
GigaFast
HomePlug Broadband Internet Router
PE904-R
User Manual
GigaFast
Copyright
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as
a whole, stored, transcribed in an information retrieval system,
translated into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any
means, mechanical, magnetic, electronic, optical, photocopying,
manual, or otherwise, without the prior written permission.
Trademarks
All products, company, brand names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies. They are used for
identification purpose only. Specifications are subject to be changed
without prior notice.
Copyright© 2004, Gigafast Inc., All Right Reserved
2

GigaFast
FCC Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against radio interference in a
commercial environment. This equipment can generate, use and radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions in this manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be required
to take whatever measures are necessary to correct the interference.
CE Declaration of Conformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic
compatibility, EN 55022/A1 Class B, and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential
protection requirements of the European Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the
approximation of the laws of the member states relation to electromagnetic
compatibility.
3

GigaFast
Table of Content
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Broadband Powerline Router......6
Overview..........................................................................6
Features...........................................................................7
Panel ..............................................................................10
Wire Diagram ...............................................................12
Chapter 2: Quick installs..............................................................13
Overview........................................................................13
Cable internet setup......................................................14
DSL internet setup........................................................19
Part 3 Macintosh Setup................................................21
Part 4 Powerline Setup.................................................23
Chapter 3: Basic Configuration....................................................25
Section 1 – Broadband Router Device Status .............25
Section 2 – Broadband Router Device Info.................26
Section 3 - Administration ...........................................27
Section 4 – WAN (Wide Area Network) .....................31
Section 5 – LAN (Local Area Network)......................32
Chapter 4 – Advanced Configuration...........................................34
Section 1 – Access Control..........................................34
Section 2 – MAC Filter...............................................36
Section 3 – Service Time.............................................37
Section 4 – URL Blocking ..........................................40
Section 5 – Virtual Server..........................................41
Section 6 – DMZ..........................................................42
Section 7 – Auto 2-Way Application .........................43
Section 8 – Dynamic DNS...........................................45
4

GigaFast
Appendix A: Cabling and Pin Assignment..................................46
Appendix B: Technical Information ............................................49
Appendix C: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) .......................50
Appendix D: IP Addressing...........................................................60
What is an IP Addresses?.............................................................60
Dynamic IP Addressing................................................................60
Static IP Addressing.....................................................................60
Checking IP Address in Windows 98 / SE / ME / 2000 / XP.....61
Setting IP Address on Windows 98 / SE / ME............................64
Setting IP Address on Windows 2000 / XP.................................68
Releasing and Renew IP Address in Windows 98 / SE / ME.....72
Releasing and Renew IP Address in Windows 2000 / XP..........75
Appendix E: Local Area Network................................................79
Sharing Files (Windows 98SE / ME / 2000 / XP)........................79
Sharing Drives on Windows 98 / SE / ME / 2000 / XP...............84
Accessing Other Computers Shared Files on Windows 98/SE/ME/ 2000/XP......88
Sharing Printers on Windows 98 / SE / ME / 2000 / XP............91
Network Printer Installation for Windows 98/ SE / ME/ 2000 /XP ......95
Connecting to Internet on Windows 98 / SE / ME...................105
Accessing the Internet using Windows 2000 / XP....................112
Appendix F: Glossary..................................................................119
Appendix G: Warranty Info........................................................122
Appendix H: Contact Information..............................................123
5

GigaFast
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Broadband Powerline
Router
Overview
Congratulations on your purchase of this outstanding Gigafast PE 904R Homeplug Broadband Internet Router. Despite the fact that no one
enjoys pulling Ethernet cables out of neither the box nor buying
expensive cables. Users can now experience a total network solution
with the Gigafast HomePlug. This product is the perfect option to
connect a group of PCs to a high-speed Broadband Internet connection
or to an Ethernet based Backbone (ETTH/ETTB: Ethernet to the
Home/Building), while enjoying the usability with the easy to use
HomePlug products. Configurable as a DHCP server, this product is the
only externally recognized server device on your local area network
(LAN). Thus even a non-technical person will easily configure it to
meet other popular applications.
The Gigafast PE904-R Homeplug Broadband Internet Router operates
on the HomePlug Powerline Specification 1.0 standard, providing up to
14 Mbps bandwidth over home AC wiring. Since the home power
lines are the most pervasive medium in households with multiple
outlets in every room, the Homeplug Broadband Internet Router allows
multiple home desktops and notebooks to be networked to share
internet connection, printers, files, and play games without any
additional wiring.
This product does not only provide a complete solution to share the
Internet bandwidth, it also serves as an Internet Firewall to protect your
LAN data from being accessed by outside intruder/hacker. Since all
incoming data packets can be analyzed or monitored, all unwanted
Chapter 1
6

GigaFast
packets may be filtered-out and be recorded as an intrusion event.
PE904-R can also be configured to block some internal LAN user’s
access to the Internet for management purpose.
For security, all Gigafast HomePlug devices are equipped with 56-bit
DES encryption. The private home power grid plus encryption makes
HomePlug significantly more secure than competing technologies.
The Gigafast PE904-R Homeplug Broadband Internet Router is the best
solution for No-New-Wires home networking. With easy Plug and
Play installation, and the reliability of Gigafast Ethernet’s products, the
Gigafast Homeplug Broadband Internet Router is the best solution for
high speed networking.
Features
z Connects to 10/100M Broadband (cable or DSL) modem
or Ethernet backbone for Internet Surfing.
z Multiple WAN connection type:
Static IP : for lease line or router-router
interconnect.
DHCP client : for most cable modem service.
PPPoE : for Dial-up ADSL service,
PPTP client : for some European D ial-up ADSL
or L2-VPN application
z Equipped with a 3-port 10/100M switched Hub for LAN
users.
z DHCP Server/ DNS proxy support (can save an extra
PC/Server in LAN).
All the networked computers in LAN can retrieve TCP/IP
setting (IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS)
Chapter 1
7

GigaFast
automatically from this device.
z Simultaneously act as both DHCP Server on the LAN and
a DHCP Clien t on the WAN for most easy application.
z Connects multiple LAN PCs to the Internet with only one
dynamic-assigned IP address (NAT mode) or a range of
legal IP address (NAT/Routing mode)
z Web-based configuring
it is configurable through any networked computer’s web
browsers using Internet Explorer or Netscape browser.
z Allow/Deny remote administration through WAN
connection by Web browser.
z Firewall capability to protect LAN PCs from outside
intruder access/attack.
Avoid unwanted packet from WAN (Wide A rea Net w or k) a nd
provide a system event log to record intrusion information.
(Date/Time, Source IP address & Port)
z Virtual Server (Port forwarding) function
Internet servers (WWW, FTP, E-mail …) in LAN could be
virtually exposed to WAN for outside Internet user access.
This is a useful and secure network deployment for Internet
servers.
z DMZ (De-Militarized Zone) Host
Administrator can expose a host PC in LAN to the Internet
without any firewall protection mechanism. This option
allows a full two-way communication between the local host
PC and remote Internet node. (ex. bi-directional gam e s,
video/audio conferences …)
z Allows a user to have up to 14 Mbps bandwidth over
standard home power lines
z It is estimated range of 300 meters in wall power lines
z There is no problem for the HomePlug passing through
circuit breaker
Chapter 1
8

GigaFast
z Uses IEEE802.3 computer interface
z Plug-and-Play installation
z Built in internal power supply
z HomePlug Powerline Specification 1. 0 c om pl i ant
z 56-bit DES encryption assure data security
z Encryption done by hardware, with no sacrifice
Package Content
z One PE904-R Homeplug Broadband Internet Router
z One power cable
z One W arranty card
z One paper manual OR manual CD
Requirement
• One Ethernet based broadband Internet connection
(Cable/ADSL modem or other router)
• Microsoft Internet Explorer browser (V.4.75 or above)
• Standard home power line wiring
• One or more HomePlug Units connected to your
computer . (For setup Powerline network )
• One PC with a network card and TCP/IP protocol stack
Installed
Chapter 1
9

GigaFast
Panel
Front
PWR: On – Receive power
Off – Doesn’t receive power
RDY: Blinking fast – Self testing
Blinking every second – Ready to Go
HP: On – Detect other HomePlug devices
Off – Doesn’t detect other HomePlug devices
WAN: On – Detect Ethernet connection ( Modem, Switch,
Computer…)
Off – Doesn’t detect Ethernet connection
Ethernet LED 1-3: Blinking: Ethernet activity
On: Detect Ethernet connection
Off: Doesn’t detect Ethernet connection
Chapter 1
10

GigaFast
Back
3 LAN port
1 WAN port
RST: Rest Hole (Restore factory default settings)
AC power in
Chapter 1
11
GigaFast
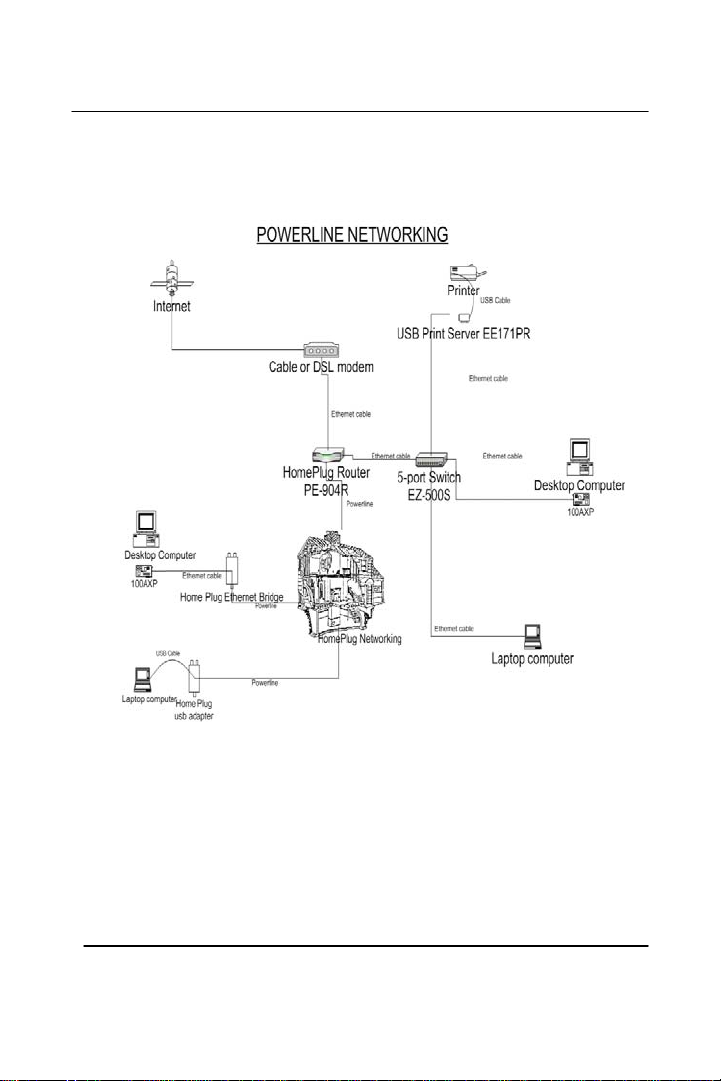
Wire Diagram
• The modem should be connected to the router’s WAN port
with an Ethernet cable(Cat 5/Cat 5e)
• Power cable should be connected to the power connector at
the back of the router
Chapter 1
12

GigaFast
• Computers are to be connected to port 1-3 on the router
(Typically with a straight through cable Cat 5/Cat 5e)
Chapter 2: Quick installs
Overview
The following steps are setup processes for most common broadband
internet service providers.
This section will be divided into three parts. Part one is for cable
internet setup, part two is for DSL internet setup and part three is for
Macintosh Users.
*Note* the http://192.168.8.1 is the main console page for the PE904-
R. Internet connection is NOT
Any computer that is connected to the router’s port 1-3 is capable of
changing the settings on the router. It does not have to be a designated
port or computer to change the settings of the router.
Before you start
Make sure the internet connection from your ISP is working. Check to
see if there is a connection coming through your ISP (modem) to your
computer. Also, check and see if the lights are properly on when the
router is connected with the computer(s) and the modem.
required upon installation of this router.
Chapter2
13
GigaFast
Cable internet setup
Section 1
1. Turn off the cable modem and the router
2. Connect an Ethernet cable from the cable modem to the WAN
port of the router
3. Connect your computers to ports 1-3(or connect using
HomePlug) with the router
* if using HomePlug to connect, please make sure they all
have the same network password to set on with the router
4. Power on the router
5. Power on the modem
6. Power on your computer
*Note* Make sure the WAN LED light and ports 1-3 LED lights
are ON at the front panel of the router.
Section 2
1. At the desktop (Windows based Operating System). Go to
2. Your internet browser should automatically open up the
‘Start’ > ‘Run’ and input this address:
press ‘enter’
‘Broadband Router’ page
http://192.168.8.1 and
Chapter2
14
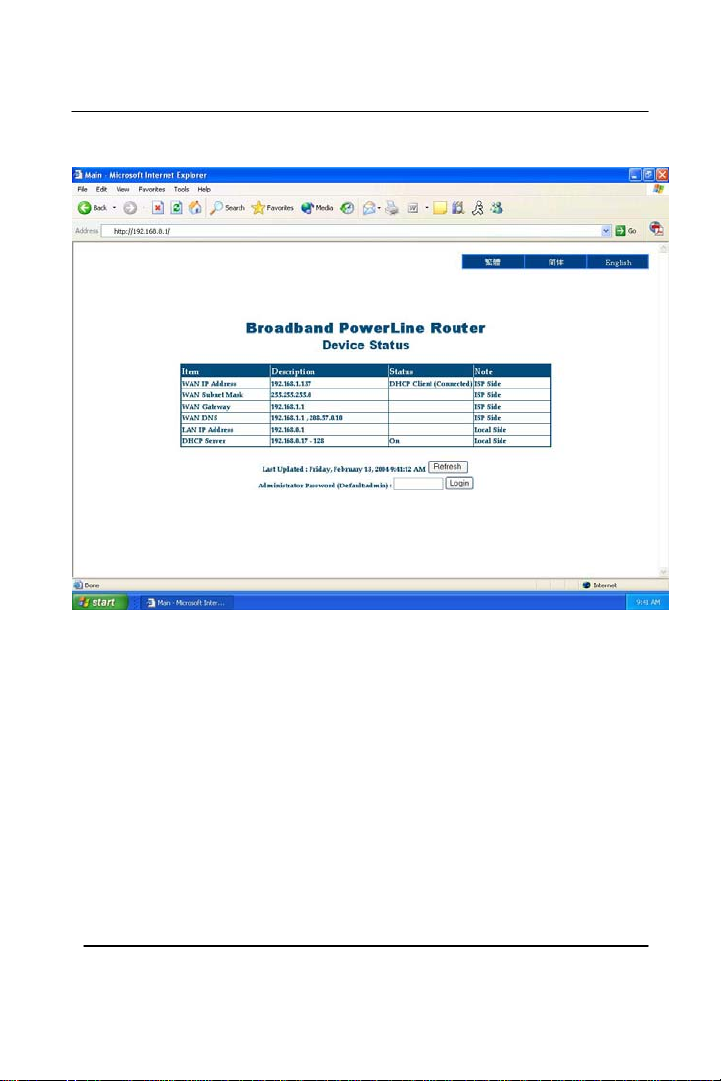
GigaFast
Example:
3. The password for the Administration Password is ‘admin’.
It is case sensitive so make sure the CAPS key is not on. Once
‘admin’ is entered, click on ‘Login’ to enter the router’s
configuration page.
*Note* Make sure the ‘WAN IP address’, ‘WAN Subnet Mask’,
‘WAN Gateway’, and ‘WAN DNS’ are filled with numbers. This
indicates that the router is communicating with the modem (your ISP).
If you are able to get those numbers, most likely you’re on the internet.
*Note* the next step is for those who can log onto the router page but
cannot get an internet connection through the ISP. (WAN IP addresses
all show 0’s)
Chapter2
15
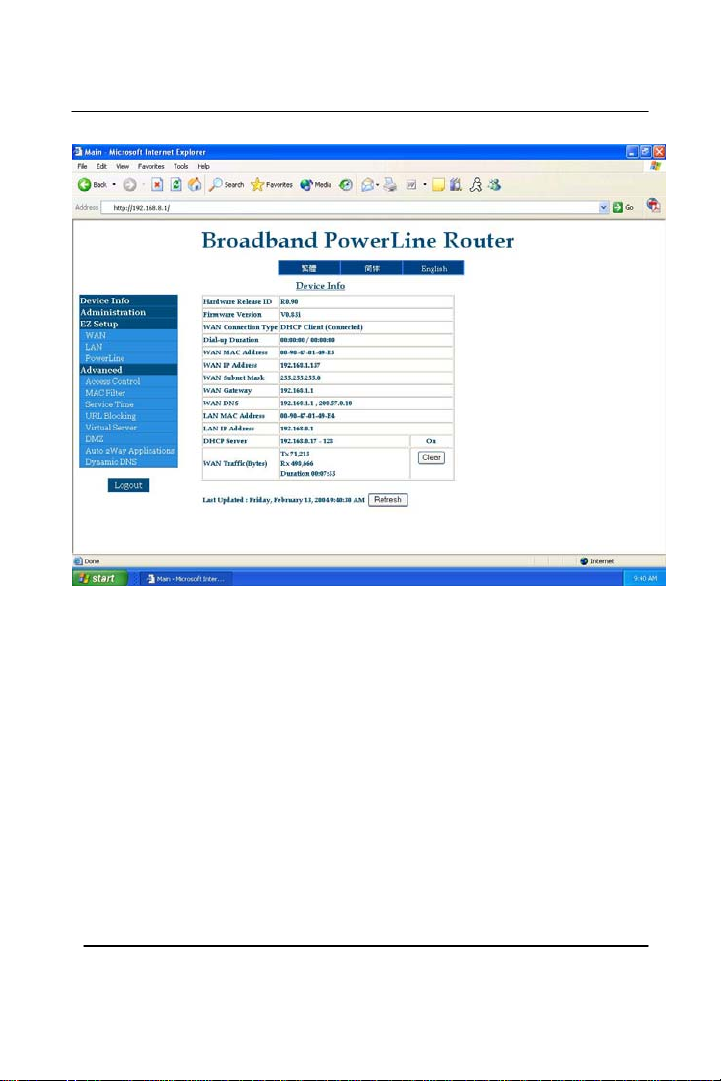
GigaFast
4. The page should look like this after you have logged onto the next
page. The next step is to click on the ‘Administration’ to the left side
of the screen.
Chapter2
16
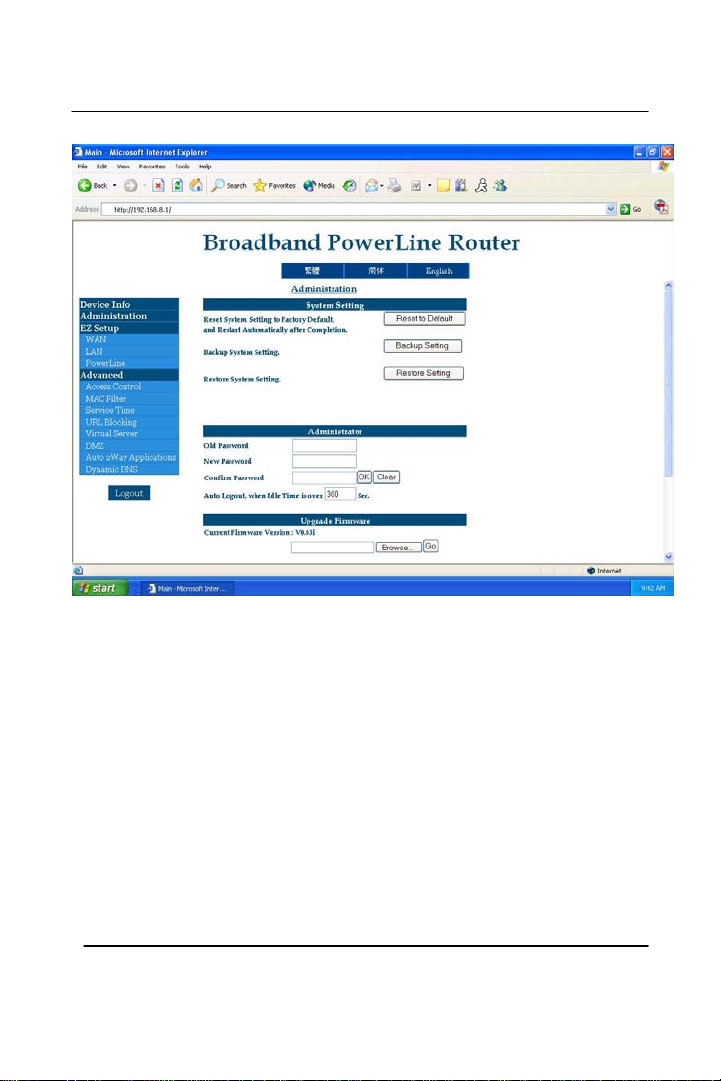
GigaFast
5. At the bottom of the ‘Administration’ section you should see
a button says ‘Clone MAC’. Click on ‘Clone MAC’ (this
will let the router copy the MAC address on the Ethernet
adapter.)
Chapter2
17
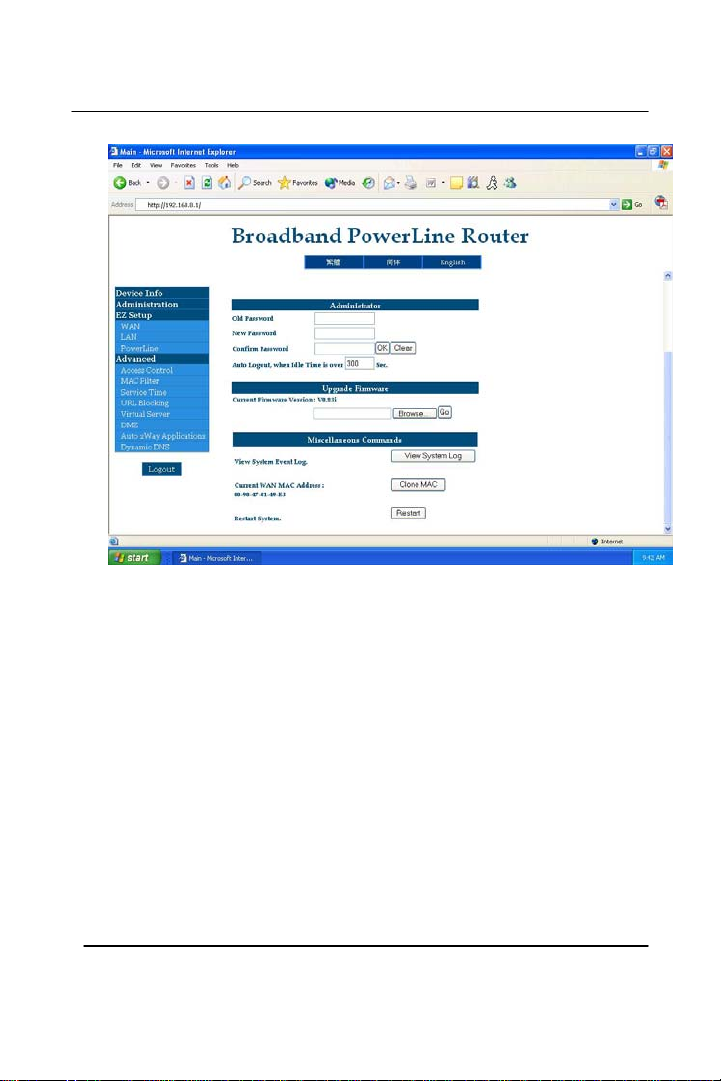
GigaFast
6. There should be a confirmation after you click on the ‘Clone
MAC’ button. Acknowledge it and restart the computer
afterwards. If you still have trouble getting an internet
connection or have other questions please follow the
instructions in our FAQ section.
Chapter2
18
GigaFast
DSL internet setup
Section 1
1. Make sure that DSL account Login ID and Password is in
2. Connect the DSL modem to the WAN Port on the router
3. Connect your computer(s) to port 1-3 on the router with
4. Turn the computer(s), DSL modem, router ON if they are
*Note* Make sure the WAN LED light and ports 1-3 LED lights
are ON in the front panel of the router.
Section 2
1. At the desktop (Windows based Operating System).
2. Enter default password ‘admin’ in the ‘Administration
3. Once you have successfully logged onto the Broadband
hand (i.e.: username@your_internet_company.net)
with an Ethernet cable
Ethernet cable(s) (or connect using HomePlug)
* If using HomePlug to connect, please make sure they all
have the same network password to set on with the router
off at this point
Click ‘Start’ > go to ‘Run’ > and type in this address in
the box:
internet browser should automatically open up the
‘Broadband Router Status’ page (See Part 1 – Section 2
{2} for image). If the page shows ‘Page cannot be
displayed’ or blank then please go to our FAQ section for
more helpful information.
Password’ column (make sure CAPS key is OFF
click ‘Login’
Router page, you should see a list of various links on the
left side of your screen. (See Part 1 – Section 2 – {4} for
http://192.168.8.1 and press ‘enter’. Your
) and
Chapter2
19
GigaFast
4. At this point the ‘WAN IP’ addresses should show all 0’s.
image)
It is usual and common because the router hasn’t been
setup to have a connection between your ISP and the
PE904-R. Please click on ‘WAN’ under ‘EZ Setup’ and
the page should look like this after:
*Note* In case if the WAN IP addresses are listed, it means the router
is getting a connection from the modem (your ISP). Try to see if you
can go onto the internet by reopening your intern et browser and inpu t a
website URL. If you still cannot get online, please see FAQ. If you do
not get any numbers and they are all 0.0.0.0 please continue with the
installation.
Chapter2
20

GigaFast
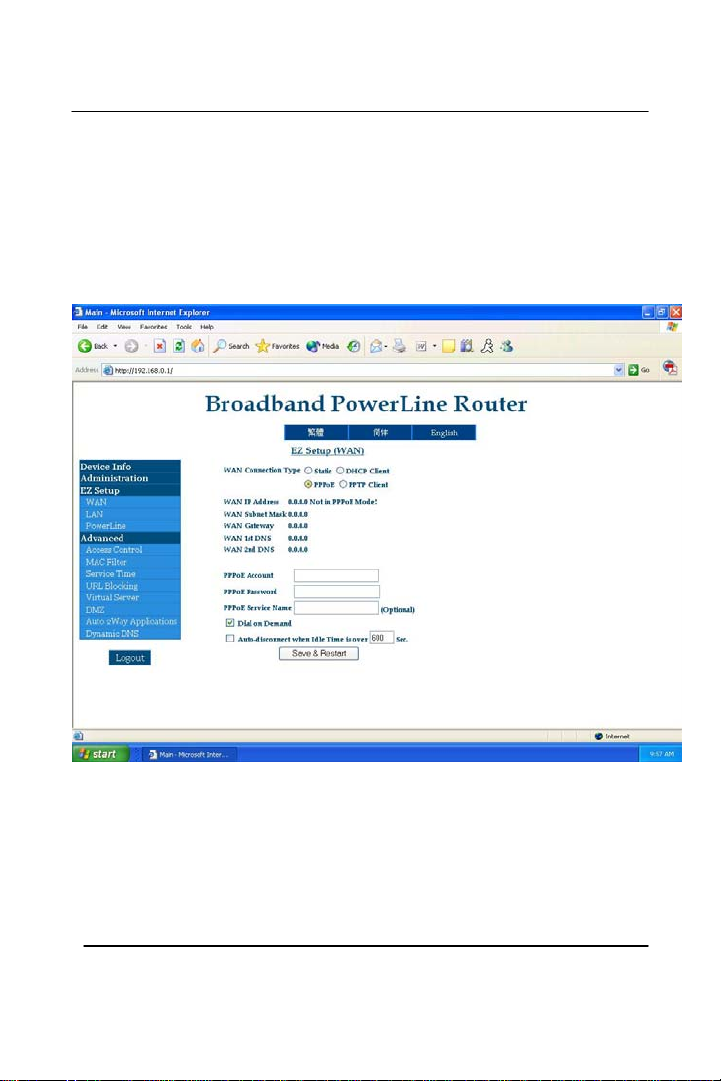
5. Most of DSL internet service providers have PPPoE type
of connection. Bubble in ‘PPPoE’ as your ‘WAN
Connection Type’ and it should bring down a longer
menu with ‘PPPoE Account’ that is where you input
your full primary e-mail address from your ISP (i.e.
username@domain.net)
* Some DSL ISP use only a username as your PPPoE
Account name
6. Next, type in the password for that e-mail account in
‘PPPoE Password’
7. ‘PPPoE Service Name’, ‘Dial on Demand’, and ‘Auto
Disconnect when Idle’ should be left as is. After
finishing the input on the ‘PPPoE Account’ and ‘PPPoE
Password’, press the ‘Save & Restart’ button for the
changes to take effect.
8. A ‘Connect’ or a ‘Disconnect’ button should appear after
the ‘Save and Restart’. If it appears to be ‘Connect’,
then click on the ‘Connect’ button and the router will try
to communicate with your ISP. Once the process is
finished, the ‘Connect’ button will become a ‘Disconnect’
button and if a ‘Disconnect’ appears, then it means you’re
already on the internet and ready to surf the net.
Part 3 Macintosh Setup
Section 1
Since Macintosh uses the same type of internet browser
(Internet Explorer, Netscape etc.), users can follow the same
procedures provided under Part 1 (for cable broadband
internet services) or Part 2 (for DSL/PPPoE based internet
services). Some Macintosh based Operating Sy st em might
require some changes under its configuration. The steps
Chapter2
21

GigaFast
below will most likely allow your Macintosh system to
communicate with the PE904-R after the changes have been
made.
Section 2
(For Macintosh OS 8.0 & 9.0)
1. Boot up your Macintosh computer
2. Make sure all cables are plugged in and all the proper lights
3. Click on the ‘Apple’ icon to bring up the menu
4. Click on ‘Control Panel’
5. Then click on ‘TCP/IP’
6. Make sure Ethernet is selected where it says ‘Connect as’ and
7. Leave the ‘DHCP Client ID’ blank and close it
8. Make sure click Save button at the end
9. Please restart your Macintosh system for the changes to take
10. After the Mac is up and running, open up your web browser
Section 3
(For Macintosh OS X or 10.00)
1. Boot up your Macintosh computer
2. Make sure all cables are plugged in and all the proper lights
3. Click on the ‘Apple’ icon
4. Go to ‘System Preference’
5. Click on ‘Network’ and choose ‘New Location’
6. Select your Ethernet card under the first configuration box
are on
change the configuration to ‘DHCP’
effect
and type in this address: ‘http://192.168.8.1’ and follow the
instructions under Part 1 and Part 2 to continue the
installation.
are on
Chapter2
22
GigaFast
7. Pick the ‘TCP/IP’ tab and change it to ‘DHCP’
8. Click on ‘Apply’ to save the settings that you have just
changed.
9. A reboot of the system might be required for the changes to
take effect
*Note* Once the settings have been changed, the Macintosh computer
should be able to log onto the router’s configuration page and setup for
the above 2 sections for your specific type of internet connection.
Please read through our FAQ guide if further assistance is needed on
setting up a Macintosh. Thank you for your patience.
Part 4 Powerline Setup
Chapter2
23

GigaFast
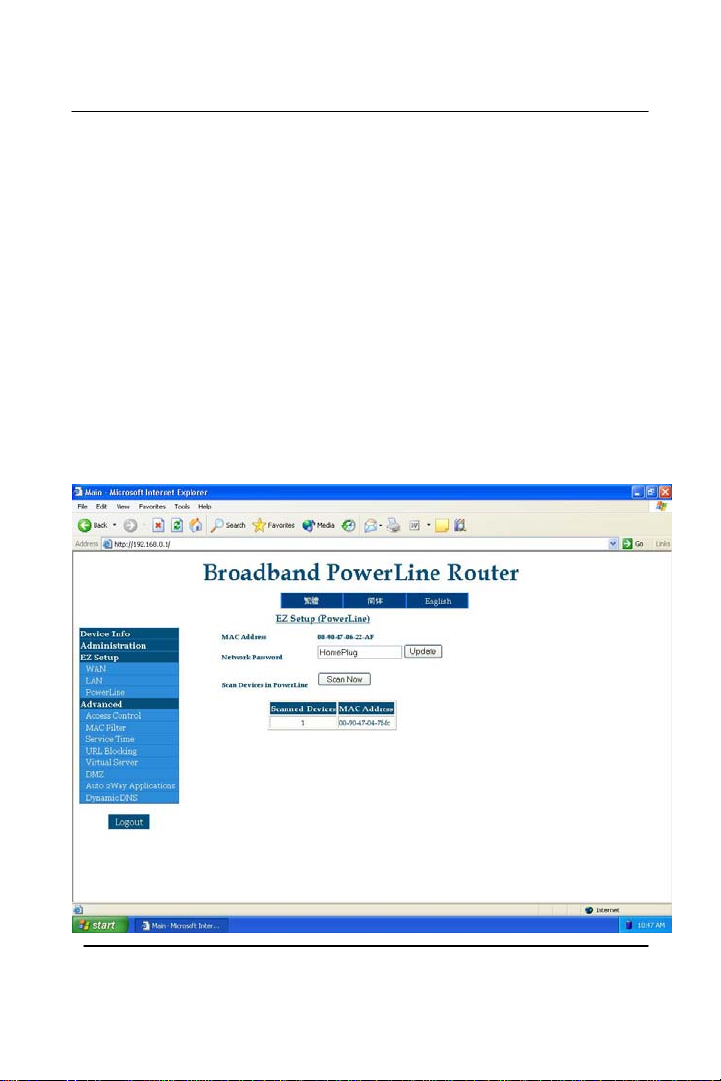
The HomePlug Portion will connect directly using the power
adapter that is provided. The Network Password is the same
password that is used with the HomePlug encryption of all
products that are on your Powerline network. By default, the
network password is “HomePlug”. You can easily change
your Broadband Powerline router network password by click
the ‘Update’ button, after you key in your new network
password. To look for all HomePlug units that are connected
to your network, click the “Scan Now” button. This will list
(in the provided area) all the HomePlug units that are
connected, including Mac Addresses.
Aftermath
Congratulations, you have just successfully installed the
PE904-R. You should notice after the connection has been
established, the ‘Broadband Router Status’ page will display
a list of ‘WAN IP Addresses’. This shows that there has been
a connection going through the modem and the router. After
this point, you don’t have use your DSL dial up software no
more on your computer.
*Note* If no connections were made or the ISP did not
establish a connection to your PE904-R, please refer to our
FAQ page. Thank you.
Chapter2
24
GigaFast
Chapter 3: Basic Configuration
The next chapter will explain in details of how each function on the
router works. It will be split a total of 5 sections. Each section will tell
you some of the most common and some advanced usages on a router.
Users can take advantage of this section to suit their own best settings
on the router.
Section 1 – Broadband Router Device Status
Chapter3
25
GigaFast
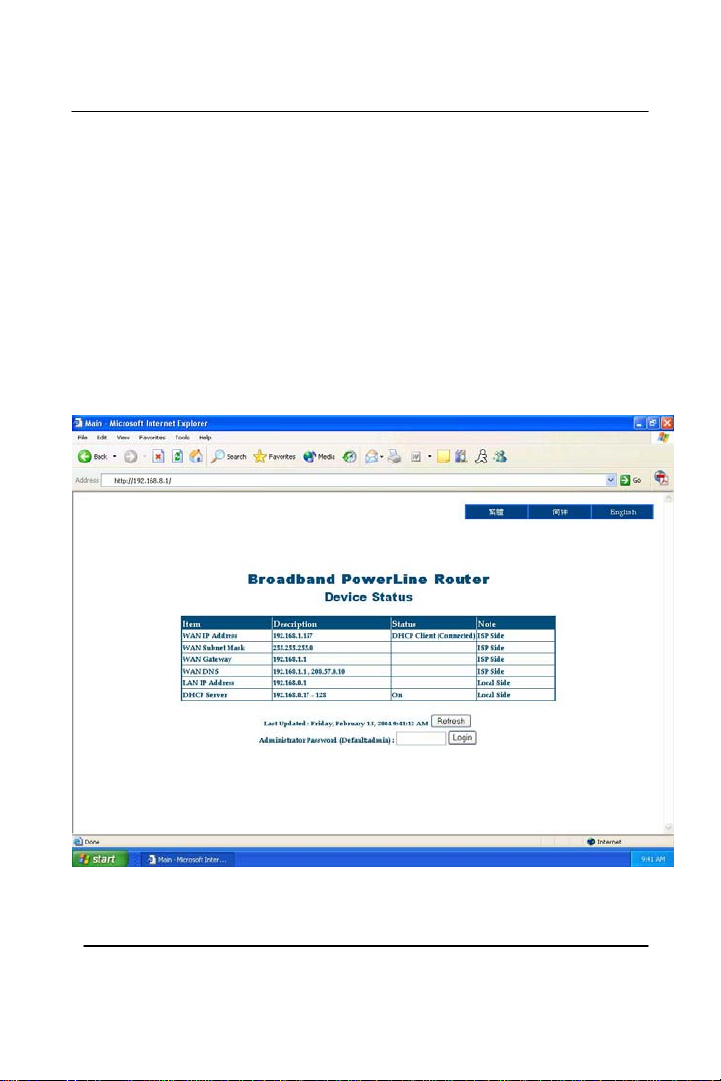
*Note* this page will be displayed after you have entered:
http://192.168.8.1 under your internet browser. The ‘Device Status’
page tells you what are the current IP addresses you’re getting from:
Your ISP (Internet Service Provider), your router, and the last log on
that was the ‘Refresh’ button will reset it back to your current login.
Press ‘Administration Password’ is where you enter the password to
log into the router’s configuration page. By default the password is
‘admin’ and it is case sensitive. The password can be changed under
‘Administration’ page once you’re logged into the router page. After
you have input the password, click on the ‘Login’ to enter the next page.
Section 2 – Broadband Router Device Info
Chapter3
26

GigaFast
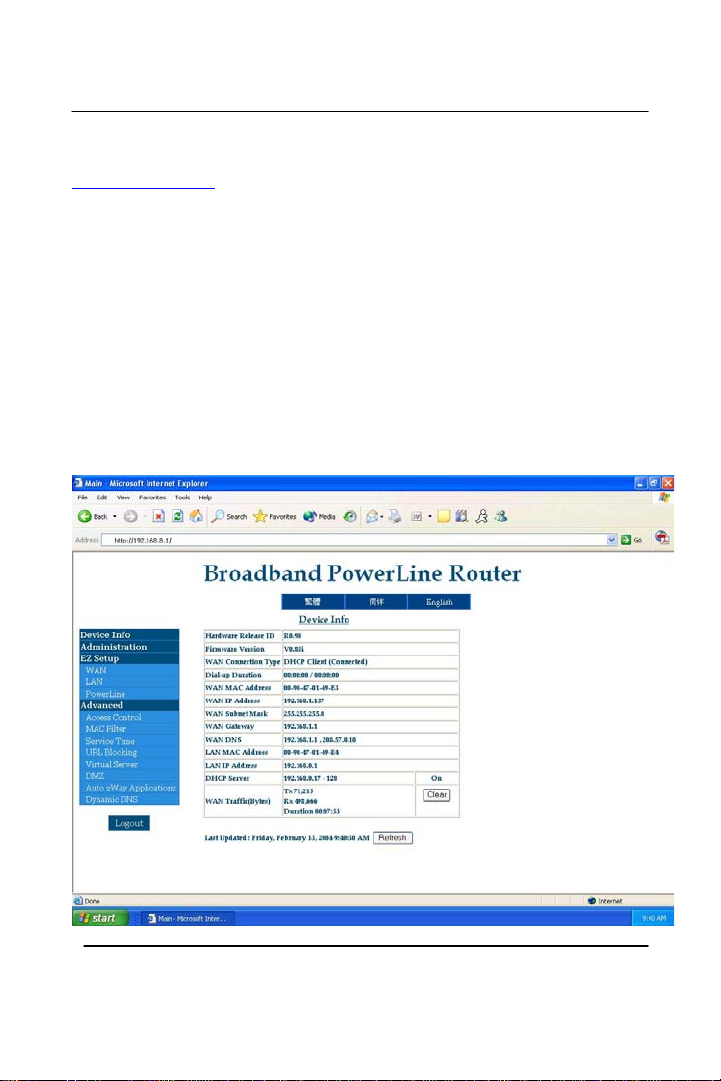
After you entered the password for the ‘Administration Password’ and
have logged onto it, a page like this will display. It is similar with the
previous page but with more options to choose from. On the left side is
where you adjust/change settings for your router. The middle (Device
Info) tells you exactly what the current version of firmware is running
and if you are getting IP addresses from outside or within your network.
The details of each selection on the left of the page will be described as
we move on to the next sections.
Section 3 - Administration (Part 1)
This page allows you to change some of the most commonly used items
on a router.
Chapter3
27

GigaFast
Reset to Default – By clicking this it will give you a confirmation on
whether or not the router should be reset back to the factory default
setting. If you have accidentally changed a setting on a router and does
not remember the setting you previously had, then it is suggested that
you click on ‘Reset to Default’ button.
Backup System Setting – This option allows storing your current
settings by saving it onto your hard-disk. It saves the current settings
on the router to your computer.
Restore System Setting – User can obtain the router settings from here
after the user has saved the information on the router. This option can
load previous settings from the hard-dis k.
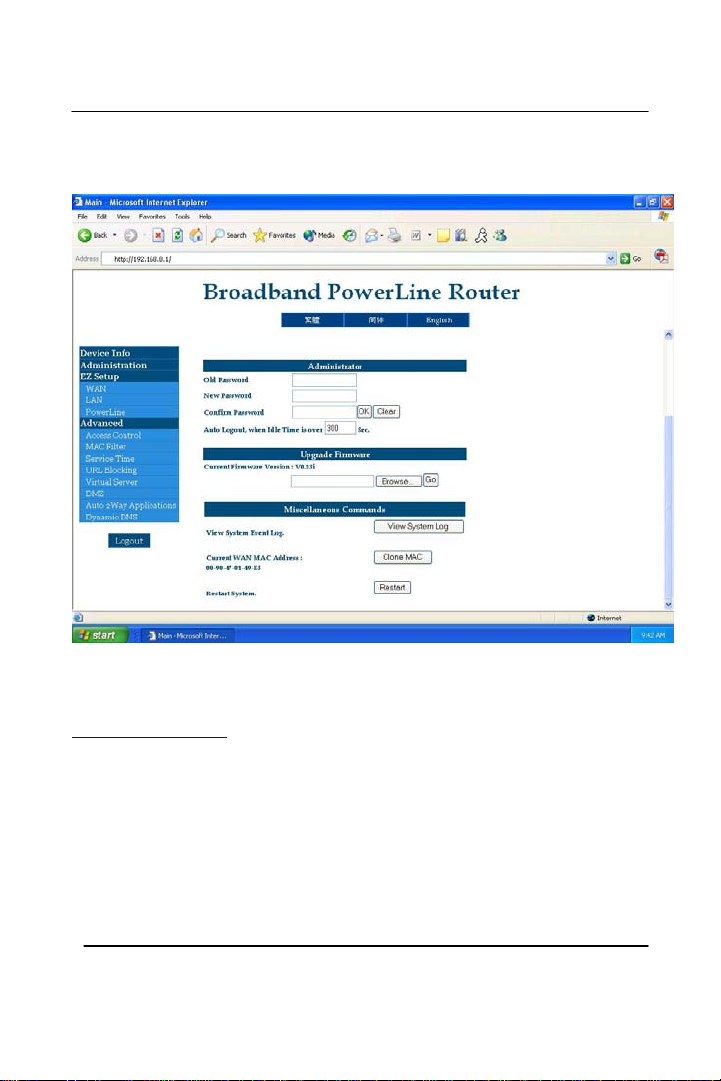
Old Password/New Password/Confirm Password – This section
allows the user to change the administration password on the router. A
user can change the default password ‘admin’ to a different password
for security reasons. (Strongly recommended)
Auto Logout, when Idle Time is over: - You can change the amount
of time for the router to take before it automatically logs out itself if
there is an idle occurred.
Chapter3
28
GigaFast
Part 2 (Administration Continued)
Upgrade Firmware – This is the place to update the firmware on the
router. Once the user has downloaded the firmware off of our website
www.Gigafast.com and saved onto a floppy or a hard-disk (hard drive):
1. Click on the ‘Browse’ button
2. Locate the firmware (file) where the user stored (Floppy, hard-
disk) and click on the ‘Go’ button.
*Note* this process should take a few moments. If the update is a
success or a failure, it will give you a confirmation on either one of the
events. Do not turn off the power of the router during the update
Chapter3
29

GigaFast
firmware process. If a user gets such error “Update failed” then please
refer to our FAQ guide.
View System Event Log – Allows users to view the most recent events
that have happened. For example, each time when a user logs onto the
ISP (Internet Service Provider) it will record it under the log. It will be
erased every time the router is unplugged, and plugged back in. This
function provides administrator a convenient diagnostic method for
troubleshooting. It also records the detailed intruder information for
analysis. Press REFRESH button to display the latest events.
Clone MAC – This allows the router to a copy of the Ethernet
adapter’s MAC address. It is used only when a user have trouble
connecting to the ISP (Internet Service Provider). Please refer to our
FAQ guide for further explanation.
Restart System – This option will refresh the router if there were any
changes made. Force router to do a system restart immediately. It is
not commonly used.
Chapter3
30

GigaFast
Section 4 – WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN Connection Type – This section allows the user to set the
proper type of WAN connection is being used. By default the ‘DHCP
Client’ is bubbled. Each type will give you some other options. For
example: After the ‘PPPoE’ is bubbled, it will give you extended
options like: PPPoE Account, PPPoE Password to fill out. Once the
settings are provided, make sure you click on the ‘Save & Restart’
button for it to take effect.
*Note* the ‘DHCP Client Domain Name’ and ‘Host name’ is
optional. It is not commonly used so users can avoid this unless the
ISP demands it.
Chapter3
31

GigaFast
Section 5 – LAN (Local Area Network)
LAN IP Address – This shows the current IP address on the LAN side.
If a user is running a static IP and cannot log onto the router page, then
changing the LAN IP Address might be needed. By default the LAN
IP Address is 192.168.8.1
DHCP Server – This allows the user to enable or disable the DHCP
Server running on the router. It is not recommended to change this
feature unless the network demands it. For example: If you’re running
a static IP address on the network and DHCP is not allowed or needed,
then disable it as needed. By default the DHCP Server is enabled.
Chapter3
32
GigaFast
DNS Proxy – If a user has a DNS Proxy that was set previously and
would like to use it without having conflicts with the router, then it is
recommended to disable this feature. By default the DNS Proxy is
enabled.
IP pool from & to – DHCP server will offer unused IP from the IP
address pool to the requesting computer. End address must be greater
then initial address. By default the range is set at: 17~128
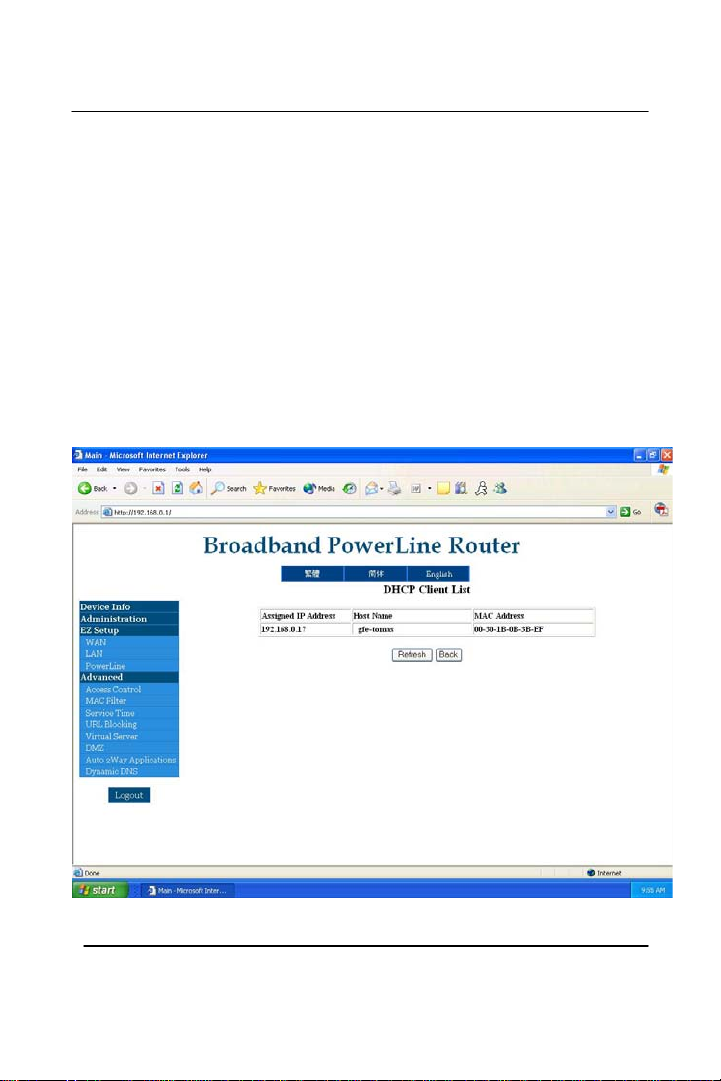
DHCP Client List – This is a list of your DHCP IP address
information. Example: what computer at which computer’s name on
what MAC address of the network card did receive what IP address.
Chapter3
33

GigaFast
Chapter 4 – Advanced Configuration
This chapter will explain great details of advanced settings on the
router. A user can change these settings for their own needs and
purposes or to fix some of the commonly known problems out there in
the industry. It will be divided into total of 10 sections and it is
recommended and accessible for both home and business users. Please
refer to our FAQ guide if there is an unexplained question regarding
the functions on the router.
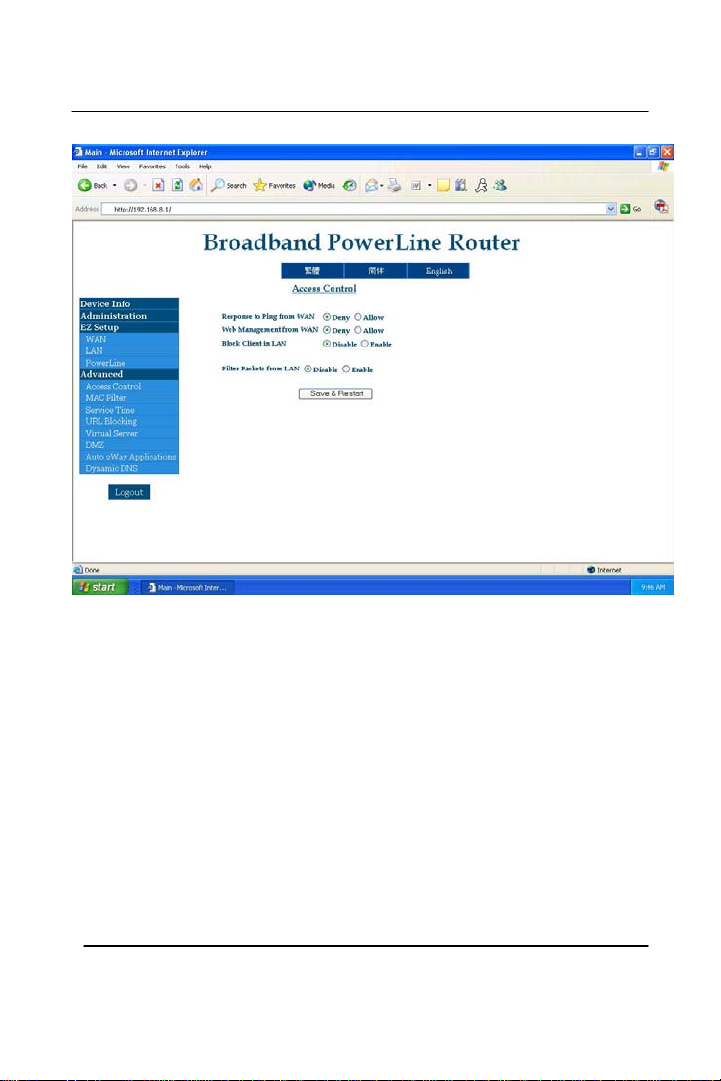
Section 1 – Access Control
Access Control allows you to set some of the security features for the
administrator. It also gives the ability to access from outside to the
router. Once the changes are made, click on ‘Save & Restart’ to have
the changes take effect.
Chapter 4
34
GigaFast
Response to Ping from WAN – If this option is allowed, others can do
a direct ping to the router from outside of your network. Due to
security reasons this option is set to ‘Deny’ by default.
Web Management from WAN – Enable administrator to log in and
configure the router remotely from internet. It is set to ‘Deny’ by
default.
Example: http://yourwanip:54321
Block Client in LAN – You can block certain internet protocols
(IP’s) within your own network and disall o w ot her clients or computers
to access other pages within the network. It is set at ‘Disable’ by
default.
Chapter 4
35

GigaFast
Filter Packets from LAN – This option allows the administrator to
block certain ports on the router so other clients can’t access them.
Section 2 – MAC Filter
MAC Filtering will block or allow the MAC addresses that are on the
Ethernet adapters. Administrator can enable this function to block or
allow certain computers or the entire network to access the router or
network.
Chapter 4
36

GigaFast
MAC Filter – Enable it to set which MAC addresses the administrator
would like to block so the blocked clients can’t make changes on the
router. The clients are still able to get onto the router, though without
making any changes. This function is set at ‘Disable’ by default.
Section 3 – Service Time
This page allows the administrator to set a time limit/duration of the
router.
Service Time Allocation – Administrator can now apply a limit on all
the clients or computers that are connected to the router. For example:
If it is set from 9:00AM~12:00PM that means the clients can only log
onto the WAN/LAN from between those times. This option is set at
‘Normal’ by default which means the connection is always allowed
Continuous – This allows users of the router to receive an internet
connection for only a certain amount of time (i.e. 2 hours) then the
internet connection will stop functioning, for a certain cool off period,
and then start up again.
Chapter 4
37

GigaFast
By time zones – This will allow users of the Router to only be
connected for a certain time period (i.e. from 8-10), after, or before the
allocated Time Zone, the Internet will not work.
Chapter 4
38

GigaFast
Chapter 4
39

GigaFast
Section 4 – URL Blocking
URL Blocking allows the administrator to block certain URL (web
addresses) so clients cannot log onto the designated pages that
administrator have blocked. By default this option is set at ‘Disable’.
URL Blocking – Administrator can enable this function and put in the
URL of a page and clients will not be able to log onto it. User can
block all the way up to 8 URLs.
Chapter 4
40

GigaFast
Section 5 – Virtual Server
Virtual Server can allow the administrator to open one or multiple ports
on the router for a LAN PC.
Virtual Server - If the user has a server behind the route he/she can
open a particular port or ports to allow incoming and outgoing traffic
through the router. This function is mainly for computers that are on
the network. By default this setting is set at ‘Disable’ if you have
trouble opening ports please r ead our FAQ section to understand more
about Virtual Server.
Chapter 4
41

GigaFast
Section 6 – DMZ
DMZ (De Militarized Zone) allows the port on your computer to be
seen outside of your network. It basically allows you to b e shown on
the WAN side. This function is mostly used for game or program
specific purposes. In comparison with the virtual server, DMZ is not
protected by firewall. Enable DMZ host are dangerous and subject to
be attacked/accessed by internet intruder/hacker. However DMZ host
is able to gain full access privilege right to internet.
A. The Host DMZ – Enable it and input the last digit of your
current IP address and it will open up you to the WAN side.
For example: 192.168.8.XX The XX marks the last digits
Chapter 4
42

GigaFast
from the IP address you’re getting on that computer. If your
IP address ends with 17, then put 17 in the empty box and
click on ‘Save & Restart’. Some users might have trouble
getting the router to communicate with their game console
servers (i.e. PlayStation2 by Sony or Xbox by Microsoft) and
if that is the case then enable DMZ and it should allow you to
enter the server after save & restart.
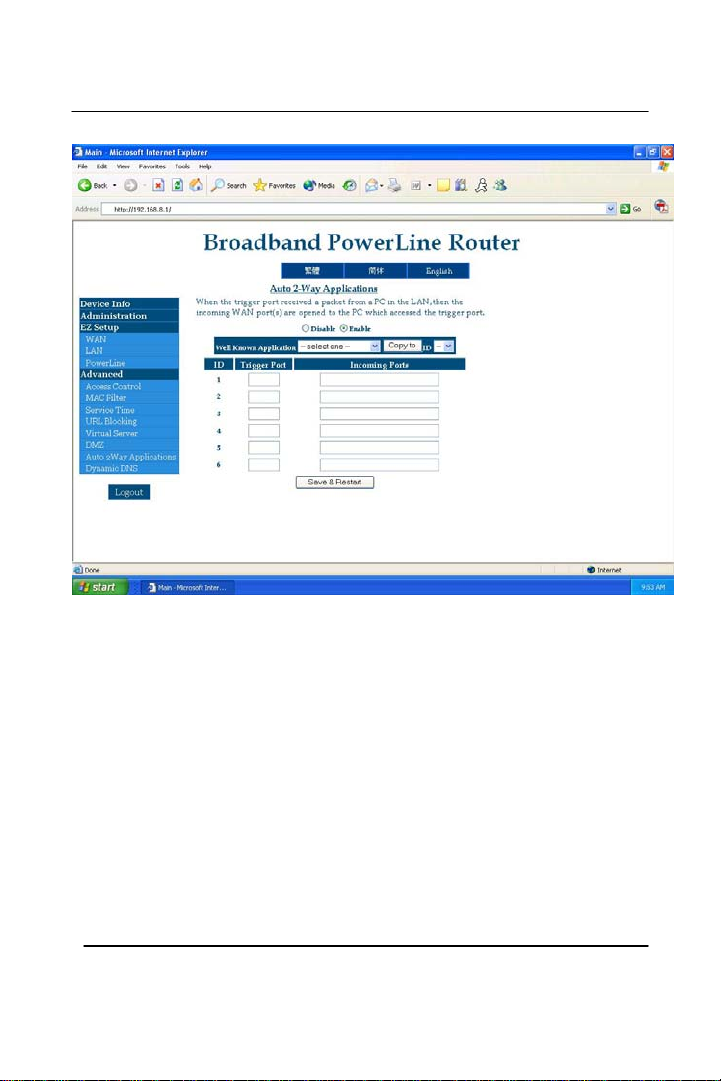
Section 7 – Auto 2-Way Application
This section can let a user open certain service ports for software.
Because there is much internet software need 2-way access right and
they open many TCP/UDP ports simultaneously such as online game or
audio/video conference, they always connect to an outside server with a
fixed destination port. Then the server would communicate with the
application in LAN by using a predefined incoming port or
range of incoming ports. If a user has trouble playing
and the games require a port to be opened, then Auto 2-Way
Application is the place to enable ports for it.
a specific
certain games
Chapter 4
43
GigaFast
Auto 2-Way Application – Once enabled, put the outgoing port in the
‘Trigger Port’ box and incoming port in the ‘Incoming Port’. All
software, games have its ports to be opened. Obtain the port numbers
and enter them under this section will allow the user to join any
particular server without being kicked or timed out. Please go to your
software website to obtain the service port information for your
software. Once a trigger is occupied, the second or later LAN PC
should not use that trigger port until the first LAN PC has released it.
Release means that the first PC doesn’t use that trigger port for more
then 5-6 minutes. By default this option is set at ‘Disable’.
Chapter 4
44
GigaFast
Section 8 – Dynamic DNS
This option will automatically translate your domain name to your
WAN IP address for others to access your page.
Dynamic DNS – If you don’t have a domain name and a host setup
then others will require a Dynamic DNS to log onto your webpage.
This enables others to see you on the WAN side and allows them to
browse your own page. Often the server will automatically update your
WAN IP address, therefore the Dynamic DNS function allow the
update to be saved so others can still browse your page without the
changes to be made manually. For further information please visit:
www.DynDNS.org and by default this function is set at ‘Disable’.
Chapter 4
45

GigaFast
Conclusion
This concludes the Basic & Advance Configuration for the PE904-R.
The most common questions are answered based on these two chapters.
If you need further assistance or perhaps require more information then
please visit our FAQ guide or contact one of our lines listed below.
Appendix A: Cabling and Pin Assignment
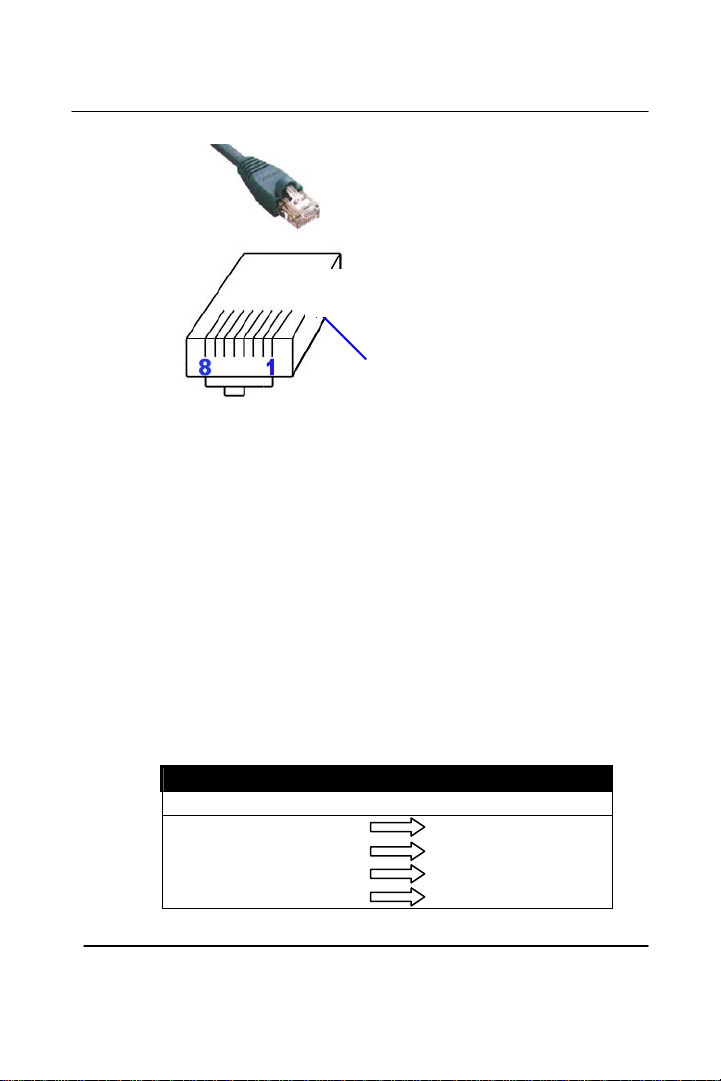
A-1 RJ-45
There are different grades, or categories, of twisted-pair cabling. Category 5 is the most
reliable and is highly recommended. Category 3 is a good second choice. Straight-
through cables are used for connecting computers’ NIC cards to a hub. Crossover
cables are used for connecting a hub to another hub. (The router provides a built-in
uplink/normal switch. Uplink mode is crossed internally, which allows you to link or
connect hubs together with a straight-through cable instead.)
A-1-1 RJ-45 pin assignment
There are 8 thin, color-coded wires inside, run from one end of the cable to
r. All 8 wires are used. the othe
Table 0-1
Wire 1 White with an Orange stripe
Wire 2 Orange
Wire 3 White with a Green Stripe
Wire 4 Blue
Wire 5 White with a Blue Stripe
Wire 6 Green
Wire 7 White with a Brown Stripe
Wire 8 Brown
RJ-45 Color Chart
GigaFast
Pin 1
*Note* To determine which wire is wire number 1, hold the
cable so that the end of the plastic RJ-45 tip (the part that goes
into a wall jack first) is facing away from you. Face the clip
down so that the copper side faces up (the springy clip will
now be facing the floor), when looking down on the copper
side, wire 1 is on the far left.
Connection between NIC card and Hub
In a straight-through cable, wire 1, 2, 3, and 6 at one end of
the cable are the same as wires 1, 2, 3, and 6 at the other end.
The straight through cable is used to connect the NIC card and
the hub.
Table 0-2
Appendix A
Straight Through Cabling
Wire Becomes
1 1
2 2
3 3
6 6
47
GigaFast
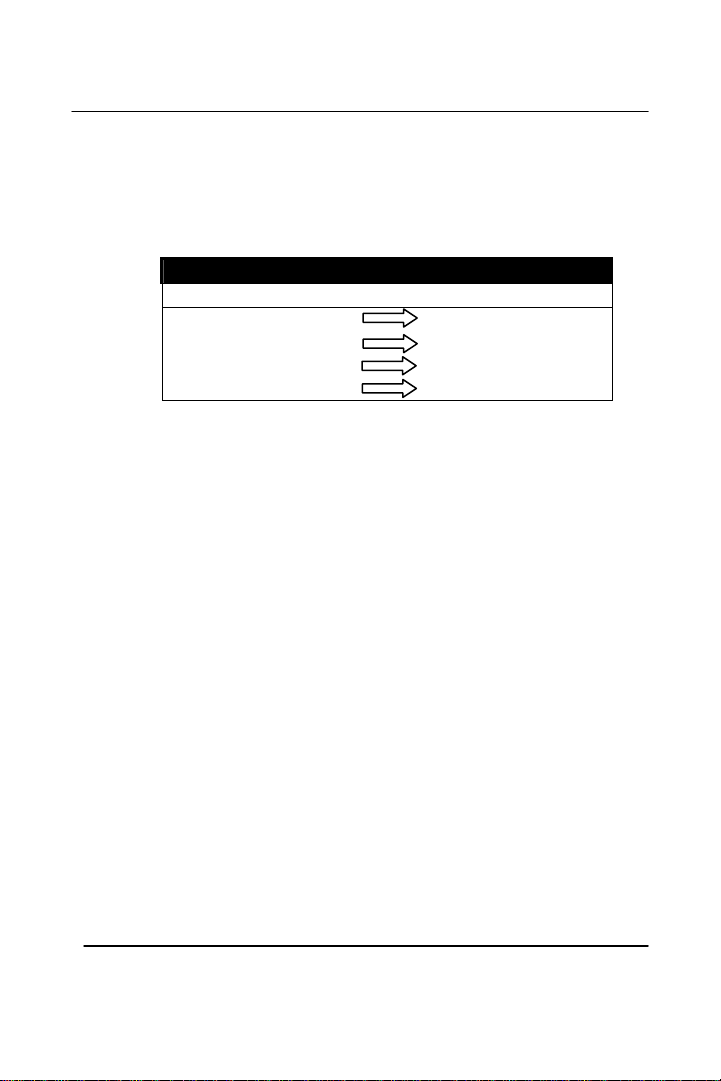
Connection between Hub and Hub
In a crossover cable, the orders of the wires change from one end to the other.
Wire 1 becomes 3, and 2 becomes 6. The crossover cable is used in
connecting hubs directly.
Table 0-3
Crossover Cabling
Wire Becomes
1 3
2 6
3 1
6 2
Appendix A
48

GigaFast
Appendix B: Technical Information
Operational
WAN I/F : One RJ-45 port, IEEE 802.3
100BaseT, CSMA/CD
WAN cabling : UTP category 5 (10/100 Mbps).
LAN I/F : Three RJ-45 ports, IEEE 802.3u
100BaseT, CSMA/CD
LAN cabling : UTP category 5 (switched 10/100
Mbps).
LED indication : Power, System Ready, Homeplug detect,
WAN Link/Act,
ETH10/100,
Button : Factory Reset default setting.
Environmental
Power Input : External, DC 7.5V/1A.
Dimensions : 255 x 185 x 93 mm (TBD)
Unit Weight : 1050g
HomePlug certification : HomePlug Powerline Specification 1.0
Certification : FCC class B, CE mark
Operating Temp : 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F)
Storage Temp : -20°C to 70°C (-4°F to 157°F)
Operating Humidity : 10% to 85% non-condensing
Appendix B
49

GigaFast
Appendix C: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Still having trouble setting up this router? Please read the following
questions and answers to solve your problems with the router.
Q: I can’t seem to log onto the ‘Broadband Powerline
router’ Configuration page (
http://192.168.8.1)
A: If you have already followed the instructions from the manual and
still can’t log onto it:
1. Please do a power reset on the router. For example: Turn the
router off for few minutes and turn it back on.
2. Use a paper-clip or a pin to do hardware reset the router. On
the router there should be a pin sized hole and that is where
you insert the pin. Once the pin is inserted, hold it down for 5
seconds and you should see the lights on the router flash for a
moment.
3. Try to ping
can’t ping the router that means the router might be defective.
Perhaps try another cable or different port on the router.
4. Make sure you have the same subnet mask between the
computers and the router.
5. If you did a ping on the router and gets a reply like
169.xx.xx.xx, that means the Ethernet cable might be bad (or
check your Ethernet card for proper installation).
http://192.168.8.1 if you can receive an IP but
Appendix C
50

GigaFast
Q: I have followed the ‘Quick Install’ but still can’t get
my router to work with my Internet Service Provider.
A: Check the following:
1. Make sure the Ethernet cable is working.
2. Make sure the lights on the router are flashing (this indicates that
there is traffic coming and going from the router to the modem).
3. See if the network adapter was installed properly and inserted into the
slot on the motherboard correctly.
4. Confirm there is internet connection (WAN Connection) coming in
from your ISP (or the modem).
5. Double check the WAN IP addresses on the router. If the WAN IP
addresses are shown but can’t connect, that means the source is being
blocked from the operating system by software or perhaps hardware.
Occasionally the anti-virus or firewall programs might stop an IP
from coming in and going out of the network. Disable the software if
you have one and try again.
*Note* if you’re not getting the router’s IP or a WAN IP address after you plug
the cables into the router and to the computer, then do an IP release and renew.
To do this:
(For Windows 95, 98, ME)
1. Go to ‘Start’ > ‘Run’ and type in: ‘winipcfg’ and press ‘Enter’ or
click ‘Ok’
2. It should bring a dialog up and give you a list of network adapters
you have on that system you’re using.
3. Select the Ethernet adapter that is connected to the router and
click on ‘Release All’ (this should take few moments and
upon completion it’ll give you all 0’s).
4. After the IP has been released, click on ‘Renew All’ (this will
refresh the IP addresses on the computer).
5. If the IP address says: 192.168.8.XX then that means there is
a connection between the modem and the router.
Appendix C
51

GigaFast
(For Windows 2000, XP)
1. Go to ‘Start’ > ‘Run’ and type in: ‘command’ and press
‘Enter’ or click ‘Ok’
2. This should bring up your MS-DOS Prompt
3. At the prompt, type in the following: ipconfig /release and
press ‘Enter’
4. After the process has finished, type in: ipconfig /renew and
pres ‘Enter’
5. This will refresh your IP addresses
To do a proper power-cycle/reset on the router, modem, computer:
1. Turn the devices listed above off
2. Turn the router back on after few minutes
3. Turn the modem back on after few minutes
4. Use a paper-clip or pin and reset the router. Insert the pin and
hold down the button for five seconds
5. Turn back on the computer(s) and see if you can go online
Q: Does the Broadband Powerline router come with
firewall protection?
A: Yes, a built-in hardware firewall is placed inside of the router. It
protects intruders hackers from vandalize your information.
Q: Can I turn the firewall function off?
A: You can’t turn the firewall off, but you can make yourself seen on
the WAN side. To do this, just enable ‘DMZ’ and that should allow
others to see you or your server.
Appendix C
52

GigaFast
Q: I’m trying to play games online with the router, but
it won’t let me.
A: Try to enable ‘DMZ’ and see if that helps. Put the last two digits of
your current IP Addresses into the empty box under DMZ and click on
‘Save & Restart’ Restart the computer afterwards. If DMZ does not
help that means the game server might need you to open some ports for
the router to play. Get the port numbers and go to Part 2 of this FAQ
to find out more information on how to fix this issue.
Q: Does the router work with AOL Broadband
Internet Service?
A: Unfortunately AOL (America Online) uses a different Proxy setting.
It requires upon log on and the router can’t bypass that. We might have
a firmware update for this issue later in the future.
Q: Is there a way to boost my internet connection to
have a faster download/upload speed with this
Broadband Powerline router?
A: A router does not provide the bandwidth from your ISP. Your ISP
decides how much bandwidth to be produced and sent in and out of
their servers. Disabling the anti-virus program or third party firewall
programs might help a little bit, but it is up to personal preferences.
Appendix C
53

GigaFast
Q: I have two computers or more and one of them is
able to go online but the other one says “IP Conflict” or
just can’t go online?
A: If you have an IP conflict within the network, do an IP release and
renew then restart the computers to see if that helps. If only one of the
computers does not work, then do the IP release and renew on that
particular computer. If none of it helps, turn the router off and turn it
back on after few minutes. If problem still exists, update the firmware
on the router.
Q: My Broadband Powerline router was working fine
for a while and all of sudden it stopped working, what
should I do?
A: If you have moved to a different place or perhaps changed to a
different ISP, try the ‘Quick Install’ and see if that helps. If the lights
on the router went out and doesn’t flash anymore then most likely the
router might be defective.
Q: How do I setup a VPN (Virtual Private Network)
PPtP?
A: Please note that this router supports only PPtP Packet PassThrough. First you need to understand that there are three protocols of
VPN software. They are the following:
1. PPtP (Point to Point Tunnel Protocol) Æ supported
2. L2tP (Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol) Æ not supported
3. IPSEC (Internet Protocol Security) Æ not supported
Appendix C
54

GigaFast
The router itself does not have a VPN function. It is allowed PPtP
Packet Pass-Through once the router has updated the firmware to
version 1.91 or above. To setup a PPtP Packet Pass-Through on
the router, please go to:
1. Virtual Server under the router’s confi gurat i on page.
2. Open service port 1723 for your VPN server (IP address).
3. Click on ‘Save & Restart’ to take effect.
The steps above will allow the packets to pass through. Reason for this
is because if this function is not enabled, the router will automatically
block the packets that are coming and out of the router.
Q: I have several static IP addresses and would like to
run them with my Broadband Powerline router, how
can I do that?
A: First off you have to go to the router’s configuration page
http://192.168.8.1):
(
1. Go to ‘WAN’ section under easy setup on the router page and
bubble in ‘Static IP’
2. Input one of your static IP address in the box and click on
‘Save & Restart’
3. Go to DMZ section, you can enable up to 8 static IP address at
one time
Q. What’s the speed of HomePlug operate over a
standard home power line network?
A. HomePlug operates up to 14 Mbps bandwidth over a standard
home power line network
Appendix C
55

GigaFast
Q. What’s the Estimated Range of HomePlug?
A. Approximately 300 meters in wall power lines(one household).
Q. Will HomePlug work in any home?
A. Any home with copper wiring built-in, since some of the older
houses built before 1950 might have older wiring, it may not work
in these instances..
Q. Will HomePlug signal pass through circuit
breakers?
A. Yes, HomePlug signal will have no problem passing through
circuit breakers but not through power transformers.
Does HomePlug work with AC input 100 – 240V?
Q.
A. Yes, HomePlug works with AC input 100 – 240V.
Q. Does HomePlug cause any interference with other
my other home networking device?
A. No, HomePlug operates in a different frequency band than other
power line control devices and can co-exist with technologies as
X-10, CEBus, and LONworks.
Appendix C
56

GigaFast
Q. Can my neighbor receive my HomePlug signal?
A. It is possible for your neighbor receive your HomePlug signal
between two adjacent homes. To prevent this happen, please
enable the 56-bit DES security encryption on your HomePlug
Device. To do that, you must run the HomePlug Configuration
Utility on each HomePlug device in your Powerline network. This
will only allow computers with the same security password to be
able to receive information.
Q. My PWR LED’s doesn’t light up after I plug the
Broadband Powerline router directly into a wall
plug?
A. Test that wall plug with other electric devices first, make sure that
wall plug is working properly. Then, try to plug your HomePlug
device again, if the same problem happens again, plug both
HomePlug units into adjacent sockets, and see if the lights light up.
If you are still having problems please contact Technical Support
(Appendix H).
Q. The Ethernet LED doesn’t light up on my
HomePlug Ethernet router?
A. Most likely, if the Ethernet LED doesn’t light on your Broadband
Powerline router is because the Ethernet port on it doesn’t detect a
LAN connection. Check your Ethernet adapter on your computer ;
make sure its enable and working properly. Also, check
your Ethernet cable, make sure you use the right type, it’s
plugged in correctly, and it’s working properly.
Appendix C
57

GigaFast
Q. I can’t connect to internet and other computers on
my Powerline network?
A. 1. Check your IP address and TCP/IP protocol are set up properly
for all the computers on your Powerline network
(Appendix D) and try to ping your gateway (Appendix D).
2. See if HomePlug Configuration Utility to detect all other
HomePlug device on your power line network. Try plugging
both HomePlug units into adjacent sockets and see if the lights light up.
If you are still having a problem, please contact Technical Support
(Appendix H).
Q. How many HomePlug devices do I need to setup a
powerline network?
A.
You must need two or more HomePlug devices to setup a
powerline network. For example, you have one broadband
powerline router connect with your modem, and one
HomePlug Ethernet bridge plug in with your pc.
Q. How many HomePlug Ethernet device that I can
install into one same Local Area Network?
A. Unlimited. But by the IP restriction, you might be able install
up to 253
Network.
units for each computer in one same Local Area
Q. Can I connect my Broadband Powerline router to
an extension cord or an UPS?
A. Yes, HomePlug devices can be plugged onto extension cords,
but please note that this will reduce the powerline signal
Appendix C
58

GigaFast
strength of the connection. Sometime it may even reduce it to
zero! Please use a wall outlet if it’s possible. HomePlug
devices do not work with UPS at this time.
Q. Can I connect my Broadband Powerline router to
my Ethernet enabled PS2/Xbox/other device?
A. Yes. Because Broadband Powerline router is a fully plug N
play device, no driver installation require.
Q. Can I use other HomePlug brands with this one?
A. Yes. However, it’s not recommended to mix HomePlug units
with other brands as the internal board may be slightly different.
As long as all HomePlug devices under the HomePlug 1.0 Specs,
then they should be OK.
Q. Will anything happen if lighting strikes my house?
A. All our HomePlug devices have lightin g pr ot ect i on buil d-in. It
will only cause the internal board of the HomePlug device to short
circuit. However, it will not damage your computer or anything
plug in with it.
Appendix C
59

GigaFast
Appendix D: IP Addressing
What is an IP Addresses?
IP Stands for Internet Protocol. An IP Address is the identifier where
other computers on the network can contact your computer, when you
are connected to the network using the TCP/IP protocols. The format
of IP addresses are 32bit numerical addresses in 4 groups o f 3. It is
ranged from 0-255. For example: 255.255.255.255. This number
allows your computer to be unique on the same network, and able to
communicate with other computers on the network.
Dynamic IP Addressing
Dynamic IP Addressing is where the computer will automatically be
assigned a new IP Address. This IP Address will be unique to the
network that it is working on, and should not be the same as any other
computer on the same network.
Static IP Addressing
Static IP Addressing is where the computer will have a preconfigured
IP Address. This Address will never change, and will always be the
same. This scheme should be used if you want to keep the same
settings on each computer all the time. If the subnet of the network
changes (subnet is the first 3 groups of the IP) the subnet of the static
computer must also change.
Appendix D
60

GigaFast
Checking IP Address in Windows 98 / SE / ME / 2000 / XP
Click Start and click Run
Appendix D
61

GigaFast
Type “Command” in the run prompt, Click OK
A Dos Command prompt will open. Type in “ipconfig” and press
Enter
Appendix D
62

GigaFast
Your IP Address will Display, along with the Subnet Mask, and your
Gateway
Appendix D
63
GigaFast
Setting IP Address on Windows 98 / SE / ME
Right Click on “Network Neighborhood” and click Properties”
Appendix D
64

GigaFast
Click on “TCP/IP” for the network adapter you want to set IP addresses
for
Click on “Specify an IP address” Type in the IP Address you wish to
use. (192.168.XXX.XXX is very standard for home networks) Click
Appendix D
65
GigaFast
on the Subnet mask, and if you know the subnet mask you want to use,
type it in, otherwise it should fill in with “255.255.255.0” which is very
standard for subnet masks.
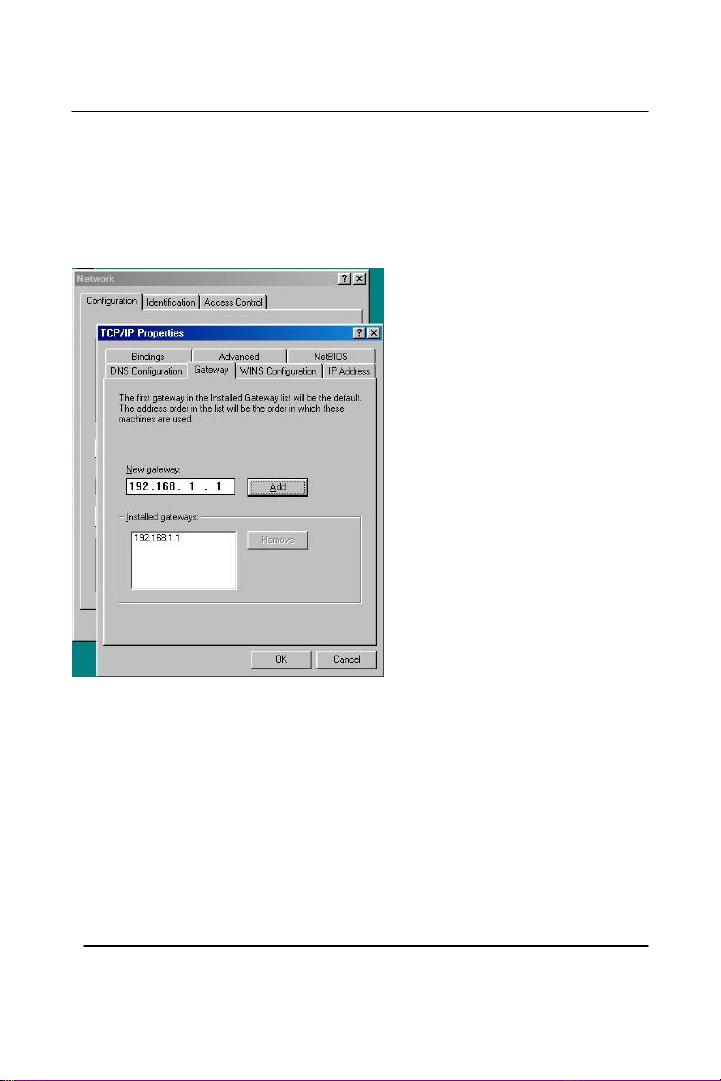
Click on the “Gateway” tab, and add in a gateway if you need to. Then
click OK
Appendix D
66

GigaFast
To save the changes you must restart, so click “YES”
Appendix D
67

GigaFast
Setting IP Address on Windows 2000 / XP
Right click My Network Places and click Properties.
Appendix D
68

GigaFast
Find and “Double Click” the Local Area Connection for the Network
adapter you want to Set IP’s for.
Click Properties
Appendix D
69
GigaFast
Click (Highlight) “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” and click “Properties”
Appendix D
70

GigaFast
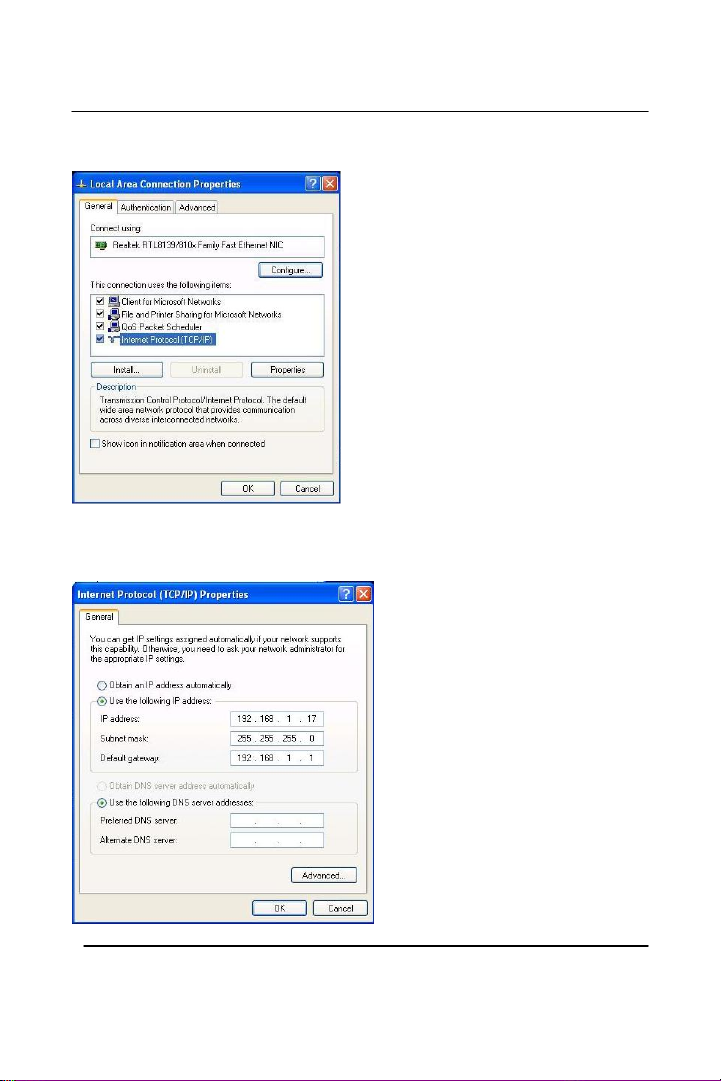
Click “Use the following IP address” Type in the IP Address you wish
to use. (192.168.XXX.XXX is very standard for home networks) Click
on the Subnet mask, and if you know the subnet mask you want to use,
type it in, otherwise it should fill in with “255.255.255.0” which is very
standard for subnet masks. Click on the Default gateway and fill that in.
If you know the DNS you are going to use, fill it in otherwise leave it
blank. Then click OK.
To check that everything is Correct, Click on “Support” and the
information you typed in should appear.
Appendix D
71

GigaFast
Releasing and Renew IP Address in Windows 98 / SE / ME
Click Start, and then click Run
Appendix D
72

GigaFast
Type “Winipcfg” and click OK
Select the Network adapter you want to release IP’s for.
Click “Release”
Appendix D
73

GigaFast
Your IP Address should turn to 0.0.0.0
Appendix D
74

GigaFast
If you Click Release, and an error saying “IP Address for adapter is
already released” then you do not need to release any more, try
“Renewing your IP”
Releasing and Renew IP Address in Windows 2000 / XP
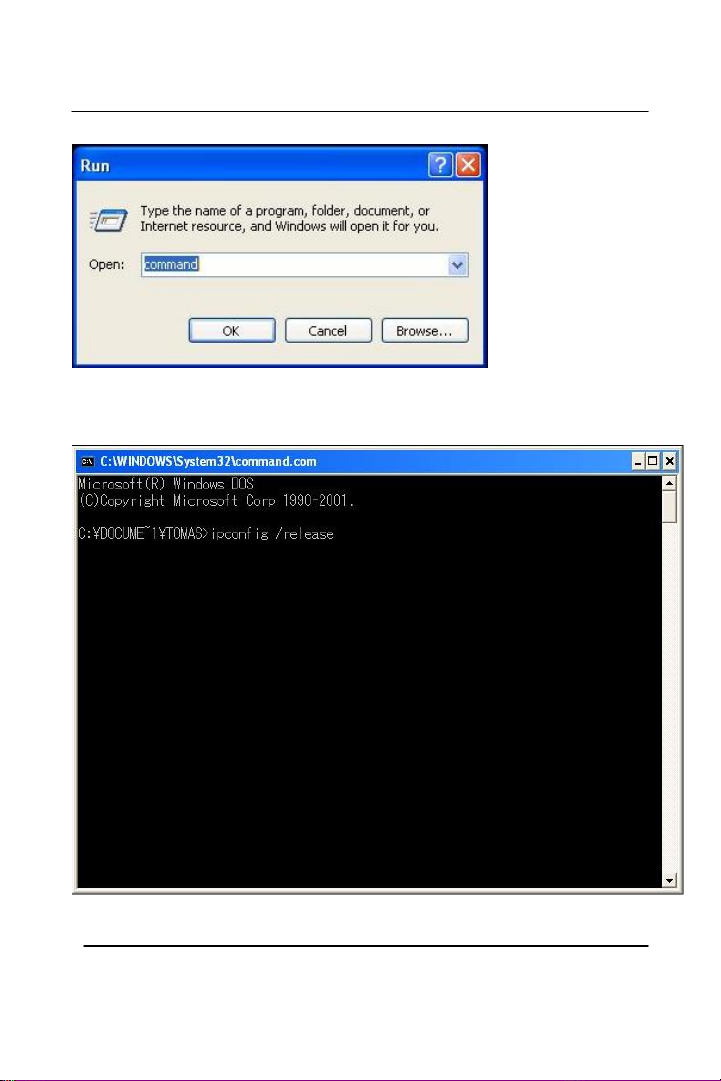
Click Start, and then click Run
Appendix D
75
GigaFast
Type Command and click OK
Appendix D
76
GigaFast
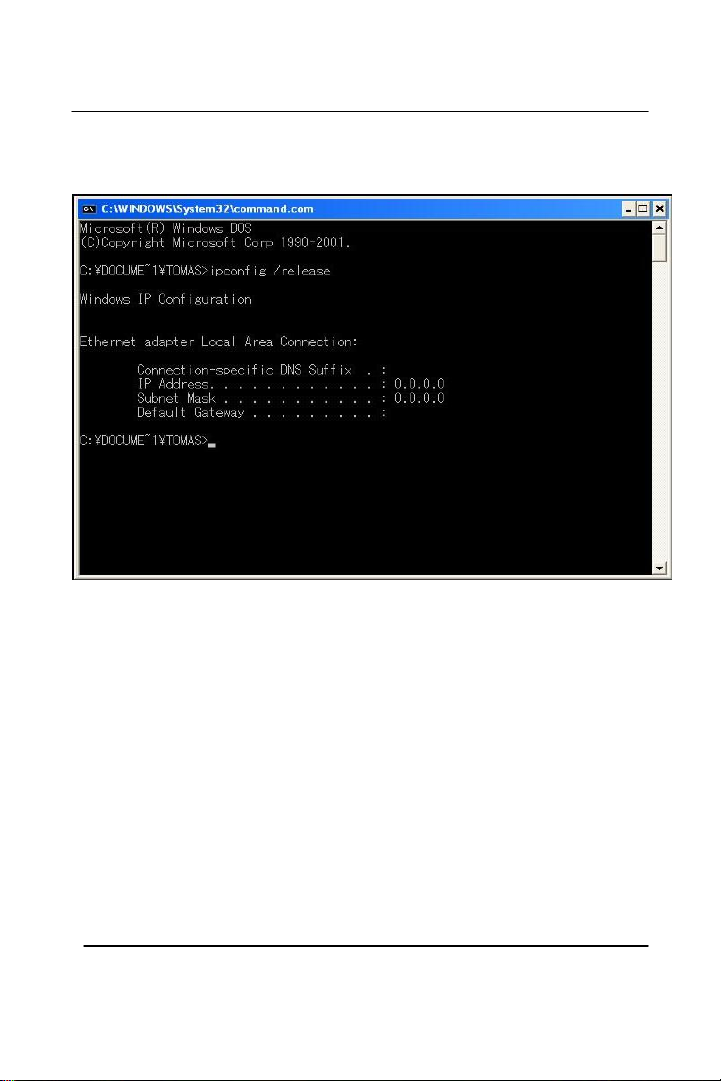
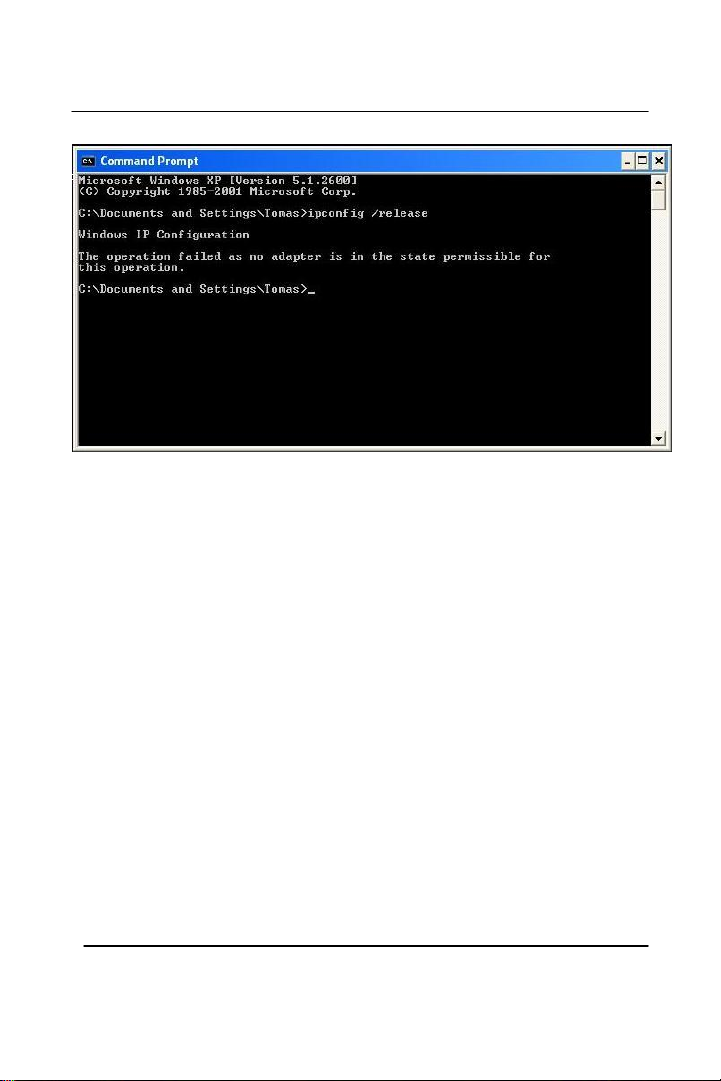
Type “ipconfig /release” and press Enter
Your IP Address should turn to 0.0.0.0. To renew your address check
Renewing IP Address.
Appendix D
77
GigaFast
If you receive an Error “The operation failed as no adapter is in the
state permissible for this operation.” Then you might need to set your
Network adapter to obtain your “IP Address Automatically”.
Appendix D
78

GigaFast
Appendix E: Local Area Network
Sharing Files (Windows 98SE / ME / 2000 / XP)
Double click “My computer”
Appendix E
79
GigaFast
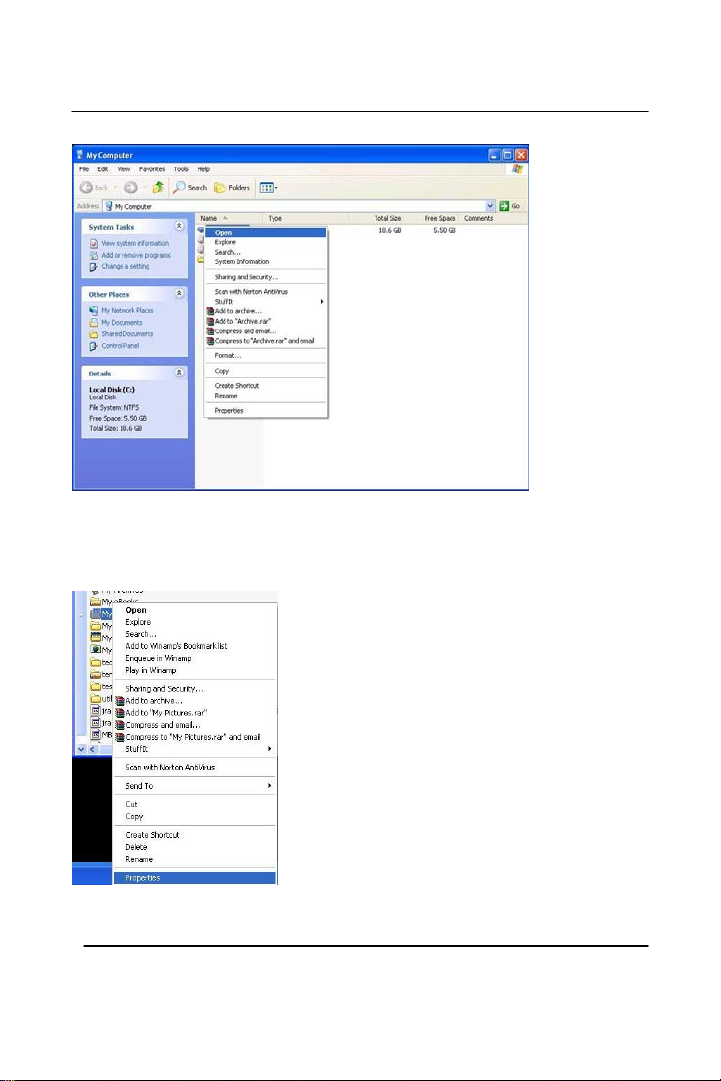
Double Click the Drive where the folder that you want to share is
located.
Right Click on the folder you want to share, and click “Properties”
Appendix E
80
GigaFast
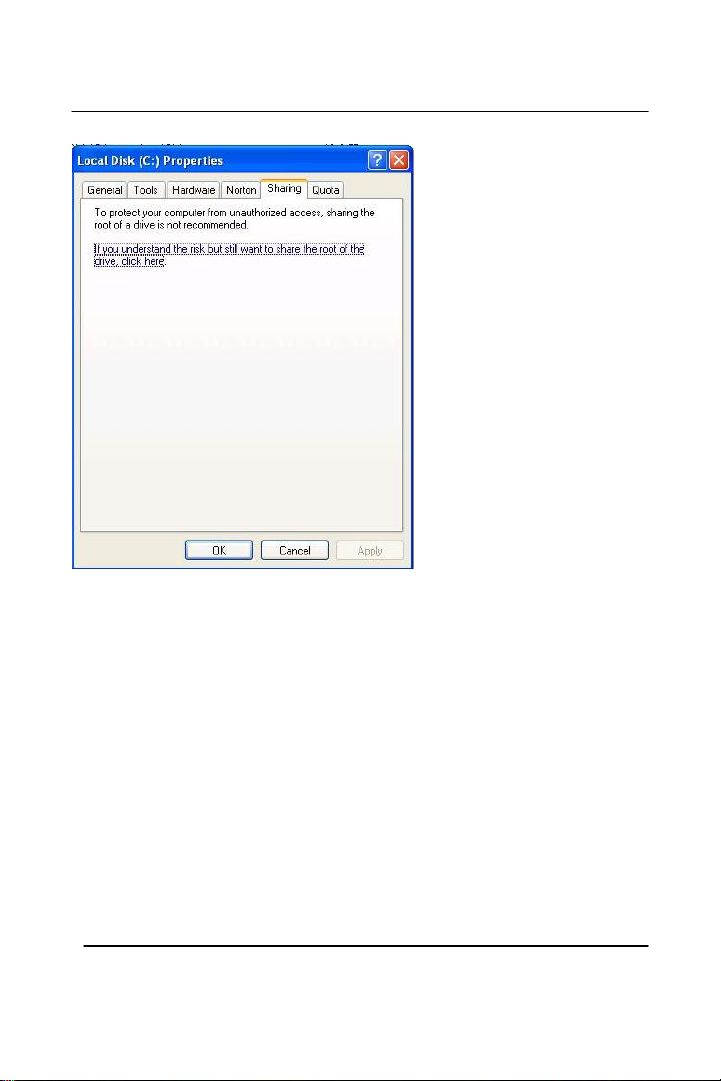
Click on the sharing tab, then “If you understand the risk but still want
to share the root of the drive, click here”
Appendix E
81

GigaFast
Click “Share this folder on the network” and specify the name you
want the folder to be seen as on the network.
Appendix E
82

GigaFast
A Hand should appear under the folder you wanted to share letting you
know that it is shared on the network.
Appendix E
83

GigaFast
Sharing Drives on Windows 98 / SE / ME / 2000 / XP
Right click on “My Computer” and click “Properties”
Appendix E
84

GigaFast
Right click on the drive you want to share and click “Properties”
Appendix E
85
GigaFast
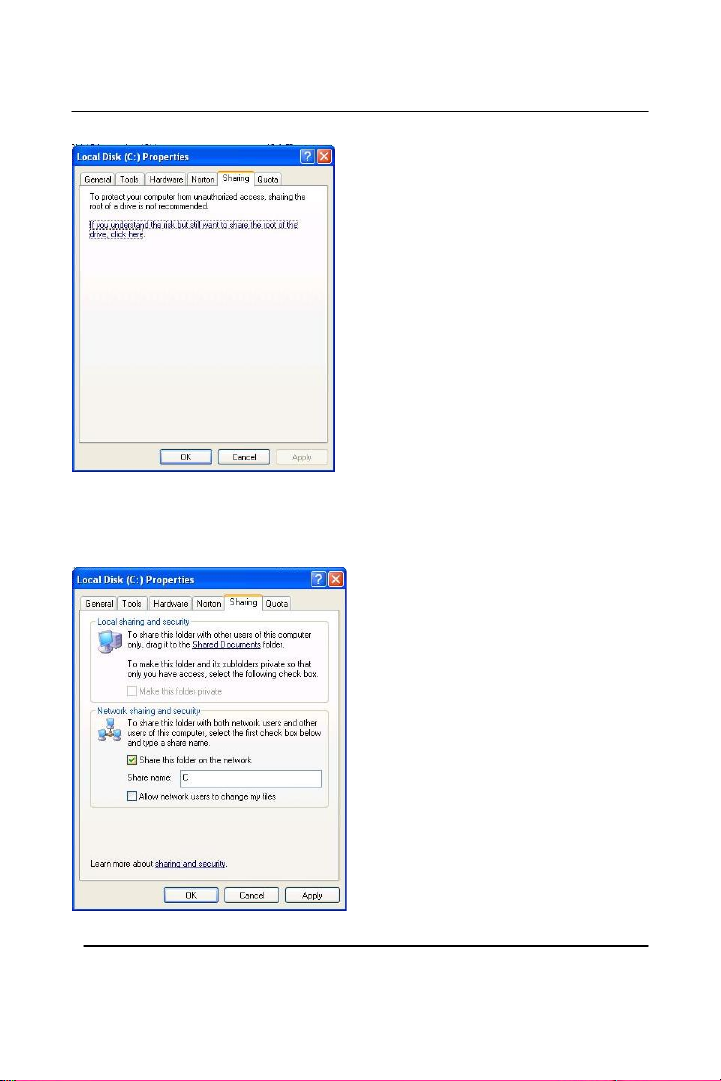
Click on the Sharing tab “If you understand the risk but still want to
share the root of the drive, click here”
Appendix E
86

GigaFast
Click on “Share this folder on the network” and specify what you want
your shared folder to be viewed as.
A hand should appear under the drive you wanted to share . Thi s let s
you know that it is shared on your network
Appendix E
87

GigaFast
Accessing Other Computers Shared Files on Windows 98/SE/ME/
2000/XP
Find the IP Address of the computer you want to access (Look at Check
IP)
Click Start, and then click Run
Appendix E
88

GigaFast
Type “\\” and the IP address of the computer you want to access.
(Format is “XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX”)
All the files that the computer you are trying to access will open in a
new window.
Appendix E
89

GigaFast
An Alternate way to do the same thing is to find the Computer Name of
the computer you are trying to access. And typing “\\______” with the
computer name in the blank
All the files that the computer you are trying to access will open in a
new window.
Appendix E
90
GigaFast
Sharing Printers on Windows 98 / SE / ME / 2000 / XP
Click “Start” and click ‘Printers and Faxes”
Appendix E
91
GigaFast
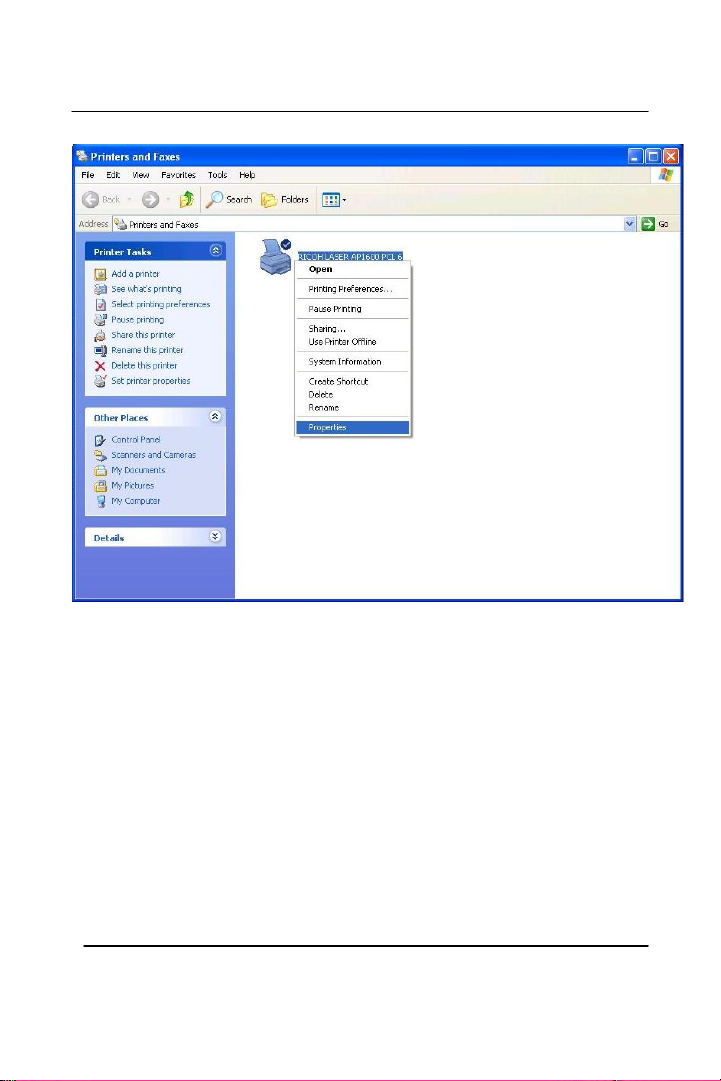
Right click on the printer you want to share and click “Properties”
Appendix E
92

GigaFast
Click the “Sharing” tab, and click “Share the printer” then specify the
name that you want the printer to be seen as on the network. Then click
“OK”
Appendix E
93

GigaFast
A hand should appear under the printer you want to share.
Appendix E
94

GigaFast
Network Printer Installation for Windows 98/ SE / ME/ 2000 /XP
Click Start and click on Printers and Faxes.
Appendix E
95
GigaFast
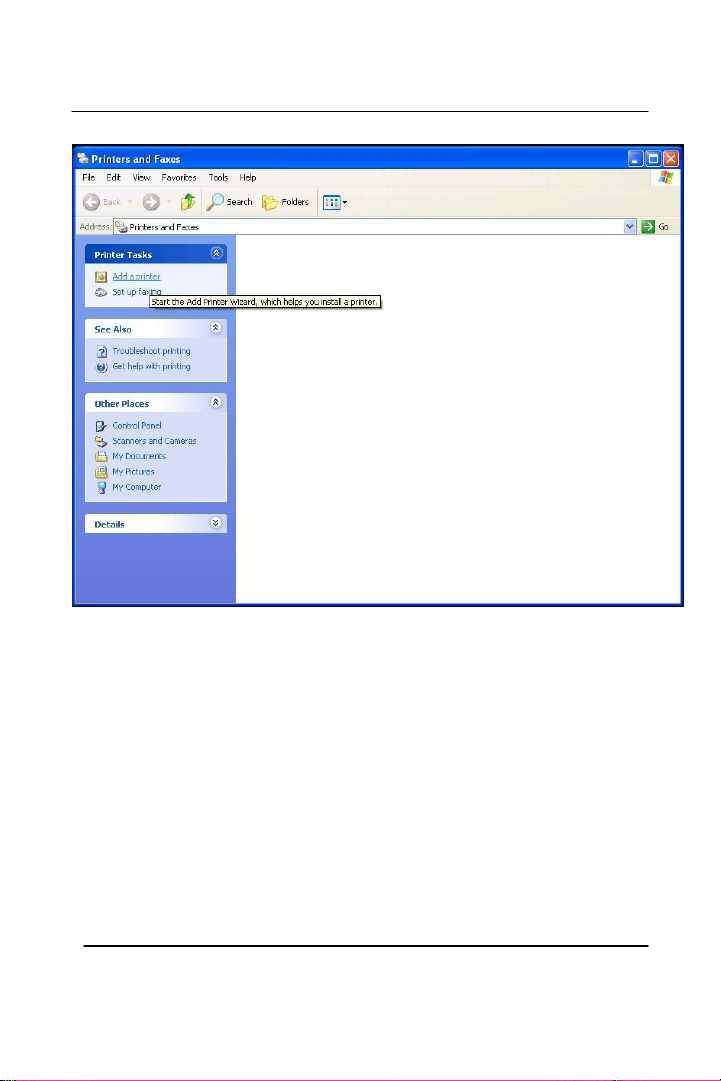
The Printers and Faxes window should open, on the left side there
should be an Add a Printer button under Printer Tasks. Click on Add a
Printer
Appendix E
96

GigaFast
The Add Printer Wizard should appear, click Next to proceed
Appendix E
97
GigaFast
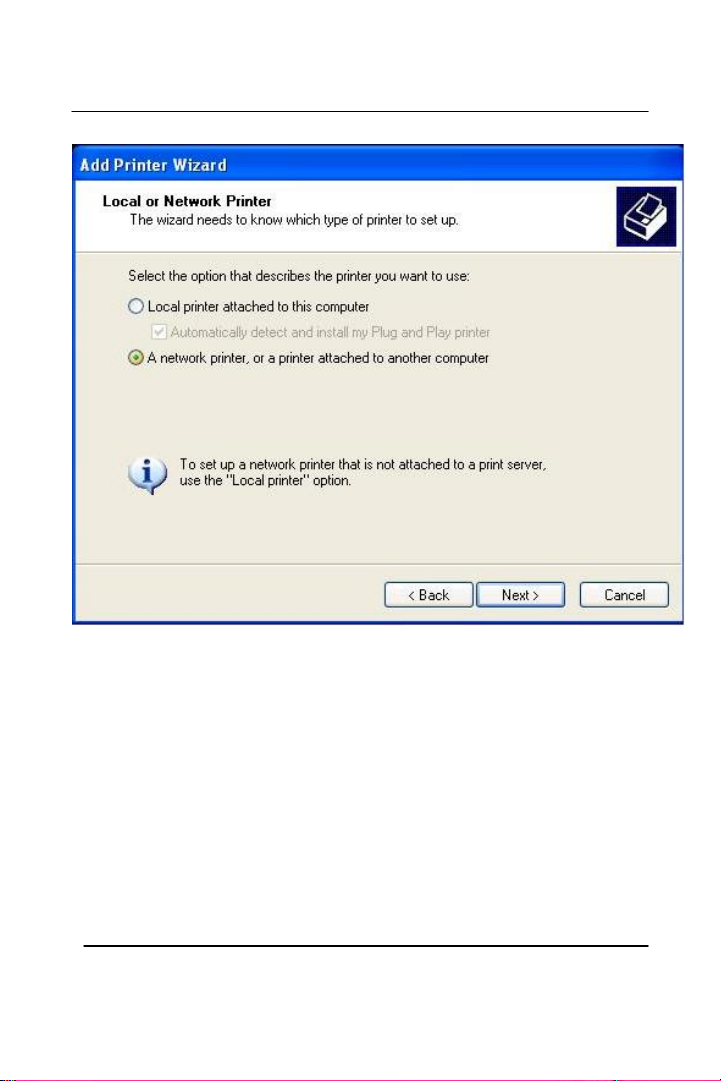
Select “A network printer or a printer attached to another computer”
and click Next
Appendix E
98
GigaFast
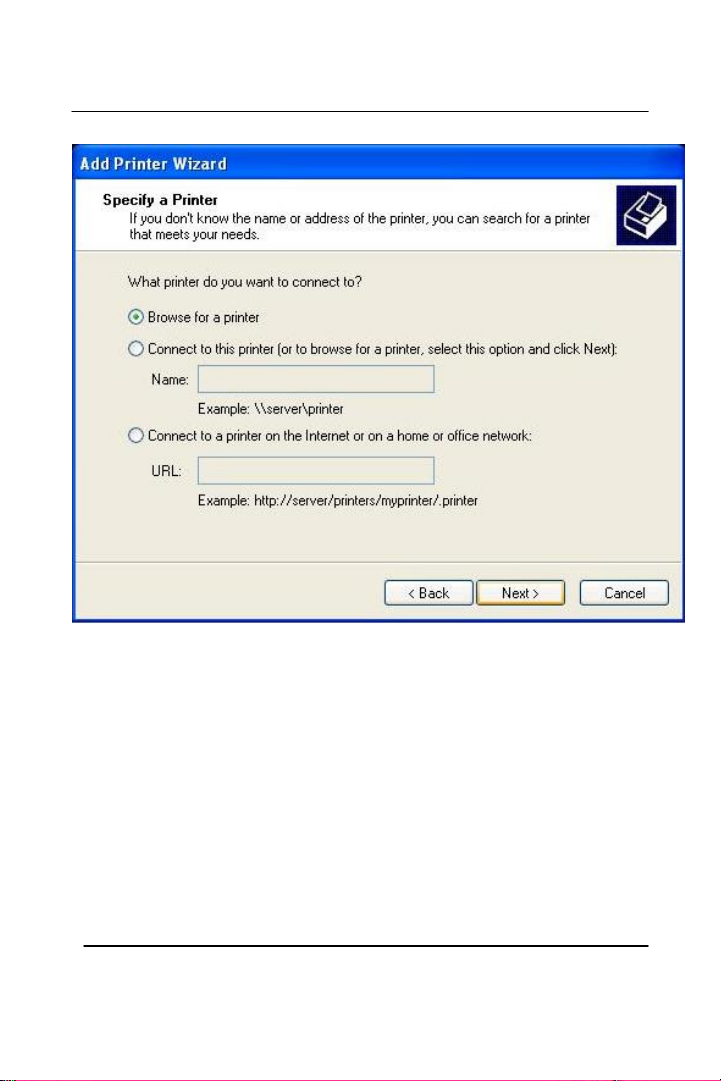
Click “Browse for a printer”, unless you know the computer name (or
IP address) of the printer, and the exact printer name. Or the printer is
at a location that can be connected to through the internet. And click
Next
Appendix E
99
GigaFast
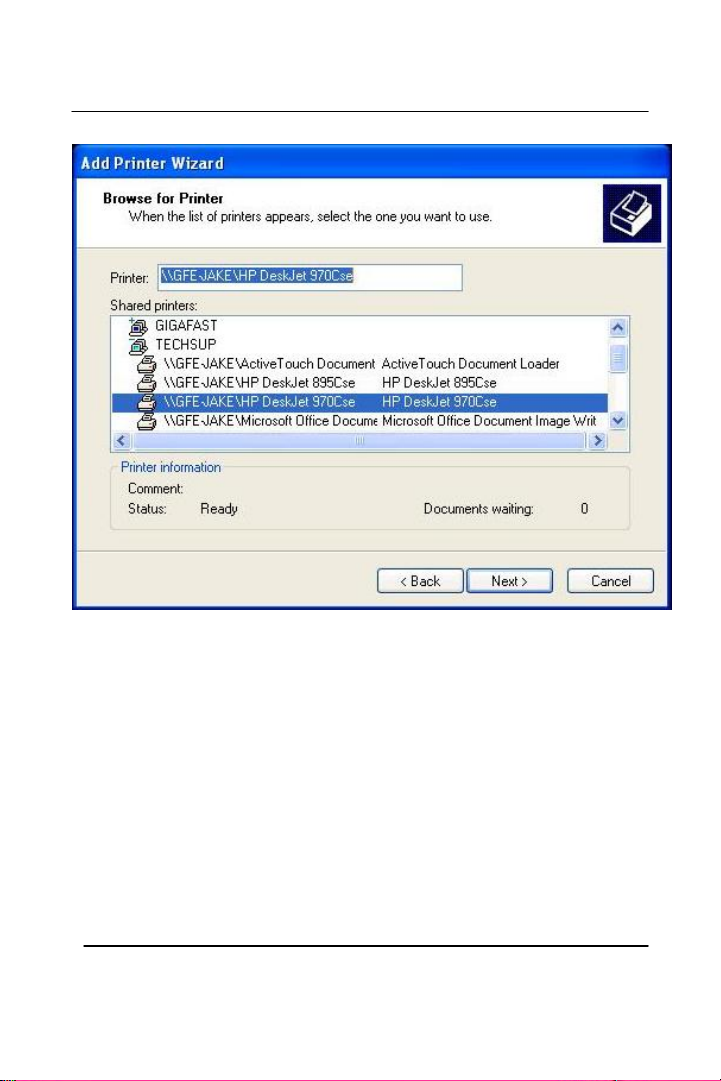
Browse through your network and select the printer that you want to
add, Highlight it, and click Next
Appendix E
100
 Loading...
Loading...