Gorman-Rupp Pumps 112E60-B User Manual

ACE OM-00905-03
July 22, 2004
Rev. B 02‐11‐14
INSTALLATION, OPERATION,
AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
WITH PARTS LIST
10 SERIES PUMP
MODEL
112E60-B
THE GORMAN‐RUPP COMPANY MANSFIELD, OHIO
www.grpumps.com
GORMAN‐RUPP OF CANADA LIMITED ST. THOMAS, ONTARIO, CANADA Printed in U.S.A.
2004 The Gorman‐Rupp Company

Register your new
Gorman‐Rupp pump online at
www.grpumps.com
Valid serial number and e‐mail address required.
RECORD YOUR PUMP MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER
Please record your pump model and serial number in the
spaces provided below. Your Gorman‐Rupp distributor
needs this information when you require parts or service.
Pump Model:
Serial Number:

TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION PAGE I - 1...................................................
SAFETY - SECTION A PAGE A - 1............................................
INSTALLATION - SECTION B PAGE B - 1.....................................
PREINSTALLATION INSPECTION PAGE B - 1............................................
POSITIONING PUMP PAGE B - 2.......................................................
Lifting PAGE B - 2.................................................................
Mounting PAGE B - 2.............................................................
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE PIPING PAGE B - 2.........................................
Materials PAGE B - 2..............................................................
Line Configuration PAGE B - 2......................................................
Connections to Pump PAGE B - 2..................................................
Gauges PAGE B - 3...............................................................
SUCTION LINES PAGE B - 3...........................................................
Fittings PAGE B - 3...............................................................
Strainers PAGE B - 3..............................................................
Sealing PAGE B - 3...............................................................
Suction Lines In Sumps PAGE B - 3.................................................
Suction Line Positioning PAGE B - 3................................................
DISCHARGE LINES PAGE B - 5........................................................
Siphoning PAGE B - 5.............................................................
Valves PAGE B - 5................................................................
Bypass Lines PAGE B - 5..........................................................
AUTOMATIC AIR RELEASE VALVE PAGE B - 6...........................................
Theory of Operation PAGE B - 6....................................................
Air Release Valve Installation PAGE B - 7............................................
ALIGNMENT PAGE B - 8..............................................................
Coupled Drives PAGE B - 8........................................................
V‐Belt Drives PAGE B - 9...........................................................
V‐BELT TENSIONING PAGE B - 9......................................................
General Rules of Tensioning PAGE B - 9.............................................
Tension Measurment PAGE B - 10...................................................
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS PAGE B - 12...............................................
OPERATION - SECTION C PAGE C - 1.......................................
PRIMING PAGE C - 1.................................................................
STARTING PAGE C - 1................................................................
Rotation PAGE C - 1..............................................................
OPERATION PAGE C - 2..............................................................
Lines With a Bypass PAGE C - 2....................................................
Lines Without a Bypass PAGE C - 2.................................................
Leakage PAGE C - 2..............................................................
Liquid Temperature And Overheating PAGE C - 2.....................................
Strainer Check PAGE C - 3.........................................................
Pump Vacuum Check PAGE C - 3..................................................
STOPPING PAGE C - 3................................................................
Cold Weather Preservation PAGE C - 3..............................................
i

TABLE OF CONTENTS
(continued)
BEARING TEMPERATURE CHECK PAGE C - 3..........................................
TROUBLESHOOTING - SECTION D PAGE D - 1...............................
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE PAGE D - 3...............................................
PUMP MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR - SECTION E PAGE E - 1.................
PERFORMANCE CURVE PAGE E - 1...................................................
PARTS LIST
Pump Model PAGE E - 3..........................................................
PUMP AND SEAL DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY PAGE E - 4.........................
Suction Check Valve Removal PAGE E - 4...........................................
Suction Elbow And Wear Plate Removal PAGE E - 4..................................
Impeller Removal PAGE E - 5......................................................
Seal Removal PAGE E - 5..........................................................
Pump Casing Removal PAGE E - 5.................................................
Shaft and Bearing Removal and Disassembly PAGE E - 6.............................
Shaft and Bearing Reassembly and Installation PAGE E - 7............................
Seal Reassembly and Installation PAGE E - 8........................................
Impeller Installation And Adjustment PAGE E - 9......................................
Pump Casing Installation PAGE E - 10................................................
Wear Plate And Suction Elbow Installation PAGE E - 10................................
Suction Check Valve Installation PAGE E - 10.........................................
Final Pump Assembly PAGE E - 10..................................................
PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE MAINTENANCE PAGE E - 11..................................
LUBRICATION PAGE E - 11.............................................................
Seal Assembly PAGE E - 11.........................................................
Bearings PAGE E - 11..............................................................
ii

10 SERIES
OM-00905
INTRODUCTION
Thank You for purchasing a Gorman‐Rupp pump.
Read this manual carefully to learn how to safely
install and operate your pump. Failure to do so
could result in personal injury or damage to the
pump.
This pump is a 10 Series, semi‐open impeller, self‐
priming centrifugal model with a suction check
valve. The pump is designed for handling most
non‐volatile, non‐flammable liquids containing
specified entrained solids. The basic material of
construction for wetted parts is gray iron, with
stainless steel impeller shaft and ductile iron wear
ing parts.
This manual will alert personnel to known proce
dures which require special attention, to those
which could damage equipment, and to those
which could be dangerous to personnel. However,
this manual cannot possibly anticipate and provide
detailed precautions for every situation that might
occur during maintenance of the unit. Therefore, it
is the responsibility of the owner/maintenance per
sonnel to ensure that only safe, established main
tenance procedures are used, and that any proce
dures not addressed in this manual are performed
only after establishing that neither personal safety
nor pump integrity are compromised by such prac
tices.
For information or technical assistance on the pow
er source, contact the power source manufactur
er's local dealer or representative.
The following are used to alert maintenance per
sonnel to procedures which require special atten
tion, to those which could damage equipment, and
to those which could be dangerous to personnel:
Immediate hazards which WILL result in
severe personal injury or death. These
instructions describe the procedure re
quired and the injury which will result
from failure to follow the procedure.
Hazards or unsafe practices which
COULD result in severe personal injury
or death. These instructions describe
the procedure required and the injury
which could result from failure to follow
the procedure.
If there are any questions regarding the pump or
its application which are not covered in this man
ual or in other literature accompanying this unit,
please contact your Gorman‐Rupp distributor, or
The Gorman‐Rupp Company:
The Gorman‐Rupp Company
P.O. Box 1217
Mansfield, Ohio 44901-1217
Phone: (419) 755-1011
or:
Gorman‐Rupp of Canada Limited
70 Burwell Road
St. Thomas, Ontario N5P 3R7
Phone: (519) 631-2870
Hazards or unsafe practices which COULD
result in minor personal injury or product
or property damage. These instructions
describe the requirements and the possi
ble damage which could result from failure
to follow the procedure.
NOTE
Instructions to aid in installation, operation,and
maintenance, or which clarify a procedure.
PAGE I - 1INTRODUCTION
10 SERIES OM-00905
SAFETY - SECTION A
This information applies to 10 Series
basic pumps. Gorman‐Rupp has no
control over or particular knowledge of
the power source which will be used.
Refer to the manual accompanying the
power source before attempting to be
gin operation.
Because pump installations are seldom
identical, this manual cannot possibly
provide detailed instructions and pre
cautions for each specific application.
Therefore, it is the owner/installer's re
sponsibility to ensure that applications
not addressed in this manual are per
formed only after establishing that nei
ther operator safety nor pump integrity
are compromised by the installation.
Before attempting to open or service the
pump:
non‐volatile, non‐flammable liquids
containing specified entrained solids.
Do not attempt to pump volatile, corro
sive, or flammable materials which may
damage the pump or endanger person
nel as a result of pump failure.
After the pump has been positioned,
make certain that the pump and all pip
ing connections are tight, properly sup
ported and secure before operation.
Do not operate the pump without the
guards in place over the rotating parts.
Exposed rotating parts can catch cloth
ing, fingers, or tools, causing severe in
jury to personnel.
1. Familiarize yourself with this man
ual.
2. Disconnect or lock out the power
source to ensure that the pump will
remain inoperative.
3. Allow the pump to completely cool
if overheated.
4. Check the temperature before
opening any covers, plates, or
plugs.
5. Close the suction and discharge
valves.
6. Vent the pump slowly and cau
tiously.
7. Drain the pump.
This pump is designed to handle most
Do not remove plates, covers, gauges,
pipe plugs, or fittings from an over
heated pump. Vapor pressure within the
pump can cause parts being disen
gaged to be ejected with great force. Al
low the pump to cool before servicing.
Do not operate the pump against a
closed discharge valve for long periods
of time. If operated against a closed dis
charge valve, pump components will
deteriorate, and the liquid could come
to a boil, build pressure, and cause the
pump casing to rupture or explode.
PAGE A - 1SAFETY

10 SERIES OM-00905
cient capacity and that they are posi
tioned so that loads will be balanced
and the pump or components will not be
Death or serious personal injury and
damage to the pump or components
can occur if proper lifting procedures
are not observed. Make certain that
hoists, chains, slings or cables are in
good working condition and of suffi
damaged when lifting. Suction and dis
charge hoses and piping must
be re
moved from the pump before lifting. Lift
the pump or component only as high as
necessary and keep personnel away
from suspended objects.
PAGE A - 2 SAFETY
10 SERIES OM-00905
INSTALLATION - SECTION B
Review all SAFETY information in Section A.
Since pump installations are seldom identical, this
section offers only general recommendations and
practices required to inspect, position, and ar
range the pump and piping.
Most of the information pertains to a standard
static lift application where the pump is positioned
above the free level of liquid to be pumped.
If installed in a flooded suction application where
the liquid is supplied to the pump under pressure,
some of the information such as mounting, line
configuration, and priming must be tailored to the
OUTLINE DRAWING
specific application. Since the pressure supplied
to the pump is critical to performance and safety,
be sure to limit the incoming pressure to 50% of the
maximum permissible operating pressure as
shown on the pump performance curve (see Sec
tion E, Page 1).
For further assistance, contact your Gorman‐Rupp
distributor or the Gorman‐Rupp Company.
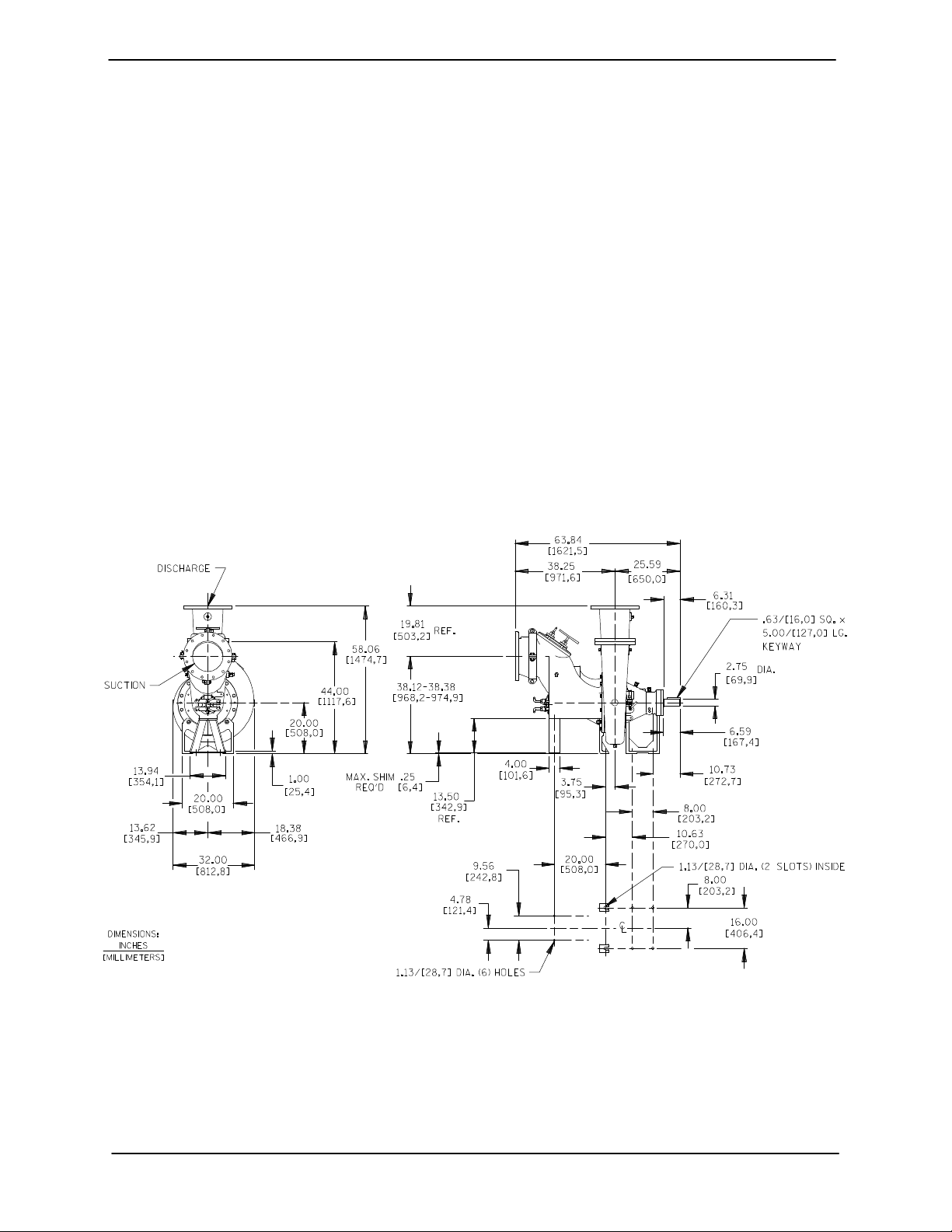
Pump Dimensions
See Figure B-1 for the approximate physical di
mensions of this pump.
Figure B-1. Pump Model 112E60-B
PREINSTALLATION INSPECTION
The pump assembly was inspected and tested be
fore shipment from the factory. Before installation,
inspect the pump for damage which may have oc
curred during shipment. Check as follows:
a. Inspect the pump, engine or motor for cracks,
dents, damaged threads, and other obvious
damage.
b. Check for and tighten loose attaching hard
ware. Since gaskets tend to shrink after dry
PAGE B - 1INSTALLATION

OM-00905 10 SERIES
ing, check for loose hardware at mating sur
faces.
c. Carefully read all tags, decals, and markings
on the pump assembly, and perform all duties
indicated. Note that the pump shaft rotates in
the required direction.
d. Check levels and lubricate as necessary. Re
fer to LUBRICATION in the MAINTENANCE
AND REPAIR section of this manual and per
form duties as instructed.
e. If the pump or
for more than 12 months, some of the compo
nents or lubricants may have exceeded their
maximum shelf life. These must be inspected
or replaced to ensure maximum pump serv
ice.
If the maximum shelf life has been exceeded, or if
anything appears to be abnormal, contact your
Gorman‐Rupp distributor or the factory to deter
mine the repair or updating policy. Do not put the
pump into service until appropriate action has
been taken.
power source have been stored
POSITIONING PUMP
Pump unit weights will vary depending on the
mounting and drive provided. Check the shipping
tag on the unit packaging for the actual weight, and
use lifting equipment with appropriate capacity.
Drain the pump and remove all customer‐installed
equipment such as suction and discharge hoses
or piping before attempting to lift existing, installed
units.
Mounting
Locate the pump in an accessible place as close as
practical to the liquid being pumped. Level mount
ing is essential for proper operation.
The pump may have to be supported or shimmed
to provide for level operation or to eliminate vibra
tion.
If the pump has been mounted on a moveable
base, make certain the base is stationary by setting
the brake and blocking the wheels before attempt
ing to operate the pump.
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE PIPING
Pump performance is adversely effected by in
creased suction lift, discharge elevation, and fric
tion losses. See the performance curve to be sure
your overall application allows the pump to operate
within the safe operation range.
Lifting
Death or serious personal injury and
damage to the pump or components
can occur if proper lifting procedures
are not observed. Make certain that
hoists, chains, slings or cables are in
good working condition and of suffi
cient capacity and that they are posi
tioned so that loads will be balanced
and the pump or components will not be
damaged when lifting. Suction and dis
charge hoses and piping must be re
moved from the pump before lifting. Lift
the pump or component only as high as
necessary and keep personnel away
from suspended objects.
Materials
Either pipe or hose maybe used for suction and
discharge lines; however, the materials must be
compatible with the liquid being pumped. If hose is
used in suction lines, it must be the rigid‐wall, rein
forced type to prevent collapse under suction. Us
ing piping couplings in suction lines is not recom
mended.
Line Configuration
Keep suction and discharge lines as straight as
possible to minimize friction losses. Make mini
mum use of elbows and fittings, which substan
tially increase friction loss. If elbows are necessary,
use the long‐radius type to minimize friction loss.
Connections to Pump
Before tightening a connecting flange, align it ex
actly with the pump port. Never pull a pipe line into
PAGE B - 2 INSTALLATION

10 SERIES OM-00905
place by tightening the flange bolts and/or cou
plings.
Lines near the pump must be independently sup
ported to avoid strain on the pump which could
cause excessive vibration, decreased bearing life,
and increased shaft and seal wear. If hose‐type
lines are used, they should have adequate support
to secure them when filled with liquid and under
pressure.
Gauges
Most pumps are drilled and tapped for installing
discharge pressure and vacuum suction gauges. If
these gauges are desired for pumps that are not
tapped, drill and tap the suction and discharge
lines not less than 18 inches (457,2 mm) from the
suction and discharge ports and install the lines.
Installation closer to the pump may result in erratic
readings.
If a strainer is not furnished with the pump, but is
installed by the pump user, make certain that the
total area of the openings in the strainer is at least
three or four times the cross section of the suction
line, and that the openings will not permit passage
of solids larger than the solids handling capability
of the pump.
This pump is designed to handle up to 2-3/4 inch
(69,9 mm) diameter spherical solids.
Sealing
Since even a slight leak will affect priming, head,
and capacity, especially when operating with a
high suction lift, all connections in the suction line
should be sealed with pipe dope to ensure an air
tight seal. Follow the sealant manufacturer's rec
ommendations when selecting and applying the
pipe dope. The pipe dope should be compatible
with the liquid being pumped.
Suction Lines In Sumps
SUCTION LINES
To avoid air pockets which could affect pump prim
ing, the suction line must be as short and direct as
possible. When operation involves a suction lift, the
line must always slope upward to the pump from
the source of the liquid being pumped; if the line
slopes down to the pump at any point along the
suction run, air pockets will be created.
Fittings
Suction lines should be the same size as the pump
inlet. If reducers are used in suction lines, they
should be the eccentric type, and should be in
stalled with the flat part of the reducers uppermost
to avoid creating air pockets. Valves are not nor
mally used in suction lines, but if a valve is used,
install it with the stem horizontal to avoid air pock
ets.
Strainers
If a single suction line is installed in a sump, it
should be positioned away from the wall of the
sump at a distance equal to 1‐1/2 times the diame
ter of the suction line.
If there is a liquid flow from an open pipe into the
sump, the flow should be kept away from the suc
tion inlet because the inflow will carry air down into
the sump, and air entering the suction line will re
duce pump efficiency.
If it is necessary to position inflow close to the suc
tion inlet, install a baffle between the inflow and the
suction inlet at a distance 1‐1/2 times the diameter
of the suction pipe. The baffle will allow entrained
air to escape from the liquid before it is drawn into
the suction inlet.
If two suction lines are installed in a single sump,
the flow paths may interact, reducing the efficiency
of one or both pumps. To avoid this, position the
suction inlets so that they are separated by a dis
tance equal to at least 3 times the diameter of the
suction pipe.
If a strainer is furnished with the pump, be certain
to use it; any spherical solids which pass through a
strainer furnished with the pump will also pass
through the pump itself.
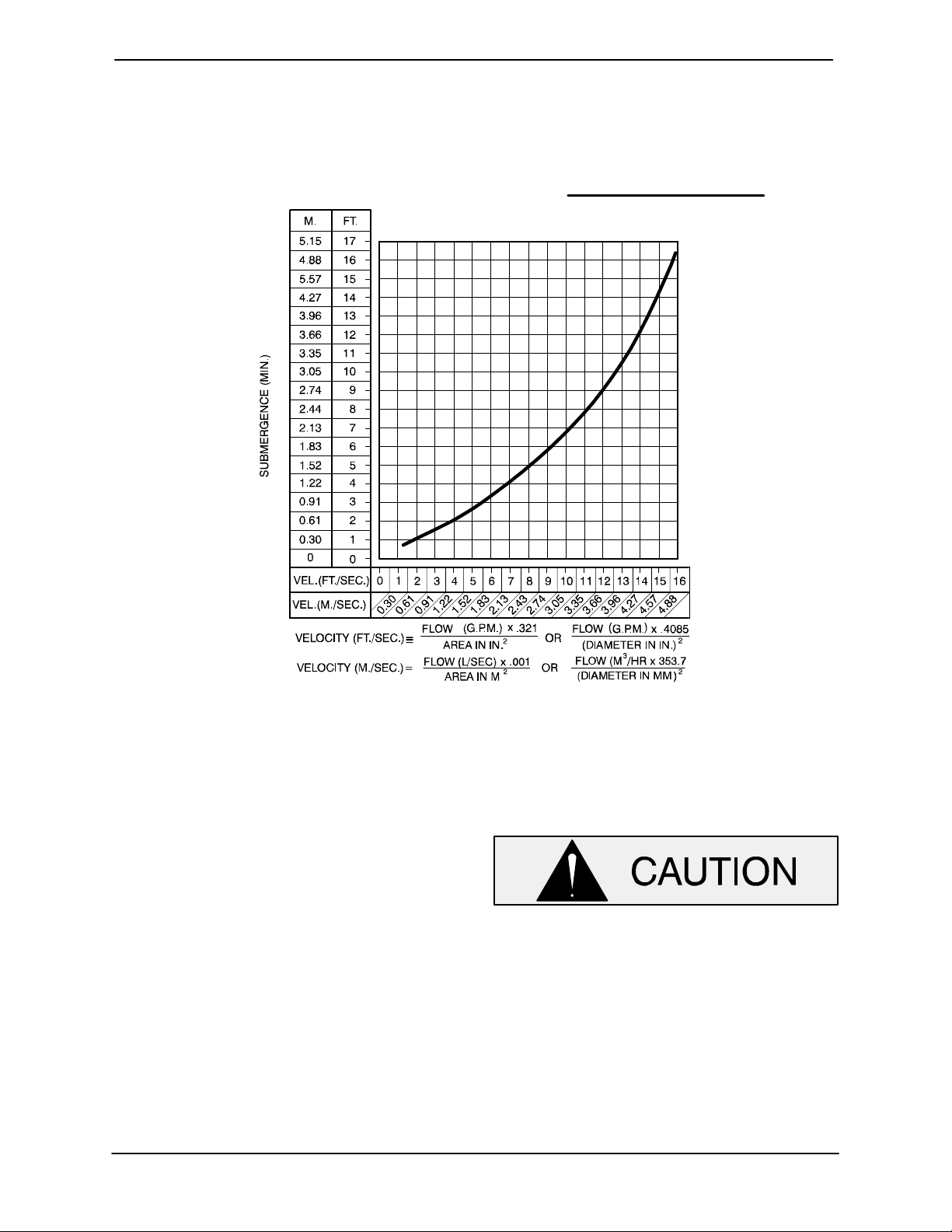
Suction Line Positioning
The depth of submergence of the suction line is
critical to efficient pump operation. Figure 2 shows
PAGE B - 3INSTALLATION
OM-00905 10 SERIES
recommended minimum submergence vs. veloc
ity.
NOTE
The pipe submergence required may be reduced
by installing a standard pipe increaser fitting at the
end of the suction line. The larger opening size will
reduce the inlet velocity. Calculate the required
submergence using the following formula based
on the increased opening size (area or diameter).
Figure 2. Recommended Minimum Suction Line Submergence vs. Velocity
DISCHARGE LINES
Siphoning
Do not terminate the discharge line at a level lower
than that of the liquid being pumped unless a si
phon breaker is used in the line. Otherwise, a si
phoning action causing damage to the pump
could result.
Valves
If a throttling valve is desired in the discharge line,
use a valve as large as the largest pipe to minimize
friction losses. Never install a throttling valve in a
suction line.
A check valve in the discharge line is normally rec
ommended, but it is not necessary in low dis
charge head applications.
With high discharge heads, it is recommended that
a throttling valve and a system check valve be in
stalled in the discharge line to protect the pump
from excessive shock pressure and reverse rota
tion when it is stopped.
If the application involves a high discharge
head, gradually close the discharge
throttling valve before stopping the pump.
Bypass Lines
Self‐priming pumps are not air compressors. Dur
ing the priming cycle, air from the suction line must
be vented to atmosphere on the discharge side. If
the discharge line is open, this air will be vented
through the discharge. However, if a check valve
has been installed in the discharge line, the dis
charge side of the pump must be opened to atmos
PAGE B - 4 INSTALLATION
 Loading...
Loading...