GIGABYTE GA-8I945P-G, GA-8I945P-G-RH, GA-8I945PL-G Owner's Manual

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller
USER’S MANUAL
12ME-IT8212-006R

Copyright
Copyright by GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. (“GBT”) No part of this manual
may be reproduced or transmitted in any from without the expressed, written
permission of GBT.
Trademarks
Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Notice
Due to rapid change in technology, some of the specifications might be out of date
before publication of this booklet.
The author assumes no responsibility for any errors or omissions which may appear
in this document nor does it make a commitment to update the information contained
herein.

Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................................4
Features ...........................................................................................................5
What is the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller.......................................6
Quick Start .................................................................................................................7
Create Your Disk Array ..................................................................................... 9
Setup Utility.............................................................................................................. 15
Using the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller Setup Utility....................15
Auto Configuration..........................................................................................17
Define RAID....................................................................................................22
Delete RAID....................................................................................................28
Rebuild RAID..................................................................................................31
RAID Card Configuration................................................................................ 36
Driver Installation .....................................................................................................38
Windows XP ................................................................................................... 39
Windows 2000................................................................................................45
Windows SE/ME............................................................................................. 53
Windows NT ................................................................................................... 61
Linux............................................................................................................... 69
Install the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller on Red Hat 7.3........................69
Application ...............................................................................................................72
Installation ......................................................................................................72
Functions Description.....................................................................................75
How to….........................................................................................................86
Q&A .........................................................................................................................88

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
Introduction
This manual is mainly to help users setup the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID
Controller and solve problems when they use it.
If it is your first time to use the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller and you are
about to install it, please refer to the “Quick Start” section on page 7. After finishing
installing it, you can get the advantages of enhancing the performance and raising
the system’s reliability.
When you face any difficulties and find anything you don’t understand while using the
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller, please refer to the “Q&A” section on page
88. In this section, you can refer to the problems users may face and find the correct
solutions. You can follow its instructions to solve your problems and then you will get
satisfactory results.
4

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
Features
Compatible with the ATA133 specification and supports two IDE channels with
4 drives.
Supports ANSI ATA proposal PIO modes 0,1,2,3,4 with flow control, DMA
Modes 0,1,2,3,4,5,6.
512 bytes FIFO for auto transfer per IDE channel to get a high performance
Supports the RAID 0/1/0+1 function
Supports the JBOD function
Supports the Scatter/Gather function for the DMA/UDMA function
Includes one embedded CPU and firmware on system to handle the RAID
function. It can reduce the driver’s loading of system CPU and improve the
system’s ability.
Low CPU utilization based on a local processor architecture
Compatible with PCI Local bus specification v2.2. Users can easily install our
systems to your PCs.
Supports PCI power Management v1.0 to reduce power consumption.
Supports the drivers for windows 98SE/Me/XP, Windows NT 4.0, Windows
2000 and Linux v2,4,1,0
5

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
What is the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller
This GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller is an excellent product resulting from
Soc concept. It includes one RAID Chip combining CPU, firmware, advanced PCI
controller and IDE controller. Its architecture can provide users a RAID system with
low CPU utilization. When a PC is in high CPU operation or PCI traffic, users won’t
have any penalties for installing RAID system. This is because this system embeds a
local CPU to deal with the RAID function and it’s unnecessary to share CPU’s
performance. It is entirely different from the traditional software RAID system.
Similarly, it also provides users more system stability. It provides users high speed
and integration and low price PC RAID system. Additionally, it also provides PCI
33MHz interface and is compatible with PCI spec. v2.2. It can be easily installed into
the PC system nowadays. Besides, we provide each OS a corresponding driver so
that users don’t have to worry that your systems and the IDE RAID system have any
compatibility issue.
This GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller can support IDE drivers ranging from
the lowest speed of PIO mode drive to the highest speed of ATA/133 drive. Thus,
users can use this characteristic to combine RAID system without any limitations.
Users can use ATA/133 drive and RAID function to achieve the best performance and
get the merit of system’s stability.
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller can support the RAID0 (striping),
RAID1 (mirroring), RAID0+1 (striping and mirroring) or JBOD (spanning) mode.
When a system is programmed to the RAID0 mode, it can read or write two drivers at
the same time to enhance the performance. When a system is programmed to the
RAID1 mode, two drivers have the same data and it will prevent data from being
damaged. Once data is damaged, the system will start the rebuild function
automatically and save data back to another new drive. Similarly, this system can use
6
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
this data-copying characteristic to let two drivers transmit at the same time and
balance the performance to raise throughput. The RAID0+1 mode uses four drivers
to get the merits of RAID0 and RAID1. As for the JBOD mode, it combines more than
two drives into a drive with a large capacity. This mode does not have the RAID
function and its merit.
Quick Start
This section leads you to quickly establish your RAID system with default settings.
The default settings can meet most people’s requirements. If you need more
advanced optimal, please refer to Setup Utility on page 15 to achieve your goal.
Warning: In order to prevent any data loss resulting from
inappropriate operation, please backup data before you start to
!
install your system.
7

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
The hard drives which are required for the installation
The hard drives, which are connected on the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller,
can support Ultra ATA/ 133, Ultra ATA/ 100, Ultra ATA/ 66, Ultra ATA/33, EIDE or Fast
ATA-2 drives. Nevertheless, for the best performance, it is suggested that you had
better use the hard drives of the same type and capacity to establish your own RAID
system. After getting ready for the hard drives, you can follow the procedures below
to install the system.
1. Exactly set up every hard drive’s master and slave setting to assure that the
hard drives can surely action and unnecessarily incorrect action of data access
won’t occur.
2. Exactly insert the hard drive’s cables into the connectors on the hard drive and
check if it’s really firmly inserted.
3. Insert every power cable connector into the corresponding hard drive and
check if it’s firmly inserted in a correct direction.
Warning: Because this system can support the hard drives of
Ultra ATA/133, it is suggested that you can use the 80-wire,
!
and efficiency. If the cable is damaged after a period of time, it is also
suggested to buy the cable of the same specification.
40-pin cable to connect the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID
Controller and hard drives in order to assure the system’s ability
8
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
Create Your Disk Array
You can create your own array using the onboard BIOS utility of the
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller with the attached hard drives. Please follow
the steps below to setup your disk array.
Warning: Please backup data in your hard drives to prevent data
!
1. Boot your system
Please attach your hard drives to the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller,
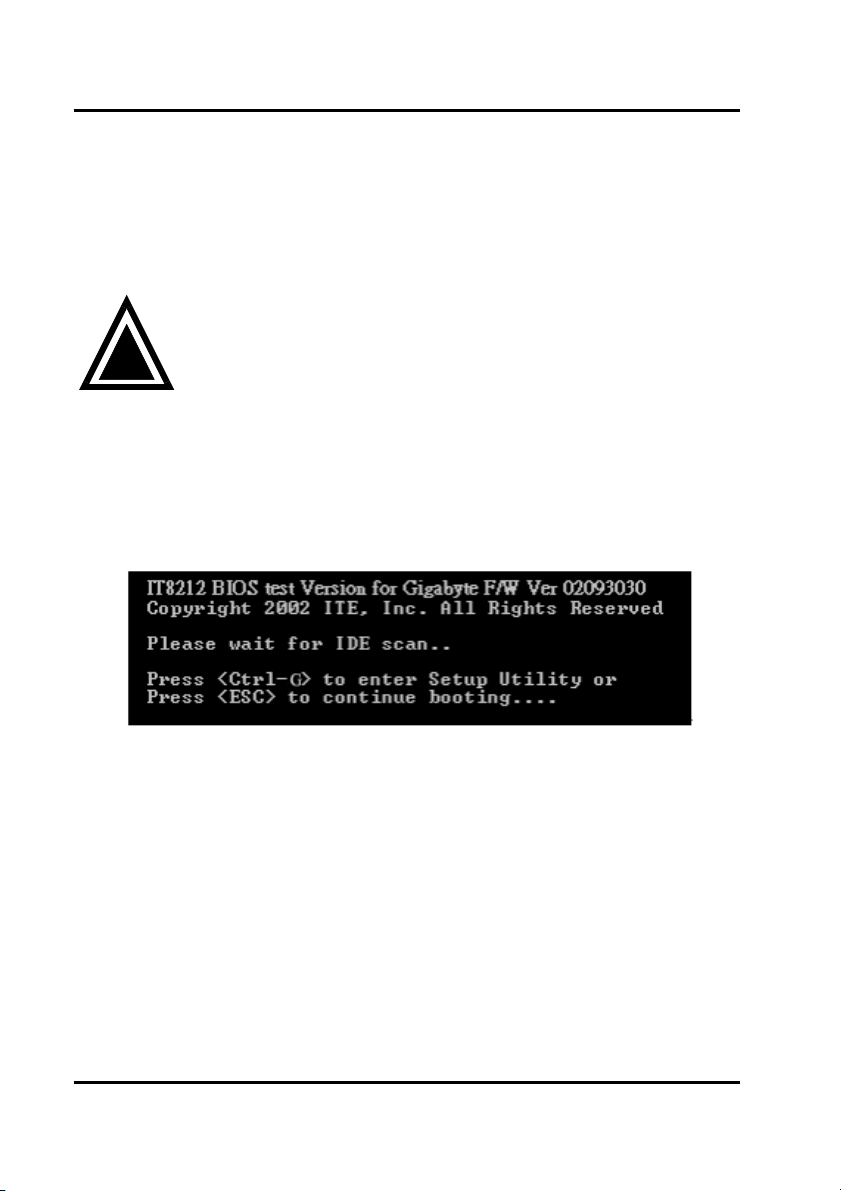
boot your system and then you will see the following message shown by the
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller onboard BIOS on the screen.
damage resulting from the unfamiliarity with the operation.
9
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
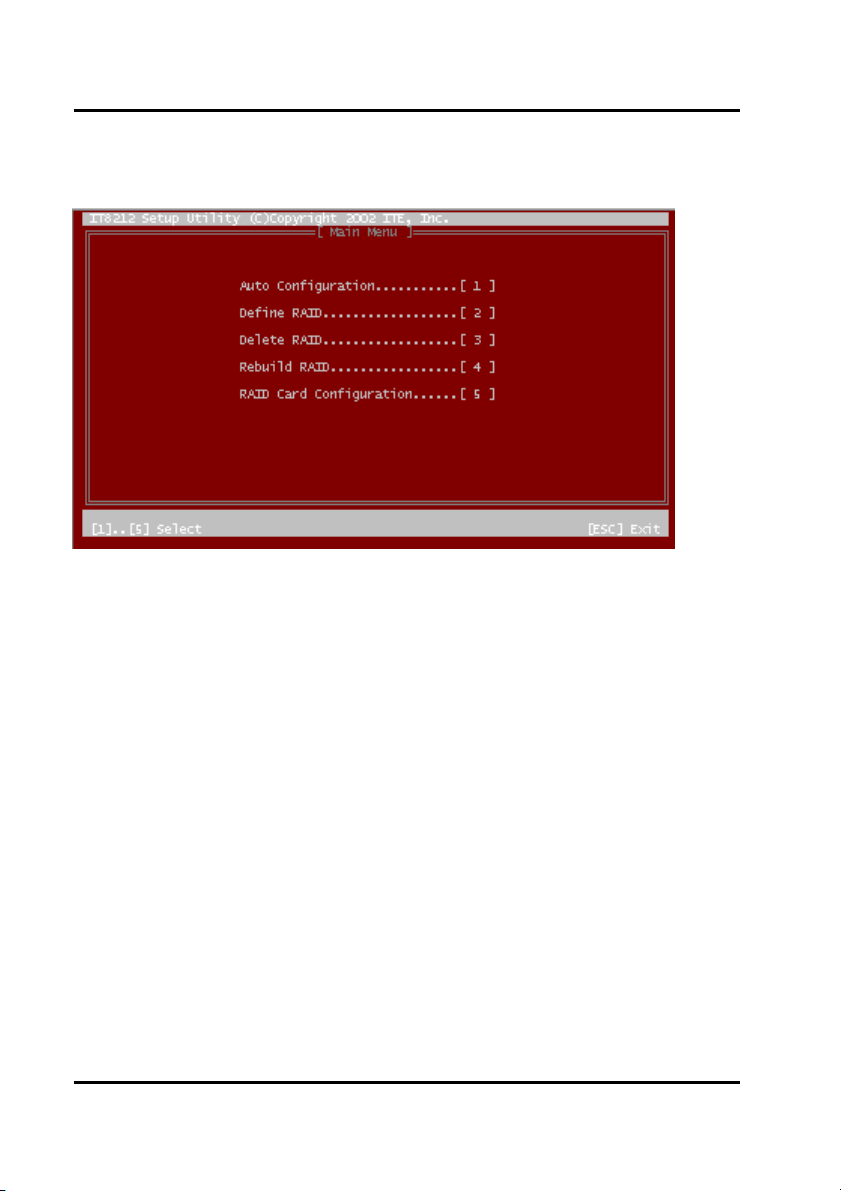
Please press “Ctrl-G” keys to enter the BIOS utility Main Menu. The screen below will
be shown.
10
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
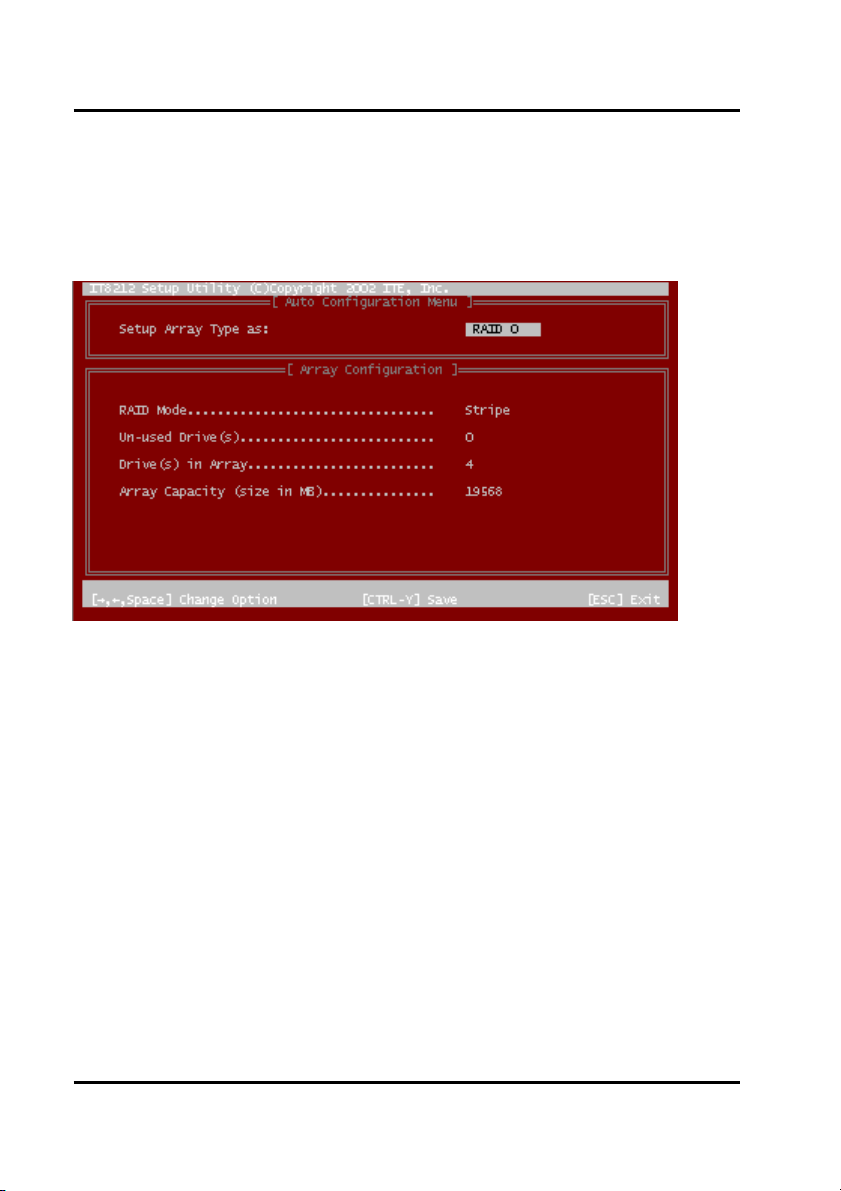
Please click ”1” to enter the Auto Configuration window. It will guide you to set an
array and this is the simplest and fastest way to create your first array. Under the
Setup Array Type as option, you can use arrow keys → and ← and the “space”
bar key to change your option to setup your array type.
11
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
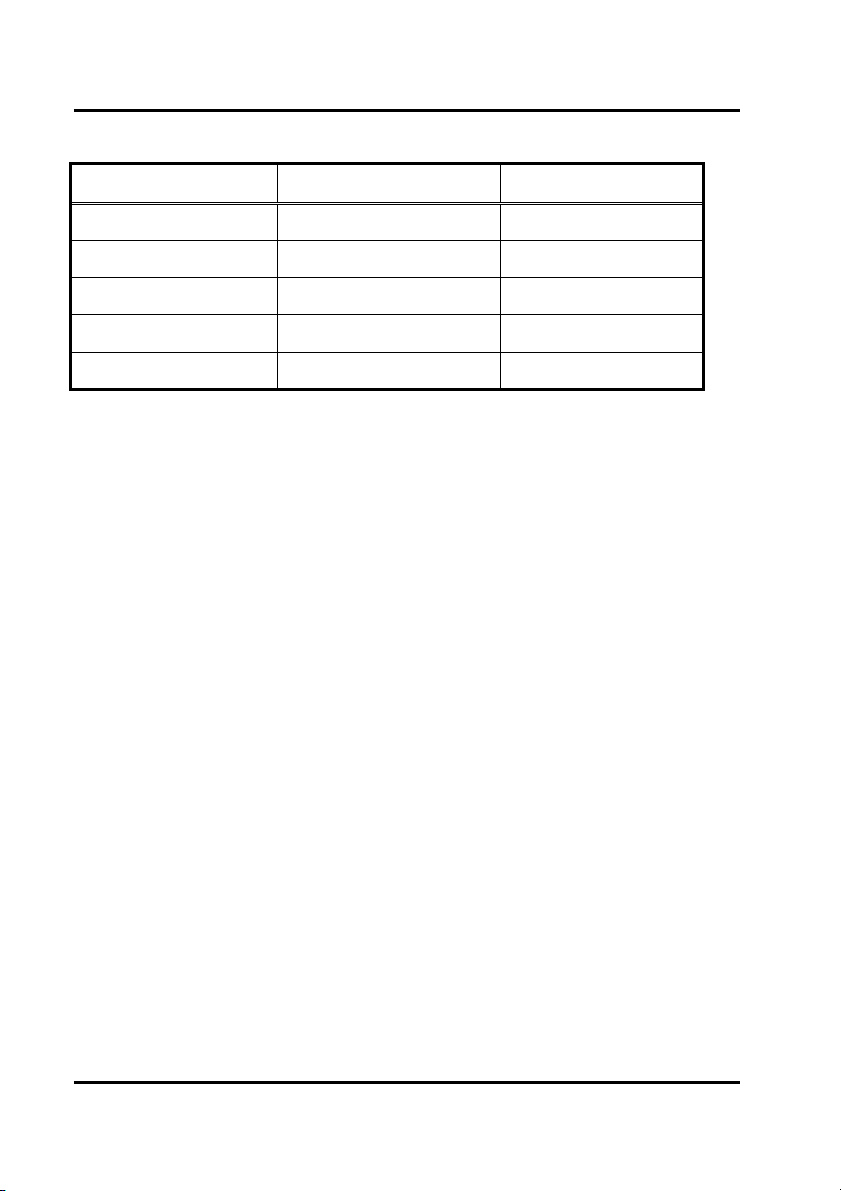
Totally, there are five configurations supported:
RAID level/Type Configurations Number of disks needed
RAID 0 Disk Striping 2 or 3 or 4
RAID 1 Disk Mirroring 2
RAID 0+1 Disk Striping + Mirroring 4
JBOD Disk Concatenation 2 or 3 or 4
Normal None 1 or 2 or 3 or 4
Setup Array for RAID 0:
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows you to use two, three or four
hard drives to set a RAID 0 (stripe) array. All the hard drives attached on the
controller will be set as array 0. When you create a striped array, files are broken into
64k (stripe size) and stripes are sent to each disk in the array. Selecting RAID 0 can
increase data transfer rate and allow the best overall performance characteristics
because of giving up redundancy.
12

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
Setup Array for RAID 1:
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows two drives to be setup as a RAID
1 (mirror) array or four drives as two arrays. The first mirrored array will be set as
array 0 and the second as array 1. RAID 1 is implemented as mirroring; a drive has
its data duplicated on the other different drive. Selecting RAID 1 can enhance read
performance and allow fault tolerance. A RAID 1 array can thoroughly backup your
files to prevent data loss.
Warning: Two hard drives that form a RAID 1 array have to be
!
attached as the same master or slave hard disks.
Setup Array for RAID 0+1:
A RAID 0+1 (mirror and stripe) array has to be formed by four hard drives. RAID 0+1
is implemented as a mirrored array whose segments are RAID 0 arrays so RAID 0+1
also has fault-tolerance capacity as RAID 1. It not only enhances hard disk access
performance but also backups data to prevent data loss. The formed array is
automatically set as array 0.
Setup Array for JBOD:
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows you to use two, three or four
hard drives to form a JBOD (Just a Bunch Of Disks) array as array 0. Although JBOD
doesn’t offer other RAID functionality, it makes the hard disks appear to be a single
one by combining the drives into one larger logical one without any capacity loss.
13
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
Setup Array for Normal:
You can use the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller as a normal IDE controller.
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows you to use one, two, three or four
hard drives. All the hard drives attached on the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID
Controller are left to act as independent drive volumes.
Please follow the procedures below to set an array:
Use the “space” bar key to select a RAID type.
Press “Ctrl-Y” keys to save and create an array. If you select RAID 0, 1, 0+1 or
JBOD, the boot sector of the new created array will be erased. If you select
Normal, the boot sector will be remained.
Warning: If you prefer to keep data in your hard drives, please
follow the procedures in Define RAID section on page 22 to
!
setup your arrays manually.
Click the “Esc” key to go back to the Main Menu on page 10.
Click the “Esc” key to quit BIOS and boot.
You need to FDISK and format your new array. The new array will be regarded
as a new hard drive by the system.
14
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
Setup Utility
Using the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller Setup
Utility
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller Setup Utility provides functions to
create, delete and rebuild an array. It also provides the information of each hard drive
and the configuration of the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller. Please attach
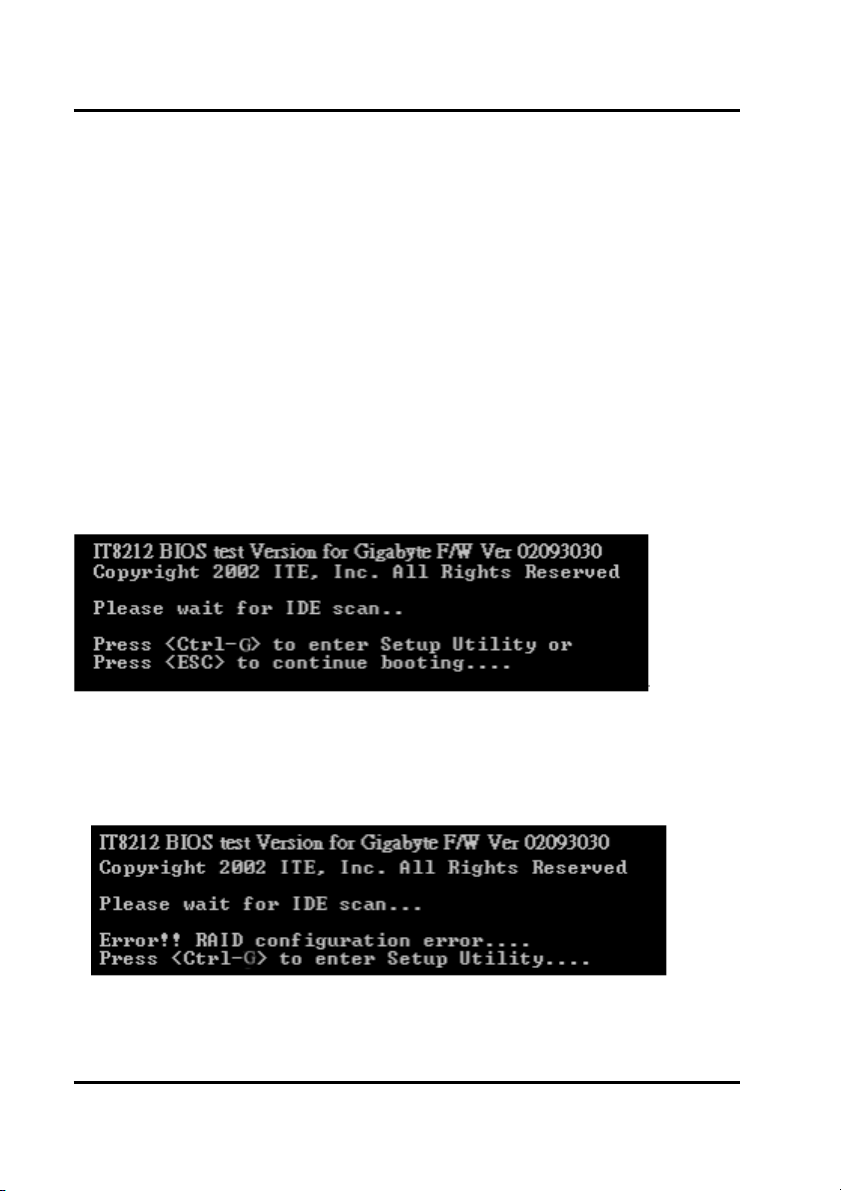
your hard drives to the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller and boot your
system. If your array’s configuration is correct, you will see the following message
shown by the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller onboard BIOS on the screen.
You can press “Ctrl-G” keys to enter Setup Utility or press the “Esc” key to skip and
boot directly.
If your array’s configuration is incorrect, you will see an error message on your
screen. You have to enter Setup Utility to reconfigure the arrays then quit utility to
boot.
15
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
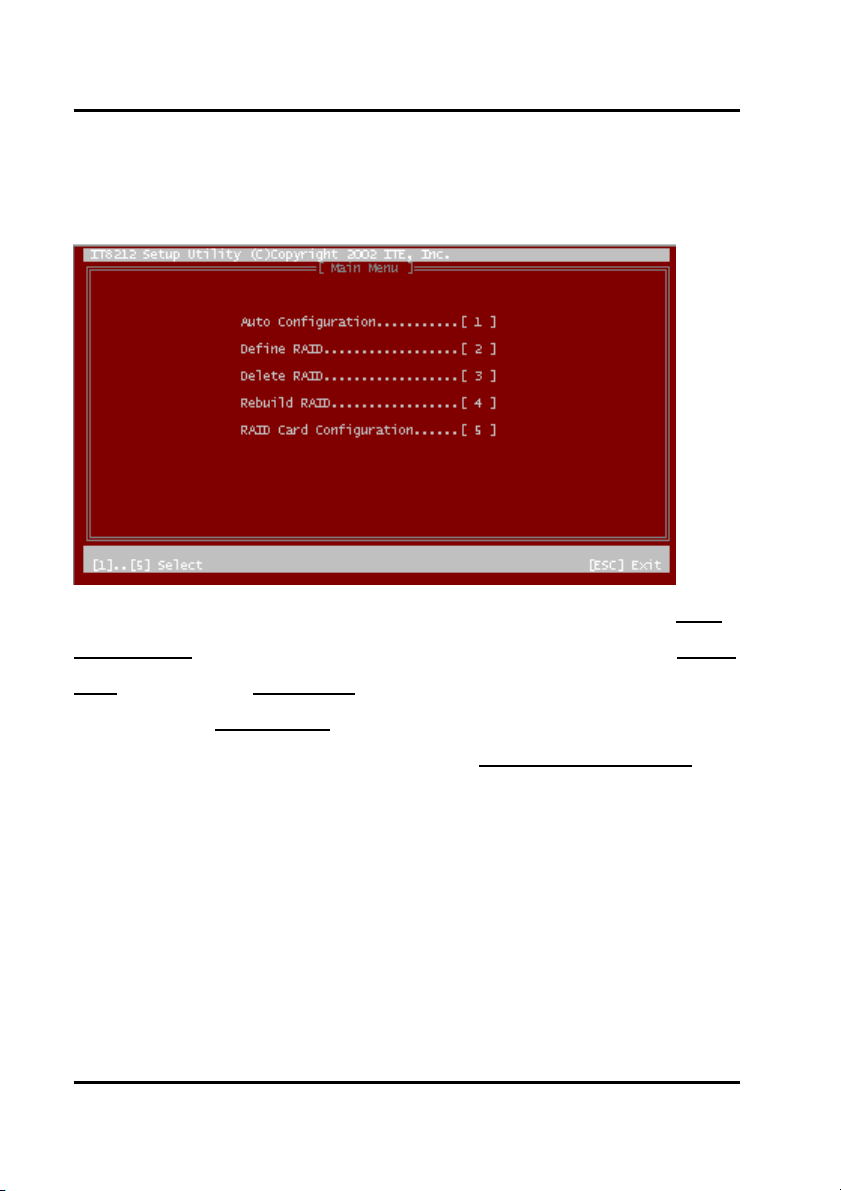
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller Setup Utility Main Menu
There are five options in the Setup Utility Main Menu, please press 1 ~ 5 to enter
the submenu or the “Esc” key to quit the Setup Utility.
If you are not familiar with the array setting, please follow the procedures in Auto
Configuration on page 17 to create new arrays automatically. You can use Define
RAID on page 22 and Delete RAID on page 28 to manually create or delete arrays.
You can also use Rebuild RAID selection on page 31 to help you rebuild a mirrored
(RAID 1 or RAID 0+1) array. Besides, you can use RAID Card Configuration on
page 36 to see the controller’s resources, each hard drive’s status and the setting of
the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller.
16
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
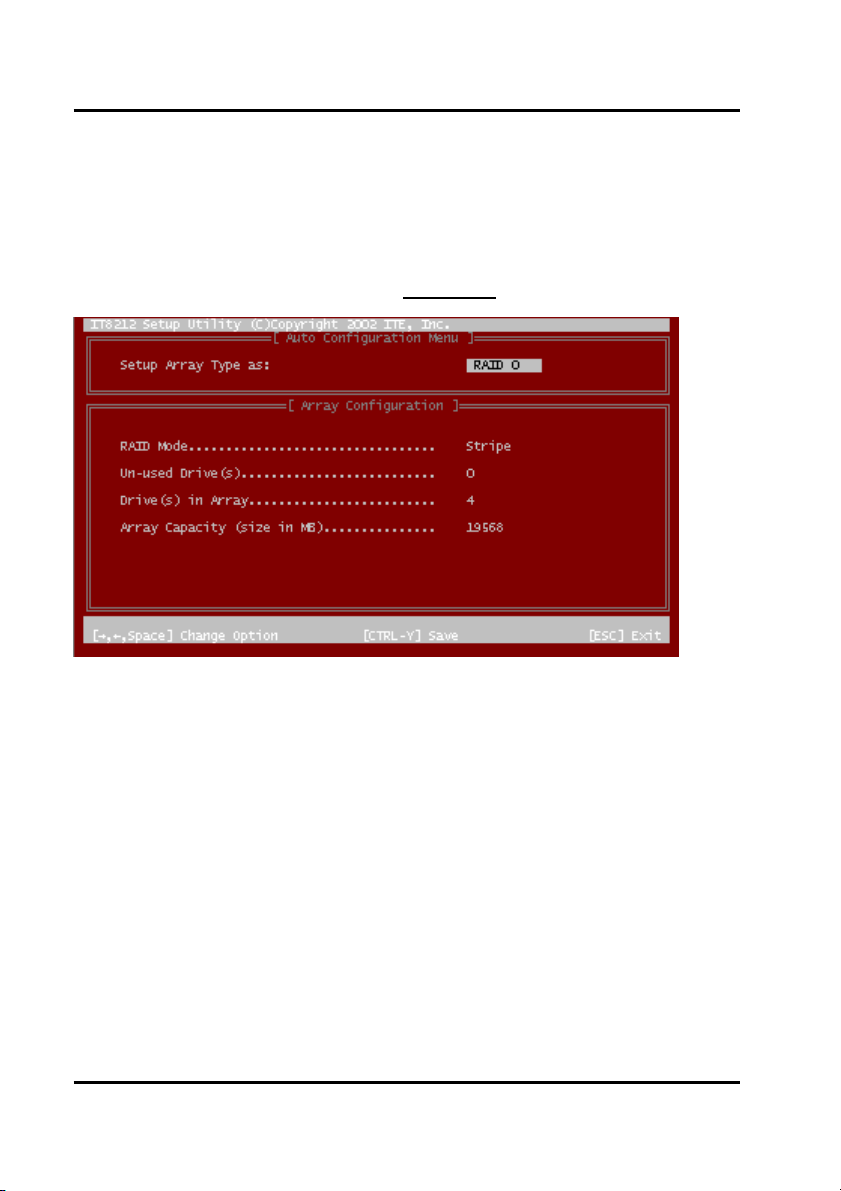
Auto Configuration
Click “1” on the Main Menu to enter Auto Configuration. You can use arrow keys →
and ← and the “space” bar key to change your option. After selecting your option,
you can press “Ctrl-Y” keys to save the setting and click the “Esc” key to leave Auto
Configuration menu and go back to the Main Menu
on page 10.
17
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
r
r
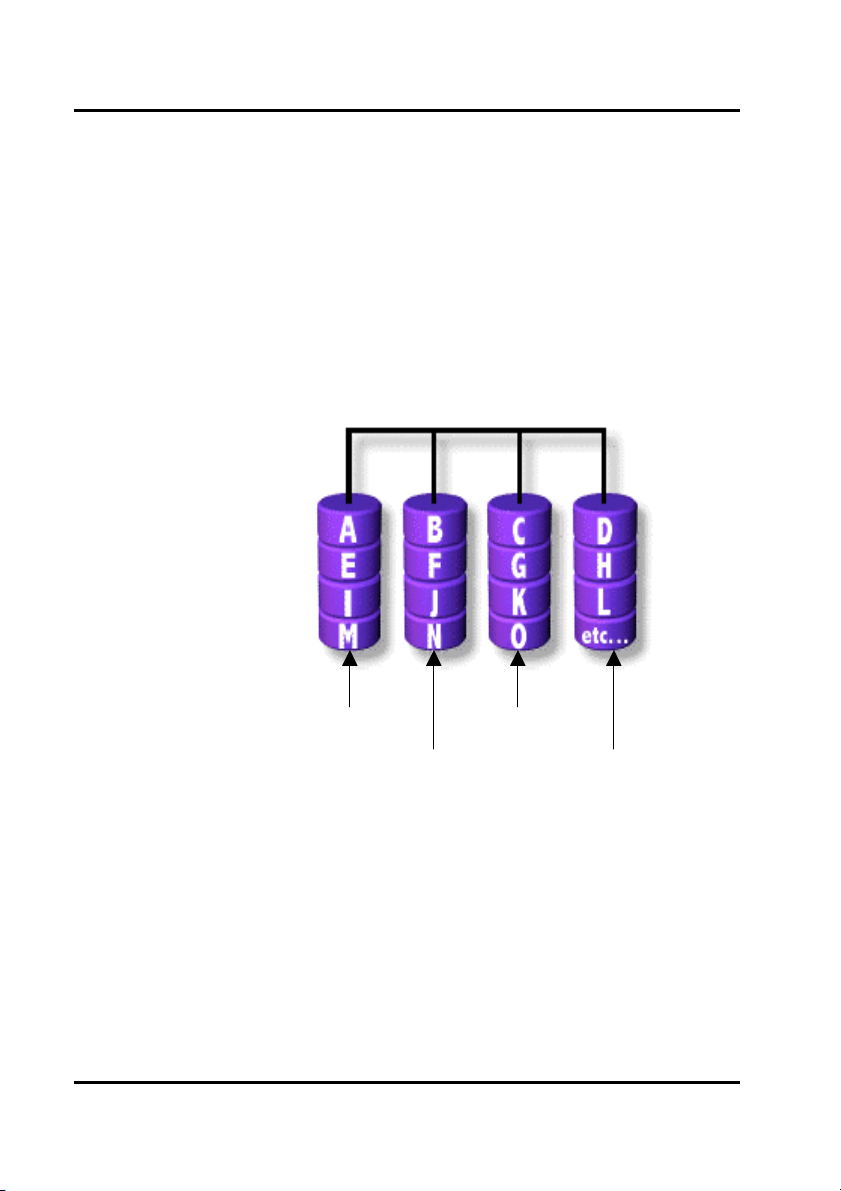
Setup Array for RAID 0:
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows you to use two, three or four
hard drives to set a RAID 0 (stripe) array. All the hard drives attached on the
controller will be set as array 0. When you create a striped array, files are broken into
64k (stripe size) and stripes are sent to each disk in the array. Selecting RAID 0 can
increase data transfer rate and allow the best overall performance characteristics
because of giving up redundancy.
RAID 0
Primary/Maste
Secondary/Maste
Primary/Slave
Secondary/Slave
18
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
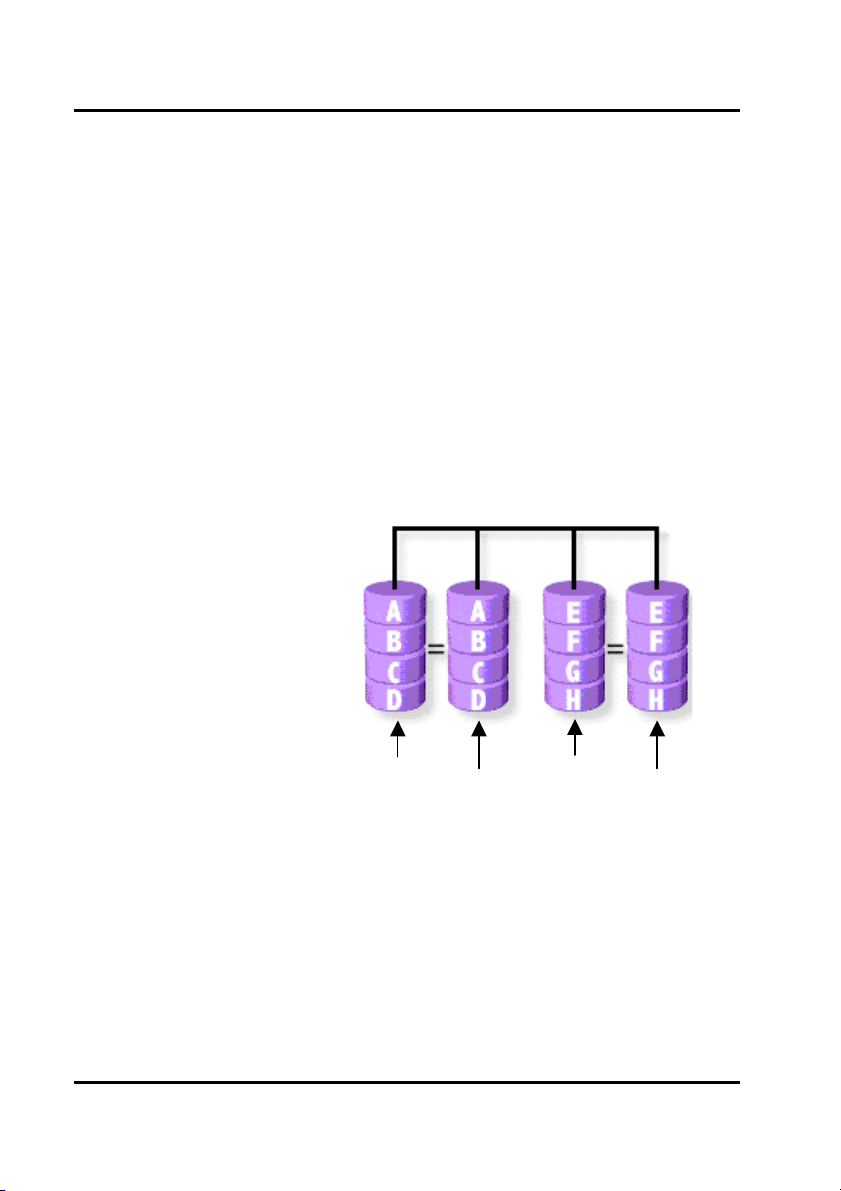
Setup Array for RAID 1:
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows two drives to be setup as a RAID
1 (mirror) array or four drives as two arrays. The first mirrored array will be set as
array 0 and the second as array 1. RAID 1 is implemented as mirroring; a drive has
its data duplicated on the other different drive. Selecting RAID 1 can enhance read
performance and allow fault tolerance. RAID 1 array can thoroughly backup your files
to prevent data loss.
Note: Two hard drives that form a RAID 1 array have to be attached as the same
master or slave hard disks.
RAID 1
Primary/Master
Secondary/Master
19
Primary/Slave
Secondary/Slave
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
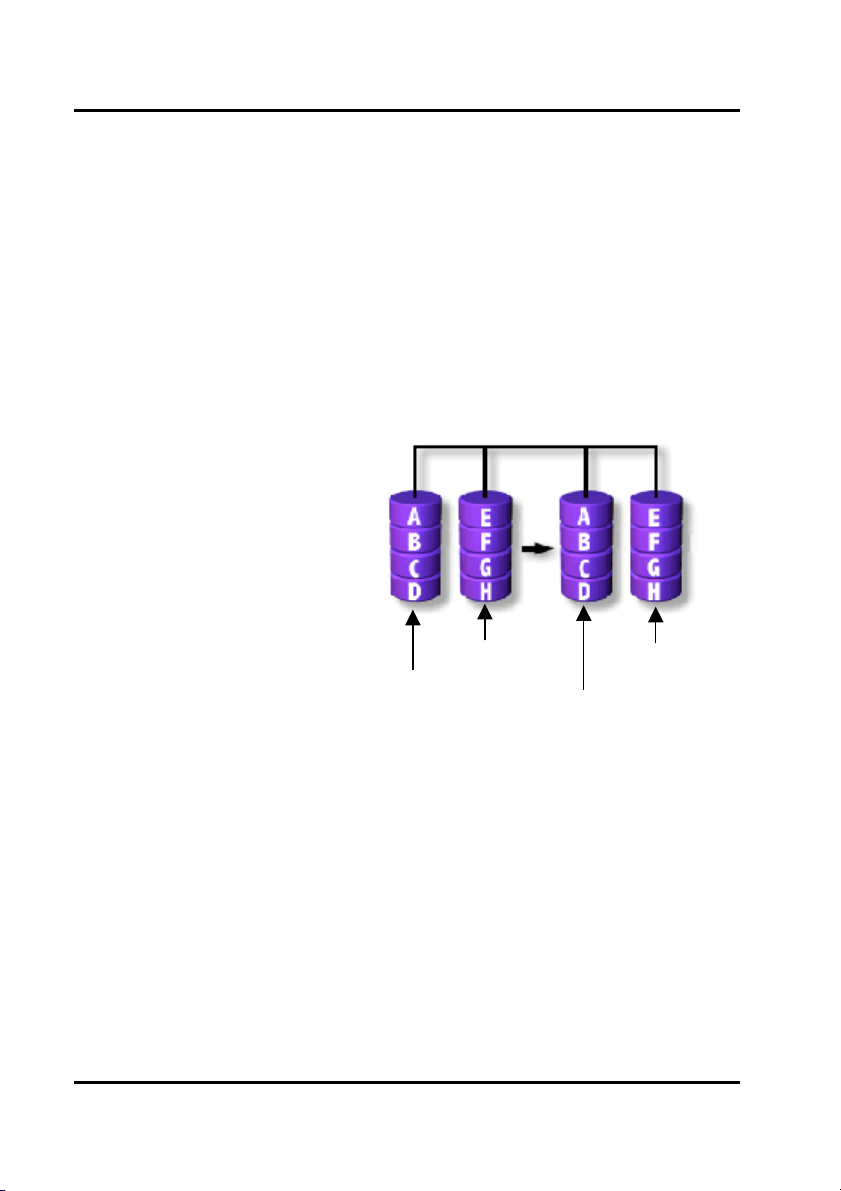
Setup Array for RAID 0+1:
A RAID 0+1 (mirror and stripe) array has to be formed by four hard drives. RAID 0+1
is implemented as a mirrored array whose segments are RAID 0 arrays so RAID 0+1
also has fault-tolerance capacity as RAID 1. It not only enhances hard disk access
performance but also backups data to prevent data loss. The formed array is
automatically set as array 0.
RAID 0+1
Primary/Slave
Secondary/Slave
Primary/Master
Secondary/Master
20

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
Setup Array for JBOD:
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows you to use two, three or four
hard drives to form a JBOD (Just a Bunch Of Disks) array as array 0. Although JBOD
doesn’t offer other RAID functionality, it makes the hard disks appear to be a single
one by combining the drives into one larger logical one without any capacity loss.
Setup Array for Normal:
You can use the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller as a normal IDE controller.
The GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller allows you to use one, two, three or four
hard drives. All the hard drives attached on the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID
Controller are left to act as independent drive volumes.
21
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
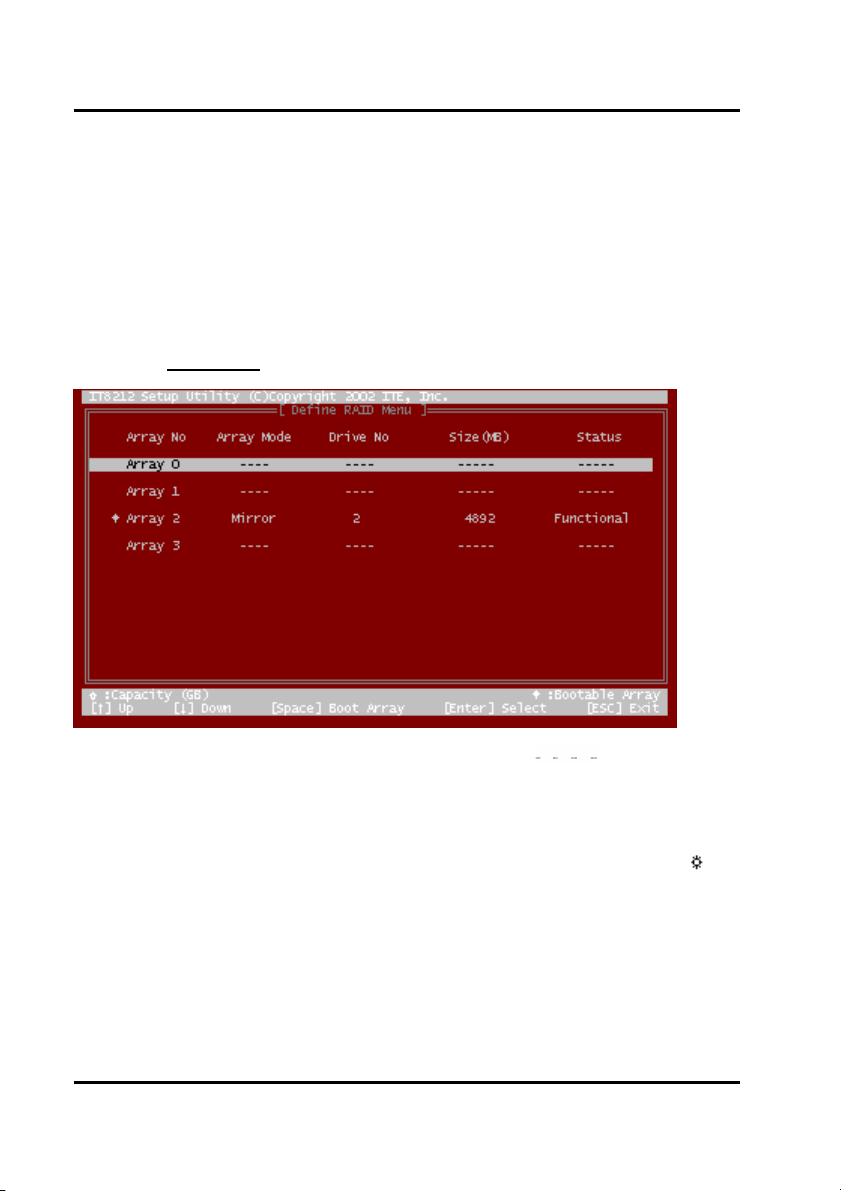
Define RAID
Click “2” on the Main Menu then you can enter the Define RAID Menu. Please use
arrow keys ↑ and ↓ to highlight the array number you want to define; use “space”
key to specify the bootable array if you like to boot your system from array attached
on GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller; and click the “Enter” key to select it and
enter the Define RAID Sub-Menu to create your array. If you want to quit and go
back to the Main Menu, please click the “Esc” key.
When an array is not assigned a RAID level, you will see “
Column “Array Mode” shows the RAID level (Stripe, Mirror, Stripe + Mirror or JBOD)
assigned to the array. Column “Drive No” shows the number of hard drive included in
the array. Column “Size” shows the array’s total capacity. If there is a symbol
shown in front of “Size”, the capacity unit is gigabyte. Column “Status” shows array
status. You will see “Functional” if the array is operational and “Non-Functional” if the
array has lost its functionality.
Please highlight the array number you want to define, click the “Enter” key, then the
Define RAID Sub-Menu will appear and allow drive assignments to the array.
” on the raw.
22
GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
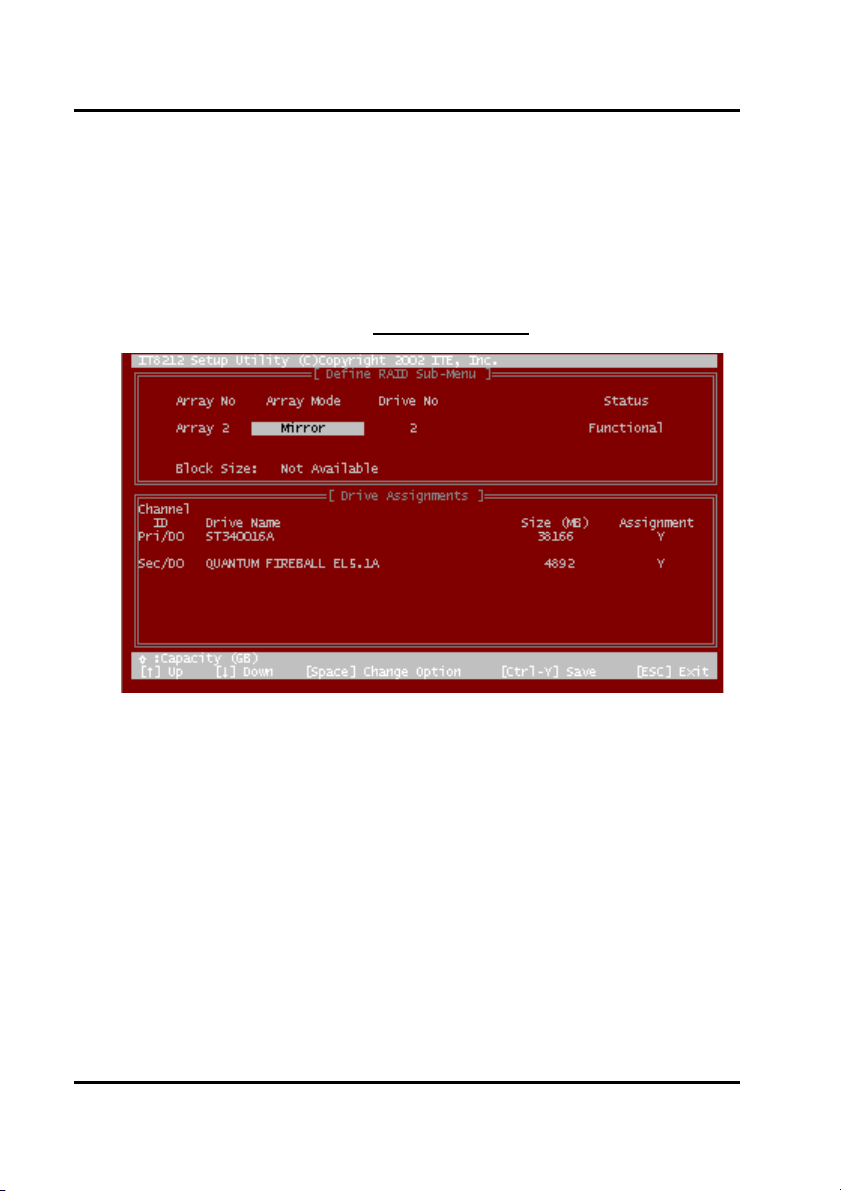
Define RAID Sub-Menu
When you highlight the array you want to define on the Define RAID Menu, click the
“Enter” key then you will enter this Define RAID Sub-Menu. You can use arrow keys
↑ and ↓ to highlight different positions. The “space” bar key can help you cycle
through the different options. “Ctrl-Y” keys can save the change and the “Esc” key
can help you quit then go back to the Define RAID Menu on page 22.
Block Size Option:
You can select Stripe Block size ranging from 1k to 64k for Stripe (RAID 0) or Stripe +
Mirror (RAID 0+1) array. The selection of block size is related to how your data is sent
and regained from hard drives. You can do some tests to decide which block size is
suitable for your system. Generally, a large block size is suitable to manage large file
transfer such as MPEG files. On the contrary, the small block size is suitable to
manage small files such as e-mail files.
Drive Assignments Option:
23

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
You can use arrow keys ↑ and ↓ to highlight the drive you want to assign to the
disk array and change the status of Assignments to “Y” by pressing the “space” bar
key.
For the meanings of “Array Mode”, “Drive No” and “Status”, please refer to Define
RAID Menu on page 22. The location of the hard drive is shown at the column
“Channel ID”. “Pri” represents the primary channel and “Sec” represents the
secondary channel. D0 represents a master hard drive while D1 represents a slave
hard drive. Column “Drive Name” shows the model name of the hard drive. Column
“Size” shows the capacity of each hard drive. When a symbol is shown before the
size, the capacity unit is gigabyte.
When you press “Ctrl-Y” keys to save your change, Setup Utility will check if the
setting is legal. If not, an error message will pop up to show you what the error is and
you have to correct the setting. Limitations are shown as below.
Stripe (RAID 0): There isn’t any specific limitation.
Mirror (RAID 1): Two hard drives that form a RAID 1 array have to be attached as the
same master or slave hard disks. For example, primary channel (Pri) master drive
(D0) and secondary channel (Sec) master drive (D0) can form a mirror array; primary
channel (Pri) slave drive (D1) and secondary channel (Sec) slave drive (D1) can form
a mirror array; but primary channel master drive and primary channel slave drive
cannot form a mirror array.
Stripe + Mirror (RAID 0+1): A RAID 0+1 array has to be formed by four hard drives.
24

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
RAID 0+1 is implemented as a mirrored array whose segments are RAID 0 arrays.
SPAN (JBOD): There isn’t any specific limitation.
Normal: If a hard drive is not included in an array (Column “Assignment” in the View
Drive Assignment is shown “Free”), this hard drive is regarded as a normal drive.
The existence of the normal hard drive sometimes will influence the array number
user specified. If the Pri/D0, Pri/D1, Sec/D0 or Sec/D1 hard drive is a normal drive,
array 0, 1, 2 or 3 cannot have the array setting respectively. However, you do not
have to concern about this limitation. If Setup Utility finds any conflicts, Array No will
be adjusted automatically. After finishing setting the array, go back to the Define
RAID Menu on page 22 then you will find the Array No is changed. This is because
the existence of the normal hard drive(s) causes the Array No to be adjusted
automatically.
When you press “Ctrl-Y” keys to save your change and your settings checked by
Setup Utility are correct, the following window will appear. You can choose to clear
the boot sector for the newly created array or not. If your RAID Mode is neither Mirror
nor Stripe + Mirror, this array setting is finished then you can click the “Esc” key to go
back to the Define RAID Menu on page 22.
25

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
If your RAID Mode selection is Mirror or Stripe + Mirror and you choose not to delete
the boot sector of the array, the following window will appear to ask whether you want
to rebuild an array. If you choose “Y”, the Rebuild RAID Menu
refer to page 31.)
If you choose not to rebuild this array for the time being, the GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA
RAID Controller cannot read data correctly because the data is inconsistent in the
will appear. (Please
26

GigaRAID (IT8212) ATA RAID Controller USER’S MANUAL
mirrored hard drives. Thus, the following window will appear.
Please press arrow keys ↑ and ↓ to highlight your selection and press the “Enter”
key to select the source disk(s) then you have finished the setting and the screen will
go back to the Define RAID Sub-Menu automatically. This array’s setup is completed.
You can press the “Esc” key to go back to the Define RAID Menu
27
on page 22.
 Loading...
Loading...