Page 1
Multi-Drug Rapid Test 1-Step Cup
DOA-R127-A1
DOA-R137-A1
DOA-R147-A1
DOA-R157-A1
DOA-R167-A1
DOA-R177-A1
DOA-R187-A1
DOA-R197-A1
DOA-R1107-A1
DOA-R1117-A1
DOA-R1127-A1
DOA-R1137-A1
DOA-R1147-A1
DOA-R1157-A1
DOA-R1167-A1
DOA-R1177-A1
DOA-R1187-A1
DUA-R127-A1
DUA-R137-A1
DUA-R147-A1
DUA-R157-A1
DUA-R167-A1
DUA-R177-A1
DUA-R187-A1
DUA-R197-A1
DUA-R1107-A1
DUA-R1117-A1
DUA-R1127-A1
DUA-R1137-A1
DUA-R1147-A1
DUA-R1157-A1
DUA-R1167-A1
DUA-R1177-A1
Test
Calibrator
Cut-off (ng/mL)
Acetaminophen (ACE )
Acetaminophen
5,000
Amphetamine (AMP)
d-Amphetamine
1,000/500/300
Barbiturates (BAR)
Secobarbital
300/200
Benzodiazepines (BZO )
Oxazepam
500/300/200/100
Buprenorphine (BUP )
Buprenorphine
10/5
Cocaine (COC)
Benzoylecgonine
300/200/150/100
Marijuana (THC)
11-nor-Δ9-THC-9 COOH
300/200/150/50/30/25/
20
Methadone (MTD )
Methadone
300/200
Methamphetamine (MET )
d-Methamphetamine
1,000/500/300
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
(MDMA )
d,l-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
1,000/500/300
Morphine (MOP/OPI)
Morphine
300/200/100
Methaqualone(MQL)
Methaqualone
300
Opiate (OPI)
Morphine
2,000/1000
Phencyclidine (PCP)
Phencyclidine
50/25
Propoxyphene (PPX)
Propoxyphene
300
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCA)
Nortriptyline
1,000/500/300
Tramadol (TML )
Cis-Tramadol
500/300/200/100
Ketamine (KET )
Ketamine
1,000/500/300/100
Oxycodone (OXY)
Oxycodone
300/100
Cotinine(COT)
Cotinine
500/300/200/100/50/10
2-ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl3,3-diphenylpyrrolidine (EDDP)
2-ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl3,3-diphenylpyrrolidine
300/100
Fentanyl (FYL)
Fentanyl
20/10/100/200/300
Synthetic Marijuana (K2)
JWH-018、JWH-073
50/30/25
6-mono-aceto-morphine (6-MAM)
6-mono-aceto-morphine
10
(±) 3,4-MethylenedioxyAmphetamine (MDA)
(±) 3,4-MethylenedioxyAmphetamine
500
Ethyl- β-D-Glucuronide (ETG)
Ethyl- β -D-Glucuronide
1,000/500/300
Clonazepam (CLO)
Clonazepam
400/150
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD)
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide
50/20/10
Methylphenidate (MPD)
Methylphenidate
300/150
Methylphenidate (MPD)
Ritalin acid
1,000
Zolpidem (ZOL)
Zolpidem
50
Diazepam (DIA)
Diazepam
300/200
Zopiclone (ZOP)
Zopiclone
50
Methcathinone (MCAT)
S(-)-Methcathinone
500
7-Aminoclonazepam (7-ACL)
7-Aminoclonazepam
300/200/100
Carfentanyl (CFYL)
Carfentanyl
500/250
Caffeine (CAF)
Caffeine
1,000
Cathine (CAT)
(+)-Norpseudoephedrine
150
Tropicamide (TRO)
Tropicamide
350
3, 4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone
(MDPV)
3, 4-methylenedioxy
pyrovalerone
1,000/500/300
Mephedrone (MEP)
Mephedrone
100/500
Alprazolam (ALP)
Alprazolam
100
AB-PINACA (ABP)
AB-PINACA
10
α-Pyrrolidinovalerophenone (α-PVP )
α-Pyrrolidinovalerophenone
2,000/1,000/500/300
Cannabinol (CNB)
Cannabinol
500
Meperidine (MPRD)
Meperidine
100
Pregabalin (PGB)
Pregabalin
50,000/500
Trazodone (TZD)
Trazodone
200
UR-144
UR-144 5-Pentanoic acid
25
Zaleplon (ZAL)
Zaleplon
100
Mescaline (MES)
Mescaline
100/300
Gabapentin (GAB)
Gabapentin
2,000
Tilidine (TLD)
Nortilidine
50
Quetiapine (QTP)
Quetiapine
1,000
Papaverine (PAP)
Papaverine
500
Kratom (KRA)
Mitragynine
300
Carisoprodol (CAR)
Carisoprodol
2,000/1,000
Fluoxetine (FLX)
Fluoxetine
500
Citalopram (CIT)
Citalopram
500
Fluoketamine (FKET)
Fluoketamine
1,000
Olanzapine (OZP)
Olanzapine
1,000
Risperidone (RPD)
Risperidone
150
Tapentadol (TAP)
Tapentadol
1,000
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (NND)
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
1,000
Scopolamine (SCOP)
Scopolamine
500
Mirtazapine (MTZ)
Desmethylmirtazapine
500
Test
Calibrator
Cut-off
Alcohol (ALC)
Alcohol
0.02%
Adulteration Pad
Reactive indicator
Buffers and non-reactive ingredients
Creatinine
0.04%
99.96%
Nitrite
0.07%
99.93%
Bleach
0.39%
99.61%
Glutaraldehyde
0.02%
99.98%
pH
0.06%
99.94%
Specific Gravity
0.25%
99.75%
Oxidants / PCC
0.36%
99.64%
Test Cups
Package Insert
Procedure Card
Timer
Cup Reader
With/Without Adulteration (Urine)
Package Insert
Instruction Sheet for testing of any combination of the following drugs:
ACE/AMP/BAR/BZO/BUP/COC/THC/MTD/MET/MDMA/MOP/MQL/OPI/PCP/PPX/TCA/TML/
KET/OXY/COT/EDDP/FYL/K2/6-MAM/MDA/ETG/CLO/LSD/MPD/ZOL/DIA/ZOP/MCAT/7-ACL
/CFYL/C AF/CAT/TRO/MDPV/MEP/ALP/ABP/ α-PVP/ CNB/MPRD/PGB/ TZD/UR-144/ZAL/
MES/GAB/TLD/QTP/PAP/KRA/CAR/FLX/CIT/FKET/OZP/RPD/TAP/NND/SCOP/MTZ/ALC
Including Specimen Validity Tests (S.V.T.) for:
Oxidants/PCC, Specific Gravity, pH, Nitrite, Glutaraldehyde, Creatinine and Bleach
A rapid test for the simultaneous, qualitative detection of multiple drugs and drug metabolites in
human urine. For healthcare professionals including professionals at point of care sites.
Immunoassay for in vitro diagnostic use only.
【INTENDED USE AND SUMMARY】
The Multi-Drug Rapid Test is a rapid chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection
of multiple drugs and drug metabolites in urine at the following cut-off concentrations that can be
performed with the use of the Cup Reader.
Configurations of the Multi-Drug Rapid Test come with any combination of the above listed drug
analytes with or without S.V.T. This assay provides only a preliminary analytical test result. A
more specific alternate chemical method must be used in order to obtain a confirmed analytical
result. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) is the preferred confirmatory method.
Clinical consideration and professional judgment should be applied to any drug of abuse test
result, particularly when preliminary positive results are indicated.
【SUMMARY OF ADULTERATION】
Adulteration is the tampering of a urine specimen with the intention of altering the test results.
The use of adulterants can cause false negative results in drug tests by either interfering with
the screening test and/or destroying the drugs present in the urine. Dilution may also be
employed in an attempt to produce false negative drug test results.
One of the best ways to test for adulteration or dilution is to determine certain urinary
characteristics such as pH, specific gravity and creatinine and to detect the presence of
oxidants/PCC, nitrites or glutaraldehyde in urine.
【PRINCIPLE (FOR DOA TESTS EXCLUDING ALCOHOL)】
During testing, a urine specimen migrates upward by capillary action. A drug, if present in the
urine specimen below its cut-off concentration, will not saturate the binding sites of its specific
antibody. The antibody will then react with the drug-protein conjugate and a visible colored line
will show up in the test region of the specific drug dipstick. The presence of drug above the
cut-off concentration will saturate all the binding sites of the antibody. Therefore, the colored
line will not form in the test region.
A drug-positive urine specimen will not generate a colored line in the specific test region of the
dipstick because of drug competition, while a drug-negative urine specimen will generate a line
in the test region because of the absence of drug competition.
To serve as a procedural control, a colored line will always appear at the control region,
indicating that proper volume of specimen has been added and membrane wicking has
occurred.
【PRINCIPLE OF ADULTERATION】
Oxidants/PCC (Pyridiniumchlorochromate) tests for the presence of oxidizing agents such
as bleach and hydrogen peroxide. Pyridiniumchlorochromate (sold under the brand name Urine
Luck) is commonly used adulterant.1 Normal human urine should not contain oxidants of PCC.
Specific gravity tests for sample dilution. The normal range is from 1.003 to 1.030. Values
outside this range may be the result of specimen dilution or adulteration.
pH tests for the presence of acidic or alkaline adulterants in urine. Normal pH levels should be in
the range of 4.0 to 9.0. Values outside of this range may indicate the sample has been altered.
Nitrite tests for commonly used commercial adulterants such as Klear and Whizzies. They work
by oxidizing the major cannabinoid metabolite THC-COOH.2 Normal urine should contain no
trace of nitrite. Positive results generally indicate the presence of an adulterant.
Glutaraldehyde tests for the presence of an aldehyde. Adulterants such as Urin Aid and Clear
Choice contain glutaraldehyde which may cause false negative results by disrupting the enzyme
used in some immunoassay tests.2 Glutaraldehyde is not normally found in urine; therefore,
detection of glutaraldehyde in a urine specimen is generally an indicator of adulteration.
Creatinine is a waste product of creatine; an amino-acid contained in muscle tissue and found
in urine.3 A person may attempt to foil a test by drinking excessive amounts of water or diuretics
such as herbal teas to “ flush” the system. Creatinine and specific gravity are two ways to check
for dilution and flushing, which are the most common mechanisms used in an attempt to
circumvent drug testing. Low Creatinine and specific gravity levels may indicate dilute urine. The
absence of Creatinine (<5 mg/dL) is indicative of a specimen not consistent with human urine.
Bleach tests for the presence of bleach bleach refers to a number of chemicals which
remove color, whiten or disinfect, often by oxidation, Bleaches are used as household
chemicals to whiten clothes and remove stains and as disinfectants. Normal human urine
should not contain bleach.
【PRINCIPLE (FOR ALCOHOL)】
The urine Alcohol Rapid Test consists of a plastic strip with a reaction pad attached at the tip.
On contact with alcohol, the reaction pad will change colors depending on the concentration of
alcohol present. This is based on the high specificity of alcohol oxidase for ethyl alcohol in the
presence of peroxidase and enzyme substrate such as TMB.
【REAGENTS (FOR DOA TESTS EXCLUDING ALCOHOL)】
Each test line contains anti-drug mouse monoclonal antibody and corresponding drug-protein
conjugates. The control line contains goat anti-rabbit IgG polyclonal antibodies and rabbit IgG.
【REAGENTS (FOR ALCOHOL)】
Tetramethylbenzidine /Alcohol Oxidase/Peroxidase
【S.V.T REAGENTS】
【PRECAUTIONS】
For healthcare professionals including professionals at point of care sites.
Immunoassay for in vitro diagnostic use only. The test should remain in the sealed pouch
until use.
All specimens should be considered potentially hazardous and handled in the same manner
as an infectious agent.
The used test should be discarded according to local regulations.
For use exclusively with the Cup Reader. Do not interpret test results visually.
【STORAGE AND STABILITY】
Store as packaged in the sealed pouch at 2-30 °C. The test is stable through the expiration date
printed on the sealed pouch. The Test Cup must remain in the sealed pouch until use. DO NOT
FREEZE. Do not use beyond the expiration date.
【SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND PREPARATION】
The urine specimen should be collected in a clean and dry container. Urine collected at any
time of the day may be used. Urine specimens exhibiting visible precipitates should be
centrifuged, filtered, or allowed to settle to obtain a clear specimen for testing.
Urine specimens may be stored at 2-8 °C for up to 48 hours prior to testing. For prolonged
storage, specimens may be frozen and stored below -20 °C. Frozen specimens should be
thawed and mixed well before testing. When testing cards with S.V.T. or Alcohol storage of
urine specimens should not exceed 2 hours at room temperature or 4 hours refrigerated prior to
testing.
【MATERIALS】
Materials Required But Not Provided
【DIRECTIONS FOR USE】
Allow the test, urine specimen, and/or controls to reach room temperature (15-30 ºC)
prior to testing.
1. Bring the pouch to room temperature before opening it. Remove the cup from the sealed
pouch and use it within 1 hour.
2. Donor provides specimen.
3. Technician replaces and secures cap while the cup is on a flat surface.
4. Check the temperature label (Temp Label) up to 4 minutes after specimen collection. A
green color will appear to indicate the temperature of the urine specimen. The proper range
for an unadulterated specimen is 32-38 °C (90-100 °F).
5. Technician dates and initials the security seal and attaches the security seal over the cup
cap.
6. Technician peels off the label on the multi-drug test cup to read results.
7. Put the cup into cup reader detection chamber at 5 min and close the chamber cap to
read the results by the cup reader. Do not read the test results visually.
Refer to your Drug Free Policy for guidelines on adulterated specimens. We recommend not
interpreting the drug test results and either retest the urine or collect another specimen in
case of any positive result for any adulteration test.
Note: For the Installation, startup, system calibration and complete test operations of the cup
reader, please refer to the Cup Reader User Manual carefully. Operator must consult the
Cup Reader User Manual prior to use and become familiar with the operations and
quality control procedures.
Urine Assay
Specimen Storage
Materials Provided
1/ 6
Page 2

【INTERPRETATION OF DOA RESULTS】
Analyte
Display
Result
MOP
POS
Positive
OXY
NEG
Negative
AMP
INV
Invalid
Analyte
Display
Result
ALC
NOR
Normal
OXI/SG
ABN/NOR
Abnormal/Normal
NIT/GLU
NOR/NOR
Normal/Normal
CRE/pH
ABN/ABN
Abnormal/Abnormal
ACE
5,000
AMP
1,000
AMP
500
AMP
300
BAR
300
BAR
200
BZO
500
BZO
300
BZO
200
BZO
100
BUP
10
Positive
Agreement
95.6%
97.1%
97.0%
96.7%
96.7%
95.0%
95.5%
96.0%
96.1%
95.8%
97.1%
Negative
Agreement
98.7%
98.7%
98.6%
98.9%
99.0%
99.0%
99.0%
98.4%
98.4%
98.5%
99.0%
Total
Results
97.6%
98.2%
98.1%
98.4%
98.5%
97.9%
98.0%
97.7%
97.8%
97.8%
98.5%
BUP 5 COC
300
COC
200
COC
150
COC
100
THC
300
THC
150
THC
50
THC
25
THC
20
THC
200
Positive
Agreement
96.4%
95.1%
96.3
95.7%
97.2%
95.8%
96.0%
96.3%
96.5%
96.1%
95.5%
Negative
Agreement
98.9%
98.9%
>98.9%
98.9%
98.9%
98.6%
99.0%
98.6%
99.0%
98.5%
99.2%
Total
Results
98.3%
97.7%
98.3%
97.8%
98.5%
97.9%
97.9%
97.6%
98.1%
97.8%
97.9%
THC
30
MET
1,000
MET
500
MET
300
MDMA
1,000
MDMA
500
MDMA
300
MOP/
OPI
300
MOP/
OPI
100
MOP/
OPI
200
PPX
300
Positive
Agreement
96.2%
95.3%
96.0%
95.8%
95.2%
95.7%
96.2%
95.0%
95.2%
95.1%
99.2%
Negative
Agreement
98.6%
99.2%
99.2%
98.6%
99.1%
99.3%
98.6%
99.0%
99.1%
98.9%
98.5%
Total
Results
98.0%
97.8%
97.9%
97.6%
97.7%
98.1%
98.0%
97.6%
98.0%
97.7%
98.8%
TCA
1,000
TCA
500
TCA
300
TML
100
TML
200
TML
300
TML
500
KET
1,000
KET
500
KET
300
KET
100
Positive
Agreement
98.9%
97.6%
96.4%
96.9%
96.7%
96.9%
96.8%
99.1%
96.8%
98.9%
99.1%
Negative
Agreement
98.7%
98.8%
99.4%
99.3%
99.4%
99.4%
99.4%
》
99.9%
98.7%
98.1%
99.3%
Total
Results
98.8%
98.4%
98.4%
98.4%
98.4%
98.0%
98.4%
99.6%
98.0%
98.4%
99.2%
OXY
100
OXY
300
COT
500
COT
200
COT
100
COT
50
COT
10
COT
300
ETG
500
ETG
1,000
ETG
300
Positive
Agreement
97.5%
96.5%
96.5%
99.1%
98.2%
96.0%
95.0%
95.0%
95.3%
98.3%
97.4%
Negative
Agreement
99.4%
99.4%
99.4%
98.5%
98.5%
99.3%
99.3%
98.8%
99.3%
98.5%
99.4%
Total
Results
98.8%
98.4%
98.4%
99.0%
98.4%
98.0%
98.1%
97.6%
97.6%
98.4%
98.8%
K2
50
K2
30
6-MAM
10
MDA
500
EDDP
300
EDDP
100
CLO
400
CLO
150
LSD
10
LSD
20
LSD
50
Positive
Agreement
98.4%
95.5%
98.2%
96.2%
99.2%
98.1%
96.1%
99.2%
95.2%
97.9%
98.9%
Negative
Agreement
99.2%
99.2%
99.3%
99.4%
99.2%
99.3%
98.6%
98.4%
98.8%
98.1%
99.4%
Total
Results
98.8%
97.6%
98.8%
98.4%
99.2%
98.8%
97.6%
98.8%
97.6%
98.0%
99.2%
MEP
100
MEP
500
ZOL
50
DIA
300
DIA
200
ZOP
50
MCAT
500
7-ACL
300
7-ACL
200
7-ACL
100
CFYL
500
Positive
Agreement
97.7%
97.5%
98.1%
96.7%
97.0%
98.6%
95.5%
98.0%
95.2%
96.3%
97.8%
Negative
Agreement
98.8%
98.8%
99.3%
99.9%
99.3%
98.9%
99.5%
99.3%
98.8%
98.8%
99.4%
Total
Results
98.4%
98.4%
98.8%
98.8%
98.4%
98.8%
98.0%
98.8%
97.6%
98.0%
98.8%
CAF
1,000
CAT
150
TRO
350
MDPV
1000
MDPV
500
α-PVP
300
α-PVP
2,000
α-PVP
500
α-PVP
1,000
CNB
500
MPRD
100
Positive
Agreement
95.2%
98.8%
96.8%
97.7%
96.9%
98.5%
95.7%
98.6%
96.0%
96.9%
95.9%
Negative
Agreement
99.5%
99.4%
99.4%
99.4%
99.5%
98.9%
99.4%
98.9%
98.7%
99.3%
99.3%
Total
Results
98.4%
99.2%
98.4%
98.8%
98.8%
98.8%
98.0%
98.8%
97.6%
98.4%
98.0%
PGB
50,000
TZD
200
UR-144
25
ZAL
100
MES
100
GAB
2,000
MQL
300
ALP
100
ABP
10
TLD
50
QTP
1,000
Positive
Agreement
95.7%
97.2%
96.9%
97.0%
97.8%
97.8%
95.7%
97.5%
96.1%
97.3%
96.2%
Negative
Agreement
98.7%
98.9%
99.5%
99.5%
99.5%
99.8%
99.1%
98.8%
99.4%
98.9%
98.8%
Total
Results
97.6%
98.4%
98.8%
98.8%
98.8%
98.4%
98.1%
98.4%
98.4%
98.4%
98.0%
PAP
500
KRA
300
TAP
1,000
FLX
500
K2
25
CIT
500
FKET
1,000
RPD
150
OPI
2,000
OPI
1,000
CFYL
250
Positive
Agreement
96.4%
98.6%
95.2%
96.5%
99.1%
96.8%
97.2%
96.4%
95.1%
97.6%
96.3%
Negative
Agreement
99.2%
99.3%
99.1%
99.3%
98.6%
99.3%
99.2%
99.1%
99.0%
99.4%
99.4%
Total
Results
98.1%
99.0%
97.5%
98.5%
98.8%
98.5%
98.5%
98.0%
97.9%
98.8%
98.4%
PGB
500
MES
300
OZP
1,000
MDPV
300
CAR
2,000
CAR
1,000
NND
1,000
SCOP
500
MTZ
500
MTD
300
MTD
200
Positive
Agreement
97.4%
97.8%
96.2%
97.7%
96.8%
97.8%
97.0%
96.4%
96.8%
95.7%
96.4%
Negative
Agreement
98.8%
99.4%
99.2%
99.4%
99.3%
98.8%
99.3%
98.8%
99.3%
98.9%
99.2%
Total
Results
97.6%
98.8%
98.0%
98.8%
98.5%
98.4%
98.5%
98.0%
98.5%
98.3%
98.8%
PCP
25
PCP
50
FYL
20
FYL
10
FYL
100
FYL
200
FYL
300
MPD
300
MPD
150
MPD
1,000
Positive
Agreement
97.9%
97.4%
98.0%
98.1%
97.4%
97.9%
96.9%
98.0%
98.6%
96.8%
Negative
Agreement
98.1%
99.4%
98.8%
98.6%
99.4%
98.1%
98.7%
98.0%
98.9%
99.3%
Total
Results
98.0%
98.8%
98.6%
98.4%
98.8%
98.0%
98.0%
98.0%
98.8%
98.5%
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
ACE
5,000
AMP
1,000
AMP
500
AMP
300
BAR
300
BAR
200
BZO
500
BZO
300
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
BZO
200
BZO
100
BUP
10
BUP 5 COC
300
COC
200
COC
150
COC
100
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
30 0 30
0
30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
30 0 30
0
30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
30 0 30
0
30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
THC
300
THC
200
THC
150
THC
50
THC
30
THC
25
THC
20
LSD
10
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + -
+
0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
FYL
100
FYL
200
FYL
300
FYL
20
FYL
10
OPI
2,000
OPI
1000
PPX
300
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
MOP/
OPI
300
MOP/
OPI
100
RPD
150
KET
1,000
KET
500
KET
300
KET
100
MQL
300
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + -
+
Results read by Cup Reader
The result of positive or negative for each analyte is determined by the Cup Reader.
Results Example:
NEGATIVE:This negative result means that the concentrations in the urine sample are below
the designated cut-off levels for a particular drug tested.
POSITIVE: The positive result means that the drug concentration in the urine sample is greater
than the designated cut-off for a specific drug.
INVALID:Insufficient specimen volume or incorrect procedural techniques are the most likely
reasons for Control line failure. Read the directions again and repeat the test with a new test. If
the result is still invalid, contact your manufacturer.
【INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS (S.V.T/ ADULTERATION AND ALCOHOL)】
Results Example:
【QUALITY CONTROL】
A procedural control is included in the test. A line appearing in the control region (C) is
considered an internal procedural control. It confirms sufficient specimen volume, adequate
membrane wicking and correct procedural technique.
Control standards are not supplied with this kit. However, it is recommended that positive and
negative controls be tested as good laboratory practice to confirm the test procedure and to
verify proper test performance.
【LIMITATIONS】
1. The Multi-Drug Rapid Test provides only a qualitative, preliminary analytical result. A
secondary analytical method must be used to obtain a confirmed result. Gas
chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) is the preferred confirmatory method.
2. There is a possibility that technical or procedural errors, as well as interfering substances in
the urine specimen may cause erroneous results.
3. Adulterants, such as bleach and/or alum, in urine specimens may produce erroneous results
regardless of the analytical method used. If adulteration is suspected, the test should be
repeated with another urine specimen.
4. A positive result does not indicate level or intoxication, administration route or concentration
in urine.
5. A negative result may not necessarily indicate drug-free urine. Negative results can be
obtained when drug is present but below the cut-off level of the test.
6. This test does not distinguish between drugs of abuse and certain medications.
7. A positive test result may be obtained from certain foods or food supplements.
【S.V.T/ADULTERATION LIMITATIONS】
1. The adulteration tests included with the product are meant to aid in the determination of
abnormal specimens. While comprehensive, these tests are not meant to be an “all-inclusive”
representation of possible adulterants.
2. Oxidants/PCC: Normal human urine should not contain oxidants or PCC. The presence of
high levels of antioxidants in the specimen, such as ascorbic acid, may result in false
negative results for the oxidants/PCC pad.
3. Specific Gravity: Elevated levels of protein in urine may cause abnormally high specific
gravity values.
4. Nitrite: Nitrite is not a normal component of human urine. However, nitrite found in urine may
indicate urinary tract infections or bacterial infections. Nitrite levels of > 20 mg/dL may
produce false positive glutaraldehyde results.
5. Glutaraldehyde: is not normally found in urine. However certain metabolic abnormalities such
as ketoacidosis (fasting, uncontrolled diabetes or high protein diets) may interfere with the
test results.
6. Creatinine: Normal Creatinine levels are between 20 and 350 mg/dL. Under rare conditions,
certain kidney diseases may show dilute urine.
7. Bleach: Normal human urine should not contain bleach. The presence of high levels of
bleach in the specimen may result in false negative results for the bleach pad.
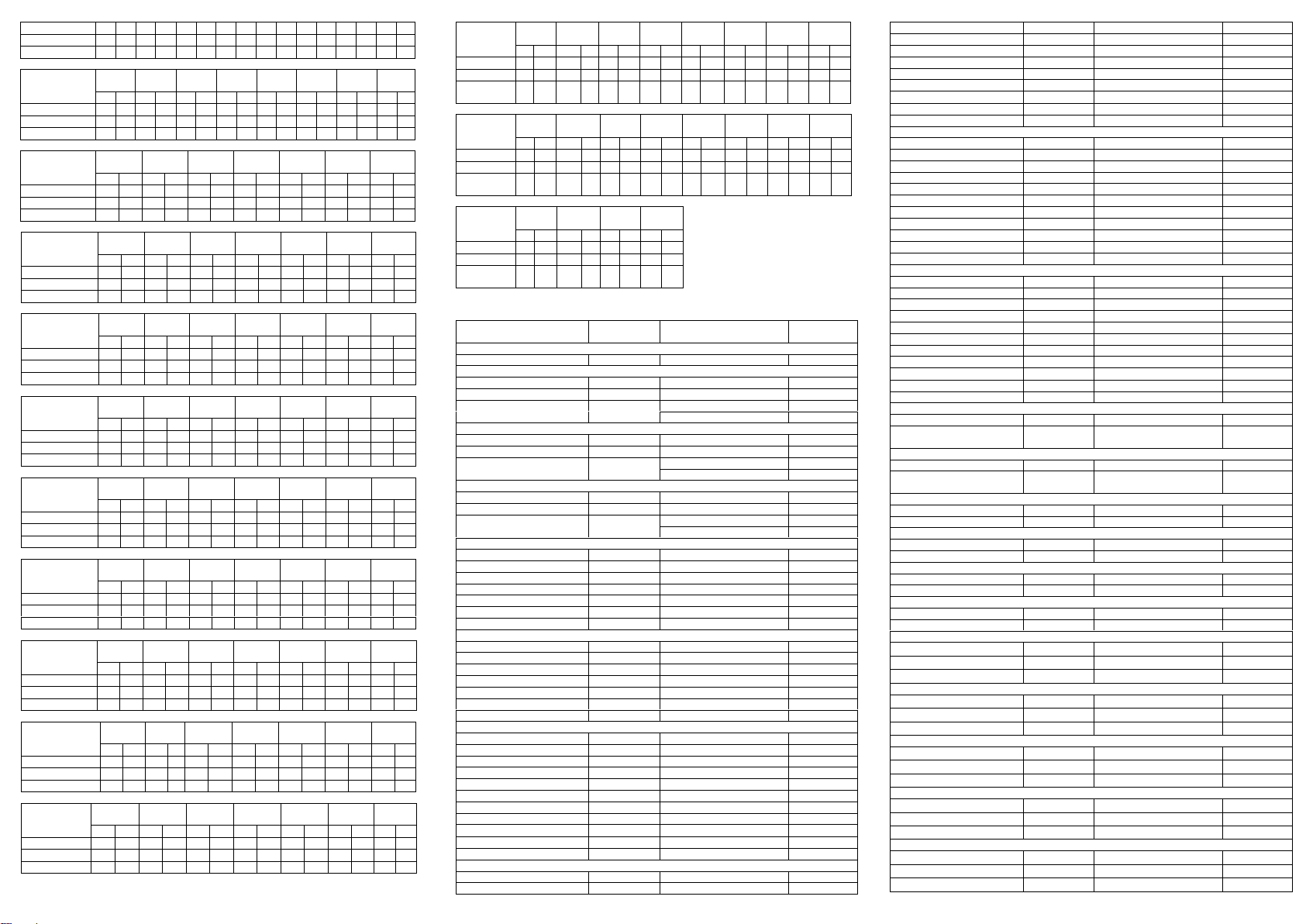
【PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS】
Accuracy
% Agreement with GC/MS
A study was conducted at three hospitals by laypersons using three different lots of product to
demonstrate the within run, between run and between operator precision. An identical card of
coded specimens, containing drugs at concentrations of negative, - 50% and 300% cut-off level,
was labeled, blinded and tested at each site. The results gained 100% accuracy in negative,
-50% and 300% cut-off level specimen.
A drug-free urine pool was spiked with drugs at the listed concentrations. The results are
summarized below.
4,5
Precision
Analytical Sensitivity
2/ 6
Page 3
0% Cut-off
30
0
30
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
-50% Cut-off
30
0
30
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30
0
30 0 30
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
OXY
100
MDMA
1,000
MDMA
500
EDDP
300
EDDP
100
MPD
300
MPD
150
K2
50
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
+300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
K2
30
6-MAM
10
MDA
500
ETG
500
ETG
1,000
CLO
400
CLO
150
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
LSD
20
LSD
50
MDPV 300
ZOL
50
MDMA
300
OXY
300
DIA
300
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 29 1 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
+300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
DIA
200
ZOP
50
MCAT
500
7-ACL
300
7-ACL
200
7-ACL
100
CFYL
500
- + - + - + - + - + - + -
+
0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 29 1 30
0
+300% Cut-off
0
30
0
30 0 30
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
CAF
1,000
CAT
150
TRO
350
MDPV
1,000
MEP
100
MEP
500
ALP
100
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
+300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
COT
500
COT
300
COT
200
COT
100
COT
50
COT
10
MPD
1,000
- + - + - + - + - + - + -
+
0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
MDPV
500
ABP
10
TAP
1,000
CNB
500
MPRD
100
PGB
50,000
TZD
200
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
UR-144
25
ZAL
100
MES
100
GAB
2,000
MOP/OPI
200
ETG
300
K2
25
- + - + - + - + - + - + -
+
0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
TLD
50
QTP
1,000
PAP
500
KRA
300
FLX
500
CAR
2000
CAR
1,000
- + - + - + - + - + -
+
-
+
0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
30
0
+300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
PGB
500
MES
300
OZP
1,000
CIT
500
FKET
1,000
MTD
300
MTD
200
- + - + - + - + - + - + -
+
0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 +300% Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
CFYL
250
α-PVP
2,000
α-PVP
500
α-PVP
300
α-PVP
1,000
NND
1,000
SCOP
500
MTZ
500
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
-50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
+300%
Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
MET
1,000
MET
500
MET
300
PCP
25
PCP
50
TCA
1,000
TCA
500
TCA
300
- + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
+300%
Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Drug
Concentration
Cut-off Range
TML
100
TML
200
TML
300
TML
500
- + - + - + - + 0% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30 0 -50% Cut-off
30 0 30 0 30 0 30
0
+300%
Cut-off
0
30 0 30 0 30 0 30
Analytes
Concentration
(ng/mL)
Analytes
Concentration
(ng/mL)
ACETAMINOPHEN (ACE 5,000)
Acetaminophen
5,000
AMPHETAMINE (AMP 1,000)
D,L-Amphetamine sulfate
300
Phentermine
1,000
L-Amphetamine
25,000
Maprotiline
50,000
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
amphetamine
500
Methoxyphenamine
6,000
D-Amphetamine
1,000
AMPHETAMINE (AMP 500)
D,L-Amphetamine sulfate
150
Phentermine
500
L-Amphetamine
12,500
Maprotiline
25,000
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
amphetamine
250
Methoxyphenamine
3,000
D-Amphetamine
500
AMPHETAMINE (AMP 300)
D,L-Amphetamine sulfate
75
Phentermine
300
L-Amphetamine
10,000
Maprotiline
15,000
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
amphetamine
150
Methoxyphenamine
2,000
D-Amphetamine
300
BARBITURATES (BAR 300)
Amobarbital
5,000
Alphenol
600
5,5-Diphenylhydantoin
8,000
Aprobarbital
500
Allobarbital
600
Butabarbital
200
Barbital
8,000
Butalbital
8,000
Talbutal
200
Butethal
500
Cyclopentobarbital
30,000
Phenobarbital
300
Pentobarbital
8,000
Secobarbital
300
BARBITURATES (BAR 200)
Amobarbital
3,000
Alphenol
400
5,5-Diphenylhydantoin
5,000
Aprobarbital
300
Allobarbital
400
Butabarbital
150
Barbital
5,000
Butalbital
5,000
Talbutal
150
Butethal
300
Cyclopentobarbital
20,000
Phenobarbital
200
Pentobarbital
5,000
Secobarbital
200
BENZODIAZEPINES (BZO 500)
Alprazolam
200
Bromazepam
1,500
a-hydroxyalprazolam
2,500
Chlordiazepoxide
1,500
Clobazam
300
Nitrazepam
300
Clonazepam
800
Norchlordiazepoxide
200
Clorazepatedipotassium
800
Nordiazepam
1,500
Delorazepam
1,500
Oxazepam
500
Desalkylflurazepam
300
Temazepam
300
Flunitrazepam
300
Diazepam
500
() Lorazepam
5,000
Estazolam
10,000
RS-Lorazepamglucuronide
300
Triazolam
5,000
Midazolam
10,000
BENZODIAZEPINES (BZO 300)
Alprazolam
100
Bromazepam
900
a-hydroxyalprazolam
1,500
Chlordiazepoxide
900
Clobazam
200
Nitrazepam
200
Clonazepam
500
Norchlordiazepoxide
100
Clorazepatedipotassium
500
Nordiazepam
900
Delorazepam
900
Oxazepam
300
Desalkylflurazepam
200
Temazepam
100
Flunitrazepam
200
Diazepam
300
() Lorazepam
3,000
Estazolam
6,000
RS-Lorazepamglucuronide
200
Triazolam
3,000
Midazolam
6,000
BENZODIAZEPINES (BZO 200)
Alprazolam
70
Bromazepam
600
a-hydroxyalprazolam
1,000
Chlordiazepoxide
600
Clobazam
120
Nitrazepam
120
Clonazepam
300
Norchlordiazepoxide
70
Clorazepatedipotassium
300
Nordiazepam
600
Delorazepam
600
Oxazepam
200
Desalkylflurazepam
120
Temazepam
70
Flunitrazepam
120
Diazepam
200
() Lorazepam
2,000
Estazolam
4,000
RS-Lorazepamglucuronide
120
Triazolam
2,000
Midazolam
4,000
BENZODIAZEPINES (BZO 100)
Alprazolam
40
Bromazepam
300
a-hydroxyalprazolam
500
Chlordiazepoxide
300
Clobazam
60
Nitrazepam
60
Clonazepam
150
Norchlordiazepoxide
40
Clorazepatedipotassium
150
Nordiazepam
300
Delorazepam
300
Oxazepam
100
Desalkylflurazepam
60
Temazepam
40
Flunitrazepam
60
Diazepam
100
() Lorazepam
1,000
Estazolam
2,000
RS-Lorazepamglucuronide
60
Triazolam
1,000
Midazolam
2,000
BUPRENORPHINE (BUP 10)
Buprenorphine
10
Norbuprenorphine
50
Buprenorphine
3-D-Glucuronide
50
Norbuprenorphine
3-D-Glucuronide
100
BUPRENORPHINE (BUP 5)
Buprenorphine
5
Norbuprenorphine
25
Buprenorphine
3-D-Glucuronide
25
Norbuprenorphine
3-D-Glucuronide
50
COCAINE (COC 300)
Benzoylecgonine
300
Cocaethylene
20,000
Cocaine HCl
200
Ecgonine
30,000
COCAINE (COC 200)
Benzoylecgonine
200
Cocaethylene
13,500
Cocaine HCl
135
Ecgonine
20,000
COCAINE (COC 150)
Benzoylecgonine
150
Cocaethylene
10,000
Cocaine HCl
120
Ecgonine
15,000
COCAINE (COC 100)
Benzoylecgonine
100
Cocaethylene
7,000
Cocaine HCl
80
Ecgonine
10,000
MARIJUANA (THC 300)
Cannabinol
200,000
△
8
-THC
100,000
11-nor-△8-THC-9 COOH
200
△
9
-THC
100,000
11-nor-△9-THC-9 COOH
300
MARIJUANA (THC 200)
Cannabinol
140,000
△
8
-THC
68,000
11-nor-△8-THC-9 COOH
120
△
9
-THC
68,000
11-nor-△9-THC-9 COOH
200
MARIJUANA (THC 150)
Cannabinol
100,000
△
8
-THC
50,000
11-nor-△8-THC-9 COOH
100
△
9
-THC
50,000
11-nor-△9-THC-9 COOH
150
MARIJUANA (THC 50)
Cannabinol
35,000
△
8
-THC
17,000
11-nor-△8-THC-9 COOH
30
△
9
-THC
17,000
11-nor-△9-THC-9 COOH
50
MARIJUANA (THC 30)
Cannabinol
20,000
△
8
-THC
10,000
11-nor-△8-THC-9 COOH
20
△
9
-THC
10,000
11-nor-△9-THC-9 COOH
30
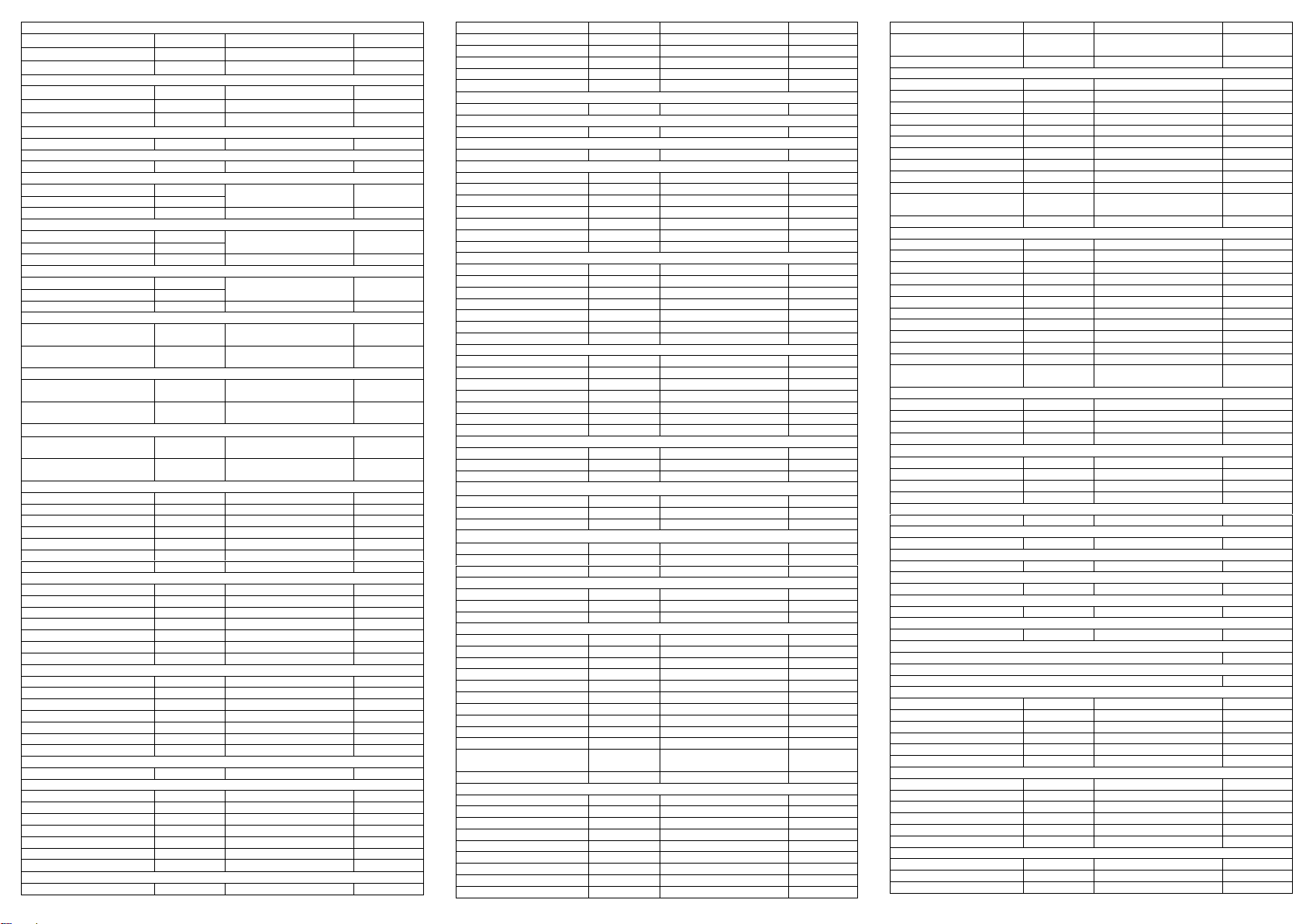
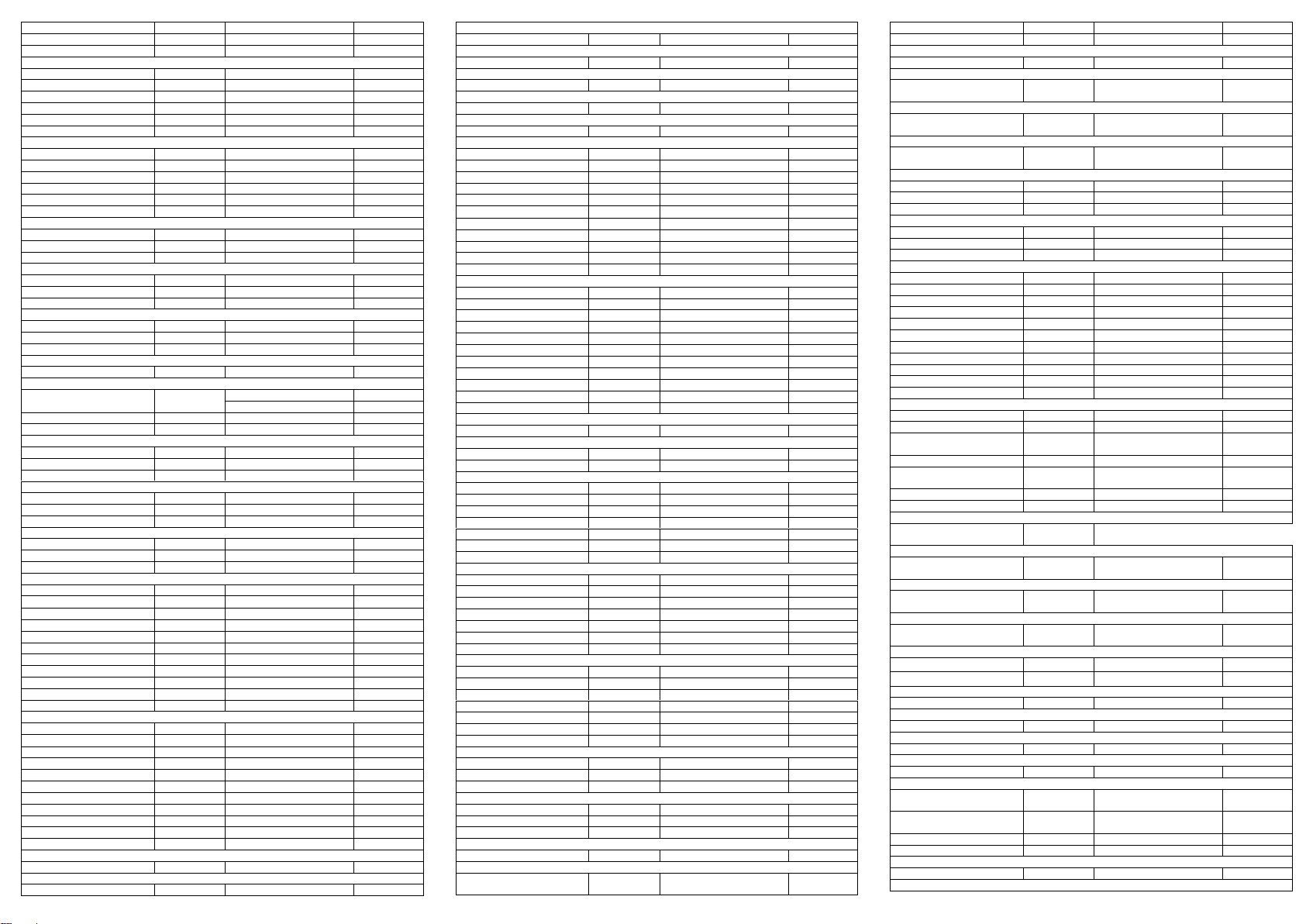
The following table lists the concentrations of compounds (ng/mL) that are detected as positive
in urine by the Multi-Drug Rapid Test at 5 minutes.
Analytical Specificity
3/ 6
Page 4
MARIJUANA (THC 25)
Cannabinol
17,500
△
8
-THC
8,500
11-nor-△8-THC-9 COOH
15
△
9
-THC
8,500
11-nor-△9-THC-9 COOH
25
MARIJUANA (THC 20)
Cannabinol
14,000
△
8
-THC
6,800
11-nor-△8-THC-9 COOH
12
△
9
-THC
6,800
11-nor-△9-THC-9 COOH
20
METHADONE (MTD 300)
Methadone
300
Doxylamine
100,000
METHADONE (MTD 200)
Methadone
200
Doxylamine
65,000
METHAMPHETAMINE (MET 1, 000)
-Hydroxymethamphetamine
25,000
()-3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
1,600
D-Methamphetamine
1,000
L-Methamphetamine
20,000
Mephentermine
50,000
METHAMPHETAMINE (MET 500)
-Hydroxymethamphetamine
12,500
()-3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
800
D-Methamphetamine
500
L-Methamphetamine
10,000
Mephentermine
25,000
METHAMPHETAMINE (MET 300)
-Hydroxymethamphetamine
7,500
()-3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
500
D-Methamphetamine
300
L-Methamphetamine
6,000
Mephentermine
15,000
METHYLENEDIOXYMETHAMPHETAMINE (MDMA 1,000) Ecstasy
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
methamphetamine HCl
1,000
3,4-Methylenedioxyethyl-amp
hetamine
600
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
amphetamine HCl
6,000
METHYLENEDIOXYMETHAMPHETAMINE (MDMA 500) Ecstasy
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
methamphetamine HCl
500
3,4-Methylenedioxyethyl-amp
hetamine
300
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
amphetamine HCl
3,000
METHYLENEDIOXYMETHAMPHETAMINE (MDMA 300) Ecstasy
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
methamphetamine HCl
300
3,4-Methylenedioxyethyl-amp
hetamine
180
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
amphetamine HCl
1,800
MORPHINE (MOP/OPI 300)
Codeine
200
Norcodeine
6,000
Levorphanol
1,500
Normorphone
50,000
Morphine-3-β-D-Glucuronide
800
Oxycodone
30,000
Ethylmorphine
6,000
Oxymorphone
50,000
Hydrocodone
50,000
Procaine
15,000
Hydromorphone
3,000
Thebaine
6,000
6-Monoacethylmorphine
300
Morphine
300
MORPHINE/OPIATE (MOP/OPI 200)
Codeine
160
Norcodeine
4,000
Levorphanol
1,000
Normorphone
40,000
Morphine-3-β-D-Glucuronide
600
Oxycodone
20,000
Ethylmorphine
4,000
Oxymorphone
40,000
Hydrocodone
40,000
Procaine
10,000
Hydromorphone
2,000
Thebaine
4,000
6-Monoacethylmorphine
200
Morphine
200
MORPHINE (MOP/OPI 100)
Codeine
80
Norcodeine
2,000
Levorphanol
500
Normorphone
20,000
Morphine-3-β-D-Glucuronide
300
Oxycodone
10,000
Ethylmorphine
2,000
Oxymorphone
20,000
Hydrocodone
20,000
Procaine
5,000
Hydromorphone
1,000
Thebaine
2,000
6-Monoacethylmorphine
100
Morphine
100
METHAQUALONE (MQL 300)
Methaqualone
300
MORPHINE/OPIATE (OPI 2,000)
Codeine
2,000
Morphine
2,000
Ethylmorphine
3,000
Norcodeine
25,000
Hydrocodone
50,000
Normorphone
50,000
Hydromorphone
15,000
Oxycodone
25,000
Levorphanol
25,000
Oxymorphone
25,000
6-Monoacetylmorphine
3,000
Procaine
50,000
Morphine 3--D-glucuronide
2,000
Thebaine
25,000
MORPHINE/OPIATE (OPI 1,000)
Codeine
1,000
Morphine
1,000
Ethylmorphine
1,500
Norcodeine
12,500
Hydrocodone
25,000
Normorphone
25,000
Hydromorphone
7,500
Oxycodone
12,500
Levorphanol
12,500
Oxymorphone
12,500
6-Monoacetylmorphine
1,500
Procaine
25,000
Morphine 3--D-glucuronide
1,000
Thebaine
12,500
PHENCYCLIDINE (PCP 25)
Phencyclidine
25
4-Hydroxyphencyclidine
12,500
PHENCYCLIDINE (PCP 50)
Phencyclidine
50
4-Hydroxyphencyclidine
25,000
PROPOXYPHENE (PPX 300)
D-Propoxyphene
300
D-Norpropoxyphene
300
TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS (TCA 1,000)
Nortriptyline
1,000
Imipramine
400
Nordoxepine
500
Clomipramine
50,000
Trimipramine
3,000
Doxepine
2,000
Amitriptyline
1,500
Maprotiline
2,000
Promazine
3,000
Promethazine
50,000
Desipramine
200
Perphenazine
50,000
Cyclobenzaprine
2,000
Dithiaden
10,000
TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS (TCA 500)
Nortriptyline
500
Imipramine
200
Nordoxepine
250
Clomipramine
25,000
Trimipramine
1,500
Doxepine
1,000
Amitriptyline
750
Maprotiline
1,000
Promazine
1,500
Promethazine
25,000
Desipramine
100
Perphenazine
25,000
Cyclobenzaprine
1,000
Dithiaden
5,000
TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS (TCA 300)
Nortriptyline
300
Imipramine
120
Nordoxepine
150
Clomipramine
15,000
Trimipramine
900
Doxepine
600
Amitriptyline
450
Maprotiline
600
Promazine
900
Promethazine
15,000
Desipramine
60
Perphenazine
15,000
Cyclobenzaprine
600
Dithiaden
3,000
TRAMADOL (TML 100)
n-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
200
o-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
10,000
Cis-tramadol
100
Phencyclidine
100,000
Procyclidine
100,000
d,l-O-Desmethyl venlafaxine
50,000
TRAMADOL (TML 200)
n-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
400
o-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
20,000
Cis-tramadol
200
Phencyclidine
200,000
Procyclidine
200,000
d,l-O-Desmethyl venlafaxine
100,000
TRAMADOL (TML 300)
n-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
600
o-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
30,000
Cis-tramadol
300
Phencyclidine
300,000
Procyclidine
300,000
d,l-O-Desmethyl venlafaxine
150,000
TRAMADOL (TML 500)
n-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
1,000
o-Desmethyl-cis-tramadol
50,000
Cis-tramadol
500
Phencyclidine
500,000
Procyclidine
500,000
d,l-O-Desmethyl venlafaxine
250,000
KETAMINE (KET 1,000)
Ketamine
1,000
Benzphetamine
25,000
Dextromethorphan
2,000
(+) Chlorpheniramine
25,000
Methoxyphenamine
25,000
Clonidine
100,000
d-Norpropoxyphene
25,000
EDDP
50,000
Promazine
25,000
4-Hydroxyphencyclidine
50,000
Promethazine
25,000
Levorphanol
50,000
Pentazocine
25,000
MDE
50,000
Phencyclidine
25,000
Meperidine
25,000
Tetrahydrozoline
500
d-Methamphetamine
50,000
Mephentermine
25,000
l-Methamphetamine
50,000
(1R, 2S) - (-)-Ephedrine
100,000
3,4-Methylendioxymethamphe
tamine (MDMA)
100,000
Disopyramide
25,000
Thioridazine
50,000
KETAMINE (KET 500)
Ketamine
500
Benzphetamine
12,500
Dextromethorphan
1,000
(+) Chlorpheniramine
12,500
Methoxyphenamine
12,500
Clonidine
50,000
d-Norpropoxyphene
12,500
EDDP
25,000
Promazine
12,500
4-Hydroxyphencyclidine
25,000
Promethazine
12,500
Levorphanol
25,000
Pentazocine
12,500
MDE
25,000
Phencyclidine
12,500
Meperidine
12,500
Tetrahydrozoline
250
d-Methamphetamine
25,000
Mephentermine
12,500
l-Methamphetamine
25,000
(1R, 2S) - (-)-Ephedrine
50,000
3,4-Methylendioxymethamphe
tamine (MDMA)
50,000
Disopyramide
12,500
Thioridazine
25,000
KETAMINE (KET 300)
Ketamine
300
Benzphetamine
6,250
Dextromethorphan
600
(+) Chlorpheniramine
6,250
Methoxyphenamine
6,250
Clonidine
30,000
d-Norpropoxyphene
6,250
EDDP
15,000
Promazine
6,250
4-Hydroxyphencyclidine
15,000
Promethazine
6,250
Levorphanol
15,000
Pentazocine
6,250
MDE
15,000
Phencyclidine
6,250
Meperidine
6,250
Tetrahydrozoline
150
d-Methamphetamine
15,000
Mephentermine
6,250
l-Methamphetamine
15,000
(1R, 2S) - (-)-Ephedrine
30,000
3,4-Methylendioxymethamphe
tamine (MDMA)
30,000
Disopyramide
6,250
Thioridazine
15,000
KETAMINE (KET 100)
Ketamine
100
Benzphetamine
2,000
Dextromethorphan
200
(+) Chlorpheniramine
2,000
Methoxyphenamine
2,000
Clonidine
10,000
d-Norpropoxyphene
2,000
EDDP
5,000
Promazine
2,000
4-Hydroxyphencyclidine
5,000
Promethazine
2,000
Levorphanol
5,000
Pentazocine
2,000
MDE
5,000
Phencyclidine
2,000
Meperidine
2,000
Tetrahydrozoline
50
d-Methamphetamine
5,000
Mephentermine
2,000
l-Methamphetamine
5,000
(1R, 2S) - (-)-Ephedrine
10,000
Thioridazine
5,000
Disopyramide
2,000
3,4-Methylendioxymethamphe
tamine (MDMA)
10,000
OXYCODONE (OXY 100)
Oxycodone
100
Hydromorphone
50,000
Oxymorphone
300
Naloxone
25,000
Levorphanol
50,000
Naltrexone
25,000
Hydrocodone
25,000
OXYCODONE (OXY 300)
Oxycodone
300
Hydromorphone
150,000
Oxymorphone
900
Naloxone
75,000
Levorphanol
150,000
Naltrexone
75,000
Hydrocodone
75,000
COTININE (COT 500)
(-)-Cotinine
500
(-)-Nicotine
12,500
COTININE (COT 300)
(-)-Cotinine
300
(-)-Nicotine
7,500
COTININE (COT 200)
(-)-Cotinine
200
(-)-Nicotine
5,000
COTININE (COT 100)
(-)-Cotinine
100
(-)-Nicotine
2,500
COTININE (COT 50)
(-)-Cotinine
50
(-)-Nicotine
1,250
COTININE (COT 10)
(-)-Cotinine
10
(-)-Nicotine
250
2-ETHYLIDENE-1,5-DIMETHYL-3,3-DIPHENYLPYRROLIDINE (EDDP 300)
2-Ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl-3,3-diphenylpyrrolidine (EDDP)
300
2-ETHYLIDENE-1,5-DIMETHYL-3,3-DIPHENYLPYRROLIDINE (EDDP 100)
2-Ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl-3,3-diphenylpyrrolidine (EDDP)
100
FENTANYL (FYL 20)
Fentanyl
20
Cyclopro Fentanyl
500
Norfentany
>100,000
(±)cis-3-Methylfentanyl
500
Butyl fentanyl
300
Valeryl Fentanyl
200
Methoxyacetyl-Fentanyl
40
Acetyl Fentanyl
40
Ocfentanil
200
para-Fluorobutyryl fentanil
200
4-Fluoro-isobutyryl Fentanyl
200
para-Fluorofentanil
100
FENTANYL (FYL 10)
Fentanyl
10
Cyclopro Fentanyl
250
Norfentany
>100,000
(±)cis-3-Methylfentanyl
250
Butyl fentanyl
150
Valeryl Fentanyl
100
Methoxyacetyl-Fentanyl
20
Acetyl Fentanyl
20
Ocfentanil
100
para-Fluorobutyryl fentanil
100
4-Fluoro-isobutyryl Fentanyl
100
para-Fluorofentanil
50
FENTANYL (FYL 100)
Fentanyl
100
Cyclopro Fentanyl
2,500
Norfentany
>100,000
(±)cis-3-Methylfentanyl
2,500
Butyl fentanyl
1,500
Valeryl Fentanyl
1,000
4/ 6
Page 5
Methoxyacetyl-Fentanyl
200
Acetyl Fentanyl
200
Ocfentanil
1,000
para-Fluorobutyryl fentanil
1,000
4-Fluoro-isobutyryl Fentanyl
1,000
para-Fluorofentanil
500
FENTANYL (FYL 200)
Fentanyl
200
Cyclopro Fentanyl
5,000
Norfentany
>100,000
(±)cis-3-Methylfentanyl
5,000
Butyl fentanyl
3,000
Valeryl Fentanyl
2,000
Methoxyacetyl-Fentanyl
400
Acetyl Fentanyl
400
Ocfentanil
2,000
para-Fluorobutyryl fentanil
2,000
4-Fluoro-isobutyryl Fentanyl
2,000
para-Fluorofentanil
1,000
FENTANYL (FYL 300)
Fentanyl
300
Cyclopro Fentanyl
7,500
Norfentany
>100,000
(±)cis-3-Methylfentanyl
7,500
Butyl fentanyl
4,500
Valeryl Fentanyl
3,000
Methoxyacetyl-Fentanyl
600
Acetyl Fentanyl
600
Ocfentanil
3,000
para-Fluorobutyryl fentanil
3,000
4-Fluoro-isobutyryl Fentanyl
3,000
para-Fluorofentanil
1,500
SYNTHETIC MARIJUANA (K2-50)
JWH-018 5-Pentanoic acid
50
JWH-073 4-butanoic acid
50
JWH-018 4-Hydroxypentyl
400
JWH-018 5-Hydroxypentyl
500
JWH-073 4-Hydroxybuty
500
SYNTHETIC MARIJUANA (K2-30)
JWH-018 5-Pentanoic acid
30
JWH-073 4-butanoic acid
30
JWH-018 4-Hydroxypentyl
250
JWH-018 5-Hydroxypentyl
300
JWH-073 4-Hydroxybuty
300
SYNTHETIC MARIJUANA (K2-25)
JWH-018 5-Pentanoic acid
25
JWH-073 4-butanoic acid
25
JWH-018 4-Hydroxypentyl
200
JWH-018 5-Hydroxypentyl
250
JWH-073 4-Hydroxybuty
250
6-MONO-ACETO-MORPHINE (6-MAM 10)
6-Monoacethylmorphine
10
Morphine
100,000
(±) 3, 4-METHYLENEDIOXYAMPHETAMINE (MDA 500)
(±) 3,4-Methylenedioxy
amphetamine
500
Methoxyphenamine
5,000
D-Amphetamine
2,000
D,L-Amphetamine sulfate
400
Phentermine
2,000
L-Amphetamine
30,000
Maprotiline
100,000
ETHYL- Β-D-GLUCURONIDE(ETG 500)
Ethyl- β -D-Glucuronide
500
Propyl β-D-glucuronide
50,000
Glucuronic Acid
100,000
Ethanol
>100,000
Methanol
>100,000
ETHYL- Β-D-GLUCURONIDE(ETG 1,000)
Ethyl- β -D-Glucuronide
1,000
Propyl β-D-glucuronide
100,000
Glucuronic Acid
>100,000
Ethanol
>100,000
Methanol
>100,000
ETHYL- Β-D-GLUCURONIDE(ETG 300)
Ethyl- β -D-Glucuronide
300
Propyl β-D-glucuronide
30,000
Glucuronic Acid
60,000
Ethanol
>100,000
Methanol
>100,000
CLONAZEPAM(CLO 400)
Clonazepam
400
Flunitrazepam
300
Alprazolam
200
() Lorazepam
1,250
a-hydroxyalprazolam
2,000
RS-Lorazepamglucuronide
250
Bromazepam
1,000
Midazolam
5,000
Chlordiazepoxide
1,000
Nitrazepam
200
Clobazam
250
Norchlordiazepoxide
200
Clorazepatedipotassium
600
Nordiazepam
1,000
Delorazepam
1,000
Oxazepam
350
Desalkylflurazepam
250
Temazepam
150
Diazepam
300
Triazolam
5,000
Estazolam
1,250
CLONAZEPAM (CLO 150)
Clonazepam
150
Flunitrazepam
120
Alprazolam
75
() Lorazepam
500
a-hydroxyalprazolam
750
RS-Lorazepamglucuronide
100
Bromazepam
400
Midazolam
2,000
Chlordiazepoxide
400
Nitrazepam
75
Clobazam
100
Norchlordiazepoxide
75
Clorazepatedipotassium
250
Nordiazepam
400
Delorazepam
400
Oxazepam
130
Desalkylflurazepam
100
Temazepam
60
Diazepam
120
Triazolam
2,000
Estazolam
500
LYSERGIC ACID DIETHYLAMIDE (LSD 10)
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide
10
LYSERGIC ACID DIETHYLAMIDE (LSD 20)
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide
20
LYSERGIC ACID DIETHYLAMIDE (LSD 50)
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide
50
METHYLPHENIDATE (MPD 1,000)
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
350
Ritalinic Acid
1,000
METHYLPHENIDATE (MPD 300)
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
300
Ritalinic Acid
1,000
METHYLPHENIDATE (MPD 150)
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
150
Ritalinic Acid
500
ZOLPIDEM(ZOL 50)
Zolpidem
50
DIAZEPAM (DIA 300)
Diazepam
300
Midazolam
6,000
Clobazam
200
Nitrazepam
200
Clonazepam
500
Norchlordiazepoxide
100
Clorazepate dipotassium
500
Nordiazepam
900
Alprazolam
100
Flunitrazepam
200
a-hydroxyalprazolam
1,500
() Lorazepam
3,000
Bromazepam
900
RS-Lorazepam glucuronide
200
Chlordiazepoxide
900
Triazolam
3,000
Estazolam
6,000
Temazepam
100
Delorazepam
900
Oxazepam
300
Desalkylflurazepam
200
DIAZEPAM (DIA 200)
Diazepam
200
Midazolam
4,000
Clobazam
120
Nitrazepam
120
Clonazepam
300
Norchlordiazepoxide
70
Clorazepate dipotassium
300
Nordiazepam
600
Alprazolam
70
Flunitrazepam
120
a-hydroxyalprazolam
1,000
() Lorazepam
2,000
Bromazepam
600
RS-Lorazepam glucuronide
120
Chlordiazepoxide
600
Triazolam
2,000
Estazolam
4,000
Temazepam
70
Delorazepam
600
Oxazepam
200
Desalkylflurazepam
120
ZOPICLONE (ZOP 50)
Zopiclone-x-oxide
50
Zopiclone
50
METHCATHINONE (MCAT 500)
S(-)-Methcathinone HCl
500
R(+)-Methcathinone HCl
1,500
Methoxyphenamine
100,000
3-Fluoromethcathinone HCl
1,500
7-AMINOCLONAZEPAM(7-ACL 300)
a-hydroxyalprazolam
6,000
Flunitrazepam
3,000
Bromazepam
6,000
RS-Lorazepam glucuronide
2,700
Chlordiazepoxide
6,000
Norchlordiazepoxide
4,500
Clobazam
9,000
Nordiazepam
15,000
Clonazepam
2,400
Temazepam
9,000
Delorazepam
6,000
7-Aminoclonazepam
300
Desalkylflurazepam
6,000
7-AMINOCLONAZEPAM(7-ACL 200)
a-hydroxyalprazolam
4,000
Flunitrazepam
2,000
Bromazepam
4,000
RS-Lorazepam glucuronide
1,800
Chlordiazepoxide
4,000
Norchlordiazepoxide
3,000
Clobazam
6,000
Nordiazepam
10,000
Clonazepam
1,600
Temazepam
6,000
Delorazepam
4,000
7-Aminoclonazepam
200
Desalkylflurazepam
4,000
7-AMINOCLONAZEPAM(7-ACL 100)
a-hydroxyalprazolam
2,000
Flunitrazepam
1,000
Bromazepam
2,000
RS-Lorazepam glucuronide
900
Chlordiazepoxide
2,000
Norchlordiazepoxide
1,500
Clobazam
3,000
Nordiazepam
5,000
Clonazepam
800
Temazepam
3,000
Delorazepam
2,000
7-Aminoclonazepam
100
Desalkylflurazepam
2,000
CARFENTANYL(CFYL 500)
Carfentanyl
500
Fentanyl
100
Sufentanil
50,000
Ramifentanil
10,000
(±)cis-3-Menthylfentanyl
20,000
Butyl fentanyl
150
CARFENTANYL(CFYL 250)
Carfentanyl
250
Fentanyl
50
Sufentanil
25,000
Ramifentanil
5,000
(±)cis-3-Menthylfentanyl
10,000
Butyl fentanyl
75
CAFFEINE (CAF 1,000)
Caffeine
1,000
CATHINE (CAT 150)
(+)-Norpseudoephedrine HCl
(Cathine)
150
(+)3,4-Methylenedioxyamphet
amine (MDA)
100
d/l-Amphetamine
100
p-Hydroxyamphetamine
100
Tryptamine
12,500
Methoxyphenamine
12,500
TROPICAMIDE (TRO 350)
Tropicamide
350
3, 4-METHYLENEDIOXYPYROVALERONE (MDPV 1,000)
3, 4-methylenedioxy
pyrovalerone
1,000
3, 4-METHYLENEDIOXYPYROVALERONE (MDPV 500)
3, 4-methylenedioxy
pyrovalerone
500
3, 4-METHYLENEDIOXYPYROVALERONE (MDPV 300)
3, 4-methylenedioxy
pyrovalerone
300
MEPHEDRONE (MEP 100)
Mephedrone HCl
100
R(+)-Methcathinone HCl
1500
S(-)-Methcathinone HCl
500
3-Fluoromethcathinone HCl
1500
4-Fluoromethcathinone HCl
300
Methoxyphenamine
100,000
MEPHEDRONE (MEP 500)
Mephedrone HCl
500
R(+)-Methcathinone HCl
7,500
S(-)-Methcathinone HCl
2,500
3-Fluoromethcathinone HCl
7,500
4-Fluoromethcathinone HCl
1,500
Methoxyphenamine
500,000
ALPRAZOLAM(ALP 100)
Benzodiazepines
300
Flunitrazepam
200
a-hydroxyalprazolam
1,500
(±) Lorazepam
3,000
Bromazepam
900
RS-Lorazepamglucuronide
200
Chlordiazepoxide
900
Midazolam
6,000
Clobazam
200
Nitrazepam
200
Clonazepam
500
Norchlordiazepoxide
100
Clorazepatedipotassium
500
Nordiazepam
900
Delorazepam
900
Oxazepam
300
Desalkylflurazepam
200
Temazepam
100
Diazepam
300
Triazolam
3,000
Estazolam
6,000
AB-PINACA (ABP 10)
AB-PINACA
10
UR-144 4-hydroxypentyl
10,000
AB-PINACA 5-Pentanoic
10
APINACA 5-hydroxypentyl
10,000
AB-PINACA 5-hydroxypentyl
10
ADB-PINACA
N-(5-hydroxypentyl)
30
AB-FUBINACA
10
ADB-PINACA Pentanoic Acid
10
AB-PINACA 4-hydroxypentyl
10,000
5-fluoro AB-PINACA
N-(4-hydroxypentyl)
30
UR-144 5-Pentanoic
5,000
5-fluoro AB-PINACA
25
UR-144 5-hydroxypentyl
10,000
ALPHA-PYRROLIDINOVALEROPHENONE (Α-PVP 2,000)
alpha-Pyrrolidinovalerophenon
e
2,000
ALPHA-PYRROLIDINOVALEROPHENONE (Α-PVP 1,000)
alpha-Pyrrolidinovalerophenon
e
1,000
ALPHA-PYRROLIDINOVALEROPHENONE (Α-PVP 500)
alpha-Pyrrolidinovalerophenon
e
500
ALPHA-PYRROLIDINOVALEROPHENONE (Α-PVP 300)
alpha-Pyrrolidinovalerophenon
e
300
CANNABINOL (CNB 500)
cannabinol
500
11-nor-9 -THC-9 COOH
300
9
-THC
10,000
MEPERIDINE (MPRD 100)
Normeperidine
100
Meperidine
100
PREGABALIN(PGB 50,000)
Pregabalin
50,000
PREGABALIN(PGB 500)
Pregabalin
500
TRAZODONE(TZD 200)
Trazodone
200
UR-144 25
UR-144 5-Pentanoic acid
25
5-fluoro AB-Pinaca
N-(4-hydroxypentyl)
10,000
UR-144 4-hydroxypentyl
10,000
ADB-PINAC
N-(4-hydroxypentyl)
>10,000
UR-144 5-hydroxypentyl
5,000
AB-PINACA 4-hydroxypentyl
>10,000
XLR-11 4-hydroxypentyl
2,000
ZALEPLON(ZAL 100)
Zaleplon
100
MESCALINE(MES 100)
5/ 6
Page 6
Mescaline
100
MESCALINE(MES 300)
Mescaline
300
GABAPENTIN(GAB 2,000)
Gabapentin
2,000
TILIDINE(TLD 50)
Nortilidine
50
Tilidine
100
QUETIAPINE(QTP 1,000)
Quetiapine
1,000
Norquetiapine
10,000
PAPAVERINE(PAP 500)
Papaverine
500
Diflunisal
1,000,000
Methortrexate
650,000
Methedrone
500,000
Pragablin
500,000
Phenelzine
8,000
Quinine
4,000
KRATOM(KRA 300)
Mitragynine
300
7-hydroxymitragynine
>50,000
CARISOPRODOL(CAR 2,000)
Carisoprodol
2,000
CARISOPRODOL(CAR 1,000)
Carisoprodol
1,000
FLUOXETINE(FLX 500)
Fluoxetine
500
OLANZAPINE(OZP 1,000)
Olanzapine
1,000
CITALOPRAM(CIT 500)
Citalopram
500
FLUOKETAMINE (FKET 1,000)
2-(2-fluorphenyl)-2-methylamin
o-cyclohexanone
1,000
RISPERIDONE (RPD 150)
Risperidone
150
TAPENTADOL (TAP 1,000)
3-((1R,2R)-3-(dimethylamino)-1
-ethyl-2-methylpropyl)phenol
1,000
N,N-DIMETHYLTRYPTAMINE(NND 1,000)
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
1,000
SCOPOLAMINE(SCOP 500)
Scopolamine
500
Atropine
3,000
MIRTAZAPINE(MTZ 500)
Desmethylmirtazapine
500
Mirtazapine
500
Acetophenetidin
Cortisone
Zomepirac
d-Pseudoephedrine
N-Acetylprocainamide
Creatinine
Ketoprofen
Quinidine
Acetylsalicylic acid
Deoxycorticosterone
Labetalol
Quinine
Aminopyrine
Dextromethorphan
Loperamide
Salicylic acid
Amoxicillin
Diclofenac
Meprobamate
Serotonin
Ampicillin
Diflunisal
Isoxsuprine
Sulfamethazine
l-Ascorbic acid
Digoxin
d,l-Propanolol
Sulindac
Apomorphine
Diphenhydramine
Nalidixic acid
Tetracycline
Aspartame
Ethyl-p-aminobenzoate
Naproxen
Tetrahydrocortisone,
Atropine
-Estradiol
Niacinamide
3-acetate
Benzilic acid
Estrone-3-sulfate
Nifedipine
Tetrahydrocortisone
Benzoic acid
Erythromycin
Norethindrone
Tetrahydrozoline
Bilirubin
Fenoprofen
Noscapine
Thiamine
d,l-Brompheniramine
Furosemide
d,l-Octopamine
Thioridazine
Caffeine
Gentisic acid
Oxalic acid
d,l-Tyrosine
Cannabidiol
Hemoglobin
Oxolinic acid
Tolbutamide
Chloral hydrate
Hydralazine
Oxymetazoline
Triamterene
Chloramphenicol
Hydrochlorothiazide
Papaverine
Trifluoperazine
Chlorothiazide
Hydrocortisone
Penicillin-G
Trimethoprim
d,l-Chlorpheniramine
o-Hydroxyhippuric acid
Perphenazine
d,l-Tryptophan
Chlorpromazine
3-Hydroxytyramine
Phenelzine
Uric acid
Cholesterol
d,l-Isoproterenol
Prednisone
Verapamil
Clonidine
【ALCOHOL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS】
Peroxidases
Strong oxidizers
Reducing agents: Ascorbic acid, Tannic acid, Pyrogallol, Mercaptans and tosylates,
Oxalic acid, Uric Acid
Bilirubin
L-dopa
L-methyldopa
Methampyrone
Consult Instructions
For Use
Contains
sufficient for
<n> tests
Authorized
Representative
in the EU
In vitro
diagnostic medical
device
Use-by date
Do not re-use
Temperature limit
2-30 °C
Batch code
Catalogue number
Do not use if package is
damaged
Manufacturer
CE mark
The detection limit on the Urine Alcohol Rapid Test is from 0.02% to 0.30% for approximate
relative blood alcohol level. The cutoff level of the Urine Alcohol Rapid Test can vary based on
local regulations and laws. Test results can be compared to reference levels with color chart on
the foil package.
【ALCOHOL ASSAY SPECIFICITY】
The Urine Alcohol Rapid Test will react with methyl, ethyl and allyl alcohols.
【ALCOHOL INTERFERING SUBSTANCES】
The following substances may interfere with the Urine Alcohol Rapid Test when using
samples other than urine. The named substances do not normally appear in sufficient quantity in
urine to interfere with the test.
A. Agents which enhance color development
B. Agents which inhibit color development
【BIBLIOGRAPHY】
1. B. Cody, J.T., “Specimen Adulteration in drug urinalysis. Forensic Sci. Rev., 1990, 2:63.
2. C. Tsai, S.C. et. al., J. Anal. Toxicol. 1998; 22 (6): 474
3. Tietz NW. Textbook of Clinical Chemistry. W.B. Saunders Company. 1986; 1735.
4. Hawks RL, CN Chiang. Urine Testing for Drugs of Abuse. National Institute for Drug Abuse
(NIDA), Research Monograph 73, 1986.
5. Baselt RC. Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man. 6th Ed. Biomedical Publ.,
Foster City, CA 2002.
Index of Symbols
Fifteen (15) urine samples of normal, high, and low specific gravity ranges (1.005-1.045) were
spiked with drugs at 50% below and 50% above cut-off levels respectively. The Multi-Drug
Rapid Test was tested in duplicate using fifteen drug-free urine and spiked urine samples. The
results demonstrate that varying ranges of urinary specific gravity do not affect the test results.
The pH of an aliquoted negative urine pool was adjusted to a pH range of 5 to 9 in 1 pH unit
increments and spiked with drugs at 50% below and 50% above cut-off levels. The spiked,
pH-adjusted urine was tested with the Multi-Drug Rapid Test The results demonstrate that
varying ranges of pH do not interfere with the performance of the test.
A study was conducted to determine the cross-reactivity of the test with compounds in either
drug-free urine or drug positive urine containing above calibrator substances. The following
compounds show no cross-reactivity when tested with the Multi-Drug Rapid Test at a
concentration of 100 µg/mL.
Effect of Urinary Specific Gravity
Non Cross-Reacting Compounds
Effect of Urinary pH
Cross-Reactivity
6/ 6
 Loading...
Loading...