Page 1

CellPipe® 7130
VDSL RESIDENTIAL GATEWAY
6Vz.A2131,6Ve.B2131 | RELEASE 1.0
USER MANUAL
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
EDITION 01
FEBRUARY 2011
Page 2

Alcatel, Lucent, Alcatel-Lucent, the Alcatel-Lucent logo, and CellPipe are trademarks of Alcatel-Lucent. All other trademarks are the property of their
respective owners.
The information presented is subject to change without notice. Alcatel-Lucent assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies contained herein.
Alcatel-Lucent provides this documentation without warranty of any kind, implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
Copyright © 2010 Alcatel-Lucent. All rights reserved.
Conformance statements
The equipment has been tested in the regulation lab and complied with the limits for VDSL device, pursuant to Europe CE/CB, Australia A-Trick and China
CCC. These limits of different regulations are designed provide reasonable protection against harmful interference or damage in a residential installation.
Security statement
In rare instances, unauthorized individuals make connections to the telecommunications network through the use of remote access features. In such an event,
applicable tariffs require the customer to pay all network charges for traffic. Alcatel-Lucent cannot be responsible for such charges and will not make any
allowance or give any credit for charges that result from unauthorized access.
IMPORTANT NOTICE: This document contains confidential information that is proprietary to Alcatel-Lucent. No part of its contents may be used, copied,
disclosed or conveyed to any party in any manner whatsoever without prior written permission from Alcatel-Lucent.
www.alcatel-lucent.com
Page 3

About this document
Purpose
This document provides information on the hardware setup, software configuration, and
administration necessary to operate the CellPipe 7130 Residential Gateway 6Vz.A2131/
6Ve.B2131.
Reason for revision
The following table shows the revision history of this document.
Revision Date Reason for reissue
Edition 01 February 2011 First release of this document
Intended audience
This document is intended for users and administrators of the CellPipe 7130 RG
6Vz.A2131/6Ve.B2131.
How to use this document
This document introduces the CellPipe 7130 RG 6Vz.A2131/6Ve.B2131 hardware,
connections, and setup. It also explains the web configuration interface and provides
parameter definitions for the fields that appear on those windows.
Conventions used
This guide uses the following typographical conventions:
Appearance Description
Italicized text
graphical user interface text or
key name
• File and directory names.
• Emphasized information.
• Titles of publications.
• A value that the user supplies.
• Text that is displayed in a graphical user
interface or in a hardware label.
• The name of a key on the keyboard.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
iii
Page 4

About this document
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Appearance Description
input text Command names and text that the user types or
selects as input to a system.
output text Text that a system displays or prints.
Press the Return or Enter key on the keyboard.
Structure of hazard statements
Overview
For the safety of you and your equipment, this document contains hazard statements.
Hazard statements are given at points where there may be a risk of damage to personnel,
equipment, or operation. Failure to follow the directions in a hazard statement may result
in personal harm, equipment damage, or network loss.
General structure
Hazard statements include the structural elements shown in the figure below.
Structure of hazard statements
Item Structure element Purpose
1 Personal injury symbol Indicates the potential for personal injury (optional).
2 Hazard type symbol Indicates hazard type (optional).
3 Signal word Indicates the severity of the hazard.
4 Hazard type Describes the source of the risk of damage or injury.
5 Damage statement Consequences if protective measures fail.
6 Avoidance message Protective measures to take to avoid the hazard.
7 Identifier The reference ID of the hazard statement (optional).
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
iv
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 5

About this document
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Signal words
The following table defines signal words that identify the hazard severity levels.
Signal words for hazard severity
Signal word Meaning
DANGER Indicates an imminently hazardous situation (high
risk) which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
WARNING Indicates a potentially hazardous situation (medium
risk) which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
CAUTION When used with the personal injury symbol:
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation (low risk)
which, if not avoided, may result in personal injury.
When used without the personal injury symbol:
Related information
The documentation set accompanying this family of routers includes this User Manual
and a Quick Installation Guide.
Technical support
For technical support, contact your local Alcatel-Lucent customer support team. See the
Alcatel-Lucent Support website (http://alcatel-lucent.com/support/) for contact
information.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation (low risk)
which, if not avoided, may result in property
damage, such as service interruption or damage to
equipment or other materials.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
v
Page 6

About this document
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
vi
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 7

Contents
1Product overview
Hardware introduction ............................................................................................................................... 1-1
Safety precautions ..................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Prerequisites .............................................................................................................................................. 1-3
Description of LEDs and interfaces .......................................................................................................... 1-3
2 Hardware installation
To mount the CellPipe 7130 RG ............................................................................................................... 2-1
To install the CellPipe 7130 RG ................................................................................................................2-2
RGAM installation of the Residential Gateway Application Module ....................................................... 2-4
3 Accessing the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool
To access the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool ..........................................................................3-1
4 Status
System Usage ............................................................................................................................................ 4-1
WAN PTM Status ...................................................................................................................................... 4-3
DSL Link Status ........................................................................................................................................4-4
Device Table ..............................................................................................................................................4-6
DHCP Lease ..............................................................................................................................................4-7
WiFi Association ....................................................................................................................................... 4-8
WAN/(W)LAN Statistics ........................................................................................................................... 4-8
IGMP Membership .................................................................................................................................. 4-10
IGMP Statistics ........................................................................................................................................4-10
.................................................................................................................................................................4-11
5Network
USB ........................................................................................................................................................... 5-1
LAN Settings .............................................................................................................................................5-3
WAN Link Selection .................................................................................................................................5-6
WAN PTM Connections ............................................................................................................................ 5-6
................................................................................................................................................................. 5-31
6WiFi setup
WiFi Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 6-1
WiFi Security .............................................................................................................................................6-4
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
vii
Page 8

Contents
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
WiFi Access Filter ..................................................................................................................................... 6-6
7 Firewall setup
Port Forwarding ........................................................................................................................................ 7-1
Demilitarized Zone .................................................................................................................................... 7-3
UPnP ......................................................................................................................................................... 7-4
Layer 2 Filter ............................................................................................................................................. 7-5
Layer 3 Filter ............................................................................................................................................. 7-7
NAT Passthrough ...................................................................................................................................... 7-8
URL Blocking ........................................................................................................................................... 7-9
Content Screening ................................................................................................................................... 7-10
Parental Control ...................................................................................................................................... 7-11
8Advanced setup
Route Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 8-1
DNS Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 8-3
Dynamic DNS ........................................................................................................................................... 8-4
System Log ................................................................................................................................................ 8-5
IGMP Proxy/Snooping .............................................................................................................................. 8-6
802.1x Config ............................................................................................................................................ 8-7
9QoS PTM setup
QoS Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 9-1
QoS Scheduler ........................................................................................................................................... 9-2
................................................................................................................................................................... 9-4
QoS Policy ................................................................................................................................................ 9-5
QoS Phone ................................................................................................................................................. 9-7
QoS ALG .................................................................................................................................................. 9-8
QoS Defaults ........................................................................................................................................... 9-10
QoS MAC ................................................................................................................................................ 9-12
10 Telephony
Account Setup ......................................................................................................................................... 10-1
Service Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 10-4
SIP Server Settings .................................................................................................................................. 10-8
RTP/Codecs settings .............................................................................................................................. 10-10
Account & Line Table ........................................................................................................................... 10-12
Call History ........................................................................................................................................... 10-13
Other Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 10-14
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
viii
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 9

Contents
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
11 Utilities
Configuration Backup ..............................................................................................................................11-1
Configuration Restore ..............................................................................................................................11-2
Firmware Upgrade ...................................................................................................................................11-3
System Settings ........................................................................................................................................11-4
Management Access Control ...................................................................................................................11-7
CWMP Management ...............................................................................................................................11-8
Connection Test .....................................................................................................................................11-10
802.1x CA Upload ................................................................................................................................. 11-11
Restore Factory Defaults ....................................................................................................................... 11-11
Reboot Gateway .....................................................................................................................................11-12
RGAM Management .............................................................................................................................11-13
A Troubleshooting
B TCP/IP configuration
C Product conformance
EU declaration of conformity ................................................................................................................... C-1
FCC 15B statement ...................................................................................................................................C-3
FCC Part 68 Statement ............................................................................................................................. C-4
Industry Canada statement ........................................................................................................................ C-5
IC TELECOM ..........................................................................................................................................C-5
GL Glossary
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
ix
Page 10

Contents
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
x
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 11

1Product overview
Overview
Purpose
This chapter provides an introduction to the physical aspects of the CellPipe 7130 RG
6Vz.A2131/6Ve.B2131 including safety precautions and features.
The CellPipe 7130 RG 6Vz.A2131/6Ve.B2131 will be referred to as
CellPipe 7130 RG throughout the rest of this document.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topics:
Hardware introduction 1-1
Safety precautions 1-2
Prerequisites 1-3
Description of LEDs and interfaces 1-3
Hardware introduction
The CellPipe 7130 RG connects residential users to a broadband WAN via an Ethernetover-VDSL link or a Gigabit Ethernet connection. For this purpose, it provides the
following WAN interfaces:
• one VDSL port
• one Gigabit Ethernet port
Note: The WAN interfaces cannot be used concurrently.
The devices on the LAN of residential users are interconnected and connected to the
WAN via IP routing or Ethernet bridging. The following interfaces can be used to connect
devices in the home:
• Four Gigabit Ethernet LAN ports (10/100/1000Base-TX)
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
1-1
Page 12

Safety precautionsProduct overview
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
• wireless access point
Safety precautions
WARNING
Risk of electric shock or fire
1. Pay attention to the power load of the electrical outlet or extension cord. An
overburdened power outlet or damaged cords and plugs may cause electric shock or
fire. Check the power cords regularly. If you find any damage, replace the cord
immediately.
2. Leave adequate space for heat dissipation to avoid any damage caused by overheating
the CellPipe 7130 RG. Do not cover the ventilation holes. Blocking the ventilation
holes may cause fire.
3. When connecting a PC or other electronic device to the CellPipe 7130 RG, make sure
you use the right cables and connect the device to the right port of the CellPipe 7130
RG. Incorrect connections may damage the device and/or CellPipe 7130 RG..
CAUTION
Potential equipment damage
Follow these recommendations to protect yourself and the CellPipe 7130 RG from harm:
1. Do not insert any sharp object into the openings of the CellPipe 7130 RG..
2. Never install telephone wiring during inclement weather; for example, during a storm.
3. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can permanently damage semiconductor devices.
Always follow ESD-prevention guidelines for equipment handling and storage.
4. Use the power adapter provided with the CellPipe 7130 RG and do not fasten the
power cable to building surfaces. Ensure the cable can move freely. Do not place
heavy objects on the cable. Check the power cords regularly. If you find any damage,
replace the cord immediately.
5. Do not put the CellPipe 7130 RG near a heat source. Avoid placing the CellPipe 7130
RG in direct sunlight.
6. Do not put the CellPipe 7130 RG in damp or wet locations. Do not spill any liquid on
the CellPipe 7130 RG..
7. Do not place the CellPipe 7130 RG on an unstable surface or support.
8. Do not place heavy objects on top of the CellPipe 7130 RG..
9. Do not use liquid or aerosol cleaners; use a soft, dry cloth for cleaning.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1-2
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 13
Product overviewPrerequisites
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have the following items before attempting to use the CellPipe 7130 RG:
• Internet services subscription (connection type, account information, and addresses)
• 10/100Base-T Ethernet NIC installed in your PC
• Operating system: Windows 98SE, Windows 2000, Windows NT, Windows ME,
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, or Mac OS
• Internet Explorer v4.0 or higher, Netscape v4.0 or higher, or Mozilla Firefox v1.5 or
higher
Note: For optimal display quality, use Internet Explorer v5.0 or Netscape v6.1.
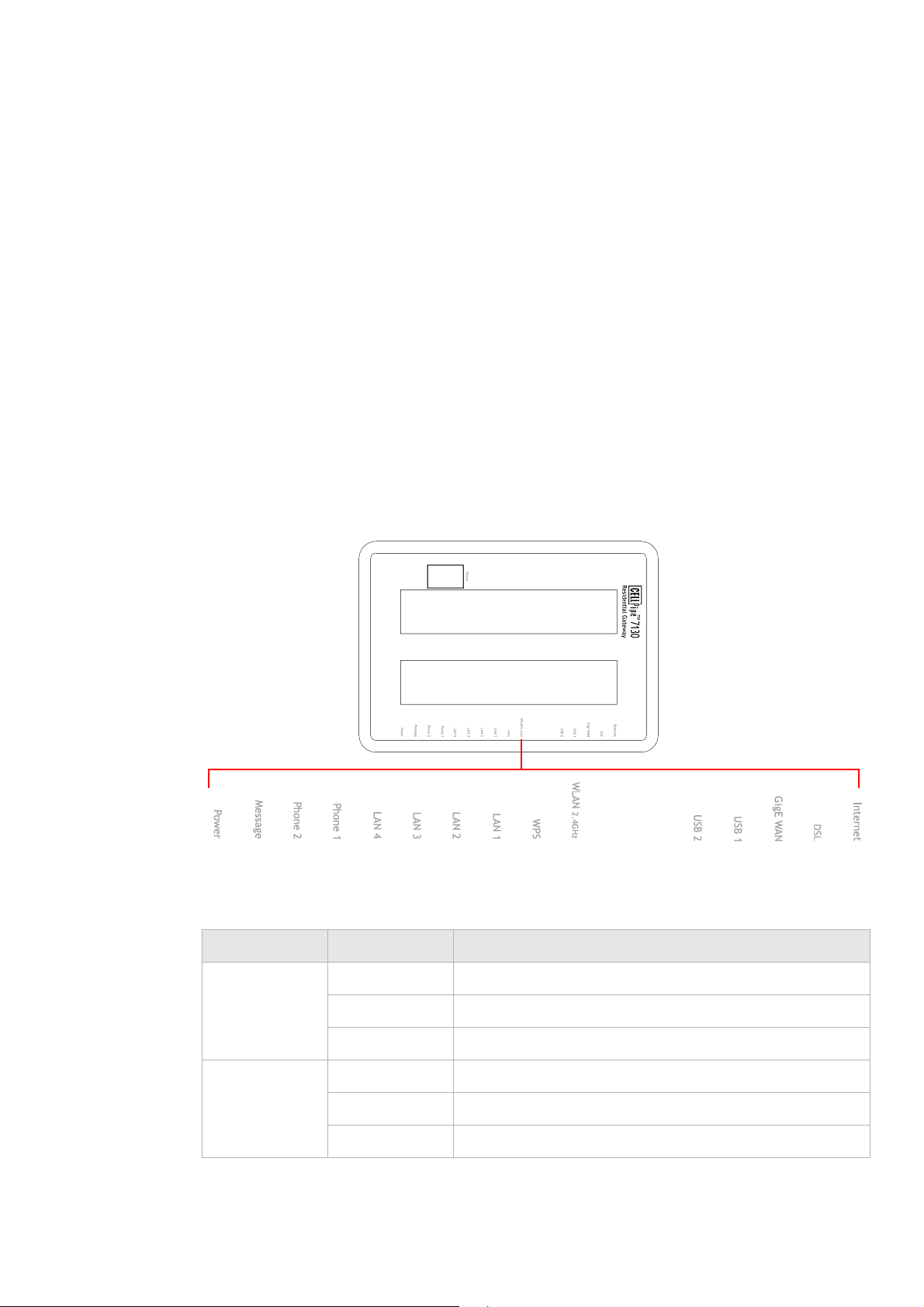
Description of LEDs and interfaces
Figure 1-1 Front panel
Table 1-1 Front panel LEDs
LED Status Description
Internet On The CellPipe 7130 RG is connected to the Internet.
Flashing Data is being transmitted over the Internet connection.
Off The CellPipe 7130 RG is not connected to the Internet.
DSL On DSL is operating.
Flashing DSL is training.
Off DSL is disconnected.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
1-3
Page 14
Description of LEDs and interfacesProduct overview
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
LED Status Description
GigE WAN On Gigabit Ethernet WAN link is up.
Flashing Data is being transmitted on the Gigabit Ethernet WAN
link.
Off Gigabit Ethernet WAN is disconnected.
USB 1 to 2 On A device is connected to the USB port.
Flashing USB port has data traffic.
Off No device is connected to USB port.
WLAN2.4GHz On Wireless function is enabled.
Flashing Data is being transmitted on the wireless link.
Off Wireless function is disabled.
WPS On WPS is enabled.
Off WPS is disabled.
LAN 1 to 4
On Ethernet LAN port 1 to 4 is connected and active.
Flashing Network activity over the corresponding ports.
Off Ethernet LAN port 1 to 4 is not active.
Phone 1 to 2 On Phone 1 to 2 is connected.
Off No phones are connected.
*
Message Slow flashing
Firmware upgrade in progress.
Off No firmware upgrade in progress.
Power On CellPipe 7130 RG is powered on.
Off Power is disconnected.
Notes:
* Slow flashing: LED flashes at the rate of 2 seconds on and 2 seconds off.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1-4
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 15

Product overviewDescription of LEDs and interfaces
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 1-2 Rear panel of 6Vz.A2131
Figure 1-3 Rear panel of 6Ve.B2131
Table 1-2 Rear panel items
Item Description
Wireless
Antennae for transmission of wireless signal.
Antennae
DSL Port DSL network connection from your ISP. The DSL port connects to an RJ-11
cable (only for 6Vz.A2131). The DSL port connects to an TAE-RJ45 cable
(only for 6Ve.B2131).
Ethernet LAN1
Four RJ-45 ports to connect up to four PCs or a Hub.
to LAN4
GigE WAN Ethernet network connection from your ISP. The GigE WAN port connects
to an RJ-45 cable.
Note: The GigE Ethernet port cannot be used simultaneously with the DSL
port.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
1-5
Page 16

Description of LEDs and interfacesProduct overview
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Item Description
USB Support USB 2.0 for file sharing, printer sharing, UPnP digital Media
sharing and sensor network interface support.
HPNA (only
One HPNA interface to connect to a HPNA device.
for
6Vz.A2131)
Phone 1 to 2
Two RJ-11 ports for connecting telephones for VoIP.
(only for
6Vz.A2131)
Reset Button Press and release to reboot the CellPipe 7130 RG. Press and hold for 10
seconds to restore to factory default settings.
Power Switch Power On/Off switch.
15VDC 2.4A DC power adapter port.
TAE (only for
6Ve.B2131)
Slot to insert the CellPipe 7130 Residential Gateway Application Module .
See Figure 1-4
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1-6
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 17

Product overviewDescription of LEDs and interfaces
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 1-4 TAE interface for the CellPipe 7130 6Ve.B2131 residential gateway
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
1-7
Page 18

Description of LEDs and interfacesProduct overview
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 1-5 Front side of 6Ve.B2131
Table 1-3 Front side items
Item Description
WPS Activates the Wireless Protected Setup (WPS) function
WLAN
Button to activate and de-activation the Wireless interface.
2.4GHz
TAE (only for
TAE phone connector
6Ve.B2131)
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1-8
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 19

Product overviewDescription of LEDs and interfaces
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
1-9
Page 20

Description of LEDs and interfacesProduct overview
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1-10
3EQ-1028-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 21

2 Hardware installation
Overview
Purpose
This chapter provides the instructions to install the CellPipe 7130 RG hardware.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topics:
To mount the CellPipe 7130 RG 2-1
To install the CellPipe 7130 RG 2-2
RGAM installation of the Residential Gateway Application Module 2-4
To mount the CellPipe 7130 RG
There are three ways to mount the CellPipe 7130 RG:
• wall mounting
• desktop mounting
• stand-up mounting
Wall mounting
Pre-Requirements
Anchors
•
• Screws
• Drill & Drill bit
1. Locate a high position on the wall that is free of obstructions and insert two screws in
the wall 5 cm (2 in.) apart. Do not insert the screws all the way into the wall.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
2-1
Page 22

To install the CellPipe 7130 RGHardware installation
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Important! Make sure that the screws are securely fixed to the wall and strong
enough to hold the weight of the CellPipe 7130 RG (recommended screw type and
size: Nylon wall plug [T8x25mm] and screws [T3.5x16mm]).
2. Align the holes on the back of the CellPipe 7130 RG with the screws on the wall and
then hang the CellPipe 7130 RG on the screws.
E ND OF STEPS
........................................................................................................................................................
Desktop mounting
Place the CellPipe 7130 RG with the rubber feet at the bottom on a flat and stable surface.
Stand-up mounting
Snap the cradle into the holes located on the side of the CellPipe 7130 RG and then place
it on a desk so that LEDs are visible.
To install the CellPipe 7130 RG
Supplies
CellPipe 7130 RG
•
• One RJ-11 telephone cable (only for 6Vz.A2131)
• One TAE-F to RJ45 cable (only for 6Ve.B2131)
• One RJ-45 category 5 Ethernet cable (yellow)
• Power adapter
Before you begin
CAUTION
Potential for equipment damage and personal harm
Before installing the CellPipe 7130 RG, ensure you have thoroughly read the Safety
precautions and Prerequisites in chapter 1.
Turn off all devices (computer, hub, CellPipe 7130 RG) before beginning this procedure.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
2-2
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 23

Hardware installationTo install the CellPipe 7130 RG
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 2-1 Cable connections of 6Vz.A2131
Figure 2-2 Cable connections of 6Ve.B2131
Procedure
1. Connect one end of the gray RJ-11 cable (omly for 6Vz.A2131) or gray TAE-RJ45
cable (only for 6Ve.B2131) into the gray DSL port on the CellPipe 7130 RG and the
other end to your telephone/VDSL service connection.
2. Connect one end of the yellow RJ-45 Ethernet cable to any of the yellow Ethernet
LAN ports (1 to 4) on the CellPipe 7130 RG. Connect the other end of the cable to
your Ethernet PC (or LAN hub if you are setting up an intranet).
3. Turn the power switch on.
E ND OF STEPS
........................................................................................................................................................
You might need to configure the Internet properties on your Ethernet PC; see Appendix B,
TCP/IP configuration, or the Quick Installation Guide for detailed instructions.
After setting up the CellPipe 7130 RG and your PC(s), you can access the web
configuration tool; see Accessing the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
2-3
Page 24

Hardware installation
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
RGAM installation of the Residential Gateway Application
Module
RGAM installation of the Residential Gateway Application Module
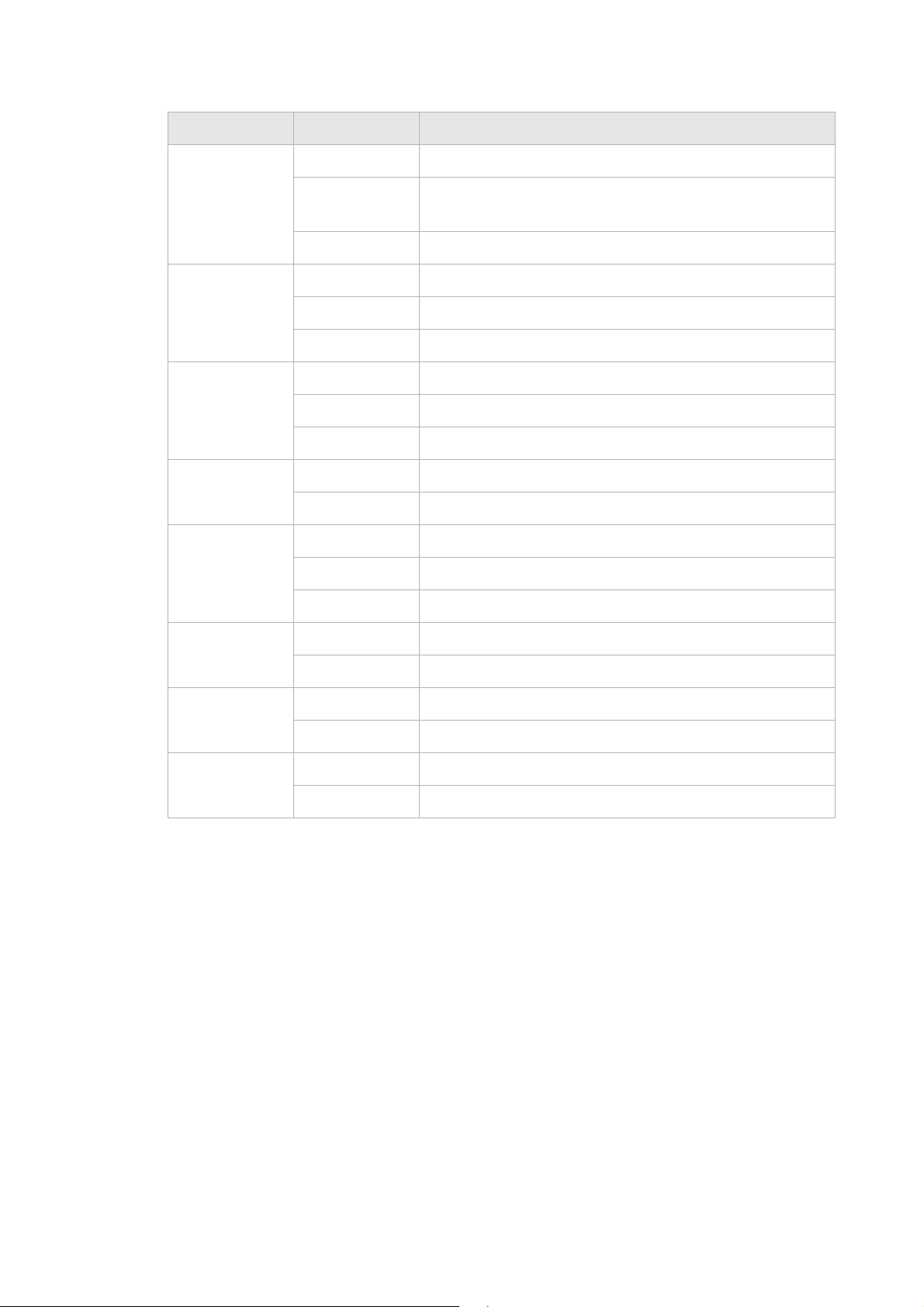
Purpose
The CellPipe 7130 Residential Gateway Application Module (RGAM) is an USB devices
which adds processing power to the residential gateway. This will allow future home
services to be deployed in your home, provided by your service provider.
Installation
As shown in the drawing, the RGAM has a USB 2.0 metal interface. This metal interface
should go into the RGAM slot first. The ventilation holes should facing up. Slide the
RGAM into the slot until it is blocked. Once inserted, the top of the RGAM will stick
outside the enclosure as illustrated below. Once the RGAM is inserted, the RGAM will
start up automatically. On the front panel of the residential gateway, the "USB 2" LED
will light up, indicating that the RGAM is up and running.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
2-4
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 25
Module
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Hardware installationRGAM installation of the Residential Gateway Application
Figure 2-3 RGAM installation
WARNING
Do not connect the RGAM to devices which are not RGAM-READY. This may damage
the RGAM or the device.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
2-5
Page 26

Hardware installation
RGAM installation of the Residential Gateway Application
Module
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
2-6
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 27

3 Accessing the CellPipe
7130 RG web
configuration tool
Overview
Purpose
This chapter explains how to access the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool by
entering the IP address and the default passwords.
The management interface software is HTML-based and can be accessed using a web
browser.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topic:
To access the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool 3-1
To access the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool
When to use
Use this procedure to access the web configuration interface of the CellPipe 7130 RG. The
configuration interface enables you to secure the CellPipe 7130 RG, limit access, set
traffic routes, modify passwords, and configure advanced settings.
Before you begin
Before you can configure the CellPipe 7130 RG, it must be installed, connected to a webenabled PC, and turned on.
To establish the initial connection with the CellPipe 7130 Gateway, your computers
should be configured to obtain automatically a network address via DHCP or via statically
configuration of the network address. In this case, the IP address should be in the range of
192.168.2.2 up to 192.168.2.99, for instance 192.168.2.10 The netmask should be
255.255.255.0
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
3-1
Page 28
To access the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration toolAccessing the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Note: If you are not sure how to configure your computer to be a DHCP client or to
set your IP address and subnet mask, please refer to Appendix B, TCP/IP
configuration, or the Quick Installation Guide for more information.
Procedure
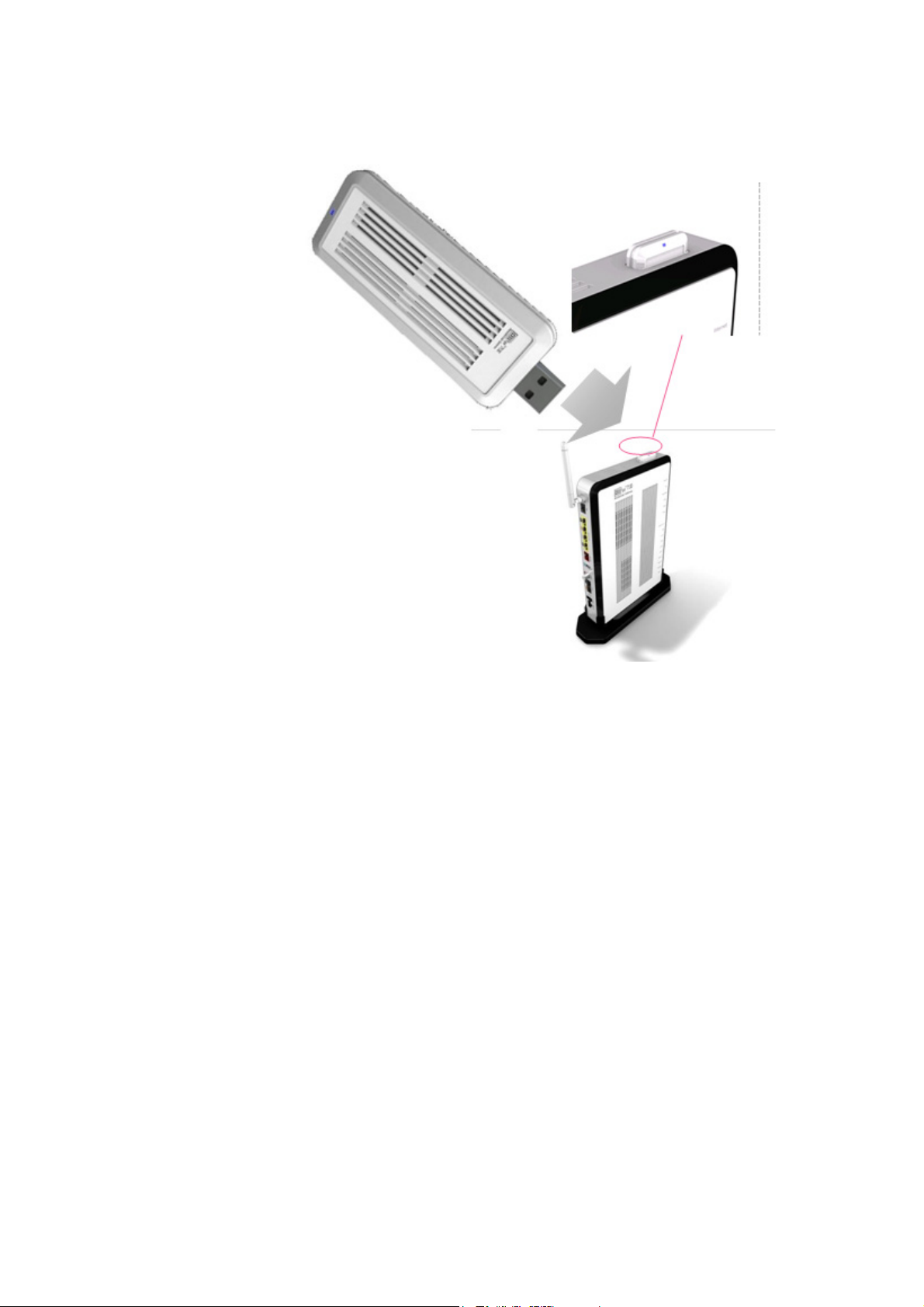
1. Open a web browser and enter the IP address of the CellPipe 7130 RG in the address
bar:
http://192.168.2.1
The login window appears; see Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Login window
2. Enter your username and password and click OK.
The default admin username is admin and the default admin password is admin.
The Status window appears; see Figure 3-2.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3-2
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 29
Accessing the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration toolTo access the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 3-2 Status window
The status window is described in Chapter 4, Status.
Note: Once you have logged in for the first time, you should change your login
password. See the System Settings section in the Utilities chapter for instructions.
3. Click the Logout button to log off; see Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Logout button
E ND OF STEPS
........................................................................................................................................................
Configuration menus
All configuration and management of the CellPipe 7130 RG is done using the web
configuration tool. Click on Status, Network, WiFi Setup, Firewall Setup, Advanced
Setup
view the configuration menus or information located in each directory.
, QoS PTM Setup, QoS ATM Setup, Te lep hon y, or Utilities in the main menu to
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
3-3
Page 30

To access the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration toolAccessing the CellPipe 7130 RG web configuration tool
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3-4
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 31

4 Status
Overview
Purpose
This chapter describes the contents of the Status menu, which contains the status
information for the CellPipe 7130 RG, its connections, and the connected hardware.
Click Status in the main menu to open the Status menu.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topics:
System Usage 4-1
WAN PTM Status 4-3
DSL Link Status 4-4
Table 4-3 Field descriptions 4-5
DHCP Lease 4-7
WiFi Association 4-8
WAN/(W)LAN Statistics 4-8
IGMP Membership 4-10
IGMP Statistics 4-10
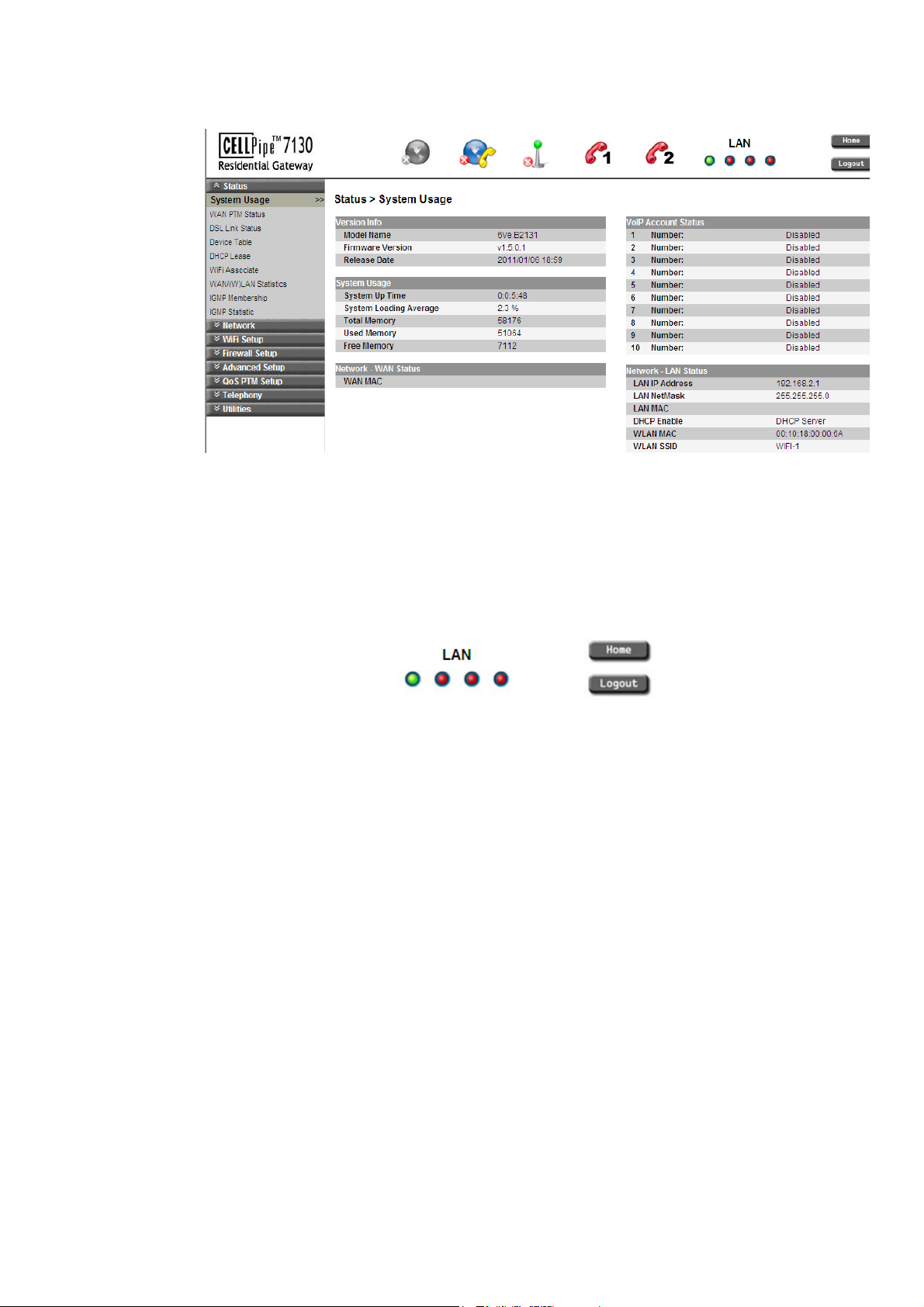
System Usage
The System Usage window shows the current status of the software, system time,
memory, WAN connection, and LAN connection.
Select System Usage in the Status menu to access the System Usage window; see
Figure 4-1.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
4-1
Page 32

System UsageStatus
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 4-1 System Usage window
Table 4-1 describes the fields of the System Usage window.
Table 4-1 Field descriptions
Field Description
Version Info
Model Name The model name of the CellPipe 7130 RG.
Firmware Version The current version of the firmware.
Release Date The release date of the firmware.
System Usage
System Up Time The amount of time the system has been operational.
System Loading Average The average loading time of the CPU.
Total Memory The memory capacity of the system in Kb.
Used Memory The amount of system memory used in Kb.
Free Memory The amount of memory available in Kb.
Network - WAN Status
WAN MAC The MAC address of the WAN connection.
VoIP Account Status
1 to 10 Number:
The status (Enabled or Disabled) of accounts 1 to
10.
Network - LAN Status
LAN IP Address The management IP address of the LAN interface.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
4-2
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 33

StatusWAN PTM Sta t u s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
LAN NetMask The subnet mask of the LAN IP address.
LAN MAC The MAC address of the LAN interface.
DHCP Enable DHCP handling method at LAN device.
WLAN MAC The MAC address of the WLAN interface.
WLAN SSID The SSID used to identify the CellPipe 7130 RG.
WAN PTM Status
This menu shows the WAN packet transfer Mode (PTM) status and data.
Select WAN PTM Status in the Status menu to access the WAN PTM Status window; see
Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2 WAN PTM Status window
Table 4-2 describes the fields of the WAN PTM Status window.
Table 4-2 Field descriptions
Field Description
Interface Name The name assigned to this connection.
Mode The connection mode:
• Static IP
• DHCP
• PPPoE
• Bridge
VLAN ID The VLAN ID number from 0 to 4094.
IP Address The IP address of the connection.
Netmask The subnet mask of the IP address.
Gateway The IP address of the gateway.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
4-3
Page 34

DSL Link StatusStatus
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
DNS 1 to 3 The IP address of the DNS.
DSL Link Status
The DSL Link Status window shows the DSL connection status and data.
Select DSL Link Status in the Status menu to access the DSL Link Status window; see
Figure 4-3.
Figure 4-3 DSL Link Status window
Table 4-3 describes the fields of the DSL Link Status window.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
4-4
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 35

StatusDSL Link Status
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Table 4-3 Field descriptions
Field Description
DSL Firmware Version The version of firmware in use.
Mode The modulation protocol
Traffic Type The channel type
Status This is the status of the DSL link.
Link Power State Displays the power management state of the DSL
connection.
Line Coding (Trellis) The Trellis Coding status of downstream and
upstream.
SNR Margin(0.1dB) This is a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) margin for
traffic going in both directions.
Atternuation(0.1dB) An estimate of the average loop attenuation
downstream and upstream.
Output Power(0.1dBm) The total output power in both directions.
Attainable Rate (Kbps): This is the maximum achievable downstream rate.
Rate (Kbps) The actual rate at which data is flowing in both
directions.
MSGc (# of bytes in overhead channel
Number of bytes in overhead channel message
message)
B (# of bytes in Mux Data Frame) Number of bytes in Mux Data Frame
M (# of Mux Data Frames in an RS
Number of Mux Data Frames in FEC Data Frame
codeword)
T (# of Mux Data Frames in a OH sub-
Mux Data Frames over sync bytes
frame)
K (number of bytes in DMT frame) This is the number of data bytes in an DSL data
frame.
R The number of redundant check bytes per Reed-
Solomon code word.
S The length of the Reed-Solomon code word, in data
frames.
L Number of bits in PMD Data Frame
D (interleabver depth) The interleaver depth.
I (interleaver block size in bytes) Number of bytes in interleaver block size
N (RS codeword size) The size of RS codeword.
Delay (msec) The delay, in microseconds, of the DSL connection.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
4-5
Page 36

Device TableStatus
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
INP (DMT symbol) INP:Impulse Noise Protection DMT:Discrete Multi-
tone
OH Frames The number of overhead frames.
OH Frame Errors The number of overhead frame errors.
Super Frames This is the total number of super frames.
Super Frame Errors The number of super frames received that had
errors.
RS Words This is the total number of Reed-Solomon code
words.
RS Correctable Errors The number of Reed-Solomon code words with
correctable errors.
RS Uncorrectable Errors The number of R-S code words that had
uncorrectable errors.
HEC Errors The total number of header error checksum errors.
OCD Errors The number of out-of-cell delineation errors.
LCD Errors The total of lost-cell-delineation errors.
Total Cells Total number of cells.
Data Cells The number of data cells.
Bit Errors The number of Bit Error.
Total ES Total number of Errored Seconds.
Total SES Total number of Severely Errored Seconds.
Total UAS Total number of Unavailable Seconds.
Device Table
The Device Table shows information about the devices that have connected to the
CellPipe 7130 RG.
Select Device Table in the Status menu to access the Device Table; see Figure 4-4.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
4-6
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 37

StatusDHCP Lease
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 4-4 Device Table
Table 4-4 describes the fields of the Device Table window.
Table 4-4 Field descriptions
Field Description
Host Name The name of the device connected to the gateway.
IP Address The IP address assigned to the device.
Attached By Method used to connect to the gateway.
MAC Address The MAC address of the attached device.
DHCP Lease
The DHCP Lease window lists the IP addresses leased to the DHCP clients in the LAN
environment.
Select DHCP Lease in the Status menu to access the DHCP Lease window; see
Figure 4-5.
Figure 4-5 DHCP Lease window
Table 4-5 describes the fields of the DHCP Lease window.
Table 4-5 Field descriptions
Field Description
No. The index number of the entry in the table.
IP Address The IP address leased to the LAN device.
MAC Address The MAC address of the LAN device.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
4-7
Page 38

WiFi AssociationStatus
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Host Name The host name of the DHCP client.
Vendor The platform of the DHCP client.
Expiry The time remaining before the lease expires.
WiFi Association
The WiFi Association window lists the wireless clients that are currently connected to the
CellPipe 7130 RG.
Select WiFi Association in the Status menu to access the WiFi Association window; see
Figure 4-6.
Figure 4-6 WiFi Association window
Table 4-6 describes the fields of the WiFi Association window.
Table 4-6 Field descriptions
Field Description
No. The index number of the entry.
MAC Address The MAC address of the wireless device connected
Rate The transmission rate of the wireless device
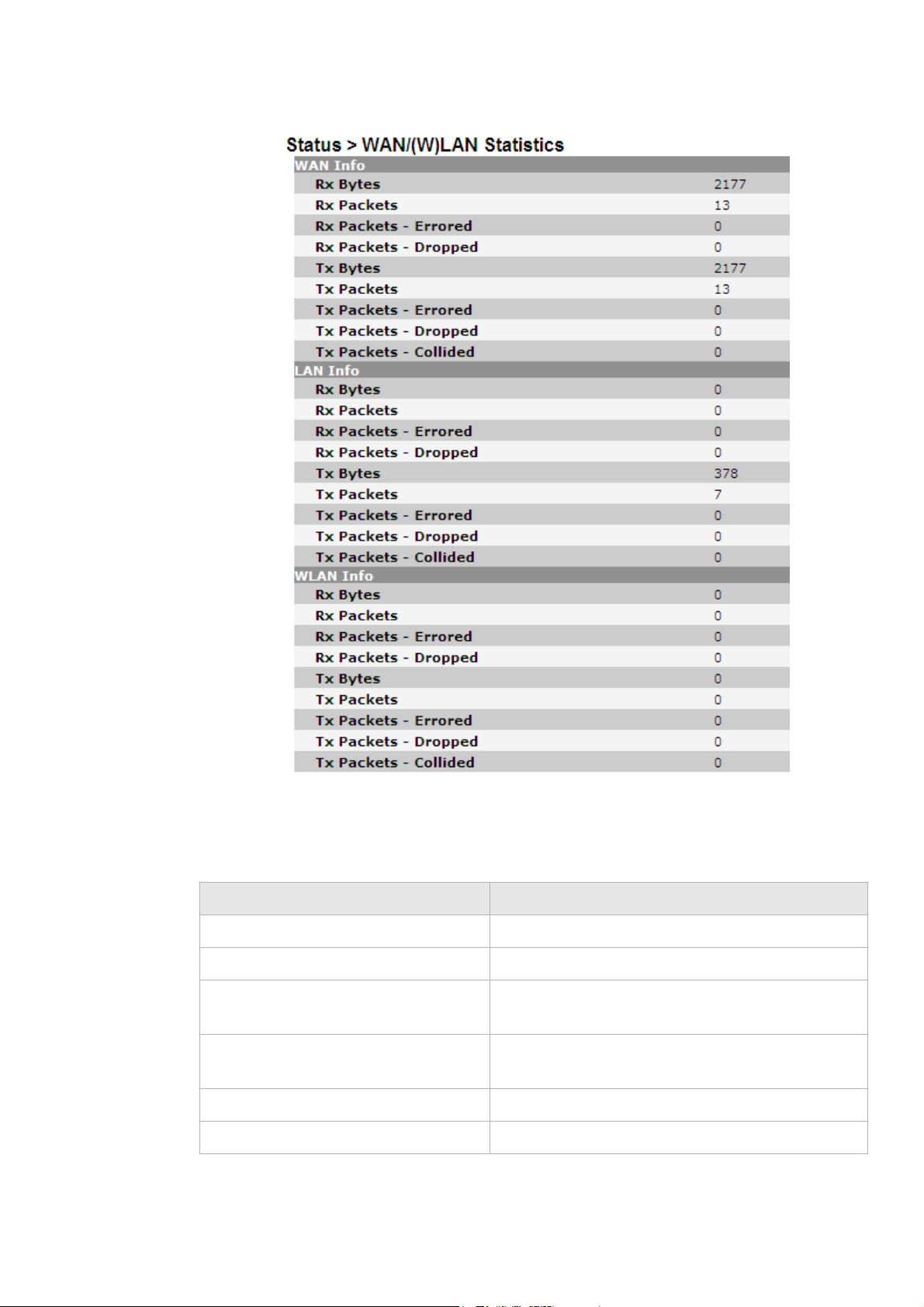
WAN/(W)LAN Statistics
The WAN/(W)LAN Statistics window shows the number of bytes that have been received
or transmitted by the WAN, LAN, and WLAN interfaces.
Select WAN/(W)LAN Statistics in the Status menu to access the WAN/(W)LAN Statistics
window; see Figure 4-7.
to the CellPipe 7130 RG.
connected to the CellPipe 7130 RG.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
4-8
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 39
StatusWAN/(W)LAN Statistics
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 4-7 WAN/(W)LAN Statistics window
Table 4-7 describes the fields of the WAN/(W)LAN Statistics window.
Table 4-7 Field descriptions
Field Description
Rx Bytes The number of bytes that have been received.
Rx Packets The number of packets that have been received.
Rx Packets-Errored The number of packets that have been received with
errors.
Rx Packets-Dropped The number of packets that have been dropped after
being received.
Tx Bytes The number of bytes that have been transmitted.
Tx Packets The number of packets that have been transmitted.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
4-9
Page 40

IGMP MembershipStatus
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Tx Packets-Errored The number of packets that have been transmitted
with errors.
Tx Packets-Dropped The number of packets that have been dropped after
being transmitted.
Tx Packets-Collided The number of packets that collided when
transmitted.
IGMP Membership
The IGMP Membership window shows the IGMP members.
Select IGMP Membership in the Status menu to access the IGMP Membership window;
see Figure 4-8.
Figure 4-8 IGMP Membership window
Table 4-8 describes the fields of the IGMP Membership window.
Table 4-8 Field descriptions
Field Description
Multicast IP Group The multicast group.
Client Lists the IP address of the client in the specific
IGMP Statistics
multicast group.
The IGMP Statistics window shows the IGMP statistics.
Note: This window only shows the IGMP activity statistics for each group within
the time period you have set.
Select IGMP Statistics in the Status menu to access the IGMP Statistics windows; see
Figure 4-9.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
4-10
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 41

Status
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 4-9 IGMP Statistics window
Table 4-9 describes the fields of the IGMP Statistics window.
Table 4-9 Field descriptions
Field Description
Period Select a time period in minutes to collect and display
the IGMP statistics.
Apply Click to show the IGMP group information for the
selected time period.
Join Number of clients in the IGMP group domain.
Leave Number of clients that have left the IGMP group
domain.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
4-11
Page 42

Status
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
4-12
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 43

5Network
Overview
Purpose
This chapter explains how to configure the network settings for the CellPipe 7130 RG.
Click the Network in the main menu to open the Network menu.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topics:
USB
USB 5-1
LAN Settings 5-3
WAN Link Selection 5-6
WAN PTM Connections 5-6
The USB windows allows you to configure services using the USB 2.0 interface. On the
USB 2.0 interface, the following devices can be connected: Printer, storage device, sensor
network interface.
By enabling the printerserver service "USB printer", you can print via your home network
to this printer. By connecting a storage devices, the gateway can be used as fileserver.
When enabling the DMS service, all digital media on the storage device will become
available on your home network. (UPnP AV)
Select
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
USB in the Network menu to access the USB&DMS window; see Figure 5-1.
5-1
Page 44

USBNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-1 USB&DMS window
Table 5-1 describes the fields of the USB&DMS window.
Table 5-1 Field descriptions
Field Description
USB Enable Select Enable to enable USB.
USB Printer Name Enter a USB printer name.
DMS Enable Select Enable to enable DMS.
DMS Server Name Enter a DMS Server name.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
Connecting storage device
When a storage device is connected, this storage can be accessed via the LAN (Home
network) and can not be accessed from the WAN side due to security reasons. The
following file-systems are supported : FAT16, FAT32, NTFS, EXT2, EXT3. No access
rights can be set, neither user accounts.
Select Disable to disable USB.
Select Disable to disable DMS.
For windows, the filesharing can be access by opening the internet explorer and typing the
IP address of the gateway. The default IP address is \\192.168.2.1\ The default userid and
password are used : guest / guest
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-2
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 45

NetworkLAN Settings
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-2 Connecting storage device
Note:
• DMS works only for devices which are directly connected to the LAN interface of the
gateway.
• The content cannot be reached from the WAN interface.
• DMS only works when an storage devices is connected to the USB 2.0 interface.
• The DMS will support UMLAUT characters
• The following file systems will be supported: FAT16, FAT32, NTFS, EXT2, EXT3
via USB
WARNING
When a storage (USB-harddisk or USB memory stick) is connected to the gateway, the
content will be automatically be available on your home network and accessible by
everybody on that home network.
If the DMS function is enabled, the gateway discovers all digital media on the connected
storage device (Harddisk/USB-memory-stick) and make this accessible via PnP AV
protocol.
LAN Settings
The LAN Settings window enables you to configure the IP address, subnet mask, DHCP
settings, DHCP relay, and static IP lease.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-3
Page 46

LAN SettingsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Select LAN Settings in the Network menu to access the LAN Settings window; see
Figure 5-3.
Figure 5-3 LAN Settings window - DHCP Server option selected
Table 5-2 describes the fields of the LAN Settings window.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-4
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 47

NetworkLAN Settings
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Table 5-2 Field descriptions
Field Description
IP Address The IP address of the LAN interface in dotted
decimal notation. The default is 192.168.2.1. You
can change this address as necessary to any address
that is reserved for private use.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask of the IP addresses in your LAN;
for example, 255.255.255.0.
DHCP Server Select DHCP Server to enable DHCP server. The
CellPipe 7130 RG automatically assigns the IP
addresses, default gateway, and DNS servers to
computers that support the DHCP client; for
example, Windows 95 or Windows NT.
Select DHCP Relay to enable DHCP Relay.
Select Disable to disable DHCP server.
Note: Figure 5-2 shows the DHCP Server options.
Selecting DHCP Relay will open the DHCP Relay
server options.
DHCP Relay Server 1 Enter the IP address of the DHCP server.(DHCP
Relay)
DHCP Relay Server 2 Enter the IP address of the second DHCP server for
a different service, if applicable.(DHCP Relay)
Mapping Vendor ID Enter the Vendor ID for DHCP Option 60. When the
client sends a DHCP request that contains vendor ID
is equal to the Vendor ID, the request will be sent to
"DHCP Relay Server 2". (DHCP Relay)
DHCP Starting IP Address
DHCP Ending IP Address
The range of IP addresses that will be assigned to the
DHCP client.
DHCP Lease Time The time period during which the computers retain
the IP addresses assigned to them.
Static Lease Assign a static IP address to DHCP clients based on
their MAC address.
Block Lease The MAC address of the client to block from
acquiring an IP address.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-5
Page 48
WAN Link SelectionNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
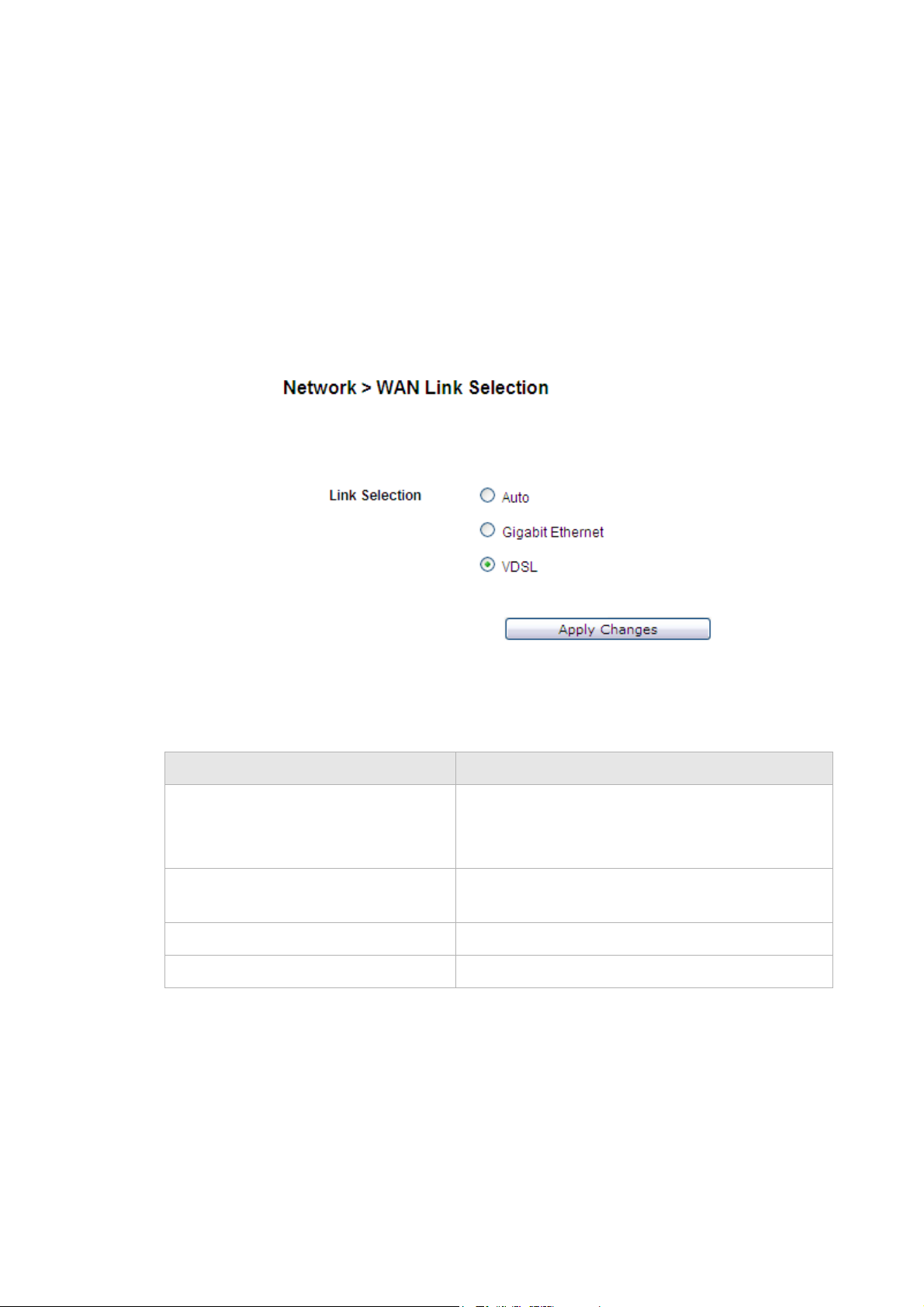
WAN Link Selection
The WAN Link Selection window specifies which link will be used for the WAN
connection, one of auto-dedicate mode, Gigabit Ethernet, or DSL.
Note: You must reboot the CellPipe 7130 RG to switch from one WAN interface to
another.
Select WAN Link Selection in the Network menu to access the WAN Link Selection
window; see Figure 5-4.
Figure 5-4 WAN Link Selection window
Table 5-3 describes the fields of the WAN Link Selection window.
Table 5-3 Field descriptions
Field Description
Auto Select to automatically detect the WAN link.
Gigabit Ethernet Select to use only the Gigabit Ethernet port as the
VDSL Select to use the VDSL port.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
WAN PTM Connections
WAN PTM connections are the connections used when the device operates in DSL-PTM
mode (if you are uncertain whether your DSL service is PTM, contact your ISP). The
WAN PTM Connections window enables you to configure multiple connections.
Note: Only one of the two LAN ports should be
physically connected.
WAN link.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-6
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 49

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
CAUTION
It is recommended that the WAN PTM connections be changed by trained service
personnel. Improper configuration can lead to loss of connectivity to the residential
gateway from the LAN side as well as the WAN side.
There are three different binding methods for the connections:
• Port based binding
• MAC based binding
• No LAN/WLAN binding
The four following types of connections can be used:
• Static IP
• DHCP Mode
• PPPoE Mode
• Bridge Mode
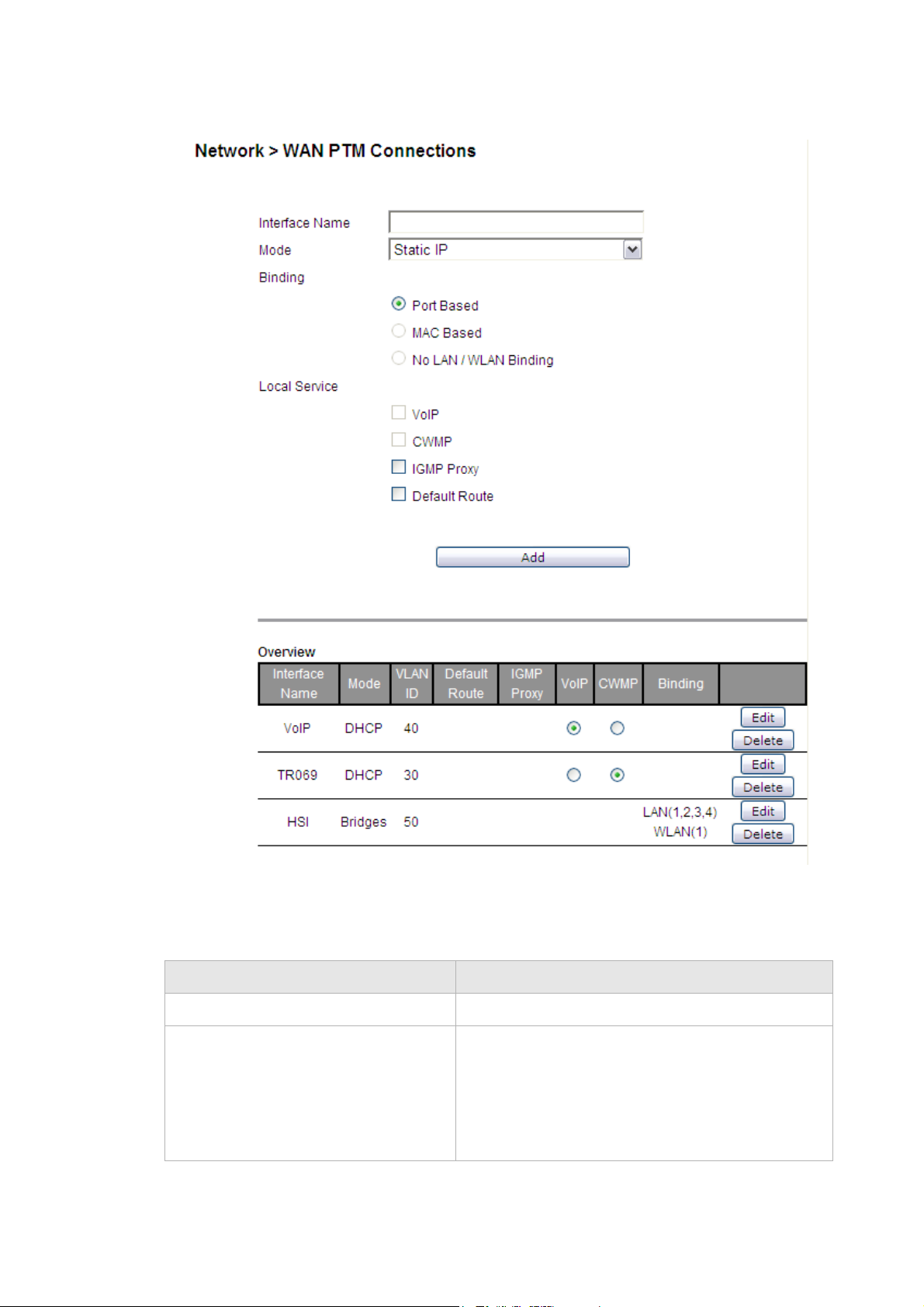
Select WAN PTM Connections in the Network menu to access the WAN PTM
Connections window; see Figure 5-5.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-7
Page 50
WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-5 WAN PTM Connections window
Table 5-4 describes the fields of the WAN PTM Connections window.
Table 5-4 Field descriptions
Field Description
Interface Name Enter a name for your new connection.
Mode Select a mode for the connection type:
• Static IP
• DHCP
• PPPoE
• Bridge
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-8
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 51

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Binding Select a binding method:
• Port Based to bind traffic to the connection by
LAN or WLAN port.
• MAC Based to bind traffic to the connection by
MAC address.
• No LAN/WLAN Binding so that the connection
does not bind traffic to any port or MAC.
Note: You cannot use a combination of Port based
and MAC based binding.
Note: When using MAC based binding, you must
define a Default connection first. This default
connection can be a routed or bridged connection.
After defining the default MAC based connection,
you can add extra bridged (not routed) connections
which are selected on basis of configurable MAC
layer based criteria.
Local Service Enable a local service:
• Enable VoI P to provide VoIP service.
• Enable CWMP to provide remote control
service. It allows a remote server to manage the
gateway
• Enable IGMP Proxy to provide service to be
used for video streaming and gaming.
• Enable Default Route to set the connection as
the gateway of last resort.
Add Click to add the new connection and proceed to the
next configuration window.
Note: After adding new connections, click
Activate WAN Settings to activate the connection.
This button will be only visible if you added a new
connection or made changes to the settings.
Interface Name (read-only) The name of the interface.
Mode (read-only) The selected mode.
VLAN ID (read-only) The VLAN ID.
Default Route All connections will be routed via the default route,
except for the connection that has special routing.
There can be only one default route between all the
connections.
IGMP Proxy Select the interface to support IGMP service.
VoIP Select the interface to support VoIP service.
CWMP Select the interface to support CWMP service.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-9
Page 52

WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Binding (read-only) Shows which ports or MAC addresses are bound on
the connection.
Delete All Click to delete all the connections.
Edit Click to modify the settings of the connection.
After changing the connection settings, press
Activate WAN Settings to activate the connection.
This button will be only visible if you made changes
to the settings or added a new connection.
Delete Click to delete the connection.
Port based binding
Port based mode enables you to bind ports to your WAN connection. You can bind LAN
ports 1 to 4 and WLAN SSID 1 to 4 in the WAN mode you selected. The default WLAN
SSID number is 1 and you can configure 2 to 4 in the WiFi Settings.
You can select the Port Based radio button for each WAN mode and then click Add to
proceed to the next configuration window.
In Port based mode, you can add up to four connections in routed mode.
Note: If you do not set a VLAN ID in the connections, you can only have one
connection in Static IP or DHCP mode and three connections maximum in PPPoE.
Note: If you already have a connection with Port based binding, you can not select
MAC based binding for any other connections.
The following WAN modes support port-based binding:
• Static IP
• DHCP
• PPPoE
• Bridge
Static IP
If you select Static IP as the mode in the WAN PTM Connections, the Static IP settings
window with Port based binding opens; see Figure 5-6.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-10
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 53

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-6 Static IP settings window with Port based binding
Table 5-5 describes the fields of Static IP settings window with Port based binding.
Table 5-5 Field descriptions
Field Description
LAN Binding
LAN Binding Select the port to which you want to bind the
connection.
WLAN Binding Select the SSID to which you want to bind the
connection.
WAN
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be used
for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0 and
4094).
802.1X Select Enable to use 802.1x or select Disable to
turn off 802.1x.
IP Address Enter the IP address provided by your ISP.
NetMask Enter the subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Gateway Enter the gateway IP address provided by your ISP.
DNS1 to 3 Enter the DNS IP address (these are optional).
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-11
Page 54

WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
MTU(Bytes) Select Auto to set the MTU to the default (1500) or
select Manual and enter a value in bytes.
Next Click to go to the QoS Defaults window.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
Activate WAN Setting Click to activate the connection.
Delete All Click to remove all WAN connections.
Edit Click to make changes to a specific connection.
Delete Click to remove a specific connection.
DHCP
If you select DHCP as the mode in the WAN PTM Connections window, the DHCP settings
window with Port based binding opens; see Figure 5-7.
Figure 5-7 DHCP settings window with Port based binding
Table 5-6 describes the fields of DHCP settings window with Port based binding.
Table 5-6 Field descriptions
Field Description
LAN Binding
LAN Binding Select the port to which you want to bind the
connection.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-12
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 55
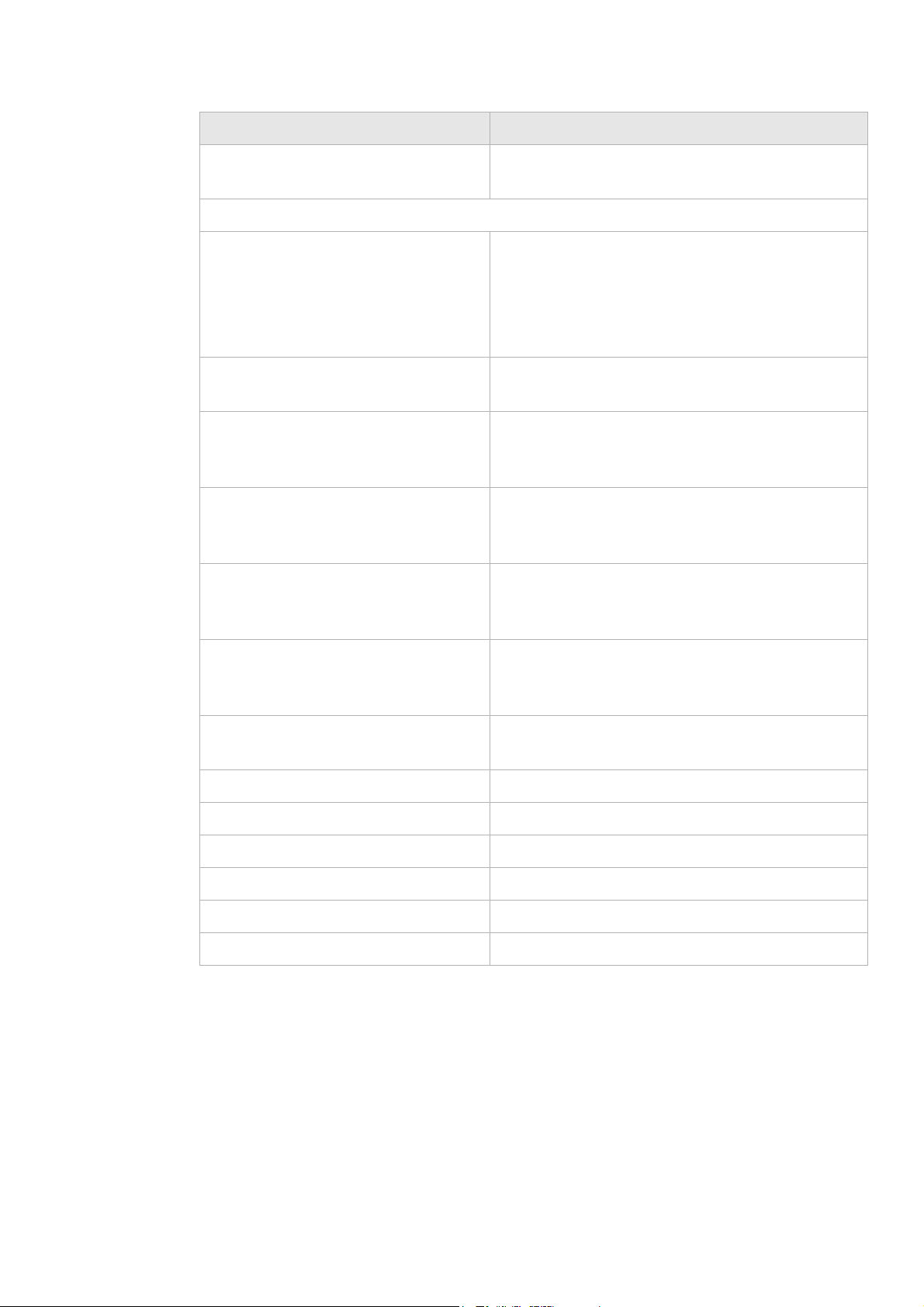
NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
WLAN Binding Select the SSID to which you want to bind the
connection.
WAN
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be used
for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0 and
4094).
802.1X Select Enable to use 802.1x or select Disable to
turn off 802.1x.
Host Name Enter the host name provided by your ISP. If you are
unsure of the host name, please consult with your
ISP for more information.
Domain Name Enter the domain name provided by your ISP. If you
are unsure of the domain name, please consult with
your ISP for more information.
Vender Class ID If required, set the vender class ID to obtain its lease
from the DHCP server. Please consult with your ISP
for more information.
Client ID If required, set the client ID to obtain its lease from
the DHCP server. Please consult with your ISP for
more information.
MTU(Bytes) Select Auto to set the MTU to the default (1500) or
select Manual and enter a value in bytes.
Activate WAN Setting Click to activate the connection.
Delete All Click to remove all WAN connections.
Edit Click to make changes to a specific connection.
Delete Click to remove a specific connection.
Next Click to go to the QoS Defaults window.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
PPPoE
If you select PPPoE as the mode in the WAN PTM Connections window, the PPPoE
settings window with Port based binding opens; see Figure 5-8.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-13
Page 56

WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-8 PPPoE settings window with Port based binding
Table 5-7 describes the fields of PPPoE settings window with Port based binding.
Table 5-7 Field descriptions
Fields Description
LAN Binding
LAN Binding Select the port to which you want to bind the
connection.
WLAN Binding Select the SSID to which you want to bind the
connection.
WAN
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be used
for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0
and 4094).
User Name Enter the username for the PPPoE connection.
Please consult with your ISP for more information.
Password Enter the password for the PPPoE connection.
Please consult with your ISP for more information.
Access Concentrator The access concentrator is optional. Please consult
with your ISP for information.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-14
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 57

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Fields Description
Service Name The service name is optional. Please consult with
your ISP for information.
Mode Select the mode:
• Select Connect on demand to allow the
gateway to connect to the Internet only when
you are trying to access it. Enter a Max idle
time. If there are no activities in the specified
time period, the CellPipe 7130 RG will
disconnect the connection.
• Select Always on to set the CellPipe 7130 RG
to always connect to the Internet.
• Select Manual and then click Connect to
manually connect the CellPipe 7130 RG to the
Internet. Click Disconnect to disconnect the
connection.
Authentication Method Select the authentication mode:
• CHAP + PAP
• Only MS-CHAP
• Only CHAP
• Only PAP
This is optional. Please consult with your ISP for
more information.
MTU (Bytes) Select Auto to set the MTU to the default (1492) or
select Manual and enter a value in bytes.
Activate WAN Setting Click to activate the connection.
Delete All Click to remove all WAN connections.
Edit Click to make changes to a specific connection.
Delete Click to remove aspecific connection
Next Click to go to the QoS Defaults window.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
Bridge
If you select Bridge as the mode in the WAN PTM Connections window, the Bridge
settings window with Port based binding opens; see Figure 5-9.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-15
Page 58
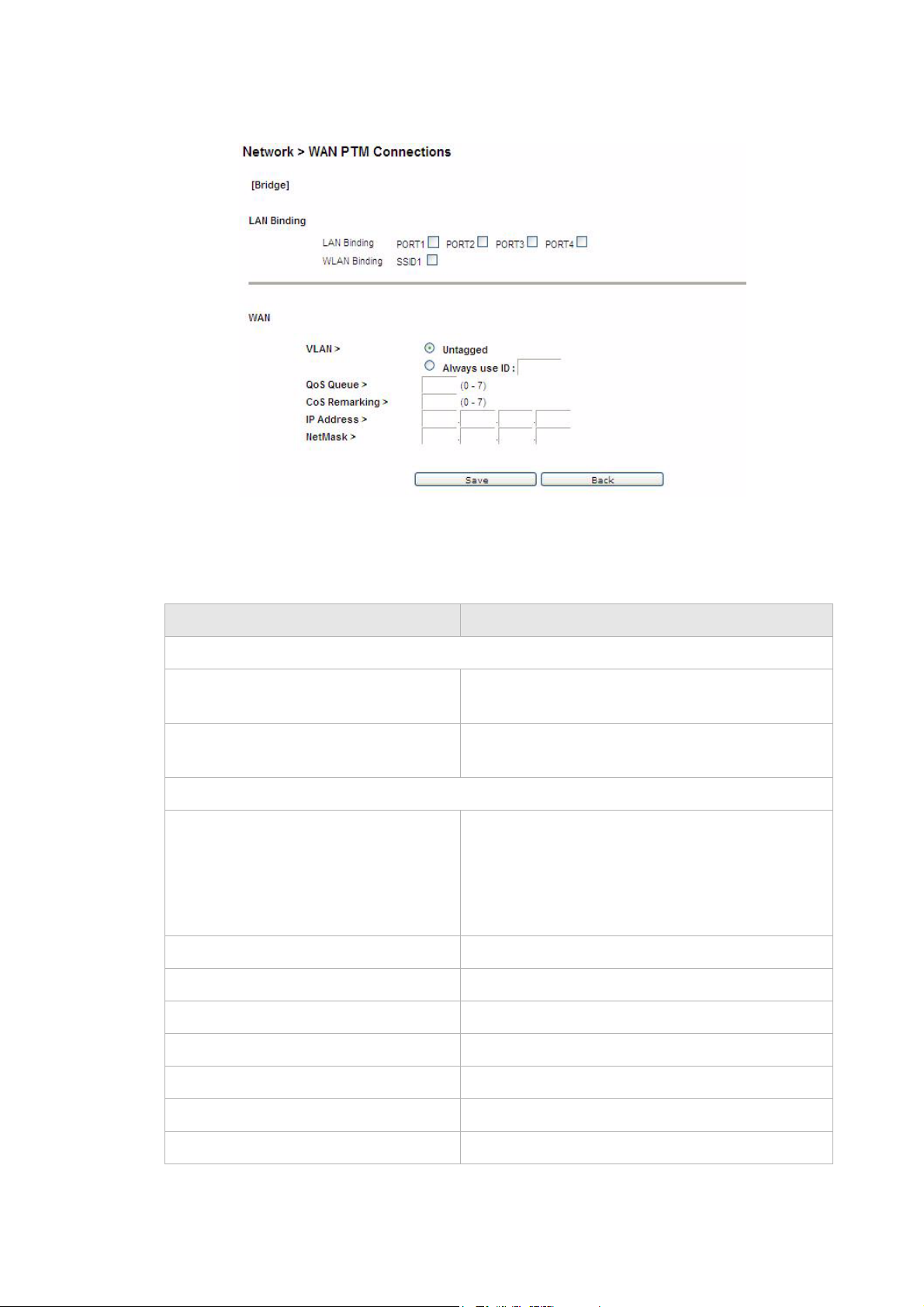
WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-9 Bridge settings window with Port based binding
Table 5-8 describes the fields of Bridge settings window with Port based binding.
Table 5-8 Field descriptions
Fields Description
LAN Binding
LAN Binding Select the port to which you want to bind the
connection.
WLAN Binding Select the SSID to which you want to bind the
connection.
WAN
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be
used for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0
and 4094).
QoS Queue Enter the QoS queue number.
CoS Remarking Enter the CoS remarking number.
IP Address Enter the IP address provided by your ISP.
NetMask Enter the subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Save Click to save your changes.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
Activate WAN Setting Click to activate the connection.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-16
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 59
NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Fields Description
Delete All Click to remove all WAN connections.
Edit Click to make changes to a specific connection.
Delete Click to remove aspecific connection
MAC based binding
MAC based mode enables you to bind your connection by DHCP Option 60, Ethernet
type, source MAC, or destination MAC.
Before you begin, you must configure a default connection. It should be routed or bridge
mode. Afterwards you can configure MAC based binding (the other binding options are
Port based and No LAN/WLAN) by DHCP Option 60, Ethernet type, source MAC, or
destination MAC.
You can select the MAC Based radio button for each WAN mode and then click Add to
enter the next configuration window.
You can set a maximum of 20 connections in MAC based binding.
Note: If you already have a connection with MAC based binding, you cannot select
Port based binding for any other connections.
The following section shows the creation of a default DHCP connection with MAC based
binding.
DHCP
If you select DHCP as the mode, the DHCP settings window with MAC based binding
opens; see Figure 5-10.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-17
Page 60

WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-10 DHCP settings window with MAC based binding
Table 5-9 describes the fields of DHCP settings window with MAC based binding.
Table 5-9 Field descriptions
Fields Description
LAN Binding
Default The first rule must be the default. After you have a
default rule you can choose the other options. For
example, you can select DHCP Option 60, Ethernet
Type, Source MAC, or Destination MAC.
DHCP Option 60 Select the radio button and enter the applicable
alphanumeric identification (wildcard * is also
applicable).
Ethernet Type Select the radio button and enter the applicable
Ethernet Type code (4 hex digits).
Source MAC Select the radio button and enter the applicable
Source MAC address in hexadecimal format.
Destination MAC Select the radio button and enter the applicable
Destination MAC address in hexadecimal format.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-18
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 61

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Fields Description
WAN
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be
used for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0
and 4094).
802.1x Select Enable to use 802.1x or select Disable to
turn off 802.1x. Please consult your ISP for more
information.
Host Name Enter the host name provided by your ISP. Please
consult with your ISP for more information.
Domain Name Enter the domain name provided by your ISP.
Please consult with your ISP for more information.
Vender Class ID If you are required, set the vender class ID to obtain
its lease from the DHCP server. Please consult with
your ISP for more information.
Client ID If you are required, set the client ID to obtain its
lease from the DHCP server. Please consult with
your ISP for more information.
MTU(Bytes) Select Auto to set the MTU to the default (1500) or
select Manual and enter a value in bytes.
Next Click to go to the QoS Defaults window.
Back Click to return to the previous page.
Now that you have a default connection, the WAN PTM Connections window with MAC
based binding opens; see Figure 5-11.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-19
Page 62
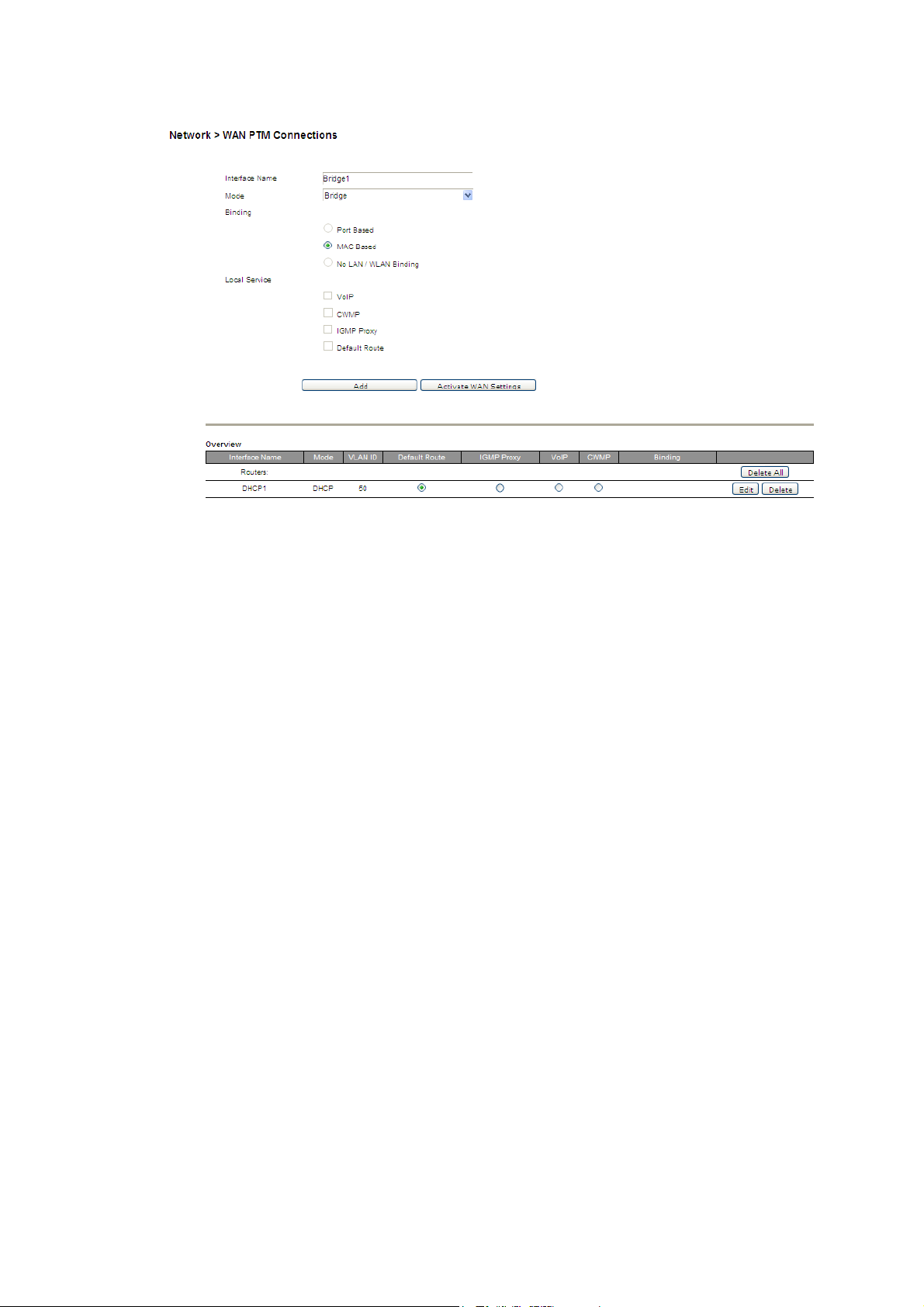
WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-11 WAN PTM Connections window with MAC based binding
After you have a default connection, you can choose the WAN Mode you want and click
Add to add a new connection. You can only choose Bridge mode with MAC based
binding. Click Add to set the configurations.
When you select Bridge mode with MAC based binding and click Add, the Bridge settings
window with MAC based binding opens; see Figure 5-12.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-20
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 63

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-12 Bridge settings window with MAC based binding
Table 5-10 describes the fields of Bridge settings window with MAC based binding.
Table 5-10 Field descriptions
Fields Description
LAN Binding
Default The first rule must be the default. After you have a
default rule you can choose the other options. For
example, you can select DHCP Option 60, Ethernet
Type, Source MAC, or Destination MAC.
DHCP Option 60 Select the radio button and enter the applicable
alphanumeric identification (wildcard * is also
applicable).
Ethernet Type Select the radio button and enter the applicable
Ethernet Type code (4 hex digits).
Source MAC Select the radio button and enter the applicable
Source MAC address in hexadecimal format.
Destination MAC Select the radio button and enter the applicable
Destination MAC address in hexadecimal format.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-21
Page 64
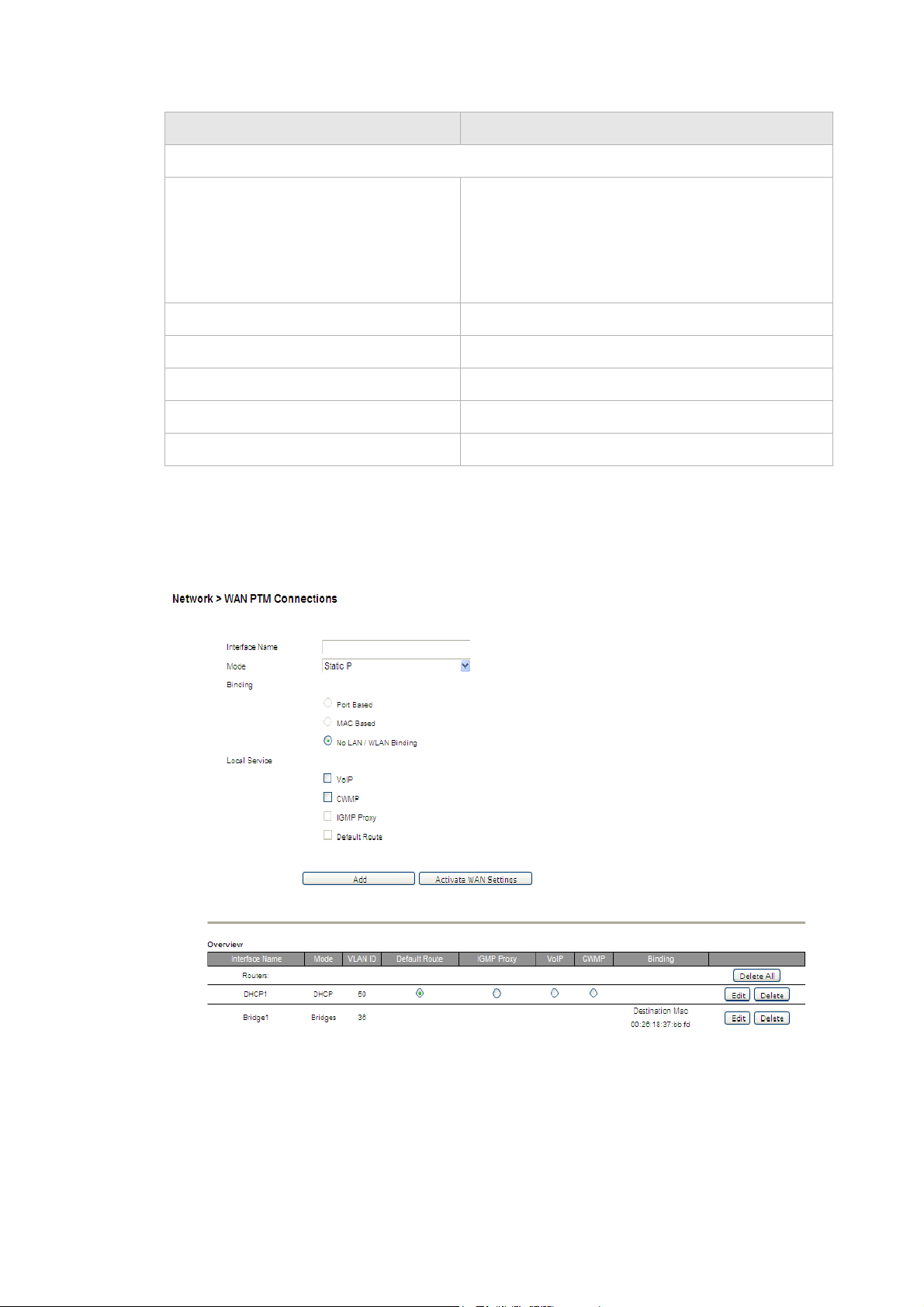
WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Fields Description
WAN
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be
used for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0
and 4094).
CoS Remarking Enter the CoS remarking number.
IP Address Enter the IP address provided by your ISP.
NetMask Enter the subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Next Click to proceed to the next step.
Back Click to return to the previous page.
After the second connection is set, you are returned to the WAN PTM Connections
window; see Figure 5-13. The two new connections, default and bridged, appear in the
Overview table.
Figure 5-13 WAN PTM Connections window with MAC based binding
You can only choose Bridge mode with MAC based binding and you can select Static IP,
DHCP, or PPPoE with No LAN/WLAN Binding for CWMP and VoIP.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-22
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 65

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
No LAN/WLAN binding
No LAN/WLAN binding enables you to configure your connection with local service
CWMP and VoIP. In order to avoid other connections using CWMP and VoIP, No
LAN/WLAN Binding is specifically for CWMP and VoIP to build an independent
connection.
Select the No LAN/WLAN Binding radio button for the binding method and then click Add
to enter the next configuration page.
Static IP
If you select Static IP as the mode and click Add, the Static IP window with No
LAN/WLAN Binding opens; see Figure 5-14.
Figure 5-14 Static IP window with No LAN/WLAN Binding
Table 5-11 describes the fields of Static IP window with No LAN/WLAN Binding.
Table 5-11 Field descriptions
Field Description
WAN
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be used
for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0 to
4094).
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-23
Page 66
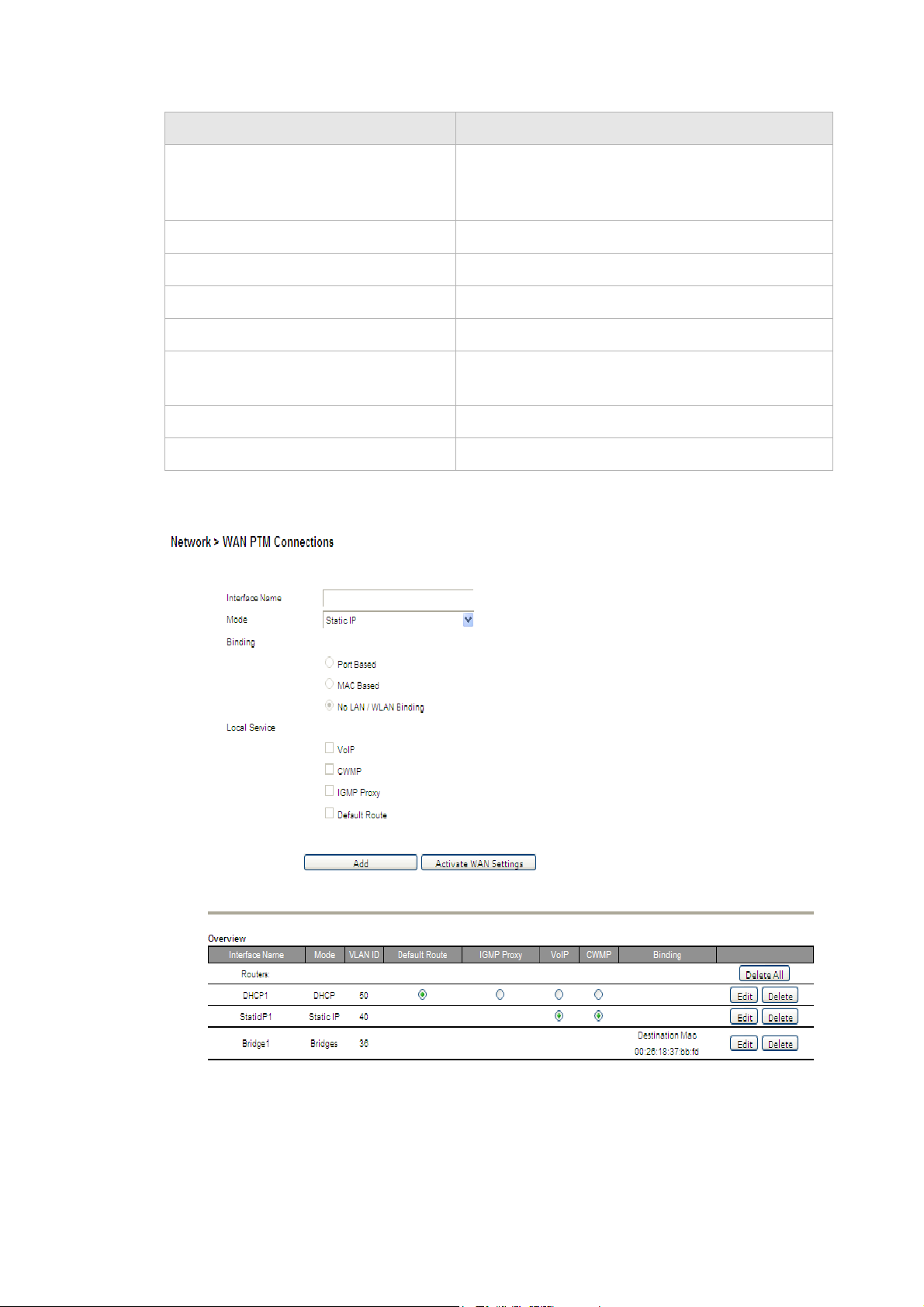
WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
802.1x Select Enable to use 802.1x or select Disable to
turn off 802.1x. Please consult your ISP for more
information.
IP Address Enter the IP address provided by your ISP.
NetMask Enter the subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Gateway Enter the gateway IP address provided by your ISP.
DNS1 to 3 Enter the DNS IP address (these are optional).
MTU(Bytes) Select Auto to set the MTU to the default (1500) or
select Manual and enter a value in bytes.
Next Click to proceed to the QoS Defaults window.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
Figure 5-15 WAN PTM Connections window with Static IP No LAN/WAN CWMP
connection created
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-24
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 67
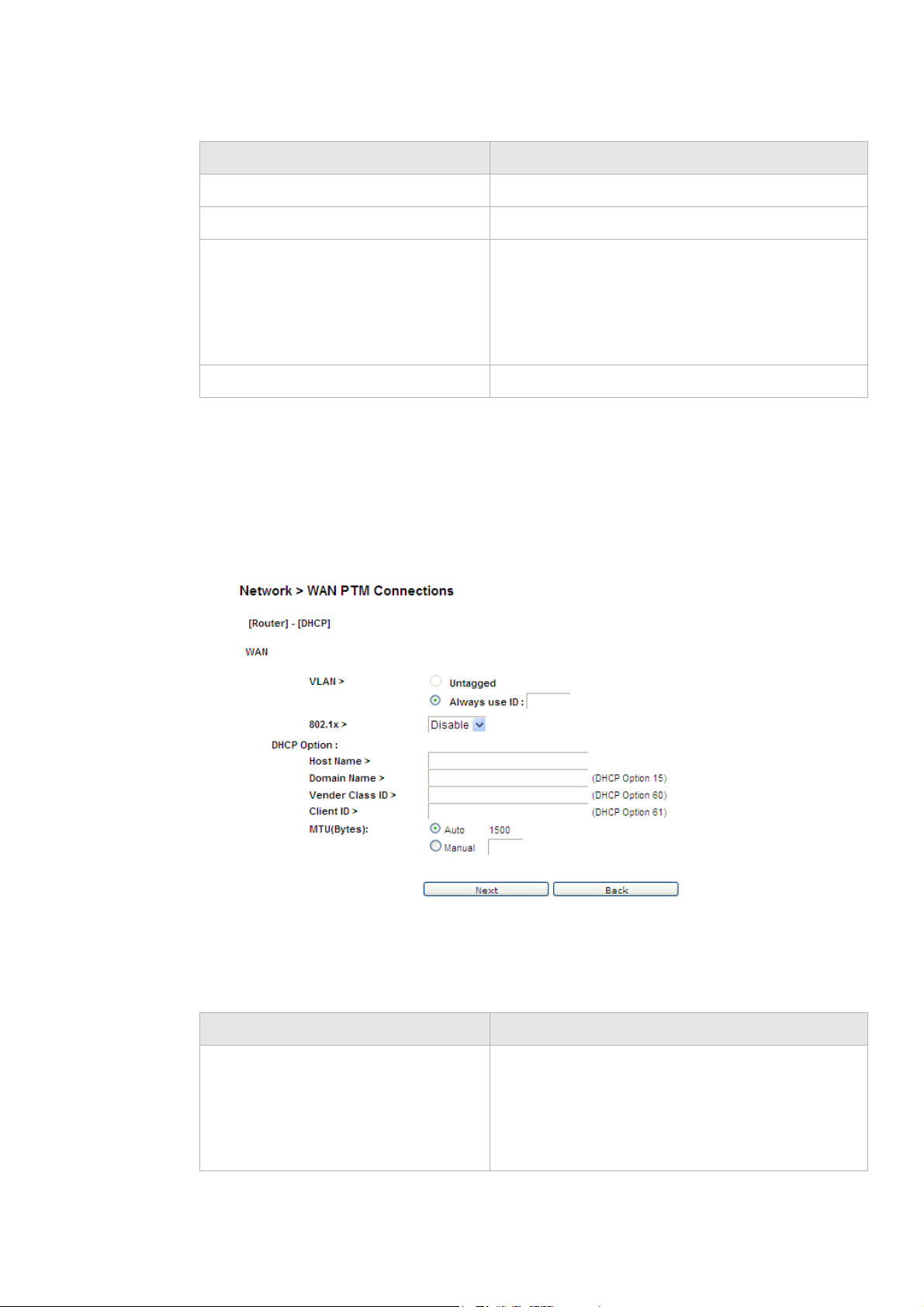
NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Table 5-12 Field descriptions
Field Description
Activate WAN Settings Click to activate the connection.
Delete All Click to delete all the connections.
Edit Click to modify the settings of the connection.
After changing the connection settings, press
Activate WAN Settings to activate the connection.
This button will be only visible if you made changes
to the settings or added a new connection.
Delete Click to delete the connection.
DHCP
If you select DHCP as the mode and click Add, the DHCP window with No LAN/WLAN
Binding opens; see Figure 5-16.
Figure 5-16 DHCP window with No LAN/WLAN Binding
Table 5-13 describes the fields of DHCP window with No LAN/WLAN Binding.
Table 5-13 Field descriptions
Field Description
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be used
for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0 and
4094).
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-25
Page 68

WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
802.1x Select Enable to use 802.1x or select Disable to
turn off 802.1x. Please consult your ISP for more
information.
Host Name Enter the host name provided by your ISP. Please
consult with your ISP for more information.
Domain Name Enter the domain name provided by your ISP. Please
consult with your ISP for more information.
Vender Class ID If you are required, set the vender class ID to obtain
its lease from the DHCP server. Please consult with
your ISP for more information.
Client ID If you are required, set the client ID to obtain its
lease from the DHCP server. Please consult with
your ISP for more information.
MTU(Bytes) Select Auto to set the MTU to the default (1500) or
select Manual and enter a value in bytes.
Next Click to go to the QoS Defaults window.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
PPPoE
If you select PPPoE as the mode and click Add, the PPPoE window with No LAN/WLAN
Binding opens; see Figure 5-17.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-26
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 69

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-17 PPPoE window with No LAN/WLAN Binding
Table 5-14 describes the fields of PPPoE window with No LAN/WLAN Binding.
Table 5-14 Field descriptions
Field Description
VLAN Select Untagged if VLAN tagging is not to be used
for this WAN connection.
Select Always use ID if VLAN tagging is to be
used and enter the VLAN ID number (between 0 to
4094).
User Name Enter the username for the PPPoE connection.
Please consult with your ISP for more information.
Password Enter the password for the PPPoE connection.
Please consult with your ISP for more information.
Access Concentrator The access concentrator is optional. Please consult
with your ISP for more information.
Service Name The service name is optional. Please consult with
your ISP for more information.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-27
Page 70
WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Mode Select the mode:
• Select Connect on demand to allow the
gateway to connect to the Internet only when
you are trying to access it. Enter a Max idle
time. If there are no activities in the specified
time period, the CellPipe 7130 RG will
disconnect the connection.
• Select Always on to set the CellPipe 7130 RG
to always connect to the Internet.
• Select Manual and then click Connect to
manually connect the CellPipe 7130 RG to the
Internet. Click Disconnect to disconnect the
connection.
Authentication Method Select the authentication mode:
• CHAP + PAP
• Only MS-CHAP
• Only CHAP
• Only PAP
QoS Defaults
This is optional. Please consult with your ISP for
more information.
MTU (Bytes) Select Auto to set the MTU to the default (1492) or
select Manual and enter a value in bytes.
Next Click to go to the QoS Defaults window.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
The QoS Defaults window enables you to configure the default QoS policy for each WAN
connection, see Figure 5-18.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-28
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 71

NetworkWAN PTM Connec t i o n s
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 5-18 QoS Defaults window
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-29
Page 72

WAN PTM Co n n e c t i o nsNetwork
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Table 5-15 describes the fields of the QoS Defaults window.
Table 5-15 Field descriptions
Field Description
QoS Classification
Queue
Original ToS Tag (First 3 bits of
DSCP)
Select Original ToS Tag to assign the queue according
to the ToS value of the packet.
Specified Queue Select Specified Queue and enter a queue number (0
to 7) to which the network traffic will be assigned.
Note: When Specified Queue is chosen, you cannot
choose Align CoS with ToS Value.
ToS/DSCP Remarking
Keep Original ToS Select Keep Original ToS to retain the original ToS
value.
New ToS Value Select New Tos Value and enter a queue number (0 to
7) to assign to the network traffic.
New DSCP Value Select New DSCP Value and enter a DSCP value (0 to
63).
CoS (p-bit) Remarking
Keep CoS Value Select Keep CoS Value to retain the original CoS value.
New CoS Value Select New CoS Value to assign CoS for network
traffic.
Align CoS with ToS Value Select to align CoS with ToS value.
Note: This field can only be set if you keep Original
To S Ta g in queue setting.
QoS LAN Classification
Queue
Original ToS Tag (First 3 bits of
DSCP)
Select Original ToS Tag to assign the queue according
to the ToS value of the packet.
Specified Queue Select Specified Queue and enter a queue number (0
to 7) to which the network traffic will be assigned.
Note: When Specified Queue is chosen, you cannot
choose Align CoS with ToS Value.
ToS/DSCP Remarking
Keep Original ToS Select Keep Original ToS to retain the original ToS
value.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-30
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 73

Network
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
New ToS Value Select New Tos Value and enter a queue number (0 to
7) to assign to the network traffic.
New DSCP Value Select New DSCP Value and enter a DSCP value (0 to
63).
Save Click to save your changes.
Back Click to return to the previous window.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
5-31
Page 74

Network
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
5-32
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 75

6 WiFi setup
Overview
Purpose
This chapter explains how to configure the WiFi settings for the CellPipe 7130 RG.
Click WiFi Setup in the main menu to open the WiFi Setup menu.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topics:
WiFi Settings 6-1
WiFi Security 6-4
WiFi Access Filter 6-6
WiFi Settings
The WiFi Settings window enables you to configure the common wireless settings.
Click on WiFi Settings in the WiFi Setup menu to access the WiFi Settings window; see
Figure 6-1.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
6-1
Page 76

WiFi SettingsWiFi setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 6-1 WiFi Settings window
Table 6-1 describes the fields of the WiFi Settings window.
Table 6-1 Field descriptions
Field Description
Common
WiFi Select Enable to turn on wireless and configure
the wireless settings. Select Disable to turn off
wireless.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
6-2
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 77

WiFi setupWiFi Settings
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Multiple SSID Select the number of SSIDs:
• 1
• 2
• 4
Tx Power Enter a value between 1 and 100 to control the
transmitting signal strength.
Radio Mode Select the wireless mode:
• 802.11b/g
• 802.11g/n
• 802.11b/g/n
• 802.11b
• 802.11g
• 802.11n
Auto Channel Select Select On to let the wireless access point
automatically select a channel with the least
interference. Select Off to configure manually.
Select Now to set the channel automatically
one time.
Channel If Auto Channel Select is off, you can manually
select a channel for the wireless access point.
The default is 1.
Beacon Period Enter a beacon period in milliseconds to
determine the frequency of the beacon to keep
the network synchronized. This is optional.
DTIM Period Enter a value to set the delivery traffic
indication message. The DTIM field is a
countdown field informing clients of the next
window for listening to broadcast and multicast
messages.
Bandwidth Select to enable channel bonding (20/40Mhz)
or disable channel bonding . If channel bonding
is selected, please also select which extension
channel is been used. Note: Not all wireless
clients support this.
Extension Channel An extension channel is a secondary channel
used to bond with the primary channel to
increase the performance.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
6-3
Page 78

WiFi SecurityWiFi setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
SSID 1 to 4
SSID Enter an SSID name (maximum of 32
characters). The SSID is an alphanumeric name
shared by all the devices on the wireless
network. It must be unique.
Broadcast SSID Select On to broadcast the SSID or select Off to
hide the SSID.
TxRate Select Auto to automatically determine the
transmission rate or manually select a
transmission rate (maximum 54Mb/s).
IGMP Enable Enable to use IGMP or disable to turn off
IGMP.
WDS Select Enable to use WDS or select Disable to
turn off WDS.
Other WDS Station Enter the wireless MAC addresses of other
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
WiFi Security
WiFi security enables you to configure the WEP, WPA, or WPA2 security settings.
Select WiFi Security in the WiFi Setup menu to access the WiFi Security window; see
Figure 6-2.
Note: If you enable WDS, ensure that all
other WDS APs are enabled, configured with
the same channel, SSID, and encryption keys,
and that each AP has a different LAN port IP
address.
wireless APs or routers that are in the same
WDS.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
6-4
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 79

WiFi setupWiFi Security
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 6-2 WiFi Security window
Table 6-2 describes the fields of the WiFi Security window.
Table 6-2 Field descriptions
Field Description
WPS Enable Push Button Control (the WPS push
button is located on the front of the CellPipe
7130 RG) or enable PIN and enter your PIN
number and click Start. The PIN number is
located in the WiFi utility of your computer.
Authentication Select one of the following encryption methods
for the wireless network:
• Open
• Shared
• WPAPSK
• WPA2PSK
• WPAPSK/WPA2PSK Mixed
• WPA
• WPA2
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
6-5
Page 80

WiFi Access FilterWiFi setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Security Type Select one of the following for the security
type:
• NONE
• WEP
• TKIP
• AES
• TKIP/AES Mixed
WEP
Passphrase Key Select a level of encryption (64 bits or 128
bits) and enter a passphrase key consisting of 8
to 63 alphanumeric characters and then click
Generate.
Key1 to 4 Select Key1 to Key4 and enter a WEP key in
the respective field. The WEP key must:
WPAPSK/WPA2PSK
Preshared Key Enter a preshared key consisting of 8 to 63
802.1x
Radius Server Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server.
Radius Port Enter the port number of the RADIUS server.
Radius Key Enter the key of the RADIUS server.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
WiFi Access Filter
• contain letters from A to F and numbers
from 0 to 9
• contain 10 characters for 64 bit and 26
characters for 128 bit encryption
alphanumeric characters.
The WiFi Access Filter window enables you to block or permit access for wireless clients
by MAC address.
Select WiFi Access Filter in the WiFi Setup menu to access the WiFi Access Filter
window; see Figure 6-3.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
6-6
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 81
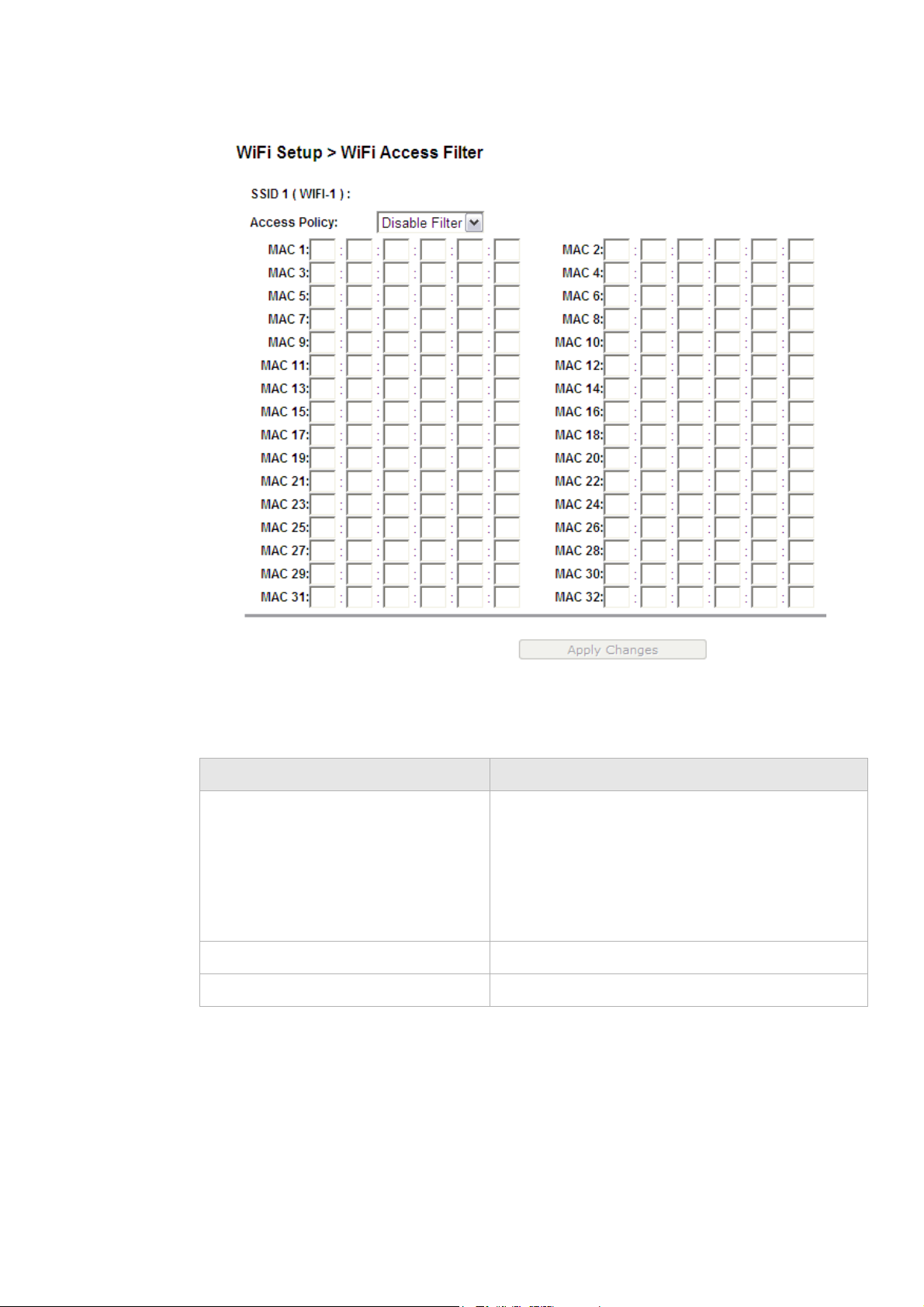
WiFi setupWiFi Access Filter
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 6-3 WiFi Access Filter window
Table 6-3 describes the fields of the WiFi Access Filter window.
Table 6-3 Field descriptions
Field Description
Access Policy Select an access policy:
• Disable Filter to turn off WiFi filtering.
• Allow to permit access from the specified MAC
address.
• Deny to deny access from the specified MAC
address.
MAC 1 to 32 Enter up to 32 MAC addresses to control access.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
6-7
Page 82

WiFi Access FilterWiFi setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
6-8
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 83

7Firewall setup
Overview
Purpose
This chapter explains how to configure the firewall for the CellPipe 7130 RG.
Click Firewall Setup in the main menu to open the Firewall Setup menu.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topics:
Port Forwarding 7-1
Demilitarized Zone 7-3
UPnP 7-4
Layer 2 Filter 7-5
Layer 3 Filter 7-7
NAT Passthrough 7-8
URL Blocking 7-9
Content Screening 7-10
Parental Control 7-11
Port Forwarding
The Port Forwarding window enables you to control the incoming requests from the
Internet to pass through the port to your local computer.
Note: It is recommended that port forwarding be configured with the assistance of
your ISP.
Select Port Forwarding in the Firewall Setup menu to open the Port Forwarding
window; see Figure 7-1.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
7-1
Page 84

Port F orwardingFirewall setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 7-1 Port Forwarding window
Table 7-1 describes the fields of the Port Forwarding window.
Table 7-1 Field descriptions
Field Description
Name Enter a name for the application you are hosting on
your LAN computer; for example, Real Audio.
Protocol Select the type of IP protocol(s) used by this
application:
• ALL
• Protocol Number and then enter the protocol
number
• Known Protocol and then select a protocol:
• TCP
• UDP
• TCP/UDP
• ICMP
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
7-2
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 85

Firewall setupDemilitarized Zone
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Port Select or enter the TCP/UDP port for which the port
forwarding route must be applied.
• Known Port and then select a port:
• FTP
• TFTP
• TELNET
• SSH
• HTTP
• HTTPS
• SMTP
• POP3
• DNS
• IMAP
• Single Port and then enter the port number
• Port Range and then enter the port range
LAN IP Address Select the first radio button to choose a pre-
LAN Port Select the first radio button to use the same port or
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
Demilitarized Zone
The Demilitarized Zone window enables you to configure a single computer on the local
side to be exposed to the Internet. All incoming packets will be forwarded to this
computer.
Note: Use the demilitarized zone setting only if the virtual server or port range
forwarding options do not provide the level of access required for certain applications.
It is recommended that you contact your ISP for assistance.
configured LAN host or select the second radio
button to enter an IP address manually.
port range as the WAN or select the second radio
button and enter the LAN port manually.
Select Demilitarized Zone in the Firewall Setup menu to access the Demilitarized Zone
window; see Figure 7-2.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
7-3
Page 86

UPnPFirewall setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 7-2 Demilitarized Zone window
UPnP
Table 7-2 describes the fields of the Demilitarized Zone window.
Table 7-2 Field descriptions
Field Description
Demilitarized Zone(DMZ) Select Enable to turn on the demilitarized zone
function. Select Disable to turn it off.
DMZ Host IP Address Select the first radio button and choose a pre-
existing LAN host or select the second radio button
to enter an IP address manually.
DMZ Timer (Option) To improve security, specify the length of time (in
seconds) during which the DMZ is active.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
UPnP is an open networking standard that allows peer-to-peer network connectivity
between devices. It enables software or devices, such as video game consoles, to function
properly using NAT.
Note: It is recommended that you contact your ISP for assistance.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
7-4
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 87

Firewall setupLayer 2 Filter
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Select UPnP in the Firewall Setup menu to access the UPnP window; see Figure 7-3.
Figure 7-3 UPnP window
Table 7-3 describes the fields of the UPnP window.
Table 7-3 Field descriptions
Field Description
UPnP Select Enable to turn on the UPnP function. Select
UPnP Log Select Enable to turn on logging activities. Select
ReadOnly Mode Select Enable to turn on the read-only mode. Select
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
Layer 2 Filter
Disable to turn off the UPnP function.
Disable to turn off the logging activities.
Disable to turn off the read-only mode.
Note: In read-only mode, users are unable to
change port forwarding settings or any other UPnP
enabled application settings.
Select Layer 2 Filter in the Firewall Setup menu to access the Layer 2 Filter window; see
Figure 7-4.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
7-5
Page 88

Layer 2 FilterFirewall setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 7-4 Layer 2 Filter window
Table 7-4 describes the fields of the Layer 2 Filter window.
Table 7-4 Field descriptions
Field Description
Filter Policy Select the policy for filters:
• Allow
• Deny
• Disable
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
7-6
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 89
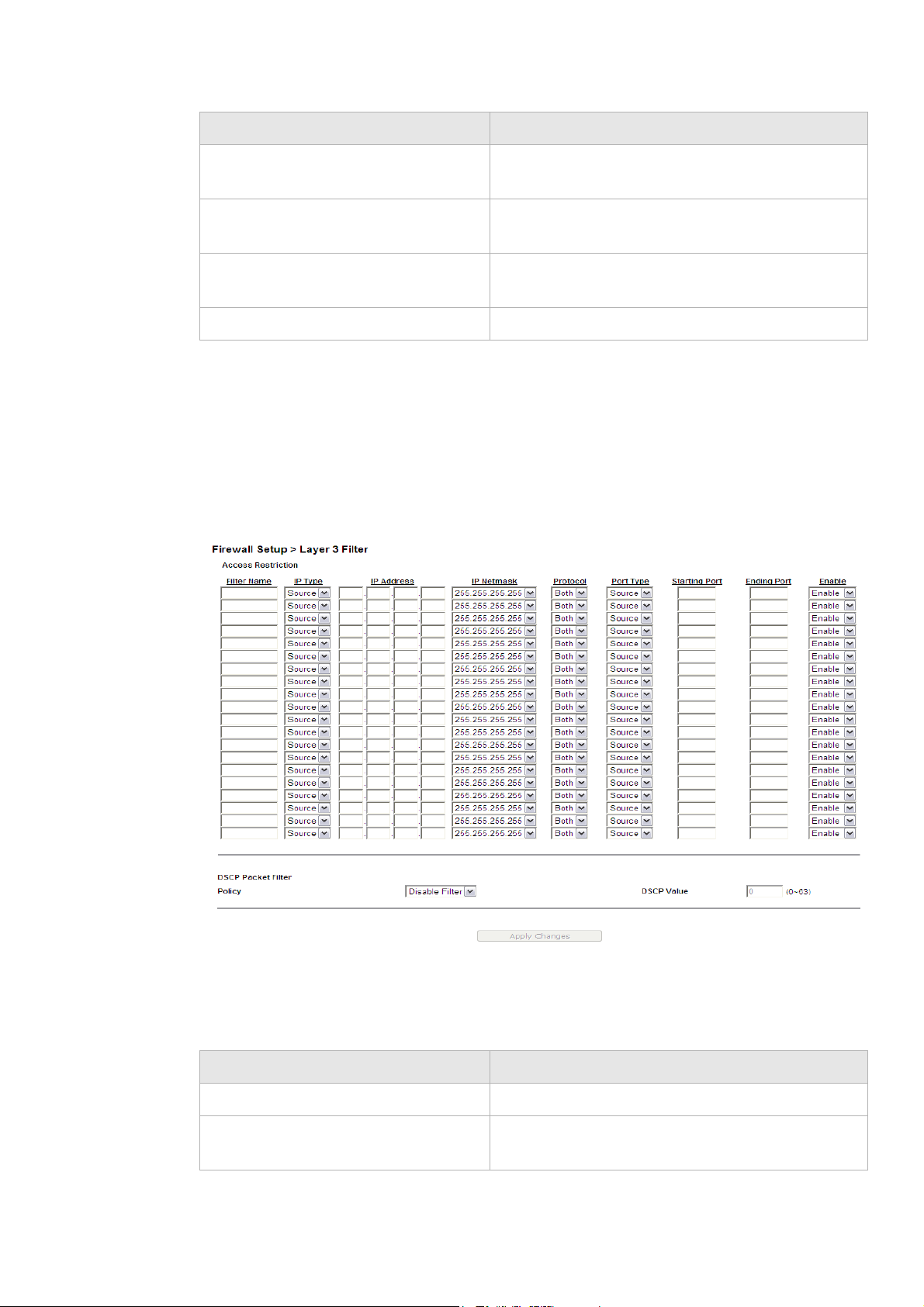
Firewall setupLayer 3 Filter
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Ethernet Type Select to use Ethernet Type as the filtering algorithm
and enter the applicable Ethernet Type code.
Source Mac Address 1 to 10 Select and then enter the source MAC address of the
device.
Destination Mac Address 1 to 10 Select and then enter the destination MAC address
of the device.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
Layer 3 Filter
Select Layer 3 Filter in the Firewall Setup menu to access the Layer 3 Filter window; see
Figure 7-5.
Figure 7-5 Layer 3 Filter window
Table 7-5 describes the fields of the Layer 3 Filter window.
Table 7-5 Field descriptions
Field Description
Filter Name Enter a name for the filtering rule.
IP Type Select Dest (destination) or Source depending on
the how the rule is going to be used.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
7-7
Page 90
NAT PassthroughFirewall setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
IP Address Enter the IP address of the host that you are
blocking.
IP Netmask Select the subnet mask of the host that you are
blocking.
Protocol Select the type of protocol(s) used by the
application:
• TCP
• UDP
• Both
Port Type Select Dest (destination) or Source depending on
the type of application.
Starting Port Enter the start port of the ports used by the
application.
Ending Port Enter the end port of the ports used by the
application.
Enable Select Enable to apply the filter rule or Disable to
DSCP Packet Filter Policy Select Disable to disable the DSCP policy. Select
DSCP Value Enter a DSCP value between 0 and 63.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
NAT Passthrough
The NAT Passthrough window allows you to enable or disable specific protocols from
passing through the gateway.
Note: This should only be configured with the help of your ISP.
turn off the filter rule.
Deny to deny packets that are accessing the Internet
with the specified DSCP value in the IP header or
select Allow to allow packets that are accessing the
Internet with the specified DSCP value in the IP
header.
Select NAT Passthrough in the Firewall Setup menu to access the NAT Passthrough
window; see Figure 7-6.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
7-8
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 91

Firewall setupURL Blocking
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 7-6 NAT Passthrough window
Table 7-6 describes the fields of the NAT Passthrough window.
Table 7-6 Field descriptions
Field Description
IPSec Passthrough Select Enable to allow IPSec passthrough. Select
L2TP Passthrough Select Enable to allow L2TP passthrough. Select
PPTP Passthrough Select Enable to allow PPTP passthrough. Select
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
URL Blocking
The URL Blocking window enables you to block requests from your local computer to
access specific websites.
Select URL Blocking in the Firewall Setup menu to access the URL Blocking window;
see Figure 7-7.
Disable to turn off the IPSec passthrough.
Disable to turn off L2TP passthrough.
Disable to turn off PPTP passthrough.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
7-9
Page 92

Content ScreeningFirewall setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 7-7 URL Blocking window
Table 7-7 describes the fields of the URL Blocking window.
Table 7-7 Field descriptions
Field Description
Name Enter a name for the URL filter.
URL Enter a URL or a prefix keyword of the URL you are
Enable Select Enable to apply the URL filter. Select
Add Click to add the URL blocking rule.
Edit Click to edit the URL blocking rule.
Delete Click to delete the URL blocking rule.
Content Screening
The Content Screening window enables you to configure keywords to screen website
content. If the keywords appear in the website content and content screening is enabled,
the firewall will block the user from accessing the website.
blocking.
Note: If the keyword is too general, you might
inadvertently block other websites.
Disable to turn off the URL filter.
Note: Compressed and secured pages are not supported.
Select Content Screening in the Firewall Setup menu to access the Content Screening
window; see Figure 7-8.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
7-10
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 93

Firewall setupParental Control
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 7-8 Content Screening window
Table 7-8 describes the fields of the Content Screening window.
Table 7-8 Field descriptions
Field Description
Content Screening Select Enable to apply content screening and block
websites that have keywords in their contents. Select
Disable to disable content screening.
Keyword Enter a keyword to be blocked. Enter only one
keyword. If you want to screen multiple keywords,
add them as separate rules. The maximum number
of keywords allowed is 254.
Note: If the keyword is too general, you might
inadvertently block other websites.
Index The index of rule. The index is created by system.
Add Click to add the keyword to the content screening
rules.
Edit Click to edit the keyword to the content screening
rules.
Delete Click to delete the keyword to the content screening
rules.
Parental Control
The Parental Control window enables you to set Internet connection limits on your
computer based on the time and day of the week.
Select Parental Control in the Firewall Setup menu to access the Parental Control
window; see Figure 7-9.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
7-11
Page 94

Parental ControlFirewall setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 7-9 Parental Control window
Table 7-9 describes the fields of the Parental Control window.
Table 7-9 Field descriptions
Field Description
Name Enter a name for the rule.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the LAN device.
Day Enable the day(s) of the week you want to limit the
Internet connection of the client. This is optional.
Time Enter a time period (in hours and minutes) that you
want to limit the Internet connection of the client.
This is optional.
Add Click to add the rule.
Edit Click to edit the rule.
Delete Click to delete the rule.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
7-12
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 95

8 Advanced setup
Overview
This chapter explains how to configure the advanced settings of the CellPipe 7130 RG
such as the route settings, DNS settings, dynamic DNS, system log, IGMP
proxy/snooping, and 802.1x.
Click Advanced Setup in the main menu to open the Advanced Setup menu.
Contents
This chapter covers the following topics:
Route Settings 8-1
DNS Settings 8-3
Dynamic DNS 8-4
System Log 8-5
IGMP Proxy/Snooping 8-6
802.1x Config 8-7
Route Settings
The Route Settings window enables you to configure static and dynamic routes for routing
packets from one network to another network.
Select Route Settings in the Advanced Setup menu to access the Route Settings window;
see Figure 8-1.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
8-1
Page 96

Route SettingsAdvanced setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Figure 8-1 Route Settings window
Table 8-1 describes the fields of the Route Settings window.
Table 8-1 Field descriptions
Field Description
Static Routing
IP Destination Enter the IP address of the destination network.
IP Netmask Select the subnet mask of the destination
network.
Gateway Enter the IP address of the gateway for the
destination network.
Metric In order to determine the best route, a value is
used to specify the cost of the route (the metric
value). Enter the metric value in the metric
field. IP routing uses hop count as measurement
of the metric.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
8-2
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 97

Advanced setupDNS Settings
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Interface Select LAN or WAN(DHCP1) interface. The
packets sent to the addresses of the destination
IP address are sent through this interface.
However, for the WAN interface it will depend
on the WAN configuration you choose and how
it is defined.
Dynamic Routing Select Enable to use dynamic routing instead
of static. Dynamic routing enables the router to
adapt to changes in the network and exchange
rating tables with other routers. Select Disable
to turn off dynamic routing.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
DNS Settings
The DNS Settings window enables you to configure the domain name and IP address of
the domain name.
Note: You can set up to 64 entries.
Select DNS Settings in the Advanced Setup menu to access the DNS Settings window;
see Figure 8-2.
Figure 8-2 DNS Settings window
Table 8-2 describes the fields of the DNS Settings window.
Table 8-2 Field descriptions
Field Description
Domain Name Enter the domain name to which you want to
connect.
IP Address Enter the IP address of the Static DNS.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
8-3
Page 98

Dynamic DNSAdvanced setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Add Click to add the DNS settings and save your
changes.
Dynamic DNS
The Dynamic DNS (DDNS) window enables you to configure your registered domain
name with a dynamic IP address.
Note: Before you can use this feature, you need to register for a DDNS service at
one of the supported DDNS service providers; see DynDNS.org or ChangeIP.com.
Click on Dynamic DNS in the Advanced Setup menu to access the Dynamic DNS
(DDNS) window; see Figure 8-3.
Figure 8-3 Dynamic DNS window
Table 8-3 describes the fields of the Dynamic DNS (DDNS) window.
Table 8-3 Field descriptions
Field Description
DDNS Service If you have registered a DDNS, select the DDNS
service. Select Disable to turn off DDNS.
User Name Enter the username of your DDNS account.
Password Enter the password of your DDNS account.
Host Name Enter the host name.
Apply Changes Click to save your changes.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
8-4
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
Page 99

Advanced setupSystem Log
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
System Log
The System Log window enables you to view the system logs and to send them to a
remote system log server.
Click on System Log in the Advanced Setup menu to access the system log window; see
Figure 8-4.
Figure 8-4 System Log window
Table 8-4 describes the fields of the System Log window.
Table 8-4 Field descriptions
Field Description
Log Size (Lines) Select the number of lines to display in the log.
Remote Logging Select LAN or WAN for the remote logging server.
Select Disable to turn off remote logging.
Remote Server Enter the IP address of the remote logging server.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
8-5
Page 100

IGMP Proxy/SnoopingAdvanced setup
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Field Description
Apply Changes Click to save your changes and to view the log.
If you are configuring remote logging, click Apply
Changes after modifying the remote logging and
remote server fields.
Time (read-only) The time that the event occurred.
Module (read-only) The type of module involved in the event.
Level (read-only) The level of logging activity:
• EMERG
• ALERT
• CRIT
• ERR
• WARNING
• NOTICE
• INFO
• DEBUG
Message The details of the event that occurred.
IGMP Proxy/Snooping
The IGMP Proxy/Snooping window enables you to setup LAN-side IGMP support that
enables the LAN-side user to receive multicast traffic.
Click on IGMP Proxy/Snooping in the Advanced Setup menu to access the IGMP
Proxy/Snooping window; see Figure 8-5.
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
8-6
3EQ-10280-AAAA-TCZZA
Edition 01 February 2011
 Loading...
Loading...