GMT G931T24U, G931T24T, G931T24D, G931T24B, G930T21U Datasheet
...
Ver: 4.5
May 13, 2002
TEL: 886-3-5788833
http://www.gmt.com.tw
1
G930/G931
Global Mixed-mode Technology Inc.
3.5V 400mA Low Dropout Regulator
Features
Dropout voltage typically 0.8V @ IO = 400mA
Output current in excess of 400mA
Output voltage accuracy +3%/-2%
Quiescent current, typically 600
µµµµ
A
Internal short circuit current limit
Internal over temperature protection
General Description
The G930/G931 positive 3.5V voltage regulator features the ability to source 400mA of output current
with a dropout voltage of typically 0.8V over the entire operating temperature range. A low quiescent
current is provided over the entire output current
range. The typical quiescent current is 0.6mA. Furthermore, the quiescent current is smaller when the
regulator is in the dropout mode (V
IN
< 3.5V).
Familiar regulator features such as over temperature
and over current protection circuits are provided to
prevent it from being damaged by abnormal operating
conditions.
Ordering Information
PIN OPTION
ORDER NUMBER PACKAGE TYPE
1 2 3
G930T21U SOT 89 V
OUT
GND V
IN
G931T24U SOT 89 GND V
IN
V
OUT
* For other package types, pin options and package, please contact us at sales @gmt.com.tw
Order Number Identification
GXXX XX X X
Packing Type
Pin Option
Package Type
Part Number
PACKAGE TYPE PIN OPTION PACKING
T2 : SOT 89
1 2 3
U & D : Tape & Reel Direction
T6 : SOT 223 1 : V
OUT
GND VIN T : Tube
T7 : SOT 23 2 : V
OUT
VIN GND B : Bag
T8 : µTO92 3 : GND V
OUT
VIN
4 : GND V
IN
V
OUT
5 : V
IN
GND V
OUT
6 : V
IN
V
OUT
GND
Typical Application Package Type
[Note 4] : Type of C
OUT
Top View
1
2
3
Top View
1
3
µTO 92
Top View
SOT 23
1
3
2
Top ViewTop View
1
2
3
SOT 89、223
Top View
2
V
IN
G930
C1
0.47µF
IQ
V
OUT
I
O
C
OUT
10µF
Top ViewTop View
1
2
3
Top View
1
3
µTO 92
Top View
SOT 23
1
3
2
Top ViewTop View
1
2
3
SOT 89、223
Top View
2
V
IN
G930
C1
0.47µF
IQ
V
OUT
I
O
C
OUT
10µF
Ver: 4.5
May 13, 2002
TEL: 886-3-5788833
http://www.gmt.com.tw
2
G930/G931
Global Mixed-mode Technology Inc.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(Note 1)
Input Voltage…………………………..……….………10V
Power Dissipation Internally Limited (Note 2)
Maximum Junction Temperature……………....……..150°C
Storage Temperature Range…..…..-65°C ≤ T
J
≤+150°C
Lead Temperature, Time for Wave Soldering
SOT-89 Package……………..………………...260°C, 4s
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +25°C)
SOT89
(1)
:…………………………………..……..…0.42W
Note
(1)
:See Recommended Minimum Footprint.
Operating Conditions
(Note 1)
Input Voltage……………………………………….4V~7V
Temperature Range……………………0°C ≤ T
J
≤125°C
Electrical Characteristics
VIN =5V, IO = 400mA, CIN = 1µF, C
OUT
=10 µF, All specifications apply for TA = TJ = 25°C. [Note 3]
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Output Voltage 5mA < IO <400mA 3.43 3.5 3.605 V
Line Regulation 4V < VIN < 7V, IO = 10mA 22 mV
Load Regulation 50mA < IO < 400mA 30 mV
Output Impedance 100mA DC and 100mA AC, fo = 120Hz 103 mΩ
Quiescent Current V
IN
= 5V 0.6 mA
Ripple Rejection fi = 120Hz, 1V
P-P,
Io = 100mA 42 dB
IO = 400mA 0.8 0.9 V
Dropout Voltage
I
O
= 100mA 125 150 mV
Short Circuit Current 0.77 A
Over Temperature 125
°C
Note 1:
Absolute Maximum Ratings are limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating
Conditions are conditions under which the device functions but the specifications might not be guaranteed. For
guaranteed specifications and test conditions see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2:
The maximum power dissipation is a function of the maximum junction temperature, T
Jmax
; total thermal re-
sistance,
θ
JA
, and ambient temperature TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient tem-
perature is T
jmax-TA
/
θ
JA
. If this dissipation is exceeded, the die temperature will rise above 130°C and IC
will go into thermal shutdown. For the G930/G931 in SOT 89 package,
θ
JA
is 250°C/W. (See Recommended Minimum Footprint). The safe operation in SOT 89, it can see “Typical Performance Characteristics” (Safe Operating Area).
Note3:
Low duty pulse techniques are used during test to maintain junction temperature as close to ambient as possible.
Note4:
The type of output capacitor should be tantalum or aluminum.
Definitions
Dropout Voltage
The input/output Voltage differential at which the regulator output no longer maintains regulation against
further reductions in input voltage. Measured when the
output drops 100mV below its nominal value, dropout
voltage is affected by junction temperature, load current and minimum input supply requirements.
Line Regulation
The change in output voltage for a change in input
voltage. The measurement is made under conditions
of low dissipation or by using pulse techniques such
that average chip temperature is not significantly affected.
Load Regulation
The change in output voltage for a change in load
current at constant chip temperature. The measurement is made under conditions of low dissipation or by
using pulse techniques such that average chip temperature is not significantly affected.
Maximum Power Dissipation
The maximum total device dissipation for which the
regulator will operate within specifications.
Quiescent Bias Current
Current which is used to operate the regulator chip
and is not delivered to the load.
Ver: 4.5
May 13, 2002
TEL: 886-3-5788833
http://www.gmt.com.tw
3
G930/G931
Global Mixed-mode Technology Inc.
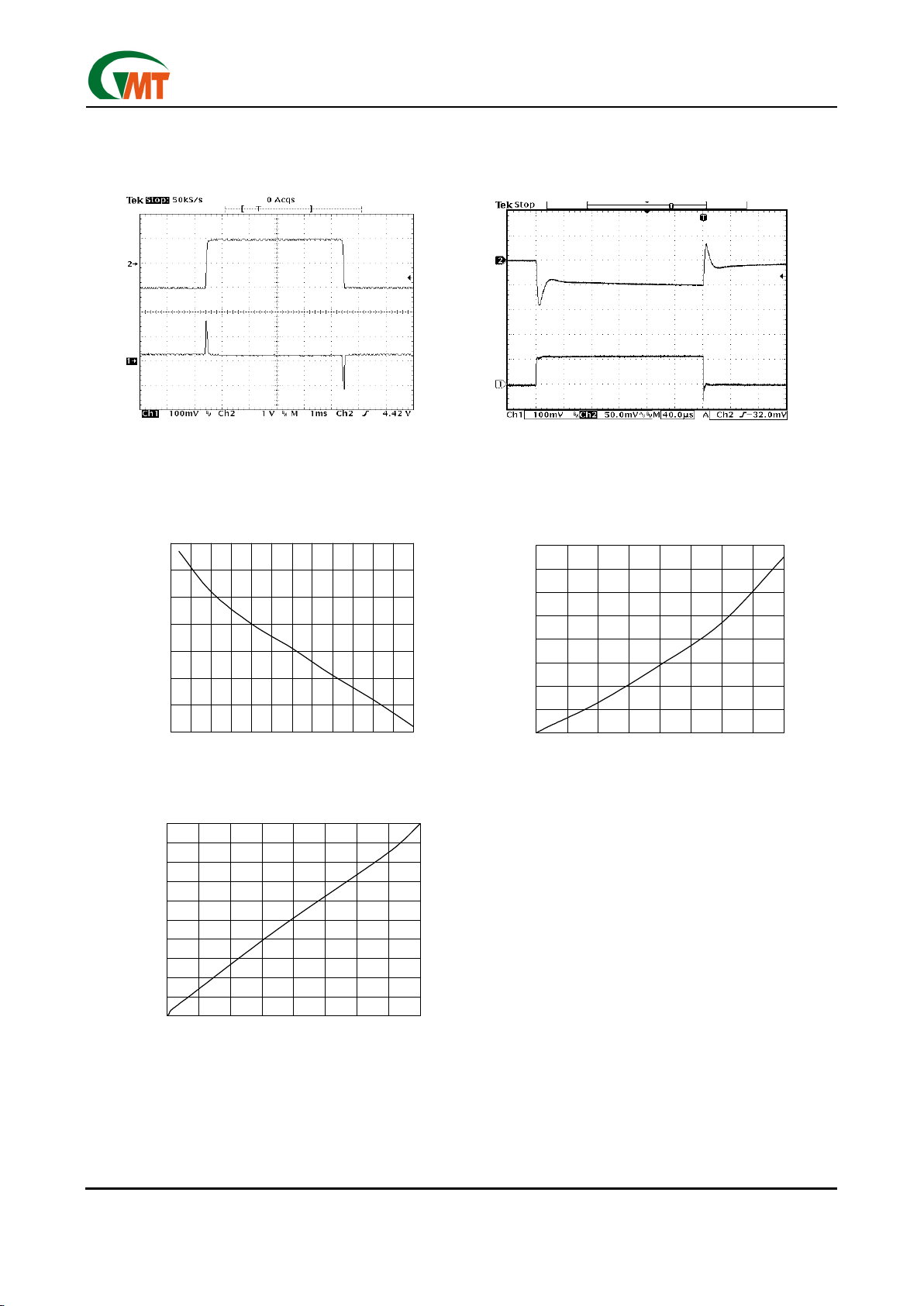
Typical Performance Characteristics
(VIN=5V, CIN=1µF , C
OUT
=10µF, TA=25°C , unless otherwise noted.)
Ch1: Vout (offset=3.50V) Ch1: Iout (400mA/div)
Ch2: Vin (offset=5.0V) Ch2: Vout (offset=3.50V)
Iout=100mA
Ground Current vs. Load Current
Line Transient Load Transient
Output Voltage vs. Load Current Dropout Voltage vs. Load Current
3.49
3.50
3.51
3.52
3.53
3.54
3.55
3.56
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Load Current (mA)
Output Voltage (V)
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
0 100 200 300 400
Load Current (mA)
Dropout Voltage (mV)
0.60
0.70
0.80
0.90
1.00
1.10
1.20
1.30
1.40
1.50
1.60
0 100 200 300 400
Load Current (mA)
Ground Current (mA)
 Loading...
Loading...