Page 1

User’s Manual
Broadband Routers
IP104 / IP104P
Page 2

Copyright
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, stored, transcribed in
an information retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any
means, mechanical, magnetic, electronic, optical, photocopying, manual, or otherwise, without the
prior written permission.
Trademarks
All product, company, brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies. They are used for identification purpose only. Specifications are subject to be changed
without prior notice.
Page 3

FCC Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against radio interference in a commercial environment. This equipment can generate, use and radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions in this manual,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be required to take
whatever measures are necessary to correct the interference.
CE Declaration of Conformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN
55022/A1 Class B, and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements of the European
Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the member states relation to
electromagnetic compatibility.
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction .............................................................................. 6
Functions and Features ........................................................................ 6
Packing List ......................................................................................... 7
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation ............................................................... 8
2.1 Panel Layout .................................................................................. 8
2.2 Installation Requirements .............................................................. 9
2.3 Procedure for Hardware Installation............................................ 10
Chapter 3 Network Settings and Software Installation........................... 11
3.1 Make Correct Network Settings of Your Computer .................... 11
3.2 Install the Software into Your Computers (Optional) .................. 12
Chapter 4 Configuring NAT Router........................................................ 15
4.1 Start-up and Log in ...................................................................... 15
4.2 Status............................................................................................ 16
4.3 Wizard.......................................................................................... 17
4.4 Basic Setting ................................................................................ 19
4.4.1 Primary Setup............................................................................ 20
4.4.2 DHCP Server ............................................................................ 24
4.4.3 Change Password...................................................................... 26
4.5 Forwarding Rules......................................................................... 27
4.5.1 Virtual Server ............................................................................ 28
4.5.2 Special AP................................................................................. 29
4.5.3 Miscellaneous Items.................................................................. 30
4.6 Security Settings .......................................................................... 31
4.6.1 Packet Filter .............................................................................. 32
4.6.2 Domain Filter............................................................................ 37
4.6.3 MAC Address Control .............................................................. 38
4.6.4 Miscellaneous Items.................................................................. 41
4.7 Advanced Setting......................................................................... 42
4.7.1 System Log ............................................................................... 43
4.7.2 Dynamic DNS........................................................................... 44
4.7.3 SNMP Setting ........................................................................... 46
4.7.4 Routing Table............................................................................ 48
4.8 Toolbox ........................................................................................ 50
4.8.1 System Log ............................................................................... 51
4.8.2 Firmware Upgrade .................................................................... 52
4.8.3 Backup Setting.......................................................................... 53
Page 5

4.8.4 Reset to default ......................................................................... 53
4.8.5 Reboot....................................................................................... 53
4.8.6 Miscellaneous Items.................................................................. 54
Chapter 5 Print Server (optional)............................................................ 55
5.1 Configuring on Windows 95/98 Platforms.................................. 55
5.2 Configuring on Windows NT Platforms...................................... 57
5.3 Configuring on Windows 2000 and XP Platforms ...................... 58
5.4 Configuring on Unix based Platforms ......................................... 62
Appendix A TCP/IP Configuration for Windows 95/98 ........................ 63
A.1 Install TCP/IP Protocol into Your PC ......................................... 63
A.2 Set TCP/IP Protocol for Working with NAT Router................... 64
Appendix B Console Mode (optional).................................................... 68
Page 6

Chapter 1 Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of this outstanding Broadband Router. This product is specifically
designed for Small Office and Home Office needs. It provides a complete SOHO solution for Internet
surfing and office resources sharing, and it is easy to configure and operate for even non-technical
users. Instructions for installing and configuring this product can be found in this manual. Before you
install and use this product, please read this manual carefully for fully exploiting the functions of this
product.
Functions and Features
Broadband modem and NAT Router
Connects multiple computers to a broadband (cable or DSL) modem or an Ethernet router to
surf the Internet.
Auto-sensing Ethernet Switch
Equipped with a 4-port auto-sensing Ethernet switch.
VPN supported
Supports multiple PPTP sessions and allows you to setup VPN server and VPN clients.
Printer sharing (Optional)
Embeds a print server to allow all of the networked computers to share one printer.
Firewall
All unwanted packets from outside intruders are blocked to protect your Intranet.
DHCP server supported
All of the networked computers can retrieve TCP/IP settings automatically from this product.
Web-based configuring
Configurable through any networked computer’s web browser using Netscape or Internet
Explorer.
Packet filter supported
Packet Filter allows you to control access to a network by analyzing the incoming and
outgoing packets and letting them pass or halting them based on the IP address of the source
and destination.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)
supported
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) enable devices such as PCs, routers or other devices to be
plugged into a network and automatically know about each other.
Virtual Server supported
Enables you to expose WWW, FTP and other services on your LAN to be accessible to
Internet users.
Page 7

User-Definable Application Sensing Tunnel
User can define the attributes to support the special applications requiring multiple
connections, like Internet gaming, video conferencing, Internet telephony and so on, then this
product can sense the application type and open multi-port tunnel for it.
DMZ Host supported
Lets a networked computer be fully exposed to the Internet; this function is used when
special application sensing tunnel feature is insufficient to allow an application to function
correctly.
Domain Filter Supported
let you prevent users under this device from accessing specific URLs.
SNMP Supported
In brief, SNMP, the Simple Network Management Protocol, is a protocol designed to give a
user the capability to remotely manage a computer network by polling and setting terminal
values and monitoring network events.
Routing Table Supported
Routing Tables allow you to determine which physical interface address to use for outgoing
IP data grams. If you have more than one routers and subnets, you will need to enable routing
table to allow packets to find proper routing path and allow different subnets to communicate
with each other.
Network time Supported
Allow you to synchronize system time with network time server.
Statistics of WAN Supported
Enables you to monitor inbound and outbound packets
Packing List
Broadband router unit
Installation CD-ROM
Power adapter
Page 8
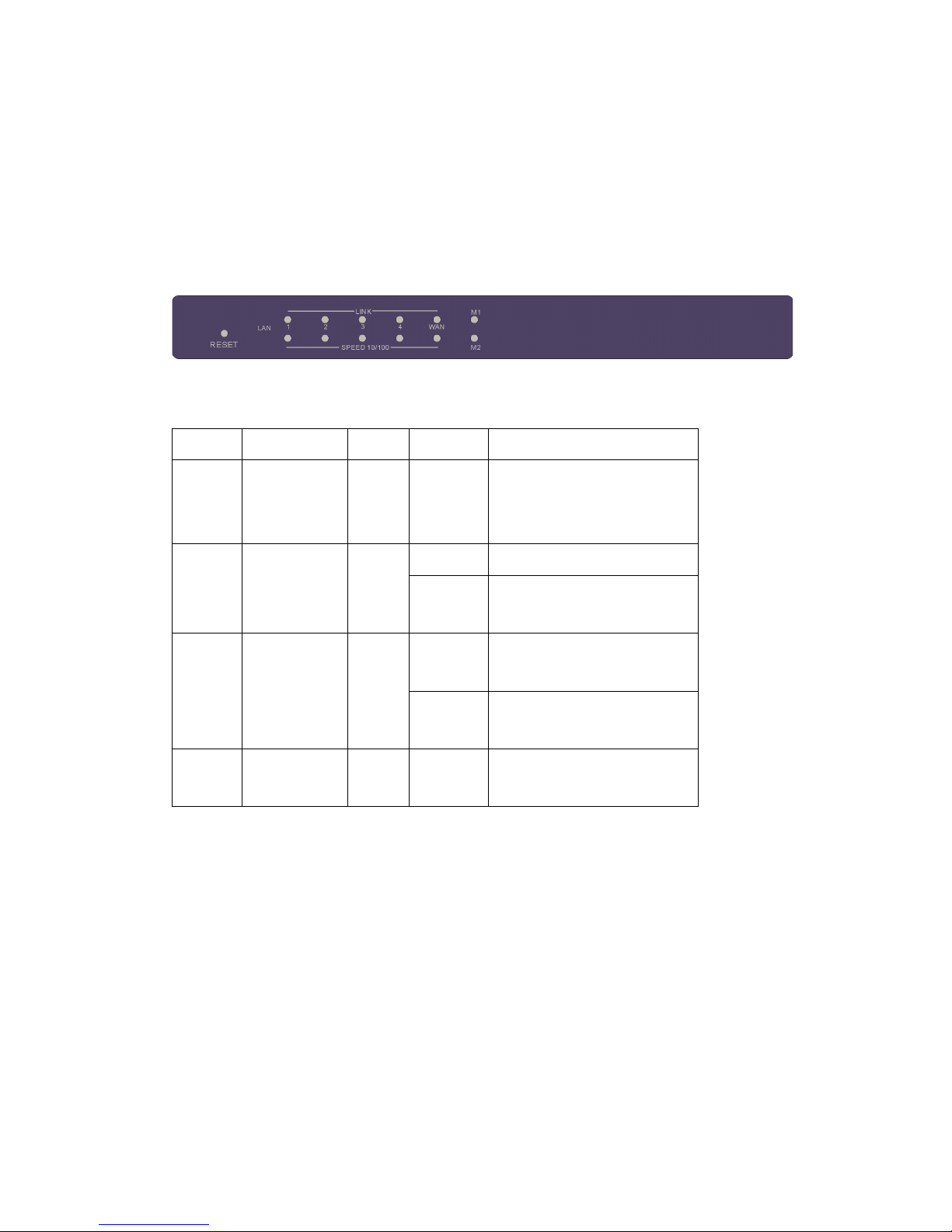
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
2.1 Panel Layout (your product may need to be modified)
2.1.1. Front Panel
Figure 2-1 Front Panel
LED:
LED Function Color Status Description
M1&M2
System status
indicators
Orange Blinking
M1 is flashed once per second to
indicate system is alive. When
system is busy, M2 is lighted.
On The WAN port is linked.
WAN
WAN port
activity
Green
Blinking
The WAN port is sending or
receiving data.
On
An active station is connected to
the corresponding LAN port.
Link/Act.
1~4
Link status Green
Blinking
The corresponding LAN port is
sending or receiving data.
Speed
10/100
Data Rate Green On
Data is transmitting in 100Mbps
on the corresponding LAN port.
Port:
RESET
To reset system settings to factory defaults, please follow the steps:
1. Power off the device,
2. Press the reset button and hold,
3. Power on the device,
4. Keep the button pressed about 5 seconds,
5. Release the button,
6. Watch the M1 LED and M2 LEDs, they will flash 8 times and then
M1 flash once per second.
Page 9

2.1.2. Rear Panel
Figure 2-2 Rear Panel
Ports:
Port Description
5VDC
Power inlet: DC 5V, 1.5A (minimum)
WAN
the port where you will connect your cable (or DSL) modem or
Ethernet router.
Port 1-4
the ports where you will connect networked computers and other
devices.
PRINTER
Printer Port (Optional)
COM
Serial port (connect analog modem or console cable)(optional)
2.2 Installation Requirements
This product can be positioned at any convenient place in your office or house. No special wiring or
cooling requirements is needed. However, you should comply with the following guidelines to install:
Place this product on a flat horizontal plane.
Keep this product away from any heating devices.
Do not place this product in dusty or wet environment.
The recommended operational specifications of this product are:
Temperature 0
o
C ~ 55 oC
Humidity 5 % ~ 90 %
In addition, remember to turn off the power, remove the power cord from the outlet, and keep your
hands dry when you try to install the hardware of this product.
Page 10

2.3 Procedure for Hardware Installation
1. Setup LAN connection: connect an Ethernet cable from your computer’s Ethernet
port to one of the LAN ports of this product.
2. Setup WAN connection: prepare an Ethernet cable for connecting this product to
your cable/xDSL modem or Ethernet backbone.
3. Power on:
Connecting the power cord to power inlet and turning the power switch on, this
product will automatically enter the self-test phase. When it is in the self-test phase,
the indicators M1 and M2 will be lighted ON for about 5 seconds, and then M1 and
M2 will be flashed 3 times to indicate that the self-test operation has finished. Finally,
the M1 will be continuously flashed once per second to indicate that this product is in
normal operation.
Page 11

Chapter 3 Network Settings and Software Installation
To use this product correctly, you have to properly configure the network settings of your computers
and install the attached setup program into your MS Windows platform (Windows 95/98/NT/2000).
3.1 Make Correct Network Settings of Your Computer
The default IP address of this product is 192.168.123.254, and the default subnet mask is
255.255.255.0. These addresses can be changed on your need, but the default values are used in this
manual. If the TCP/IP environment of your computer has not yet been configured, you can refer to
Appendix A to configure it. For example,
1. configure IP as 192.168.123.1, subnet mask as 255.255.255.0 and gateway as
192.168.123.254, or more easier,
2. configure your computers to load TCP/IP setting automatically, that is, via DHCP server of
this product.
After installing the TCP/IP communication protocol, you can use the ping command to check if your
computer has successfully connected to this product. The following example shows the ping procedure
for Windows 95 platforms. First, execute the ping command
ping 192.168.123.254
If the following messages appear:
Pinging 192.168.123.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.123.254: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=64
a communication link between your computer and this product has been successfully established.
Otherwise, if you get the following messages,
Pinging 192.168.123.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
There must be something wrong in your installation procedure. You have to check the following items
in sequence:
1. Is the Ethernet cable correctly connected between this product and your computer?
Tip: The LAN LED of this product and the link LED of network card on your computer must be
lighted.
2. Is the TCP/IP environment of your computers properly configured?
Tip: If the IP address of this product is 192.168.123.254, the IP address of your computer must
be 192.168.123.X and default gateway must be 192.168.123.254.
Page 12

3.2 Install the Software into Your Computers (Optional)
Skip this section if you do not want to use the print server function of this product.
Step 1: Insert the installation CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive. The following window will be
shown automatically. If it isn’t, please run “install.exe” on the CD-ROM.
Page 13
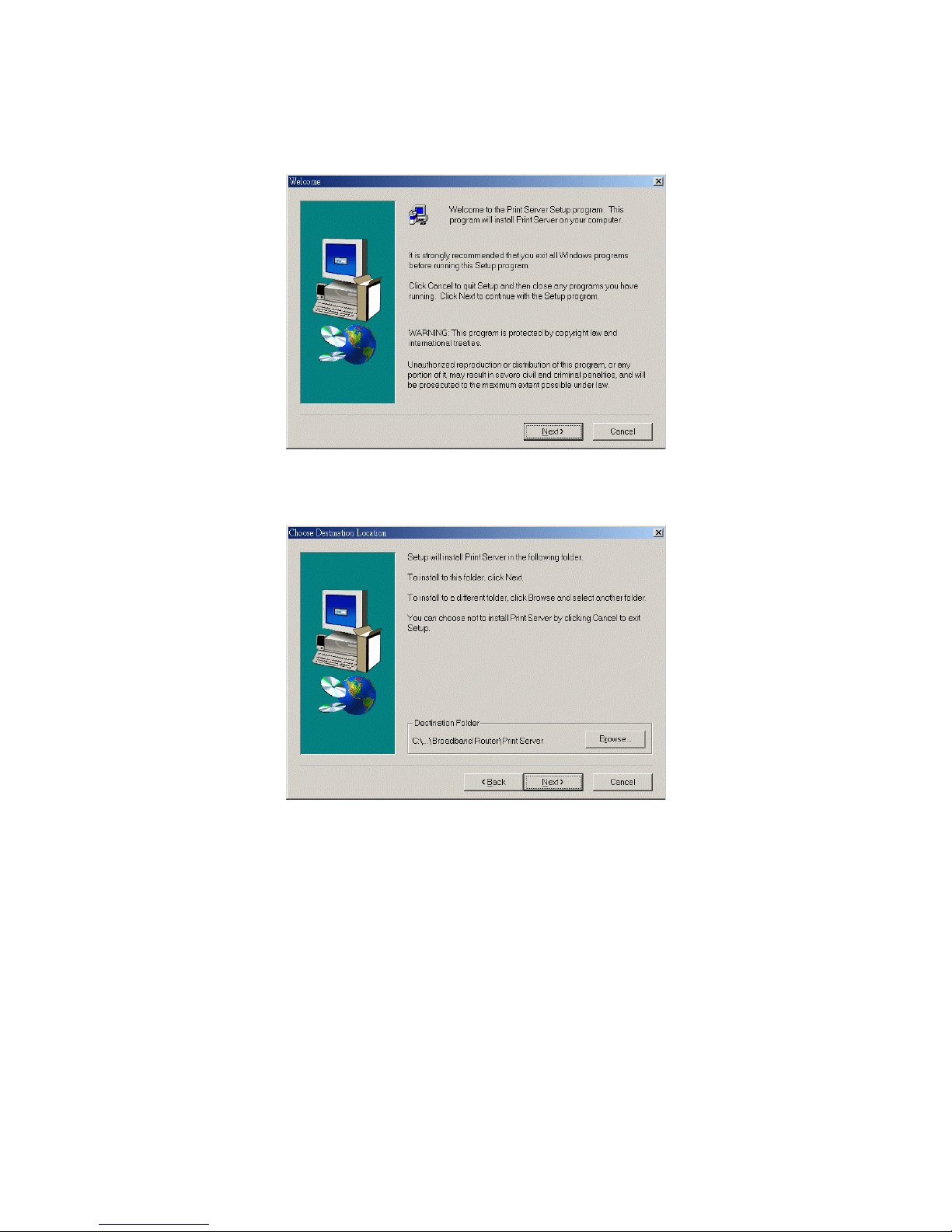
Step 2: Click on the INSTALL button. Wait until the following We lcome dialog to appear, and click on
the Next button.
Step 3: Select the destination folder and click on the Next button. Then, the setup program will begin to
install the programs into the destination folder.
Page 14
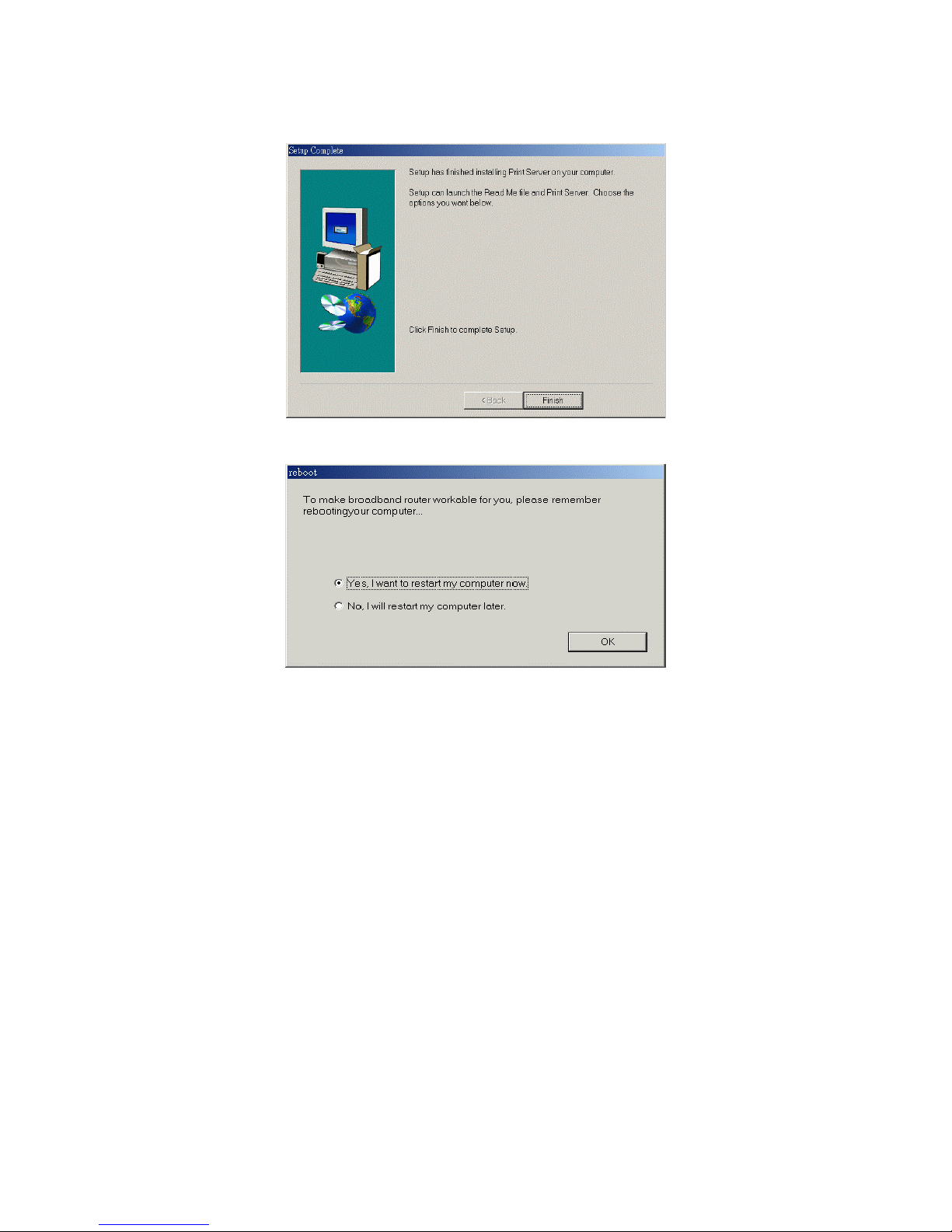
Step 4: When the following window is displayed, click on the Finish button.
Step 5: Select the item to restart the computer and then click the OK button to reboot your computer.
Step 6: After rebooting your computer, the software installation procedure is finished.
Now, you can configure the NAT Router (refer to Chapter 4) and setup the Print Server (refer to
Chapter 5).
Page 15
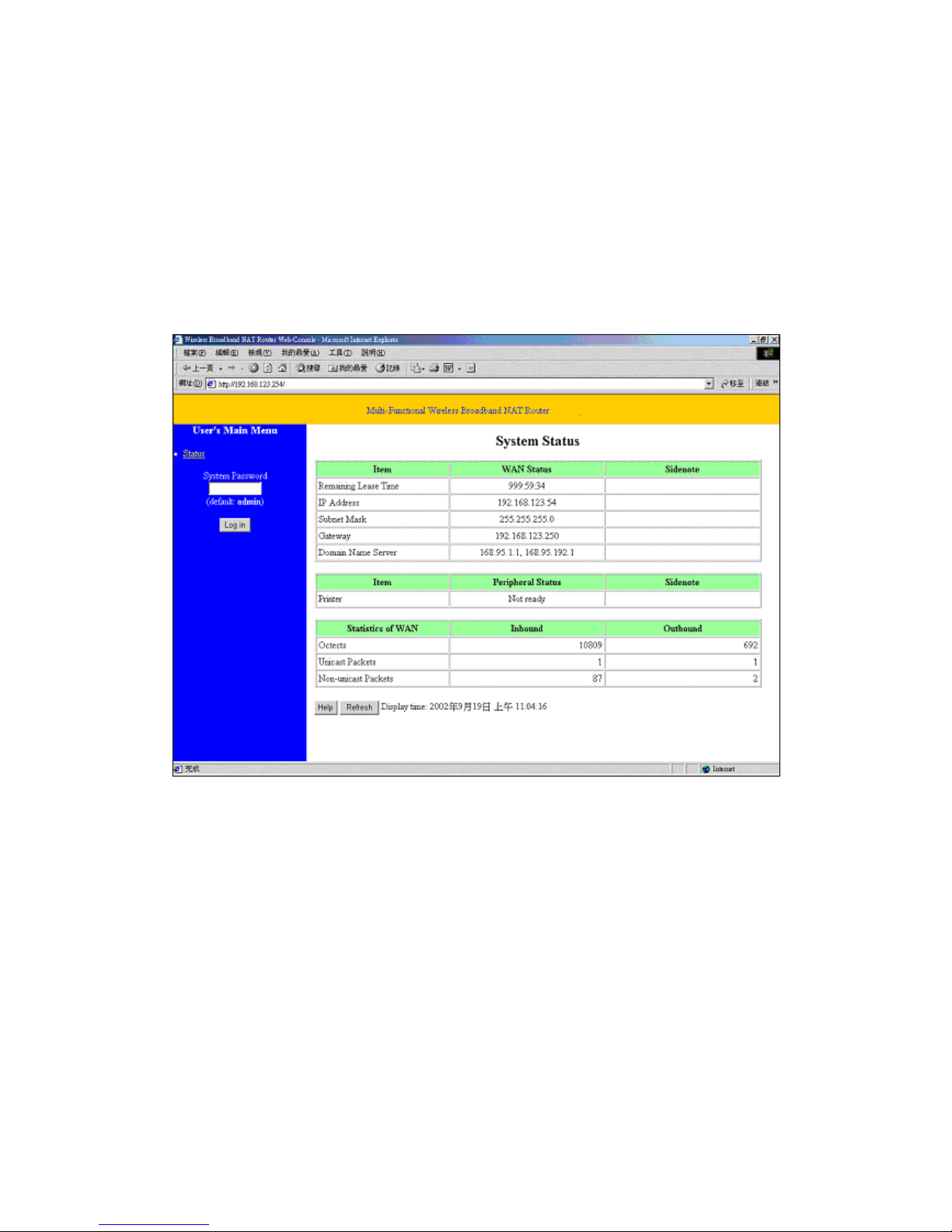
Chapter 4 Configuring NAT Router
This product provides Web based configuration scheme, that is, configuring by your Web browser, such
as Netscape Communicator or Internet Explorer. This approach can be adopted in any MS Windows,
Macintosh or UNIX based platforms.
4.1 Start-up and Log in
Activate your browser, and disable the proxy or add the IP address of this product into the exceptions.
Then, type this product’s IP address in the Location (for Netscape) or Address (for IE) field and press
ENTER. For example: http://192.168.123.254.
After the connection is established, you will see the web user interface of this product. There are two
appearances of web user interface: for general users and for system administrator.
To log in as an administrator, enter the system password (the factory setting is ”admin”) in the System
Password field and click on the Log in button. If the password is correct, the web appearance will be
changed into administrator configure mode. As listed in its main menu, there are several options for
system administration.
Page 16
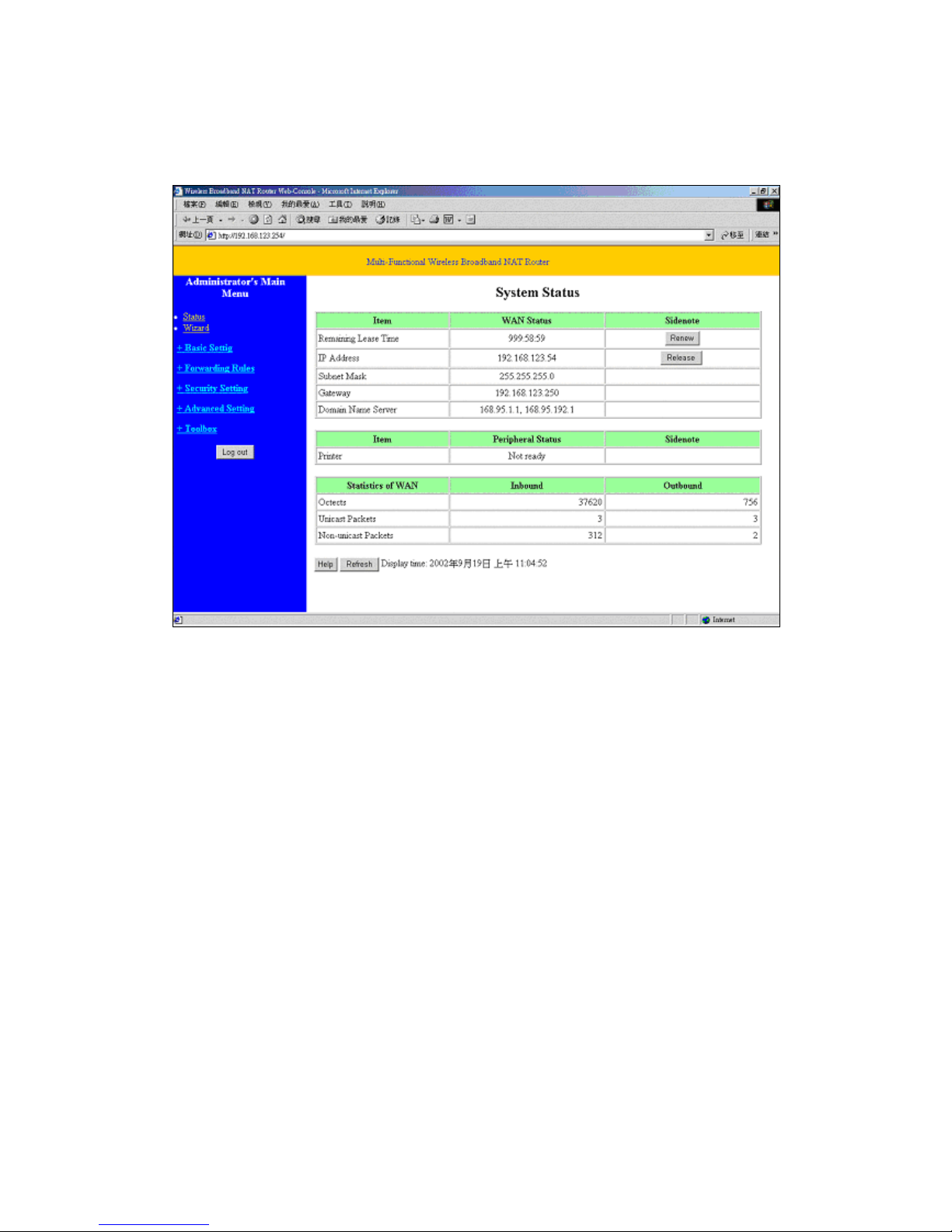
4.2 Status
This option provides the function for observing this product’s working status:
A. WAN Port Status.
If the WAN port is assigned a dynamic IP, there may appear a “Renew” or “Release” button
on the Sidenote column. You can click this button to renew or release IP manually.
B. Modem Status.
C. Printer Status. The possible kinds of printer status include “Ready”, “Not ready”,
“Printing…”, and “Device error”.
When a job is printing, there may appear a “Kill Job” button on the Sidenote column. You
can click this button to kill current printing job manually.
D. Statistics of WAN: enables you to monitor inbound and outbound packets
Page 17
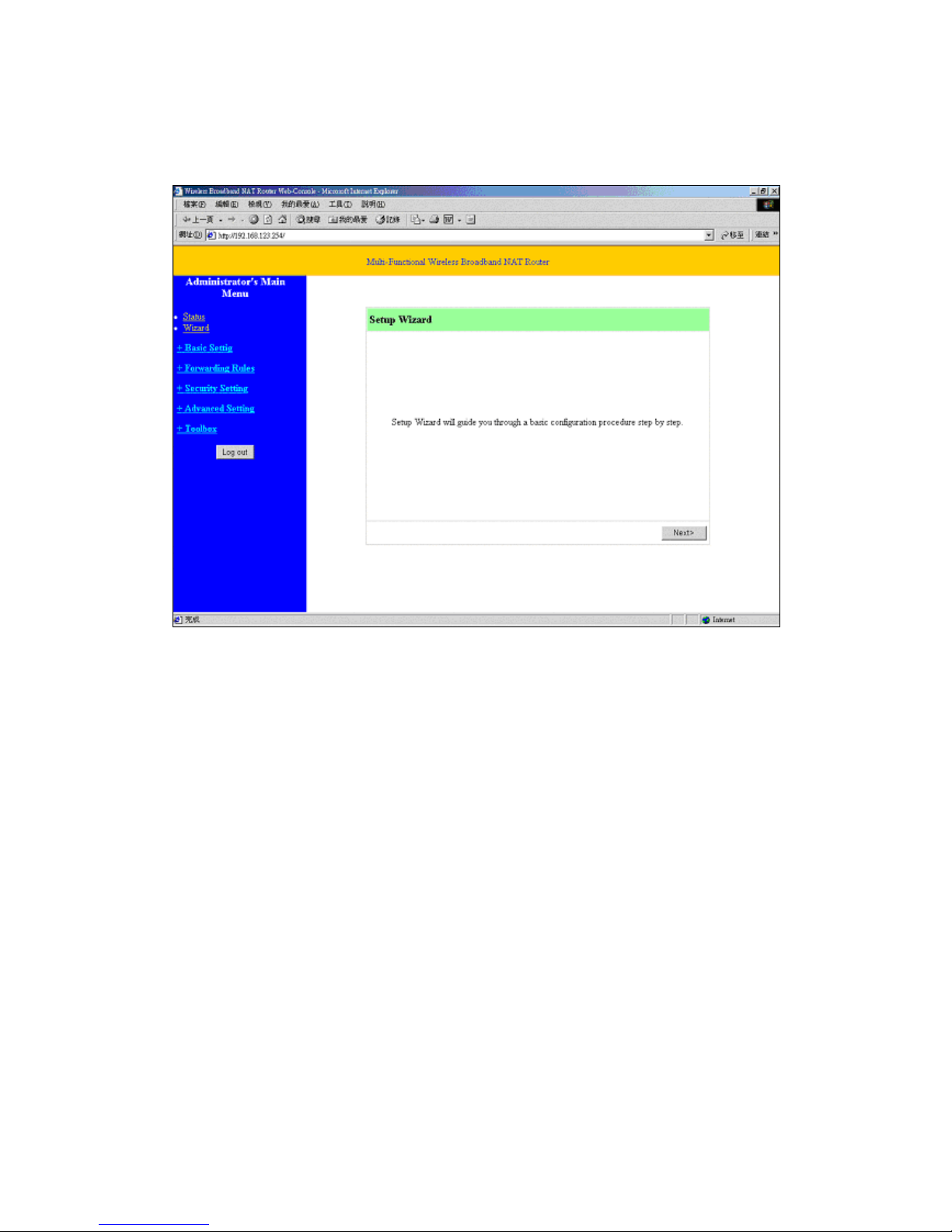
4.3 Wizard
Setup Wizard will guide you through a basic configuration procedure step by step.
Press ”Next >”
Page 18
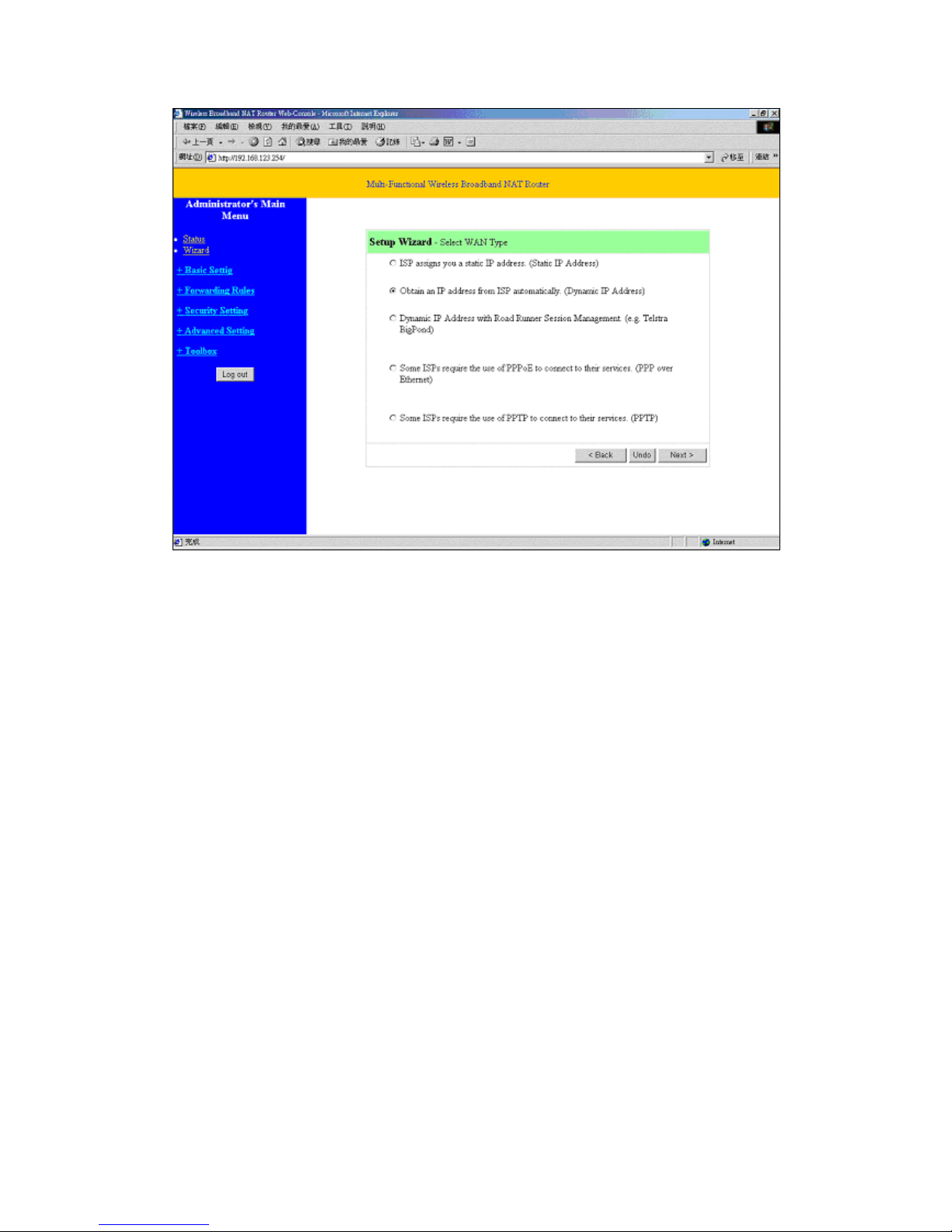
Setup Wizard - Select WAN Type: For detail settings, please refer to 4.4.1 primary
setup.
Page 19
4.4 Basic Setting
Page 20
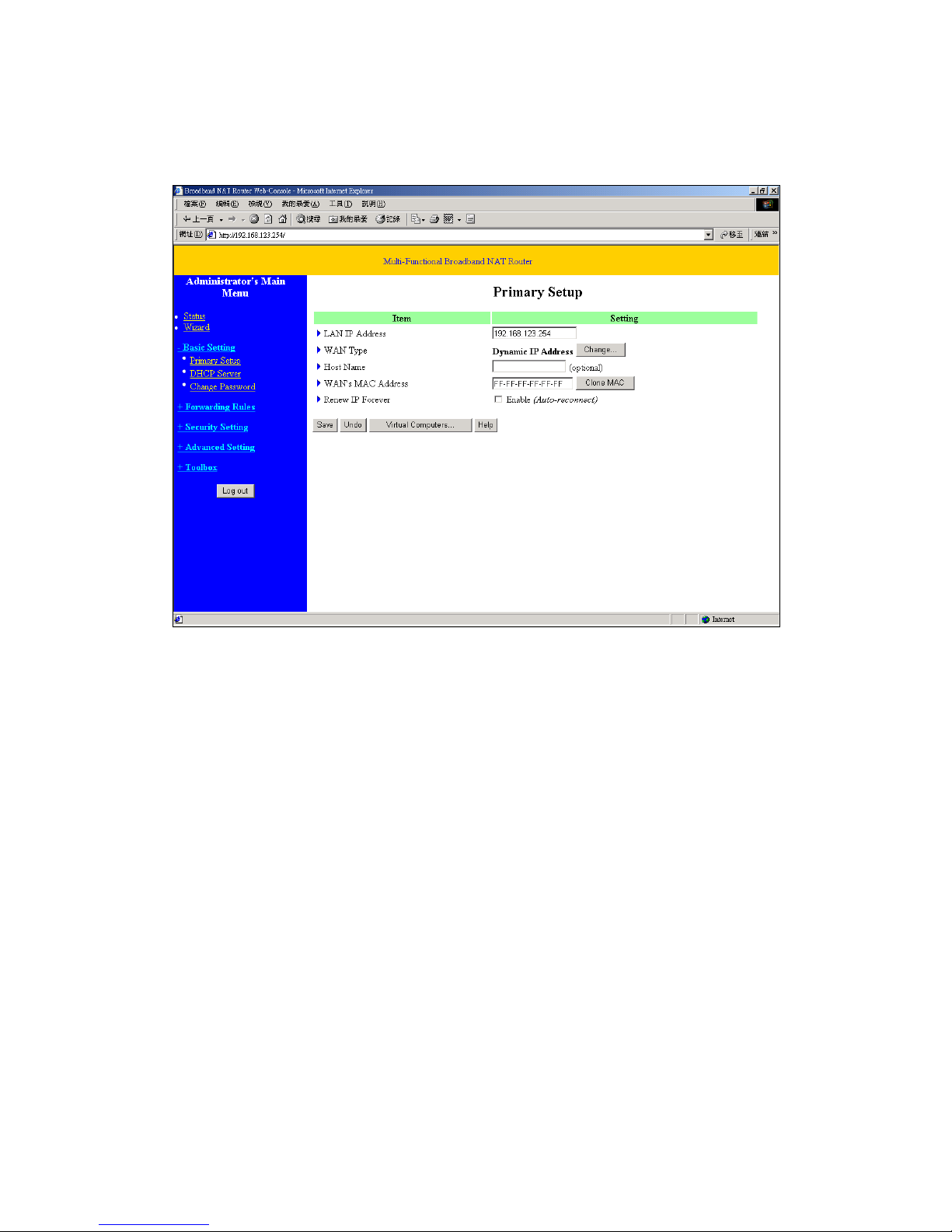
4.4.1 Primary Setup
Press “Change”
Page 21
This option is primary to enable this product to work properly. The setting items and the web
appearance depend on the WAN type. Choose correct WAN type before you start.
1. LAN IP Address: the local IP address of this device. The computers on your network must use the
LAN IP address of your product as their Default Gateway. You can change it if necessary.
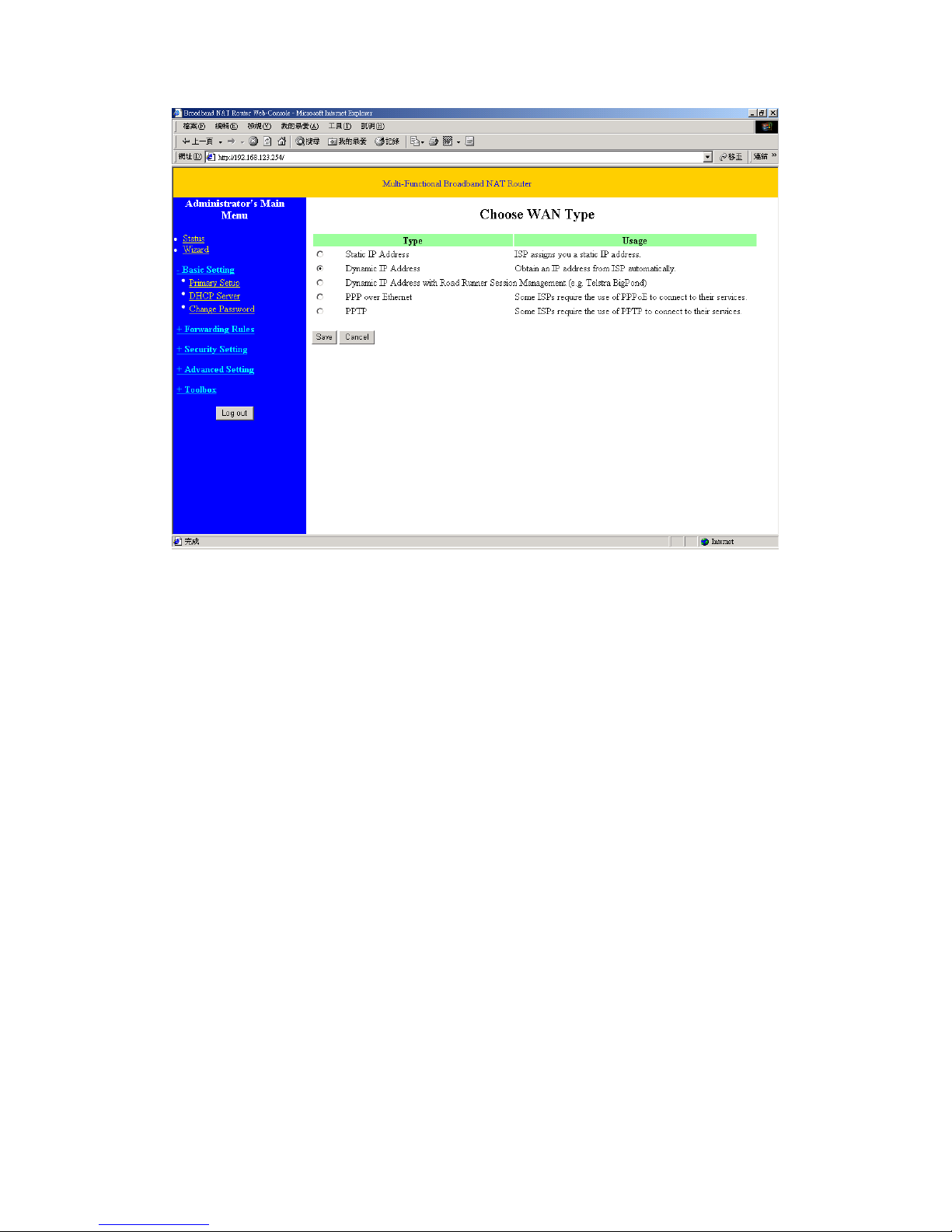
2. WAN Type: WAN connection type of your ISP. You can click Change button to choose a correct
one from the following four options:
A. Static IP Address: ISP assigns you a static IP address.
B. Dynamic IP Address: Obtain an IP address from ISP automatically.
C. Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management.(e.g. Telstra BigPond)
D. PPP over Ethernet: Some ISPs require the use of PPPoE to connect to their services.
E. Dial-up Network: To surf the Internet via PSTN/ISDN.
4.4.1.1 Static IP Address
WAN IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Primary and Secondary DNS: enter the proper setting
provided by your ISP.
4.4.1.2 Dynamic IP Address
1. Host Name: optional. Required by some ISPs, for example, @Home.
2. Renew IP Forever: this feature enables this product to renew your IP address automatically when
the lease time is expiring-- even when the system is idle.
Page 22

4.4.1.3 Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management.(e.g. Telstra BigPond)
LAN IP Address is the IP address of this product. It must be the default gateway of your
computers.
WAN Type is Dynamic IP Address. If the WAN type is not correct, change it!
Host Name: optional. Required by some ISPs, e.g. @Home.
•
Renew IP Forever: this feature enable this product renew IP address
automatically when the lease time is being expired even the system is in idle
state.
4.4.1.4 PPP over Ethernet
1. PPPoE Account and Password: the account and password your ISP assigned to you. For security,
this field appears blank. If you don't want to change the password, leave it empty.
2. PPPoE Service Name: optional. Input the service name if your ISP requires it. Otherwise, leave it
blank.
3. Maximum Idle Time: the amount of time of inactivity before disconnecting your PPPoE session.
Set it to zero or enable Auto-reconnect to disable this feature.
4.4.1.5 PPTP
1. My IP Address and My Subnet Mask: the private IP address and subnet mask your ISP assigned
to you.
2. Server IP Address: the IP address of the PPTP server.
3. PPTP Account and Password: the account and password your ISP assigned to you. If you don't
want to change the password, keep it empty.
4. Connection ID: optional. Input the connection ID if your ISP requires it.
5. Maximum Idle Time: the time of no activity to disconnect your PPTP session. Set it to zero or
enable Auto-reconnect to disable this feature. If Auto-reconnect is enabled, this product will
automatically connect to ISP after system is restarted or connection is dropped.
Page 23

4.6.6 Dial-up Network
1. Dial-up Telephone, Account and Password: assigned by your ISP. For security, this field appears
blank. If you don't want to change the password, leave it empty.
2. Primary and Secondary DNS: If they are configured as "0.0.0.0.", they will be automatically
assigned upon connection.
3. Maximum Idle Time: the amount of time of inactivity before disconnecting your dial-up session.
4. Baud Rate: the communication speed between this product and your MODEM or ISDN TA.
5. Extra Setting: (initialization string) optional. Used to optimize the communication quality
between the ISP and your MODEM or ISDN TA
Page 24

4.4.2 DHCP Server
Press “More>>”
Page 25

The settings of a TCP/IP environment include host IP, Subnet Mask, Gateway, and DNS configurations.
It is not easy to manually configure all the computers and devices in your network. Fortunately, DHCP
Server provides a rather simple approach to handle all these settings. This product supports the function
of DHCP server. If you enable this product’s DHCP server and configure your computers as “automatic
IP allocation” mode, then when your computer is powered on, it will automatically load the proper
TCP/IP settings from this product. The settings of DHCP server include the following items:
1. DHCP Server: Choose “Disable” or “Enable.”
2. IP pool starting Address/ IP pool starting Address: Whenever there is a request, the DHCP
server will automatically allocate an unused IP address from the IP address pool to the
requesting computer. You must specify the starting and ending address of the IP address pool.
3. Domain Name: Optional, this information will be passed to the client.
4. Primary DNS/Secondary DNS: This feature allows you to assign DNS Servers
5. Primary WINS/Secondary WINS: This feature allows you to assign WINS Servers
6. Gateway: The Gateway Address would be the IP address of an alternate Gateway.
This function enables you to assign another gateway to your PC, when DHCP server offers an
IP to your PC.
Page 26

4.4.3 Change Password
You can change Password here. We strongly recommend you to change the system
password for security reason.
Page 27

4.5 Forwarding Rules
Page 28

4.5.1 Virtual Server
This product’s NAT firewall filters out unrecognized packets to protect your Intranet, so all hosts
behind this product are invisible to the outside world. If you wish, you can make some of them
accessible by enabling the Virtual Server Mapping.
A virtual server is defined as a Service Port, and all requests to this port will be redirected to the
computer specified by the Server IP.
For example, if you have an FTP server (port 21) at 192.168.123.1, a Web server (port 80) at
192.168.123.2, and a VPN server at 192.168.123.6, then you need to specify the following virtual
server mapping table:
Service Port Server IP Enable
21 192.168.123.1 V
80 192.168.123.2 V
1723 192.168.123.6 V
Page 29

4.5.2 Special AP
Some applications require multiple connections, like Internet games, Video conferencing, Internet
telephony, etc. Because of the firewall function, these applications cannot work with a pure NAT router.
The Special Applications feature allows some of these applications to work with this product. If the
mechanism of Special Applications fails to make an application work, try setting your computer as the
DMZ host instead.
1. Trigger: the outbound port number issued by the application..
2. Incoming Ports: when the trigger packet is detected, the inbound packets sent to the specified
port numbers are allowed to pass through the firewall.
This product provides some predefined settings Select your application and click Copy to to add the
predefined setting to your list.
Note! At any given time, only one PC can use each Special Application tunnel.
Page 30

4.5.3 Miscellaneous Items
IP Address of DMZ Host
DMZ (DeMilitarized Zone) Host is a host without the protection of firewall. It allows a computer to be
exposed to unrestricted 2-way communication for Internet games, Video conferencing, Internet
telephony and other special applications.
NOTE: This feature should be used only when needed.
Non-standard FTP port
You have to configure this item if you want to access an FTP server whose port number is not 21. This
setting will be lost after rebooting.
Page 31

4.6 Security Settings
Page 32

4.6.1 Packet Filter
Packet Filter enables you to control what packets are allowed to pass the router. Outbound filter applies
on all outbound packets. However, Inbound filter applies on packets that destined to Virtual Servers or
DMZ host only. You can select one of the two filtering policies:
1. Allow all to pass except those match the specified rules
2. Deny all to pass except those match the specified rules
You can specify 8 rules for each direction: inbound or outbound. For each rule, you can define the
following:
• Source IP address
• Source port address
• Destination IP address
• Destination port address
• Protocol: TCP or UDP or both.
Page 33

For source or destination IP address, you can define a single IP address (4.3.2.1) or a range of IP
addresses (4.3.2.1-4.3.2.254). An empty implies all IP addresses.
For source or destination port, you can define a single port (80) or a range of ports (1000-1999). Add
prefix "T" or "U" to specify TCP or UDP protocol. For example, T80, U53, U2000-2999. No prefix
indicates both TCP and UDP are defined. An empty implies all port addresses.
Each rule can be enabled or disabled individually.
Inbound Filter:
To enable Inbound Packet Filter click the check box next to Enable in the Inbound
Packet Filter field.
Suppose you have SMTP Server (25), POP Server (110), Web Server (80), FTP
Server (21), and News Server (119) defined in Virtual Server or DMZ Host.
Example 1:
(1.2.3.100-1.2.3.149) They are allow to send mail (port 25), receive mail (port 110),
and browse the Internet (port 80)
Page 34

(1.2.3.10-1.2.3.20) They can do everything (block nothing)
Others are all blocked.
Example 2:
(1.2.3.100-1.2.3.119) They can do everything except read net news (port 119) and
transfer files via FTP (port 21)
Others are all allowed.
After Inbound Packet Filter setting is configured, click the save button.
Outbound Filter:
To enable Outbound Packet Filter click the check box next to Enable in the
Outbound Packet Filter field.
Page 35

Example 1:
(192.168.123.100-192.168.123.149) They are allowed to send mail (port 25), receive
mail (port 110), and browse Internet (port 80); port 53 (DNS) is necessary to resolve
the domain name.
(192.168.123.10-192.168.123.20) They can do everything (block nothing)
Others are all blocked.
Page 36

Example 2:
(192.168.123.100-192.168.123.119) They can do everything except read net news
(port 119) and transfer files via FTP (port 21)
Others are allowed
After Outbound Packet Filter setting is configured, click the save button.
Page 37

4.6.2 Domain Filter
Domain Filter let you prevent users under this device from accessing specific URLs.
Domain Filter Enable
Checke if you want to enable Domain Filter.
Log DNS Query
Checke if you want to log the action when someone accesses the specific URLs.
Privilege IP Addresses Range
Setting a group of hosts and privilege these hosts to access network without restriction.
Domain Suffix
A suffix of URL to be restricted. For example, ".com", "xxx.com".
Action
When someone is accessing the URL met the domain-suffix, what kind of action you want.
Checke drop to block the access. Checke log to log these access.
Enable
Checke to enable each rule.
Page 38

Example:
In this example:
1. URL include “sex.com” will be blocked, and the action will be record in log-file.
2. URL include “girl.com” will not be blocked, but the action will be record in log-file.
3. URL include “erotica.com” will be blocked, but the action will not be record in log-file.
4. IP address X.X.X.1~ X.X.X.10 can access network without restriction.
4.6.3 MAC Address Control
Page 39

MAC Address Control allows you to assign different access right for different users and to assign a
specific IP address to a certain MAC address.
MAC Address Control Check “Enable” to enable the “MAC Address Control”. All of the
settings in this page will take effect only when “Enable” is checked.
Connection control Check "Connection control" to enable the controlling of which wired
clients can connect to this device. If a client is denied to connect to this
device, it means the client can't access to the Internet either. Choose
"allow" or "deny" to allow or deny the clients, whose MAC addresses are
not in the "Control table" (please see below), to connect to this device.
Page 40

MAC Address
MAC address indicates a specific client.
IP Address
Expected IP address of the corresponding
client. Keep it empty if you don't care its
IP address.
C
When "Connection control" is checked,
check "C" will allow the corresponding
client to connect to this device.
In this page, we provides the following Combobox and button to help you to input the MAC address.
You can select a specific client in the “DHCP clients” Combobox, and then click on the “Copy to”
button to copy the MAC address of the client you select to the ID selected in the “ID” Combobox.
Previous page and Next Page To make this setup page simple and clear, we have divided the
“Control table” into several pages. You can use these buttons to
navigate to different pages.
Page 41

4.6.4 Miscellaneous Items
Remote Administrator Host/Port
In general, only Intranet user can browse the built-in web pages to perform administration task. This
feature enables you to perform administration task from remote host. If this feature is enabled, only the
specified IP address can perform remote administration. If the specified IP address is 0.0.0.0, any host
can connect to this product to perform administration task. You can use subnet mask bits "/nn" notation
to specified a group of trusted IP addresses. For example, "10.1.2.0/24".
NOTE: When Remote Administration is enabled, the web server port will be shifted to 88. You can
change web server port to other port, too.
Administrator Time-out
The time of no activity to logout automatically. Set it to zero to disable this feature.
Discard PING from WAN side
When this feature is enabled, any host on the WAN cannot ping this product.
Page 42

4.7 Advanced Setting
Page 43

4.7.1 System Log
This page support two methods to export system logs to specific destination by means
of syslog(UDP) and SMTP(TCP). The items you have to setup including:
IP Address for Syslogd
Host IP of destination where syslogs will be sent to.
Check Enable to enable this function.
IP Address of Outgoing Mail Server
Input the IP Address of Outgoing Mail Server.
For example, "192.168.1.100".
Log or Alert Recipient
The recipients who will receive these logs.Check Enable to enable Email alert(send
syslog via email).
.
Page 44

4.7.2 Dynamic DNS
To host your server on a changing IP address, you have to use dynamic domain name
service (DDNS).
So that anyone wishing to reach your host only needs to know the name of it. Dynamic
DNS will map the name of your host to your current IP address, which changes each
time you connect your Internet service provider.
Before you enable Dynamic DNS, you need to register an account on one of these
Dynamic DNS servers that we list in provider field.
To enable Dynamic DNS click the check box next to Enable in the DDNS field.
Next you can enter the appropriate information about your Dynamic DNS Server.
You have to define:
Provider
Page 45

Host Name
Username/E-mail
Password/Key
You will get this information when you register an account on a Dynamic DNS server.
Example:
After Dynamic DNS setting is configured, click the save button.
Page 46

4.7.3 SNMP Setting
In brief, SNMP, the Simple Network Management Protocol, is a protocol designed to give a user the
capability to remotely manage a computer network by polling and setting terminal values and
monitoring network events.
Enable SNMP
You must check either Local or Remote or both to enable SNMP function. If Local is checked, this
device will response request from LAN. If Remote
is checked, this device will response request
from WAN.
Get Community
Setting the community of GetRequest your device will response.
Set Community
Setting the community of SetRequest your device will accept.
Page 47

Example:
1. This device will response to SNMP client which’s get community is set as “public”
2. This device will response to SNMP client which’s set community is set as “private”
3. This device will response request from both LAN and WAN
Page 48

4.7.4 Routing Table
Routing Tables allow you to determine which physical interface address to use for outgoing
IP data grams. If you have more than one routers and subnets, you will need to enable routing
table to allow packets to find proper routing path and allow different subnets to communicate
with each other.
Routing Table settings are settings used to setup the functions of static and dynamic routing.
Static Routing: For static routing, you can specify up to 8 routing rules. You can
enter the destination IP address, subnet mask, gateway, hop for each routing rule, and
then enable or disable the rule by checking or unchecking the Enable checkbox.
Page 49

Example:
So if, for example, the host wanted to send an IP data gram to 192.168.3.88, it would use the above
table to determine that it had to go via 192.168.1.33 (a gateway),
And if it sends Packets to 192.168.5.77 will go via 192.168.1.55
Each rule can be enabled or disabled individually.
After routing table setting is configured, click the save button.
Page 50

4.8 Toolbox
Page 51

4.8.1 System Log
You can View system log by clicking the View Log button
Page 52

4.8.2 Firmware Upgrade
You can upgrade firmware by clicking Firmware Upgrade button.
Page 53

4.8.3 Backup Setting
You can backup your settings by clicking the Backup Setting button and save it as a
bin file. Once you want to restore these settings, please click Firmware Upgrade
button and use the bin file you saved.
4.8.4 Reset to default
You can also reset this product to factory default by clicking the Reset to default button.
4.8.5 Reboot
You can also reboot this product by clicking the Reboot button.
Page 54

4.8.6 Miscellaneous Items
MAC Address for Wake-on-LAN
Wake-on-LAN is a technology that enables you to power up a networked device remotely. In order to
enjoy this feature, the target device must be Wake-on-LAN enabled and you have to know the MAC
address of this device, say 00-11-22-33-44-55. Clicking "Wake up" button will make the router to send
the wake-up frame to the target device immediately.
Page 55

Chapter 5 Print Server (optional)
This product provides the function of network print server for MS Windows 95/98/NT/2000 and Unix
based platforms. (If the product you purchased doesn’t have printer port, please skip this chapter.)
5.1 Configuring on Windows 95/98 Platforms
After you finished the software installation procedure described in Chapter 3, your computer has
possessed the network printing facility provided by this product. For convenience, we call the printer
connected to the printer port of this product as server printer. On a Windows 95/98 platform, open the
Printers window in the
My Computer menu:
Now, yon can configure the print server of this product:
Page 56

1. Find out the corresponding icon of your server printer, for example, the HP
LaserJet 6L. Click the mouse’s right button on that icon, and then select the Properties item:
2. Click the Details item:
3. Choose the “PRTmate: (All-in-1)” from the list attached at the Print To item. Be sure that the
Printer Driver item is configured to the correct driver of your server printer.
4. Click on the button of Port Settings:
Type in the IP address of this product and then click the OK button.
4. Make sure that all settings mentioned above are correct and then click the OK button.
Page 57

5.2 Configuring on Windows NT Platforms
The configuration procedure for a Windows NT platform is similar to that of Windows 95/98 except
the screen of printer Properties:
Compared to the procedure in last section, the selection of Details is equivalent to the selection of
Ports, and Port Settings is equivalent to Configure Port.
Page 58

5.3 Configuring on Windows 2000 and XP Platforms
Windows 2000 and XP have built-in LPR client, users could utilize this feature to
Print.
1. Open Printers and Faxs.
Page 59

2. Click Create a new port, and then click LPR Port
Page 60

3. Click Next and then provide the following information:
Type address of server providing LPD that is our NAT device:192.168.123.254
Page 61

4. Type print queue on that server. Ours is” lp“ lowercase letter
And enable “LPR Byte counting Enabled”
Page 62

5. Apply your settings
5.4 Configuring on Unix based Platforms
Please follow the traditional configuration procedure on Unix platforms to setup the print server of this
product. The printer name is “lp.”
Page 63

Appendix A TCP/IP Configuration for Windows 95/98
This section introduces you how to install TCP/IP protocol into your personal computer. And suppose
you have been successfully installed one network card on your personal computer. If not, please refer
to your network card manual. Moreover, the Section B.2 tells you how to set TCP/IP values for
working with this NAT Router correctly.
A.1 Install TCP/IP Protocol into Your PC
1. Click Start button and choose Settings, then click Control Panel.
2. Double click Network icon and select Configuration tab in the Network window.
3. Click Add button to add network component into your PC.
4. Double click Protocol to add TCP/IP protocol.
5. Select Microsoft item in the manufactures list. And choose TCP/IP in the Network Protocols.
Click OK button to return to Network window.
6. The TCP/IP protocol shall be listed in the Network window. Click OK to complete the install
procedure and restart your PC to enable the TCP/IP protocol.
Page 64

A.2 Set TCP/IP Protocol for Working with NAT Router
1. Click Start button and choose Settings, then click Control Panel.
2. Double click Network icon. Select the TCP/IP line that has been associated to your network card
in the Configuration tab of the Network window.
3. Click Properties button to set the TCP/IP protocol for this NAT Router.
Page 65

4. Now, you have two setting methods:
A. Get IP via DHCP server
a. Select Obtain an IP address automatically in the IP Address tab.
b. Don’t input any value in the Gateway tab.
Page 66

c. Choose Disable DNS in the DNS Configuration tab.
B. Configure IP manually
a. Select Specify an IP address in the IP Address tab. The default IP address of this
product is 192.168.123.254. So please use 192.168.123.xxx (xxx is between 1 and 253)
for IP Address field and 255.255.255.0 for Subnet Mask field.
Page 67

b. In the Gateway tab, add the IP address of this product (default IP is 192.168.123.254)
in the New gateway field and click Add button.
c. In the DNS Configuration tab, add the DNS values which are provided by the ISP into
DNS Server Search Order field and click Add button.
Page 68

Appendix B Console Mode (optional)
When you forget the system password or the IP address of this product, you need enter console mode to
reset them.
Before invoking the console program, be sure to find a null modem cable and use it to connect from
this product’s COM port to your computer’s COM port. Then, execute a terminal program, such as the
Hyper Terminal of MS Windows 95. The connection parameters should be set to 19200 8-N-1. And,
reboot this product. When the M1 indicator starts flashing regularly, you can press the “Enter” key of
the keyboard several times, there should be some messages and console prompt ">" appeared in the
terminal.
In the console mode, you may reset the IP address and the system password of this product. Please
remember to execute the SR command to save the changes you have made. For example,
IP 192.168.123.254
PW admin
SR
 Loading...
Loading...