Page 1
‡ SIGNET 2714-2717 Twist-Lock pH and ORP Electrodes
50
3
PSIBAR
50
12275167
25
77
0
10
32
50
25
2
75
5
100
7
°F
°C
2714
2714-HF
ENGLISH
3-2714.090-1
G-1/02 English
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1. Depressurize and vent system prior to installation or removal.
2. Confirm chemical compatibility before use.
3. Do not exceed maximum temperature/pressure specifications.
4. Wear safety goggles or faceshield during installation/service.
5. Do not alter product construction.
6. When using chemicals or solvents care should be taken and appropriate eye, face, hand, body,
and/or respiratory protection should be used.
1. Technical Data
1.1 General
Compatibility: +GF+ SIGNET 2720 Twist-Lock Preamplifier
Pipe Size Range:
1
/2 in. and up.
•
• Use +GF+ SIGNET installation fittings to 4 in.
• Use pipe adapter in pipes over 4 in.
• Submersion with 2720 pre-amplifier requires
ISO 7-R 3/4 in. male threaded extensions
Efficiency: >97% @ 25°C (77° F)
Wetted Materials: CPVC Body
Glass
FPM O-rings
Porous UHMW Polyethylene reference
junctions
ORP: Platinum sensing surface
Primary Functions: 2714, 2715: Flat surface resists fouling
2716, 2717: Bulb surface for general use
2714-HF: Extended use in applications
with trace hydrofluoric acid (<2%)
2716-DI: Extended use in pure waters
(<100 µS)
Secondary Junction: Nylon Filament
Element: Ag/AgCl
Shipping Weight: 0.2 kg (0.4 lb)
1.2 2714 and 2716 pH Electrodes
Operating Range: 0 to 14 pH (2714-HF: 0 to 12 pH)
Reference: Electrolyte: Solidified Acrylamide Gel
3.5M KCI (2714, 2714-HF, 2716)
0.1 M KCl (2716-DI)
Temperature Sensor: 3KΩ Balco (3000Ω = 25°C)
ResponseTime: <5 s for 95% of signal change
Response Time, τ: 140 s (2714), 196 s (2716)
1.3 2715/2717 ORP Electrodes
Operating Range: -999 to +999 mV
Reference: Electrolyte: Solidified Acrlyamide Gel
Response Time: Application dependent
3.5M KCL
3
/4 in. NPT or
1.4 Temperature and pressure specifications
ORP electrode operating Temperature/Pressure
• 6.89 bar @ 0°C to 65ºC (100 psi @ 32° to 149° F)
• 4.00 bar @ 66ºC to 85°C (58 psi @150° to 185°F)
2716 and 2716-DI pH electrode operating Temperature/Pressure
• 6.89 bar @ 0°C to 65ºC (100 psi @ 32° to 149° F)
• 4.00 bar @ 66ºC to 85°C (58 psi @150° to 185°F)
2714 pH electrode operating Temperature/Pressure
• 6.89 bar @ 10°C to 65ºC (100 psi @ 50° to 149° F)
• 4.00 bar @ 66ºC to 85°C (58 psi @150° to 185°F)
2714-HF pH electrode operating Temperature/Pressure
• 6.89 bar @ 0°C to 50ºC (100 psi @ 32° to 122° F)
Storage Temperature: > -12° C (11° F)
1.5 Dimensions
1.0 in.
(27 mm)
(104 mm)
3.4 in.
(86 mm)
4.1 in.
1.2 in.
(30.5 mm)
2.6 in.
(65 mm)
1.0 in.
(27 mm)
(97 mm)
3.4 in.
(86 mm)
3.8 in.
1.2 in.
(30.5 mm)
2.6 in.
(65 mm)
0.9 in.
(23 mm)
0.9 in.
(23 mm)
Flat electrode Bulb electrode
page 1 of 4‡ SIGNET 2714-2717 Twist-Lock pH and ORP Electrodes
Page 2
2. Electrode care and application
pH/ORP electrodes are similar to batteries; they age with time and usage. The following information will help maximize electrode life.
2.1 Conditions to Avoid:
• High temperatures, strong acids or caustics will elevate electrochemical reactions and speed electrode aging.
• Coatings on the glass or junction surfaces (i.e. proteins) cause extended response time and inaccurate measurement.
• Never store the electrode tip in deionized (DI) water.
• Never expose electrode to temperatures below -12 °C (10 °F) or allow it to dehydrate. These conditions will damage the electrode.
• Never scrape or sand the glass electrode surface.
• Treat glass electrode surfaces with care. The glass is very thin and requires care to prevent accidental breakage.
2.2 Submersible Installation Tips:
• Mount electrodes in a location with ample clearance for removal for
periodic cleaning and recalibration. Choose a location that keeps the
YES
YES
electrode glass completely submerged at all times.
• Place the electrode tip in pH 4 buffer during system maintenance or
storage to avoid dehydration.
• Mount the electrode near tank outlet away from reagent addition areas.
2.3 In-Line Installation Tips:
• pH and ORP electrodes respond best in moving fluids.
30°
NO
30°
NO
• The internal measuring electrode chamber contains a wire within a liquid
and a slight amount of air. The electrode must be mounted at least 30°
from horizontal to ensure proper sensing. Mounting angles less than 30°
will impede performance.
NO
3. pH Electrode Calibration
All pH electrodes are designed to ensure linearity during their lifespan. The following
sections define proper electrode operation.
3.1 Offset (STD)
Electrode offsets occur due to:
• Clogged reference junction
• Aged or contaminated reference solution/wire
Check offsets in a pH 7 buffer @ 25 °C. The theoretical output is 0 mV. Any deviation from
0 mV is the pH electrode offset.
pH Electrode Offset pH 7 buffer @ 25°C Theoretical: 7.0 pH (0.0 mV)
New: pH 7 ± 0.25 pH (±15 mV)
Reliable: pH 7 ± 0.85 pH (± 50 mV)
Electrode offsets greater than 0.85 pH (50 mV) indicate the electrode requires cleaning or replacement. See section 5: Maintenance and
cleaning.
3.2 Slope (SLP)
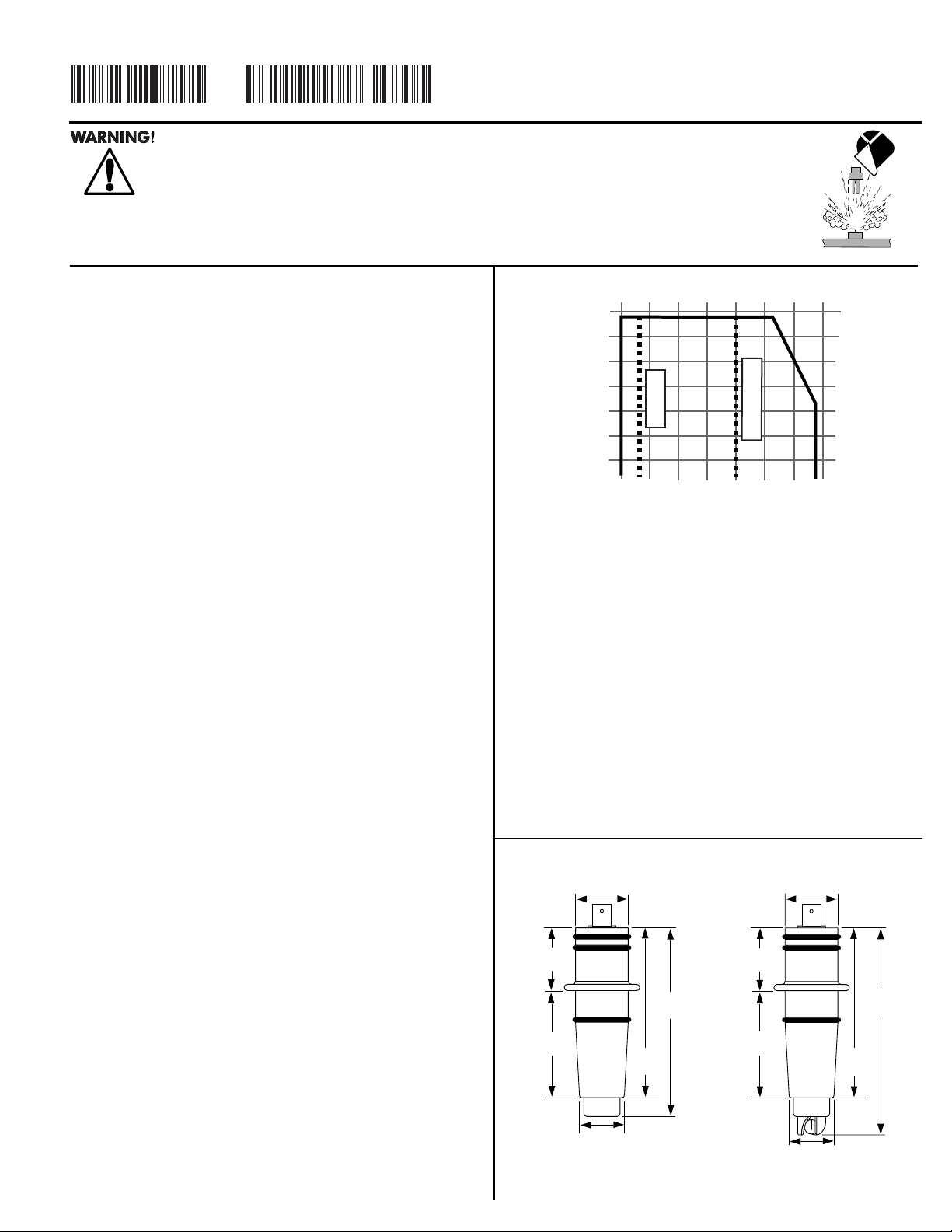
Electrode slope is the number of mV per pH unit. At 25°C the
theoretical slope is 59.16 mV per pH. Temperature has an
appreciable affect on electrode slope. Reliable instrumentation
includes temperature compensation. The graph below illustrates
potential pH error when a temperature compensated instrument
is not used.
°C pH Error
23456789101112
15 0.15 0.12 0.09 0.06 0.03 0 0.03 0.06 0.09 0.12 0.15
25 00000000000
35 0.15 0.12 0.09 0.06 0.03 0 0.03 0.06 0.09 0.12 0.15
45 0.3 0.24 0.18 0.12 0.06 0 0.06 0.12 0.18 0.24 0.3
55 0.45 0.36 0.27 0.18 0.09 0 0.09 0.18 0.27 0.36 0.45
Recommendations:
• Calibrate temperature before calibrating the standard and slope.
• The mV offset will track across the entire pH range. The slope is usually not affected by offset changes.
(i.e. pH 7= +10 mV, pH 4= +187 mV); slope = 59 mV
• Coatings on the glass may affect sensor slopes. See section 5 maintenance and cleaning.
•A constant output near 0 mV in all buffer solutions indicates a shorted electrode that must be replaced.
Theoretical mV Values @ 25°C
pH mV
2+ 295 mV
3+ 236 mV
4 +177 mV
5 +118 mV
6+ 59 mV
70 mV
8- 59 mV
9 - 118 mV
10 - 177 mV
11 - 236 mV
12 - 295 mV
3.3 Response Time/Stability
Response time and stability are affected by the condition of the pH electrode's glass surface (ORP electrode - Platinum surface),
reference junction, and reference solution. Restoration to acceptable levels can often be accomplished by cleaning the electrode's glass
surface (ORP electrode - Platinum surface) and reference junction.
Electrode mV values should remain stable ±3 mV. Conditions that may cause fluctuations are:
1. Electrode coating
2. Ground fault: If proper operation is observed in the beaker, but is unstable in the application, a ground fault probably exists.
• Using instrumentation with isolated inputs and outputs may restore stable operation.
• Solution grounding may also restore stable operation.
page 2 of 4 ‡ SIGNET 2714-2717 Twist Lock pH and ORP Electrodes
Page 3

4. ORP Electrode Calibration
All ORP electrodes are designed to ensure linearity during their lifespan. The following sections define proper electrode operation.
4.1 Offset (STD)
Electrode offsets occur due to:
• Clogged reference junction
• Aged or contaminated reference solution/wire
Offsets are easily checked in pH 7 buffer saturated with quinhydrone @ 25 °C; since the theoretical output is +87 mV. Any deviation
from +87 mV is the ORP electrode offset (i.e. +90 mV). Quinhydrone is the oxidizer measured by the ORP electrode and is required for
calibration. To guarantee buffer saturation, mix 1/8g quinhydrone per 50 mL of pH buffer.
ORP Electrode Offset:
Solution: pH 7 or pH 4 buffer saturated with Quinhydrone @ 25 °C
pH 7 + Quinhydrone pH 4 + Quinhydrone
Theoretical mV: + 87 mV + 264 mV
New: 87 ± 15 mV +264 ± 15 mV
Reliable: 87 ± 50 mV +264 ± 50 mV
Electrode offsets greater than ±50 mV indicate the electrode requires cleaning or replacement, see section 5.2.
4.2 Slope (SLP)
ORP slope errors are generally caused by contamination of the platinum electrode surface. Cleaning the electrode surface will usually
restore proper values, response time, and stability.
Common ORP Values
Reaction mV
-
3
-
+ e
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 913
- 440
- 407
- 400
- 370
- 250
- 126
- 37
0
+ 771
+ 799
+ 800
+ 1060
+ 1066
+ 1160
+ 1188
+ 1369
Cr → Cr2+ + 2e
Fe → Fe2+ + 2e
Cr2+ →Cr3+ + e
4OH- → O2 + 2H2O + 4e - 401
2I- → I2 + 2e
Ti2+ → Ti3+ + e
Ni → Ni2+ + 2e
Pb → Pb2+ + 2e
Fe → Fe3+ + 3e
H2 → 2H+ + 2e
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e
Ag → Ag+ + e
Pb → Pb4+ + 4e
3Br- → Br
2Br- → Br2 + 2e
-
ClO
→ ClO2 + e
2
Pt → Pt2+ + 2e
Ag → Ag2+ + 2e
Many systems require both pH and ORP calibration. To conserve calibration reference solutions, use pH 7 and 4 buffers for pH
calibration first. ORP calibration can be performed with the same buffers by adding quinhydrone.
5. Maintenance and Cleaning
5.1 Maintenance
Variables can affect long term pH or ORP electrode life. For this reason, a maintenance log is recommended for trend analysis. When
storing boxed sensors, lay the sensor flat to maximize hydration of the glass surface. Keep the glass surface wet at all times. Soak the
sensor tip in pH 4.0 buffer during system maintenance intervals. In-line applications should be plumbed with a depression (trap) so liquid
is maintained around the sensor tip. If the sensor dehydrates, soak the sensor tip in pH 4 buffer for 24 to 48 hours, then visually inspect
the electrode for surface cracks, swelling, or discoloration. Severely dehydrated electrodes cannot be restored to normal operation.
page 3 of 4‡ SIGNET 2714-2717 Twist-Lock pH and ORP Electrodes
Page 4

a
b
c
d
e
f
g
o
l
k
j
i
h
n
m
c
5.2 Cleaning
Cleaning techniques vary depending on the type of coating present on the glass electrode surface or reference junction.
• Soft coatings can be removed by vigorous stirring, or with directed spray of an applicable detergent or solvent onto the glass
electrode surface. Chlorine bleach or mild detergent may be used to remove soft coatings. Always rinse electrode tip in clean water
after cleaning.
• Hard coatings can be chemically removed. Use the least harsh chemical which will remove the contaminant within two (2) minutes
without attacking the materials of construction. e.g. calcium carbonate may be removed with a 5% HCL (muriatic acid) solution.
• Oily or organic coatings can be removed with detergents or an appropriate solvent that does not attack the materials of
construction e.g. isopropyl alcohol may be used but acetone must be avoided to prevent damage to the CPVC sensor body.
• ORP electrode surface (platinum rod) can be gently sanded with 600 grit wet and dry silicone or carbide sandpaper, jewelers rouge,
crocus cloth, or very fine steel wool.
WARNING!
Wear appropriate eye, face, hand, body, and respiratory protection when using chemicals or solvents.
6. Replacement parts and accessories
Mfr. Part No. Code Description
3-2714 198 844 300 Flat pH Electrode
3-2714-HF 198 844 305 Flat pH Electrode, HF Resistsant
3-2715 198 844 301 Flat ORP Electrode
3-2716 198 844 302 Bulb pH Electrode
3-2716-DI 198 844 306 Bulb pH Electrode, DI Resistant
3-2717 198 844 303 Bulb ORP Electrode
3-2759 159 000 762 pH/ORP Simulator/System Tester
3-2759.393 159 000 765 Adapter Cable for use with 2720
3-2720 198 864 602 Preamplifier,
3-2720-2 198 864 603 Preamplifier, ISO 7-R 3/4 in.
P31515-0P200 159 000 630 PVC Pipe Adapter
P31515-0C200 159 000 631 CPVC Pipe Adapter
P31515-0V200 159 000 459 PVDF Pipe Adapter
3-0700.390 198 864 403 pH Buffer Kit
1220-0021 198 801 186 O-ring, FPM (standard)
1224-0021 198 820 006 O-ring, EPR
1228-0021 198 820 007 O-ring, Kalrez
CAUTION!
Apply O-ring lubricant to sensor O-rings prior to assembly.
Unlubricated O-rings may score the sealing surface in the 2720.
3
/4 in. NPT
3-2759 pH/ORP
Simulator/System Tester
ORP
pH
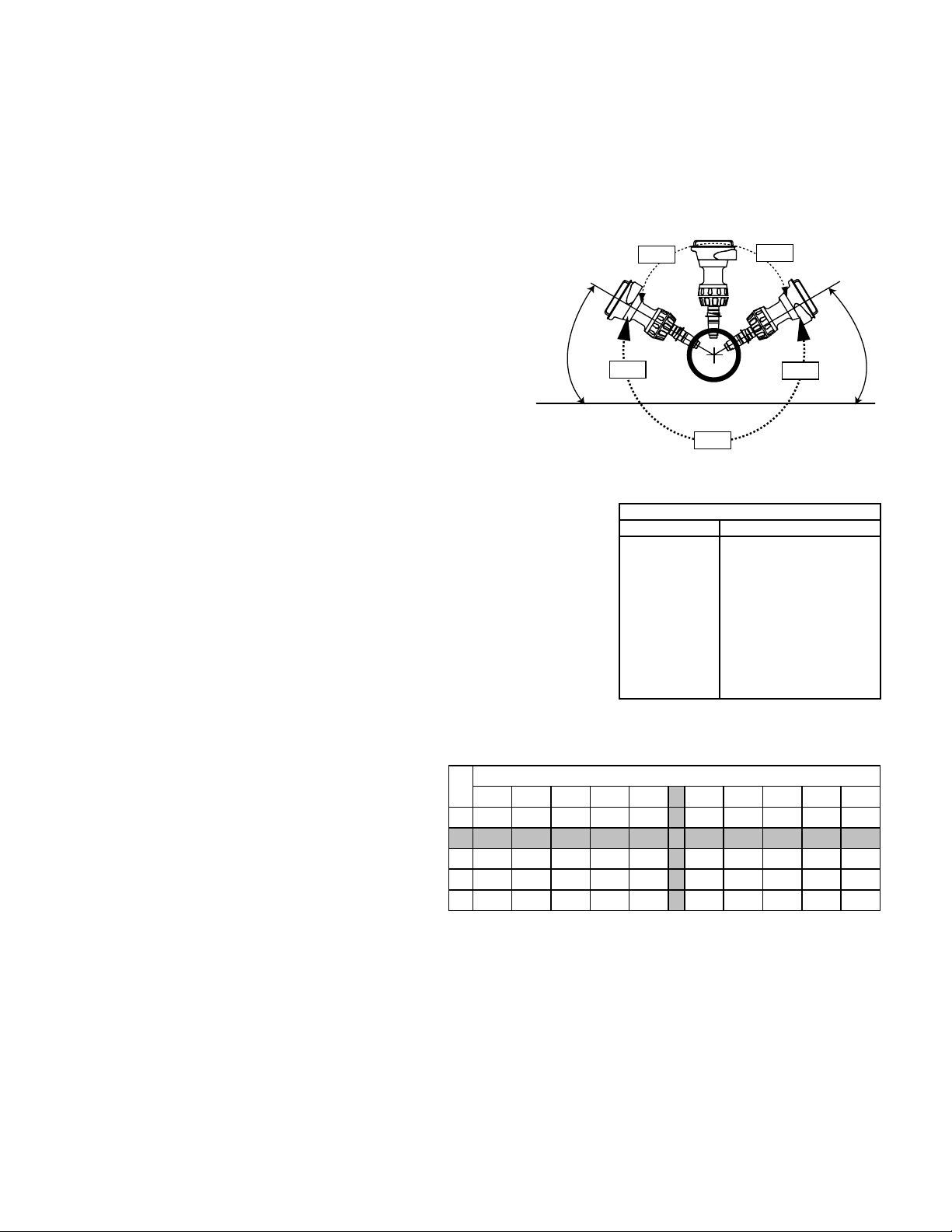
Technical Features
a) Male BNC connector
b) Keyed for a simple sure fit
c) Viton® O-rings
d) Silicone-bushing seal
e) Double junction
f) Ag/AgCl reference element
g) Platinum sensing surface (ORP) or flat pH glass
h) Porous UHMW polyethylene reference junction
‡ SIGNET
Signet Scientific Company, 3401 Aerojet Avenue, El Monte, CA 91731-2882 U.S.A. • Tel. (626) 571-2770 • Fax (626) 573-2057
For Worldwide Sales and Service, visit our website: www.gfsignet.com • Or call (in the U.S.): (800) 854-4090
i) 3K Balco thermistor
j) Solidified acrylamide reference
electrolyte
k) Ag/AgCl measuring element
l) Large reference volume
m) Epoxy seal
n) Shielding
o) 10KΩ I.D. resistor for ORP sensor
GEORGE FISCHER ‡ Piping Systems
3-2714.090-1/(G-1/02) English © Signet Scientific Company 2001 Printed in U.S.A. on recycled paper
page 4 of 4 ‡ SIGNET 2714-2717 Twist Lock pH and ORP Electrodes
 Loading...
Loading...