Page 1

1
GD-GEO20
Page 2

2
Table of contents
1 Conventions Used in this Document ..................................................................................... 4
Abbreviation List ................................................................................................................... 5
2 Packing list ............................................................................................................................ 7
3 Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 8
3.1 Deployment Scenarios .................................................................................................... 8
3.1.1 HotSpot .................................................................................................................... 8
3.1.2 Point to Multipoint ................................................................................................... 8
3.1.3 Light PTP ................................................................................................................. 9
4 Device Setup ........................................................................................................................ 10
4.1 AP Setup ....................................................................................................................... 10
4.2 Station Setup ................................................................................................................. 13
5 Network Mode ..................................................................................................................... 17
5.1 Bridge Mode ................................................................................................................. 17
5.2 Router Mode ................................................................................................................. 17
6 Device Operation ................................................................................................................. 18
6.1 Web Management Structure .......................................................................................... 18
6.2 Appling and Saving Configuration Changes ................................................................ 19
7 Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 20
7.1 Status ............................................................................................................................. 20
7.1.1 Information ............................................................................................................ 20
7.1.2 Status Network ...................................................................................................... 21
7.1.3 Wireless ................................................................................................................. 21
7.1.4 Routes .................................................................................................................... 22
7.1.5 ARP ....................................................................................................................... 22
7.2 Configuration ................................................................................................................ 23
7.2.1 Network ................................................................................................................. 23
7.2.2 Bridge Mode .......................................................................................................... 23
7.2.3 Router Mode .......................................................................................................... 25
7.2.4 Wireless ................................................................................................................. 30
7.2.5 Wireless Mode: Access Point ................................................................................ 31
7.2.6 Wireless Mode: Station ......................................................................................... 35
7.2.7 Wireless Mode: iPoll Access Point ....................................................................... 38
7.2.8 Wireless Mode: iPoll Station ................................................................................. 40
7.2.9 Virtual AP .............................................................................................................. 42
Page 3

7.2.10 Wireless ACL ........................................................................................................ 43
7.2.11 Traffic Shaping ...................................................................................................... 44
7.2.12 Port Forwarding ..................................................................................................... 45
7.2.13 Static Routes .......................................................................................................... 46
7.3 Services ......................................................................................................................... 46
7.3.1 WNMS ................................................................................................................... 46
7.3.2 System alerts .......................................................................................................... 47
7.3.3 SNMP .................................................................................................................... 48
7.3.4 Clock/NTP ............................................................................................................. 49
7.3.5 SSH ........................................................................................................................ 50
7.3.6 HTTP ..................................................................................................................... 50
7.4 System ........................................................................................................................... 51
7.4.1 Administration ....................................................................................................... 51
7.4.2 Log ......................................................................................................................... 52
3
7.4.3 LED Control .......................................................................................................... 53
7.4.4 Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................. 54
7.5 Tools ............................................................................................................................. 56
7.5.1 Antenna Alignment................................................................................................ 56
7.5.2 Site Survey ............................................................................................................. 56
7.5.3 Delayed Reboot ..................................................................................................... 57
7.5.4 Ping ........................................................................................................................ 58
7.5.5 Trace route ............................................................................................................. 58
7.5.6 Spectrum Analyser ................................................................................................ 59
8 Universal Acces Method ..................................................................................................... 61
8.1 UAM Overview ............................................................................................................ 61
8.2 UAM Configuration ...................................................................................................... 61
8.2.1 White/Black List .................................................................................................... 64
9 Appendix ............................................................................................................................. 66
9.1 Resetting Device to Factory Defaults ............................................................................ 66
9.2 RADIUS Attributes ....................................................................................................... 67
9.2.1 General Attributes .................................................................................................. 67
9.2.2 WISPr Attributes ................................................................................................... 69
9.2.3 ChilliSpot Attributes .............................................................................................. 69
Page 4

1 Conventions Used in this Document
The following typographic conventions and symbols are used throughout document:
Additional information that may be helpful but which is not required.
Important information that should be observed.
bold Menu commands, buttons, input fields, links, and configuration keys are displayed in bold
italic References to sections inside the document are displayed in italic.
code
File names, directory names, form names, system-generated output, and user
typed entries are displayed in constant-width type
4
Page 5
Abbreviation
Description
ACL
Access Control List
AES
Advanced Encryption Standard
AMSDU
Aggregated Mac Service Data Unit
AP
Access Point
CRC
Cyclic Redundancy Check
DHCP
Dynamic Host Control Protocol
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol
GHz
Gigahertz
GMT
Greenwich Mean Time.
GUI
Graphical User Interface
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
ISP
Internet Service Provider
IP
Internet Protocol
LAN
Local Area Network
LED
Light-Emitting Diode
MAC
Media Access Control
Mbps
Megabits per second
MHz
Megahertz
MIMO
Multiple Input, Multiple Output
MSCHAPv2
Microsoft version of the Challenge-handshake authentication protocol, CHAP.
NAT
Network address translation – translation of IP addresses (and ports)
PC
Personal Computer
PDA
Personal Digital Assistant
PTP
Point To Point
PTMP
Point To Multi Point
PSK
Pre-Shared Key
QoS
Quality of Service
PEAP
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol
RSSI
Received Signal Strength Indication – received signal strength in mV,
measured on BNC outdoor unit connector
RX
Receive
SISO
Simple Input, Simple Output
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
SSID
Service Set Identifier
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
TKIP
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
TTLS
Tunneled Transport Layer Security (EAP-TTLS) protocol
TX
Transmission
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
Abbreviation List
5
Page 6

UAM
Universal Access Method
VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network
VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol
WDS
Wireless Distribution System
WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy
WISPr
Wireless Internet Service Provider roaming
WLAN
Wireless Local Area Network
WPA
Wi-Fi Protected Access
WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access 2
6
Page 7

2 Packing list
1 piece power cable
1 piece power adapter
1 piece connector
1 piece bent threaded rod
1 piece bracket
1 piece screw
4 pieces nuts
+
1 piece user manual CD
1 piece GD-GEO20-TP
7
Page 8
3 Introduction
GD-GEO20 offers reliable, great performance and cost-effective point-to-multipoint outdoor and indoor
wireless solutions perfectly suited for access technology, private network and hotspots. Beside that
APC (Access Point/Customer Premises Equipment) can be used for a light point-to-point applications.
APC works in unlicensed 2.4 or 5 GHz frequency band, which is attractive solution for quick
network creation with minimum investment. These products support newest WLAN standards IEEE
802.11n and are compatible with IEEE 802.11a/b/g, also have options for SISO and MIMO
functionality. The private protocol named iPoll offers effective point-to-multipoint deployment scenario.
and simple
3.1 Deployment Scenarios
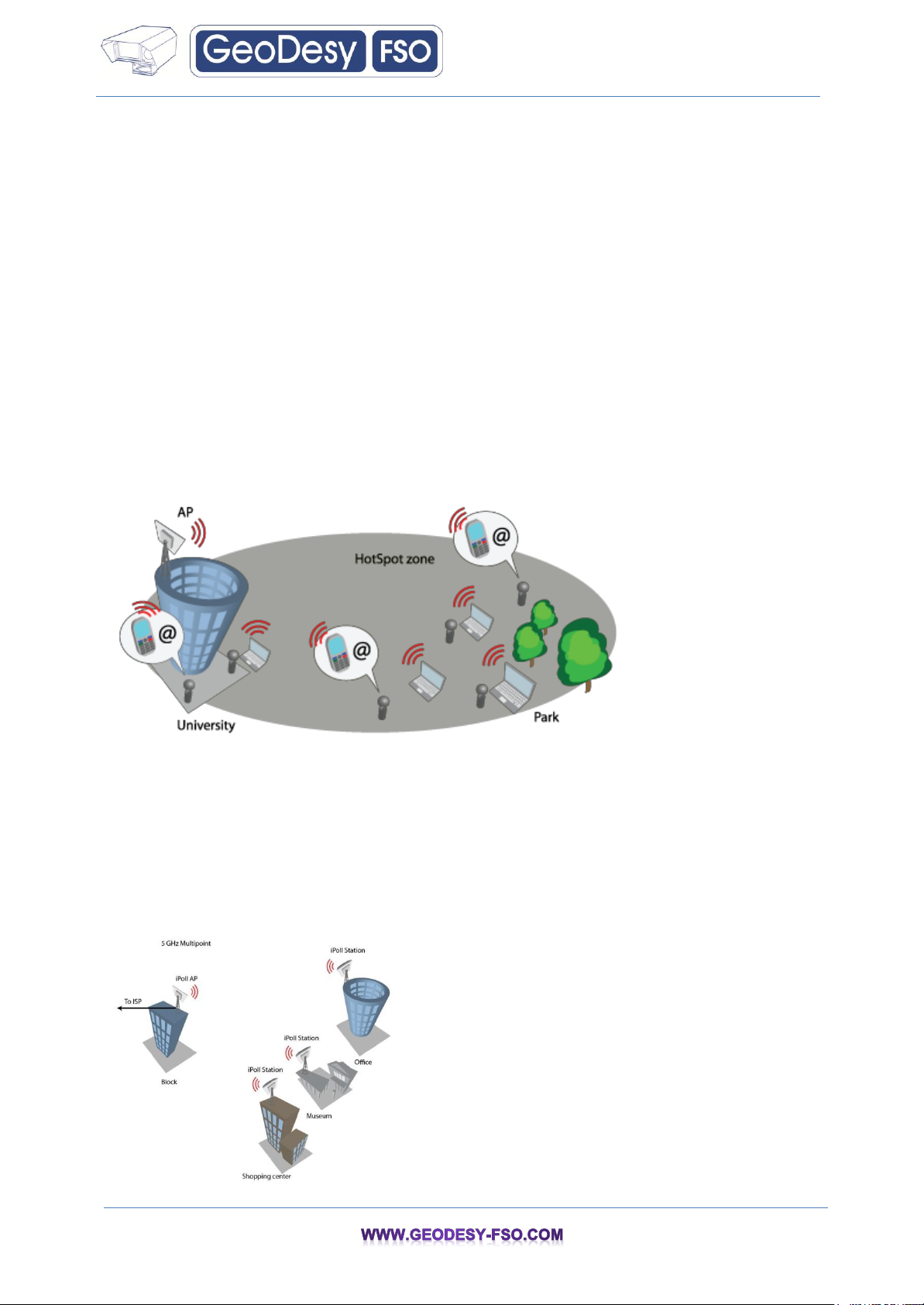
3.1.1 HotSpot
AP can easily create hotspot‟s zone network on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz unlicensed band. IEEE 11n lets
achieve (depending on laptop, smart-phone or PDA capabilities) great throughput and support all
possible client equipment (based on IEEE 802.a/b/g). Hotspot zones can be created indoor or
outdoor.
8
HotSpot Scenario
3.1.2 Point to Multipoint
This is the IEEE 802.11n wireless multipoint which delivers several times higher throughput than
802.11a/g. The APC supports a private wireless point to multipoint protocol called iPoll which allows
connecting more than one iPoll Stations to the iPoll Access Point thus creating a robust point to multi
point network.
Page 9
Point to Multipoint Scenario
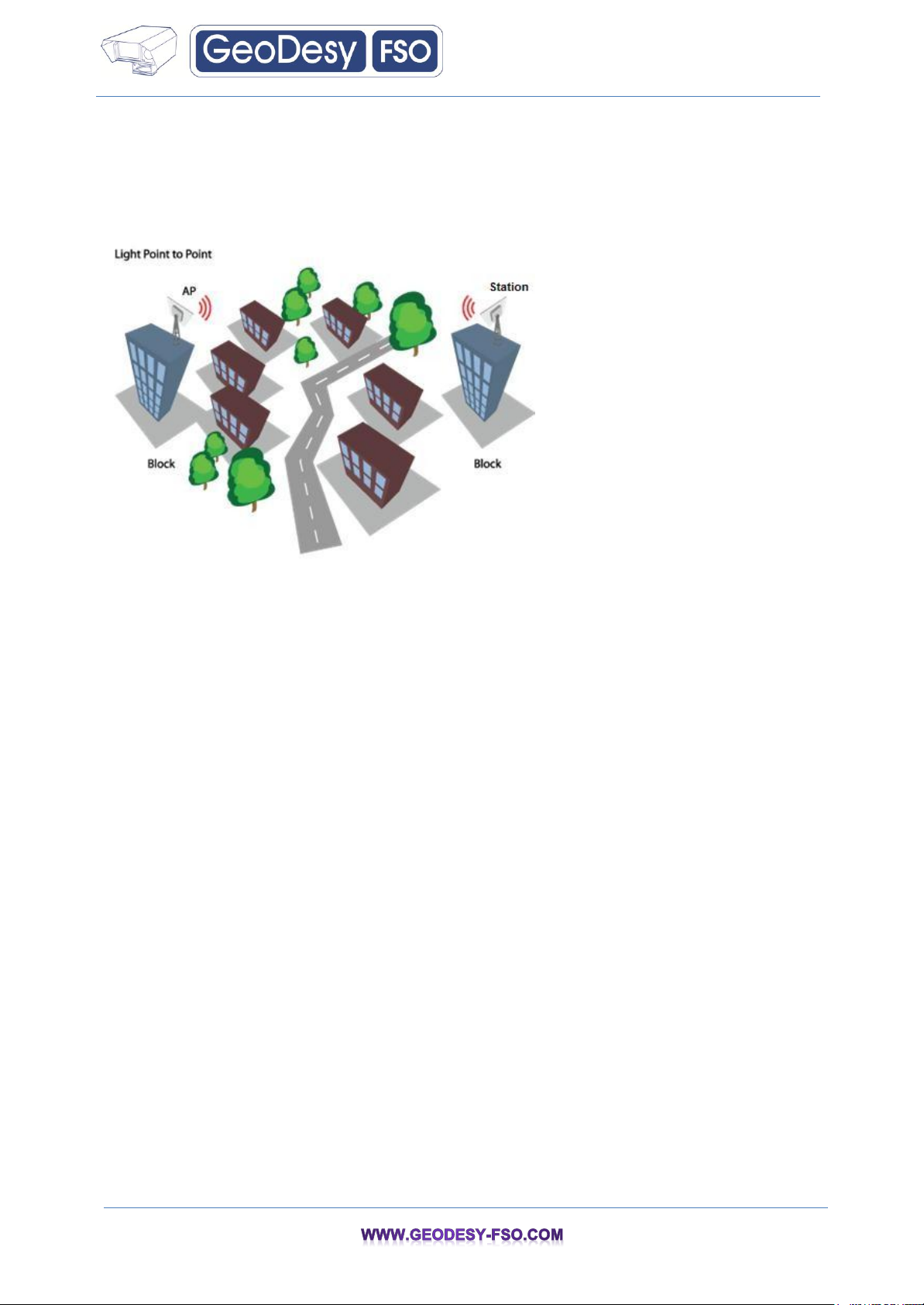
3.1.3 Light PTP
GD-GEO20 supports access point and station operating modes, therefore point-to-point can be created
From AP and Station or from 2 Station’s or from 2 AP‟s. For simplicity two Stations can be used
Because they have integrated directional antennas. There are available options for SISO and MIMO
PTPs. Maximum achievable real data throughput is up to 160 Mbps.
9
Light PTP Scenario
Page 10
4 Device Setup
The default product address is 192.168.2.66.
To access the Web management interface, configure your PC with a static IP address on the
192.168.2.0 subnet with mask 255.255.255.0. Connect the AP device in to the same physical network
as your PC. Open the Web browser and type the default IP address of the AP device
https://192.168.2.66/ and the login page will be loaded. Enter default administrator login
settings:
10
Login Page
The default administrator login settings are:
Login: admin
Password: admin01
After successful administrator login you will see the main page of the device Web management
interface. The device now is ready for configuration.
4.1 AP Setup
Follow the steps for initial wireless Access Point setup that will be prepared to accept wireless Station
connections (refer to the section Initial Station Setup for instructions).
Step 1. Connect an Ethernet cable between your computer and the AP.
Step 2. Make sure your computer is set to the same subnet as the AP, i.e. 192.168.2.150
Step 3. Start your Web browser.
Step 4. Each device uses following default settings:
WAN IP: 192.168.2.66
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Username: admin
Password: admin01
Step 5. Enter the default password, and then press the Login button to enter the AP web
management page.
Page 11
Step 6. Navigate to the Configuration | Network tab and choose the Router network mode
with NAT enabled, Static IP enabled on WAN side, LAN settings with DHCP server enabled (to loan
an IP addresses for connected clients) on LAN side and click Save Apply:
11
Step 7. Navigate to the Configuration | Wireless tab, choose Access Point wireless mode with WDS
enabled, specify the SSID with Broadcast enabled, Security parameters and IEEE mode and click
Save&Apply:
Page 12
12
Step 8. Verify connection. Navigate to Status | Information menu to check if the Station are
successfully connected to the APC device:
Page 13
13
4.2 Station Setup
Follow the steps for initial wireless client setup that will be connected to the previously configured AP
(refer to the section Initial AP Setup).
Step 1. Connect an Ethernet cable between your computer and the GD-GEO20 device.
Step 2. Make sure your computer is set to the same subnet as the APC, i.e. 192.168.2.150
Step 3. Start your Web browser.
Step 4. Each APC devices uses following default settings:
WAN IP: 192.168.2.66
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Username: admin
Password: admin01
Page 14
Step 5. Enter the default password, and then press the Login button to enter the APC web
management page.
Step 6. Navigate to the Configuration | Network tab and choose the bridge network mode
with, Dynamic IP enabled (be sure that AP to which the device will be associated has a DHCP server
running ((refer to the section Initial AP Setup for instructions)), specify the DHCP fallback settings in
case the DHCP server will be unreachable and click Save Apply button:
14
Step 7. Navigate to the Configuration | Wireless tab, choose Station WDS wireless mode,
click Scan button near the SSID entry field to choose the SSID of the AP where the station will be
associated to. Specify the Security parameters for the AP, check IEEE mode (these settings must
conform to AP wireless settings) and click Save Apply:
Page 15
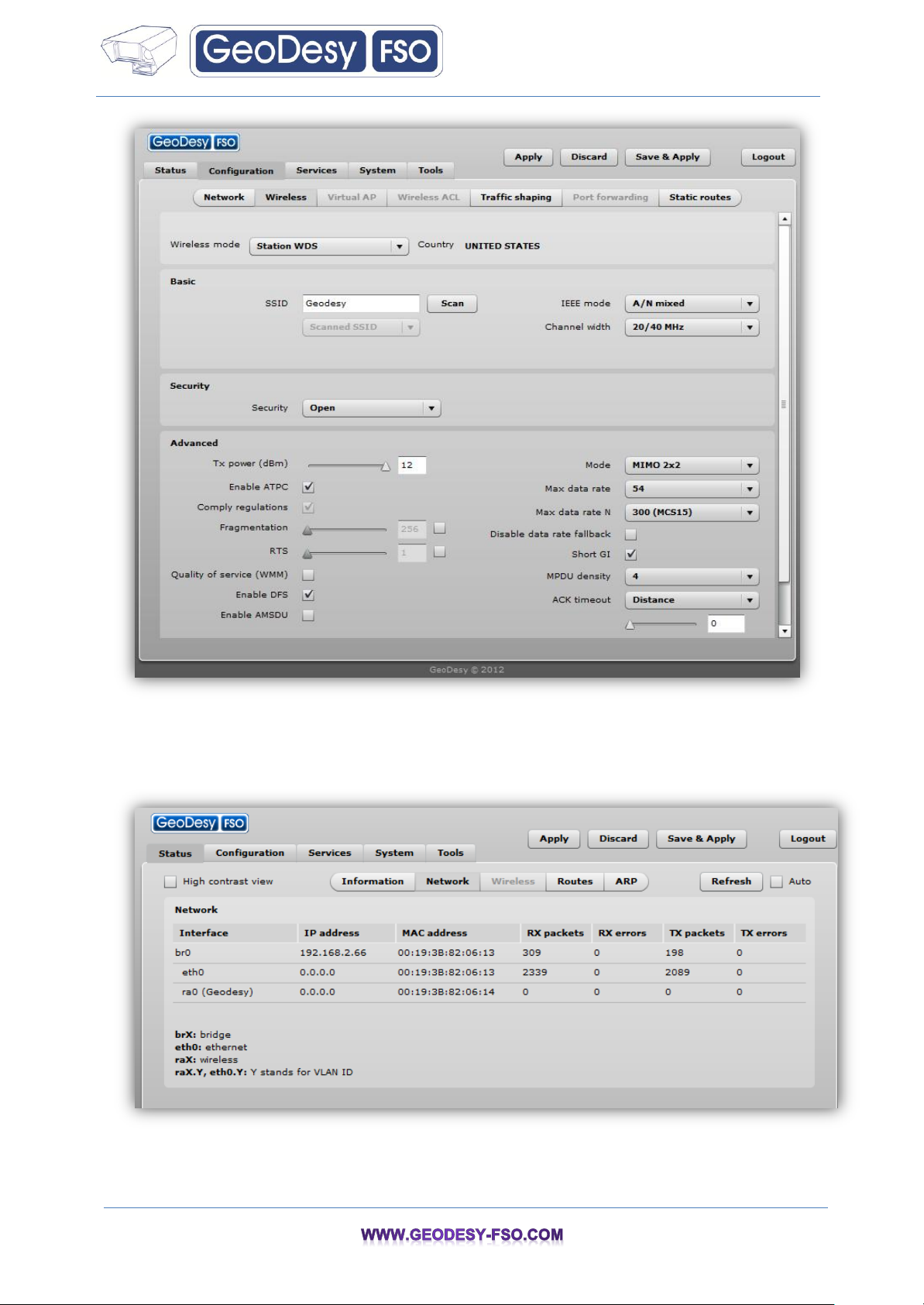
15
Step 8. Verify connection. Navigate to the Status | Network page. The Network page will
show main network information about association with AP:
The main Status | Information page will display wireless information of the link with access point.
Page 16
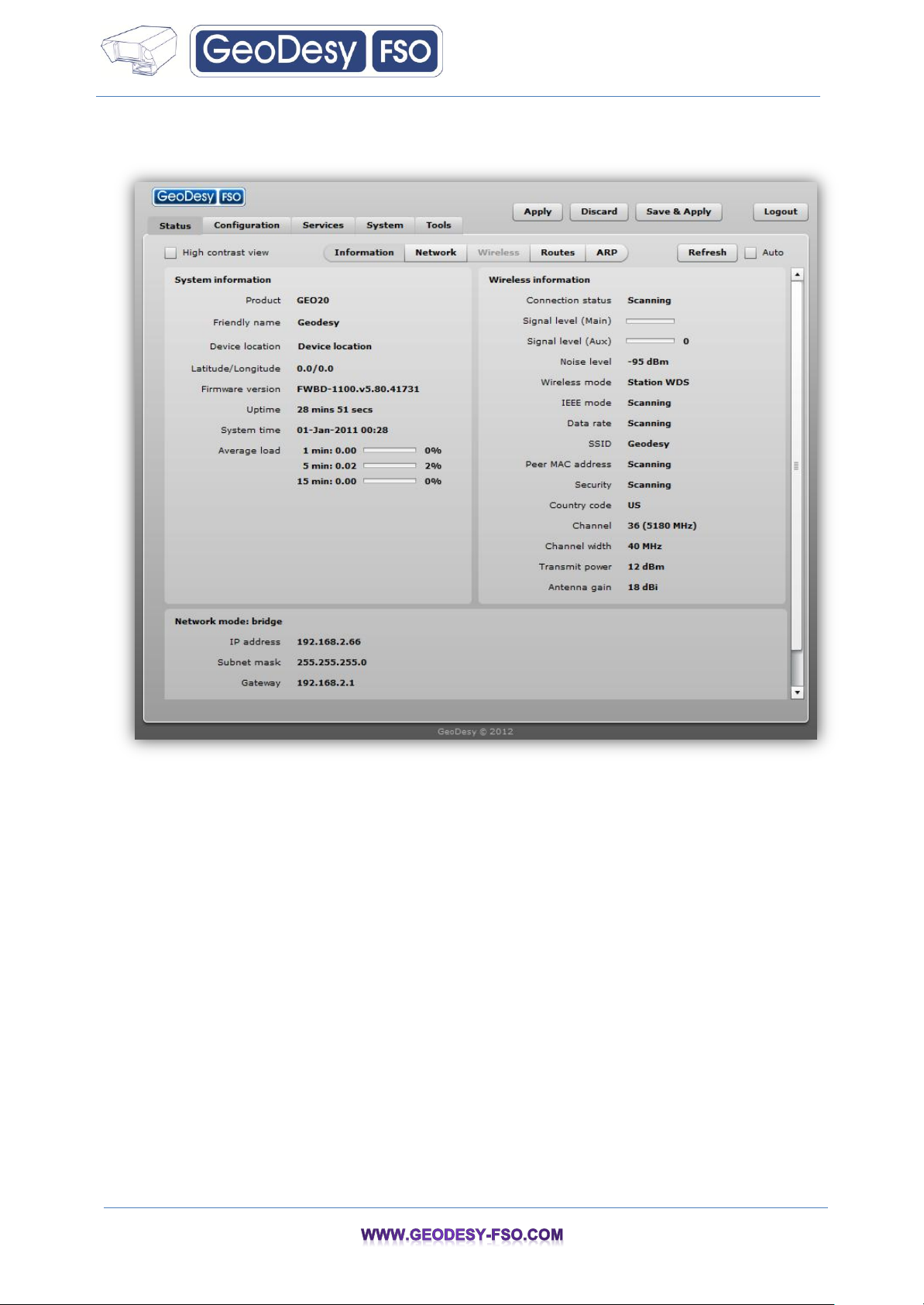
The connection status must be displayed as Connected and progress bars indicating the quality of the
connection must be displayed:
16
Page 17
5 Network Mode
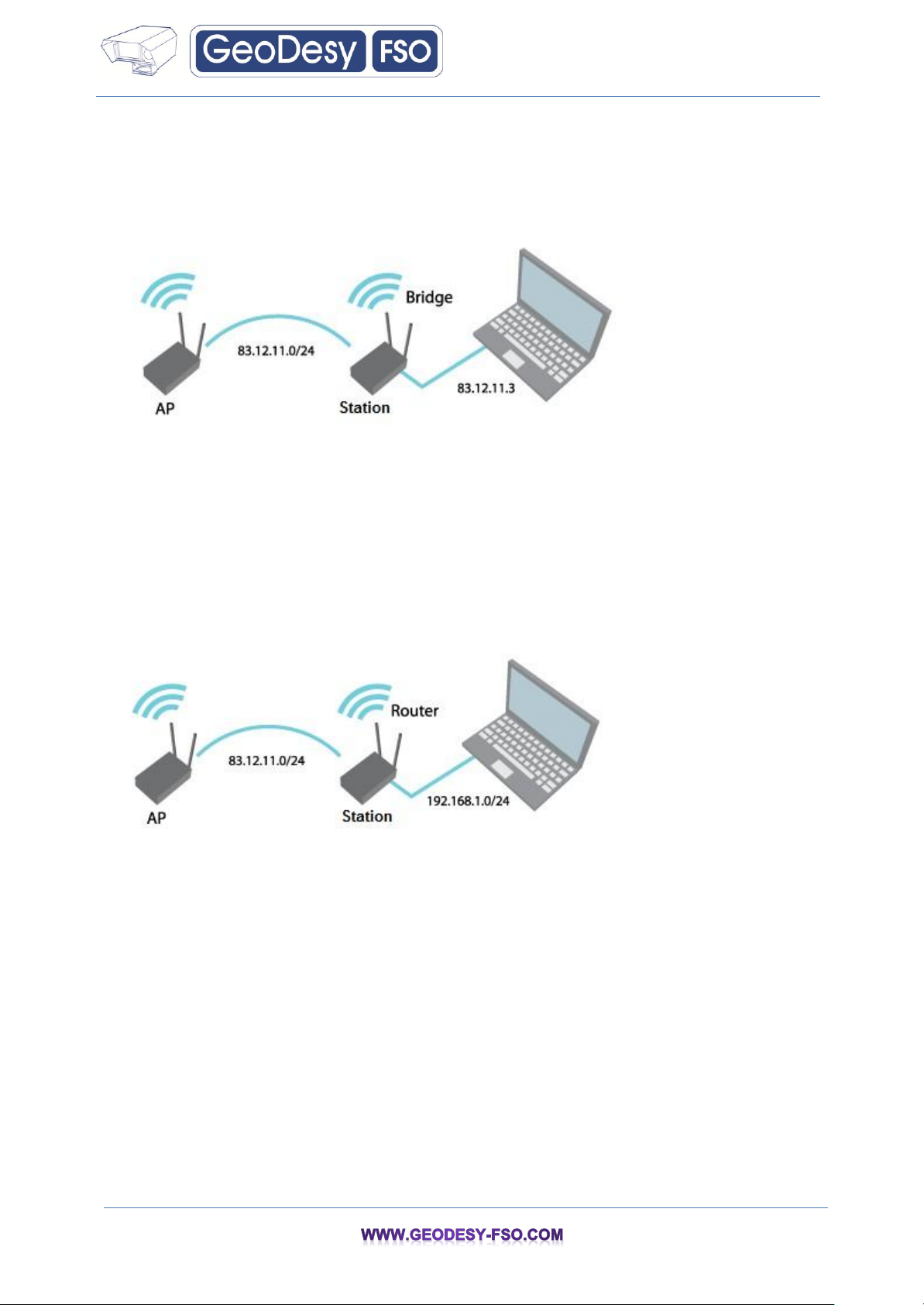
5.1 Bridge Mode
The device can act as a wireless network bridge and establish wireless links with other APs. In this
mode all LAN port and Wireless interface will be a part of the Bridge.
17
Bridge Mode
With a Bridge, all connected computers are in the same network subnet. The only data that is allowed
to cross the bridge is data that is being sent to a valid address on the other side of the bridge.
5.2 Router Mode
In router mode the device will receive internet through WAN port and will share it to the LAN ports that
will be separated with a different IP range. The type of connection to the WAN interface can be made
by Static IP, DHCP client or PPPoE client.
Router Mode
Page 18
GD-GEO20
6 Device Operation
6.1 Web Management Structure
The main web management menu is displayed after successfully login into the system (see the figure
below). From this menu all essential configuration pages are accessed. The active menu tab is
displayed in a different color:
18
Figure 7 – Main Web Management Menu
By default the Status | Information menu is activated where the main device information is displayed.
The AP web management menu has the following structure:
Status
Information – displays general information of the device.
Network – displays main network and wireless statistics of the device.
Wireless – displays information about connected stations on the particular interface (only on
Station wireless mode).
Routes – displays
unit’s
route table.
ARP – displays ARP table.
Configuration
Network – network mode, Ethernet speed, IP settings, management and data VLANs, DHCP,
PPPoE.
Wireless – specify wireless mode (AP, Station, iPoll AP, iPoll Station), country, SSID, IEEE
Mode, channel configuration, security, advanced radio settings.
Virtual AP – create and setup virtual AP (only in AP wireless mode).
Wireless ACL – access control by MAC address (only in AP and IPoll AP wireless modes).
Page 19

Traffic shaping – download and upload traffic control.
Port forwarding – port forwarding rules (only in router network mode for AP and IPoll AP).
Static routes – static route rules (only in router network mode for AP and IPoll AP).
Services
WNMS – set WNMS server/collector URL allowing remote device configuration and monitoring.
System Alerts – set alerts which can be sent via SNMP Traps or/and SMTP notifications. SNMP
– SNMP service settings allowing remote device monitoring.
Clock/NTP – set device date manually or enable and configure NTP service.
SSH – control SSH connection.
HTTP – control HTTP connection.
System
Administration – change password, reboot, restore factory default settings, backup/restore
configuration, troubleshooting file support.
Log – view device log, set system log forwarding settings.
LED – control operation of LEDs.
Firmware upgrade – upgrade device firmware.
Tools
Antenna alignment – measure received signal quality of the wireless link to align antenna in the
best direction.
Site Survey – information about other wireless networks in the local area.
Delayed reboot – setup delayed reboot for APC unit.
Ping – perform ping command.
Traceroute – perform graphical traceroute command.
Spectrum analyzer – check the signal strength on available channels.
6.2 Appling and Saving Configuration Changes
19
There are three general buttons located on the right top corner of the WEB GUI allowing managing
device configuration:
Apply – if pressed new configuration settings are applied instantly. It will take few seconds and
the device will be running with new settings. It should be noted that pressing Apply button
settings are not written to the permanent memory. Therefore, if the device is rebooted it will
start with old configuration settings.
Discard – if pressed parameter changes are discarded. It should be noted that if Apply or
Save Apply is pressed it is not possible to discard changes.
Save Apply – if pressed new configuration settings are applied instantly and written to the
Permanent memory.
It is not required to press Apply or Save Apply in every Web GUI tab. The device remembers all
changes made in every tab and after action button is used, all changes will be applied.
Page 20
7 Configuration
7.1 Status
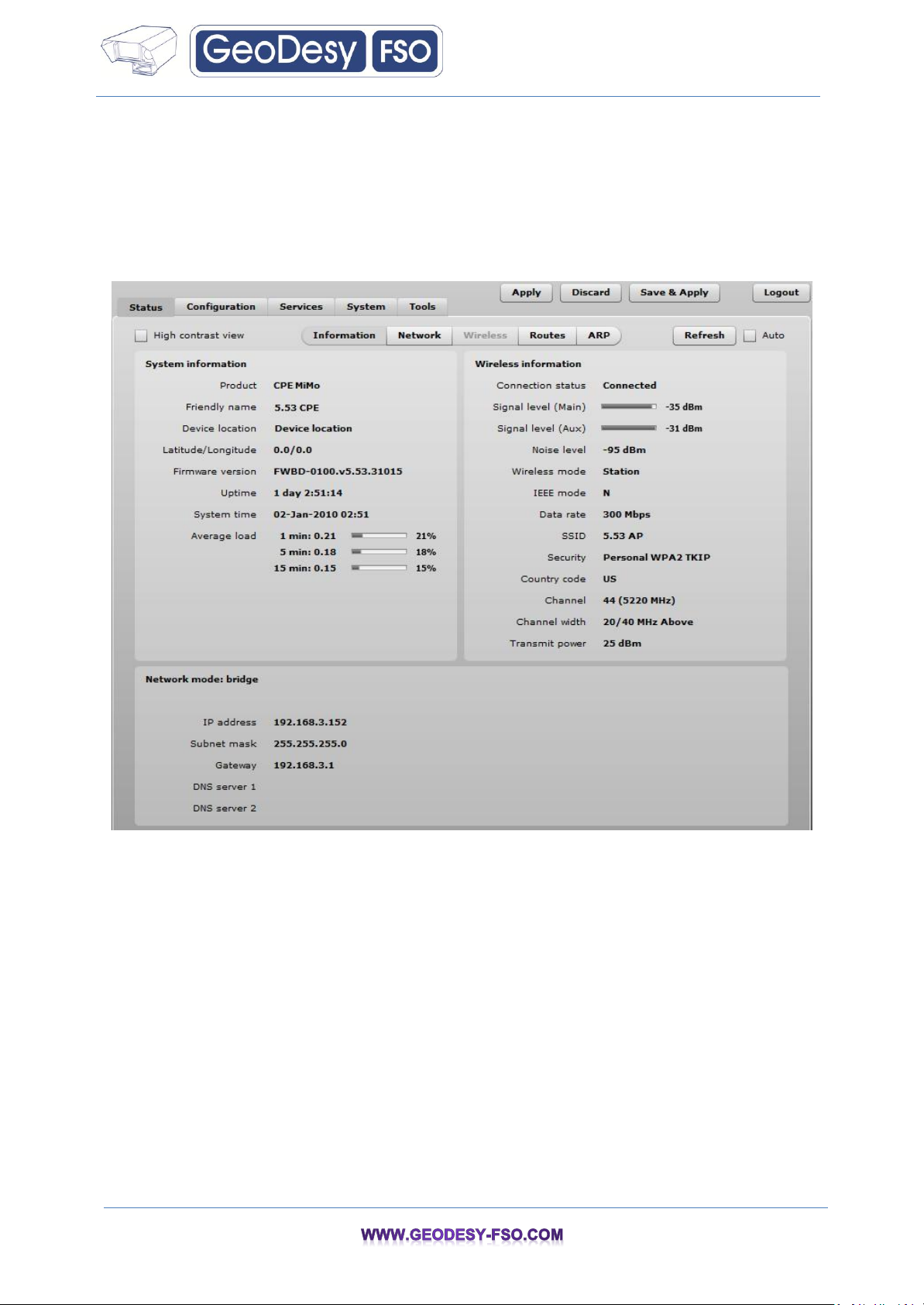
7.1.1 Information
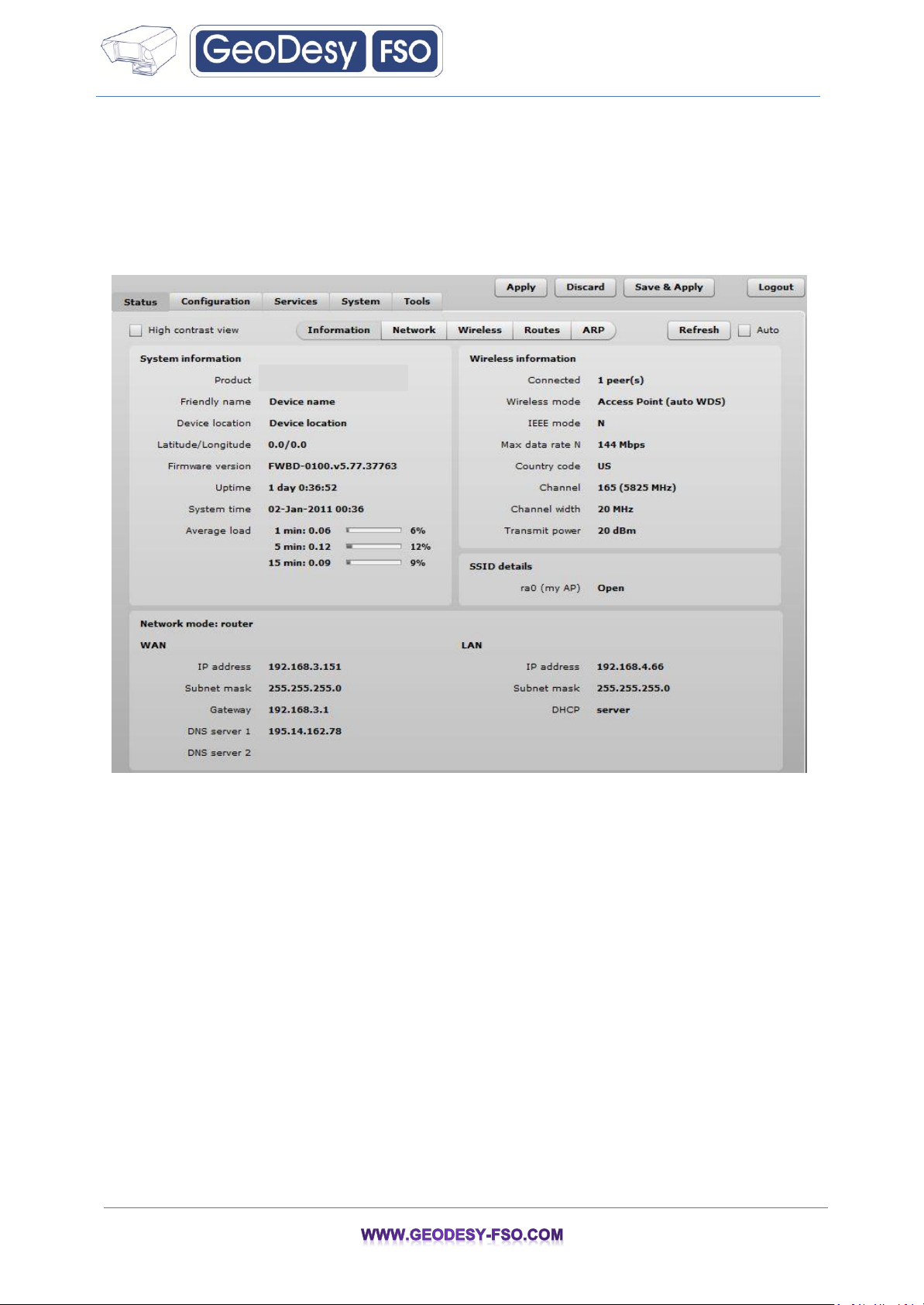
The Information page displays a summary of status information of your device. It shows important
information for the APC operating mode, network settings.
20
System information – displays general information about the device.
Wireless information – displays general information about the wireless network. The wireless
information will differ on Access Point, Station, iPoll wireless modes:
AP mode – displays access point operating information, number of connected clients and SSID
details (including VAPs).
Station mode – displays settings at which the station is connected to the access point.
iPoll AP – displays iPoll access point operating information, number of connected wireless
Stations.
iPoll Station – displays settings at which the iPoll wireless station is connected to the iPoll
Access point.
Network mode – displays short summary of the APC current network configuration (bridge or router).
Page 21
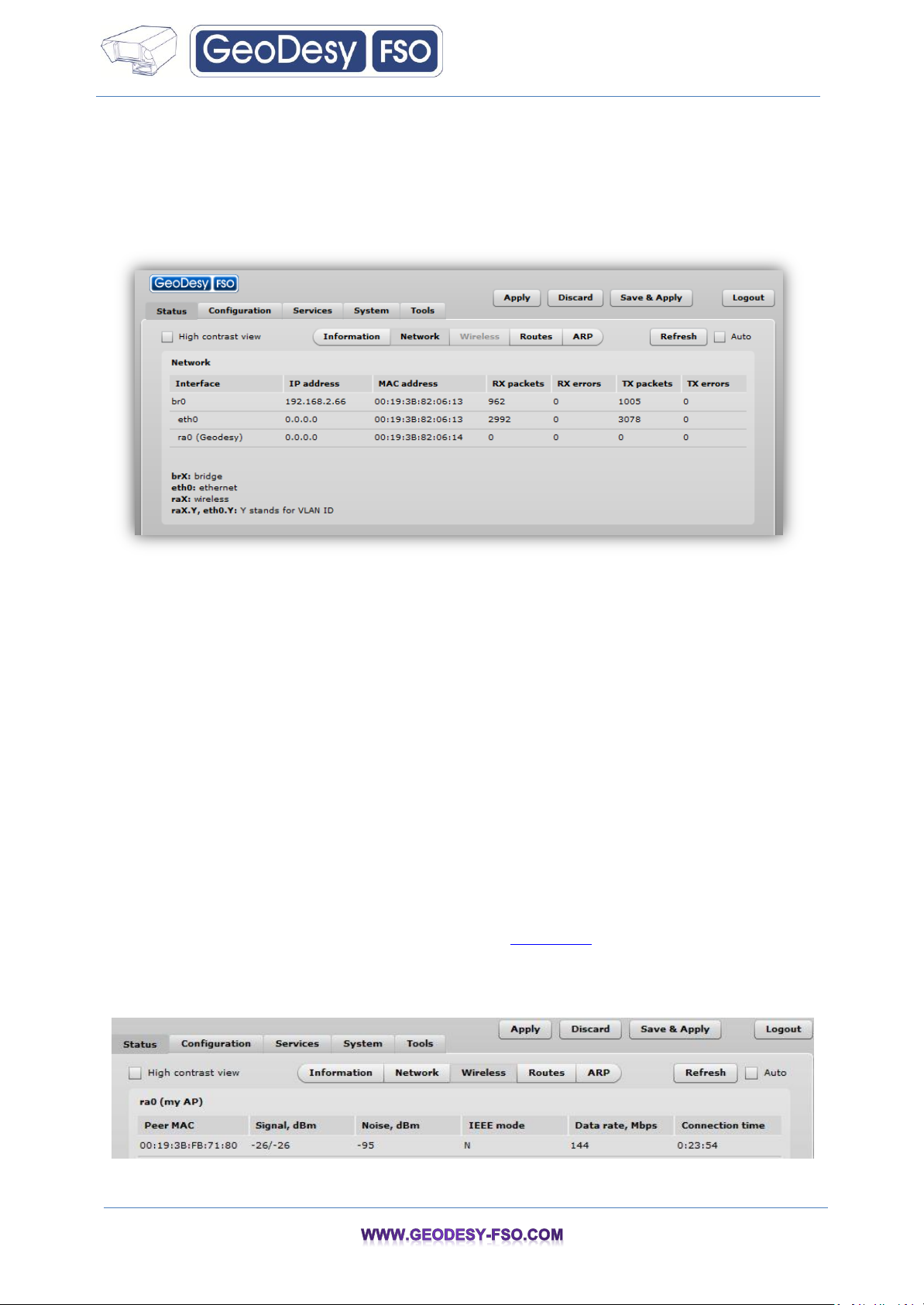
7.1.2 Status Network
The Network sections displays statistics of the network interfaces and DHCP leases (depending on
network mode):
21
Figure 9 – Network Statistics
Interface – displays the interface name. The SSID name is displayed in the brackets near the radio
interface (and VAPs).
IP address – displays the IP address of the particular interface.
MAC – displays the MAC address of the particular interface.
Received – displays the number of received packets.
RX errors – displays the number of the RX errors.
Transmitted – displays the number of transmitted packets.
TX errors – displays the number of the TX errors.
DHCP leases – table displays information about leased DHCP addresses.
7.1.3 Wireless
Status Wireless section is not available if APC is operating in Station wireless mode. All necessary
information about wireless connection with AP unit is under Information section.
The Wireless statistics displays the receive/transmit statistics of successfully associated wireless
clients:
In case the access point has more than one wireless interface (VAPs), the appropriate number of
Page 22

tables with information about connected wireless clients will be displayed.
Peer MAC – displays MAC address of the successfully connected wireless client.
Signal – indicates the signal strength of the access point main and auxiliary antennas that the station
communicates with displayed dB.
Noise – displays the noise level in dBm.
IEEE mode – displays the IEEE mode at which the access point communicates with the particular
station.
Data rate – displays the data rate at which the access point communicates with the particular station.
Connection time – displays the duration of the session.
7.1.4 Routes
The Routes page displays the routing table for each interface:
22
7.1.5 ARP
The ARP page displays the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table currently recorded on the
device. Use Refresh button to reload ARP table results.
Page 23

7.2 Configuration
7.2.1 Network
The Configuration | Network page allows you to control the network configuration and settings of the
device. First, the device operation mode must be defined to work as a bridge or router. The content of
the window varies depending on your selection:
23
Network mode - choose the device operating mode [bridge/router]
Bridge – in this mode the device works as transparent bridge interconnecting wireless network
and LAN port. The Firewall related functions and NAT are not available in this mode.
Router – in this mode the device works as router between wireless network and all LAN ports.
Ethernet speed – configures the Ethernet link speed and the duplex mode of the Ethernet port.
Choose "auto" for automatic detection of link speed and duplex mode.
Network settings will vary according to the selected Network mode. The Bridge mode allows
configuring device LAN IP settings, while the Router mode requires more parameters such as LAN
network settings, WAN network settings, LAN DHCP settings.
7.2.2 Bridge Mode
Port forwarding and Static routes are not available on Bridge mode.
When device is configured to operate in Bridge mode, only device LAN settings should be configured
on the Network page:
Page 24

24
IP Settings
When assigning IP address make sure that the chosen IP address is unused and belongs to the same
IP subnet as your wired LAN, otherwise you will lose the connection to the device from your current PC.
If you enable the DHCP client, the browser will lose the connection after saving, because the IP
address assigned by the DHCP server is not predictable.
Method – specify IP reception method: IP addresses can either be retrieved from a DHCP server or
configured manually:
Static IP – the IP address must be specified manually.
Dynamic IP – the IP address for this device will be assigned from the DHCP server. If DHCP
Server is not available; the device will try to get an IP. If has no success, it will use a fallback IP
address (default fallback IP is 192.168.2.66). The fallback IP settings can be changed to custom
values.
IP Address – specify IP address for device
Subnet mask – specify a subnet mask for device.
Default gateway – specify a gateway IP address for device.
DNS server – specify the Domain Naming Server.
Enable IP alias – specify the alternative IP address and the netmask for APC unit management.
VLAN to SSID Mapping
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) are logical groupings of network resources.
VLAN to SSID mapping – specify the VLAN ID for traffic tagging on required radio interface [2-4095].
The Station devices that associate using the particular SSID will be grouped into this VLAN.
Page 25

25
Management VLAN
Available only on Bridge network mode.
Access to the AP for management purposes can further be limited using VLAN tagging. By defining
Management VLAN, the device will only accept management frames that have the appropriate
Management VLAN ID. All other frames using any management protocol will be rejected.
When you specify a new management VLAN, your HTTP connection to the device will be lost. For
this reason, you should have a connection between your management station and a port in the
new management VLAN or connect to the new management VLAN through a multi-VLAN router.
Enable – select to enable a VLAN tagging for management traffic.
Management VLAN ID – specify the VLAN ID [2-4095]. When device interfaces are configured with a
specific VLAN ID value, only management frames that matching configured VLAN ID will be accepted
by device.
Restrict management to interfaces – select interfaces that will be restricted with management
VLAN.
7.2.3 Router Mode
This section allows customizing parameters of the Router to suit the needs of network, including
ability to use the built-in DHCP server. When device is configured to operate as Router, the following
sections should be specified: WAN network settings, LAN network settings and LAN DHCP settings.
Page 26

26
Enable NAT – select to enable NAT (Network Address Translation), that functions by transforming the
private IP address of packets originating from hosts on your network so that they appear to be coming
from a single public IP address and by restoring the destination public IP address to the appropriate
private IP address for packets entering the private network, the multiple PCs on your network would
then appear as a single client to the WAN interface.
WAN Settings
WAN network settings include settings related to the WAN interface. The access type of the WAN
interface can be configured as: Static IP, Dynamic IP, PPPoE client.
WAN mode – choose Static IP to specify IP settings for device WAN interface
MAC address – specify the clone MAC address if required. The ISPs registers the MAC address
router, and allows only that MAC address to connect to their network. In such case if there is need to
of the
Page 27

change hardware (router), you need to notify your ISP about MAC address change, or simply set
The
router’s
VLAN ID – specify the VLAN ID for traffic tagging on required radio interface [2-4095]. The Station
devices that associate using the particular SSID will be grouped into this VLAN.
WAN mode – choose Static IP to specify IP settings manually. This option needs parameters listed
below:
IP address – specify static IP address.
Subnet mask – specify a subnet mask.
Default gateway – specify a gateway.
DNS server – specify primary and/or secondary DNS server
Enable IP alias – specify the alternative IP address and the netmask for APC unit management.
MAC address to the MAC address of the previously router/computer.
WAN mode – choose Dynamic IP to enable DHCP client on the WAN side. This option does not need
Any parameters.
27
MAC address – specify the clone MAC address if required. The ISPs registers the MAC address
router, and allows only that MAC address to connect to their network. In such case if there is need to
change hardware (router), you need to notify your ISP about MAC address change, or simply set
The
router’s
VLAN ID – specify the VLAN ID for traffic tagging on required radio interface [2-4095]. The Station
devices that associate using the particular SSID will be grouped into this VLAN.
DHCP fallback setting – specify IP address, Subnet mask, Default gateway and optionally DNS
server for DHCP fallback. In case the APC unit will not get the IP address from the DHCP, the
specified fallback IP settings will be used.
Enable IP alias – specify the alternative IP address and the netmask for APC unit management.
MAC address to the MAC address of the previously router/computer.
of the
Page 28

WAN mode – choose PPPoE to configure WAN interface to connect to an ISP via a PPPoE:
28
MAC address – specify the clone MAC address if required. The ISPs registers the MAC address
of the
router, and allows only that MAC address to connect to their network. In such case if there is need to
change hardware (router), you need to notify your ISP about MAC address change, or simply set
The
router’s
MAC address to the MAC address of the previously router/computer.
VLAN ID – specify the VLAN ID for traffic tagging on required radio interface [2-4095]. The Station
devices that associate using the particular SSID will be grouped into this VLAN.
User name – specify the user name for PPPoE.
Password – specify the password for PPPoE.
MTU – specify the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit). The default value is 1500 bytes.
DNS settings – allows selecting if automatically assigned or alternative DNS servers should be used.
Enable IP alias – specify the alternative IP address and the netmask for APC unit management.
LAN Network Settings
LAN network settings includes settings related to the LAN interface
Page 29

IP address – specify the IP address of the device LAN interface.
Subnet mask – specify the subnet mask of the device LAN interface.
LAN DHCP Settings
DHCP mode – choose disabled to disable DHCP on LAN interface.
29
DHCP mode – choose relay to enable DHCP relay. The DHCP relay forwards DHCP messages
between subnets with different sub layer broadcast domains.
DHCP mode – choose server to enable DHCP server on LAN interface.
IP address from – specify the starting IP address of the DHCP address pool.
IP address to – specify the ending IP address of DHCP address pool.
Subnet mask – specify the subnet mask.
Default gateway – specify DHCP gateway IP address.
Lease time – specify the expiration time in seconds for the IP address assigned by the DHCP server.
DNS server – specify the DNS server IP address.
Page 30

7.2.4 Wireless
The Wireless tab is divided in three sections: Basic, Security and Advanced configuration sections.
The Basic section contains all parameters that required to configure in order have working wireless
link. Security section is used to select authentication and encryption settings. Advanced section
contains parameters allowing optimizing the link capacity.
Before changing radio settings manually verify that your settings will comply with local
government regulations. At all times, it is the responsibility of the end-user to ensure that the
installation complies with local radio regulations.
The APC device can operate in four wireless modes: Access Point, Station, Station WDS, iPoll
Access Point and iPoll Station.
30
Depending on the wireless operation mode selection some of the displayed configuration parameters
will differ (e.g. security or advanced wireless settings).
Wireless mode – select wireless operation mode:
Access Point (auto WDS)) – enables the APC radio function as an access point. When in AP
mode, wireless clients can see the AP broadcast and associate to it if settings are configured
correctly.
Station – sets the radio to run in client mode. In this mode wireless station does not broadcast an
SSID and clients cannot connect to it. Station mode allows the APC radio to connect to other
radios functioning as an AP.
Station WDS – a wireless station will communicate with access point in WDS mode. Station WDS
Mode enables packet forwarding at layer 2 level.
iPoll Access Point – enables APC radio function as access point for point-to-multipoint solution.
The iPoll Access Point accepts only iPoll Station requests.
iPoll Station – enables APC radio function as wireless station for point-to-multipoint solution. The
iPoll Station can establish a link only with iPoll Access point.
Be sure that both ends of the link have the appropriate wireless mode, otherwise the
connection will be not established (e.g. iPoll Station is able to establish a connection only with
iPoll AP).
Country – choose from the drop-down list the country in which the APC will operate. The channel list,
transmit power limits, IEEE 802.11 mode will be adjusted according to the regulations of the selected
country.
Page 31

7.2.5 Wireless Mode: Access Point
Use Basic Wireless Settings to setup radio interface of the device.
31
Basic Wireless Settings
SSID – specify the SSID of the wireless network device.
Page 32

Broadcast SSID – enables or disables the broadcasting of the SSID for AP.
IEEE mode – specify the wireless network mode.
Channel width – The default channel bandwidth for 802.11 radio is 20MHz. The 802.11n allow
channel bonding in such way the total channel width becomes 40MHz.
Channel – select the channel from the drop-down list or option Auto for auto channel. Automatic
channel selection allows Access Point to select a channel which is not used by an y other wireless
device or, if there are no free channels available - to select a channel which is least occupied.
Channel list – select the channels to create a channel list for auto channel.
Security Settings
Both sides (AP and Station) of the link must have the same security settings.
Device supports various
Open – no encryption.
WEP – 64bit and 128bit key.
Personal – preshared key encryption with WPA/WPA2 using AES or TKIP.
Enterprise – RADIUS server based authentication with WPA/WPA2 encryption using AES or
TKIP (requires configured RADIUS server).
UAM – Web browser based user authentication method. UAM authentication is available only if
Access Point is working in router mode. For UAM configuration details refer at the respective
chapter Universal Access Method (UAM).
By default there is no encryption enabled on the device:
authentication/encryption
methods:
32
WEP encryption can be either 64bit or 128bit:
WEP passkey – specify the passkey, for the chosen WEP security:
For WEP 64bit encryption – 5 HEX pairs (e.g. aa:bb:cc:dd:ee), or 5 ASCII characters (e.g.
abcde);
For WEP 128bit encryption – 13 HEX pairs (e.g.
aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff:gg:hh:00:11:22:33:44),
or 13
ASCII characters (e.g. abcdefghijklm);
To setup Personal WPA/WPA2 encryption, need to specify the pre-shared key and encryption with
chosen AES, TKIP or Auto method:
Page 33

33
Passphrase – specify WPA or WPA2 passphrase [8-63 characters]. The passphrase will be
converted to key format, selected above.
Encryption – specify WPA/WPA2 encryption algorithm:
AES – APC will accept clients with passphrase encrypted with AES method only;
TKIP – APC will accept clients with passphrase encrypted with TKIP method only;
Auto – APC will accept clients with passphrase encrypted with both: AES and TKIP methods;
AP has possibility to configure Enterprise WPA/WPA2 encryption with RADIUS authentication.
Properly configured AP will accept wireless stations requests and will send the information to
configured RADIUS server for client authentication.
The properly configured RADIUS server is required for Enterprise WPA/WPA2 encryption.
Encryption – specify WPA/WPA2 encryption algorithm:
AES – AP will accept clients with passphrase encrypted with AES method;
TKIP – AP will accept clients with passphrase encrypted with TKIP method;
Auto – AP will accept clients with passphrase encrypted with both: AES and TKIP methods;
RADIUS authentication settings:
RADIUS IP – specify the IP address of the authentication RADIUS server where the authentication
requests will be send to.
RADIUS port – specify the network port used to communicate with the RADIUS authentication server.
Default: 1812 for authentication.
RADIUS key – specify the secret key of the authentication server [string]. The shared secret is used
to encrypt data packets transmitted between RADIUS server and client.
Shared secrets must be the same on the RADIUS servers and the RADIUS client.
Advanced Wireless Settings
Advanced parameters allow configuring the device to get the best performance/capacity of the link.
Page 34

34
Tx power – set the
unit’s
transmitting power at which the device will transmit data. The larger the
distance, the higher transmit power is required. To set transmit power level use the slider or enter the
value manually. When entering the transmit power value manually, the slider position will change
according to the entered value. The maximum transmit power level is limited to the allowed value by
country in which device is operating regulatory agency.
Enable ATPC – select to enable Automatic Transmit Power Control (ATPC). If enabled, device radio
will continuously communicate with remote
unit’s
radio in order to adjust the optimal transmit power
Automatically.
Antenna Gain, dBi – displays integrated antenna gain in dBi. This entry field will be editable for the
connectorized antennas where the custom value of the antenna gain must be specified.
Comply regulations – if enabled, the APC will automatically adjust radio settings (transmit power and
DFS) to conform regulatory rules of the selected country.
Fragmentation – specify the Fragmentation threshold using slider or enter the value manually [256-
2346 bytes]. This is the maximum size for a packet before data is fragmented into multiple packets.
Setting the Fragmentation threshold too low may result in poor network performance. Only minor
modifications of this value are recommended.
RTS – specify the RTS threshold using slider or enter the value manually [0-2347 bytes]. The RTS
threshold determines the packet size of a transmission and, through the use of an access point, helps
control traffic flow.
Quality of service (WMM) – enable to support quality of service for traffic prioritizing.
Client isolation – select to enable the layer 2 isolation that blocks clients from communicating with
each other. Client isolations is available only in Access Point (auto WDS) mode.
Enable DFS – select to enable radar detection. With enabled DFS, APC unit monitors the operating
frequency for radar signals. If radar signals are detected on the channel, the APC unit randomly
selects a different channel.
Enable AMSDU – enable the AMSDU packet aggregation. If enabled, the maximum size of the
802.11 MAC frames will be increased.
Mode – choose the AP antenna operating mode:
SISO – single input single output. The device will use only one antenna for data transfer. The
antenna will be chosen automatically.
MIMO – multiple input multiple outputs. The device will use two antennas for data transfer (two
Simultaneous streams).
Max data rate – choose the maximum data rate in Mbps at which should transmit packets. The APC
Will attempts to transmit data at the highest data rate set. If there will be an interference encountered,
Page 35

The APC will step down to the highest rate that allows data transmission.
Max data rate N – choose the data rates in Mbps at which should transmit packets for the selected
802.11n mode. The APC will attempts to transmit data at the highest data rate set. If there will be an
interference encountered, the APC will step down to the highest rate that allows data transmission.
Disable data rate fallback – when this option is selected, the constant Max data rate will be set
without a step back to the next highest data rate for APC data transmission.
Short GI – enable short guard interval. If selected, then 400ns value will be used, else 800ns.
MPDU density – define minimum time between PPDU‟s.
ACK timeout – specify the ACK timeout using slider or enter the value manually. Ack timeout can be
entered by defining the link distance or specifying time value. Too low value of the ACK timeout will
give very low throughput. A high value may slow down the link in noisy environment. A low value is far
worse than a value slightly too high. ACK Timeout value should be tuned to the optimal value for the
maximum link throughput.
7.2.6 Wireless Mode: Station
Station WDS has the same wireless settings.
The Station wireless settings a bit differ from the Access
SSID of the surrounding APs and choose the required one.
Use Wireless Settings to setup radio interface of the device.
Point’s
settings: there is possibility to scan
35
Basic Wireless Settings
SSID – specify the SSID of the wireless network device.
Scan – click this button to scan for surrounding wireless networks. Found network
SSID‟s
will be
Available in drop down menu.
IEEE mode – specify the wireless network mode.
Channel width - The default channel bandwidth for 802.11 radio is 20MHz. The 802.11n allow
channel bonding in such way the total channel width becomes 40MHz.
Security Settings
Both sides (AP and Station) of the link must have the same security settings.
Device supports various
Open – no encryption.
WEP – 64bit and 128bit key.
Personal – preshared key encryption with WPA/WPA2 using AES or TKIP.
Enterprise – RADIUS server based authentication with WPA/WPA2 encryption using AES or
TKIP (requires configured RADIUS
By default there is no encryption enabled on the device:
authentication/encryption
server).
methods:
Page 36

36
WEP encryption can be either 64bit or 128bit:
WEP passkey – specify the passkey, for the chosen WEP security:
For WEP 64bit encryption – 5 HEX pairs (e.g. aa:bb:cc:dd:ee), or 5 ASCII characters (e.g.
abcde);
For WEP 128bit encryption – 13 HEX pairs (e.g.
ASCII characters (e.g.
abcdefghijklm);
aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff:gg:hh:00:11:22:33:44),
or 13
Personal WPA/WPA2 encryption must be specified with the pre-shared key, encrypted with chosen
AES or TKIP method (Auto mode on Station is not available):
Passphrase – specify the WPA or WPA2 passphrase [8-63 characters]. The passphrase will be
converted to key format, selected above.
Encryption – specify the encryption algorithm:
AES – passphrase encrypted with AES method.
TKIP – passphrase encrypted with TKIP method.
APC has possibility to use Enterprise WPA/WPA2 encryption with RADIUS authentication. Station
will send requests to AP, which will redirect authentication parameters to required RADIUS server.
Encryption – choose WPA/WPA2 encryption type:
AES – data encrypted with AES method;
TKIP – data encrypted with TKIP method;
EAP method – choose EAP method:
EAP-TTLS-MSCHAPv2
Page 37

PEAP/ MSCHAPv2
Identity – specify the identity of the authentication to the RADIUS server.
Password – specify the password of the authentication to the RADIUS server.
Identity and Password on the APC must match the identity and password running on the
RADIUS server's user list.
Advanced Wireless Settings
Advanced parameters allow configuring the device to get the best performance/capacity of the link.
37
Tx power – set the
unit’s
transmitting power at which the device will transmit data. The larger the
distance, the higher transmit power is required. To set transmit power level use the slider or enter the
value manually. When entering the transmit power value manuall y, the slider position will change
according to the entered value. The maximum transmit power level is limited to the allowed value by
country in which device is operating regulatory agency.
Enable ATPC – select to enable Automatic Transmit Power Control (ATPC). If enabled, device radio
will continuously communicate with remote
unit’s
radio in order to adjust the optimal transmit power
Automatically.
Antenna Gain, dBi – displays integrated antenna gain in dBi. This entry field will be editable for the
connectorized antennas where the custom value of the antenna gain must be specified.
Comply regulations – if enabled, the APC will automatically adjust radio settings (transmit power and
DFS) to conform regulatory rules of the selected country.
Fragmentation – specify the Fragmentation threshold using slider or enter the value manually [256-
2346 bytes]. This is the maximum size for a packet before data is fragmented into multiple packets.
Setting the Fragmentation threshold too low may result in poor network performance. Only minor
modifications of this value are recommended.
RTS – specify the RTS threshold using slider or enter the value manually [0-2347 bytes]. The RTS
threshold determines the packet size of a transmission and, through the use of an access point, helps
control traffic flow.
Quality of service (WMM) – enable to support quality of service for traffic prioritizing.
Enable DFS – select to enable radar detection. With enabled DFS, APC unit monitors the operating
frequency for radar signals. If radar signals are detected on the channel, the APC unit randomly
selects a different channel.
Enable AMSDU – enable the AMSDU packet aggregation. If enabled, the maximum size of the
802.11 MAC frames will be increased.
Mode – choose the AP antenna operating mode:
SISO – single input single output. The device will use only one antenna for data transfer. The
Page 38

antenna will be chosen automatically.
MIMO – multiple input multiple outputs. The device will use two antennas for data transfer (two
Simultaneous streams).
Max data rate – choose the maximum data rate in Mbps at which should transmit packets. The APC
Will attempts to transmit data at the highest data rate set. If there will be an interference encountered,
The APC will step down to the highest rate that allows data transmission.
Max data rate N – choose the data rates in Mbps at which should transmit packets for the selected
802.11n mode. The APC will attempts to transmit data at the highest data rate set. If there will be an
Interference encountered, the APC will step down to the highest rate that allows data transmission.
Disable data rate fallback – when this option is selected, the constant Max data rate will be set
without a step back to the next highest data rate for APC data transmission.
Short GI – enable short guard interval. If selected, then 400ns value will be used, else 800ns.
MPDU density – define minimum time between PPDU‟s.
ACK timeout – specify the ACK timeout using slider or enter the value manually. Ack timeout can be
entered by defining the link distance or specifying time value. Too low value of the ACK timeout will
give very low throughput. A high value may slow down the link in noisy environment. A low value is far
worse than a value slightly too high. ACK Timeout value should be tuned to the optimal value for the
maximum link throughput.
7.2.7 Wireless Mode: iPoll Access Point
38
The iPoll wireless mode is designed for point to multipoint wireless solutions. The iPoll Access Point
establishes a connection only with iPoll Stations thus creating a reliable network
Basic Settings
Use Basic section to setup basic operating settings of the iPoll Access
iPoll Access Point and iPoll Station will operate in 802.11n IEEE mode
SSID – specify the SSID of the wireless network device.
Point’s
radio.
only.
Broadcast SSID – enables or disables the broadcasting of the SSID for AP.
Channel width – The default channel bandwidth for 802.11n radio is 20MHz. The 802.11n allow
channel bonding in such way the total channel width becomes 40MHz.
Channel – select the channel from the drop-down list or option Auto for auto channel. Automatic
Page 39

channel selection allows iPoll Access Point to select a channel which is not used by any other
wireless device or, if there are no free channels available - to select a channel which is least
occupied.
Channel list – select the channels to create a channel list for auto channel.
Security Settings
Both sides (iPoll Access Point and iPoll Station) of the link must have the same security
settings.
The APC device working, in iPoll Access Point wireless mode, supports authentication/encryption
methods listed below:
Open – no encryption.
Personal WPA – preshared key encryption with WPA using AES method.
Personal WPA 2 – preshared key encryption with WPA2 using AES method.
By default there is no encryption enabled on the device:
39
Personal WPA/WPA2 encryption must be specified with the pre-shared key:
Passphrase – specify the WPA or WPA2 passphrase [8-63 characters]. The passphrase will be
converted to key format, selected above.
Advanced Wireless Settings
Advanced wireless settings allow configuring the APC unit to get the best
link:
performance/capacity
of the
Transmit power – set the
unit’s
transmitting power at which the device will transmit data. The larger
Page 40

the distance, the higher transmit power is required. To set transmit power level use the slider or enter
the value manually. When entering the transmit power value manually, the slider position will change
according to the entered value. The maximum transmit power level is limited to the allowed value by
country in which device is operating regulatory agency.
Enable ATPC – select to enable Automatic Transmit Power Control (ATPC). If enabled, device radio
will continuously communicate with remote
Automatically.
Antenna Gain, dBi – displays integrated antenna gain in dBi. This entry field will be editable for the
connectorized antennas where the custom value of the antenna gain must be specified.
Comply regulations – if enabled, the APC will automatically adjust radio settings (transmit power and
DFS) to conform regulatory rules of the selected country.
Enable DFS – select to enable radar detection. With enabled DFS, APC unit monitors the operating
frequency for radar signals. If radar signals are detected on the channel, the unit randomly selects a
different channel.
Mode – choose the
SISO – single input single output. The device will use only one antenna for data transfer. The
unit’s
antenna operating mode:
antenna will be chosen automatically.
MIMO – multiple input multiple outputs. The device will use two antennas for data transfer (two
Simultaneous streams).
Max data rate – select the device data transmission rates in Mbps from the drop-down list. The APC
Will attempt to transmit data at the highest data rate set. If there will be an interference encountered,
The APC will step down to the highest rate that allows data transmission.
Transmit queue length, frames – specify the length in frames of the transmit queue.
unit’s
radio in order to adjust the optimal transmit power
40
7.2.8 Wireless Mode: iPoll Station
The iPoll Station is a wireless client mode which can connect to the iPoll Access Points.
Page 41

Basic Settings
Use this section to setup basic operating settings of the iPoll Station radio.
iPoll Access Point and iPoll Station will operate in 802.11n IEEE mode only.
SSID – specify the SSID of the wireless network device manually, or use Scan functionality.
41
Scan – click this button to scan for surrounding iPoll Access Points. Found network
SSID‟s
will be
Available in drop down menu.
Channel width – The default channel bandwidth for 802.11 N radio is 20/40MHz. The 802.11n allow
channel bonding in such way the total channel width becomes 40MHz.
Security Settings
Both sides (iPoll Access Point and iPoll Station) of the link must have the same security
settings.
The APC device working, in iPoll Station wireless mode, supports authentication/encryption methods
listed below:
Open – no encryption.
Personal WPA – preshared key encryption with WPA using AES method.
Personal WPA 2 – preshared key encryption with WPA2 using AES method.
By default there is no encryption enabled on the device:
Personal WPA/WPA2 encryption must be specified with the pre-shared key:
Passphrase – specify the WPA or WPA2 passphrase [8-63 characters]. The passphrase will be
converted to key format, selected above.
Advanced Wireless Settings
Advanced wireless settings allow configuring the APC unit to get the best
link:
performance/capacity
of the
Page 42

42
Transmit power – set the
unit’s
transmitting power at which the device will transmit data. The larger
the distance, the higher transmit power is required. To set transmit power level use the slider or enter
the value manually. When entering the transmit power value manually, the slider position will change
according to the entered value. The maximum transmit power level is limited to the allowed value by
country in which device is operating regulatory agency.
Enable ATPC – select to enable Automatic Transmit Power Control (ATPC). If enabled, device radio
will continuously communicate with remote
unit’s
radio in order to adjust the optimal transmit power
Automatically.
Antenna Gain, dBi – displays integrated antenna gain in dBi. This entry field will be editable for the
connectorized antennas where the custom value of the antenna gain must be specified.
Comply regulations – if enabled, the APC will automatically adjust radio settings (transmit power and
DFS) to conform regulatory rules of the selected country.
Enable DFS – select to enable the radar detection. With enabled DFS, APC unit monitors the
operating frequency for radar signals. If radar signals are detected on the channel, the unit randomly
selects a different channel.
Mode – choose the
SISO – single input single output. The device will use only one antenna for data transfer. The
unit’s
antenna operating mode:
antenna will be chosen automatically.
MIMO – multiple input multiple outputs. The device will use two antennas for data transfer (two
Simultaneous streams).
Max data rate – select the device data transmission rates in Mbps from the drop-down list. The APC
Will attempt to transmit data at the highest data rate set. If there will be an interference encountered,
The APC will step down to the highest rate that allows data transmission.
Transmit queue length, frames – specify the length in frames of the transmit queue.
7.2.9 Virtual AP
Virtual AP functionality is available only in Access Point (auto WDS) wireless mode.
Use the Configuration | Virtual AP page to configure to create up to 3 additional Virtual AP
interfaces. The Virtual AP defines a logical wireless network, and the APC can be configured to
provide additional 3 wireless networks on each device radio. All the VAPs may be active at the same
time meaning that client devices can associate to the APC using any of the VAP SSID.
The Virtual AP table displays a summary of all virtual radio interfaces running on the APC:
Page 43

43
To create a new Virtual AP, click on + button to add new entry on the VAP table, then select this entry
and specify required parameters:
SSID – specify the unique name for the VAP [string].
Broadcast SSID – when this option is selected the particular SSID is visible during network scans on
a wireless station. When unselected, the VAP SSID is not visible and not broadcasted to wireless
stations.
Quality of service (WMM) – enable to support quality of service for prioritizing traffic.
User isolation – enable the user Layer 2 isolation. The Layer 2 isolation blocks the wireless clients
from communicating with each other.
Each VAP security is configured by default as an “open system”, which broadcasts a beacon signal
Including the configured SSID. For more secure network choose one of the security mechanisms for
Each VAP interface.
Security – choose the wireless security and encryption method from the drop-down list (for detailed
security configuration, refer to the respective section Access Point (auto WDS) Security Settings).
Open – no encryption.
WEP – 64bit and 128bit key.
Personal – preshared key encryption with WPA/WPA2 using AES or TKIP.
Enterprise – RADIUS server based authentication with WPA/WPA2 encryption using AES or
TKIP (requires configured RADIUS server).
UAM – Web browser based user authentication method. UAM authentication is available only if
Access Point is working in router mode. For UAM configuration details refer at the respective
chapter Universal Access Method (UAM).
Wireless clients must be able to process the WPA or WPA2 information element and
respond with a specific security configuration.
7.2.10 Wireless ACL
Wireless ACL is active only in Access Point (auto WDS) and iPoll Access Point wireless mode.
Page 44

Access Control provides the ability to limit associations wirelessly based on MAC address to an AP by
creating an Access Control List (ACL).
44
Policy – define the policy:
Open – no rules applied
Allow MAC in the list – only listed MAC clients can connect to the AP (white list).
Deny MAC in the list – only listed MAC clients can NOT connect to the AP (black list).
To add new rule, press the “+” button.
To remove the rule, first select the rule then press the “–” button.
To edit the rule double click on the field.
7.2.11 Traffic Shaping
Use Traffic Shaping to control download or upload bandwidth in order to optimize or guarantee
performance. There are two methods to control network traffic:
Limit all traffic – limits overall APC upload and download traffic.
Limit per IP traffic – limits upload and download traffic for a specified IP addresses.
Limit all traffic
Enable download shaping – select to enable limitation of the download traffic.
Download limit, kbps – specify the maximum download (from wireless interface to Ethernet
interface) bandwidth value in Kbps.
Download burst, kbytes – specify the download burst size in kbytes.
Enable upload shaping – select to enable limitation of the upload traffic.
Page 45

Upload limit, kbps – specify the maximum upload (from Ethernet interface to wireless interface)
bandwidth value in Kbps.
Upload burst, kbytes – specify the upload burst size in kbytes
Limit per IP traffic
Use + button to create new traffic limitation rules
45
IP address – specify IP address for which the traffic will be limited.
Down rate, kbps – specify the maximum download (from wireless interface to Ethernet interface)
bandwidth value in Kbps.
Down burst, kbytes – specify the download burst size in kbytes.
UP rate, kbps – specify the maximum upload (from Ethernet interface to wireless interface)
bandwidth value in Kbps.
UP burst, kbytes – specify the download burst size in kbytes
7.2.12 Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is active only in Router network mode..
Port Forwarding, UPnP and DMZ is effective only if NAT is enabled.
The Port forwarding section gives the ability to pass traffic behind an interface that has NAT
Enabled. For instance if the unit is in router mode with NAT enabled on the WAN interface, no devices
on the outside of the WAN interface can see any private IPs on the LAN side of the unit. By using port
forwarding or DMZ it is possible to pass traffic through to these private IP addresses.
Enable UPnP – select to enable UPnP (Universal Plug and Play connectivity) service. The UPnP
enables APC communicate with other network devices automatically opening required ports, without
manual intervention.
Page 46

Enable DMZ – select to enable DMZ. DMZ opens all TCP/UDP ports to particular IP address.
setting up servers behind the APC. The feature is used commonly for setting up VoIP or Multi- Media
servers.
Public port – specify the port that will be accessed externally using the public IP address.
Private host – specify the IP address behind NAT that public traffic will get forwarded to.
Private port – specify the listening port on private computer behind NAT.
Protocol – select type of forwarding traffic: TCP or UDP.
It allows
7.2.13 Static Routes
Static routes is active only in Router network mode.
A routing rule is defined by the destination subnet (Destination IP address and netmask), interface
and/or gateway where to route the target traffic. A data packet that is directed to the destination
Network is routed to the specified
Route, specify the following
parameters:
router’s
interface or to another gateway router. To add a new static
46
Destination IP – specify the destination IP address.
Netmask – specify destination netmask.
Gateway – specify the gateway address for the route. 0.0.0.0 Stands for the default gateway of the
selected interface.
Interface – select interface for the route.
7.3 Services
7.3.1 WNMS
Wireless Network Management System (WNMS) is a centralized monitoring and management system
for wireless network devices. The communication between managed devices and the WNMS server is
always initiated by WNMS client service running on every device.
Page 47

Enable WNMS agent – select to enable WNMS agent.
Server/Collector URL – specify the URL of the WMS server to which that heartbeat notifications will
be sent to.
7.3.2 System alerts
The device is able to send external alerts when there are system errors. The alerts can be sent via
SNMP Traps or/and SMTP notifications.
47
Enable alerts – select to enable alert notifications on the system.
System check interval, s – specify interval in seconds at which the device will send notifications of
unexpected system behavior.
System alerts:
Wireless link status change – system will send notification on Wireless link status change.
Ethernet link status change – system will send notification on Ethernet link status change.
RSSI level lower than – system will send notification when RSSI reach value lower than specified.
Default: 25
Noise level greater than – system will send notification when signal noise will reach value greater
than specified. Default: -60 dBm.
RX drop greater than – system will send notification when percent of RX dropped packets become
higher than specified value. Default: 250 packets per seconds.
TX retry greater than – system will send notification when percent of TX retries becomes higher than
specified value. Default: 250 packets per seconds.
Device reboot – system will send notification about unexpected or administrator initiated device
reboot.
Page 48

48
SNMP Traps Settings
Manager address – specify the IP address or hostname of SNMP Trap receiver.
Manager port – specify the port number of the Trap receiver. Default port number is 162.
Trap community - specify the SNMP community string. This community string acts as password
between SNMP manager and device by default Trap community string is "public".
Use informs – select to wait for an acknowledgment from SNMP manager that trap was received.
Retry count – specifies maximum number of times to resend an inform request [1-10]. Default: 5.
Retry timeout – specifies number in seconds to wait for an acknowledgment before resending
request [1-10]. Default: 1.
SMTP Settings
Server address – specify the IP address or hostname of the networked SMTP server.
Server port – specify the SMTP Port Number is the port number used by the networked SMTP
server. By default the port number is 25.
Source e-mail address – specify the e-mail address that will be used by the device.
Destination e-mail address – specify the e-mail address where the device will send the alert
messages.
E-
sent
after unexpected system behavior.
7.3.3 SNMP
SNMP is the standard protocol that is widely used for remote network management over the Internet.
With the SNMP service enabled, the device will act as SNMP agent.
Mail notification interval – specify interval in seconds at which the e-mail notification will be
from the device [0-86400]. If 0 specified, then device will send an e-mail notification immediately
Page 49

49
Enable SNMP – specify the SNMP service status.
Friendly name – displays name of the APC that will be used to identify the unit. This name has the
same value as Friendly name in the Device settings.
Link location – displays the physical location of the device. This name has the same value as Device
location in the Device settings.
Contact information – spe cify the identification of the contact person for this managed device,
together with information on how to contact this person.
R/O community – specify the read-only community name for SNMP version 1 and version 2c. The
read-only community allows a manager to read values, but denies any attempt to change values.
R/O user – specify the user name for read-only SNMPv3 access. The read-only community allows a
manager to read values, but denies any attempt to change values.
R/O user password – specify the password for read-only SNMPv3 access [string].
7.3.4 Clock/NTP
Use this section to manage the system time and date on the device automatically, using the Network
Time Protocol (NTP), or manually, by setting the time and date on the device.
The NTP (Network Time Protocol) client synchronizes the clock of the device with the defined time
server. Choose NTP from the configuration menu, select your location time zone and enter NTP
server in order to use the NTP service.
Page 50

Configuration – choose the system clock configuration mode [NTP/Manual].
Time zone – select the time zone. Time zone should be specified as a difference between local
time and GMT time.
Save last known time – select to recall the timestamp that was saved on last reboot. When NTP is
enabled, this option will set system clock to last reboot time if no NTP servers are available.
NTP server – specify the trusted NTP server IP or hostname for synchronizing time with [IP address].
To adjust the clock settings manually, choose the configuration mode as Manual and specify the
following settings:
Configuration – choose the system clock configuration mode [NTP/Manual].
50
Time zone – select the time zone. Time zone should be specified as a difference between local
time and GMT time.
Save last known time – select to recall the timestamp that was saved on last reboot.
Date – specify the new date value in format MM/DD/YYYY
Time – specify the time in format hh:mm.
7.3.5 SSH
Use this menu to manage access to the device via SSH port:
Enabled – enable or disable SSH access to device.
Port – the SSH service port. By default SSH port is 22.
7.3.6 HTTP
Use this menu to control HTTP connection on device web management:
Page 51

51
Enable management through HTTP – select tis option to enable or disable HTTP access to the
device management.
Port – specify HTTP port. Standard HTTP port is 80.
HTTPS connection via the standard port 8080 is always enabled.
7.4 System
7.4.1 Administration
For security reasons it is recommended to change the default administrator username and
password as soon as possible.
System menu allows you to manage main system settings and perform main system actions (reboot,
restore configuration, etc.). The section is divided into further three sections: Device settings, Account
settings and system functions.
Device settings
Friendly name – specify name of the APC that will be used to identify the unit.
Device location – describe the location of the device [maximum 255 ASCII characters].
Page 52

Longitude – specify the longitude coordinates of the device [specific decimal format, e.q. 54.869446].
52
Latitude – specify the latitude coordinates of the device [specific decimal format, e.q.
23.891058]. Both
coordinates helps indicate accurate location of the device.
Account settings
The Administrative Account menu is for changing the
Default administrator logon settings are:
Username: admin
Password: admin01
Username – change the
administrator’s
username.
Old password – enter the old administrator password.
New password – enter the new administrator password for user authentication.
Verify password – re-enter the new password to verify its accuracy.
The only way to gain access to the web management if you forget the administrator
password is to reset the unit to factory default settings.
administrator’s
password.
System functions
Reboot device – reboot device with the last saved configuration.
Reset device to factory defaults – click to restore unit's factory configuration.
Resetting the device is an irreversible process. Current configuration and the administrator
password will be set back to the factory default.
Download troubleshooting file – click to download the troubleshooting file. The troubleshooting file
contains valuable information about device configuration, routes, log files, command outputs, etc.
When using the troubleshooting file, the device quickly gathers troubleshooting information
automatically, rather than requiring you to gather each piece of information manually. This is helpful
for submitting problems to the support team.
Backup configuration file – click to save the current configuration file. The saved configuration file is
useful to restore a configuration in case of a device misconfiguration or to upload a standard
configuration to multiple devices without the need to manually configure each device through the web
interface.
Restore configuration from file – click to upload an existing configuration file to the device.
7.4.2 Log
Use the log tab to configure device to view or save log messages to the local or remote server using
standard syslog facility:
Page 53

53
View system log – click to view current trace messages. The system log viewer utility provides debug
information about the system services and protocols. If the device's malfunction occurs recorded
messages can help operators to locate misconfiguration and system errors.
Message level – specify system's message tracing level. The level determines the importance of the
message and the volume of messages generated by the device. The levels are in incr eased
importance order [emergency, alert, critical, error, warning, notice, information, debug]. Default: info.
The device can be configured to send system log messages to a remote server:
Syslog forward – select to enable remote system logging.
Forward server – specify the remote host IP address or hostname where syslog messages will be
sent.
Forward port – specify the port to which syslog messages will be forwarded [0-65535]. Default: 514.
Forward message level – specify the level of the message which will be sent to the remote syslog
server. The level determines the importance of the message and the volume of messages generated
by the device. The levels are in order of increasing importance
[emergency/alert/critical/error/warning/notice/information/debug].
Default: information.
Forward backup – select to enable remote syslog logging backup.
Backup server – specify the backup host IP address or hostname where syslog messages will be
send to.
Backup port – specify the port to which syslog messages will be forwarded [0-65535]. Default: 514.
7.4.3 LED Control
The APC is equipped with 6 LEDs: power, LAN and 4 RSSI LEDs that indicates the signal strength of
current connection. The signal level is classified into 4 levels, thus corresponding 4 LEDs switches on
as soon as indicated threshold is reached.
Page 54

54
Enable – select to enable LEDs on the device. If this option is not selected, then no LED activity will
be visible on the device.
RSSI thresholds – specify the RSSI threshold at which corresponding LED will switch on.
The Signal LEDs are working only when the connection is established. Therefore, please make
sure all wireless settings are correct and the connection is established.
LAN LED – select to enable LAN LED. The red LED will be blinking on LAN activity, off – no LAN
connection.
Power LED – select to enable Power LED. The steady red LED when power is on, off – no power.
7.4.4 Firmware Upgrade
To update your device firmware use the System | Firmware upgrade menu. Press Upload
firmware, select the firmware file and click the Upload button:
Current version – displays version of the current firmware.
Upload firmware – click the button to select the new firmware image for uploading it to the device.
The device system firmware upgrade is compatible with all configuration settings. When the device is
Upgraded with a newer version or the same version builds, all the
system’s
configuration will be
Preserved after the upgrade.
The new firmware image is uploaded to the
Firmware into the device permanent memory. Click the Upgrade button:
controller’s
temporary memory. It is necessary to save the
Page 55

55
Upgrade – upgrade device with the uploaded image and reboot the system.
Do not switch off and do not disconnect the device from the power supply during the
firmware upgrade process as the device could be damaged.
Page 56

7.5 Tools
7.5.1 Antenna Alignment
The Antenna Alignment tool measures signal quality between the Station and AP. For best results
during the antenna alignment test, turn off all wireless networking devices within range of the device
except the device(s) with which you are trying to align the antenna. Watch the constantly updated
display in the Alignment Test window as you adjust the antenna.
56
Start – press this button to start antenna alignment.
Stop – press this button to stop antenna alignment.
Average – if this option selected, the graph will display the average RSSI of both antennas.
7.5.2 Site Survey
The Site Survey tool shows overview information for wireless networks in a local geographic area.
Using this test, an administrator can scan for working access points, check their operating channels,
encryption and see signal/noise levels.
To perform the Site Survey test currently, click the Start scan:
Page 57

57
Last updated before – displays when the last scan was
performed.
The results of the Site Survey test are converted to handy two graphs: AP count and RSSI. An
administrator can use this to identify the best channel for device operation that will not receive
interference from adjacent APs.
7.5.3 Delayed Reboot
This tool is extremely useful while tuning radio settings – once you defined hypothetic radio
parameters and set them with Apply button (not written to the permanent memory), device starts
Page 58

Operating with the new settings, and in case the link fails, device will be rebooted in specified minutes,
thus the old settings will be set back.
58
Reboot after – specify time in minutes, after which the device will be rebooted.
Start/Stop – click to start or stop delayed reboot tool.
7.5.4 Ping
This command is used to test whether a particular host is reachable across an IP network. The Ping
results will be displayed graphically:
IP address or Host name – specify the destination IP address or Host name.
Packet size – specify the packet size.
7.5.5 Trace route
This tool is a route-tracing utility used to determine the path that an IP packet has taken to reach a
destination. This is useful when trying to find out why destination is unreachable, as you will be able to
see where the connection fails.
Page 59

59
Destination IP or Hostname – specify hostname or IP address of the target host.
Max Hops –Specifies the maximum number of hops to search for target.
Start/Stop – click to start or stop traceroute tool.
7.5.6 Spectrum Analyser
The Spectrum analyzer test displays detailed information about signal level of each APC
Antenna on each available frequency. This enables administrator choose the best available
Frequency/channel for the unit operation. The frequency list depends on the Country at which the unit
is operating, and chosen channel width.
Do not use the Spectrum analyzer on the remote unit of the link, as the connection to the device will
be lost during the test.
Click Start button to perform the test:
unit’s
Page 60

60
Operating frequency range – displays the channel frequency range at which the APC unit is
operating currently.
Maximum – color indicates the maximum achieved signal level on the appropriate frequency.
Current – color indicates the current signal level on the appropriate frequency.
Average – indicates average of the signal level on the appropriate frequency.iversal Access Method
(UAM)
Universal Access Method (UAM) is a simple Web browser based user authentication method. On
Initial HTTP request to any Web site,
To the network. The login page can be served by internal Web server or by external Web Application
Server.
client’s
browser is redirected to the authentication page for login
Page 61

8 Universal Acces Method
8.1 UAM Overview
When using internal UAM, the Login page is the first page a client receives when he starts his Web
browser and enters any URL. To get access to the network, the user should enter his authentication
settings: login name and password and click the login button:
61
The GD-GEO20 could be shared by several Wireless Internet Service Providers (WISP). They
are uniquely identified by specifying WISP domain name in addition to subscriber user name
when logging in. APC can be configured to send authentication and accounting information to
different
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) servers associated with different WISP domains.
S
ubscriber’s
username
login format:
8.2 UAM Configuration
UAM authentication is available on radio interfaces (including VAPs) only if GD-GEO20 is
working as router in Access Point (auto WDS) wireless mode.
The APC allows user authentication through external or internal Web portal. This authentication
method is called UAM. User provides login credentials and then Web portal attempts to authenticate
and authorize the client using the provided information. Client will not send any authentication
requests directly to the APC, the Web portal will do this. On success, APC will allow access to the
Internet; otherwise Web portal will display failure notice.
Page 62

Use Security section on Wireless or VAP (depending on the interface on which the UAM will be
configured) page for UAM configuration: choose the security option UAM:
62
RADIUS Settings
NAS ID – specify the NAS identifier.
RADIUS server 1 – specify the name or IP address of the primary RADIUS server.
RADIUS server 2 – specify the name or IP address of the secondary RADIUS server.
RADIUS Secret – specify the RADIUS shared secret.
RADIUS authentication port – specify the UDP port number to use for radius authentication
requests, default 1812
RADIUS accounting port – specify the UDP port number to use for radius accounting requests,
default 1813
RADIUS WEB page type – choose the authentication Web portal type:
Internal – use the built in authentication Web page. If selected, then when a user’s first tries to
access the Internet, they will be blocked, and re-directed to the built-in login page. The logon data
will be sent to the Radius Server for authentication.
External – specify the external authentication Web page URL and settings. If selected, then when
A user first tries to access the Internet; they will be blocked, and re-directed to the URL specified
below.
Custom internal – upload a customized internal page.
Use HTTPS – enable to use the HTTPS protocol for connection and authentication.
Page 63

Key – upload a PEM formatted private key file.
Certificate – upload a PEM formatted certificate file.
63
Page 64

WISPr Settings
WISPr location name – specify the WISPr location name.
64
Operator name – specify the
operator‟s
name
Network name – specify the network name
ISO country code – specify the country code in ISO standard.
E.164 country code – specify the country code in E.164 standard.
E.164 area code – specify the area code in E.164 standard.
WISPr default max bandwidth – specify the default bandwidth limitation for clients. Note that if the
External RADIUS server has traffic limitations preconfigured, and then RADIUS overrides these settings.
Download, kbps – specify max download bandwidth in kbps.
Upload, kbps – specify the max upload bandwidth in kbps.
Interface IP address – specify the LAN interface IP address. Note that LAN settings on Network
Menu will be disabled if UAM is enabled.
DHCP settings – specify the dynamic IP settings for the connected users:
Network – specify the network for IP address pool.
Subnet mask – specify the subnet mask for the DHCP.
DNS server – specify the primary and the secondary DNS servers.
Data encryption settings – choose the data encryption method:
Open – no encryption.
Personal WPA – preshared key encryption with WPA using AES method.
Personal WPA 2 – preshared key encryption with WPA2 using AES method.
8.2.1 White/Black List
The white and black access lists control user access to Web content through the APC. The
unauthenticated users will be allowed to access sites from white list while access to the sites from black
list will be denied even for authenticated users.
Use “+” sign to add new entry to the list, and “–” sign to remove required one.
White list
Host/IP address – specify the IP addresses or hosts for free access even for unauthenticated users.
Notes – add a description for the specified host or IP address.
Black list
Host/IP address – specify the IP addresses or hosts that will be not accessible even for the
authenticated users.
Notes – a description for the specified host or IP address.
Page 65

65
Page 66

9 Appendix
9.1 Resetting Device to Factory Defaults
Device has the capability of being reset to defaults by pinging the device with a certain packet size when the
radio is booting. During the startup of the device, when the drivers of the Ethernet interfaces are loaded, the
discovery daemon is started. The daemon suspends startup process for 3
"echo request" packet of length 369 bytes. If the packet received, the discovery resets the device to
default configuration.
It is recommended to connect PC to the device via switch, as depending on PC OS settings, the
ARP table might be flushed during wired link status change (connecting the device that will be
reset).
Steps to reset to default settings:
Step 1. Power off the APC device.
Step 2. Obtain the device MAC address.
Step 3. Connect a PC to the same physical subnet as the device.
Step 4. Execute 'arp -s' command to assign the IP address (IP address should be from the same
subnet as PC) to the device MAC address:
arp -s <IP address to assign> <device MAC address>
Note that syntax of MAC address differs depending on OS:
Linux OS: AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF
Windows OS: AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF
Step 5. Start ping the device:
For Linux users: ping <IP address> -s 369
For Windows users: ping <IP address> -l 369 -t -w 0.2
Step 6. Power up APC device and wait about 30sec or more (depending on device hardware).
Step 7. Stop pinging the device, and let the device boot as usual. The device should start up with
factory default settings.
seconds and
waits for ICMP
66
Page 67

Attribute
Description
User-name (1)
Full username as entered by the user.
User-Password (2)
Used for UAM as alternative to CHAP-Password and CHAP-Challenge.
CHAP-Password (3)
Used for UAM CHAP Authentication
CHAP-Challenge (60)
Used for UAM CHAP Authentication
EAP-Message (79)
Used for WPA Authentication
NAS-IP-Address (4)
IP address of Chilli (set by the nasip or radiuslisten option, and
otherwise "0.0.0.0")
Service-Type (6)
Set to Login (1) for normal authentication requests. The Access-Accept
message from the
Radius server for configuration management messages must also
be set to Administrative-User.
Framed-IP-Address (8)
IP address of the user, which is configurable during MAC
authentication in the Access-Accept.
Filter-ID (11)
Filter ID pass on to scripts possibly.
Reply-Message (18)
Reason of reject if present.
State (24)
Sent to chilli in Acc ess-Accept or Access-Challenge. Used
transparently in subsequent Access-Request.
Class (25)
Copied transparently by chilli from Access-Accept to AccountingRequest.
Session-Timeout (27)
Logout once session timeout is reached (seconds)
Idle-Timeout (28)
Logout once idle timeout is reached (seconds)
alled-Station-ID (30)
Set to the nasmac option or the MAC address of chilli.
Calling-Station-ID (31)
MAC address of client
NAS-Identifier (32)
Set to radiusnasid option if present.
Acct-Status-Type (40)
1=Start, 2=Stop, 3=Interim-Update
Acct-Input-Octets (42)
Number of octets received from client.
Acct-Output-Octets (43)
Number of octets transmitted to client.
Acct-Session-ID (44)
Unique ID to link Access-Request and Accounting-Request messages.
Acct-Session-Time (46)
Session duration in seconds.
Acct-Input-Packets (47)
Number of packets received from client.
Acct-Output-Packets (48)
Number of packets transmitted to client.
Acct-Terminate-Cause (49)
1=User-Request, 2=Lost-Carrier, 4=Idle-Timeout, 5=Session-Timeout,
11=NAS-Reboot
Acct-Input-Gigawords (52)
Number of times the Acct-Input-Octets counter has wrapped around.
Acct-Output-Gigawords (53)
Number of times the Acct-Output-Octets counter has wrapped around.
NAS-Port-Type (61)
19=Wireless-IEEE-802.11
9.2 RADIUS Attributes
The following RADIUS attributes and messages are supported by the GD-GEO20.
9.2.1 General Attributes
67
Page 68

Message-Authenticator (80)
Is always included in Access-Request. If present in Access-Accept,
Access-Challenge or
Access-reject chilli will validate that the Message-Authenticator is
correct.
68
Page 69

Attribute
Description
Acct-Interim-Interval (85)
If present in Access-Accept chilli will generate interim accounting
records with the specified interval (seconds).
MS-MPPE-Send-Key
(311,16)
Used for WPA
MS-MPPE-Recv-Key
(311,17)
Used for WPA
Attribute
Description
WISPr-Location-ID (14122, 1)
Location ID is set to the radiuslocationid option if present.
Should be in the format: isocc=, cc≤
E.164_Country_Code>, ac≤E.164_Area_Code>,
network≤ssid/ZONE>
WISPr-Location-Name (14122, 2)
Location Name is set to the radiuslocationname option if
present. Should be in the format: ,
WISPr-Logoff-URL (14122, 3)
Included in Access-Request to notify the operator of the
log off URL. Defaults to " http://uamlisten:uamport/logoff".
WISPr-Redirection-URL (14122, 4)
If present the client will be redirected to this URL once
authenticated.
This URL should include a link to WISPr-Logoff-URL in
order to enable the client to log off.
WISPr-Bandwidth-Max-Up (14122, 7)
Maximum transmit rate (b/s). Limits the bandwidth of the
connection.
Note that this attribute is specified in bits per second.
WISPr-Bandwidth-Max-Down
(14122, 8)
Maximum receive rate (b/s). Limits the bandwidth of the
connection.
Note that this attribute is specified in bits per second.
WISPr-Session-Terminate-Time
(14122, 9)
The time when the user should be disconnected in ISO
8601 format (YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssTZD).
If TZD is not specified local time is assumed.
For example a disconnect on 18 December 2001 at 7:00
PM UTC would be specified as 2001-1218T19:00:00+00:00.
Attribute
Description
ChilliSpot-Max-Input-Octets (14559, 1)
Maximum number of octets the user is allowed to transmit.
After this limit has been reached the user will be
disconnected.
ChilliSpot-Max-Output-Octets
(14559, 2)
Maximum number of octets the user is allowed to receive.
After this limit has been reached the user will be
disconnected.
ChilliSpot-Max-Total-Octets
(14559, 3)
Maximum total octets the user is allowed to send or
receive.
After this limit has been reached the user will be
disconnected.
ChilliSpot-Bandwidth-Max-Up
(14559, 4)
Maximum bandwidth up
9.2.2 WISPr Attributes
69
9.2.3 ChilliSpot Attributes
Page 70

Attribute
Description
ChilliSpot-Bandwidth-Max-Down
(14559, 5)
Maximum bandwidth down
ChilliSpot-Config (14559, 6)
Configurations passed between chilli and back-end as
name value pairs
ChilliSpot-Lang (14559, 7)
Language selected in user interface
ChilliSpot-Version (14559, 8)
Version of Chilli sending this AccessRequest
 Loading...
Loading...