Page 1

Siemens Cellular Engine
Version: 02.8xb
DocID: MC46_HD_V02.8xb
Hardware
Interface
Description
Page 2

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Document Name:
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
Version: 02.8xb
Date: August 21, 2003
DocId: MC46_HD_V02.8xb
Status: DRAFT
General note
Product is deemed accepted by Recipient and is provided without interface to Recipient´s products.
The Product constitutes pre-release version and code and may be changed substantially before
commercial release. The Product is provided on an “as is” basis only and may contain deficiencies or
inadequacies. The Product is provided without warranty of any kind, express or implied. To the
maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Siemens further disclaims all warranties, including
without limitation any implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose and
noninfringement of third-party rights. The entire risk arising out of the use or performance of the
Product and documentation remains with Recipient. This Product is not intended for use in life support
appliances, devices or systems where a malfunction of the product can reasonably be expected to
result in personal injury. Applications incorporating the described product must be designed to be in
accordance with the technical specifications provided in these guidelines. Failure to comply with any of
the required procedures can result in malfunctions or serious discrepancies in results. Furthermore, all
safety instructions regarding the use of mobile technical systems, including GSM products, which also
apply to cellular phones must be followed. Siemens AG customers using or selling this product for use
in any applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Siemens for any damages
resulting from illegal use or resale. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, in no event
shall Siemens or its suppliers be liable for any consequential, incidental, direct, indirect, punitive or
other damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits,
business interruption, loss of business information or data, or other pecuniary loss) arising out the use
of or inability to use the Product, even if Siemens has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
Subject to change without notice at any time.
Copyright
Transmittal, reproduction, dissemination and/or editing of this document as well as utilization of its
contents and communication thereof to others without express authorization are prohibited. Offenders
will be held liable for payment of damages. All rights created by patent grant or registration of a utility
model or design patent are reserved.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2003
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 2 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 3

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Contents
0 Document History ...................................................................................................... 7
1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 8
1.1 Related documents ............................................................................................. 8
1.2 Terms and abbreviations..................................................................................... 9
1.3 Type approval ....................................................................................................12
1.4 Safety precautions .............................................................................................14
2 Product concept........................................................................................................16
2.1 MC46 key features at a glance...........................................................................17
2.2 Circuit concept ...................................................................................................20
3 Application Interface.................................................................................................21
3.1 Operating modes ...............................................................................................22
3.2 Power supply .....................................................................................................24
3.2.1 Power supply pins on the board-to-board connector.............................24
3.2.2 Minimizing power losses.......................................................................25
3.2.3 Monitoring power supply.......................................................................25
3.3 Power up / down scenarios ................................................................................26
3.3.1 Turn on MC46 ......................................................................................26
3.3.1.1 Turn on MC46 using the ignition line /IGT (Power on)...............27
3.3.1.2 Timing of the ignition process ...................................................28
3.3.1.3 Turn on MC46 using the POWER signal...................................29
3.3.1.4 Turn on MC46 using the RTC (Alarm mode).............................29
3.3.2 Turn off MC46 ......................................................................................31
3.3.2.1 Turn off MC46 using AT command ...........................................31
3.3.2.2 Maximum number of turn-on / turn-off cycles............................32
3.3.2.3 Emergency shutdown using /EMERGOFF pin...........................32
3.3.3 Automatic shutdown .............................................................................33
3.3.3.1 Temperature dependent shutdown............................................33
3.3.3.2 Temperature control during emergency call ..............................34
3.3.3.3 Undervoltage shutdown if battery NTC is present .....................34
3.3.3.4 Undervoltage shutdown if no battery NTC is present ................35
3.3.3.5 Overvoltage shutdown ..............................................................35
3.4 Automatic GPRS Multislot Class change............................................................35
3.5 Charging control.................................................................................................36
3.5.1 Battery pack characteristics..................................................................37
3.5.1.1 Recommended battery pack .....................................................38
3.5.2 Implemented charging technique..........................................................39
3.5.3 Operating modes during charging ........................................................40
3.5.4 Charger requirements ..........................................................................41
3.6 Power saving .....................................................................................................42
3.6.1 No power saving (AT+CFUN=1)...........................................................42
3.6.2 NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode (AT+CFUN=0) .........................................42
3.6.3 CYCLIC SLEEP mode (AT+CFUN=5, 6, 7 and 8) ................................43
3.6.4 Timing of the /CTS signal in CYCLIC SLEEP modes ...........................43
3.6.5 Wake up MC46 from SLEEP mode ......................................................45
3.7 Summary of state transitions (except SLEEP mode)..........................................46
3.8 RTC backup.......................................................................................................47
3.9 Serial interfaces .................................................................................................48
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 3 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 4

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.9.1 Features supported on first and second serial interface .......................49
3.10 Audio interfaces .................................................................................................51
3.10.1 Microphone circuit ................................................................................52
3.10.2 Speech processing...............................................................................53
3.10.3 DAI timing.............................................................................................53
3.11 SIM interface......................................................................................................55
3.11.1 Requirements for using the CCIN pin ...................................................56
3.11.2 Design considerations for SIM card holder...........................................57
3.12 Control signals ...................................................................................................58
3.12.1 Inputs ...................................................................................................58
3.12.2 Outputs.................................................................................................59
3.12.2.1 Synchronization signal.........................................................59
3.12.2.2 Using the SYNC pin to control a status LED ........................60
3.12.2.3 Behavior of the /RING0 line (ASC0 interface only)...............61
4 Antenna interface......................................................................................................63
4.1 Antenna installation............................................................................................63
4.1.1 Antenna pad.........................................................................................65
4.1.1.1 Suitable cable types..................................................................65
4.1.2 Hirose antenna connector ....................................................................66
5 Electrical, reliability and radio characteristics .......................................................70
5.1 Absolute maximum ratings.................................................................................70
5.2 Operating temperatures .....................................................................................70
5.3 Electrical specifications of the application interface............................................71
5.4 Power supply ratings..........................................................................................76
5.4.1 Current consumption during transmit burst...........................................77
5.5 Electrical characteristics of the voiceband part...................................................78
5.5.1 Setting audio parameters by AT commands.........................................78
5.5.2 Audio programming model ...................................................................79
5.5.3 Characteristics of audio modes ............................................................80
5.5.4 Voiceband receive path ........................................................................81
5.5.5 Voiceband transmit path.......................................................................82
5.6 Air interface........................................................................................................83
5.7 Electrostatic discharge.......................................................................................85
5.8 Reliability characteristics ....................................................................................86
6 Mechanics..................................................................................................................87
6.1 Mechanical dimensions of MC46........................................................................87
6.2 Mounting MC46 onto the application platform ....................................................90
6.3 Board-to-board connector ..................................................................................91
6.3.1 Mechanical dimensions of the Hirose DF12 connector .........................92
6.3.2 Adapter cabling ....................................................................................92
6.4 Heat sinks and thermally conductive tapes ........................................................93
6.4.1 Test conditions and results...................................................................93
7 Reference Approval ..................................................................................................95
7.1 Reference Equipment for Type Approval ...........................................................95
7.2 Compliance with FCC Rules and Regulations ....................................................96
8 List of parts and accessories...................................................................................97
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 4 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 5

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Figures
Figure 1: MC46 block diagram .............................................................................................20
Figure 2: Power supply limits during transmit burst ..............................................................25
Figure 3: Power-on by ignition signal....................................................................................27
Figure 4: Timing of power-on process if VDDLP is not used ................................................28
Figure 5: Timing of power-on process if VDDLP is fed from external source........................28
Figure 6: Deactivating GSM engine by /EMERGOFF signal.................................................32
Figure 7: Schematic of approved charging transistor, trickle charging and ESD protection ..36
Figure 8: Battery pack circuit diagram ..................................................................................37
Figure 9: Charging process..................................................................................................39
Figure 10: Timing of /CTS signal (example for a 2.12 s paging cycle)..................................44
Figure 11: Beginning of power saving if CFUN=5 or 7..........................................................44
Figure 12: RTC supply from capacitor..................................................................................47
Figure 13: RTC supply from rechargeable battery................................................................47
Figure 14: RTC supply from non-chargeable battery............................................................47
Figure 15: Serial interfaces ..................................................................................................48
Figure 16: Audio block diagram............................................................................................51
Figure 17: Schematic of microphone inputs .........................................................................52
Figure 18: DAI timing on transmit path .................................................................................54
Figure 19: DAI timing on receive path ..................................................................................54
Figure 20: SIM card holder of DSB45 Support Box ..............................................................57
Figure 21: Pin numbers of Molex SIM card holder on DSB45 Support Box ..........................57
Figure 22: SYNC signal during transmit burst ......................................................................59
Figure 23: LED Circuit (Example).........................................................................................60
Figure 24: Incoming voice call ..............................................................................................61
Figure 25: Incoming data call ...............................................................................................61
Figure 26: URC transmission ...............................................................................................61
Figure 27: U.FL-R-SMT connector .......................................................................................63
Figure 28: Antenna pad and GND pad .................................................................................63
Figure 29: Never use antenna connector and antenna pad at the same time.......................64
Figure 30: Restricted area around antenna pad ...................................................................64
Figure 31: Mechanical dimensions of U.FL-R-SMT connector..............................................66
Figure 32: U.FL-R-SMT connector with U.FL-LP-040 plug ...................................................67
Figure 33: U.FL-R-SMT connector with U.FL-LP-066 plug ...................................................67
Figure 34: Specifications of U.FL-LP-(V)-040(01) plug.........................................................68
Figure 35: Pin assignment (top view on MC46) ....................................................................71
Figure 36: Maximum burst peak current during transmit burst in mA....................................77
Figure 37: AT audio programming model .............................................................................79
Figure 38: MC46 – top view..................................................................................................87
Figure 39: Mechanical dimensions of MC46.........................................................................88
Figure 40: MC46 bottom view...............................................................................................89
Figure 41: Hirose DF12C receptacle on MC46.....................................................................91
Figure 42: Header Hirose DF12 series.................................................................................91
Figure 43: Mechanical dimensions of Hirose DF12 connector..............................................92
Figure 44: Reference equipment for approval ......................................................................95
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 5 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 6

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Tables
Table 1: MC46 key features .................................................................................................17
Table 2: Coding schemes and maximum net data rates over air interface ...........................19
Table 3: Overview of operating modes.................................................................................22
Table 4: Power supply pins of board-to-board connector .....................................................24
Table 5: AT commands available in Alarm mode .................................................................29
Table 6: Temperature dependent behavior ..........................................................................34
Table 7: Bill of material for external charging circuit .............................................................36
Table 8: Specifications of XWODA battery pack ..................................................................38
Table 9: Comparison Charge-only and Charge mode ..........................................................40
Table 10: AT commands available in Charge-only mode......................................................41
Table 11: Wake-up events in NON-CYCLIC and CYCLIC SLEEP modes............................45
Table 12: State transitions of MC46 (except SLEEP mode) .................................................46
Table 13: DCE-DTE wiring of 1st serial interface .................................................................49
Table 14: DCE-DTE wiring of 2nd serial interface ................................................................50
Table 15: Signals of the SIM interface (board-to-board connector) ......................................55
Table 16 : Pin assignment of Molex SIM card holder on DSB45 Support Box ......................57
Table 17: Input control signals of the MC46 module.............................................................58
Table 18: MC46 synchronization signal (if SYNC pin is set to mode 0 via AT^SSYNC)........59
Table 19: Coding of the status LED......................................................................................60
Table 20: MC46 ring signal...................................................................................................62
Table 21: Return loss ...........................................................................................................63
Table 22: Product specifications of U.FL-R-SMT connector .................................................66
Table 23: Material and finish of U.FL-R-SMT connector and recommended plugs...............67
Table 24: Ordering information for Hirose U.FL Series.........................................................69
Table 25: Absolute maximum ratings ...................................................................................70
Table 26: Operating temperatures........................................................................................70
Table 27: Electrical description of application interface ........................................................72
Table 28: Power supply ratings ............................................................................................76
Table 29: Audio parameters adjustable by AT command .....................................................78
Table 30: Voiceband characteristics (typical) .......................................................................80
Table 31: Voiceband receive path ........................................................................................81
Table 32: Voiceband transmit path.......................................................................................82
Table 33: Air Interface..........................................................................................................83
Table 34: Local oscillator and intermediate frequencies used by MC46 ...............................84
Table 35: Measured electrostatic values ..............................................................................85
Table 36: Summary of reliability test conditions....................................................................86
Table 37: Ordering information DF12 series.........................................................................91
Table 38: Electrical and mechanical characteristics of the Hirose DF12C connector............91
Table 39: Tested heat sinks and thermally conductive tapes and test results ......................94
Table 40: List of parts and accessories ................................................................................97
Table 41: Molex sales contacts (subject to change) .............................................................98
Table 42: Hirose sales contacts (subject to change) ............................................................98
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 6 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 7

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
0 Document History
Preceding document: "MC46 Hardware Interface Description" Version 02.8xa
New document: "MC46 Hardware Interface Description" Version 02.8xb
7.2 96 Added chapter related to FCC certification.
3.4 35 More detailed description of GPRS Multislot Class change.
Preceding document: "MC46 Hardware Interface Description" Version 02.8x
New document: "MC46 Hardware Interface Description" Version 02.8xa
3.3.2.1 31 To keep /EMERGOFF pin and output pins of the serial interfaces from
floating when in high impedance state use additional resistors.
3.3.2.3 32 Added example when /EMERGOFF might be needed.
3.12.2.2 60 LED mode of the SYNC pin recommended for testing and evaluating product
design.
3.12.2.3 61 Recommendations for utilizing /RING0 line added.
4.1.1 65 More detailed information on how to connect the antenna ground pad.
5.4.1 77 More detailed description of current consumption during transmit burst.
Added Smith chart.
5.3 71ff Table 27 - /EMERGOFF pin and output pins of serial interface: To keep
output pins from floating when in high impedance state use additional
resistors.
5.6 83f Table 34: Channel numbers of GSM 850 MHz frequency band corrected.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 7 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 8

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
1 Introduction
This document describes the hardware interface of the Siemens MC46 module that connects
to the cellular device application and the air interface. As MC46 is intended to integrate with
a wide range of application platforms, all functional components are described in great detail.
So this guide covers all information you need to design and set up cellular applications
incorporating the MC46 module. It helps you quickly retrieve interface specifications,
electrical and mechanical details and, last but not least, information on the requirements to
be considered for integrating further components.
1.1 Related documents
[1] MC46 AT Command, Version 02.8xb
[2] MC46 Release Notes, Version 02.8xb
[3] GPRS Startup User's Guide
[4] Remote-SAT User's Guide
[5] DSB45 Support Box - Evaluation Kit for Siemens Cellular Engines
[6] Application Note 23: Installing MC46 on DSB45
[7] Application Note 16: Upgrading MC46 Firmware, Version 0.5
[8] Application Note 14: Audio and Battery Parameter Download
[9] Application Note 02: Audio Interface Design
[10] Multiplexer User's Guide
[11] Multiplex Driver Developer’s Guide for Windows 2000 and Windows XP
[12] Multiplex Driver Installation Guide for Windows 2000 and Windows XP
[13] Application Note 22: Using TTY / CTM equipment with MC46
[14] Application Note 24: Application Developer’s Guide
Prior to using the MC46 engines or upgrading to a new firmware release, be sure to carefully
read the latest product information.
To visit the Siemens Website you can use the following link:
http://www.siemens.com/wm
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 8 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 9

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
1.2 Terms and abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
ADC Analog-to-Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control
AGC Automatic Gain Control
ANSI American National Standards Institute
ARFCN Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number
ARP Antenna Reference Point
ASC0 / ASC1 Asynchronous Controller. Abbreviations used for first and second serial interface of
MC46
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
B Thermistor Constant
B2B Board-to-board connector
BER Bit Error Rate
BTS Base Transceiver Station
CB or CBM Cell Broadcast Message
CE Conformité Européene (European Conformity)
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CPU Central Processing Unit
CS Coding Scheme
CSD Circuit Switched Data
CTS Clear to Send
DAC Digital-to-Analog Converter
DAI Digital Audio Interface
dBm0 Digital level, 3.14dBm0 corresponds to full scale, see ITU G.711, A-law
DCE Data Communication Equipment (typically modems, e.g. Siemens GSM engine)
DCS 1800 Digital Cellular System, also referred to as PCN
DRX Discontinuous Reception
DSB Development Support Box
DSP Digital Signal Processor
DSR Data Set Ready
DTE Data Terminal Equipment (typically computer, terminal, printer or, for example, GSM
application)
DTR Data Terminal Ready
DTX Discontinuous Transmission
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
EGSM Enhanced GSM
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 9 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 10

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Abbreviation Description
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
ETS European Telecommunication Standard
FCC Federal Communications Commission (U.S.)
FDMA Frequency Division Multiple Access
FR Full Rate
GMSK Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GSM Global Standard for Mobile Communications
HiZ High Impedance
HR Half Rate
I/O Input/Output
IC Integrated Circuit
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity
ISO International Standards Organization
ITU International Telecommunications Union
kbps kbits per second
LED Light Emitting Diode
Li-Ion Lithium-Ion
Mbps Mbits per second
MMI Man Machine Interface
MO Mobile Originated
MS Mobile Station (GSM engine), also referred to as TE
MSISDN Mobile Station International ISDN number
MT Mobile Terminated
NTC Negative Temperature Coefficient
OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer
PA Power Amplifier
PAP Password Authentication Protocol
PBCCH Packet Switched Broadcast Control Channel
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PCL Power Control Level
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PCN Personal Communications Network, also referred to as DCS 1800
PCS Personal Communication System, also referred to as GSM 1900
PDU Protocol Data Unit
PLL Phase Locked Loop
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 10 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 11

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Abbreviation Description
PPP Point-to-point protocol
PSU Power Supply Unit
R&TTE Radio and Telecommunication Terminal Equipment
RAM Random Access Memory
RF Radio Frequency
RMS Root Mean Square (value)
ROM Read-only Memory
RTC Real Time Clock
Rx Receive Direction
SAR Specific Absorption Rate
SELV Safety Extra Low Voltage
SIM Subscriber Identification Module
SMS Short Message Service
SRAM Static Random Access Memory
TA Terminal adapter (e.g. GSM engine)
TDMA Time Division Multiple Access
TE Terminal Equipment, also referred to as DTE
Tx Transmit Direction
UART Universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter
URC Unsolicited Result Code
USSD Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
Phonebook abbreviations
FD SIM fixdialing phonebook
LD SIM last dialing phonebook (list of numbers most recently dialed)
MC Mobile Equipment list of unanswered MT calls (missed calls)
ME Mobile Equipment phonebook
ON Own numbers (MSISDNs) stored on SIM or ME
RC Mobile Equipment list of received calls
SM SIM phonebook
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 11 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 12

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
1.3 Type approval
MC46 is designed to comply with the directives and standards listed below. Please
note that the product is still in a pre-release state and, therefore, type approval and
testing procedures have not yet been completed.
European directives
99/05/EC “Directive of the European Parliament and of the council of 9 March
1999 on radio equipment and telecommunications terminal
equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity”, in short
referred to as R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC
89/336/EC Directive on electromagnetic compatibility
73/23/EC Directive on electrical equipment designed for use within certain
voltage limits (Low Voltage Directive)
Standards of North American Type Approval
CFR Title 47 “Code of Federal Regulations, Part 2 and Part 24
(Telecommunications, PCS)”
US Equipment Authorization FCC
UL 60 950 “Product Safety Certification” (Safety requirements)
NAPRD.0s3 “Overview of PCS Type certification review board
Mobile Equipment Type Certification and IMEI control”
PCS Type Certification Review board (PTCRB)
Standards of European Type Approval
3GPP TS 51.010-1 “Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2); Mobile
Station (MS) conformance specification”.
ETSI EN 301 511 “V7.0.1 (2000-12) Candidate Harmonized European Standard
(Telecommunications series) Global System for Mobile
communications (GSM); Harmonized standard for mobile stations in
the GSM 900 and DCS 1800 bands covering essential requirements
under article 3.2 of the R&TTE directive (1999/5/EC) (GSM 13.11
version 7.0.1 Release 1998)”
GCF-CC “Global Certification Forum - Certification Criteria”
ETSI EN 301 489-1 “V1.1.1 (2000-09) Candidate Harmonized European Standard
(Telecommunications series) Electro Magnetic Compatibility and
Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electro Magnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common
Technical Requirements”
ETSI EN 301 489-7 “V1.1.1 (2000-09) Candidate Harmonized European Standard
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 12 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 13

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
(Telecommunications series) Electro Magnetic Compatibility and
Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electro Magnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 7: Specific
conditions for mobile and portable radio and ancillary equipment of
digital cellular radio telecommunications systems (GSM and DCS)”
EN 60 950 Safety of information technology equipment (2000)
Requirements of quality
IEC 60068 Environmental testing
DIN EN 60529 IP codes
Compliance with international rules and regulations
Manufacturers of mobile, fixed or portable devices incorporating MC46 modules are advised
to have their completed product tested and approved for compliance with all applicable
national and international regulations. As a tri-band GSM/GPRS engine designed for use on
any GSM network in the world, MC46 is required to pass all approvals relevant to operation
on the European and North American markets. For the North American market this includes
the Rules and Regulations of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and PTCRB,
for the European market the R&TTE Directives and GCF Certification Criteria must be fully
satisfied.
The FCC Equipment Authorization planned for MC46 Siemens reference application is valid
only for the equipment described in Chapter 7.
SAR requirements specific to handheld mobiles
Mobile phones, PDAs or other handheld transmitters and receivers incorporating a GSM
module must be in accordance with the guidelines for human exposure to radio frequency
energy. This requires the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) of handheld MC46 based
applications to be evaluated and approved for compliance with national and/or international
regulations.
Since the SAR value varies significantly with the individual product design manufacturers are
advised to submit their product for approval if designed for handheld operation. For
European and US markets the relevant directives are mentioned below. It is the
responsibility of the manufacturer of the final product to verify whether or not further
standards, recommendations of directives are in force outside these areas.
Products intended for sale on US markets
ES 59005/ANSI C95.1 Considerations for evaluation of human exposure to
Electromagnetic Fields (EMFs) from Mobile Telecommunication
Equipment (MTE) in the frequency range 30MHz-6GHz
Products intended for sale on European markets
EN 50360 Product standard to demonstrate the compliance of mobile phones
with the basic restrictions related to human exposure to
electromagnetic fields (300 MHz - 3 GHz)
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 13 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 14
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
1.4 Safety precautions
The following safety precautions must be observed during all phases of the operation,
usage, service or repair of any cellular terminal or mobile incorporating MC46. Manufacturers
of the cellular terminal are advised to convey the following safety information to users and
operating personnel and to incorporate these guidelines into all manuals supplied with the
product. Failure to comply with these precautions violates safety standards of design,
manufacture and intended use of the product. Siemens AG assumes no liability for customer
failure to comply with these precautions.
When in a hospital or other health care facility, observe the restrictions on the
use of mobiles. Switch the cellular terminal or mobile off, if instructed to do so
by the guidelines posted in sensitive areas. Medical equipment may be
sensitive to RF energy.
The operation of cardiac pacemakers, other implanted medical equipment
and hearing aids can be affected by interference from cellular terminals or
mobiles placed close to the device. If in doubt about potential danger, contact
the physician or the manufacturer of the device to verify that the equipment is
properly shielded. Pacemaker patients are advised to keep their hand-held
mobile away from the pacemaker, while it is on.
Switch off the cellular terminal or mobile before boarding an aircraft. Make
sure it cannot be switched on inadvertently. The operation of wireless
appliances in an aircraft is forbidden to prevent interference with
communications systems. Failure to observe these instructions may lead to
the suspension or denial of cellular services to the offender, legal action, or
both.
Do not operate the cellular terminal or mobile in the presence of flammable
gases or fumes. Switch off the cellular terminal when you are near petrol
stations, fuel depots, chemical plants or where blasting operations are in
progress. Operation of any electrical equipment in potentially explosive
atmospheres can constitute a safety hazard.
Your cellular terminal or mobile receives and transmits radio frequency
energy while switched on. Remember that interference can occur if it is used
close to TV sets, radios, computers or inadequately shielded equipment.
Follow any special regulations and always switch off the cellular terminal or
mobile wherever forbidden, or when you suspect that it may cause
interference or danger.
Road safety comes first! Do not use a hand-held cellular terminal or mobile
when driving a vehicle, unless it is securely mounted in a holder for handsfree
operation. Before making a call with a hand-held terminal or mobile, park the
vehicle.
Handsfree devices must be installed by qualified personnel. Faulty installation
or operation can constitute a safety hazard.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 14 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 15

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
IMPORTANT!
SOS
Cellular terminals or mobiles operate using radio signals and cellular
networks cannot be guaranteed to connect in all conditions. Therefore, you
should never rely solely upon any wireless device for essential
communications, for example emergency calls.
Remember, in order to make or receive calls, the cellular terminal or mobile
must be switched on and in a service area with adequate cellular signal
strength.
Some networks do not allow for emergency calls if certain network services
or phone features are in use (e.g. lock functions, fixed dialing etc.). You may
need to deactivate those features before you can make an emergency call.
Some networks require that a valid SIM card be properly inserted in the
cellular terminal or mobile.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 15 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 16

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
2 Product concept
Designed for use on any GSM network in the world, Siemens MC46 is a tri-band GSM/GPRS
engine that works on the three frequencies GSM 850 MHz, GSM 1800 MHz and GSM
1900 MHz. MC46 features GPRS multislot class 10 and supports the GPRS coding schemes
CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4.
To save space on the application platform, MC46 comes as an extremely slim and compact
module. This makes it ideally suited for a broad range of mobile computing devices, such as
laptops, notebooks, multimedia appliances, and particularly offers easy integration with
PDAs, pocket organizers or miniature mobile phones.
The tiny MC46 module incorporates all you need to create high-performance GSM/GPRS
solutions: baseband processor, power supply ASIC, complete radio frequency circuit
including a power amplifier and antenna interface. The power amplifier is directly fed from
the supply voltage BATT+. The MC46 software is residing in a flash memory device. An
additional SRAM enables MC46 to meet the demanding requirements of GPRS connectivity.
The physical interface to the cellular application is made through a board-to-board
connector. It consists of 50 pins, required for controlling the unit, transferring data and audio
signals and providing power supply lines.
MC46 comprises two serial interfaces (ASC0 and ASC1) giving you maximum flexibility for
easy integration with the Man-Machine Interface (MMI).
An extremely versatile audio concept offers various audio interfaces, each available on the
board-to-board connector: a digital audio interface (DAI) and two analog audio interfaces.
This allows you to connect up to three audio devices in any combination, all at the same
time. Using AT commands you can easily switch back and forth and select different audio
modes.
The external dual-band or triple-band antenna can be connected optionally to a connector on
the top side or to a pad on the bottom side.
The power saving technique minimizes current consumption to as low as 3mA. In SLEEP
mode, MC46 is able to wake up on demand and to resume power saving automatically if no
activity is required.
For battery powered applications, MC46 features a charging control which can be used to
charge a Li-Ion battery. The charging circuit must be implemented outside the module on the
application platform.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 16 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 17

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
2.1 MC46 key features at a glance
Table 1: MC46 key features
Feature Implementation
Power supply Single supply voltage 3.2V – 4.5V
Power saving Minimizes power consumption in SLEEP mode to 3mA
Charging Supports charging control for Li-Ion battery
Frequency bands
GSM class Small MS
Transmit power
GPRS connectivity
Temperature range
Temperature control
and auto switch-off
DATA GPRS:
CSD:
WAP:
· Tri-band GSM 850, GSM 1800, GSM 1900
· Compliant to GSM Phase 2/2+
· Class 4 (2W) at GSM 850
· Class 1 (1W) at GSM 1800 and GSM 1900
· GPRS multi-slot class 10
· GPRS mobile station class B
· Normal operation: -20°C to +55°C
· Restricted operation: -25°C to -20°C and +55°C to +70°C
· Constant temperature control prevents damage to MC46 when the
specified temperature is exceeded. When an emergency call is in
progress the automatic temperature shutdown functionality is
deactivated.
· GPRS data downlink transfer: max. 85.6 kbps (see Table 2)
· GPRS data uplink transfer: max. 42.8 kbps (see Table 2)
· Coding scheme: CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4
· MC46 supports the two protocols PAP (Password Authentication
Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol)
commonly used for PPP connections.
· Support of Packet Switched Broadcast Control Channel (PBCCH) allows
you to benefit from enhanced GPRS performance when offered by the
network operators.
· CSD transmission rates: 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 14.4 kbps, non-transparent, V.110
· Unstructured Supplementary Services Data (USSD) support
· WAP compliant
SMS
FAX Group 3: Class 1, Class 2
SIM interface
External antenna Connected via 50 Ohm antenna connector or antenna pad
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 17 of 98 21.08.2003
· MT, MO, CB, Text and PDU mode
· SMS storage: SIM card plus 25 SMS locations in the mobile equipment
· Transmission of SMS alternatively over CSD or GPRS. Preferred mode
can be user-defined.
· Supported SIM card: 3V
· External SIM card reader has to be connected via interface connector
(note that card reader is not part of MC46)
Page 18

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Feature Implementation
Audio interfaces Two analog audio interfaces, one digital audio interface (DAI)
Audio features Speech codec modes:
· Half Rate (ETS 06.20)
· Full Rate (ETS 06.10)
· Enhanced Full Rate (ETS 06.50 / 06.60 / 06.80)
· Adaptive Multi Rate (AMR)
Handsfree operation
· Echo cancellation
· Noise reduction
Two serial interfaces:
ASC0, ASC1
Phonebook
management
SIM Application Toolkit Supports SAT class 3, GSM 11.14 Release 98
Ringing tones Offers a choice of 7 different ringing tones / melodies, easily selectable with
Real time clock Implemented
Timer function Programmable via AT command
Support of TTY/CTM To benefit from TTY communication via GSM, CTM equipment can be
Physical characteristics Size: 53 +0.15 x 34 +0.15 x 3.5+0.3 mm
· 2.65V level, bi-directional bus for AT commands and data
· ASC0 – full-featured 8-wire serial interface. Supports RTS0/CTS0
hardware handshake and software XON/XOFF flow control. Multiplex
ability according to GSM 07.10 Multiplexer Protocol.
· ASC1 - 4-wire serial interface. Supports RTS1/CTS1 hardware
handshake and software XON/XOFF flow control.
· Baud rate: 300bps ... 230kbps on ASC0 and ASC1
· Autobauding (on ASC0 only) detects 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200,
38400, 57600, 115200, 230400 bps
Supported phonebook types: SM, FD, LD, MC, RC, ON, ME
AT command
connected to one of the three audio interfaces.
Weight: 10g
Firmware upgrade Firmware upgradable over serial interface and SIM interface
Evaluation kit The DSB45 Support Box is an evaluation kit designed to test and type
approve Siemens cellular engines and provide a sample configuration for
application engineering. See Chapter 8 for ordering information.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 18 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 19
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 2: Coding schemes and maximum net data rates over air interface
Coding scheme 1 Timeslot 2 Timeslots 4 Timeslots
CS-1: 9.05 kbps 18.1 kbps 36.2 kbps
CS-2: 13.4 kbps 26.8 kbps 53.6 kbps
CS-3: 15.6 kbps 31.2 kbps 62.4 kbps
CS-4: 21.4 kbps 42.8 kbps 85.6 kbps
Please note that the values stated above are maximum ratings which, in practice, are influenced by a
great variety of factors, primarily, for example, traffic variations and network coverage.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 19 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 20
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
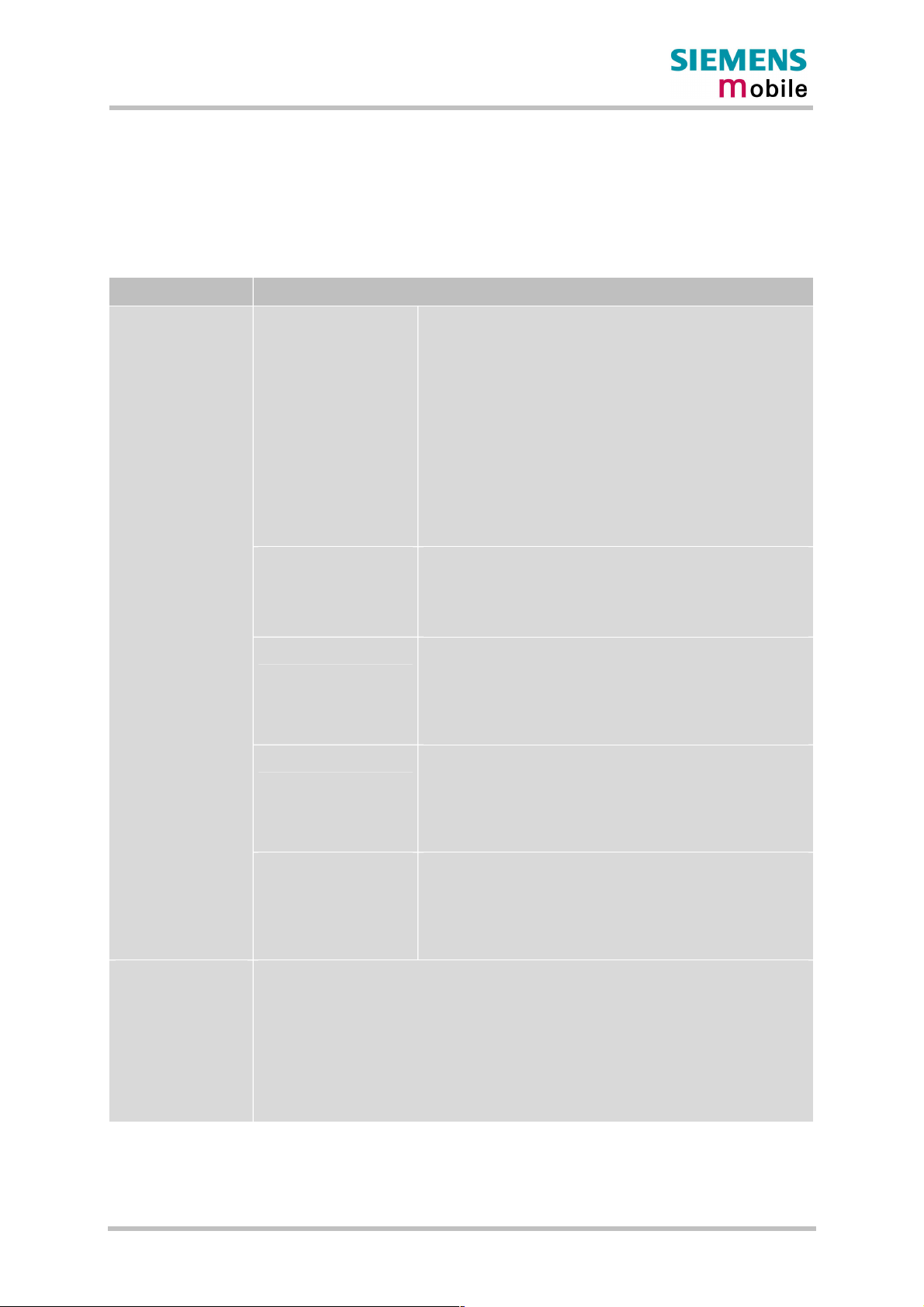
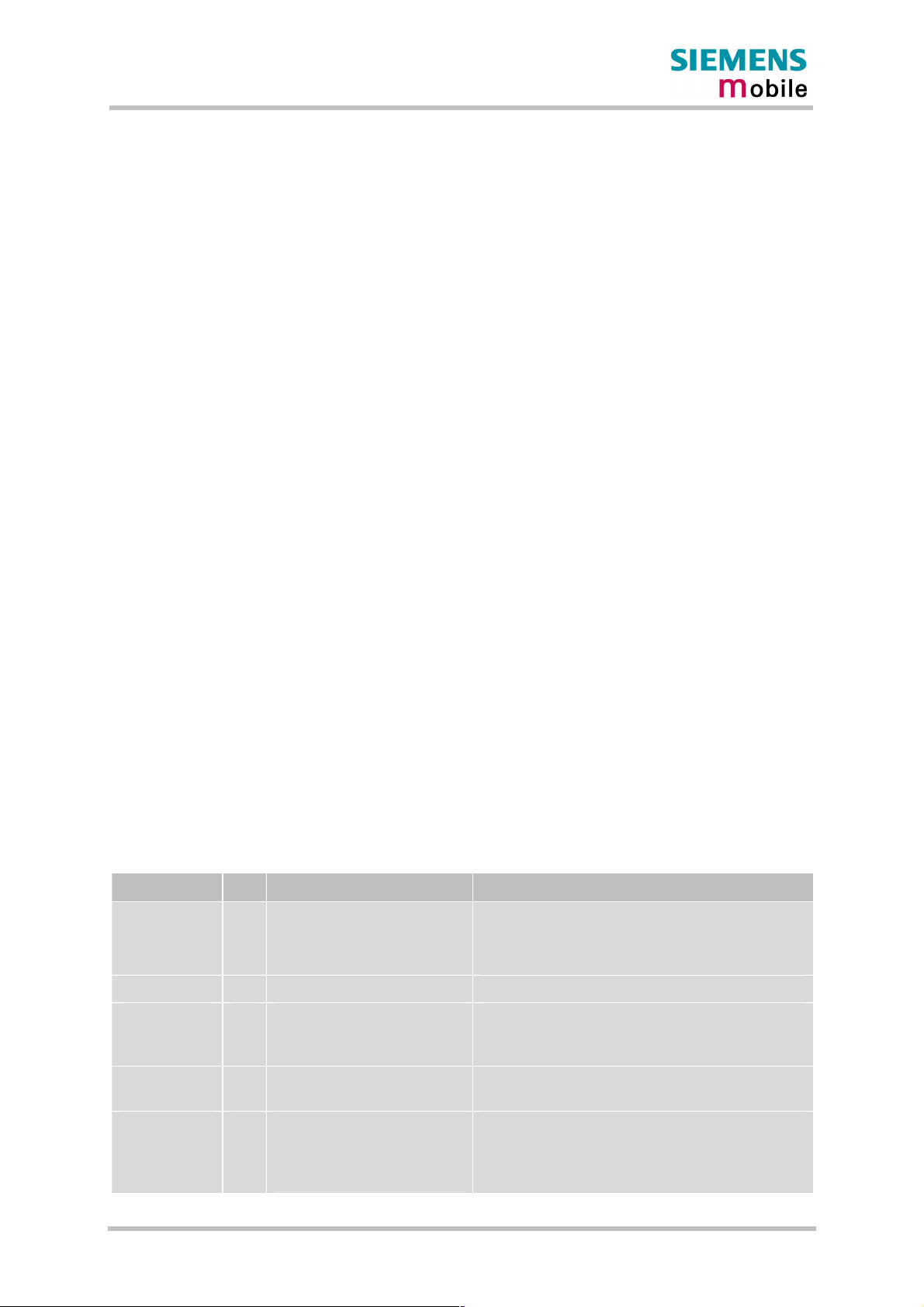
2.2 Circuit concept
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the MC46 module and illustrates the major functional
components:
GSM / GPRS baseband block:
· Baseband controller operating at 26MHz
· Power supply ASIC
· Flash
· SRAM
· Application interface (board-to-board connector)
GSM RF block:
· RF transceiver
· RF power amplifier
· RF frontend (antenna connector)
RF Power
Amplifier
RF Section
MC46
Measuring
Network
Interface
RF - Baseband
Send
Receive
Control
Baseband
Controller
CCRST
CCCLK
CCIO
4
CCIN
CCVCC
(GND)
2
Power
Supply
ASIC
Figure 1: MC46 block diagram
Data
Adr
Control
Data
Adr
Control
5
9
8
4
6
SIM Interface
/EMERGOFF
POWER
CHARGE
5
5
BATT_TEMP
DAI
2x Audio
ASC0
ASC1
SYNC
VDD
VDDLP
/IGT
BATT+
GND
SRAM
Flash
CCIN
CCVCC
4
SIM
(50 pins)
Application Interface
Ext.
Charging
Circuit
Charger
input
NTC
+
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 20 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 21

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3 Application Interface
MC46 is equipped with a 50-pin 0.5mm pitch board-to-board connector that connects to the
cellular application platform. The host interface incorporates several sub-interfaces
described in the following chapters:
· Power supply and charging control (see Chapters 3.2 and 3.3)
· Dual serial interface (see Chapter 3.9)
· Two analog audio interfaces and a digital audio interface (see Chapter 3.10)
· SIM interface (see Chapter 3.11)
Electrical and mechanical characteristics of the board-to-board connector are specified in
Chapter 6.3. Ordering information for mating connectors and cables are included.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 21 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 22
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.1 Operating modes
The table below briefly summarizes the various operating modes referred to in the following
chapters.
Table 3: Overview of operating modes
Mode Function
Normal operation
GSM / GPRS SLEEP Various powersave modes set with AT+CFUN
command.
Software is active to minimum extent. If the module was
registered to the GSM network in IDLE mode, it is
registered and paging with the BTS in SLEEP mode,
too. Power saving can be chosen at different levels: The
NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode (AT+CFUN=0) disables the
AT interface. The CYCLIC SLEEP modes AT+CFUN=5,
6, 7 and 8 alternatingly activate and deactivate the AT
interfaces to allow permanent access to all AT
commands.
GSM IDLE Software is active. Once registered to the GSM network,
paging with BTS is carried out. The module is ready to
send and receive.
GSM TALK Connection between two subscribers is in progress.
Power consumption depends on network coverage
individual settings, such as DTX off/on, FR/EFR/HR,
hopping sequences, antenna.
GPRS IDLE Module is ready for GPRS data transfer, but no data is
currently sent or received. Power consumption depends
on network settings and GPRS configuration (e.g.
multislot settings).
GPRS DATA GPRS data transfer in progress. Power consumption
depends on network settings (e.g. power control level),
uplink / downlink data rates and GPRS configuration
(e.g. used multislot settings).
POWER DOWN Normal shutdown after sending the AT^SMSO command.
The Power Supply ASIC (PSU-ASIC) disconnects the supply voltage from the
baseband part of the circuit. Only a voltage regulator in the PSU-ASIC is active
for powering the RTC. Software is not active. The serial interfaces are not
accessible.
Operating voltage (connected to BATT+) remains applied.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 22 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 23

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Mode Function
Alarm mode Restricted operation launched by RTC alert function while the module is in
POWER DOWN mode. Module will not be registered to GSM network. Limited
number of AT commands is accessible.
If application is battery powered: No charging functionality in Alarm mode.
Charge-only mode Limited operation for battery powered applications. Enables charging while
module is detached from GSM network. Limited number of AT commands is
accessible. There are several ways to launch Charge-only mode:
· From POWER DOWN mode: Connect charger to the charger input pin of the
external charging circuit and the module’s POWER pin when MC46 was
powered down by AT^SMSO.
· From Normal mode: Connect charger to the charger input pin of the external
charging circuit and the module’s POWER pin, then enter AT^SMSO.
Charge mode
during normal
operation
Normal operation (SLEEP, IDLE, TALK, GPRS IDLE, GPRS DATA) and
charging running in parallel. Charge mode changes to Charge-only mode when
the module is powered down before charging has been completed.
See Table 11 and Table 12 for the various options of waking up MC46 and proceeding from one mode
to another.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 23 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 24
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.2 Power supply
The power supply of MC46 has to be a single voltage source of V
= 3.2V...4.5V. It must
BATT+
be able to provide sufficient current in a transmit burst which typically rises to 2A. Beyond
that, the power supply must be able to account for increased current consumption if the
module is exposed to inappropriate conditions, for example antenna mismatch. For further
details see Chapters 3.2.2 and 5.4.1.
All the key functions for supplying power to the device are handled by an ASIC power
supply. The ASIC provides the following features:
· Stabilizes the supply voltages for the GSM baseband using low drop linear voltage
regulators.
· Controls the module's power up and power down procedures.
A watchdog logic implemented in the baseband processor periodically sends signals to
the ASIC, allowing it to maintain the supply voltage for all digital MC46 components.
Whenever the watchdog pulses fail to arrive constantly, the module is turned off.
· Delivers, across the VDD pin, a regulated voltage of 2.9V. The output voltage VDD may
be used to supply, for example, an external LED or a level shifter. However, the external
circuitry must not cause any spikes or glitches on voltage VDD. This voltage is not
available in POWER DOWN mode. Therefore, the VDD pin can be used to indicate
whether or not MC46 is in POWER DOWN mode.
· Provides power to the SIM interface.
The RF power amplifier is driven directly from BATT+.
3.2.1 Power supply pins on the board-to-board connector
Five BATT+ pins of the board-to-board connector are dedicated to connect the supply
voltage, five GND pins are recommended for grounding. The values stated below must be
measured directly at the reference points on the MC46 board (TP BATT+ and TP GND
illustrated in Figure 40).
The POWER and CHARGE pins serve as control signals for charging a Li-Ion battery.
VDDLP can be used to back up the RTC.
Table 4: Power supply pins of board-to-board connector
Signal name I/O Description Parameter
BATT+ I/O Positive operating voltage
Reference points are the
test points
GND - Ground 0 V
POWER I This line signalizes to the
processor that the charger
is connected.
CHARGE O Control signal for external
charging transistor
VDDLP I/O Can be used to back up the
RTC when V
applied.
See Chapter 3.8
BATT+
is not
3.2 V...4.5 V, I
The minimum operating voltage must not fall
below 3.2 V, not even in case of voltage drop.
U
UIN = 2.0 V...5.5 V
Ri = 1kW
I
in,max
OUT,max
= 30µA
< V
£ 2 A during transmit burst
typ
BATT+
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 24 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 25
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
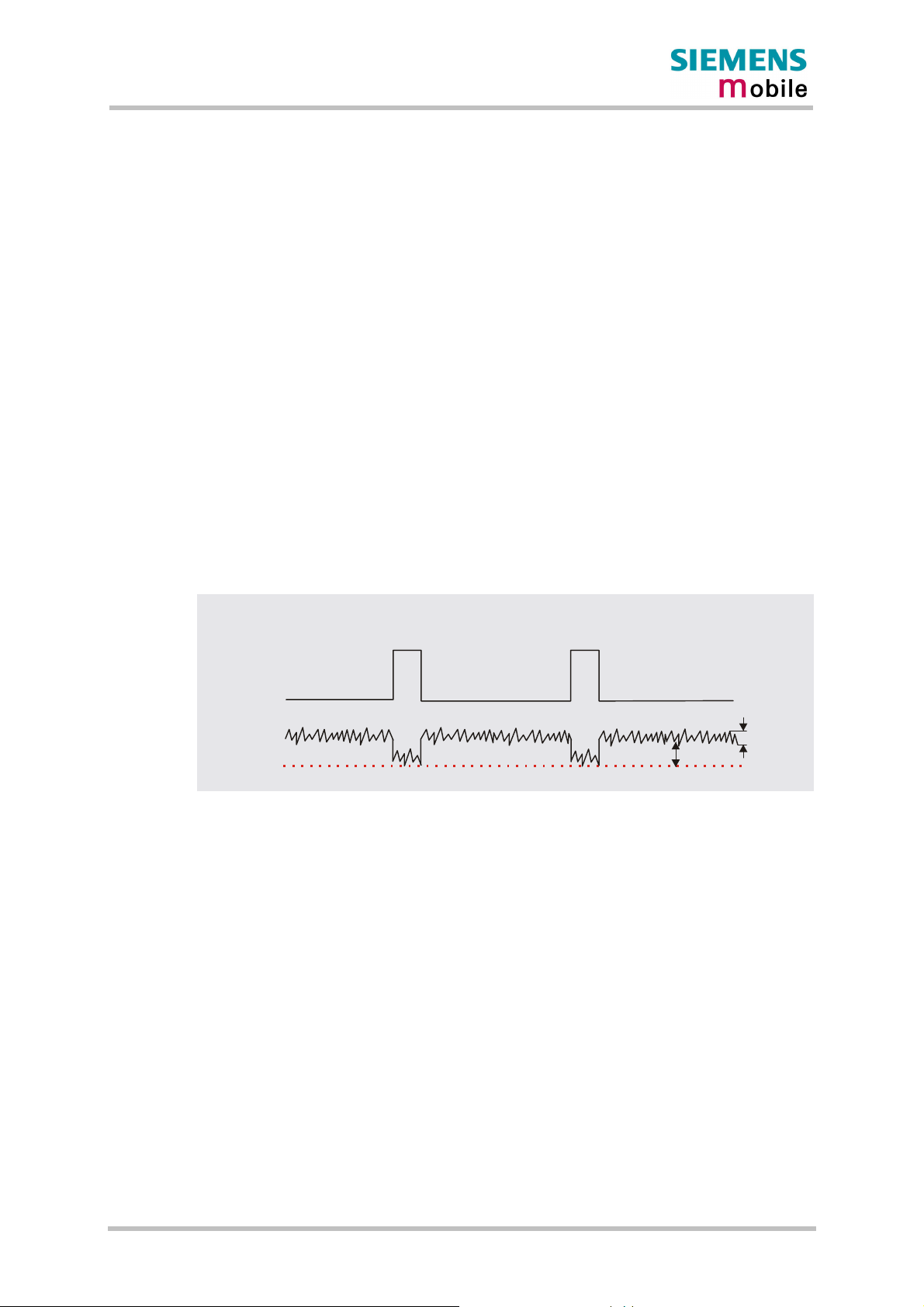
3.2.2 Minimizing power losses
When designing the power supply for your application please pay specific attention to power
losses. Ensure that the input voltage V
even in a transmit burst where current consumption can rise to typical peaks of 2A. It should
be noted that MC46 switches off when exceeding these limits. Any voltage drops that may
occur in a transmit burst should not exceed 400mV. For further details see Chapter 5.4.
The best approach to reducing voltage drops is to use a board-to-board connection as
recommended, and a low impedance power source. The resistance of the power supply lines
on the host board and of a battery pack should also be considered.
Note: If the application design requires an adapter cable between both board-to-board
connectors, use a flex cable as short as possible in order to minimize power
losses.
Example: If the length of the flex cable reaches the maximum length of 200mm, this
connection may cause, for example, a resistance of 50m! in the BATT+ line and
50m! in the GND line. As a result, a 2A transmit burst would add up to a total
voltage drop of 200mV. Plus, if a battery pack is involved, further losses may
occur due to the resistance across the battery lines and the internal resistance of
the battery.
Transmit
burst 2A
BATT+
min. 3.2V
never drops below 3.2 V on the MC46 board, not
BATT+
Transmit
burst 2A
Drop
Ripple
Figure 2: Power supply limits during transmit burst
The input voltage V
must be measured directly at the test points on the MC46 board (TP
BATT+
BATT+ and TP GND illustrated in Figure 40).
3.2.3 Monitoring power supply
To help you monitor the supply voltage you can use the AT^SBV command which returns the
voltage measured at TP BATT+ and GND.
The voltage is continuously measured at intervals depending on the operating mode on the
RF interface. The duration of measuring ranges from 0.5s in TALK/DATA mode to 50s when
MC46 is deregistered. The displayed voltage (in mV) is averaged over the last measuring
period before the AT^SBV command was executed.
For details please refer to [1].
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 25 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 26

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.3 Power up / down scenarios
In general, be sure not to turn on MC46 while it is out of the operating range of voltage and
temperature stated in Chapters 5.2 and 5.3. MC46 would immediately switch off after having
started and detected these inappropriate conditions.
3.3.1 Turn on MC46
MC46 can be activated in a variety of ways, which are described in the following chapters:
· via ignition line /IGT: starts normal operating state (see Chapters 3.3.1.1 and 3.3.1.2)
· via POWER line: starts charging algorithm (see Chapters 3.5.3 and 3.3.1.3)
· via RTC interrupt: starts Alarm mode (see Chapter 3.3.1.4)
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 26 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 27
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
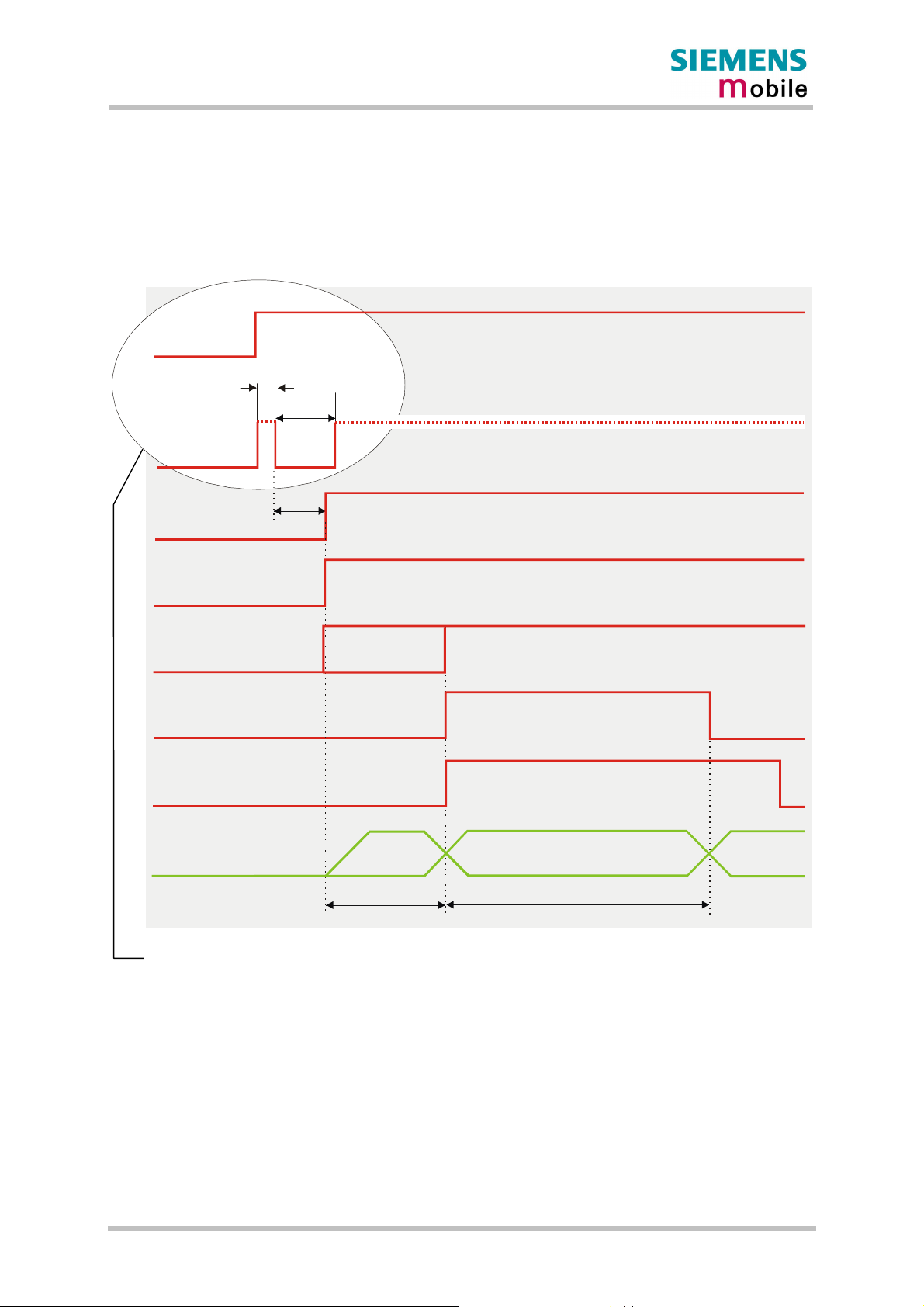
3.3.1.1 Turn on MC46 using the ignition line /IGT (Power on)
To switch on MC46 the /IGT (Ignition) signal needs to be driven to ground level for at least
100ms and not earlier than 10ms after the last falling edge of VDD. This can be
accomplished using an open drain/collector driver in order to avoid current flowing into this
pin.
BATT+
min. 10ms
min.
/IGT
HiZ
ca. 60ms
100ms
HiZ
VDD
/TXD0
/TXD1
/DSR0
/EMERGOFF
Serial interfaces
ASC0 and ASC1
For details please see Chapter 3.3.1.2
Software
controlled
Undefined
ca. 300ms ca. 900ms
Inactive
Active
Figure 3: Power-on by ignition signal
If configured to a fix baud rate, MC46 will send the result code ^SYSSTART to indicate that it
is ready to operate. This result code does not appear when autobauding is active. See
Chapter AT+IPR in [1].
In a battery operated MC46 application, the duration of the /IGT signal must be 1s minimum
when the charger is connected and you may want to go from charging to Normal mode.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 27 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 28
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.3.1.2 Timing of the ignition process
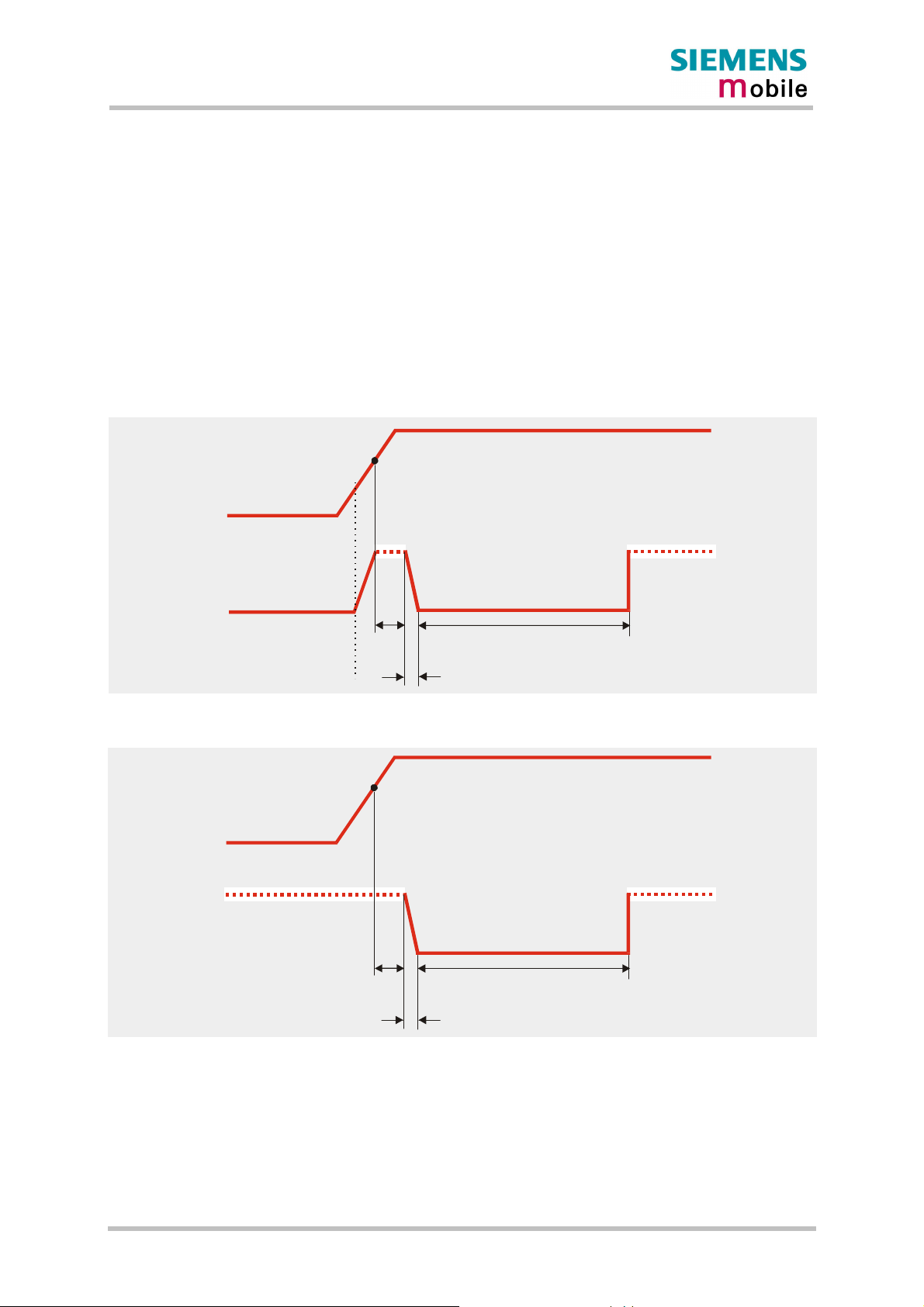
When designing your application platform take into account that powering up MC46 requires
the following steps.
· The ignition line cannot be operated until V
· The ignition line shall not be operated earlier than 10ms after the last falling edge of VDD.
· 10ms after V
has reached 3.0V the ignition line can be switched low. The duration of
BATT+
the falling edge must not exceed 1ms.
· Another 100ms are required to power up the module.
· Ensure that V
does not fall below 3.0V while the ignition line is driven. Otherwise the
BATT+
module cannot be activated.
· If the VDDLP line is fed from an external power supply as explained in Chapter 3.8, the
/IGT line is HiZ before the rising edge of BATT+.
3.0V
passes the level of 3.0V.
BATT+
BATT+
/IGT
BATT+
/IGT
0V
HiZ
10ms
min. 100ms
max. 1ms
Figure 4: Timing of power-on process if VDDLP is not used
3.0V
0V
HiZ
HiZ
HiZ
10ms
min. 100ms
max. 1ms
Figure 5: Timing of power-on process if VDDLP is fed from external source
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 28 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 29

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.3.1.3 Turn on MC46 using the POWER signal
As detailed in Chapter 3.5.3, the charging adapter can be connected regardless of the
module’s operating mode (except for Alarm mode).
If the charger is connected to the charger input of the external charging circuit and the
module’s POWER pin while MC46 is off, processor controlled fast charging starts (see
Chapter 3.5.2). MC46 enters a restricted mode, referred to as Charge-only mode where only
the charging algorithm will be launched.
During the Charge-only mode MC46 is neither logged on to the GSM network nor are the
serial interfaces fully accessible. To switch to normal operation and log on to the GSM
network, the /IGT line needs to be activated.
3.3.1.4 Turn on MC46 using the RTC (Alarm mode)
Another power-on approach is to use the RTC, which is constantly supplied with power from
a separate voltage regulator in the power supply ASIC. The RTC provides an alert function
which allows to wake up MC46 while power is off. To prevent the engine from unintentionally
logging into the GSM network, this procedure only enables restricted operation, referred to
as Alarm mode. It must not be confused with a wake-up or alarm call that can be activated
by using the same AT command, but without switching off power.
Use the AT+CALA command to set the alarm time. The RTC retains the alarm time if MC46
was powered down by AT^SMSO. Once the alarm is timed out and executed, MC46 enters
into the Alarm mode. This is indicated by an Unsolicited Result Code (URC) which reads:
^SYSSTART ALARM MODE
Note that this URC is the only indication of the Alarm mode and will not appear when
autobauding was activated (due to the missing synchronization between DTE and DCE upon
start-up). Therefore, it is recommended to select a fixed baudrate before using the Alarm
mode. In Alarm mode only a limited number of AT commands is available. For further
instructions refer to the AT Command Set.
Table 5: AT commands available in Alarm mode
AT command Use
AT+CALA Set alarm time
AT+CCLK Set date and time of RTC
AT^SBC In Alarm mode, you can only query the present current consumption and check
whether or not a charger is connected. The battery capacity is returned as 0,
regardless of the actual voltage (since the values measured directly on the cell are
not delivered to the module).
AT^SCTM Query temperature range, enable/disable URCs to report critical temperature ranges
AT^SMSO Power down GSM engine
For the GSM engine to change from the Alarm mode to full operation (normal operating
mode) it is necessary to drive the ignition line to ground. This must be implemented in your
host application as described in Chapter 3.3.1.1.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 29 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 30

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
If your application is battery powered note that charging cannot be started while the engine
is in Alarm mode, i.e. charging will not begin even though the charger connects to the
charger input of the external charging circuit and the module’s POWER pin. See also
Chapter 3.7 which summarizes the various options of changing the mode of operation.
If your host application uses the SYNC pin to control a status LED as described in Chapter
3.12.2.2, please note that the LED is off while the GSM engine is in Alarm mode.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 30 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 31

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.3.2 Turn off MC46
To switch the module off the following procedures may be used:
· Normal shutdown procedure: Software controlled by sending the AT^SMSO command
over the serial application interface. See Chapter 3.3.2.1.
· Emergency shutdown: Hardware driven by switching the /EMERGOFF line of the board-
to-board-connector to ground = immediate shutdown of supply voltages, only applicable
if the software controlled procedure fails! See Chapter 3.3.2.3.
· Automatic shutdown: See Chapter 3.3.3
a) Takes effect if undervoltage is detected.
b) Takes effect if MC46 board temperature exceeds critical limit.
3.3.2.1 Turn off MC46 using AT command
The best and safest approach to powering down MC46 is to issue the AT^SMSO command.
This procedure lets MC46 log off from the network and allows the software to enter into a
secure state and safe data before disconnecting the power supply. The mode is referred to
as POWER DOWN mode. In this mode, only the RTC stays active.
Before switching off the device sends the following response:
^SMSO: MS OFF
OK
^SHUTDOWN
After sending AT^SMSO do not enter any other AT commands. There are two ways to verify
when the module turns off:
· Wait for the URC “^SHUTDOWN”. It indicates that all important data have been stored to
the Flash and that the complete system turns off in less than 1 second.
· Also, you can monitor the VDD pin. The low state of VDD definitely indicates that the
module is switched off.
Be sure not to disconnect the operating voltage V
before the URC “^SHUTDOWN” has
BATT+
been issued or the VDD signal has gone low. Otherwise you run the risk of losing data.
While MC46 is in POWER DOWN mode the application interface is switched off and must
not be fed from any other source. Therefore, your application must be designed to avoid any
current flow into any digital pins of the application interface.
Note: In POWER DOWN mode, the /EMERGOFF pin, the output pins of the ASC0 interface
/RXD0, /CTS0, /DCD0, /DSR0, /RING0 and the output pins of the ASC1 interface
/RXD1 and /CTS1 are switched to high impedance state.
If this causes the associated input pins of your application to float, you are advised to
integrate an additional resistor (100 kOhms – 1 MOhm) at each line. In the case of the
/EMERGOFF pin use a pull-down resistor tied to GND. In the case of the serial
interface pins you can either connect pull-up resistors to the VDD line, or pull-down
resistors to GND.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 31 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 32

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
r
r
f
DRAFT
3.3.2.2 Maximum number of turn-on / turn-off cycles
Each time the module is shut down, data will be written from volatile memory to flash
memory. The guaranteed maximum number of write cycles is limited to 100.000.
3.3.2.3 Emergency shutdown using /EMERGOFF pin
Caution: Use the /EMERGOFF pin only when, due to serious problems, the software is
not responding for more than 5 seconds. Pulling the /EMERGOFF pin causes
the loss of all information stored in the volatile memory since power is cut off
immediately. Therefore, this procedure is intended only for use in case of
emergency, e.g. if the host controller experienced a watchdog reset and
afterwards MC46 fails to shut down properly or fails to respond.
The /EMERGOFF signal is available on the board-to-board connector. To control the
/EMERGOFF line it is recommended to use an open drain / collector driver. To turn the GSM
engine off, the /EMERGOFF line has to be driven to ground for ³ 3.2s.
BATT+
/IGT
VDD
Internal reset
/EMERGOFF
Controlled by MC46 software
Figure 6: Deactivating GSM engine by /EMERGOFF signal
max. 3.2s
Controlled by external application
How does it work:
· Voltage V
is permanently
batt+
applied to the module.
· The module is active while the
internal reset signal is kept at
high level.
During operation of MC46 the
baseband controller generates
watchdog pulses at regula
intervals.
Once the EMERGOFF pin is
grounded these watchdog
pulses are cut off from the
power supply ASIC. The powe
supply ASIC shuts down the
internal supply voltages o
MC46 after max. 3.2s and the
module turns off.
Consequently, the output
voltage at VDD is switched off.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 32 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 33

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.3.3 Automatic shutdown
Automatic shutdown takes effect if
· the MC46 board is exceeding the critical limits of overtemperature or undertemperature
· the battery is exceeding the critical limits of overtemperature or undertemperature
· undervoltage is detected
The automatic shutdown procedure is equivalent to the power-down initiated with the
AT^SMSO command, i.e. MC46 logs off from the network and the software enters a secure
state avoiding loss of data. NOTE: This is not true for overvoltage conditions, and if an
unrecoverable hardware or software error occurs, see below for details
Alert messages transmitted before the device switches off are implemented as Unsolicited
Result Codes (URCs). The presentation of these URCs can be enabled or disabled with the
two AT commands AT^SBC and AT^SCTM. The URC presentation mode varies with the
condition, please see Chapters 3.3.3.1 to 3.3.3.4 for details. For further instructions on AT
commands refer to [1].
3.3.3.1 Temperature dependent shutdown
The board temperature is constantly monitored by an internal NTC resistor located on the
PCB. The NTC that detects the battery temperature must be part of the battery pack circuit
as described in Chapter 3.5. The values detected by either NTC resistor are measured
directly on the board or the battery and therefore, are not fully identical with the ambient
temperature.
Each time the board or battery temperature goes out of range or back to normal, MC46
instantly displays an alert (if enabled).
· URCs indicating the level "1" or "-1" allow the user to take appropriate precautions, such
as protecting the module from exposure to extreme conditions. The presentation of the
URCs depends on the settings selected with the AT^SCTM write command:
AT^SCTM=1: Presentation of URCs is always enabled.
AT^SCTM=0 (default): Presentation of URCs is enabled for 15 seconds time after
start-up of MC46. After 15 seconds operation, the presentation will be disabled, i.e.
no alert messages can be generated.
· URCs indicating the level "2" or "-2" are instantly followed by an orderly shutdown. The
presentation of these URCs is always enabled, i.e. they will be output even though the
factory setting AT^SCTM=0 was never changed.
The maximum temperature ratings are stated in Table 26. Refer to Table 6 for the
associated URCs. All statements are based on test conditions according to IEC 60068-2-2
(still air).
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 33 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 34

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 6: Temperature dependent behavior
Sending temperature alert (15 s after start-up, otherwise only if URC presentation enabled)
^SCTM_A: 1 Caution: T
^SCTM_B: 1 Caution: T
^SCTM_A: -1 Caution: T
^SCTM_B: -1 Caution: T
^SCTM_A: 0 Battery back to uncritical temperature range.
^SCTM_B: 0 Board back to uncritical temperature range.
Automatic shutdown (URC appears no matter whether or not presentation was enabled)
^SCTM_A: 2 Alert: T
^SCTM_B: 2 Alert: T
^SCTM_A: -2 Alert: T
^SCTM_B: -2 Alert: T
of battery close to overtemperature limit.
amb
of board close to overtemperature limit.
amb
of battery close to undertemperature limit.
amb
of board close to undertemperature limit.
amb
of battery equal or beyond overtemperature limit. MC46 switches off.
amb
of board equal or beyond overtemperature limit. MC46 switches off.
amb
of battery equal or below undertemperature limit. MC46 switches off.
amb
of board equal or below undertemperature limit. MC46 switches off.
amb
3.3.3.2 Temperature control during emergency call
If the temperature limit is exceeded while an emergency call is in progress the engine
continues to measure the temperature and to deliver alert messages, but deactivates the
shutdown functionality.
Once the call is terminated the temperature control will be resumed. If the temperature is still
out of range MC46 switches off immediately.
3.3.3.3 Undervoltage shutdown if battery NTC is present
In applications where the module’s charging technique is used and an NTC is connected to
the BATT_TEMP terminal, the software constantly monitors the applied voltage. If the
measured battery voltage is no more sufficient to set up a call the following URC will be
presented:
^SBC: Undervoltage.
The message will be reported, for example, when you attempt to make a call while the
voltage is close to the critical limit and further power loss is caused during the transmit burst.
To remind you that the battery needs to be charged soon, the URC appears several times
before the module switches off.
To enable or disable the URC use the AT^SBC command. The URC will be enabled when
you enter the write command and specify the power consumption of your GSM application.
Step by step instructions are provided in [1].
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 34 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 35

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.3.3.4 Undervoltage shutdown if no battery NTC is present
The undervoltage protection is also effective in applications, where no NTC connects to the
BATT_TEMP terminal. Thus, you can take advantage of this feature even though the
application handles the charging process or MC46 is fed by a fixed supply voltage. All you
need to do is executing the write command AT^SBC=<current> which automatically enables
the presentation of URCs. You do not need to specify <current>.
Whenever the supply voltage falls below the specified value (see Table 28) the URC
^SBC: Undervoltage
appears several times before the module switches off.
3.3.3.5 Overvoltage shutdown
If the supply voltage raises to V
>5.8V, or an unrecoverable hardware or software error
BATT+
occurs, the PSU-ASIC immediately cuts off the power supply to all components it is
connected to. In contrast to undervoltage shutdown, loss of data cannot be avoided.
Furthermore, there is no URC function available for overvoltage conditions, i.e. no alert will
be sent prior to shutdown.
Keep in mind that several MC46 components are directly linked to BATT+ and, therefore,
power remains applied at major parts of MC46. Particular attention must be paid to the
power amplifier which is very sensitive to high voltage and might even be destroyed.
Generally, to avoid that the MC46 application violates GSM specifications, be sure that the
supply voltage does not exceed the maximum value of 4.5V stated in Table 28.
3.4 Automatic GPRS Multislot Class change
XC18 features an integrated temperature control for GPRS multislot operation. If the board
temperature increases to the limit specified for restricted operation
transmitted over GPRS, it is likely that the module automatically reverts to a lower GPRS
Multislot Class, for example from Class 10 (2 Tx) to Class 8 (1Tx). This reduces the current
consumption and, consequently, causes the board’s temperature to decrease. Once the
temperature drops to a value of 5 degrees below the limit of restricted operation, XC18
returns to the higher Multislot Class. If the temperature stays at the critical level or even
continues to rise, XC18 will not switch back to the higher class.
If the temperature rises and drops in a rapid succession within less than a minute, the
transition from one Multislot Class to another takes at least one minute.
Please note that there is not one single cause of switching over to a lower GPRS Multislot
Class. Rather it is the result of an interaction of several factors, such as the board
temperature that depends largely on the ambient temperature, the operating mode and the
transmit power.
1)
See Table 26 for temperature limits known as restricted operation.
1)
while data are
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 35 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 36
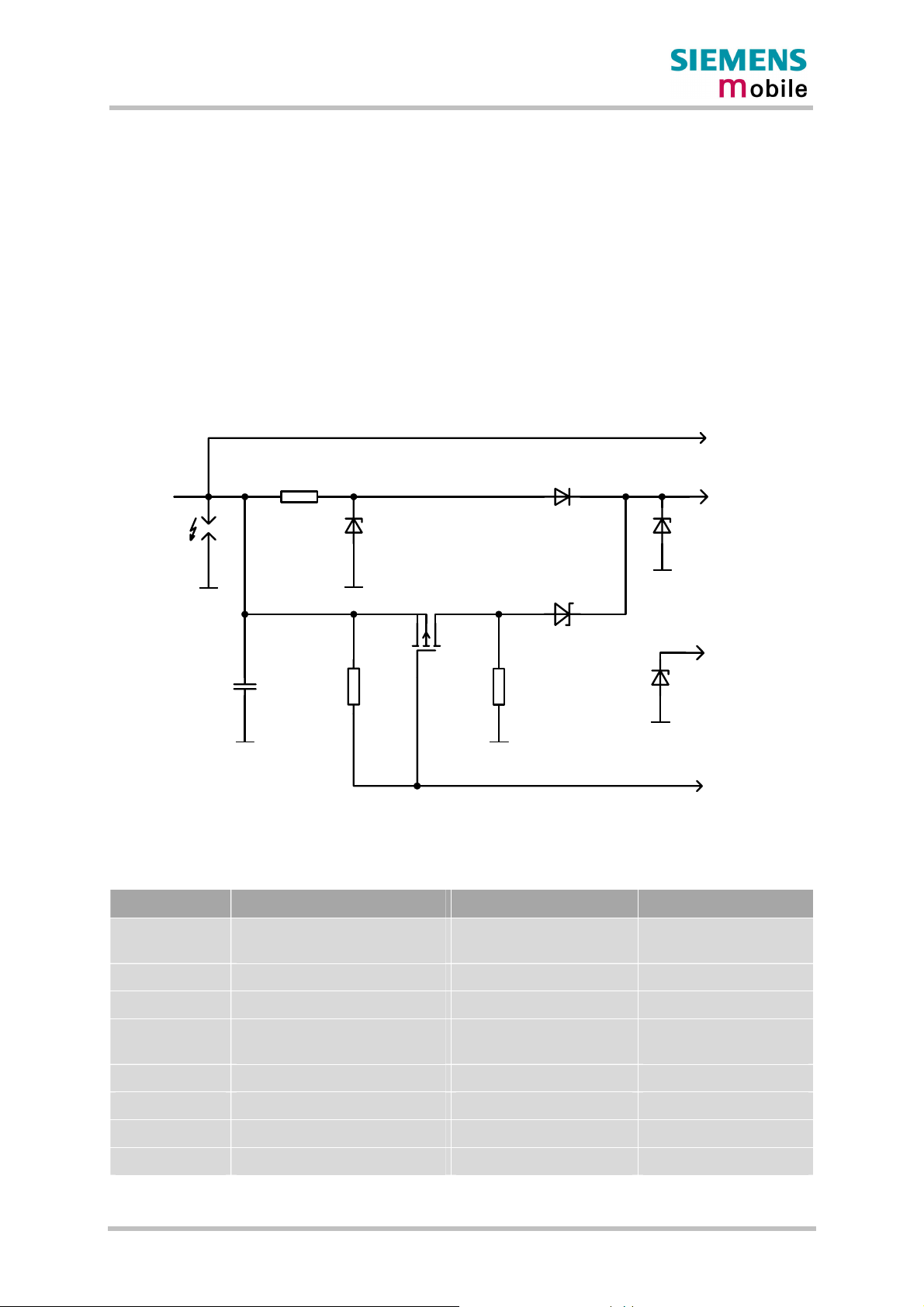
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.5 Charging control
MC46 integrates a charging management for Li-Ion batteries. You can skip this chapter if
charging is not your concern, or if you are not using the implemented charging algorithm.
MC46 has no on-board charging circuit. To benefit from the implemented charging
management you are required to install a charging circuit within your application. In this
case, MC46 needs to be powered from a Li-Ion battery pack, e.g. as specified in Table 8.
The module only delivers, via its POWER line and CHARGE line, the control signals needed
to start and stop the charging process. The charging circuit should include a transistor and
should be designed as illustrated in Figure 7. A list of parts recommended for the external
circuit is given in Table 7.
Input from
charger
(5.5V - 8V)
under load
470R
1SS355
to POWER
to BATT+
pcb spark
gap
4V3
SI3441DV
CRS04
1
/5 ESDA6V1-5W6
BATT_TEMP
100nF 10k
3k3
1
/5 ESDA6V1-5W6
CHARGE
Figure 7: Schematic of approved charging transistor, trickle charging and ESD protection
Table 7: Bill of material for external charging circuit
Part Description First supplier Second supplier
SI3441DV
1SS355 100mA Si-diode (UMD2) ROHM: 1SS355TE-18 Toshiba: 1SS352TPH3
p-chan 2.5V (G-S) MOSFET
(TSOP-6)
VISHAY: SI3441DV-T1 NEC: UPA1911TE-T1
CRS04 1A Shottky diode Toshiba: CRS04 -
4V3
250mW; 200mA;
4.3V Z-Diode (SOD323)
Philips: PDZ4.3B
ROHM: UDZS4.3B
UDZ4.3B
ESDA6V1-5W6 ESD protection transil array STM: ESDA6V1-5W6 -
470R, 3k3, 10k Resistor, e.g. 0805 or 0603 - -
100nF Ceramic capacitor 50V - -
PCB spark gap 0.2mm spark gap on PCB - -
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 36 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 37
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.5.1 Battery pack characteristics
The charging algorithm has been optimized for a Li-Ion battery pack that meets the
characteristics listed below. It is recommended that the battery pack you want to integrate
into your MC46 application is compliant with these specifications. This ensures reliable
operation, proper charging and, particularly, allows you to monitor the battery capacity using
the AT^SBC command (see [1] for details). Failure to comply with these specifications might
cause AT^SBC to deliver incorrect battery capacity values. A battery pack especially
designed to operate with MC46 modules is specified in Chapter 3.5.1.1.
· Li-Ion battery pack specified for a maximum charging voltage of 4.2 V and a capacity of
800 mAh. Battery packs with a capacity down to 600 mAh or more than 800 mAh are
allowed, too.
· Since charging and discharging largely depend on the battery temperature, the battery
pack should include an NTC resistor. If the NTC is not inside the battery it must be in
thermal contact with the battery. The NTC resistor must be connected between
BATT_TEMP and GND. Required NTC characteristics are: 10 kΩ +
3435K +
3% (alternatively acceptable: 10 kΩ +2% @ 25°C, B
25/50
5% @ 25°C, B
= 3370K +3%). Please
note that the NTC is indispensable for proper charging, i.e. the charging process will not
start if no NTC is present.
· Ensure that the pack incorporates a protection circuit capable of detecting overvoltage
(protection against overcharging), undervoltage (protection against deep discharging)
and overcurrent. The circuit must be insensitive to pulsed current.
· On the MC46 module, a built-in measuring circuit constantly monitors the supply voltage.
In the event of undervoltage, it causes MC46 to power down. Undervoltage thresholds
are specific to the battery pack and must be evaluated for the intended model. When you
evaluate undervoltage thresholds, consider both the current consumption of MC46 and
the application circuit.
· The internal resistance of the battery and the protection should be as low as possible. It
is recommended not to exceed 150m", even in extreme conditions at low temperature.
The battery cell must be insensitive to rupture, fire and gasing under extreme conditions
of temperature and charging (voltage, current).
· The battery pack must be protected from reverse pole connection. For example, the
casing should be designed to prevent the user from mounting the battery in reverse
orientation.
· The battery pack must be approved to satisfy the requirements of CE conformity.
Figure 8 shows the circuit diagram of a typical
to BATT+
to BATT_TEMP to GND
battery pack design that includes the
protection elements described above.
J
25/85
=
of
NTC
Protection Circuit
-
+
Figure 8: Battery pack circuit diagram
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 37 of 98 21.08.2003
Battery cell
Polyfuse
Page 38

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.5.1.1 Recommended battery pack
The following battery pack has been especially designed for use with MC46 modules.
Table 8: Specifications of XWODA battery pack
Product name, type XWODA, Li-Ion, 3.6V, 800mAh
Vendor
To place orders or obtain more
information please contact:
Shenzhen Xwoda Electronic Co., Ltd
Building C, Tongfukang Industrial Zone
Shiyan Town, Bao’an District
Shenzen
P.R.China
Contact:
Waichard Tsui
Phone: +86-755-27623789 ext. 370
Fax: +86-755-27623078
Email: waichard@xwoda.com.cn
Nominal voltage 3.6V
Capacity 800mAh
NTC 10k" ± 5% @ 25°C, B (25/85)=3435K ± 3%
Overcharge detection voltage 4.325 ± 0.025V
Overcharge release voltage 4.075 ± 0.025V
Overdischarge detection voltage 2.5 ± 0.05V
Overdischarge release voltage 2.9 ± 0.5V
Overcurrent detection 3 ± 0.5A
Nominal working current <5µA
Current of low voltage detection 0.5µA
Overcurrent detection delay time 8~16ms
Short detection delay time 50µs
Overdischarge detection delay time 31~125ms
Overcharge detection delay time 1s
Internal resistance <130m"
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 38 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 39

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.5.2 Implemented charging technique
If the external charging circuit follows the recommendation of Figure 7, the charging process
consists of trickle charging and processor controlled fast charging. For this solution, the fast
charging current provided by the charger or any other external source must be limited to
500mA.
Trickle charging
· Trickle charging starts when the charger is connected to the charger input of the external
charging circuit and the module’s POWER pin. The charging current depends on the
voltage difference between the charger input of the external charging circuit and BATT+
of the module.
· Trickle charging stops when the battery voltage reaches 3.6V.
Fast charging
· After trickle charging has raised the battery voltage to 3.2V within 60 minutes +
connecting the charger, the power ASIC turns on and wakes up the baseband processor.
Now, processor controlled fast charging begins.
If the battery voltage was already above 3.2V, processor controlled fast charging starts
just after the charger was connected to the charger input of the external charging circuit
and the module’s POWER pin. If MC46 was in POWER DOWN mode, it turns on and
enters the Charge-only mode along with fast charging (see also Chapter 3.3.1.3).
· Fast charging delivers a constant current until the battery voltage reaches 4.2V and then
proceeds with varying charge pulses. As shown in Figure 5, the pulse duty cycle is
reduced to adjust the charging procedure and prevent the voltage from overshooting
beyond 4.2V. Once the pulse width reaches the minimum of 100ms and the duty cycle
does not change for 2 minutes, fast charging is completed.
· Fast charging can only be accomplished in a temperature range from 0°C to +45°C.
Voltage
10% from
4.3
4.2
3.8
3.4
3.0
Constant current
100ms 2 ... 0.1s
t
= 100 ms
OFF
100ms 0.1 ... 2s
t
= 100 ms
ON
Time
Figure 9: Charging process
Note: Do not connect the charger to the BATT+ lines. Only the charger input of the
external charging circuit is intended as input for charging current! The POWER pin
of MC46 is the input only for indicating a connected charger!
The battery manufacturer must guarantee that the battery complies with the
described charging technique.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 39 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 40

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
What to do if software controlled charging does not start up?
If trickle charging fails to raise the battery voltage to 3.2V within 60 minutes +
10%, processor
controlled charging does not begin. To start fast charging you can do one of the following:
· Once the voltage has risen above its minimum of 3V, you can try to start software
controlled charging by pulling the /IGT line to ground.
· If the voltage is still below 3V, driving the /IGT line to ground switches the timer off.
Without the timer running, MC46 will not proceed to software controlled charging. To
restart the timer you are required to shortly disconnect and reconnect the charger.
3.5.3 Operating modes during charging
Of course, the battery can be charged regardless of the engine's operating mode. When the
GSM engine is in Normal mode (SLEEP, IDLE, TALK, GPRS IDLE or GPRS DATA mode), it
remains operational while charging is in progress (provided that sufficient voltage is applied).
The charging process during the Normal mode is referred to as Charge mode.
If the charger is connected to the charger input of the external charging circuit and the
module’s POWER pin while MC46 is in POWER DOWN mode, MC46 goes into Charge-only
mode.
Table 9: Comparison Charge-only and Charge mode
How to activate mode Features
Connect charger to charger input of
external charging circuit and module’s
POWER pin while MC46 is
· operating, e.g. in IDLE or TALK mode
· in SLEEP mode
Charge mode
Connect charger to charger input of
external charging circuit and module’s
POWER pin while MC46 is
· in POWER DOWN mode
· in Normal mode: Connect charger to
the POWER pin, then enter
AT^SMSO.
IMPORTANT: While trickle charging is in
progress, be sure that the application is
switched off. If the application is fed from
Charge-only mode
the trickle charge current the module
might be prevented from proceeding to
software controlled charging since the
current would not be sufficient.
· Battery can be charged while GSM engine
remains operational and registered to the
GSM network.
· In IDLE and TALK mode, the serial interfaces
are accessible. AT command set can be used
to full extent.
· In the NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode, the serial
interfaces are not accessible at all. During the
CYCLIC SLEEP mode it can be used as
described in Chapter 3.6.3.
· Battery can be charged while GSM engine is
deregistered from GSM network.
· Charging runs smoothly due to constant
current consumption.
· The AT interface is accessible and allows to
use the commands listed below.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 40 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 41

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Features of Charge-only mode
Once the GSM engine enters the Charge-only mode, the AT command interface presents an
Unsolicited Result Code (URC) which reads:
^SYSSTART CHARGE-ONLY MODE
Note that this URC will not appear when autobauding was activated (due to the missing
synchronization between DTE and DCE upon start-up). Therefore, it is recommended to
select a fixed baudrate before using the Charge-only mode.
While the Charge-only mode is in progress, you can only use the AT commands listed in
Table 10. For further instructions refer to the AT Command Set supplied with your GSM
engine.
Table 10: AT commands available in Charge-only mode
AT command Use
AT+CALA Set alarm time
AT+CCLK Set date and time of RTC
AT^SBC Monitor charging process
Note: While charging is in progress, no battery capacity value is available. To query
the battery capacity disconnect the charger.
If the charger connects externally to the host device no charging parameters are
transferred to the module. In this case, the command cannot be used.
AT^SCTM Query temperature range, enable/disable URCs to report critical temperature ranges
AT^SMSO Power down GSM engine
To proceed from Charge-only mode to normal operation, it is necessary to drive the ignition
line to ground. This must be implemented in your host application as described in Chapter
3.3.1.1. When the engine is in Alarm mode there is no direct way to start charging, i.e.
charging will not begin even though the charger connects to the charger input of the external
charging circuit and the module’s POWER pin. See also Chapter 3.7 which summarizes the
various options of changing the mode of operation.
If your host application uses the SYNC pin to control a status LED as described in Chapter
3.12.2.2, please note that the LED is off while the GSM engine is in Charge-only mode.
3.5.4 Charger requirements
If you are using the implemented charging technique and the charging circuit recommended
in Figure 7, the charger must be designed to meet the following requirements:
a) Simple transformer power plug
- Output voltage: 5.5V...8V (under load)
- The charge current must be limited to 500mA
- Voltage spikes that may occur while you connect or disconnect the charger must be
limited.
- There must not be any capacitor on the secondary side of the power plug (avoidance of
current spikes at the beginning of charging)
b) Supplementary requirements for a) to ensure a regulated power supply
- When current is switched off a voltage peak of 10V is allowed for a maximum 1ms
- When current is switched on a spike of 1.6A for 1ms is allowed
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 41 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 42

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.6 Power saving
SLEEP mode reduces the functionality of the MC46 module to a minimum and, thus,
minimizes the current consumption to the lowest level. SLEEP mode is set with the
AT+CFUN command which provides the choice of the functionality levels <fun>=0, 1, 5, 6, 7
or 8, all explained below. Further instructions of how to use AT+CFUN can be found in [1].
IMPORTANT: The AT+CFUN command can be executed before or after entering PIN1.
Nevertheless, please keep in mind that power saving works properly only while the module is
registered to the GSM network. If you attempt to activate power saving while the module is
detached, the selected <fun> level will be set, though power saving does not take effect.
To check whether power saving is on, you can query the status of AT+CFUN if you have
chosen CYCLIC SLEEP mode. If available, you can take advantage of the status LED
controlled by the SYNC pin (see Chapter 3.12.2.2). The LED stops flashing once the module
starts power saving.
The wake-up procedures are quite different depending on the selected SLEEP mode. Table
11 compares the wake-up events that can occur in NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode and in the
four CYCLIC SLEEP modes.
3.6.1 No power saving (AT+CFUN=1)
The functionality level <fun>=1 is where power saving is switched off. This is the default after
startup.
3.6.2 NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode (AT+CFUN=0)
If level 0 has been selected (AT+CFUN=0), the serial interface is blocked. The module
shortly deactivates power saving to listen to a paging message sent from the base station
and then immediately resumes power saving. Level 0 is called NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode,
since the serial interface is not alternatingly made accessible as in CYCLIC SLEEP mode.
The first wake-up event fully activates the module, enables the serial interface and
terminates the power saving mode. In short, it takes MC46 back to the highest level of
functionality <fun>=1.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 42 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 43

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.6.3 CYCLIC SLEEP mode (AT+CFUN=5, 6, 7 and 8)
The functionality levels AT+CFUN=5, AT+CFUN=6, AT+CFUN=7 and AT+CFUN=8 are
referred to as CYCLIC SLEEP modes. The major benefit over the NON-CYCLIC SLEEP
mode is that the serial interface is not permanently blocked and that packet switched calls
may go on without terminating the selected CYCLIC SLEEP mode. This allows MC46 to
become active, for example to perform a GPRS data transfer, and to resume power saving
after the GPRS data transfer is completed.
The four CYCLIC SLEEP modes give you greater flexibility regarding the wake-up
procedures: For example, in all CYCLIC SLEEP modes, you can enter AT+CFUN=1 to
permanently wake up the module. The best choice is using CFUN=7 or 8, since in these
modes MC46 automatically resumes power saving, after you have sent or received a short
message or made a call. CFUN=5 and 6 do not offer this feature, and therefore, are only
supported for compatibility with earlier releases. Please refer to Table 11 for a summary of
all modes.
The CYCLIC SLEEP mode is a dynamic process which alternatingly enables and disables
the serial interface. By setting/resetting the /CTS signal, the module indicates to the
application whether or not the UART is active. The timing of the /CTS signal is described
below.
Both the application and the module must be configured to use hardware flow control
(RTS/CTS handshake). The default setting of MC46 is AT\Q0 (no flow control) which must
be altered to AT\Q3. See [1] for details.
Note: If both serial interfaces ASC0 and ASC1 are connected, both are synchronized. This
means that SLEEP mode takes effect on both, no matter on which interface the AT
command was issued. Although not explicitly stated, all explanations given in this
chapter refer equally to ASC0 and ASC1, and accordingly to /CTS0 and /CTS1.
3.6.4 Timing of the /CTS signal in CYCLIC SLEEP modes
The /CTS signal is enabled in synchrony with the module’s paging cycle. It goes active low
each time when the module starts listening to a paging message block from the base station.
The timing of the paging cycle varies with the base station. The duration of a paging interval
can be calculated from the following formula:
4.615 ms (TDMA frame duration) * 51 (number of frames) * DRX value.
DRX (Discontinuous Reception) is a value from 2 to 9, resulting in paging intervals from 0.47
to 2.12 seconds. The DRX value of the base station is assigned by the network operator.
Each listening period causes the /CTS signal to go active low: If DRX is 2, the /CTS signal is
activated every 0.47 seconds, if DRX is 3, the /CTS signal is activated every 0.71 seconds
and if DRX is 9, the /CTS signal is activated every 2.1 seconds.
The /CTS signal is active low for 4.6 ms. This is followed by another 4.6 ms UART activity. If
the start bit of a received character is detected within these 9.2 ms, /CTS will be activated
and the proper reception of the character will be guaranteed.
/CTS will also be activated if any character is to be sent from the module to the application.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 43 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 44

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
s
DRAFT
After the last character was sent or received the interface will remain active for another
· 2 seconds, if AT+CFUN=5 or 7 or
· 10 minutes, if AT+CFUN=6 or 8.
In the pauses between listening to paging messages, while /CTS is high, the module
resumes power saving and the AT interface is not accessible. See Figure 10 and Figure 11.
Paging message Paging message Paging message
/CTS
4.6
ms
AT interface disabled
4.6 ms
2.12 s
2.12 s
4.6
ms
4.6 ms
AT interface enabled
4.6
ms
4.6 ms
Paging message
2.12 s
4.6
ms
4.6 ms
Figure 10: Timing of /CTS signal (example for a 2.12 s paging cycle)
Figure 11 illustrates the CFUN=5 and CFUN=7 modes, which reset the /CTS signal 2
seconds after the last character was sent or received.
Paging message Paging message
2.12 s
2.12 s
Paging message
Paging message
2.12 s
Beginning of power saving
/CTS
1 characterstLast character
AT interface disabled
2 s
AT interface enabled
4.6 ms
4.6
ms
4.6 ms
4.6
ms
4.6 m
Figure 11: Beginning of power saving if CFUN=5 or 7
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 44 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 45

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.6.5 Wake up MC46 from SLEEP mode
A wake-up event is any event that switches off the SLEEP mode and causes MC46 to return
to full functionality. In short, it takes MC46 back to AT+CFUN=1.
Definitions of the state transitions described in Table 11:
Yes = MC46 exits SLEEP mode.
No = MC46 does not exit SLEEP mode.
Table 11: Wake-up events in NON-CYCLIC and CYCLIC SLEEP modes
Event From SLEEP mode
AT+CFUN=0 to
AT+CFUN=1
Ignition line No No No
/RTS0 or /RTS1
(falling edge)
Unsolicited Result Code
(URC)
Incoming voice or data call Yes Yes No
Any AT command
(incl. outgoing voice or data
call, outgoing SMS)
Incoming SMS depending on
mode selected by AT+CNMI:
AT+CNMI=0,0 (= default, no
indication of received SMS)
AT+CNMI=1,1 (= displays
URC upon receipt of SMS)
GPRS data transfer Not possible
Yes1) No1) No1)
Yes Yes No
Not possible
(UART disabled)
No
Yes
(UART disabled)
From SLEEP mode
AT+CFUN=5 or 6 to
AT+CFUN=1
No No
No
Yes
No No
From SLEEP mode
AT+CFUN=7 or 8 to
AT+CFUN=1
No
No
RTC alarm2) Yes Yes No
AT+CFUN=1 Not possible (UART
disabled)
Yes Yes
1)
During all CYCLIC SLEEP modes, /RTS0 and /RTS1 are conventionally used for flow
control: The assertion of /RTS0 or /RTS1 signals that the application is ready to
receive data - without waking up the module. Be aware that this behavior is different if
CFUN=0: In this case, the assertion of /RTS0 and /RTS1 serves as a wake-up event,
giving the application the possibility to intentionally terminate power saving.
2)
Recommendation: In NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode, you can set an RTC alarm to wake
up MC46 and return to full functionality. This is a useful approach because, in this
mode, the AT interface is not accessible.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 45 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 46

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.7 Summary of state transitions (except SLEEP mode)
Table 12: State transitions of MC46 (except SLEEP mode)
The table shows how to proceed from one mode to another (gray column = present mode, white columns = intended modes)
Further mode
Present mode
èèè
POWER DOWN Normal mode
**)
Charge-only mode*) Charging in normal
mode
*)**)
Alarm mode
POWER DOWN
mode without charger
POWER DOWN
mode with charger
(high level at POWER
--- /IGT >100 ms at low
level
--- /IGT >1 s at low level,
if battery is fully
charged
pins of MC46)
Normal mode
**)
AT^SMSO
or
--- No automatic transition,
exceptionally /EMERGOFF
pin > 3.2s at low level
Charge-only mode *) Disconnect charger (MC46
POWER pin at low level)
AT^SMSO or
or
exceptionally /EMERGOFF
3.2s at low level
pin >
Charging in normal
mode*)
**)
AT^SMSO è “Charge-only
mode”, again AT^SMSO;
exceptionally
or
/EMERGOFF pin >
3.2s at
No automatic
transition, but via
“Charge in Normal
mode”
Disconnect charger
from input of ext.
charging circuit and
module’s POWER pin
low level
Alarm mode AT^SMSO or
exceptionally /EMERGOFF
3.2s at low level
*)
See Chapter 3.5.3 for details on the charging mode
pin >
/IGT >100ms at low
level
Connect charger to
input of ext. charging
circuit and POWER pin
No direct transition, but
via “Charge-only mode” or
“Normal mode”
Wake-up from POWER
DOWN mode (if
activated with AT+CALA)
(high level at POWER)
100ms < /IGT < 500ms
at low level
/IGT >1 s at low level Wake-up from POW ER
DOWN mode (if
activated with AT+CALA)
but via “POWER
DOWN”
Connect charger to
POWER pin at MC46
(high level at POWER)
AT+CALA followed by
AT^SMSO. MC46 enters
Alarm mode when
specified time is reached.
--- /IGT >1s at low level AT+CALA followed by
AT^SMSO. MC46 enters
Alarm mode when
specified time is reached
BATT+
>3.2V
and V
AT^SMSO --- No direct transition
No transition /IGT >100ms at low level ---
**)
Normal mode covers TALK, DATA, GPRS, IDLE and SLEEP modes
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 46 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 47

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.8 RTC backup
The internal Real Time Clock of MC46 is supplied from a separate voltage regulator in the
power supply ASIC which is also active when MC46 is in POWER DOWN status. An alarm
function is provided that allows to wake up MC46 without logging on to the GSM network.
In addition, you can use the VDDLP pin on the board-to-board connector to backup the RTC
from an external capacitor or a battery (rechargeable or non-chargeable). The capacitor is
charged by the BATT+ line of MC46. If the voltage supply at BATT+ is disconnected the
RTC can be powered by the capacitor. The size of the capacitor determines the duration of
buffering when no voltage is applied to MC46, i.e. the greater capacitor the longer MC46 will
save the date and time.
The following figures show various sample configurations. The voltage applied at VDDLP
can be in the range from 2 to 5.5V. Please refer to Table 27 for the parameters required.
Baseband
processor
RTC
PSU
1k
B2B
BATT+
VDDLP
+
Figure 12: RTC supply from capacitor
BATT+
Baseband
processor
RTC
PSU
B2B
1k
VDDLP
+
Figure 13: RTC supply from rechargeable battery
BATT+
Baseband
processor
PSU
RTC
B2B
1k
VDDLP
+
+
Figure 14: RTC supply from non-chargeable battery
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 47 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 48

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.9 Serial interfaces
MC46 offers two unbalanced, asynchronous serial interfaces conforming to ITU-T V.24
protocol DCE signaling. The electrical characteristics do not comply with ITU-T V.28. The
significant levels are 0V (for low data bit or ON condition) and 2.65V (for high data bit or OFF
condition). For electrical characteristics please refer to Table 38.
The GSM engine is designed for use as a DCE. Based on the conventions for DCE-DTE
connections it communicates with the customer application (DTE) using the following
signals:
ASC0
· Port /TXD @ application sends data to the module’s /TXD0 signal line
· Port /RXD @ application receives data from the module’s /RXD0 signal line
ASC1
· Port /TXD @ application sends data to module’s /TXD1 signal line
· Port /RXD @ application receives data from the module’s /RXD1 signal line
GSM module
(DCE)
ASC0 interface
/TXD0
/RXD0
/RTS0
/CTS0
/DTR0
/DSR0
/DCD0
/RING0
/TXD1
/RXD1
/RTS1
/TXD
/RXD
/RTS
/CTS
/DTR
/DSR
/DCD
/RING
/TXD
/RXD
/RTS
Application
(DTE)
serial interface
st
1
/CTS1
ASC1 interface
Figure 15: Serial interfaces
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 48 of 98 21.08.2003
/CTS
serial interface
nd
2
Page 49
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.9.1 Features supported on first and second serial interface
ASC0
· 8-wire serial interface
· Includes the data lines /TXD0 and /RXD0, the status lines /RTS0 and /CTS0 and, in
addition, the modem control lines /DTR0, /DSR0, /DCD0 and /RING0.
· It is primarily designed for voice calls, CSD calls, fax calls and GPRS services and for
controlling the GSM engine with AT commands. Full Multiplex capability allows the
interface to be partitioned into three virtual channels, yet with CSD and fax services only
available on the first logical channel. Please note that when the ASC0 interface runs in
Multiplex mode, ASC1 cannot be used. For more detailed characteristics see [10].
· The /DTR0 signal will only be polled once per second from the internal firmware of
MC46.
· The /RING0 signal serves to indicate incoming calls and other types of URCs
(Unsolicited Result Code). It can also be used to send pulses to the host application, for
example to wake up the application from power saving state. For further details see
Chapter 3.12.2.3.
· Autobauding is only selectable on ASC0 and supports the following bit rates: 1200, 2400,
4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, 230400 bps.
· Autobauding is not compatible with multiplex mode, see [10].
ASC1
· 4-wire serial interface
· Includes only the data lines /TXD1 and /RXD1 plus /RTS1 and /CTS1 for hardware
handshake. This interface is intended for voice calls, GPRS services and for controlling
the GSM engine with AT commands. It is not suited for CSD calls, fax calls and Multiplex
mode.
· On ASC1 no RING line is available. The indication of URCs on the second interface
depends on the settings made with the AT^SCFG command. For details refer to [1].
ASC0 and ASC1
· Both interfaces are configured for 8 data bits, no parity and 1 stop bit, and can be
operated at bit rates from 300bps to 230400 bps.
· XON/XOFF software flow control can be used on both interfaces (except if power saving
is active).
Table 13: DCE-DTE wiring of 1st serial interface
DCE DTE V.24
circuit
103 /TXD0 Input /TXD Output
104 /RXD0 Output /RXD Input
105 /RTS0 Input /RTS Output
106 /CTS0 Output /CTS Input
108/2 /DTR0 Input /DTR Output
107 /DSR0 Output /DSR Input
109 /DCD0 Output /DCD Input
125 /RING0 Output /RING Input
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 49 of 98 21.08.2003
Pin function Signal direction Pin function Signal direction
Page 50

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 14: DCE-DTE wiring of 2nd serial interface
DCE DTE V.24
circuit
103 /TXD1 Input /TXD Output
104 /RXD1 Output /RXD Input
105 /RTS1 Input /RTS Output
106 /CTS1 Output /CTS Input
Pin function Signal direction Pin function Signal direction
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 50 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 51
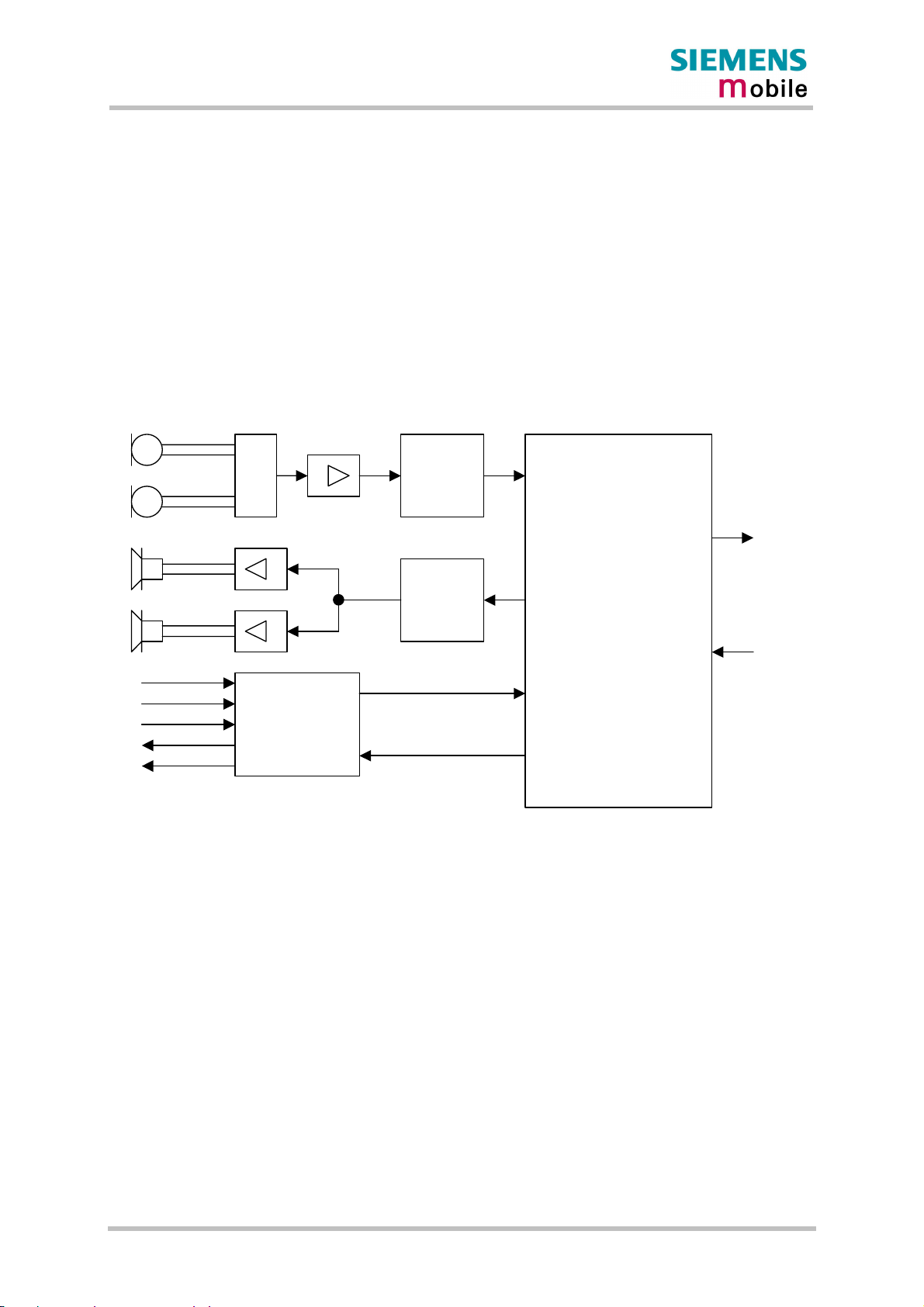
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
Air
A
(
)
DRAFT
3.10 Audio interfaces
MC46 comprises three audio interfaces available on the board-to-board connector:
· Two analog audio interfaces, each with a balanced analog microphone input and a
balanced analog earpiece output. The second analog interface provides a supply circuit
to feed an active microphone.
· Serial digital audio interface (DAI) using PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) to encode analog
voice signals into digital bit streams.
This means you can connect up to three audio devices in any combination, all at the same
time. Using the AT^SAIC command you can easily switch back and forth.
MICP1
MICN1
MICP2
MICN2
EPP1
M
U
X
ADC
EPN1
EPP2
DAC
DSP
Interface
EPN2
SCLK
RXDDAI
RFSDAI
TXDDAI
TFSDAI
MC46 offers six audio modes which can be selected with the AT^SNFS command, no matter
which of the three interfaces is currently active. The electrical characteristics of the
voiceband part vary with the audio mode. For example, sending and receiving amplification,
sidetone paths, noise suppression etc. depend on the selected mode and can be altered with
AT commands (except for mode 1).
On each audio interface you can use all audio AT commands specified in [1] to alter
parameters. The only exception are the DAC and ADC gain amplifier attenuation
<outBbcGain> and <inBbcGain> which cannot be modified when the digital audio interface is
used, since in this case the DAC and ADC are switched off.
Please refer to Chapter 5.5 for specifications of the audio interface and an overview of the
audio parameters. Detailed instructions on using AT commands are presented in the "MC46
AT Command Set" [1]. Table 30 on page 80 summarizes the characteristics of the various
audio modes and shows what parameters are supported in each mode.
Digital
udio
Interface
DAI
Figure 16: Audio block diagram
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 51 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 52

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
When shipped from factory, all audio parameters of MC46 are set to interface 1 and audio
mode 1. This is the default configuration optimized for the Votronic HH-SI-30.3/V1.1/0
handset and used for type approving the Siemens reference configuration. Audio mode 1
has fix parameters which cannot be modified. To adjust the settings of the Votronic handset
simply change to another audio mode.
In transmit direction, all audio modes contain internal scaling factors (digital amplification)
that are not accessible by the user. To avoid saturation with a full scale digital input signal on
the DAI, and to obtain a one-to-one digital access to the speech coder in audio mode 5
and 6, it is recommended to set the parameter <inCalibrate> of the selected audio mode as
follows:
Audio mode 1 and 4: 23196
Audio mode 2: 17396
Audio mode 3: 21901
Audio mode 5 and 6: 21402
3.10.1 Microphone circuit
Interface 1
This interface has no microphone supply circuit and therefore, has an impedance of 50k
W.
When connecting a microphone or another signal source to interface 1 you are required to
add two 100 nF capacitors, one to each line.
Interface 2
This interface comes with a microphone supply circuit and can be used to feed an active
microphone. It has an impedance of 2k
W. If you do not use it or if you want to connect
another type of signal source, for example, an op amp or a dynamic microphone, it needs to
be decoupled with capacitors. The power supply can be switched off and on by using the
command AT^SNFM. For details see [1].
Figure 17 shows the microphone inputs at both analog interfaces of MC46.
2.65 V
Power down
MICP1
MICN1
Ri=50k"
to ADC
1
k" 1 k"
MICP2
MICN2
10 µF
1 k" 1 k"
k"
Ri=2
Figure 17: Schematic of microphone inputs
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 52 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 53

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.10.2 Speech processing
The speech samples from the ADC or DAI are handled by the DSP of the baseband
controller to calculate e.g. amplifications, sidetone, echo cancellation or noise suppression
depending on the configuration of the active audio mode. These processed samples are
passed to the speech encoder. Received samples from the speech decoder are passed to
the DAC or DAI after post processing (frequency response correction, adding sidetone etc.).
Full rate, half rate, enhanced full rate, adaptive multi rate (AMR), speech and channel
encoding including voice activity detection (VAD) and discontinuous transmission (DTX) and
digital GMSK modulation are also performed on the GSM baseband processor.
Customer specific audio parameters can be evaluated and supplied by Siemens on request.
These parameters can be downloaded to MC46 using an AT command. For further
information refer to [8] or contact your Siemens distributor.
3.10.3 DAI timing
To support the DAI function, MC46 integrates a simple five-line serial interface with one input
data clock line (SCLK) and input / output data and frame lines (TXDDAI, TFSDAI, RXDDAI,
RFSDAI).
The serial interface is always active if the external input data clock SLCK is present, i.e. the
serial interface is not clocked by the DSP of the MC46 baseband processor. SLCK must be
supplied from the application and can be in a frequency range between 0.2 and 10 MHz.
Serial transfer of 16-bit words is done in both directions.
Data transfer to the application is initiated by the module through a short pulse of TFSDAI.
The duration of the TFSDAI pulse is one SCLK period, starting at the rising edge of SLCK.
During the following 16 SLCK cycles, the 16-bit sample will be transferred on the TXDDAI
line. The next outgoing sample will be transferred after the next TFSDAI pulse which occurs
every 125 µs.
The TFSDAI pulse is the master clock of the sample transfer. From the rising edge of the
TFSDAI pulse, the application has 100 µs to transfer the 16-bit input sample on the RXDDAI
line. The rising edge of the RFSDAI pulse (supplied by the application) may coincide with the
falling edge of TFSDAI or occur slightly later - it is only significant that, in any case, the
transfer of the LSB input sample will be completed within the specified duration of 100 µs.
Audio samples are transferred from the module to the application in an average of 125µs.
This is determined by the 8kHz sampling rate, which is derived from and synchronized to the
GSM network. As SLCK is independent of the GSM network, the distance between two
succeeding sample transfers may vary about +
The application is required to adapt its sampling rate to the TFSDAI rate. Failure to
synchronize the timing between the module and the application may cause audible pops and
clicks in a conversation. The timing characteristics of both data transfer directions are shown
in Figure 18 and Figure 19.
1 SLCK period.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 53 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 54
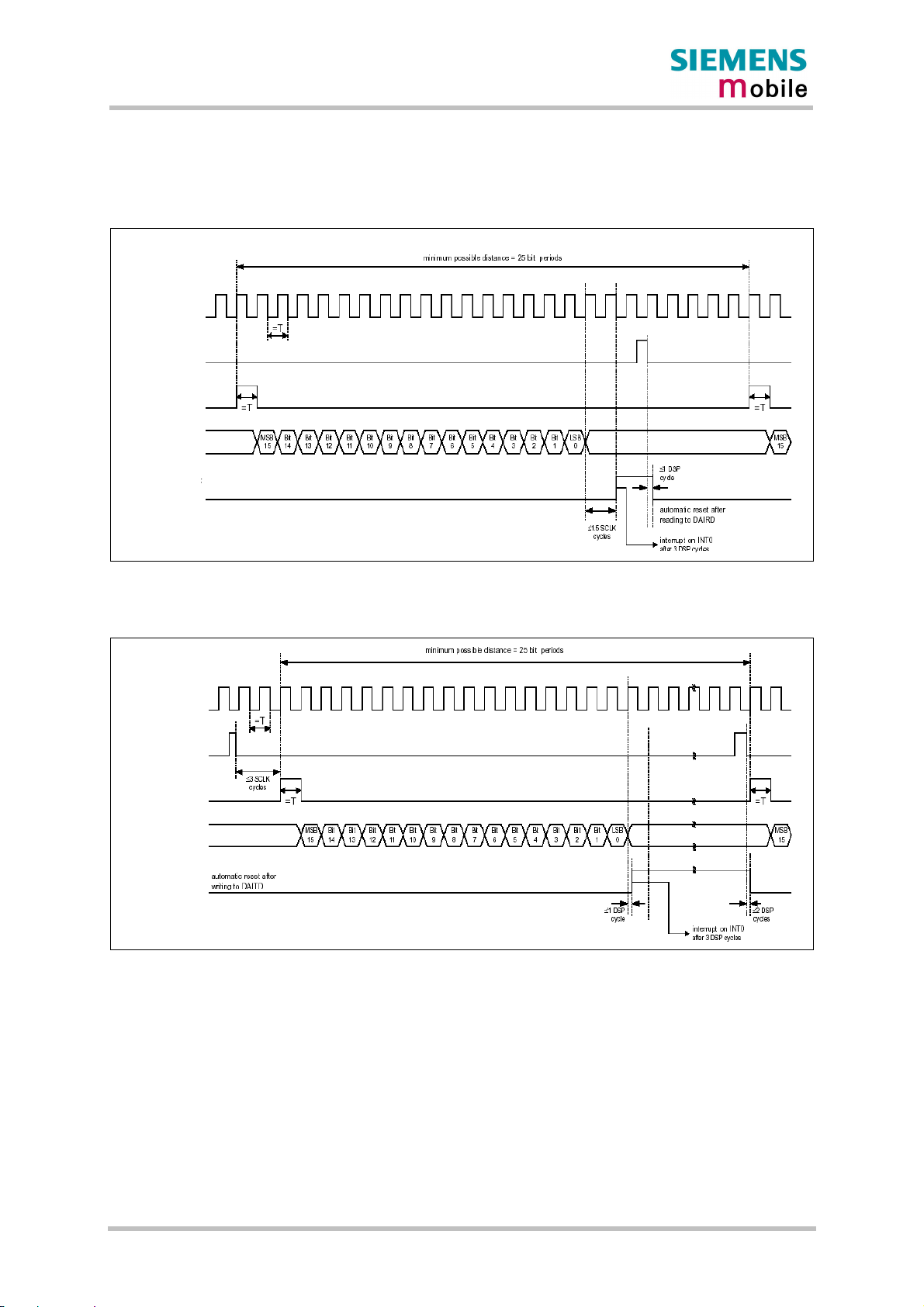
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Note: Before starting the data transfer the clock SCLK should be available for at least
three cycles.
After the transfer of the LSB0 the clock SCLK should be still available for at least
three cycles.
SLCK
(input)
Internal
signal
RFSDAI
(input)
RXDDAI
(input)
Flag
SLCK
(input)
Internal
signal
T = 100ns to 5,000 ns
Figure 18: DAI timing on transmit path
T = 100ns to 5,000 ns
TFSDAI
(output)
TXDDAI
(output)
Flag
Figure 19: DAI timing on receive path
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 54 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 55

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.11 SIM interface
The baseband processor has an integrated SIM interface compatible with the ISO 7816 IC
Card standard. This is wired to the host interface (board-to-board connector) in order to be
connected to an external SIM card holder. Six pins on the board-to-board connector are
reserved for the SIM interface.
The CCIN pin serves to detect whether a tray (with SIM card) is present in the card holder.
Using the CCIN pin is mandatory for compliance with the GSM 11.11 recommendation if the
mechanical design of the host application allows the user to remove the SIM card during
operation. See Chapter 3.11.1 for details.
It is recommended that the total cable length between the board-to-board connector pins on
MC46 and the pins of the SIM card holder does not exceed 200 mm in order to meet the
specifications of 3GPP TS 51.010-1 and to satisfy the requirements of EMC compliance.
Table 15: Signals of the SIM interface (board-to-board connector)
Signal Description
CCGND Separate ground connection for SIM card to improve EMC.
CCCLK Chipcard clock, various clock rates can be set in the baseband processor.
CCVCC SIM supply voltage from PSU-ASIC
CCIO Serial data line, input and output.
CCRST Chipcard reset, provided by baseband processor.
CCIN Input on the baseband processor for detecting a SIM card tray in the holder.
The CCIN pin is mandatory for applications that allow the user to remove the SIM card
during operation.
The CCIN pin is solely intended for use with a SIM card. It must not be used for any other
purposes. Failure to comply with this requirement may invalidate the type approval of
MC46.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 55 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 56

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.11.1 Requirements for using the CCIN pin
SIM card is removed during operation. Therefore, the signal at the CCIN pin must go low
before the SIM card contacts are mechanically detached from the SIM interface contacts.
This shut-down procedure is particularly required to protect the SIM card as well as the SIM
interface of MC46 from damage.
An appropriate SIM card detect switch is required on the card holder. For example, this is
true for the model supplied by Molex, which has been tested to operate with MC46 and is
part of the Siemens reference equipment submitted for type approval. Molex ordering
number is 91228-0001, see also Chapter 8.
The module’s startup procedure involves a SIM card initialization performed within 1 second
after getting started. An important issue is whether the initialization procedure ends up with a
high or low level of the CCIN signal:
a) If, during startup of MC46, the CCIN signal on the SIM interface is high, then the status
of the SIM card holder can be recognized each time the card is inserted or ejected.
A low level of CCIN indicates that no SIM card tray is inserted into the holder. In this
case, the module keeps searching, at regular intervals, for the SIM card. Once the SIM
card tray with a SIM card is inserted, CCIN is taken high again.
b) If, during startup of MC46, the CCIN signal is low, the module will also attempt to
initialize the SIM card. In this case, the initialization will only be successful when the
card is present.
If the SIM card initialization has been done, but the card is no more operational or
removed, then the module will never search again for a SIM card and only emergency
calls can be made.
Removing and inserting the SIM card during operation requires the software to be
reinitialized. Therefore, after reinserting the SIM card it is necessary to restart MC46.
It is strongly recommended to connect the contacts of the SIM card detect switch to the
CCIN input and to the CCVCC output of the module as illustrated in the sample diagram in
Figure 20.
Note: No guarantee can be given, nor any liability accepted, if loss of data is encountered
after removing the SIM card during operation.
Also, no guarantee can be given for properly initializing any SIM card that the user
inserts after having removed a SIM card during operation. In this case, the application
must restart MC46.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 56 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 57
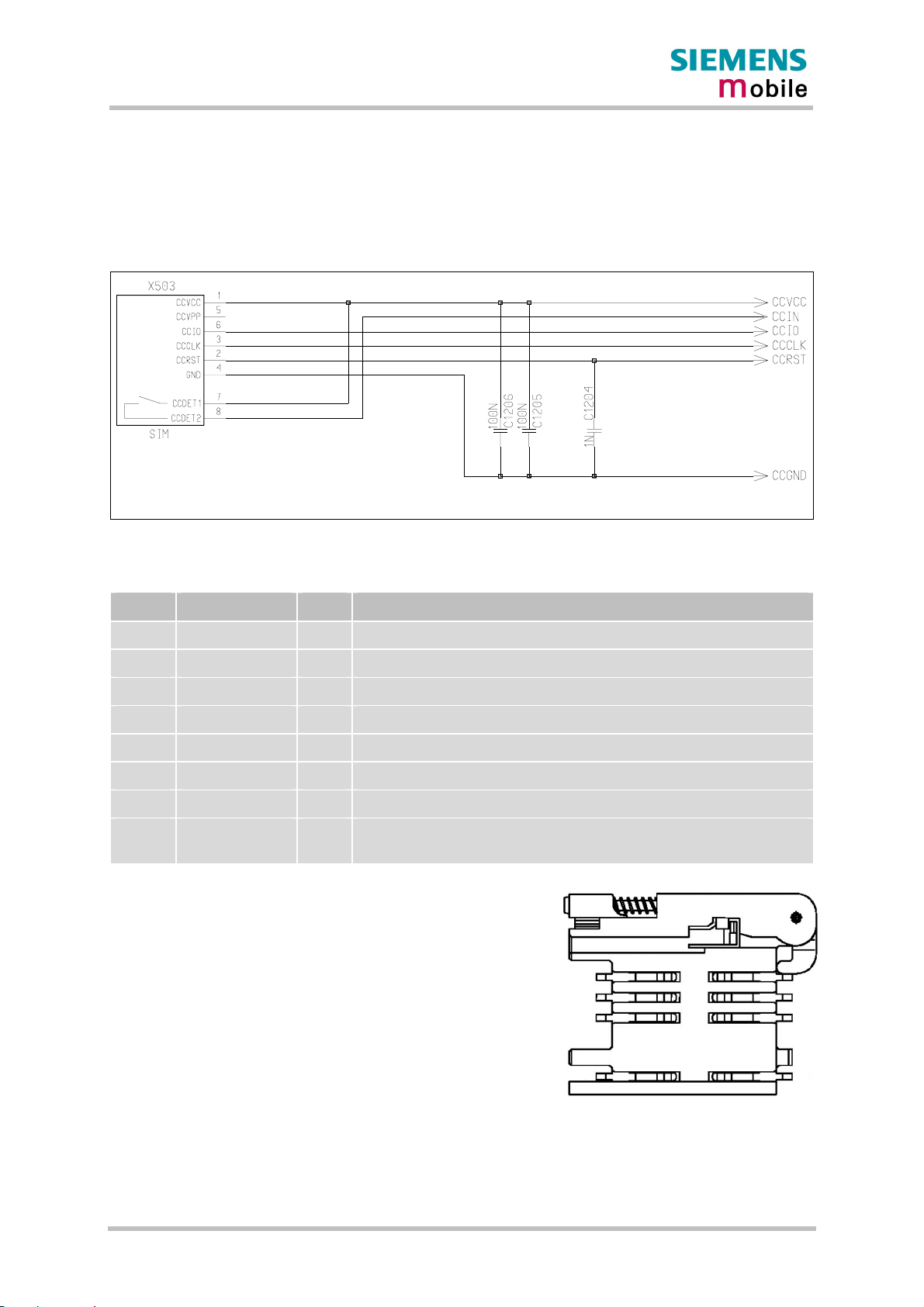
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.11.2 Design considerations for SIM card holder
The schematic below is a sample configuration that illustrates the Molex SIM card holder
located on the DSB45 Support Box (evaluation kit used for type approval of the Siemens
MC46 reference setup, see [5]). X503 is the designation used for the SIM card holder in [5].
Molex card holder
Figure 20: SIM card holder of DSB45 Support Box
Table 16 : Pin assignment of Molex SIM card holder on DSB45 Support Box
Pin no. Signal name I/O Function
1 CCVCC I Supply voltage for SIM card, generated by the GSM engine
2 CCRST I Chip card reset, prompted by the GSM engine
3 CCCLK I Chip card clock
4 CCGND - Individual ground line for the SIM card to improve EMC
5 CCVPP - Not connected
6 CCIO I/O Serial data line, bi-directional
7 CCDET1 - Connect to CCVCC
8 CCDET2 Connects to the CCIN input of the GSM engine. Serves to
recognize whether a SIM card is in the holder.
GSM module
Pins 1 through 8 (except for 5) are the minimum
requirement according to the GSM Recommendations,
where pins 7 and 8 are needed for SIM card tray
detection through the CCIN pin.
4
5
6
1
2
3
Figure 21: Pin numbers of Molex SIM card holder on DSB45
Support Box
8
7
Place the capacitors C1205 and C1206 (or instead one capacitor of 200nF) as close as
possible to the pins 1 (CCVCC) and 4 (GND) of the card holder. Connect the capacitors to
the pins via low resistance tracks.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 57 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 58

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.12 Control signals
3.12.1 Inputs
Table 17: Input control signals of the MC46 module
Signal Pin Pin status Function Remarks
Ignition
Emergency
shutdown
/IGT
/EMERGOFF
(HiZ = high impedance)
Falling edge Power up MC46
Left open or HiZ No operation
Low Power down MC46
Left open or HiZ No operation
Active low ³ 100ms (Open
drain/collector driver to GND
required in cellular device
application).
Note: If a charger and a
battery is connected to the
customer application the /IGT
signal must be 1s minimum.
Active low ³ 3.2s (Open
drain/collector driver required
in cellular device application).
At the /EMERGOFF signal the
watchdog signal of the GSM
engine can be traced (see
description in Table 27).
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 58 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 59

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.12.2 Outputs
3.12.2.1 Synchronization signal
The synchronization signal serves to indicate growing power consumption during the
transmit burst. The signal is generated by the SYNC pin (pin number 32). Please note that
this pin can adopt two different operating modes which you can select by using the
AT^SSYNC command (mode 0 and 1). For details refer to the following chapter and to [1].
To generate the synchronization signal the pin needs to be configured to mode 0 (= default).
This setting is recommended if you want your application to use the synchronization signal
for better power supply control. Your platform design must be such that the incoming signal
accommodates sufficient power supply to the MC46 module if required. This can be
achieved by lowering the current drawn from other components installed in your application.
The characteristics of the synchronization signal are explained below.
Table 18: MC46 synchronization signal (if SYNC pin is set to mode 0 via AT^SSYNC)
Function Pin Pin status Description
Low No operation Synchronization SYNC
High Indicates increased power consumption
during transmission.
1 Tx 577 µs every 4.616 ms
2 Tx 1154 µs every 4.616 ms
Transmit burst
SYNC signal
*)
300 µs
Figure 22: SYNC signal during transmit burst
*)
The duration of the SYNC signal is always equal, no matter whether the traffic or the
access burst are active.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 59 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 60

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
3.12.2.2 Using the SYNC pin to control a status LED
As an alternative to generating the synchronization signal, the SYNC pin can be used to
control a status LED on your application platform.
To avail of this feature you need to set the SYNC pin to mode 1 by using the AT^SSYNC
command. For details see [1].
When controlled from the SYNC pin the LED can display the functions listed in Table 19.
Especially in the development and test phase of an application, system integrators are
advised to use the LED mode of the SYNC pin in order to evaluate their product design and
identify the source of errors.
Table 19: Coding of the status LED
LED mode Operating status
Off MC46 is off or run in SLEEP, Alarm or Charge-only mode
600 ms On / 600ms Off No SIM card inserted or no PIN entered, or network search in
progress, or ongoing user authentication, or network login in
progress.
75 ms On / 3 s Off Logged to network (monitoring control channels and user
interactions). No call in progress.
75 ms on / 75 ms Off / 75 ms On /
3 s Off
Flashing Indicates GPRS data transfer: When a GPRS transfer is in
On Depending on type of call:
LED Off = SYNC pin low. LED On = SYNC pin high (if LED is connected as illustrated in Figure 23)
One or more GPRS contexts activated.
progress, the LED goes on within 1 second after data packets
were exchanged. Flash duration is approximately 0.5 s.
Voice call: Connected to remote party.
Data call: Connected to remote party or exchange of
parameters while setting up or disconnecting a call.
To operate the LED a buffer, e.g. a transistor or gate,
must be included in your application. A sample
configuration can be gathered from Figure 23. Power
consumption in the LED mode is the same as for the
synchronization signal mode. For details see Table 27,
SYNC pin.
Figure 23: LED Circuit (Example)
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 60 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 61

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
/
DRAFT
3.12.2.3 Behavior of the /RING0 line (ASC0 interface only)
The /RING0 line is available on the first serial interface ASC0 (see also chapter 3.9). The
signal serves to indicate incoming calls and other types of URCs (Unsolicited Result Code).
Although not mandatory for use in a host application, it is strongly suggested that you
connect the /RING0 line to an interrupt line of your application. In this case, the application
can be designed to receive an interrupt when a falling edge on /RING0 occurs. This solution
is most effective, particularly, for waking up an application from power saving. Note that if
the /RING0 line is not wired, the application would be required to permanently poll the data
and status lines of the serial interface at the expense of a higher current consumption.
Therefore, utilizing the /RING0 line provides an option to significantly reduce the overall
current consumption of your application.
The behavior of the /RING0 line varies with the type of event:
· When a voice call comes in the /RING0 line goes low for 1s and high for another 4s.
Every 5 seconds the ring string is generated and sent over the /RXD0 line.
If there is a call in progress and call waiting is activated for a connected handset or
handsfree device, the /RING0 line switches to ground in order to generate acoustic
signals that indicate the waiting call.
4s
4s
/RING0
1s
Ring
string
Figure 24: Incoming voice call
1s
Ring
string
1s
Ring
string
· Likewise, when a Fax or data call is received, /RING0 goes low. However, in contrast to
voice calls, the line remains low. Every 5 seconds the ring string is generated and sent
over the /RXD0 line.
5s
Ring
string
/RING0
Ring
string
5s
Ring
string
Figure 25: Incoming data call
· All types of Unsolicited Result Codes (URCs) also cause the
/RING0 line to go low, however for 1 second only.
RING0
For example, MC46 may be configured to output a URC
upon the receipt of an SMS. As a result, if this URC type
was activated with AT+CNMI=1,1, each incoming SMS
causes the /RING0 line to go low. See [1] for detailed
1s
URC
information on URCs.
Figure 26: URC transmission
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 61 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 62

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 20: MC46 ring signal
Function Pin Status Description
Ring indication /RING0
0 Indicates an incoming call or URC. If in NON-CYCLIC
SLEEP mode CFUN=0 or CYCLIC SLEEP mode
CFUN=5 or 6, the module is caused to wake up to full
functionality. If CFUN=7 or 8, power saving is resumed
after URC transmission or end of call.
1 No operation
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 62 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 63

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
4 Antenna interface
The RF interface has an impedance of 50". MC46 is capable of sustaining a total mismatch
at the antenna connector or pad without any damage, even when transmitting at maximum
RF power.
The external antenna must be matched properly to achieve best performance regarding
radiated power, DC-power consumption and harmonic suppression. Matching networks are
not included on the MC46 PCB and should be placed in the host application.
Regarding the return loss MC46 provides the following values:
Table 21: Return loss
State of module Return loss of module Recommended return loss of application
Receive > 8dB > 12dB
Transmit not applicable > 12dB
Idle < 5dB not applicable
The connection of the antenna or other equipment must be decoupled from DC voltage.
4.1 Antenna installation
To suit the physical design of individual applications MC46 offers two alternative approaches
to connecting the antenna:
· Recommended approach: U.FL-R-SMT antenna connector from Hirose assembled on
the component side of the PCB (top view on MC46). See Chapter 4.1.2 for details.
· Antenna pad and grounding plane placed on the bottom side. See Chapter 4.1.1.
Figure 27: U.FL-R-SMT connector Figure 28: Antenna pad and GND pad
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 63 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 64

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
r
t
t
DRAFT
The U.FL-R-SMT connector has been chosen as antenna reference point (ARP) for the
Siemens reference equipment submitted to type approve MC46. All RF data specified
throughout this manual are related to the ARP. For compliance with the test results of the
Siemens type approval you are advised to give priority to the connector, rather than using
the antenna pad.
IMPORTANT: Both solutions can only be applied alternatively. This means, whenever an
antenna is plugged to the Hirose connector, the pad must not be used. Vice versa, if the
antenna is connected to the pad, then the Hirose connector must be left empty.
Antenna connected to Hirose connector:
Module
Antenna or
measurement
PAD
50Ohm
U.FL
equipment
50Ohm
Antenna connected to pad:
Module
PAD
50Ohm
U.FL
Z
Z
Antenna o
measuremen
equipmen
50Ohm
Figure 29: Never use antenna connector and antenna pad at the same time
No matter which option you choose, ensure that the antenna pad does not come into contact
with the holding device or any other components of the host application. It needs to be
surrounded by a restricted area filled with air, which must also be reserved 0.8 mm in height.
U.FL antenna connector
RF section
MC46 PCB
Antenna pad
Figure 30: Restricted area around antenna pad
Restricted area
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 64 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 65

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
4.1.1 Antenna pad
The antenna can be soldered to the pad, or attached via contact springs. To provide a
proper ground for the antenna, MC46 comes with a grounding pad located close to the
antenna pad. The positions of both pads can be seen from Figure 28 and Figure 40. The
grounding pad should be connected to the ground plane of the application.
When you decide to use the antenna pad take into account that the pad has not been
intended as antenna reference point (ARP) for the Siemens MC46 type approval. The
antenna pad is provided only as an alternative option which can be used, for example, if the
recommended Hirose connection does not fit into your antenna design.
Also, consider that according to the GSM recommendations TS 45.005 and TS 51.010-01 a
50" connector is mandatory for type approval measurements. This requires GSM devices
with an integral antenna to be temporarily equipped with a suitable connector or a low loss
RF cable with adapter.
To prevent damage to the module and to obtain long-term solder joint properties you are
advised to maintain the standards of good engineering practice for soldering.
MC46 material properties:
MC46 PCB: FR4
Antenna pad: Gold plated pad
4.1.1.1 Suitable cable types
For direct solder attachment, we suggest to use the following cable types:
· RG316/U 50 Ohm coaxial cable
· 1671A 50 Ohm coaxial cable
Suitable cables are offered, for example, by IMS Connector Systems. For further details and
other cable types please contact http://www.imscs.com
.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 65 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 66

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
4.1.2 Hirose antenna connector
MC46 uses an ultra-miniature SMT antenna connector supplied
from Hirose Ltd. The product name is:
U.FL-R-SMT
The position of the antenna connector on the MC46 board can be
seen in Figure 39.
Figure 31: Mechanical dimensions of U.FL-R-SMT connector
Table 22: Product specifications of U.FL-R-SMT connector
Item Specification Conditions
Ratings
Nominal impedance
Rated frequency DC to 3 GHz
Mechanical characteristics
Female contact holding
force
Repetitive operation Contact resistance:
Vibration No momentary disconnections of
Shock No momentary disconnections of
Environmental characteristics
Humidity resistance No damage, cracks and looseness
50 W
0.15 N min
Center 25 mW
Outside 15mW
1 µs;
No damage, cracks and looseness
of parts
1 µs.
No damage, cracks and looseness
of parts.
of parts.
Insulation resistance:
100 MW min. at high humidity
500 MW min when dry
Operating temp:-40°c to + 90°C
Operating humidity: max. 90%
Measured with a Æ 0.475 pin
gauge
30 cycles of insertion and
disengagement
Frequency of 10 to 100 Hz, single
amplitude of 1.5 mm,
acceleration of 59 m/s2, for 5
cycles in the direction of each of
the 3 axes
Acceleration of 735 m/s2, 11 ms
duration for 6 cycles in the
direction of each of the 3 axes
Exposure to 40°C, humidity of
95% for a total of 96 hours
Temperature cycle No damage, cracks and looseness
of parts.
Contact resistance:
Center 25 mW
Outside 15mW
Salt spray test No excessive corrosion 48 hours continuous exposure to
Temperature: +40°C ® 5 to 35°C
® +90°C ® 5 to 35°C
Time: 30 min. ® within 5 min. ®
30 min. within 5 min
5% salt water
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 66 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 67

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 23: Material and finish of U.FL-R-SMT connector and recommended plugs
Part Material Finish
Shell Phosphor bronze Silver plating
Male center contact Brass Gold plating
Female center contact Phosphor bronze Gold plating
Insulator Plug: PBT
Receptacle: LCP
Black
Beige
Mating plugs and cables can be chosen from the Hirose U.FL Series. Examples are shown
below and listed in Table 24. For latest product information please contact your Hirose
dealer or visit the Hirose home page, for example http://www.hirose.com
.
Figure 32: U.FL-R-SMT connector with U.FL-LP-040 plug
Figure 33: U.FL-R-SMT connector with U.FL-LP-066 plug
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 67 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 68
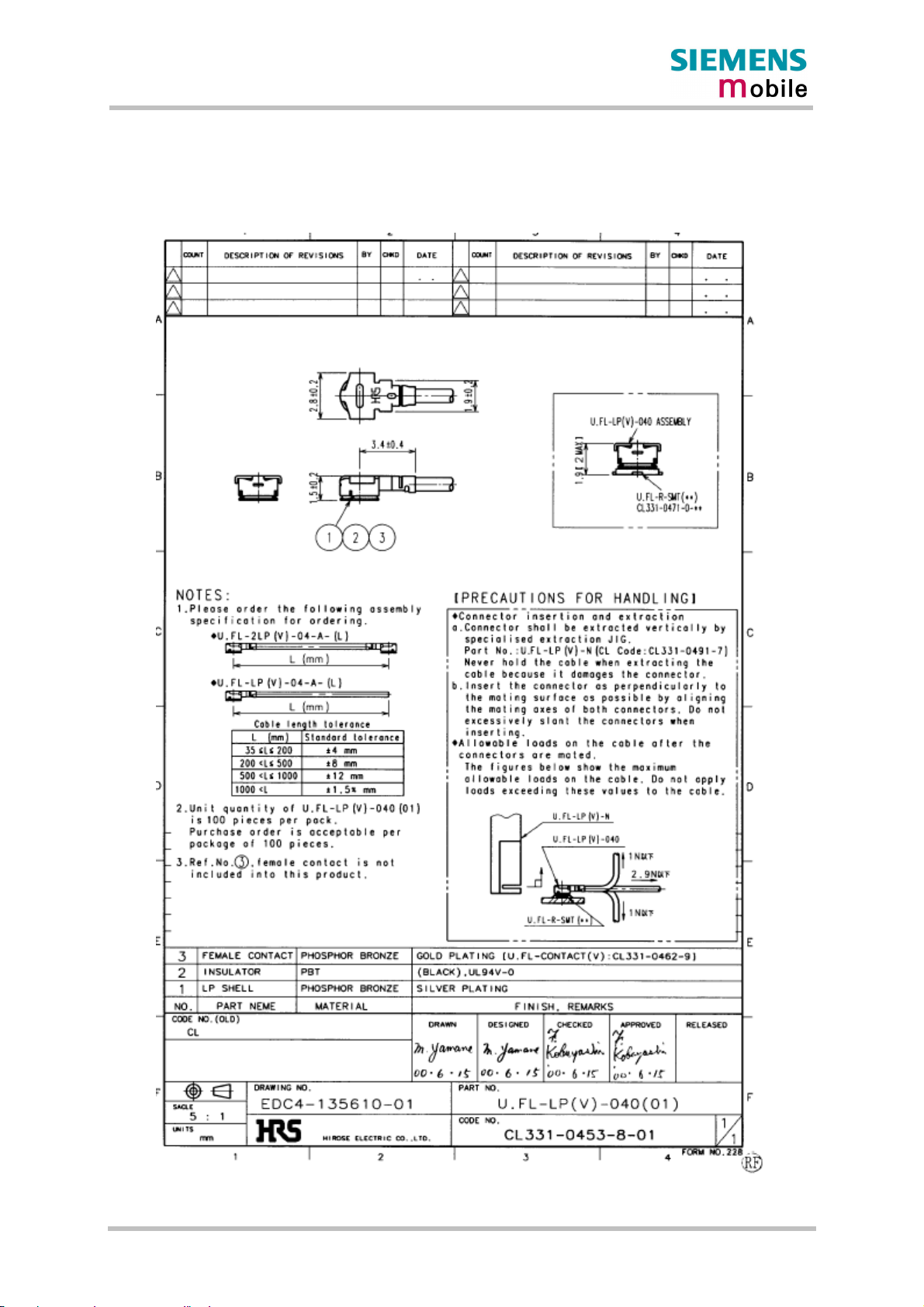
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
In addition to the connectors illustrated above, the U.FL-LP-(V)-040(01) version is offered as
an extremely space saving solution. This plug is intended for use with extra fine cable (up to
Æ 0.81 mm) and minimizes the mating height to 2 mm. See Figure 34 which shows the
Hirose datasheet.
Figure 34: Specifications of U.FL-LP-(V)-040(01) plug
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 68 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 69
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 24: Ordering information for Hirose U.FL Series
Item Part number HRS number
Connector on MC46 U.FL-R-SMT CL331-0471-0-10
Right-angle plug shell for
Æ 0.81 mm cable
Right-angle plug for
Æ 0.81 mm cable
Right-angle plug for
Æ 1.13 mm cable
Right-angle plug for
Æ 1.32 mm cable
Extraction jig E.FL-LP-N CL331-04441-9
U.FL-LP-040 CL331-0451-2
U.FL-LP(V)-040 (01) CL331-053-8-01
U.FL-LP-066 CL331-0452-5
U.FL-LP-066 CL331-0452-5
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 69 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 70

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5 Electrical, reliability and radio characteristics
5.1 Absolute maximum ratings
Absolute maximum ratings for supply voltage and voltages on digital and analog pins of
MC46 are listed in Table 25. Exceeding these values will cause permanent damage to
MC46.
The power supply shall be compliant with the SELV safety standard defined in EN60950.
The supply current must be limited according to Table 25.
Table 25: Absolute maximum ratings
Parameter Min Max Unit
Peak current of power supply 0 4.0 A
RMS current of power supply (during one TDMA-frame) 0 0.7 A
Voltage at digital pins -0.3 3.3 V
Voltage at analog pins -0.3 3.0 V
Voltage at digital / analog pins in POWER DOWN mode -0.25 +0.25 V
Voltage at POWER pin 15 V
Voltage at CHARGE pin 15 V
Differential load resistance between EPNx and EPPx 15
W
5.2 Operating temperatures
Test conditions were specified in accordance with IEC 60068-2 (still air). The values stated
below are in compliance with GSM recommendation TS 51.010-01.
Table 26: Operating temperatures
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Ambient temperature (according to GSM 11.10) -20 25 55 °C
Restricted operation *) -25 to -20 55 to 70 °C
Automatic shutdown
MC46 board temperature
Battery temperature
Charging temperature (software controlled fast charging) 0 +45 °C
*)
MC46 works, but deviations from the GSM specification may occur.
**)
Consider the ratio of output power, supply voltage and operating temperature: To achieve
T
4.0V.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 70 of 98 21.08.2003
= 70°C and, for example, GSM 850 PCL5 the supply voltage must not be higher than
amb max
-29
-18
>70
>60
**)
°C
°C
Page 71
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.3 Electrical specifications of the application interface
Please note that the reference voltages listed in Table 27 are the values measured directly
on the MC46 module. They do not apply to the accessories connected.
If an input pin is specified for V
value 3.3V is an absolute maximum rating.
The Hirose DF12C board-to-board connector on MC46 is a 50-pin double-row receptacle.
The names and the positions of the pins can be seen from Figure 35 which shows the top
view of MC46.
26
50
BATT+ GND
BATT+ GND
BATT+ GND
BATT+ GND
BATT+ GND
VDD CHARGE
/RING0 POWER
/DSR0 VDDLP
/RTS0 /TXD0
/DTR0 /TXD1
/RTS1 /RXD0
/CTS0 /RXD1
/CTS1 SYNC
/DCD0 BATT_TEMP
/EMERGOFF RFSDAI
/IGT TXDDAI
GND SCLK
MICN1 TFSDAI
MICP1 RXDDAI
MICP2 CCGND
MICN2 CCIN
EPN1 CCRST
EPP1 CCIO
EPP2 CCVCC
EPN2 CCCLK
= 3.3V, be sure never to exceed the stated voltage. The
i,h,max
25
1
Figure 35: Pin assignment (top view on MC46)
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 71 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 72

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 27: Electrical description of application interface
Function Signal name IO Signal form and level Comments
Power
supply
Charge
interface
External
supply
voltage
BATT+ I VI = 3.2V to 4.5V
VInorm = 4.1V
Inorm # 2A, Imax < 3A (during Tx burst)
GND
1 Tx, peak current 577µs every 4.616ms
2 Tx, peak current 1154µs every 4.616ms
POWER I
V
min = 3.0V
I
V
max = 15V
I
BATT_TEMP I
Connect NTC with R
to ground.
CHARGE O
VDD O
= -300µA ... -600µA
I
CHARGE
@ 3V < V
CHARGE
VDDmin = 2.84V, VDDmax = 2.96V
Imax = -10mA
C
max = 1µF
L
< V
# 10kW @ 25°C
NTC
LOAD
Power supply input.
5 BATT+ pins to be
connected in parallel.
5 GND pins to be
connected in parallel.
The power supply must be
able to meet the
requirements of current
consumption in a Tx burst
(up to 3A).
Sending with two timeslots
doubles the duration of
current pulses to 1154µs
(every 4.616ms)!
This line signalizes to the
processor that the charger
is connected.
If unused keep pin open.
Input to measure the
battery temperature over
NTC resistor.
NTC should be installed
inside or near battery pack
to enable the charging
algorithm and deliver
temperature values.
If unused keep pin open.
This line is a current
source for the charge FET
with a 10kW resistance
between gate and source.
If unused keep pin open.
Supply voltage, e.g. for an
external LED or level
shifter. The external digital
logic must not cause any
spikes or glitches on
voltage VDD.
Not available in POWER
DOWN mode.
VDD signalizes the “ON”
state of the module.
If unused VDD keep pin
open.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 72 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 73
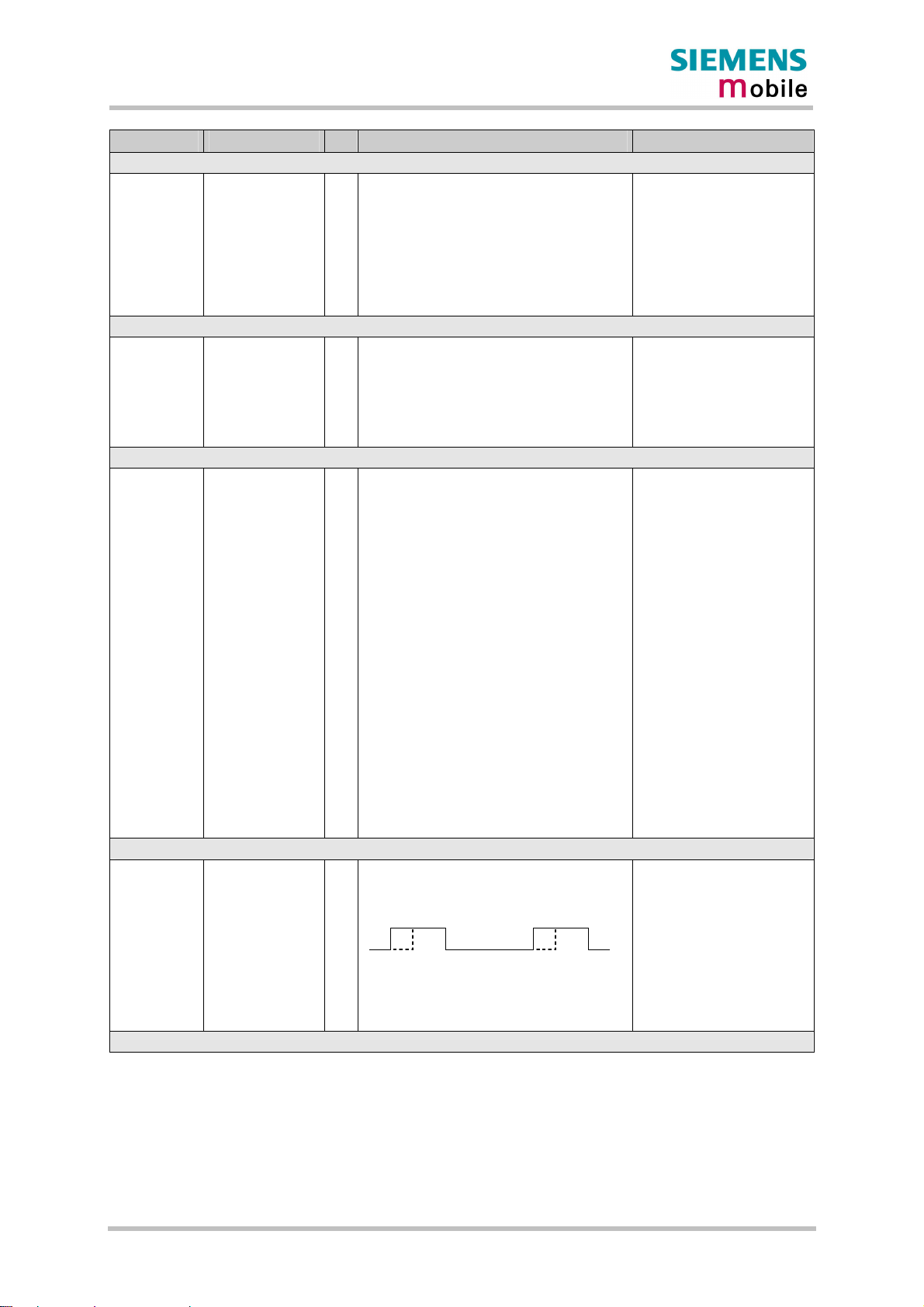
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Function Signal name IO Signal form and level Comments
VDD Low
Power
Ignition /IGT I
Emergency
shutdown
(Watchdog)
Synchronization
VDDLP I/O
RI =1kW
V
max # 4.0V (output)
O
V
min = 2.2V, VImax = 5.5V (input)
I
I
typ = 10µA at BATT+ = 0V
I
Mobile in POWER DOWN mode:
VImin = 1.2V
RI # 100kW, CI # 1nF
V
max = 0.5V at Imax = -20µA
IL
V
max = 2.3V
Open
~~~
ON
/EMERGOFF I
RI #22kW
V
max = 0.5V at Imax = -100µA
IL
V
max = 2.73V
Open
Signal
Watchdog:
max = 0.35V at I = 10µA
V
OL
V
min= 2.25V at I = -10µA
OH
f
min = 0.16Hz
O
f
max = 1.55Hz
O
SYNC O
VOLmax = 0.2V at I = 1mA
V
min = 2.35V at I = -1mA
OH
V
max = 2.73V
OH
1 Tx, 877µs impulse each 4.616ms and
2 Tx, 1454µs impulse each 4.616ms, with
300µs forward time.
|____|
~~~
|______|
~~~
Active Low ³ 100ms
~~~
Active Low ³ 3.2s
Supplies the RTC with
power via an external
capacitor or buffer battery
if no V
BATT+
If unused keep pin open.
Input to switch the mobile
ON.
The line must be driven
low by an Open Drain or
Open Collector driver.
This line must be driven by
an Open Drain or Open
Collector driver.
Emergency shutdown
deactivates the power
supply to the module.
The module can be reset if
/IGT is activated after
emergency shutdown.
To switch the mobile off
use the AT^SMSO
command.
/EMERGOFF also
indicates the internal
watchdog function.
To avoid floating if pin is
high impedance, use pulldown resistor tied to VDD.
See chapter 3.3.2.1.
If unused keep pin open.
Indicates increased current
consumption during uplink
transmission burst. Note
that timing is different
during handover.
Alternatively used to
control status LED (see
Chapter 3.12.2.2).
If unused keep pin open.
is applied.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 73 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 74

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Function Signal name IO Signal form and level Comments
SIM interface
CCIN I
CCRST O
CCIO IO
CCCLK O
CCVCC O
RI # 100kW
V
max = 0.5V
IL
V
min = 2.15V at I = 20µA,
IH
V
max=3.3V at I = 30µA
IH
RO #47W
V
max = 0.25V at I = 1mA
OL
V
min = 2.3V at I = -1mA
OH
V
max = 2.73V
OH
RI #10kW
V
max = 0.5V
IL
V
min = 1.95V, VIHmax=3.3V
IH
#220W
R
O
V
max = 0.4V at I = 1mA
OL
V
min = 2.15V at I = -1mA
OH
V
min = 2.55V at I = -20µA
OH
V
max = 2.96V
OH
RO #220W
V
max = 0.4V at I = 1mA
OL
V
min = 2.15V at I = -1mA
OH
V
max = 2.73V
OH
ROmax = 5W
CCIN = high, SIM card
holder closed (no card
recognition)
Maximum cable length
200mm to SIM card holder.
All signals of SIM interface
are protected against ESD
with a special diode array.
Usage of CCGND is
mandatory.
CCVCCmin = 2.84V,
CCVCCmax = 2.96V
Imax = -20mA
CCGND Ground
ASC0
interface
/RXD0 O
/TXD0 I
/CTS0 O
/RTS0 I
/DTR0 I
/DCD0 O
VOLmax = 0.2V at I = 1mA
V
min = 2.35V at I = -1mA
OH
V
max = 2.73V
OH
VILmax = 0.5V
V
min = 1.95V, VIHmax=3.3V
IH
/DTR0, RTS0: Imax = -90µA at V
/TXD0: Imax = -30µA at V
/DSR0 O
= 0V
IN
= 0V
IN
First serial interface for AT
commands or data stream.
To avoid floating if output
pins are high-impedance,
use pull-up resistors tied to
VDD or pull-down resistors
tied to GND. See chapter
3.3.2.1.
If unused keep pins open.
/RING0 O
ASC1
interface
/RXD1 O
/TXD1 I
max = 0.2V at I = 1mA
V
OL
V
min = 2.35V at I = -1mA
OH
V
max = 2.73V
OH
VILmax = 0.5V
V
min = 1.95V, VIHmax=3.3V
/CTS1 O
/RTS1 I
IH
max = -90µA at VIN = 0V
I
I
Second serial interface for
AT commands.
To avoid floating if output
pins are high-impedance,
use pull-up resistors tied to
VDD or pull-down resistors
tied to GND. See chapter
3.3.2.1.
If unused keep pins open.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 74 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 75

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Function Signal name IO Signal form and level Comments
Digital audio
interface
Analog audio
interfaces
Explanation of signal names:
P = positive, N = negative
RFSDAI I
RXDDAI I
SCLK I
TFSDAI O
TXDDAI O
EPP2 O
EPN2 O
EPP1 O
EPN1 O
MICP1 I
MICN1 I
MICP2 I
MICN2 I
AGND Separate ground
VOLmax = 0.2V at I = 1mA
V
min = 2.35V at I = -1mA
OH
V
max = 2.73V
OH
VILmax = 0.5V
V
min = 1.95V, VIHmax=3.3V
IH
I
max = 330µA at VIN = 3.3V
I
VOmax = 3.7Vpp
See also Table 31.
VOmax = 3.7Vpp
See also Table 31.
RI # 50kW differential
max = 1.03Vpp
V
I
See also Table 32.
RI = 2kW differential
max = 1.03Vpp
V
I
See also Table 32.
If unused keep pins open.
The audio output is
balanced and can directly
operate an earpiece.
If unused keep pins open.
Balanced audio output.
Can be used to directly
operate an earpiece.
If unused keep pins open.
Balanced microphone
input. To be decoupled
with 2 capacitors (C
100nF), if connected to a
microphone or another
device.
If unused keep pins open.
Balanced microphone
input. Can be used to
directly feed an active
microphone.
If used for another signal
source, e.g. op amp, to be
decoupled with capacitors.
If unused keep pins open.
connection for external
audio circuits.
=
K
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 75 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 76

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.4 Power supply ratings
Table 28: Power supply ratings
Parameter Description Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
BATT+
I
BATT+
Supply voltage Reference points on MC46:
TP BATT+ and TP GND (see
Figure 40).
Voltage must stay within the
min/max values, including voltage
drop, ripple, spikes.
Voltage drop during
transmit burst
Normal condition, power control
level for P
out max
Voltage ripple Normal condition, power control
level for P
out max
@ f<200kHz
@ f>200kHz
Average supply
current3)
POWER DOW N mode 50 100 µA
SLEEP mode @ DRX = 6 3 mA
IDLE mode GSM 850
GSM 1800/1900
TALK mode GSM 8501)
GSM 1800/19002)
IDLE GPRS GSM 850
3.2 4.1 4.5 V
400 mV
mV
50
2
15
mA
15
300
400 mA
270
15
mA
Peak supply current
(during transmission
slot every 4.6ms)
1)
Power control level PCL 5
2)
Power control level PCL 0
3)
All average supply current values @ I
GSM 1800/1900
DATA mode GPRS,
(4 Rx, 1 Tx) GSM 8501)
GSM 1800/19002)
360
330
DATA mode GPRS,
(3 Rx, 2 Tx) GSM 8501)
GSM 1800/19002)
590
540
Power control level 1)
= 0mA
VDD
15
460 mA
840 mA
2 3 A
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 76 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 77

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.4.1 Current consumption during transmit burst
A Smith chart shows the complex impedance plane. The Smith chart in Figure 36 illustrates the
dependence between the typical peak current consumption of the application during a transmit
burst and an impedance connected to the antenna reference point (ARP).
As shown in Figure 36, the typical current consumption is about 2000 mA, but the current is
maximized when the minimum supply voltage is used together with a total reflection at the
RF interface.
The Smith chart in Figure 36 shows the channel with the highest current consumption:
· 836.4 MHz (Channel 189)
· at the minimum supply voltage of 3.35 V during a transmit burst
This measurement case was performed with a total resistance of about 100m" in the current
path.
Conditions: 836.4 MHz ( Channel 189 ); miminum supply voltage during burst = 3.35 V at 3.5A; T
Figure 36: Maximum burst peak current during transmit burst in mA
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 77 of 98 21.08.2003
= 25°C
amb
Page 78

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.5 Electrical characteristics of the voiceband part
5.5.1 Setting audio parameters by AT commands
The audio modes 2 to 6 can be adjusted according to the parameters listed below. Each
audio mode is assigned a separate set of parameters.
Table 29: Audio parameters adjustable by AT command
Parameter Influence to Range Gain range Calculation
inBbcGain MICP/MICN analog amplifier gain of
baseband controller before ADC
inCalibrate digital attenuation of input signal
after ADC
outBbcGain EPP/EPN analog output gain of
baseband controller after DAC
outCalibrate[n]
n = 0...4
sideTone digital attenuation of sidetone
digital attenuation of output signal
after speech decoder, before
summation of sidetone and DAC
present for each volume step[n]
is corrected internally by outBbcGain
to obtain a constant sidetone
independent of output volume
0...7 0...42dB 6dB steps
0...32767 -$...0dB 20 * log
(inCalibrate/
32768)
0...3 0...-18dB 6dB steps
0...32767 -$...+6dB 20 * log (2 *
outCalibrate[n]/
32768)
0...32767 -$...0dB 20 * log
(sideTone/
32768)
Note: The parameters inCalibrate, outCalibrate and sideTone accept also values from 32768
to 65535. These values are internally truncated to 32767.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 78 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 79

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
A
DRAFT
5.5.2 Audio programming model
The audio programming model shows how the signal path can be influenced by varying the
AT command parameters. The model is the same for all three interfaces, except for the
parameters <outBbcGain> and <inBbcGain> which cannot be modified if the digital audio
interface is being used, since in this case the DAC is switched off.
The parameters inBbcGain and inCalibrate can be set with AT^SNFI. All the other
parameters are adjusted with AT^SNFO.
2,65V
1k
MIC2
10uF
1k
1k
1k
inBbcGain
+0...42dB in 6dB steps
A
D
inCalibrate
-¥...0dB
Speech coder
outBbcGain
0dB; -6db, -12dB; -18dB
Figure 37: AT audio programming model
sideTone
D
A
+
outCalibrate[n]
Speech decoder
n = 0...4
T parameters
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 79 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 80
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.5.3 Characteristics of audio modes
The electrical characteristics of the voiceband part depend on the current audio mode set
with the AT^SNFS command.
Table 30: Voiceband characteristics (typical)
Audio mode no.
AT^SNFS=
1 (Default
settings, not
2 3 4 5 6
adjustable)
Name Default
Handset
Purpose DSB with
Votronic
handset
Gain setting via AT
command. Defaults:
inBbcGain
outBbcGain
Default audio
Fix
4 (24dB)
1 (-6dB)
1 2 2 1 1 2 4)
Basic
Handsfree
Siemens Car
Kit Portable
Adjustable
2 (12dB)
1 (-6dB)
Headset User
Handset
Siemens
Headset
DSB with
individual
handset
Adjustable
5 (30dB)
2 (-12dB)
Adjustable
4 (24dB)
1 (-6dB)
Plain
Codec 1
Direct
access to
speech
coder
Adjustable
0 (0dB)
0 (0dB)
Plain
Codec 2
Direct
access to
speech
coder
Adjustable
0 (0dB)
0 (0dB)
interface
Power supply
ON (2.65V) ON (2.65V) ON (2.65V) ON (2.65V) OFF (GND) OFF (GND)
Sidetone ON --- Adjustable Adjustable Adjustable Adjustable
Volume control OFF Adjustable Adjustable Adjustable Adjustable Adjustable
Limiter (receive) ON ON ON ON --- ---
Compressor
--- ON1) --- --- --- ---
(receive)
AGC (send) --- --- ON --- --- ---
Echo control (send) Suppression Cancellation +
suppression
--- Suppression
--- ---
Noise suppression2) --- up to 10dB 10dB --- --- ---
MIC input signal for
0dBm0 @ 1024 Hz
(default gain)
EP output signal in
mV rms. @ 0dBm0,
1024 Hz, no load
(default gain);
@ 3.14 dBm0
Sidetone gain at
default settings
1)
Adaptive, receive volume increases with higher ambient noise level.
2)
In audio modes with noise reduction, the microphone input signal for 0dBm0 shall be measured
23mV 58mV 7.5mV @
-3dBm0 due
to AGC
284mV 120mV
default @
max volume
300mV
default @
max volume
22.8dB -$ dB Affected by
AGC, 13dB
@ 7.5mV
(MIC)
23mV 315mV 315mV
284mV
default @
max
volume
22.8dB -2.5dB
895mV
3.7Vpp
@
sideTone
= 81923)
895mV
3.7Vpp
-2.5dB
@
sideTone
= 81923)
with a sine burst signal for a tone duration of 5 seconds and a pause of 2 sec. The sine signal
appears as noise and, after approx. 12 sec, is attenuated by the noise reduction by up to 10dB.
3)
See AT^SNFO command in [1].
4)
Audio mode 5 and 6 are identical. With AT^SAIC, you can easily switch mode 5 to the second
interface. Therefore, audio mode 6 is only kept for compatibility to earlier Siemens GSM products.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 80 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 81

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Note: With regard to acoustic shock, the cellular application must be designed to avoid
sending false AT commands that might increase amplification, e.g. for a high
sensitive earpiece. A protection circuit should be implemented in the cellular
application.
5.5.4 Voiceband receive path
Test conditions:
· The values specified below were tested to 1kHz and 0dB gain stage, unless otherwise
stated.
· Parameter setup: gs = 0dB means audio mode = 5 for EPP1 to EPN1 and 6 for EPP2 to
EPN2, inBbcGain= 0, inCalibrate = 32767, outBbcGain = 0, OutCalibrate = 16384,
sideTone = 0.
Table 31: Voiceband receive path
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test condition / remark
Differential output
voltage (peak to peak)
Differential output gain
settings (gs) at 6dB
stages (outBbcGain)
Fine scaling by DSP
(outCalibrate)
Output differential
DC offset
Differential output
resistance
Differential load
capacitance
Absolute gain accuracy 0.8 dB Variation due to change in
Attenuation distortion
3.33 3.7 4.07 V from EPPx to EPNx
gs = 0dB @ 3.14 dBm0
no load
-18 0 dB Set with AT^SNFO
-$ 0 dB Set with AT^SNFO
100 mV gs = 0dB, outBbcGain = 0 and -6dB
2 " from EPPx to EPNx
1000 pF from EPPx to EPNx
temperature and life time
1 dB for 300...3900Hz,
@ EPPx/EPNx (333Hz) /
@ EPPx/EPNx (3.66kHz)
Out-of-band
discrimination
60 dB for f > 4kHz with in-band test
signal@ 1kHz and 1kHz RBW
gs = gain setting
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 81 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 82
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.5.5 Voiceband transmit path
Test conditions:
· The values specified below were tested to 1kHz and 0dB gain stage, unless otherwise
stated.
· Parameter setup: Audio mode = 5 for MICP1 to MICN1 and 6 for MICP2 to MICN2,
inBbcGain= 0, inCalibrate = 32767, outBbcGain = 0, OutCalibrate = 16384, sideTone = 0
Table 32: Voiceband transmit path
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test condition/Remark
Input voltage (peak to peak)
MICP1 to MICN1, MICP2 to
MICN2
Input amplifier gain in 6dB steps
(inBbcGain)
Fine scaling by DSP (inCalibrate) -$ 0 dB Set with AT^SNFI
Input impedance MIC1 50 k"
Input impedance MIC2 2.0 k"
Microphone supply voltage ON
Ri = 4k" (MIC2 only)
Microphone supply voltage OFF
Ri = 4k" (MIC2 only)
Microphone supply in POWER
DOWN mode
1.03 V
0 42 dB Set with AT^SNFI
2.57
2.17
1.77
0 V
See Figure 17
2.65
2.25
1.85
2.73
2.33
1.93
V
V
V
no supply current
@ 100µA
@ 200µA
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 82 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 83
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.6 Air interface
Test conditions: All measurements have been performed at T
= 25°C, V
amb
BATT+ nom
= 4.1V.
The reference points used on MC46 are the BATT+ and GND contacts (test points are
shown in Figure 40).
Table 33: Air Interface
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
GSM 850 824.2 848.8 MHz Frequency range
Uplink (MS ® BTS)
GSM 1900 1850 1910 MHz
Downlink (BTS ® MS)
GSM 1900 1930 1990 MHz
RF power @ ARP with 50" load
Number of carriers
GSM 1800 1710 1785 MHz
GSM 850 869.2 893.8 MHz Frequency range
GSM 1800 1805 1880 MHz
GSM 8501) 31 33 35 dBm
GSM 18002) 28 30 32 dBm
GSM 1900 28 30 32
GSM 850 123
GSM 1800 374
GSM 1900 299
GSM 850 45 MHz Duplex spacing
GSM 1800 95 MHz
GSM 1900 80
Carrier spacing 200 kHz
Multiplex, Duplex TDMA / FDMA, FDD
Time slots per TDMA frame 8
Frame duration 4.615 ms
Time slot duration 577 µs
Modulation GMSK
Receiver input sensitivity @ ARP
BER Class II < 2.4%
GSM 850 -102 -106 dBm
GSM 1800 -102 -105 dBm
GSM 1900 -102 -105 dBm
1)
Power control level PCL 5
2)
Power control level PCL 0
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 83 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 84
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 34: Local oscillator and intermediate frequencies used by MC46
All frequencies in MHz
GSM 850
PCN 1800
PCS 1900
Frequency Band Channel Local Oscillator Intermediate
Frequency
TX 824.2 – 848.8 128 - 251 3612.8 – 3723.2 79
RX 869.2 – 893.8 128 - 251 3476.0 – 3575.2 0
TX 1710.2 – 1733.0 512 – 626 3580.4 – 3626.0 80
TX 1733.2 – 1759.8 627 – 760 3628.4 – 3681.6 81
TX 1760.0 – 1784.8 761 – 885 3680.0 – 3729.6 80
RX 1805.2 – 1879.8 512 – 885 3610.4 – 3759.6 0
TX 1850.2 – 1909.8 512 – 810 3860.4 – 3979.6 80
RX 1930.2 – 1989.8 512 – 810 3860.4 – 3979.6 0
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 84 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 85

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.7 Electrostatic discharge
The GSM engine is not protected against Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) in general.
Consequently, it is subject to ESD handling precautions that typically apply to ESD sensitive
components. Proper ESD handling and packaging procedures must be applied throughout
the processing, handling and operation of any application that incorporates a MC46 module.
Special ESD protection provided on MC46:
Antenna interface: one spark discharge line (spark gap)
SIM interface: clamp diodes for protection against overvoltage.
The remaining ports of MC46 are not accessible to the user of the final product (since they
are installed within the device) and therefore, are only protected according to the “Human
Body Model” requirements.
MC46 has been tested according to the EN 61000-4-2 standard. The measured values can
be gathered from the following table.
Table 35: Measured electrostatic values
Specification / Requirements Contact discharge Air discharge
ETSI EN 301 489-7
ESD at SIM port
ESD at antenna port
Human Body Model (Test conditions: 1.5 kW, 100 pF)
ESD at the module
± 4kV ± 8kV
± 4kV ± 8kV
± 1kV
Note: Please note that the values may vary with the individual application design. For
example, it matters whether or not the application platform is grounded over
external devices like a computer or other equipment, such as the Siemens
reference application described in Chapter 7.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 85 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 86

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
5.8 Reliability characteristics
The test conditions stated below are an extract of the complete test specifications.
Table 36: Summary of reliability test conditions
Type of test Conditions Standard
Vibration Frequency range: 10-20 Hz; acceleration: 3.1mm
amplitude
Frequency range: 20-500 Hz; acceleration: 5g
Duration: 2h per axis = 10 cycles; 3 axes
Shock half-sinus Acceleration: 500g
Shock duration: 1msec
1 shock per axis
6 positions (± x, y and z)
Dry heat Temperature: +70 ±2°C
Test duration: 16 h
Humidity in the test chamber: < 50%
Temperature
change (shock)
Damp heat cyclic High temperature: +55°C ±2°C
Low temperature: -40°C ±2°C
High temperature: +85°C ±2°C
Changeover time: < 30s (dual chamber system)
Test duration: 1 h
Number of repetitions: 100
DIN IEC 68-2-6
DIN IEC 68-2-27
EN 60068-2-2 Bb ETS
300019-2-7
DIN IEC 68-2-14 Na
ETS 300019-2-7
DIN IEC 68-2-30 Db
Cold (constant
exposure)
Low temperature: +25°C ±2°C
Humidity: 93% ±3%
Number of repetitions: 6
Test duration: 12h + 12h
Temperature: -40 ±2°C
Test duration: 16 h
ETS 300019-2-5
DIN IEC 68-2-1
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 86 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 87
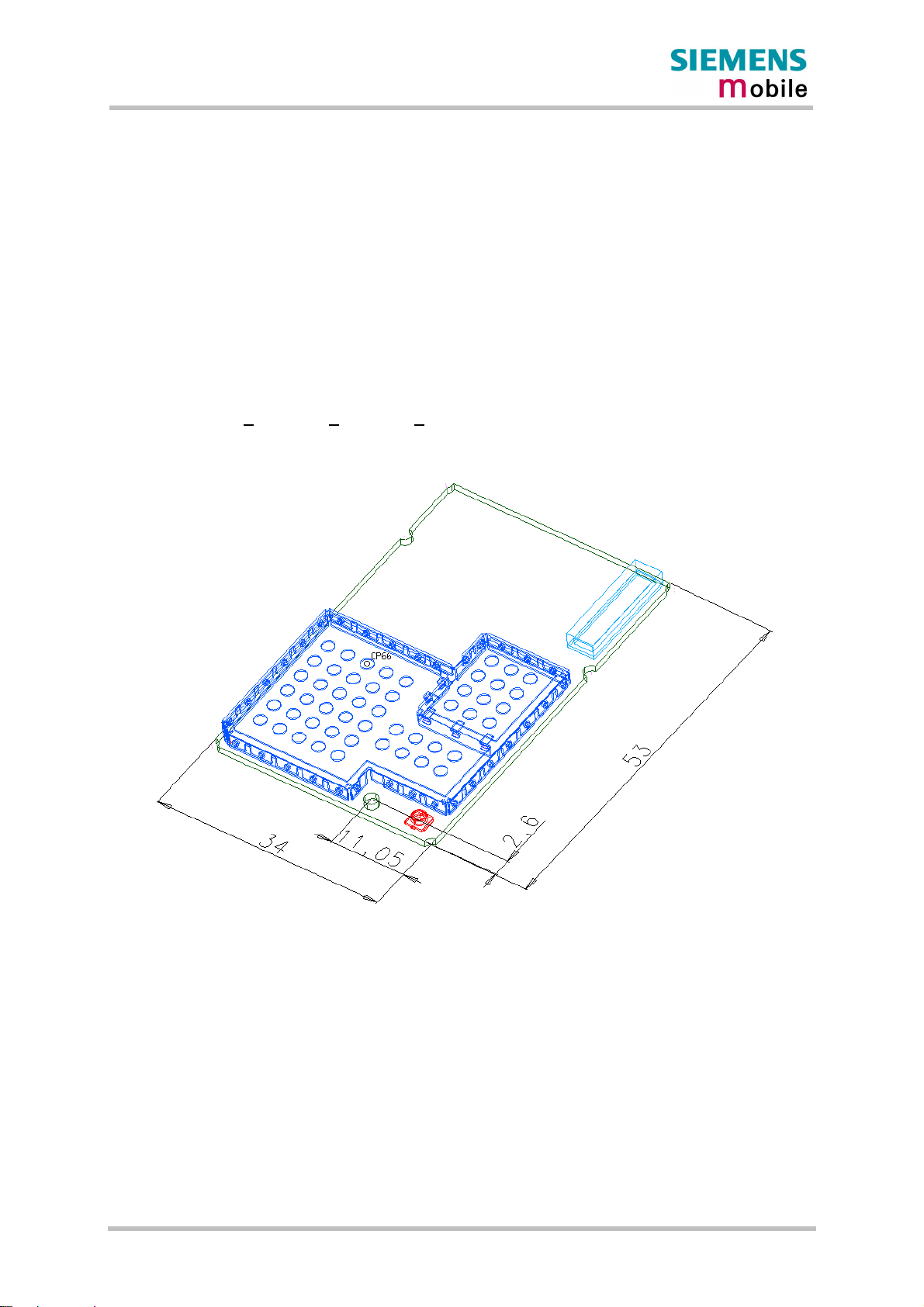
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
6 Mechanics
The following chapters describe the mechanical dimensions of MC46 and give
recommendations for integrating MC46 into the host application.
6.1 Mechanical dimensions of MC46
Figure 38 shows the top view on MC46 and provides an overview of the mechanical
dimensions of the board. For further details see Figure 39.
Size: 53 +
Weight: 10g
0.15 x 34 +0.15 x 3.5+0.3 mm
Figure 38: MC46 – top view
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 87 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 88
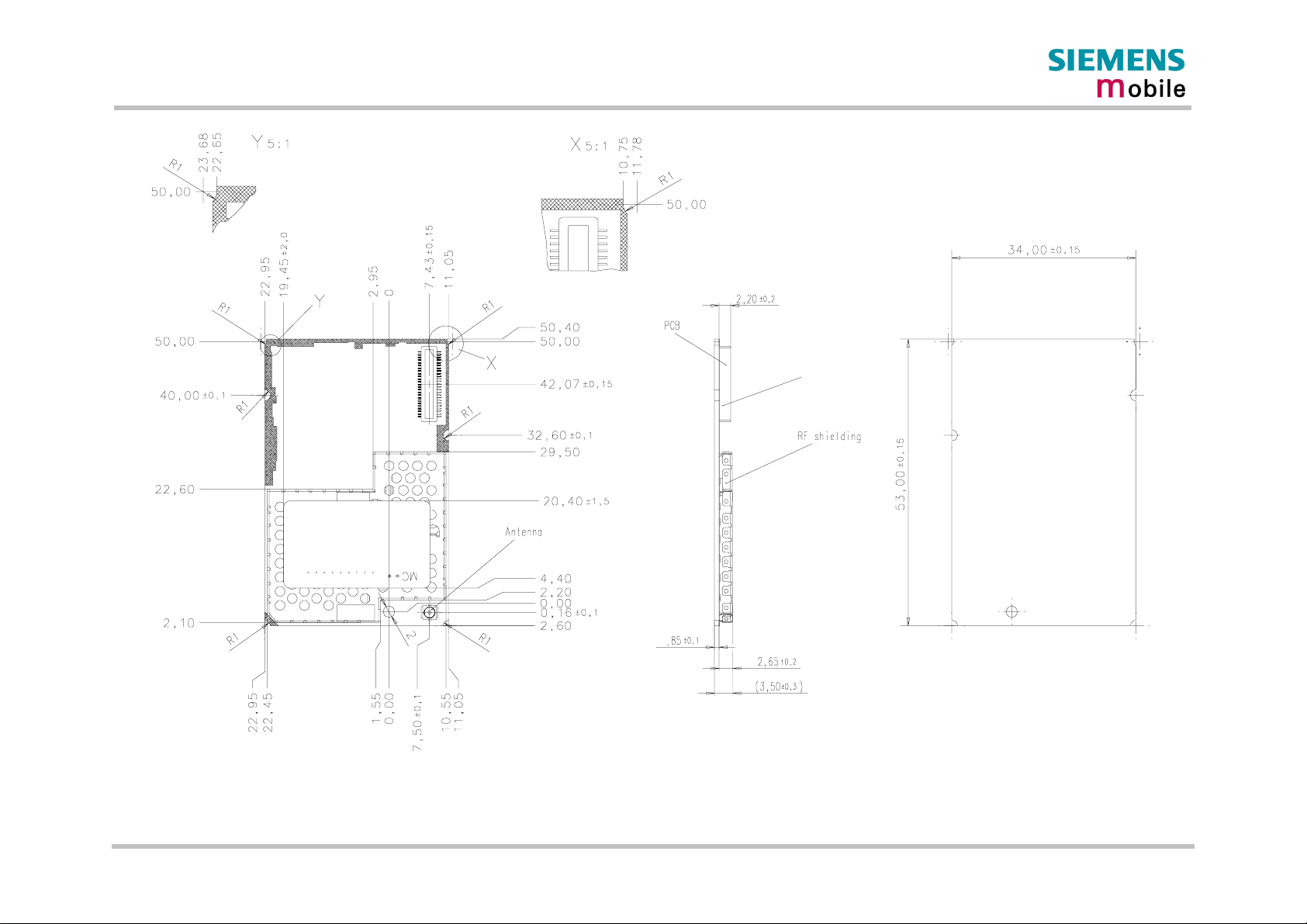
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Board-to-board connector
All dimensions in millimeter
Figure 39: Mechanical dimensions of MC46
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 88 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 89

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Ground pad, e.g. for heatsink
or connection to host device
Ø
1
.
1
TP 402
14.42
4.75
0.00
10.60
0
TP GND
TP BATT+
Figure 40: MC46 bottom view
0
9
4
.
.
6
4
2
2
0
5
.
5
1
0
0
.
0
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 89 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 90

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
6.2 Mounting MC46 onto the application platform
There are many ways to properly install MC46 in the host device. An efficient approach is to
mount the MC46 PCB to a frame, plate, rack or chassis.
Fasteners can be M1.6 or M1.8 screws plus suitable washers, circuit board spacers, or
customized screws, clamps, or brackets. Screws must be inserted with the screw head on
the bottom of the MC46 PCB. This is necessary to avoid contacting the shielding covers on
top.
In addition, the board-to-board connection can also be utilized to achieve better support.
MC46 provides a number of ground pads, all of them illustrated in Figure 40. If the bottom of
MC46 faces the holding device, only use the ground pads for the connection. To avoid short
circuits ensure that the remaining sections of the MC46 PCB do not come into contact with
the host device since there are a number of test points. The largest ground pad in the middle
of the board can also be used to attach cooling elements, e.g. a heat sink or thermally
conductive tape. Refer to Chapter 6.4 for an overview on a variety of cooling elements.
Particular attention should be paid to the test point TP 402. Placed beneath the large ground
pad it has been added for manufacturing only. When the pad is used for grounding the unit
or connecting a heat sink, extra care must be taken not to contact this test point. Figure 40
shows the positions of all test points.
To prevent mechanical damage, be careful not to force, bend or twist the module. Be sure it
is positioned flat against the host device.
All the information you need to install an antenna is summarized in Chapter . Note that the
antenna pad on the bottom of the MC46 PCB must not be influenced by any other PCBs,
components or by the housing of the host device. It needs to be surrounded by a restricted
space as described in Chapter 4.1.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 90 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 91

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
6.3 Board-to-board connector
This chapter provides specifications for the 50-pin board-to-board connector which serves as
physical interface to the host application. The receptacle assembled on the MC46 PCB is
type Hirose DF12C. Mating headers from Hirose are available in different stacking heights.
Figure 41: Hirose DF12C receptacle on MC46
Table 37: Ordering information DF12 series
Figure 42: Header Hirose DF12 series
Item Part number Stacking
HRS number
height (mm)
Receptacle on MC46 DF12C(3.0)-50DS-0.5V(81) 3 - 5 537-0694-9-81
Headers DF12 series DF12E(3.0)-50DP-0.5V(81)
DF12E(3.5)-50DP-0.5V(81)
DF12E(4.0)-50DP-0.5V(81)
DF12E(5.0)-50DP-0.5V(81)
3.0
3.5
4.0
5.0
537-0834-6-**
537-0534-2-**
537-0559-3-**
537-0584-0-**
Notes: The headers listed above are without boss and metal fitting. Please contact Hirose for details on
other types of mating headers. Asterixed HRS numbers denote different types of packaging.
Table 38: Electrical and mechanical characteristics of the Hirose DF12C connector
Parameter Specification (50 pin board-to-board connector)
Number of contacts 50
Quantity delivered 2000 connectors per tape & reel
Voltage 50V
Rated current 0.3A max per contact
Resistance 0.05 Ohm per contact
Dielectric withstanding voltage 500V RMS min
Operating temperature -45°C...+125°C
Contact material phosphor bronze (surface: gold plated)
Insulator material PA , beige natural
Stacking height 3.0 mm ; 3.5 mm ; 4.0 mm ; 5.0 mm
Insertion force 21.8N
Withdrawal force 1st 10N
Withdrawal force 50th 10N
Maximum connection cycles 50
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 91 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 92

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
6.3.1 Mechanical dimensions of the Hirose DF12 connector
Figure 43: Mechanical dimensions of Hirose DF12 connector
6.3.2 Adapter cabling
The board-to-board connection is primarily intended for direct contact between both
connectors. If this assembly solution does not fit into your application design ensure that the
used adapter cable meets the following requirements:
· Maximum length: 200 mm
It is recommended that the total cable length between the board-to-board connector pins
on MC46 and the pins of the card holder does not exceed 200 mm in order to meet the
specifications of 3GPP TS 51.010-1 and to satisfy the requirements of EMC compliance.
· Type of cable: Flexible cable or flexible printed circuit board designed to mate with the
Hirose receptacle and headers specified above.
The equipment submitted for type approving the Siemens reference setup of MC46 includes
a 160mm adapter cable. See Chapter 7.1.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 92 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 93

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
6.4 Heat sinks and thermally conductive tapes
Thermal management solutions vary largely according to the usage of the final product and
the design of the host device. Therefore, the focus of this chapter is on a brief overview of
standard heat sinks and thermally conductive tapes that have been tested with MC46.
6.4.1 Test conditions and results
Table 39 shows the results of extensive testing based on different combinations of heat
sinks and thermally conductive tapes.
All measurements were performed under the same test conditions:
· GPRS connection, Power control level 5, GSM Band: 850MHz
· GPRS Class 10 (3x downlink, 2x uplink), Coding Scheme CS-4
· V
BATT+ nom
· Ambient temperature: 55°C
· The conductive tapes were attached either to entire bottom area of the module (in Table
39 referred to as “Full area”), or only to the ground pad near the power amplifier (in Table
39 referred to as “PA only”).
= 4.2V
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 93 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 94

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 39: Tested heat sinks and thermally conductive tapes and test results
Manufacturer Product name Description Rth Website Temperature
reduction
Test condition: Thermally conductive tape T2022 combined with different heat sinks (material characteristics of T2022: adhesive on both sides, silicon free,
100µm, Rth > 0,1 K/W, manufacturer: Balkhausen)
Fischerelektronik SK18 65mm x 37.5mm 3.75 K/W www.fischerelektronik.de 12-15°C Full area
5-10°C PA only
Fischerelektronik ICK R 19 K/W www.fischerelektronik.de 4-5°C PA only
Fischerelektronik ICK C17 17 K/W www.fischerelektronik.de 3-4°C PA only
Fischerelektronik SFP 060-50
Alumininum Profile
Fischerelektronik SFP 007-50
Alumininum Profile
Wakefield Spezial A&D 13mm x 5mm 32 K/W www.wakefield.com 2°C PA only
Wakefield Spezial A&D 19mm x 8mm 27 K/W www.wakefield.com 2°C PA only
Test condition: Heat sink SK 18 with conductive tape TAP 005
80mm x 50mm x 8mm Not specified www.fischerelektronik.de 4-6°C Full area
40mm x 50mm x 5mm Not specified www.fischerelektronik.de 1°C Full area
Conductive tape
positioned on
Balkhausen TAP 005 adhesive on both
sides, silicon free,
125µm
>0,1 K/W www.balkhausen.com
10-13°C Full area
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 94 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 95

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
7 Reference Approval
7.1 Reference Equipment for Type Approval
The Siemens reference setup that will be submitted to type approve MC46 consists of the
following components:
· Siemens MC46 cellular engine
· Development Support Box (DSB45)
· Flex cable (160 mm) from Hirose DF12C receptacle on MC46 to Hirose DF12 connector
on DSB45. Please note that this cable is not included in the scope of delivery of DSB45.
· SIM card reader integrated on DSB45
· Handset type Votronic HH-SI-30.3/V1.1/0
· PC as MMI
Antenna or 50 W
cable to system
simulator
Antenna
PC
Power supply
RS-232
Figure 44: Reference equipment for approval
DSB45
Flex cable
160mm
DAI cable for
acoustic measuring
SIM
Handset
GSM engine
DAI Box
Acoustic tester
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 95 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 96

MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
7.2 Compliance with FCC Rules and Regulations
The FCC Equipment Authorization Certification for the MC46 reference application described
in Chapter 7.1 will be listed under the
FCC identifier QIPMC45,
granted to Siemens AG.
The MC46 reference application registered under the above identifier is certified to be in
accordance with the following Rules and Regulations of the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC).
“This device is to be used only for mobile and fixed applications. The antenna(s) used
for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm
from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter. Users and installers must be provided with antenna installation
instructions and transmitter operating conditions for satisfying RF exposure
compliance.
This device is approved as a module to be installed in other devices. Each OEM must
obtain their own Certification for each device containing this module.”
IMPORTANT: Manufacturers of mobile, fixed or portable devices incorporating MC46
modules are advised to clarify any regulatory questions and to have their completed product
tested and approved for FCC compliance.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 96 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 97
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
8 List of parts and accessories
Table 40: List of parts and accessories
Description Supplier Ordering information
MC46 Siemens Siemens ordering number: L36880-N8320-A100
Siemens Car Kit Portable Siemens Siemens ordering number: L36880-N3015-A117
DSB45 Support Box Siemens Siemens ordering number: L36880-N8301-A100
BB35 Bootbox Siemens Siemens ordering number: L36880-N8102-A100-1
Votronic Handset VOTRONIC Votronic HH-SI-30.3/V1.1/0
VOTRONIC
Entwicklungs- und Produktionsgesellschaft für
elektronische Geräte mbH
Saarbrücker Str. 8
D-66386 St. Ingbert
SIM card holder incl. push
button ejector and slide-in
tray
Battery cell XWODA Shenzhen
DF12C board-to-board
connector
Molex Ordering numbers: 91228
Xwoda
Electronic Co.,
Ltd
Hirose See Chapter 6.3 for details on receptacle on MC46
Phone: 06 89 4 / 92 55-0
Fax: 06 89 4 / 92 55-88
e-mail: contact@votronic.com
91236
Sales contacts are listed in Table 41.
To place orders or obtain more information please
contact:
Shenzhen Xwoda Electronic Co., Ltd
Building C, Tongfukang Industrial Zone
Shiyan Town, Bao’an District
Shenzen
P.R.China
Contact:
Waichard Tsui
Phone: +86-755-27623789 ext. 370
Fax: +86-755-27623078
Email: waichard@xwoda.com.cn
Info:
Http://xwoda.com.cn
and mating headers.
U.FL-R-SMT antenna
connector
Hirose See Chapter 4.1.2 for details on U.FL-R-SMT
Sales contacts are listed in Table 42.
connector, mating plugs and cables.
Sales contacts are listed in Table 42.
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 97 of 98 21.08.2003
Page 98
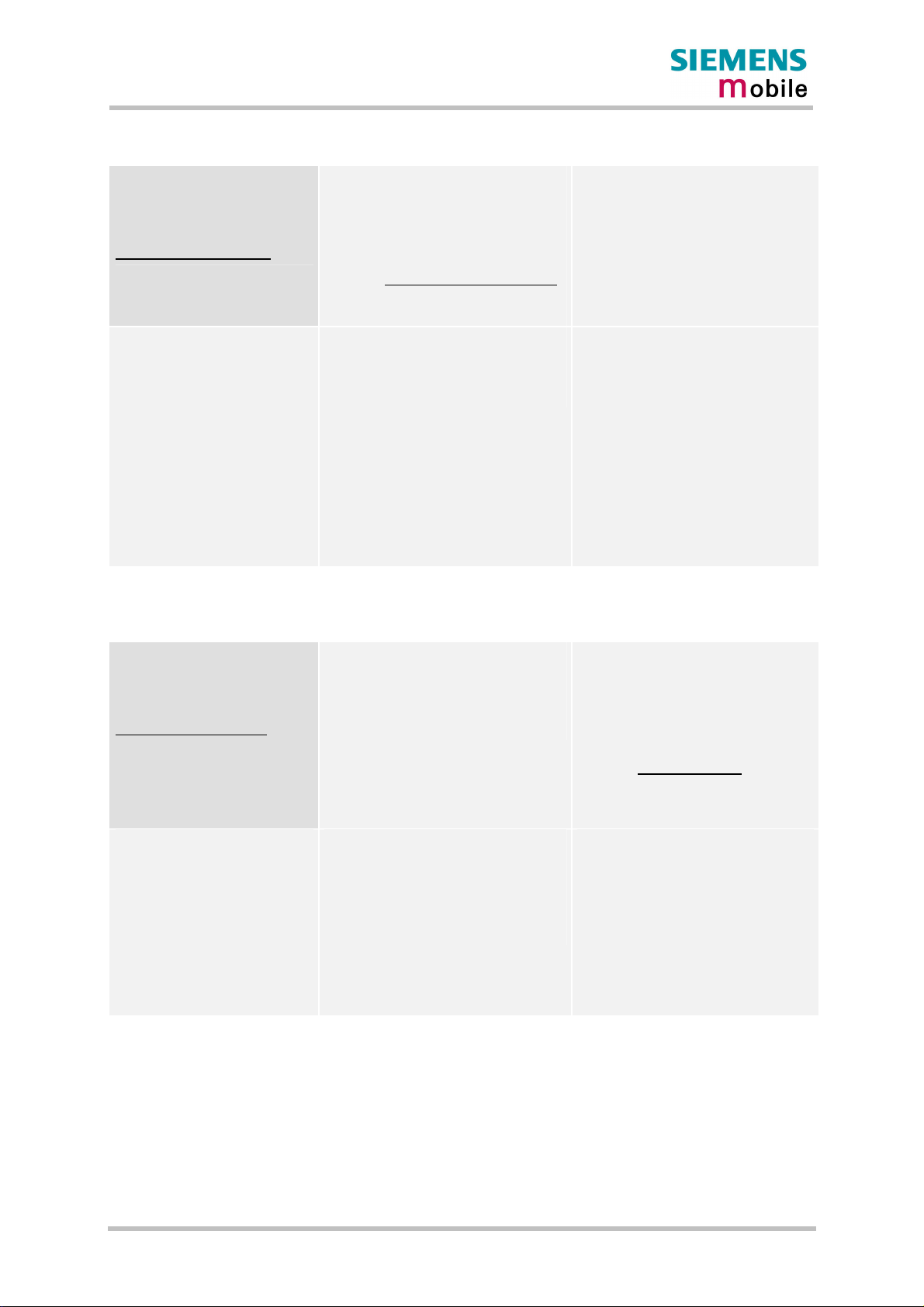
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
DRAFT
Table 41: Molex sales contacts (subject to change)
Molex
For further information
please click:
http://www.molex.com/
Molex China Distributors
Beijing,
Room 1319, Tower B,
COFCO Plaza
No. 8, Jian Guo Men Nei
Street, 100005
Beijing People's Republic of
China
Phone: 86-10-6526-9628
Phone: 86-10-6526-9728
Phone: 86-10-6526-9731
Fax: 86-10-6526-9730
Molex Deutschland GmbH
Felix-Wankel-Str. 11
D-74078 Heilbronn-Biberach
Phone: +49(7066)9555 0
Fax: +49(7066)9555 29
Email: mxgermany@molex.com
Molex Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Jurong, Singapore
Phone: 65-268-6868
Fax: 65-265-6044
Table 42: Hirose sales contacts (subject to change)
American Headquarters
Lisle, Illinois 60532 U.S.A.
Phone: 1-800-78MOLEX
Fax: 630-969-1352
Molex Japan Co. Ltd.
Yamato, Kanagawa, Japan
Phone: 81-462-65-2324
Fax: 81-462-65-2366
Hirose Ltd.
For further information
please click:
http://www.hirose.com
Hirose Electric UK, Ltd
Crownhill Business Centre
22 Vincent Avenue,
Crownhill
Milton Keynes, MK8 OAB
Phone: 44-1908-305400
Fax: 44-1908-305401
Hirose Electric (U.S.A.) Inc
2688 Westhills Court
Simi Valley, CA 93065
Phone: 805-522-7958
Fax: 805-522-3217
Hirose Electric Co., Ltd.
5-23, Osaki 5 Chome,
Shinagawa-Ku
Tokyo 141, Japan
Phone: 03-3491-9741
Fax: 03-3493-2933
Hirose Electric GmbH
Zeppelinstrasse 42
73760 Ostfildern
Kemnat 4
Phone: +49 711 4560-021
Fax +49 711 4560-729
E-mail info@hirose.de
Hirose Electric Co., Ltd.
Eroupean Brance
First class Building 4F
Beechavenue 46, 1119PV
Schiphol-Rijk, Netherlands
Phone: 31-20-6557-460
Fax: 31-20-6557-469
MC46_HD_V02.8xb Page 98 of 98 21.08.2003
 Loading...
Loading...