Page 1

Page 2

2
PREFACE
The service manual has been specially prepared to provide all the necessary
information for the proper maintenance and servicing.
You have now a new type of scooter that has many techinal features such as:
V-belt drive automatic transmission
Forced air-cooling system
CDI ignition system
Electric starter system
Those who will be servicing the scooter should carefully review the manual before
performing any repair or services. Major modifications and changes incorporated
later will be advised to GENERIC product distributor in each market. Therefore, if
newest information is requested in the future, please contact the local GENERIC
distributor.
The scooters distributed in your country mignt differ in minor respects from the
standard specification and, if they do, it is because some minor modifications had to
be made to comply with the statutory requirements of your country.
Page 3

3
GENERAL INFORMATION
TYPE IDENTIFICATION
FUEL AND ENGINE OIL
BREAK-IN PROCEDURE
PRECAUTIONS AND GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
CONTENT
Page 4

4
TYPE IDENTIFICATION
ENGINE NUMBER
ENGINE NUMBER ① is carved on rear crankcase
as
Shown in figure.
Both FRAME NUBER AND ENGINE NUMBER are
designed specially for registering your scooter
and ordering spare parts.
FUEL AND ENGINE OIL
Be sure to use specified fuel and engine oil.
Some specifications are as follows:
FUEL
Unleaded, the minimum octane number is 95 or more.
ENGINE OIL
For GENERIC CCI SYSTEM, we recommend special engine oil, you can choose high
quality two-stroke engine oil (without being diluted) if without special oil.
GEAR OIL
Use high quality, all-purpose SAE90 engine oil for scooter.
BREAK-IN TIME
General requirements are as follows:
Limit break-in speed:
At the first 1000KMS(600 miles)mileage,play throttle less than 4/5 throttle;
After mileage exceeds 1000KMS(600 miles),play full throttle;
Don’t run engine too long during break-in time, and try to change throttle
position.
1
Page 5

5
PRECAUTIONS AND GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
Correctly abide by the following items when disassembling and assembling scooter:
□ Don’t run engine indoors without ventilation;
□ Be sure to replace new bushings, circlips, O-rings and cotter pins with new ones;
CAUTION
It is forbidden to use the circlip removed from shaft, only use new one;
Be very carefull to install new circlip for fear that the end hatch of circlip exceeds
required sliding surface for shaft;
After installing circlip, inspect whether it has been completely clipped into the
groove.
□ Fix bigger diameter bolt first when tightening cylinder head or cylinder, and tighten
to specified torque gradually from inside to outside at diagonal order.
□ Use special tools for some special requirements;
□ Use original components and recommended engine oil;
□ Keep each other’s safety when several persons do;
□ Inspect looseness and operating state of components after reassembling them.;
□ Take high care of gasoline, which is explosive, and never use gasoline as lotion.
The words like warning, notice, note may turn out incessantly in the manual,
which means:
WARNING The personal safety of the rider may be involved. Disregarding the
information could result in injury to the rider.
CAUTION These instructions point out special service procedures or
precautions that must be followed to avoid damaging the machine.
NOTE it provides some special information, which keeps maintenance
easier and important instructions clearer..
REPLACEMENT COMPONENTS
Be sure to use genuine GENERIC components or their equivalent.. Genuine
GENERIC components are high quality parts which are designed specially for
GENERIC vehicle.
CAUTION
Damage to the scooter may result from use of replacement components which are
not
Equivalent in quality to genuine GENERIC parts, and it can lead to performance
problems.
Page 6

6
SPECIFICATIONS
DIMENSION AND NET WEIGHT
OVERALL LENGTH 1830
mm
OVERALL LENGTH 695
mm
OVERALL HEIGHT 1160
mm
WHEELBASE 1295 mm
NET WEIGHT 92 kg
CHASSIS
Front shock absorber spring, no damp
Rear shock absorber spring, oil damp
Turning angle 48º
Front wheel 120/70-12
Rear wheel
130/70-12
Front brake Discφ190
Rear brake
Drumφ110
ENGINE
Type two-stroke, air
cooled
Intake system piston-reed valve
Cylinder QTY. 1
Bore 40.0mm
Stroke 39.6mm
Discharge 49.8mL
Compression ratio 6.9:1
Carburetor flat inhale stopper
style
Air cleaner dry
Starting system electric and kicking
start
Lubricating system pressure
lubricating
ELECTRIC
Ignition mode CDI
Ignition timing 15
0
at 1500RPM
Spark plug BP8HS
Storage battery YTX5L-BS
Generator AC magneto
Fuse 8A
Headlight 12V—55W
Turning light 12V/10W
Taillight 12V—21/5W
Meter light 12V/1.7W
Oil level signal indicator light 12V/3W
Turning signal indicator light 12V/3W
CAPACITY
FUEL TANK 5.2L
ENGINE OIL TANK 1L
GEAR OIL 0.1L
Transmission system
Clutch system dry auto a centric
Gearshift mechanism CVT stepless
Operating mode of gears shift
mechanism Automatic
a centric
Step less shift range 0.86~2.64
*the above data may be modified
without any notification.
Page 7
7
Periodic maintenance and service
Periodic maintenance and service schedule
Maintenance and service procedures
Storage battery
Spark plug
Cylinder head nut and exhaust pipe bolt
Cylinder head and cylinder
Fuel level line
Air cleaner
Throttle cable
Engine idle speed
Oil pump
Gear oil
Braking
Tire
Steering
Front shock absorber
Rear shock absorber
Vehicle bolts and nuts
CONTENTS
Page 8
8
Periodic maintenance and service schedule
The following table lists all required intervals for maintenance and service,following
which, you are assured to have your scooter perform in the best way.
Note
Do more frequent maintenance when often riding on bad road
Periodic maintenance table
Interval
(first 500 than all
3000km)
Kilometer 500 3500 6500 9500 12500
Storage battery I
I I I I
Cylinder head nut and exhaust pipe
bolt
T
T T T T
Cylinder head and cylinder (change
all 12000 km)
—
C R C R
Spark plug —
R R R R
Air cleaner Clean every 3000KM(2000 miles)
Idle speed rpm
I I I I I
Throttle cable play
I I I I I
Oil pump
I I I I I
Gear oil (75W90) R — R — R
I I I I
I
Fuel line
Replace every 4 years
Brake
I I I I I
I I I I I
Brake hose
Replace every 4 years
I I I I I
Brake fluid
Replace every 2 years
Steering
I I I I I
Front fork
I I I I I
Rear shock absorber
I I I I I
Tire
I I I I I
Vehicle body boot and nut T
T T T T
Note
I=inspect,clean,adjust,lubricate,or replace if necessary;
A=adjust; C=clean; R=replace; T=tighten
Page 9

9
Maintenance and adjustment procedures
The section describes the servicing procedures for each item of the Periodic
Maintenance requirements.
Storage battery
Inspect at initially 1000KM(600 miles,2
months),and every 6000KM(4000 miles,
12 months)thereafter
□ Uncover seat, and then remove the battery box cap in the
Middle of helmet barrel.
□ Disconnect negative pole line end, positive end, and then remove battery;
□ Measure the voltage between the two ends of
battery with
voltage gauge,charge if the voltage is below
11,9V
Page 10
10
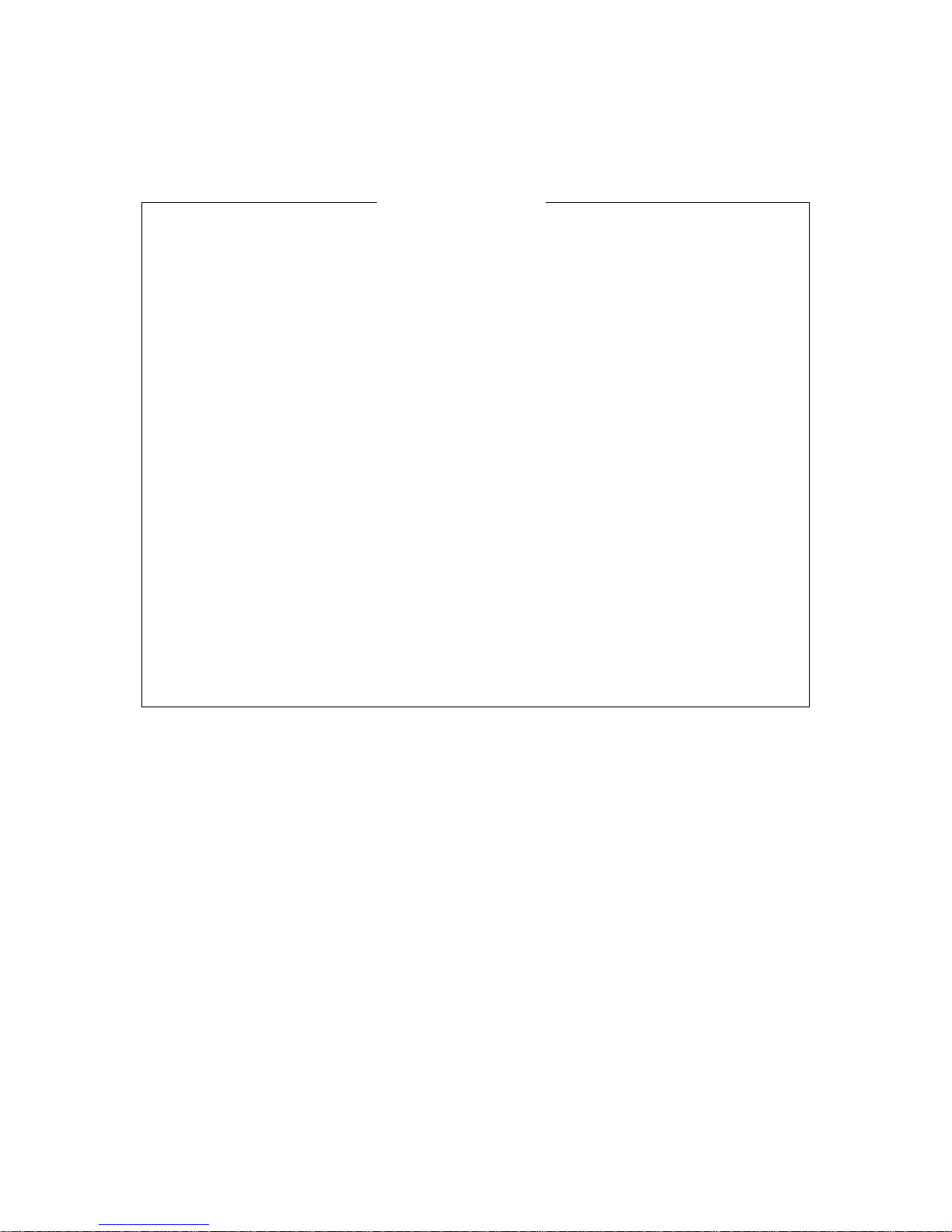
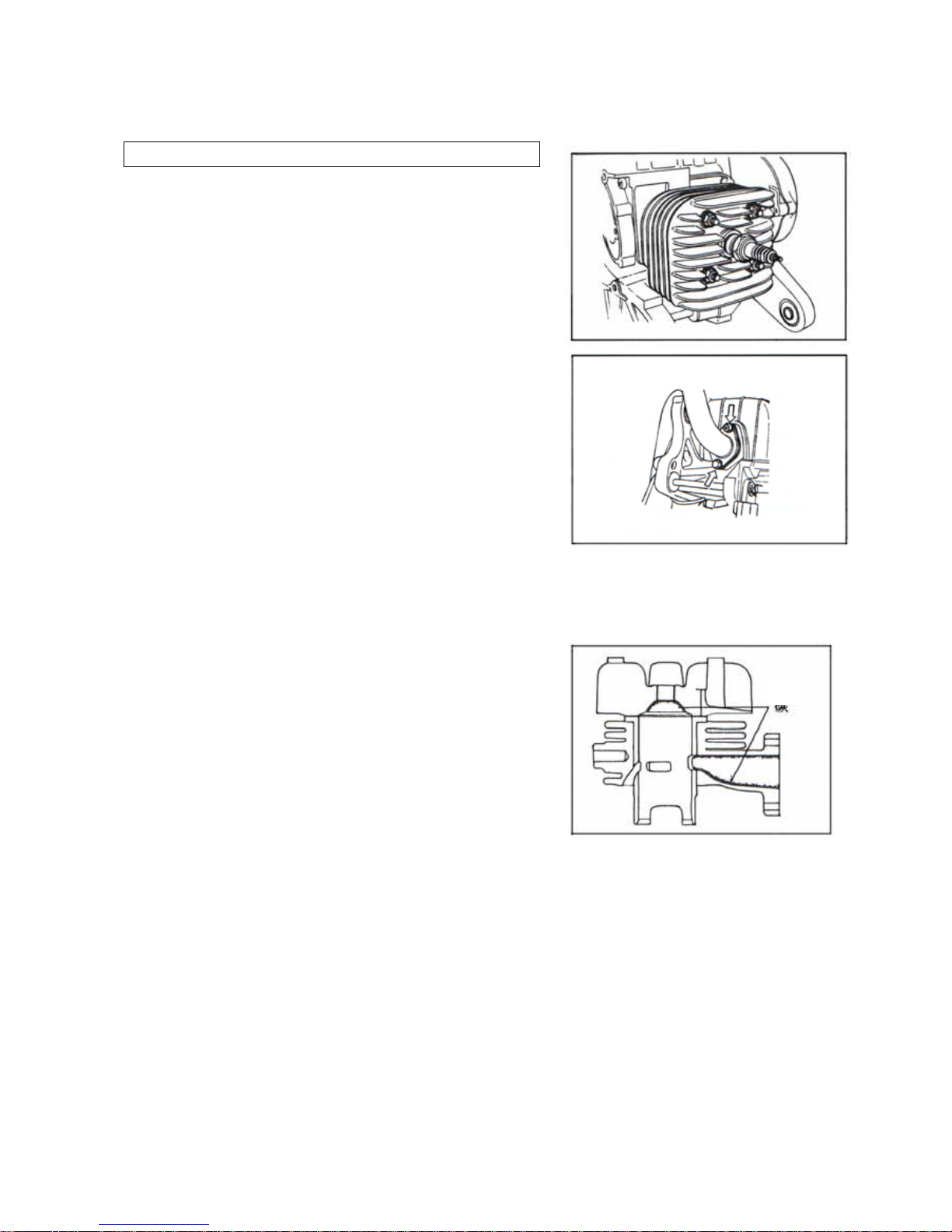
Cylinder head nuts and exhaust pipe bolts
Tighten at 500 km, and each service.
If cylinder head nuts are not tightened to the
specified torque, may result in leakage of
compressed fuel-air mixture and reduce
output, tighten the cylinder head nuts in the
following procedures::
1. Remove the frame lower covers.
2. Remove the cylinder head cover bolt.
3. Remove spark plug cap.
4. Tighten the nuts evenly one by one to the their
specified torque. Tighten the nuts in the order
indicated.
Tightening torque:
Cylinder head nut:15-18N.m
Exhaust pipe bolt:15-18N.m
Cylinder and cylinder head
Remove carbon every 6000 km(4000 miles,12
months)
Carbon deposits in the combustion chamber
and the cylinder head will raise the compression
ratio and may cause preignition and
overheating. Carbon deposited at the exhaust
port of the cylinder will prevent the flow of
exhaust gases, reducing the output. Remove
carbon deposits periodically.
Page 11
11
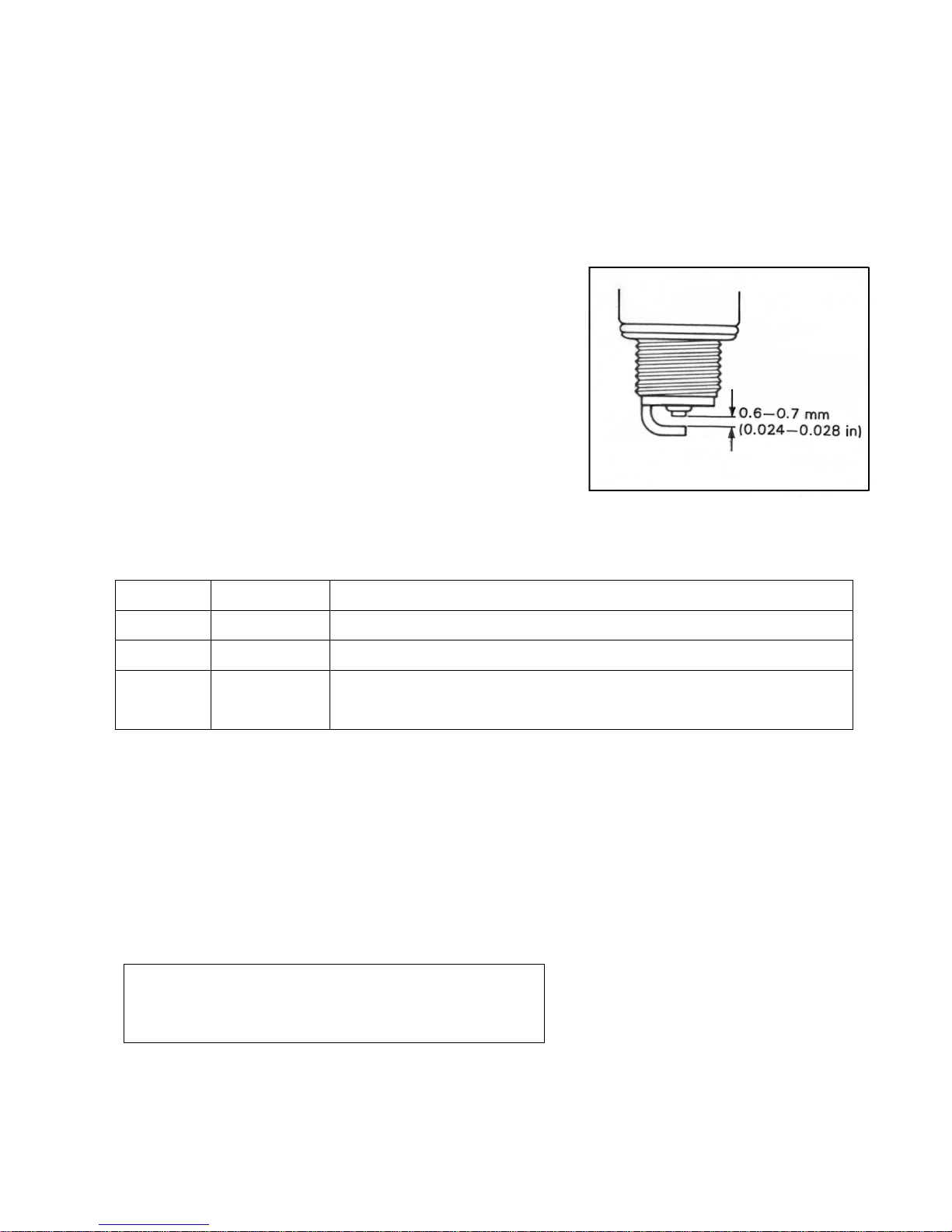
SPARK PLUG
Neglecting the spark plug maintenance eventually leads to difficult starting and poor
performance. If the spark plug is used for a long time, the electrode gradually burns
away and carbon builds up along the inside part. In accordance with the periodic
table, the plug should be removed for inspection, cleaning and to reset the gap.
z Carbon deposits on the spark plug will prevent
good sparking and cause misfiring. Clean the
deposits periodically.
z If the center electrode is fairly worn down, the
plug should be replaced and the plug gap set to
the specified gap using a thickness gauge.
Thickness gauge
Spark plug gap:0.6-0.7 mm (0.024-0.028 inch)
Check the spark plug for burnt condition. If
abnormal replace the spark plug as indicated in the
chart.
NGK TROCH REMARKS
BPR7HS E8RTC If the standard plug is apt to get wet, replace with the plug.
BPR8HS E7RTC Standard
BPR9HS E6RTC
If the standard plug is apt to overheat, replace with the
plug.
z Tighten the spark plug to the specified torque.
Spark plug
Tightening torque:15-18N.m
NOTE:
z To check the spark plug, first make sure that the fuel used is unleaded gasoline,
and if plug is either sooty with carbon or burnt white, replace it.
z Confirm the thread size and reach when replacing the plug.
FUEL LINE
Inspect at initially 500 km and every service,
replace every 4 years.
Page 12

12
AIR CLEANER
Clean every 3000KM(2000 miles)
If the air cleaner is clogged with dust, intake resistance will, be increased with a resultant
decrease in power output and an increase in fuel consumption. Check and clean the element
in the following manner.
Remove screw 1 and screw 2,take down air cleaner
Unscrew tapping screw 3,remove air cleaner cap 4
Fill a washing pan of a proper size with Non-flammable
cleaning solvent. Immerse the air Cleaner in the cleaning
solvent and wash them clean.
Squeeze the cleaning solvent out of the washed element
By pressing it between the palms of both hands: do not
twist
or wring the air cleaner filter core element or it will
develop tears.,
Immerse cleaned filter core of air cleaner in CCI or CCI
SUPER oil, and squeeze the oil out of the core,which
may be slightly wet with oil.
Install air cleaner filter core in the reverse order of
removal.
CAUTION:
Before and during the cleaning operation, inspect the core
for tears. A tore core must be replaced
Be sure to position the filter core, so that no incoming air will
bypass it. Remember, rapid wear of piston rings and
cylinder bore is ofter caused by defective or poorly fitted
filter core.
А Non-flammable cleaning solvent
Б CCI or CCI SUPER oil
THROTTLE CABLE
Adjust at initially 1000KM(600 miles,2 months),and
every 6000 km(4000 miles,12 months)
Loosen locknut ,and adjust throttle cable play by turning
adjuster in or out to obtain the following cable play. After
adjusting the calbe play,tighten the locknut.
Cable play:0.5-1.0MM(0.02.-0.040 inch)
Engine idle speed
Adjust at initially 1000KM(600 mil es,2 months) and
every 6000 km(4000 miles,12 months)thereafter.
Adjust the throttle cable play.
warm up the engine.
Note:
Warm up engine for 10 minutes.
Connect an electric tachometer to the connecting protion of the
magneto lead wire as shown in the illustration. Use the selector
key “C’ position.
3
Page 13

13
Tachometer
Adjust the throttle stop screw to obtain the idle
r/min as follows:
Idle speed:1400±100r/min
Finally adjust the throttle cable play.
OIL PUMP
Inspect at initially 500km and every
year.
The engine oil is fed by the oil pump to the engine. The amount of oil fed to it is
regulated by engine speed and oil pump control lever which is controlled by amount
of throttle opening.
Check the oil pump in the following manner to confirm correct operation for throttle
valve full opening position.
Turn the throttle grip full open.
Check whether the red mark on the oil pump control lever
Is aligned with the index mark when the throttle valve is positioned as above.
If the marks are not aligned, loosen lock nuts and turn the adjuster in or out to
align the marks.
After align the marks, tighten the locknuts.
Caution:
Oil pump calbe adjustment must be done after
throttle cable adjustment.
Page 14

14
GEAR OIL
Change as shown in the
service schedule.
Inspect gear oil periodically as follows:
Remove the cover and hose
Remove the kicking starter lever
Remove clutch cover
Remove oil level bolt and inspect oil level,
if oil level is below oil hole, add oil until oil
flows from the level hole.
Tighten oil level bolt to the specified torque.
Tightening toque:9-15N.m
(0.9-1.5 kg-m ,6.5-11.0 lb-ft)
BRAKES
Inspect at initially 500 km and every service,
replace brake fluid every 2 years, replace
brake hose every 4 years.
Front brake fluid level
Keep the scooter upright and place the
handlebar staight.
Check brake fluid level by observing the
lower limit line on the brake fluid reservoir.
When the level is below the lower limit line,
replenish with brake fluid that meets the
following specification.
Specification and classification:DOT4
WARNING:
The brake system of the scooter is filled with a glycol-based brake the lowest line
Fluid. Do not use or mix different types of fluid such as silicone-based and
petroleum-based. Do not use any brake fluid taken from old, used or unsealed
containers. Never reuse the brake fluid left over from the last servicing and stored for
long periods.
Page 15

15
WARNING:
Brake fluid, if it leaks, will interfere with safe running and immediately
discolor painted surfaces.
Check the brake hoses for cracks and hose joints for leakage before
riding.
Brake pads
Wearing condition of brake pads can be checked by
observing the limit line marked on the pad. When the
wear exceeds the limit mark, replace the pads with
new ones.
Bleeding air from the brake fluid circuit
Air trapped in the fluid circuit acts like a cushion to
absorb a large proportion of the pressure developed by
the master cylinder and thus interferes with the full
braking performance of the brake caliper. The
presence of air is indicated by “sponginess” of the
brake lever and also by lack of braking force.
Considering the danger to which such trapped air
exposes the machine and rider, it is essential that, after
remounting the brake and restoring the brake system
to the normal condition, the brake fluid circuit be
purged of air in the following manner:
Fill up the master cyliner reservoir to the upper end
of the inspection window. Replace the reservoir cap
to prevent entry of dirt.
Attach a pipe to the caliper bleeder valve, and insert
the free end of the pipe into a receptacle.
Bleed air from the bleeder valve.
Squeeze and release the brake level several times
in rapid succession. And squeeze the lever fully
without releasing it. loosen the bleeder valve by
turning it a quarter of a turn so that the brake fluid
runs into the receptacles: the will remove the
tension of the brake lever causing it to touch the
handlebar grip. Then, close the valve, pump and
squeeze the lever, and open the valve. Repeat the
process until the fluid flowing into the receptacle no
longer contains air bubbles.
Page 16

16
NOTE:when bleeding the braking system, replenish the brake fluid reservoir if
necessary. Make sure that there is always some fluid visible in the reservoir.
Close the bleeder vavle, disconnect the pipe. Fill the reservoir with brake fluid to
the upper end of the inspection window.
BLEEDER VALVE
TIGHTENING TORQUE: 6-9N.m(0.6-0.9kg-m,4.5-6.5lb-ft)
CAUTION:
Handle brake fluid with care: the fluid
reacts chemically with paint, plastics,
rubber materials, etc.
Rear brake
T urn adjusting nut so that the the play of the
brake lever is 15-25MM as shown in the
illustration.
Brake shoe wear:
The vehicle is equipped with the brake
lining limit Indicator on the rear brake.
Inspect brake lining limit as follows:
1. First check if the brake system is properly
adjusted.
2. when operating the brake, check to see
that the tip of indicator is within the range.
3. if the tip of indicator is beyond the range,
the brake shoe assembly should be
raplaced with anew set of shoe.
Page 17

17
Tire
Inspect at initially 1000KM ( 600 miles , 2
months) and every 6000KM(4000 miles,12
months)thereafter
Tire pressure:
If the pressure is too high, the scooter will tend to rede
stiffly and have poor traction. Conversely, if tire
pressure is too low, stability will be adversely affected.
Thereafter , maintain the correct tire pressure for good
roadability and to prolong tire life.
CAUTION:
The standard air pressure of tires is 175/196Kpa, the use
of other than standard may cause handling instability . It is
highly recommended to use a GENERIC genuine tire.
Tire tread condition:
Operating the scooter with the excessively worn tires
will decrease riding stability and consequently invite
dangerous situation. It is highly recommended to
replace the tire when the remaining depth of tire tread
reaches the following specification.
Front and rear:1.6MM(0.064IN)
Tire depth gauge
Steering
inspect at initially 500km and every
service.
Steering should be adjusted properly for smooth turning
of handlebars and safe running. Too stiff steering
prevents smooth turning of handlebars and too loose
steering will cause poor stability.
Check that there is no play in the front fork assembly by
supporting the machine so that the front wheel is off the
ground, with wheel staight ahead, grasp lower shock
absorber near the axle and pull forward. If play i s found,
perform steering bearing adjustment.
Page 18
18
Front shock absorber
Adjust at initially 500km and each
service.
Inspect the front shock absorber for oil leakage or other damage, and replace the
defective parts, if necessary.
Rear shock absorber
Adjust at initially 500km and each
service.
Inspect front shock absorber for oil leakage and other damage, and replace the
defective parts if necessary.
No. Item N•m Kg-m
1 Front axle nut 55-60 5.5-6
2 Handle tightenging nut 37-44 3.7-4.4
3 Steering sterm locknut 37-44 3.7-4.4
4 Disc brake caliper fixing bolt 22-29 2.2-2.9
5
Disc brake master cylinder hose fixing
bolt
22-29 2.2-2.9
6 Disc brake fixing bolt 5-9 0.5-0.9
7 Front shock absorber fixing bolt 37-44 3.7-4.4
8 Engine pivot fixing nut 55-60 5.5-6
9 Engine bracket fixing nut 37-44 3.7-4.4
10 Rear wheel fixing nut 100-130 10-13
11 Rear brake rocker arm fixing bolt 5-9 0.5-0.9
12 Rear shock absorber under fixing bolt 22-29 2.2-2.9
13 Start pedal mounting screw 15-20 1.5-2
14 Rear shock absorber top fixing bolt 37-44 3.7-4.4
Page 19

19
③
①
②
④
⑤
⑥
⑦
⑧
⑨
⑩
14
Page 20

20
LUBRICATION
Proper lubrication is important for smooth operation and long life of each working
part of the scooter. The major lubrication points are indicated below:
NOTE:
1. Lubricate exposed parts which aare subject to ruse with engine oil.
2. Before lubricating each part, clean off any rusty spots and wipe off any grease,
oil dirt of grime.
WARNING:Be careful not to apply too much grease to the rear brake camshaft,
otherwise brake slippage will result from the presence of grease in brake drum.
steering stem bearing
front wheel bearing
engine bracket
rear brake camshaft
side stand
rear brake shaft and rear brake cable
speedometer cable and gear box
main stand
A: lubrication
A
A
A
A
A
③A
Page 21

21
ENGINE
CONTENS
Engine components removal with the engine in place
Engine removal and remounting
Engine removal
Engine remounting
Engine disassembly
Engine components inspection and servicing
Bearings
Oil seals
crankshaft
automatic clutch inspection
cylinder head
cylinder
piston
reed valve
engine remounting
oil seals
bearings
bushings
crankshaft
crankcase
rear axle shaft
transmission
starter pinion and starter gear
Movable driven and clutch
Movable drive
Kicking starter
Piston
Oil pump and oil pump driven gear
Intake pipe
Magneto
Page 22

22
Engine components removable with the engine in place
The parts listed below can be removed and reinstalled without removing the engine
from the frame.
Engine left side
Kicking starter lever
Clutch brake pad kit
Driver left face
V-belt
Driver belt right face
Electric starter gear
Super clutch
Driven face
Engine center
Carburetor
Intake pipe
Reed valve
Oil pump
Worm wheel
Cylinder head
Cylinder
Piston
Engine right side
cooling fan
Magneto
Starter motor
Page 23

23
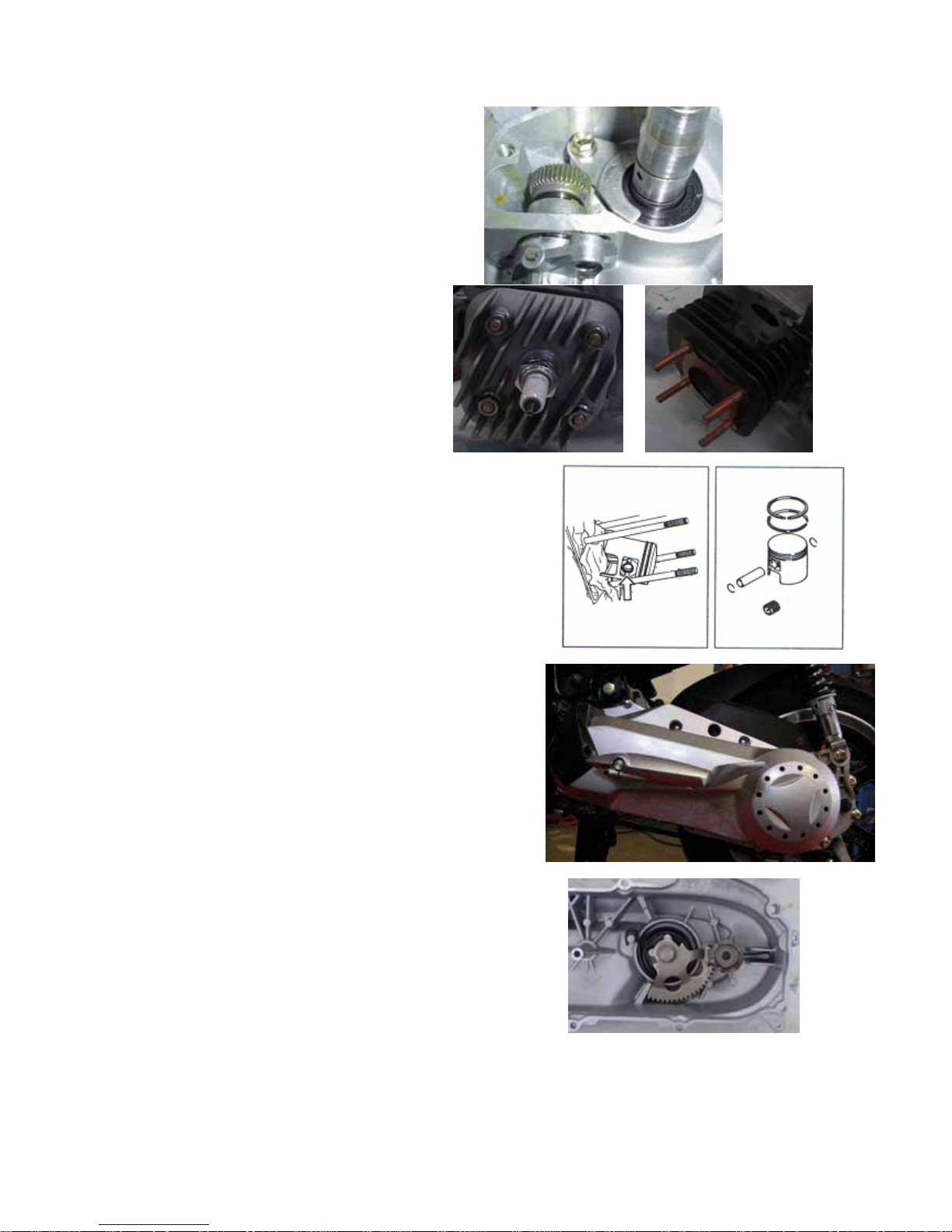
ENGINE ASSY.
z Remove the muffler
z Remove cooling fan cover
z Remove cylinder cover
z Remove cooling fan
z Remove magneto nut with special tools.
z remove magneto rotor and half circle key with
special tools.
z remove magneto stator and paper gasket
z remove oil pump
Page 24
24
Remove worm wheel and oil seal press board
z remove cylinder head and
cylinder
z Place a cloth stopper beneath the piston
and remove the circlip with a plier.
z remove the piston pin and piston.
z Remove the kick starter lever.
z Remove side cover
z Remove movable ratchet wheel and clip
Page 25

25
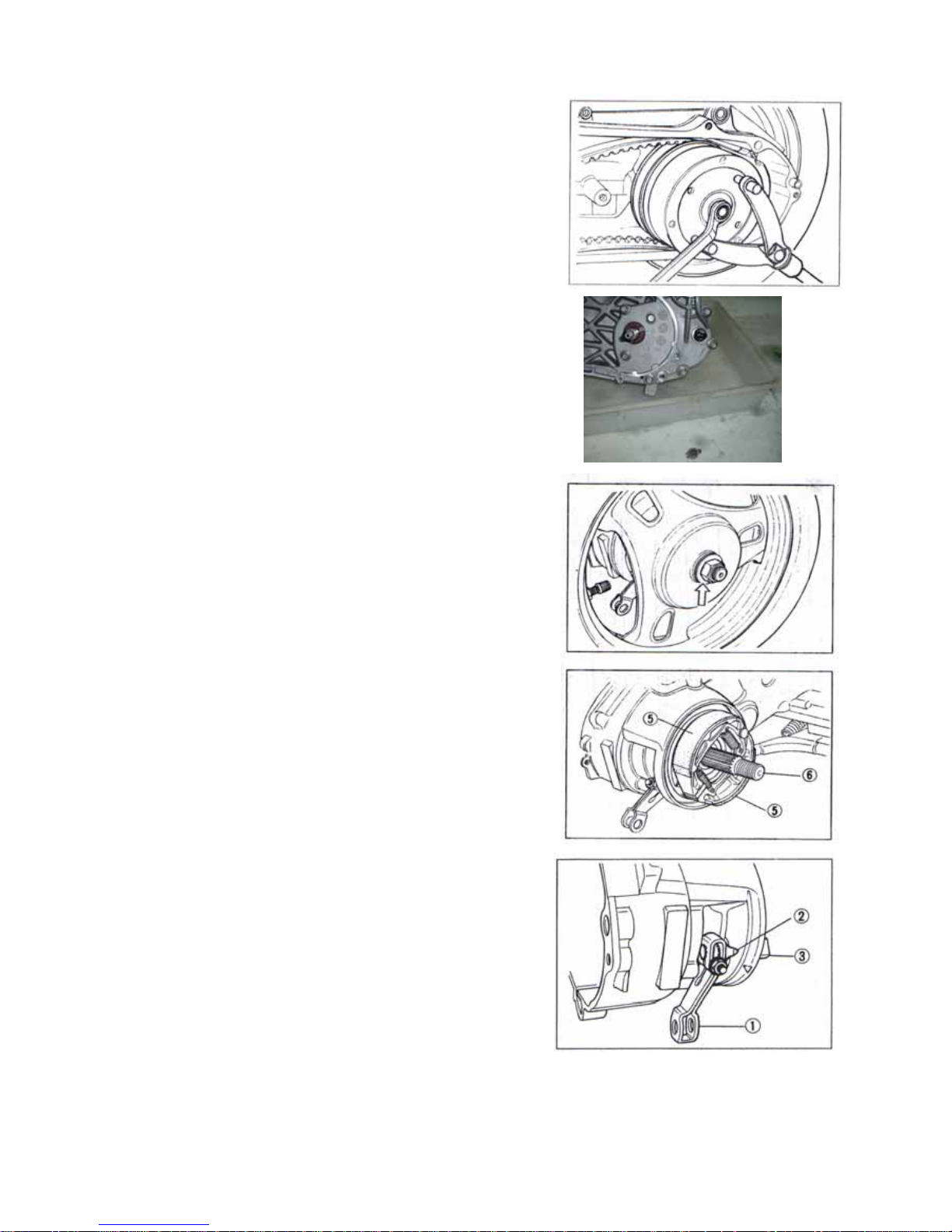
z Remove starting driven ratchet wheel by removing the nuts.
z Remove fan and V-belt.
z Disassemble the movable drive
face.
z Remove electric gear press board, electric
gear and super clutch
z Remove starter motor
Page 26
26
z Remove the clutch housing with the special tool.
(Peg key)
z drain gear oil
z remove rear axle nut
z remove rear wheel
z remove brake shoe and rear axle。
z Remove the rear brake cam lever,indicator
plate and camshaft.
Page 27

27
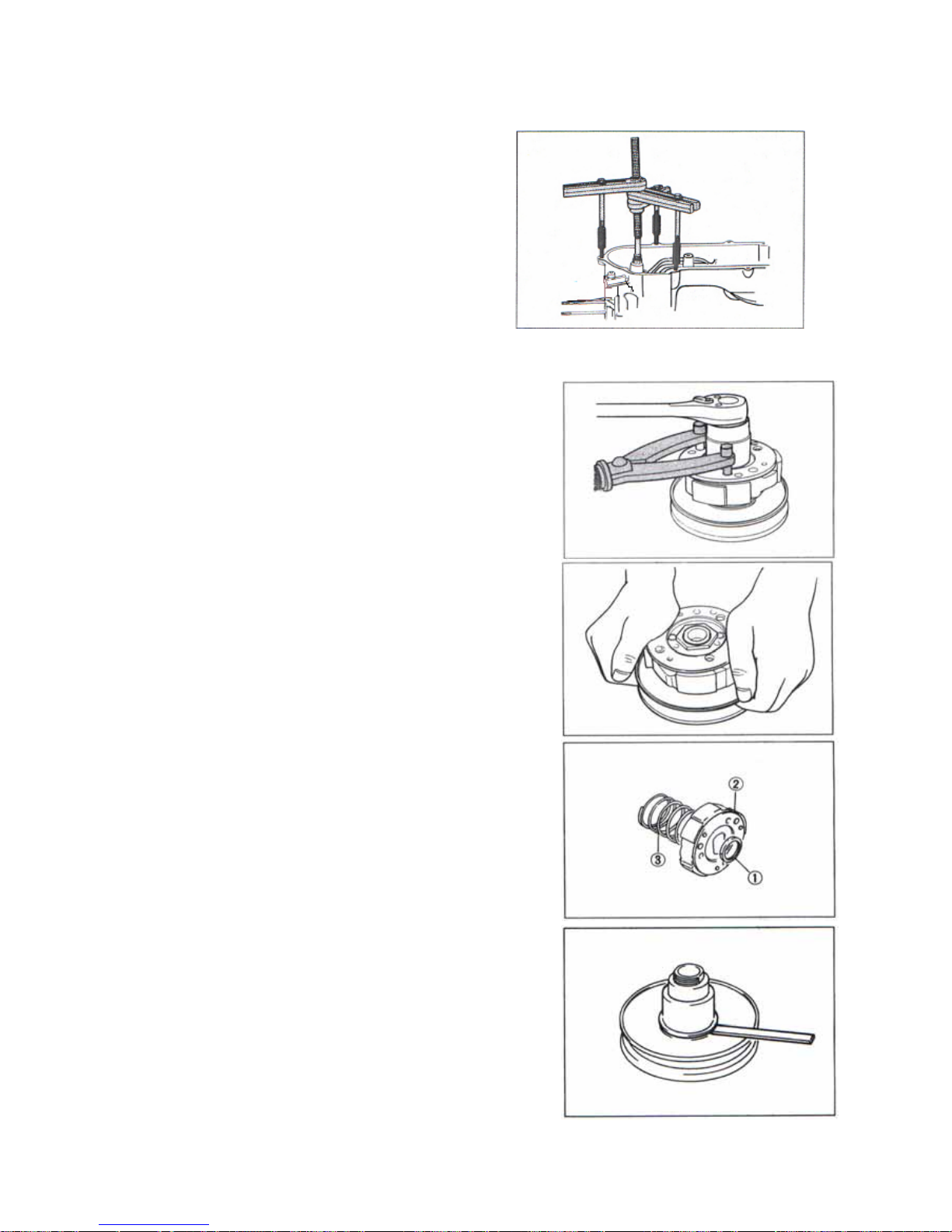
z remove spring
z remove cotter pin and shaft
z remove main stand
z remove gearcase cover
z Remove paper gasket and middle
gear assy.,
z Remove output gear assy.
z remove carburetor
z remove intake pipe
z remove reed valve and paper gasket.
z Remove crankcase fixing shaft
Page 28
28
z disassemble crankcase with special tools
z first remove right crankcase cover.
z Remove crankcase with special tools
z Remove crankshaft bearing with special tools
SLIDING SHAFT
Warning use a new sliding shaft.
Unscrew clutch shoe nut with special tools.
z Remove the nut while holding down clutch
shoe assy. by both hands as shown in the
illustration.
WARNING:Gradually back off the clutch shoe assy,
pressed down by hands to counter the clutch
sparing load. Releasing the hand suddenly may
cause the following parts to fly apart.
nut
clutch shoe
spring
CAUTION:
Do not attempt to disassemble the clutch
shoe assy. Otherwise the clutch shoe
may be damaged.
z Using a screwdriver or the like, pry up the
movable driven face spring guide.
Page 29
29
Remove the pins, movable driven face and
fixed driven face.
Remove circlip
z Remove bearing with special tool.
CAUTION:Replace the removed bearing with a new
one.
z Remove inner bearing with special tool.
CAUTION:Replace the removed bearing with a new
one.
z Remove the spacer
Remove the oil seal from the gearcase cover
with the speical tool.
CAUTION: Replace the removed oil seal
with a new one.
z Remove gearcase cover bearing with special
tool
Page 30
30
Remove left crankcase oil seal
z with special tool
warning:use a new oil seal
z remove left crankcase bearing with special tool
warning:use a new one
z remove left crankcase shock absorber bushing
with special tool
warning:use a new bushing
wrap the oil seal with two appropriate size of sheet
irons and clamp it, shown as fig.
z Remove right crankcase oil seal with special tool
Warning:use a new oil seal
z remove right crankcase bearing
sliding bearing
warning:use a new bearing
Page 31

31
ENGINE COMPONENTS INSPECTION AND SERVICING
BEARINGS
Clear bears with solvent and lubricate
with engine oil before inspecting.
T urn the inner ring and check to see that
the inner rieng turns smoothly. If it does
not turn lightly , quietly and smoothly , or if
noise is heard, the bearing is defective
and must be replaced with a new one.
OIL SEAL
Damage to the lip of the oil seal may result in leakage of the fuel-air mixture or oil.
Inspect for damage and be sure to replace the damaged seal if found.
CRANKSHAFT
CRANKSHAFT RUNOUT
Support crankshaft by“V” block, with the dial gauge
rigged to read the runout as shown.
Service limit:0.05mm(0.002in)
Excessive crankshaft runout is often responsible for
abnormal engine vibration. Such vibration shortens
engine life.
Condition of big end bearing
Turn the crankshaft with the connecting rod to feel the
smoothness of rotary motion in the big end. Move the
rod up and down while holding the crankshaft rigidly to
be sure that there is no rattle in the big end.
Wear on the big end of the connecting rod can be
estimated by checking the movement of the small end
of the rod. The method can also check the extent of
wear on the parts of the connecting rod ‘s big end. If
wear exceeds the limit, replace connecting rod, crank
pin and crank pin bearing.
Service limit:3.0mm(0.12in)
Page 32

32
Connecting rod small end inside diameter
Measure the connecting rod small end diameter with
a caliper gauge.
Service limit:14.040mm
Page 33

33
Automatic clutch inspection
The scooter is equipped with an automatic clutch
and variable ratio belt drive transmission. The
engagement of the clutch is governed by engine
RMPS and centrifugal mechanism located in the
clutch.
To insure proper performance and long lifespan of
the clutch, it is essentiall that the clutch engages
smoothly and gradually. Two inspection checks must
be performed to thoroughly check the operation o f
the drivetrain. Follow the procedures listed.
1.Inspect initial engagement
Warm up the scooter to normal operating
temperature.
Remove the right frame side cover.
Connect an electric tachmeter to the connecting
portion of the magneto lead wire (black with red
tracer).
Seated on the scooter with the scooter on level
ground, increase the engine RPMs slowly and note
the RPM at which the scooter begins to move
forward.
Tachometer
Standard 2900r/min
tolerance ±300r/min
2.Clutch “LOCK-UP” inspection
Perform the inspection to determine if the clutch is
engaging fully and not slipping.
Warm the engine to normal operating
temperatures.
Connect the electric tachomter to the magneto
lead wire.
Apply the rear brake as firm as possible.
Briefly open the throttle fully and note the
maximum engine RPMs sustained during the test
cycle.
CAUTION:
Do not apply full power for more than 10 seconds
or damage to the clutch or engine may occur.
LOCK-UP R/MIN
Standard 5800r/min
Tolerance ±400r/min
Page 34

34
If the engine R/MIN doesn’t coincide with the specified r/min range, then
disassemble the clutch.
Clutch shoe---inspect the shoes visually for chips, cracking, uneven wear and burning,
and check the thickness of the shoes with vernier calipers. If the thickness is less than
the following service limit, replace them as a set.
Clutch springs -----visually inspect the clutch springs for strectched coils or broken
coils.
Service limit::2.0mm(0.08in)
CAUTION : clutch shoes or springs must be
changed as a set and never individually.
Clutch wheel—inspect visually the condition of the
inner clutch wheel surface for scrolling, cracks, or
uneven wear. Measure inside diameter of the clutch
wheel with inside calipers. Measure the diameter at
several points to check for an out-of-round condition
as well as wear.
Service limit:110.50mm(4.350in)
DRIVE BELT
Remove the drive belt and check for cracks, wear
and separation. Measure the drive belt width with a
vernier calipers. Replace it if the belt width is less
than the service limit or and defect has been found.
Service limit:16.0mm(0.630in)
CAUTION;Always keep the drive belt away
from any geasy matter.
Drive face
Inspect the belt contact surface of the dirve faces
for wear, scratches or any abnormality. If there is
something unusual, replace the drive face with a
new one.
Page 35

35
Roller and sliding surface
Inspect each roller and sliding surface for wear or
damage.
Driving face spring
Measure the free distance of the driven face spring. If
the length is shoter than the service limit, replace the
spring with a new one.
service limit: 104.5mm(4.11in)
Driven face pin and oil seal
T urn the driven face and check to see that the driven
faces turn smoothly. If any stickiness or hitches are
found, visually inspect the lip of oil seal, driven face
sliding surface and sliding pins for wear or damage.
Driven face
inspect the belt contacting surface of bothdriven
faces for any scratches, wear and damage.
Replace driven face with a new one if there are
any abnormality.
Cylinder head
Decarbon the combusion chamber.
Check the surface of the clinder head as shown
in the illustration for distortion with a straightedge
and thickness gauge, taking a clearance reading
at several places.
service limit:0.05mm(0.002in)
Page 36

36
If the largest reading at any portion of the
staightedge excees the limit, rework the surface by
rubbing it against emery paper laid flat on the
surface plate in a lapping manner. The surface must
ge smooth and perfectly falt in order to secure a tight
join: a leaky joint can be the cause of reduced power
output and increased fuel consumption.
CYLINDER
Decarbon exhaust port and upper part of the
cylinder, taking care not to damage the cylinder wall
surface. The wear of the cylinder wall is determined
from diameter reading taken at 20mm from the top
of the cylinder with a cylinder gauge. If the wear thus
determined exceeds the limit indicated below, rework
the bore to the next oversize by using a boring
machine or replace the cylinder with a new one.
Oversize pistions are available in two sizes: 0.5mm
and 1.0mm. (cylinder gauge)
service limit:40.075mm(1.5778in)
after reworking the bore to an oversize , be sure to
chamfer the edges of ports and smooth the
chamfered edges with emery paper. To chamfer,
use a scraper, taking care not to nick the wall
surface.
NOTE
:
Minor surface flaws on the cylinder wall durto seizure
or similar abnormalities can be corrected by grinding
the flaws off with fine-grain emery paper . If the flaws
are deep grooves or otherwise persist, the cyliner
must be reworked with a boring machine to the next
oversize.
PISTON
cylinder and piston clearance
cylinder –piston clearance is the difference between
piston diameter and cylinder bore diameter. Be sure
to take the maked diameter at right angles to the
piston pin. The value of elevation ,A is prescribed to
be 20mm from the skirt end.
(micrometer)
service limit:39.885mm(1.5703in)
As a result of the above measurement, if the
piston-to-cylinder clearance exceeds the following
limit, overhaul the cylinder and use an oversize piston,
replace both cylinder and piston. The measurement
for the bore diameter should be taken in the
intake-to-exhaust port direction and at 20mm from
the cylinder top surface.
Page 37

37
Unit:mm
Piston pin bore
Use a caliper gauge to measure the piston pin bore inside diameter,. If reading
exceeds the following service limit, replace it with a new one.
(Dial caliper)
Limit service: 12.30mm(0.4736in)
Piston pin outside diameter:
Use a micrometer to measure the piston outside
diameter at three positions.
(Micrometer(0-25mm))
service limit:11.980mm(0.4717in)
Piston rings
Check each ring for end gap, reading the gap with a
thickness gauge shown in the illustration. If the end gap
is found to exceed the limit, indicated below, replace it
with a new one.
The end gap of each ring is to be measued with the ring
fitted squarely into the cylidner bore and held at the
least worn part near the cylidner bottom, as shown in
the illustration.
Service limit:0.75mm(0.030in)
As the piston ring wears, its end gap increases reducing
reducing engine power output becaust of the resultant
blow by through the enlarged gap. Here lies the
importance of using piston rings with end gaps with the
limit. Measure the piston ring free end gap to check the
spring tension.
service limit:3.6mm(0.14in)
Fix the piston ring in the piston ring groove, measure the ring side clearance with the
thicknes gauge while matching the sliding surface of piston and ring.
Standard service
limit
Cylinde
r
40.005-40.0
20
40.075
Piston 39.94-39.955 39.885
Cylinder to
piston
0.06-0.07 0.120
Page 38

38
Standard clearance
1st:0.04-0.06mm(0.0016-0.0024in)
2nd:0.02-0.04mm(0.0008-0.0016in)
Reed valve
Check the clearance A betw een reed valve and its
seat and the dimension B. If the clearance A is noted
to exceed 0.2mm, replace the reed valve assembly.
The dimension B is at least 1mm.
ENGINE Reassembly
Reassembly is generally performed in the reverse
order of disassembly, but there are a number of
reassembling steps that demand or deserve detailed
explanation or emphasis. These steps will be taken
up for respective parts and components.
Oil seals
fit the oil seals to the crankcase following the
procedure below. Replace removed oil seals with
new ones.
z Lubricate the edge of oil seal
z Install oil seal into crankcase
carefully with special tool.
Oil seal installation
Bearing
Install new bearing with
special tool
Install bearing
First heat up the cover and
cool down the bearing. The
install would be much easier
and better for the bearing.
Page 39

39
shock absorber bushing
positon
install bearing in the cover. Don’t install
the bearings on the crankshaft.
Install shock absorber bushing
Install crankshaft (without bearings)
Page 40

40
CRANKCASE
z Wipe the crankcase mating surfaces with
clraning solvent.
z Apply GENERIC NO.1215 evenly to the mating
surface of the right half of the crankcase
z Tighten the crankcase screws securely.
z Check if crankshaft rotates smoothly.
Install gearcase bearing
Install new bearing and oil seal into gearcase cover with special tool, and tighten
anchor pin.
Page 41

41
z install output axle
z gearshift
z install middle gear , position pin by installing middle
gear axle, gasket and thrust gasket
z install gearcase cover into
crankcase and lock bolt.
z tighten each screw
z screw oil drain nut,11
tightening torque:4-7 N.m
(0.4-0.7kg-m,3.0-5.0 Ib-ft)
Page 42

42
z install the bearing in the fixed driven face with the
special tool.
z install sliding bearing 。
Page 43

43
z Install the bearing with special tool
z install the spacer and circlip:
z install the new oil seals and to the movable
driven face with the special tool.
z apply grease to the lip of oil seals and
groove of inside of movable driven face.
GENERIC special super grease
NOTE:
When reinstalling the movable face to the fixed
face, make sure that the oil seal is positoned
properly.
z install the pin at three places on the driven
face hub.
z Apply grease lightly to the cam part where the
pins are placed.
z Install two O-RINGs.
Page 44

44
z Install the movable driven face seat.
z install the clutch shoe assembly and nut.
z tighten the nut to the specified torque with the
special tool.
tightening torque:40-60 Nm
(4.0-6.0kg.m 29.0-43.5Ib-ft)
z insert the V-belt between the driven faces as
deep inside possible while pulling the movable
driven face all the way outside to provide the
maximum ble clearance.
CAUTION:
the belt should be positioned so that the arrows
on the belt periphery point the normal turning
direction.
The V-belt contact face on the driven faces should
be thoroughly cleaned to be free from oil.
z Thoroughly clean the clutch housing to be free
from oil and position it over the clutch shoe
assembly.
z tighten the clutch housing nut to the specified
torque with the special tool.
Torque:40-60 Nm
(4.0-6.0kg.m 29.0-43.5Ib-ft)
Page 45

45
z Apply grease to all the sliding and rolling surfaces
for six roller weights. For each weight,
approximately 1.5g of grease should be used.
GENERIC super grease
z Mount the three dampers on the movable drive
plate and install it on the movable drive face.
z Position the O-RING on the movable drive
face.
z Install the movable drive face cover.
NOTE:
1. Make sure that the mova ble drive plate is fully
positioned inside, or the weight roller may
come off.
Page 46

46
z Insert the spacer
z Position the movable drive face
subassembly on the crankshaft as shown in
illustration.
NOTE
:
Thoroughly clean the belt contact to be
free from oil.
z Install the fixed drive fan.
z tighten the nut to the specified torque with
special tool.
Connecting rod fixer
Tightening torque:40-60Nm
(4.0-6.0kg-m, 29.0-43.5Ib-ft)
z fill grease in the groove provided inside sliding
surface of the kick driven gear and install on the
end of the crankshaft. Wipe off excess grease.
QIANJIANG super grease
Install washer and spring.
NOTE:
When Installing washer,face the resin surface
of washer to outside.
z install the retainer.
z continue turning the fixed drive face by hand
until the belt is seated in and both the drive and
driven faces will move together smoothly with
slip.
fill the final gear box with engine oil up to the
level hole.
Oil capacity: 90ml
z tighten the oil level bolt to the specified torque.
Tightening torque:9-15Nm
Page 47

47
Starter assy.
z Inject lubrication into start bearing and
lubrication in the end of starter shaft
GENERIC SPECIAL LUBRICATION
z Tighten starter shaft gasket
Install starter ratchet wheel and circlip
Page 48

48
z Install the dowel pins
z install the new gaskets( and )
z apply GENERIC bond no. 1215 to the clutch
cover as shown in the illustration.
GENERIC bond no. 1215
NOTE: Install the kick starter lever as
shown in the illustration.
Tightening toque:8-12Nm
(0.8-1.2kg-m, 6.0-8.5Ib-ft)
PISTON
z install the piston rings on the piston.
The first and the second ring: keystone ring.
NOTE:
Position the ring so that the marking is on
upside.
z it is extremely important that, when the
piston is fed into the cylinder , each ring in
place should be so positioned as to hug
the locating pin as shown in illustration.
Page 49

49
z apply oil for the piston and install the piston to
the connecting rod.
NOTE
:
The arrow mark on the piston head should
point the exhaust side.
z The circlip should be mounted in such a
position that the mating ends of the circlip do
not coincide with the grovve portion of the
piston.
z apply oil on the position and cyoinder wall
surfaces and install the cylinder over the
piston carefully.
z tighten the cylinder head nut to the
specification.
tightening torque:18-28Nm
z install right crankcase oil seal press board
z install worm, and lubricater it with GENERIC
special lubrication.
Oil pump
z install oil pump into crankcase
torque:3-5Nm
(0.3-0.5kg-m, 2.3-3.7Ib-ft)
OUTSIDE
Page 50

50
Reed valve
z install a new reed valve paper
gasket.
z Install reed valve
z Install oil hose
Intake pipe
z install intake pipe
Magneto
z clear crankshaft and magneto rotor
z install half circle key
z install paper gasket and stator coil, and fix them
z tighten to specified torque with special tool
specified torque:35-45Nm
(3.5-4.5kg.m,25.5-31.0Ib-ft)
Page 51

51
z install cooling fan
z install guiding cover
z install fan guiding cover
z install pipe screw and screw for tightening muffler
to their specified torque.
:8-12Nm (0.8-1.2kg.m,6.0-8.5Ib-ft)
:18-28Nm (1.8-2.8kg.m,13.0-20.0Ib-ft)
z lubricate brake cam shaft with GENERIC grease.
Page 52

52
CHAPTER 4 FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM
CONTENTS
FUEL SWITCH
CARBURETOR
OIL PUMP
Page 53

53
FUEL SWITCH
When the engine has started, a negative pressure (vacuum) is generated at the intake
port. The negative pressure acts upon the diaphragm of the fuel switch and it pressed
down the spring which supports the diaphragm so that the fuel passageway is opened
and fuel is fed to the carburetor.
When the engine has stopped, the spring presses the valve, the fuel passageway is
closed, and no fuel flows to the engine.
Fuel switch
Page 54

54
CARBURETOR
CARBURETOR
Carburetor
manufacturer/type
Identification code
Throat tube diameter
Main jet size
Idle needle jet size
Oil needle clamp position
Idle air adjusting screw
Float height
equal vacuum
PZ19JB
19mm
#80
#57.5
3
rd
groove
extrude 1
2
1
±
2
1
turnout
13±1mm
Page 55

55
CARBURETION
Proper carburetion is determined according to the results of various tests, mainly
concerning engine poer , fuel consumption and cooling effect of feul on engine, and jet
settings ard made so as to satisfy and balance all of these conditions. Therefore, the
jet should not be replaced with a size other than the original. And the positions of
adjustable parts should not be changed except wh en compensation for the mixture
ratio due to altitude differences or other climatic conditions. When adjustment is
necessary, refer to the following.
OIL PUMP
OIL LEAKAGE throughout
Whenever evidence is noted of some air having leaked into the oil pipe from the oil
tannk in a machine brought in for servicing, be sure to carry out an air bleeding
operation with the oil pump in place before returning the machine to the user. T o bleed
air, hold the machine in standstill condition.
Page 56

56
CHAPTER 5 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
CONTENS
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHARGING AND LIGHTING SYSTEM
STARTER SYSTEM
FUEL GAUGE
OIL LEVEL CHECK LIGHT AND TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR
SWITCHS
BARTERY
Page 57

57
IGNITION SYSTEM
The ignition system consists of a flywheel magneto, a CDI&Ignition coil unit and a
spark plug.
As the rotor tatates, an AC current is induced in the coil. Then current induced in the
,A direction charges up the capacitor.
As the rotor rotates further, the current is induced in the reverse direction (dirction,B).
the current causes a voltage applied through the ground to the gate of SCR.
As the SCR conducts, the energy which has been charged in the capacitor is
instantaneously discharged through the primary winding of the ignition coil.
CDI UNIT AND IGNITION COIL INSPECTION
CHECKING WITH ELECTRO TESTER
Connect the CDI test lead to the coil”s primary
connector.
Connect the high tension leads, red,+ lead to the
spark plug cord and the black,— lead to the black
lead of the test lead.
z Set the test selector knob to “P.E.I”.
z Connect the power lead to the appropriate AC source.
z Switch the power on.
Switch Black
red
CDI test lead
MAGNETO
CDI&Ignition coil unit
Spark plug
Page 58

58
Note the spark in the spark gap window. It should
be strong and continuous, not intermittent, acrossa
preset 8mm(0.32in) gap. Allow the spark to jump
the test gap for at least five minutes continuously.
To insure proper operation under the temperature
of actual riding.
Electronic tester
Ignition coil testing lead
Use portable tester to check it.
Test the resistance between i gntion ground wire and
spark plug cap.
Ignition coil second resistance:12-18 KQ
MAGNETO EXCITING COIL
z remove the right frame side cover
z disconnect the exciting coil lead wire(black with
red tracer).
z Using a pocket tester, measure the resistance
between the B/R lead wire and ground. If the
resistance checked is incorrect, re plac e the coil.
Exciting coil restance:140-220
Page 59

59
CHARGING AND LIGHTING SYSTEM
The charging system uses the flywheel magnetoas shown in the figure. The charging
and lighting coils are mounted on the magneto stator and generate AC as the
flywheel rotor turns. AC generated in the charging coil flows to the regulator/recifier
which changes AC to DC. The DC Then charges the battery.
Charging output check
start the engine and keep it running at 5000r/min
with lighting switch turned on.
NOTE:
When making the test, be sure that the batteryis
in fully charged condition.
Tachometer
Standard charging output:13-16v at 5000r/min
Fuse
Battery
Page 60

60
NO-LOAD PERFORMANCE
z Disconnect the magneto lead wire coupler.
z Start the engine and keep it running at 5000r/min.
z Using a pocket tester, mea sure the AC voltage between the white and red trace r
lead wire and ground. If the tester reading is as follows, magneto is in good
condition.
Standard no-load performance: more than
65v(AC)AT 5000R/MIN.
STATOR COILS
Inducing coils
Use procket tester to measure the resistance
between the lead wire and ground. If the resistance
checked is not correct, replace the coil.
Rregulator/rectifier
Disconnect the lead wire couple.
Using the pocket tester( × 1KQ RANGE), measurethe resistance between the
terminals as shown in the following table. If the resitance checked is incorrect, replace
the regulator/rectifier.
UNIT:
NOTES:
Including the components such as
transistor,capacitance, regulator
diode and so on, so tested
resistance may be different from
actual resistance.
Standard
resistance
W/R-GROUND 0.6-1.1Q
W/R-GROUND 0.5-0.8 Q
Page 61

61
STARTER SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The starter system is shown in the diagram bel ow: namely, the starter motor, relay,
starter switch and battery. depressing the starter button while squeezing the front or
rear brake lever energizes the relay, causing the contact points to close which
connects the starter motor to the battery.
Starter motor removal and disassembly
Remove the starter motor
Disassemble the starter motor as shown in the
illustration
Page 62

62
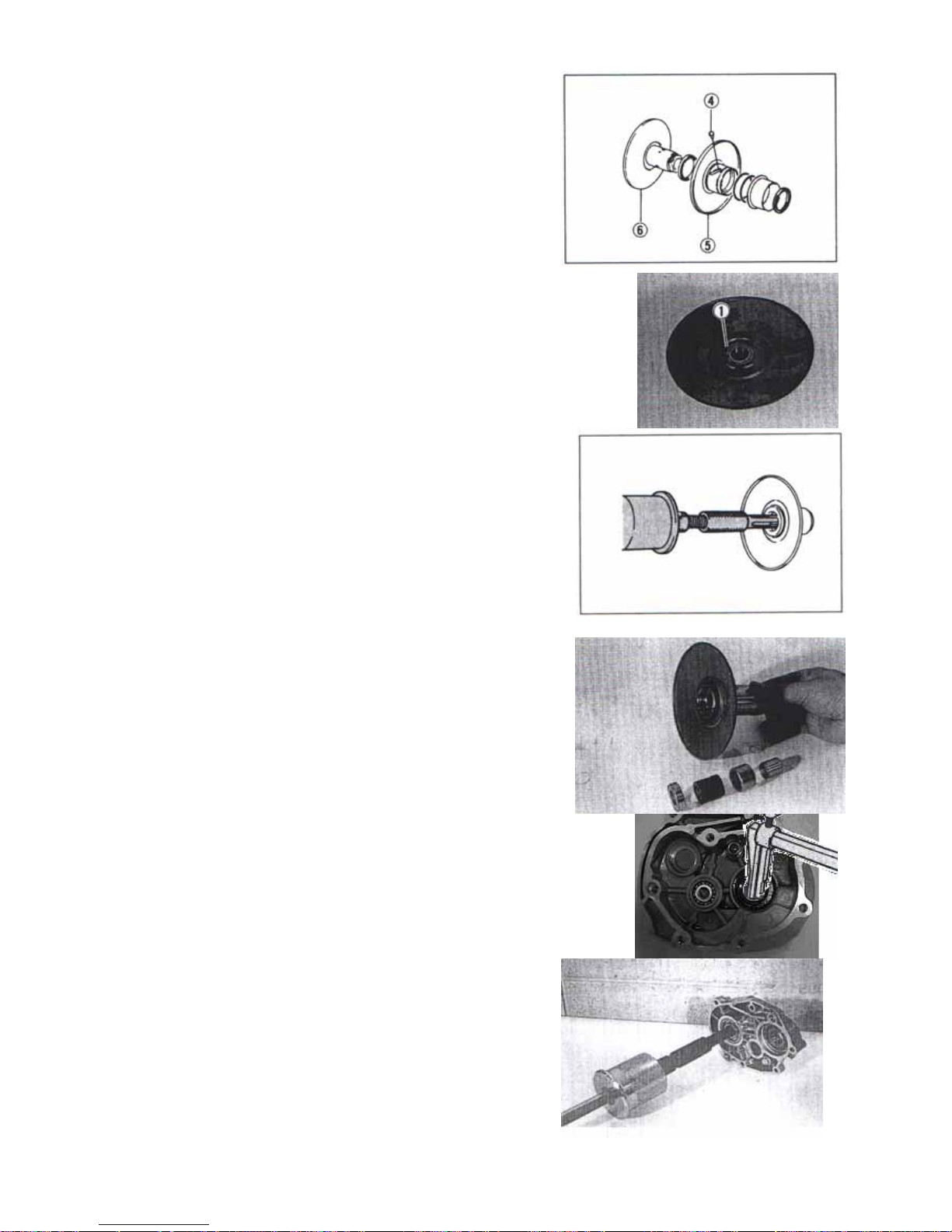
STARTER MOTOR INSPECITION
CARBON BRUSHES
When the brushes are worn, the motor will be
unable to produce sufficient torque, and the engine
will be difficult to turn over. To prevent the ,
periodically inspect the length of the brushes and
replace them when they are too short or chipping.
Service limit:3.5mm(0.14in)
Commutator
If the commutator surface is dirty, starting
performance will decrease. Polish the commutator
with #400 or similar fine emery paper when it is dirty.
Service limit:0.2mm(0.008in)
Armature coil
using the pocket tester , check the coil for open and
ground by plcing probe pins on each commutator
segment and rotor core and on any two segments
at various places. With the brushes lifted off the
commutator surface. If the coil is found to be
open-circuited or grounded, replace the armatrue.
Starter relay inspection
z Disconnect lead wire (R/W) of the starter motor.
T urn on the igniton switch and squeeze the front
or rear brake lever, then inspect the continuity
between the Red and Red/White lead wires at
the starter relay when pushing the starter
button.
If the starter relay is in sound condition,
continuity is found.
• Disconnect the starter relay lead wire couple.
Check the coil for “open”, “ground” and ohic
resistance. The coil is in good condition, if the
resistance is as follows:
STANDARD RESTANCE::80-150Q
Segment
Mica
Page 63

63
FUEL LEVEL METER/GAUGE
FUEL METER INSPECTION
T o test the Fuel Meter two different checks may be used. The first,and simplest test will
tell if the mete is operating but will not indicate the meters accuracy throughout the
range.To perform the test,lift the seat and remove the right frame cover,then
disconnect the B/W and Y/B lead connector of the fuel gauge sending unit.Connect a
jumper wire between B/M and Y/B wiers coming from the main wiring harness.With the
ignition switch tuined ON,the fuel meter should indicate“F”.
The second test will check the accuracy of the meter in
the full and empty positions.Connect a 90-ohm resistor
between the Y/B and B/W lead wires.The fuel meter is normal
if its pointer indicates the E(empty) position when the
specified voltage is applied to the circuit and if its
pointer indicates the F(full) position when the resistor is
changed to 10 ohms.If either one or both indications are
abnormal,replace the fuel meter with a new one.
FUEL GUAGE SENDING UNIT INSPECTION
Disconnect the lead wires coming out of the fuel
gauge and check resistance of eadn podition.
If the resistance measured is incorrect, erplace the
fuel gaue assembly with a new one.
The relation between the position of the fuel guage float and
resistance is shown in the following table.
FLOAT POSITION RESISTANCE
F(FULL)
APPROX.33
1/2 APPROX.200
E(EMPTY)
APPROX.566
CABLE ASSY.
33
Page 64

64
SIGNAL SYSTEM
The same bulb is used tor both oil level check light and turn signal indicator light.The
circuitry is shown below.When the oil level has fallen to a certain level (the remaining
amount of oil has become approximately 160 ml,the oil level check light turns on and
remains lit.When the turn signal switch is turned on and the turn signal light flashes,the
turn signal indicator light (oil level check light)also flashes,both being not concurrently
but alternatively as one being lit white the other unit.
Fig. 7
OIL LEVEL SWITCH INSPECTION
Check the oil level switch for continuity between the lead wire.If the tester does not
show the value of 0-1 ohm when the switch ring is in bottom position,file the contact
surface or replace the unit.
Page 65

65
SWITCH
DARK GREEN
OFF
ON
HORN SWITCH
RED/WITHE
OFF
OFF
ON
RED/SWITCH
LOCK
BREAK SWITCH
RED
ON
RED/WHITE
MA IN SWITCH
BROWN
TURN RIGHT
TURN LEFT
DIRECTION SWITCH
ORANGE
GREEN
/BLACK
GREEN/WHITE
PASSING LIGHT
YELLOW/RED
PURPLE
DIPPED
HEADLIGHT
HIGH BEAM
OFF
BULE AZURY
EXCHANGE LIGHT SWITCH
GREEN/RED
BLACK
HEAD LIGHT
YELLOW/RED
YELLOW
LIGHT CONTROL SWITCH
YELLOW
PINK
Page 66

66
BATTERY
SPECIFICATIONS
Type designation YB4L-B
Capacity 12V 4Ah
Standard electrolyte 1.28(20)
INITIAL CHARGING
FILLNG ELECTROLYTE
Remove the aluminum tape sealing the battery electrolyte filler holes.
Remove the caps .
NOTE:
* After filling the electrolyte completely ,use the removed cap
as the sealed caps of battery-filler holes.
* Do not remove or pierce the sealed areas of the
electrolyte container.
Insert the nozzles of the electrolyte container into the
battery`s electrolyte filler holes,holding the container
firmly so that it doer not fall.Take precaution not to
allow any of the fluid to spill.
Make sure air bubbles are coming up each electrolyte
container ,and leave in the positon for about more than 20
minutes.
Test the battery after the filling process. If
necessary charge the battery about 20 minutes
with the charger.
Page 67

67
RECHARGING OPERATION
Apply multimeter to measure the voltage of battery. If the reading is below 12.0V,it
should be charged.
NOTE:
When recharging, remove the battery form the vehicle.
NOTE:
When recharging, don’t remove the sealing cap off battery top.
Recharging time:0.4A or for 5 hours or 4.0A for 1 hour.
NOTE:
The current should be not more than 4A at any time.
After recharging, wait for more than 30 minutes and apply multimeter to meas ure the
battery voltage.
If the battery voltage is less than12.5V,please rechare the battery again.
If battery voltage is still less than 12.5V,please replace the battery with a new one.
When the battery is left for a long term without using, it is subject to discharge. When th
scooter is not used for more than 1 month (especially dring the winter season),
recharge the battery once a month at least.
Page 68

68
CHAPTER 6 CHASSIS
CONTENTS
LEG SHIELD AND FRAME SIDE COVERS
LEG SHIELD REMOVAL
LEG SHIELD REMOUNTING
FARME SIDE COVER REMOVAL
FARME SIDE COVER REMOUNTING
HANDLEBAR COVERS
REMOVAL
REMORNTING
FRONT WHEEL
REMORAL
INSPECTION AND DISASSEMBLY
REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING
FRONT BRAKE
BRAKE PAD REPLACEMENT
CALIPER REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
CALIPER AND DISC INSPECTION
CALIPER REASSEMBLY
MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
MASTER CYLINDER INSPECTION
MASTER CYLINDER REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING
STEERING STEM AND FRONT SUSPENSION
REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING
IGNITION SWITCH
REAR WHEEL AND BRAKE
REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING
Page 69

69
Side cover removal
1. remove seat and helmet barrel by opening
seat and loosing tightening screw .
2. loose hexad screw and remove decorating
cap , rear carrier and oil tank lock ,remove
side cover by loosing side cover screw ;
3. unlock oil pump cap and remove it, two
tapping screw are exposed, remove
them; remove tapping screw;then remove
side cover
side installation
4. the sequence of installation is the reverse of removal.
④
③
⑦
②
③
⑦
⑧
⑩ ⑩
⑨
Page 70

70
under cover removal
1. unscrew screw and bolt
2. removing under cover by loosing the left and right tapping screws ;
under cover installation
3. The sequence if installation is ther reverse of removal.
front cover removal
1.Unscrew tapping screw , and remove front cover by removing front cover screw
②
①
①
②
①
③
①
② ②
②
①
Page 71

71
LEGSHIELD AND PEDAL REMOVAL
1. Remove power lock housing by unscrewing bolt.
3. remove legshield and pedal by
unscrewing the four bolts
Legshield and pedal installation
4. the sequence of legshield and
pedal is the reverse of reomval;
②
③
①
Page 72

72
HANDLE COVER REMOVAL
1. Remove front handle cover by
unscrewing the six tapping screws
2. Remove master cylinder by removing
the bolt ;
①③
①①
①①
①①
①②
Page 73

73
3. Disconnect throttle cable and oil pump cable
4.Remove rear brake cable adjusting nut
①③
①④
①⑤
Page 74

74
Handle cover removal
5. remove all cables;
6.Remove handle cover by unscrewing bolt
Handle cover unstallation
7. The sequence of removal is the reverse of reomval
⑥
Page 75

75
Front wheel
1. front rim
2. middle bushing
3. oil seal
4. roller bearing GB6201-2RS
5. tire
6. valve mouth
7. nut GB6817
8. front shaft
9. front wheel left bushing
10. gearcase
11. valve mouth cap
remove
Remove the front brake caliper by removing the
mounting
bolts.
NOTE: Do not operate the front brake lever while
dismounting caliper
∙remove mounting bolt
∙remove the left decorating cover and right one .
∙remove under front fender
∙support the scooter by jack or wood
shelf.
∙Remove front wheel by removing
front axle shaft.
① ②
③
⑤
④
⑥
Page 76

76
INSPECTION AND DISASSEMBLY
WHEEL BEARING
Inspect the play of bearing inner ring by hand while
mounted in the wheel.
Rotate the inner ring by hand to inspect if any abnormal
noise occurs or rotating smoothly,
Replace the bearing if there is anything ucusual.
∙Remove the dust seal.
CAUTION:
The removed dust seal and bearing should be replaced with new ones.
AXLE SHAFT
Check the axle shaft runout with a micrometer and
replace it if the runout exceeds the limit.
Service limit:0.25mm (0.010in)
WHEEL RIM
Make sure that the wheel rim runout does not exceed
the service limit when checked as shown.
An excessive runout is usually due to worn or loose
wheel bearings and can be reduced by replacing the
bearings.If bearing replacement fails to reduce the
runout,replace the wheel.
Service Limit:2.0mm (0.08in))
Page 77

77
Reassembly and remounting
Reassemble and remount this front wheel in the reverse order of removal, and also
carry out the following steps:
install this wheel bearing with the special tools as shown in this illustration.
CAUTION: Install this wheel bearing for left side..
Install the brake disc as shown in photo.
When installing this speedometer gear box, align the
two driving pawls with the two recesses of the wheel
hub.
Tighten the nut with special tool.
Page 78

78
FRONT BRAKE SYSTEM
RAKE PAD REPLACEMENT
Remove the calliper by removing the mounting bolts .
NOTE:
Do not operate the front brake lever while dismounting the calliper.
1. disc brake assy.
2. disc brake handle
lever
3. tightening bolt
4. nut M6
5. master cylinder
6. tightening seat
7. bolt M6X23
8. brake hose assy.
9. brake caliper
10. connecting
board tightening
bolt
11. hose mounting
bolt
12. seal gasket
13. front gasket
14. rear gasket
15. brake pad 1
16. brake pad 2
17. master cylinder
rubber bushing
18. front brake
switch
①
Page 79

79
∙Remove the brake pads.
CAUTION:
Replace the brake pads as a set,otherwise braking
performance will be adversely affected.
Reassemble and remount the calliper.
CALIPER REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
Remove the brake hose and catch the brake fluid in a suitable
receptacle.
CAUTION:
Nevere re-use the brake fluid left over from the last
servicing and stored for long periods.
∙Remove the calliper.
∙Remove the brake pads.
∙Remove the spring and pad holder.
∙Place a rag over the piston to prevent popping up.Froce out the piston with a air gun.
CAUTION:
Do not use high pressure air to prevent piston damage.
∙Remove the dust seal and piston seal .
Page 80

80
CALIPER AND DISC INSPECTION
Inspect the calipe cylinder bore wall or
micks,scratches or other damage.
Inspect piston for damage and wear.
Inspect each rubber part for damage and wear.
Check the disc for wear with a micrometer.Its
thickness can be checked with disc and wheel in
place. Ralpace the dise if the thickness exceeds the
service limit.
Service Limit:3.5 mm (0.14 in)
With the disc mounted on the wheel, check the dids
for face runout with a dial gauge as shown.
Replace the disc if the runout exceeds the service
limit.
Service Limit:0.3 mm(0.012 in)
Page 81

81
BRAKE CALIPER REASSEMBLY
Reassemble and remount the calliper in the reverse
order of removal and disassembly, and also carry out
the following steps.
CAUTION:
Wash the calliper components with fresh brake fluid
before reassembly. Never use cleaning solvent or
gasoline to wash them.Apply brake fluid to the calliper
bore and piston to be inserted into the bore.
Reassemble and remount the calliper. (refer to preceding bove pages)
WARNING:
Bleed air after remounting the calliper. (refer to above pages)
MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
Remove the handlebar cover. (Refer to above page)
Disconnect the front brake light switch lead wires.
Place a cloth underneath the union bolt on the master
cylinder to catch spilled drops of brake fluid. Unscrew
the union bolt and disconnect the brake hose master
cylinder joint.
CAUTION:
Completely wipe off any brake fluid adhering to any part of motorcycle. The fluid reacts
chemically with paint, plastics, rubber materials, etc.
Remove the master cylinder.
Page 82

82
Remove the brake lever and brake switch.
Remove the dust boot.
Remove the circlip with the special tool.
Remove the piston/primary cup with return spring.
Remove the reservoir cap and diaphragn.
Drain brake fluid.
MASTER CYLINDER INSPECTION
Inspect the master cylinder bore for any
scratches or other damage.
Page 83

83
Inspect the piston surface for scratches or other damage.
Inspect the primary cup and dust boot for wear or damage.
MASTER CYLINDER REASSEMBLY AND
ERMOUNTING
Reassemble and remount the master cylinder in the
reverse order of removal and disassembly,and also
carry out the following steps.
CAUTION:
Wash the master cylinder components with fresh
brake fluis before reassembly. Never use cleaning solvent or gasoline to wash them.
Apply brake fluid to the cylinder bore and all the internals to be inserted into the bore.
Reassemble and remount the master cylinder, When remounting the master cylinder
on the handlebar, first tighten the clamp bolt for upside.
CAUTION:
Bleed air after remounting the master cylinder.
Page 84

84
STEERING STEM AND FRONT SUSPENSION
REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY
(Refer to preceding page)
□ remove the handle cover(refer to preceding page)
□ remove under decorating cover(refer to the preceding page)
□ remove legshield(refer to preceding
page)
□ remove front wheel(refer to preceding
page)
□ disconnect the front and rear brake
light switch lead wires .
□ Remove the rear brake cable .
□ Remove throttle grip case .
□ Remove throttle cable .
1. handle jointing assy.
2. bolt GB5789
M10X1.25X45
3. nut GB6187 M10X1.25
4. left handlebar
5. throttle grip assy.
6. screw GB818 M5X10
7. rear brake cable assy.
8. throttle cable assy.
9. left switch comp.
10. right switch comp.
11. anti-dust cover
12. steel ball ¢5
13. lower outer steel bowl
14. connecting steel bowl
15. under connecting borad
assy.
16. lower inner steel bowl
17. bolt GB5789
M10X1.25X30
18. locknut
① ③
④
②
Page 85

85
□ remove disc brake system by unscrewing tightening bolt.
□ remove handle by removing tightening bolt
□ unscrew locknut with special tool
□ remove fornt fork assy. by removing upper outer steel bowl
NOTE:
Not drop the steering stem balls.
□ remove front fork
□ remove bearing lower race by chisel.
□ Remove steel balls.
Number of steel balls:
Upper:21
lower:21
□ remove the upper and lower bearing inner races with a
appropriate bar
Page 86

86
Page 87

87
INSPECTION
□ inspect the removed parts for the following abnormalities.
bearing race wear and brinelling.
Worn and damaged steel balls
Distortion of steering stem or handlebar.
□ Inspect the suspension for damage
Page 88

88
Reassembly and remounting
reassemble and remount the steering stem, handlebar
and front fork in the reverse order of disassembly
andremoval, and also carry out the following steps.
Install the right left suspension arms.
Steel ball
Apply grease when installing the upper and lower
steel balls.
QTY:upper :21
lower :21
Tighten the steering outer race with special tool,
then extrude it 1/8-1/4round.
NOTE:adjustment will vary from scooter to scooter. B e
sure that the steering turns smoothly and easily, left to
right.
□ install a locknut by installing locknut and
anti-dust cover
□ screw locknut with special tool, and adjust
front fork bearing to get smooth turning.
Page 89

89
install handlebar and tighten the screw and bolt
to the specified torque:37-44N.M
NOTE:
After performing the adjustment and installing the handlebar, rock the front wheel
forward and backward to ensure that there Is not play and that the procuder is
accomplished correctly. If play is noticeable, raadjust the steering outer race nut.
Page 90

90
REAR WHEEL AND BRAKE
1. Tire 130/70-12
2. rear rim assy.
3. brake pad kit
assy.
4. brake pad kit
spring
5. rear brake
tension
6. rear indicator
7. anti-dust cover
8. rear brake
camshaft
9. bolt M6Χ30
10. valve
11. nut M16Χ1.5
12. rear brake arm
13. valve ca
p
Page 91

91
REMOVE
□ Place the scooter on level ground.
□ Remove muffler.
□ Remove rear small fender.
□ Remove locknut and rear wheel.
□ Remove brake shoes.
INSPECTION
REAR RIM
Measure inner diameter of rear rim hub with
micrometer, if measured diameter exceeds 110.7,
replace it with a new one.
Brake shoes
Check the brake shoe and decide whether it should be replaced or not from the
thickness of the brake shoe lining.
Service limit:2.5mm(0.09in)
Page 92

92
REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING
Reassemble and remount the rear wheel and
brake in the reverse of removal, and also
carry out the following steps:
□ Turn the punched mark on the camshaft
to the rear axle shaft side.
□ Install the protrusion of indicator plate to the
groove of Camshaft.
□ When installing the brake cam shaft, aligh the groove
of camshaft with the slit of on cam shaft.
□ When installing brake shoes, be sure to daub
camshaft with adequate grease.
CAUTION:
Be careful not to daub the camshaft with too
much grease.
If grease gets on the lining, brake effectiveness will be lost.
Page 93

93
SERVICING INFORAMTION
Troubleshooting
Battery
Vehicle
Wiring diagram
Wire, cable and brake hose routing
Special tools
Thread parts tightening torque
Service data
CONTENTS
Page 94

94
TROUBLESHOOTING
ENGINE
Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy
Engine does
not start, or
is hard to
start.
Compression too low
Excessively worn cylinder or piston rings.
Stiff piston ring in place.
Gas leaks from the joint in crankcase, cylinder or
cylinder head.
Damaged reed valve.
Spark plug too loose.
Broken, cracked or otherwise failed piston.
Plug not sparking
Damaged spark plug or spark plug cap.
Dirty or wet spark plug.
Defective CDI & ignition coil unit or stator coil.
Open or short n high-tension cord.
Defective ignition switch.
No fuel reaching the carburetor
Clogged hole in the fuel tank cap.
Clogged or defective fuel cock.
Defective carburetor float valve.
Clogged fuel hose or defective vacuum hose.
Replace.
Repair or replace.
Repair or replace.
Replace.
Tig ht en
Replace.
Replace.
Clean and dry.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Clean.
Clean or replace.
Replace.
Clean or replace.
Engine stalls
easily.
Carbon deposited on the spark plug.
Defective CDI & ignition coil unit.
Clogged fuel hose.
Clogged jets in carburetor.
Clogged exhaust pipe.
Clean.
Replace.
Clean.
Clean.
Clean.
Noisy engine. Noise appears to come from piston
Piston or cylinder worn down.
Combustion chamber fouled with carbon.
Piston pin, bearing or piston pin bore worn.
Piston rings or ring grooves worn.
Noise seems to come from crankshaft
Worn or burnt crankshaft bearings.
Worn or burnt conrod big-end bearings.
Noise seems to come from final gear box
Gears worn or rubbing.
Badly worn splines.
Worn or damaged bearing of drive shaft or rear axle
shaft.
Replace.
Clean.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Slipping
clutch
Worn or damaged clutch shoes.
Worn clutch drum.
Replace.
Replace.
Engine idles
poorly.
Excessively worn cylinder or piston rings.
Stiff piston ring in place.
Gas leaks from crankshaft oil seal.
Spark plug gaps too wide.
Defective CDI & ignition coil unit.
Defective magneto stator coil.
Float-chamber fuel level out of adjustment in
carburetor.
Clogged jets in carburetor.
Broken or damaged reed valve.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Adjust or replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Clean or adjust.
Replace.
Page 95

95
Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy
Engine runs
poorly in
high-speed
range.
Excessively worn cylinder or piston rings.
Stiff piston ring in place.
Spark plug gaps to narrow.
Ignition not advanced sufficiently due to poorly working
CDI & ignition coil unit.
Defective magneto stator coil.
Float-chamber fuel level too low.
Clogged air cleaner element.
Clogged fuel hose, resulting in inadequate fuel supply to
carburetor.
Clogged fuel cock vacuum pipe.
Replace.
Replace.
Adjust.
Replace.
Replace.
Adjust or replace.
Clean.
Clean and prime.
Clean.
Dirty or
heavy
exhaust
smoke.
Too much engine oil to the engine.
Use of incorrect engine oil.
Check oil pump.
Change.
Engine
lacks
power.
Excessively worn cylinder or piston rings.
Stiff piston rings in place.
Gas leaks from crankshaft oil seal.
Spark plug gaps incorrect.
Clogged air cleaner element.
Float-chamber fuel level out of adjustment.
Clogged air cleaner element.
Fouled spark plug,
Sucking air from intake pipe.
. Slipping or worn V-belt.
Damaged/worn rollers in the movable drive face.
. Weakened movable driven face spring.
. Too rich fuel/air mixture due to defective starter system.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Adjust or replace.
Clean.
Adjust or replace.
Clean.
Clean or replace.
Retighten or replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Engine
overheats.
Heavy carbon deposit on piston crown.
Defective oil pump or clogged oil circuit.
Fuel level too low in float chamber.
Air leakage from intake pipe.
Use of incorrect engine oil.
Use lf improper spark plug.
Clogged exhaust pipe/muffler.
Clean.
Replace and clean.
Adjust or replace.
Retighten or replace.
Change.
Change.
Clean or replace.
Page 96

96
CARBURETOR
Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy
Trouble
with
starting.
Starter jet is clogged.
Air leaking from a joint between starter body and
carburetor.
Air leaking from carburetors joint or vacuum hose joint.
Starter plunger is not operating properly.
Clean.
Check starter body and
carburetor for tightness,
and replace gasket.
Check and replace.
Check and replace.
Idling or
low-spee
d
troubles.
Pilot jet, pilot air jet are clogged or loose.
Air leaking from carburetors joint, vacuum pipe joint, or
starter.
Pilot outlet is clogged.
Starter plunger is not fully close.
Check and clean.
Check and replace.
Check and clean.
Check and replace.
Mediumor
high-spee
d trouble.
Main jet or main air jet is clogged.
Needle jet is clogged.
Fuel level is improperly set.
Throttle valve is not operating properly.
Fuel filter is clogged.
Check and clean.
Check and clean.
Check and replace.
Check throttle valve for
operation.
Check and clean.
Overflow
and fuel
level
fluctuatio
ns.
Needle valve is worn or damaged.
Spring in needle valve is broken.
Float is not working properly.
Foreign matter has adhered to needle valve.
Fuel level is too high or low.
Replace.
Replace.
Check and adjust.
Clean.
Adjust and replace.
Page 97

97
ELECTRICAL
Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy
No sparking
or poor
sparking.
Defective CDI & ignition coil unit.
Defective spark plug.
Defective magneto stator coil.
Loose connection of lead wire.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Connect/tighten.
Spark plug
soon
becomes
fouled with
carbon.
Mixture too rich.
Idling speed set too high.
Incorrect gasoline.
Dirty element in air cleaner.
Spark plug loose.
Incorrect engine oil.
Adjust carburetor.
Adjust carburetor.
Change.
Clean.
Replace by hot type plug.
Replace.
Spark plug
electrodes
overheat or
burn.
Spark plug too hot.
The engine overheats.
Spark plug loose.
Mixture too lean.
Not enough engine oil.
Replace by cold type plug,
Tune up.
Retighten.
Adjust carburetor.
Check oil pump.
Magneto
does not
charge.
Open or short in lead wires, or loose lead
connections.
Shorted, grounded or open magneto coil.
Shorted or open regulator/rectifier.
Repair or retighten.
Replace.
Replace.
Magneto
charge, but
charging
rate is
below the
specificatio
ns.
Lead wires tend to get shorted or
open-circuited or loosely connected at terminal.
Grounded or open-circuited stator coils of
magneto.
Defective regulator/rectifier.
Defective cell plates in the battery,
Repair or retighten.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace the battery.
Magneto
overcharge
s.
Internal short-circuit in the battery.
Resistor element in the regulator/rectifier
damaged or defective.
Regulator/rectifier unit poorly grounded.
Replace the battery.
Replace.
Clean and tighten ground
connection.
Unstable
charging.
Defective regulator/rectifier.
Lead wire insulation frayed due to vibration,
resulting in intermittent shorting.
Magneto coil internally shorted.
Repair or replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Starter
button is not
effective.
Battery run down.
Defective switch contacts.
Brushes not seating properly on commutator in
starter motor.
Defective starter relay.
Defective starter pinion gears
Defective front or rear brake light switch circuit.
Recharge and replace.
Replace.
Repair or replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Repair or replace.
Page 98

98
BATTERY
Complaint
Symptom and possible causes Remedy
Battery runs
down
quickly.
The charging method is not
correct.
Cell plates have lost much of
their active material as a result of
over-charging.
A short-circuit condition exists
within the battery due to excessive
accumulation of sediments caused
by the incorrect electrolyte.
Battery is too old.
Check the magneto and regulator/rectifier
circuit connections, and make necessary
adjustments to obtain specified charging
operation.
Replace the battery, and correct the
charging system.
Replace the battery.
Replace the battery.
Reversed
battery
polarity.
The battery has been connected
the wrong way round in the system,
so that it is being charged in the
reverse direction.
Replace the battery and be sure to connect
the battery properly.
Battery
discharges
too rapidly.
Dirty container top and sides.
Battery is too old.
Clean.
Replace.
Page 99

99
CHASSIS
Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy
Handling feels
too heavy.
Steering stem nut overtightened.
Broken bearing/race in steering
stem.
Distorted steering stem.
Not enough pressure in tires.
Adjust.
Replace.
Replace.
Adjust.
Wobbly
handle.
Loss of balance between right
and left front suspension.
Distorted front axle or crooked
tire.
Replace.
Replace.
Wobbly front
wheel.
Distorted wheel rim.
Worn front wheel bearings.
Defective or incorrect tire.
Loose nut on axle.
Loose nuts on the rear shock.
Worn engine mounting bushing.
Loose nuts or bolts for engine
mounting.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Retighten.
Retighten.
Replace.
Tighten.
Front
suspension
too soft.
Weakened springs.
Oil leakage of shock absorber,
Replace.
Replace.
Front
suspension
too stiff.
Not enough grease,
Worn suspension arm spacer
Refill.
Replace.
Noisy front
suspension.
Not enough grease.
Loose nuts on suspension.
Refill.
Retighten.
Wobbly rear
wheel.
Distorted wheel rim.
Defective or incorrect tire.
Loose nuts on the rear shock
absorber.
Worn engine mounting bushing.
Loose nuts or bolts for engine
mounting.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Retighten.
Rear
suspension
too soft.
Weakened spring.
Oil leakage of rear shock
absorber.
Replace.
Add lubrication
Noisy rear
suspension.
Loose nuts on shock absorber,
lubrication leakage.
Adjust
Add lubrication.
Page 100

100
BRAKES
Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy
Insufficient
brake
power.
Leakage of brake fluid from hydraulic
system.
Worn pad.
Oil adhesion on engaging surface of
pad.
Worn disc.
Air entered into hydraulic system.
Worn shoe.
Friction surfaces of shoes are dirty
with oil.
Excessively worn drum.
Too much brake lever play.
Repair or replace.
Replace.
Clean disc and pads.
Replace.
Bleed air.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace.
Adjust.
Brake
squeaking.
Carbon adhesion on pad surface.
Tilted pad.
Damaged wheel bearing.
Worn pad.
Foreign substance entered into brake
fluid.
Clogged return port of master
cylinder.
Brake shoe surface glazed.
Loose front-wheel axle or rear-wheel
axle nut.
Worn shoe.
Repair surface with sandpaper.
Modify and fitting.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace brake fluid.
Disassemble and clean master cylinder.
Repair surface with sandpaper,
Ti ghten to specified torque.
Replace.
Excessive
brake lever
stroke.
Air entered into hydraulic system.
Insufficient brake fluid.
Improper quality of brake fluid.
Worn brake cam lever.
Excessively worn shoes and/or
drum.
Adjust
Refill
Replace
Replace
Replace
Leakage of
brake fluid.
Insufficient tightening of connection
joints.
Cracked hose.
Worn piston seal.
Replace or repair
Replace.
Replace.
Brake
drags.
1. Rusty moving parts. replace
 Loading...
Loading...