Page 1
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Employees Traffic
Visitor Traffic
Internal Servers
Employe
LAN
WLAN
WAN
P-560
Internet Router
Visitor
Figure 146 – User Access
Step 1 Configure your RADIUS server to use the "Billing-Class-of-Service" attribute as
defined in the WISPr vendor specific attribute set (see appendix: Vendor Specific
Attributes). If this BCoS attribute is set to the value "visitor_access" during the
authentication response, the AC will allow routing between the WLAN port and the
LAN port for this specific user.
Step 2 Use the system | access | NAV menu and enable visitor access function on ixp0
(LAN).
Such a user (visitor) will have employee access rights and access to servers running in the LAN (see
Figure 146 – User Access, employee traffic). In other words, the P-560 controls the client’s access to
the LAN via RADIUS attributes specifically addressing which clients are allowed to connect to the
LAN.
Visitor access on selected interface can only function with enabled
authentication. RADIUS server should authenticate the user, in order to control
user’s access to LAN.
If authentication is on enabled (visitor access enabled) user only receives the access to the Internet
independently from his/her access rights.
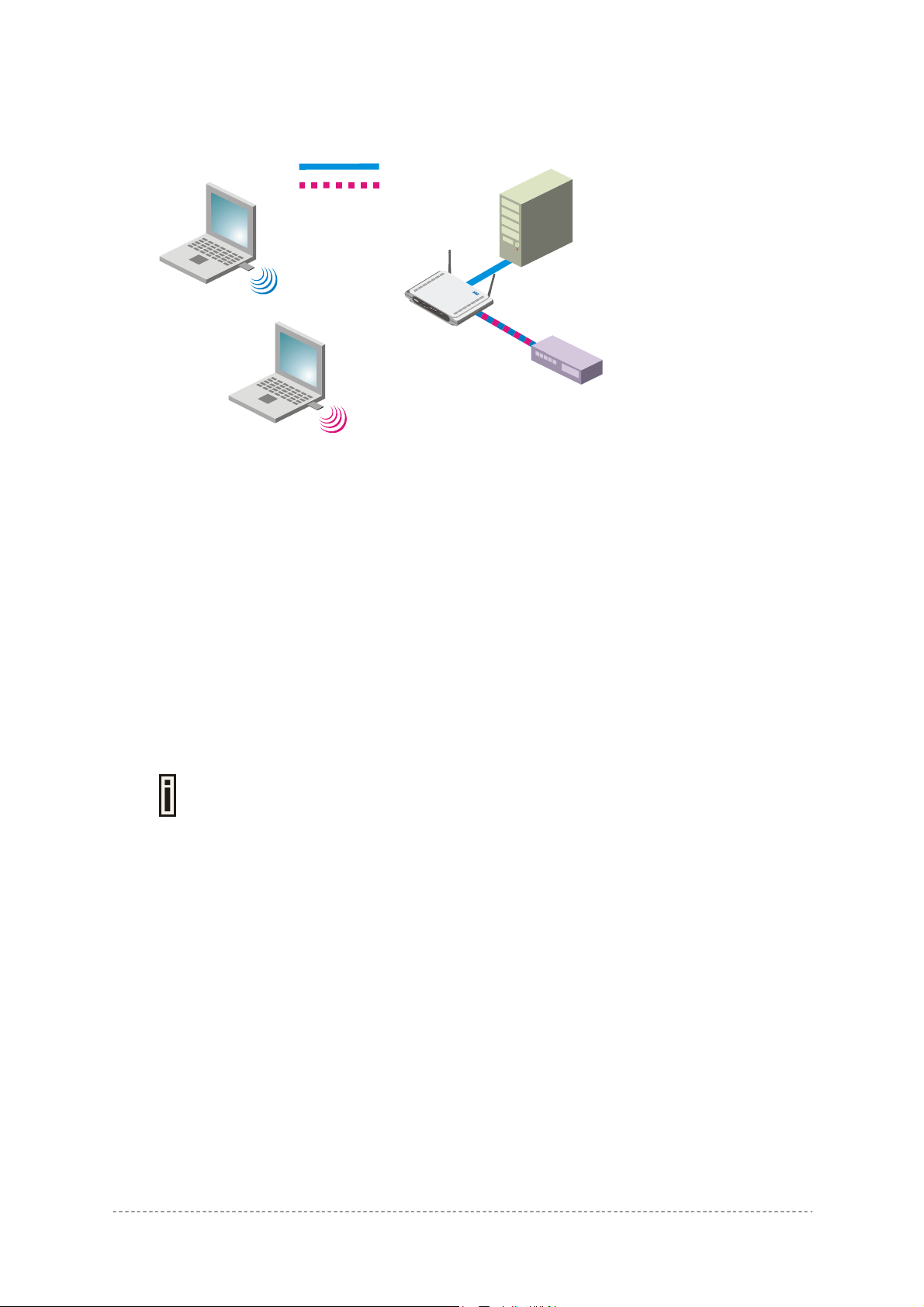
System | Access | SNMP
SNMP is the standard protocol that regulates network management over the Internet. With enabled
SNMP service Hotspot-in-a-Box can act as SNMP agent. To communicate with SNMP manager you
must set up the same SNMP communities and identifiers on both ends: manager and agent. For more
information about SNMP see Chapter 6 – SNMP Management.
Use the system | access | SNMP menu to enable/disable SNMP service or change current SNMP
configuration on your P560 controller.
Gemtek Systems Page 101
Page 2
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Figure 147 – SNMP Settings
SNMP Table:
SNMP Service – enable or disable SNMP service on AC [enabled/disabled]. By default SNMP service
is enabled. With service enabled the AC acts as the SNMP agent.
If enabled, then device can be configured via SNMP:
SNMP Name – An administratively assigned name for this managed node [0-99 any string]. By
convention, this is the node’s fully qualified domain name.
SNMP Location – The physical location of this node (e.g., `telephone closet, 3rd floor') [0-99 any
string].
SNMP Contact – The textual identification of the contact person for this managed node, together with
information on how to contact this person [0-99 any string].
SNMP Read-Only Community – Community name is used in SNMP version 1 and version 2c. Readonly (public) community allows reading values, but denies any attempt to change values [1-32 all
ASCII printable characters, no spaces].
SNMP Read-Write Community – Community name is used in SNMP version 1 and version 2c.
Read-write (private) community allows to read and (where possible) change values [1-32 all ASCII
printable characters, no spaces].
Default Trap Community Name – The default SNMP community name used for traps without
specified communities. The default community by most systems is "public". The community string
must match the community string used by the SNMP network management system (NMS) 1-32 all
ASCII printable characters, no spaces].
Authentication Failure Taps Generation – select [enable/disable] getting the authentication failure
traps from your AC.
Gemtek Systems Page 102
Page 3
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
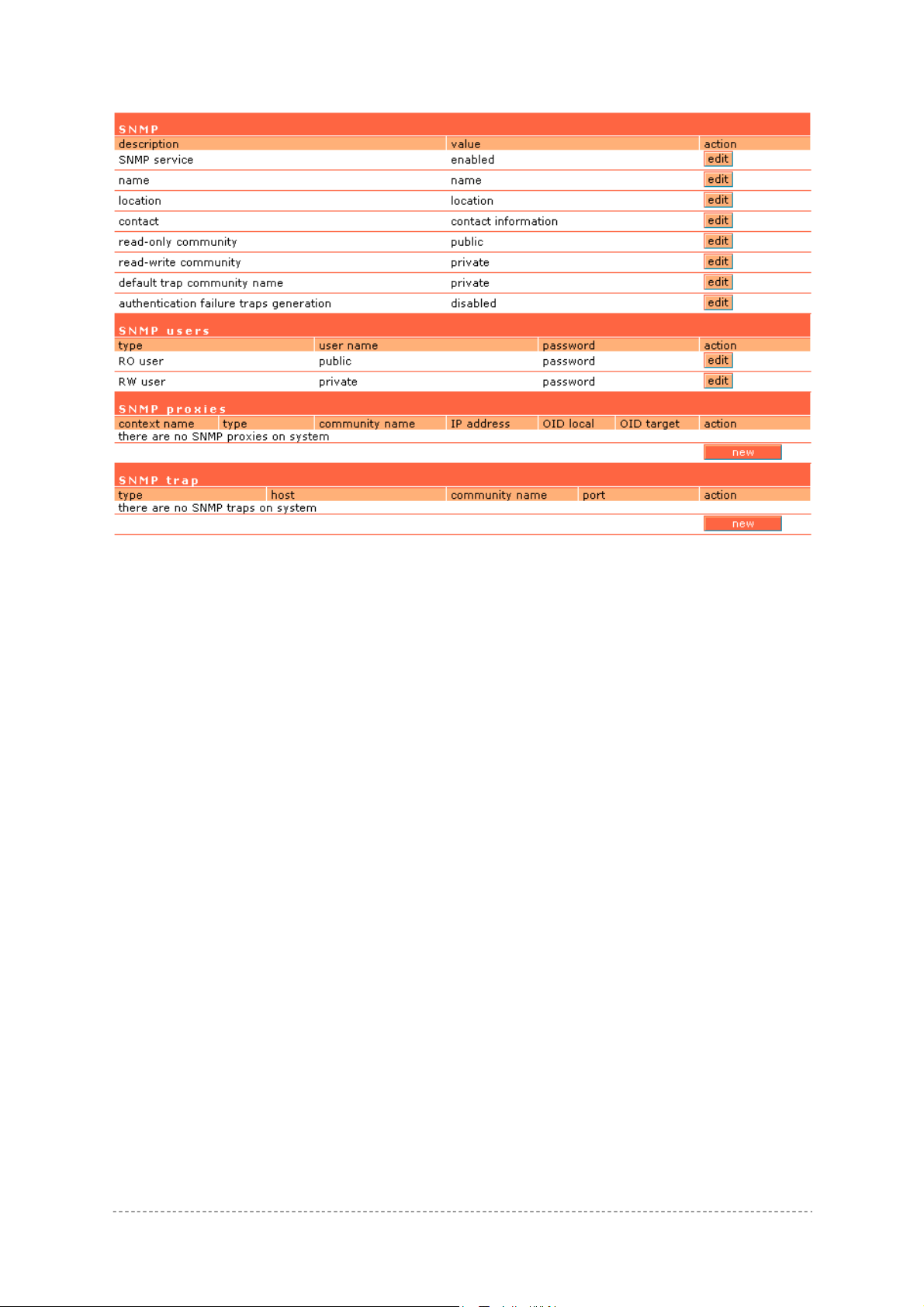
SNMP Users Table:
SNMP Users table is only used for SNMP v3.
SNMP Users – Users are used in SNMP version 3. They have the same access rights as
communities, but instead of a single community name there are user name and password. Strong
encryption is supported in SNMPv3.
User Name – enter user name for read-only (RO) or read-write (RW) SNMP access [1-32 all ASCII
printable characters, no spaces].
Password – enter password for read-only (RO) or read-write (RW) SNMP access [8-32 all ASCII
characters, no spaces].
SNMP Proxies Table:
SNMP Proxies – SNMP proxy configuration specifies that any incoming SNMP requests can be send
to another host. SNMP proxy can be configured in such a way that can proxy only specified SNMP
request under specific OID (OID local). Click the new button to create SNMP proxy:
Figure 148 – Add SNMP Proxies
Context Name – enter the context name for SNMP proxy rule between client and AC. Context name
only works with SNMP v3. If a "context name" is specified, it assigns the proxy rule to a particular
context name within the local agent [1-32 all ASCII printable characters, no spaces]:
P-560
WAN
Administrator
SNMP v3
with Context Name
LAN
SNMP v1/v2c
Figure 149 – SNMP and Content Name
This is the proper way to query multiple SNMP agents through a single proxy. Assign each remote
agent to a different context name. Then you can use "snmpwalk -n contextname1" to walk one
remote proxied agent and "snmpwalk -n contextname2" to walk another, assuming you are using
SNMPv3 to talk to the proxy (snmpv1 and snmpv2c context mappings aren’t currently supported but
might be in the future) (see the Figure 149 – SNMP and Content Name).
Type – select SNMP version for SNMP proxy rule between AP and AC [v1/v2c].
Community Name – enter community name for communicating with the host (see Figure 149 –
SNMP and Content Name, the host is AP in this case) [1-32 all ASCII printable characters, no
spaces].
Gemtek Systems Page 103
Page 4
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
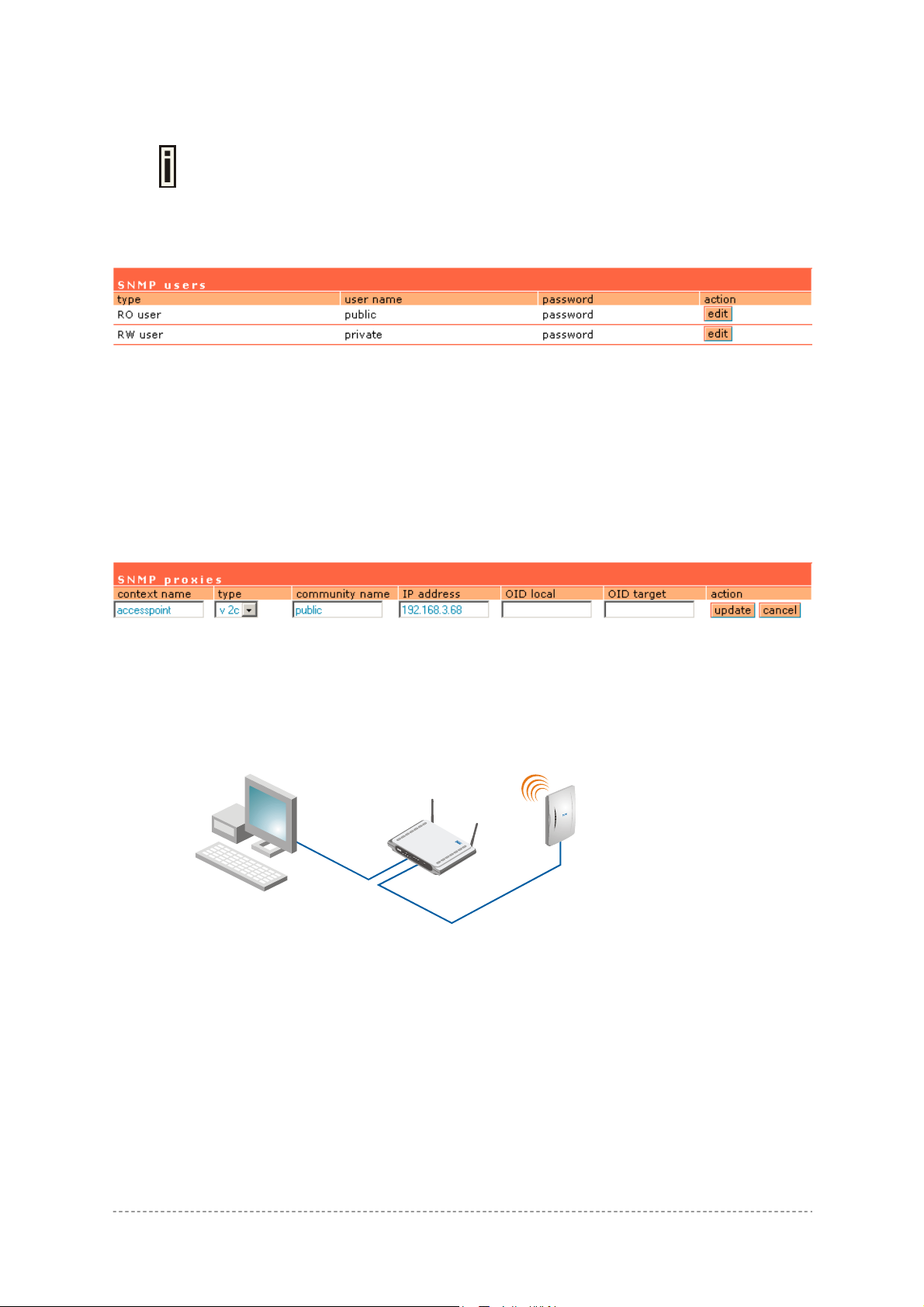
IP Address – specify the host address (AP in our case) to which any incoming requests should be resent [dots and digits].
OID Local – enter Object Identifier (OID) of MIB tree if you want to proxy only the specified SNMP
requests under the specific OID in the MIB tree. That part is specified by OID local tree [optional,
number and dots].
OID Target – Optionally, you can relocate the "OID local” tree to the new location at the "OID target"
If no OID is specified all SNMP request to the controller will be redirected to a
specific host.
SNMP Trap Table:
You can configure your SNMP agent to send SNMP Traps (and/or inform notifications) under the
defined host (SNMP manager) and community name (optional).
Type – select trap message type [v1/v2/inform].
Host – enter SNMP manager IP address [dots and digits].
Community Name – specify the community name at a SNMP trap message. This community will be
used in trap messages to authenticate the SNMP manager. If not defined, the default trap community
name will be used (specified in the SNMP table) [1-32 all ASCII printable characters, no spaces].
Port – enter the port number the trap messages should be send through [number].
System | Status
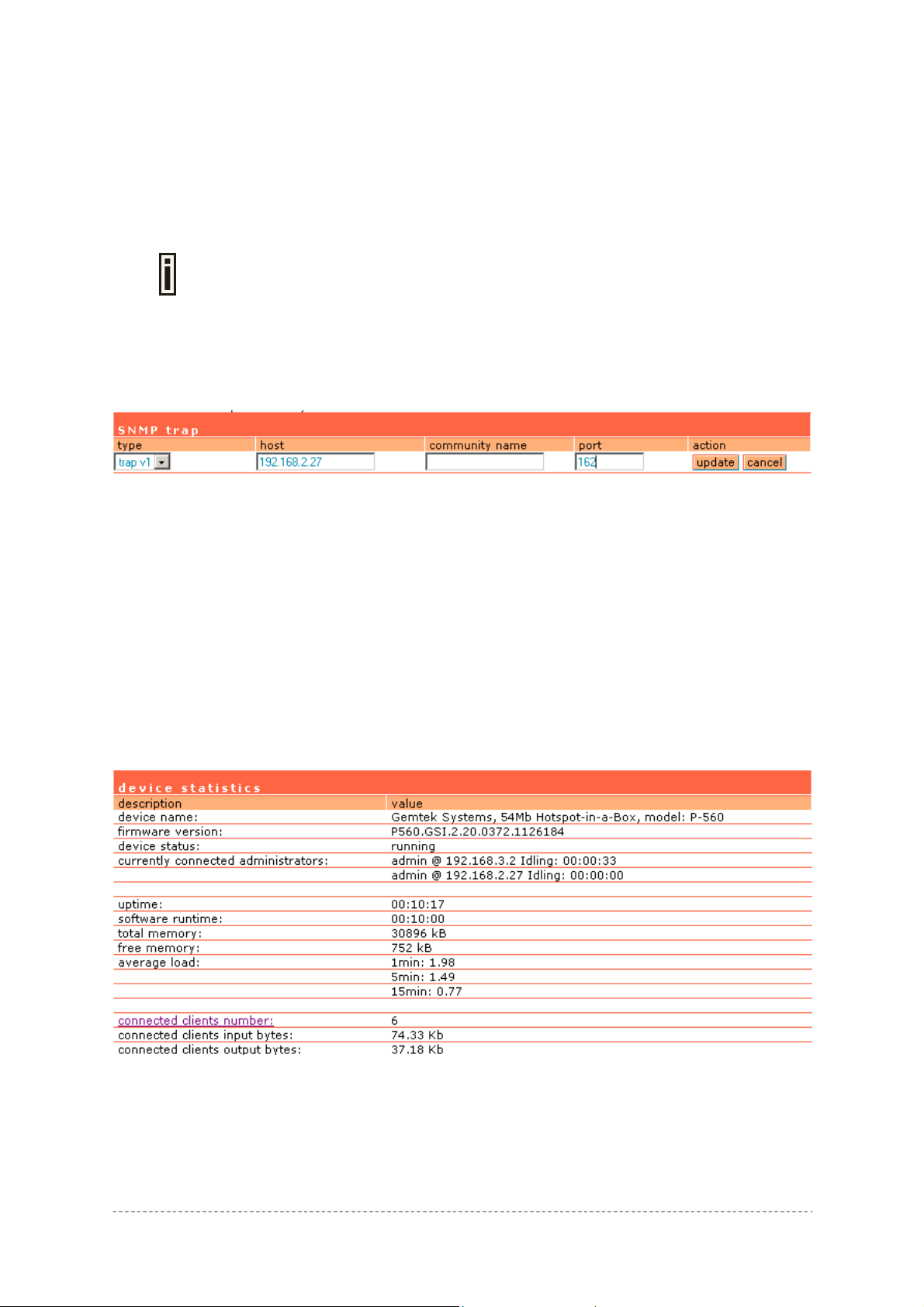
Use the system | status menu to check the P-560 current status:
Device statistics (including device name, model, firmware version, status, logged administrators,
general uptime, memory, load, connected clients)
Figure 150 – Device Statistics
Device Name – full device name and model.
Firmware Version – the current version of the firmware.
Device Status – current device status: running/warning.
Gemtek Systems Page 104
Page 5
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Currently Connected Administrators – logged administrators list in format: [administrator name, IP
address, and idling time in hours/minutes/seconds].
Uptime – indicates the time, expressed in days, hours and minutes since the system was last
rebooted [days/hours/minutes/seconds].
Software Runtime – indicates the time, expressed in days, hours and minutes since the software
reboot. The system itself can restart the software without rebooting the device
[days/hours/minutes/seconds].
Total Memory – total operational memory of your P-560 [kB].
Free Memory – indicates the memory currently available in the controller [kB].
Average Load – indicates the average load of the P-560 processor in the period of the last 1minute,
5 minutes and 15 minutes (a larger value means a larger average load on the processor).
Minimum load – 0.0
Normal load – should not exceed 1.0 (including)
Processor is busy – more than 1.00.
Connected Clients Number – total number of current connected clients on WAN interface. Click on
the settings and get detailed connected clients list (clients page under the connection | user):
Figure 151 – Connected Clients Detailed List
Connected Clients Input Bytes – current connected clients’ total Input bytes [K, KB, MB, GB].
Connected Clients Output Bytes – current connected clients’ total Output bytes [K, KB, MB, GB].
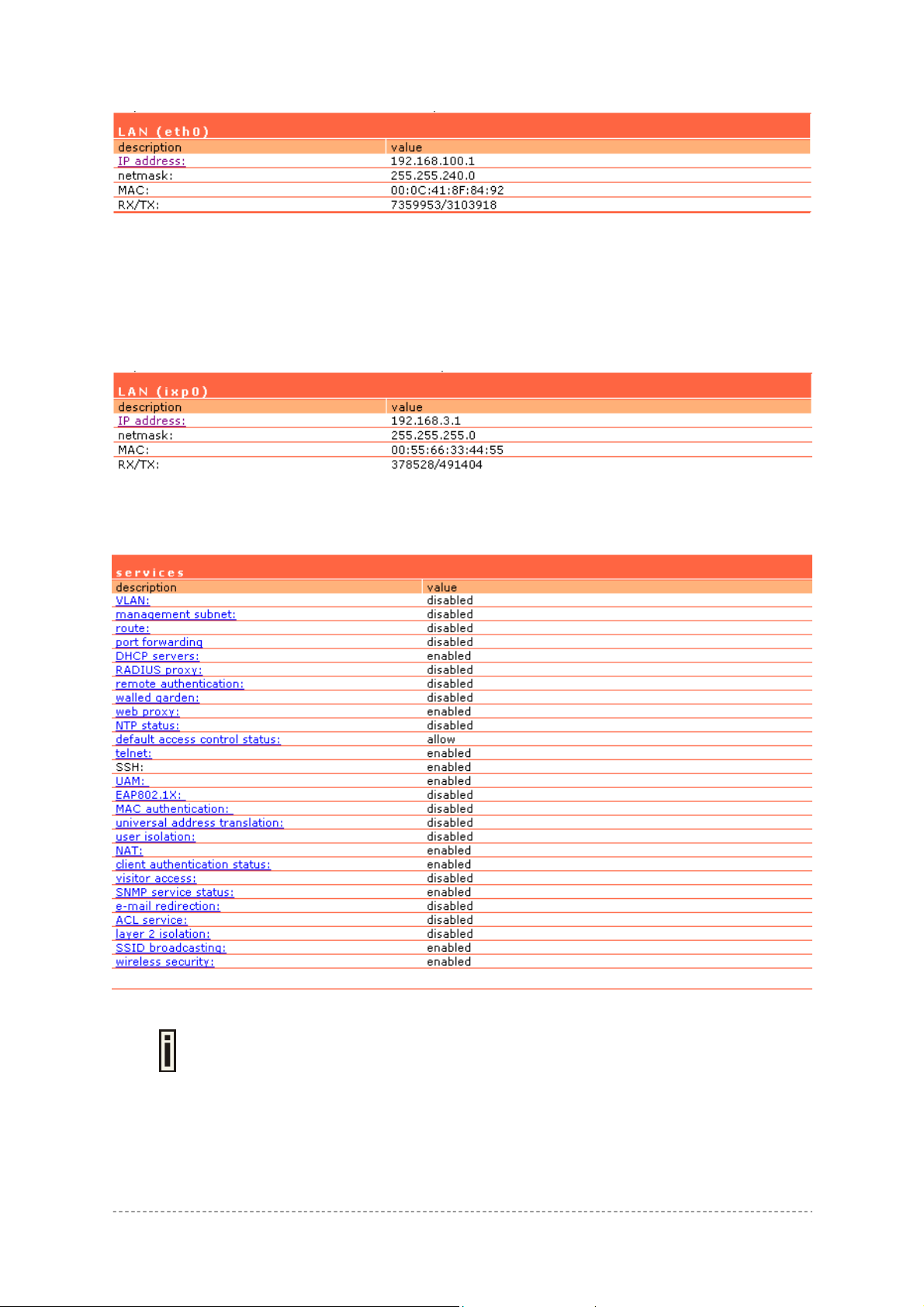
WAN interface (ixp1) (including the IP address, netmask, gateway, MAC address of the WAN
interface, DNS servers, RX/TX statistics)
Figure 152 – WAN Interface Statistics
RX – indicates data volume received on the WAN interface since reboot.
TX – indicates data volume transmitted to the WAN interface since reboot.
Wireless LAN interface (eth0) (including the IP address, netmask, MAC address of the WLAN
interface, RX/TX statistics)
Gemtek Systems Page 105
Page 6
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Figure 153 – LAN Interface Statistics
RX – indicates data volume received on the WLAN interface since reboot.
TX – indicates data volume transmitted to the WLAN interface since reboot.
LAN interface (ixp0) (including the IP address, netmask, MAC address of the LAN interface,
RX/TX statistics)
RX – indicates data volume received on the WLAN interface since reboot.
TX – indicates data volume transmitted to the WLAN interface since reboot.
Services (all services list with its status: enabled/disabled)
Services are displayed as a link to the respective menu where status can be
configured.
Refresh – click the button to refresh device status statistics.
Gemtek Systems Page 106
Page 7
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
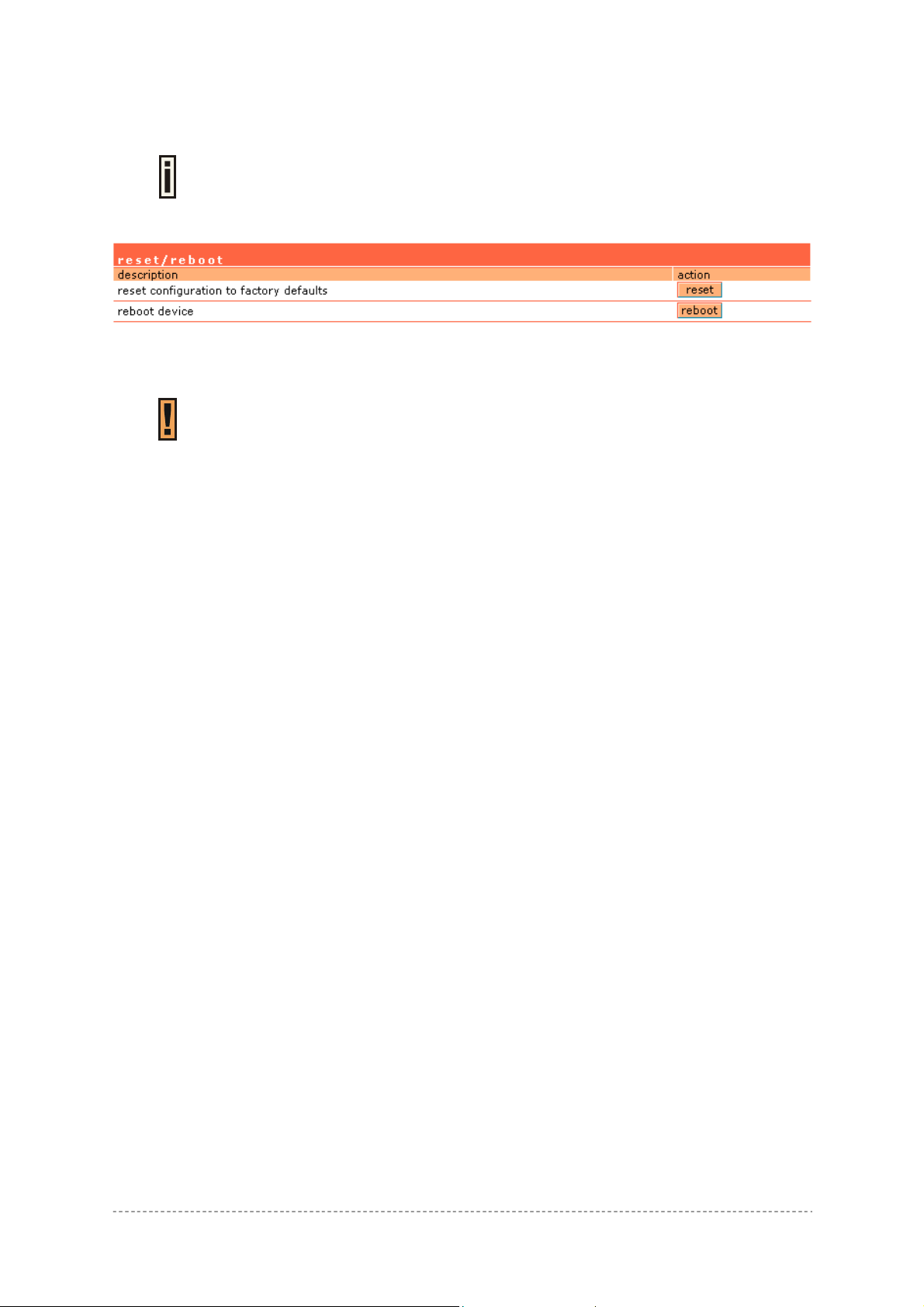
System | Reset
Check the Factory defaults values in the Appendix section: B) Factory Defaults
If you need to reboot your device or reset to factory defaults select the system | reset menu:
Figure 154 – Reset and Reboot
Reset – reset device to factory default values.
Reboot – reboot device with the last saved configuration.
for the Access Controller.
Keep in mind that resetting the device is an irreversible process.
Please note that even the administrator password will be set back to the factory
default.
Gemtek Systems Page 107
Page 8
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
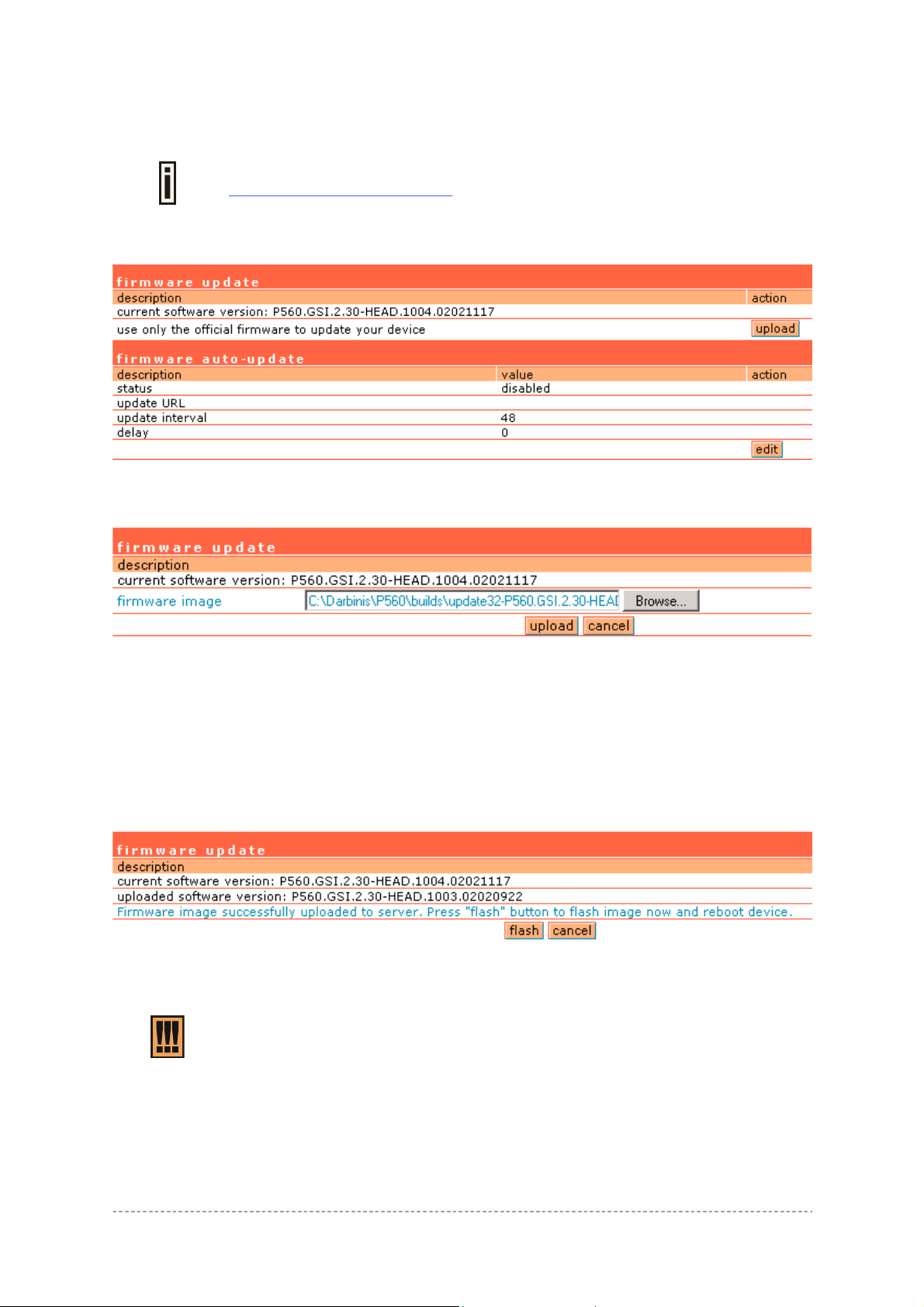
System | Update
Check for new product updates at the Gemtek Systems website:
To update your device firmware, use only the original firmware image and under system | update
menu click the upload button:
Figure 155 – Firmware Update
Specify the full path to the new firmware image and click the upload button:
http://www.gemtek-systems.com
Figure 156 – New Firmware Upload
Firmware Image – enter the firmware image using the full path.
Browse – click the button to specify the new image location.
Upload – upload with new firmware.
Cancel – cancel the upload process.
New firmware image is uploaded into the controller. Now you need to upload this new firmware into
the controller’s FLASH memory, click the flash button:
Figure 157 – Flash New Image
Flash – flash new image, reboots the system.
Do not switch off and do not disconnect the P-560 from the power supply during the
firmware update process because the device could be damaged.
Firmware auto-update:
Auto-update function allows update device firmware automatically. This function will help for large
enterprises, having hundreds of AC's, to keep them up to date.
Gemtek Systems Page 108
Page 9

User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Figure 158 – Firmware Auto-update Configuration
Status - defines if auto-update is enabled or disabled. Default value disabled.
Update URL - defines where firmware should be downloaded from. It points directly to firmware
update file. URL should be accessible without any user authentication. URL can use HTTP, HTTPS
and FTP protocols. Default value - empty string.
Update interval – time interval between each update in hours [1-9999]. Time is counted from last
device boot-on. Default value is 48 hours.
Delay – delays update process by given amount of hours. This should prevent from getting hundreds
requests for firmware download at the same time [0-24]. Default value is 0.
Save - save new firmware auto-update settings.
On boot auto-update feature checks for available updates on specified server at
given URL. If there is different version - device downloads, installs firmware update
and reboots. If firmware version matches current version on device - no update
takes place.
Gemtek Systems Page 109
Page 10
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Connection
Use the connection menu to view the connected user’s statistics, set outgoing mail server or observe
the connected station availability.
Figure 159 – Connection Menu
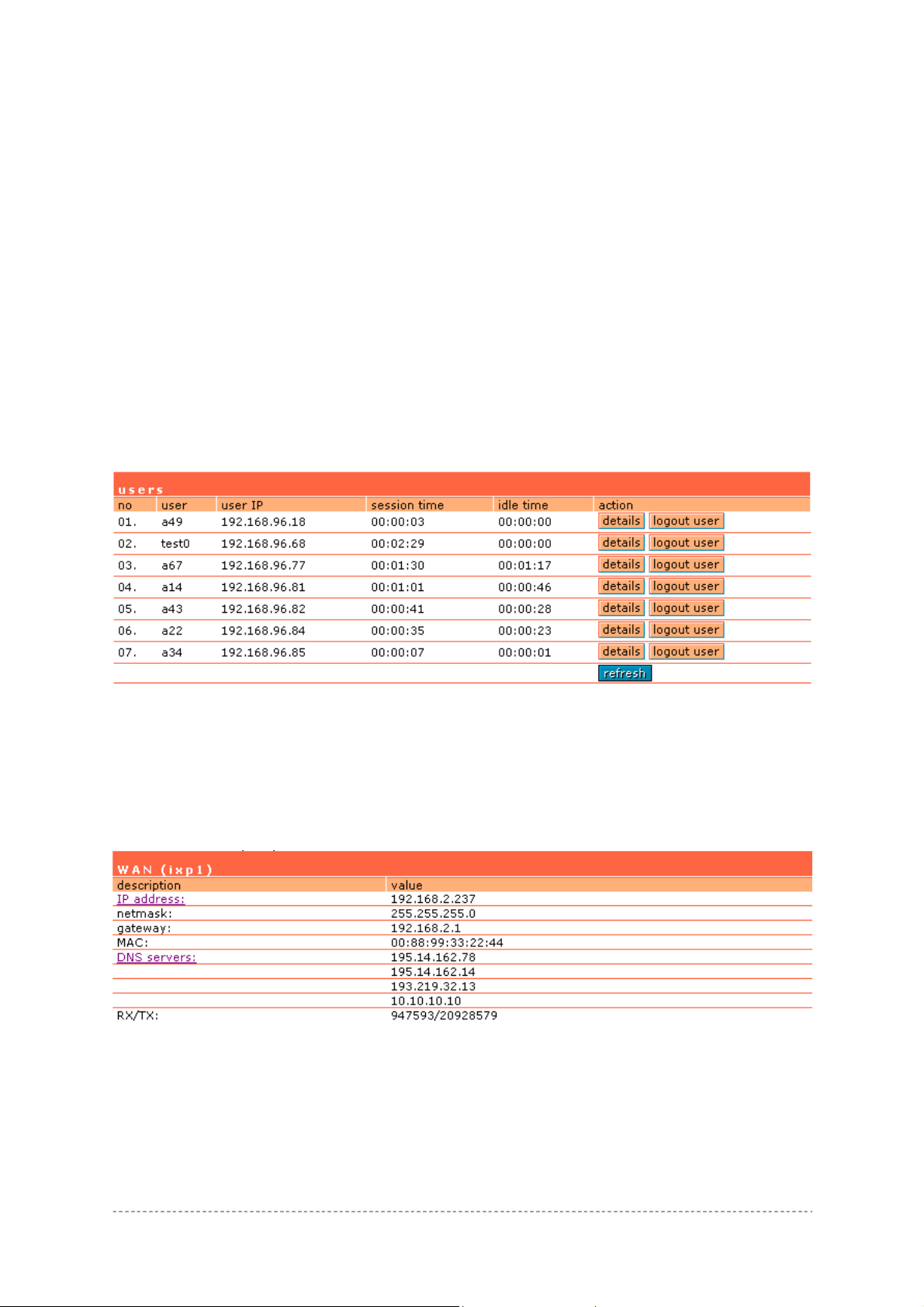
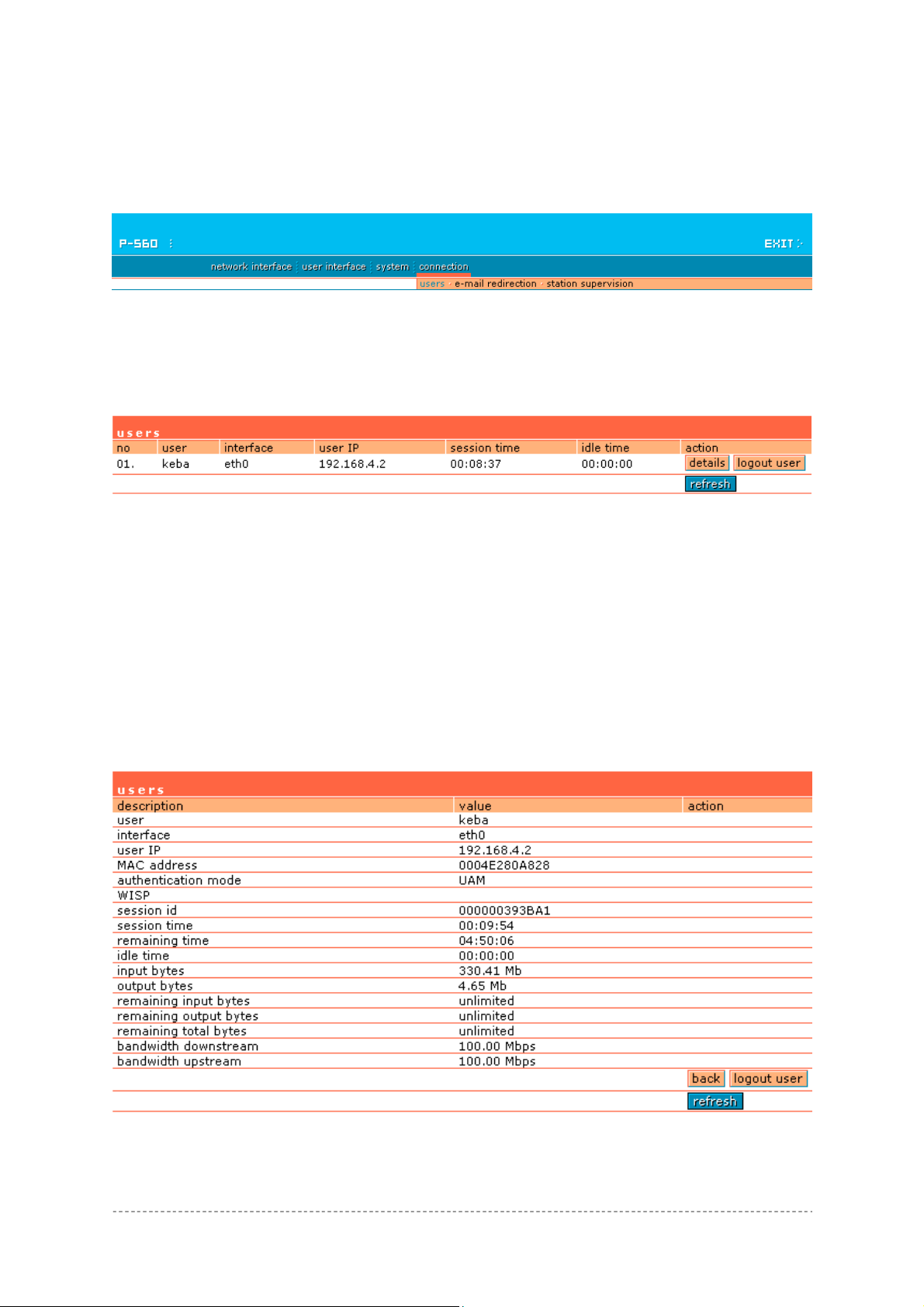
Connection | Users
The users menu is for viewing the connected users’ statistics. Also ability to logout user from the
system is implemented here:
Figure 160 – Users’ Statistics
The users’ statistics parameters are as follows:
No – number of the user’s session connection.
User – username of the connected client.
Interface – name of interface, through which client is connected [eth0/ixp0].
User IP – IP address, from which the user’s connection is established. Address is presented in digits
and dots notation.
Session Time - session duration since the user login.
Idle Time - amount of user inactivity time [hours: minutes: seconds].
Details – click on user details to get more information about the client:
Figure 161 – User’s Details
User – the username of the connected client.
Gemtek Systems Page 110
Page 11

User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Interface – name of interface, through which client is connected.
User IP – IP address, from which the user’s connection is established. Address is presented in digits
and dots notation.
MAC Address – hardware address of the network device from which the user is connected.
Authentication mode – authentication method which user uses to connect.
WISP – WISP domain name where the user belongs.
Session ID – the unique user’s session ID number. This can be used for troubleshooting purposes.
Session Time – session time duration since user login [hours: minutes: seconds/unlimited].
Remaining Time – remaining user’s session time [hours: minutes: seconds/unlimited]. Session time
for user is defined in the RADIUS server.
Idle Time - amount of user inactivity time [hours: minutes: seconds].
Input Bytes - amount of data in bytes, which the user network device has received [Bytes].
Output Bytes - amount of data in bytes, transmitted by the user network device [Bytes].
Remaining input/output/total bytes – user session remaining input/output bytes. WISP Operator
can define the user session in bytes. Remaining bytes is received from RADIUS [Bytes/unlimited].
Bandwidth downstream/upstream – user upstream and downstream bandwidth [in bps].
Back – returns to connected client’s statistics list.
Logout User – click this button to explicitly logout user from the network.
Refresh – click the button to refresh users’ statistics.
Gemtek Systems Page 111
Page 12
User’s Guide Chapter 7 – Reference Manual
Connection | E-mail Redirection
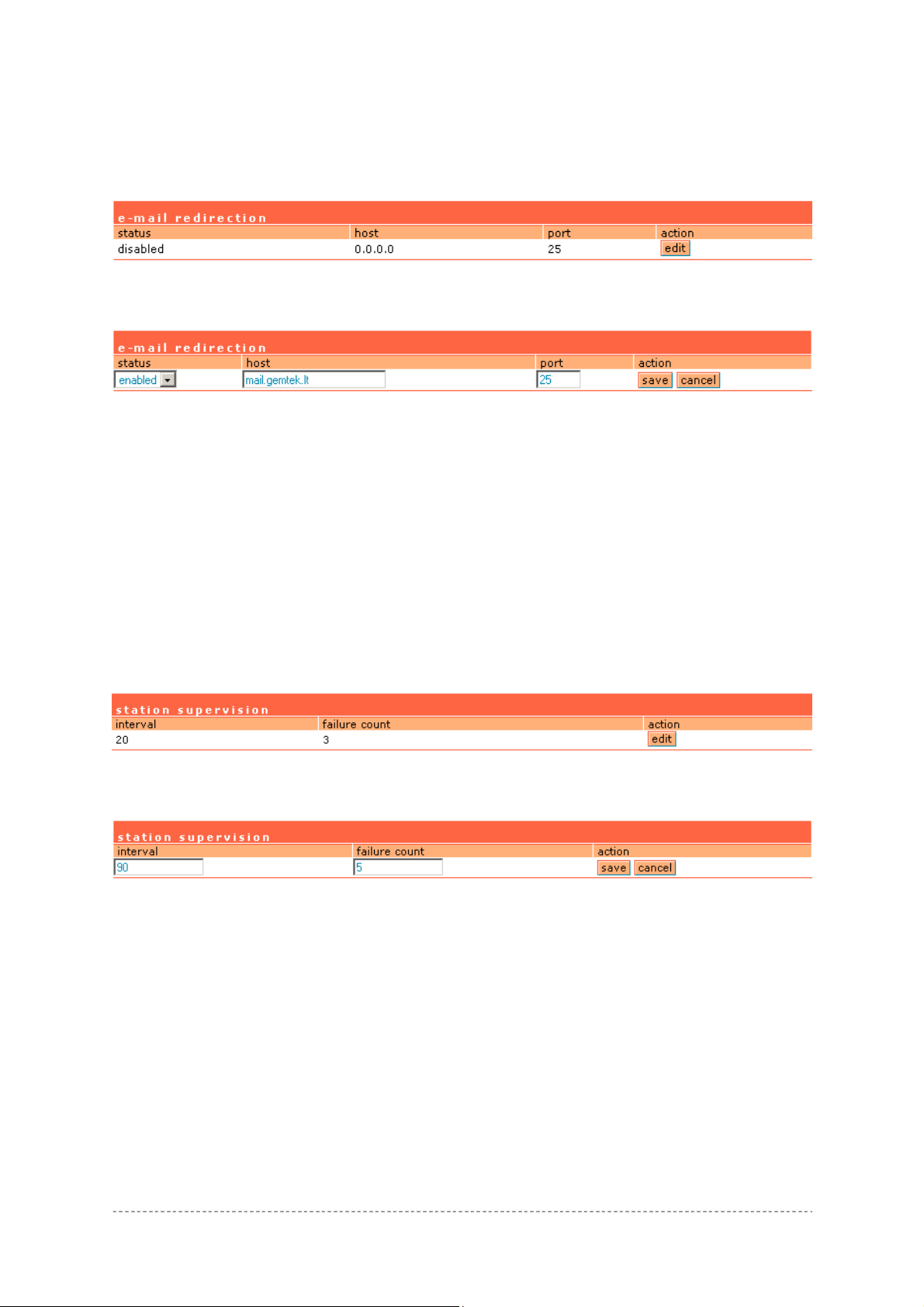
The outgoing mail (SMTP) server redirection is performed using the e-mail redirection menu. By
default such redirection settings is displayed:
Figure 162 – E-mail Redirection Settings
Click the edit button to specify your outgoing mail server settings.
Figure 163 – Edit E-mail Redirection
Status – enable/disable e-mail redirection function.
Host – SMTP server address where to redirect the outgoing clients e-mails [enter host name or host
IP address].
Port – port number [number, by default: 25].
Save – save new e-mail redirection settings.
Connection | Station Supervision
The station supervision function is used to monitor the connected host station availability. This
monitoring is performed with ping. If the specified number of ping failures is reached (failure count),
the user is logged out from the AC.
Figure 164 – Station Supervision
To adjust the ping interval/failure count, click the Edit button.
Figure 165 – Edit Station Supervision
Interval – define interval of sending ping to host [in seconds].
Failure Count – failure count value after which the user is logged out from the system.
Save – save station supervision settings.
Cancel – cancel changes.
Gemtek Systems Page 112
Page 13

User’s Guide Appendix
Appendix
A) Access Controller Specification
Technical Data
Wireless
Standard
Data Rate
Client Stations
Typical range 50 meters in indoor environments, up to 300m outdoors
Transmit Power Max. 17 dBm (EIRP)
Antennas Two 2dBi dipole antennas with space diversity, SMA connectors.
Encryption WPA, TKIP, WEP64, WEP128
WDS Wireless Distribution System for up to 7 APs
IEEE 802.11g (OFDM), IEEE 802.11b (DSSS), 2.4GHz ISM band, Wi-Fi
compliant
802.11g: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, 6 Mbps, 802.11b: 11Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 2,
1Mbps (auto fall back)
Max. 250 simultaneous client stations (depending on SW license Bronze,
Silver, Gold)
Network and Hotspot Access Control
IP Router with NAT/PAT, firewall filters Hotspot access controller with web browser log-
on (UAM) and 802.1x/EAP support, Smart Client
support, MAC authentication, WISPr compliant
(Wi-Fi alliance)
AAA RADIUS client and proxy server
with EAP support
Universal address translation and web
proxy support (any client configuration
is accepted)
VPN client (PPTP, GRE) IEEE 802.1x authenticator with EAP-SIM, MD-5,
WPA support DHCP server, DHCP relay gateway, DHCP client
VPN pass-through Layer 2 user isolation
E-mail redirection Bandwidth management via RADIUS
Universal access method (web browser log-on)
with XML support and walled garden (free web
sites)
WISPr compatible log-on via web browser,
SSL/TLS support UAT
TLS, TTLS, PEAP
Interface
WAN 10/100Mb Ethernet, auto sensing, RJ-45
LAN
WLAN Two SMA antenna connectors
Four 10/100Mb Ethernet port switched, auto sensing, RJ-45, 802.1q
VLAN support
Management
Interfaces
Software Update Remote software update via HTTPs
Reset Remote reset / Manufacturing reset
HTTPs, Telnet, SNMP (MIB II, Ethernet MIB, bridge MIB, private MIB),
Terminal
Physical Specification
Dimension 195 mm x 160 mm x 27 mm
Gemtek Systems Page 113
Page 14

User’s Guide Appendix
Weight -
Environment Specification
Temperature Humidity
Operating 0 to 55°C 10 % to 95%, non-condensing
Power Supply
External 100-230V AC, 50/60Hz
LEDs
8 LEDs Power, Online, WAN link, WLAN link, 4x LAN-link
Warranty
2 years
Package Contents
P560 Hotspot-in-a-Box Mounting Kit including tool to remove AP from
wall mounting
Two Ethernet patch cables External power supply, 100-230 V, 50/60 Hz
Two detachable antenna’s SMA
connector type
CD-ROM with software and
documentation
Power cord for EU
Printed warranty note, release note
Related Products
Controllers: G-6000/G-4000/G-4100 Public Access Controller
Access Points: P-520 54Mb Operator P-360 11Mb Hotspot-in-a-Box
P-380 11MB Outdoor Router
Client Adapters: T-316 11Mb Ethernet Client (2.4 GHz)
Gemtek Systems Page 114
Page 15

User’s Guide Appendix
B) Factory Defaults for the Access Controller
Network Interface Configuration Settings
Configuration | Interface Configuration
Interface Eth0
Status Enabled
Type LAN
IP Address 192.168.4.1
Netmask 255.255.255.0
Gateway Ixp1
Interface Ixp1
Status Enabled
Type WAN
IP Address 192.168.2.66
Netmask 255.255.255.0
Gateway 192.168.2.1
Interface Ixp0
Status Enabled
Type LAN
IP Address 192.168.3.1
Netmask 255.255.255.0
Gateway Ixp1
Configuration | VLAN
No VLAN entries are defined on system.
Configuration | Route
No routes are defined on system.
Configuration | Port Forwarding
No port forwards defined.
Configuration | Management Subnet
Interface Eth0
Status Disabled
IP Address 0.0.0.0
Netmask 0.0.0.0
Remote Network 0.0.0.0
Remote Netmask 0.0.0.0
Interface Ixp0
Status Disabled
IP Address 0.0.0.0
Netmask 0.0.0.0
Remote Network 0.0.0.0
Remote Netmask 0.0.0.0
Gemtek Systems Page 115
Page 16

User’s Guide Appendix
DNS
Hostname None
Domain None
Type Primary
IP Address 0.0.0.0
Type Secondary
IP Address 0.0.0.0
DHCP
Status DHCP Server
Interface Eth0
IP Address from 192.168.4.2
IP Address to 192.168.4.254
WINS Address 0.0.0.0
Status DHCP Server
Interface Ixp0
IP Address from 192.168.3.2
IP Address to 192.168.3.254
WINS Address 0.0.0.0
RADIUS Settings
RADIUS Retries 5
RADIUS Timeout 2
NAS Server ID -
User Session Timeout 18000
User Accounting Update 600
User Accounting Update Retry 60
User Idle Timeout 900
Location ISO Country Code US
Location E.164 Country Code 1
Location E.164 Area Code 408
Location Network Gemtek_Systems
Hotspot Operator Name Gemtek_Systems
Location Terminal_Worldwide
Bandwidth Up 128 Kbits
Bandwidth Down 128 Kbits
RADIUS Servers
Name DEFAULT (default)
Type Authentication
IP Address 0.0.0.0
Port 1812
Secret password (case sensitive)
Type Accounting
IP Address 0.0.0.0
Gemtek Systems Page 116
Page 17

User’s Guide Appendix
Port 1813
Secret secret (case sensitive)
Reverse Accounting disabled
Strip WISP enabled
UAM authentication method PAP
WISP
No WISP defined on system.
Accounting Backup
Description Backup via syslog
Status Disabled
Host 0.0.0.0
Description Backup to local file
Status Disabled
Host -
Tunnels | PPPoE/PPTP/GRE
PPPoE/PPTP/GRE services are disabled.
Tunnels | PPTP Client for VPN
No PPTP client for VPN entries defined on system.
Tunnels | GRE Client for VPN
GRE Status Disabled
GRE Remote Host 0.0.0.0
GRE Interface IP 0.0.0.0
GRE Interface Netmask 0.0.0.0
GRE Route 0.0.0.0/24
Wireless | Basic
Primary SSID P560
Wireless Network Mode Mixed/G (WiFi)
Regulatory Domain Manual
Default Channel 11
Wireless | Advanced
Layer 2 Isolation Disabled
SSID Broadcasting Enabled
Fragmentation Threshold 2346
RTS Threshold 2347
Output Power 10
Antenna Gain 2
Wireless | Security
WEP/WPA Disabled
Wireless | ACL
ACL Service Disabled
Default ACL Policy Allow
Gemtek Systems Page 117
Page 18

User’s Guide Appendix
Wireless | WDS
No WDS links are specified.
User Interface Configuration Settings
Pages
Page Welcome
Use Internal
Status Enabled
Location Welcome.xsl
Page Login
Use Internal
Status -
Page Logout
Use Internal
Status -
Location Logout.xsl
Page Help
Use Internal
Status -
Location Images/help.html
Page Unauthorized
Use Internal
Status -
Location Images/unauthorized.html
Caching
Description Enabled
Headers
Description Content-Type
Status Disabled
Description Content-Language
Status Disabled
Remote Authentication
Remote Authentication Disabled
Shared Secret None
Administrator
Username admin (case sensitive)
Start Page
Start Page URL http://www.gemtek-systems.com
Walled Garden
Gemtek Systems Page 118
Page 19

User’s Guide Appendix
No free site (or walled garden) URL is specified.
Web Proxy
Web Proxy Enabled
Port 3128, 8080
System Configuration Settings
Configuration | Syslog
Remote Log Status Disabled
Host 0.0.0.0
Level Debug
Configuration | Trace System
History Size 100
Level Debug
Configuration | Clock
Date Time No further known parameter.
Configuration | NTP
NTP Service Disabled
Host 0.0.0.0
Configuration | Certificate
By default Gemtek System certificate is uploaded in the system with following certificate information:
Issuer Organization Name Gemtek Systems
Subject Organization Name Gemtek Systems
Validity Not Before Oct 7 7:46:53 2002 GMT
Validity Not After Mar 12 7:46:53 2019 GMT
Configuration | Save and Restore
No further known parameters.
Configuration | Pronto
Gold Pronto Status Disabled
HNS server URL 0.0.0.0:9989
Heartbeat interval Disabled
Remote host 0.0.0.0
Remote port 7788
Access | Access Control
Default Access Status Deny
Network Address All
SNMP Service Allow
Network Address All
Access | Telnet
Telnet Status Disabled
Gemtek Systems Page 119
Page 20

User’s Guide Appendix
Access | AAA
UAM Enabled
EAP802.1x Disabled
MAC Disabled
Use Password RADIUS secret
Password password (case sensitive)
Access | UAT
Interface Eth0
UAT Status Disabled
IP Address 0.0.0.0
Netmask 0.0.0.0
Interface Ixp0
UAT Status Disabled
IP Address 0.0.0.0
Netmask 0.0.0.0
Access | Isolation
Bindmac Disabled
Isolation Disabled
Access | NAV
Interface Eth0
IP Address 192.168.3.1
NAT Enabled
Authentication Enabled
Visitor Access Disabled
Interface Ixp0
IP Address 192.168.2.4.1
NAT Enabled
Authentication Enabled
Visitor Access Disabled
Access | SNMP
SNMP Service Enabled
Name Name
Location Location
Contact Contact information
Public Community Name Public
Private Community Name Private
Default Trap Community Name Private
Authentication Failure Traps Generation Disabled
Type RO User
User Name public (case sensitive)
Password password (case sensitive)
Type RW User
Gemtek Systems Page 120
Page 21

User’s Guide Appendix
User Name private (case sensitive)
Password password (case sensitive)
There are no SNMP proxies on system.
There are no SNMP traps on system.
Update
Status Disabled
Update URL None
Update interval 48
Delay 0
Connection Settings
E-mail Redirection
Status Disabled
Host 0.0.0.0
Port 25
Station Supervision
Interval 20
Failure count 3
Gemtek Systems Page 121
Page 22

User’s Guide Appendix
C) Regulatory Domain/Channels
Channels
Identifiers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Frequency in
MHz
2412
2417
2422
2427
2432
2437
2442
2447
2452
2457
2462
2467
2472
2484
USA,
Canada
(FCC)
—
—
— — — — —
European
Union
WORLD
(CE/FCC)
France China Japan Manual
(CE/ETSI)
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • • • • • •
• • • • • • •
•
•
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
• • • •
• • • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• •
Maximum Power Levels 30dBm 20dBm 20dBm 20dBm 20dBm 20dBm 20dBm
Mexico is included in the Americas regulatory domain; however, channels 1
through 8 are for indoor use only while channels 9 through 11 can be used indoors
and outdoors. Users are responsible for ensuring that the channel set configuration
complies with the regulatory standards of Mexico.
Gemtek Systems Page 122
Page 23

User’s Guide Appendix
D) CLI Commands and Parameters
Network Commands
network
configuration Network Interfaces configuration.
dhcp Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol services configuration.
dns DNS Server settings.
radius Configuration set for changing RADIUS Server settings.
tunnels Tunnels configuration commands.
network configuration
interface Network Interfaces configuration.
portforward Port forwarding setup.
routes Static IP routing settings.
subnet Management subnet configuration.
vlans VLANs configuration.
network configuration interface
<interface> Standard UNIX interface name. This name cannot be changed.
-s <status> The interface status. Possible values are enabled and disabled.
-a <ip_address> Interface IP address in digits and dots notation, e.g. 192.168.2.27.
-m <netmask> Interface subnet mask e.g. 255.255.255.0.
-g <gateway>
-d <dhcpclient>
-q <masquerade> Masquerade status for interface: enabled or disabled.
-u <authentication> Authentication status on interface: enabled and disabled.
-v <visitor_access> Visitor access for interface: values enabled and disabled.
network configuration portforward
Interface gateway in digits and dots notation or name of other
interface.
The status of dhcp client for the interface. May have values
enabled and disabled. Can be used with WAN interface only.
<action> Action to take upon Port Forwarding entry: A(dd), E(dit), D(elete).
<id> Port Forwarding entry id. Needed with actions E(dit) and D(elete).
-s <status> PortForwarding rule status: enabled or disabled.
-p <protocol> Rule protocol.
-a <ip> Source ip address.
-l <port> Source port.
-d <ip> Destination ip address.
-r <port> Destination port.
network configuration routes
<action>
<id> Route id. Needed only with actions E and D.
<status> Route status. May have values active or inactive.
Action to take upon the route. May have values A(dd), E(dit),
D(elete).
Gemtek Systems Page 123
Page 24

User’s Guide Appendix
<device> Interface name.
<target> Target ip address.
<netmask> Target netmask.
<gateway> Gateway for the target address.
network configuration subnet
<interface> Interface name on which the management subnet is configured.
-s <status> Interface ip address for management subnet.
-a <ip_address> Interface ip address for management subnet.
-m <netmask> Interface netmask for management subnet.
-n <filterNetwork>
-t <filterNetmask>
network configuration vlans
<action> Action to take upon VLAN interface: A(dd), E(dit), D(elete).
<id> Vlan interface id. Needed only when adding VLAN interface.
<interface>
<name>
network dhcp
Network from which users are allowed to access management
subnet.
Netmask of network from which users are allowed to access
management subnet.
Name of interface on which VLAN interface exists. Needed only
when adding VLAN interface.
Name of VLAN interface. Needed only when editing or deleting
VLAN interface.
<interface> Interface name for DHCP server instance.
-s <status>
-f <from>
-t <to>
-w <wins>
-l <lease_time> DHCP Server lease time. Needed only with server status.
-d <domain> DHCP domain name. Needed only with server status.
-c <circuit_id>
-n <dns_list> List of up to two DNS servers IP addresses.
network dns
<type> DNS Server type. May be primary or secondary.
<nameserver>
Status of DHCP server for interface. May be server, relay or
disabled.
Start of IP address range supported for DHCP service. Needed
only with server status.
End of IP address range supported for DHCP service. Needed
only with server status.
WINS Address (Windows Internet Naming Service Address) if it is
available on the network. Needed only with server status.
Circuit ID - a unique NAS identifier. MAC address will be used by
default. Needed only with relay status.
DNS Server IP address in digits and dots notation, e.g.
192.168.2.27.
Network Radius Commands
network radius
accounting_log For sending RADIUS accounting via syslog.
proxy RADIUS Proxy configuration.
servers Up to 32 different RADIUS servers' configuration.
Gemtek Systems Page 124
Page 25

User’s Guide Appendix
settings General RADIUS settings configuration.
wisp WISP information and setup.
network accounting_log
-l <status>
-r <status>
-a <host> The host IP address where to send the accounting information.
network radius servers
accounting Accounting RADIUS servers' configuration.
authentication Authentication RADIUS servers' configuration.
backup Accounting information backup servers configuration.
network radius servers accounting
<id> RADIUS server id.
-a <ip_address> RADIUS server IP address used for Radius accounting.
-p <port> RADIUS server port used for Radius accounting.
-s <secret>
network radius servers authentication
<action>
<id> RADIUS server id.
-n <name> RADIUS server name.
-a <ip_address> RADIUS server IP address.
-p <port> RADIUS server port.
-s <secret>
-d <default>
-r <status> Reverse accounting. May have values enabled or disabled.
-w <status>
-u <method>
network radius servers backup
Local accounting log status. Possible values are enabled or
disabled.
Remote accounting log status. Possible values are enabled or
disabled.
Shared secret key for accounting (must be the same on RADIUS
server and RADIUS client).
Action to take uppon radius server. May have values A(dd), E(dit),
D(elete).
Shared secret key (must be the same on RADIUS server and
RADIUS client).
Sets the server as default. Possible values: yes. Note: there can
be only one default Radius server.
Strip WISP name before sending to RADIUS. May have values
enabled or disabled.
UAM authentication method for RADIUS server. May have values
pap, chap, mschap1 and mschap2.
<id> RADIUS server id.
-b <status>
-a <ip_address> Backup RADIUS server IP address used for Radius accounting.
-p <port> Backup RADIUS server port used for Radius accounting.
-s <secret>
If RADIUS Backup Server feature is on. May have values enabled
or disabled.
Shared secret key for backup server(must be the same on
RADIUS server and RADIUS client).
network radius settings
-r <retries> Retry count of sending RADIUS packets before giving up.
Gemtek Systems Page 125
Page 26

User’s Guide Appendix
-t <timeout>
-n <nas> NAS Server identification string.
-o <user_timeout>
-a <acct_update>
-c <acct_retry>
-i <idle>
-u <bandwidth> Default Radius user upload bandwidth.
-d <bandwidth> Default Radius user download bandwidth.
network radius wisp
<action> A(dd), D(elete)
<id> WISP Id. Usable only with D action.
<name> WISP name. Usable only with A action.
<radius_id>
<interface>
Maximal amount of time before retrying RADIUS packets (in
seconds).
Amount of time from user side (no network carrier) before closing
the connection (in seconds).
Period after which server should update accounting information
(in seconds).
Retry time period in which server should try to update accounting
information before giving up (in seconds).
Amount of user inactivity time, before automatically disconnecting
user from the network (in seconds).
WISP Radius server id (from Radius authentication server list).
Usable only with A action.
Interface name to which the WISP should be bound or none.
Usable only with A action.
Network Tunnels Commands
network tunnels
gre GRE client setup.
ppp PPTP, PPPoE and GRE setup.
pptp4vpn PPTP for VPN setup.
network tunnels gre
-s <status>
-r <ip> Remote host ip.
-d <ip> GRE device ip
-m <netmask> GRE device netmask. e.g. 255.255.255.0
-n <ip/netmask> Gre route. e.g. 192.168.6.0/24.
network tunnels ppp
-s <status> Status: disabled/PPTP/PPPoE/GRE.
-n <name> PPPoE/PPTP username.
-p <password> PPPoE/PPTP password.
-e <encryption>: PPPoE/PPTP encryption status: enabled or disabled.
-a <server> PPTP server ip address/GRE remote address.
-i <ip> GRE interface address.
-m <netmask> GRE interface netmask.
network tunnels pptp4vpn
Gre status: enabled or disabled. When enabling, gre tunnel will be
created.
<action> A(dd), D(elete) or E(dit) entry.
Gemtek Systems Page 126
Page 27

User’s Guide Appendix
-c <channel> PPTP channel. Used only with A and E actions.
-s <server> PPTP server ip address. Used only with A and E actions.
-u <username> PPTP username. Used only with A and E actions.
-p <password> PPTP password. Used only with A and E actions.
-e <encryption>
-a <network> PPTP remote network address. Used only with A and E actions.
-m <netmask> PPTP remote network netmask. Used only with A and E actions.
PPTP encryption status: enabled or disabled. Used only with A
and E actions.
Wireless Commands
wireless
acl Static ACL configuration.
advanced Advanced wireless settings
basic Basic wireless settings.
security Wireless security configuration.
wds Wireless Distribution System (WDS) configuration.
wireless acl
-s <status> Static ACL status: enabled or disabled.
-d <policy> Default ACL policy: allow or deny.
-aa <mac> Add MAC address to 'allow' list.
-ad <mac> Add MAC address to 'deny' list.
-ra <mac> Remove MAC address from 'allow' list.
-rd <mac> Remove MAC address from 'deny' list.
wireless advanced
-i <isolation> Layer 2 isolation: enabled or disabled.
-s <ssid_broadcasting SSID broadcasting: enabled or disabled.
-f <fragmentation> Fragmentation threshold: 256-2346.
-r <rts> RTS threshold: 0-2347.
-p <power> Wireless card output power in dBm.
-a Print valid output power range for current regulatory domain.
-g <gain> Wireless card antenna gain in dBi.
wireless basic
-s <ssid> SSID name.
-d <domain> Regulatory domain name.
-l Print available regulatory domains.
-m <mode>
-c <channel> Channel selection.
-a Print available channels for current regulatory domain
Wireless network mode: B-only, B(WiFi), Mixed(WiFi), Mixed,
Mixed/G (WiFi), G(WiFi).
wireless security
-s <mode> Wireless security mode: disabled, wep64, wep128, wpakey.
-k <key> Pre-shared key.
Gemtek Systems Page 127
Page 28

User’s Guide Appendix
wireless wds
-a <mac> Add WDS MAC address.
-r <mac> Remove WDS MAC address.
User Commands
user
administrator Administrator login and password change.
connected Connected users list.
start_page Definition of first URL after user login.
walled_garden Free Web sites list.
webproxy Web proxy configuration.
user administrator
Enter for wizard Follow the wizard and complete administrator settings changes.
user connected
<action> D(etail) user statistics for or L(ogout) user with specified ip.
<ip> User ip address.
user start_page
<url> The web page to which the user is redirected after login.
user walled_garden
host Configures free web sites that are not displayed to users.
url Configure free web sites that are displayed to users.
user walled_garden host
<action>
<id>
-h <host> Host address.
-p <port> Network port, which is used to reach the host.
-t <type> Used protocol type. May have values tcp or udp.
-m <netmask> Host subnet mask e.g. 255.255.255.255.
user walled_garden url
<action>
<id>
-u <url> URL address used for link.
-s <display> URL description visible for user.
user webproxy
-s <status> Web proxy status: enabled or disabled.
-a <port> [<port>... [<port>]] Add list of Web proxy ports.
-d <port> [<port>... [<port>]] Delete list of Web proxy ports.
Action to take on free web site. May have values A(add), E(edit),
D(delete).
Walled Garden entry id. Used only with E(dit) and D(elete)
actions.
Action to take on free web site. May have values A(add), E(edit),
D(delete).
Walled Garden entry id. Used only with E(dit) and D(elete)
actions.
Gemtek Systems Page 128
Page 29

User’s Guide Appendix
System Commands
system
access System access configuration.
configuration System configuration.
system access
aaa Multimode settings.
control
isolation Isolation setup.
snmp Configuration of SNMP service.
telnet Enabling or disabling of telnet protocol.
uat Universal Address Translation of all IP and proxy settings.
system configuration
clock Manual setting of internal device clock
ntp Configuration of Network time Protocol service.
syslog For sending system and debug messages via syslog protocol.
trace Displays the last logged messages.
Allow or deny management access depending on user network
address.
System Access Commands
system access aaa
-m <mode_list>
-u <use_password>
-p <password> User defined mac authentication password.
system access control
<action>
<id>
-s <service>
-a <ip/bitmask> 'all' or network ip address and bitmask to (dis)allow service to.
-p <policy> Management access policy: allow or deny(default is deny).
system access isolation
-b <status> Mac binding status: enabled or disabled.
-i <status> Isolation status: enabled or disabled.
system access snmp
Either disabled or space separated list of modes. Modes may be:
uam, 802.1x, mac.
Mac authentication mode password usage: 'radius' - use radius
shared secret key, 'user' - use of user-defined password.
Action to take upon management access entry: A(dd), E(dit),
D(elete) or default.
Management access entry id. Needed only when editing or
deleting entry.
Services for which the policy should be set: ssh, snmp, telnet or
all.
proxies SNMP proxies settings.
settings SNMP service settings.
traps SNMP traps settings.
users SNMP users settings.
Gemtek Systems Page 129
Page 30

User’s Guide Appendix
system access snmp proxies
<action> Action to take upon SNMP proxy entry: A(dd), E(dit) or D(elete).
<id> Entry id. Needed only with Edit and Delete actions.
-t <type>
-a <ip_address> Proxy ip address.
-c <community_name> Proxy community name.
-l <oid_local> Proxy local OID.
-r <oid_target> Proxy target OID.
Proxy type. May have values v1, v2c. Can be used only when
adding or editing proxy.
system access snmp settings
-s <status> Status of SNMP service.
-n <name> System name.
-l <location> Location of the device.
-c <contact> Contact information.
-b <public_name> Public name of SNMP service.
-r <private_name>: Private name of SNMP service.
system access snmp traps
<action> Action to take upon SNMP trap entry: A(dd), E(dit) or D(elete)
<id> Entry id. Needed only with Edit and Delete actions.
-c <community> SNMP community string.
-a <ip_address> SNMP trap host address.
-p <port> SNMP trap port.
-t <type> SNMP trap type: v1, v2 or inform.
system access snmp users
<id> User id.
-n <name> SNMP user name.
-p <password> SNMP user password.
system access telnet
<status> Change telnet service status: enabled or disabled.
system access uat
<interface> Active LAN interface.
-s <status> UAT status on interface.
-a <ip> Network of UAT address pool.
-m <netmask> Netmask of UAT address pool.
System Configuration Commands
system configuration
clock Manual setting of internal device clock.
ntp Configuration of Network time Protocol service.
syslog For sending system and debug messages via syslog protocol.
trace Displays the last logged messages.
Gemtek Systems Page 130
Page 31

User’s Guide Appendix
system configuration clock
<date> New date values in YYYY.MM.DD format.
<time> New time in hh:mm format.
<zone> New time zone (time from GMT in minutes).
system configuration ntp
<action> Action: A(dd), E(dit), D(elete) server or set NTP S(tatus).
<id> Server id. Needed only with E and D actions.
-a <server> NTP server address.
-s <status>
NTP service status: enabled or disabled. Needed only with S
action.
system configuration pronto
-s <status> Pronto compatibility agent status: enabled or disabled.
-u <server_url> HNS server url in format host:port.
-h <interval>
-a <remote_host> Remote host ip address.
-p <remote_port> Remote host port.
Heartbeat interval in seconds, 'disabled' or 'server' to obtain it
from the server.
system configuration syslog
-s <status> Syslog status. Possible values are enabled or disabled.
-h <host>
-l <level>
The host IP address where to send the syslog. Needed only when
enabling syslog.
The lowest level of messages that will be logged. Possible levels:
debug, info, warning, error, fatal.
system configuration trace
clear Clears trace history.
size <number> Sets trace history size.
level <level>
Sets level of trace messages. Possible levels: debug, info,
warning, error, fatal.
Status Commands
status
device General system information.
network Network information.
service Services information.
Connection Commands
connection
email Outgoing Main (SMTP) Redirection settings.
supervision Settings for station availability monitoring with ARP-Pings.
connection email
Gemtek Systems Page 131
Page 32

User’s Guide Appendix
<status> SMTP redirection status: enabled or disabled.
<host> New SMTP server host IP address.
<port> New port number.
connection supervision
<seconds> <number>
ARP-Ping interval in seconds and failure number after reaching
which user is automatically logged out.
Gemtek Systems Page 132
Page 33

User’s Guide Appendix
E) Standard RADIUS Attributes
The following standard RADIUS attributes and messages are supported by the Hotspot-in-a-Box.
The Gemtek System vendor specific attributes are described at the client point of
view (reverse accounting is disabled).
Required Attribute # Type Auth Req Auth
Acctg Req Comment
Reply
User-Name 1 String X X User enters full NAI
User – Password 2 String X
NAS–IP–Address 4 Ipaddr X X
Service-Type 6 Integer X Must be set to Login (1)
Framed-IP-Address 8 Ipaddr X X IP Address of the User
Reply-Message 18 String X
State 24 String X X
Class 25 String X X
Session-Timeout 27 Integer X
Idle-Timeout 28 Integer X
Called-Station-ID 30 String X X
NAS-Identifier 32 String X X String identifying the NAS
Acct-Status-Type 40 Integer X
Acct-Delay-Time 41 Integer X
Acct-Input-Octets 42 Integer X
Acct-Output Octets 43 Integer X
Acct-Session-ID 44 String X X X
Password of the user to be
authenticated
IP Address of the Hotspot-ina-Box
Text of reject reason if
present
AC does not interpret the
attribute locally
Attribute provided by the
Auth. Server, forwarded to
the accounting server
Forced logout once timeout
period reached (seconds)
Implicit logout inactivity
timeout period (seconds)
This field should contain the
MAC address or other
information identifying the
Hotspot-in-a-Box
1=Start, 2=Stop, 3=Interim
Update
Delay (seconds) between
Acctg Event and when AcctReq sent (doesn’t include
estimated network transit
time)
Indicates how many octets
have been received from
the port over the course of
this service being provided
Indicates how many octets
have been sent to the port in
the course of delivering this
service
Unique Accounting ID to
make it easy to match start
and stop records in a log file
Gemtek Systems Page 133
Page 34

User’s Guide Appendix
Acct-Session-Time 46 Integer X
Acct-Input-Packets 47 Integer X
Acct-Output
Packets
Acct-TerminateCause
Acct-InputGigawords
Acct-OutputGigawords
NAS-Port-Type 61 Integer X X 15=Ethernet, 19=802.11
Acct-Interim-Interval 85 Integer X
48 Integer X
49 Integer X
52 Integer X
53 Integer X
Call duration in seconds
(already compensated for idle
timeout)
Indicates how many packets
have been received from
the port over the course of
this service being provided
Indicates how many packets
have been sent to the port in
the course of delivering this
service
1=Explicit Logoff, 4=Idle
Timeout, 5=Session Timeout,
6=Admin Reset, 9=NAS
Error, 10=NAS Request,
11=NAS Reboot
This attribute indicates how
many times the Acct-InputOctets counter has wrapped
around 2
this service being provided
This attribute indicates how
many times the Acct-OutputOctets counter has wrapped
around 2
delivering this service
Interval (seconds) to send
accounting updates
32
over the course of
32
in the course of
Vendor Specific Attributes
The Wi-Fi Alliance recommends a list of certain Vendor Specific Attributes (VSA). The VSA values are
intended to provide location information to the backend processing system or to deliver service type
information back to the Hotspot-in-a-Box.
The Wi-Fi Alliance has registered an IANA Private Enterprise Number (PEN) of 14122, which can be
used to pass Vendor-Specific attributes to international roaming partners.
WISPr Vendor Specific
Atributes
Location-ID 1 String X X Hotspot Location Identifier
Location-Name 2 String X X
Logoff-URL 3 String X
Redirection-URL 4 String X URL of Start Page
Bandwidth-Min-Up 5 Integer X Minimum Transmit Rate (bps)
Bandwidth-MinDown
Bandwidth-Max-Up 7 Integer X
Bandwidth-MaxDown
# Type Auth Req Auth
Acctg Req Comment
Reply
Hotspot Location and
Operator’s Name
URL for user to perform
explicit logoff
6 Integer X Minimum Receive Rate (bps)
Maximum Transmit Rate
(bps)
8 Integer X Maximum Receive Rate (bps)
Gemtek Systems Page 134
Page 35

User’s Guide Appendix
Session-TerminateTime
Session-TerminateTime-End-of-Day
Billing-Class-OfService
Gemtek Systems
Vendor Specific
The Gemtek System vendor specific attributes are described at the client point of view
(reverse accounting is disabled).
9 String X
10 Integer X
11 String X
# Type Auth Req Auth
Reply
Atributes
Acct-Session-InputOctets
Acct-Session-InputGigawords
Acct-SessionOutput-Octets
Acct-SessionOutput-Gigawords
Acct-Session-Octets 25 Integer X
Acct-SessionGigawords
21 Integer X
22 Integer X
23 Integer X
24 Integer X
26 Integer X
YYYY-MMDDThh:mm:ssTZD
Flag zero or one indicating
termination rule.
Text string indicating service
type e.g. used for the visitor
access feature
Acctg Req Comment
Session download volume
limitation in bytes. Forced
logout once volume limitation
is reached.
Session download volume
limitation in bytes. Forced
logout once volume limitation
is reached
Session upload volume
limitation in bytes. Forced
logout once volume limitation
is reached
Session upload volume
limitation in bytes. Forced
logout once volume limitation
is reached
Upload and download
limitation
Upload and download
limitation
Gemtek Systems Page 135
Page 36

User’s Guide Appendix
F) Location ID and ISO Country Codes
This list states the country names (official short names in English) in alphabetical order as given in
ISO 3166-1 and the corresponding ISO 3166-1-alpha-2 code elements.
It lists 239 official short names and code elements.
Location ID Country Location ID Country
AF Afghanistan LI Liechtenstein
AL Albania LT Lithuania
DZ Algeria LU Luxembourg
AS American Samoa MO Macao
AD Andorra MK
AO Angola MG
AI Anguilla MW Malawi
AQ Antarctica MY Malaysia
AG Antigua and Barbuda MV Maldives
AR Argentina ML Mali
AM Armenia MT Malta
AW Aruba MH Marshall islands
AU Australia MQ Martinique
AT Austria MR Mauritania
AZ Azerbaijan MU Mauritius
BS Bahamas YT Mayotte
BH Bahrain MX Mexico
BD Bangladesh FM
BB Barbados MD Moldova, republic of
BY Belarus MC Monaco
BE Belgium MN Mongolia
BZ Belize MS
BJ Benin MA Morocco
BM Bermuda MZ Mozambique
BT Bhutan MM
BO NA Namibia
BA Bosnia and Herzegovina Nauru
BW Botswana NP Nepal
BV Bouvet island NL Netherlands
BR Brazil AN Netherlands Antilles
IO
BN Brunei Darussalam NZ New Zealand
BG Bulgaria NI Nicaragua
BF Burkina Faso NE Niger
BI Burundi NG Nigeria
Bolivia
NR
British Indian ocean territory NC New Caledonia
Macedonia, the former Yugoslav
republic of
Madagascar
Micronesia, federated states of
Montserrat
Myanmar
Gemtek Systems Page 136
Page 37

User’s Guide Appendix
KH Cambodia NU Niue
CM Cameroon NF Norfolk island
CA Canada MP Northern Mariana islands
CV Cape Verde NO Norway
KY Cayman islands OM
CF Central African republic PK Pakistan
TD Chad Palau
CL Chile PS Palestinian territory, occupied
CN China PA Panama
CX Christmas island Papua new guinea
CC Cocos (keeling) islands PY Paraguay
CO Colombia PE Peru
KM Comoros PH Philippines
CG Congo PN Pitcairn
CD Congo, the democratic republic of the PL Poland
CK Cook islands PT
CR Costa Rica PR Puerto Rico
CI Côte d'ivoire Qatar
HR Réunion
CU Cuba RO Romania
CY Cyprus RU Russian federation
CZ Czech republic RW
DK SH Saint Helena
DJ Djibouti KN Saint Kitts and Nevis
DM LC Saint Lucia
DO PM
EC VC Saint Vincent and the grenadines
EG WS
SV El Salvador San Marino
GQ Sao tome and Principe
ER Eritrea SA Saudi Arabia
EE Estonia SN Senegal
ET Ethiopia SC Seychelles
FK Falkland islands (malvinas) SL Sierra Leone
FO Faroe islands SG Singapore
FJ Fiji SK Slovakia
FI Finland SI Slovenia
FR France SB Solomon islands
GF French Guiana SO Somalia
PF French Polynesia ZA South Africa
TF French southern territories GS
Croatia RE
Denmark
Dominica
Dominican republic Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Ecuador
Egypt Samoa
Equatorial guinea ST
PW
PG
QA
SM
Oman
Portugal
Rwanda
South Georgia and the south
sandwich islands
Gemtek Systems Page 137
Page 38

User’s Guide Appendix
GA Gabon ES
GM Gambia LK Sri Lanka
GE Georgia SD Sudan
DE Germany SR
GH Ghana SJ Svalbard and Jan Mayan
GI Gibraltar SZ Swaziland
GR Greece SE Sweden
GL Greenland CH Switzerland
GD Grenada SY Syrian Arab republic
GP Guadeloupe TW Taiwan, province of china
GU Guam TJ Tajikistan
GT Guatemala Tanzania, united republic of
GN
GW Guinea-Bissau TL Timor-leste
GY Guyana TG Togo
HT
HM Heard island and McDonald islands TO Tonga
VA Holy see (Vatican city state) TT Trinidad and Tobago
HN Honduras TN Tunisia
HK TR Turkey
HU Hungary TM Turkmenistan
IS Iceland TC
IN India TV
ID Indonesia UG Uganda
IR Iran, Islamic republic of Ukraine
IQ Iraq AE United Arab emirates
IE Ireland GB United kingdom
IL Israel US United states
IT Italy UM United states minor outlying islands
JM Jamaica Uruguay
JP
JO Jordan VU Vanuatu
KZ Kazakhstan
KE Kenya VE
KI Kiribati VN Viet nam
KP
KR
KW Kuwait WF Wallis and Futuna
KG Kyrgyzstan Western Sahara
LA Lao people's democratic republic YE Yemen
LV Latvia YU Yugoslavia
Guinea TH Thailand
Haiti TK Tokelau
Hong Kong
Japan UZ Uzbekistan
Korea, democratic people's republic
of
Korea, republic of VI Virgin islands, u.s.
TZ
UA
UY
VG Virgin islands, British
EH
Spain
Suriname
Turks and Caicos islands
Tuvalu
Vatican city state see holy see
Venezuela
Gemtek Systems Page 138
Page 39

User’s Guide Appendix
LB Lebanon
LS Lesotho ZM Zambia
LR ZW Zimbabwe
LY Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
Liberia
Zaire see Congo, the democratic
republic of the
Gemtek Systems Page 139
Page 40

User’s Guide Appendix
G) User Pages Templates Syntax
In this section you will find syntax for the writing of the user pages with examples for the writing of
XSL templates. The P560 web server creates XML, having data inside its structure:
Example:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<Gemtek>
<Header Script_Name="login.user" Title="Login" charset="; charset=ISO88591" language="en"/>
<Data nasid="TestLab" version="P-560" help="images/help.html"
ip="192.168.4.1"
mac="00923456789A" original_url="https://192.168.4.4:7777/login.user"
type="2" username="g1">
<entry descr="Gemtek Baltic" id="0" url="http://www.gemtek.lt"/>
<entry descr="Gemtek Systems, Inc." id="1" url="http://www.gemtek-
systems.com"/>;
</Data>
<WISPAccessGatewayParam MessageType="120" ResponseCode="100">
<entry ReplyMessage="Your password has expired."/>
</WISPAccessGatewayParam>
<Errors id="4102"/>
</Gemtek>
;
;
Current script filename (to be used in forms action attribute) can be located in the XML tree at:
/Gemtek/Header/@Script_Name
Page title at:
/Gemtek/Header/@Title
Custom char set (if enabled on administration pages) for user pages at:
/Gemtek/Header/@charset
Welcome.xsl
Welcome page is the first page that the user sees while not registered on the network. This page
provides welcome text to the user who is connected to the controller and supplies a link to the login
page.
Attribute in XML tree at /Gemtek/Data/@cmd defines the link to the login page. This link should be
used to point the user from the welcome screen to login screen. The Welcome page also lists
defined walled garden entries, informing the user where to browse without registering on the network.
Walled Garden information is located in the XML tree under /Gemtek/Data with multiple "entry"
branches. These branches have the following attributes:
descr - website description;
url - website URL;
id - website id for P560 configuration, which is not needed for the user connecting to the network
through the P560.
Login.xsl
Login page appears when the user is not registered to the network and tries to open a webpage. The
user proceeds to the login page, following the link from the welcome page. The Login page has
variables that can be used:
/Gemtek/Header/@Script_Name - script name to send back to the P560 user login information;
/Gemtek/Data/@username - the username to be entered into the user name field – usually the
name the user entered before while unsuccessful in registering on the network;
Gemtek Systems Page 140
Page 41

User’s Guide Appendix
/Gemtek/Data/@ip - detected user IP from which he/she tries to register on the network;
/Gemtek/Data/@mac - detected users MAC address;
/Gemtek/Errors/@id - returned error code, which can be as follows:
error description
4101 Failed to authorize.
4102 Login or/and password incorrect.
4103 Network connection failed.
4104 Accounting error.
4105 Unknown authorization error.
4106 Could not get redirection URL.
4107 Already logged in.
/Gemtek/Data/@type - returns to P560 response for login request. Type values are as follows:
error description
0 Ok - logged in, redirect user to start page
1
2 Login or/and password incorrect
3 Network connection failed
4 Accounting error
5
Failed to authorize
User already logged in
It is advisable to first check the error codes, because they return more precise information. Branch
"Type" returns RADIUS server response, which gives additional information about the user status.
This can help in detecting whether the user is just logged in or has come to this page while already
logged-in.
/Gemtek/WISPAccessGatewayParam/entry/@ReplyMessage - the RADIUS server response
message on user logon [optional]. This parameter supports multiple messages.
This optional RADIUS Reply-Message's could provide more detailed information, why user logon
failed.
/Gemtek/Data/@cmd - link to logout page. The logout page displays network usage statistics and
provides the logout from the network function.
/Gemtek/Data/@url - the URL of start page to where the user is redirected after successful login.
Usually it can be the website of the company or organization providing the P560 controller and
configuring the users to visit their website.
/Gemtek/Data/@help - link to help page regarding how the user should register on the network.
When the user clicks the login button, information is sent to: /Gemtek/Header/@Script_Name
location with following information:
username - user name to register to network;
password - user password.
When the form is submitted, user information is checked and indication of success or failure is
returned.
Logout.xsl
The logout page displays network usage statistics and the user ability to logout from the network. The
Logout page is displayed after the successful login and with usage statistics which are automatically
refreshed after a defined time period.
Gemtek Systems Page 141
Page 42

User’s Guide Appendix
Logout page has variables:
/Gemtek/Header/@Script_Name - current script name, to send command to logout or refresh the
statistics on page.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@auth - authentication method.
/Gemtek/Errors/@id - returned error code. Error code is a follows:
error description
4107
Following error codes are sent when other than the LOGOUT command is submitted:
Already logged in. This error code usually comes from
login screen, when redirecting.
error description
4201 Failed to authorize.
4202 Login failed.
4203
4204
4205 Undefined error return from RADIUS client on P560.
4206 Already logged in.
Following error codes are sent when other than LOGOUT command is submitted:
Network connection failed.
Accounting error.
error description
4210 Already logged in.
4211 Failed authorization.
4212 Login failed.
4213 Network connection failed.
4214 Accounting error.
4215 Undefined error return from RADIUS client on P560.
/Gemtek/Data/@cmd - link to logout page.
/Gemtek/Data/@login - link to login page. This is used when the user is logged-off and to provide
a quick link to be used to register again.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@username - username with which user is logged in.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@ip - detected user IP address from which the user has made his attempt to
register on the network.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@mac - detected users MAC address.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@time - session time.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@idle - idle time.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@in - input bytes sent.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@out - output bytes sent.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@remain_down - input bytes left.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@remain_up - output bytes left.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@remain_total - total bytes left.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@remain_time - session time remaining.
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@down - bandwidth downstream.
Gemtek Systems Page 142
Page 43

User’s Guide Appendix
/Gemtek/Data/entry/@up - bandwidth upstream.
If there is no /Gemtek/Data/entry in XML tree, it indicates that the user is not logged in.
Logout page has two purposes:
Log off the user
Show the user usage statistics.
To log off the user, call the script defined in /Gemtek/Header/@Script_Name with variable cmd
set to logout. This could be done trough POST or simply GET methods supplying simple link with
parameters:
<a href="/logout.user?cmd=logout">.
To get user usage statistics, simply refresh the script defined in /Gemtek/Header/@Script_Name
with no variables set. This could be done by defining the simple link:
<a href="/logout.user">.
Help.html
This is a HTML file with no embedded cgi prepared. It is advisable to write instructions for the user on
how to register to the network or what to do in the case of troubleshooting.
Unauthorized.html
This page appears if the user is not registered on the network or the web authentication is not
provided on the AC. It is recommended to include information on how to contact the network
administrator (e.g. phone number).
Smart Client
The P560 cannot only be used with a browser, but with a smart client connected to the P560 through
HTTPS connection; thus, retrieving information given as XML in the same login.user output. To
support a smart client, the following lines should be included in all user XSL templates:
<xsl:import href="xml-in-comments.xsl"/>
<xsl:apply-templates select="Gemtek/WISPAccessGatewayParam"/>
Commands for User Pages
A user who is not logged in and trying to browse the Internet will be redirected to the welcome page
automatically.
The welcome page address is:
https://P560_ip_address/welcome.user
The login page address is:
https://P560_ip_address/login.user
The logout and session information page address is:
https://P560_ip_address/logout.user
For the user who is logged in, the form should be posted to /login.user address and the form
should have the following parameters:
username - username to log on;
password - user password;
'cmd' with value 'login'.
To receive connected user session information, the following address should be used:
https://P560_ip_address/logout.user
To disconnect a user who is currently connected, the following address should be used:
Gemtek Systems Page 143
Page 44

User’s Guide Appendix
https://P560_ip_address/logout.user with parameter 'cmd' with value 'logout'.
Entering the following address into the browser will disconnect the currently logged in user:
https://P560_ip_address/logout.user?cmd=logout
Upload Templates
All user pages files (welcome.xsl, login.xsl, logout.xsl, help.html, unauthorized.html) can be on an
external server or on the P560. Which templates are to be used is found in user interface |
configuration | pages. The P560 has default user templates that can be replaced by uploading new
templates. Any uploaded templates and images overrides the default templates.
Next to predefined templates, there are supported image types:
PNG
GIF
JPG
Supported cascading style sheets:
CSS
Uploaded file types are detected by their extension.
Use of cascading style sheets (css) is not required, but recommended.
The Hotspot-in-a-Box administrator is responsible to conduct tests to ensure that all uploaded
templates are correct and work as expected. After the upload, the controller does not verify the
correctness of the uploaded templates. If the controller is not able to load the uploaded xsl template,
it will use the default build-in templates.
Image Location
Designers who prepare custom user templates should take note of the location of the images used.
All uploaded images, style sheets and static HTML pages (help.html and unauthorized.html) are
located at the virtual directory 'images'. Uploaded image example.gif will be accessible at the
following path: 'images/example.gif'
Using other paths like 'webserver/example.gif' or 'example.gif' will redirect to
images/unauthorized.html' or if UAM is enabled to user page (welcome.user, login.user or logout.user
depending on device configuration and user status).
This is an example of how to use an image in a XSL template:
<img name="example" src="images/example.gif" />
Gemtek Systems Page 144
Page 45
User’s Guide Glossary
Glossary
Symbols:
802.11: 802.11 is a family of specifications for
wireless local area networks (WLANs)
developed by a working group of the Institute
of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
The original specification provides for an
Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) and
several physical layer (PHY) options, the most
popular of which uses GFSK modulation at
2.4GHz, enabling data rates of 1 or 2Mbps.
Since its inception, two major PHY
enhancements have been adopted and
become "industry standards".
802.11b adds CCK modulation enabling data
rates of up to 11Mbps, and 802.11a specifies
OFDM modulation in frequency bands in the 5
to 6GHz range, and enables data rates up to
54Mbps.
A
AAA: Authentication, Authorization and
Accounting. A method for transmitting roaming
access requests in the form of user credentials
(typically user@domain and password),
service authorization, and session accounting
details between devices and networks in a
real-time manner.
authentication: The process of establishing the
identity of another unit (client, user, device)
prior to exchanging sensitive information.
B
backbone: The primary connectivity mechanism
of a hierarchical distributed system. All
systems, which have connectivity to an
intermediate system on the backbone, are
assured of connectivity to each other. This
does not prevent systems from setting up
private arrangements with each other to
bypass the backbone for reasons of cost,
performance, or security.
Bandwidth: Technically, the difference, in Hertz
(Hz), between the highest and lowest
frequencies of a transmission channel.
However, as typically used, the amount of data
that can be sent through a given
communications circuit. For example, typical
Ethernet has a bandwidth of 100Mbps.
bps: bits per second. A measure of the data
transmission rate.
D
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) is a communications protocol that lets
network administrators manage centrally and
automate the assignment of Internet Protocol
(IP) addresses in an organization's network.
Using the Internet Protocol, each machine that
can connect to the Internet needs a unique IP
address. When an organization sets up its
computer users with a connection to the
Internet, an IP address must be assigned to
each machine. Without DHCP, the IP address
must be entered manually at each computer
and, if computers move to another location in
another part of the network, a new IP address
must be entered. DHCP lets a network
administrator supervise and distribute IP
addresses from a central point and
automatically sends a new IP address when a
computer is plugged into a different place in
the network.
DNS: Domain Name Service. An Internet
service that translates a domain name such as
gemtek-systems.com to an IP address, in the
form xx.xx.xx.xx, where xx is an 8 bit hex
number.
E
EAP: Extensible Authentication Protocol.
Defined in [RFC2284] and used by IEEE
802.1x Port Based Authentication Protocol
[8021x] that provides additional authentication
methods. EAP-TLS (Transport Level Security)
provides for mutual authentication, integrityprotected ciphersuite negotiation and key
exchange between two endpoints [RFC2716].
EAP-TTLS (Tunneled TLS Authentication
Protocol) provides an authentication
negotiation enhancement to TLS (see InternetDraft <draft-ietf-pppext-eap-ttls-00.txt>).
Gemtek Systems Page 145
Page 46

User’s Guide Glossary
G
gateway: A gateway is a network point that acts
as an entrance to another network. On the
Internet, a node or stopping point can be either
a gateway node or a host (end-point) node.
Both the computers of Internet users and the
computers that serve pages to users are host
nodes. The computers that control traffic within
your company's network or at your local
Internet service provider (ISP) are gateway
nodes.
H
hotspot: A hotspot is wireless public access
system that allows subscribers to be
connected to a wireless network in order to
access the Internet or other devices, such as
printers. Hot-spots are created by WLAN
access points, installed in public venues.
Common locations for public access are
hotels, airport lounges, railway stations or
coffee shops.
hotspot operator: An entity that operates a facility
consisting of a Wi-Fi public access network
and participates in the authentication.
HTTP: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
is the set of rules for exchanging files (text,
graphic images, sound, video, and other
multimedia files) on the World Wide Web.
Relative to the TCP/IP suite of protocols
(which are the basis for information exchange
on the Internet), HTTP is an application
protocol.
HTTPS: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol
over Secure Socket Layer, or HTTP over SSL)
is a Web protocol developed by Netscape and
built into its browser that encrypts and
decrypts user page requests as well as the
pages that are returned by the Web server.
HTTPS is really just the use of Netscape's
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) as a sublayer
under its regular HTTP application layering.
I
ICMP: ICMP (Internet Control Message
Protocol) is a message control and errorreporting protocol between a host server and a
gateway to the Internet. ICMP uses Internet
Protocol (IP) datagrams, but the messages are
processed by the IP software and are not
directly apparent to the application user.
IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers. The IEEE describes itself as the
world's largest professional society. The IEEE
fosters the development of standards that
often become national and international
standards, such as 802.11.
IP: The Internet Protocol (IP) is the method or
protocol by which data is sent from one
computer to another on the Internet. Each
computer (known as a host) on the Internet
has at least one IP address that uniquely
identifies it from all other computers on the
Internet. When you send or receive data (for
example, an e-mail note or a Web page), the
message gets divided into little chunks called
packets. Each of these packets contains both
the sender's Internet address and the
receiver's address. Any packet is sent first to a
gateway computer that understands a small
part of the Internet. The gateway computer
reads the destination address and forwards
the packet to an adjacent gateway that in turn
reads the destination address and so forth
across the Internet until one gateway
recognizes the packet as belonging to a
computer within its immediate neighborhood or
domain. That gateway then forwards the
packet directly to the computer whose address
is specified.
IPsec: IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) is a
developing standard for security at the network
or packet processing layer of network
communication. Earlier security approaches
have inserted security at the application layer
of the communications model. IPsec will be
especially useful for implementing virtual
private networks and for remote user access
through dial-up connection to private networks.
A big advantage of IPsec is that security
arrangements can be handled without
requiring changes to individual user
computers. Cisco has been a leader in
proposing IPsec as a standard (or combination
of standards and technologies) and has
included support for it in its network routers.
IPsec provides two choices of security service:
Authentication Header (AH), which essentially
allows authentication of the sender of data,
and Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP),
which supports both authentication of the
sender and encryption of data as well. The
specific information associated with each of
these services is inserted into the packet in a
header that follows the IP packet header.
Separate key protocols can be selected, such
as the ISAKMP/Oakley protocol.
Gemtek Systems Page 146
Page 47

User’s Guide Glossary
ISP: An ISP (Internet Service Provider) is a
company that provides individuals and other
companies access to the Internet and other
related services such as Web site building and
virtual hosting. An ISP has the equipment and
the telecommunication line access required to
have a point-of-presence on the Internet for
the geographic area served.
L
LAN: A local area network (LAN) is a group of
computers and associated devices that share
a common communications line and typically
share the resources of a single processor or
server within a small geographic area (for
example, within an office building). Usually,
the server has applications and data storage
that are shared in common by multiple
computer users. A local area network may
serve as few as two or three users (for
example, in a home network) or many as
thousands of users (for example, in an FDDI
network).
M
MAC: Medium Access Control. In a WLAN
network card, the MAC is the radio controller
protocol. It corresponds to the ISO Network
Model's level 2 Data Link layer. The IEEE
802.11 standard specifies the MAC protocol
for medium sharing, packet formatting and
addressing, and error detection.
N
NAT: NAT (Network Address Translation) is the
translation of an Internet Protocol address (IP
address) used within one network to a different
IP address known within another network. One
network is designated the inside network and
the other is the outside. Typically, a company
maps its local inside network addresses to one
or more global outside IP addresses and
unmaps the global IP addresses on incoming
packets back into local IP addresses.
P
POP3: POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) is the
most recent version of a standard protocol for
receiving e-mail. POP3 is a client/server
protocol in which e-mail is received and held
for you by your Internet server. Periodically,
you (or your client e-mail receiver) check your
mail-box on the server and download any mail.
POP3 is built into the Netmanage suite of
Internet products and one of the most popular
e-mail products, Eudora. It's also built into the
Netscape and Microsoft Internet Explorer
browsers.
PPP: PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol
for communication between two computers
using a serial interface, typically a personal
computer connected by phone line to a server.
PPP uses the Internet protocol (IP) (and is
designed to handle others). It is sometimes
considered a member of the TCP/IP suite of
protocols. Relative to the Open Systems
Interconnection (OSI) reference model, PPP
provides layer 2 (data-link layer) service.
Essentially, it packages your computer's
TCP/IP packets and forwards them to the
server where they can actually be put on the
Internet.
PPP is a full-duplex protocol that can be used
on various physical media, including twisted
pair or fiber optic lines or satellite
transmission. It uses a variation of High Speed
Data Link Control (HDLC) for packet
encapsulation.
PPP is usually preferred over the earlier de
facto standard Serial Line Internet Protocol
(SLIP) because it can handle synchronous as
well as asynchronous communication. PPP
can share a line with other users and it has
error detection that SLIP lacks. Where a
choice is possible, PPP is preferred.
NAT is included as part of a router and is often
part of a corporate firewall.
Gemtek Systems Page 147
Page 48

User’s Guide Glossary
PPPoE: PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over
Ethernet) is a specification for connecting
multiple computer users on an Ethernet local
area network to a remote site through common
customer premises equipment, which is the
telephone company's term for a modem and
similar devices. PPPoE can be used to have
an office or building-full of users share a
common Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), cable
modem, or wireless connection to the Internet.
PPPoE combines the Point-to-Point Protocol
(PPP), commonly used in dialup connections,
with the Ethernet protocol, which supports
multiple users in a local area network. The
PPP protocol information is encapsulated
within an Ethernet frame.
PPPoE has the advantage that neither the
telephone company nor the Internet service
provider (ISP) needs to provide any special
support. Unlike dialup connections, DSL and
cable modem connections are "always on."
Since a number of different users are sharing
the same physical connection to the remote
service provider, a way is needed to keep
track of which user traffic should go to and
which user should be billed. PPPoE provides
for each user-remote site session to learn
each other's network addresses (during an
initial exchange called "discovery"). Once a
session is established between an individual
user and the remote site (for example, an
Internet service provider), the session can be
monitored for billing purposes.
PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
(PPTP) is a protocol (set of communication
rules) that allows corporations to extend their
own corporate network through private
"tunnels" over the public Internet. Effectively, a
corporation uses a wide-area network as a
single large local area network. This kind of
interconnection is known as a virtual private
network (VPN).
R
RADIUS: RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-
In User Service) is a client/server protocol and
software that enables remote access servers
to communicate with a central server to
authenticate dial-in users and authorize their
access to the requested system or service.
RADIUS allows a company to maintain user
profiles in a central database that all remote
servers can share. It provides better security,
allowing a company to set up a policy that can
be applied at a single administered network
point. Having a central service also means that
it's easier to track usage for billing and for
keeping network statistics.
S
SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP) is the protocol governing network
management and the monitoring of network
devices and their functions. It is not
necessarily limited to TCP/IP networks.
SNMP is described formally in the Internet
Engineering Task Force (IETF) Request for
Comment (RFC) 1157 and in a number of
other related RFCs.
SSL: The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a
commonly-used protocol for managing the
security of a message transmission on the
Internet. SSL has recently been succeeded by
Transport Layer Security (TLS), which is
based on SSL. SSL uses a program layer
located between the Internet's Hypertext
Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Transport
Control Protocol (TCP) layers. The "sockets"
part of the term refers to the sockets method
of passing data back and forth between a
client and a server program in a network or
between program layers in the same
computer. SSL uses the public-and-private key
encryption system from RSA, which also
includes the use of a digital certificate.
T
TCP: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a
set of rules (protocol) used along with the
Internet Protocol (IP) to send data in the form
of message units between computers over the
Internet. While IP takes care of handling the
actual delivery of the data, TCP takes care of
keeping track of the individual units of data
(called packets) that a message is divided into
for efficient routing through the Internet.
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, which
means that a connection is established and
maintained until such time as the message or
messages to be exchanged by the application
programs at each end have been exchanged.
TCP is responsible for ensuring that a
message is divided into the packets that IP
manages and for reassembling the packets
back into the complete message at the other
end. In the Open Systems Interconnection
(OSI) communication model, TCP is in layer 4,
the Transport Layer.
Gemtek Systems Page 148
Page 49

User’s Guide Glossary
TCP/IP: TCP/IP (Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol) is the basic
communication language or protocol of the
Internet. It can also be used as a
communications protocol in a private network
(either an intranet or an extranet). When you
are set up with direct access to the Internet,
your computer is provided with a copy of the
TCP/IP program just as every other computer
that you may send messages to or get
information from also has a copy of TCP/IP.
TCP/IP is a two-layer program. The higher
layer, Transmission Control Protocol,
manages the assembling of a message or file
into smaller packets that are transmitted over
the Internet and received by a TCP layer that
reassembles the packets into the original
message. The lower layer, Internet Protocol,
handles the address part of each packet so
that it gets to the right destination.
Telnet: Telnet is the way to access someone
else's computer, assuming they have given
permission. (Such a computer is frequently
called a host computer.) More technically,
Telnet is a user command and an underlying
TCP/IP protocol for accessing remote
computers. On the Web, HTTP and FTP
protocols allow to request specific files from
remote computers, but not to actually be
logged on as a user of that computer.
U
UAM: Universal Access Method is the current
recommended methodology for providing
secure web-based service presentment,
authentication, authorization and accounting of
users is a WISP network. This methodology
enables any standard Wi-Fi enabled TCP/IP
device with a browser to gain access to the
WISP network.
W
WAN: A wide area network (WAN) is a
geographically dispersed telecommunications
network. The term distinguishes a broader
telecommunication structure from a local area
network (LAN). A wide area network may be
privately owned or rented, but the term usually
connotes the inclusion of public (shared user)
networks. An intermediate form of network in
terms of geography is a metropolitan area
network (MAN).
X
XSL (Extensible Style sheet Language),
formerly called Extensible Style Language, is a
language for creating a style sheet that
describes how data sent over the Web using
the Extensible Markup Language (XML) is to
be presented to the user.
Gemtek Systems Page 149
Page 50

Index
A
AAA, 9
configuration, 99
AC specification, 114
access AC
using KickStart utility, 17
using Web-browser, 16
access control on device, 97
ACL
configuration, 79
administrator, 87
antenna gain, 78
authentication, 101
B
back pannel, 13
C
certificates upload, 94
CLI, 41
connection commands, 132
network commands, 124
network RADIUS commands, 125
network tunnels commands, 127
status commands, 132
system commands, 130
system configuration commands, 131
user commands, 129
wireless commands, 128
CLI commands
connection, 41
exit, 47
login, 41
network, 42
reboot, 47
reset, 47
status, 46
system, 46
telnet, 47
user, 45
wireless, 44
clock, 92
command line interface, 40
connect
to CLI, 40
connect the access controller, 15
connectors, 14
create log-on, 20
D
Defaults, 76
DHCP, 60
DNS, 59
E
e-mail redirection, 113
extended UAM, 34
F
factory defaults values, 116
Features list, 9
G
GRE tunnel, 73
H
hardware introduction, 12
headers, 84
help page, 27, 83
I
initilization, 16
installation
connecting the controller, 11
package content, 11
interface configuration, 53
introduction
kickstart, 16
IP router, 9
ISO country codes, 137
L
LAN switch, 10
LED's, 13
location ID, 137
login, 20, 25, 83
logout, 26, 83
M
Management, 10
management subnet, 58
N
NAT, 101
Page 51

User’s Guide Index
NTP, 93
O
output power, 78
P
port forwarding, 57
PPPoE/PPPTP for DSL, 71
PPTP client for VPN, 72
Product overview, 8
proxy
configuration, 68
R
RADIUS
WISP, 68
RADIUS, 63
accounting backup, 70
attributes, 134, 135
servers, 66
settings, 64
redirection URL, 88
regulatory domain, 123
remote authentication, 85, 86
restore settings, 95
route
configuration, 56
T
technical data, 114
telnet access, 98
trace system, 92
trace system levels, 92
tunnels, 71
U
UAT, 22, 100
upgrade, 109
user isolation, 101
user pages
help, 27
logon, 25
logout, 26
unauthorized, 27
welcome, 25
user pages templates, 141
user pages upload, 84
users statistics, 111
V
visitor access, 101
scheme, 101
VLAN
configuration, 55
VPN, 9, 72
S
save settings, 95
SNMP, 48, 102
start up
administrator password, 21
e-mail redirection, 21
start-up
create welcome, 20
DNS set-up, 19
interface, 19
IP address management, 19
RADIUS set-up, 19
station supervision, 113
step by step, 19
support, 7
syslog, 91
system, 91
system reset, 108
system status, 105
W
walled garden, 88
WDS
configuration, 81
web interface
connection, 111
menu, 51
user, 83
web proxy, 90
welcome, 25, 83
wireless advanced
configuration, 78
wireless basic
configuration, 76
wireless interface, 76
wireless security
configuration, 78
WLAN, 9
Gemtek Systems Page 151
 Loading...
Loading...