Page 1
Dual Radio 2.4GHz/5GHz Access Point
P-720
User’s Guide v1.0
Page 2

Within the 5.15 to 5.25 GHz band (5GHz radio channels 34 to 48) the U-NII devices
are restricted to indoor operations to reduce any potential harmful interference to
MSS operations.
FCC Warning
FCC Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could
void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator &
your body.
If this device is going to be operated in 5.15 ~ 5.25GHz frequency range, then it is restricted in indoor
environment only.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
P-720 is limited in CH1~CH11 for 2.4GHz by specified firmware controlled in U.S.A
Page 1 of 51
Page 3

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Contents
FCC Warning.......................................................................................................................................1
CONTENTS ............................................................................................................................................2
ABOUT THIS GUIDE..............................................................................................................................4
Purpose...............................................................................................................................................4
Prerequisite Skills and Knowledge......................................................................................................4
Conventions Used in this Document...................................................................................................4
CHAPTER 1 – INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................5
Product Overview................................................................................................................................5
Features Highlight...............................................................................................................................6
CHAPTER 2 - INSTALLATION..............................................................................................................8
The Product Package..........................................................................................................................8
Hardware Introduction.........................................................................................................................8
General Overview............................................................................................................................8
Bottom Cover...................................................................................................................................9
LEDs................................................................................................................................................9
Connectors.....................................................................................................................................10
Connect to the Power Source and Local Network ............................................................................11
Software Installation..........................................................................................................................12
Initialization....................................................................................................................................12
CHAPTER 3 – APPLICATION MODE .................................................................................................14
AP + AP Mode...................................................................................................................................14
AP + Bridge Mode.............................................................................................................................14
CHAPTER 4 – REFERENCE MANUAL...............................................................................................16
Web Interface....................................................................................................................................16
Status ................................................................................................................................................17
Status | Device Status ...................................................................................................................17
Status | Wireless Status.................................................................................................................17
Network .............................................................................................................................................18
Network | Interface.........................................................................................................................18
Network | RADIUS Server .............................................................................................................20
Network | DHCP Settings ..............................................................................................................21
Wireless.............................................................................................................................................26
Wireless | Basic .............................................................................................................................26
Wireless | Advance........................................................................................................................30
Wireless | WEP..............................................................................................................................35
Wireless | MAC ACL......................................................................................................................36
System...............................................................................................................................................39
System | Security...........................................................................................................................39
System | SNMP..............................................................................................................................39
System | Telnet..............................................................................................................................41
System | Configuration ..................................................................................................................41
System | Reset...............................................................................................................................43
System | Upgrade..........................................................................................................................43
APPENDIX............................................................................................................................................45
A) Specification .................................................................................................................................45
B) Factory Defaults for the P-720......................................................................................................46
Page 2 of 51
Page 4

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
C) Regulatory Channels/Power ...........................................................................................46
D) Location ID and ISO Country Codes............................................................................................48
Page 3 of 51
Page 5
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
About this Guide
Purpose
This document provides information and procedures on hardware installation, setup, configuration,
and management of the high performance Dual Radio 2.4GHz/5GHz AP P-720.
Prerequisite Skills and Knowledge
To use this document effectively, you should have a working knowledge of Local Area Networking
(LAN) concepts and wireless Internet access infrastructures. In addition, you should be familiar with
the following:
Hardware installers should have a working knowledge of basic electronics and mechanical
assembly, and should understand related local building codes.
Network administrators should have a solid understanding of software installation proced ures for
network operating systems under Microsoft Windows 95, 98, Millennium, 2000, NT, and Windows
XP and general networking operations and troubleshooting knowledge.
Conventions Used in this Document
The following typographic conventions and symbols are used througho ut this document:
Very important information. Failure to observe this may result in damage.
Important information that should be observed.
bold
code
<value>
[value]
Additional information that may be helpful but which is not required.
Menu commands, buttons and input fields are displayed in bold
File names, directory names, form names, and system-generated output
such as error messages are displayed in constant-width type
Placeholder for certain values, e.g. user inputs
Input field format, limitations, and/or restrictions.
Page 4 of 51
Page 6

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Chapter 1 – Introduction
Thank you for choosing the Dual Radio Access Point P-720.
The P-720 operates simultaneously in the 5-GHz and 2.4-GHz frequency bands and is fully compliant
to 802.11b/g and 802.11a standard with its high performance and enhance d security.
The two Dual-Band radio (a/g + a/g) that this product provides supplies the furthest in flexibility and
makes sure low interference and large coverage. The a+g operation mode and Multiple BSSID that
this product provides differentiates it from traditional indoor AP product.
Product Overview
Flexibility and high performance
The P-720 is a high performance indoor AP for multiple service. The two dual-band radios and
AP/Bridge working mode supply the furthest flexibility for wireless applications:
z Simultaneously supports 802.11a/b/g in one platform
z Dual AP configuration for high client density environment
z Dual AP configuration for supporting all kinds of client (11a/b/g) simultaneously
z Dual Bridge configuration for wireless repeating and wireless bridging areas
Secure and reliable wireless networking
The P-720 supplies multiple methods to protect the wireless network:
z Supports VLAN, up to 16 VLAN tagging
z IEEE 802.1x/EAP with certificates and SIM card (EAP/TLS, EAP/PEAP, EAP/SIM and
EAP/TTLS)
z 64bits/128bits static and dynamic WEP key
z WPA(TKIP and AES)
z WPA2
z Layer 2 Isolation for preventing snooping on the same BSS
z MAC ACL for preventing illegal attacking from Internet
Multiple BSSID
Supports up to16 BSSID, each BSSID can be configured independently, such as Multiple SSID,
security policy, authentication method, RADIUS server and VLAN tag. With this, P-720 can supply
multiple services, including multiple VLAN partition and multiple security policy.
Simple Installation
Support IEEE 802.3af Power-over-Ethernet as well as external power supply by power adaptor. This
reduces the cost and the effort of installation and maintenance dramatically.
Easy remote management and maintenance
Page 5 of 51
Page 7

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
The P-720 can be remote managed by HTTPs, CLISH and SNMP.
z Web-based user interface based on HTTPs and CLISH config uration based on SSHv2 supplies
secure remote management
z NMS product supplies the system management solution
z DHCP Server/DHCP Relay service supplies flexibility for different network setup
z Remote software upgrading via HTTPs
Management Option
You can use the Access Point management systems through the following interfaces:
Web-browser interface
Command Line interface (CLI) with optional SSH
Simple Network Management Protocol
P-720 management system pages are organized the same way for the web-browser interface and the
CLI. This user manual provides detailed description of each management option.
with HTTPS
Features Highlight
Super AP
Multiple BSSID (up to 16)
SSID per BSSID
Enabled or Disabled Hidden SSID per BSSID
VLAN ID per BSSID
AAA way per BSSID, 802.1x and web login
Co-existence of 802.1x and web login
Security policy per BSSID
WPA pass-through
RADIUS server per BSSID
AAA
RADIUS client supporting
802.1x supporting(EAP/TLS,EAP/TTLS, EAP/PEAP and EAP/SIM)
Security
Static 64/128bits WEP, Dynamic 64/128bits WEP
WPA/TKIP and WPA/AES support
MAC ACL
Access Control (accept rule and deny rule) based on MAC addre ss
Layer 2 Isolation
Hidden SSID
Management
Secure management via HTTPS, CLISH, SNMP
Standard MIB
Remote firmware update via WEB UI
Backup/Restore configuration file
Page 6 of 51
Page 8

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
DHCP Server
Super Brige
802.11a/b/g compliant
108Mbps raw data rate supporting
Up to 8 bridge links supporting
Special radio for Bridge
WPA/PSK over Bridge link
Page 7 of 51
Page 9

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Chapter 2 - Installation
This chapter provides installation instructions for the hardware and software components of the
Access Point P-720. It also includes the procedures for the following tasks:
Hardware Introduction (LEDs, Connectors)
Connecting the Access Point
First Configuration
The Product Package
The product comes with the following:
Dual Radio Access Point (model: P-720)
Screw Bag for Mounting Kit
Antenna (Dual-band Dipole Antennas with TNC plug connector, 2 units)
Ethernet patch cable (Cat5 UTP, 1.8m length, 1 unit)
External power supply (Input:100-230VAC, 50-60Hz, Output: 12VDC, 1 unit)
Installation CD containing:
P-720 User Guide in PDF format
Product Firmware
Release Notes
Adobe Acrobat Readers
Readme
Printed Release Note
Hardware Introduction
General Overview
Figure 1 – P-720 General View
The front panel of P-720 contains:
There are 4 indicator lights (LEDs) that help to describe the state of various networkin g and
connection operations.
The Bottom cover of P-720 contains:
Connectors which enable you to make different network connections for the device
Reset button enables you to reboot or reset the device configuration to the factory defaults
Press the Reset button for less than 5 seconds to reboot the device.
Press the Reset button for more than 5 seconds to set the device to factory
Page 8 of 51
Page 10
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
defaults.
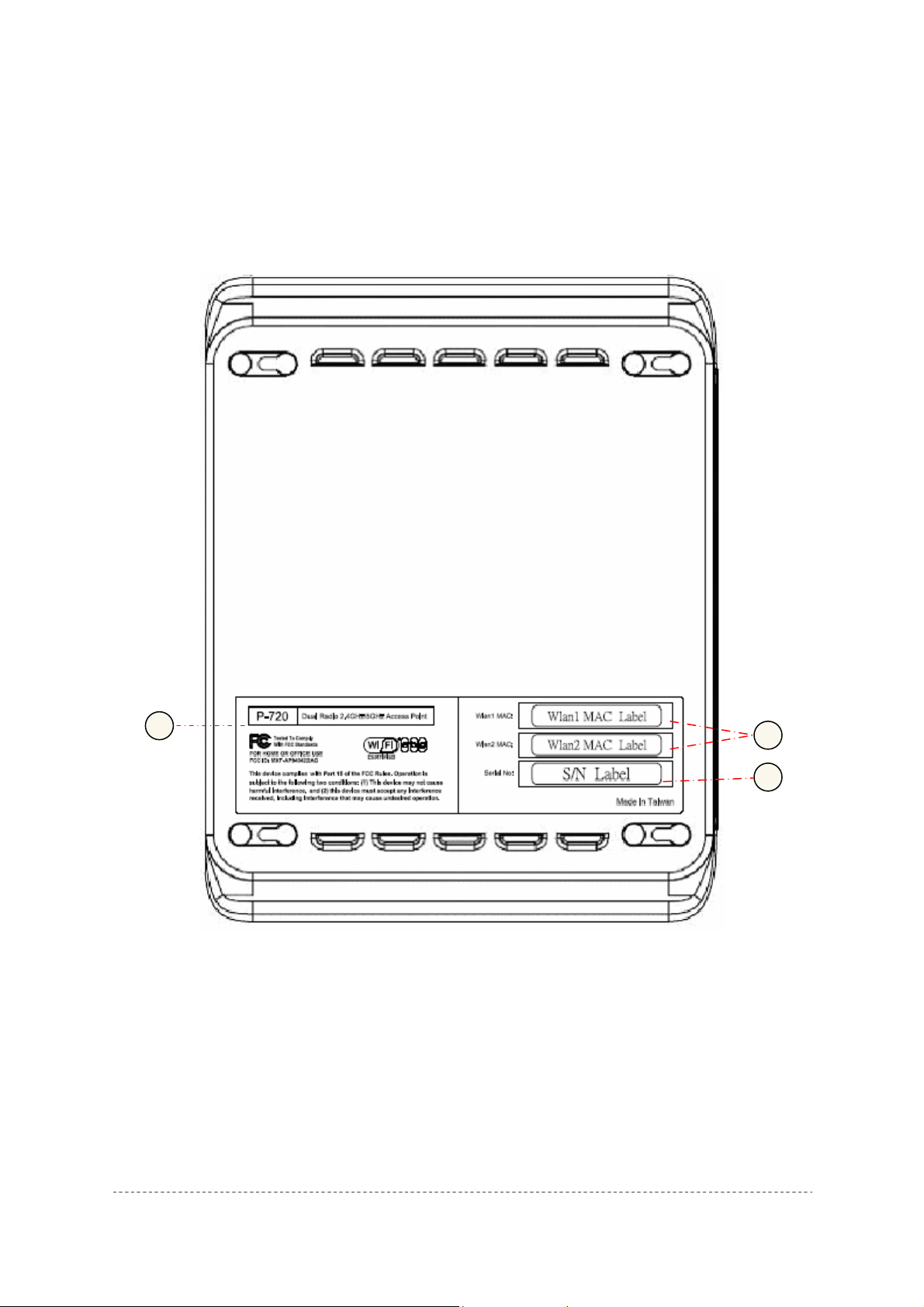
Bottom Cover
1
Figure 2 –Bottom Cover of the P-720
The Bottom Cover of the P-720 contains:
1. Back Label with Model and Device name. The official device name is Dual Radio 2.4GHz/5GHz
Access Point, model P-720.
2. MAC address labels of the device. The two labels show the WLAN1 and WLAN2 interface MAC
address of the device.
3. Serial Number label of the device.
2
3
LEDs
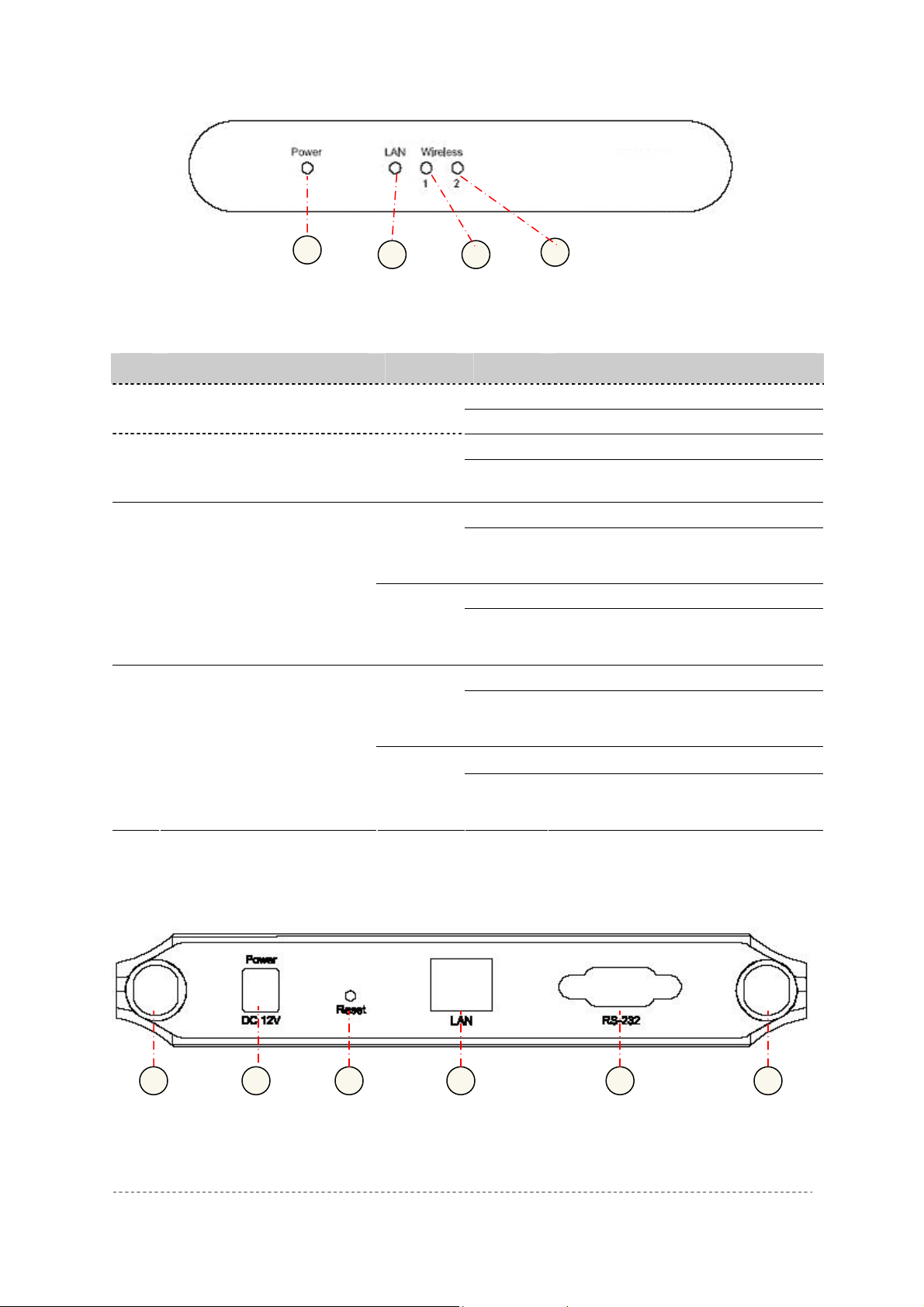
The P-720 Access Point has 3 LEDs located on the front panel:
Page 9 of 51
Page 11
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
1
Figure 3 – LEDs of the P-720
The various states of the LEDs indicate different networking and connection operations as follows:
2 3
4
Item LED Color Status Indication
On P-720 is active/working 1 Power Green
Blink P-720 is booting
On P-720 Ethernet Port Link Active 2 LAN Green
P-720 Ethernet Port is Transmitting
and Receiving data
P-720 WLAN1 RF card is
Transmitting and Receiving data
P-720 WLAN1 RF card is
Transmitting and Receiving data
P-720 WLAN2 RF card is
Transmitting and Receiving data
P-720 WLAN2 RF card is
Transmitting and Receiving data
3 Wireless1
4 Wireless2
(802.11g
module is
functional)
Amber
(802.11a
module is
functional)
(802.11g
module is
functional)
Amber
(802.11a
module is
functional)
Blink
On P-720 WLAN1 RF card Active Green
Blink
On P-720 WLAN1 RF card Active
Blink
On P-720 WLAN2 RF card Active Green
Blink
On P-720 WLAN2 RF card Active
Blink
Connectors
The P-720 has several connectors on the rear panel:
1 23 4 5 6
Figure 4 –RF Connectors
Descriptions of the connectors are given in the following table:
Page 10 of 51
Page 12
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Item Connector Description
1 WLAN1 For WLAN1 RF card connecting to Antenna
2 WLAN2 For WLAN2 RF card connecting to Antenna
3 Power For power supply
4 Reset Reboot or reset to factory defaults.
Press the reset button for less than 5 seconds to reboot the
Access Point. Press the reset button for more than 5
seconds to set the Access Point to factory defaults.
5 LAN To your company LAN
6 Console For console connection
Connect to the Power Source and Local Network
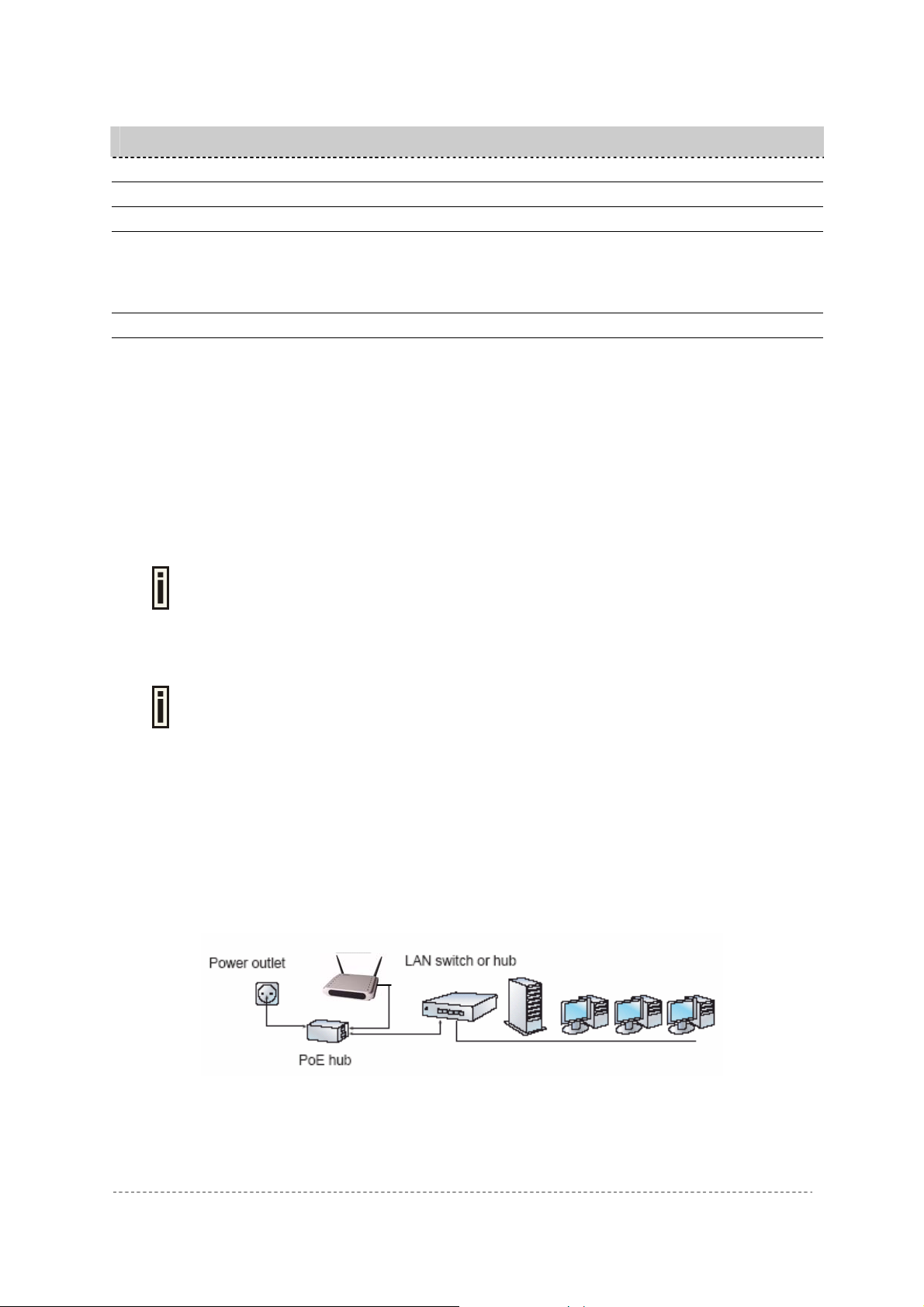
There are two power supply methods can be used by P-720:
♦ Power-over-Ethernet equipment
♦ External Power Supply
Case 1 Use the Power-over-Ethernet Equipment:
Use the enclosed power cord or any IEEE802.3af Compliant POE Power Source
Devices to supply your P-720 Access Point.
Step 1 Place the Access Point on a flat work surface or hang on the wall.
Use the enclosed 4 screws to put the rear side of the Access Point hanging on the
wall.
Step 2 Connect the Ethernet cable from the P-720 route to an IEEE802.3-2003 compliant Power
source Equipment.
Step 3 If you use a POE HUB, please connect the P-720 LAN port to the PWR-LAN OUT port of
the POE HUB and connect the LAN-IN port of the POE HUB to the Switch or hub in the
local network.
Figure 5 – Connecting P-720 to Power source and network by PoE HUB
Case 2 Use External Power Supply
Page 11 of 51
Page 13
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Step 1 Place the Access Point on a flat work surface or hang on the wall.
Step 2 Use the enclosed Ethernet patch cable to connect the LAN port of the Access Point to the
Switch or hub in the local network.
Step 3 Connect the power supply to the Access Point.
Software Installation
Initialization
For the first web browser connection to your P-720, please use your Web browser
The default network settings for your new access point are:
LAN port: IP 192.168.2.2 subnet 255.255.255.0
Step 1 Configure your PC with a static IP address on the 192.168.2.0 subnet with mask
255.255.255.0. Connect the P-720 in to the same physical network as your PC. Open
the Web browser and type the default IP address of the P-720:
https://192.168.2.2
Step 2 Enter the P-720 administrator login details to access the Web management.
The default administrator log on settings for all access point interfaces are:
User Name: admin
Password: admin01
Page 12 of 51
Page 14
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Step 3 After successful administrator log on you will see the main page of the P-720’s Web
interface:
Now you are enabled to perform your configuration.
Page 13 of 51
Page 15
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Chapter 3 – Application Mode
The two Dual-Band chips (a/g + a/g) that this product provides supplies the furthest flexible
application. Three application modes are supplied by P-720:
z AP + AP mode
z AP + Bridge mode
AP + AP Mode
AP + AP configuration can be for client density environment.
The typical usage is: 11g AP + 11a AP.
Figure 6 – AP +AP application mode
AP + Bridge Mode
AP + Bridge configuration is for environment with last mile issue.
The typical usage is: 11g AP + 11a Bridge.
Page 14 of 51
Page 16

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 7 – AP +Bridge application mode
Page 15 of 51
Page 17
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Chapter 4 – Reference Manual
This chapter contains web management reference information.
The web management main menu consists of the following sub menus:
Status
Network – device settings affecting networking
Wireless – device settings related to the wireless part of the P-720
System – device system settings directly applicable to the P-720
Exit – click exit and leave the web management then close your web-browser window.
– device status showing
Web Interface
The main web management menu is displayed at the top of the page after successfully logging into
the system (see the figure below). From this menu all essential configuration pages are accessed.
Figure 8 – Main Configuration Management Menu
The web management menu has the following structure:
Status
Device Status – show the status related with the whole device
Wireless Status – show the status of the two radios
Network
Interface – TCP/IP settings of P-720 LAN (Bridge) port
RADIUS Server – specify the settings of RADIUS server which is used by 802.1x or WPA
DHCP Settings– specify the settings of DHCP server or DHCP relay service
Wireless
Basic
– specify the basic settings related with wireless part
Advance
WEP – specify the WEP settings related with static WEP encryption
MAC ACL – MAC ACL settings for P-720
System
Security – set access permission to your P-720
SNMP – SNMP service
Telnet
Configuration
Reset – reboot device and restore systems to factory default
Upgrade – Upgrade the firmware remotely
In the following sections, short references for all menu items are presented.
– specify the settings of multiple BSSID or Bridge
– Telnet/SSH service
– system configuration utilities, including Backup/Upload configuration
Page 16 of 51
Page 18
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Status
Status | Device Status
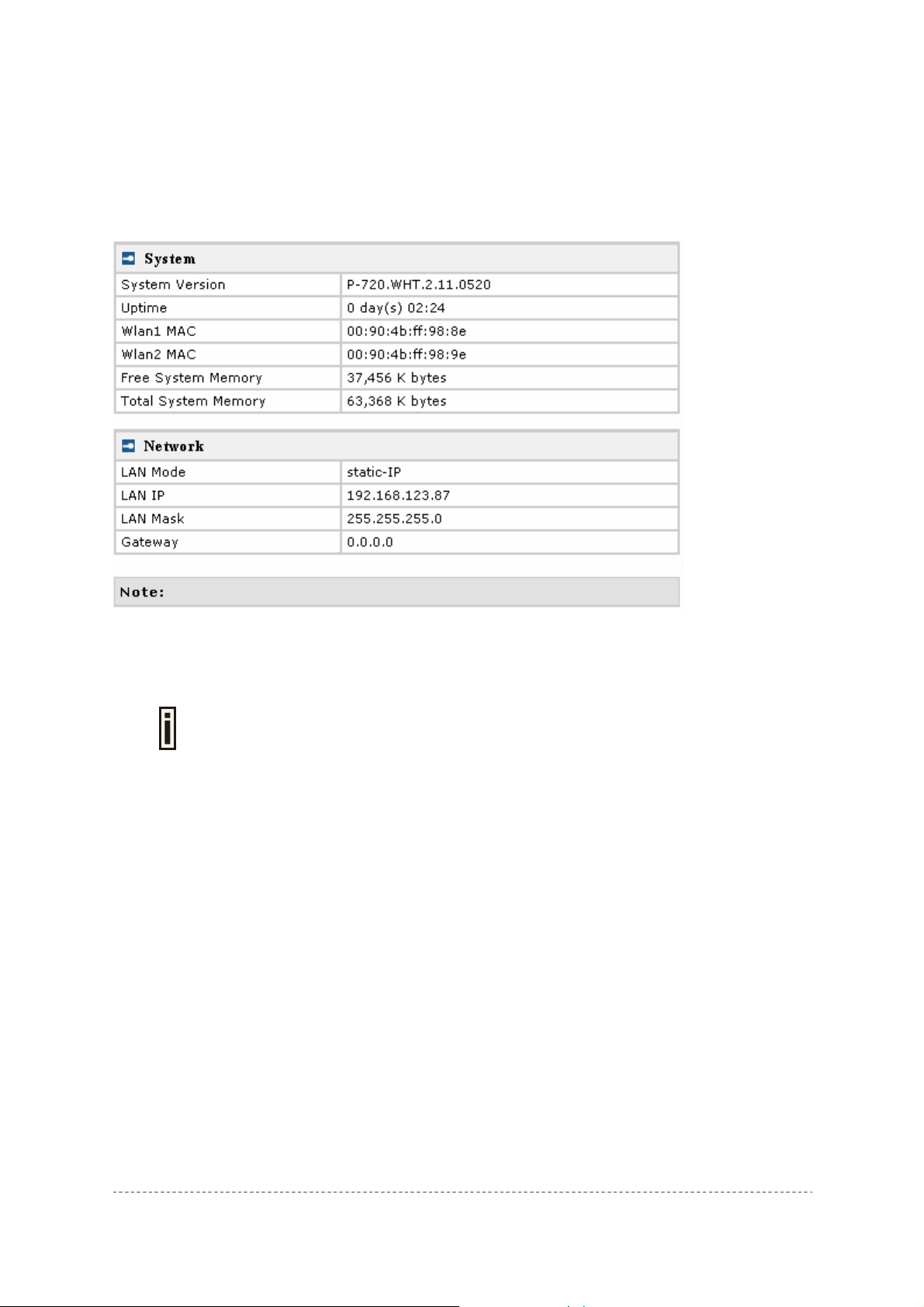
The device status page shows important information for the P-720, its system status and network
configuration.
Figure 9 – Device Status
System Version display the current version of the firmware loaded to the AP
This is important information for support requests and for preparing firmware
Uptime indicates the time, expressed in days, hours and minutes since the system was last rebooted.
Wlan1 MAC / Wlan 2 MAC shows the MAC addresses of the two wireless interfaces of the P-720
Free System Memory indicates the memory currently available in the P-720
Total System Memory indicates the total memory in the P-720
LAN Mode indicate static IP or DHCP client is used for P-720 LAN IP address
LAN IP shows the LAN IP address of P-720
LAN Mask shows the LAN Network Mask of P-720
Gateway shows the default gateway of P-720
upgrading
Status | Wireless Status
The wireless status shows the information related with P-720 two wireless interfaces.
Page 17 of 51
Page 19

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
US
US
Figure 10 – Wireless Status
Radio1 / Radio2 relates with two wireless interfaces
Channel indicates which channel is in use.
Mode AP or Bridge mode is be used for this wireless interface
Band specify which band is in use for wireless interface
Layer2 Isolation specify the status of Layer2 Isolation service on this wireless interface
Total Connected Clients indicates number of the currently connected clients to your P-720
Antenna Gain indicates antenna Gain value.
Total Output Power (EIRP) indicates EIRP value set to the P-720
MAC ACL indicates the status of MAC ACL feature on P-720
Network
Network | Interface
The interface configured is bridge device therefore only one interface is displayed
here for configuration.
Bridge interface and its settings are listed in the Interface page.
Page 18 of 51
Page 20
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
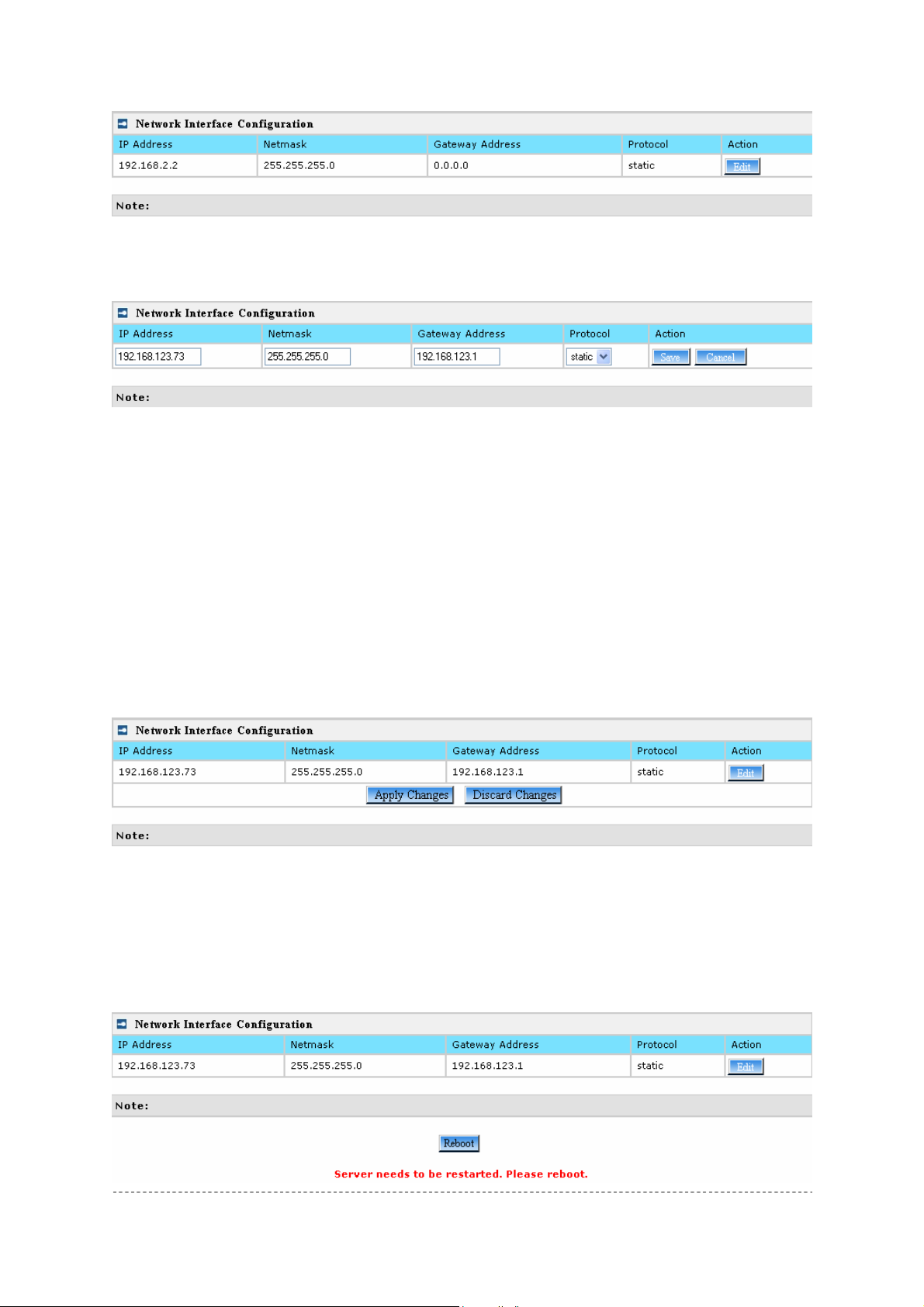
Figure 11 – Interface Configuration Table
To change network interface (bridge) configuration properties clic k the Edit button in the Action
column. The status can be changed now:
Figure 12 – Edit Interface Configuration Settings
IP Address - specify new interface IP address [in digits and dots notation, e.g. 192.168.123.70].
Netmask – specify the subnet mask [[0-255].[0-255].[0-255].[0-255]].These numbers are a binary
mask of the IP address, which defines IP address order and the number of IP addresses in the subnet.
Gateway Address – interface gateway. For Bridge type interfaces, the gateway is always the
gateway router.
Protocol – specify static for setting IP address manually and dhcp for getting IP address dynamically
acting as DHCP client.
Save – save the entered values.
Cancel – restore all previous values.
Change status or leave in the default state if no editing is necessary and click the Save button.
Figure 13 – Apply or Discard Interface Configuration Changes
Apply Changes – to save all changes in the interface table at once.
Discard Changes – restore all previous values.
For such each change of settings, the P-720 needs to be restarted to apply all settings changes when
clicking Apply Changes. Request for reboot server appears:
Page 19 of 51
Page 21

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 14 – Reboot Server
Reboot – Click the button to restart the server and apply the changes.
If there is no other setting needed to be modified, click the Reboot button for
To reboot at once, click Reboot button and then it is necessary to wait a moment. And the message
of reboot appears just like bellows:
applying all modifications.
And if there are still other setting modifications needed, go ahead to finish all
changes and then click Reboot button to restart and apply all settings together.
Figure 15 – Reboot Information
Network | RADIUS Server
Up to 32 different RADIUS servers can be configured under the RADIUS servers
By default, one RADIUS server is specified for the system:
Page 20 of 51
menu.
Page 22

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 16 – RADIUS Servers Settings
Add – add new RADIUS server.
Click Add to configure RADIUS server settings.
Figure 17 – RADIUS Server's Details
Name – specify the new RADIUS server name which is used for selecting RADIUS server.
Server IP – authentication RADIUS server IP address [dots and digits].
Server Port – specify the network port used to communicate with RADIUS [1-65535].
The port default value of 1812 is based on RFC 2138 "Remote Authentication Dialin User Service (RADIUS)".
Secret – shared secret string that is used to make sure the integrity of data frames used for
authentication server.
Save – add new specified RADIUS server.
Cancel – restore all previous values.
After adding a new RADIUS server or editing an existing one, the following control appears:
Edit – edit an existing RADIUS server settings
Delete – delete an existing RADIUS server settings
Reboot – restart the controller to make applied changes work.
If there is no other setting needed to be modified, click the Reboot button for
applying all modifications.
And if there are still other setting modifications needed, go ahead to finish all
changes and then click Reboot button to restart and apply all settings together.
Network | DHCP Settings
P-720 can act as DHCP server or DHCP relay. The DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
service is supported on physical interfaces.
Page 21 of 51
Page 23

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
DHCP server and DHCP relay is disabled by default.
Figure 18 –DHCP Settings
Edit – edit the wireless basic settings
To change DHCP setting properties click the Edit button, the DHCP server or DHCP relay service
should be configured:
Figure 19 –DHCP Settings
Status – Select status from the drop-down menu.
Disabled – Disable the DHCP server service.
DHCP Server – Enable the DHCP server service.
DHCP Relay – Enable the DHCP Relay service.
Choose DHCP Server to enable DHCP server service. Choose DHCP Relay to enable DHCP relay
service.
DHCP Server
This DHCP server service enables clients on the LAN to request configuration information, su ch as IP
address, from a server. Settings of the DHCP service can be viewed just like the follow page.
Figure 20 –DHCP server Settings
Page 22 of 51
Page 24

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
By default, DHCP server is disabled for P-720.
IP Address from / IP Address to – specify the IP address range to be dynamically allocated by the
DHCP server.
Netmask – enter the netmask for IP pool range.
Gateway – enter the gateway IP for wireless clients.
WINS Address (Windows Internet Naming Service) – specify server IP address if it is available on the
network [dots and digits].
Lease Time – specify the IP address lease interval in seconds [1-1000000].
DNS address – specify the DNS server’s IP address [in digits and dots notation].
DNS secondary address – specify the secondary DNS server’s IP address [in digits and dots
notation].
Change status or leave in the default state if no editing is necessary and click the Save button.
Figure 21 –Apply or Discard DHCP server Settings
The DHCP server settings will be automatically adjusted to match the network
For each change of settings, the P-720 needs to be restarted to apply all settings changes when
clicking Apply Changes. Request for reboot server appears:
interface settings.
The Gateway of DHCP server settings must be same with the Gateway of P-72 0
Page 23 of 51
Page 25

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 22 – Reboot information
Reboot – Click the button to restart the server and apply the changes.
If there is no other setting needed to be modified, click the Reboot button for
When P-720 uses DHCP to get IP address, the similar WEB UI will be appears:
applying all modifications.
And if there are still other setting modifications needed, go ahead to finish all
changes and then click Reboot button to restart and apply all settings together.
When P-720 network Interface uses DHCP to get IP address dynamically, DHCP
server service cannot be enabled.
Figure 23 – Warning information
Page 24 of 51
Page 26

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
DHCP Relay
To route DHCP through the external server, enable the DHCP Relay service.
Figure 24 – DHCP Relay settings
Server IP: enter the IP address of the external DHCP server.
Change status or leave in the default state if no editing is necessary and click the Save button.
Figure 25 –Apply or Discard DHCP relay Settings
For each change of settings, the P-720 needs to be restarted to apply all settings changes when
clicking Apply Changes. Request for reboot server appears:
Figure 26 – Reboot information
Reboot – Click the button to restart the server and apply the changes.
If there is no other setting needed to be modified, click the Reboot button for
applying all modifications.
And if there are still other setting modifications needed, go ahead to finish all
changes and then click Reboot button to restart and apply all settings together.
Page 25 of 51
Page 27
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Wireless
Wireless | Basic
Use the wireless | Basic menu to configure such wireless settings as regulatory channel,
band, and power, layer2isolation. Click the edit button on the setting you need to change:
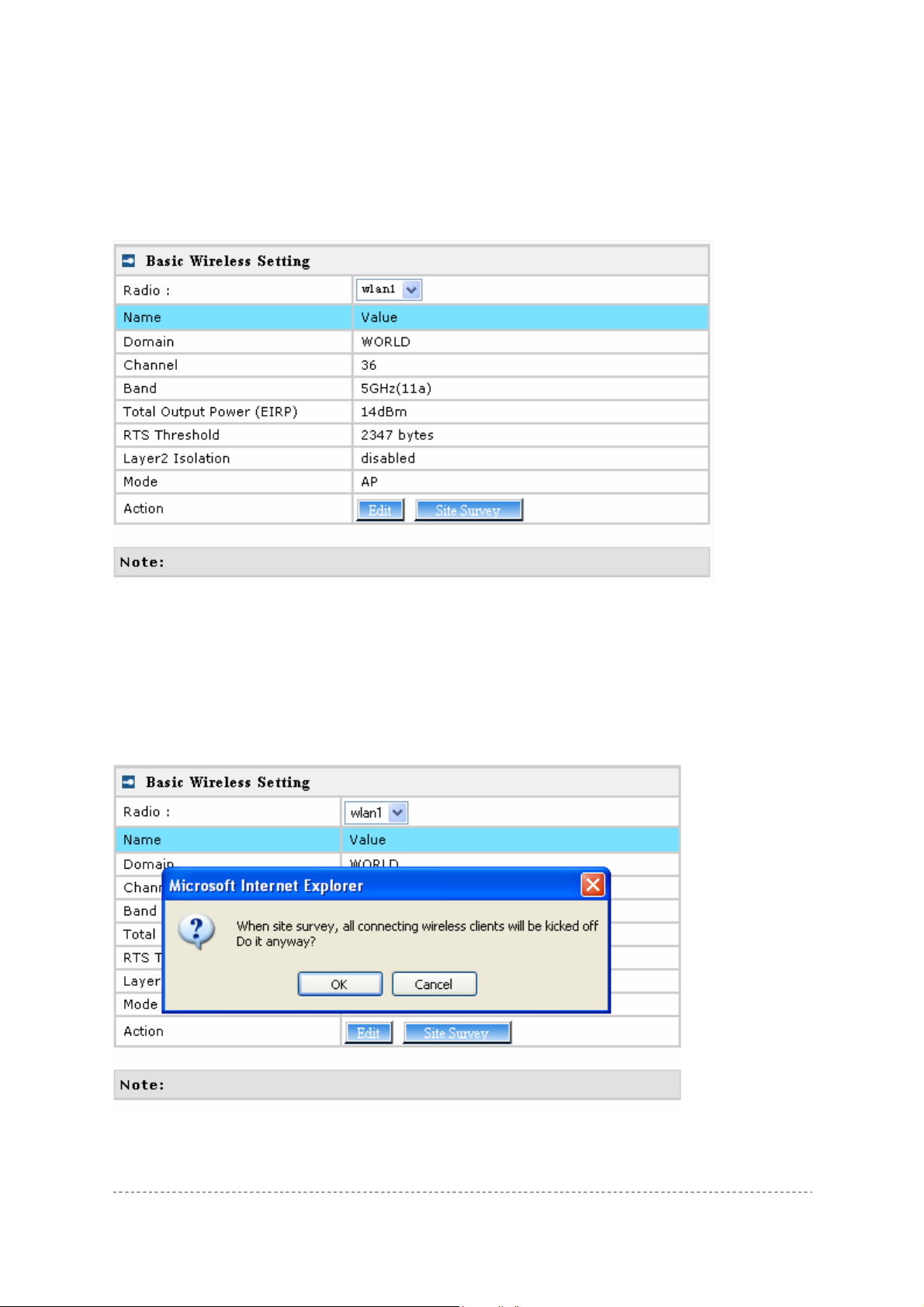
Figure 27 – Basic Wireless Settings
Site Survey –perform survey to show overview information for wireless networks in a local geography.
The site survey shows overview information for wireless networks in a local geographic area. Using
this survey, administrator can scan for working access points, check their operating channels, and see
RSSI levels. To start the scan, simply click the Site Survey menu.
After clicking Site Survey, you will get the follow warning:
Figure 28 – Site Survey warning
Page 26 of 51
Page 28

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
US
Click OK to continue site survey and get the similar UI:
Figure 29 – Site Survey information
To refresh the statistics click the Rescan button.
During Site Survey, all wireless clients which are connecting with P-720 would be
kicked off.
Site Survey takes some minutes to perform. Please wait and don’t power off AP
during site survey.
Edit – edit the wireless basic settings
To change basic wireless setting properties click the Edit button in the Action column. The status
can be changed now:
Figure 30 – Edit Basic Wireless Settings
Change status or leave in the default state if no editing is necessary and click the Save button.
Page 27 of 51
Page 29

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 31 – Apply or Discard Basic Wireless Settings
Radio – specify which wireless interface of P-720 is shown
Channels – select the channel that the access point will use to transmit and receive information. If
one channel is defined, it acts as default channel. Channels list will vary depending on selected
regulatory selected band. Multiple frequency channels are used to avoid interference
between two radios of this AP, and between nearby access points. If you wish to operate more than
one access point in overlapping coverage areas, we recommend a distance of at least four channels
between the chosen channels. For example, for three Access Points in close proximity choose
channels 1, 6 and 11 for 11b/g or channels 36, 40 and 64 for 11a.
Band – working bands on which your radios are working.
Six bands are supplied: 5GHz(11a), 5GHz(Turbo Mode 11a), 2.4GHz(Mixed 11g), 2.4GHz(1 1g
only), 2.4GHz(Mixed 11g WiFi) and 2.4GHz(11g only WiFi).
If 2.4GHz(Mixed 11g) or 2.4GHz(11g only) is selected, the radio will work on 2.4GHz for a better
performance. 2.4GHz (11g only) mode only allows 11g client access. 2.4GHz(Mixed 11g) mode
allows 11b/11g client access.
2.4GHz(Mixed 11g WiFi) or 2.4GHz(11g only WiFi) can make sure to compatible with Wi-Fi.
If 5GHz (11a) or 5GHz(Turbo Mode 11a) is selected, the radio will work on 5GHz 11A mode.
5GHz(Turbo Mode 11a) can supply 108 raw data rate.
Only under Bridge mode, Turbo Mode 11a can be set.
Page 28 of 51
Page 30

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
FCC
US
Total Output Power (EIRP) – the P-720 transmission output power (EIRP) in dBm. Seven levels are
specified: 17dBm, 16dBm, 15dBm, 14dBm, 10dBm, 4dBm and 0dBm. Default is 14dBm.
Total Output Power (EIRP) = Antenna Gain + RF card output power
The range of the EIRP varies with channel.
RTS Threshold – when set, this settings specifies the maximum packet size beyond which RTS/CTS
mechanism is be invokes. The value range of this is [0 …2347]. Default is 2347 which means that
RTS is disabled.
Layer 2 Isolation – Layer2 wireless client separation. Connected clients with user isolation function
enabled cannot access each other directly. The clients are isolated from each other using their MAC
addresses [enabled/disabled].
Mode – two modes are supplied: AP mode and Bridge mode.
For such each change of settings, the P-720 needs to be restarted to apply all settings changes when
clicking Apply Changes. Request for reboot server appears:
Figure 32 – Reboot Server
Reboot – Click the button to restart the server and apply the changes.
If there is no other setting needed to be modified, click the Reboot button for
applying all modifications.
And if there are still other setting modifications needed, go ahead to finish all
changes and then click Reboot button to restart and apply all settings together.
Page 29 of 51
Page 31

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Wireless | Advance
P-720 supports Multiple BSSID (MBSSID) function. You can configure up to 16 BSSIDs per radio on
P-720 and assign different configuration settings to each BSSID. For wireless users, they can think P720 as single AP with multi service supporting, including different security policy, different VLAN ID,
different authentication etc. All the BSSIDs are active at the same time that means client devices can
associate to the access point for specific service. Use the Wireless | Advance menu to configure
properties related to Multiple BSSID, including configure SSID, Hidden SSID, VLAN, and Security for
each SSID.
Each BSSID can have its own SSID. In this case, Multiple BSSID is the same with
Also, P-720 supports Bridge function, it can support up to 8 Bridge links per radio. Different bridge
link can use different WEP key index.
AP Mode:
Multiple ESSID. Wireless users can think P-720 as multiple virtual APs, each
supporting different service, and connects one SSID for the special services.
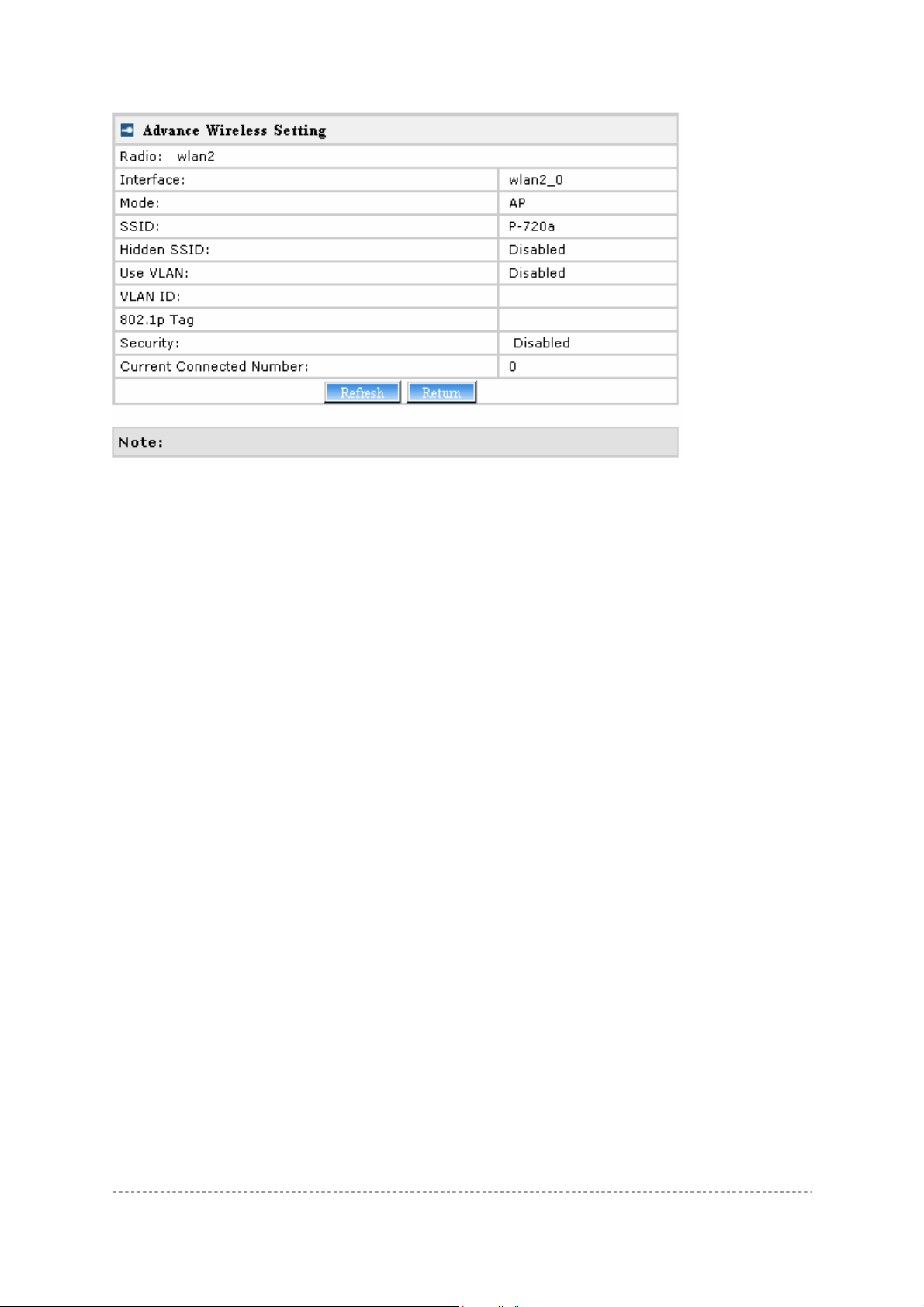
Figure 33 – Advanced Wireless Setting (AP Mode)
Radio – specify which RF card (wlan1 or wlan2) is needed to be configured since P-720 has two
Dual-Band radios
Mode – specify the operation mode of P-720 (AP or Bridge)
Interface – Choose the specified MBSSID entry you want to configure. Each Interface maps to a
BSSID
Hidden – Show the status of Hidden SSID feature
Security – Show which security policy is used for this MBSSID entry
Current Connect # – Show the number of current wireless clients who are connecting with this
MBSSID
New – Create a new MBSSID entry
Detail – Show the detail information of this MBSSID entry
Edit – Edit the selected MBSSID entry you want to configure
Delete – Delete the selected MBSSID entry. When in AP mode, you can not delete the last entry
Clicking Detail, a similar page will be appears as below:
Page 30 of 51
Page 32
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 34 – Detail for MBSSID entry
Detail – Show the MAC address of current connected clients
Return – Return to the wireless advance settings page
Clicking New or Edit on AP mode, the settings of MBSSID entry appears:
Page 31 of 51
Page 33

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 35 – Multiple BSSID Setting
Radio – showing which RF card (wlan1 or wlan2) is being configured.
Mode – showing the current operation mode of P-720 (AP or Bridge).
Interface – showing the current MBSSID | Bridge link entry
SSID – a unique ID for your wireless network. It is case sensitive and must not exceed 32 characters.
The default SSID is "P-720" but you should change this to a personal wireless network name. The
SSID is important for clients when connecting to the access point. All client stations must have their
client SSID settings configured and must use the same SSID.
Each MBSSID entry (BSSID) can has its own SSID. And SSID can be same for
different BSSID
Hidden SSID – When enabled, the SSID of this Interface is invisible in the networks list while
scanning the available networks for wireless client (SSID is not broadcasted with its Beacons). When
disabled, the AP’s SSID is visible in the available network list [enabled/disabled]. By default the
Hidden SSID is disabled.
Use VLAN – When enabled, the outgoing packets from this SSID device will be tagged with VLAN ID
and 802.1p tag (If have).
VLAN ID – Configure VLAN ID for each Multiple SSID devices. Valid numbers are from 1 to 4094.
Page 32 of 51
Page 34

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
802.1p Tag – Configure 802.1p Tag for remote APC’s or Router’s QoS uses. Valid numbers are
from 0 to 7.
VLAN ID and 802.1p tag must cooperate with remote Router or APC.
Security – Specify the security policy.
WEP – When selected, the privacy of MSSID entry will be set to WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy).
WEP Key Index – Select the default key Index to make it the Default key and encrypt the
data before being transmitted. All stations, including this MSSID Entry, always transmit data
encrypted using this Default Key. The key number (1,2,3,4) is also transmitted. The receiving
station will use the key number to determine which key to use for decryption. If the key value
does not match with the transmitting station, the decryption will fail. The key value is set in
Wireless | WEP web page.
802.1x – When selected, the MSSID entry will be configured as an 802.1x authenticator. It
supports multiple authentication types based on EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) like
EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, EAP-PEAP, EAP-SIM. The privacy will be configured as dynamic WEP.
RADIUS Server Profile – Select the default radius server name. If not, please configure
Network | RADIUS Servers Web page first.
Dynamic Key Length – Select the dynamic 64-bits / 128-bits encryption.
WPA – Wi-Fi Protected Access, When selected, the encrypt method will be WPA with RADIUS
Sever.
RADIUS Server Profile – The same as 802.1x.
Algorithm – Choose WPA algorithm (TKIP, AES).
Use ReKey – If not selected, indicates that Group Key will not be rekeyed. If selected, must
specify the time in minutes, after which the group key will be updated.
Every … minutes – Specify amount of minutes and WPA automatically will generate a new
Group Key.
WPA-PSK – When selected, the encrypt method will be WPA without RADIUS Server.
Use Pre-Shared Key – Specify more than 8 characters and less than 64 characters for WPA
with pre-shared key encryption.
Algorithm – The same as WPA.
Use Rekey – The same as WPA.
Every … minutes – The same as WPA.
MAC Auth – MAC authentication. When selected, the MAC address of username and password
will be passed to RADIUS server for PAP authentication when wireless client connects with P-720.
RADIUS Server Profile – The same as 802.1x.
Disabled – When selected, you don’t select any security policy.
Bridge Mode
Page 33 of 51
Page 35

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 36 – Advanced Wireless Setting (Bridge Mode)
Radio – specify which RF card (wlan1 or wlan2) is needed to be configured since P-720 has two
Dual-Band radios
Mode – specify the operation mode of P-720 (AP or Bridge)
Interface – Choose the specified Bridge link entry you want to configure.
Remote MAC – Specify the remote peer’s MAC address of this Bridge
Security – Specify which security policy is used
New – Create a new Bridge link entry
Detail – Show the detail information of this Bridge link entry
Edit – Edit the selected Bridge link entry you want to configure
Delete – Delete the selected Bridge link entry.
Clicking Detail, the similar page will be appears:
Figure 37 – Detail of one bridge entry
Clicking Edit for editing an existed bridge link or New for adding a new bridge link , you can see the
figure like this.
Page 34 of 51
Page 36

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 38 – Bridge Link Setting
Remote MAC – Add the remote peer’s MAC address you want to configure as a bridge link
Security – Specify WEP or WPA-PSK (TKIP or AES) is used for security policy. WPA-PSK or static
WEP can be used for encrypt each bridge link
Each Bridge link can have its own WEP key/keyIndex for encryption.
Only WEP can be used as security policy for Bridge links now. More enhanced
security policy is in developing.
By default, four WEP keys are all set to “aaaaa”. They can be modified in
Wireless | WEP.
Wireless | WEP
Use the Wireless | WEP menu to configure static WEP settings.
This menu only set static WEP key value related with 4 key indexes for each RF
card (wlan1 or wlan2). Enable or Disable static WEP is in the Wireless | Advance
menu.
Figure 39 – WEP Settings
Page 35 of 51
Page 37

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Radio – specify which RF card (wlan1 or wlan2) is needed to be set.
Click Edit to edit the existing wepkey1 to wepkey4.
By default, four WEP keys are all set to “aaaaa”. They can be modified according to
Figure 40 – Edit WEP Key
real need.
Wireless | MAC ACL
Use the MAC ACL service to control the default access to the wireless interface of the P-720 or
define special access rules for mobile clients. Configure the ACL using the Wireless | MAC ACL menu:
Figure 41 – MAC ACL Service
Radio – Two wireless interfaces wlan1 and wlan2 can be selected for each radio’s MAC ACL rules.
Only AP mode has the MAC ACL service. The wireless interface whose mode is
Bridge hasn’t MAC ACL settings.
Policy Setting – click the edit button to choose Allow, Deny or disable the access control service on
device. By default the ACL service is disabled and all wireless clients connecting to the P-720 are
allowed (no ACL rules are applied to the wireless clients).
Select Allow means only the wireless clients whose MAC are listed in the MAC List would be
permitted to access this AP. Other wireless client cannot access this AP.
Select Deny means only the wireless clients whose MAC are listed in the MAC List would be
prevented from accessing. Other wireless clients can access th is AP.
Page 36 of 51
Page 38

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Select Disabled means no ACL service.
Figure 42 – MAC ACL settings
You must create MAC List to work with Policy setting. The access control list is based on the
network device’s MAC address. In the MAC ACL Configuration table, you only need to specify the
MAC address of wireless client. Click the Add button to create a new MAC entry:
Figure 43 – Add MAC entry
MAC Address – enter the physical address of the network device you need to (MAC address) The
format is a list of colon separated hexadecimal numbers (for example: 00:AA:A2:5C:89:56).
Save – click the button to save the new MAC entry.
Figure 44 – Apply or Discard MAC ACL Configuration Changes
Apply Changes – to save all changes made in the interface table at once.
Discard Changes – restore all previous values.
For such each change of settings, the P-720 needs to be restarted to apply all settings changes when
clicking Apply Changes. Request for reboot server appears:
Page 37 of 51
Page 39

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 45 – Reboot Server
Reboot – Click the button to restart the server and apply the changes.
If there is no other setting needed to be modified, click the Reboot button for
applying all modifications.
And if there are still other setting modifications needed, go ahead to finish all
changes and then click Reboot button to restart and apply all settings together.
Page 38 of 51
Page 40

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
System
System | Security
Use the System | Security service to configure the name and password administrator:
Figure 46 – system security settings
User Name – administrator username for access to P-720 (e.g. web interface, CLI mode) [1-32
symbols, spaces not allowed].
Old Password – old password value.
New Password –new password value used for user authentication in the system [4-8 characters,
spaces not allowed].
Confirm Password – re-enter the new password to verify its accuracy.
Save – click to save new administrator settings.
Default administrator logon settings are:
User Name: admin
Password: admin01
Password length is from 4 to 8 characters.
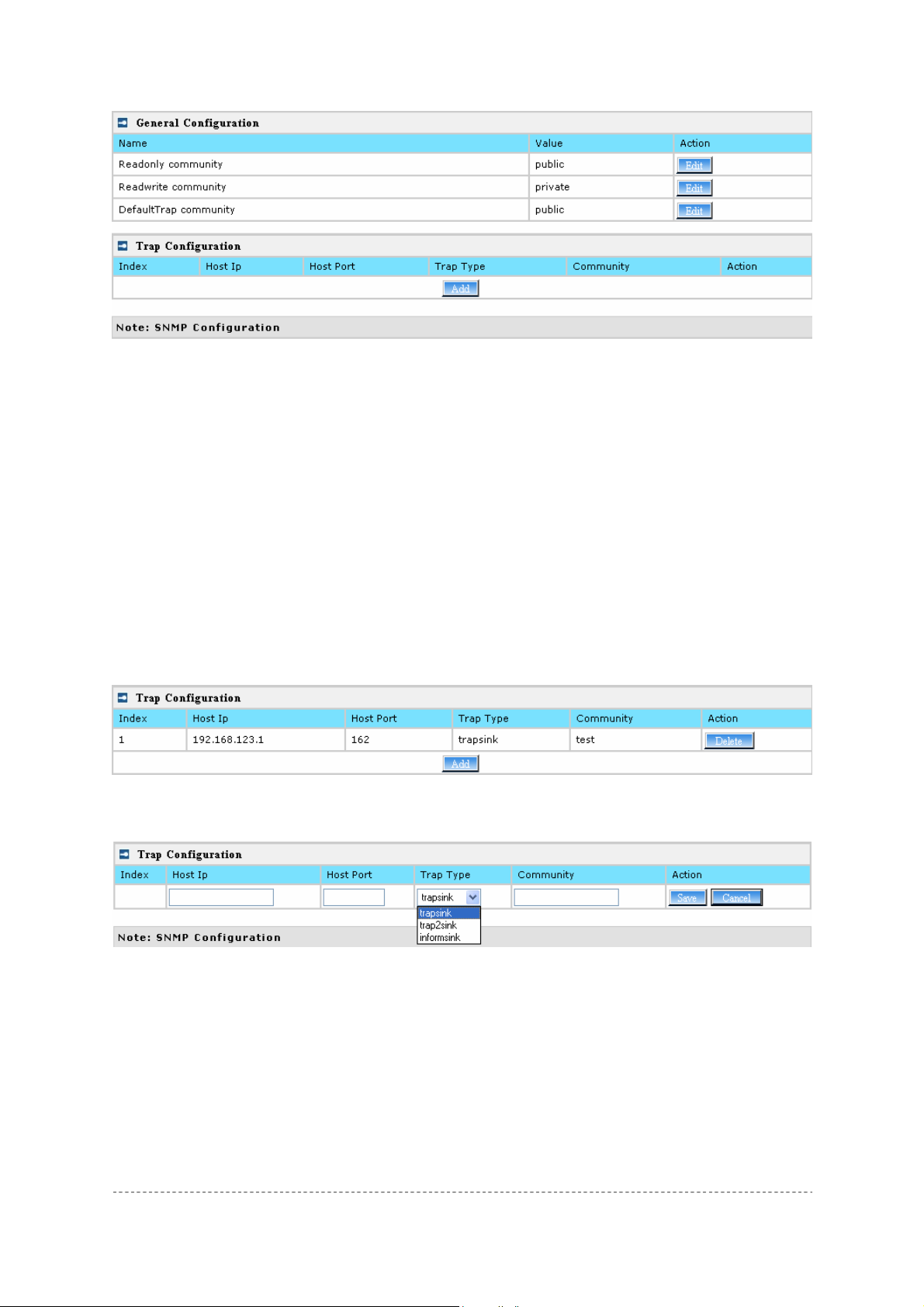
System | SNMP
SNMP is the standard protocol that regulates network management over the Internet. To
communicate with SNMP manager you must set up the same SNMP communities and identifiers on
both ends: manager and agent.
Use the System | SNMP menu to change current SNMP configuration.
Page 39 of 51
Page 41
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 47 – SNMP settings
Readonly community – Community name is used in SNMP version 1 and version 2c. Read-only
(public) community allows reading values, but denies any attempt to change values [1-32 all ASCII
printable characters, no spaces].
Readwrite community – Community name is used in SNMP version 1 and version 2c. Read-write
(private) community allows to read and (where possible) change values [1-32 all ASCII printable
characters, no spaces].
Default Trap community – The default SNMP community name used for traps without specified
communities. The default community by most systems is "public". The community string must match
the community string used by the SNMP network management system (NMS) [1-32 all ASCII
printable characters, no spaces].
Trap Configuration Table:
You can configure your SNMP agent to send SNMP Traps (and/or inform notifications) under the
defined host (SNMP manager) and community name (optional).
Figure 48 – SNMP Trap table settings
Click Add to add a new SNMP manager or Delete to delete a specific SNMP manager. Clicking Add:
Figure 49 – Add SNMP Trap
Host IP – enter SNMP manager IP address [dots and digits].
Host Port – enter the port number the trap messages should be send through [numbe r].
Trap Type – select trap message type [v1/v2/inform].
Community – specify the community name at a SNMP trap message. This community will be used in
trap messages to authenticate the SNMP manager. If not defined, the default trap community name
will be used (specified in the SNMP table) [1-32 all ASCII printable characters, no spaces].
Save – save all current settings
Cancel – restore the last settings
Page 40 of 51
Page 42

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
System | Telnet
Use System | Telnet menu to manage the telnet/SSH service of y our P-720.
Figure 50 – System Configuration settings
Telnet Service – Enable or disable telnet service of P-720
SSH Service – Enable or disable SSH service of P-720.
The default of these two services are all Enabled. The current IETF SSH (SSHv2) is supported for
security of accessing P-720 via telnet/CLISH.
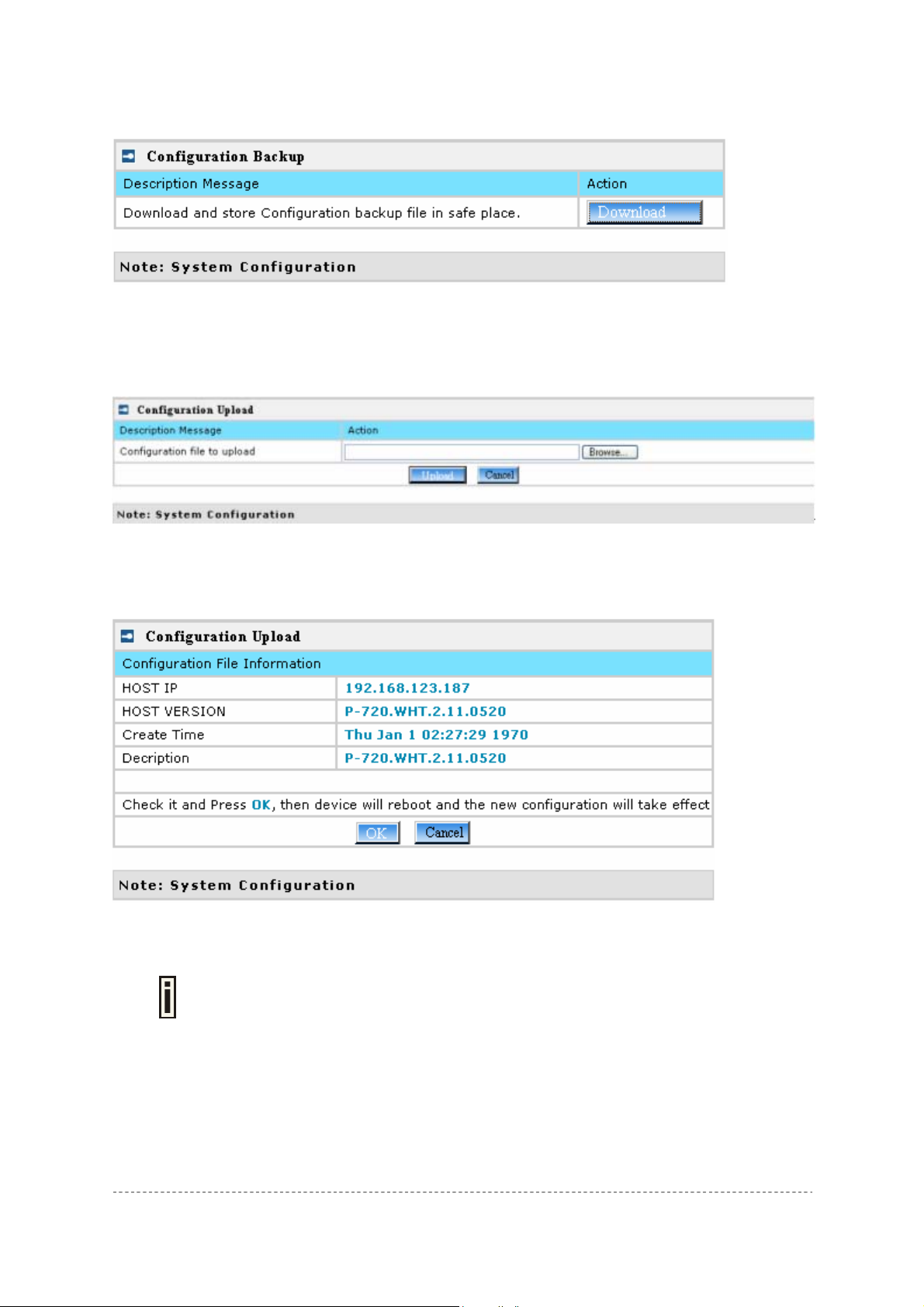
System | Configuration
Use the System | Configuration menu to configure such system utilities:
Backup – download current working system configuration for backup
Upload/Restore – upload system configuration for restore
Figure 51 – System Configuration settings
You can save your current device configuration file locally using the Backup menu under the System
| Configuration | Backup menu:
Figure 52 – Backup settings
Such device configuration is saved in the specific format file (.cfg).
Description Message shows the current version of firmware.
Click the Preparation button to start saving the configuration file.
Click the Download button to download current working configuration into your local PC.
Page 41 of 51
Page 43
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 53 – Download system configuration
You can upload saved configuration file any time you want to restore this configuration to the device
by using the Browse button Select the configuration file and upload it on the device:
Figure 54 – Configuration Upload/Restore
Click Upload for upload the specified configuration and then the similar UI appea rs
Figure 55 – configuration information
HOST IP – show the IP address in the configuration file that needs to upload.
Please remember this IP address for accessing P-720 after the configuration file is
uploaded.
HOST VERSION – show the firmware version in the configuration file that needs to upload.
OK – click the button to apply configuration setting to the device.
If everything is right, click OK button for upload/restore.
Page 42 of 51
Page 44

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
System | Reset
Figure 56 – System Reset setting
Reboot – Reboot the device
Reset – Reset System to Factory Defaults
To reboot the device, click Reboot and then the below appears to make sure:
Figure 57 – Reboot the device
To reset device to factory defaults, click Reset on Figure 56 and then the below appears to make sure:
Figure 58 – Reset the device
Please note that all settings including the administrator settings will be set back to
the factory default when Reset is selected.
System | Upgrade
Upload – Update your device firmware.
Page 43 of 51
Page 45

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Figure 59 – Firmware Upgrade
Click the Upload and then the follow appears. Specify the full path to the new firmware image and
click the Upload button:
Figure 60 – Firmware Upgrade
To flash the uploaded firmware image to upgrade the firmware is done by click the Upgrade button.
Please make sure the firmware is correct for P-720. Otherwise the upgrade will be
Figure 61 – Device Statistics
failed.
Do not switch off and do not disconnect the P-720 from the power supply during the
firmware update process because the device could be damaged. It is best to use
the Ethernet connection (not wireless) for the firmware update process.
Page 44 of 51
Page 46

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
Appendix
A) Specification
Wireless
Standard IEEE 802.11b(DSSS), IEEE 802.11g(OFDM) and IEEE 802.11a(OFDM)
802.11a: 54,48,36,24,18,12,9,6Mbps;802.11g:
Data Rate
Transmit Power
(adjustable RF power)
Antennas 2 Dual-band Dipole Antennas with reverse: R-TNC plug connector
Encryption
Bridge Up to 8 bridge links
Interface
54,48,36,24,12,9,6,11,5,5,2,1Mbps (auto fall back)
Turbo 802.11a: 108Mbps
Max. 17 dBm ± 1.5dBm @6~24Mbps
Max. 13 dBm ± 1.5dBm @54Mbps (Maximum power will vary by channel,
rate)
WPA(TKIP and CCMP-AES), Dynamic/static 64bits and 128bits WEP
LAN 10/100Mb Ethernet, auto sensing, RJ-45
Console
1×DB-9 Male (RS232) for serial configuration
Management
Interfaces HTTPs, Secure Telnet(SSHv2), SNMP
Software Update Remote software update via HTTPs
Restore default H/W and S/W remote restore factory default
Physical Specification
Dimension 195 mm x 160 mm x 27 mm
Weight 500g
Environment Specification
Temperature Humidity
Operating 0 to 50°C 95%, non-condensing
Power Supply
POE 48V, IEEE802.3af-2003 compliance
Power adaptor External power supply, input: 100-230 VAC, 50-60Hz and output: 12VDC
LEDs
4 LEDs Power, LAN, WLAN1, WLAN2
Warranty
1 years
Package Contents
P-720 Dual Radio 2.4GHz/5GHz
Access Point
Printed Release note Ethernet patch cable (1.8m)
International power supply Console
Antenna Mount kit package
Page 45 of 51
CD-ROM with User Manuals (*.pdf)
Page 47

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
B) Factory Defaults for the P-720
General Configuration Settings
Administrator Username admin
Administrator Password admin01
Get Community Public
Set Community Private
Network Configuration Settings
IP address (static IP) 192.168.2.2
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway 0.0.0.0
Wireless Configuration Settings
RF Card 1(WLAN1)
Default Mode 11g Access Point
SSID P-720
Default channel 11
RTS Threshold 2347 bytes
RF Output Power 14dBm
Authentication Type Open System
Encryption Off
RF Card 2(WLAN2)
Default Mode 11a Access Point
SSID P-720
Default channel 60
RTS Threshold 2347 bytes
RF Output Power 17dBm
Authentication Type Open System
Encryption Off
C) Regulatory Channels/Power
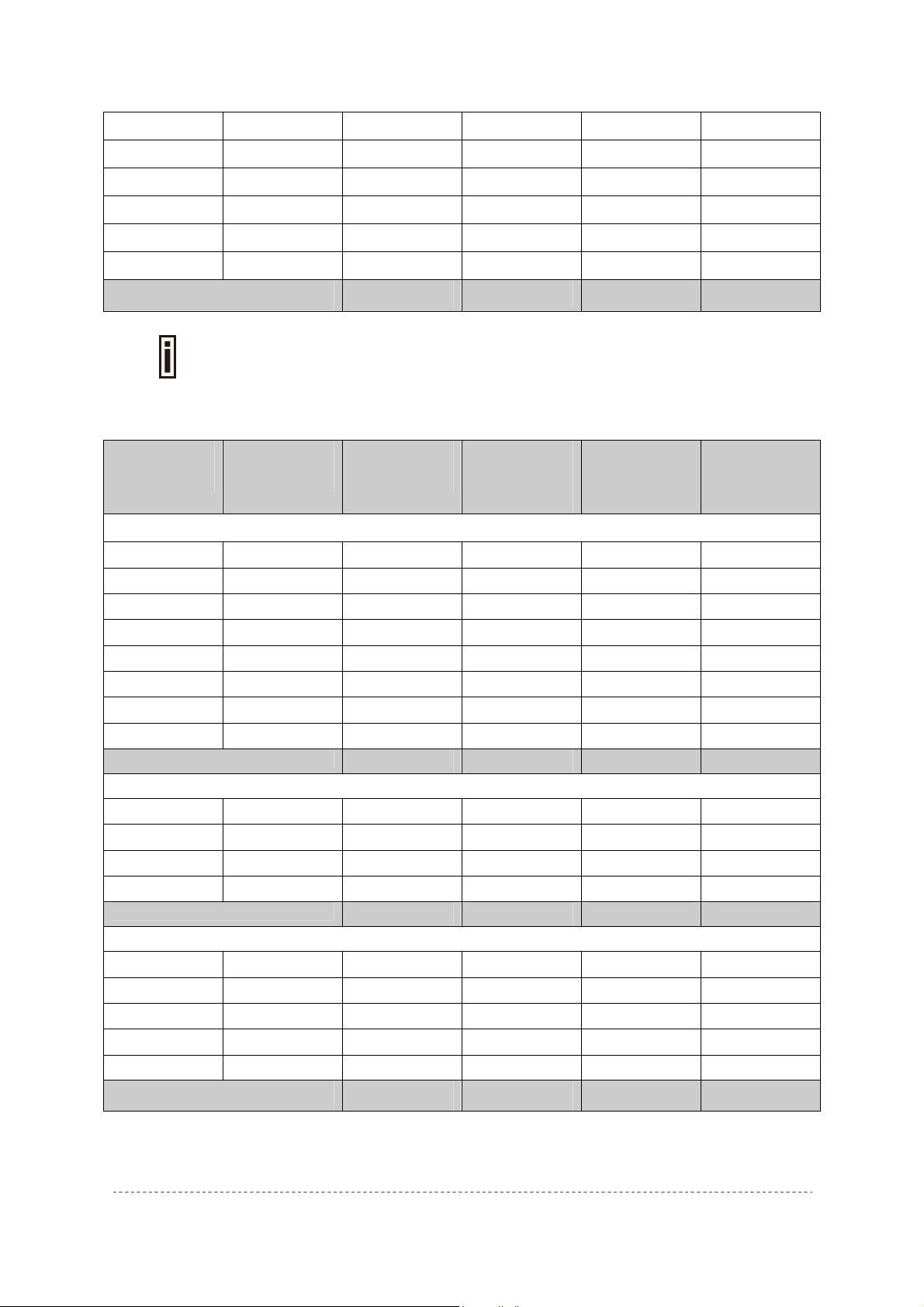
Channels and Maximum output power for the P-720 11g radio:
Channels
Identifiers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Frequency in
MHz
2412
2417
2422
2427
2432
2437
2442
2447
USA, Canada
(FCC)
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
European
Union
(CE/ETSI)
Japan
(TELEC)
Page 46 of 51
Page 48
P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
9
10
11
12
13
14
2452
2457
2462
2467
2472
2484
Maximum output Power
For channel 1 and channel 11, the maximum output power will be 18.5dBm in the
Channels and Maximum power for the P-720 11a radio:
Channels
Identifiers
case of the setting of FCC.
Frequency in
MHz
USA, Canada
(FCC)
• • •
• • •
• • •
—
—
— — —
18.5dBm 14dBm 14dBm
European
Union
(CE/ETSI)
U-NII lower band (5150 – 5250 MHz)
34 5170
36 5180
38 5190
40 5200
42 5210
44 5220
46 5230
48 5240
Maximum Output Power
U-NII middle band (5250 – 5350 MHz)
52 5260
56 5280
60 5300
64 5320
Maximum Output Power
U-NII upper band ( 5725 – 5875 MHz)
149 5745
153 5765
157 5785
161 5805
165 5825
Maximum Output Power
— —
• •
— —
• •
— —
• •
— —
• •
17dBm 17 dBm 15 dBm
• •
• •
• •
• •
17 dBm 17 dBm —
•
•
•
•
— —
17 dBm 17 dBm —
•
•
•
•
Japan
(TELEC)
•
—
•
—
•
—
•
—
—
—
—
—
— —
— —
— —
— —
Page 47 of 51
Page 49

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
D) Location ID and ISO Country Codes
This list states the country names (official short names in English) in alphabetical order as given in
ISO 3166-1 and the corresponding ISO 3166-1-alpha-2 code elements.
It lists 239 official short names and code elements.
Location
ID
AF Afghanistan LI Liechtenstein
AL Albania LT Lithuania
DZ Algeria LU Luxembourg
AS American Samoa MO Macao
AD Andorra MK
AO Angola MG Madagascar
AI Anguilla MW Malawi
AQ Antarctica MY Malaysia
AG Antigua and Barbuda MV Maldives
AR Argentina ML Mali
AM Armenia MT Malta
AW Aruba MH Marshall islands
AU Australia MQ Martinique
AT Austria MR Mauritania
AZ Azerbaijan MU Mauritius
BS Bahamas YT Mayotte
BH Bahrain MX Mexico
BD Bangladesh FM Micronesia, federated states of
BB Barbados MD Moldova, republic of
BY Belarus MC Monaco
BE Belgium MN Mongolia
BZ Belize MS Montserrat
BJ Benin MA Morocco
BM Bermuda MZ Mozambique
BT Bhutan MM Myanmar
BO Bolivia NA Namibia
BA Bosnia and Herzegovina NR Nauru
BW Botswana NP Nepal
BV Bouvet island NL Netherlands
BR Brazil AN Netherlands Antilles
IO British Indian ocean territory NC New Caledonia
BN Brunei Darussalam NZ Ne w Zealand
BG Bulgaria NI Nicaragua
Country Location
ID
Country
Macedonia, the former Yugoslav
republic of
Page 48 of 51
Page 50

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
BF Burkina Faso NE Niger
BI Burundi NG Nigeria
KH Cambodia NU Niue
CM Cameroon NF Norfolk island
CA Canada MP Northern Mariana islands
CV Cape Verde NO Norway
KY Cayman islands OM Oman
CF Central Africa n republic PK Pakistan
TD Chad PW Palau
CL Chile PS Palestinian territory, occupied
CN China PA Panama
CX Christmas island PG Papua new guinea
CC Cocos (keeling) islands PY Paraguay
CO Colombia PE Peru
KM Comoros PH Philippines
CG Congo PN Pitcairn
CD Congo, the democratic republic of the PL Poland
CK Cook islands PT Portugal
CR Costa Rica PR Puerto Rico
CI Côte d'ivoire QA Qatar
HR Croatia RE Réunion
CU Cuba RO Romania
CY Cyprus RU Russian federation
CZ Czech republic RW Rwanda
DK Denmark SH Saint Helena
DJ Djibouti KN Saint Kitts and Nevis
DM Dominica LC Saint Lucia
DO Dominican republic PM Saint Pierre and Miquelon
EC Ecuador VC Saint Vincent and the grenadines
EG Egypt WS Samoa
SV El Salvador SM San Marino
GQ Equatorial guinea ST Sao tome and Principe
ER Eritrea SA Saudi Arabia
EE Estonia SN Senegal
ET Ethiopia SC Seychelles
FK Falkland islands (malvinas) SL Sierra Leone
FO Faroe islands SG Singapore
FJ Fiji SK Slovakia
FI Finland SI Slovenia
FR France SB Solomon islands
GF French Guiana SO Somalia
Page 49 of 51
Page 51

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
PF French Polynesia ZA South Africa
TF French southern territories GS
GA Gabon ES Spain
GM Gambia LK Sri Lanka
GE Georgia SD Sudan
DE Germany SR Suriname
GH Ghana SJ Svalbard and Jan Mayan
GI Gibraltar SZ Swaziland
GR Greece SE Sweden
GL Greenland CH Switzerland
GD Grenada SY Syrian Arab republic
GP Guadeloupe TW Taiwan, province of china
GU Guam TJ Tajikistan
GT Guatemala TZ Tanzania, united republic of
GN Guinea TH Thailand
GW Guinea-Bissau TL Timor-leste
GY Guyana TG Togo
HT Haiti TK Tokelau
HM Heard island and McDonald islands TO Tonga
VA Holy see (Vatican city state) TT Trinidad and Tobago
HN Honduras TN Tunisia
HK Hong Kong TR Turkey
HU Hungary TM Turkmenistan
IS Iceland TC Turks and Caicos islands
IN India TV Tuvalu
ID Indonesia UG Uganda
IR Iran, Islami c republic of UA Ukraine
IQ Iraq AE United Arab emirates
IE Ireland GB United kingdom
IL Israel US United states
IT Italy UM United states minor outlying islands
JM Jamaica UY Uruguay
JP Japan UZ Uzbekistan
JO Jordan VU Vanuatu
KZ Kazakhstan
KE Kenya VE Venezuela
KI Kiribati VN Viet nam
KP
KR Korea, republic of VI Virgin islands, u.s.
KW Kuwait WF Wallis and Futuna
Korea, democratic people's republic
of
VG Virgin islands, British
South Georgia and the south
sandwich islands
Vatican city state see holy see
Page 50 of 51
Page 52

P-720 User’s Guide v1.0 Jun 10, 2005
KG Kyrgyzstan EH Western Sahara
LA Lao people's democratic republic YE Yemen
LV Latvia YU Yugoslavia
LB Lebanon
LS Lesotho ZM Zambia
LR Liberia ZW Zimbabwe
LY Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
Zaire see Congo, the democratic
republic of the
Page 51 of 51
 Loading...
Loading...