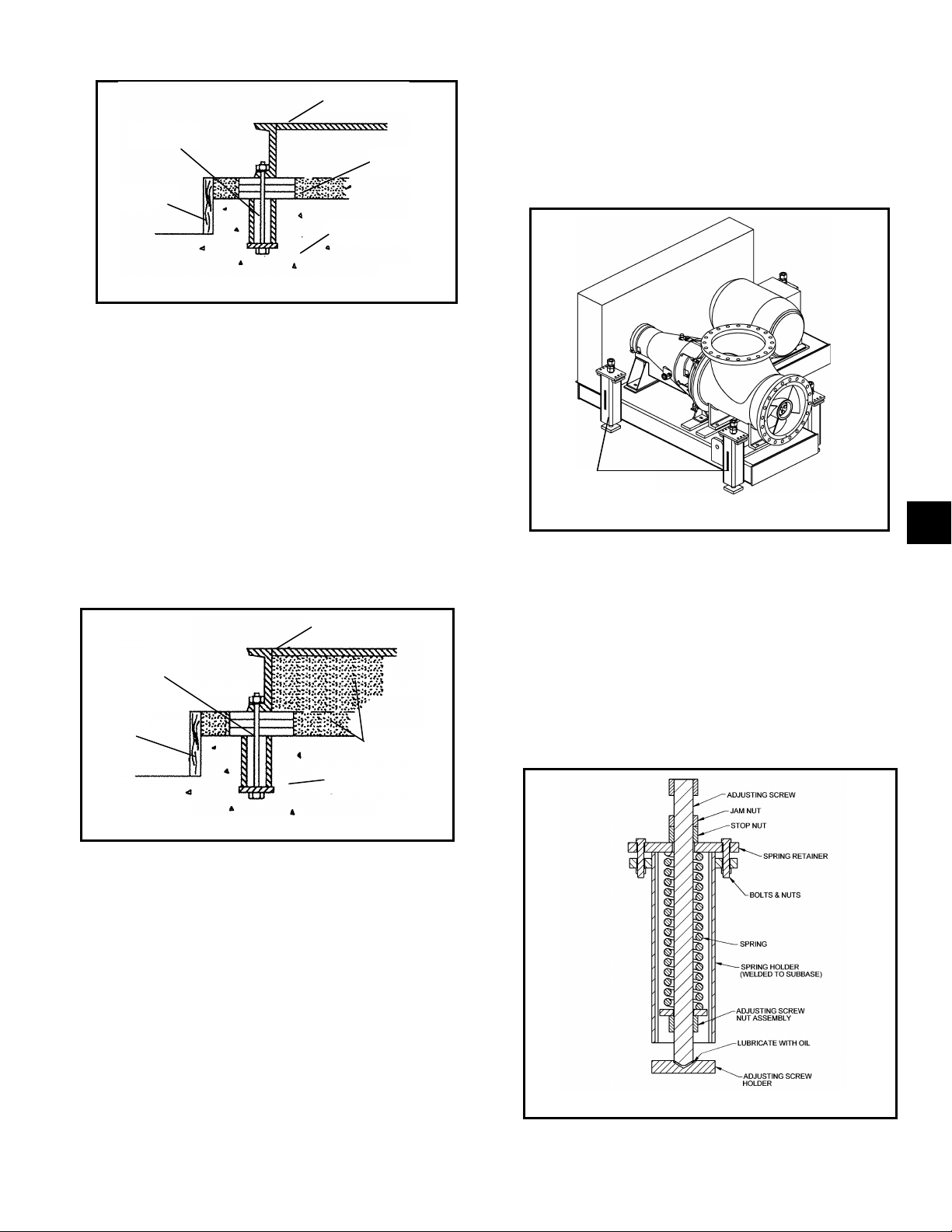
Fig. 10
SPRING
POCKETS
Fig. 8
BOLT
BASEPLATE
GROU
DAM
GROUT
FOUNDATION
Fig. 6
BOLT
BASEPLATE
DAM
GROUT
FOUNDATION
Fig. 7
3
SPRING MOUNTED BASE
Fig. 8 shows a V-belt driven AF pump on a spring
mounted sub-base. Sub-bases supported by spring
pockets assure that the pump remains level,
regardless of vertical movement due to thermal pipe
expansion during operation.
6. Pour grout through the grout holes in the sub-base,
up to level of dam. Remove air bubbles from grout
as it is poured by puddling, using a vibrator, or
pumping the grout into place. Non-shrink grout is
recommended.
7. Allow grout to set.
8. Fill remainder of sub-base with grout. Remove air
as before (Fig. 7)
9. Allow grout to set at least 48 hours.
10. Tighten foundation bolts.
Fig. 8
The following is a brief description of the spring pocket
components and their function (see Fig. 9). The
adjusting screw is used to compress or relax the
spring. Turning the screw causes the adjusting screw
nut assembly to move vertically and change the
amount of force the spring exerts against the spring
retainer, which is fastened to the sub-base. The stop
nut is to limit the vertical up motion of the sub-base in
case part of the load is removed from the pump unit
AF (42-66) IOM 17
Fig. 9
Fig. 9
Page 18
1/16”
FLANGE
BOLTS
BLOCKS
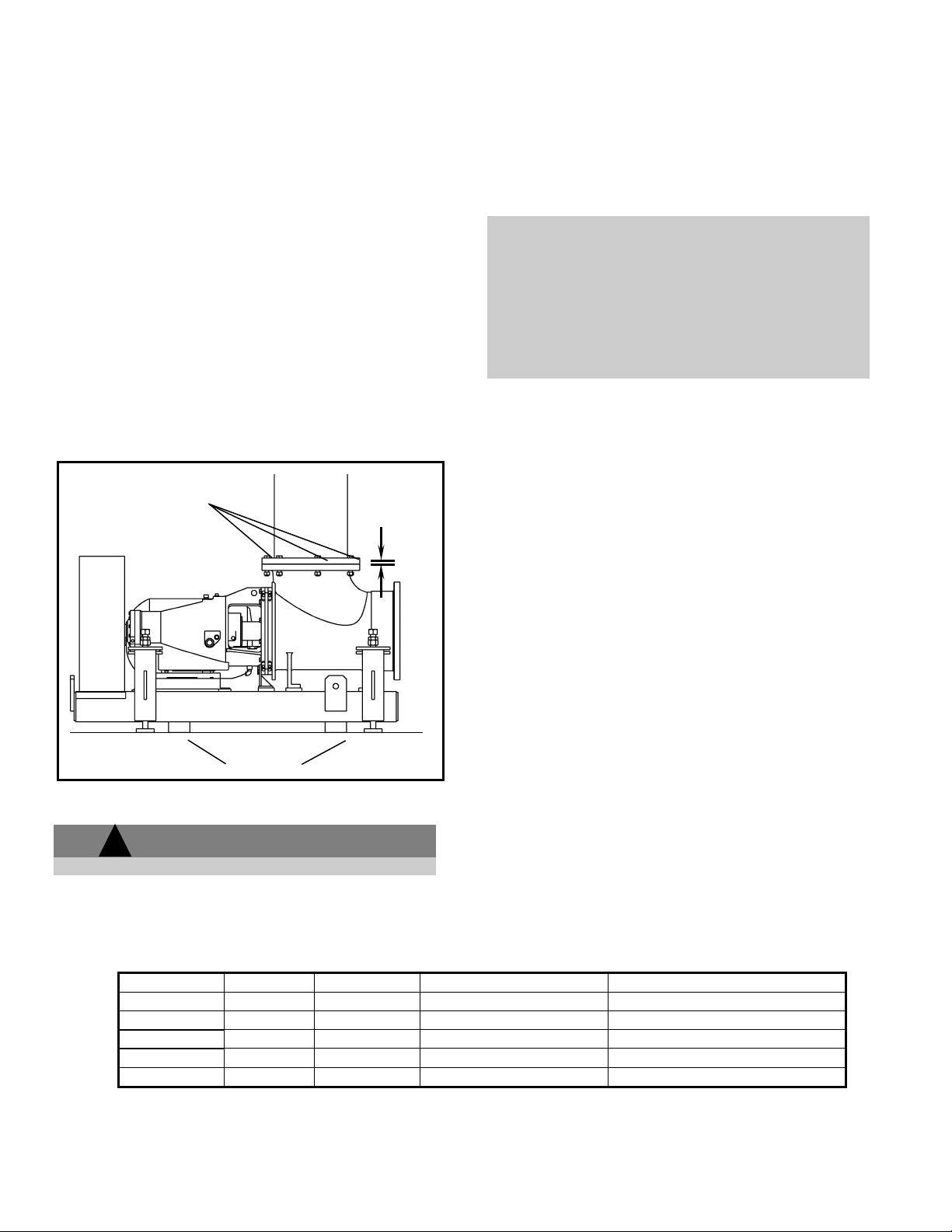
Spring Size
Wire Size
Spring Rate
Adjusting Screw Size
Load Change per Full Turn
1
.812”
1140 #/in.
1-1/2”-6 UNC
190 #
2
.750”
760 #/in.
1-1/2”-6 UNC
127 #
3
.532”
560 #/in.
1-1/2”-6 UNC
93 #
4
1.00”
1000 #/in.
2”-4-1/2 UNC
222 #
5
.375”
133 #/in.
¾”-10 UNC
13 #
Table 1
!
when the system is cold. The jam nut keeps the stop
nut from turning during normal operation when the subbase has been pushed down from the thermal
expansion. The adjusting screw holder is a bearing
surface for the end of the adjusting screw and serves
to hold the end of the screw in a fixed location.
The adjusting screw was lubricated at the factory but
should be re-lubricated with heavy protective grease
during the pump installation. The springs and other
parts should be coated with an agent to protect the
surface from corrosion, and a heavy lubricant should
be applied to the adjusting screw holder pocket.
The following steps are used to set the springs and
level the sub-base:
1. Place blocks under the sub-base, near each spring
holder, and position the sub-base level on the blocks.
A small gap (approx. 1/16" or 1.6 mm) should exist
between the flange of the vertical pipe and the pump
elbow with the gasket in place (Fig. 10).
allow the required horizontal motion without having the
adjusting screw nut assembly hit the walls of the spring
holder. Make sure there is sufficient clearance
between the adjusting screw holder and the bottom of
the sub-base for vertical thermal expansion, this
clearance is usually shown on the pump installation
drawing.
NOTE: Each spring carries a share of the unit load
but generally do not carry equal loads. Each
holder has a small "window” to check the spring
coil spacing, which is an indication of the relative
load on the spring. The ins tallation drawing may
indicate the approximate number of turns required
for each spring loca tion, especially if the unit uses
more than (4) springs. If necessary refer to table 1
for spring rate information.
4. Turn the adjusting screws until the bottom of the
sub-base just clears each block. Next adjust each
screw evenly until the pump flange and gasket are less
than 1/32” (0.8 mm) away from the pipe flange.
Careful adjustment is necessary to keep the pump
level and obtain better weight distribution on the
springs. After the springs have been loaded and
adjusted, the base should be off the support blocks
and level.
5. Check the alignment of the impeller and the pump
elbow. If necessary, correct the alignment by adjusting
the springs or by using shims.
NOTE: If the flange gap is over 1/32” (0.8 mm), turn
the adjusting screws a uniform amount to close the
gap. For a gap of 1/32” (0.8 mm) or less, omit this
step.
Fig. 10
2. Install several flange bolts to help maintain
alignment of the flanges.
6. Tighten the vertical pipe flange bolts, recheck the
alignment and connect the horizontal pipe flange to the
elbow. The pump unit should be level and there
should not be any rubbing of the impeller in the elbow
when the shaft is turned by hand.
WARNING
Do not tighten bolts.
3. Position the adjusting screw holders, while the
adjusting screw end is seated in the hole, in the
direction of the horizontal thermal expansion. This will
18 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 19
Never draw piping into place by
damage to the equipment.
3
!
7. Run each stop nut down to make light contact with
the spring retainer. Lock in place by turning the
jam nut down tight against the stop nut.
8. Inspect each spring holder to check the gap
between the coils of the spring. There must be
enough total gap to accommodate the downward
thermal expansion of the system without having
them compressed solid.
NOTE: Pumps with oil lubrication should be
checked for oil level while thermal expansion is
taking place. It may be necessary to add oil to the
bearing housing to provide the proper oil level to
the higher bearing. A line parallel with the subbase deck through the pr o p er oil level line will
show the correct level at the highest end of the
bearing housing. A hori zontal line back from that
point will establish the proper level mark on the
sight gauge.
The system should be operated at normal temperature
before the adjusting screw holders are grouted in
place. Some customers operate their units with the
adjusting screw holders ungrouted.
If it becomes necessary to remove a spring assembly
from a spring pocket, for safety the following steps
should be strictly adhered to:
1. Make sure the spring is relaxed. If the spring
cannot be relaxed with the adjusting screw, the safest
method is to pry off the Plexiglas cover and cut the
coils using a torch.
2. Remove the bolts or cap screws, which fasten
the spring retainer to the holder and lift out the entire
assembly.
3. When the pump is connected to the system and
a spring is removed, there should be support under the
sub-base near the spring location until the spring has
been replaced and adjusted. Distortion of the subbase will affect the pump alignment, and the weight of
the components is more likely to cause distortion when
the pump is connected to the rigid pipe system.
4. If a spring is replaced while the system is hot,
the stop nut should not be set until the system is cold.
The springs must be allowed to push the base back to
its cold position.
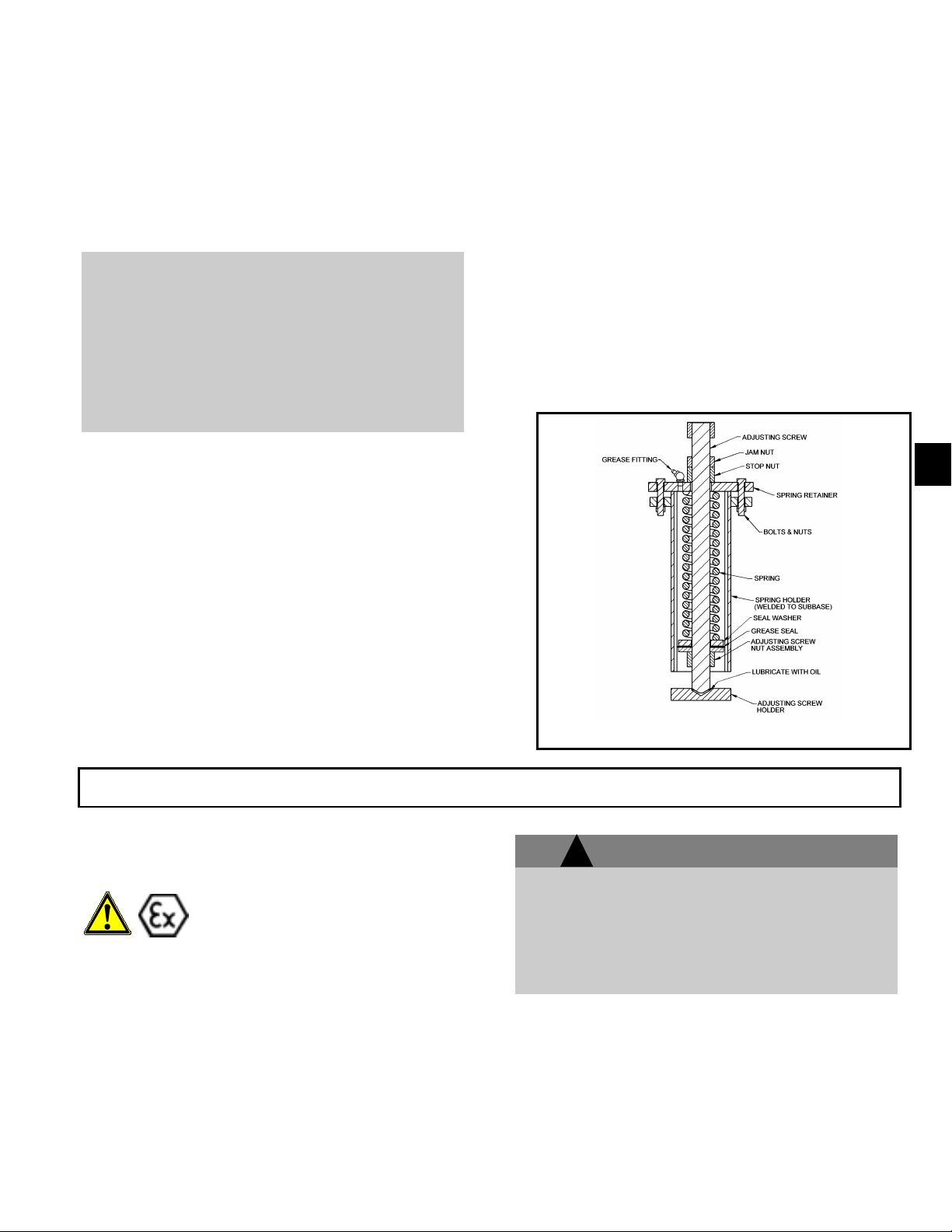
An optional grease filled spring pocket is shown in
figure 11. The difference between the standard pocket
and the grease filled pocket is the addition of a grease
fitting and grease seal. Adjustment and setting of the
grease filled pocket are identical.
Fig. 11
GENERAL
forcing at the flanged connections of
the pump. This may impose
dangerous strains on the unit and
cause misalignment between pump
and driver. Pipe strain will adversely
effect the operation of the pump
resulting in physical injury and
Guidelines for piping are given in the “Hydraulic
Institutes Standards” available from: Hydraulic
Institute, 30200 Detroit Road, Cleveland OH 441451967 and must be reviewed prior to pump installation.
AF (42-66) IOM 19
CONNECTION OF PIPI NG
WARNING
Never draw piping into place by forcing at the
flanged connections of the pump. This may
impose dangerous strains on the unit and cause
misalignment between the pu m p and driver. Pipe
strain will adversely affect the operation of the
pump resulting in physical injury and damage to
the equipment.
1. All piping must be supported independently of, and
line up with the pump flanges.
2. Piping runs should be as short as possible to
minimize friction losses
Page 20

!
3. DO NOT connect piping to the pump until the
pump and driver hold-down bolts have been
tightened.
4. It is suggested that expansion loops or joints be
properly installed in suction and /or discharge lines
when handling liquids at elevated temperatures, so
linear expansion of piping will not draw pump out
of alignment.
5. The piping should be arranged to allow pump
flushing prior to removal of the unit on services
handling corrosive liquids.
6. Carefully clean all pipe parts, valves and fittings,
and pump branches prior to assembly.
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE P IPING
WARNING
NPSHA must always exceed NPSHR as shown on
Goulds performance curves received with order.
(Reference Hydraulic Institute for NPSH and pipe
friction values needed to evaluate suction piping
Properly installed suction piping is a necessity for
trouble-free pump operation. Suction piping should be
flushed BEFORE connection to the pump.
1. Use of elbows close to the pump suction flange
should be avoided. There should be a minimum of
2 pipe diameters of straight pipe between the
elbow and suction inlet. Where used, elbows
should be long radius.
2. Use suction pipe one or two sizes larger than the
pump suction, with a reducer at the suction flange.
Suction piping should never be of smaller diameter
than the pump suction.
3. To prevent suction cavitation, horizontal reducers
should be eccentric with the sloping side down and
concentric for vertical applications.
5. Pump must never be throttled on suction side.
7. Separate suction lines are recommended when
more than one pump is operating from the same
source of supply.
Suction lift conditions
1. Suction pipe must be free from air pockets.
2. Suction piping must slope upwards to pump.
3. All joints must be airtight.
Suction head/Flooded suction conditions
1. An isolation valve should be installed in the suction
line at least two pipe diameters from the suction to
permit closing of the line for pump inspection and
maintenance.
2. Keep suction pipe free from air pockets.
3. Piping should be level or slope gradually
downward from the source of supply.
4. No portion of the piping should extend below pump
suction flange.
5. The size of entrance from supply should be one or
two sizes larger than the suction pipe.
6. The suction pipe must be adequately submerged
below the liquid surface to prevent vortices and air
entrainment at the supply.
Discharge piping
1. Isolation and check valves should be installed in
discharge line. Locate the check valve between
isolation valve and pump, this will permit inspection
of the check valve. The isolation valve is required
for priming, regulation of flow, and for inspection
and maintenance of pump. The check valve
prevents pump or seal damage due to reverse flow
through the pump when the driver is turned off.
2. Increasers, if used, should be placed between
pump and check valves.
3. Cushioning devices should be used to protect the
pump from surges and water hammer if quickclosing valves are installed in system.
Final Piping Check
1. Rotate shaft several times by hand to be sure that
there is no binding and all parts are free.
2. Check alignment, per the impeller alignment
procedure outlined on pg. 28 to determine
absence of pipe strain. If pipe strain exists, correct
the piping.
20 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 21

Foundation
Pipe
Shaft
Level Sub-base
be Parallel
be Parallel
level .005”/ft
3
PIPE HUNG INSTALLATION
LOCATION OF UNIT
The pump should be located in a clean, dry area free
from flooding. The area should provide adequate
space for maintenance and repair, considering
complete disassembly and handling of equipment.
The unit should be positioned to provide the most
efficient pipeline system.
PIPING
Short, direct suction and discharge pipelines having a
minimum of elbows and fittings will result in the least
amount of pipe friction. Excessive friction losses will
result in insufficient capacity and cavitation. Future
access to the pump impeller and shaft will require
removal of a section of discharge pipe (spool piece).
NOTE: The horizontal pipe flange must be parallel
with the pump flange before the bolts are
tightened. If the flanges are not parallel, forcing
them parallel by tightening the bolts may put
excessive strain on the pump.
INSTALLATION OF PUMP IN PIPELINE
1. Connect the pump top flange to the vertical
pipe and tighten flange bolts. Level pump
within .005” (0.42 mm)/Meter.
2. Check the impeller clearance in the casing so
that it is reasonably well centered using the
criteria that the minimum gap at the vane.
3. O.D. is at least 50% of the maximum gap (see
the impeller alignment worksheet, pg. 28 for
instructions)
4. Connect the casing flange to the spool piece
and tighten the flange bolts.
INSTALLATION OF THE DRIVER
Install the driver (motor and reduction gear on a
separate sub-base) as indicated on the installation
drawing for the pump. The universal joint drive shaft
requires the gear and pump shafts be parallel within 1
degree but off-set as indicated on the drawing. The
optimal universal joint life is obtained with off-set shaft
angles of 1 to 3 degrees.
Level the driver base relative to the pump, in
accordance with the proceeding paragraph using
leveling wedges adjacent to the anchor bolts. Partially
tighten the anchor bolt nuts and check the shaft
alignment between the motor and reduction gear. If the
alignment is reasonably satisfactory, grout the base in
place.
After the grout has hardened, tighten the anchor bolt
nuts. Check and correct the motor shaft alignment. We
recommend the actual shaft misalignment for the
flexible couplings be considerably less than the
maximum allowed by the coupling manufacturer for
long coupling life and reduced vibration levels.
CONNECTION TO PUMP DRI VER
The pipe hung pump is connected to the driver via a
drive shaft and universal joints at each end. Follow the
drive shaft installation instructions and the angle limits
per the pump installation drawing. An extendable guard
is provided for the drive shaft and should be used any
time the pump driver is rotating.
AF (42-66) IOM 21
Motor
Extendable
Guard
Reduction
Gear
Flanges must
Drive
Shaft Offset
+/- 1 to 3 deg.
Vertical
Spool Piece
Flanges must
Pump must be
Horizontal
Pipe
Fig. 11A
Page 22

injury.
Fig. 12
!
DRIVE ALIGNMENT PROCEDURES
Alignment procedures must be followed to
prevent unintended contact of rotating parts.
Follow coupling manufacturer’s installation and
operation procedures.
WARNING
Before beginning any alignment procedure, make
sure driver power is locked out. Failure to lock out
driver power will result in serious physical injury.
Lock out driver power to prevent electric
shock, accidental start-up and physical
The AF pump comes with two drive variations, V-belt
and gear driven. Accurate alignment of both systems
is essential to long pump life and reduced pump
problems.
The points at which alignment are checked and
adjusted are:
• Initial Alignment is done prior to operation
when the pump and the driver are at ambient
temperature.
• Final Ali g n ment is done after operation when
the pump and driver are at operating temperature.
Alignment is achieved by adding or removing shims
from under the feet of the driver and gearbox and
shifting equipment horizontally by adjusting bolts as
needed.
NOTE: Proper alignment is the responsibility of
the installer and user of the unit.
Trouble free operation can be accomplished by
following these procedures.
Initial Alignment (Cold Alignment)
• Before Grouting Sub-base - To ensure alignment
can be attained. After Grouting Sub-base - To
ensure no changes have occurred during the mounting
process.
• After Spring Setting – To ensure no changes
have occurred during the leveling process.
After Connecting Piping - To ensure pipe strains
have not altered alignment. If changes have occurred,
alter piping to remove pipe strains on pump flanges.
• Final Ali g n ment (Hot Alignment)
• After First Run - To obtain correct alignment
when both pump and driver are at operating
22 AF (42-66) IOM
temperature. Thereafter, alignment should be
checked periodically in accordance with plant
operating procedures.
NOTE: Alignment check must be made if process
temperature changes , piping changes, and or
pump service is performed.
V-BELT DRIVE (SHEAVES)
Well designed and properly installed V-belt drives are
capable of running for years. AF pumps come in
several different belt drive configurations i.e. side by
side, overhead, underslung or “Z” mount. Installation
and alignment procedures are similar for all
configurations. Remove the guard or guards by
referring to the assembly/disassembly instructions.
There are a few items that should be checked during
installation and alignment.
Sheave Alignment - Alignment must be maintained
for full power transmission, minimum vibration, and
long drive life. A dial indicator can be used to check
runout on the periphery and face of each sheave. A
straight edge can be used to check parallel and
angular alignment of the pump and drive sheaves, see
Fig. 12.
Belt Installation - When installing new belts, shorten
center distance between sheaves so that belts can be
placed on the sheave without the use of force. Never
'roll' or "Pry" the belts into place, as this could damage
the belt cords.
Page 23

!
3
1. Check Belt Fit - Regardless of the belt section
used, the belt should never be allowed to bottom
in the groove. This will cause the belts to lose
their wedging action and slippage can occur.
Sheaves or belts that permit such a condition to
occur should be changed.
2. Maintain Proper Belt Tension - Proper tension
is essential for long belt life. Improper tension
could cause belt fatigue and/or hot bearings.
3. Impeller Alignment after Belt Tensioning – If
the impeller was aligned prior to belt tensioning a
check should be made to determine that it is still
centered. An off center impeller may rub and
cause unnecessary pump damage. Belt Tension
will usually cause impeller misalignment opposite
the motor. Be sure to align or re-align in
accordance with the Impeller Alignment section
page 26.
The general method of tensioning belts is given
below, and should satisfy most drive requirements.
General Method:
STEP 1. Reduce the center distance so that the belts
may be placed over the sheaves and in the grooves
without forcing them over the sides of the grooves.
Arrange the belts so that both belt spans have a
proximately the same sag between the sheaves.
Apply tension to the belts by increasing the center
distance until the belts are snug, see Fig. 13.
Fig. 13
WARNING
Do not operate the pump without the proper drive
guard in place. Failure to observe this warning
could result in perso n al injury to operating
personnel
STEP 2. Operate the drive a few minutes to seat the
belts in the sheave grooves. Observe the operation of
the drive under its highest load condition (usually
starting). A Slight bowing of the slack side of the drive
indicates proper tension. If the slack side remains
taut during the peak load, the drive is too tight.
Excessive bowing or slippage indicates insufficient
tension. If the belts squeal as the motor begins
operation or at some subsequent peak load, they are
not tight enough to deliver the torque demanded by the
drive machine. The drive should be stopped and the
belts tightened.
STEP 3. Check the tension on a new drive frequently
during the first day by observing the slack side span.
After a few days of operation the belts will seat
themselves in the sheave grooves and it may become
necessary to readjust so that the drive again shows a
slight bow in the slack side.
Other methods of determining proper belt tension can
be obtained from the drive manufacturer.
5. Use Belt Guards - Belt guards protect personnel
from danger and the drive from contamination.
Inspect periodically to assure that belts do not rub
against guard.
6. Keep Belts Clean - Dirt and grease reduce belt life.
An occasional wiping with a dry cloth to remove any
build-up of a foreign material can extend the life of
the belt. Should oil or grease splatter onto the
belts, clean with soap and water.
Belt dressing affects performance only temporarily and
is never recommended. Maintaining a clean drive is a
better practice.
If any questions arise pertaining to the drive limitations,
consult the manufacturer.
GEAR DRIVE (COUPLINGS)
The coupling used in an ATEX classified
environment must be properly certified.
Remove the guard or guards by referring to the
assembly/disassembly instructions. Disconnect
motor/gearbox and the pump/gearbox coupling halves
before proceeding with the alignment. First, align the
pump/gearbox coupling then the motor/gearbox
coupling. Check both coupling connections for parallel
and angular alignment by either the Dial Indicator or
Straight-Edge Method outlined below.
Good alignment is achieved when the dial indicator
readings, for both parallel and angular misalignment,
are .003" (.076mm) Total Indicated Reading (T.I.R.) or
less when the pump and driver are at operating
temperature (Final Alignment). Fig. 14 describes what
to look for.
AF (42-66) IOM 23
Page 24

Fig. 14
1. Mount two dial indicators off one half of the
coupling (X) so they contact the other coupling half (Y)
(Fig. 15).
Fig. 15
2. Check setting of indicators by rotating coupling
half (X) to ensure indicators stay in contact with
coupling half (Y) but do not bottom out. Adjust
indicators accordingly.
MEASUREMENT
3. To ensure accuracy of indicator readings, always
rotate both coupling halves together so indicators
contact the same point on coupling half (Y). This will
eliminate any measurement problems due to runout
on coupling half (Y).
4. Take indicator measurements with hold-down bolts
tightened. Loosen hold down bolts prior to making
alignment corrections.
5. Take care not to damage indicators when moving
driver during alignment corrections.
Keep this instruction manual handy for reference.
Further information can be obtained by contacting
Goulds Pumps, 240 Fall St., Seneca Falls, New York
13148 or your local representative.
ALIGNMENT PROCEDURE
On gear driven AF pumps angular and parallel
misalignment are corrected in the vertical direction by
means of shims under the motor or gearbox mounting
feet, and in the horizontal direction by adjusting bolts
that slide the motor or gearbox in the proper direction.
After each adjustment, it is necessary to recheck the
alignment of the coupling halves. Adjustment in one
direction may disturb adjustments already made in
another direction. It should not be necessary to adjust
the pump in any way.
ANGULAR ALIGNMENT
Couplings are in angular alignment when indicator “A“
(Angular Indicator), Fig 15, does not vary by more than
.003” (.076mm) as measured at four points on the
coupling periphery 90° apart at operating temperature.
Outlined below are two acceptable methods to achieve
the desired alignment.
METHOD 1 - Dial Indicator Method
For steps 1 through 5 refer to Fig. 16 on the following
page.
1. Zero indicator “A” at position 1 of coupling half (Y).
Mark this position on both flanges.
2. Rotate both flanges 180° to position 3. Observe
needle and record reading.
3. Negative Reading - The coupling halves are
further apart at position 3 than position 1.
Positive Reading - The coupling halves are closer
at position 3 than position 1.
24 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 25

3
Directions for viewing coupling
View from front end of pump
Fig. 16
4. Correct any misalignment by shimming the under
the motor or gearbox feet to attain the proper
alignment.
When using positions 2 and 4 in steps 1-3, correct
any misalignment by sliding the motor back and forth
to attain the proper alignment.
5. Repeat steps 1-4 substituting position 2 for
position 1 and position 4 for position 3. Use the
same marks made on the coupling from position 1
and be sure to turn the coupling halves together.
METHOD 2 - Feeler Gauge Method
For the following steps refer to Fig. 16.
1. Insert a feeler gauge at position 1 at the periphery
of the couplings. Mark this position on both
flanges.
2. Record the largest gauge size that fits snugly
between the two flanges.
3. Rotate both flanges to position 3 - 180°.
4. Insert a feeler gauge at the periphery of the
couplings at position 3
5. Record the largest gauge size that fits snugly
between the two flanges.
6. Calculate the difference between the readings at
positions 1 and 3. The difference should not be
greater than .003" (.076mm).
7. Correct any misalignment by shimming under the
motor or gearbox feet to attain the proper
alignment.
When using positions 2 and 4 in steps 1 - 6, correct
any misalignment by sliding the motor or gearbox
back and forth to attain the proper alignment.
8. Repeat steps 1-6 substituting positions 2 and 4 for
position 1 and 3 respectively. Use the same marks
made on the coupling from position 1 and be sure
to turn the coupling halves together.
Parallel Alignment
The unit is in parallel alignment when indicator “P”
(Parallel Indicator) does not vary by more than .003”
(.076mm) as measured at four points on the coupling
periphery 90' apart at operating temperature. There are
two methods outlined below that are acceptable to
achieve the desired alignment.
NOTE: Equal amounts of shims must be added to
or removed from eac h d river foot. Otherwise the
vertical angular alignment will be affected.
METHOD I - Dial Indicator Method
For the following steps, refer to Fig. 16.
1. Zero the indicator “P” at position 1 of coupling half
(Y). Mark this position on both flanges.
2. Rotate both flanges 180° to position 3. Observe
needle and record reading.
3. Negative Reading - Coupling half (Y) is shifted
toward position 1.
If the value is greater than .003” (.076mm), correct the
misalignment by evenly (at equal amounts on both
sides) shimming the motor higher.
When using positions 2 and 4 in steps 1 - 2, correct any
misalignment by sliding the motor evenly toward
position 2.
Positive Reading - Coupling half (Y) is shifted
toward position 3.
If the value is greater than .003" (.076mm), correct the
misalignment by evenly (at equal amounts on both
sides) shimming the motor or gearbox lower.
When using positions 2 and 4 in steps 1 - 2, correct any
misalignment by sliding the motor or gearbox evenly
toward position 4.
4. Repeat steps 1-3 until indicator “P” reads .003"
(.076mm) or less.
AF (42-66) IOM 25
Page 26

5. Once the ideal alignment is reached, repeat steps
1-4 substituting position 2 for position 1 and
position 4 for position 3.
METHOD 2 - Straight-Edge Method
For the following steps refer to Fig. 16.
1. Place a straight edge across the two coupling
flanges at position 1 and mark the spot on both
flanges.
2. Adjust the motor or gearbox so that the straightedge rests evenly on both flanges (within .003"
.076mm).
3. Rotate both flanges 90° to positions 2 and repeat
steps one and two.
4. The unit will be in parallel alignment when the
straight edge rests evenly (within .003” .076mm)
on the coupling periphery at both positions along
the periphery.
NOTE: Care must be taken to h ave the straight
edge parallel to the axis of the shafts
Complete Alignment
A unit is in complete alignment when both indicators
“A” (angular) and “P” (parallel) do not vary by more
than .003” (.076 mm) as measured at four points 90°
apart.
Vertical Correction (Top-to-Bottom)
1. Zero indicators “A” and “P” at top dead center (12
o'clock) of coupling half (Y).
2. Rotate indicator to bottom dead center (6 o'clock).
Observe the needles and record the readings.
3. Make corrections as outlined previously.
Horizontal Correction (Side-to-Side)
1. Zero indicators “A” and “P” on the left side of
coupling half (Y), 90° from top dead center (9
o'clock).
2. Rotate indicators through, top dead center to the
right side, 180° from the start (3 o'clock), Observe
the needle, measure and record the reading.
3. Make corrections as outlined previously.
4. Recheck both vertical and horizontal readings to
ensure adjustment of one did not disturb the
other. Correct as necessary.
Factors that may disturb alignment
The unit should be checked periodically for alignment.
If the unit does not stay in line after being properly
installed, the following are possible causes:
1. Settling or spring of the foundation.
2. Wear of bearings.
3. Pipe strains distorting or shifting the machine.
4. Shifting of the sub-base due to heat created from
an adjacent heat source.
5. Shifting of the building structure due to variable
loading or other causes.
6. Loose nuts or bolts on the pump or driver
assembly.
NOTE: With experience, the installer will
understand the interaction between angular and
parallel and will make corrections appropriately.
26 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 27

Improper impeller adjustment could cause
generation.
The impeller clearance setting procedure
heat generation and equipment damage.
3
IMPELLER ALIGNMENT
GENERAL
contact between the rotating and stationary
parts, resulting in a spark and heat
must be followed. Improperly setting the
clearance or not following any of the proper
procedures can result in sparks, unexpected
The AF impeller has been aligned at the factory but
should be checked prior to pump operation. The
impeller requires several thousandths of and inch of
clearance to prevent rubbing due to the action of
hydraulic forces when the pump is operating. Many
corrosion-resistant alloys will gall and build up if
rubbing occurs, therefore, pumps using these alloys
need to be free from any rubbing.
Turn the shaft by hand, if the impeller rubs the inside of
the casing it must be realigned. The following steps
are used to align the impeller.
Note: Impeller rubbing is often caused by pipe
strain or belt tension. Pipe strain must be
eliminated prior to impeller alignment. The
impeller should aligned after proper belt
tensioning.
Clearance measurement - The alignment worksheet
on page 27 is used to align the impeller of the AF
pump. The measurement procedure is as follows:
Make sure the cap screws fastening the casing to the
elbow are tight, so an accurate measurement of the
impeller clearances can be made prior to adjustment.
Mark each blade 1, 2, 3 and 4 and then align the
impeller blades as shown on the impeller alignment
worksheet (approx. 2, 4, 8, and 10 o’clock)
Rotate the shaft and measure the gap between each
blade and the casing at all four clock positions
indicated on the worksheet. The value of interest is
the largest value of feeler gage thickness that will slide
easily the whole length of the vane tip.
Add the measurements for all positions together and
divide by the number of measurements. This will give
the average measurement.
Divide the average measurement by 2. This will give
the minimum clearance.
If any blade has a clearance in any position smaller
than the calculated minimum clearance the prop is not
sufficiently centered and should be adjusted.
Impeller Alignment
1. Loosen the bolts that attach the casing to the
elbow.
2. Use the adjusting bolts attached to the elbow to
adjust the impeller clearance. The adjusting bolts
are used to raise and lower the casing and shift the
casing left to right relative to the impeller.
3. Move the casing relative to the impeller until the
impeller is centered. At this point it is
recommended that the Impeller Alignment
Worksheet (on the following page) be filled out and
filed with the pump maintenance records for future
reference.
4. Tighten the bolts between the casing and the
elbow and re-check the clearance to be sure the
adjustments have centered the impeller. If the
impeller is centered the casing may be taper
pinned to the elbow to maintain alignment.
AF (42-66) IOM 27
Page 28

(1.16 mm )
(0.58 mm )
28 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 29

When installing in a potentially explosive
properly certified.
3
ROTATION CHECK
Before the V-belts or couplings are installed, the
motor should be wired and the direction of rotation
checked. A rotation arrow is located on the
bearing housing (134C).
Serious damage could occur if the pump is run the
wrong direction.
environment, ensure that the motor is
AF (42-66) IOM 29
Page 30

THIS PAGE
INTENTIONALLY
LEFT BLANK
30 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 31

When installing in a potentially explosive
properly certified.
The coupling guard used in an ATEX
from a non-sparking material.
4
!
!
OPERATION
PREPARATION FOR OPERATION ............................................................. 31
STARTING THE PUMP ............................................................................... 35
OPERATION ................................................................................................ 36
SHUTDOWN ................................................................................................ 37
FINAL ALIGNMENT .................................................................................... 38
PREPARATION FOR OPERATION
CHECKING ROTATIO N
environment, ensure that the motor is
Damage occurs
from:
1. Increased vibration levels-affects bearings, stuffing
box or seal chamber and mechanical seal
2. Increased radial loads Stresses on shaft and
bearings
3. Heat build up-Vaporization causing rotating parts to
score or seize
4. Cavitation-Damage to internal surfaces of pump
CAUTION
Serious damage may result if pump is run in the
wrong direction.
WARNING
Lock out power to prevent accidental start-up and
physical injury.
Serious damage may result if the pump is
run in the wrong direction.
A check must be made to be sure motor rotation
coincides with the pump rotation direction. Depending
on your pump arrangement (V-belt or
gear-drive) use one of the following methods to check
motor rotation.
Direct Connect
1. Lock out power to the driver.
2. Remove the pump coupling guard.
3. Make sure the coupling halves are securely
fastened to shafts.
4. Unlock driver power.
5. Make sure everyone is clear. Jog the driver just
long enough to determine direction of rotation of
the output shaft of the gearbox. Rotation must
correspond to an arrow on bearing housing.
6. Lock out power to driver.
7. Replace the pump coupling guard.
classified environment must be constructed
V-BELT
1. Lock out power to the driver.
2. Remove the V-belt guard.
3. Make sure the sheaves are securely fastened to
shafts.
AF (42-66) IOM 31
Page 32

Bearings must be lubricated properly in
sparks and premature failure.
AXIAL FLOW PUMP
APPROX. OIL VOLUME
Pump Size
Quarts
Liters
42” / 1200mm / 54”
74
70.5
60” / 66”
62
59
Table 2
4. Unlock driver power.
5. Make sure everyone is clear. Jog the driver just
long enough to determine direction of rotation.
Rotation must correspond to an arrow on bearing
housing.
6. Lock out power to driver.
7. Replace the V-belt guard.
CHECK IMPELLER CLEA RANCE
Check impeller clearance before installing the pump.
The impeller mus t not rub when the shaft is turned by
hand, therefore it is recommended that the Impeller
Alignment Worksheet (shown on pg. 27) is filled out
and filed with the pump m aintenance records f or future
reference.
CHECK FOR FREE TURNING
Before the pump is started, rotate the pump by hand to
be sure it turns freely, and does not rub or bind.
BEARINGS
The bearing assembly uses spherical roller bearings to
carry the radial load, and a spherical roller thrust
bearing to carry the axial thrust load from the impeller.
The bearing housing has a horizontal split along the
centerline for ease of assembly and inspection.
Approximate values only. Always fill using sight glass to verify level. Oil level should be at t he center of the sight glass. See comments in this sec tion.
LUBRICATION
The bearing uses oil bath lubrication. Oil lubricated
bearing assemblies are shipped without oil. Oil must be
added to the bearing housing before starting. Remove
the bearing housing breather (113A) and add oil until oil
level is at the center of the sight glass. If the unit has
an external oil lube system, fill the bearing housing and
the reservoir to satisfy the system requirements.
Replace the breather. Table 2.shows the oil volume
required.
order to prevent excess heat generation,
Run the pump for 1 minute to fill the oil galleys and in
and around each bearing. Check the sight glass and
add oil accordingly. Monitor the oil level indicator for
the first 24 hours of operation and maintain fill level.
OIL TYPE
Use an industrial quality lubrication oil such as Mobil
DTE series, Exxon Teresstic, or similar of ISO VG68.
ISO VG46 may be used in ambient temperatures
below 40F.
In any case the operating temperature viscosity must
be a minimum of 150SSU.
An oil with a higher viscosity than required will
increase the bearing operating temperature because
of the extra viscous drag, but never to the point where
the viscosity becomes lower than required from the
increased heat generation. It is therefore better for the
bearings to have an oil that is too heavy rather than
too light.
Change the oil after the first 200 hours of operation.
For normal operating conditions, change the oil at
least four (4) times a year. If the bearing assembly is
exposed to dirty or moist conditions, the oil should be
changed more often.
OIL LEVEL CONTROL
If the level of oil in the bearing housing (134C) is too
high, excessive heat may be generated due to
churning. If the level is too low, excessive heat may be
generated due to inadequate lubrication. A liquid level
switch connected to the oil sump can be used to warn
of a dangerous oil level condition.
Observe the oil level requirements shown on the
assembly drawing furnished with the pump. If
excessive heat is experienced within these levels,
consult the factory. Be sure that the shaft centerline is
horizontal through the bearing housing
NORMAL BEARING TEMPERATURE
The running temperature for a bearing assembly
depends on many factors such as speed, bearing
loads, lubrication, ambient air temperatures, and
condition of bearings. Temperatures higher than the
human hand can tolerate are very satisfactory for
good bearing operation and should not cause any
alarm.
For a given speed and loading, the bearing housing
temperature will stabilize at some temperature, usually
32 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 33

PACKING RINGS
CORRECT
INCORRECT
4
below 200°F., which will be the normal temperature for
temperature, without any change in speed or loading
can mean a lubrication difficulty or the approach of
bearing failure.
INSTALLING A BEARING
Long bearing life is dependent on careful handling of
the bearing when it is out of the housing and during the
installation procedure. Dirt and rough handling are
prime enemies of precision bearings. Bearings should
be pressed, not “hammered” into place. If heat is used
to facilitate the installation, a hot oil bath is the best
method.
THRUST BEARING ORIENTATION
Fig. 20 at the end of this section shows the axial thrust
bearing (112C) in the outboard location. This is used
for top suction pumps.
End suction pumps have the flow and axial thrust in
the opposite direction. Therefore, the complete thrust
bearing assembly is reoriented in the opposite
direction. This does not change the basic disassembly
procedure, other than the sequence of installing the
thrust bearing assembly components on the shaft.
The illustration shows the thrust bearing (112C)
mounted on a sleeve (196). For the other bearing
orientation, the bearing is mounted on an extension of
the spacer (443), eliminating the separate sleeve.
SHAFT SEALING
A packed stuffing box or mechanical seal is used to
seal the AF pump shaft. Both methods are described
below.
PACKED STUFFING BOX
The original equipment packing is a suitable grade for
the service intended. To pack the standard stuffing
box use the following procedure: For the special (6)
ring packing arrangement see the appendix 1.
1. Stuffing box and shaft sleeve must be clean and
free of grit.
2. Form packing over shaft or mandrel of same
diameter. Carefully cut to packing length. Discard
rings cut too short.
3. Pre-form each ring by coiling 1 -1 /2 turns.
the installation.
4. To install packing rings, do not pull straight.
Expand the coil as a coil spring, see Fig 17 for the
correct and incorrect method of installing packing.
Fig. 17
Expand the first coil as shown and insert into stuffing
box. Tamp packing to stuffing box shoulder firmly with
the gland. Note, where the cut is positioned.
5. Install the first lantern ring into the stuffing box.
6. Install the second and third coil as required by
7. Install the second lantern ring into stuffing box,
8. Install the third and fourth coil as required by
9. After packing and lantern rings are properly
10. Turn lubricant supply on, start pump, and adjust
11. Periodic maintenance is absolutely required for all
Packed stuffing boxes are not allowed in an
ATEX classified environment.
Failure to property locate the lantern ring with the
flush port will result in insufficient packing
lubrication.
sectional drawing, staggering the cut 90° to 120°.
carefully noting its proper position on the sectional
drawing.
sectional drawing, staggering the cut 90° to 120°.
installed, insert gland into stuffing box. Tighten
gland nuts finger tight only. The shaft should turn
freely.
the gland as described in Section III-E Stuffing Box
Adjustment.
packed pumps. Normal shaft run-out should be
under .005” to avoid pounding of stuffing box
packing. With excessive shaft run-out, shaft
straightening or replacement is necessary.
AF (42-66) IOM 33
Page 34

The mechanical seal used in an ATEX
certified.
The mechanical seal must always be properly
heat generation and seal failure.
!
GLAND ADJUSTMENT
Adjust the stuffing box if packing is used. When the
pump is first started, there should be considerable
leakage by the gland to cool the packing. Gradually
tighten the gland nuts on flat at a time while observing
the leakage and stuffing box temperature. Packing
requires time to “run-in” and extra coolant (leakage)
while it is being “run-in”. If the leakage is reduced too
quickly, the packing will overheat and may be destroyed.
The shaft sleeve may also be damaged.
LEAKAGE
Normal leakage for a properly adjusted box,
depending on shaft size and speed, varies
from a few drops a second to a small trickle
out of the gland.
MECHANICAL SEAL
classified environment must be properly
through the seal gland. Clear, grit-free liquid is
necessary. Goulds Pumps strongly recommends the
stocking of replacement sealing elements.
WARNING
Do not make shaft adjustments on mechanical seal
installations without consulting seal instructions and the
pump assembly drawing. Damage to the mechanical
seal may result.
Dynamic seals are not allowed in an ATEX
classified environment.
flushed. Failure to do so will result in excess
Most mechanical seals are installed and adjusted at the
factory. A common seal type used on the AF pump is
the cartridge type. Cartridge seals are preset at the seal
manufacturer’s facility and require no field settings. Due
to size and design, some installed mechanical seals are
supplied with holding clips. These clips keep the sealing
faces apart to avoid damage during transport. The clips
must be removed before the shaft is to be rotated.
Pumps with retained seal faces will be specifically
marked and instructions from the seal manufacturer for
clip removal will be provided.
If the seal has been installed in the pump at the Goulds
factory, these clips have already been removed. For
other types of mechanical seals, refer to the seal
manufacturer’s instructions for installation and setting.
Mechanical seals have a stationary and a rotating
sealing face. Commonly, these sealing rings are of
carbon and ceramic material, brittle in nature, and easily
damaged. As the sealing rings seat with the operation of
the pump, a compatible wear pattern develops between
the mating surfaces.
To disassemble the mechanical seal after the wear
pattern is established would necessitate the replacement
of the rotating element and stationary sealing elements.
Do not replace only one component.
To insure the life and sealing characteristics of the
mechanical seal, lubricating liquid must be circulated
34 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 35

When starting pump, immediately observe
.
4
!
!
STARTING THE PUMP
PRIMING PUMP
Pumps that are not self-priming must be fully
primed at all times during operation.
Start up Precautions
1. All equipment and personal safety related devices
and controls must be installed and operating properly.
2. To prevent premature pump failure at initial start
up due to dirt or debris in the pipe system, ensure the
system has been adequately cleaned and flushed.
3. Variable speed drivers should be brought to rated
speed as quickly as possible.
4. Variable speed drivers should not be adjusted or
checked for speed governor or overspeed trip settings
while coupled to the pump at initial start up If settings
have not been verified, uncouple the unit and refer to
driver manufacturers instructions for assistance.
5. Pumpage tempartatures in excess of 200°F will
require warmup of pump prior to operation. Circulate a
small amount of pumpage throught the pump until the
casing temperature is within 100°F of the pumpage
temperature and evenly heated.
pressure gauges. If discharge pressure is
not quickly attained, stop driver, re-prime and
attempt to restart
6. Never start the pump until it has been properly
primed. Check the pump impeller for submergence.
The pump must be full of liquid with specified
submergence head above the impeller. Do not run the
pump dry, as this might damage pump and seal
components.
7. Lubricating liquid must be flowing to the stuffing
box before pump is started.
FLUSH FLOWS
Packing or mechanical seals are used to seal the
rotating shaft. Generally, a clear liquid such as water
is used to lubricate and cool the sealing elements. The
lubricating liquid pressure must be 10 -15 psi higher
than the pressure inside the elbow to prevent pumpage
from entering the sealing elements. The lubricating
liquid must be clean and free of grit. Shaft scoring,
packing destruction, and mechanical seal face damage
will result from contaminated lubricant.
The stuffing box may be on the suction or the
discharge side of the impeller, depending on the
direction of flow through the elbow ordered by the
customer. If the pressure inside the elbow is unknown,
it should be measured with a pressure gauge when the
pump is operating. The standard stuffing box is
furnished with (2) N.P.T. holes for piping the lubricating
liquid. The lubricating liquid is piped into one of them.
Some users simply plug the other hole. For additional
cooling of the sealing elements, an outlet pipe with a
valve can be installed to allow more liquid to flow
through the stuffing box.
For special (6) row packing arrangement see appendix
1 at the end of this manual for flush pressures and flow
rates.
(Mechanical seals have no leakage and usually require
a lubricant flow through the stuffing box for cooling).
The lubricating flow should be regulated by the valve in
the outlet pipe rather than by throttling the flow in the
supply pipe.
DRIVER
Start driver.
CAUTION
Immediately observe pressure gauges. If discharge
pressure is not quickly attained-stop driver, check
submergence level and attempt to restart
SET DESIRED FLOW
If your system is equipped with a variable frequency
drive (VFD) or a variable speed V-belt drive, you may
at this point want to set your speed for the desired flow.
CAUTION
Observe pump for vibration levels, bearing
temperature and excessive noise. If normal levels are
exceeded shut down and resolve.
AF (42-66) IOM 35
Page 36

Service temperature in an ATEX classified
ATEX identification section.
Do not operate pump below
pump failure and physical injury.
Observe pump for vibration levels,
shut down and resolve.
recirculation.
Always vary capacity with regulating
curves received with order.
!
OPERATION
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
environment is limited by the table in the
minimum rated flows or with suction
and/or discharge valve closed.
These conditions may create an
explosive hazard due to vaporization
of pumpage and can quickly lead to
Reference Hydraulic Institute for NPSH and pipe
friction values needed to evaluate suction piping.
Most axial flow pumps are in evaporator circulation
service and since the evaporator performance and the
amount of product depends on the rate of liquid
circulation, care should be taken to maintain these
pumps in good operating condition.
bearing temperature and excessive
noise. If normal levels are exceeded,
Always operate the pump at or near
the rated conditions to prevent
damage resulting form cavitation or
valve in the discharge line. NEVER
throttle flow from the suction side.
Pump must never be throttled on
suction side.
NPSHa must always exceed NPSHr
as shown on Goulds performane
When production drops off, it is usually due to lower
circulation rate. An approximation of this rate can be
made by several methods:
• Temperature drop across the heat exchanger.
• Visual inspection of flow in evaporator body.
• Testing the circulating pump.
Items (1) and (2) above are covered by the evaporator
manufacturer.
While field conditions preclude absolute accuracy, a
check of pump performance will give reasonably close
results. This can be done by installing a mercury
manometer at pipe taps located at least-one pipe
diameter away from the suction and discharge flanges
of the pump. If-gauges are used, the pressure
differential times 2.31 divided by the specific gravity of
the slurry indicates the TDH against which the pump is
actually operating. If a manometer is used, then
inches of mercury times 1.0455 divided by specific
gravity equals TDH, providing water is in both legs of
the manometer and connecting lines.
Check the pump speed and determine flow rate (gpm)
from the pump curve. This curve will also give
efficiency from which the hp requirement can be
determined. A double check is to take motor ammeter
readings, convert to hp, figure 90% drive efficiency,
and use it against the pump curve to get GPM. This is
only an approximate check, as the hp curve on some
applications is rather flat, but is probably within 7-1/2%.
It is important to take and record these readings when
the equipment is new, so that later readings can be
judged on a relative basis.
OPERATING AT REDUCED CAPACITY
WARNING
DO NOT operate pump below minimum rated flows
or with a discharge valve closed. This condition
may create an explosive hazard due to
vaporization of pumpage and can quickly lead to
pump failure and physic al injury.
Driver may overload if the pumpage
specific gravity (density) is greater
than originally assumed, or the rated
flow rate is exceeded.
36 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 37

4
Listed below are some causes for circulation loss.
Keep in mind that operation at reduced capacities can
cause damage to the pump.
1. Increase in TDH against which pump operates
could be caused by:
a) Heat exchanger tubes partially plugged.
b) Too many heat exchanger tubes blanked off.
c) Improperly sized or partially plugged strainer.
2. Viscosity of slurry higher than it should be.
3. Pump speed low. V-belt drive may be slipping and
operating pump below design speed.
4. Pump throttled on suction side. This could be
caused by:
a) rubber lining pulling away from the suction pipe
and partially collapsing,
b) large solids dropping into the suction, or
c) by an improperly sized or-plugged strainer in
the suction pipe.
5. Pump partially plugged by large solid jammed
between two impeller blades. This will also cause
rough operation with excessive vibration.
6. Incorrect pump rotation. When changing motors
for any reason or after any electrical system
changes or modifications, always check motors for
correct direction of rotation.
7. Worn pump impeller and/or casing. On a new
pump, clearance between tip of impeller blade and
casing is carefully determined. As this clearance
increases, pump performance decreases.
It is not practical to predict performance at any given
clearance without running a test at this clearance. On
small pumps, this effect is magnified as the
percentage of impeller blade area lost from wear and
corrosion is higher.
Other pump conditions and possible causes
are:
HIGH HP DEMAND
1. Increased head or viscosity
2. Pump speed too high
3. Specific-gravity of slurry higher-than normal
4. Packing gland pulled up too tight
5. Impeller rubbing in casing
NOISY OR ROUGH OPERATION
1. Throttled suction or plugging
2. Impeller rubbing in casing
DAMAGE OCCURS FROM:
1. Increased vibration levels - Affects bearings,
stuffing box seal chamber, and mechanical seals.
2. Heat build up - Vaporization causing rotating parts
to score or seize.
3. Cavitation - Damage to internal surfaces of pump.
4. Loose impeller
5. Broken impeller blade
6. Bearings not properly lubricated
7. Bent shaft
8. Impeller out of balance.
Operating under freezing conditions
Exposure to freezing conditions, while pump is idle,
could cause liquid to freeze and damage the pump.
Liquid inside pump should be drained.
AF (42-66) IOM 37
Page 38

!
SHUTDOWN
1. Turn off power to pump motor.
2. In case of necessary maintenance or pump
inspection, lock driver to prevent accidental rotation.
FINAL ALIGNMENT
1. Run the pump under ac tual conditions for a sufficient
length of time to bring the pump and driver up to
operating temperature.
WARNING
When handling hazardous and/or toxic fluids, skin
and eye protection are required. If pump is being
drained, precautio n s must be taken to prevent
physical injury. Pumpage must be handled and
disposed of in conformance with applicable
environmental regul ation.
2. Check alignment per alignment procedure
outlined earlier.
38 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 39

The preventive maintenance section must
classification for the equipment.
Inspection intervals should be shortened
classified as potentially explosive.
applicable environment regulations.
5
PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
GENERAL COMMENTS .............................................................................. 39
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE ...................................................................... 39
MAINTENANCE OF BEARINGS ................................................................. 40
MAINTENANCE OF SHAFT SEALS ........................................................... 41
PUMP TROUBLE SHOOTING ................................................................ 43-44
GENERAL COMMENTS
A routine maintenance progr am can extend the life of your pump. Well
maintained equipment w ill last longer and require fewer repairs. You should ke ep
maintenance records, this will help pinpoint cause s of problems.
Condition Monitoring
For additional safety precautions, and where noted in this manual, condition monitoring devices should
be used.
This includes, but is not limited to:
• Pressure gauges
• Flow meters
• Level indicators
• Motor load readings
For assistance in selecting the proper instrumentation and its use, please contact your ITT/Goulds representative.
• Temperature detectors
• Bearing monitors
• Leak detectors
• PumpSmart control system
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
be adhered to in order to keep the
applicable ATEX classification of the
equipment. Failure to follow these
procedures will void the ATEX
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
• Bearing lubrication
• Seal monitoring
• Vibration analysis
• Discharge pressure
• Temperature monitoring
appropriately if the pumpage is abrasive
and/or corrosive, or if the environment is
When handling hazardous and / or
toxic fluids, proper personal protective
equipment should be worn. If pump is
being drained, precautions must be
taken to prevent physical injury.
Pumpage must be handled and
disposed of in conformance with
AF (42-66) IOM 39
Page 40

and pump seizure.
Throughout this section on bearing
APPROX. OIL VOLUME
Pump Size
Quarts
Litres
42” / 1200mm / 54”
74
70.5
60” / 66”
62
59
Bearings must be lubricated properly in order
and premature failure.
ROUTINE INSPECTIONS
• Check for unusual noise, vibration and bearing
temperatures.
• Inspect pump and piping for leaks
• Check seal chamber/stuffing box leakage
• Packing: Excessive leakage requires adjustment
or possible packing replacement. Refer to page
35 for packing gland adjustment.
• Mechanical Seal: Should be no leakage.
3 MONTH INSPECTIONS
• Check foundation and hold down bolts for
tightness.
• If pump has been idle, check packing. Replace if
necessary.
• If any rubbing noise has been noticed, re-align the
impeller.
• Oil should be changed at least every 3 months
(2000 hrs) or more often if there are any adverse
atmospheric conditions that might contaminate or
break down the oil, or if it is cloudy or
contaminated as seen through the sight glass.
ANNUAL INSPECTIONS
• Check pump capacity, pressure and power. If
pump performance does not satisfy your process
requirements, and process requirements have not
changed, pump should be disassembled,
inspected, and worn parts should be replaced,
otherwise, a system inspection should be done.
Operation of the unit without proper
lubrication will cause bearing failure,
lubrication, different pumpage
temperatures are listed. If the
equipment is ATEX certified and the
listed temperature exceeds the
applicable value shown in the table
under ATEX identification, then that
temperature is not valid. Should this
situation occur, please consult with
your ITT/Goulds representative.
OIL LUBRICATED BEARINGS
Remove the bearing housing breather (113A) and add
oil until oil level is at the center of the sight glass. If the
unit has an external oil lube system, fill the bearing
housing and the reservoir to satisfy the system
requirements. Replace the breather. Table 3. shows
the oil volume required.
MAINTENANCE OF BEARINGS
AXIAL FLOW PUMP
Approximate values only. Always fill using sight glass to verify l evel. Oil level should be at the cent er of the sight glass. See comments in this section.
Table 3
Run the pump for 1 minute to fill the oil galleys and in
and around each bearing. Check the sight glass and
add oil accordingly. Monitor the oil level indicator for
the first 24 hours of operation and maintain fill level.
to prevent excess heat generation, sparks
40 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 41

5
!
OIL TYPE
A good SAE#30 or #40 is usually satisfactory. Consult
a reputable supplier for acceptable substitutes for the
oils mentioned. The viscosity of the oil should be 150
SSU at the operating temperature to prevent
accelerated bearing wear 150° F is the maximum
temperature at which a typical 30 wt. oil will supply the
required viscosity.
For the best results, the minimum oil viscosity should
be maintained as follows:
Operating temp. below 150 °F - SAE 30
Operating temp. 150 - 160 °F - SAE 40
Operating temp. 160 - 180 °F - SAE 50
An oil with a higher viscosity than required will increase
the bearing operating temperature because of the extra
viscous drag, but never to the point where the viscosity
becomes lower than required from the increased heat
generation. It is therefore better for the bearings to
have an oil that is too heavy rather than too light.
Change the oil after the first 200 hours of operation.
For normal operating conditions, change the oil at least
four (4) times a year. If the bearing assembly is
exposed to dirty or moist conditions, the oil should be
changed more often.
OIL LEVEL CONTROL
If the level of oil in the bearing housing (134C) is too
high, excessive heat may be generated due to
churning. If the level is too low, excessive heat may
be generated due to inadequate lubrication. A liquid
level switch connected to the oil sump can be used to
warn of a dangerous oil level condition.
Observe the oil level requirements shown on the
assembly drawing furnished with the pump. If
excessive heat is experienced within these levels,
consult the factory. Be sure that the shaft centerline is
horizontal through the bearing housing.
NORMAL BEARING TEMPERATURE
The running temperature for a bearing assembly
depends on many factors such as speed, bearing
loads, lubrication, ambient air temperatures, and
condition of bearings. Temperatures higher than the
human hand can tolerate are very satisfactory for
good bearing operation and should not cause any
alarm.
For a given speed and loading, the bearing housing
temperature will stabilize at some temperature, usually
below 200°F., which will be the normal temperature for
the installation. Higher temperatures than this normal
temperature, without any change in speed or loading
can mean a lubrication difficulty or the approach of
bearing failure..
MAINTENANCE OF SHAFT SEALS
MECHANICAL SEAL
When mechanical seals are furnished, a
manufacturer’s reference drawing is supplied with the
data package. This drawing should be kept for future
use when performing maintenance and adjusting the
seal. The seal drawing will also specify required flush
liquid attachment points. The seal and all flush piping
must be checked and installed as needed prior to
starting the pump.
AF (42-66) IOM 41
The life of a mechanical seal depends on various
factors such as cleanliness of the liquid handled and
its lubricating properties. Due to the diversity of
operating conditions it is, however, not possible to give
definite indications as to its life.
WARNING
Never operate the pum p without liquid supplied to
the mechanical seal. Running a mechanical seal
dry, even for a few seconds, can cause seal
damage and must be avoided. Physical injury can
occur if the mechanical seal fails.
Page 42

Fig. 19
PACKING RINGS
CORRECT
INCORRECT
PACKED STUFFING BOX
If the axial flow pump has a standard stuffing box to
seal the rotating shaft the packing rings were installed
at the factory, but at some point during the life of the
pump they must be replaced. The following steps are
used to replace the standard packing:
1. Drain the system or isolate the pumpage from the
pump before replacing the packing.
2. Remove the nuts from the gland studs that hold the
gland in place.
3. Use a packing puller remove the first (2) rows of
packing from the box.
4. Use threaded rods or a packing puller to remove
the lantern ring from the box.
5. Use a packing puller remove the second (2) rings
of packing from the box.
6. Use threaded rods or a packing puller to remove
the second lantern ring from the box.
7. Use a packing puller remove the final ring of
packing from the bottom of the box
8. Clean the stuffing box of any grit or build-up. Clean
the shaft sleeve prior to replacing the packing. If the
sleeve is damaged now is the time to replace it.
9. Install the packing and lantern ring in the reverse
order of removal, 1 rings of packing, lantern ring, 2
rings of packing, lantern ring, 2 rings of packing, and
the gland. Firmly seat each ring. Stagger joints in each
ring 90°. Make sure middle of lantern ring lines up with
flush tap in the stuffing box.
10. Die formed packing rings are used when re-
packing a box. Care must be used during their
installation. To install packing, twist the ring sideways
just enough to get it around the shaft. Do not attempt
to pull rings straight out, see Fig. 18.
11. Insert the lantern ring with tapped extractor holes
facing outward from the box, be sure it is aligned with
the flush ports in the stuffing box, see Fig. 19.
12. Install the gland nuts finger tight. Then with the
lubricating supply on and the pump running,
gradually tighten the gland nuts one flat at a time,
while observing the leakage and stuffing box
temperature. Pac king requires time to run-in. Allow a
minimum of ½ hour between adjustments. If the
leakage is reduced quickly, the packing will overheat
and may be destroyed. The shaft sleeve may also
become damaged. T he norm al leakage for a properly
adjusted stuffing box, depending on the shaf t size and
speed, varies from a f ew drops per second to a small
trickle out of the gland.
LABYRINTH SEALS
Labyrinth seals are found on the inboard and outboard
end caps of the bearing housing to prevent
contaminants from entering the bearing housing.
On some older models lip seals were used. These
were assisted by cast slingers that fling contaminant
fluids away prior to reaching the lip seals. Lip seals do
not require any preventative maintenance but should
be replaced during any rebuild operations. They can
be cleaned occasionally from the outside by removing
the slingers.
42 AF (42-66) IOM
Fig. 18
Page 43

Pump Troubleshooting
Impeller clogged with foreign material
Back flush pump or manually clean impeller
Excess air entrapped in liquid
Install vent in piping or eliminate air source
Suction and/or discharge valve closed or clogged
Open valves to remove partially blocked condition
Pump not producing rated flow
Speed (rpm) too low
New drive or gear box to obtain higher pump speed
Instruments give erroneous readings
Check and calibrate instruments, replace if necessary
is accelerated
Analyze pumpage and correct or change pump wet end materials to
harder composition
Packing gland improperly adjusted
Tighten gland nuts
Excessive leakage
125% of BEP
Packing has short life
Pump not assembled correctly
Compare pump assembly to instruction manual
5
CONNECTION OF SEALING LIQUID
If stuffing box pressure is above atmospheric pressure
and the pumpage is clean, normal gland leakage of 4060 drops per minute is usually sufficient to lubricate and
cool packing and sealing liquid is not required.
NOTE: Otherwise an external flush should be used
to lubricate and cool pa cking.
An external sealing liquid is required when:
1. Abrasive particles in the pumpage could score
the shaft sleeve.
2. Stuffing box pressure is below atmospheric
pressure due to pump running when suction
source is under vacuum. Under these
PROBLEM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
Pump not primed or prime lost, liquid level does not completely fill elbow Fill system piping completely so the impeller is submerged
Suction inlet clogged Remove obstructions from pump inlet
NOTE: Most pack ing requires lubrication. Failure
to lubricate packing may shorten the life of the
packing and pump.
conditions, packing will not be cooled and
lubricated and air will be drawn into the pump.
If an outside source of clean compatible liquid
is required,
The pressure should be 15-20 psi
(1.1-1.4 kg/cm
pressure. The piping should be
connected to the stuffing box flush
port inlet.
3. Under extreme temperature and pressure a
pipe should also be connected to the flush
port outlet.
2
) above suction
No liquid delivered or
intermittent flow
Air leak in suction line Test suction piping for leaks
Speed (rpm) too low New drive or gear box to obtain higher pump speed
Insufficient suction head Fill system piping so the liquid level is above the pump impeller centerline
Pump not primed or prime lost, pump does not completely fill elbow Fill system piping completely so the impeller is submerged
or head
Incorrect impeller or impeller diameter Check vane angles and/ or impeller clearances
System head too high Check system curve calculations, reduce system resistance
Pump assembled incorrectly Compare pump assembly to instruction manual
Insufficient NPSH available Increase liquid level or lower pump
Wear of internal wetted parts
Pump assembled incorrectly Compare pump assembly to instruction manual
Higher solids concentration than specifi ed
from stuffing box Worn mechanical seal parts Replace worn parts
Overheating mechanical seal Check lubrication and cooling lines
Shaft sleeve scored Re-machine or replace as required
Pump run off design point
Packing gland not properly adjusted Replace packing and readjust gland as specified in the operating manual
Packing not properly installed Check packing manufacturer's instructions.
Suction and /or discharge valve closed or clogged Open valves to remove shut-off condition
Wrong direction of rotation
Suction piping incorrect Replace or modify suction piping
Insufficient NPSH available Increase liquid level or lower pump
Impeller partly clogged Back flush pump or manually clean impeller
Suction piping incorrect Replace or modify suction piping
Excessive air entrapped in liquid Install vent in piping or eliminate air source
Incorrect rotation Check motor wiring
Worn or broken impeller, bent vanes Inspect and replace if necessary
Chemicals in liquid other than specified
Stuffing box improperly packed Check packing and re-pack box
Shaft/shaft sleeve worn Replace shaft or shaft sleeve if necessary
Change rotation to concur with direction indicated by the arrow on the
bearing housing
Analyze pumpage and correct or change pump wet end materials to suit
pumpage composition
Check head and flow, AF’s should normally be run between 75% and
AF (42-66) IOM 43
Table 3
Page 44

Pump Troubleshooting (Cont’d)
Inadequate lubricant cooling
Check pumpage temperature and add oil cooling system if necessary
a regular basis
Check pump and drive component vibration levels, rebalance coupling if
Impeller out of balance
Check pump vibrations, if necessary rebalance impeller
125% of BEP
Viscosity higher than specified
Analyze pumpage and compare to specified viscosity
Imbalance
Impeller out of balance
Check impeller balance
operation, maintenance manual
necessary
Impeller clearances too tight
Check impeller clearances adjust if necessary
125% of BEP
High rate of mechanical seal
failure
125% of BEP
Check pump and drive component vibration levels, rebalance coupling if
Sub-base not installed correctly
Compare pump sub-base installation to instruction manual
power
Stuffing box packing too tight
Readjust packing. Replace if worn
Rotating parts binding, internal clearances too tight
Check internal wearing parts for proper clearances
PROBLEM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
Lubricant level Be sure the oil level is at center line of sight glass
Improper lubricant Check lubricant for suitability
Not lubricated enough Increase frequency of grease lubrication
Broken or bent impeller vanes Check impeller dimensions and vane layout
Excessive shaft misalignment Check shaft run-out and consult factory
Bearings run hot and or fail on
Coupling out of balance
Suction pressure too high Check liquid levels and static suction pressure
Bearing incorrectly installed Check bearing orientation to sectional drawing
Pump run off design point
Pump and/or driver not secured to sub-base Check fasteners, if loose check alignment and re-tighten
Specific gravity higher than specified Analyze pumpage and compare to specified gravity
Broken or bent impeller or shaft Replace as required
Pump foundation not rigid or sub-base not completely secured Tighten hold down bolts on sub-base Check foundation rigidity
Improper coupling lubrication
Coupling out of balance
Pump operating speed too close to system’s natural frequency Change speed to be +/- 20% of the pumps natural frequency
Pump is noisy or vibrates at
higher than normal levels
Pump run off design point
W or n bearings Replace
Suction or discharge piping not anchored or properly supported Anchor per Hydraulic Institute Strandards Manual recommendation
Suction and/or discharge valve closed or clogged Open valves to remove partially blocked condition
Excessive shaft misalignment Check shaft run-out and consult factory
Insufficient NPSH available Increase liquid level or lower pump
Excessive shaft misalignment Check shaft run-out and consult factory
Impeller out of balance Check pump vibrations, if necessary rebalance impeller
Overheating of seal faces Check flush flow with mfgr’s recommendation, increase if necessary
Pump run off design point
Shaft/shaft sleeve worn Replace shaft or shaft sleeve if necessary
Coupling out of balance
Axial thrust or radial load higher than bearing rating Calculate bearing life for make and model bearing
Improper coupling lubrication
Excessive shaft deflection Check shaft diameter, sag and deflection, consult factory
Lubricant contamination Inspect oil or grease for contaminants
Piping not properly anchored Check to see if excessive pipe strain is being transferred to pump flanges
Pump assembled incorrectly Compare pump assembly to instruction manual
Partly clogged impeller causing
Motor not secure Check motor fasteners
Bearing incorrectly installed Check bearing orientation to sectional drawing
Impeller partly clogged Back flush pump or manually clean impeller
Pump assembled incorrectly Compare pump assembly to instruction manual
Excessive shaft deflection Check shaft diameter, sag and deflection, consult factory
Pump assembled incorrectly Compare pump assembly to instruction manual
Pump is cavitating, insufficient NPSH available System problem, increase liquid level or lower pump
Suction pressure too high Check liquid levels and static suction pressure
Bearing installed incorrectly Check bearing orientation to sectional drawing
Excessive shaft deflection Check shaft diameter, sag and deflection, consult factory
Lack of seal flush to seal faces Check shaft diameter, sag and deflection, consult factory
Incorrect seal installation Check seal materials vs. pumpage to determine compatibility
Pump is run dry Fill system piping completely so the impeller is submerged
Check coupling lubrication schedule in manufacturers installation,
operation, maintenance manual
necessary
Check head and flow, AF’s should normally be run between 75% and
Back flush pump or manually clean impeller
Check coupling lubrication schedule in manufacturers installation,
Check pump and drive component vibration levels, rebalance coupling if
Check head and flow, AF’s should normally be run between 75% and
Check head and flow, AF’s should normally be run between 75% and
necessary
Piping not properly anchored Check to see if excessive pipe strain is being transferred to pump flanges
Pump and/or driver not secured to sub-base Check fasteners, if loose check alignment and re-tighten
Specific gravity higher than specified Analyze pumpage and compare to specified gravity
Motor requires excessive
Pump run off design point Check measured head and flow to specified head and flow
Bearing failing Replace if necessary
Viscosity higher than specified Analyze pumpage and compare to specified viscosity
Pump assembled incorrectly Compare pump assembly to instruction manual
Head higher than rating. Reduced flow Check for fouling in the piping or obstruction in discharge
Liquid heavier than expected Check specific gravity and viscosity
Incorrect rotation Jog motor and check rotation
44 AF (42-66) IOM AF (42-66) IO
Table 3 (Cont’d)
Page 45

6
DISASSEMBLY & RE-ASSEMBLY
PUMP DISASSEMBLY & RE-ASSEMBLY .................................................. 45
Disassembly of Pump ....................................................................... 46
Re-Assembly of Pump ....................................................................... 46
LM & LMR POWER END DISASSEMBLY & RE-ASSEMBLY .................... 46
Power E nd Disassembly ................................................................... 46
Power E nd Re-Assembly .................................................................. 47
INSPECTIONS ............................................................................................. 48
Impeller .............................................................................................. 48
Shaft ................................................................................................... 48
Shaft Sleeve ....................................................................................... 48
Bearings ............................................................................................. 48
Oil Seals, O-Rings, Gaskets.............................................................. 48
PUMP DISASSEMBLY & RE-ASSEMBLY
Refer to the pump part list (pg. 50) and sectional
drawings (Fig.’s 22, 23) for proper part designation in
these instructions. The order of steps for
disassembly and assembly of the liquid end and
power end is the suggested method. However, any
workable sequence to accomplish the desired results
may be used.
Pump Disassembly
1. Remove all auxiliary water lines to pump and
completely drain pump and pipeline. Remove bolts
which fasten pump to suction and discharge piping.
2. If the pump is pipe mounted remove it from the
piping and support it on adequate cribbing. If the
pump is base mounted the casing (100) and power
end may be removed while the elbow (315A)
remains attached to the base.
3. Support the casing (100) by the lifting eye on top.
Loosen and remove all of the bolts and nuts that
secure the casing to the elbow (315A). With the
casing supported, swing it away from the impeller
(101) until it clears and set it down on a hard surface.
Be careful not to damage the mating gasket or o-ring
surfaces.
4. Disconnect coupling halves and remove any
intermediate shafting.
Support the impeller (101) with a chain around top
vane. Remove the impeller end cap (9988).
Remove the screws (370C) that secure the impeller
(101) and shaft washer (9985) to the shaft (122).
Tapped holes in the hub of the impeller on the
discharge side are provided for pulling the impeller
from the shaft. If no holes are provided, strapping or
chains around the impeller vanes will provide a
means of pulling the impeller from the shaft. Always
use the shaft center for the center point of a puller.
Be sure to retain the impeller key (178).
NOTE: If chains are used for pulling, place
blocking between chain and impeller vanes.
5. Support bearing housing (134) and impeller end
of shaft (122). Remove hex head bolts (370G) that
secure bearing housing (134) to suction elbow
(315A).
6. If packing is used, disassemble the gland (107),
packing (106), and lantern rings (105) from stuffing
box. If mechanical seal (383) was used, please see
the mechanical seal IOM for proper removal of seal.
7. With the power end properly supported. Carefully
pull it from suction elbow (315A).
8. The shaft sleeve (126) can be removed by
loosening set screw and sliding the sleeve from shaft
(122). Be sure to retain the sleeve key (128D).
AF (42-66) IOM 45
Page 46

!
!
PUMP RE-ASSEMBLY
1. Be sure shaft (122) and sleeve (126) are clean and
free of all burrs. Slide shaft sleeve (126) over shaft
(122), making sure that O-rings are in place as
indicated on assembly drawing. Secure sleeve with
set screw (222C) and key (128D).
2. Provide adequate support for bearing housing
(134) and shaft (122). Carefully slide shaft through
stuffing box of suction elbow. Bolt bearing housing to
suction elbow (315A).
3. Install shaft O-rings (496C & 496D) on shaft (122).
Place the shaft key (178) in the keyway. Lubricate the
O-rings as required.
4. Carefully install impeller (101) on shaft (122). With
shaft washer (9985) in place, install (4) cap screws
(370C) to secure the impeller to the shaft. Install
impeller end cap (9988) with o-ring (496B) as required.
5. Bolt casing (100) to elbow (315A) with (6) bolts
evenly spaced around bolt circle. Leave bolts loose
enough to shift casing for alignment with impeller. The
actual adjustment of casing is accomplished by turning
the (3) adjusting screws (370B) against casing flange.
6. The procedure for setting impeller clearance is
described in the ALIGNMENT section of these
instructions. When acceptable alignment has been
achieved, secure the initial (6) bolts, then install the
remaining bolts and tighten.
7. Before connecting the coupling halves, check
direction of motor rotation. Manually turn pump shaft
to insure no rubbing. Be sure the pump and gear box
shafts are in alignment according to the previously
discussed alignment procedure.
8. Connect coupling halves and any intermediate
shafting.
9. Assemble discharge piping to casing.
10. If packing is used, assemble gland, packing,
lantern rings and sleeve into stuffing box. Do not
compress too tightly until after start-up. The packing
will need to be "run-in" and adjusted for proper flow of
lubricating water. If a mechanical seal is used, please
see the mechanical seal IOM for proper installation of
seal.
11. Connect seal water and cooling lines to pump. Fill
the oil lubrication system. Be sure bearing housing oil
is level with the center of the sight glass.
LM & LMR POWER END DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY
Power End Disassembly (See Fig.’s 20, 21)
WARNING
Lockout driver power to prevent accidental
startup.
1. Lockout power supply to motor.
2. Close suction and discharge valve.
WARNING
The pump may handle hazardo u s and/or toxic
fluids. Skin and eye protection may be required.
Precautions must be taken to prevent injury or
environmental damage.
1. Remove piping from pump.
2. Remove coupling guard and coupling (direct
connect) or belt guard and belts (belt drive).
3. Drain oil from bearing housing, disconnect oil
circulation system, and remove pump from sub-base.
4. Wash down pump with appropriate cleaner.
5. Disassemble Pump per instructions per that
section. Discharge piping and impeller (101) will be
disassembled. The power end with the shaft (122) will
be removed from the elbow (315A).
6. Remove cap screws (370H) fastening thrust
bearing retainer (109) to bearing housing (134).
Carefully pull retainer over shaft. Top suction pumps
have thrust bearing (112C) at the outboard location
and the thrust bearing stationary race and (6) small
springs (9890) may be jarred free. Do not damage oil
seal (332).
7. Be sure overhung portion of shaft is supported.
8. Remove cap screws (370F) fastening radial
bearing retainer (119B) to bearing housing (134).
Carefully pull retainer away from bearing housing
without damaging lip seal (333).
46 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 47

9. Disassemble bearing halves by removing bolts and
knocking out taper pins. Carefully lift top half. The
shaft (122) with bearings can be lif ted fr om bottom half
of housing
10. Remove thrust end locknut (136) and lockwasher
(382).
a. For top suction pumps (Fig.20), the thrust
bearing (112C), thrust bearing sleeve (196) and thrust
bearing spacer (237) can be pulled from shaft (122).
Press or pull radial bearing (112) from shaft by
applying force on inner race bearing.
b. For end suction pumps (Fig.21), press the entire
thrust bearing stack off by pushing against stationary
race of thrust bearing (112C).
11. Loosen set screws and pull oil wheel (248) off
shaft.
12. Push inboard radial bearing (168C) off shaft
toward coupling end by applying force on bearing inner
race with a press.
POW ER END RE-ASSEMBLY
1. Be sure shaft is clean and free from all burrs.
2. Heat inboard radial bearing (168C) in a 200 deg. F
oil bath or by induction heater. Slide bearing on shaft
(122), butting against shaft shoulder. Position oil
wheel (248) on shaft (122) and secure with set screws.
3. Heat thrust end bearings (112) & (112C) and
sleeve (if used), in 200 deg. F oil bath. If thrust
bearing rotating race mounts on spacer (443), install
race on collar and heat collar with bearing mounted in
oil bath.
a) For top suction pumps (Fig. 20), slide bearing
(112), spacer (237), and sleeve into position, tight
against each other and against shaft shoulder.
After sleeve has cooled, install thrust bearing
(112C).
4. When the thrust bearing is in the outboard position
the stationary race will usually fit over the lock nut and
washer. This saves the trouble of trying to keep the
race in position because it can be set aside until
retainer (109) is installed.
a) For end suction pumps (Fig.21), slide spacer
(443) with mounted thrust bearing (112C),
including stationary race, into position against shaft
shoulder. If a spacer drive key is used, be sure it
is installed. Install bearing (112) against collar.
5. Secure bearings with lockwasher (382) and
locknut (136). Retighten locknut while components are
cooling to keep them tight together.
6. Install (6) thrust bearings springs (9890) in thrust
bearing retainer (109) or bearing housing (134) halves.
Use thick grease in each hole to help hold springs until
assembly.
7. Lower shaft (122) into bottom half of bearing
housing (134). Be careful not to damage bearings
or machined fits.
8. If springs (9890) are located in the housing, keep
the shaft about 3/8" outboard of normal position so
springs are not compressed.
9. Lower top half of housing into position, align with
taper pins, and secure together with bolts.
10. Install thrust bearing retainer. Do not damage lip
seal.
11. Slide thrust bearing retainer (109) and gasket
(360R) onto shaft to contact bearing housing
(134). Do not damage lip seal (332). Fasten
retainer to bearing housing with cap screws.
AF (42-66) IOM 47
Page 48

INSPECTIONS
IMPELLER
1. Inspect impeller vanes for damage (101). Check
the vane O.D. for erosion. Check the vane surfaces,
replace if grooved, worn, or eroded deeper than 3/16
in. (5.0 mm.) Excessive impeller wear may cause a
reduction in performance.
2. Inspect the leading and trailing edges of the vanes
for pitting, erosion or corrosion damage replace if
grooved, or worn deeper than 3/16 in. (5.0 mm.)
3. Inspect the root (vane attach point at hub) of each
vane for cracks. Impeller vane failure can cause
unbalance in the rotating assembly that will lead to
catastrophic failure of the pump.
4. Inspect the keyway and stepped bores for signs of
pitting, wear or corrosion damage.
5. Check the O-ring groove and bolt holes for signs of
pitting or corrosion.
SHAFT
1. Check the shaft (122) for straightness, wear,
corrosion, and radial run-out. Maximum run-out for
non-contact portions of the shaft is .002 in. (.05 mm)
max.
2. Bearing seats and seal areas must be smooth and
free of scratches and grooves. Shaft hole threads must
be in good condition. Replace if necessary.
SHAFT SLEEVE
1. The shaft sleeve (126) should be replaced if badly
grooved or worn. Localized wear or grooving
greater than 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) deep is cause for
replacement, see Fig. 50.
BEARINGS
The bearings (112, 112C, and 168C) should be
inspected for contamination and damage. The
condition of the bearing will provide useful information
on operating conditions in the bearing housing.
Lubrication condition and residue should be noted.
Bearing damage should be investigated to determine
the cause. If cause is not normal wear, it should be
corrected before the pump is returned to service.
DO NOT RE-USE BEARINGS.
OIL SEALS, O-RINGS, GASKETS
Although the oil seals (332, 333), O-rings (351A, 351B,
496A, 496B, 496C) and gaskets (360R, 360X,) may
seem OK during inspection and examination, DO NOT
RE-USE SEALS when rebuilding the pump. Replace
them while pump is disassembled.
48 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 49

7
SPARE PARTS
When ordering spare parts, always state Goulds Serial No., and indicate part name and
item number from relevant sectional drawing. It is imperative for service reliability to have a
sufficient stock of readily available spares.
RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS
Suggested Spare Parts
• Elbow and or Casing (100, 315A)
• Impeller (101)
• Gaskets (360R, 360X)
• O-Rings (351A, 351B, 496B, 496C, 496D)
• Shaft (122)
• Inboard Radial Bearing (168C)
• Outboard Thrust Bearings (112, 112C)
• Bearing Lockwasher (382)
• Bearing Locknut (136)
• Outboard Oil Seal (332)
• Inboard Oil Seal (333)
• Shaft Sleeve (126) (Optional)
• Sleeve O-rings (496A) (Optional)
• Stuffing Box Bushing (473) (Optional)
• Lantern Ring (105) (Optional)
• Stuffing Box Packing (106) (Optional)
• Packing Gland (107) (Optional)
HOW TO ORDER PARTS
When ordering parts c a ll
1-800-446-8537
or your local Goulds Representative
EMERGENCY SERVICE
Emergency parts service is available
24 hours a day, 365 days/year
Call 1-800-446-8537
AF (42-66) IOM 49
Page 50

Item
Part Description
Item
Part Description
101
PROPELLER
355
HEX NUT, GLAND
105
LANTERN RING
357D
NUT, ELBOW TO CASING
106
PACKING, PACKED BOX
358U
PIPE PLUG [½-14 NPT]
107
GLAND
358V
PIPE PLUG [1”-11.5 NPT]
109
RETAINER, THRUST BEARING
360X
GASKET, BRG., OUTBOARD
113A
BREATHER
370B
CAP SCREW
119B
RETAINER, RADIAL BEARING
370C
SCREW, SHAFT WASHER
122
SHAFT
370D
SCREW, ELBOW TO CASING
126
SHAFT SLEEVE
370E
CAP SCREW-ALIGNMENT
134
BEARING HOUSING ASSEMBLY
370G
HEX HD CAP SCREW, BEARING FRAME
Part of 134 assy
SCREW,HHC 1"-8 X 4-1/2"LG
370H
HEX HD CAP SCREW, THRUST RETAINER
Part of 134 assy
NUT,HEX 1"- 8 HVY
370I
NUT, HEX, BEARING FRAME TO ELBOW
136
LOCKNUT, THRUST BEARING
400
KEY, COUPLING
168C
BEARING, RADIAL, INBOARD
408N
PIPE PLUG [3/8-18 NPT]
178
PROPELLER KEY
415
JAM NUT
196
SLEEVE, THRUST BEARING
415A
JAM NUT
222
SET SCREW, OIL WHEEL
443
SPACER, THRUST BEARING
237
SPACER, THRUST BEARING
496B
O-RING, PROPELLER CAP
248
OIL WHEEL
496C
O-RING, SHAFT
315A
ELBOW
972G
MALE CONNECTOR
319
SIGHT WINDOW
972H
FEMALE CONNECTOR
319A
SIGHT WINDOW
984A
COOLING COIL
333
OIL SEAL, OUTBOARD
9985
SHAFT WASHER/PROPELLER LOCKPLATE
351A
CASING O-RING
9988
PROPELLER END COVER
351B
CASING O-RING
AF PARTS LIST–42-54 inch Pumps
100 CASING 353 STUD, GLAND
112 BEARING, RADIAL, OUTBOARD 360R GASKET, BRG., INBOARD
112C BEARING, THRUST 370A SCREW, PROPELLER END COVER
128D SLEEVE KEY 370F HEX HD CAP SCREW, RADIAL BEARING
RETAINER
TO ELBOW
TO BEARING FRAME
Part of 134 assy PIN,TAPER #10 X 3-1/2" (PLN) 382 LOCKWASHER, THRUST BEARING
222C SET SCREW, SLEEVE KEY 496A O-RING, SHAFT SLEEVE
332 OIL SEAL, INBOARD 9890 SPRINGS, THRUST BRG
50 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 51

42–54 (End Suction) AF with LM Bearings
42–54 (Top Suction) AF with LMR Bearings
Fig. 20
Fig. 21
AF (42-66) IOM 51
Page 52

42–54 AF with LMR Be a rings / Mechanical
Fig. 22
Seal / and Casing Gasket seal
52 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 53

42–54 AF with LM Bearings / Special Packing
Fig. 23
Arrangement / Dual Casing O-ring seal
AF (42-66) IOM 53
Page 54

Item
Part Description
Item
Part Description
100
CASING
357D
HEX NUT, ELBOW TO CASING
105
LANTERN RING
358V
PIPE PLUG [1"-11.5 NPT] (NOT SHOWNl
106
PACKING, PACKED BOX
360R
GASKET, BRG., INBOARD
107
GLAND
360X
GASKET, BRG., OUTBOARD
109
RETAINER, THRUST BEARING
370A
STUD, PROPELLER END COVER
112
BEARING, RADIAL, OUTBOARD
370B
CAP SCREW - SUCTION ALIGNMENT
113A
BREATHER
370D
STUD, ELBOW TO CASING
119B
RETAINER, RADIAL BEARING
370E
CAP SCREW-ALIGNMENT
122
SHAFT
370F
CAP SCREW, RADIAL BEARING RETAINER
126
SHAFT, SLEEVE
370G
CAP SCREW, BEARING FRAME TO ELBOW
128D
SLEEVE KEY
370H
CAP SCREW, THRUST RETAINER TOBEARING
AME TO ELBOW
136
LOCKNUT, THRUST BEARING
382
LOCKNUT CLIP
168C
BEARING, RADIAL INBOARD
383
MECHANICAL SEAL
178
PROPELLER KEY
400
KEY, COUPLING
196
SLEEVE, THRUST BEARING
408A
PIPE PLUG [ 1"-11.5 NPTJ
248
OIL WHEEL
415A
JAM NUT - ALIGNMENT
315A
ELBOW
443
SPACER, BEARING
319
SIGHT WINDOW
467A
HEX BUSHING - BREATHER
319A
SIGHT WINDOW
473
THROAT BUSHING
332
OIL SEAL, OUTBOARD
494
FRAME COOLER ASSEMBLY
351A
CASING 0-RING
496B
O-RING. PROPELLER END COVER
351B
CASING 0-RING
496C
O-RING, SHAFT TO PROPELLER
353
STUD, GLAND
9890
SPRINGS, THRUST BEARING
355
HEX NUT, GLAND
9985
SHAFT WASHER / PROPELLER LOCKPLATE
9988
PROPELLER END COVER
AF PARTS LIST–60-66 inch
Top Suction Pumps
101 PROPELLER 358U PIPE PLUG [1/2-14 NPT] (NOT SHOWN)
112C BEARING, THRUST 370C CAP SCREW, SHAFT WASHER
FRAME
134 BEARING FRAME ASSEMBLY 370I HEX NUT, BEARING FR
222 SET SCREW, OIL WHEEL 408H PLUG - PROPELLER CAP
222C SET SCREW, SLEEVE KEY 415 JAM NUT - SUCTION ALIGNMENT
333 0 I L SEAL, INBOARD 496A O-RING, SHAFT SLEEVE
54 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 55

60–66 (Top Suction) AF with LMR Bearings
Fig. 24
AF (42-66) IOM 55
Page 56

60–66 AF with LMR Be a rings / Mechanical
Fig. 25
Seal / and Casing Gasket seal
56 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 57

Item
Part Description
Item
Part Description
100
CASING
357D
HEX NUT, ELBOW TO CASING
105
LANTERN RING
358V
PIPE PLUG [1"-11.5 NPT] (NOT SHOWNl
106
PACKING, PACKED BOX
360R
GASKET, BRG., INBOARD
107
GLAND
360X
GASKET, BRG., OUTBOARD
109
RETAINER, THRUST BEARING
370A
STUD, PROPELLER END COVER
112
BEARING, RADIAL, OUTBOARD
370B
CAP SCREW - SUCTION ALIGNMENT
113A
BREATHER
370D
STUD, ELBOW TO CASING
119B
RETAINER, RADIAL BEARING
370E
CAP SCREW-ALIGNMENT
122
SHAFT
370F
CAP SCREW, RADIAL BEARING RETAINER
126
SHAFT, SLEEVE
370G
CAP SCREW, BEARING FRAME TO ELBOW
128D
SLEEVE KEY
370H
CAP SCREW, THRUST RETAINER TOBEARING
HEX NUT, BEARING FRAME TO ELBOW
136
LOCKNUT, THRUST BEARING
382
LOCKNUT CLIP
168C
BEARING, RADIAL INBOARD
383
MECHANICAL SEAL
178
PROPELLER KEY
400
KEY, COUPLING
196
SLEEVE, THRUST BEARING
408A
PIPE PLUG [ 1"-11.5 NPTJ
248
OIL WHEEL
415A
JAM NUT - ALIGNMENT
315A
ELBOW
443
SPACER, BEARING
319
SIGHT WINDOW
467A
HEX BUSHING - BREATHER
319A
SIGHT WINDOW
473
THROAT BUSHING
332
OIL SEAL, OUTBOARD
494
FRAME COOLER ASSEMBLY
351A
CASING 0-RING
496B
O-RING,. PROPELLER END COVER
351B
CASING 0-RING
496C
O-RING, SHAFT TO PROPELLER
353
STUD, GLAND
9890
SPRINGS, THRUST BEARING
355
HEX NUT, GLAND
9985
SHAFT WASHER / PROPELLER LOCKPLATE
9988
PROPELLER END COVER
AF PARTS LIST–60-66 inch
End Suction Pumps
101 PROPELLER 358U PIPE PLUG [1/2-14 NPT] (NOT SHOWN)
112C BEARING, THRUST 370C CAP SCREW, SHAFT WASHER
FRAME
134 BEARING FRAME ASSEMBLY 370I
222 SET SCREW, OIL WHEEL 408H PLUG - PROPELLER CAP
222C SET SCREW, SLEEVE KEY 415 JAM NUT - SUCTION ALIGNMENT
333 0 I L SEAL, INBOARD 496A O-RING, SHAFT SLEEVE
AF (42-66) IOM 57
Page 58

60–66 (End Suction) AF with LM Bearings
Fig. 26
58 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 59

60–66 AF with LM Bearings / Special Packing
Fig. 27
Arrangement / Dual Casing O-ring seal
AF (42-66) IOM 59
Page 60

THIS PAGE
INTENTIONALLY
LEFT BLANK
60 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 61

Fig. 24
Sleeve dia. Flush flow
Inlet
Outlet
8
APPENDIX 1
SPECIAL PACKING
ARRANGEMENT
(High pressure, dual flush packing)
The following information covers the installation,
operation and maintenance of the high pressure, dual
flush packing arrangement. This arrangement was
developed for high pressure, to minimize product
dilution, and to minimize external packing leakage.
DESCRIPTION
The arrangement consists of (6) rings of packing
(106), (2) lantern rings (105), and (1) restrictor
bushing arranged as follows: 3P, 1L, 2P, 1L, 1P, 1RB
from the gland face to the bottom of the stuffing box,
See fig. 24 below.
The flush flow depends on the application, the more
heat generated the higher the flows must be to
effectively remove the heat. The table below can be
used as a starting point for initial setting: The table
below represents the flow required with one flush line,
for a dual flush arrangement the flow can be divided
up equally.
(inches) (gpm)
2 .05
3 .15
4 .30
6 1.3
8 2.5
10 5.0
12 8.0
The stuffing box is furnished with (2) inlet and (2)
outlet ports for piping of the flush liquid. The inlets are
chosen based on shaft rotation direction so the flush
flow travels the longer route to the outlet ports (see fig
25). The outlet ports may be plugged, but for
improved cooling of the sealing elements, outlet pipes
are installed to allow more flow through the stuffing
box. With this setup flush flows are regulated by a
valve on the outlet line rather than by throttling the
flow on the inlet li ne
The inner lantern ring uses product flush to minimize
product dilution. This flush should be filtered to
reduce particle size and minimize sleeve / packing
wear.
The outer lantern ring is supplied with water and is
used as with any other packing arrangement to
lubricate and cool the packing as the shaft rotates
and generates heat.
The flush pressures should be 10% higher than the
pressure inside the pump. For end suction pumps
this will also include pump discharge pressure.
Product flush pressure to the inner lantern ring may
be slightly less than the water flush pressure to
ensure flow toward the inside of the pump.
AF (42-66) IOM 61
Page 62

PACKING RINGS
CORRECT
INCORRECT
INSTALLATION
1. Be sure the stuffing box and shaft sleeve (126)
must be clean and free of grit.
2. A Teflon restrictor bushing is used in the bottom of
the box and is installed similar to packing (see Fig. 26).
With the restrictor bushing wrapped around the shaft,
push it squarely into the stuffing box until it bottoms out.
Be sure the ends have not separated and that it sits
square in the bottom of the box. Note, where the cut is
positioned.
3. Form packing over a mandrel of same shaft
diameter and carefully cut packing to length. Discard
rings cut too short.
4. Pre-form each ring by coiling 1 -1 /2 turns.
5. To install packing rings, do not pull straight.
Expand the coil as a coil spring, see Fig 26 for the
correct and incorrect method of installing packing.
Fig. 26
6. Expand the first coil as shown and insert into
stuffing box. Tamp the packing up against the restrictor
bushing shoulder firmly with a nylon bar or wood rod.
Note, where the cut is positioned.
7. Assemble the first lantern ring around the shaft and
push it squarely into the stuffing box until it bottoms out
against the first ring of packing. Failure to property
locate the lantern ring with respect to the flush ports will
result in insufficient packing lubrication. Packing and
shaft sleeve damage may result.
8. Install the second and third coil as required by the
sectional drawing, staggering the cuts 90° to 120°.
9. Assemble the second lantern ring around the shaft
and push it squarely into the stuffing box until it bottoms
out on the third ring of packing. Failure to property
locate the lantern ring with respect to the flush ports will
result in insufficient packing lubrication. Packing and
shaft sleeve damage may result.
10. Install the third, fourth and fifth packing ring as
required by the sectional drawing, staggering the cuts
90° to 120°.
11. After all packing and lantern rings have been
properly installed, insert gland into stuffing box. Tighten
gland nuts finger tight only. The shaft should turn freely.
12. Turn lubricant supply on, start pump, and adjust the
gland as described in the operation section that follows.
13. Periodic maintenance is absolutely required for all
packed pumps. Normal shaft run-out should be under
.005” to avoid pounding of stuffing box packing. With
excessive shaft run-out, shaft straightening or
replacement is necessary.
GLAND ADJUSTMENT
Adjust the stuffing box if packing is used. When the
pump is first started, there should be considerable
leakage by the gland to cool the packing. Gradually
tighten the gland nuts on flat at a time while observing
the leakage and stuffing box temperature. Packing
requires time to “run-in” and extra coolant (leakage)
while it is being “run-in”. If the leakage is reduced too
quickly, the packing will overheat and may be
destroyed. The shaft sleeve may also be damaged.
LEAKAGE
Normal leakage for a properly adjusted box,
depending on shaft size and speed, varies
from a few drops a second to a small trickle
out of the gland.
62 AF (42-66) IOM
Page 63

THIS PAGE
INTENTIONALLY
LEFT BLANK
Page 64

HOW TO ORDER
EMERGENCY SERVICE
Form No. IAF (42-66) 04/14
When ordering parts call
1-800-446-8537
or your local Goulds Representative
Emergency parts service is available
24 hours/day, 365 days/year . . .
Call 1-800-446-8537
Visit our website at w w w .gouldspumps.com
2014 Goulds Pumps, Incorporated
a subsidiary of ITT Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...