
GigaFast WF728-AEX IEEE 802.11 B/G WLAN CardBus
User Manual
Version 1.1
M090403V11

No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any
derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written permission fro m the
copyright owner.
All the other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Statement of Conditions
We may make improvements or changes in the product described in this documentation at any time. The
information regarding to the product in this manual are subject to change without notice.
We assume no responsibility for errors contained here in or for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or cons equential
damages with the furnishing, performance, or use of this manual or equipment supplied with it, even if the
suppliers have been advised of the possibility of such damages.
Electronic Emission Notices
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
FCC INFORMATION
The Federal Communication Commission Radio Frequency Interference Statement includes the following
paragraph:
The equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B Digital Device, pursuant to part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are desig ned to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in
a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction, may cause harmful interference to radio communication.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to overcome the interfer ence by one or more of the following measures:
--Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
--Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
--Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
--Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The equipment is for home or office use.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of the Directive 1999/5/EC of the European p arliament and the
council of 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication terminal Equipment and the mutual
recognition of their conformity(R&TTE).
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC. As of April 8, 2000.
IMPORTANT NOTE
FCC RF Radiation Exposure S t atement: This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth
for an uncontrolled environment. This device has been tested for compliance with FCC RF Exposure
(SAR) limits in typical laptop configurations, and this transmitter must not be co-located or operating in
conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Caution: Changes or modifications not ex pressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user's authority to operate the equipment.

T
able of Contents
INTRODUCTION ...... ........................... .......................... .......................... ........................... ............................. 1
1.1 FEATURES ............................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 PRODUCT PACKAGE ........................................................................................................................... 1
1.3 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS.................................................................................................................. 2
INSTALLATION OF THE 802.11b/g WLAN CARDBUS............................................................................ 3
2.1 INSTALLATION PROCEDURES .......................................................................................................... 3
2.2 VERIFYING A SUCCESSFUL INSTALLATION ................................................................................. 6
WLAN-G CONFIGURATION TOOL BASICS ... ... .... .... ...................... .... .... . ... ...................... .... .. .. .... .......... 7
3.1 RIGHT-CLICK MENU OF THE TRAY ICON ...................................................................................... 7
Wireless Radio On .............................................................................................. 7
Wireless Radio Off.............................................................................................. 7
Remove Status Icon ........................................................................................... 7
Wireless Network Status ..................................................................................... 8
Advanced Configuration ...................................................................................... 8
WEP Encryption ................................................................................................. 8
IBSS Channel .................................................................................................... 8
Country/Domain ................................................................................................ 8
Version Information ........................................................................................... 8
3.2 PROGRAM CONTROLS ....................................................................................................................... 9
The Status Tab .................................................................................................. 9
The Configuration Tab ...................................................................................... 11
The Encryption Tab .......................................................................................... 12
The Site Survey Tab ......................................................................................... 14
The IBSS Tab .................................................................................................. 14
The Domain Tab .................................................. .. ...... ...... ... ..... ..... .... ..... ... ..... 15
The About Tab................................................................................................. 16
APPENDIX A: TROUBLESHOO TING ........................... . ... ... ....................... ...................... ........................ 18
DISABLE 802.11b/g WLAN CARDBUS................................................................................................... 18
UNINSTALL WLAN-G CONFIGURATION TOOL AND THE CARD’S DRIVER .................... ........ ... . 18
802.11b/g WLAN CARDBUS DOES NOT WORK PROPERLY .............................................................. 21
APPENDIX B: SPECIF ICATIO NS. ........................ .. . ... .... .... ......................................... ............................... 22

Table of Figures
FIGURE 2-1: THE FOUND NEW HARDWARE WIZARD DIALOG BOX .................................................................3
FIGURE 2-2: THE WLAN IEEE802.11b/g SETUP WINDOW .......................................................................................4
FIGURE 2-3: THE SETUP STATUS SCREEN .................................................................................................................4
FIGURE 2-4: THE HARD WARE INSTALLATION DIALOG BOX..............................................................................5
FIGURE 2-5: THE COMPLETE SCREEN.......................................................................................................................5
FIGURE 2-6: THE WLAN-G CONFIGURATION TOOL TRAY ICON..................... ....................... . ......................... . .5
FIGURE 2-7: THE DEVICE MANAGER DIALOG BOX...............................................................................................6
FIGURE 3-1: RIGHT-CLICK MENU OF THE TRAY ICON ............................................................................................7
FIGURE 3-2: THE REMOVE WIRELESS STATUS ICON DIALOG BOX .................................................................8
FIGURE 3-3: THE WIRELESS SETTINGS DIALOG BOX...........................................................................................9
FIGURE 3-4: THE STATUS T AB ............................... ..... ... ... ...... . ...... .. .... .... ... ... .... ..... ... .... .... ... ... .... ..... ... .... .... .. ... ..........10
FIGURE 3-5: THE CONFIGURATION T A B ....................... ... ... .......................... .. ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .... ..... ... ... ...... .. ... .... .... 11
FIGURE 3-6: THE ENCRYPTION TAB........................ ....... . ...... . ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .... ..... ... ... ...................13
FIGURE 3-7: THE SITE SURVEY TAB ......................................................... .. .... ... .... .... ... ...... .. .... ... .... .... ... ..... ... .... ... ...1 4
FIGURE 3-8: THE IBSS TAB................. ...... .... ..... .... ....... ...... .... ... ...... ...... ....... .... .. ....... ...... ....... .. .... ....... ...... ... ................15
FIGURE 3-9: THE DOMAIN T AB .. ......................... .. ..... ... ... ...... . ...... .. .... .... ... ... .... ..... ... .... .... ... ... .... ..... ... .... .... ... ... . ........16
FIGURE 3-10: THE ABOUT TA B .......................... ............................ ............................. ............................. ...................17
FIGURE 4-1: THE DEVICE MANAGER DIALOG BOX.............................................................................................18
FIGURE 4-2: THE CONFIRM DEVICE REMOVAL MESSAGE BOX ......................................................................19
FIGURE 4-3: THE ADD OR REMOVE PROGRAMS DIALOG BOX.......... ........................ . ........................ .. . ..........19
FIGURE 4-4: THE WLAN IEEE802.11b/g SETUP WINDOW .....................................................................................20
FIGURE 4-5: THE WLAN IEEE802.11b/g SETUP MESSAGE BOX ..........................................................................20
FIGURE 4-6: THE MAINTENANCE COMPLETE SCREEN .....................................................................................21

INTRODUCTION
Being five times faster than the speed of 802.11b network standard devices, the innovative 802.11g
standard lets the wireless network become incredibly easier and faster (up to 54Mbps) than ever. Your
802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus surely will bring you into such a high-speed network sphere. This document
describes how to install your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus, which aims to let your computer communicate
with 802.11 networks quickly and seamlessly. Wireless LAN is local area networking without wires,
which uses radio frequencies to transmit and receive data between PCs or other network devices.
Additionally, wireless LAN is able to configure either independent networks, which is also known as
peer-to-peer or ad-hoc network, or infrastructure networks. The former is suitable for small or
temporary peer-to-peer configurations, and the later is offering fully distributed data connectivity via
micro cells and roaming.
To obtain most benefits your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus brings, please read this manual carefully
before using it.
1.1 Features
With 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus, you can:
g establish a wireless connection without the hassles and cost of cabling
g operate Ad-Hoc or Infrastructure mode
g utilize up to 128-bit WEP encryption
g enjoy high-speed data transfer rate up to 54 Mbps
g employ automatic data rate switching which offers maximum reliability, throughput and
connectivity
g possess the network’s range up to 100 meters indoor and 400 meters outdoor
g monitor and configure the network via the supplied friendly-interfaced application –
WLAN-G Configuration Tool
1.2 Product Package
Before starting the installation, please make sure the package you purchased includes the following
items:
g One 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus.
g One Setup Wizard CD with User Manual
g One Quick Installation Guide
If any of the items above is missing or damaged, please contact your distributor.
1

1.3 System Requirements
To properly operate your Card, your computer should meet the following minimum requirements:
g Microsoft Windows 98/98 Second Edition/ME/2000 or Windows XP
g Minimum 5 Mbytes free disk sp ace for installing the driver and the utility program
g 32 MB RAM or above
g A CD-ROM drive
g 300 MHz processor or higher
g Cardbus interface
2
INSTALLATION of THE 802.11b/g WLAN CARDBUS
It’s free and easy for you to install your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus and the attached program –
WLAN-G Configuration Tool. Simply with a few clicks of the mouse, you will succeed the
completion of installation.
To have the 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus operated appro priately, please read and go along with the
instructions below carefully. Here, we will illustrate the installation instructions based on Windows XP
operating system.
2.1 Installation Procedures
a) Insert the 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus into your PC’s Cardbus slot. The Found New
Hardware Wizard dialog box will appear because the system has detected the
insertion of the Card.
b) In the Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box, choose Cancel.
Figure 2-1: The Found New Hard ware Wizard Dialog Box
c) Insert the supplied CD into your CD-ROM drive, and double-click setup.exe under the
CD’s directory to execute it.
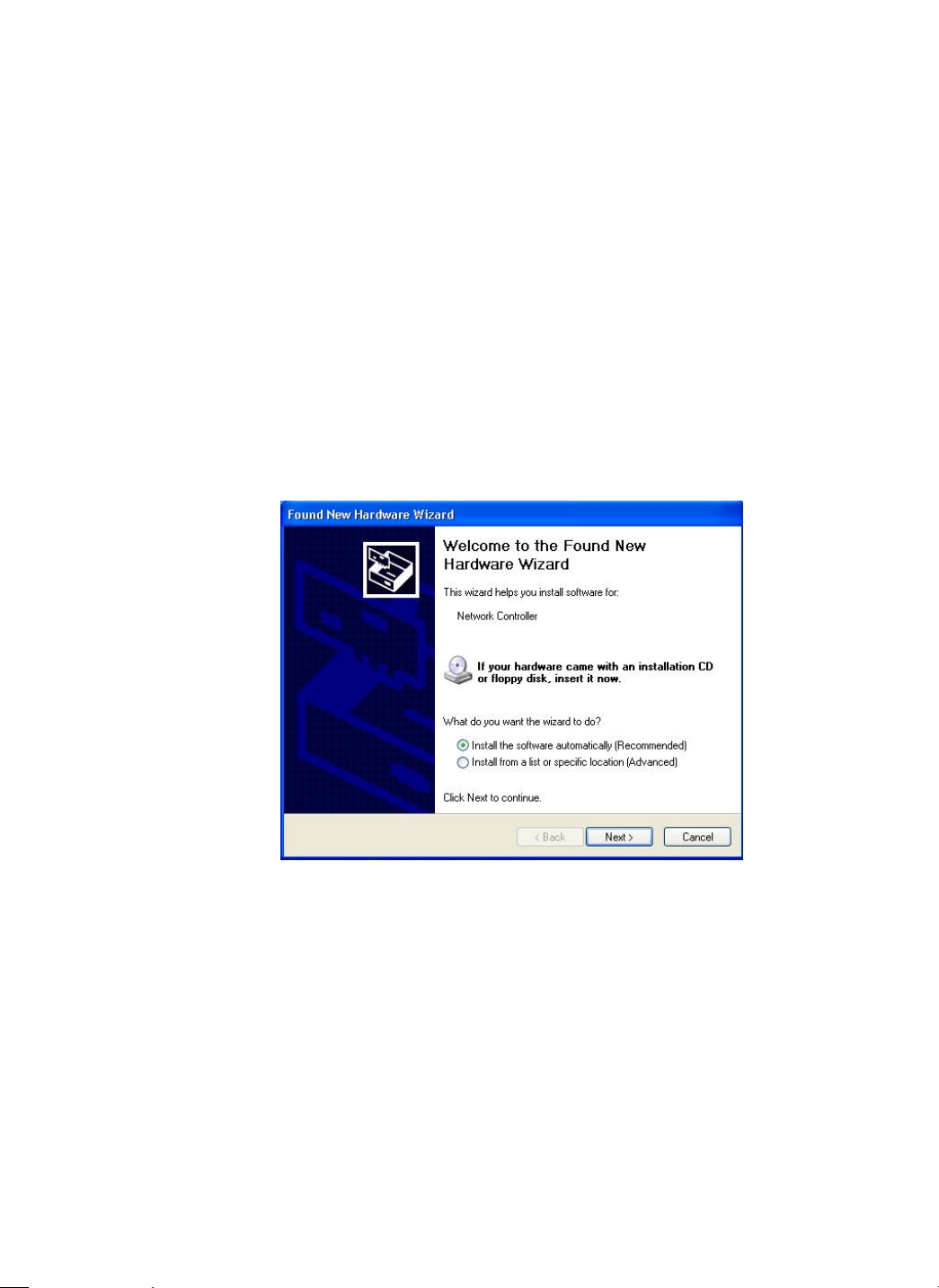
d) In the prompted WLAN IEEE802.11b/ g Setup window, choose Next to continue.
3
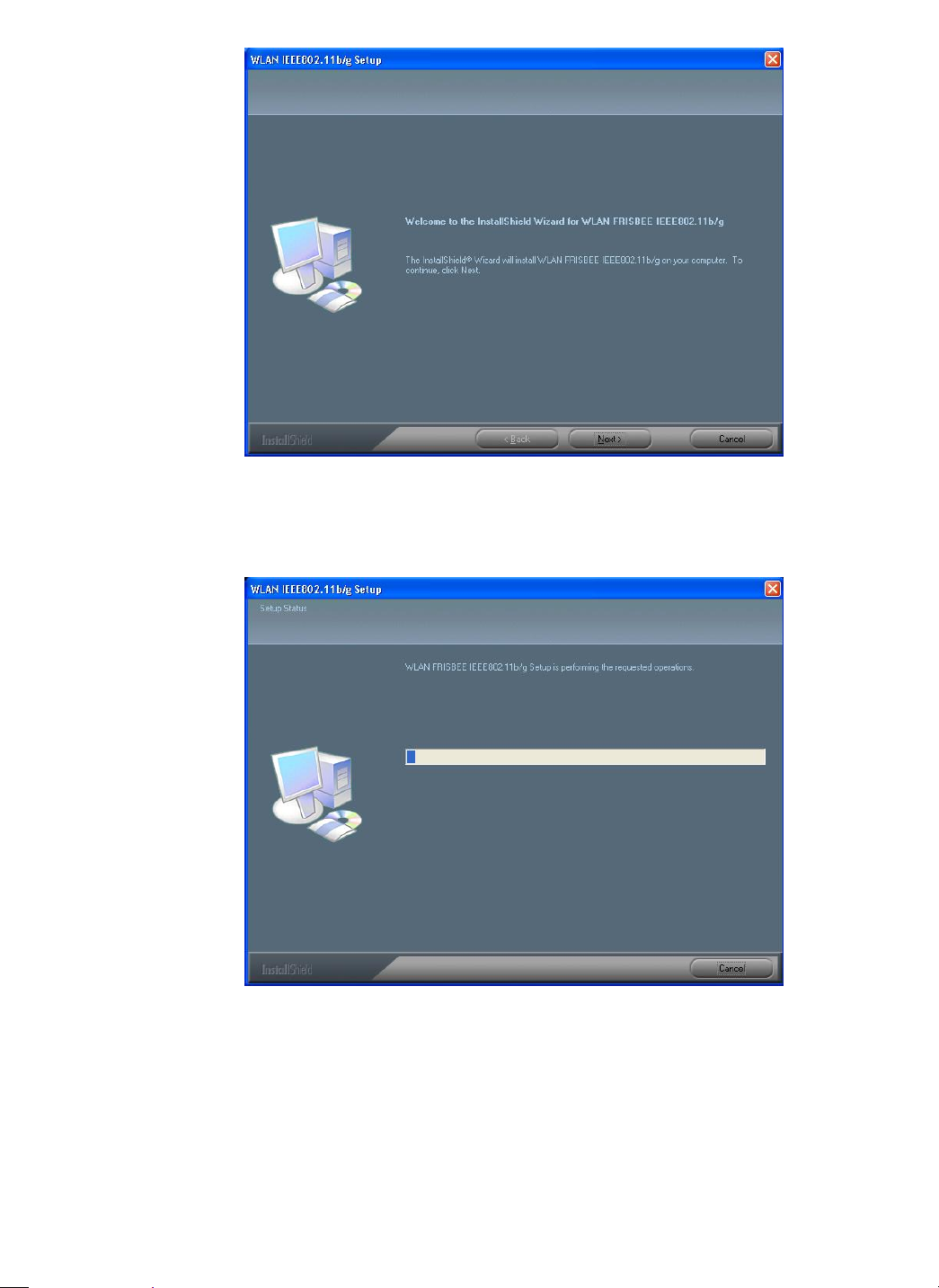
e) The system will start to copy the drivers found. It may take a couple of minutes.
Figure 2-2: The WLAN IEEE802.11b/g Setup Window
f) Windows will notify you that the driver has not passed the Windows Logo testing.
Because the Card has been tested to work with Windows XP, please choose Continue
Anyway.
Figure 2-3: The Setup St atus Scre en
4
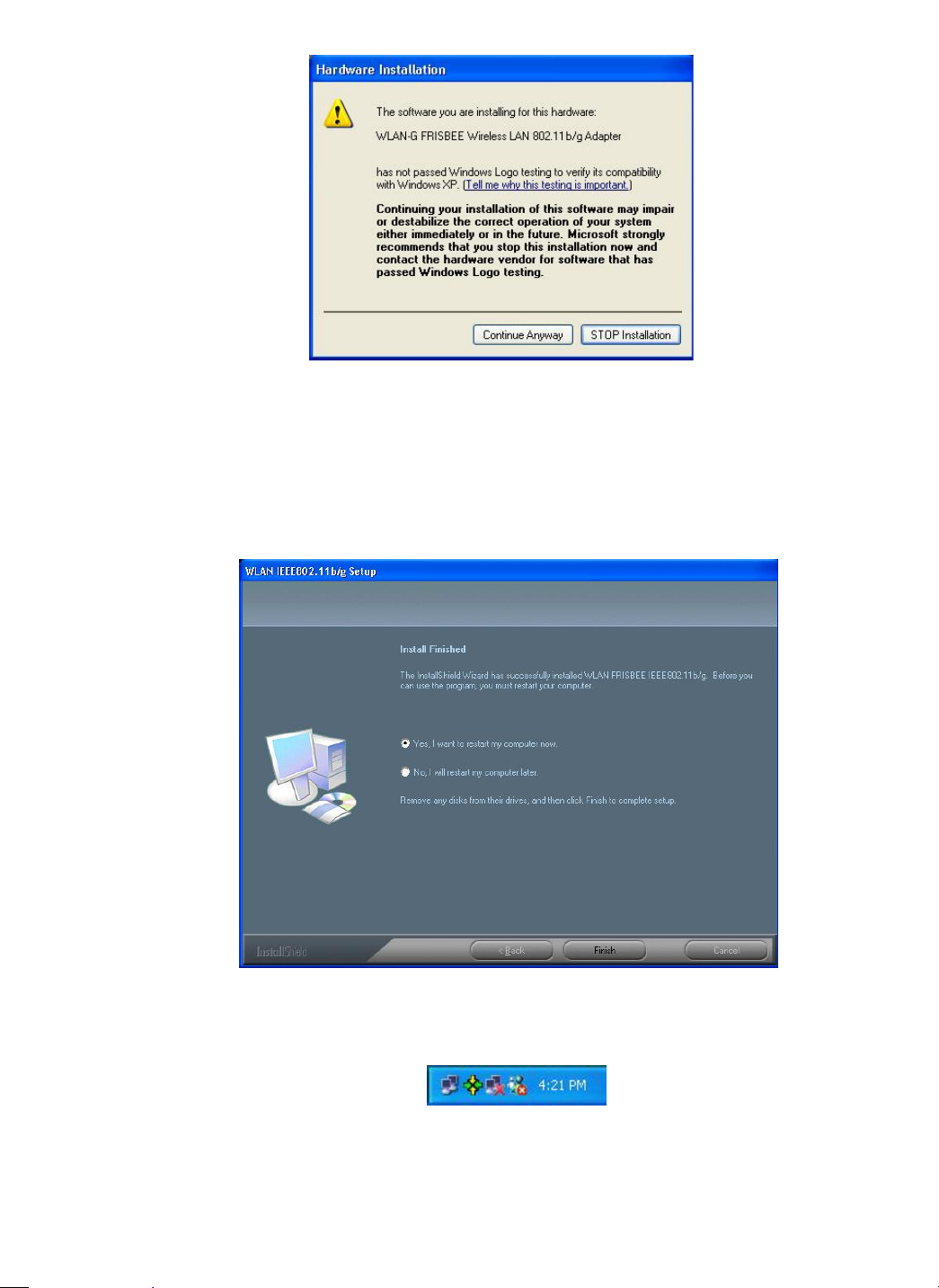
Figure 2-4: The Hardware Installation Dialog Box
g) From the Install Finished screen, if you are operating Windows 98 or ME, choose Yes, I
want to restart my computer now; on the other hand, if your current system is
Windows 2000 or XP, choose No, I will restart my computer later instead. Then click
Finish to finish the install a t ion.
Figure 2-5: The Complete Screen
h) Then, y ou will f ind the WLAN-G Configuration Tool icon appeared in the system tray.
Figure 2-6: The WLAN-G Configuration Tool Tray Icon
Double-click the icon to launch the application and open the Wireless Settings dialog
box, in which seven tabs are contained. Now you may start to monitor and configure
5

the network via WLAN-G Configuration Tool. For more details about the program,
please refer to the next chapter -- WLAN-G Configuration Tool Basics.
2.2 Verifying a Successful Installation
To confirm that your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus is properly installed, please go along with the
procedures below.
1. Right-click the My Computer desktop icon and choose Properties from its menu.
2. In the System Properties dialog box, choose Device Manager if you are under Windows
98 or ME. If you are operating Windows 2000 or XP, click the Hardware tab, and then
choose the Device Manager button.
3. In the opened window, expand Network adapters to find the input device – WLAN-G
FRISBEE Wireless LAN 802.11b/g Adapter. Right-click over the item and choose
Properties.
4. From the opened dialog box, on the General tab, find the descriptions under the Device
Status pane to learn if the card is working properly. However, if there’s an error message
shown, please choose Uninstall from the opened menu while right-clicking over the
Cardbus item, to which a red or yellow icon is attached beside, in the Device Manager
dialog box. Then restart your system and go through the inst allation procedures again.
The following picture indicates a successful installation of the 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus.
Figure 2-7: The Dev i ce Manager Dialog Box

WLAN-G CONFIGURATION TOOL BASICS
Once you insert your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus, it will operate with the factory default settings.
However, you may configure the desired settings by double-clicking the WLAN-G Configuration Tool
icon,
, on the system tray. In the prompted Wireless Settings dialog box, there are seven tabs,
including Status, Configuration, Encryption, Site Survey, IBSS, Domain, and About, and each
proffers various functions to assist you in configuring the connection to the networks.
This chapter is divided into the two sections: Right-Click Menu of the Tray Icon and Program
Controls. Please refer to the preferred topic to obtain more information and enjoy vast advantages
WLAN-G Configuration Tool brings.
3.1 Right-Click Menu of the Tray Icon
Right-clicking the WLAN-G Configuration Tool icon in the system tray will open a menu as the
following picture:
Figure 3-1: Right-Click Menu of the Tray Icon
Check the descriptions below to obtain detailed information about each command in the menu.
Wireless Radio On
Choose the Wireless Radio On command to receive the radio frequency signal.
Wireless Radio Off
Choosing the Wireless Radio Off command will stop receiving the radio frequency signal.
Remove Status Icon
If you do not wish to have the WLAN-G Configuration Tool icon displayed in the system tray,
choose this command to open the Remove Wireless St atus Icon dialog box, and then choose Yes to
have the icon disappeared. The icon will reappear next time when you restart the computer. If you
intend to remove it permanently, put a tick in the checkbox next to the Remove Status Icon
Permanently option. To launch the utility hereafter, click Start on the taskbar, choose Program from
the menu, and then point to WLAN-G Configuration Tool of the submenu of WLAN-G TOOLS.
7

Clicking No will undo the removal.
Figure 3-2: The Remove Wireless Status Icon Dialog Box
Wireless Network Status
Choose this command to launch the Status tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. For more
details about the tab, please refer to The Status Tab in the Program Controls section below .
Advanced Configuration
Choose this command to launch the Configuration tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. Please
refer to The Configuration Tab in the Program Controls section below to gain more information
about the tab.
WEP Encryption
Choose this command to launch the Encryption tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. This tab
offers you a number of options to maintain the secure management in a wireless LAN environment.
See the explanations in The Encryption Tab under the Program Controls section below for more
details.
IBSS Channel
Choosing this command will launch the IBSS tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. To obtain more
information about the tab, please refer to The IBSS Tab in the Program Controls section below.
Country/Domain
Choosing this command will launch the Domain tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. Detailed
information about this tab is presented in The Domain Tab of the Program Controls section.
Version Information
Choosing this command will launch the About tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. The About t ab
reveals general information on your 8 0 2.11b/g WLAN Cardbus, including the release version of driver
and the WLAN-G Configuration Tool and the card’s MAC Address.
8

3.2 Program Controls
When you double-click the WLAN-G Configuration Tool tray icon, the Wireless Settings dialog box
will be prompted as the picture shown below. The application is a window-based program, which is
consisted of seven tabs, including Status, Configuration, Encryption, Site Survey, IBSS, Domain,
and About.
Check the desired items below to obtain more information about these tabs.
The Status Tab
In the Wireless Settings dialog box, click the Status tab, and you will see the following display. Here
presents the status of your current connection. To close the window, click OK.
Note: Choosing the Wireless Network Status command from the right-click menu of WLAN-G
Configuration Tool tray icon will launch this tab too.
Figure 3-3: The Wireless Settings Dialog Box
9

Figure 3-4: The Status Tab
Note: The texts before ” Wireless Settings” in the caption bar of the dialog box is the profile name of the current
connection. Thus, the caption contexts vary according to the connectivity at the given time. From the above
picture, the associated profile is named “Wireless”.
From the window, the general information on the status of currently connected entry is presented. You
may want to click the Rescan button to reinitiate the scanning process and update the status. Later the
result of scanning will be renewed and displayed i n the window. If you wish to stop the networking
connection, click the Disable Radio button to stop scanning. However, if you are already in the
disabled radio mode, you will find the Enable Radio button here instead. Click Enable Radio to regain
the link then.
State
Here displays either the MAC Address of the current associated access point in the Infrastructure
mode or a BSSID from any computer joining in the Ad-Hoc net work.
Current Tx Rate
This feature indicates the transmission rate of the current connection.
Current Channel
Here reveals the current channel operated in the wireless network. Note that the channel number
differs as the radio scans any available channels in the Infrastructure mode.
Throughout (bytes/sec)
This feature indicates the rates of transmitting (Tx) and receiving (Rx) data package of your
802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus within a short period of time; thus, the values vary on a time basis.
10

Link Quality
Link Quality is based on the percentage of successfully transmitted or received signal of the
associated access point beacon within a limited period. The higher the percent age, the bett er the link
quality . The bar graph beside also provides a visual interpretation of the current link quality . It is noted
that the Link Quality and Signal Strength features only apply to the Infrastructure mode. They are
inapplicable in the Ad-Hoc mode since data will be transferred from many different computers.
Signal Strength
You may learn the received signal strength of the baseband processor of the beacon signal from the
Signal Strength bar beside, and it’s also presented in terms of percentage. As the signal gets
stronger, the signal percentage rate gets higher. It is noted that the Signal Strength and Link
Quality features only apply to the Infrastructure mode. They are inapplicable in the Ad-Hoc mode
since data will be transferred from many dif f erent comput ers.
The Configuration Tab
Click this tab to edit diff erent prof iles for different network configurations. When finish changing the
settings, please click Apply to perform the new configuration at last.
Note: Choosing the Advanced Configuration command from the right-click menu of WLAN-G
Configuration Tool tray icon will launch this tab too.
Profile Name
Enter texts in the Profile Name field to identify a new profile. After defining the configurations below,
Figure 3-5: The Configuration Tab
click the Apply button to establish the profile. To switch between any existing profiles,
11

simply click the arrow button at the right of the Profile Name field to open the pull-down menu and
then select the intended one from it.
Note: You will have at least one profile named Default. When selecting any link from the list under the Site
Survey tab, the common information on this chosen link will be illustrated under the Configuration tab.
Network Name
Network Name, also known as SSID (Service Set Identifier), must be unique to distinguish itself as
a particular wireless network, while all wireless points in this network area share the same SSID.
Type the identical SSID in the Network Name field to associate with access points or stations
within the specified wireless LAN. T o change the Network N ame, highlight the name in the box, edit
a new SSID, and then click Apply to save the changes.
Network Type
Two network types are offered here: Access Point and Peer-to-Peer. Choose the intended type
from the two options. The Access Point mode, which is also known as the Infrastructure mode,
allows you to communicate with a wired network via an access point. If you attempt to operate this
mode, you must indicate the identical Network Name to make a communication with the intended
access point. On the other hand, the Peer-to-Peer mode provides you with the so-called Ad-Hoc
communication, which means each wireless-equipped computers within a group is able to
connect with each other as an independent wireless LAN without the use of an access point. Each
station within this Ad-Hoc network has to define the same Net work Name.
The Encryption Tab
Click the Encryption tab to define the encryption settings for a specific profile. It offers you various
options concerning the so-called WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) to maintain the secure
management in a wireless LAN environment. See the explanations below for more details, and
before making an activation of any new settings, click Apply. To leave the window, click OK. To undo
the new settings, select the Cancel button.
Note: Choosing the WEP Encryption command from the right-click menu of WLAN-G Configuration Tool
tray icon will launch this tab too.
12

Figure 3-6: The Encryption Tab
Encryption (WEP security)
If you choose Disabled from the pull-down list, you will have the 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus
communicated with all stations within the same networking community without any data
encryption. Otherwise, two key lengths are offered: 64 bit and 128 bit. Specify a preferred one from
the two, so that you may use the identical WEP key to make a communication with the chosen
access point.
Create Keys Manually
Once you set the Encryption type as 64 bit or 128 bit, you may choose to edit WEP keys
manually or create them via the passphrase of your wireless network. If you choose the Create Key
Manually option, you may directly enter up to 4 WEP keys for use in WEP encryption. To generate
the WEP keys, please define the key entry method as Alphanumeric or Hexadecimal
(for hexadecimal characters, only digits 0-9 and letters A-F are valid). Then edit the texts in the blank
fields below, from Key 1 to Key 4, as the encryption codes. Note that these codes/keys shall be
identical between the wireless nodes within the range and the access point only. Check the table
below to find valid key length of each encryption type:
64 bit 128 bit
Alphanumeric 5 characters 13 characters
Hexadecimal 10 digits 26 digits
Use WEP Key
Indicate which WEP key you intend to apply to activate the WEP encryption from the pull-down menu.
Make sure that the intended access point on the wireless network shares the same keys.
13

By default, Key 1 will be used.
Create Keys with Passphrase
Choose this command when the associated wireless network uses a passphrase to create WEP
keys. Enter the passphrase string in the Passphrase filed to generate four encryption keys in the
Key fields above. Note that only letters A-F are valid for the Passphrase feature.
Note: When entering the passphrase here, ensure that you have specified an accurate type of the
Encryption (WEP security) above according to the associated agent’s configuration. Otherwise, the
inaccuracy will cause any failure of performance.
After finish configuring the Encryption features, remember to click the Apply button to initiate the new
settings.
The Site Survey Tab
First of all, while entering this tab, please do choose the Rescan button to reinitiate the scanning
process and update the list. Later the result of scanning will be renewed and displayed afterwards.
From the offered information, you may learn the general information on the status of current scan lines,
including BSSID, SSID, signal strength, the channel number , WEP ty pe, and network type.
In addition, to directly make an association with any site on the list, double-click the intended entry , and
you will be led to the Status tab then.
Figure 3-7: The Site Survey Tab
The IBSS Tab
If you, as a creator of the wireless network, are communicating with other stations via the IBSS
(802.11 Ad- hoc) mode to form peer-to-peer networks, click the IBSS (Independent Basic Service
Set) tab to specify an operating radio frequency channel from the pull-down list under the IBSS
14

Channel Selection section.
Note: Choosing the IBSS Channel command from the right-click menu of WLAN-G Configuration Tool
tray icon will launch this tab too.
Note that the available channels differ from country to country, and the channel number must be the
same between the entries/stations within the range, so that each can communicate with each other . Or
you may simply click Defaults to automatically determine the channel number for you. When done,
click Apply to activate the new configuration.
On the other hand, while in the Access Point mode, you will find the channel number is the same as
the associated access point. Thus, there’s no need to manually set the value.
Figure 3-8: The IBSS Tab
The Domain Tab
While in the 5GHz range, the network operation may differ from country to country, or domain to
domain. This is because the 802.11d protocol was established. To have the oper ation normally
processed, choose the Domain tab to change relevant settings.
Note: Choosing the Country/Domain command from the right-click menu of WLAN-G Configuration Tool
tray icon will launch this tab too.
15

Figure 3-9: The Domain Tab
802.11d Support
802.1 1d Support lets you operate multi-country roaming. To automatically adjust regulatory domain
while operating network in different countries, choose either Strict or Flexible according to your
need. If you choose None, the task will be terminated.
Countries/Domains
Define the regulatory domain from the drop-down menu of this command according to the country
you are located in. More deta iled information about the defined country/domain will be listed below
afterwards.
When you are done, remember to click Apply to let the new settings take eff ect.
The About Tab
This tab reveals general information on your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardb us, including the following
items:
Note: Choosing the Version Information command from the right-click menu of WLAN-G Configuration
Tool tray icon will launch this tab too.
16

Figure 3-10: The About Tab
Network Driver
Displays the current version and released date of the 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus’ driver.
Configuration Utility
Displays the current version and released date of the WLAN-G Configuration Tool application.
NIC Firmware
Displays the current NIC card f irmware version and the MAC (Media Access Control) address of your
wireless card. It is consisted of 12-digit hexadecimal numbers (48 bits in length) to identify your
computer's physical address on the local area network.
17

Frequently Asked Questions
A
k
r
t
t
o
s
A
s
r
s
1. When I plugged the card into my available PCMCIA the operating system doe s not detect the card,does it wo rk even
after I have installed the drivers on the CD, or does not fit into my PCMCIA slot why?
: One of the most common problems is that some users might have a 16bit PCMCIA slot. The 32bit card will not wor
with a 16bit but on the other hand the 32bit PCMCIA slot will work with any 16 bit card. Please refer your user manual fo
your laptop and find out whether if it has a 16bit or a 32bit slot. Please do not MAKE the card fit, if you push too hard i
might damage the card, the PCMCIA slot or both, the card should only require a little resistance to lock into place. If you
feel its requiring too much force, it probably is, stop and check to see that you are using the right bit slot.
2. I have installed the card, the drivers, and it does appear under ‘Device Manager’, but for some reason I can’t get it to
connect to my wireless router, why?
A: Please refer to our ‘Setting up Wireless Connection’ and see i f that helps. If not, please call o ur technical suppor
line a better understanding on how to troubleshoot your network with our wireless adapter.
3. I can’t seem to find the drivers on the CD. It appears that the CD does not contain anything that can allow me t
install this card, what should I do?
A: If the product never came with a CD or perhaps drivers, please go to our website at: www.gigafast.com and
download the latest driver for your PCMCIA wireless adapter.
4. Will this card work with my wireless router?
A: As long as the router is 802.11b or g compatible then you should be able to have your wireless connection set up.
5. Everything runs fine and there is a connection going through, but how come my connection is extremely slow?
A: Make sure the ‘encryption’ is not set too high. Some users might tend to set it at 128bit encryption and that slow
down the time for the bandwidth to go through your wireless connection. Adjust the encryption and set it to 64bit or have
it off for a moment and see if that helps.
6. How do I make the ‘signal strength’ better so I can have a better and faster connection?
: The closer the laptop is to the router the more solid the connection is. It depends on if there are any other device
around you that might interfere with the connection. An open area with less walls and objects usually gets a bette
connection than the one that is in a room where there is microwave oven around.
7. Does the encryption on the card and the wireless router have to be the same?
A: Yes, that includes the SSID, too has be the same.
8. I’m trying to use the Realtek Wireless Utility that came with the installation CD, but for some reason when I click on
the ‘Configure’ and ‘Advanced’ button it does not seem to do anything, why?
A: Uncheck the ‘Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings’ box and click ‘OK’ to take effect. Thi
option has to be disabled if you want to use the Realtek Wireless Utility.

k
o
9. Where do I change the SSID, Channel, and Network Type on the wireless card?
A: First you have to get to ‘Device Manager’. Once you’re there, highlight the wireless card listed under ‘Networ
Adapters’ and click on ‘Properties’. Click on the ‘Advanced’ button and you should see it there. The dialog should
look like this:
*Note* it is required that the settings needs to be changed according to the settings on the wireless router. If the
‘Channel’ on your wireless router is ‘3’ then change the value on the card to ‘3’. This applies on the SSID also.
10. How do I determine the type of chipset I have on the wireless adapter?
A: The back of each wireless adapter will have a S/N f ollow by a nu mber. The first letter represent s a different chipset.
The first letter of the S/N represents a different manufacture. For example:
C – Realtek
A – Admel
R – Realtek
T – Cybertan
That is the list of current manufactures that makes our wireless network cards. A user might require a chipset name t
download the driver for his/her operating systems.

APPENDIX A: TROUBLESHOOTING
This section provides solutions to problems that you might encounter during the installation and
operation of your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus. Please refer to the desired topics below and read the
description to solve your problems.
Disable 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus
Supposed you do not need the 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus to establish the wireless connectivity for any
reason, you can directly unplug and remove your 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus from the Cardbus slot on
your computer, or click Disable Radio on the Status tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. Once
the device is removed, the connection to the network stops. Thus, be sure that you have closed all the
network applications before processing the removal.
Uninstall WLAN-G Configuration Tool and the Card’s Driver
Prior to starting uninstalling, please make sure that the utility is closed, and then go along with the
procedures below to entirely uninstall WLAN-G Configuration Tool and the card driver.
1. Right-click the My Computer desktop icon and choose Properties from its menu.
2. In the System Properties dialog box, choose Device Manager if you are under Windows
98 or ME. If you are operating Windows 2000 or XP, click the Hardware tab, and then
choose the Device Manager button.
3. In the opened window, expand Network adapters to find the input device – WLAN-G
FRISBEE Wireless LAN 802.11b/g Adapter. Right-click over the item and choose
Uninstall.
Figure 4-1: The Device Manager Dialog Box
18

4. In the Confirm Device Removal message box, click OK to proceed with the removal of the
hardware.
Figure 4-2: The Confirm Device Removal Message Box
5. Click Start on the taskbar and choose Control Panel from the Settings menu.
6. Select Add or Remove Programs to open the dialog box shown as below.
Figure 4-3: The Add or Remove Programs Dialog Box
7. Click the Change/Remove button under WLAN FRISBEE IEEE802.11b/g.
8. In the prompted WLAN IEEE802.11b/g Setup window, choose Remove and then click the
Next button to begin uninstalling the program.
19

Figure 4-4: The WLAN IEEE802.11b/g Setup Window
9. Choose Yes when the following message box appears.
Figure 4-5: The WLA N IEEE802.11b/ g Setup Message Box
10. From the Maintenance Complete screen, choose Yes, I want to restart my computer now
if you are running Windows 98 or ME; on the other hand, if your current system is Windows
2000 or XP, choose No, I will restart my computer later. Then choose Finish to entirely
complete the removal.
20

Figure 4-6: The Ma intenance Complete Screen
802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus Does Not Work Properly
If this happens, follow the guidelines below.
g Unplug and replug the 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus into your PC’s Cardbus slot.
g Right-click the My Computer desktop icon and choose Properties to open the System
Properties dialog box. If you are under Windows 98 or Me, choose the Device Manager tab,
or if your system is Windows 2000 or XP, click the Hardware tab, and then choose the
Device Manager button. In the opened window , find your Cardbus to see if t he inst allation is
successful. If you see a yellow exclamation mark beside the item, please go along with the
steps below to reinstall the drivers:
1. Uninstall the software and hardware drivers from your PC. (Please refer to the
previous topic for details)
2. Restart your computer and repeat the installation procedures as indicated in Chapter
2: Installation.
3. When finished, open the Device Manager window again to verify if the installation is
approved. The yellow exclamation mark shall be removed for this time.
21

APPENDIX B: SPECIFICATIONS
Product Name 802.11b/g WLAN Cardbus
Host Interface 32-bit Cardbus
Standards IEEE 802.11, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g
Frequency Band 2.400 ~ 2.4835GHz (subject to local regulations)
Current Drain Power save mode=22mA, Standby mode=7mA, Transmit mode=460mA,
Receive mode=410mA
Spreading DSSS (11b), OFDM (11g)
Data Rate 1Mpbs, 2Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 6Mbps, 9Mbps, 11Mbps, 12Mbps, 18Mbps,
24Mbps, 36Mbps, 48Mbps, 54Mbps
Transmit Power 802.11b≧17dBm
802.11g
6/9Mbps≧17dBm
12/18Mbps≧15dBm
24Mbps≧14dBm
36Mbps≧14dBm
48Mbps≧12dBm
54Mbps≧12dBm
Receive Sensitivity 802.11b
8% FER@1Mbps≦-91dBm
8% FER@2Mbps≦-88dBm
8% FER@5.5Mbps≦-85dBm
8% FER@11Mbps≦-83dBm
802.11g
10% PER@6Mbps≦-88dBm
10% PER@9Mbps≦-87dBm
10% PER@12Mbps≦-84dBm
10% PER@18Mbps≦-82dBm
10% PER@24Mbps≦-79dBm
10% PER@36Mbps≦-75dBm
10% PER@48Mbps≦-69dBm
10% PER@54Mbps≦-68dBm
Modulation CCK (11b), BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM (11g)
Security 64/128 bit WEP Encryption
802.1x, WPA (Windows XP SP1 and Windows 2000 SP4 only)
Internal Antenna Type Dual Antenna Diversity Switching
22

Media Access Control RF activity
Supplied Driver CSMA/CA with ACK
Warranty 1 year
Temperature Range 0~65°C (Operating)
Humidity Max. 95% Non-condensing
Operating Range Open Space: up to 400meters; Indoor: up to 100meters
The transmission speed varies in the surrounding environment.
CIS Customer Defined
 Loading...
Loading...