Page 1

Microwave Data Systems
MDS FIVE Series Digital
Radio Transceiver
User Reference and Installation Guide
Document Number: 05-4498A01, Rev. G
Date: 13 July 2006
Page 2

Page 3

© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved.
This book and the information contained herein is the proprietary and confidential information of
Microwave Data Systems Inc. that is provided by Microwave Data Systems
TM
exclusively for
evaluating the purchase of Microwave Data Systems Inc. technology and is protected by copyright
and trade secret laws.
No part of this document may be disclosed, reproduced, or transmitted in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, for any purpose without the express writt en permission of Microwave Data
Systems Inc.
For permissions, contact Micro wav e Data Systems Inc. Marketing Group at 1-585-241-5510 or 1-585242-8369 (FAX).
Notice of Disclaimer
The information and specifications provided in this document are subject to change without notice.
Microwave Data Systems Inc. reserves the right to make changes in design or components as
progress in engineering and manufacturing may warrant.
The Warranty(s) that accompany Microwave Data Systems Inc., products are set forth in the sales
agreement/contract between Microwave Data Systems Inc. and its customer. Please consult the
sales agreement for the terms and conditions of the Warranty(s) proved by Microwave Data Systems
Inc. To obtain a copy of the Warranty(s), contact your Microwave Data Systems Inc. Sales
Representative at 1-585-241-5510 or 1-585-242-8369 (FAX).
The information provided in this Microwave Data Systems Inc., document is provided “as is” without
warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties
of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or non-infringement. Some jurisdictions do not
allow the exclusion of implied warranties, so the above exclusion may not apply to you.
In no event shall Microwave Data Systems Inc. be liable for any damages whatsoever – including
special, indirect, consequential or incidental damages or damages for loss of profits, revenue, use, or
data whether brought in contract or tort, arising out of or connected with any Microwave Data
Systems Inc., document or the use, reliance upon or performance of any material contained in or
accessed from this Microwave Data Systems Inc. document. Microwave Data Systems’s license
agreement may be provided upon request. Additional Terms and Conditions will be finalized upon
negotiation or a purchase.
The above information shall not be constructed to imply any additional warranties for Microwave Data
Systems Inc. equipment including, but not limited to, warranties of merchantability or fitness for an
intended use.
Trademark Information
Software Defined Indoor Unit
TM
(SDIDUTM) is a product and trademark of CarrierComm Inc.
JavaTM is a trademark of Sun Microsystems Inc.
Windows® is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation
All other brand or product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies or organizations.
Part Number: 05-4498A01
Page 4
Table of Contents
1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS......................................................................................................................1-1
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION.......................................................................................................................2-1
2.1 About This Manual............................................................................................................................2-1
2.2 Introduction.......................................................................................................................................2-1
2.3 System Features...............................................................................................................................2-4
2.4 Physical Description ........................................................................................................................2-5
2.4.1 Model Types................................................................................................................................2-5
2.4.2 Options ........................................................................................................................................2-6
2.4.3 Front Panel Indicators .................................................................................................................2-7
2.4.4 Front Panel Connections.............................................................................................................2-8
2.5 System Description........................................................................................................................2-11
2.6 Consecutive Point Architecture....................................................................................................2-14
2.7 2 + 0 (East-West) Configuration....................................................................................................2-16
2.8 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).......................................................................................................2-17
2.9 1+1 Protection.................................................................................................................................2-17
2.9.1 Protected Non-Diversity (Hot Standby).....................................................................................2-18
2.9.2 Protected Diversity ....................................................................................................................2-18
2.10 1 + 1 Multi-hop Repeater Configuration.......................................................................................2-19
2.11 Data Interfaces................................................................................................................................2-21
2.12 Crosspoint Switch..........................................................................................................................2-21
2.13 Power Management........................................................................................................................2-22
2.14 MDS FIVE Series Software and Network Management...............................................................2-23
2.14.1 IP Address.................................................................................................................................2-24
2.14.2 Network......................................................................................................................................2-24
2.14.3 NMS Network Operational Principles........................................................................................2-24
2.14.4 Third Party Network Management Software Support................................................................2-25
2.15 System Loopbacks.........................................................................................................................2-25
3 INSTALLATION.....................................................................................................................................3-1
3.1 Unpacking..........................................................................................................................................3-1
3.2 Notices...............................................................................................................................................3-2
3.3 Required Tools..................................................................................................................................3-2
3.3.1 SDIDUTM Tools............................................................................................................................3-2
3.3.2 ODU Tools...................................................................................................................................3-2
3.4 PRE-INSTALLATION NOTES ...........................................................................................................3-3
3.5 Overview of Installation and Testing Process...............................................................................3-3
3.6 Site Evaluation..................................................................................................................................3-5
3.6.1 Preparing for a Site Evaluation....................................................................................................3-6
3.6.2 Site Evaluation Process...............................................................................................................3-7
3.6.3 Critical System Calculations......................................................................................................3-12
3.6.4 Frequency Plan Determination..................................................................................................3-13
3.6.5 Antenna Planning......................................................................................................................3-15
Page 5

3.6.6 ODU Transmit Power Setup......................................................................................................3-15
3.6.7 Documenting a Site Evaluation.................................................................................................3-18
3.7 Installation of the MDS FIVE Series..............................................................................................3-21
3.7.1 Installing the MDS FIVE Series Software Defined IDUTM..........................................................3-21
3.7.2 Installing the MDS FIVE Series ODU........................................................................................3-22
3.7.3 Routing the ODU/ SDIDUTM Interconnect Cable.......................................................................3-24
3.8 Quick Start Guide ...........................................................................................................................3-26
3.8.1 Materials Required ....................................................................................................................3-26
3.8.2 Grounding the ODU...................................................................................................................3-26
3.8.3 Grounding the SDIDUTM............................................................................................................3-28
3.8.4 Connecting the SDIDUTM to the PC and Power Source............................................................3-28
3.8.5 SDIDUTM Configuration..............................................................................................................3-29
3.8.6 ODU Antenna Alignment...........................................................................................................3-31
3.8.7 Quick Start Settings...................................................................................................................3-32
3.9 SDIDU™ Service .............................................................................................................................3-33
3.9.1 Removing a Module...................................................................................................................3-33
3.9.2 Installing a Module.....................................................................................................................3-34
3.10 Documenting MDS FIVE Series Configuration............................................................................3-35
4 SUMMARY SPECIFICATION................................................................................................................4-1
5 FRONT PANEL CONNECTORS...........................................................................................................5-1
5.1 DC Input (Power) Connector............................................................................................................5-1
5.2 Ethernet 100BaseTX Payload Connector 1-2.................................................................................5-1
5.3 SONET Payload Connector..............................................................................................................5-2
5.4 STM-1 Payload Connector...............................................................................................................5-2
5.5 DS-3/E-3/STS-1 Payload Connector................................................................................................5-2
5.6 NMS 10/100BaseTX Connector 1-2.................................................................................................5-3
5.7 Alarm/Serial Port Connector............................................................................................................5-3
5.8 ODU Connector.................................................................................................................................5-4
5.9 T1/E1 - Channels 1-2 Connector .....................................................................................................5-4
5.10 T1/E1 - Channels 3-16 Connector ...................................................................................................5-5
5.11 USB ....................................................................................................................................................5-7
5.12 Voice Order Wire...............................................................................................................................5-7
5.13 Data Order Wire ................................................................................................................................5-8
5.13.1 RS422..........................................................................................................................................5-8
5.13.2 RS-232.........................................................................................................................................5-8
6 APPENDIX.............................................................................................................................................6-1
6.1 Alarm Descriptions...........................................................................................................................6-1
6.2 Abbreviations & Acronyms............................................................................................................6-16
Page 6
1 Safety Precautions
PLEASE READ THESE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS!
RF Energy Health Hazard
The radio equipment described in this guide uses radio frequency transmitters. Although the
power level is low, the concentrated energy from a directional antenna may pose a health hazard.
Do not allow people to come in close proximity to the front of the antenna while the transmitter is
operating. The antenna will be professional installed on fixed-mounted outdoor permanent
structures to provide separation from any other antenna and all persons as detailed on page
1-3.
Protection from Lightning
Article 810 of the US National Electric Department of Energy Handbook 1996 specifies that radio
and television lead-in cables must have adequate surge protection at or near the point of entry to
the building. The code specifies that any shielded cable from an external antenna must have the
shield directly connected to a 10 AWG wire that connects to the building ground electrode.
Warning – This is a Class A product
Warning – This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Warning – Turn off all power before servicing
Warning – Turn off all power before servicing.
Safety Requirements
Safety requirements require a switch be employed between the SDIDU™ external power supply
and the SDIDU™ power supplies.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc.
All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 7
User Reference and Installation Guide 1-2
Proper Disposal
The manufacture of the equipment described herein
has required the extraction and use of
natural resources. Improper disposal may contaminate the environment and prese nt a health risk
due to the release of hazardous substances contained within. To avoid dissemination of these
substances into our environment, and to lessen the demand on natural resources, we encourage
you to use the appropriate recycling systems for disposal. These systems will reuse or recycle
most of the materials found in this equipment in a sound way. Please contact Microwave Data
Systems or your supplier for more information on the proper disposal of this equipment.
FCC Notice, USA
Microwave Data Systems Digital Radios comply with Part 15 of the FCC rules. The radios are
specifically designed to be used under Part 15, Section 15.247 of the FCC rules and regulations.
Operation is subject to following conditions:
• The device to utilize a fix
• The de
vice to be installed by qualified installation/deployment personnel. When the
device is operating, a minimum separation must exist between the device and persons as
shown in the table below. The following method was used to calculate the RF safety
distance:
which is solved for the minimum separation distance
ed mount antenna, for use on a permanent outdoor structure.
= PG/4πr
S
MPE
r
= (PG/4πS
min
2
= EIRP/4πr
min
1/2
)
= (EIRP/4πS
MPE
min
2
1/2
)
MPE
where P = power input to the antenna (mW), EIRP = Equivalent (effective) isotropic
radiated power, S = maximum permissible exposure (mW/cm
antenna relative to an isotropic radiator, and r
the center of radiation (cm). The resulting separation distances are dependent on
frequency band.
Frequency Band Minimum Distance (cm)
UNII Band (nominal frequency = 5.25 GHz) 9
ISM Band (nominal frequency = 5.725 GHz) 371
• The de
vice installers and operators should be aware of the transmitter operating
conditions, specified in the installation manual and other associated user documentation,
as well as the antenna co-location requirements of Part 1.1307 (b) (3), of FCC rules,
pertaining to RF exposure.
• The device
• The de
may not cause harmful interference.
vice must accept interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc.
2
), G = numeric gain of the
is the minimum separation distance to
min
All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 8

User Reference and Installation Guide 1-3
The device is intended to be used only when installed in accordance with instructions outlined in
this manual. Failure to comply with these instructions may void the user's authority to operate
this device and/or the manufacturer's warranty. Furthermore, any unauthorized modification or
changes to this device without the express approval of Microwave Data Systems may also void
the user's authority to operate this device.
FCC Part 15 Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area may cause harmful
interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his expense.
Any external data or audio connection to this equipment must use shielded cables.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 9

2 System Description
2.1 About This Manual
This manual is written for those who are involved in the “hands-on” installation of the
MDS FIVE Series Digital Transceiver, such as installation technicians, site evaluators, project
managers, and network engineers. It assumes the reader has a basic understanding of how to
install hardware, use Windows® based software, and operate test equipment.
The MDS FIVE Series includes a Software Defined Indoor Unit
(ODU). The SDIDU
TM
is a product and trademark of CarrierComm.
TM
(SDIDUTM) and outdoor unit
2.2 Introduction
The Microwave Data Systems family of digital radios provides high capacity transmission,
flexibility, features, and convenience for wireless digital communications networks. The
Microwave Data Systems digital point-to-point radios represent a new microwave architecture
that is designed to address universal applications for both PDH and SDH platforms. This
advanced technology platform is designed to provide the flexibility to customers for their current
and future network needs.
The Microwave Data Systems radio family is based upon a common platform to support a wide
range of network interfaces and configurations. It supports links for 16 x E1/T1, 100BaseTX
Ethernet, and DS-3/E-3/STS-1 (optional, consult factory for availability). The radio family is
spectrum and data rate scalable, enabling service providers or organizations to trade-off system
gain with spectral efficiency and channel availability for optimal network connectivity. The
Microwave Data Systems digital radio family enables network operators (mobile and private),
government and access service provides to offer a portfolio of secure, scalable wireless
applications for data, video, and Voice over IP (VoIP).
The MDS FIVE Series digital radio family operates in the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM)
band of 5.725 to 5.850 GHz, which is generically referred to as 5.8 GHz, and the Unlicensed
National Information Infrastructure (U-NII) band of 5.25 to 5.35 GHz, which is generically referred
to as 5.3 GHz. The MDS FIVE Series supports three types of user data payload connectivity:
• 100Base-TX intelligent bridging between two locations without the delay and expense of
installing cable or traditional microwave.
• Scalable Ethernet capability of 25 and 50 Mbps is included. These scalable radios provide
LAN connectivity and offer performance trade-offs between operational bandwidths, data
rates, and distance.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc.
All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 10
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-2
• 16E1 or T1 for cellular backhaul, enterprise voice applications and voice network redundancy
For customers such as cellular carriers requiring backhaul and backbone extension as well
as service providers requiring network redundancy, new Points of Presence (POPs), and last mile
access, the MDS FIVE Series radio is a cost effective alternative to leased lines with carrier-class
quality of performance. The MDS FIVE Series is a cost effective solution to meet the growing
demand for enterprise Local Area Network (LAN) connectivity between buildings and campuses
as well as service providers requiring reliable products for infrastructure expansion, extending
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) fiber access, and network redundancy.
The MDS FIVE Series includes integrated Network Management functionality and design features
enabling simple commissioning when the radio network is initially set up in the field at the
customer’s premises. Furthermore, a highlight of MDS radio products is scalability and the
capability to support a ring-type architecture. This ring or consecutive point radio architecture is
self-healing in the event of an outage in the link and automatically re-routes data traffic, thereby
ensuring that service to the end user is not interrupted.
TM
The MDS FIVE Series is composed of a Software Defined Indoor Unit
(SDIDUTM) and Outdoor
Unit (ODU). It supports 1+0 and 1+1 protection and ring architectures in a single 1 RU chassis.
The modem and power supply functions are supported using easily replaceable plug-in modules.
An additional feature of the SDIDU
TM
is provision for a second plug-in modem/IF module to
provide repeater or east/west network configurations.
The overall architecture consists of a single 1RU rack mount Software Defined Indoor Unit
SDIDU
(
TM
) with a cable connecting to an Outdoor Unit (ODU) with an external antenna.
Core Access
Network
Outdoor
Outdoor
Unit
Unit
Outdoor
Unit
Outdoor
Unit
Indoor Unit
Indoor Unit
Outdoor
Unit
Outdoor
Unit
Indoor Unit
Figure 2-1. MDS FIVE Series SDIDUTM /ODU Architecture
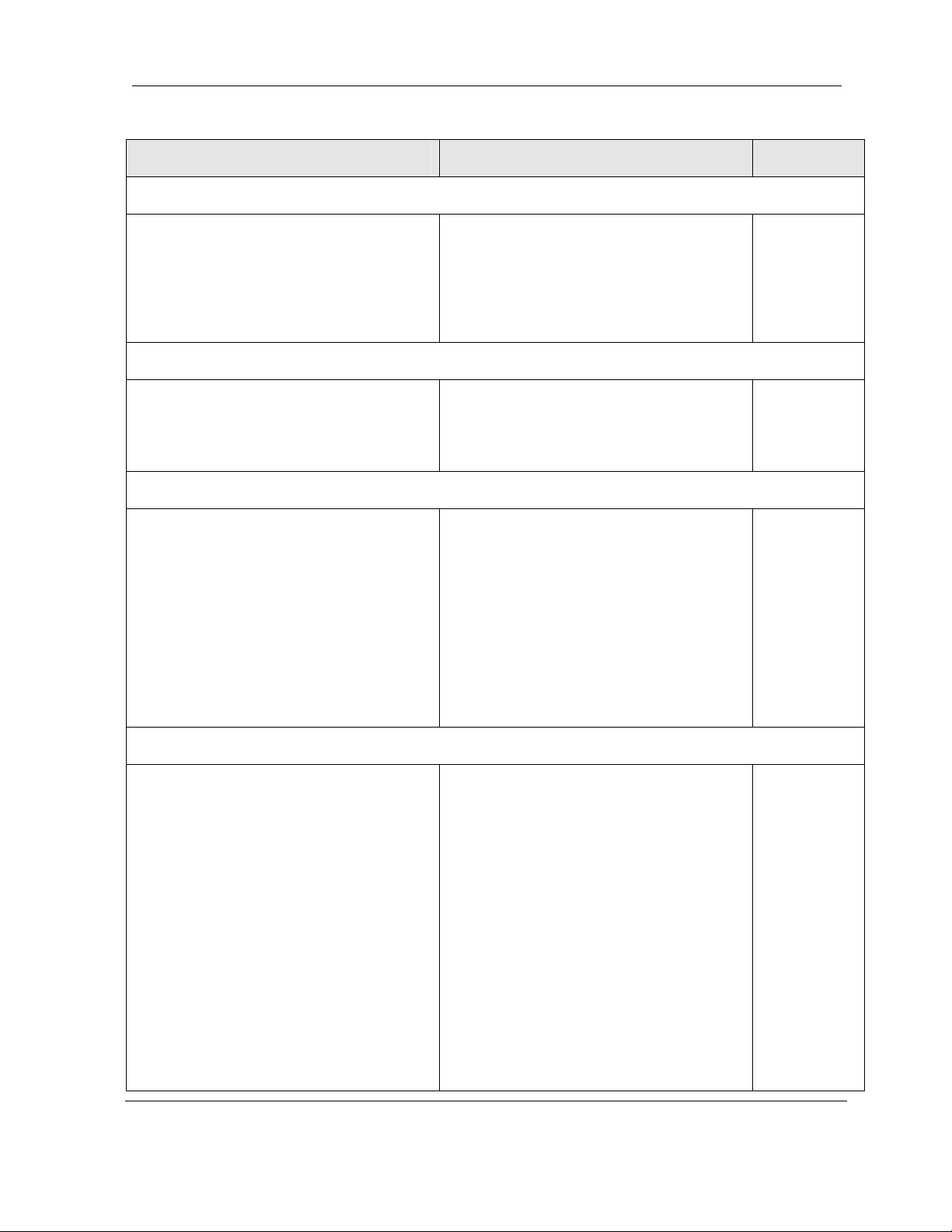
Table 2-1 lists key features that MDS FIVE Series technology offers to those involved in the
design, deployment and support of broadband fixed wireless networks.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 11
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-3
Table 2-1 Key Benefits and Advantages of MDS FIVE Series Radios
Benefits Advantages to Providers/Customers Reference
Wireless license-exempt system
ISM bands do not require expensive
license band fees or incur licensing delays.
Wireless connectivity supplements existing
cable (Ethernet).
Easy to install units
Straightforward modular system enables
fast deployment and activation.
Carrier-class reliability.
Complete support of payload capacity with additional wayside channels
Aggregate capacity beyond basic payload
(34 Mbps or 50 Mbps or 100 Mbps).
Scalable and spectrally efficient system.
Separate networks for radio
overhead/management and user payload.
Fast return on investment.
Lower total cost of total ownership.
Media diversity avoids single points of
failure.
Fast return on investment.
No monthly leased line fees.
Increases available bandwidth of network.
Allows customer full use of revenue-
generating payload channel.
Up to 16 T1/E1 wayside channels supports
extension of PBX connectivity between
buildings without additional leased-line
costs.
2.2 –2.4
3.5
2.2– 0
Lowers total cost of ownership.
Ring Architecture
Supports a ring (consecutive point)
configuration, thus creating a self-healing
redundancy that is more reliable than
traditional point-to-point networks.
In the event of an outage, traffic is
automatically rerouted via another part of
the ring without service interruption.
Ring/consecutive point networks can
overcome line-of-sight issues and reach
more buildings than other traditional
wireless networks.
Networks can be expanded by adding
more MDS FIVE Series
without interruption of service.
units or more rings
Enables network scalability.
Increases deployment scenarios for initial
deployment as well as network expansion
with reduced line-of-sight issues.
Increases network reliability due to selfhealing redundancy of the network.
Minimizes total cost of ownership and
maintenance of the network.
Allows for mass deployment.
2.6,2.7,2.10
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 12
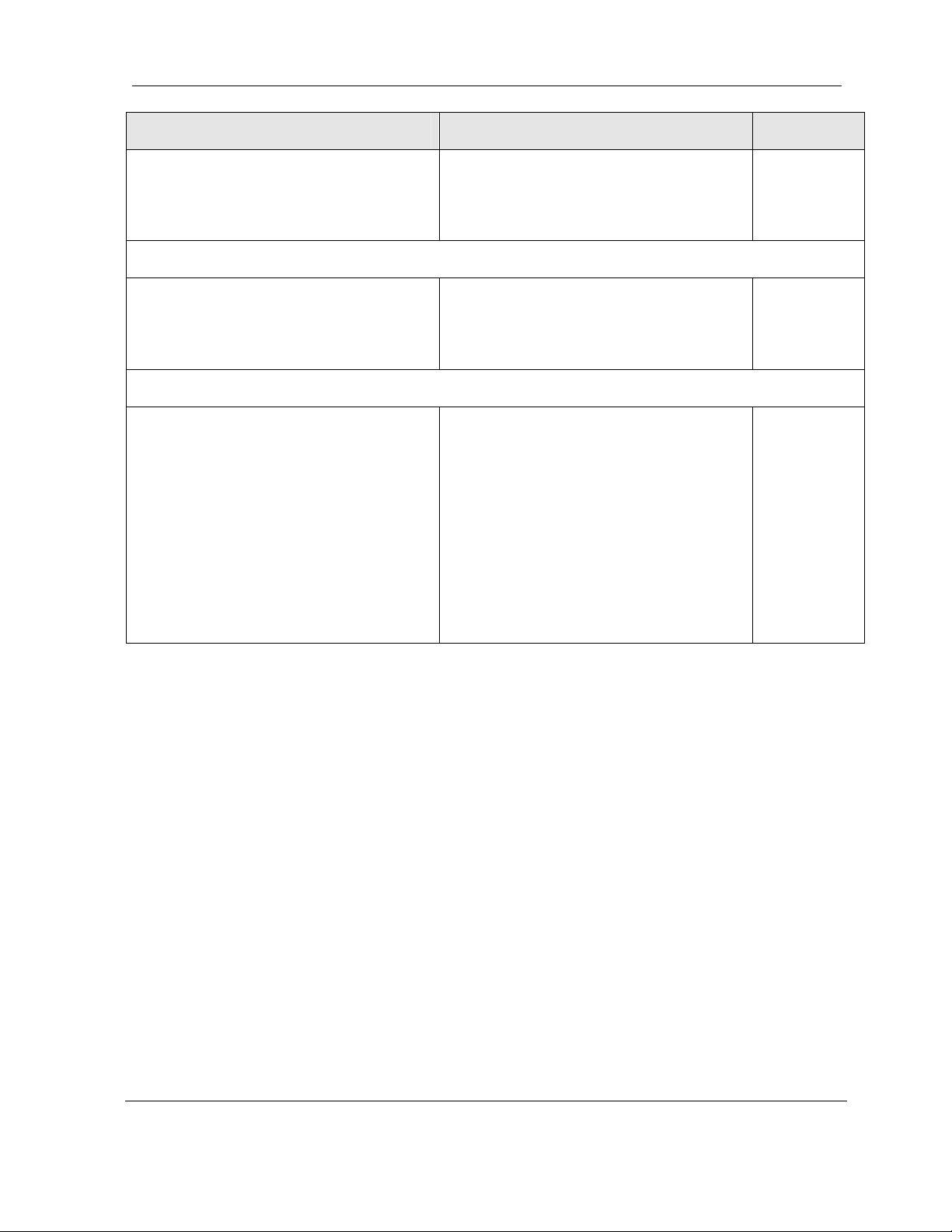
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-4
Benefits Advantages to Providers/Customers Reference
A separate management channel allows
for a dedicated maintenance ring with
connections to each MDS FIVE Series
Digital Radio on the ring.
Adaptive Power Control
Automatically adjusts transmit power in
discrete increments in response to RF
interference.
Comprehensive Link/Network Management Software
A graphical user interface offers security,
configuration, fault, and performance
management via standard craft interfaces.
Suite of SNMP-compatible network
management tools that provide robust
local and remote management capabilities.
Enables dense deployment.
Simplifies deployment and network
management.
Simplifies management of radio network
and minimizes resources as entire network
can be centrally managed out of any
location.
Simplifies troubleshooting of single radios,
links, or entire networks.
Simplifies network upgrades with remote
software upgrades.
Allows for mass deployment.
2.3 System Features
2.12
2.14
Selectable Rates and Interfaces
o Up to 16 x E1/T1 (wayside channels)
o
100BaseTX/Ethernet: Scalable 25-100 Mbps
DS-3/E-3/STS-1 (option; consult factory for availability)
o
Support for multiple configurations
o 1+0, 1+1 protection/diversity
o Hot Standby
o East/West Repeater (2 + 0)
Selectable Spectral Efficiency of 0.8 to 6.25 bits/Hz (including FEC and spectral shaping
effects)
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 13

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-5
QPSK, 16 – 64 QAM Modulation
Powerful Trellis Coded Modulation concatenated with Reed-Solomon Error Correction
Built-in Adaptive Equalizer
Support of Voice Orderwire Channels
Peak output power at antenna port
o
30 dBm at 5.8 GHz
o
12 dBm at 5.3 GHz
Receive Sensitivity: -84 dBm to -72 dBm (depending on data rate/modulation/FEC/ODU)
Adaptive Power Control
Built-in Network Management System (NMS)
Consecutive Point ring architecture
Built-in performance statistics
o
Built-in Bit Error Rate (BER) performance monitoring
Data encryption of all payload data and T1/E1 wayside channels for MDS FIVE Series-
100 and MDS FIVE Series-50 Ethernet models (Consult factory for availability)
2.4 Physical Description
The following section details the physical features of the MDS FIVE Series digital radios
• Model types
• Front panel indicators
• Front panel connections
2.4.1 Model Types
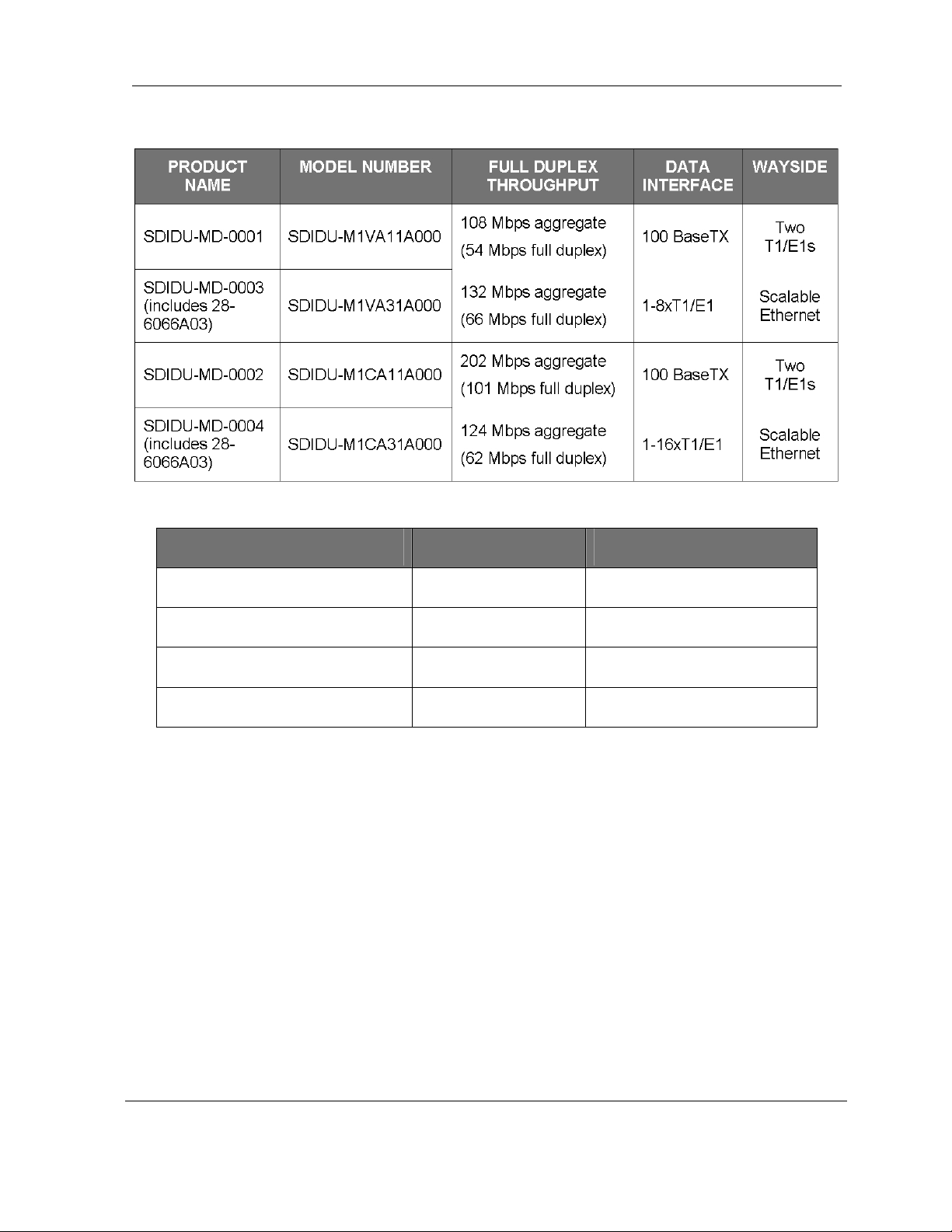
Table 2-2 lists the MDS FIVE Series digital radios according to model number and associated
capabilities of throughput, data interface, and wayside channel.
numbers.
Table 2-3 lists the ODU model
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 14
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-6
Table 2-2 MDS FIVE Series SDIDU™ Model Type
Table 2-3 MDS FIVE Series ODU Model Types
PRODUCT NAME MODEL NUMBER ANTENNA
MDS FIVE Series 5.8 ODU-I ODU5800MIP
MDS FIVE Series 5.8 ODU-E ODU5800MEP
MDS FIVE Series 5.3 ODU-I ODU5300MIP
MDS FIVE Series 5.3 ODU-E ODU5300MEP
2.4.2 Options
The following items are also available:
• AC/DC power supply
• Data Encryption
• Upgrade 50Mbps Ethernet systems to 100Mbps capability
• OC-3/STM-1 Mini-IO Module
Please consult the factory for more information.
Integrated antenna
External antenna required
Integrated antenna
External antenna required
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 15
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-7
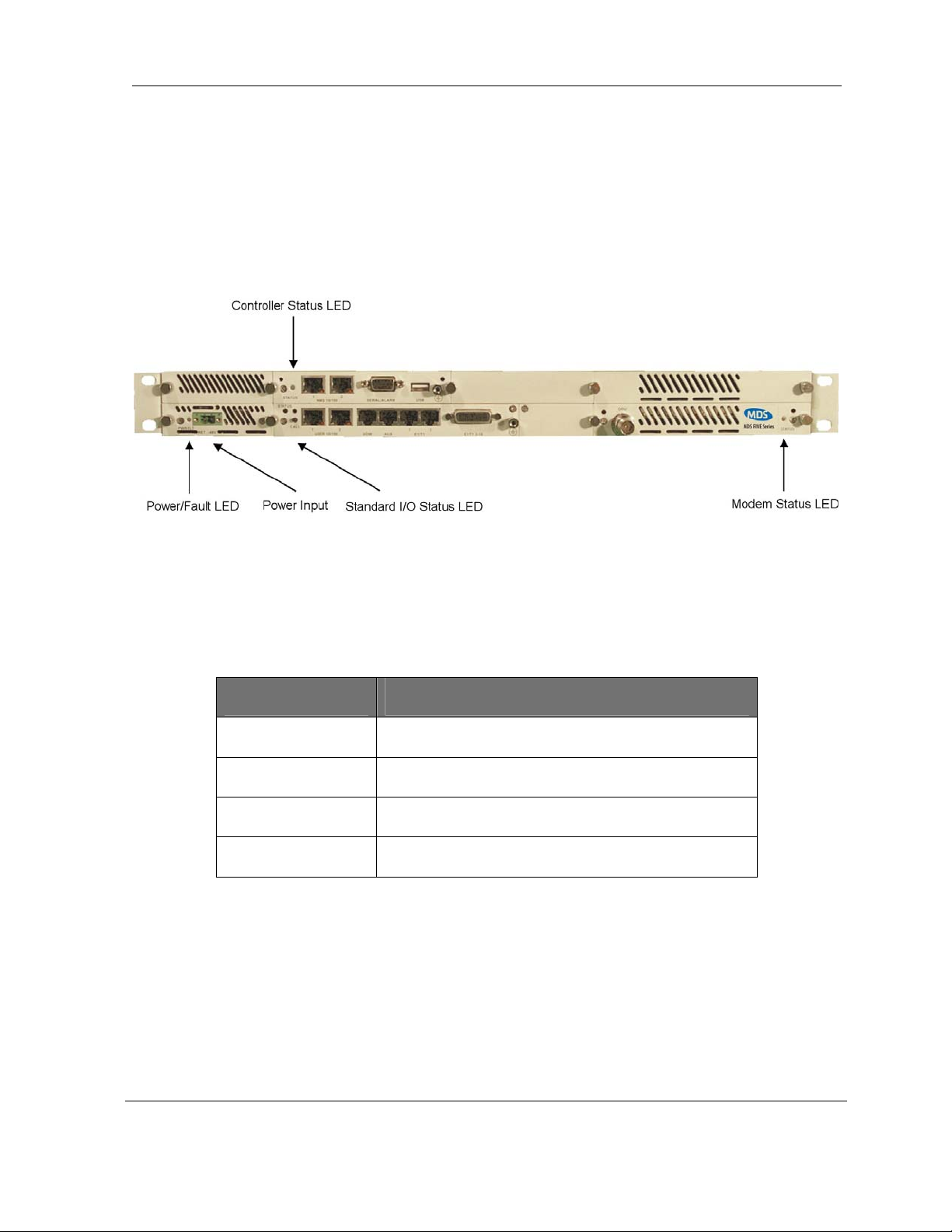
2.4.3 Front Panel Indicators
All models of the MDS FIVE Series support a variety of front panel configurations that are
dependent on the network interface and capacity configurations.
Figure 2-2 provides an example of the MDS FIVE Series 1+0 configuration and the associated
LEDs displayed on the
SDIDU
TM
front panel. The controller, standard I/O, and each modem card
have a status LED.
Figure 2-2. MDS FIVE Series LEDs: SDIDUTM Front Panel Configuration for MDS FIVE Series,
1+0 Configuration
The modem status LED indicates the modem status as described in Table 2-4.
Table 2-4. Modem status LED.
LED STATUS
Green
Orange
Flashing Green
Flashing Orange
Standby Locked Link (1+1 Non-Diversity Only)
Active Locked Link
Low SNR
Unlocked
The controller status LED is the primary front panel indicator of alarms. An alarm is generated
when a specific condition is identified and is cleared when the specified condition is no longer
detected. When an alarm is posted,
1. The controller status LED turns orange for 5 seconds
2. The controller status LED turns off for 5 seconds
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 16
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-8
3. The controller status LED flashes orange the number of times specified by the first digit of
the alarm code
4. The controller status LED turns off for 3 seconds
5. The controller status LED flashes orange the number of times specified by the second
digit of the alarm code
Steps 2-5 are repeated for each alarm posted. The entire process is repeated as long as the
alarms are still posted.
The standard I/O and modem status LEDs are set to red when certain alarms are posted. A
complete list of alarms is provided in Appendix
The alarm description is also displayed in the Graphical User Interface (GUI) as described in the
User Interface Reference Manual.
6.1.
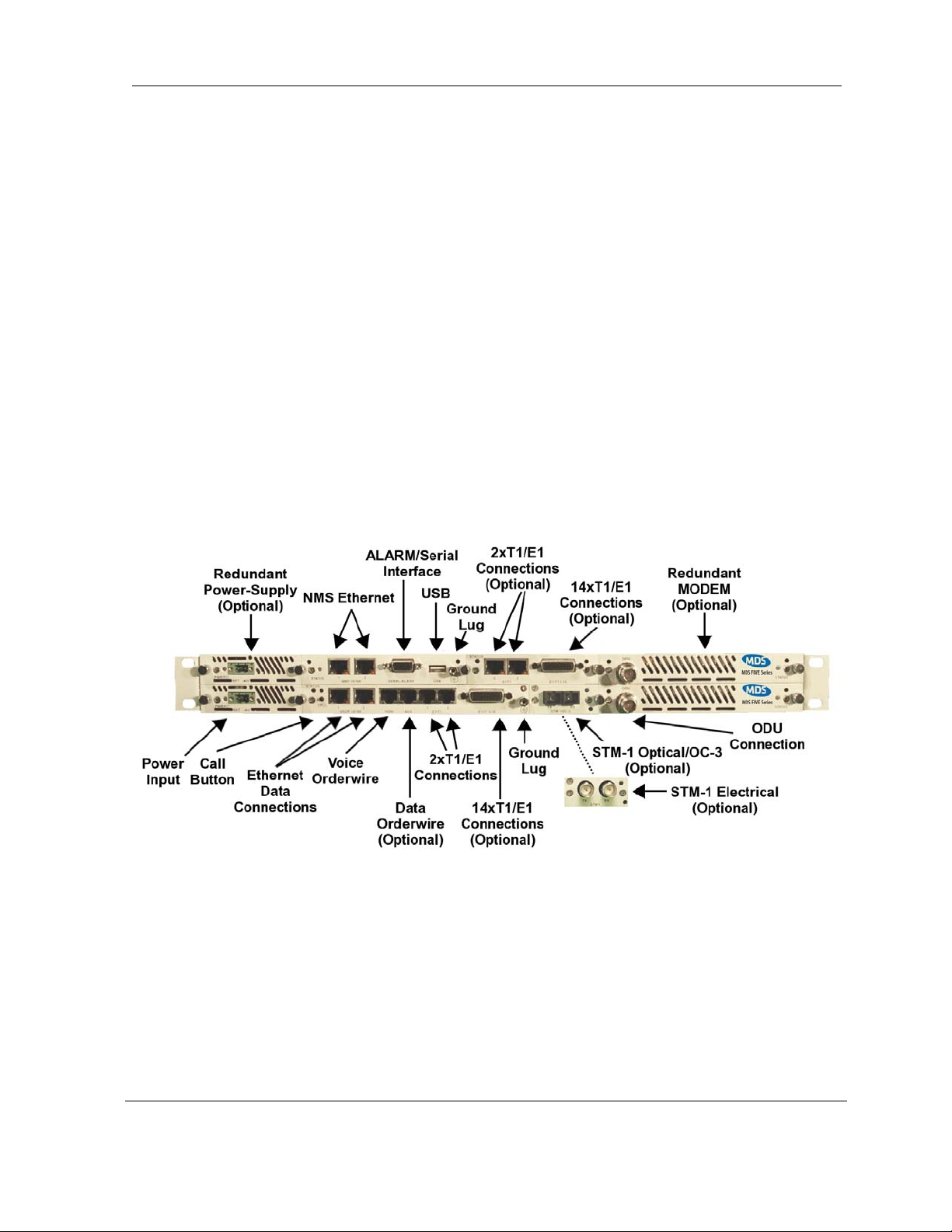
2.4.4 Front Panel Connections
Please refer to the
followed by a descriptive text of the connections.
Figure 2-3 for an example of a MDS FIVE Series SDIDUTM front panel
Figure 2-3. SDIDUTM Front Panel Connections
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 17
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-9
Power Supply Input
DC Input
-48 VDC
-48v (Isolated Input); 2-pin captive power connector. The
MDS FIVE Series requires an input of -48 volts dc ±10% at
the front panel DC Input connector. The total required power
is dependent on the option cards and protection configuration
(1+0, 1+1). The SDIDU
TM
front panel power connector pin
numbering is 1 through 2, from left to right, when facing the
unit front panel. Pin 1 is the power supply return and is
connected to unit chassis ground internally. Pin 2 should be
supplied with a nominal -48 V dc, with respect to the unit
chassis (ground). A ground-isolated supply may be used,
provided it will tolerate grounding of its most positive output.
The recommended power input is -44 to -52 V dc at 2 Amps
minimum. It is recommended that any power supply used be
able to supply a minimum of 100 W to the SDIDU
A mating power cable connector is supplied with the MDS
FIVE Series SDIDU
TM
. It is a 2-pin plug, 5 mm pitch,
TM
.
manufactured by Phoenix Contact, P/N 17 86 83 1
(connector type MSTB 2,5/2-STF). This connector has
screw clamp terminals that accommodate 24 AWG to 12
AWG wire. The power cable wire should be selected to
provide the appropriate current with minimal voltage drop,
based on the power supply voltage and length of cable
required. The recommended wire size for power cables
under 10 feet in length supplying -48 Vdc is 18 AWG.
TM
The SDIDU
the ODU/SDIDU
Series SDIDU
DC power is connected to the SDIDU
supplies the ODU with all required power via
TM
Interconnect cable. The MDS FIVE
TM
does not have a power on/off switch. When
TM
, the digital radio
powers up and is operational. There can be up to 320 mW of
RF power present at the antenna port (external antenna
version). The antenna should be directed safely when power
is applied.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 18

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-10
Alarm/Serial Interface
Alarms/Serial DB-15HD female connector for two Form-C relay alarm
outputs (rated load: 1A @ 24 VDC), two TTL alarm outputs,
four TTL alarm inputs, and Serial Console. The two Form-C
relay alarm outputs can be configured to emulate TTL alarm
outputs.
USB Interface
USB USB connector, reserved.
Voice Orderwire Connector
Call Button The voice orderwire provides a PTP connection via a PTT
handset and buzzer. The call button initiates a ring. Only the
SDIDU™’s link partner will receive the ring. VOW does not
ring all nodes or support “party line” calls.
Voice
RJ-45 modular port connector for voice orderwire interface.
Orderwire
Data Orderwire Connector
Data Orderwire RJ-45 modular port connector for RS422/RS-232 data at 64
kbps.
NMS 10/100 Network Management System Connections
NMS 10/100 1 10/100Base-TX RJ-45 modular local port connector for
access to the Network Management System (SNMP) and
GUI.
NMS 10/100 2 10/100BaseTX RJ-45 modular remote port connector for
access to the Network Management System (SNMP). This
port to be used for consecutive point networks.
100/Ethernet Models: Ethernet 100BaseT Connections
USER 10/100 1 100Base-TX RJ-45 modular port connector for the local Fast
Ethernet interface.
USER 10/100 1 100Base-TX RJ-45 modular port connector. This port to be
used for consecutive point networks.
T1 Channels
T1 1-2 Two T1/E1 (RJ-48C) interface connections.
T1 3-16 Fourteen T1/E1 high density interface connector
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 19
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-11
Ground Connection
Ground Lug Two ground lugs are provided on the front panel. Either may
be used to connect the SDIDU™ to ground.
2.5 System Description
The overall digital radio architecture consists of a single 1RU rack mount Software Defined Indoor
TM
(SDIDUTM) with a cable connecting to an Outdoor Unit (ODU). The ODU is available with
Unit
an integrated antenna or connectors to support an external antenna. Two ODU types are
available servicing the 5.8 GHz band or the 5.3 GHz band. This SDIDU
advantageous when compared to a single IDU with external mount antenna since supporting a
signal of 5.8 GHz from the IDU rack to the antenna will result in significant signal degradation,
which would require expensive coaxial cable or waveguide.
TM
/ODU architecture is
Figure 2-4 shows the SDIDUTM and interfaces from a functional point of view. The functional
partitions for the I/O, Modem/IF, and power supply modules are shown. The SDIDU
TM
comes
with the standard I/O capability that can be upgraded. In addition, the Modem/IF function is
modular. This allows the addition of a second Modem to support protection or ring architectures.
The power supply is similarly modular.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 20
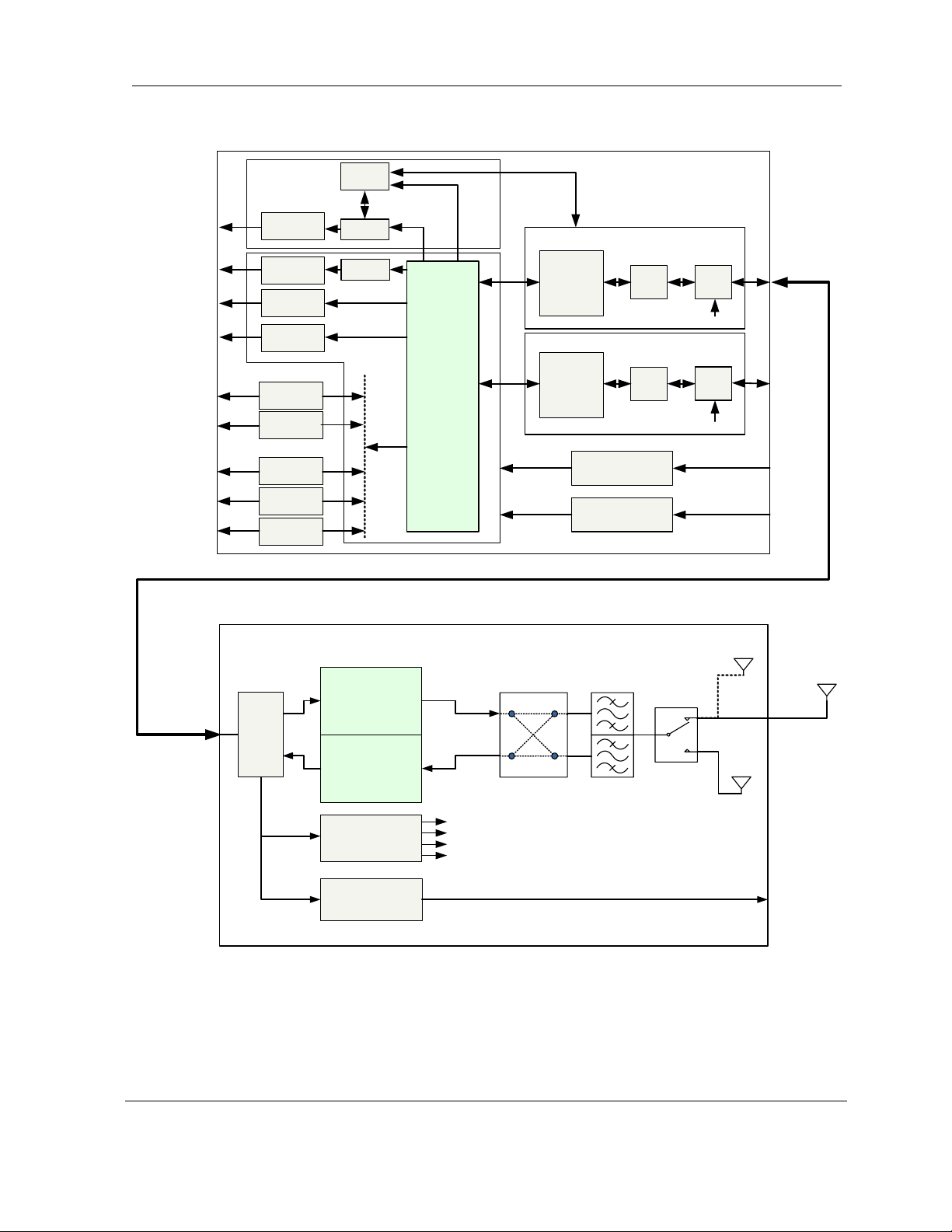
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-12
IDU
Modem Control
Telemetry
East/Primary Modem
MODEM/
FEC ASIC
West/Secondary Modem
MODEM/
FEC ASIC
Secondary Power
Digital
Digital
Primary Power
Supply
Supply
Multiplexed
Quad
IF
IF
Mux
-48Vdc
Quad
Mux
-48Vdc
IF
Multiplexed
IF
-48Vdc
-48Vdc
2x 100 Mbps
2x 100 Mbps
16x 1.544/2.048
Mbps
155.52 Mbps
4x44.736/34.368/
51.84 Mbps
2x 155.52 Mbps
4x44.736/34.368/
51.84 Mbps
IDU
CONTROLLER
SNMP 2x
100Base-Tx
User 2x
100Base-Tx
16 T1/E1
64 kbps
Voice
Standard I/O Cards
Optional I/O Cards
(Small Slot)
STM-1/OC3
DS-3/ES/
STS-1
Optional I/O Cards
(Large Slot)
2xSTM-1/
OC3
4xDS3/ES/
STS1
Future
CPU
Switch
Switch
Serial
RCH Serial
FRAMER
ODU
Vertical
Antenna
350
TNC
Quad
Mux
MHz
MHz
-48Vdc
5/10
MHz
140
Transmitter
Up-Converter
Receiver
Down-Converter
DC/DC
Converters
Commlink
& Processor
5.3/
5.8
GHz
+10Vdc
+5Vdc
+3Vdc
-5Vdc
Figure 2-4. MDS FIVE Series System Block Diagram
The SDIDUTM interfaces with the ODU to receive and provide modulated transmit and receive
waveforms. The SDIDU
TM
interfaces provide Fast Ethernet 100Base-T (MDS FIVE Series-100)
connections to the network. Contact factory for availability of SONET OC-3 (MDS FIVE Series-
155) connections. In addition, two E1/T1 channels are provided for PBX extension. SNMP is
provided on 10/100BaseT ports.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
Transfer
Switch
Duplexer
Diversity
Switch
Internal/
Horizontal
Antenna
BNC
05-4498A01, Rev. G
N-type
External
Antenna
RSL
(Received
Signal Level)
Voltage
Page 21
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-13
The ODU RF Up/Down Converter card provides the interface to the antenna. The transmit
section up converts and amplifies the modulated Intermediate Frequency (IF) of 350 MHz from
the IF Processor and provides additional filtering. The receive section down converts the
received signal, provides additional filtering, and outputs an IF of 140 MHz to the IF Processor.
The 64-QAM Modem performs the modulation and demodulation of the payload and forward error
correction using advanced modulation and coding techniques. Using all-digital processing, the
64-QAM Modem uses robust modulation and forward error correction coding to minimize the
number of bit errors and optimize the radio and network performance. The 64-QAM Modem also
scrambles, descrambles and interleaves/deinterleaves the data stream in accordance with
Intelsat standards to ensure modulation efficiency and resilience to sustained burst errors. The
modulation will vary by application, data rate, and frequency spectrum. The highest order
modulation mode supported is 64 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
Table 2-5
summarizes the TCM/convolutional code rates for each modulation type supported by the MDS
FIVE Series.
Table 2-5. MDS FIVE Series TCM/Convolutional Code Rates
Modulation Type Available Code
Rates
QPSK 1/2, 3/4, 7/8
16-QAM 3/4, 7/8, 11/12
32-QAM 4/5, 9/10
64-QAM 5/6, 11/12
The major functions of the SDIDUTM can be summarized as follows:
TM
• I/O Processing – The SDIDU
comes with a standard I/O capability that includes support for up to
16xT1/E1 and 2x100Base-TX user payloads, 2x100Base-TX for SNMP, and voice orderwire. In
addition, option cards for DS-3/E3/STS-1, 1-2 x STM-1/OC-3, and 4xDS-3/E3/STS-1 may be
added. The SDIDU
TM
architecture is flexible and allows for the addition of other I/O types in the
future.
TM
• Switch/Framing – The SDIDU
includes an Ethernet Switch and a proprietary Framer that are
designed to support 1+1 protection switching, ring architecture routing, and overall network control
functions.
TM
• Network Processor – The SDIDU
includes a Network Processor that performs SNMP and
Network Management functions.
TM
• Modem/IF – The SDIDU
Modem performs forward-error-correction (FEC) encoding, PSK/QAM
modulation and demodulation, equalization, and FEC decoding functions. The IF chain provides a
350 MHz carrier, receives 140 a MHz carrier, processes OOK telemetry, and provides –48V
power. Two modems can be used for 1+1 protection or ring architectures.
TM
• Power Supply – The SDIDU
power supply accepts -48 Vdc and supplies the SDIDUTM and ODU
with power. A second redundant power supply may be added as an optional module.
The Modem Processor and its associated RAM, ROM, and peripherals control the digital and analog
Modem operation. It also provides configuration and control for both the IF and I/O cards.
The
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 22

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-14
SDIDU
TM
interfaces with the ODU to receive and provide modulated transmit and receive
waveforms.
The SDIDUTM also provides the physical interface for the user payload and network management.
In transmit mode, the Framer merges user payload with radio overhead-encapsulated network
management data. This combined data stream is transmitted without any loss of user bandwidth.
In the receive mode, the Framer separates the combined data stream received from the 64-QAM
Modem. The SDIDU
100BaseT data interface port. The SDIDU
TM
supports Scalable Ethernet data rates, such as 25 or 50 Mbps via the
TM
provides network management data on 10 Mbps
ports accessible via the 10/100BaseTX port. The Central Processor Unit (CPU) provides the
embedded control and network element functionality of the NMS. The CPU also communicates
with other functions within the SDIDU
TM
for configuration, control, and status monitoring.
In Ethernet models, the payload of each user Ethernet data packet and all T1 can be encrypted
using an AES encryption algorithm. In addition, the encryption engine is re-seeded with a new,
randomly generated key stream every 10 seconds, in order to provide enhanced security. The
initial key is based off of a pass phrase entered into each MDS FIVE Series unit by the network
administrator. Consult factory for the availability of this encryption function.
The power supply converts -48 Vdc to the DC voltage levels required by each component in the
system.
2.6 Consecutive Point Architecture
The consecutive point network architecture is based upon the proven SONET/SDH ring.
Telecommunications service providers traditionally use the SONET/SDH ring architecture to
implement their access networks. A typical SONET/SDH network consists of the service
provider’s Point of Presence (POP) site and several customer sites with fiber optic cables
connecting these sites in a ring configuration (see
deliver high bandwidth with high availability to their customers.
Figure 2-5). This architecture lets providers
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 23
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-15
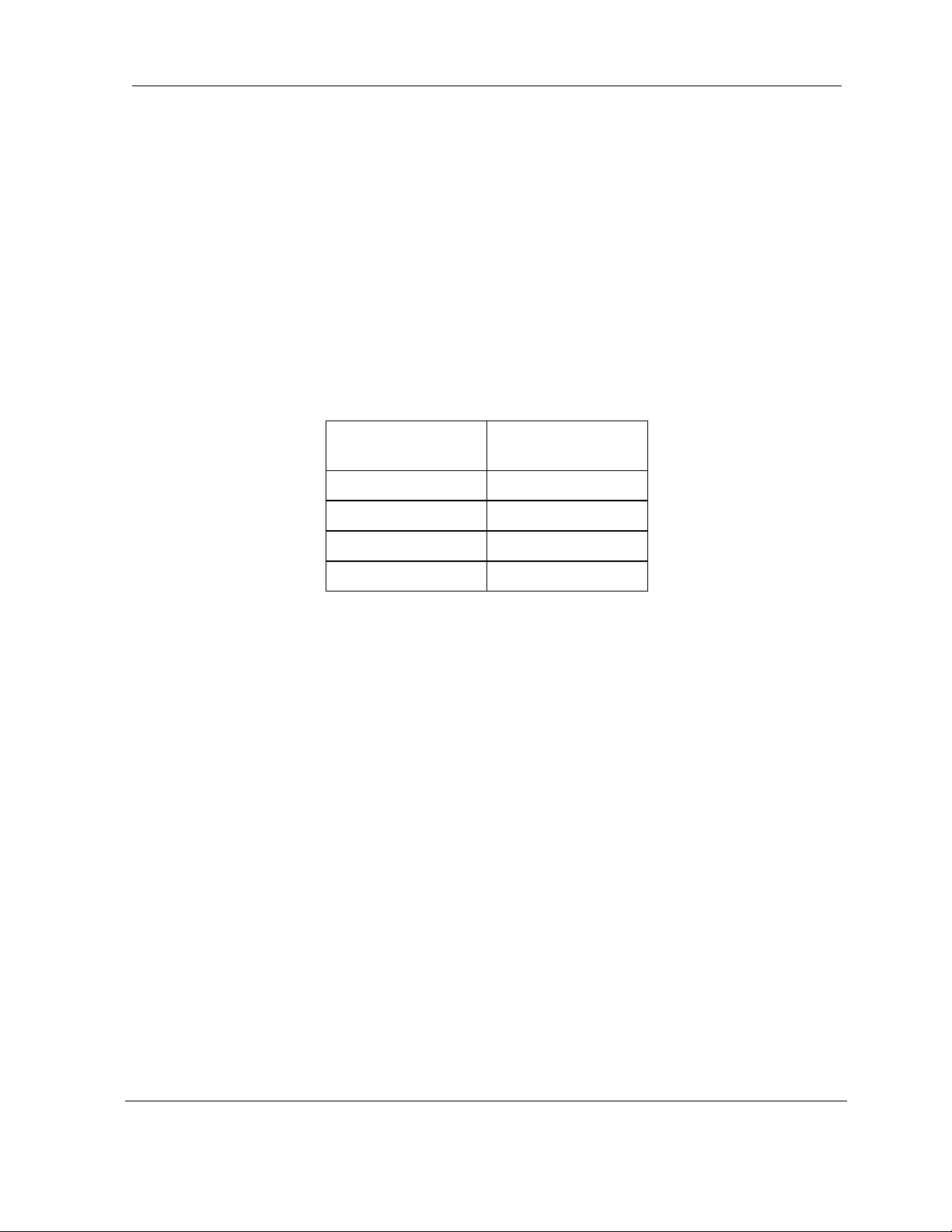
Figure 2-5. Ring Configuration.
SONET/SDH rings are inherently self-healing. Each ring has both an active path and a standby
path. Network traffic normally uses the active path. Should one section of the ring fail, the network
will switch to the standby path. Switchover occurs in seconds. There may be a brief delay in
service, but no loss of payload, thus maintaining high levels of network availability.
The consecutive point architecture implemented in the MDS FIVE Series Digital Radio family is
based on a point-to-point-to-point topology that mimics fiber rings, with broadband wireless links
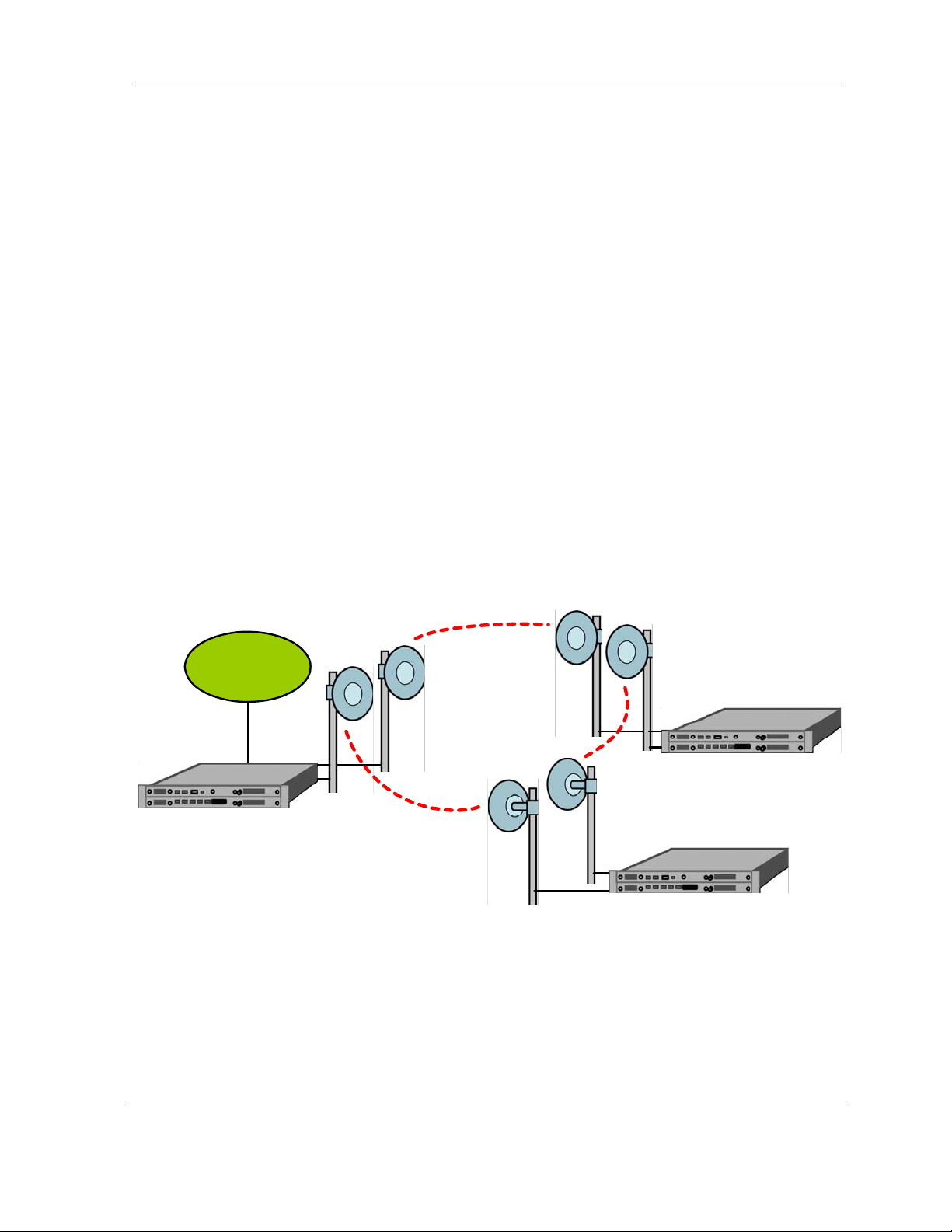
replacing in-ground fiber cable. A typical consecutive point network consists of a POP and
several customer sites connected using MDS FIVE Series units. These units are typically in a
building in an east/west configuration. Using east/west configurations, each unit installed at a
customer site is logically connected to two other units via an over-the-air radio frequency (RF) link
to a unit at an adjacent site.
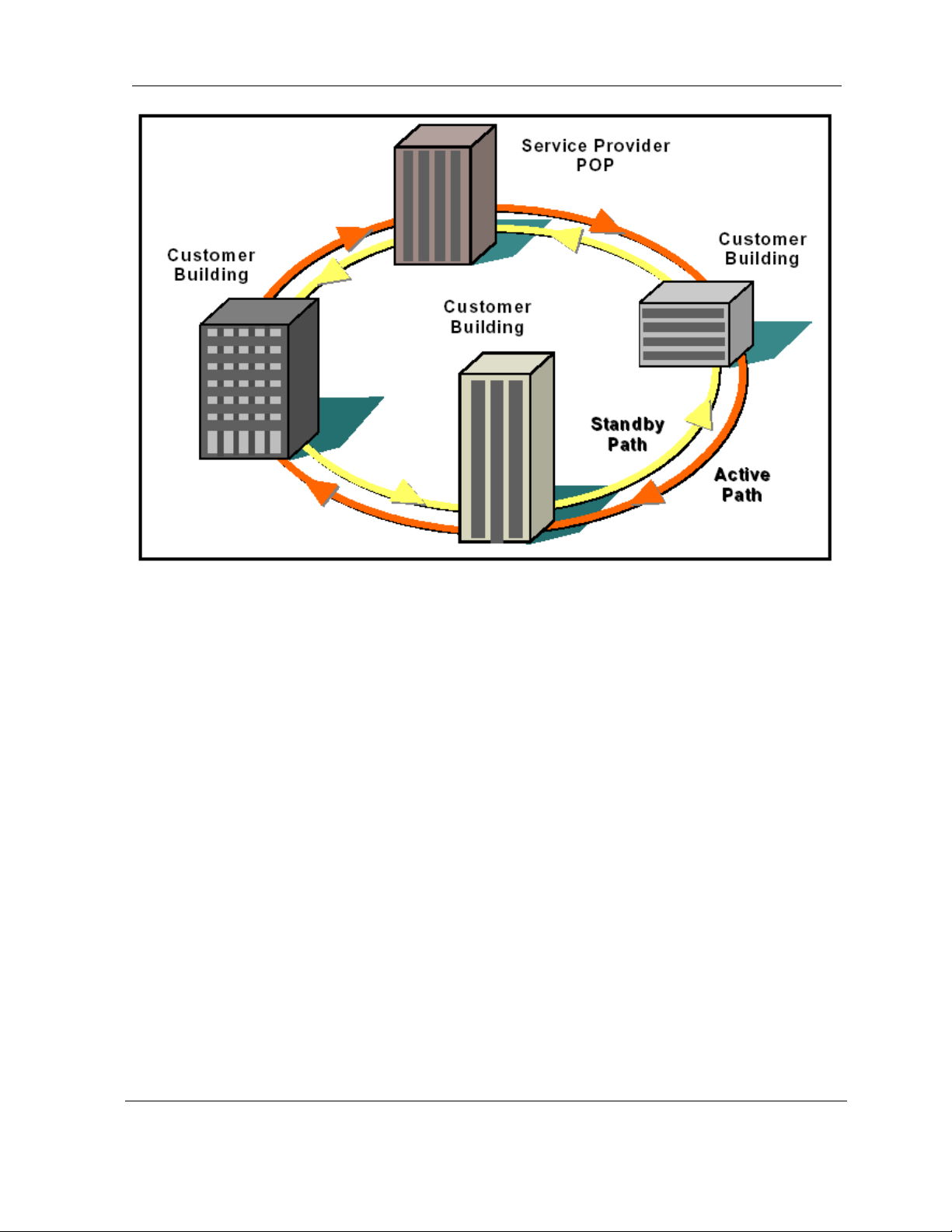
Each consecutive point network typically starts and ends at a POP. A pattern of wireless links and
in-building connections is repeated at each site until all buildings in the network are connected in
a ring as shown in
need to be jumpered between two SDIDU
there is a single SDIDU
Figure 2-6. . For 2 x 1+0 and 2 x 1+1 nodes payload and NMS connections
TM
. For SDH or SONET payloads, the configuration is similar but an
TM
s. For 1 x 2+0 nodes, there is no need for jumpers as
external add/drop mux and a second SDH/SONET interface card are required.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 24
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-16
Figure 2-6. Consecutive Point Network
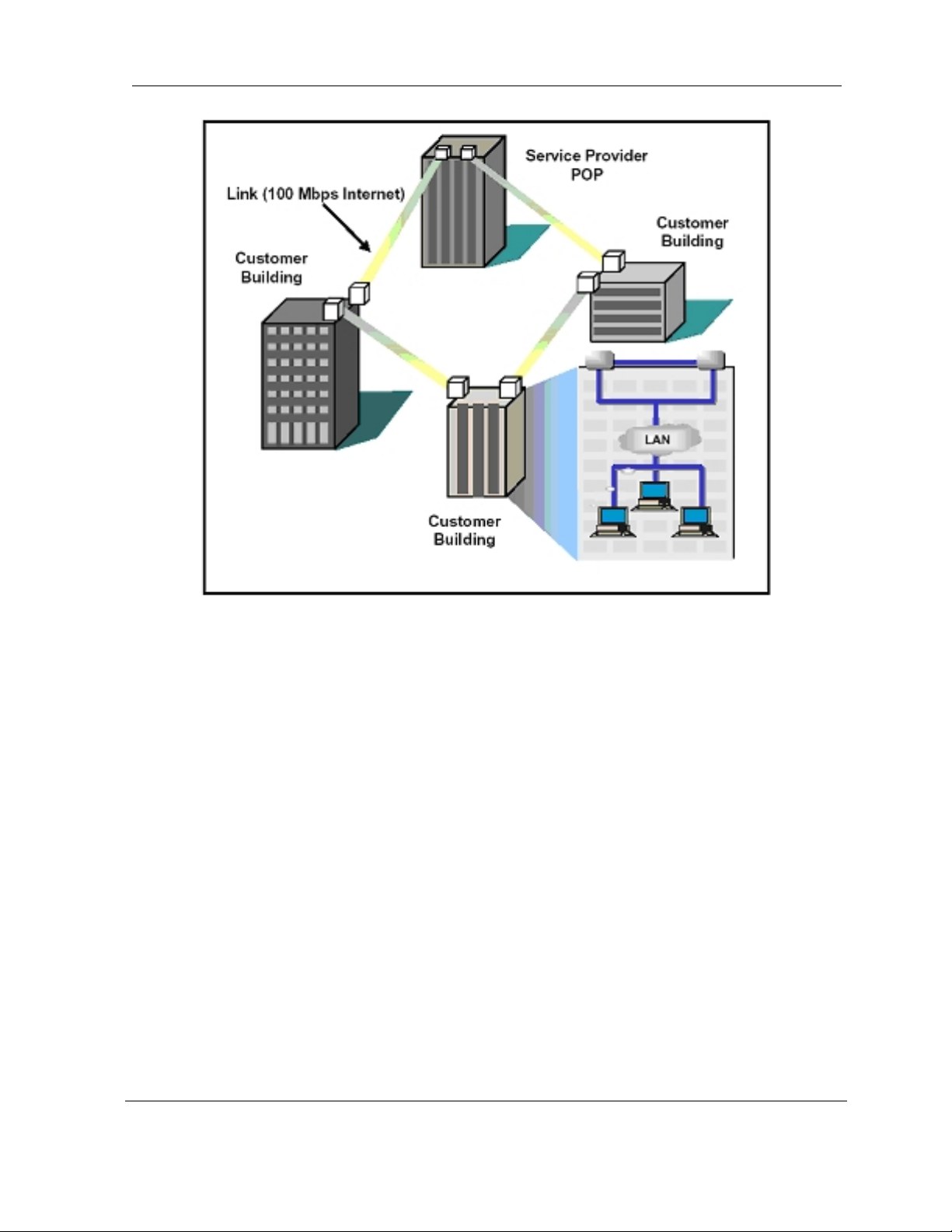
2.7 2 + 0 (East-West) Configuration
The SDIDUTM supports an east/west, or 2+0, configuration that allows a consecutive point
architecture to be achieved with only a single 1 RU chassis at each location. In this configuration
the SDIDU
is referred to as the west modem and the other as the east modem. The SDIDU
to two ODUs, one broadcasting/receiving in one direction of the ring architecture and t he other
broadcasting/receiving in the other as shown in
TM
contains two modems supplies and may contain two power supplies. One modem
Figure 2-7.
TM
is connected
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 25
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-17
Connected to
west modem
Connected to
east modem
Connected to
east modem
Connected to
east modem
Connected to
west modem
Connected to
west modem
Connected to
east modem
Connected to
west modem
Figure 2-7. 2+0 (East-West) configuration.
2.8 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Spanning Tree Protocol STP keeps Ethernet loops from forming in a ring architecture. Without
STP, loops would flood a network with packets. STP prevents loops by creating an artificial
network break. In the event of a network outage, STP automatically removes the artificial break,
restoring connectivity.
2.9 1+1 Protection
The MDS FIVE Series supports 1+1 protection as an option for a critical link. In this
configuration, protection is provided in a single 1 RU chassis. The SDIDU
supplies and two modems. The power supply, ODU, IF/telemetry and modem are protected. The
digital framing and LIUs are not. One modem is referred to as the west modem and the other as
the east modem. 1+1 protection can be run in two modes called Protected Non-Diversity and
Protected Diversity.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
TM
contains two power
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 26
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-18
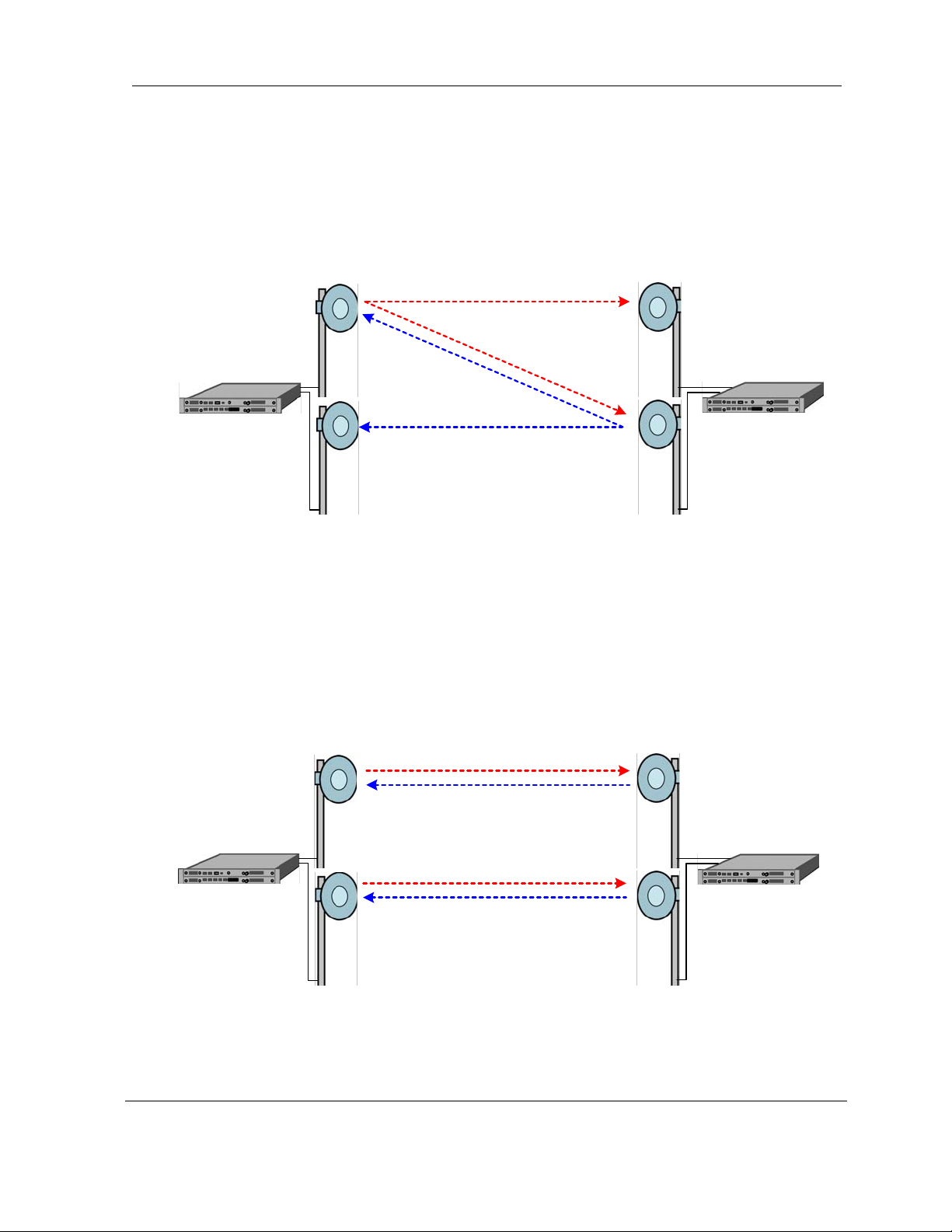
2.9.1 Protected Non-Diversity (Hot Standby)
Figure 2-8Error! Reference source not found. shows operation in Protected Non-Diversity
mode, also called Hot Standby. In this mode, one ODU at each location transmits to two ODUs
at the other location. This mode does not require the extra bandwidth or interference protection.
It provides hitless receive switching and hot standby. The SDIDU
transmit ODU upon appropriate ODU alarm or ODU interface error, minimizing transmit outage
time.
TM
automatically switches
Connected to
west modem
Connected to
east modem
Connected to
west modem
Connected to
east modem
Figure 2-8. 1+1 protection in non-diversity mode
2.9.2 Protected Diversity
In Protected Diversity mode, the link between each pair of modems is the same, as shown in
Figure 2-9Error! Reference source not found., providing complete redundancy. This
arrangement requires bandwidth for both links and non-interference between the links, but it
provides hitless receive and transmit switching. The SDIDU
spatial diversity.
TM
supports both frequency and
Connected to
west modem
Connected to
east modem
Connected to
west modem
Connected to
east modem
Figure 2-9. 1+1 protection in diversity mode
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 27

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-19
2.9.2.1 Frequency Diversity
In frequency diversity, two frequencies are used to achieve non-interference. The proprietary
framer chooses the best, or error-free, data stream and forwards it to the Line Interface Units
(LIUs).
2.9.2.2 Spatial Diversity
In spatial diversity, two non-interfering paths are used. The proprietary framer chooses the best,
or error-free, data stream and forwards it to the Line Interface Units (LIUs).
2.9.2.2.1 Single Transmitter Protected Non-Diversity, or Hot Standby, is also refered to as Single Transmitter Spatial Diversity.
For more information on this mode, see Section
2.9.2.2.2 Dual Transmitter When using Dual Transmitter Spatial Diversity, two active transmitters are physically isolated to
avoid crosstalk.
2.9.1.
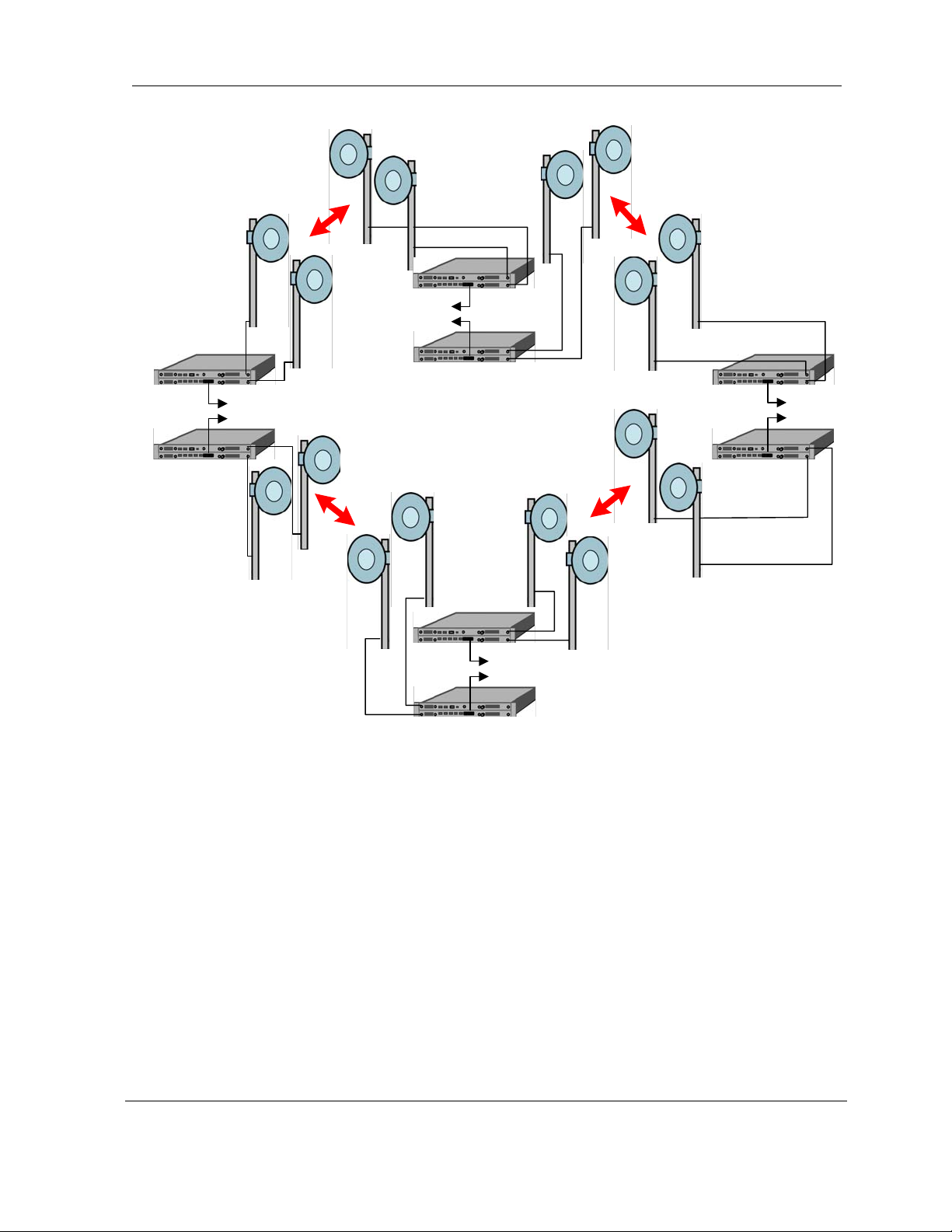
2.10 1 + 1 Multi-hop Repeater Configuration
The MDS FIVE Series supports a 1 + 1 multi-hop repeater configuration with drop/insert
capability as shown in
described in section
architecture as described in section
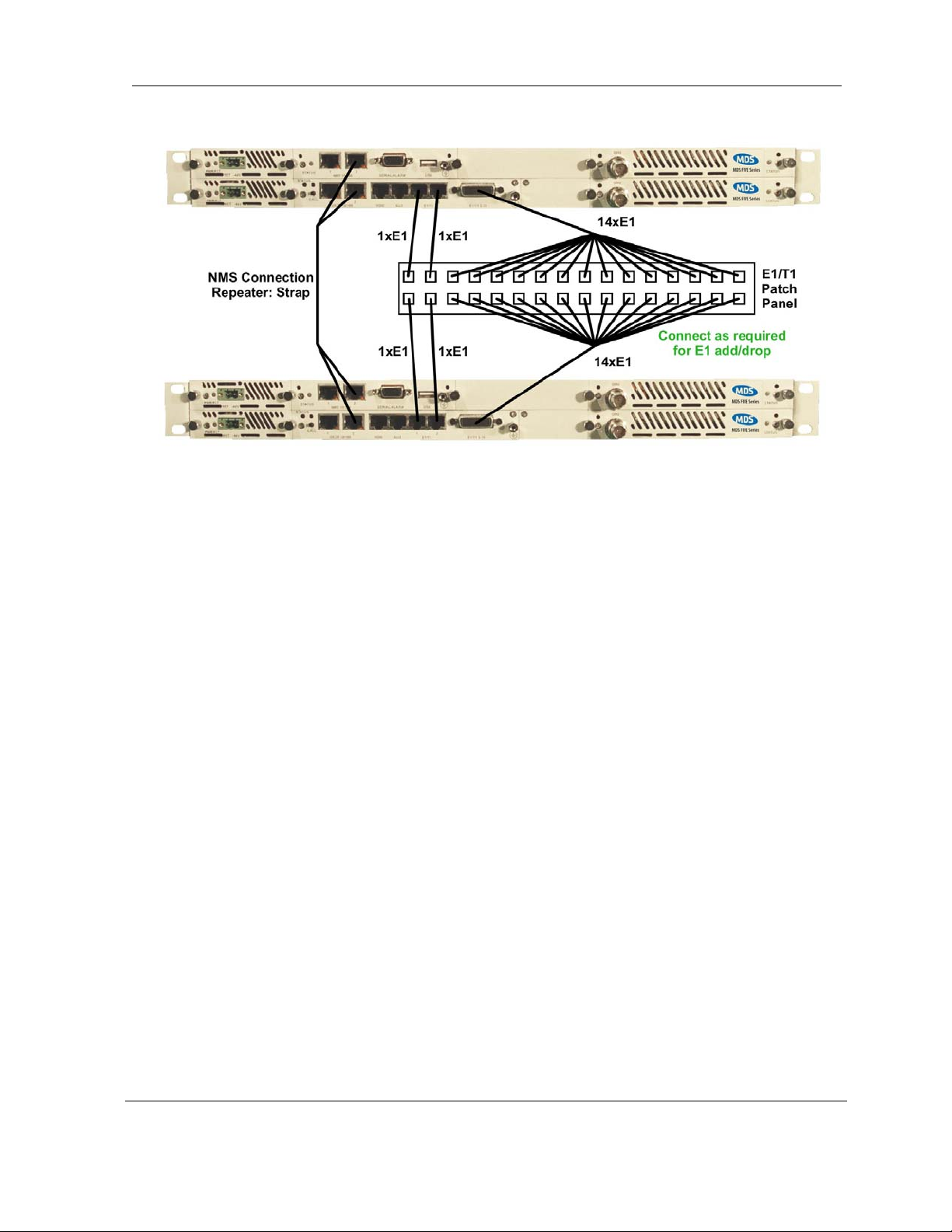
dropped or inserted. Front panel connections for drop/insert capability are shown in
In this configuration each SDIDU
Figure 2-10. This configuration provides individual 1 + 1 link protection as
2.8, as well as the full-scale protection inherent in the consecutive point
2.6. At each location within the network, data may be
TM
contains two power supplies and two modems.
Figure 2-11.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 28
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-20
Protected
Data
drop/insert
Link
drop/insert
Protected
Link
Protected
Link
Data
Data
drop/insert
Protected
Link
Data
drop/insert
Figure 2-10. 1 + 1 Multi-hop Repeater Configuration
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 29
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-21
Figure 2-11. Front Panel connections in 1 + 1 multi-hop repeater configuration
2.11 Data Interfaces
The I/O card has 2x100BaseTX interfaces that can be configured as either primary payload, or
secondary wayside channels. The Over-the-air channel has a data-bandwidth capacity that is set
by the frequency-bandwidth, modulation, and coding. The data-bandwidth may be allocated to
various I/O card interfaces, including 155.52 Mbps for STM-1, 2 Mbps per E1, up to 100 Mbps
Ethernet, and up to 1 Mbps NMS. Only up to 100 Mbps of data-bandwidth may be allocated for
either net data, and the two I/O card 100BaseTX interfaces will share that 100 Mbps databandwidth.
There is also an option mini-I/O card, which provides STM-1 Optical/OC-3 or STM-1 Electrical
interfaces. The optical interface is single mode at 1300 nm. Consult factory for availability of
Mini-IO STM-1/OC-3 Module.
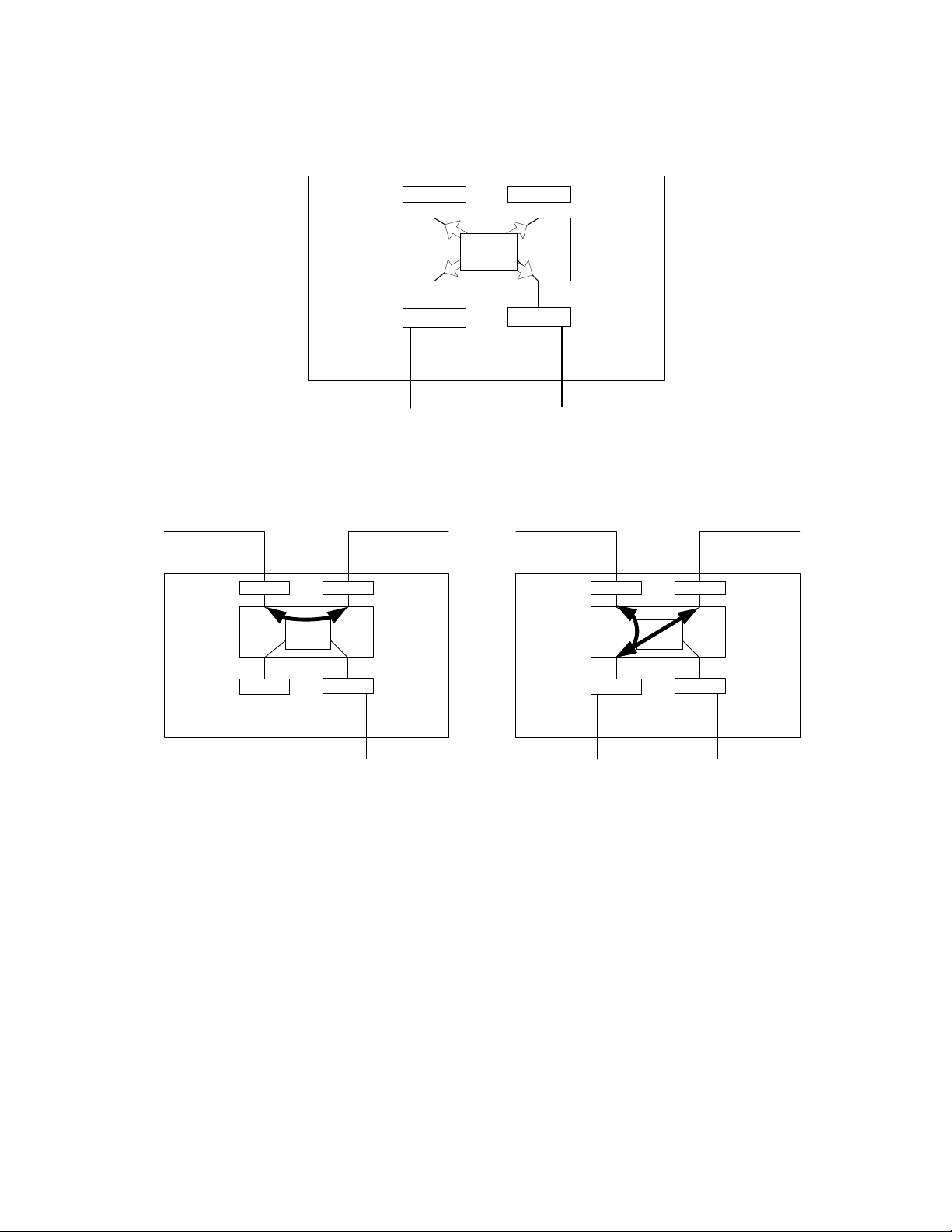
2.12 Crosspoint Switch
The SDIDU™ crosspoint switch provides any-to-any E1/T1 routing between front panel ports and
RF links, as shown in
routings or custom routing. Custom routings are uploaded to the SDIDU™ via FTP. Two
examples of the crosspoint capability are to use the crosspoint switch to configure a repeater or
an add/drop. These examples are shown in
Crosspoint Switch is used as a passthrough to send E1/T1s from the east modem to the west
modem. In the add/drop example, the crosspoint switch connects E1/T1s from the modems to
the front-panel ports.
Figure 2-12. Flexible channel mapping allows selection from predefined
Figure 2-13. In the repeater example, the
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 30
User Reference and Installation Guide 2-22
Repeater Example
Up to 32 E1
Modem East Modem West
Up to 32 E1
Modem East Modem West
Framer
Up to 16E1
Crosspoint
Switch
IO
Optional IO
Up to 16E1
Figure 2-12 Crosspoint switch
Up to 32 E1
Up to 32 E1
Up to 32 E1
Add/Drop Example
Up to 32 E1
Modem East Modem West
Up to 16E1
Framer
IO
Crosspoint
Switch
Optional IO
Up to 16E1
Up to 16E1
Framer
IO
Crosspoint
Switch
Optional IO
Up to 16E1
Figure 2-13 (a) Crosspoint switch used a passthrough in repeater configuration. (b)
Crosspoint switch allows access for add/drop.
2.13 Power Management
RF power management is a radio design feature that controls the power level (typically expressed
in dBm) of the RF signal received from a transmitter by a receiver. The traditional goal of power
management is to ensure that the RF signal at a receiver is strong enough to maintain the radio
link under changing weather and link conditions.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 31

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-23
Traditional power management techniques such as Constant Transmit Power Control (CTPC)
and Automatic Transmit Power Control (ATPC) transmit at a high power level to overcome the
effects of fading and interference. However, these techniques continue to operate at a higher
power level than needed to maintain the link in clear weather. Because transmit power remains
high when the weather clears, the level of system interference increases.
Radios operating at high transmit power will interfere with other radios, even if the interfering
source is miles away from the victim. High interference levels can degrade signal quality to the
point that wireless radio links become unreliable and network availability suffers. The traditional
solution to system interference is to increase the distance between radios. However, the resulting
sparse deployment model is inappropriate for metropolitan areas.
In response to the need for a high-density deployment model t he MDS FIVE Series use a unique
power control technique called A
minimum power level necessary to maintain a link regardless of the prevailing weather and
interference conditions. The MDS FIVE Series is designed and manufactured to not exceed the
+30 dBm maximum power allowed. The purpose of power management is to minimize transmit
power level when lower power levels are sufficient. A
management by controlling not only the power (dBm) of the RF signal, but its quality (signal-tonoise ratio) as well.
TPC. AdTPC enables MDS FIVE Series units to transmit at the
d
TPC also extends the concept of power
d
In contrast to ATPC, the A
the actual strength and quality of the signal. Networked MDS FIVE Series units constantly
monitor receive power and maintain 10
climate conditions. Each MDS FIVE Series unit can detect when there is a degradation in the
received signal level of quality and adjust the transmit power level of the far-end MDS FIVE
Series unit to correct for it.
TPC provides maximum power in periods of heavy interference and fading and minimum power
A
d
when conditions are clear. Minimal transmit power reduces potential for co-channel and adjacent
channel interference with other RF devices in the service area, thereby ensuring maximum
frequency re-use. The resulting benefit is that operators are able to deploy more MDS FIVE
Series units in a smaller area.
TPC technique dynamically adjusts the output power based on both
d
-12
BER performance under varying interference and
2.14 MDS FIVE Series Software and Network Management
All of the MDS FIVE Series parameters are accessible in three ways:
1. Using a standard web-browser via HTTP to access the built in webserver.
2. Via SNMP using the fully featured MIB, allowing for automation of data collection and
network management.
3. Via a command line client accessible from a terminal client connected to the serial port, or
telnet over the NMS Ethernet.
The GUI, SNMP, and CLI control are discussed in the MDS FIVE Series User Interface Manual.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 32

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-24
2.14.1 IP Address
Each SDIDU™ is configured independently for network parameters such as IP address, subnet,
and gateway. However, the SDIDU™ also supports acting as a DHCP client, in which case the
IP address can be assigned to the SDIDU™ using a DHCP server. A specific IP address may be
associated with a particular SDIDU™ by configuring the DHCP server to server IP address based
upon the SDIDU™ Ethernet MAC address.
2.14.2 Network
The SDIDU™ uses an “Out-of-Band” NMS network which is separated from the payload Ethernet
network. Each SDIDU™ contains a managed Layer 2 Ethernet switch that supports SpanningTree Protocol (STP) for managing NMS traffic. This allows the SDIDU™ to be configured in a
protected ring configuration where the STP will prevent an Ethernet loop in the ring. This will alow
allow the ring to re-configure in the event of an outage. The SDIDU acts as a network bridge via
the Ethernet switch and STP. The SDIDU™ does not currently support NMS routing capability.
2.14.3 NMS Network Operational Principles
The SDIDU™ does not provide routing capability. Therefore, all SDIDUs™ must be on the same
subnet as the PC being used to access the SDIDUs™. If the SDIDUs™ and/or the PC are on
different subnets, a router must be used, with the gateway addresses set appropriately.
shows the PC and both SDIDUs™ in the same subnet. In this case, no router is required.
2-14
Figure 2-15 shows the PC and one of the SDIDUs™ in one subnet and the other SDIDU™ in
another. In this case, a router is required. Note how the GW addreses are set to allow
communication from the PC to the SDIDU™ in the other subnet.
Figure
SWITCH
TM
SDIDU
192.168.1.22
SUBNET
PC
192.168.1.10
TM
SDIDU
192.168.1.21
Figure 2-14. PC and SDIDUs™ on same subnet
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 33

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-25
SUBNET 1
PC
IP: 192.168.1.10
GW: 192.168. 1 . 1
SWITCH
TM
SDIDU
IP: 192.168.1.21
GW: 192.168.1.1
ROUTER
IP1: 192.168.1.1
IP2: 192.168.2.1
Figure 2-15. SDIDUs™ on different subnets.
2.14.4 Third Party Network Management Software Support
SUBNET 2
TM
SDIDU
IP: 192.168.2.33
GW: 192.168.2.1
The SDIDU™ supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3 protocols for use with third party
network management software. The SNMP agent will send SNMP traps to specified IP
addresses when an alarm is set or cleared. Information contained in the trap includes:
IP address
System uptime
System time
Alarm name
Alarm set/clear detail
The SDIDU™ may also be managed via HTTP, TELNET, and SSH protocols.
2.15 System Loopbacks
The SDIDU™ provides system loopbacks as a means for test and verification of a unit, link,
and/or network. A variety of loopback points, included LIU selection, are available, Loopback
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 34

User Reference and Installation Guide 2-26
points are easily selected through the Graphical User Interface, for more information see the User
Interface Guide. Loopback duration is also selectable.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 35

3 Installation
3.1 Unpacking
The following is a list of possible included items.
Description Quantity
Digital Radio SDIDUTM (1RU chassis) 1
ODU (with hardware) 1
Manual and/or Quick Start Guide 1
ODU
Figure 3-1. MDS FIVE Series Components
Be sure to retain the original boxes and packing material in case of return shipping. Inspect all
items for damage and/or loose parts. Contact the shipping company immediately if anything
appears damaged. If any of the listed parts are missing, call the distributor or the factory
immediately to resolve the problem.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc.
All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
SDIDU
TM
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 36

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-2
3.2 Notices
CAUTION
DO NOT OPERATE EXTERNAL ANTENNA ODU UNITS WITHOUT AN ANTENNA,
ATTENUATOR, OR LOAD CONNECTED TO THE ANTENNA PORT. DAMAGE MAY OCCUR
TO THE TRANSMITTER DUE TO EXCESSIVE REFLECTED RF ENERGY.
ALWAYS ATTENUATE THE SIGNAL INTO THE RECEIVER ANTENNA PORT TO LESS THAN
–20 dBm. THIS WILL PREVENT OVERLOAD AND POSSIBLE DAMAGE TO THE RECEIVER
MODULE.
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE IS PRESENT INSIDE THE ODU and SDIDUTM WHEN THE UNIT IS
PLUGGED IN. TO PREVENT ELECTRICAL SHOCK, UNPLUG THE POWER CABLE
BEFORE SERVICING. UNIT SHOULD BE SERVICED BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
3.3 Required Tools
The following tools are needed for installation.
3.3.1 SDIDU
• 1/8” Slotted screwdriver for securing power supply connector
• Screwdriver for rack mount assembly. Size and types depends on rack mount screws
(not included).
3.3.2 ODU Tools
• 13 mm or adjustable wrench for ODU bracket mounting bolts
• 17 mm or adjustable wrench for U-Bolt
TM
Tools
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 37

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-3
3.4 PRE-INSTALLATION NOTES
It may be useful to gain familiarity with the MDS FIVE Series via back-to-back bench testing prior
to final installation. We highly recommend installation of lightning protectors on the
ODU/SDIDU
Back-to-back bench testing prior to final installation is highly recommended in order to gain
familiarity with the product. The following additional equipment is required for back-to-back
testing:
• Low-loss cables, N-male connectors on ODU interfaces.
• Two inline RF attenuators, 30 dB each, rated for ODU frequency.
TM
Interconnect Cable to prevent line surges from damaging expensive components.
The SDIDU
Figure 3-2. When equipment is connected in operational configuration, no errors should be
in
reported on the front panel.
TM
and ODUs must be configured in an operational configuration and set-up a s shown
Ant. Port
ODU - 1
To IDU
SDIDU - 1
TM TM
Figure 3-2. MDS FIVE Series Back-to-Back Testing Configuration
30 dB 30 dB
Ant. Port
ODU - 2
SDIDU - 2
3.5 Overview of Installation and Testing Process
The installation and testing process is accomplished by performing a series of separate, yet
interrelated, procedures, each of which is required for the successful implementation of a
production MDS FIVE Series network. These procedures are as follows:
• Site Evaluation: gathering specific information about potential MDS FIVE Series installation
sites.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 38

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-4
• Cable and Installation: Testing and installing MDS FIVE Series ODU cables and optional
interface devices at installation sites.
• MDS FIVE Series ODU Mounting and Alignment: Mounting ODUs to a pole or wall,
performing link alignment and radio frequency (RF) verification.
• MDS FIVE Series Digital Radio Configuration: Using MDS FIVE Series Link Manager
software to install network- and site-specific parameters in the radios.
• MDS FIVE Series Digital Radio Testing: Performing cable continuity checks and RF tests for
links, the payload/radio overhead channel, and the management channel.
The following diagram shows where installation and commissioning resides within the MDS FIVE
Series network deployment life cycle and defines the sequence in which the processes that
comprise installation and commissioning should be performed.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 39

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-5
Network Life Cycle
Customer
Requirements
RF Planning
& Network
Design
Site Selection
& Acquisition
PDH SDH
Installation &
Commissioning
Perform Site
Evaluation
Mount and Align
ODUs
Install Cables
Configure Digital
Software Defined
TM
IDU
Type of
Network?
Operation &
Maintenance
Network
Network
Upgrade &
Expansion
Perform Fast
PDH Network Test
Installation &
Commissioning
Complete
Perform
SDH Network Test
03-01-013b
3.6 Site Evaluation
A site evaluation consists of a series of procedures for gathering specific information about
potential MDS FIVE Series locations. This information is critical to the successful design and
deployment of a network.
Site evaluations are required to confirm whether or not a building meets network design
requirements. The main objectives are as follows:
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 40

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-6
• Confirm
• Line of sight for each link
• MDS FIVE Series ODU mounting locations
• Site equipment locations
• Cable routes
• Any other potential RF sources
• Prepare site drawings and record site information
3.6.1 Preparing for a Site Evaluation
The following tools are required to perform a site evaluation:
• RF and network design diagrams (as required)
• Binoculars
• Global positioning system (GPS) or range finder
• Compass
• Measuring tape and/or wheel
• Digital camera
• Area map
• Aerial photograph (if available)
• List of potential installation sites (“targeted buildings”)
The following tasks must be completed prior to performing a site evaluation:
• Prepare the initial network design by performing the following:
• Identify potential buildings by identifying targeted customers (applicable if you’re a service
provider)
• Identify potential links by selecting buildings based on the high probability of line of sight
• Arrange for access with the facility personnel into the buildings, equipment rooms, and
architectural plans to become familiar with the location of all ducts, risers, etc.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 41

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-7
3.6.2 Site Evaluation Process
The following steps must be completed to perform a successful site evaluation. Each step in the
process is detailed in the following subparagraphs:
• Ensure RF Safety compliance: Ensure that appropriate warning signs are properly placed
and posted at the equipment site or access entry. For a complete list of warnings, refer
the Safety Precautions listed at the beginning of this manual.
• Ensure Compliance with Laws, Regulations, Codes, and Agreements: Ensure that any
installation performed as a result of the site evaluation is in full compliance with applicable
federal and local laws, regulations, electrical codes, building codes, and fire codes.
• Establish Radio Line of Sight between MDS FIVE Series Radios: The most critical step
in conducting a site evaluation is confirming a clear visual and radio Line of Sight
(LOS) between a near MDS FIVE Series Radio and a far MDS FIVE Series Radio. If
LOS does not exist, another location must be used.
MDS FIVE Series Radios in a link must have a clear view of each other, or visual “line of
sight”. Binoculars may be used evaluate the path from the desired location of the near
MDS FIVE Series Radio to the desired location of the far MDS FIVE Series Radio.
To confirm Line of Sight:
- Ensure that no obstructions are close to the transmitting/receiving path. Take into
consideration trees, bridges, construction of new buildings, unexpected aerial traffic,
window washing units, etc.
- Ensure that each MDS FIVE Series can be mounted in the position required to
correctly align the MDS FIVE Series with its link partner.
MDS FIVE Series Radios must also have a clear radio line of sight. If a hard object, such
as a mountain ridge or building, is too close to the signal path, it can damage the r adio
signal or reduce its strength. This happens even though the obstacle does not obscure
the direct, visual line of sight. The Fresnel zone for a radio beam is an elliptical area
immediately surrounding the visual path. It varies in thickness depending on the length of
the signal path and the frequency of the signal. The necessary clearance for the Fresnel
zone can be calculated, and it must be taken into account when designing a wireless
links.
As shown in the picture above, when a hard object protrudes into the signal path within
the Fresnel zone, knife-edge diffraction can deflect part of the signal and cause it to reach
the receiving antenna slightly later than the direct signal. Since these deflected signals
are out of phase with the direct signal, they can reduce its power or cancel it out
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 42

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-8
altogether. If trees or other 'soft' objects protrude into the Fresnel zone, they can
attenuate (reduced the strength of) a passing signal. In short, the fact that you can see a
location does not mean that you can establish a quality radio link to that location.
Microwave Data Systems provides a link planner spreadsheet that calculates the Fresnel
ratio and helps determine link feasibility. Contact your technical support representative
for a copy of the spreadsheet.
Determine MDS FIVE Series ODU Mounting Requirements: MDS FIVE Series ODUs can
be mounted on an antenna mast, brick, masonry or wall. Refer to detailed installation
sections.
TM
• Determine MDS FIVE Series SDIDU
Installation Location: MDS FIVE Series SDIDUsTM
can be installed tabletop or cabinet, wall mount, or rack mount. The site must provide DC
power or an optional AC/DC converter may be used. Refer to detailed installation
sections.
• Document Potential Sources of Co-location Interference: When MDS FIVE Series ODUs
are located on a roof or pole with other transmitters and receivers, an interference
analysis may be required to determine and resolve potential interference issues. The
interference analysis needs to be performed by an RF engineer. The specific information
required for each transmitter and receiver includes the following:
- Transmitting and/or receiving frequency
- Type of antenna
- Distance from MDS FIVE Series ODU (horizontal and vertical)
- Polarity (horizontal or vert ical)
- Transmit power level
- Antenna direction
• Measure the Link Distance: The two ways to measure link distance are as follows:
- GPS: record the latitude and longitude for the ne ar and far MDS FIVE Series ODU
sites and calculate the link distance. Record the mapping datum used by the GPS
unit and ensure the same mapping datum is used for all site evaluations in a given
network.
- Range finder: measure the link distance (imperial or metric units may be used).
Once the link distance has been measured, verify that the link distance meets the
availability requirements of the link. Microwave Data Systems has created a spreadsheet
tool that calculates the link availability based on the details of the link. The Microsoft Excel
spreadsheet is available on internet, at http://www.microwavedata.com/, and is shown on
the following page. The following parameters should be entered (items in yellow):
• Operating Frequency: Enter 5800 or 5300
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 43

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-9
• Transmit Antenna Gain: Enter 23 for the internal antenna or enter the gain of the external
antenna if used.
• Transmit Output Power: Selectable between +5 to +23dB (5.8 GHz) and –18 to +5 (5.3
GHz) in 1 dB steps.
• Receive Antenna Gain: Enter 23 for the internal antenna or enter the gain of the external
antenna if used.
• Link Distance: Enter distance in miles or kilometers (must select the correct units: miles or
kilometers)
• Fresnel Clearance Ratio: This is a factor indicating the radio line of sight. A clear radio
line of site has a fresnel clearance ratio of +0.60. As the curvature of the earth or other
obstacles degrade the radio line of sight, the ratio can drop to –1. A separate spreadsheet
is provided to calculate the appropriate ratio. In this spreadsheet the path length, tower
heights and heights of any obstructions or ridges in the path of the link are entered.
• Climate Factor: Enter 0.1 for dry, 0.25 for average and 0.5 for humid environments
• Terrain Factor: Enter 0.25 for mountainous, 1 for average, and 4 for smooth (water)
TM
• Determine the Length of Interconnect Cable from ODU to SDIDU
consideration for the outdoor interconnect cable from the ODU to SDIDU
and route between the ODU and SDIDU
3-1
.
Table 3-1. Maximum cable lengths
Cable Type 140 MHz 350 MHz
LMR-200 12.6 20.1 100 m
LMR-300 7.6 12.1 165 m
LMR-400 4.9 7.8 256 m
RG-214 8 13.1 153 m
Belden 7808 8.6 14 143 m
Loss at (dB/100 m)
TM
. Maximum cable lengths are listed in Table
Maximum
Length*
: The primary
TM
is the distance
* Does not account for connector loss.
The link availability, dispersive fade margin and expected signal strength readings are calculated
based on the entered parameters. Maximum link distances based on the antenna and transmitter
power settings are also displayed.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 44

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-10
)
1,2
(
)
4
4
5
5
4
4
%
%
%
5
5
5
5
4
5
5
5
6
5
6
(
)
MDS FIVE series Link Planner: 5.3GHz Availability
Parameter
Operating Frequency (MHz)
Transmit Antenna Gain (dBi)
Transmitte r O utput Power (dBm
Receive Antenna Gain (dBi)
Link Distance
Fresnel Clearance Ratio
Climate Factor
Terrain Factor
Value
5300
3.93
0.60
0.25
23
6
23
miles
1
Sens itivity
3
Receiver
3
dBm
99.9
9
9
9
8
7
9
9
9
9
Marg in ( d B)
Max Distance
for Various Availability
Link Fade
99.99
32
32
MDS FIVE series Mode
5.3GHz Band
5.3G-25FE1 31.112E+6 30.0 -83 12 -71
5.3G-25FE2 31.112E+6 20.0 -82 11 -71
5.3G-25FE3 31.112E+6 13.3 -82 11 -71
5.3G-50FE1 56.733E+6 30.0 -80 9 -71
5.3G-50FE2 56.733E+6 20.0 -77 6 -71
5.3G-50FE3 56.733E+6 13.3 -72 1 -71
5.3G-100FE1 107.797E+6 30.0 -73 2 -71
5.3G-16E1-2 36.918E+6 20.0 -82 11 -71
5.3G-16T1-2 28.655E+6 20.0 -84 13 -71
5.3G-16E1-3 36.918E+6 13.3 -82 11 -71
5.3G-16T1-3 28.655E+6 13.3 -84 13 -71
Note1: FCC's definition; negative clearance indicates no optical LOS; range is [-1,…,0.6]; 0.6 is radio LO S condition.
Note2: Accounting for single knife-edge diffraction loss only.
Note3: BER<<1e-6.
Note4: Listed data rates inlcudes 2 E1 Wayside channels, except for 16E1/T1 modes.
MDS FIVE series Mode
5.3G-25FE 1 QPSK 3/4 -83
5.3G-25FE2 16QAM 3/4 -82
5.3G-25FE3 16QAM 3/4 -82
5.3G-50FE1 16QAM 3/4 -80
5.3G-50FE2 32QAM 4/5 -77
5.3G-50FE3 64QAM 11/12 -72
5.3G-100FE1 32QAM 9/10 -73
5.3G-16E1-2 16QAM 3/4 -82
5.3G-16T1-2 16QAM 3/4 -84
5.3G-16E1-3 16QAM 7/8 -82
5.3G-16T1-3 16QAM 7/8 -84
Modem Data
Rate (M bp s )
Modulation
and Code
Rate
Channel
Bandwidth
(MHz)
Receiver
Sens itivity
dBm
ODU RSSI
(dBm)
(miles)
99.999
3
3
3
3
2
3
3
3
3
Ava i lability
(%)
99.9987
99.998
99.998
99.997
99.9950
99.984
99.9876
99.998
99.9990
99.998
99.9990
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 45

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-11
Path Length (Km) 10
TX Tower Height (m) 30
RX Tow er He igh t ( m) 30
Frequency (MHz) 5800
Calculat ed Fresnel Clearance Ratio 0.48
MDS FIVE series Li nk P lanner: Fresnel Zone Clearance
Radio LOS (60%
1st
Distance
Note1: Earth Curvature is based on a spherical Earth model w ith a nominal radius of 6371Km and a typical K-factor of 1.33.
Optical
from TX
(Km)
Height (m)
0.0 30.0 0.0 30.0 30.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.3 30.0 3.5 26.5 27.9 0.1 0.0 0.1
0.5 30.0 5.0 25.0 27.0 0.3 0.0 0.3
0.8 30.0 6.0 24.0 26.4 0.4 0.0 0.4
1.0 30.0 6.8 23.2 25.9 0.5 0.0 0.5
1.3 30.0 7.5 22.5 25.5 0.6 0.0 0.6
1.5 30.0 8.1 21.9 25.1 0.8 0.0 0.8
1.8 30.0 8.6 21.4 24.8 0.8 20.8
2.0 30.0 9.1 20.9 24.5 0.9 10.9
2.3 30.0 9.5 20.5 24.3 1.0 11.0
2.5 30.0 9.8 20.2 24.1 1.1 24.1
2.8 30.0 10.1 19.9 23.9 1.2 25.2
3.0 30.0 10.4 19.6 23.8 1.2 0.0 1.2
3.3 30.0 10.6 19.4 23.6 1.3 0.0 1.3
3.5 30.0 10.8 19.2 23.5 1.3 0.0 1.3
3.8 30.0 11.0 19.0 23.4 1.4 0.0 1.4
4.0 30.0 11.1 18.9 23.3 1.4 11.4
4.3 30.0 11.2 18.8 23.3 1.4 0.0 1.4
4.5 30.0 11.3 18.7 23.2 1.5 0.0 1.5
4.8 30.0 11.3 18.7 23.2 1.5 0.0 1.5
5.0 30.0 11.4 18.6 23.2 1.5 0.0 1.5
5.3 30.0 11.3 18.7 23.2 1.5 0.0 1.5
5.5 30.0 11.3 18.7 23.2 1.5 0.0 1.5
5.8 30.0 11.2 18.8 23.3 1.4 0.0 1.4
6.0 30.0 11.1 18.9 23.3 1.4 0.0 1.4
6.3 30.0 11.0 19.0 23.4 1.4 0.0 1.4
6.5 30.0 10.8 19.2 23.5 1.3 19.8
6.8 30.0 10.6 19.4 23.6 1.3 0.0 1.3
7.0 30.0 10.4 19.6 23.8 1.2 0.0 1.2
7.3 30.0 10.1 19.9 23.9 1.2 0.0 1.2
7.5 30.0 9.8 20.2 24.1 1.1 0.0 1.1
7.8 30.0 9.5 20.5 24.3 1.0 0.0 1.0
8.0 30.0 9.1 20.9 24.5 0.9 0.0 0.9
8.3 30.0 8.6 21.4 24.8 0.8 0.0 0.8
8.5 30.0 8.1 21.9 25.1 0.8 0.0 0.8
8.8 30.0 7.5 22.5 25.5 0.6 0.0 0.6
9.0 30.0 6.8 23.2 25.9 0.5 0.0 0.5
9.3 30.0 6.0 24.0 26.4 0.4 0.0 0.4
9.5 30.0 5.0 25.0 27.0 0.3 0.0 0.3
9.8 30.0 3.5 26.5 27.9 0.1 0.0 0.1
10.0 30.0 0.0 30.0 30.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
LOS
1st
Fre snel
Zone
Radius (m)
Fre snel
Zone
Height (m )
Fre snel
Clearance) Zone
Height (m)
Ear th
Curvatur e
(m)
Obs truction
1
Height (m)
20.0
10.0
10.0
23.0
24.0
10.0
18.5
Total Earth
Terr ain
Height (m)
Fre snel
Clearance
Ratio
8.42
6.00
4.95
4.32
3.91
3.61
1.06
2.10
2.00
0.60
0.48
2.76
2.70
2.65
2.60
1.67
2.54
2.53
2.52
2.51
2.52
2.53
2.54
2.57
2.60
0.94
2.70
2.76
2.84
2.94
3.05
3.20
3.38
3.61
3.91
4.32
4.95
6.00
8.42
-
-
Optical LOS 1st Fresnel Radio LOS Earth Curvature Obstructions
35.0
30.0
25.0
20.0
Height (m)
15.0
10.0
5.0
0.0
0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0
Distance (km)
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 46

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-12
Select the Grounding Location for both the MDS FIVE Series ODU and SDIDU
TM
: The MDS
FIVE Series must be properly grounded in order to protect it and the structure it is installed on
from lightning damage. This requires
- Grounding all ODUs as specified by supplier
- Grounding all SDIDU
TM
to the rack.
• Confirm the Presence of DC Power for the MDS FIVE Series SDIDUTM.
• Ensure Building Aesthetics: Ensure that the ODU can be mounted so that it is
aesthetically pleasing to the environment and to the property owner. Aesthetics must be
approved by the property owner and the network engineer.
• Take Site Photographs
• Sketch the Site
3.6.3 Critical System Calculations
3.6.3.1 Received Signal Level (RSL) and Link Budget
The received signal level (RSL) can be estimated using the following formula:
RSL (dBm) = P
TX
+ G
TX ANT
– L
Path
+ G
RX ANT
Where: PTX is the transmitter output power (in dBm)
G
G
L
is the Path loss, defined by:
Path
L
(dB) = 36.6 + 20log10(F*D)
P
is the gain of the transmit antenna (in dB), 23 dBi for ODU’s internal antenna
TX ANT
is the gain of the receive antenna (in dB), 23 dBi for ODU’s internal antenna
RX ANT
Where: F is the Frequency in MHz (5800 or 5300), D is the Distance of path in miles
This link budget is very important in determining any potential problems during installation. The
expected RSL and measured RSL should be close (+/- 5 to 10 dB)
3.6.3.2 Fade Margin Calculation
The fade margin is the difference between the actual received signal and the MDS FIVE Series
Radio’s threshold for the modulation mode selected. The fade margin can be used to determine
availability and should be at least 10 dB.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 47

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-13
3.6.3.3 Availability Calculation
Availability of the microwave path is a prediction of the percent of time that the link will operate
without producing an excessive BER due to multipath fading. Availability is affected by the
following:
• Path length
• Fade margin
• Frequency
• Terrain (smooth, average, mountainous, valleys)
• Climate (dry, temperate, hot, humid)
Depending on the type of traffic carried over the link and the overall network design redundancy,
fade margin should be included to support the desired availability rate. Critical data and voice
may require a very high availability rate (99.999% or 5.3 minutes of predicted outage per year).
To improve availability, the fade margin can be increased by shortening the path length,
transmitting at a higher power level, or by using higher gain antennas.
Availability can be computed using the following formula, which is known as the Vigants Barnett
Method.
Availability = 100
P = 2.5
× 10
× (1 – P)
-9
× C × F × D
3
× 10
(-FM/10)
Where F is the frequency in MHz (5300 or 5800)
D is the distance in miles
FM is the fade margin in dB
C is the climate/terrain factor as defined below:
Humid/Over Water: C = 4 (worst case channel)
Average Conditions: C = 1
Dry/Mountains: C = 0.25 (best case channel)
Example: Assume 21 dB fade margin, over 5 miles with average climate/terrain, at 5.8 GHz. The
availability comes out to be 99.9986. This corresponds to the link being unavailable for 7.6
minutes per year.
3.6.4 Frequency Plan Determination
When configuring MDS FIVE Series units in a point-to-point or consecutive point configuration,
careful engineering of the MDS FIVE Series frequency plans and antenna locations should be
performed in order to minimize potential interference between nearby radios. Nearby radios
should operate on different frequencies, transmitting in the same band (high side or low side).
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 48

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-14
When designing multi-radio configurations, antenna size, antenna polarization, and antenna
location are critical.
The frequency plan must be selected based on desired data rate and expected link conditions. In
a high interference environment or with lower gain antennas, higher bandwidth, more robust
modulation formats must be employed. The available frequency plans are illustrated in
and Figure 3-4.
3-3
Figure
The channel assignments shown in the figures correspond to the channel numbers entered vi a
the graphical user interface (GUI) or SNMP.
1 Channel Operation, 30MHz Bandwidth
1 Channel Operation, 30MHz Bandwidth
A Tx
A Tx
B Rx
B Rx
5725
5725
1A Tx
1A Tx
1A Tx
1B Rx
1B Rx
1B Rx
5725
5725
5725
5725
5725
5725
5725
5725
5725
5737
5737
5737
1A Tx
1A Tx
1A Tx
1B Rx
1B Rx
1B Rx
5733 5841
5733 5841
5733 5841
1A Tx
1A Tx
1A Tx
1B Rx
1B Rx
1B Rx
5731
5731
5731
5750 5825
5750 5825
2A Tx
2A Tx
2A Tx
2B Rx
2B Rx
2B Rx
5762
5762
5762
3A Tx
3A Tx
2A Tx
2A Tx
2A Tx
2B Rx
2B Rx
2B Rx
5743
5743
5743
2A Tx
2A Tx
2A Tx
2B Rx
2B Rx
2B Rx
5750
5750
5750
5756
5756
5756
3A Tx
3A Tx
3A Tx
3B Rx
3B Rx
3B Rx
3A Tx
3B Rx
3B Rx
3B Rx
5766
5766
5766
4A Tx
4A Tx
4A Tx
4B Rx
4B Rx
4B Rx
5768
5768
5768
Diplexer
Diplexer
2 Channel Operation, 25MHz Bandwidth
2 Channel Operation, 25MHz Bandwidth
2 Channel Operation, 25MHz Bandwidth
1A Rx
1A Rx
1A Rx
1A Rx
1A Rx
1B Tx
1B Tx
1B Tx
5808
5808
5808
1A Rx
1A Rx
1A Rx
1B Tx
1B Tx
1B Tx
5806
5806
5806
1A Rx
1B Tx
1B Tx
1B Tx
5812
5812
5812
2A Rx
2A Rx
2A Rx
2B Tx
2B Tx
2B Tx
5818 5831
5818 5831
5818 5831
Diplexer
Diplexer
Diplexer
3 Channel Operation, 16.7MHz Bandwidth
3 Channel Operation, 16.7MHz Bandwidth
3 Channel Operation, 16.7MHz Bandwidth
Diplexer
Diplexer
Diplexer
4 Channel Operation, 12.5MHz Bandwidth
4 Channel Operation, 12.5MHz Bandwidth
4 Channel Operation, 12.5MHz Bandwidth
Diplexer
Diplexer
Diplexer
2A Rx
2A Rx
2A Rx
2B Tx
2B Tx
2B Tx
A Rx
A Rx
B Tx
B Tx
5825
5825
5825
3A Rx
3A Rx
3A Rx
3B Tx
3B Tx
3B Tx
2A Rx
2A Rx
2A Rx
2B Tx
2B Tx
2B Tx
5837
5837
5837
3A Rx
3A Rx
3A Rx
3B Tx
3B Tx
3B Tx
4A Rx
4A Rx
4A Rx
4B Tx
4B Tx
4B Tx
5843
5843
5843
5850
5850
5850
5850
5850
5850
5850
5850
5850
5850
5850
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
Figure 3-3. MDS FIVE Series Channel 5.8 GHz Frequency Plan
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 49

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-15
1 Channel Operation, 30MHz Bandwidth
1 Channel Operation, 30MHz Bandwidth
A Tx
A Tx
B Rx
B Rx
5270 5330
5250
5250
1A Tx
1A Tx
1A Tx
1B Rx
1B Rx
1B Rx
5250
5250
5250
5250
5250
5250
5260
5260
5260
1A Tx
1A Tx
1A Tx
1B Rx
1B Rx
1B Rx
5257 5343
5257 5343
5257 5343
5270 5330
2A Tx
2A Tx
2A Tx
2B Rx
2B Rx
2B Rx
5280
5280
5280
3A Tx
3A Tx
2A Tx
2A Tx
2A Tx
2B Rx
2B Rx
2B Rx
5270
5270
5270
3A Tx
3B Rx
3B Rx
3B Rx
5283
5283
5283
Diplexer
Diplexer
2 Channel Operation, 20MHz Bandwidth
2 Channel Operation, 20MHz Bandwidth
2 Channel Operation, 20MHz Bandwidth
1A Rx
1A Rx
1A Rx
1A Rx
1A Rx
1B Tx
1B Tx
1B Tx
5317
5317
5317
1A Rx
1B Tx
1B Tx
1B Tx
5320
5320
5320
Diplexer
Diplexer
Diplexer
3 Channel Operation, 13.3MHz Bandwidth
3 Channel Operation, 13.3MHz Bandwidth
3 Channel Operation, 13.3MHz Bandwidth
Diplexer
Diplexer
Diplexer
A Rx
A Rx
B Tx
B Tx
2A Rx
2A Rx
2A Rx
2B Tx
2B Tx
2B Tx
5330
5330
5330
2A Rx
2A Rx
2A Rx
2B Tx
2B Tx
2B Tx
5340
5340
5340
3A Rx
3A Rx
3A Rx
3B Tx
3B Tx
3B Tx
5350
5350
5350
5350
5350
5350
5350
5350
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
F, MHz
Figure 3-4. MDS FIVE Series Channel 5.3 GHz Frequency Plan
3.6.5 Antenna Planning
The ODU comes with a built in 23 dBi gain antenna. This should provide adequate link
performance for most applications.
Larger antennas have the advantage of providing narrower beamwidths and high isotropic gain,
which yields better link performance (higher fade margin, better availability), and improves
immunity to spatial interference (due to the smaller beamwidths). However, larger antennas are
more costly to purchase and install than smaller antennas and in some cases, they require
special equipment for installation due to narrower beamwidths. They are also more easily
affected by wind.
Only directional antennas can be used with MDS FIVE Series radios. Consult factory for antenna
manufacturer options.
The ISM (5.8 GHz) band does not restrict antenna gain or EIRP, therefore there is no need to
back off transmit power due to excessive antenna gain.
1. Select where the cable will enter the building from the outside.
2. Determine the length of cable required. Allow three extra feet on each end to allow for strain
relief, as well as any bends and turns.
3.6.6 ODU Transmit Power Setup
Setting the ODU transmit power is conditional on the band and application. The installer of
this equipment is responsible for proper selection of allowable power settings.
If there are
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 50

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-16
any questions on power settings refer to your professional installer in order to maintain
the FCC legal ERP limits.
The SDIDU
TM
employs spectrally efficient shaped Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). This
waveform is not a constant envelope waveform. Therefore, the average power and peak power
are different. The difference in peak and average power depends on the constellation type and
shaping factor, where spectral efficiency such as more constellation points or lower shaping
factor leading to peak powers higher than average powers. The peak power is typically 5-7 dB
greater than the average power in the SDIDU
TM
, and never exceeds 7 dB. Regulatory
requirements are usually based on peak EIRP which is based on peak power and antenna gain.
3.6.6.1 5.8 GHz Band
For fixed point-to-point applications in the United States the maximum EIRP (Effective Isotropic
Radiated Power) is unlimited when using directional antennas in accordance with FCC part
15.247b(3). The ODU 5800 may therefore be operated at its maximum output power, +23 dBm,
for maximum system gain.
EIRP is calculated for link budget with external antennas as,
EIRP(avg) dBm = External Antenna Gain (dBi) + 23 dBm
For internal antenna (23 dBi) EIRP is,
EIRP(avg) = 46 dBm
3.6.6.2 5.3 GHz Band
In the 5.3 GHz U-NII band the peak EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) is limited to +30
dBm at the antenna for bandwidths above 20 MHz and is reduced for narrower bandwidths in
accordance with FCC part 15.407a(3).
The installer is responsible during set up of transmit power to not exceed FCC limits on
transmission power. These maximum power levels are provided in Table 3-1 for both internal
antenna and external antenna ODU configurations, along with the operational bandwidths.
Note that though regulatory limits are stated in terms of peak power, the system transmit power
levels are calibrated as averaged power readings. Average power is used for link calculations.
Therefore the levels provided in the following table is average power levels that have been
certified to correspond with the maximum peak EIRP allowed.
3.6.6.2.1 ODU with Internal Antenna Table 3-1 indicates the maximum average transmit power setting that may be selected ODU 5300
with internal (23 dBi) antenna.
The number of supported channels per band (low band or high band) is shown in the link
configuration wizard. The greater number of channels supported the lower the emission
bandwidth for each channel.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 51

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-17
For link budget, EIRP(Avg) = 23 dBi + Tx Power Setting (dBm).
3.6.6.2.2 ODU with External Antenna When using external antennas with gains greater than 23 dBi, the transmit power must be
reduced in dB from that given in Table 3-1 by the antenna gain difference above 23 dBi for the
mode that is being used.
For example, using a 6 foot dish antenna with 37 dBi gain, the output power would be dropped by
Antenna Gain (External) – 23 dBi = Antenna Gain Difference
37.6 dBi – 23 dBi = 14.6 dB
For mode 100FE1 (single channel configuration with 30MHz emission bandwidth) the power
would be lowered from
Tx Power (Internal Antenna) – Antenna Gain Difference = Tx Power (External Ant)
+5 dBm – 14.6 dB = -9.6 dBm (-10 dBm).
Table 3-1 also presents transmit power settings for various antenna dish sizes.
For link budget, EIRP(Avg) dBm = 37 dBi + Tx Power Setting (dBm).
Table 3-2. Maximum Power Settings for 5.3GHz U-NII Band Operation (US).
Antenna
Diameter
Antenna
Gain, dBi*
(example)
Maximum Tx
Power
Setting, dBm
1 Channel
Mode
(30MHz BW)
Maximum Tx
Power
Setting, dBm
2 Channel
Mode
(20MHz BW)
6 foot dish 37.6 -10 -11 -12
4 foot dish 34.6 -7 -8 -9
3 foot dish 31.2 -3 -4 -5
2 foot dish 28.0 0 -1 -2
1.5 foot dish 25.3 +3 +2 +1
Internal 23.0 +5 +4 +3
Maximum Tx
Power
Setting, dBm
3 Channel
Mode
(13.3MHz
BW)
* Note: Many antenna manufacturers rate antenna gain in dBd (dB referred to a dipole antenna)
in their literature. To convert to dBi, add 2.15 dB.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 52

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-18
Power settings for other modes of operation can be easily extrapolated from
Table 3-2. For link
budget calculations,
EIRP(Avg) dBm= Antenna Gain (dBi) + Tx Power Setting (dBm).
Though transmitter radiated power is limited in the 5.3 GHz band regardless of antenna size, the
receiver benefits from gain of larger antennas.
3.6.7 Documenting a Site Evaluation
Use the site evaluation form provided on the following pages to document the results of your site
evaluation. Optimally, this complete site form would be stored with the SDIDU
reference.
TM
for future
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 53

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-19
Site Evaluation Form
Address Site Engineer
Contact Person
Phone
Site No Site Agent
Site Type
ODU Roof Location
# Latitude Longitude
Mapping Datum (ex. NDA27)
ODU
Example Information Information Infor mation
ODU# 4
Clear Line of Sight Yes
Mounting Method Wall or Pole
FCC Compliance Y es
Collocation
Aesthetics
ODU Azimuth 60 degrees
GPS Reading 80 21' 48"
Cable Lengths
Alarm
Interconnect Cable 250 feet
Grounding/Lighting
Instructions
Photographs*
Photo 1
Photo 2
Roof Requirements
Photo 3
Sketches**
Sketch 1
Sketch 2
Recommendations for Site Photographs and Sketches
*Photographs
Photo 1 - ODU mounting location Sketch 1- Roof and cable route to entry point
Phone 2 - View from the ODU mounting location to the link partner Sketch 2 - Details for grounding and lighting protection
Photo 3 - IDU location Sketch 3 - IDU room and cable routes from entry port
**Sketches
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 54

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-20
A
A
p
Site Evaluation
Parameters
Source
Tx and/or Rx
Frequency
Distance from ODU
Owner
zimuth
Elevation
ntenna Type
Power
Colocated
Power
Parameters
IDU room Identified
Space for cabinet Yes
Phone line
TM
48 VDC available?
Cables
Take Photo 3
SDIDU
Sketch 3
Front View
Example Information
2 degrees downtilt
Example Information
Equipment Dimensions
PCS
Tx/Rx
2.1 GHz
5 feet
Sprint PCS
210 degrees
14W
Yes
Need to install
Yes
Confirm cables
Information Information Information
Information Information Information
Top View Side View
Equipment Cabinet
ace
Batteries
Indoor S
Note
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 55

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-21
3.7 Installation of the MDS FIVE Series
The following sections provide installation guides for:
• SDIDU
TM
Installation
• ODU Installation
3.7.1 Installing the MDS FIVE Series Software Defined IDU
The MDS FIVE Series SDIDU
TM
can be installed in the following three options:
TM
1. Table top or cabinet
2. Wall mount
3. Rack mount
The MDS FIVE Series SDIDU
TM
should be:
• Located where you can easily connect to a power supply and any other equipment used in
your network, such as a router or PC.
• In a relatively clean, dust-free environment that allows easy access to the rear grounding post
as well as the front panel controls and indicators. Air must be able to pass freely over the
chassis.
• Accessible for service and troubleshooting.
• Protected from rain and extremes of temperature (it is designed for indoor use).
3.7.1.1 Installing on a Table Top or Cabinet
The MDS FIVE Series SDIDUTM can be placed on a tabletop or cabinet shelf. In order to prevent
possible disruption, it is recommended to use a strap to secure the SDIDU
TM
.
3.7.1.2 Installing on a Wall
An installation option for the SDIDUTM is mounting the unit to a wall. If the wall mount option is
being considered, plan to position the MDS FIVE Series SDIDU
the connectors on the front panel, and the rear grounding post to be visible at all times and easily
accessible. Also, including plastic clamps to support and arrange the ODU/ SDIDU
TM
at a height that allows LEDs,
TM
Interconnect Cable should also be considered.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 56

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-22
3.7.1.3 Installing in a Rack
To rack-mount the SDIDUTM, use the supplied mounting brackets to secure the chassis to a 19
inch rack cabinet. As shown in
enclosure. An optional 21 inch rack mount kit is also available (consult factory for details).
Figure 3-5. MDS FIVE Series SDIDUTM Dimensions
Figure 3-5, the brackets can be attached to the front sides of the
3.7.2 Installing the MDS FIVE Series ODU
The MDS FIVE Series ODU is intended for mounting on either a pole or antenna mast.
Each site must be assessed for the mounting method, location, and height. After defining the
mounting location and height for the MDS FIVE Series ODU, re-confirm the line of sight.
When operating a 1+1 configured SDIDU™, i.e. an SDIDU™ with two power supplies and two
modem modules installed, in 1+0 mode, the ODU must be connected to the modem in the bottom
slot. If the ODU is connected to the modem in the top slot, the SDIDU™ will not communicate
with the ODU, and a link cannot be established.
3.7.2.1 Installing the Mounting Poles
First install the mounting poles, on which you will mount the MDS FIVE Series ODU. It is
important to note the direction in which the ODU will point when installing the mounting pole.
The mounting pole must be mounted in a vertical position. Failure to do so may result in
improper alignment of the ODU. Vertical tilt of the ODU is accomplished from the tilt mounting
bracket.
The mounting pole must be grounded.
Now that you have installed the mounting pole, you are ready to install the MDS FIVE Series
ODU onto the mounting poles. Reference
Figure 3-6 through Figure 3-9.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 57

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-23
Figure 3-6. Mounting Parts for the MDS FIVE Series ODU
1. Remove the pole mount portion of the tilt bracket from the ODU by loosening the middle
bolts and removing the top and bottom bolts on each side.
2. Mount the tilt bracket to the mounting pole using the U-Bolts and nuts. Insert the U-bolts
around the pole and through the holes in the tilt bracket. Install a washer and nut to each
side of the threaded U-bolt and hand tighten. Repeat this step for the second U-bolt.
3. Place the MDS FIVE Series ODU on the mating half of the tilt bracket connected by the
two center bolts.
4. Add the remaining four bolts to the tilt bracket but do not tighten until the antenna
alignment is complete (only applies for internal antenna ODUs).
5. Manually point the ODU in the direction of the link partner ODU.
Figure 3-7. MDS FIVE Series ODU Rear View
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 58

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-24
Figure 3-8. Tilt Bracket
Figure 3-9. MDS FIVE Series ODU with Mounted Tilt Bracket
3.7.3 Routing the ODU/ SDIDU
TM
Interconnect Cable
1. Select where the cable will enter the building from outside.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 59

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-25
2. Determine the length of cable required. Allow three extra feet on each end to allow for strain
relief, as well as any bends and turns.
3. Route the cable.
The SDIDU
TM
is equipped with TNC female connector on the front of the chassis. Depending on
the ODU type, it will be equipped with either a N-type or TNC female connector at its
interconnecting port. A length of coaxial cable (such as Times Microwave Systems LMR-400,
LMR-300 or LMR-200) fitted with the appropriate N-type or TNC male connectors is required to
connect the ODU to the SDIDU
TM
. This cable assembly may be supplied in fixed lengths with the
digital radio. Bulk coaxial cable of equivalent specification may also be used, with terminating
connectors applied during cable installation.
TM
Based on an evaluation of the cable routing path, pull the ODU/SDIDU
one unit to the other, utilizing cable trays, ducts, or conduit as required. Take care that the ODU/
SDIDU
protect the TNC connectors from stress, damage and contamination during installation (do not
pull the cable by the connectors). If multiple ODU/ SDIDU
TM
Interconnect cable is not kinked or damaged in any way during installation. Be sure to
TM
Interconnect cables are to be
installed along the same route, the cables should all be pulled at one time. Be sure the installed
cable does not have any bends that exceed the specified cable bend radius. The ODU/ SDIDU
Interconnect cable from
TM
Interconnect cable should be adequately supported on horizontal runs and should be restraine d
by hangers or ties on vertical runs to reduce stress on the cable. Outside the building, support
and restrain the cable as required by routing and environmental conditions (wind, ice).
TM
The MDS FIVE Series ODU/SDIDU
and interconnection must be properly grounded in order to
protect it and the structure it is installed on from lightning damage. This requires that the ODU,
any mounting pole or mast and any exposed interconnect cable be grounded on the outside of
the structure. The SDIDU
TM
must be grounded to a rack or structure ground that also has direct
path to earth ground.
The ODU must be directly connected to a ground rod or equivalent earth ground. The ODU/
SDIDU
TM
interconnect cable should also be grounded at the ODU, where the cable enters the
structure and at intermediate points if the exposed cable run is long (typically at intervals of 100
ft), with the cable manufacturer’s grounding kits. Lightning protection devices used with the
interconnect cable must be appropriate for the transmission of the interconnect signals (DC to
350 MHz).
Provide a sufficient but not excessive length of cable at each end to allow easy connection to the
ODU and SDIDU
outdoors, should be avoided to minimize signal attenuation and provide a more robust and
reliable installation. If installing using bulk coaxial cable, terminate the ODU/ SDIDU
Interconnect cable at each end with a TNC male connector on the SDIDU
TM
without stress or tension on the cable. Excessive cable length, especially
TM
side and either a N-
TM
type or TNC male connector on the ODU side that is appropriate for the cable type. Use of
connectors, tools and termination procedures specified by the cable manufacturer is
recommended.
Once the cable has been installed but before connection has been made to either unit, a simple
DC continuity test should be made to verify the integrity of the installed cable. A DC continuity
tester or digital multimeter may be used to verify a lack of DC continuity between the cable center
conductor and outer conductor, with the opposite end of the cable unconnected. With a
temporary test lead or shorting adapter connected to one end of the cable, DC continuity should
be verified between the center and outer conductors at the opposite end.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 60

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-26
3.8 Quick Start Guide
3.8.1 Materials Required
1. Power supply (-48 V DC @ 2 Amps) OR optional AC/DC power supply and power cable
(A Phoenix Contact P/N 17 86 83 1 connector is provided)
2. Digital voltmeter with test leads and BNC connector (optional, for ODU alignment).
3. SDIDU
4. Computer with networking capability, consisting of either:
- Laptop computer and Ethernet card with any necessary adapters and a Cat-5 Ethernet
regular or crossover cable
or
- Networked computer and an additiona l Ethernet cable providing access to the network.
With the following system requirements:
Minimum:
• Pentium II 400MHz
• 128MB RAM
• 30MB available hard drive space
• Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, or Windows XP
• Internet Explorer 5.5 (available at
• Sun Java JVM 1.5.0 or above (available at
Recommended:
• Pentium III 500MHz
• 256 RAM
• 30MB available hard drive space
• Windows 98SE, Windows NT, Windows 2000, or Windows XP
• Internet Explorer 5.5 (available at
• Sun Java JVM 1.5.0 or above (available at
TM
Serial Cable (Optional)
Firefox 1.0.6 (available at
Firefox 1.0.6 (available at
http://www.microsoft.com) and above or Mozilla
http://www.firefox.com) with default settings.
http://www.java.com)
http://www.microsoft.com) and above or Mozilla
http://www.firefox.com) with default settings.
http://www.java.com)
5. Site engineering folder with site drawings, or equivalent SDIDU
information
6. 1/8” slotted screwdriver
TM
configuration
3.8.2 Grounding the ODU
1. Place the grounding rod so as to allow for the shortest possible path from the grounding
cable to the ODU.
2. Drive the grounding rod into the ground at least eight inches from the ground surface.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 61

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-27
3. Attach a grounding clamp to the grounding rod. You will use this clamp to attach
grounding wires for both the ODU and SDIDU
TM
, reference Figure 3-10.
Figure 3-10 Ground Connections to ODU
4. Connect a ground lug to one end of the grounding wire.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 62

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-28
5. Remove one of the lower mounting screws of the mounting pole. Insert a screw through
the grounding lug terminal and re-install it to the mounting pole.
6. Attach the grounding wire to the clamp on the grounding rod. If necessary, use wire
staples to secure the grounding wire to the outside wall.
3.8.3 Grounding the SDIDU
TM
1. The SDIDU™ should be able to be connected to a system or building electrical ground
point (rack ground or power third-wire ground) with a cable of 36” or less.
2. Connect the grounding wire to either grounding point on the front panel. Use 6-32x5/16
maximum length screws (not provided) to fasten the lug of the grounding cable.
3. Connect the other end of the ground to the local source of ground in an appropriate
manner.
3.8.4 Connecting the SDIDU
TM
to the PC and Power Source
1. Using the supplied power cable connector, pin 2 (labeled -V) should be connected to the
power supply terminal supplying -48 V dc, while pin 1 (labeled RET) should be connected
to the power supply return. Refer to
inappropriate ground reference may cause damage to the SDIDU
Figure 3-11. Use of a power supply with an
TM
and/or the supply.
2 1
Figure 3-11. SDIDUTM DC Power Cable Connector
2. Connect the SDIDUTM power cable to the -48 V dc power supply, and place the voltmeter
probes on the unconnected SDIDU
TM
end of the power cable, with the positive voltmeter
probe on pin 2 (-V) of the cable connector and the negative probe on pin 1(RET). The
connector terminal screw heads may be used as convenient monitor points. Refer to
Figure 3-11.
3. Turn on the –48 V dc supply. Verify that the digital voltmeter reads between -44 V dc and
-52 V dc when monitoring the cable points specified above. Adjust the power supply
output voltage and/or change the connections at the power supply to achieve this reading.
4. Turn the -48 V dc supply off.
5. Plug the SDIDU
TM
power cable into the SDIDUTM front panel DC Power connector (DC
Input). Place the voltmeter probes on the cable connector terminal screw heads as per
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 63

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-29
step 2 above. Refer to
Figure 3-11. Note that the MDS FIVE Series SDIDUTM does not
have a power on/off switch. When DC power is connected, the digital radio powers up
and is operational. There can be up to 320 mW of RF power present at the antenna port.
The antenna should be directed safely when power is applied.
6. Turn on the -48 V dc power supply, and verify that the reading on the digital voltmeter is
as specified in step 3 above.
TM
7. Connect the SDIDU
the SDIDU
cable to the NMS 1 or 2 connector on the SDIDU
the SDIDU
TM
to a computer network, using a Cat-5 Ethernet cable. Connect the Ethernet
TM
front panel connections.
to the laptop computer, using a Cat-5 Ethernet cable or connect
TM
front panel. Refer to Figure 3-12 for
Figure 3-12. MDS FIVE Series-SB, 1+1 Protection: SDIDU
3.8.5 SDIDU
Although basic configuration of the MDS FIVE Series SDIDU
the ODU, it is recommended that the ODU and SDIDU
SDIDU
TM
TM
Configuration
TM
. A connection to the ODU must be established prior to running the Link Configuration
TM
Front Panel Connections
TM
does not require a connection to
are connected prior to configuring the
process (section 5.2) in order to configure ODU related parameters.
3.8.5.1 Setting the SDIDU™ IP Address
1. The PC’s network configuration must be set with the parameters provided at the end of
this guide.
2. The IDU should be accessible from your PC at the default IP address provided at the end
of this guide. A network ‘ping’ can be done to verify connectivity to the IDU.
3. Start web browser and use the SDIDU
TM
default IP address as the url.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 64

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-30
4. Log in at the login prompt. The username and password are provided at the end of this
guide.
5. The GUI includes a navigation menu in the left frame. If this navigation menu is not
visible, make sure the Java environment is properly installed and active. In the navigation
menu, select Administration, then Network Configuration, and then General. The IP
address, IP Netmask, and IP Gateway are shown.
6. Enter the new IP address, IP Netmask, and IP Gateway. The gateway must be in the
same subnet as the IP address for proper operation. Click “Update” to change the
values.
7. To verify the new IP address, change the PC's network configuration to be on the same
subnet as the new IP address set in the unit and a network 'ping' may be pe rformed to the
new address.
8. To continue using the GUI, point the web browser to the new IP address.
3.8.5.2 Link Configuration
1. Start the SDIDUTM GUI.
2. Use the frame on the left side of the window to navigate to “Link Configuration”, then
“Radio Link.”
3. Select the subcategory “Link Configuration.”
4. Select the operating mode. If the SDIDU
one ODU, select standard. If the SDIDU
TM
has one modem installed and is connected to
TM
has two modems installed and is connected to
two ODUs, select 1+1 diversity or 1+1 non-diversity for a protected link or east-west for a
2+0 ring configuration.
5. Follow the wizard located here to enter the rest of the required settings.
3.8.5.3 Setting SDIDUTM Site Attributes
1. Start the SDIDUTM GUI.
2. In the navig ation menu, select Administration, then Device Information, and then Device
Names.
3. Enter the O wner, Contact, Description, and Location. These values are not required for
operation, but will help keep a system organized.
3.8.5.4 Power on Reset to Factory Defaults
The SDIDU™ may be reset to factory defaults during power up. A power on reset affects the IP
address and the user logins/passwords. To perform a power on reset:
1. Power on the SDIDU™
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 65

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-31
2. During bootup, the SDIDU™ will flash the controller-card LED alternating red/green for
five seconds.
3. Make sure the call button is not active at the start of this five second period.
4. While the LED is flashing, press the call button and release it one second prior to the LED
changing to static green.
3.8.5.5 CLI Access via NMS Ethernet
The CLI may be accessed via NMS Ethernet after connecting and configuring the PC as
described in the previous section. Then using a Telnet client, telnet to the SDIDU
TM
IP address.
You will be prompted for a username and password. Use the username and password supplied
at the end of this guide.
3.8.5.6 CLI Access via Serial Port
The CLI for configuring/monitoring the SDIDUTM may be accessed via the front-panel serial port.
Table 3-3 shows the pinout for constructing a DB-9 to HD-15 cable.
Table 3-3: Serial Cable Pinout
DB-9 Pin HDB-15 Pin
2 2
3 3
5 5
The serial port parameters are show in Table 3-4.
Table 3-4: Serial Port Parameters
Parameter Value
Speed 38400
Bits 8
Stop-Bits 1
Parity None
Flow-Control None
After powering-on the SDIDUTM, the CLI may be accessed by connecting the serial cable
between the PC and the SDIDU
TM
, launching and configuring a terminal program (e.g.
Hyperterm) and pressing the enter key. You will be prompted for a username and password,
which are supplied at the end of this guide.
3.8.6 ODU Antenna Alignment
To use the built-in tuning of the ODU antenna, a complete link is required, with both ends of the
link roughly pointed at each other, and transmitting.
Once the links are roughly pointed, connect the voltmeter to the RSSI (Receive Signal Strength
Indication) BNC connector seen on the ODU. This mode outputs 0 to +3 Volts. Adjust the
antenna for maximum voltage. The RSSI voltage is linearly calibrated from 2.5 Volts for maximum
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 66

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-32
RSL (received signal level) at –20 dBm to 0Volts for minimum RSL at -90 dBm. This mapping
characteristic is plotted below in
Figure 3-13.
3
2
1
RSSI Output (V)
0
-100 -80 -60 -40 -20 0
RSSI - Mapped Voltage Outpu t
Received Signal Level (dBm)
Figure 3-13. ODU RSSI Output vs. Received Signal.
3.8.7 Quick Start Settings
PC Network Configuration
The Web GUI may be accessed via NMS by connecting a CAT5 patch cable between
the SDIDUTM front-panel NMS port and a PC. The PCs network interface must be
configured to an open IP address within the same subnet. For the default SDIDUTM
configuration, the IP address of the PC needs to be 192.168.0.x, where x (between 2
and 253) provides an available IP address. DHCP may also be used to set the PC IP
address if a DHCP server is configured on the same subnet.
SDIDUTM Default IP Address
Parameter Value
IP Address 192.168.0.1
Netmask 255.255.255.0
Gateway 192.168.0.254
After configuring the PCs network interface, a web browser may be launched and the
following URL entered to access the Web GUI:
http://192.168.0.1/
Username and Password
A dialog box will show requesting a username and password:
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 67

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-33
• User: administrator
• Pass: d1scovery
3.9 SDIDU™ Service
At times, it may be necessary to service the SDIDU™. This may include installing, removing, or
replacing an SDIDU™ module. There may be up to 8 modules installed in a single SDIDU™
chassis.
procedure for removing and installing a module is common to all the modules, with slight
variations for the Power Supply Module, Controller Module, and Mini IO Module. These basic
procedures are described below. Variations are described in sub-items beneath each step.
Figure 3-14 shows the front panel of the SDIDU™ with each module labeled. The basic
Figure 3-14 SDIDU™ Modules
3.9.1 Removing a Module
1. Modules are static sensitive and should only be handled in an ESD-safe environment.
When packaging modules for shipment or storage, place in an ESD bag.
2. Remove front panel connections to the module.
3. Remove the two thumbscrews on either side of the module. Figure 3-15 shows the
locations of these thumb screws.
4. The thumbscrew for the Standard IO Module is located on the right side of the Mini IO
Module slot.
5. If a Mini IO module is installed and the Standard IO Module is to be removed, both
modules will be removed as one unit.
When removing only the Mini IO card, remove the corner screw indicated in Figure 3-15
6.
and one thumb screw.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 68

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-34
Figure 3-15 Thumbscrew and Corner Screw Locations
7. Thread thumbscrew(s) into hole(s) shown in Figure 3-16. Remove the module by
grasping the thumbscrew(s) and pulling module straight out of the SDIDU™. Both
thumbscrews should be used for all modules except the Power Supply and the Mini IO
Modules.
The Power Supply and Mini IO Modules have only one threaded hole each.
8.
When removing the Standard IO Module, the ground lug indicated in Figure 3-16 is used
9.
as the second threaded hole. If the SDIDU™ is to remain powered on and the ground lug
is being used to ground the unit, first move the ground connection to the ground lug
located on the Controller Module.
The SDIDU™ retains its current configuration when a module is removed, unless that
module is the Controller Module. In which case, the IP addresses will need to be
reprogrammed.
Figure 3-16 Threaded Hole Locations
3.9.2 Installing a Module
1. Modules are static sensitive and should only be handled in an ESD-safe environment.
When packaging modules for shipment or storage, place in an ESD bag.
2. Line up the module board with the guides in the chassis and slide the module into the
SDIDU™.
with the face of the SDIDU™, connectors on the back of the module will engage with the
SDIDU™ backplane. It is possible to encounter interference from adjacent module front
panels. If this occurs, loosen the thumbscrews holding the neighboring panels and shift
them as necessary to ensure fit.
Figure 3-17 shows a photo of the guides. As the module face plate comes flush
a. The Mini IO Module only has one guide on the right side. Take care to insert the Mini
IO module carefully and correctly engage the rear connector with its mate on the
Standard IO Module.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 69

User Reference and Installation Guide 3-35
Guide
Figure 3-17 Guides
3. Install thumbscrews on either side of the module as shown in Figure 3-15.
a. The Mini IO card has a corner screw which should be installed. This corner screw is
shown in
4. Make front panel connections to the module and power on the SDIDU™ if necessary.
5. Verify proper operation of the unit.
a. If the Controller Module has been changed, reprogram the IP addresses.
Figure 3-15.
3.10 Documenting MDS FIVE Series Configuration
Use the MDS FIVE Series configuration form provided at the end of this section, or a similar form,
to document the results of the SDIDU
form would be stored with the SDIDU
TM
configuration procedure. Optimally, this complete site
TM
for future reference.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 70

Link ID Digital Radio Configuration Form
Radio Type(A/B) A = Low band, Horizontal polarization, odd serial number
Radio ID # Radio S/N
Site Name
B= High band & Vertical polarization, even serial number
Network Administration
Adresses Comissioning
Near IP Far IP Rain Model
Routing Frequency TX R X
Net Mask IP EMS 1 Grade of Service
NTP IP EMS 2 Rain Region
Gateway IP EMS 3
IP EMS 4 Link Distance GPS Location
SNMP Community Names Distance (meters) Near Latitude deg min sec
Trap Super User OR Near Longitude deg min sec
Read/Write Read Far Latitude deg min sec
Radio Type(A/B) A = Low band, Horizontal polarization, odd serial number
Radio ID # Radio S/N
Site Name
B= High band & Vertical polarization, even serial number
1
Link Administration
Far Longitude deg min sec
2
Network Administration Link Administration
Adresses Comissioning
Near IP Far IP Rain Model
Routing Frequency TX R X
Net Mask IP EMS 1 Grade of Service
NTP IP EMS 2 Rain Region
Gateway IP EMS 3
IP EMS 4 Link Distance GPS Location
SNMP Community Names Distance (meters) Near Latitude deg min sec
Trap Super User OR Near Longitude deg min sec
Read/Write Read Far Latitude deg min sec
Far Longitude deg min sec
Page 71

4 Summary Specification
Parameter 5.8 GHz 5.3 GHz
System
Capacity 100 Mbps Ethernet
1-16 T1/E1
Various combinations of above
Output Power – Average*
(at antenna port)
Output Power – Peak*
(at antenna port)
Input Sensitivity -84 dBm (or higher, based on
Maximum Input Power -20 dBm -20 dBm
Modulation QPSK to 64-QAM QPSK to 64-QAM
Channelization 12.5, 16.7, 25, 30 MHz 13.3, 20, 30 MHz
Radio Interfaces
External Antenna N Type Female N Type Female
SDIDUTM /ODU Link
RSSI BNC Female BNC Female
Data Interfaces
+5 to 23 dBm -18 to +5 dBm (Ext. Antenna)
30 dBm 12 dBm
selected mode)
TNC Female TNC Female
100 Mbps Ethernet
1-16 T1/E1
Various combinations of above
-6 to +5 (Int. Antenna)
-84 dBm (or higher, based on
selected mode)
Payload
Ethernet
2 T1/E1
14 T1/E1
SNMP
Control
Network Management SNMP, web/http browser SNMP, web/http browser
NMS Connector 10Base-T/100Base-Tx 10Base-T/100Base-Tx
Voice Orderwire RJ-45 for PTT handset RJ-45 for PTT handset
Auxiliary Data (64 kbps) RS422 via RJ-45 RS422 via RJ-45
Encryption Proprietary, AES (optional) Proprietary, AES (optional)
100Base-Tx RJ-45
100 Ω / 120 Ω Balanced
RJ-48C Female (2)
100 Ω / 120 Ω Balanced
Molex High-Density 60-pin
10Base-T/100Base-Tx RJ-45
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc.
100Base-Tx RJ-45
100 Ω / 120 Ω Balanced
RJ-48C Female (2)
100 Ω / 120 Ω Balanced
Molex High-Density 60-pin
10Base-T/100Base-Tx RJ-
Female
All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
45 Female
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 72

User Reference and Installation Guide 4-2
Parameter 5.8 GHz 5.3 GHz
Alarm Port 2 Form C (SPDT), 2 TTL
Output, 4 TTL Input, DB-15HD
Power/Environment
DC Power -48 Volts ±10%, <70 W -48 Volts ±10%, <70 W
SDIDUTM Operational
Temperature
ODU Operational
Temperature
SDIDUTM Humidity
ODU Humidity Up to 100% at 45º C Up to 100% at 45º C
Altitude 15,000 feet/4572 meters,
Physical Dimensions
SDIDUTM Size (WxHxD)
0 to 95%, non-condensing 0 to 95%, non-condensing
17.2 x 1.75 x 14.5 inches
SDIDUTM Weight
SDIDUTM
EIA Rack Mount 19 inch/48.2 cm, 1 rack unit 19 inch/48.2 cm, 1 rack unit
-5º to 55º C -5º to 55º C
-30º to 55º C -30º to 55º C
maximum
(43.7 x 4.5 x 36.0 cm)
7 lbs (3.12 Kg) 7 lbs (3.12 Kg)
2 Form C (SPDT), 2 TTL
Output, 4 TTL Input, DB-15HD
15,000 feet/4572 meters,
maximum
17.2 x 1.75 x 14.5 inches
(43.7 x 4.5 x 36.0 cm)
ODU Size (W x H x D) 14.6 x 15.4 x 2.6 inches 14.6 x 15.4 x 2.6 inches
ODU Weight 15 lbs (6.8 Kgs) 15 lbs (6.8 Kg)
ODU
Mounting Custom Bracket Custom Bracket
* For definitions of peak and average power, see Section3.6.6
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 73

5 Front Panel Connectors
5.1 DC Input (Power) Connector
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
Two-pin male
12
1 POWER Power supply return
2 POWER -48 Vdc, nominal
5.2 Ethernet 100BaseTX Payload Connector 1-2
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
RJ-45 Female
12 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 INPUT RX+
2 INPUT RX3 OUTPUT TX+
4 N/A N/A
5 N/A N/A
6 OUTPUT TX 7 N/A N/A
8 N/A N/A
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc.
All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 74

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-2
5.3 SONET Payload Connector
Consult factor for Mini-IO Optical Module for availability.
SC Duplex Female Fiber
INOUT
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
OUT OUTPUT SONET OC-3 payload output (optical)
IN INPUT SONET OC-3 payload input (optical)
5.4 STM-1 Payload Connector
Consult factor for Mini-IO Optical Module for availability.
BNC Duplex
RXTX
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
TX OUTPUT SDH STM-1 payload output (electrical)
RX INPUT SDH STM-1 payload input (electrical)
5.5 DS-3/E-3/STS-1 Payload Connector
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
BNC Duplex
RXTX
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
TX OUTPUT DS-3/E-3/STS-1 payload output
RX INPUT DS-3/E-3/STS-1 payload input
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 75

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-3
5.6 NMS 10/100BaseTX Connector 1-2
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
RJ-45 Female
1 OUTPUT TX+
2 OUTPUT TX-
12 3 4 5 6 7 8
3 INPUT RX+
4 N/A N/A
5 N/A N/A
6 INPUT RX 7 N/A N/A
8 N/A N/A
5.7 Alarm/Serial Port Connector
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
DB-15HD Female
1 OUTPUT TTL Alarm Output 3
1
2
INPUT/
RS-232 RX/TX
Output
1
3
OUTPUT/
RS-232 TX/RX
Input
4 OUTPUT TTL Alarm Output 4
5 N/A GROUND
6
7
8
2
2
2
N/A Alarm 1 Form C Contact Normally Open
N/A Alarm 1 Form C Contact Normally Closed
N/A Alarm 2 Form C Contact Common
1
Pins 2 and 3 are hardware jumper configurable for DCE or DTE operation.
2
Form C Contacts are hardware jumper configurable to emulate TTL outputs.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 76

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-4
9 INPUT TTL Alarm Input 1
10 INPUT TTL Alarm Input 3
11
12
13
14 INPUT TTL Alarm Input 2
15 Input TTL Alarm Input 4
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
2
2
2
5.8 ODU Connector
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
TNC coaxial female
Center I/O 350 MHz TX IF / 140 MHz RX IF / -48 VDC
N/A Alarm 1 Form C Contact Common
N/A Alarm 2 Form C Contact Normally Open
N/A Alarm 2 Form C Contact Normally Closed
Shield N/A Shield / Chassis GND
5.9 T1/E1 - Channels 1-2 Connector
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
RJ-45 Female
100 Ω / 120 Ω Balanced
12 3 4 5 6 7 8
6 N/A GND
7 N/A N/A
1 INPUT RX+
2 INPUT RX-
3 N/A GND
4 OUTPUT TX+
5 OUTPUT TX-
8 N/A N/A
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 77

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-5
5.10 T1/E1 - Channels 3-16 Connector
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
60-pin Molex
100 Ω / 120 Ω Balanced
5 OUTPUT T1 Chan nel 9 Transmit Tip
6 OUTPUT T1 Chan nel 10 Transmit Tip
7 OUTPUT T1 Chan nel 11 Transmit Tip
8 OUTPUT T1 Chan nel 12 Transmit Tip
9 OUTPUT T1 Chan nel 5 Transmit Tip
10 OUTPUT T1 Channel 6 Transmit Tip
11 OUTPUT T1 Channel 7 Transmit Tip
12 OUTPUT T1 Channel 8 Transmit Tip
1 OUTPUT T1 Channel 13 Transmit Tip
2 OUTPUT T1 Channel 14 Transmit Tip
3 OUTPUT T1 Channel 15 Transmit Tip
4 OUTPUT T1 Channel 16 Transmit Tip
13 OUTPUT T1 Channel 3 Transmit Tip
14 OUTPUT T1 Channel 4 Transmit Tip
15 NC NC
16 NC NC
17 OUTPUT T1 Channel 4 Transmit Ring
18 OUTPUT T1 Channel 3 Transmit Ring
19 OUTPUT T1 Channel 8 Transmit Ring
20 OUTPUT T1 Channel 7 Transmit Ring
21 OUTPUT T1 Channel 6 Transmit Ring
22 OUTPUT T1 Channel 5 Transmit Ring
23 OUTPUT T1 Channel 12 Transmit Ring
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 78

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-6
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
24 OUTPUT T1 Channel 11 Transmit Ring
25 OUTPUT T1 Channel 10 Transmit Ring
26 OUTPUT T1 Channel 9 Transmit Ring
27 OUTPUT T1 Channel 16 Transmit Ring
28 OUTPUT T1 Channel 15 Transmit Ring
29 OUTPUT T1 Channel 14 Transmit Ring
30 OUTPUT T1 Channel 13 Transmit Ring
31 INPUT T1 Channel 16 Receive Tip
32 INPUT T1 Channel 15 Receive Tip
33 INPUT T1 Channel 9 Receive Tip
34 INPUT T1 Channel 14 Receive Tip
35 INPUT T1 Channel 10 Receive Tip
36 INPUT T1 Channel 13 Receive Tip
37 INPUT T1 Channel 11 Receive Tip
38 INPUT T1 Channel 4 Receive Tip
39 INPUT T1 Channel 12 Receive Tip
40 INPUT T1 Channel 3 Receive Tip
41 INPUT T1 Channel 5 Receive Tip
42 INPUT T1 Channel 8 Receive Tip
43 INPUT T1 Channel 6 Receive Tip
44 INPUT T1 Channel 7 Receive Tip
45 NC NC
46 NC NC
47 INPUT T1 Channel 7 Receive Ring
48 INPUT T1 Channel 6 Receive Ring
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 79

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-7
49 INPUT T1 Channel 8 Receive Ring
50 INPUT T1 Channel 5 Receive Ring
51 INPUT T1 Channel 3 Receive Ring
52 INPUT T1 Channel 12 Receive Ring
53 INPUT T1 Channel 4 Receive Ring
54 INPUT T1 Channel 11 Receive Ring
55 INPUT T1 Channel 13 Receive Ring
56 INPUT T1 Channel 10 Receive Ring
57 INPUT T1 Channel 14 Receive Ring
58 INPUT T1 Channel 9 Receive Ring
59 INPUT T1 Channel 15 Receive Ring
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
60 INPUT T1 Channel 16 Receive Ring
5.11 USB
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
USB Type A
1 OUTPUT +5V
2 I/O -Data
3 I/O +Data
4 N/A GND
5.12 Voice Order Wire
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
RJ-45 Female 1 N/A NC
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 80

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-8
6 INPUT TI 7 N/A GND
8 N/A NC
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
2 INPUT PTT
3 N/A GND
4 OUTPUT PO-
5 OUTPUT PO+
5.13 Data Order Wire
5.13.1 RS422
RJ-45 Female
12 3 4 5 6 7 8
6 OUTPUT TX Data +
7 INPUT RX Clock 8 INPUT RX Clock +
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
1 OUTPUT TX Clock -
2 OUTPUT TX Clock +
3 OUTPUT TX Data -
4 INPUT RX Data -
5 INPUT RX Data +
5.13.2 RS-232
RJ-45 Female 1 N/A NC
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 81

User Reference and Installation Guide 5-9
PIN TYPE SIGNAL
2 N/A NC
3 N/A Signal GND
4 N/A NC
5 INPUT RX Data +
6 OUTPUT TX Data +
7 N/A NC
8 N/A NC
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 82

6 Appendix
6.1 Alarm Descriptions
Alarm
Modem Fault
Lower
Modem Comm
Failiure Lower
Modem Card
Removed Lower
Modem Card
Installed Lower
Affected
Component
Modem The specified Modem card
has indicated a fault. Fault
detection is via reading
Modem Hardware Status
from MODEM during start-up
and polling GPIO for MODEM
fault indication. Polling
interval 5 sec.
Modem The Controller Card is unable
to communicate with the
specified Modem card.
Modem
Modem The specified Modem card
The specified Modem card has
been removed from the IDU
(only if the specified Modem
card has been enabled for
use). Fault detection via carddetect logic.
has been installed into the
IDU (only if the specified
Modem card is not enabled
for use). Fault detection via
card-detect logic. Alarm is
raised then lowered.
Description
LED to
RED
N/A 11 Critical
Modem
Lower
N/A 13 Major
Modem
Lower
Alarm
Code
12 Critical
14 Info
Severity
Modem Unlock
Lower
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc.
Modem The demodulation functional
N/A N/A Critical
components of the modem
have lost lock to the incoming
signal. The data received
through the RF link is not
valid. Fault detection via
modem status polling. Polling
interval: 1 sec.
All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 83

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-2
Alarm
Affected
Component
Description
RSL Low Lower Modem RSSI is approaching the
minimum operational level of
the link as set during
configuration. Fault detection
via modem status polling,
comparing RSSI value to
threshold value in
configuration table. Polling
interval 5 sec.
Synthesizer
Unlock Lower
Modem Modem synthesizer has
unlocked. Fault detection via
modem status polling. Polling
is done in conjunction with
Modem Unlock polling.
SNR Low Lower Modem The signal-to-noise ratio is
below the minimum
operational level of the link as
set during configuration. Fault
detection via modem status
polling, comparing Eb/N0
value to threshold value in
configuration table. Polling
interval 5 sec.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A N/A Major
N/A N/A Critical
N/A N/A Major
Modem Fault
Upper
Modem The specified Modem card
has indicated a fault. Fault
N/A 16 Critical
detection is via reading
Modem Hardware Status
from MODEM during start-up
and polling GPIO for MODEM
fault indication. Polling
interval 5 sec.
Modem Comm
Failiure Upper
Modem The Controller Card is unable
to communicate with the
Modem
Lower
17 Critical
specified Modem card.
Modem Card
Removed Upper
Modem The specified Modem card
has been removed from the
N/A 18 Major
IDU (only if the specified
Modem card has been
enabled for use). Fault
detection via card-detect
logic.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 84

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-3
Alarm
Modem Card
Installed Upper
Affected
Component
Description
Modem The specified Modem card
has been installed into the
IDU (only if the specified
Modem card is not enabled
for use). Fault detection via
card-detect logic. Alarm is
raised then lowered.
Modem Unlock
Upper
Modem The demodulation functional
components of the modem
have lost lock to the incoming
signal. The data received
through the RF link is not
valid. Fault detection via
modem status polling. Polling
interval 1 sec.
RSL Low Upper Modem RSSI is approaching the
minimum operational level of
the link as set during
configuration. Fault detection
via modem status polling,
comparing RSSI value to
threshold value in
configuration table. Polling
interval 5 sec.
LED to
RED
Modem
Alarm
Code
Severity
19 Info
Upper
N/A N/A Critical
N/A N/A Major
SNR Low Upper Modem The signal-to-noise ratio is
N/A N/A Major
below the minimum
operational level of the link as
set during configuration. Fault
detection via modem status
polling, comparing Eb/N0
value to threshold value in
configuration table. Polling
interval 5 sec.
Synthesizer
Unlock Upper
Modem Modem synthesizer has
unlocked. Fault detection via
N/A N/A Critical
modem status polling. Polling
is done in conjunction with
Modem Unlock polling.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 85

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-4
Alarm
Affected
Component
Description
Fan Failure Controller The Fan rotational speed is
too low. (Controller card LED
flashed red rather than
orange). Fault detection via
polling fan controller status.
Polling interval 10 sec.
Controller Card
Fault
Controller The CPU has detected a fault
in the controller card.
(Controller card LED flashes
red rather than orange). Fault
detection via software.
Low Battery
Voltage
Controller The CPU has detected a low-
battery voltage condition.
(Controller card LED flashes
red rather than orange). Fault
detection via software polling
RTC via controller FPGA.
Power Supply
Fault Lower
Power Supply The Power Supply card has
indicated a fault. Fault
detection via polling GPIO.
Polling interval 5 sec.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
Controller 21 Major
Controller 22 Critical
Controller 23 Info
N/A 31 Critical
Power Supply
Card Removed
Lower
Power Supply The specified Power Supply
card has been removed from
the IDU. Fault detection via
N/A 32 Major
card-detect logic.
Power Supply
Fault Upper
Power Supply The Power Supply card has
indicated a fault. Fault
N/A 36 Critical
detection via polling GPIO.
Polling interval 5 sec.
Power Supply
Card Removed
Upper
Power Supply The specified Power Supply
card has been removed from
the IDU. Fault detection via
N/A 37 Major
card-detect logic.
Standard I/O
Card Removed
StdIO The Standard I/O card has
been removed from the IDU.
N/A 41 Critical
Fault detect via card-detect
logic.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 86

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-5
Alarm
Ethernet
Payload
Disconnect
Framer
Initialization
Timeout
Mini I/O Card
Removed
Affected
Component
Description
StdIO There is no cable detected at
either Ethernet payload on
Standard I/O card (only if
Ethernet mode enabled).
Fault detection via polling of
Ethernet PHY. Polling interval
5 sec.
StdIO There is an Initalization wait
for Framer to turn ON the
Framer Receiver side after
turning ON the Modem/ODU.
Fault detection via polling.
Poll only after timeout to
detect.
MiniIO The Mini I/O card has been
removed from the IDU (only if
Mini I/O card has been
enabled for use). Fault
detection via card-detect
logic.
LED to
RED
Standard
I/O
Standard
I/O
Standard
I/O
Alarm
Code
Severity
42 Critical
43 Critical
46 Critical
Mini I/O Card
Installed
Optional I/O
Card Removed
Optional I/O
Card Installed
MiniIO The Mini I/O card has been
installed into the IDU (only if
Mini I/O card is noted
enabled for use). Fault
detection via card-detect
logic. Alarm is raised then
lowered.
OptIO The Optional I/O card has
been removed from the IDU
(only if the Optional I/O card
has been enabled for use).
Fault detection via carddetect logic.
OptIO The Optional I/O card has
been installed into the IDU
(only if the Optional I/O card
is not enabled for use). Fault
detection via card-detect
logic. Alarm is cleared after 5
minutes.
Standard
47 Info
I/O
N/A 26 Critical
Optional
27 Info
I/O
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 87

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-6
Alarm
T1/E1 Channel
Alarm Ch x
T1/E1 Test
Mode
Affected
Component
StdIO (1-16)
There is either no cable
Description
detected at the specified
OptIO (17-32)
E1/T1 channel port on
Standard I/O Card or there is
an AIS condition detected
(only for active T1/E1
channels). Fault detection via
polling of LIUs on Standart
I/O card and Optional I/O
Card when installed. Polling
interval 2 channels per 1 sec.
Report of this alarm in the
GUI/Syslog/Alarm history
shall indicate whether this is
a disconnect or AIS condition.
If both conditions are present,
then the disconnect alarm
shall take precedence over
the AIS alarm.
StdIO The user has selected a
T1/E1 test mode (loopback or
Tx Data). This alarm shall be
set when the user sets the
testmode for any of the T1/E1
channels, and cleared when
all T1/E1 channels are not in
loopback and Tx Data is
normal.
LED to
RED
Standard
I/O when
Alarm
Code
51-58
(1-16)
Severity
Critical
1-16
61-68
Optional
I/O when
17-32
Turn LED
(17-
32)
orange
rather
than RED
N/A 59 Info
BERT/LB/CW
Test Mode
StdIO This alarm shall be set when
the user enables either
N/A 69 Info
BERT,, Loopback, or CW
mode, and cleared when all
BERT, Loopback and CW
modes are disabled.
ODU Fault
Lower
ODU The ODU has indicated a
fault condition. Fault
N/A 71 Critical
detection via polling of ODU
or unsolicited message, if
supported. Polling interval 5
sec. Polling done via API
functional call. Report of this
alarm in the
GUI/Syslog/Alarm history
shall indicate the fault code
from the ODU.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 88

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-7
Alarm
ODU Comm
Failure Lower
ODU Fault
Upper
ODU Comm
Failure Upper
Affected
Component
Description
ODU The IDU is unable to
communicate with the ODU.
This could be a problem with
the ODU or a problem with
the cable connecting the
ODU to the IDU.
ODU The ODU has indicated a
fault condition or unsolicited
message, if supported. Fault
detection via polling of ODU.
Polling interval 5 sec. Polling
done via API function call.
Report of this alarm in the
GUI/Syslog/Alarm history
shall indicate the fault code
from the ODU.
ODU The IDU is unable to
communicate with the ODU.
This could be a problem with
the ODU or a problem with
the cable connecting the
ODU to the IDU.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A 72 Critical
N/A 73 Critical
N/A 74 Critical
Protection
Switch
East ATPC Tx at
Max Power
MODEM/ODU This alarm shall be set when
an AL1 command is received
from the active
MODEM/ODU, then cleared
when an AL2 command is
received from the standby
MODEM/ODU. Report of this
alarm in the
GUI/Syslog/Alarm history
shall indicate the fault code
from the ODU, if received.
ODU The IDU is unable to increase
the Tx Power as requested
by link partner due to
maximum power being
reached. Maximum power is
specified in the configuration
table.
N/A 75 Major
N/A 76 Info
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 89

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-8
Alarm
West ATPC Tx
at Max Power
Affected
Component
Description
ODU The IDU is unable to increase
the Tx Power as requested
by link partner due to
maximum power being
reached. Maximum power is
specified in the configuration
table.
Link Fault IDU Failed to receive link
heartbeat from link partner
via Radio Overhead (ROH)
channel. Fault detection via
timeout counter, which is
reset via reception of link
heartbeat message.
Remote Fault IDU Link Partner IDU indicating it
has a fault condition. Local
IDU receives Link Partner
Fault detection via Radio
Overhead (ROH) channel
message.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A 78 Info
N/A 81 Critical
N/A 82 Info
Encryption
Failure
IDU Data is not being decrypted
properly due to encryption
key mismatch between link
partners. Fault detection via
software detection of
unreadable ROH messages
from link partner.
Encryption
OneWay
IDU Only one IDU has data
encryption enabled. Fault
detection via software
messages to/from link
partner.
External Alarm 1 External The external Alarm 1 input
has been activated. Fault
detection via polling GPIO.
Polling interval 1 sec.
External Alarm 2 External The external Alarm 2 input
has been activated. Fault
detection via polling GPIO.
Polling interval 1 sec.
N/A 83 Critical
N/A 84 Major
N/A 91 Info
N/A 92 Info
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 90

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-9
Alarm
Affected
Component
Description
External Alarm 3 External The external Alarm 3 input
has been activated. Fault
detection via polling GPIO.
Polling interval 1 sec.
External Alarm 4 External The external Alarm 4 input
has been activated. Fault
detection via polling GPIO.
Polling interval 1 sec.
Remote IDU
Alarm
Link Partner
IDU
The link partner IDU has
indicated an alarm condition
via ROH.
Remote IDU
External Alarm 1
Link Partner
External
The link partner IDU has
indicated via ROH its external
alarm input 1 has been
activated.
Remote IDU
External Alarm 2
Link Partner
External
The link partner IDU has
indicated via ROH its external
alarm input 2 has been
activated.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A 93 Info
N/A 94 Info
N/A 95 Major
N/A 96 Info
N/A 97 Info
Remote IDU
External Alarm 3
Link Partner
External
The link partner IDU has
indicated via ROH its external
alarm input 3 has been
activated.
Remote IDU
External Alarm 4
Link Partner
External
The link partner IDU has
indicated via ROH its external
alarm input 4 has been
activated.
STM Loss of
Clock
IDU The SDH/SONET clock has
lost lock. Fault detection via
polling of LIU.
STM RS_LOS IDU The SDH/SONET has a Loss
of Signal Defect. Fault
detection via polling of LIU.
N/A 98 Info
N/A 99 Info
N/A Solid Critical
N/A Solid Critical
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 91

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-10
Alarm
Affected
Component
Description
STM RS_B1 IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has a B1 Defect.
Fault detection via polling of
RS_B1_T bit in STM-1 Core.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
STM RS_LOF IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has a Loss of
Frame Defect. Fault detection
via polling of RS_LOF_T bit
in STM-1 Core. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
STM RS_OOF IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has a Out of
Frame Defect. Fault detection
via polling of RS_OOF_T bit
in STM-1 Core. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Critical
N/A Solid Critical
STM RS_TIM IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has a Trace
Identifier Mismatch Defect.
Fault detection via polling of
RS_TIM_T bit in STM-1 Core.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
STM MS-AIS IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has detected an
AIS at the Multiplexer Level.
Fault detection via polling of
MS_AIS_T bit in STM-1 Core.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Critical
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 92

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-11
Alarm
Affected
Component
Description
STM MS-REI IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has detected a
Remote Error at the
Multiplexer Level. Fault
detection via polling of
MS_REI_T bit in STM-1
Core. Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
STM MS-RDI IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has detected an
Remote Defect at the
Multiplexer Level. Fault
detection via polling of
MS_RDI_T bit in STM-1
Core. Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
STM MS_B2 IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux has a B2 Defect
at the Multiplex level. Fault
detection via polling of
MS_B2_T bit in STM-1 Core.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Major
STM AU-AIS x IDU The SDH/SONET
N/A Solid Critical
Mux/Demux has detected an
AIS at the AU Level. Fault
detection via polling of
AU_AIS_T bit in STM-1 Core.
Where ‘x’ is the HP index.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
STM AU-LOP x IDU The SDH/SONET
N/A Solid Critical
Mux/Demux has detected an
Loss of Pointer Defect at the
AU Level. Fault detection via
polling of AU_LOP_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘x’ is the
HP index. Alternate detection
via Interrupt enabled in STM1 core.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 93

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-12
Alarm
Affected
Component
Description
STM HP-UNEQ x IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux HP number ‘x’ is
Unequipped. Fault detection
via polling of HP_UNEQ_T bit
in STM-1 Core. Where ‘x’ is
the HP index. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
STM HP-TIM x IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux HP number ‘x’
has a Trace Identifier
Mismatch. Fault detection via
polling of HP_TM_TIM_T bit
in STM-1 Core. Where ‘x’ is
the HP index. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
STM HP-REI x IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux HP number ‘x’
has a Remote Error
Indication. Fault detection via
polling of HP_REI_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘x’ is the
HP index. Alternate detection
via Interrupt enabled in STM1 core.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A Solid Critical
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Major
STM HP-RDI x IDU The SDH/SONET
N/A Solid Major
Mux/Demux HP number ‘x’
has a Remote Defect
Indication. Fault detection via
polling of HP_RDI_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘x’ is the
HP index. Alternate detection
via Interrupt enabled in STM1 core.
STM HP-PLM x IDU The SDH/SONET
N/A Solid Critical
Mux/Demux HP number ‘x’
has a Path Identifier
Mismatch. Fault detection via
polling of HP_PLM_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘x’ is the
HP index. Alternate detection
via Interrupt enabled in STM1 core.
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 94

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-13
Alarm
Affected
Component
Description
STM HP_B3 x IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux HP number ‘x’
has a CRC Error. Fault
detection via polling of
HP_B3_T bit in STM-1 Core.
Where ‘x’ is the HP index.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
STM TU-LOM
lkm
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux TU number ‘x’
has a Loss of Multiframe.
Fault detection via polling of
TU_LOMF_T bit in STM-1
Core. Where ‘lkm’ is the TU
index as LKM numbering.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Critical
STM TU-AIS
lkm
STM TU-LOP
lkm
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux TU number ‘x’
has an AIS. Fault detection
via polling of TU_AIS_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘lkm’ is
the TU index as LKM
numbering. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux TU number ‘x’
has a Loss of Pointer Defect.
Fault detection via polling of
TU_LOP_T bit in STM-1
Core. Where ‘lkm’ is the TU
index as LKM numbering.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
N/A Solid Critical
N/A Solid Critical
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 95

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-14
Alarm
STM LP-UNEQ
lkm
STM LP-TIM
lkm
Affected
Component
Description
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux LP number ‘x’ is
Unequipped. Fault detection
via polling of LP_UNEQ_T bit
in STM-1 Core. Where ‘lkm’
is the LP index as LKM
numbering. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux LP number ‘x’
has a Trace Identifier
Mismatch. Fault detection via
polling of LP_TM_TIM_T bit
in STM-1 Core. Where ‘lkm’
is the LP index as LKM
numbering. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Major
STM LP-REI lkm IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux LP number ‘x’
has a Remote Error
Indication. Fault detection via
polling of LP_REI_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘lkm’ is
the LP index as LKM
numbering. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
STM LP-RDI
lkm
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux LP number ‘x’
has a Remote Defect
Indication. Fault detection via
polling of LP_RDI_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘lkm’ is
the LP index as LKM
numbering. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Major
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 96

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-15
Alarm
STM LP-PLM
lkm
Affected
Component
Description
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux LP number ‘x’
has a Path Identifier
Mismatch. Fault detection via
polling of LP_PLM_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘lkm’ is
the LP index as LKM
numbering. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
STM LP-RFI lkm IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux LP number ‘x’
has a Remote Fault
Indication. Fault detection via
polling of LP_RFI_T bit in
STM-1 Core. Where ‘lkm’ is
the LP index as LKM
numbering. Alternate
detection via Interrupt
enabled in STM-1 core.
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A Solid Critical
N/A Solid Critical
STM LP-BIP2
lkm
IDU The SDH/SONET
Mux/Demux LP number ‘x’
has a CRC Error. Fault
detection via polling of
LP_BIP2_T bit in STM-1
Core. Where ‘lkm’ is the LP
index as LKM numbering.
Alternate detection via
Interrupt enabled in STM-1
core.
SDIDU PowerUp
IDU During power-up raise then
lower this alarm.
SDIDU Re-boot IDU When a user reboots the
SDIDU, raise then lower this
alarm prior to re-booting.
NTP Update IDU When the system time is
updated via NTP raise then
lower this alarm. The
previous system time and
new system time should be
noted in the alarm log, snmp
trap, and syslog messages.
N/A Solid Major
N/A Solid Info
N/A Solid Info
N/A Solid Info
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 97

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-16
Alarm
Remote
Reconfiguration
Failure
Affected
Component
Description
IDU When a remote
reconfiguration fails and the
original configuration is
restored after timeout, raise
then lower this alarm.
FPGA
Programming
Failure
Reconfiguration
Failure
IDU When the FPGA
programming fails, this alarm
shall be set.
IDU When the local SDIDU
configuration fails raise then
lower this alarm.
6.2 Abbreviations & Acronyms
LED to
RED
Alarm
Code
Severity
N/A Solid Info
N/A Solid Critical
N/A Solid Info
AdTPC Adaptive Power Control
AIS Alarm Indication Signal
BER Bit Error Rate
Codec Coder-Decoder
CPU Central Processing Unit
DB Decibel
DBm Decibel relative to 1 mW
DCE Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment
DTE Data Terminal Equipment
EIRP Effective Isotropic Radiated Power
FCC Federal Communications Commi ssion
FEC Forward Error Correction
FPGA Field Programmable Gate Array
GPIO General Purpose Input/Output
IF Intermediate frequency
IP Internet Protocol
LED Light-emitting diode
LOS Line of Sight
MIB Management Information Base
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 98

User Reference and Installation Guide 6-17
Modem Modulator-demodulator
ms Millisecond
NC Normally closed
NMS Network Management System
OAM&P Operations, Administration, Maintenance, and Provisioning
OC-3 Optical Carrier level 3
ODU Outdoor Unit
PCB Printed circuit board
POP Point of Presence
QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QPSK Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
RF Radio Frequency
RSL Received Signal Level (in dBm)
RSSI Received Signal Strength Indicator/Indication
RX Receiver
SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
SNR Signal-to-Noise Ratio
SDIDU
TM
Software Defined Indoor Unit (CarrierComm trademark)
SONET Synchronous Optical Network
STM-1 Synchronous Transport Module 1
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TTL Transistor-transistor logic
TX Transmitter
© 2006 Microwave Data Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved. MDS FIVE Series
05-4498A01, Rev. G
Page 99

IN CASE OF DIFFICULTY...
MDS products are designed for long life and trouble-free operation. However, this equipment, as
with all electronic equipment, may have an occasional component failure. The following
information will assist you in the event that servicing becomes necessary.
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
Technical assistance for MDS products is available from our Technical Support Department
during business hours (8:00 A.M.–5:30 P.M. Eastern Time). When calling, please give the
complete model number of the radio, along with a description of the trouble/symptom(s) that you
are experiencing. In many cases, problems can be resolved over the telephone, without the need
for returning the unit to the factory. Please use one of the following means for product assistance:
Phone: 585 241-5510 E-Mail:
mailto:TechSupport@microwavedata.com
FAX: 585 242-8369 Web: http://www.microwavedata.com/
FACTORY SERVICE
Component level repair of radio equipment is not recommended in the field. Many components
are installed using surface mount technology, which requires specialized training and equipment
for proper servicing. For this reason, the equipment should be returned to the factory for any PC
board repairs. The factory is best equipped to diagnose, repair and align your radio to its proper
operating specifications.
If return of the equipment is necessary, you will be issued a Service Request Order (SRO)
number and return shipping address. The SRO number will help expedite the repair so that the
equipment can be repaired and returned to you as quickly as possible. Please be sure to include
the SRO number on the outside of the shipping box, and on any correspondence relating to the
repair. No equipment will be accepted for repair without an SRO number.
A statement should accompany the radio describing, in detail, the trouble symptom(s), and a
description of any associated equipment normally connected to the radio. It is also important to
include the name and telephone number of a person in your organization who can be contacted if
additional information is required.
The radio must be properly packed for return to the factory. The original shipping container and
packaging materials should be used whenever possible.
When repairs have been completed, the equipment will be returned to you by the same shipping
method used to send it to the factory. Please specify if you wish to make different shipping
arrangements. To inquire about an in-process repair, you may contact our Product Services
Group at 585-241-5540 (FAX: 585-242-8400), or via e-mail at:
ProductServices@microwavedata.com
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...