
GigaFast EE 410-R Broadband
Router
User Guide

2

FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
regulations for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of
the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with this
user’s guide, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case the
user will be required to correct the interference at his or her
expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this
product may cause radio interference, in which case the user
may be required to take adequate measures.


TABLE OF CONTENT
About This Guide.................................................................................. 1
Purpose............................................................................................1
Overview of this User’s Guide..........................................................1
Introduction...........................................................................................3
Applications:..................................................................................... 3
Features:..........................................................................................4
Unpacking and Setup...........................................................................5
Unpacking ........................................................................................5
Setup................................................................................................5
Hardware Installation............................................................................ 7
Front Panel.......................................................................................7
Rear Panel ....................................................................................... 8
Hardware connections......................................................................9
Connect the Internet Broadband Router.......................................9
Check the installation ................................................................. 10
PC Network TCP/IP Setting................................................................11
Windows 95/98/ME.........................................................................11
Windows 2000................................................................................13
Windows NT4.0..............................................................................14
Windows XP...................................................................................15
Internet Broadband Router Configuration...........................................17
Login to the Internet Broadband Router ......................................... 17
Quick Setup....................................................................................18
Advance Setup............................................................................... 22
Technical Specifications..................................................................... 37


ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Congratulations on your purchase of this 4-port Broadband
Router. This device integrates 100Mbps Fast Ethernet and
10Mbps Ethernet network capabilities in a highly flexible
desktop package. It provides a complete solution for Internet
surfing and office resources sharing, and it is easy to configure
and operate for even non-technical users.
Purpose
This manual discusses how to install the 4-port Broadband
Router.
Overview of this User’s Guide
Introduction: Describes the Broadband Router and its
features.
Unpacking and Setup: Helps you get started with the basic
installation of the Router.
Identifying External Components: Describes the front panel,
rear panel and LED indicators of the Router.
Connecting your Router: This section tells a user how to
connect the router to the network physically.
Technical Specifications: Lists the technical (general,
physical and environmental, performance and Routers settings)
specifications of the Broadband Router.
1

2

INTRODUCTION
With the explosive growth of the Internet, accessing information
and services at any time, day or night has become a standard
requirement for most people. The era of the standalone PC is
waning. Networking technology is moving out of the exclusive
domain of corporations and into homes with at least two
computers.
Broadband network access is also gaining ground. However,
allowing more than two computers to access the Internet at the
same time means less affordable, higher costs. Thus, there is a
need to share one legal IP address over a single Internet
connection to link the home with the Internet.
The scarcity of IP addresses and using a shared Internet
connection through an Internet sharing device can solve high
network access costs. All linked computers can make full use of
broadband capabilities over such a device.
This device not only comes equipped with a wide range of
features, but also can be installed and configured right out of
the box. This device supports a simple local area network and
Internet access share, offering great cost savings.
The local area network connects up home computers while also
allowing any of the computers to access the Internet, share
resources, or play online games—the basis of the family
computing lifestyle.
Applications:
Broadband Internet access:
Several computers can share one high-speed broadband
connection (LAN and WAN-Internet).
3
Resource sharing:
Share resources such as printers, scanners and other
peripherals.
File sharing:
Exchange data, messages, and distribute files thus making
good use of hard disk space.
Online gaming:
Through the local area network, online gaming and e-commerce
services can be easily setup.
Firewall:
A built-in firewall functions for security and anti-hack system.
Features:
¾ Supports NAT for share 1 IP address to all LAN users.
¾ Supports PPPoE and PPTP protocol for Dial-Up ADSL.
¾ Supports DHCP Server / Client.
¾ Supports UPnP (Universal Plug and Play).
¾ Supports virtual server mapping.
¾ Supports packet filtering.
¾ Simple Firewall protection.
¾ Upgradeable firmware for future function.
¾ Simple setting using Quick Setup.
¾ Easy configuration via WEB Browser.
4

UNPACKING AND SETUP
This chapter provides unpacking and setup information for the
Broadband Router.
Unpacking
Open the box of the Broadband Router and carefully unpack it.
The box should contain the following items:
One 4-port Broadband Router
One external power adapter
This User’s Guide
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your
local reseller for replacement.
Setup
The setup of the Broadband Router can be performed using the
following steps:
The power outlet should be within 1.82 meters (6 feet) of
the Broadband Router.
Visually inspect the DC power jack and make sure that it
is fully secured to the power adapter.
Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation from and
adequate ventilation around the Broadband Router. Do
not place heavy objects on the Broadband Router.
5

HARDWARE INSTALLATION
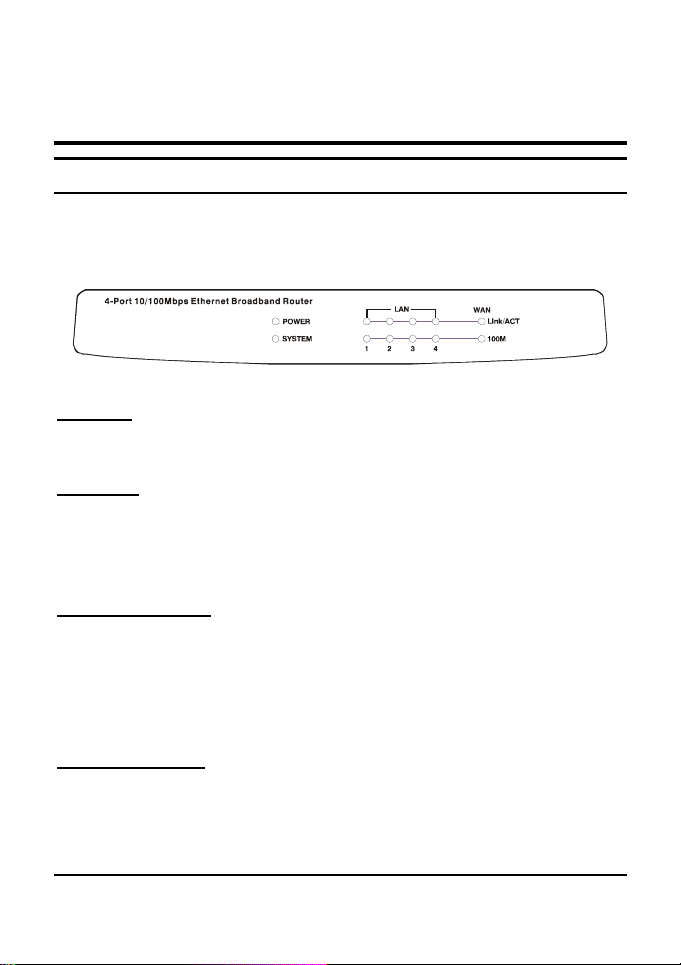
Front Panel
The figure below shows the front panel of the Broadband
Router.
4 Port 10/100Mbps Ethernet Broadband Router Front Panel
POWER
This indicator lights green when the hub is receives power,
otherwise, it is off.
SYSTEM
This indicator blinks green means the Internet Broadband
Router is working successful. Otherwise, this indicator always
on or off means the function of the Internet Broadband Router is
fail.
WAN (Link/ACT)
This indicator lights green when the WAN port is connected to
an xDSL/Cable modem successfully.
This indicator blinks green while the WAN port is transmitting or
receiving data on the xDSL/Cable modem.
LAN (Link/ACT)
From port 1 to port 4 indicator lights green when the LAN port is
connected to a 100Mbps Fast Ethernet station, if the indicator
7

blinks green while transmitting or receiving data on the
100Mbps Fast Ethernet or 10Mbps Ethernet network.
Rear Panel
The figure below shows the rear panel of the Broadband Router.
- +
RESET
II X
WAN
4 Port 10/100Mbps Ethernet Broadband Router Rear Panel
4
WAN
In the four port broadband router, there are two RJ-45 ports for
the WAN, the port can be either connected to “II” which is for
hub/switch or “X” port for crossover, and this will fit the
xDSL/Cable modem’s specification need.
NOTE: Only one port can be plug-in to the WAN port, either the “II” port or “X” port.
LAN (1-4)
These ports are the four RJ-45 10/100Mbps auto-sensing ports
for connecting to either 10Mbps or 100Mbps Ethernet
connections.
RESET
Use a pin-shape item to push to reset this device to factory
default settings. It will be useful too when the manager forgot
the password to login, but the setting will be back to default
setting.
123
8

Hardware connections
C
xDSL Modem
P
O
W
E
R
S
L
Y
A
S
N
T
E
M
1
2
3
4
P
PC
PC
PC
L
i
n
k
A
/
C
T
1
0
0
M
Internet Broadband Router
Connect the Internet Broadband Router
1. Plug in one end of the network cable to the WAN port of the
four ports Internet Broadband Router, either the “X” or “II”
port to be connected, depends of what the broadband
modem specification is using.
2. Plug in one end of the network cable to the WAN port of the
four port Internet Broadband Router, the port need to
connect to hub/switch, using the crossover cable depends
on what the broadband modem specification needs.
3. Plug in the other end of the network cable to the Ethernet
port of the xDSL or Cable modem.
4. Use another network cable to connect to the Ethernet card
on the computer system, the other end of the cable
connects to the LAN port of the Internet Broadband Router.
Since the Internet Broadband Router has four ports, you
can connect up to four computers directly to the unit. There
you do not have to buy a switch to connect these
computers since one Internet Broadband Router functions
both as a connection-sharing unit and as a switch.
9

Check the installation
The control LEDs of the Internet Broadband Router are clearly
visible and the status of the network link can be seen instantly:
1. With the power source on, once the device is connected to
the broadband modem, the Power, CPU, LAN and WAN
port link LEDs of the Internet Broadband Router will light up
indicating a normal status.
2. By using a Straight through Cable on the four port
broadband router, the WAN’s “X” port must connect to MDI
uplink port, and the WAN’s “II” port must connect to MDII
regular port.
3. If the WAN Port’s Link indicator does not light up then
replace the RJ-45 cable that plugged onto WAN’s “X” port
to the “II” port or from the “II” port to the “X” port at the rear
or using a crossover cable to connect on the WAN port to
meet the specification need of the xDSL or Cable modem.
4. While the LAN is link up to the computer system, the LAN
port’s Link/ACT LED will light up.
10

PC NETWORK TCP/IP SETTING
The network TCP/IP settings differ based on the computer’s
operating system (Win95/98/ME/NT/2000) and are as follows.
Windows 95/98/ME
1. Click on the “Network neighborhood” icon found on the
desktop.
2. Click the right mouse button and a context menu will be
show.
3. Select “Properties” to enter the TCP/IP setting screen.
4. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” on the “IP
address” field.
11

5. Select “Disable DNS” in the “DNS” field.
6. Select “None” for the “Gateway address” field.
12

Windows 2000
Double click on the “My computer” icon on the desktop. When
“My computer” window opens, open the “Control panel” and
then open the “Network dialup connection” applet. Double
click on the “Local area network connection” icon. Select
“Properties” to enter the TCP/IP setting window.
1. In the “Local area network status” window, click on
“Properties.”
2. In the “Local area network connection” window, first
select TCP/IP setting and then select “Properties.”
3. Set both “IP address” and “DNS” to Automatic
configuration.
13

Windows NT4.0
Click on the “Start” button located on the lower left corner of the
menu bar.
Select “Settings” and then “Control panel.”
In the “Control panel” window, select “Network” to enter the
TCP/IP setting window.
1. Set “IP address” to “Obtain an IP address automatically.”
2. Set “DNS” to “Disable DNS.”
14

Windows XP
Point the cursor and click the right button on the “My Network
Place” icon.
Select “properties” to enter the TCP/IP setting window.
1. Set “IP address” to “Obtain an IP address
automatically.”
2. Set “DNS” to “Obtain DNS server address
automatically.”
15


INTERNET BROADBAND ROUTER CONFIGURATION
First make sure that the network connections are functioning
normally.
This Internet Broadband Router can be configured using
Internet Explorer 4.0 or newer web browser versions.
Login to the Internet Broadband Router
Before you configure this device, note that when the Broadband
Router is configured through an Ethernet connection, make
sure the host PC must be set on the IP sub network that can
be accessed by the xDSL/Cable modem. For example, when
the default network address of the xDSL/Cable modem Ethernet
interface is 192.168.1.x, then the host PC should be set at
192.168.1.xxx (where xxx is a number between 2 and 254), and
the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
1. Open Internet Explorer 4.0 or above Internet browser.
2. Enter IP address
address setting) to the URL web address location.
3. When the following dialog box appears, remain blank (first
login) or enter the password and press Login to enter the
main configuration window.
http://192.168.1.1 (the factory-default IP
Note: If needed to set a password, then refer to the Administrator Setting.
17

4. After entering the password, the main web page comes up,
there are two choices for setting, Quick Setup or Advanced
Setup, it is recommended that the beginner to use the
Quick Setup, it will lead you step by step to configure the
Broadband Router.
Quick Setup
In the main web page, select “Quick Setup” to specify the Time
Zone and the WAN connection type: Cable modem (DHCP),
Fixed IP, or Dial-up xDSL (PPPoE).
1-1 Time Zone
To set the time zone in order to synchronize the system clock in
the global through the SNTP Server.
18

1-2 WAN Connection Type
To select which the WAN connection type will be connected to,
point the cursor to the Cable modem (DHCP), Fixed IP, or Dialup xDSL (PPPoE) to process.
1-2-1 Cable modem (DHCP)
To connect a cable modem with the Broadband Router, check
the cable modem with the related user’s guide, then the Cable
modem will automatically configure itself; the Broadband Router
is configured to automatically assign addresses to each PC.
Fill up the MAC Address of the network adapter when the DNS
server need a certain address with the network adapter, or
press the “Clone MAC Address” button to get the manager’s PC
MAC Address.
19

1-2-2 Fixed IP
If the Internet Service Providers assign a fixed IP address,
choose this option and enter the assigned IP address, subnet
mask, gateway IP and DNS IP addresses for your Broadband
Router.
1-2-3 Dial-up xDSL (PPPoE)
If connected to the Internet using a Dial-up xDSL (PPPoE)
Modem, the ISP will provide a Password and User Name, and
then the ISP uses PPPoE. Choose this option and enter the
required information, if the ISP provided a Service Name, enter
it in the column of the Service Name field, otherwise, leave it
blank.
The MTU feature specifies the largest packet size permitted for
network transmission. Enter the value desired, for most DSL
users, it is recommended to use 1492. By default, MTU is set at
1492.
The Maximum Idle Time
feature can control the
connection time while user’s
need to save the cost of
connection fee from ISP
provider (default time=0,
always connect). Click on
the Connect-on-demand
20

button to dial up to the ISP when only on demand, while there is
a need of connecting to the ISP automatically.
1-2-4 PPTP
If connected to the Internet
using a (PPTP) xDSL
Modem, enter the PPTP
Account Name, PPTP
Password, Host Name,
Service IP Address, Your IP
Address, Your Subnet Mask
required by your ISP in the
appropriate fields. If your
ISP has provided you with a
Connection ID, enter it in the Connection ID field, otherwise,
leave it zeros.
The MTU feature specifies the largest packet size permitted for
network transmission. Enter the value desired, for most DSL
users, it is recommended to use 1460. By default, MTU is set at
1460
The Maximum Idle Time feature can control the connection time
while user’s need to save the cost of connection fee from ISP
provider (default time=0, always connect). Click on the
Connect-on-demand button to dial up to the ISP when only on
demand, while there is a need of connecting to the ISP
automatically.
1-3 DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the way that Internet
domain names are
21

located and translated into Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
If your ISP provided at least one DNS Server IP Address, type
that IP Address in the Primary DNS address fields. You can
type up to another DNS Server IP Addresses. The Router will
utilize these for quicker access to functioning DNS Servers.
1-4 Status
When finish configuring the Quick
Setup, the Status screen will list up the
connection status for the Broadband
Routers' WAN/LAN interfaces,
firmware and hardware version
numbers, and the number of
connected clients to the network.
Advance Setup
The Broadband Router supports advanced functions like
System setting WAN setting, LAN setting, NAT Setting and
Firewall setting.
22

2-1 System
This page includes all the basic configuration tools for the
Broadband Router. Point the selections in the left side of the
menu screen.
2-1-1 System Time
Connecting to a Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server
allows the Broadband Router to synchronize the system clock
to the global Internet
through the SNTP Server.
The synchronized clock in
the Broadband Router is
used to record the system
log and control client filtering.
2-1-2 Administrator Settings
z Password Settings
Set a password to restrict management access to the
Broadband Router.
z Remote Management from Internet
23

To manage the Broadband Router from a remote location
(outside of the local network through WAN port), it must specify
the IP address of the remote PC, otherwise, leave the IP
address 0.0.0.0, means all legal IP address can access the
device.
2-1-3 Firmware Upgrade
You can enhance the phone by upgrading a new firmware for
the Broadband Router to improve functionality and performance.
Enter the path and name of
the upgrade file then click
the APPLY button below.
You will be prompted to
confirm the upgrade.
While updating the firmware, please wait after pressing the
APPLY button, and follow the instruction on the screen, the
System Light on the front panel will start blinking when the
firmware upgraded successfully.
24

2-1-4 Configuration Tools
Use the "Backup Settings" tool to save the Broadband Router's
current configuration to a file named "config.bin" on your PC.
You can then use the "Restore Settings" tool to restore the
saved configuration of the Broadband Router that you set
before. Alternately, you can use the "Restore to Factory
Defaults" tool to force the Broadband Router to perform reset
and restore the original factory settings.
z Restore Factory Default
To restore the factory default settings of the Broadband
Router, click on the “Restore” button.
z Backup Settings
Press the “Backup Settings” button to save the current
setting in a filed “config.bin” or given filename.
z Restore Settings
To restore the backup file to the Broadband Router, enter
the path and filename on the
restore settings.
2-1-5 Status
Use the Status screen to see the
connection status for the Broadband
Routers' WAN/LAN interfaces,
firmware and hardware version
numbers, and the number of
connected clients to the network.
25

2-1-6 System Log
View any attempts that have been made to gain access to the
network.
2-1-7 Reset
In the event that the Broadband Router stops responding
correctly or in some way stops functioning, perform the reset
function. The settings will not be changed. To perform the reset,
click on the "Reset" button. The reset will be complete when the
system light starts blinking.
26

2-2 WAN
The Broadband Router can be connected to the service
provider in any of the following ways: Dynamic IP Address,
Static IP Address, PPPoE and PPTP.
2-2-1 Dynamic IP
The Host Name is optional, but may be required by some
Service Providers. The default MAC address is set to the
WAN's physical interface on the Broadband Router. If the
Service Provider requires the host name, using the "Clone MAC
Address" button to copy the MAC address of the Network
Interface Card installed in the selected PC and replaces the
WAN MAC address with this MAC address.
The road runner management is optional. If the ISP needs to
run the road runner management (sometimes called Big Pond),
enable it.
27

2-2-2 Static IP
If the Service Provider has assigned a fixed IP address, enter
the assigned IP address subnet mask and gateway address
provided. Click “yes” if using two or more IP addresses.
2-2-3 Dial-up xDSL (PPPoE)
If connected to the Internet using a Dial-up xDSL (PPPoE)
Modem, the ISP will provide a Password and User Name, and
then the ISP uses PPPoE. Choose this option and enter the
required information, if the ISP provided a Service Name, enter
it in the column of the Service Name field, otherwise, leave it
blank.
The MTU feature specifies the largest packet size permitted for
network transmission. Enter the value desired, for most DSL
users, it is recommended to use 1492. By default, MTU is set at
1492.
The Maximum Idle Time feature can control the connection time
while user’s need to save the cost of connection fee from ISP
provider (default time=0, always connect). Click on the
Connect-on-demand button to dial up to the ISP when only on
demand, while there is a need of connecting to the ISP
automatically.
28

2-2-4 PPTP
If connected to the Internet
using a (PPTP) xDSL
Modem, enter the PPTP
Account Name, PPTP
Password, Host Name,
Service IP Address, Your IP
Address, Your Subnet Mask
required by your ISP in the
appropriate fields. If your
ISP has provided you with a
Connection ID, enter it in the Connection ID field, otherwise,
leave it zero.
The MTU feature specifies the largest packet size permitted for
network transmission. Enter the value desired, for most DSL
users, it is recommended to use 1460. By default, MTU is set at
1460
The Maximum Idle Time feature can control the connection time
while user’s need to save the cost of connection fee from ISP
provider (default time=0, always connect). Click on the
Connect-on-demand button to dial up to the ISP when only on
demand, while there is a need of connecting to the ISP
automatically.
29

2-2-5 DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the way that Internet
domain names are located and translated into Internet Protocol
(IP) addresses.
If your ISP provided at least one DNS Server IP Address, type
that IP Address in the Primary DNS address fields. You can
type up to another DNS Server IP Addresses. The Router will
utilize these for quicker access to functioning DNS Servers.
2-3 LAN
This section is to set the LAN’s IP Address and DHCP Service.
2-3-1 LAN Settings
The default value is 192.168.1.1 for the IP address and
255.255.255.0 for the Subnet Mask. And you can also change
the value for your
needs.
To enable the DHCP
server for dynamic IP
address allocation to
the clients PCs, click
the “Enable”. The
client can get the IP Addresses from a range from IP Pool
Starting Address to IP Pool Ending Address; also, you can
change the IP Pool range value.
The Lease Time is the amount of time a network user will be
allowed connection to the Router with their current dynamic IP
30

address. Enter the amount of time, in hours, days or weeks,
which the user will be “leased” this dynamic IP address.
You can enter your local domain name in the Local Domain
Name fields.
2-3-2 DHCP Client List
The DHCP client list allows you to see which clients are
connected to the Barricade via IP address, host name, and
MAC address.
2-4 NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows multiple users at the
local site to access the Internet through a single public IP
address. NAT can also prevent hacker attacks by mapping local
addresses to public addresses for key services such as the
Web or FTP.
2-4-1 Special Application
Some applications require multiple connections, such as
Internet gaming, video conferencing, Internet telephony and
others. These applications cannot work when Network Address
Translation (NAT) is enabled. When users send this type of
request to your network via the Internet, the Router will forward
those requests to the appropriate PC. If you need to run
applications that require multiple connections, specify the port
normally associated with an application in the "Trigger Port"
field, select the protocol type as TCP or UDP, then enter the
public ports associated with the trigger port to open them for
inbound traffic.
31

z TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A method (protocol)
used along with the Internet Protocol (Internet Protocol) to
send data in the form of message units between
computers over the Internet. While IP takes care of
handling the actual delivery of the data, TCP takes care of
keeping track of the individual units of data (called packets)
that a message is divided into for efficient routing through
the Internet.
z UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - A communications
method (protocol) that offers a limited amount of service
when messages are exchanged between computers in a
network that uses the Internet Protocol (IP). UDP is an
alternative to the TCP and, together with IP, is sometimes
referred to as UDP/IP. Like the Transmission Control
Protocol, UDP uses the Internet Protocol to actually get a
data unit (called a datagram) from one computer to
another. Unlike TCP, however, UDP does not provide the
service of dividing a message into packets (datagram’s)
and reassembling it at the other end. Specifically, UDP
doesn't provide sequencing of the packets that the data
arrives in. This means that the application program that
uses UDP must be able to make sure that the entire
message has arrived and is in the right order. Network
applications that want to save processing time because
they have very small data units to exchange (and
therefore very little message reassembling to do) may
prefer UDP to TCP.
32

Example:
ID Trigger Port
1 28800 UDP 2300-2400, 47624 UDP MSN Game Zone
2 28800 UDP 2300-2400, 47624 TCP MSN Game Zone
3 6112 UDP 6112 UDP Battle.net
Trigger
Type
Public Port
Public
Type
Comment
2-4-2 Virtual Server
Configure the Broadband Router as a virtual server to allow the
Router to watch outgoing data for specific port numbers. The IP
address of the computer that sends the matching data is
remembered by the Router, so that when the requested data
returns through the Router, the data is pulled back to the proper
computer by way of IP address and port mapping rules such as
the Web or FTP at the local site via public IP addresses can be
automatically redirected to local servers configured with private
IP addresses. In other words, depending on the requested
service (TCP/UDP port number), the Broadband Router
redirects the external service request to the appropriate server.
33

Example:
ID Server IP Mapping Port Type Comment
1 192.168.2.20 80 TCP Web Server
2 192.168.2.12 20 TCP FTP Server
3 192.168.2.12 21 TCP FTP Server
4 192.168.2.28 23 TCP Telnet Server
2-5 Firewall
The Broadband Router provides extensive firewall protection by
restricting connection parameters to limit the risk of hacker
attack, and defending against a wide array of common hacker
attacks.
The Broadband Router provides packet filtering rules by
restricting service ports, IP address or MAC address. However,
for applications those require unrestricted access to the Internet;
configure a specific client/server as a demilitarized zone (DMZ).
2-5-1 Block WAN Ping
When the "Block WAN Ping" activated, it is causing the public
WAN IP address on the Broadband Router not to respond to
ping commands. Pinging public WAN IP addresses is a
34

common method used by hackers to test whether the WAN IP
address is valid and supports a network.
2-5-2 Client Filtering
To block a certain client PCs accessing the Internet based on
time.
You can filter Internet access for local clients based on IP
addresses, application types, (i.e., HTTP port), and time of day.
For example, this screen shows that clients in the address
range 192.168.2.50-99 are permanently restricted from using
FTP (Port 21), while clients in the address range
192.168.2.110-119 are blocked from browsing the Internet (port
80) from Monday to Friday and from 0:00AM to 11:00 PM.
Example:
2-5-3 MAC Control
You can block certain client PCs accessing the Internet based
on MAC addresses.
35

2-5-4 DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
If a local client PC cannot run an Internet application properly
from behind the NAT firewall, open the client up to unrestricted
two-way Internet access by defining a virtual DMZ Host.
36

TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
General
Standards IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
ANSI/IEEE 802.3 Auto-negotiation
Protocol CSMA/CD
Data Transfer
Rate
Topology Star
Network
Cables
Number of
Ports
DC inputs 4 port Broadband Router: DC 7.5V 1A
Power
Consumption
Temperature
Humidity Operating: 10% ~ 90%, Storage: 5% ~ 90%
Dimensions 171 x 100 x 33 mm (W x H x D)
EMI: FCC Class B, CE Mark B, VCCI-II
Ethernet: 10Mbps (half duplex), 20Mbps (full-duplex)
Fast Ethernet: 100Mbps (half duplex), 200Mbps (full- duplex)
10BASET: 2-pair UTP Cat. 3,4,5 (100 m), EIA/TIA- 568 100-ohm
STP (100 m)
100BASE-TX: 2-pair UTP Cat. 5 (100 m), EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm STP
(100 m)
LAN: 4 x 10/100Mbps auto-negotiation
4 port Broadband Router: 1 x 10/100Mbps “II” port connect to the
hub/switch or 1 x 10/100Mbps “X” port connect to the LAN Card
(either “II” or “X” can be used)
Physical and Environmental
4 port Broadband Router: 3W (Max)
Operating: 0° ~ 40° C, Storage: -10° ~ 70° C
37
 Loading...
Loading...