Page 1

High
Models
Frequency
Operating Instructions
Global® Pneumatic
Roller Vibrators
GCL-4400 GCD-4400
GCL-5000 GCD-5000
GCL-5500 GCD-5500
GCL-6500 GCD-6500
AIR BLASTERSVIBRATORSVIBRATORS
GlobalManufacturing.com
GCD
GCL
Global Manufacturing Inc.
1801 East 22nd St
Little Rock, Arkansas 72206
501.374.7416 TEL
800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
501.376.7147 FAX
®
GCL-GCD_03/02/16 Copyright © 2016 by Global Manufacturing, Inc
Page 2

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
Table of Contents Page
I. Introduction 2
II. Installation Procedures 3
III. Mounting 4 - 5
I V. Operation 6
V. Assembly & Disassembly Procedures 6 - 7
VI. Vibrating Wet Concrete 8 - 10
VII. Vibrator Orientation 11
VIII. Parts Explosion - GCD 12
IX. Parts Explosion - GCL 13
X. Vibrator Dimensions - GCD & GCL 14
XI. Bracket Dimensions 15
XII. Performance Data & Lubrication 16
XIII. Troubleshooting 17
I. Introduction
You have purchased a GCL-4400/GCD-4400, GCL-5000/GCD-5000, GCL-5500/GCD-5500, or GCL-6500/
GCD-6500 High Frequency vibrator manufactured by Global Manufacturing, Inc.® They are excellent
roller style high frequency pneumatic vibrators used on forms for concrete consolidation. The GCL model
ts the standard cradle lug brackets commonly used on concrete forms. The GCD models are bolt-on for
a more permanent mount, although they can also be attached to portable brackets.
For optimum performance, cycle the vibrator on and off. Vibrator act as a friction reducer and once the
bulk solid is set into motion, gravity does the rest. Do not operate the vibrator on an empty hopper as
this may cause structural damage to the hopper. Operate vibrators only when discharge gates are open.
Vibration will compact the material inside the structure if the discharge gate is closed.
Vibration has two important elements – Frequency and Amplitude. Frequency is the speed (RPM) or the
number of vibrations per minute. It is controlled by the air ow to a pneumatic vibrator. Amplitude is
the unbalance or amount of force produced by the eccentric weight. The faster the eccentric weights turn
the more force output generated. Force and frequency work together. It is not necessary to use a lot of
force when you have adequate frequency.
• Follow all mounting instructions.
• Always use a safety cable or chain for support.
• Do not operate vibrators when structure is empty.
• Do not operate vibrators when gate is closed or conveyor is stopped unless consolidation of
material is desired.
• Wear ear protection for 90+ decibel levels.
• Do not operate the pneumatic vibrators above 100 p.s.i.
• To prevent explosive hazard, do not use combustible gases to drive the pneumatic motor.
• Do not use hydrocarbons (fuel or kerosene) as a lubricant or de-icer.
• Always operate pneumatic vibrator with a regulator, lter, and lubricator.
• Always disconnect air line before maintenance.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
2
Page 3

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
II. Installation Procedures
Caution!
Do not mount the vibrator directly to the
structure wall. Use a channel iron stiffener for
proper mount rigidity and as the transducer of
the vibrational energy.
The key to successful
vibration is a proper mount
because rotary vibration
resonates the material
inside the structure, when
the vibrator is mounted
correctly. Rotary vibrators
should appear motionless
and make minimal noise.
Channel Irons - Size & Mounting
Stitch weld channel iron
Do not weld the ends of the channel
iron. This allows the vibrational force to
"escape". Solid welded ends trap the force
which can cause stress cracks.
Mounting GCL cradle lug model - Stitch weld a
GCL Bracket to the back of the channel iron. Do not
weld the ends. Mount the vibrator in the bracket by
sliding the foot into the GCL Bracket, lowering the
latch bolt into the ngers on the vibrator housing,
and securely tighten the nut.
Piggy-back
channel
Important!
Install a channel iron that is at least twothirds of the height of the sloped portion of
the hopper but no greater than 10 feet (3 m).
Install channel iron at least two-thirds the height
of the sloped portion of the hopper, but not less
than 6 feet (1.83 m) in length and the width not
less than the base width of the vibrator. See
chart below for recommended channel si zes. Do
not install more than one vibrator on the same
channel iron or use a channel iron shorter than the
recommended length. A short channel may ex
the bin wall.
Channel Iron Designation
Model
GC L- 4400
GCD-4400
GC L- 5000
GCD-5000
GC L- 5500
GC L- 6500
GCD- 5500
GCD- 6500
Channel
Iron
C4" x 5.4 lb/ft 60"
C100 x 8 kg/m 1524 mm
C4" x 5.4 lb/ft 72"
C100 x 8 kg/m 1829 mm
C4" x 7.25 lb/ft 72"
C100 x 11 kg/m 1829 mm
Attaching the vibrator to the channel iron.
Stitch weld nuts to the back of the channel iron
or the channel iron may be drilled and tapped to
accept the mounting bolts. An alternate method is
to cut a second channel iron slightly longer than
the footprint of the vibrator. Stitch weld the second
channel iron to the rst. Do not weld the ends.
Mount the vibrator to the second channel iron.
Minimum
Length
Stitch weld
GCL Bracket
Stitch weld
channel iron
Do not weld the ends of the
channel iron. This allows the
vibrational force to “escape”.
Solid welded ends trap the force
which can cause stress cracks.
to channel
Hopper
Stitch weld the channel iron vertically to the
sloped portion of the bin wall. Weld 3 inches
(7.5 cm), skip 1 inch (2.5 cm), weld 3 inches (7.5
cm), etc... Leave 1 inch (2.5 cm) un-welded on
the ends and corners. This allows the vibration to
dissipate out the ends of channel without causing
stress cracks to the hopper or bin. By doing so,
should the weld fail, the entire mount will not fall
off. Do not mount the channel iron horizontally.
Secure the vibrator to the channel iron with
SAE coarse thread grade 8 plated bolts with
lock washers or an adhesive such as Loctite
®
262. Tighten bolts in a sequential process. At least
two passes are required in most situations. Give
all bolts the same torque value. Grade 8 bolts can
handle more torque than standard bolts. If Loctite
®
is not used, retorque the bolt after the vibrator has
operated for a few minutes and check tightness
often. If Loctite® is used do not retorque the bolts
as this will break the Loctite® bond.
Attach a safety cable to a stronghold (not the
channel iron mount), which is higher than the
mounted vibrator and capable of holding the
vibrator’s weight.
3
Page 4
Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
H
⅓
of H
⅔
of H
⅓
of H
⅔
of H
H
¾
of
H
¼
of H
½
of H
⅔
of H
⅓
of H
⅔
of
H
⅔
of H
H
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
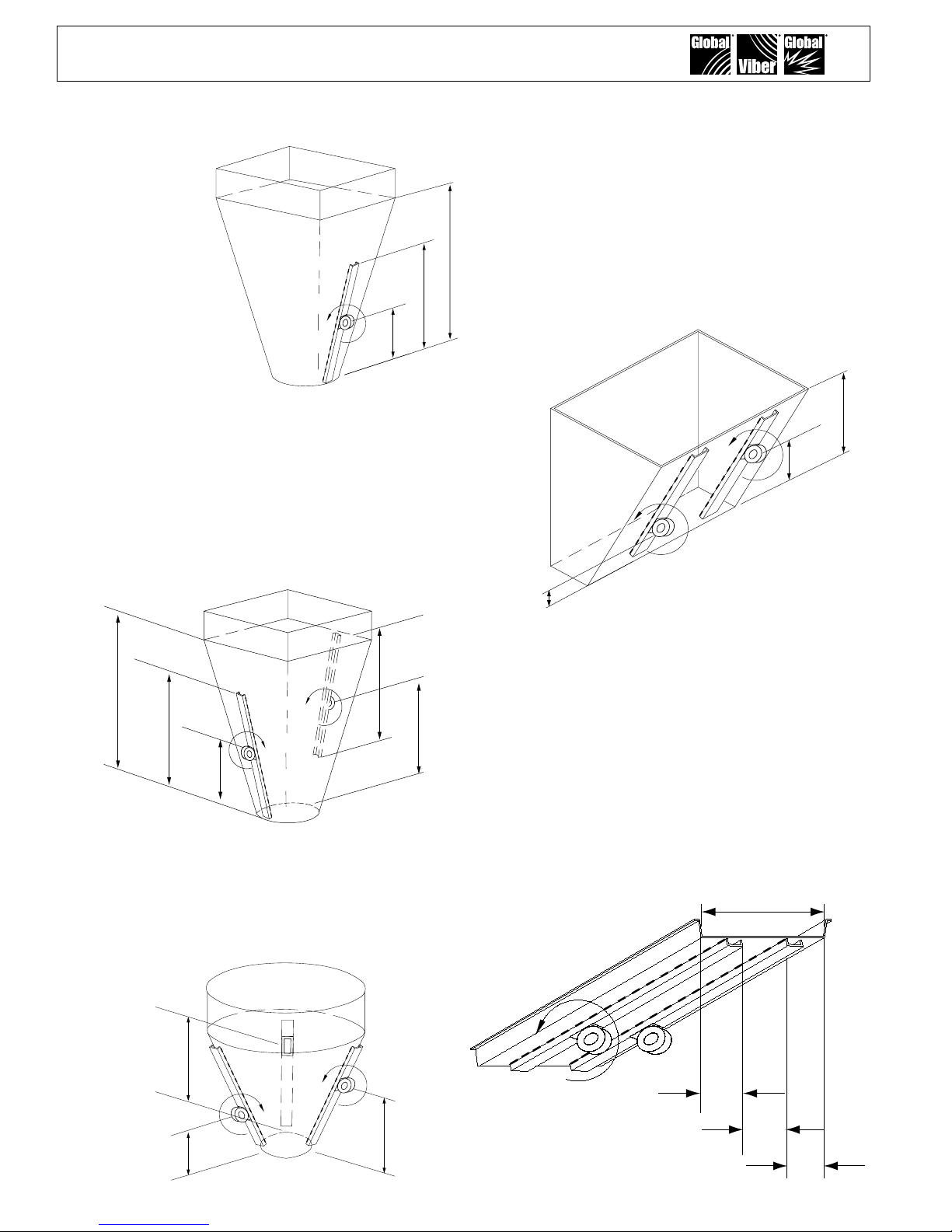
III. Mounting Locations
Single Vibrator
Install a channel
iron stiffener on
the outside of the
sloping wall 1⁄3 the
distance above the
discharge opening.
Multiple Vibrators
Use more than one vibrator when the diameter or
width of any wall is greater than 12 feet (3.66 m).
Always mount the vibrators on different planes.
Two Vibrators on Round or Square Hoppers
Install channel iron stiffeners 180° apart. Install
one vibrator on the outside of the sloping wall 1⁄3
the distance above the discharge opening. Install
the second vibrator on the outside of the opposite
sloping wall 2⁄3 the distance above the discharge
opening.
Two Vibrators on Rectangular Hoppers
Install channel iron stiffeners on opposite sides of
the long walls. Install one vibrator on the outside of
the sloping wall 1⁄3 the distance from the discharge
opening. Install the second vibrator on the outside
of the opposite sloping wall 2⁄3 the distance above
the discharge opening. When only one wall slopes,
mount both stiffeners on it. Equally space the
stiffeners on the wall. Place one vibrator 1⁄3 above
the discharge opening on one channel iron and the
other vibrator 2⁄3 above the bin’s discharge opening
on the second channel.
Three Vibrators
Install channel iron stiffeners mounted 120° apart.
Install the rst vibrator on the outside of the
sloping wall ¼ the distance above the discharge
opening. Install the second vibrator on a separate
channel iron at ½ the distance above the discharge
opening. Install the third vibrator on the remaining
channel iron at ¾ the distance above the discharge
opening.
Installation on Chutes and Flow Pipes
Mount channel iron stiffeners vertically or in the
direction of material ow. Center the channel if the
chute is less than 6 ft (1.83 m) in width. If the
chute is greater than 6' in width, use two vibrators
on separate channel irons. To maximize each
vibrator’s radius of inuence; center each channel
iron in each half of the chute. Each channel iron
should be located ¼ of the chute width from the
edge and ½ of the chute width apart. (e.g. –
a chute 8' wide, the channel iron locations would
be 2' from each edge and 4' apart.) When wall
thickness is less than ⅛", additional reinforcement
may be required.
Width is more than 6'
¼ of Width
½ of Width
4
¼ of Width
Page 5

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
Placement on Channel Iron
Orient the direction-of-rotation of the unbalance
(roller weight) so that it turns in the direction of
material ow. Position lug bolt on the high side
(uphill side) of the channel iron.
R
o
t
a
t
i
o
Direction of Material Flow
Keyway
Inlet
Hopper
n
Lug
Bolt
Installation on Railcars
Place GCL vibrator in a GCL-GBMX Bracket or a
GCL-GBM Bracket. The vibrator on the bracket slides
into the standard railcar bracket on the hopper car.
If two vibrators are used on one railcar, use an air
regulator to run them at different speeds.
GCL-GBMX Bracket
Has handy handle
for ease of use.
Channel Iron
stitch welded
to hopper
Securing Vibrator to GCL Bracket
Attach the vibrator to the cradle lug bracket by
placing the tab at the base of the vibrator under
the bar on the end of bracket. Rotate the vibrator
towards the bracket until it is fully seated. Rotate
the bracket bolt until it ts between the two ngers
on the vibrator housing and secure it using the
cradle lug nut. Use a standard open-end or box
wrench to tightened. Repeated tightening with an
air wrench will eventually cause excessive wear to
the ngers on the vibrator housing.
Mounting on Truck Bed
Weld GCL bracket to an independent channel
iron. The GCL vibrator inserts quickly into bracket.
Locate the channel iron as close as possible to the
material flow problem area.
Channel Iron
Vibrator
For correct vibrator
rotation, the hose
barb is on the left side
of the handle.
GCL Vibrator
Keyway
GBF Bracket
Wedge Pocket Bracket is
standard on most railcars.
GCL-GBM
Bracket
GCD-GBM
Bracket
GCD Vibrator
Railcar
Wedge Pocket Bracket standard on most railcars
5
Page 6

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
IV. Operation
Global High Frequency External Vibrators are
pneumatic with dual rollers. Their ease of operation
and low maintenance is due in part to the fact that
these vibrators contain no bearings or motors.
The vibrator may run continuously at speeds
up to the rated running conditions shown in our
performance data. Use a ball valve or solenoid
valve to turn the vibrator on and off. A regulator
provides constant speed control even as the plant
air pressure varies.
Install a filter, regulator, gauge, and lubricator in
the air line within 10 to 12 feet (3 - 3.7 m).
Filtration
Do not connect the vibrator directly to plant air. Use
a 64 micron filter. Drain the airline filter regularly
and examine the element for signs of clogging.
Regulation
Operate the vibrator on ltered, regulated, lubricated
air between 40 - 80 psi (2.8 - 5.5 bar) at 45 - 60
cfm (21 - 28 Lps).
Lubrication
Use a lightweight lubricant. Replenish the airline
lubricator as required and set to give the following
drop rate minimum. Will operate in temperatures
of 32° F (0° C) to 250° F (120° C).
Filter & Lubrication Requirements
Pipe and Hose Connections
The vibrator has a barb tting to accept a ¾"
I.D. hose. Clamp the hose securely to the tting
with a Band-It, Punch-Lok
worm driven clamp is not recommended since the
vibration may cause the clamp to loosen and allow
the hose to blow off the fitting.
The table below shows the recommended hose size
according to the amount of air required.
Hose Length and I.D.
SCFM
Flow
(Lps)
20 (9)
30 (14)
60 (28)
80 (38)
0 - 25'
(7.6 m)
5
⁄16" ⅜" ½"
⅜" ½" ½"
½" ¾" ¾"
¾" 1" 1"
If the vibrator will be moved or disconnected
frequently, a hose whip is recommended (see
illustration below). The whip is a short piece of hose
(12" - 18") atttached to the shaft with a clamp.
Attach a quick coupling, such as a Dixon
coupling, to the free end of the whip. Add a ball
valve to the plant air line to shut off the air before
disconnecting the quick coupling.
®,
or a similar clamp. A
Hose Length
26' - 50'
(7.6 - 15 m)
50' - 200'
(15 - 61 m)
Hose I.D.
®
hose
Filtration Required Lubrication Required
64 Micron
10 -1 2 Drops per Minute
10 Weight Oil
Recommended Lubricants
Shell: Tellus 37
B.P.: Energol HL65
Castrol: Hyspin 70
Mobil: Alma oil No 1
®
Vibrator
6
Punch-loks
=
H
o
s
e
W
h
V. Assembly & Disassembly
For proper vibration operation, it may be necessary
to change the direction of rotation or the position
of the vane. Both the GCD and GCL models are
disassembled and assembled in the same manner.
Tools Required:
• Press
• Torque Wrench
• ⅜" Wrench
Dixon
Hose Ends
p
i
Ball
Valve
Hose Whip Assembly
part number 260197
Hose
Nipple
Air Line
Page 7

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
Roller
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
Disassembly:
Note 1: The vibrator shaft is pressed into the
side plates. The side plates have a slip t in
the housing.
1. Remove the four ⅜" hex bolts and lock washers
from each side plate.
2. Opposite the air inlet, using a press, carefully
press against the backside of the shaft. This
will push out the (exhaust) side plate and the
shaft (as one assembly). Protect the air inlet
connection. The inner and outer rollers will
come out with the shaft. Remove blind side
plate if necessary.
3. Lift air vane from shaft. Inspect side plates,
shaft, and vane for wear. Any grooving on the
side plates or noticeable wear on the inner
roller, shaft, or vane requires component
replacement.
Assembly:
It is important to keep in mind the mounted
orientation of the vibrator. The vane and side plates
must be properly positioned to place the vane on
top of the shaft to give the proper direction of
rotation when mounted.
Note 2: Below is an exploded view of the GCD
vibrator. Notice the position of the blind side plate,
which has three slots milled halfway through
the plate, and the exhaust side plate, which has
three slots milled all the way through the plate.
The slots of the side plates must be directly
across from each other. These plates must be
positioned with the grooves in the vane facing
away from these three slots.
1. Assemble the shaft. Press or tap the keys into
the keyways in the shaft. Place the vane in the
shaft so that the grooves in the vane will be
facing away from the three milled slots of each
side plate. See page 11 for orientation of vane.
2. Exhaust side plate installation: Using the key as
a guide, align the shaft/key with the keyway on
the exhaust side plate. Press air inlet end of the
shaft into the exhaust side plate until it stops.
3. Install the exhaust side plate/shaft assembly
into the vibrator housing. Be sure its orientation
will place the vane on top of the shaft and
give the desired direction of rotation when the
vibrator is in the mounted position. Align the
bolt holes in the side plate with the threaded
holes in the vibrator housing. Install the hex
®
bolts and lock washers with Loctite
262 and
tighten the bolts to 33 ft·lb torque (44 Nm).
4. Make sure all foreign material is out of the
vibrator housing and the rollers. Place the
rollers on the shaft inside the housing. Place
smaller roller inside the larger roller.
5. Press the blind side plate onto the end of the
shaft and into the vibrator housing. Align the
bolt holes and the keyway of the blind side
plate. Install the hex bolts and lock washers
with Loctite® 262 and tighten the bolts to 33
ft·lb torque (44 Nm).
Exhaust
Vane
Ports
Blind
Side Plate
Sliding
Surface
Blind Slots
Housing
Keyway
n
o
i
t
R
Vane
Grooves
Shaft
Keys
a
t
o
Air
Inlet
Outer Roller
Inner
Roller
Outer
Through
Slots
Exhaust
Side Plate
Inner
Roller
Hose
Barb
Key
7
Page 8

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
VI. Vibrating Wet Concrete
Concrete Consolidation by vibration is achieved by
adding a mechanically-induced combination of force
and frequency allowing those forces to act on the
freshly-poured concrete within the vibrator's area
of inuence. The proper combination of force and
frequency will ensure that the concrete will retain
its homogeneity while allowing the entrapped air to
escape through the surface. A frequency of 9,000
– 12,000 vibrations per minute initiates resonance
in (or “excites”) the cement, causing the ultra-ne
cement particles to release the extremely small
air pockets that have adhered to the cement, so
that the mortar lls in all of the spaces around the
aggregate. Vibration evenly distributes the cement
and aggregates resulting in a more dense and a
smoother concrete nish.
When enough of the entrapped air has risen to the
surface to achieve concrete consistent with the
intended strength of the mixture, the vibration is
complete. In practical terms, it is neither possible
nor necessary to remove all of the entrapped air in
the consolidation process.
How to Select an External Vibrator
There is not an exact method or science when using
external vibrators for concrete consolidation. Mixes
vary, and therefore, consolidation procedures and
preferred vibrator styles vary. “Experts” become
experts through trial and error. What makes every
application different is that the mixes will vary due
to the slump, any chemical additives, aggregate
sizes/shape, cement content, consistency of the
mixture, weather conditions, and even the type of
form work used. Following these general rules may
be helpful in selecting the number and placement
of external vibrators for effective concrete consolidation.
In selecting External Vibrators, the contractor
should initially consider the workability of the
concrete and the rigidity of the forms. Plastic
concrete (slump > 3") responds better to high
frequency vibration, while stiffer mixtures
(slump < 3") require higher amplitude vibration to
initiate uidization. While properly-sized external
vibrators can be successfully used on virtually any
concrete formwork, using a too-powerful vibrator
on lightweight forms can cause damage to the
formwork. This has caused some contractors to
mistakenly believe that external vibrators cannot
be used on lightweight concrete formwork.
Vibrator Selection
Depending on specic conditions, external vibrators
with speeds between 3,000 and 12,000 rpm may be
suitable for form vibration. However, because the
natural resonant frequency of Portland Cement is
between 9,000 – 12,000 rpm, pneumatic vibrators
are often the only equipment capable of delivering
this necessary frequency.
After determining the approximate combined
weight of the formwork and concrete to be vibrated,
the contractor should select a vibrator producing the
amount of force specied by the table below. It will
often be necessary to use more than one vibrator
to produce the total amount of force required.
Note: If specific density of the concrete is
unavailable, use a standardized weight of 150 pounds
per cubic foot (2,400 kg / m3) for approximation.
Vibrator Selection
for Concrete Consolidation
Consistency Slump Vibrator Selection
Vibrator force output
Very stiff
concrete
Stiff
or
stiff plastic
concrete
Plastic
or
owing
concrete
<0.5"
0.5" - 2.0"
>2.0"
should be equal to
200-300% of the total
weight of the concrete
and form.
Vibrator force output
should be equal to
130-150% of the total
weight of the concrete
and form.
Vibrator force output
should be equal to
the total weight of the
concrete and form.
8
Page 9

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
Tips for using External Vibrators for
concrete consolidation:
Proper placement of the external vibrators is critical
to ensure that the vibration is distributed over the
desired area of the concrete. Depending on the
concrete consistency, density of embedments and
the quality of the mounting, External Vibrators
produce an Area-of-Inuence determined by the
force and frequency of the vibrator and the duration
of the vibrating time.
The following guidelines for spacing External
Vibrators have been developed, but contractors
should determine specic spacing requirements
for each project to ensure complete coverage of
vibration and successful consolidation.
Vibrator Spacing
for Concrete Consolidation
Distance
Consistency Slump
Very stiff or
stiff concrete
< 1.0"
< 25 mm
between
Vibrators
5' Apart
1524 mm
If the thickness of the concrete to be consolidated
is greater than the area of inuence of the vibrator,
or if a higher-quality nished surface is required on
both sides, the contractor should locate alternate
vibrators on opposite form walls. For instance, the
rst vibrator is placed on the front wall and the
next is 5' (1.5 m) away but on the back wall. See
illustration below.
Alternating the vibrators on a concrete form
Vibrators on the opposite
side of the form.
Vibrators on the near
side of the form.
Stiff plastic
concrete
Plastic
concrete
Flowing
concrete
1.0 − 2.0"
25 − 50 mm
2.0 − 5.0"
50 − 127 mm
> 5.0"
> 127 mm
6' Apart
1828 mm
7' Apart
2134 mm
8' Apart
2438 mm
Vibrating times for external vibrators may be
longer than for immersed internal vibrators. Most
operators will initially vibrate for approximately
two minutes per lift, and i n cr e as e or decrease
vibrating times as needed. Note that the same
criteria should be used to determine when the
consolidation is complete (no air bubbles at the top
surface, a thin lm of mortar on the top surface
and a stabilization of the speed of the vibrator).
Pour concrete into the forms in evenly dispersed
layers (lifts). Do not exceed a 20" lift height
otherwise the weight of the concrete can prevent
the entrapped air from escaping. Operate vibrators
in conjunction with each lift until the concrete is
fully consolidated. As each subsequent lift is placed,
locate additional vibrators for operation (or move
them from the previous level). Some operators
prefer to operate the previous lift’s vibrators for
a short period of time to promote “knitting” of the
two layers together.
In some cases, when the thickness of the concrete
to be consolidated is extraordinarily large,
contractors may choose to use Internal Vibrators
in the center section, with External Vibrators used
simultaneously along the outer edges.
Important!
Forms should be well made to withstand the
strains of vibration.
1. If using wooden forms, use screws instead of
nails (which may back out with vibration).
2. Forms need to be well braced to prevent bulging.
3. Joints need to be closely t to prevent leaking.
4. Monitor forms during placement of concrete.
Tighten as needed.
9
Page 10

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
Examples of Mounting External Vibrators
Poor Mount = Poorly Finished Concrete
The vibrator is mounted directly to the form wall.
Without a channel iron, the force output is
concentrated where the vibrator is attached,
causing the wall to ex and may cause stress
cracks. The vibration is not evenly distributed
resulting in a poor concrete nish.
Excellent Mount
Excellent Mount = Superior Finished Concrete
The vibrator is mounted on a channel iron, which
acts as the transducer of the energy. The vibration
is evenly distributed along the length of the channel
iron, which results in an excellent concrete nish.
Do not weld the channel iron to horizontal
stiffeners. Cut out the channel to t over stiffeners.
10
Excellent Mount
Page 11

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
D
i
r
e
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
R
o
t
a
t
i
o
n
D
i
r
e
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
R
o
t
a
t
i
o
n
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
VII. Vibrator Orientation
Whenever possible, mount the vibrator with the
shaft in the horizontal position.
To ensure proper direction-of-rotation, the GCL
vibrators are assembled for either a hopper or a
concrete form application. This only applies to the
GCL due to the way it sits in its bracket. To reverse
direction of rotation, the shaft and side plates must
be removed and swapped, so that, the shaft air
inlet is on the opposite side of the housing. Always
observe vane and exhaust port orientation. See
page 7, Note 2).
On a Hopper Wall: The direction of rotation is
in the direction of material ow - the roller weight
rotates toward the hopper and down. Facing the
hopper, the shaft/hose bard will be on the left.
GCL
The direction of rotation is determined by looking
at the side plate with the hose barb and exhaust
slots. The air enters the vibrator through the shaft
and pushes up the vane. (The vane is opposite the
keyway in the shaft.) The slots in the vane force
the air to one side only. The air carries the inner
roller with it as it travels around the shaft to get to
the exhaust slots. If the vane is facing the wrong
direction the air will have a direct path to the
exhaust without having to circle the shaft. If the
vane is not on the top of the shaft, but instead on
the side or bottom, the weight of the roller will not
press the vane back into the shaft and the vibrator
may not start.
On a Concrete Form: The rotation of
vibrator roller (weight) is counterclockwise.
This helps force the air bubbles to the surface.
Facing the concrete form the shaft/hose barb
will be on the right.
GCL
Material
Flow
Material
Flow
Hopper
Hopper
Vane
Key
Vane
Keyway
i
r
D
e
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
R
o
t
a
t
i
o
n
Hose Barb
i
r
D
e
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
R
o
t
a
t
i
o
n
Hose Barb
Key
Assembly Table
GCD GCD
Plan View
Assembly Table
Keyway
Assembly Table
Plan View
Assembly Table
Hose Barb
Vane
Key
Concrete Form
Air bubbles
rise to the
surface
GCLGCL
Concrete Form
Hose Barb
Vane
Key
Air bubbles
rise to the
surface
Plan View
Plan View
11
Page 12

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
VIII. Parts Explosion - GCD Models
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
7
10
8
7
2
1
Parts List for GCD High Frequency Vibrators
GCD-4400 (pn 522044)
GCD-5000 (pn 522050)
# Description PART # Qty # Description Part # Qty
1 Bolt Hex ⅜ - 16 x 1¼" 330212 8 5 Roller 192100 1
2 Lock Washer ⅜" 338106 8 6 Housing 141102 1
3 Side Plate - Blind 117000 1 7 Key 346205 2
4a Roller Weight - 4400* 192144 1 8 Shaft 205000 1
4b Roller Weight - 5000* 192150 1 9 Vane 270001 1
4c Roller Weight - 5500* 192155 1 10 Side Plate - Exhaust 117031 1
4d Roller Weight - 6500* 192165 1 * 1 weight per vibrator - determines force output
12
GCD-5500 (pn 522055)
GCD-6500 (pn 522065)
Page 13
Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
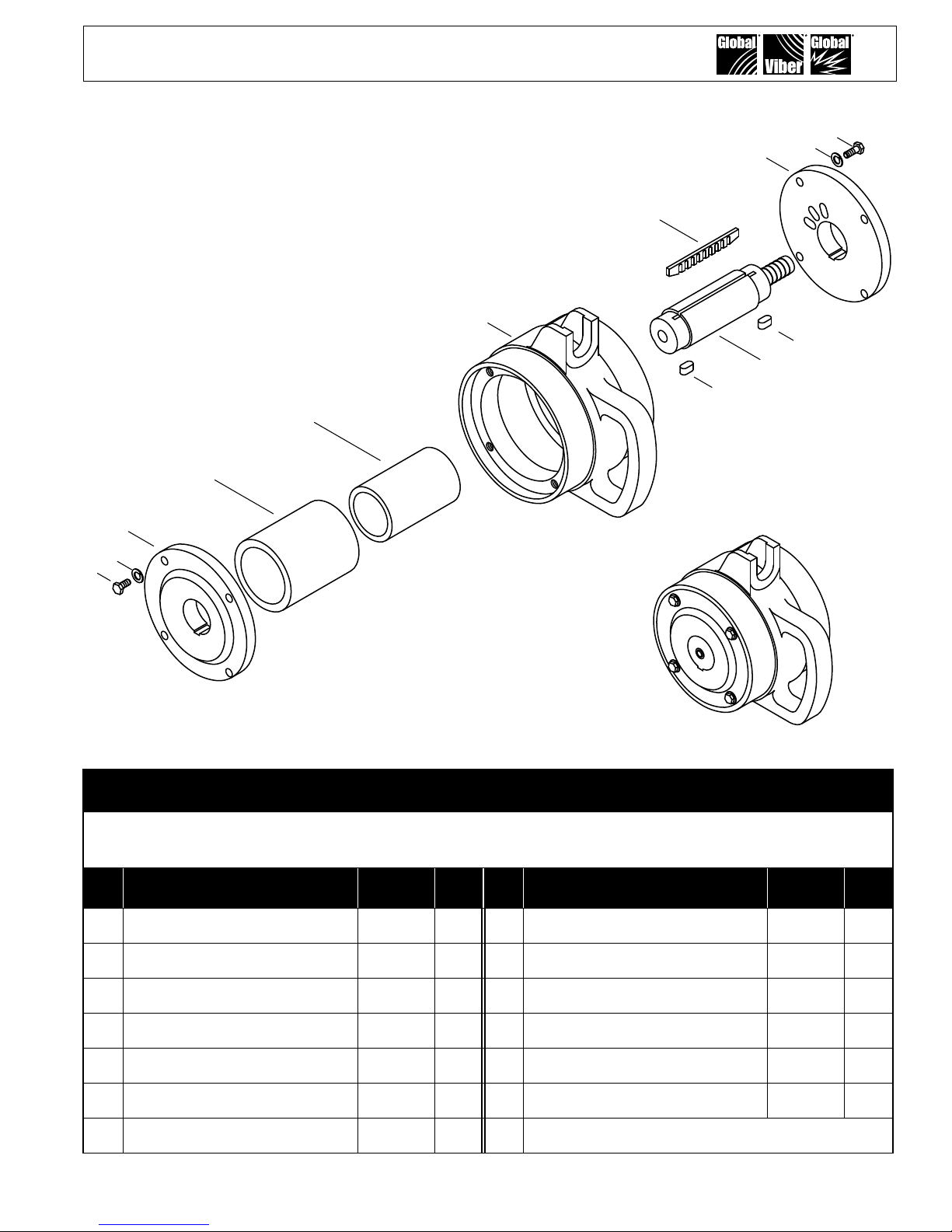
IX. Parts Explosion - GCL Models
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
7
10
8
7
2
1
Parts List for GCL High Frequency Vibrators
GCL-4400 (pn 524044)
GCL-5000 (pn 524050)
# Description PART # Qty # Description Part # Qty
1 Bolt Hex ⅜ - 16 x 1¼" 330212 8 5 Roller 192100 1
2 Lock Washer ⅜" 338106 8 6 Housing 141104 1
3 Side Plate - Blind 117000 1 7 Key 346205 2
4a Roller Weight - 4400* 192144 1 8 Shaft 205000 1
4b Roller Weight - 5000* 192150 1 9 Vane 270001 1
4c Roller Weight - 5500* 192155 1 10 Side Plate - Exhaust 117031 1
4d Roller Weight - 6500* 192165 1 * 1 weight per vibrator - determines force output
GCL-5500 (pn 524055)
GCL-6500 (pn 524065)
13
Page 14

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
X. Dimensions of GCD and GCL Vibrators
GCD GCL
G
D
C
Vibrator
Model
GCD-4400
GCD-5000
GCD-5500
GCD-6500
GCL-4400
GCL-5000
GCL-5500
GCL-6500
G
A
F
E
B
A
D
B
High Frequency Dual Roller Vibrator Dimensions
Weight
lb in in in in in in in
kg mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
34.8 6.7 9.2 7.4 5.7 3/4 0.7 7.5 X 3.8
15.8 170 234 188 145 19 18 190 X 95
35.2 6.7 9.2 7.4 5.7 3/4 0.7 7.5 X 3.8
16.0 170 234 188 145 19 18 190 X 95
35.4 6.7 9.2 7.4 5.7 3/4 0.7 7.5 X 3.8
16.1 170 234 188 145 19 18 190 X 95
38.7 6.7 9.2 7.4 5.7 3/4 0.7 7.5 X 3.8
17.6 170 234 188 145 19 18 190 X 95
32.8 8.5 9.4 7.3 5.5 3/4
14.9 216 239 185 140 19
33.2 8.5 9.4 7.3 5.5 3/4
15.1 216 239 185 140 19
33.4 8.5 9.4 7.3 5.5 3/4
15.1 216 239 185 140 19
36.8 8.5 9.4 7.3 5.5 3/4
16.7 216 239 185 140 19
A B C D E F G
Height Length Width Hsg Width Inlet ID Bolt Hole Bolt Centers
E
N/A Fits GCL Bracket
N/A Fits GCL Bracket
N/A Fits GCL Bracket
N/A Fits GCL Bracket
C
14
Page 15
Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
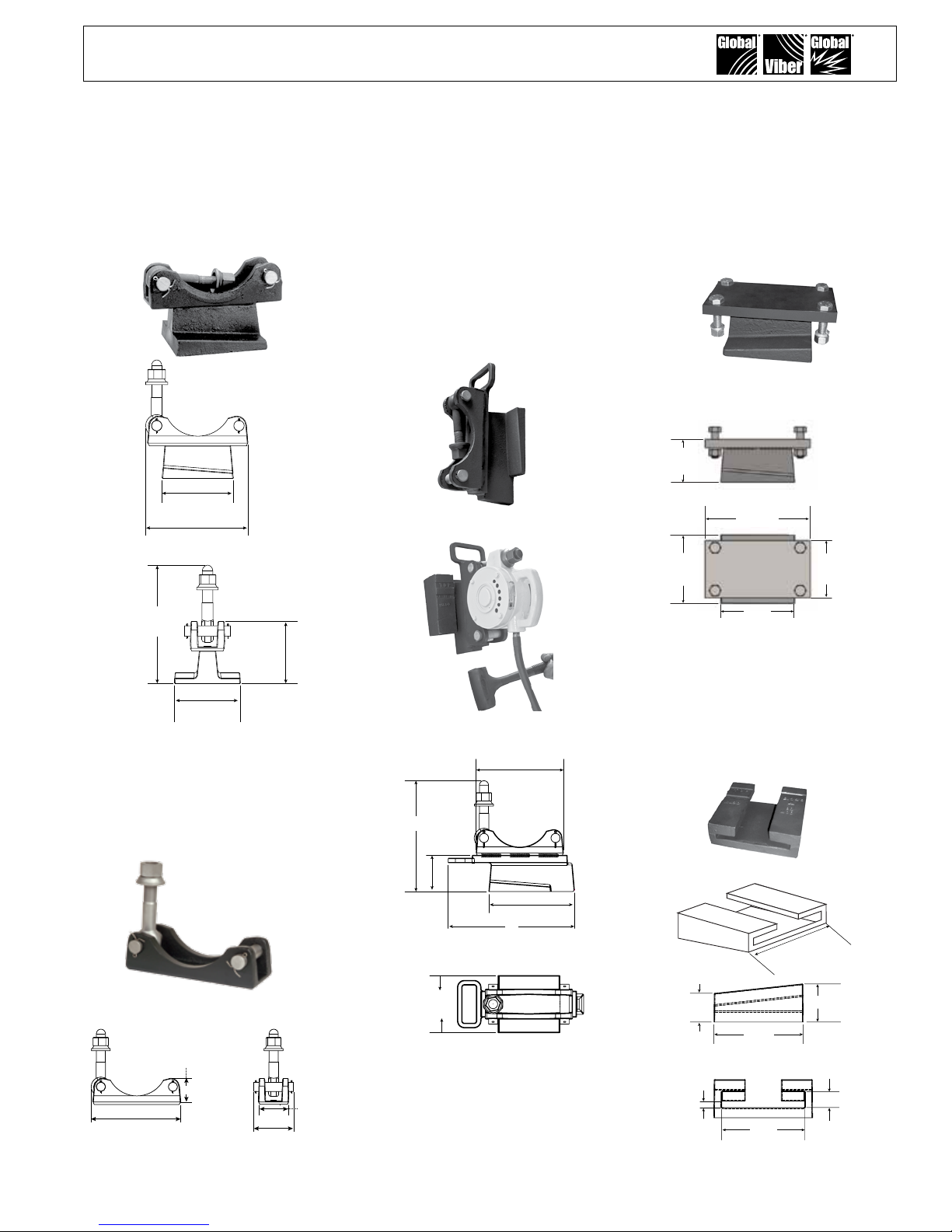
XI. Brackets Dimensions
GCL-GBM Bracket (pn 167020)
Bracket ts into the GBF Bracket
found on railcars.
6.50"
mm
165
9.44"
mm
240
B
10.81"
275
mm
6.00
152
5.51"
mm
140
A
"
mm
C
GCL Bracket (pn 168001)
Universal cradle-lug bracket.
Competitive vibrator brands with
cradle-lug housing prole t into
this bracket.
GCL-GBMX Bracket (pn 167120)
Bracket ts into the GBF Bracket
found on railcars. This bracket
has an unitized construction,
which helps it hold up to abuse.
It also has a hammer strike plate
to help when the bracket gets
stuck in railcar bracket. There is
a handle for ease of portability.
9.15"
232
mm
11.61"
A
295
mm
mm
3.80"
97
8.98"
228
B
13.23"
336 mm
mm
GCD-GBM Bracket (pn 167030)
Bracket ts into the GBF Bracket
found on railcars.
3.75"
mm
95
A
9.25"
532
mm
B
6.00
152
"
mm
C
6.50"
mm
561
5.00"
127
mm
D
GBF Bracket (pn 167071)
This bracket is the female wedge
pocket for the male brackets. The
bracket is often found on railcars.
7.75"
196.85
mm
C
2.69"
mm
68.33
9.44"
240
A
mm
B
106
4.16"
C
mm
3.50"
88.9
D
mm
6.00"
152 mm
2.99"
mm
A
1.24"
31.5
75.95
mm
mm
C
2.26"
57.4
.51"
12.95
mm
mm
7.00"
177.8
mm
B
6.50"
165.10
D
15
Page 16

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
XII. Performance and Lubrication Charts
High Frequency Vibrators Performance Data
40 psi 60 psi 80 psi
2.8 bar 4.1 bar 5.5 bar
Start-Up
Pressure
Speed Flow Force Speed Flow Force Speed Flow Force
rpm
9,500
9,350
8,800
7,600
cfm lbf
46.0 1,538
47.0 1,986
48.0 3,079 9,000 59.0 3,221
49.0 4,593 8,200 60.0 5,347
rpm
12,000
11,800
Model
GCD-4400
GCL-4400
GCD-5000
GCL-5000
GCD-5500
GCL-5500
GCD-6500
GCL-6500
Unbalance
lb-in psi
kg-mm bar Lpm kN Lpm kN Lpm kN
0.60 12
7 0.8 1,303 6.8 1,529 10.9 1,727 18.0
0.80 14
9 1.0 1,331 8.8 1,614 14.1 1,784 21.2
1.40 15
16 1.0 1,359 13.7 1,671 14.3 1,812 23.4
2.80 20
32 1.4 1,388 20.4 1,699 23.8 1,897 35.4
cfm lbf
54.0 2,454
57.0 3,164
rpm
15,400
14,500
11,500
10,000
cfm lbf
61.0 4,041
63.0 4,777
64.0 5,258
67.0 7,952
Pneumatic Motor Filter & Lubrication Requirements
Filtration Required Lubrication Required
64 Micron
Recommended Lubricants: Shell - Tellus 37, B.P. - Energol HL65, Castrol - Hyspin 70,
Mobil - Alma oil No 1
10 -1 2 Drops per Minute
10 Weight Oil*
16
Page 17

Global Manufacturing, Inc ® 800.551.3569 TOLL FREE USA & CANADA
1801 East 22nd Street 501.374.7416 TEL 501.376.7147 FAX
Little Rock, AR 72206 USA www.GlobalManufacturing.com
XIII. Troubleshooting
Problem Probable Cause Solution
Vibrator will
not operate
Excessive noise
Airline blocked
Locate obstruction and remove. Check
for kinked airline. Check filter.
Increase regulator setting or reduce
Inadequate air supply
number of units in use at same time.
Check capacity of compressor.
Airline too small for
distance used
Contamination in
vibrator
Use larger airline.
Disassemble and clean.
Clogged filter Clean or replace filter.
Foreign matter in
vibrator jamming vane
Disassemble and clean.
Disassemble and position shaft and
Vane is in wrong position
vane according to this manual. Rollers
must set on top of vane.
Insufficient mount
Damaged housing or
covers
Replace with stronger mounting
apparatus.
Replace the housing or covers.
Vibrator
operates
slowly
Change in
vibrator sound
Airline leaking or
constricted
Airline too small for
distance used
Replace airline, valve, or filter.
Replace airline with larger size air line.
Filter clogged Clean, repair, or replace.
Contamination in
vibrator
Lack of lubrication or
oil has thickened due to
cold weather which may
cause vane to stick
Disassemble and clean.
Increase amount of lubrication. Thin oil
with alcohol or antifreeze. Switch to a
lighter weight oil.
Side plates are worn Replace or resurface side plates.
Insufficient mount
Check for loose bolts, broken welds,
and damaged brackets.
Worn vane or side plates Replace parts.
Insufficient lubrication Increase amount of lubrication.
17
 Loading...
Loading...