Page 1

WIRELESS 11G PCI ADAPTER
WPI-100G
User Guide
Version 1.0 - Aug. 2003
Page 2

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
CONTENTS
Introduction…………………………………………………………………….. 2
Planning Your Wire less Network ………..……………………………………… 3
Network Topology …...……………………………………………………… 3
Ad-Hoc versus Infrastructure Mode…………. ………………………….…. 3
Getting to Know the Wireless-G PCI Adapter………………………………… 4
Software Installation and Confituration for Window 98SE , Me , and 2000 ….. 4
Driver Installation and Configuration for Windows XP ……………………...... 6
Driver Installation for Windows XP …………………………………….…… 6
Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration ………………………………….. 6
Troubleshooting …………………………………………………………………… 8
Common Problems and Solutions ………………………………………….… 8
Frequently Asked Questions ……………………………………………….. 8
Specifications ………………………….……………………………………… 10
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
1
Page 3

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing your WPI-100G Wireless PCI Adapter.
This user guide will assist you with the installation procedure.
The Gemtek Wireless-G PCI Adapter installs in most desktops and lets you put your
computer almost anywhere in the building, without the cost and hassle of running network
cables. Now you don't have to drill holes in your walls and climb through the attic or cellar
to get connected to the network. Once you're connected, you can keep in touch with your
e-mail, access the Internet, use instant messaging to chat with friends, and share files and
other resources such as printers and network storage with other computers on the network.
The Wireless-G PCI Adapter connects you with Wireless-G networks at an incredible
54Mbps! And for added versatility, it can also interoperate with all the 11Mbps Wireless-B
(802.11b) products found in homes, businesses, and public wireless hotspots around the
country. And in either mode, your wireless communications are protected by up to 128-bit
encryption, so your data stays secure.
So don't hassle with running cables through your house - get your desktop connected the
easy way with the Gemtek Wireless-G PCI Adapter.
The package you have received should contain the following items:
• Operates in the 2.4Ghz frequency spectrum with throughput of up to 54 Mbps
• Complies with IEEE 802.11g draft standards, and backwards compatible with IEEE
802.11b products
• Up to 128-bit WEP encryption
• 32-bit PCI Interface
• Compatible with Windows 98SE, Millennium, 2000 and XP
Note: if anything is missing, please contact your vendor
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
2
Page 4

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is exactly like a regular local area network(LAN),
except that each computer in t he WLAN uses a wireless d evice to connect to the network.
Computers in a WLAN share the same frequency channel and SSID, which is an
identification name for wireless devices.
Your Wireless PCI adapter should be placed in a safe and secure location. To ensure proper
operation, please keep the unit away from water and other damaging elements.
Ad-Hoc versus Infrastructure Mode
Unlike wired networks, wireless networks have two different modes in which they ma y be
set up: infrastructure and ad-hoc. In an infrastruct ure configuration a WLAN and wired
LAN communicate to each other through an access point. In ad-hoc configuration,
wireless-equipped computers communicate directly with each other. Choosing between
these two modes depends on whether or not the wireless network needs to share data or
peripherals with a wired network or not.
If the computers on the wireless network need to
be accessed by a wired network or need to share a
peripheral, such as a printer, with the wired
network computers, the wireless network should
be set up in infrastructure mode.(See Figure 2-1.)
The basis of infrastructure mode centers around
an access point, which serves as the main point of
communications between a wired and wireless
network. Access points transmit data to PCs equipped with wireless network adapters,
which can roam within a certain radial range of the access point. Multiple access points
can be arranged to work in succession to extend the roaming range, and can be set up to
communicate with your Ethernet (wired) hardware as well.
If the wireless network is relativel y small and needs to share resources onlywith the other
computers on the wireless network, then the ad-hoc mode can be used. Ad-hoc mode
allows computers equipped with wireless transmitters and receivers to communicate
directly with each other, eliminating the need for an access point. Communication betwe en
the wireless-equipped computers is limited by the distance and interference directly
between them.
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
3
Page 5

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
Getting to Know the Wireless-G PCI Adapter
ACT LED Green. The ACT LED lights up when the Adapter is powered on.
Antenna Port Attach the PCI Adapter’s antenna here and position it for maximum
performance, which is usually perpendicular to the horizon.
Software Installation and Confituration for Window 98SE , Me ,
and 2000
1. To install the Adapter, click the Install button on the Welcome screen, Figure 4-1. Click
User Guide to view the User Guide or click Exit to exit the Setup Wizard.
2. After reading the License Agreement, shown in Figure 4-2, click the Next button to
continue the installation, or click the Cancel button to end the installation.
Figure 4-2
3. The Setup Wizard will display a screen similar to that shown in Figure 4-3, asking you
to choose a wireless mode. Click the Infrastructure Mode radio button if you want your
wireless computers to network with computers on your wired network using a wireless
access point. Click the Ad-HocMode radio button if you want multiple wireless computers
to network directly with each other. Do not use Ad-Hoc mode if you want your wireless
computers to communicate with computers on your wired network.
In the SSID field, enter the SSID of your wireless network. The SSID must be identical for
all devices in the network.
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
Figure 4-3
4
Page 6

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
4. If you chose Infrastructure Mode, go to Step 5 now. If you chose Ad-HocMode, you’ll
see a screen similar to that shown in Figure 4-4. Select the correct operating channel for
your network from the Channel drop-down menu. Then, select the Network Mode from the
drop-down menu. Click the Next button, and go to Step 4. Click the Back button to change
any settings.
Channel - The channel you choose should match the channel set on the other devices in
your wireless network. If you are unsure about which channel to use, select the default
channel (Channel 6).
Figure 4-4
5. The Setup Wizard will ask you to review your settings (as in Figure 4-5) before it starts
to copy files. Click the Next button to save these settings, or click the Back button to
change any settings.
Figure 4-5
6. After the files have been successfully copied, the screen in Figure 4-6 will appear. Click
the Exit button.
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
Figure 4-6
5
Page 7
WPI-100G PCI Adapter
Driver Installation and Configuration for Windows XP
Driver Installation for Windows XP
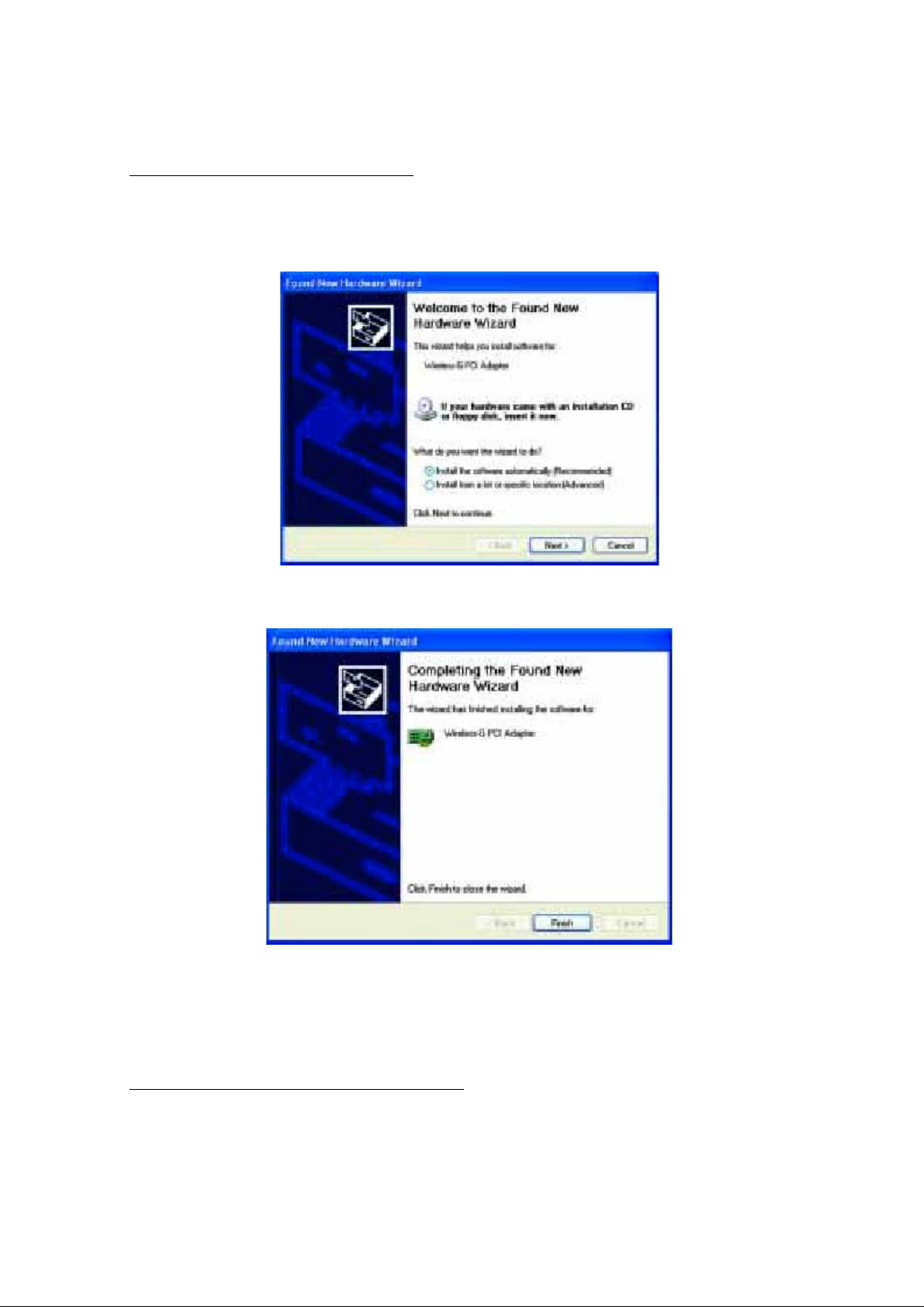
1. Windows XP will automatically detect the Adapter. Insert the Setup CDROM into the
CD-ROM drive and the screen in Figure 5-1 should appear. Click the radio button next to
Install the software automatically (Recommended). Then click the Next button.
Figure 5-1
2. When Windows has finished installing the driver, click the Finish button.
Figure 5-2
You have now completed the driver installation for the Adapter. To configure the
Adapter, proceed to the next section, “Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration.”
Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration
1. After installing the Adapter, the Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration icon will
appear in your computer’s system tray. Double click the icon.
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
6
Page 8
WPI-100G PCI Adapter
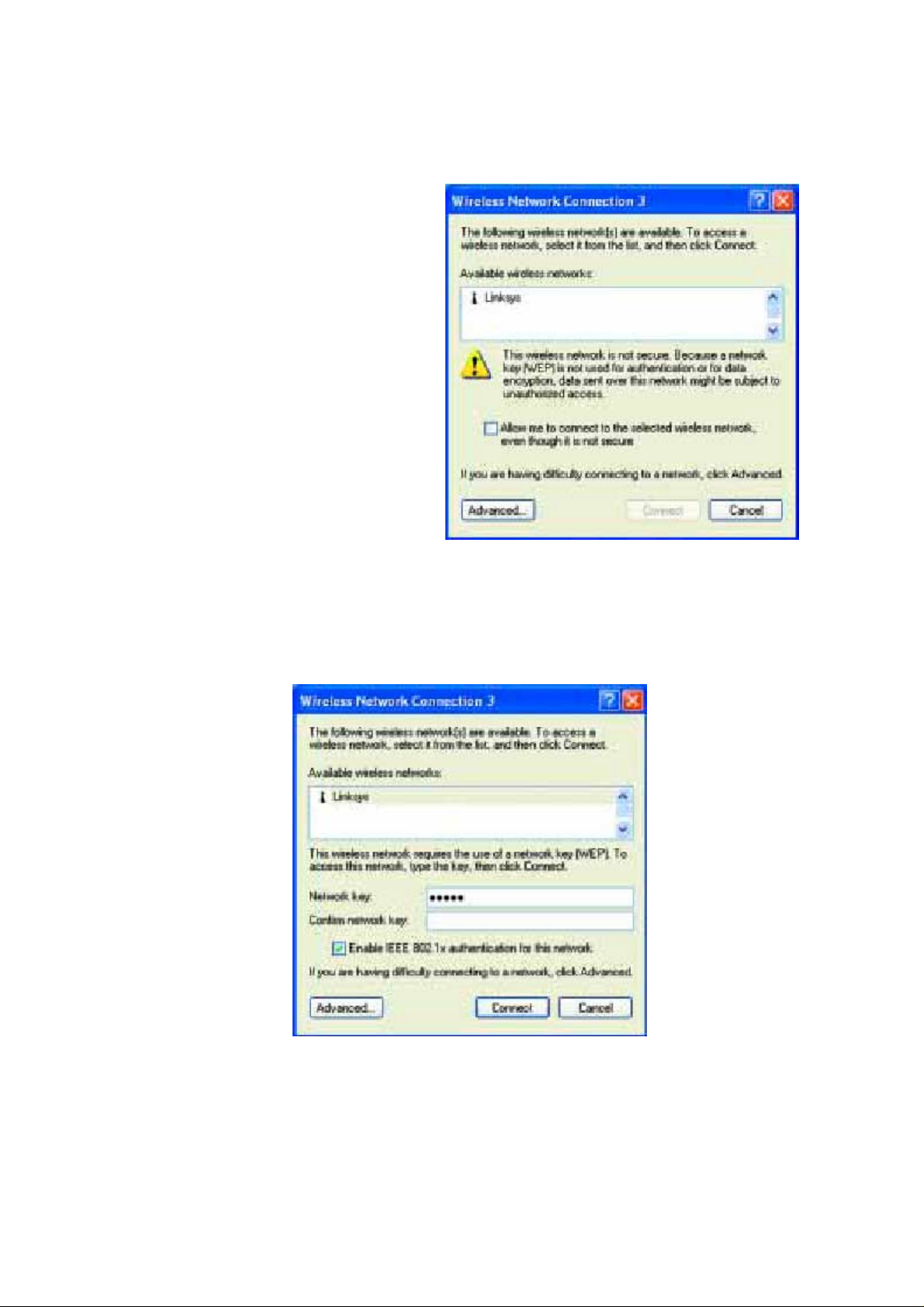
2. The screen that appears will show any available wireless network. Select the network
you want. If you have already enabled WEP encryption on your network, skip ahead
to step 3.
If you have NOT enabled WEP
encryption on your network, the screen
in Figure 5-3 will appear. Check the
box next to Allow me to connect to the
selected wireless network, even though
it is not secure. Then click the Connect
button and continue to step 4.
Figure 5-3
3. The screen in Figure 5-4 will appear. Enter the WEP key of your wireless network in the
Network key field, and re-enter it in the Confirm network key field. Then, click the
Connect button.
Your PC is now connected to your wireless network.
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
Figure 5-4
Congratulations!
7
Page 9

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
Troubshooting
Common Problems and Solution
This chapter provides solutions to problems that may occur during the installation and
operation of the Wireless-G PCI Adapter. Read the descriptions below to solve your
problems. If you can’t find an answer here, check the Gemtek website at
www.gemtek.com.tw
1. The Wireless-G PCI Adapter does not work properly.
• Reinsert the Wireless-G PCI Adapter into your PC’s PCI slot.
• Right click on My Computer and s elect Properties. Select the device mana ger and cl ick
on the Network Adapter. You will find the Wireless-G PCI Adapter if it is installed
successfully. If you see the yellow exclam ation mark, the resources are conflicting. You
will see the status of the Wireless-G PCI Adapter. If there is a yellow question mark,
please check the following:
• Make sure that your PC has a free IRQ (Interrupt ReQuest, a hardware interrupt on a PC.)
• Make sure that you have inserted the right adapter and installed the proper driver.
If the Wireless-G PCI Adapter does not function after attempting the above steps, remove
the adapter and do the following:
• Uninstall the driver software from your PC.
• Restart your PC and repeat the hardware and software installation as specified in this
User Guide.
2. I cannot communicate with the other computers linked via Ethernet in the
Infrastructure configuration.
• Make sure that the PC to which the Wireless-G PCI Adapter is associated is powered on.
• Make sure that your Wireless-G PC I Adapter is confi gured on the same cha nn el and with
the same security options as with the other computers in the Infrastructure configuration.
8. The Congratulations screen (Figure 7-15) will appear next. Click Activate new settings
now to implement the new settings immediately and return to the Link Information screen.
Click Activate new settings later to keep the current settings active, and return to the
Profiles screen so that you can edit your profile or create another profile.
Frequently Aske d Questions
Can I run an application from a remote computer over the wireless network?
This will depend on whether or not the application is designed to be used over a network.
Consult the application’s user guide to determine if it supports operation over a network.
Can I play computer games with other members of the wireless network?
Yes, as long as the game supports multiple players over a LAN (local area network). Refer
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
8
Page 10

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
to the game’s user guide for more information.
What is the IEEE 802.11b standard?
It is one of the IEEE standards for wireless networks. The 802.11b standard allows
wireless networking hardware from different manufacturers to communicate, provided that
the hardware complies with the 802.11b standard. Th e 802.11b standard states a max imum
data transfer rate of 11Mbps and an operating frequency of 2.4GHz.
What is ad-hoc mode?
When a wireless network is set to ad-hoc mode, the wireless-equipped computers are
configured to communicate directly with each oth er. The ad-hoc wi reless network will not
communicate with any wired network.
What is infrastructure mode?
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth for
unlicensed use in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band. Spectrum in the
vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made available wo rldwide. This presents a trul y
revolutionary opportunity to place convenient high-speed wireless capabilities in the hands
of users around the globe.
What is Spread Spectrum?
Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio frequency technique developed by the
military for use in reliable, secure, mission-critical communications sys tems. It is designed
to trade off bandwidth efficiency for reliability, integrity, and security. In other words,
more bandwidth is consumed than in the case of nar rowband transmission, but the tradeoff produces a signal that is, in effect, louder and thus easier to detect, provided that the
receiver knows the parameters of the spread-spectrum signal being broadcast. If a receiv er
is not tuned to the right frequency, a spread-spectrum signal looks like background noise.
There are two main alternatives, Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency
Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS).
What is roam ing?
Roaming is the ability of a portable computer user to communicate continuously while
moving freely throughout an area greater than that covered by a single access point. Before
using the roaming function, the workstation must make sure that it is the same channel
number with the access point of dedicated coverage area.
Would the information be intercepted while transmitting on air?
WLAN features two-fold protection in security. On the hardware side, as with Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum technology, it has the inherent securit y feature of scrambling.
On the software side, WLAN offers the encryption function (WEP) to enhance security
and access control.
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
9
Page 11

WPI-100G PCI Adapter
Specification
Standards: Draft 802.11g, 802.11b
Modulation: 802.11b: CCK (11 Mbps), DQPSK (2 Mbps),DBPSK (1 Mbps);
802.11g: OFDM
Channels: 802.11b, 11 Channels (USA) draft 802.11g 13 Channels (Europe)
14 Channels (Japan)
Network Protocol: TCP/IP, IPX, NDIS 4, NDIS 5, NDIS 5.1, NetBEUI
Interface: PCI
Transmit Power: 15 dBm
Sensitivity: -80 dBm
LED: ACT
WEP Key Bits: 64-Bit and 128-Bit
Dimensions: 4.8" x 8.66" x 0.91" (122 mm x 220 mm x 23 mm)
Unit Weight: 4.5 oz. (0.13 kg)
Power: 3.3V
Certifications: FCC
Operating Temp.: 32ºF to 150ºF (0ºC to 65ºC)
Storage Temp.: -40ºF to 185ºF (-40ºC to 85ºC)
Operating Humidity: 0% to 95%, Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity: 0% to 95%, Non-Condensing
Wireless Broadband Anywhere
10
Page 12

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit diff erent from that to which the receiver is
connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, any changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this
equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interf erence that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
 Loading...
Loading...