
Upgradeable PDU
Instruction Manual
geistglobal.com

2
Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual
Table of Contents
Part I Specifications
................................................................................................................................... 41 Overview
................................................................................................................................... 42 Environmental
.......................................................................................................................................................... 4Temperature
.......................................................................................................................................................... 4Humidity
.......................................................................................................................................................... 4Elevation
................................................................................................................................... 43 Electrical
................................................................................................................................... 54 Receptacle Ratings
................................................................................................................................... 55 Networking
.......................................................................................................................................................... 5Ethernet Link Speed
.......................................................................................................................................................... 5Protocols
.......................................................................................................................................................... 5User Interfaces
................................................................................................................................... 56 EMC Verification
Part II Installation
................................................................................................................................... 61 Guidelines
................................................................................................................................... 72 Mounting
Part III Interchangeable Monitoring Device
................................................................................................................................... 161 Basic
................................................................................................................................... 162 Monitored
................................................................................................................................... 173 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
................................................................................................................................... 174 Network Setup
.......................................................................................................................................................... 18Windows
.......................................................................................................................................................... 21Mac
................................................................................................................................... 225 Removal
................................................................................................................................... 246 Installation
4
6
16
Part IV Web Interface
................................................................................................................................... 251 Sensors Page
.......................................................................................................................................................... 25Overview
.......................................................................................................................................................... 28Alarms & Warnings
................................................................................................................................... 322 System
.......................................................................................................................................................... 32User Accounts
.......................................................................................................................................................... 34Network
.......................................................................................................................................................... 35Email
.......................................................................................................................................................... 37SNMP
.......................................................................................................................................................... 39Syslog
.......................................................................................................................................................... 39Admin
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
25
......................................................................................................................................................... 26Configuration and Operation
......................................................................................................................................................... 29Add/Modify Alarms & Warnings
© 2015 Geist

................................................................................................................................... 413 Help
3Table Of Contents
.......................................................................................................................................................... 39Locale
.......................................................................................................................................................... 40Restore Defaults
.......................................................................................................................................................... 40Firmware Update
.......................................................................................................................................................... 41Info
.......................................................................................................................................................... 41Support Site
Part V Technical Support
................................................................................................................................... 421 Resetting PDU
................................................................................................................................... 422 Service and Maintance
................................................................................................................................... 423 More Technical Support
................................................................................................................................... 424 Using Microsoft Exchange as an SMTP server
42
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
3
Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual4
Operating
10°C (50°F)
min
45°C (122°F) max (full nameplate
current load)
60°C (140°F) max (50% of max
nameplate and receptacle current
rating)
Storage
-25°C (-13°F)
min
65°C (149°F) max
Operating
5% min
95% max (non-condensing)
Storage
5% min
95% max (non-condensing)
Operating
0 m (0 ft) min
3050 m (10000 ft) max
Storage
0 m (0 ft) min
15240 m (50000 ft) max
1 Specifications
1.1 Overview
The new Geist Upgradeable PDU gives data-center managers the flexibility to install
the intelligence they require today, with the option to upgrade technology as needs
evolve. From basic power to power monitoring, the Geist Upgradeable product line
adapts to your business well into the future.
To establish this extraordinary upgrade path, our engineers took Geist's robust PDU
design and incorporated an Interchangeable Monitoring Device (IMD). Geist's rugged
PDUs last for many years, and with the new IMD design, users will be able to upgrade
their PDUs to newer monitoring technologies in the future without having to replace the
entire PDU. The hot-swappable IMD can be changed out in a few simple steps,
without interrupting power to critical servers.
1.2 Environmental
1.2.1 Temperature
1.2.2 Humidity
1.2.3 Elevation
1.3 Electrical
See nameplate for unit ratings.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
1.4 Receptacle Ratings
Type
Ratings
NEMA 5-15R or L5-15R
125Vac, 15A
NEMA 5-20R or L5-20R
125Vac, 20A
NEMA 6-20R or L6-20R
250Vac, 20A
NEMA L5-30R
125Vac, 30A
NEMA L6-30R
250Vac, 30A
IEC-60320 C13
250Vac, 10A (UL & CSA 15A, 250Vac)
IEC-60320 C19
250Vac, 16A (UL & CSA 20A, 250Vac)
1.5 Networking
1.5.1 Ethernet Link Speed
10/100 Mbit; full-duplex
1.5.2 Protocols
Specifications 5
ARP, IPv4, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, NDP, TCP, UDP, DNS, HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP,
SMTPS, DHCP, SNMP (v1/v2c/v3), Syslog
1.5.3 User Interfaces
JSON API, SNMP, Web GUI
1.6 EMC Verification
This Class A device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual6
2 Installation
2.1 Guidelines
For standard temperature models, the ambient temperature of the installation
location, such as an IT rack, should be no greater than 45°C if the PDU is loaded to
its full nameplate current rating. The ambient temperature of the installation location
should be not greater than 60°C if the PDU normal current load is a maximum 50%
of the nameplate and individual receptacle ratings. (Note: load up to full nameplate
rating are permitted during short term abnormal operating conditions).
Install the PDU such that the amount of airflow required for safe operation of
equipment is not compromised.
Mount the PDU so that a hazardous condition is not achieved due to uneven
mechanical loading.
Follow nameplate ratings when connecting equipment to the branch circuit. Take
into consideration the effect that overloading of the circuits might have on
overcurrent protection and supplied wiring.
The PDU relies on the building installation for protection from overcurrent. A
certified overcurrent protection device is required in the building installation. The
overcurrent protection device should be sized according to the PDU’s nameplate
ratings and local/national electrical code.
Reliable earthing of rack-mount equipment should be maintained. Particular
attention should be given to supply connections other than direct connections to the
branch circuit. The PDU must be connected to an earthed socket outlet.
PDU is intended for restricted-access locations. Only qualified service personnel
should install and access the PDU.
For pluggable equipment, install the PDU so the input plug or appliance coupler may
be disconnected for service.
The PDU is intended for indoor use only. Do not install the unit in wet or outdoor
environments, and do not install it next to water tanks or plumbing.
The PDU is intended for use with TN, TT, or IT power supply systems.
Installation
1. Using appropriate hardware, mount unit to rack. (See next section for examples.)
2. Plug PDU into an appropriately-rated and protected branch-circuit receptacle.
3. Plug in the devices to be powered by the PDU.
4. Turn on each device connected to the PDU. Sequential power-up is recommended
to avoid high inrush current.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
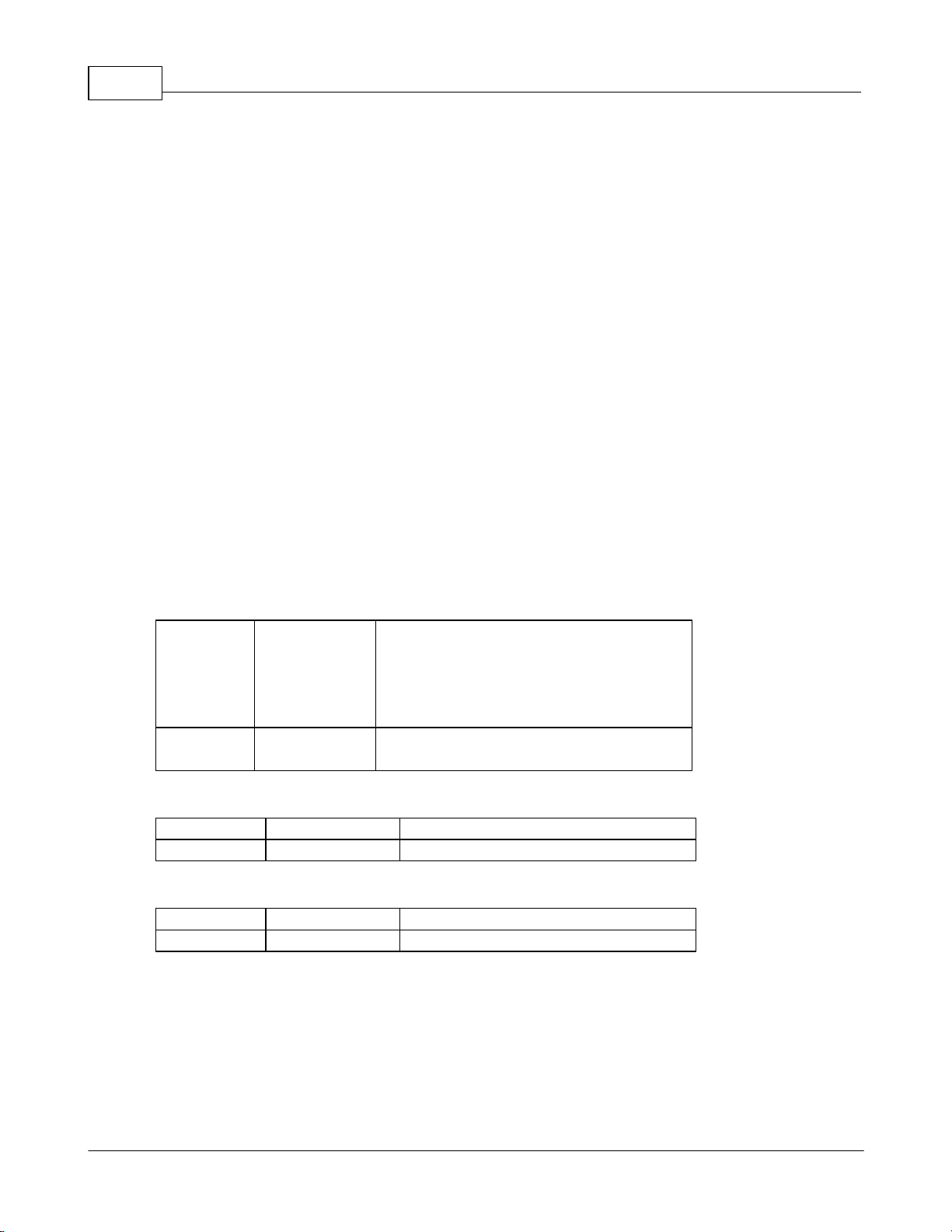
2.2 Mounting
Installation 7
Figure 1: Full-Length Bracket
Using the full-length bracket, mount PDU to rack as shown
Figure 2: Mini "L" Brackets
Using the mini “L” brackets, attach PDU to rack as shown
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
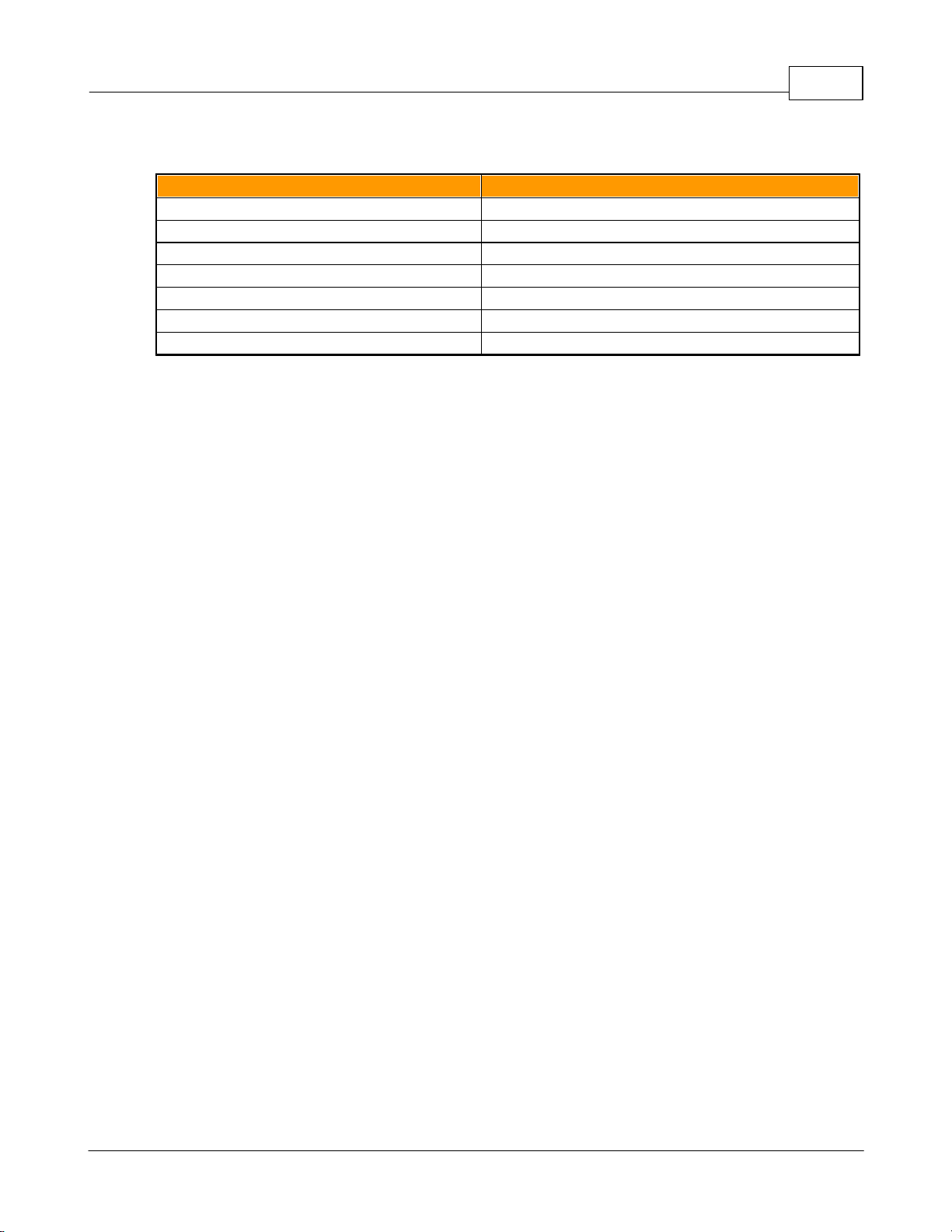
Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual8
Figure 3: Vertical-Extension Brackets
Using the vertical-extension brackets, attach PDU to rack as shown
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
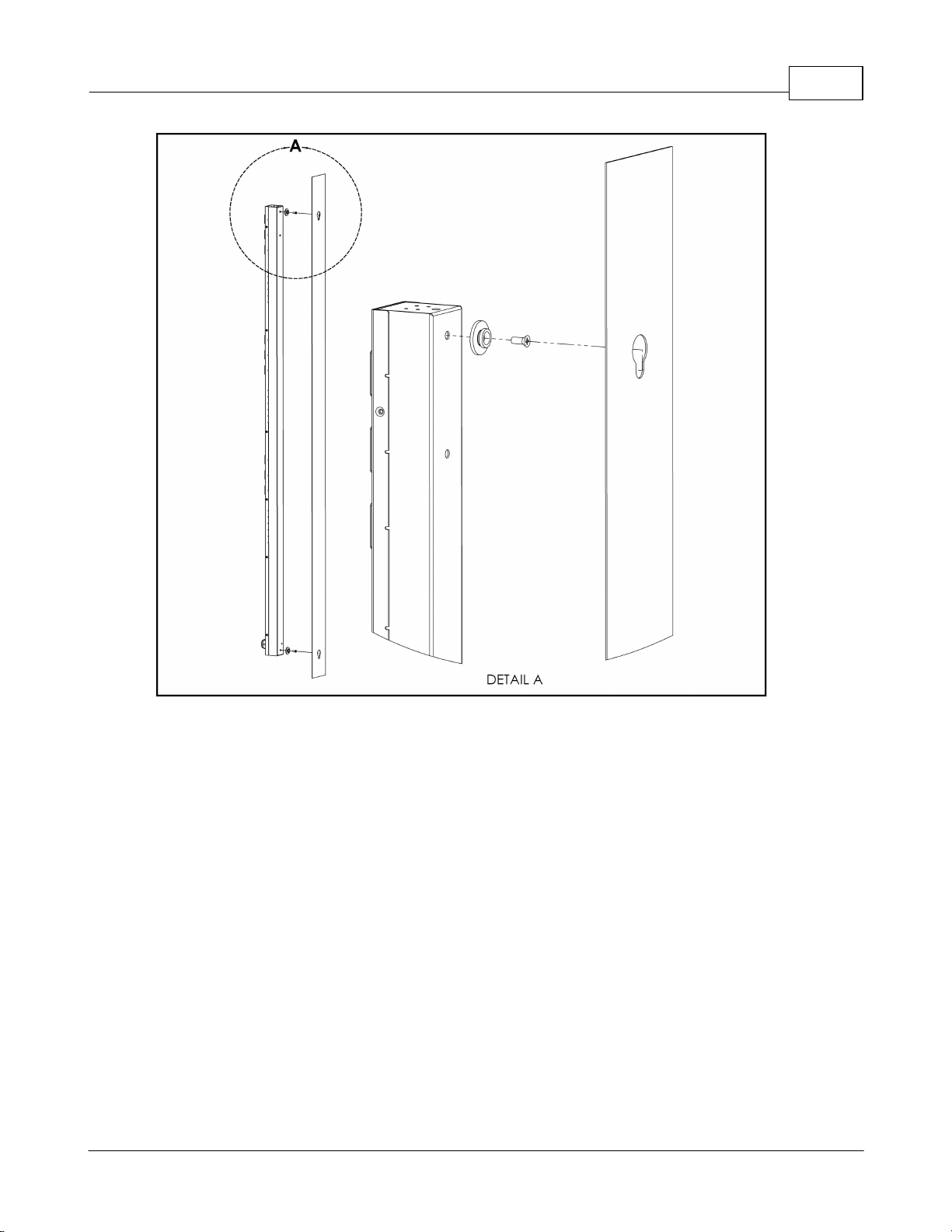
Installation 9
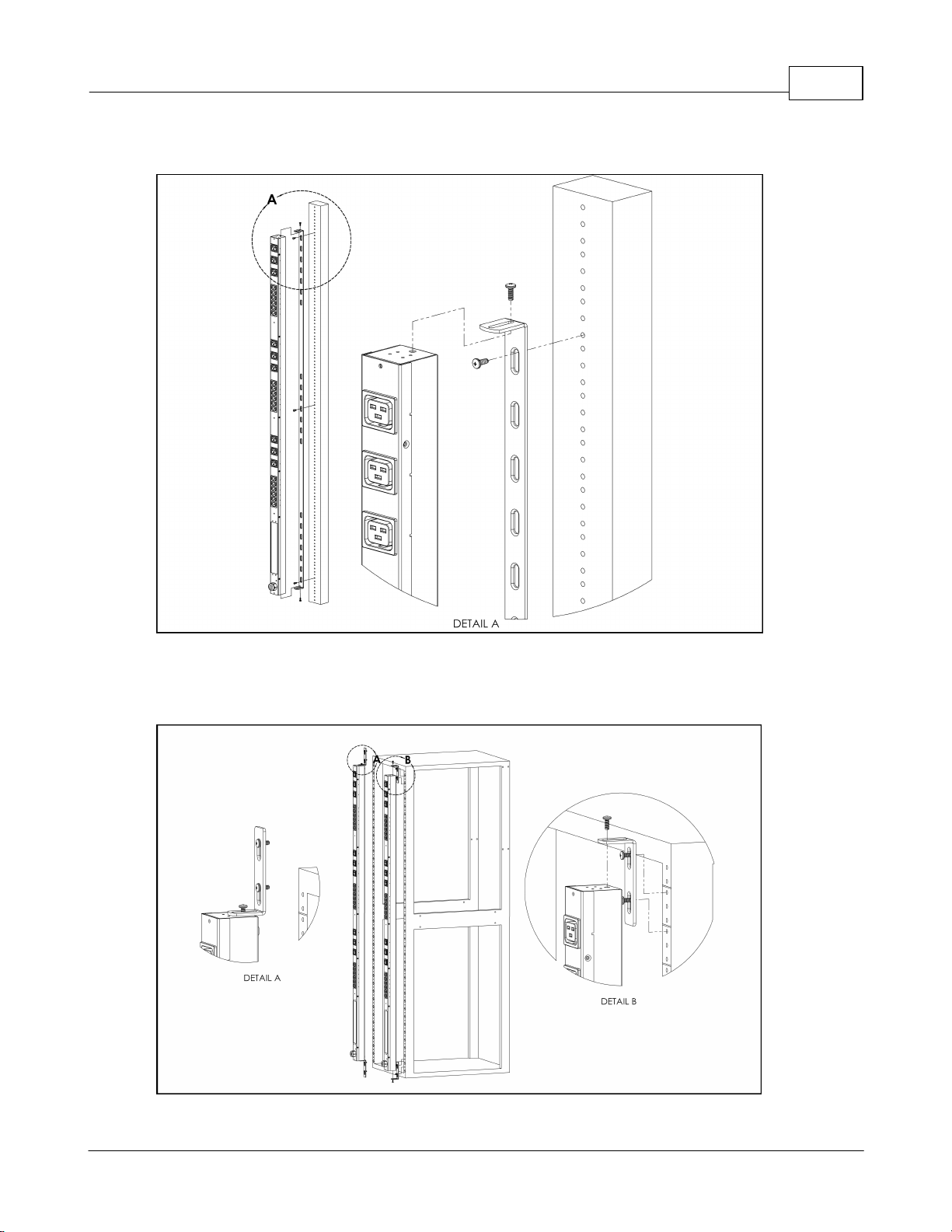
Figure 4: Toolless Mounting Hardware
Secure the toolless mounting buttons to PDU as shown. Use toolless buttons with keyholed slots built into the cabinet, or with optional Geist key-holed brackets.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
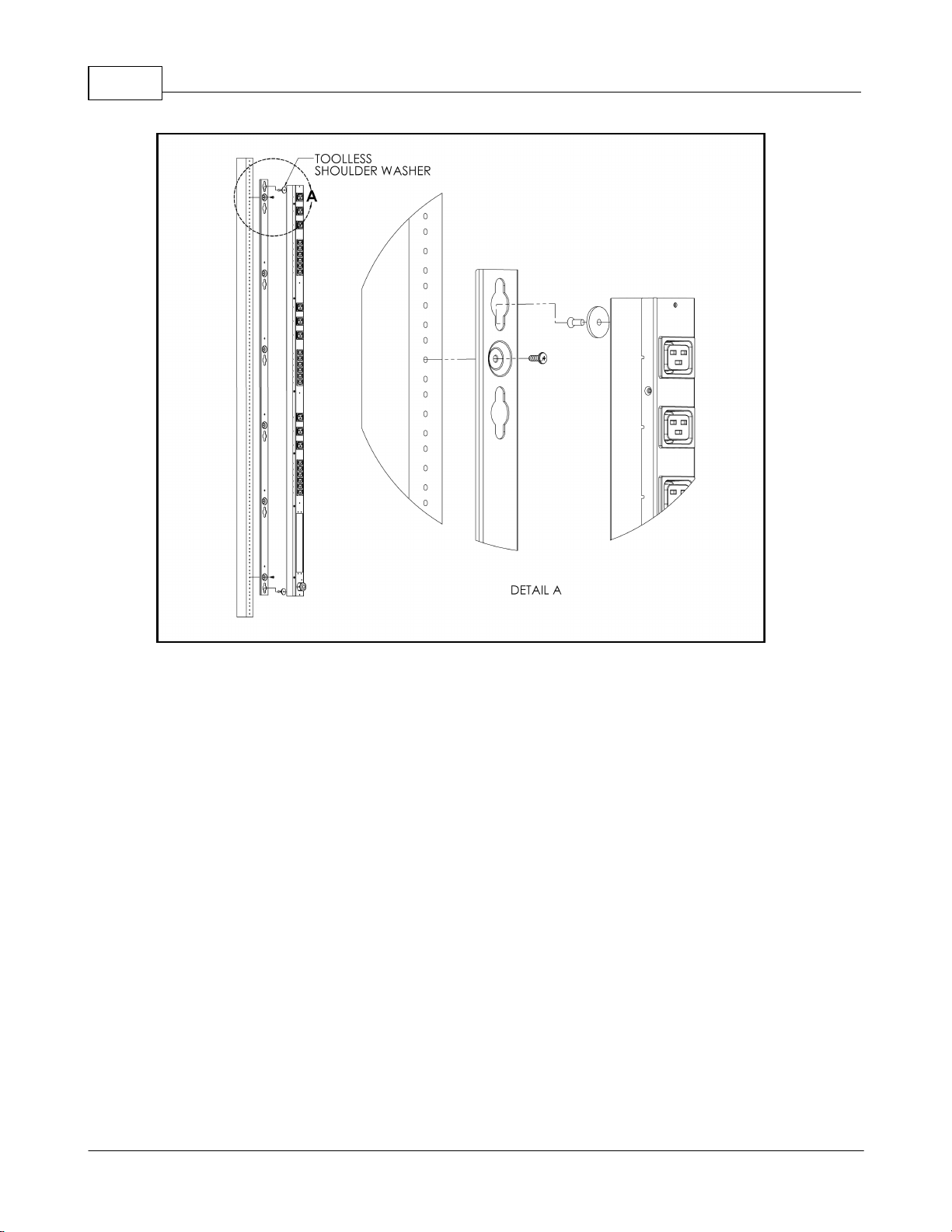
Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual10
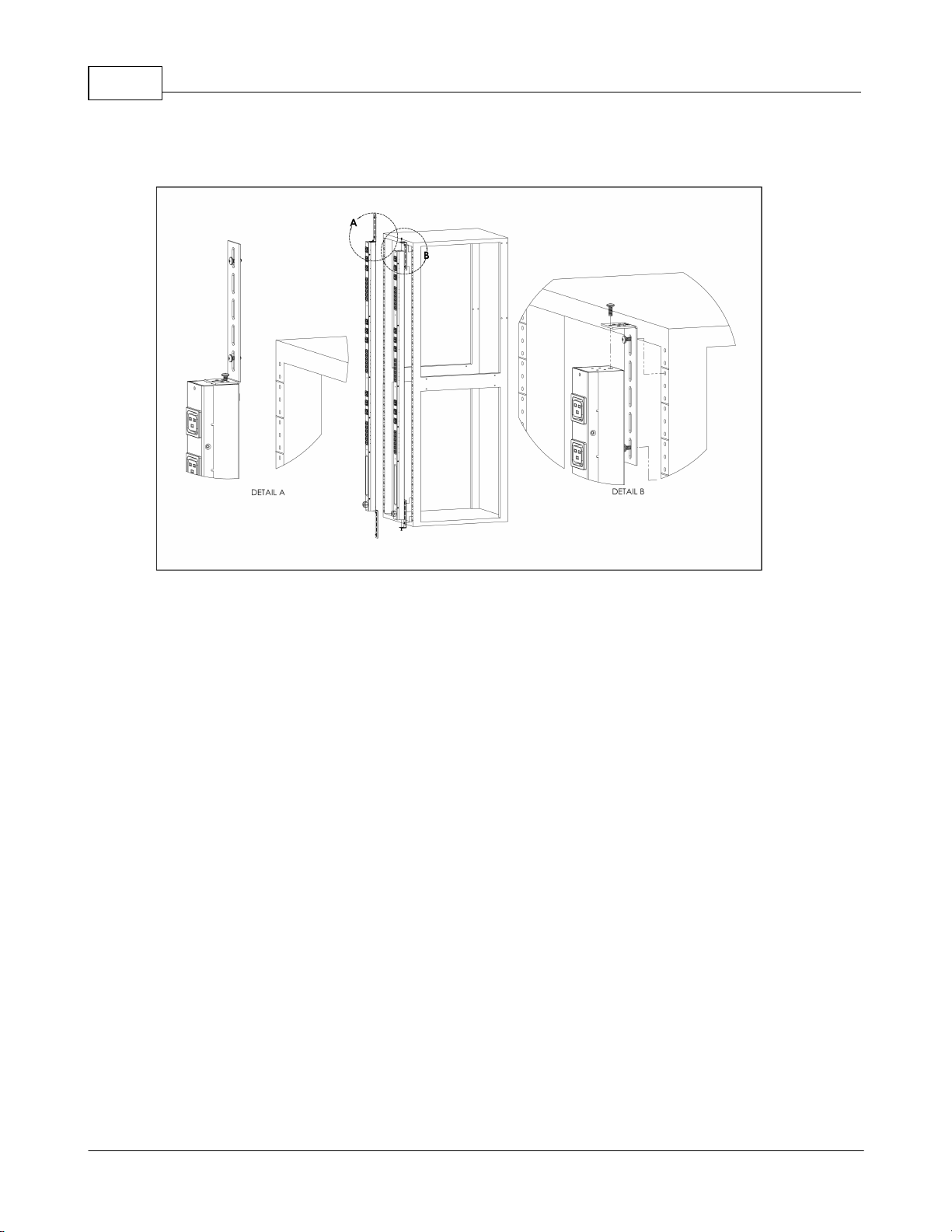
Figure 5: Toolless Full-Length Bracket
Using the full-length toolless bracket and toolless mounting buttons, attach PDU to
rack as shown
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
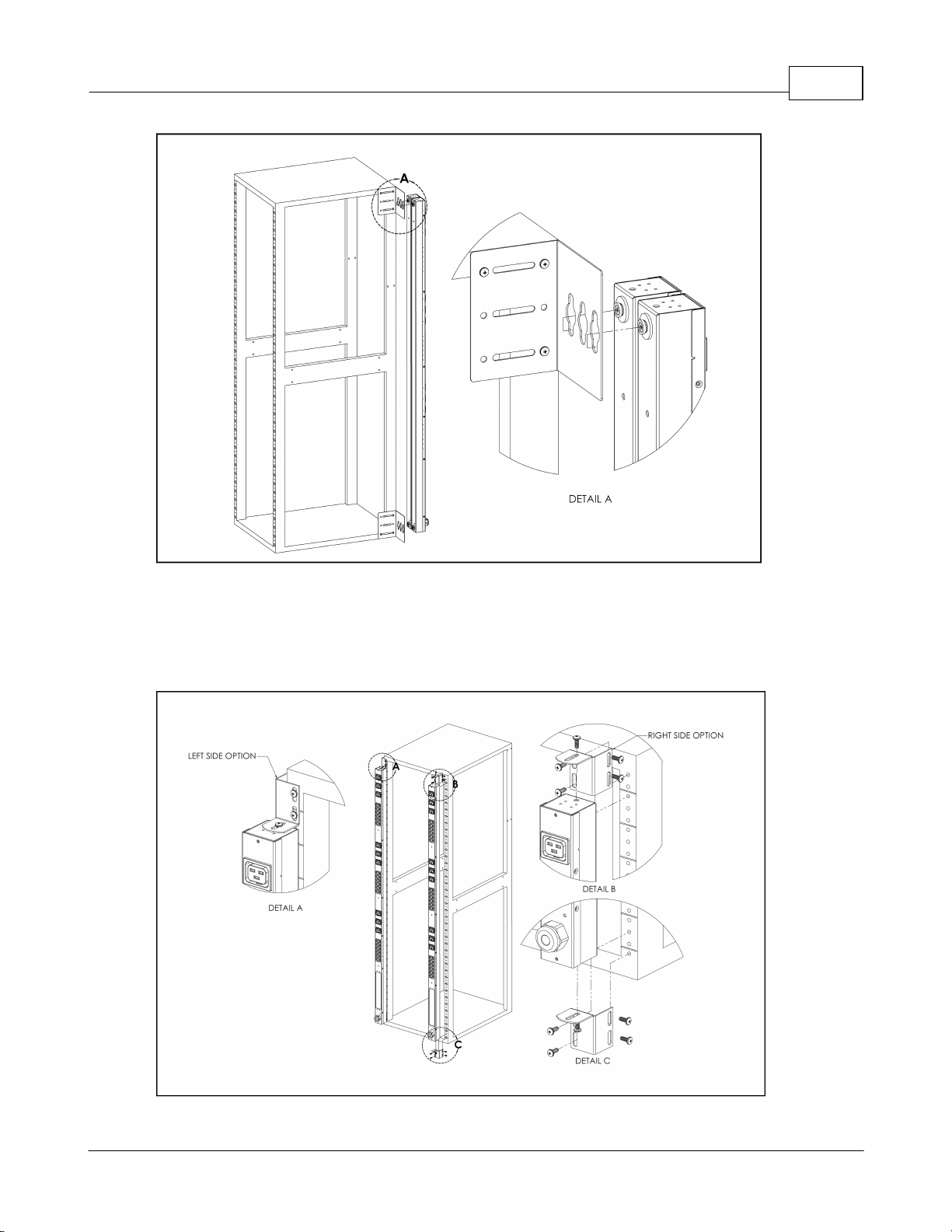
Installation 11
Figure 6: Single-Side-Mount 2-Unit Brackets
Using the single-side-mount 2-unit brackets and toolless mounting buttons, attach
PDU to rack as shown
Figure 7: Offset/Side-Mount Brackets
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
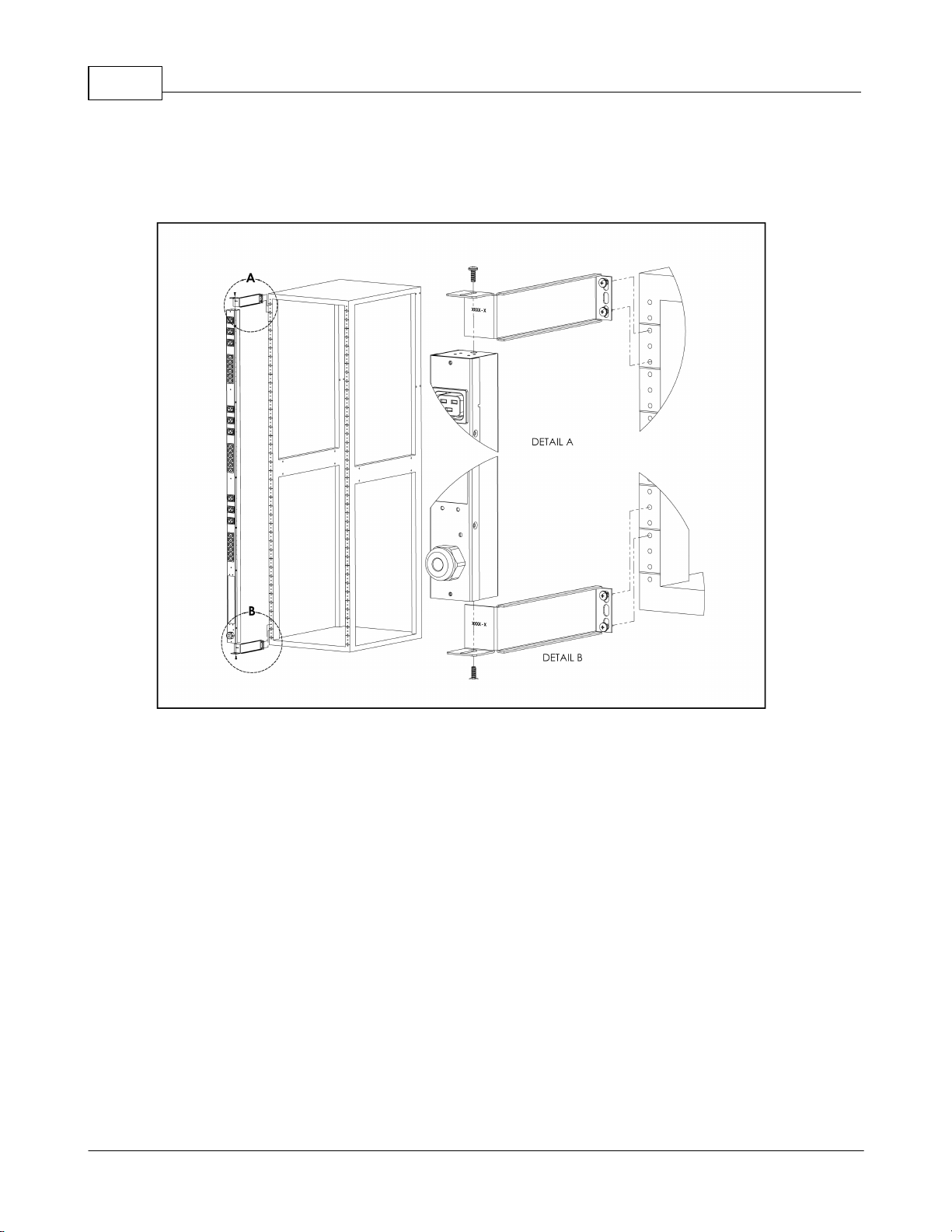
Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual12
Using the offset/side-mount brackets, attach PDU to rack as shown.
Figure 8: 7" Extension Brackets
Using the 7” extension brackets, attach PDU to rack as shown
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
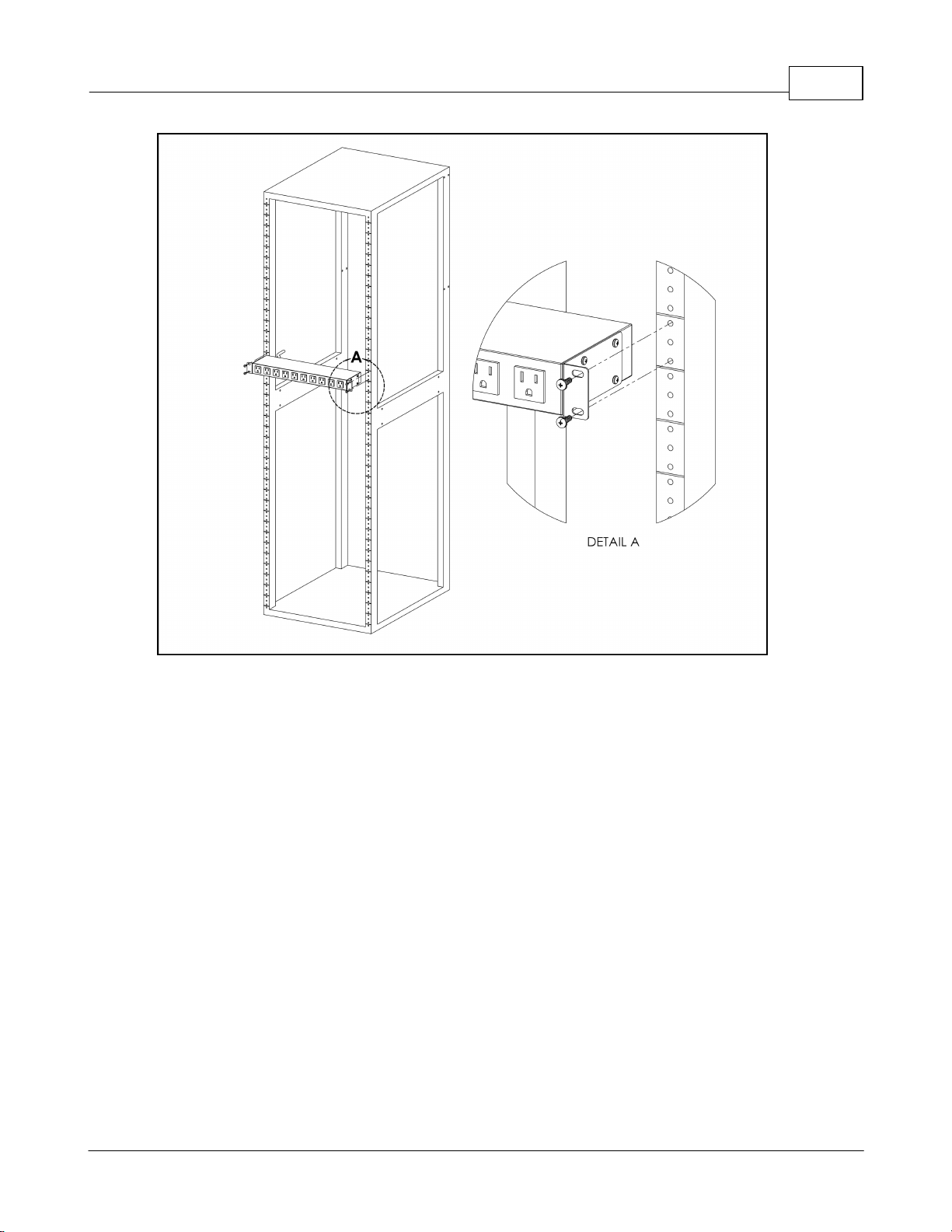
Installation 13
Figure 9: Flush-Mount Brackets
Using the flush-mount brackets, attach PDU to rack as shown
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual14
Figure 10: Adjustable-Mount Brackets
Using the adjustable-mount brackets, attach PDU to rack as shown
Figure 12: 23" Conversion-Mounting Brackets
Using the 23" conversion-mounting brackets, attach 19” PDU to 23” rack as shown
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Installation 15
Figure 13: 19" Horizontal/Panel-Mount Brackets
Using the 19” horizontal/panel-mount brackets, attach PDU to rack as shown
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual16
3 Interchangeable Monitoring Device
The Interchangeable Monitoring Device (IMD) is the core behind the Geist Upgradable
line of power products. The IMD can be replaced and upgraded to allow data-center
managers to future-proof their locations.
3.1 Basic
The Basic Geist Upgradable PDU is the baseline for the GU line of products. It is built
with the IMD-01X module, and provides low cost power distribution with the option of
being able to upgrade to add monitoring and other features in the future.
3.2 Monitored
The Monitored Geist Upgradable PDU is an advanced option for data centers that
need full remote monitoring and alarms. It is built with the IMD-02X module, which
provides dual Ethernet ports and a local display.
1. Dual Ethernet Ports: The Dual Ethernet ports act as a 2-port Ethernet switch,
allowing for multiple devices to be daisy-chained.
2. Hard-Reboot Button: Pressing the hard-reboot button reboots the IMD. This acts
as a power-cycle for the IMD, and does not change or remove any user
information.
3. Network-Reset Button: Holding the network-reset button for 15 seconds during
normal operation will restore the default IP address and reset the user accounts.
Holding the network-reset button during power-up will reset all of the unit's settings
back to factory-default values.
4. Local Display: The local display will display the phase, line, and circuit current
values (in Amperes).
5. Display Buttons: There are 3 buttons near the IMD display; a back button, a
forward button, and a center button. The functions of these buttons are as follows:
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Interchangeable Monitoring Device 17
Back Button
Decrement to the previous channel.
Forward Button
Increment to the next channel.
Center Button
Toggle between scrolling and static display modes.
Holding this button for 10 seconds will perform a network
reset, restoring the default IP address and resetting user
account information
and
Flip the display 180 degrees. (Both buttons must be
pressed at the same time.)
and
Display the unit's primary IPv4 address. (Both buttons
must be pressed at the same time.)
3.3 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
Geist Upgradable monitored devices built with the IMD-02X include two Ethernet ports
which act together as an internal Ethernet bridge. One of these ports can be used to
connect the IMD to an existing network, or both ports can be used at the same time to
connect one IMD to another in a daisy-chain configuration.
When both network interfaces are connected, the IMD implements a network bridging
protocol called the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). RSTP is an IEEE standard
that is implemented by all managed bridges. Using RSTP, bridges in the network
exchange information to find redundant paths, or loops.
When a loop is detected, the bridges in the network work together to temporarily
disable the redundant paths. This allows the network to avoid broadcast storms
caused by the loops. In addition, RSTP regularly checks for changes in the network
topology. When a connection is lost, RSTP allows the bridges to quickly switch to a
redundant path.
Since every IMD-02X runs RSTP, a chain of only IMDs can be connected redundantly
to an external switch, even an unmanaged (dumb) switch. In this configuration, if a link
of the chain is disconnected, the IMDs will quickly switch to the alternate path and
connectivity will not be lost.
The only limitation is that the RSTP protocol imposes a limit of 40 links between
bridges, including IMDs.
3.4 Network Setup
The Monitored Geist Upgradeable PDU has a default IP address for initial setup and
access to the unit. Once you have assigned an IP address to a unit, the default IP
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual18
IP Address:
192.168.123.123
Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.0
Gateway:
192.168.123.1
address will no longer be active. To restore the default IP address and reset all user-
account information if the user-assigned address or passwords are lost or forgotten,
press and hold the network-reset button located below the #2 Ethernet port for 15
seconds during normal operation. Holding the center button of the LED display for 10
seconds will also reset the network and user account information.
To completely erase all of the user settings and restore the unit back to its "out-of-thebox" factory-default state, disconnect power from the PDU, then press and hold the
network-reset button while powering up the PDU.
The Network page (located under the System Tab) allows you to assign the network
properties manually, or use DHCP to connect to your network. Access to the unit
requires the IP address to be known, so using a static IP or a reserved DHCP is
recommended. The default address is shown on the front of the unit:
To access the unit for the first time, you will need to temporarily change your
computer's network settings to match the 192.168.123.xxx subnet. To set up the unit,
connect it to your computer's Ethernet port, then follow the appropriate instructions for
your computer's operating system in the following section(s).
Note: Some computers may require the use of a "crossover" Ethernet cable to make
this type of direct connection. If you find that you are unable to connect to the unit
even after following the instructions below, try using one of these cables.
3.4.1 Windows
Windows 2000 / XP / Server 2003:
Click the Start button, choose Settings, then Network Connections.
Windows 7 / Server 2008:
Click the Start button, then choose Control Panel >> Adjust Your Computer's
Settings >> View Network Status and Tasks >> Change Adapter Settings.
(Alternatively, on some Windows 7 machines, this may be Start, then Settings >>
Control Panel >> Network and Sharing Center >> Change Adapter Settings.)
Windows 8 / Server 2012:
Move the mouse cursor to the bottom or top right corner of the screen, click the
Settings icon, then select Control Panel. Change the view type from Category to
Large or Small Icons if necessary, then select Network and Sharing Center, then
Change Adapter Settings.
Locate the entry under LAN or High-Speed Internet which corresponds to the
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Interchangeable Monitoring Device 19
network card (NIC) which the unit is connected to. (Note: Most computers will only
have a single Ethernet NIC installed, but a WiFi or 3G adapter will also show as a NIC
in this list, so be sure to choose the correct entry.)
Double-click on the network adapter's entry in the Network Connections list to open
its status dialog box, then click the Properties button to open the Local Properties
window.
Find the entry titled "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" in the list, then click
the Properties button to open the Internet Protocol Properties window. If you see
more than one TCP/IP entry, as in the example above, the computer may be
configured for IPv6 support as well as IPv4; make sure to select the entry for the IPv4
protocol.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual20
Choose the Use the following IP address option, then set IP address to
192.168.123.1 and Subnet Mask to 255.255.255.0. For this initial setup, Default
Gateway and the DNS Server entries can be left blank. Select OK, then OK again to
close both the Internet Protocol Properties and Local Properties windows.
Once the NIC settings are configured properly, you should be able to access the unit
by typing http://192.168.123.123 into the address bar of your web browser. If
you are setting up the unit for the first time, or if the unit has been reset back to
factory defaults via the network-reset button, the unit will require you to create an
Admin account and password before you can proceed.
Once you have created the Admin account and logged into it, the unit's default
Sensors page should come up by default. Navigate to the System tab, then the
Network page to configure the device's network properties. The unit's IP Address,
Subnet Mask, Gateway, and DNS settings can either be assigned manually, or
acquired via DHCP.
Note that the new settings will take effect instantly when the Save button is clicked, so
the browser will no longer be able to reload the web page from the 192.168.123.123
address and will probably display a "page not found" or "host unavailable" message.
This behavior is normal. Once you have finished configuring the unit's IP address,
simply repeat the steps above, and change the computer's Ethernet NIC card settings
back to the ones you wrote down prior to changing them, to restore its normal
network and internet settings.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

3.4.2 Mac
Click the System Preferences icon on the Dock, and choose Network.
Interchangeable Monitoring Device 21
Be sure Ethernet is highlighted on the left side of the NIC window. (In most cases,
there will only be one Ethernet entry on a Mac.)
Select Manually from the Configure IPv4 drop-down list, then set IP Address to
192.168.123.1 and Subnet Mask to 255.255.255.0. (The Router and DNS Server
settings can be left blank for this initial setup.) Click Apply when finished.
Once the NIC settings are configured properly, you should be able to access the unit
by typing http://192.168.123.123 into the address bar of your web browser. If
you are setting up the unit for the first time, or if the unit has been reset back to
factory defaults via the network-reset button, the unit will require you to create an
Admin account and password before you can proceed.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual22
Once you have created the Admin account and logged into it, the unit's default
Sensors page should come up by default. Navigate to the System tab, then the
Network page to configure the device's network properties. The unit's IP Address,
Subnet Mask, Gateway, and DNS settings can either be assigned manually, or
acquired via DHCP.
Note that the new settings will take effect instantly when the Save button is clicked, so
the browser will no longer be able to reload the web page from the 192.168.123.123
address and will probably display a "page not found" or "host unavailable" message.
This behavior is normal. Once you have finished configuring the unit's IP address,
simply repeat the steps above, and change the computer's Ethernet NIC card settings
back to the ones you wrote down prior to changing them, to restore its normal
network and internet settings.
3.5 Removal
The IMD is designed to be field replaceable by qualified service personnel only.
The IMD module is hot-swappable, meaning it is designed to be replaced while the
PDU is still connected to AC power. If the Geist Upgradable PDU is going to be
upgraded by replacing the IMD module, follow the procedure described here:
Note: Be sure to have the new IMD module ready for installation immediately after
removal of the old IMD.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Interchangeable Monitoring Device 23
1. Peel off the two overlays, to reveal the openings for the internal locking
mechanisms.
2. Insert a flat-head screwdriver into one of the side openings, and pry the screwdriver
as shown to undo the locking mechanism. (CAUTION: Be careful not to insert the
screwdriver further than about 1" (2.5cm), and do not apply excessive force, or you
may damage the locking mechanism.)
3. While holding the screwdriver in position to keep the locking mechanism
disengaged, grip the IMD firmly and carefully pull on IMD until it comes loose from
the PDU.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 on the opposite side opening, then pull the IMD straight out.
Be careful not to pull too far, as there is only about 4 inches (10cm) of cable slack
built into the device.
5. Gently unplug the connector from the IMD.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual24
3.6 Installation
1. Connect the cable to the replacement IMD module.
2. Place cable into the strain-relief slot in the IMD's housing. as shown.
3. Tuck the excess cable back into the PDU, and slide the IMD straight in.
4. Press with both thumbs until the IMD snaps into place.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

4 Web Interface
The unit is accessible via a standard, unencrypted HTTP connection, or via an
encrypted HTTPS (SSL) connection. The following web pages are available:
4.1 Sensors Page
4.1.1 Overview
The front page, Sensors Overview, gives both current and historical views of the unit’s
data. Real-time readings are provided for all PDU data and individual circuits' data.
Interchangeable Monitoring Device 25
1. Geist Logo
Clicking on this logo from any page will reload the Sensor Overview page.
2. Sensors, System, and Help Tab
Mouse over to show sub-menus:
Sensors: available options are "Overview" (this page) and "Alarms &
Warnings" (see next section)
System: available options are "Users", "Network", "Email", "SNMP", "Syslog",
"Admin", "Locale", "Restore Defaults", and "Firmware Update." (Refer to the
appropriate section under "System")
Help: available options are "Info" and "Support Site" (Refer to the appropriate
section under "Help")
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual26
3. Log In / Log Out
Click to log in or log out of the unit. Note that both user-name and password are
case sensitive; prohibited characters are: $&`:<>[ ] { }"+%@/ ; =?\^|~',
4. Alarms and Warnings
Indicates the number of Alarms and Warnings currently occurring, if any.
5. Device Label
Displays the user-assigned label of this unit (see "Configuration and Operation",
"Device Labeling")
6. Device ID
Unique product identification. May be required for technical support.
7. Total and Individual Phase Monitor
Displays AC current, voltage, and power statistics for each individual phase, and
for the total of all phases combined.
8. Current Monitor
Displays AC current draw statistics for each individual circuit on the PDU.
Configuration Icon Operation Icon
4.1.1.1 Configuration and Operation
Note that you must log in before making any changes. Only users with Control-level
authorizations have access to these settings.
Device Labeling
1. Click the desired Configuration icon, and change the device's Label. (Name is the
PDU's factory name or model, and cannot be changed.)
2. Once done, click Save.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Web Interface 27
Phase and Circuit Labels Naming
1. Click the desired Configuration icon, and change the phase or circuit's Label.
(Name is the physical phase or circuit, and cannot be changed.)
2. Once done, click Save.
Resetting Energy (kWh) and Current (Minimum and Maximum) Values
1. Click the Operation icon.
2. Select the operation you wish to perform.
3. Click Submit to execute operation.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual28
4.1.2 Alarms & Warnings
The Alarms & Warnings page allows the user to establish alarm or warning conditions
(hereafter referred to as "Events") for each power and circuit readings. Events are
triggered when a measurement exceeds a user-defined threshold, either going above
the threshold ("high-trip") or below it ("low-trip"). Events are displayed in different
sections, based on the device or measurement the Event is associated with. Each
Event can have one or more Actions to be taken when the Event occurs.
1. State: Shows the status of each Event.
Empty: No alert condition.
: This symbol indicates that this particular "Warning" Event has been tripped.
A tripped Warning Event displays in orange.
: This symbol indicates that this particular "Alarm" Event has been tripped. A
tripped Alarm Event displays in red.
: This symbol will indicate that this Event has been acknowledged by user
after being tripped. It will remain this way until the condition being measured by
this Event returns to normal (i.e. ceases to exceed the trigger threshold for this
Event.)
2. Configuration: Add/Delete/Modify Alarms & Warnings.
: Add new Alarms & Warnings.
: Modify existing Alarms & Warnings.
: Delete Existing Alarms & Warnings.
3. Notification: Notify user of tripped Events, and request acknowledgment.
Empty: No alert condition.
: Acknowledge button. When a Warning or Alarm Event has occurred; the user
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

can click on this symbol to acknowledge the Event and stop the unit from sending
any more notifications about it. (Note that clicking this symbol does not clear the
Warning or Alarm Event, it just stops the notifications from repeating.)
4. The actual conditions for the various Alarms & Warnings settings are shown here.
4.1.2.1 Add/Modify Alarms & Warnings
To add a new Alarm or Warning Event:
1. Click the Add/Modify Alarms & Warnings button:
Web Interface 29
2. Set the desired conditions for this Event as follows:
a. Select the Name of the phase or circuit you wish to set an Event on.
b. Select the measurement (current, voltage, etc.) you want to Trigger the Event.
c. Set the Severity level ("Warning", or "Alarm") for this Event.
d. Select the threshold Type, "high" (trips if the measurement goes above the
threshold) or "low" (trips if the measurement goes below the threshold).
e. Type in the desired Threshold Value (any number between -999.0 ~ 999.0 is
valid).
f. Type in the desired Clear Delay time in seconds. Any value other than "0"
means that once this Event is tripped, the measurement must return to normal for
this many seconds before the Event will clear and reset. Clear Delay can be up
to 14400 seconds (4 hours).
g. Type in the desired Trip Delay time in seconds. Any value other than "0" means
that the measurement must exceed the threshold for this many seconds before
the Event will be tripped. Trip Delay can be up to 14400 seconds (4 hours).
h. Latching Mode: If enabled, this Event and its associated Actions (see below)
remain active until the Event is acknowledged, even if the measurement
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual30
subsequently returns to normal.
i. To determine where the alert notifications will be sent to when this particular
Alarm or Warning Event occurs, click the Add icon to create a new Action, then
select the desired options from the drop-down menu:
Target is the e-mail address or SNMP manager to which notifications should be sent
when the Event is tripped.
Delay determines how long this Event must remain tripped for before this Action's
first notification is sent. (Note that this is different from the Trip Delay, above; Trip
Delay determines how long the threshold value has to be exceeded before the Event
itself is tripped; this delay determines how long the Event must remain tripped
before this Action occurs.) Delay can be up to 14400 seconds (4 hours). A Delay
of 0 will send the notification immediately.
Repeat detemines whether multiple notifications will be sent for this Event Action.
Repeat notifications are sent at the specified intervals until the Event is
acknowledged, or until the Event is cleared and reset. The Repeat interval can be
up to 14400 seconds (4 hours). A Repeat of 0 disables this feature, and only one
notification will be sent.
Then, click Save to save this notification Action.
More than one Action can be set for an Alarm or Warning; to add multiple Actions, just
click the Add icon again and set each one as desired. Each alert can have up to 32
Actions associated with it.
To change an existing notification Action, click the Modify icon next to the Action you
wish to change, then modify its settings as above.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Web Interface 31
Once an Action has been added, each Action has its own checkbox in the "enabled"
column at the far left. The default is unchecked (disabled) when you first add each
Action; set the checkbox to enable it. (This allows you to selectively turn different
Actions on and off for testing.)
To remove a notification Action entirely, click the Delete icon to remove the Action
from the list, then click Delete to confirm:
3. When finished, click Save to save this Alarm or Warning event.
To change an existing Alarm or Warning Event:
Click the Modify icon next to the Alarm or Warning Event you wish to change, then
modify its settings as above.
To delete an existing Alarm or Warning Event:
Click the Delete icon next to the Alarm or Warning Event you wish to change, then
click Delete to confirm.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual32
4.2 System
4.2.1 User Accounts
The User Accounts page allows you to manage or restrict access to the unit's features
by creating accounts for different users.
There are three buttons available on the User Accounts page:
1. Add New User Account
2. Modify User's Account
3. Delete User's Account
Note that only an Administrator-level account can Add, Modify, or Delete users.
Control-level and View-Only accounts can change their own passwords via the Modify
button, but cannot Add or Delete accounts, or Modify other accounts. The Guest
account cannot Add, Delete, or Modify any account, not even itself.
To Add or Modify a user uccounts:
1. Click the Add or Modify User icon.
2. Create or modify the account information as follows:
a. Username: the name of this account. User names may be up to 24 characters
long, are case-sensitive, and may not contain spaces or any of these prohibited
characters: $&`:<>[ ] { }"+%@/ ; =?\^|~', Note that an account's username
cannot be changed after the account is created.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Web Interface 33
b. Administrator: if set to True, this account has Administrator-level access to the
unit, and can change any setting.
c. Control: if set to True, this account has Control-level access. (Setting
Administrator to True will automatically set Control to True as well.) Setting this
to False makes the account a View-Only account.
d. New Password: account passwords may be up to 24 characters long, are case-
sensitive, and may not contain spaces or any of these prohibited characters:
$&`:<>[ ] { }"+%@/ ; =?\^|~',
e. Verify New Password: retype the account password from (d), above. Both
fields must match for the password to be accepted.
f. Account Status: set the account to Enabled or Disabled. Disabling an account
prevents it from being used to log in, but does not delete it from the account list.
3. Click the Save button when finished.
Account Types:
Administrator: Administrator accounts (accounts with both Administrator and
Control authority set to True, as above) have full control over all available
functions and settings on the device, including the ability to modify System settings
and add, modify, or delete other users' accounts.
Control: Control accounts (accounts with only Control set to True) have control
over all settings pertaining to the device's sensors. They can add, modify, or
delete Alarms & Warning Events and notification Actions, and can change the
names or labels of the device and its sensors. Control accounts cannot, however,
modify System settings or make changes to other users' accounts.
View: If both Administrator and Control are set to False, the account is a View-
Only account. The only changes a View-Only account is permitted to make are
changing their own account's password, and changing the preferred language for
their own account. View-Only accounts cannot change any device or system
settings.
Guest: Anyone who brings up the unit's web page without logging in will
automatically be viewing the unit as Guest. By default, the Guest account is a
View-Only account, and cannot make changes to any settings, although the
Administrator can elevate the Guest account to Control-level access if desired,
allowing anyone to make changes to names, labels, alarm events, and
notifications without logging in. The Guest account cannot be deleted.
Note: Once a user has logged in to their account, they can change their password or
language preference by clicking their username, shown next to the Log Out hyperlink
at the top right-hand corner of the web page, as shown here:
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual34
4.2.2 Network
The unit’s network configuration is set on the Network tab of the Configuration page.
Settings pertaining to the unit’s network connection are:
DHCP: Allows the unit to request a dynamic IP address from a server on the
network when Enabled. (The default is Disabled, or static IP addressing.)
Gateway (IPv4): The IP address of the network gateway bridging your private
network (LAN) to the public internet network. This is required if the unit needs to
reach any services on the internet, such as a public email or NTP server. (If DHCP
is Enabled, this field will automatically be filled in when the DHCP service assigns
the unit an IP address.)
IP Address: Displays the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses currently being used by the unit.
Clicking on the Modify icon will allow you to change the unit's IPv4 address and
Netmask. (Note that if DHCP is enabled, then there will be no Modify icon,
indicating that this address can't be changed by the user.) The IPv6 address is a
"Link Local" address inherent to the unit, and cannot be changed.
DNS: Allows the unit to resolve host names for Email, NTP and SNMP servers as
well as cameras.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Web Interface 35
HTTP Interface: Enables/disables access via HTTP. HTTPS interface will always
be enabled. Available options are: Enabled or Disabled. It is not possible to disable
the web interface completely.
HTTP/HTTPS Server Port: Allows you to change the TCP ports which the HTTP
and HTTPS services listen to for incoming connections. The defaults are port 80 for
HTTP, and 443 for HTTPS.
Note that any changes you make to the Network settings will take effect instantly once
the Save button is clicked! If you have changed the IP address or HTTP/HTTPS
ports, it will appear as if the unit is no longer responding because the browser will not
be able to reload the web page. Just stop or close the browser window, then type in
the new IP address into the browser's address bar, and the unit will be accessible.
4.2.3 Email
The unit is capable of sending e-mail notifications to up to five e-mail addresses when
an Alarm or Warning Event occurs.
To send e-mails, the unit must be configured to access the mail server, as follows:
SMTP Server: the name or IP address of a suitable SMTP or ESMTP server.
Port: the TCP port which the SMTP Server uses to provide mail services. (Typical
values would be port 25 for an unencrypted connection, or 465 for a TLS/SSLencrypted connection, but these may vary depending on the mail server's
configuration.)
Enable SSL: If Enabled, the unit will attempt to connect to the server using a fullyencrypted TLS/SSL connection. Note that only fully-encrypted sessions are
supported; the "Start-TLS" method, where the session starts out as unencrypted
and then switches to encrypted partway through the session, is not supported.
"From" Email Address: the address which the unit's e-mails should appear to
come from. Note that many hosted e-mail services, such as Gmail, will require this
to be the e-mail account of a valid user.
Username and Password: the login credentials for the e-mail server. If your server
does not require authentication (open relay), these can be left blank.
Microsoft Exchange servers will have to be set to allow SMTP relay from the IP
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual36
address of the unit. In addition, the Exchange server will need to be set to allow
"Basic Authentication", so that the unit will be able to log in with the AUTH LOGIN
method of sending its login credentials. (Other methods, such as AUTH PLAIN, AUTH
MD5, etc. are not supported.)
Target e-mail addresses can be configured as follows:
Legend of icons/buttons:
1. Add new target email address.
2. Modify existing target email address.
3. Delete existing target email address.
4. Send test email.
To Add or Modify a Target Email address:
1. Click on the Add or Modify icon.
2. Type email address and then click Save.
To Delete a Target Email address:
1. Click on the Delete icon next to the address you wish to delete.
2. Click the Delete button on the pop-up window to confirm.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

To send a test e-mail:
1. Click on the Test Email icon next to the address you wish to test.
2. A pop-up window will indicate that the test e-mail is being sent. Click OK to
dismiss the pop-up.
4.2.4 SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) can be used to monitor the unit's
measurements and status, if desired. SNMP v1, v2c and v3 are supported. In
addition, alarm traps can be sent to up to two IP addresses.
Web Interface 37
The SNMP Service can be enabled or disabled, as desired. The service will normally
listen for data-read requests (a.k.a. "Get requests") on Port 161, which is the usual
default for SNMP services; this can also be changed if desired.
The MIB is can be downloaded from the unit, if needed, via the MIB link at the top of
the web page. Clicking this link will download a .ZIP archive containing both the MIB
file itself, and a CSV-formatted spreadsheet describing the available OIDs in a humanreadable form to assist you in setting up your SNMP manager to read data from the
unit.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual38
The Users section allows you to configure the various Read, Write, and Trap
communities for SNMP services. You can also configure the authentication types and
encryption methods used for the SNMP v3 communities, if desired.
Traps allows you to define the IP address(es) and SNMP types that you wish the
traps to be sent to.
To configure a trap destination:
1. Locate the Traps section of the SNMP page, and click on the Modify icon.
2. Enter the IP Address which the trap should be sent to, select the trap Version
to be used (v1, v2c, or v3), and click Save.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

A test trap may be sent by clicking on the Test icon next to the trap destination.
4.2.5 Syslog
Syslog data can be captured remotely but must first be setup and enabled via the
Syslog page. Note that this function is primarily only useful for diagnostic purposes,
and should normally be left Disabled unless advised to enable it by Geist's technical
support for troubleshooting a specific issue.
4.2.6 Admin
The Admin page allows the administrator of the device to save their contact
information along with the device description and location. Once the info is saved by
an administrator, other (non-administrator) users can view the information. Also, the
System Label can be modified on this page; this label is typically shown in the title bar
of the web browser's window, and/or on the browser tab(s) currently viewing the
device.
Web Interface 39
Note that this information is strictly for the users' and administrator's convenience; the
unit will not attempt to send e-mails to the "Administrator Email" address, and this
address cannot be chosen as the Target of an Event Action when configuring an Alarm
or Warning Event.
4.2.7 Locale
The Locale page sets the default Language and Temperature Units for the device.
These settings will become the default viewing options for the device, although
individual users can change these options for their own accounts. (The Guest account
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual40
will only be able to view the device with the options set here.)
4.2.8 Restore Defaults
The Restore Defaults page allows the user to restore the unit's settings to the factory
defaults. There are two options:
All Settings: erases all of the unit's settings, including all Network and User Accounts
settings, effectively reverting the entire unit back to its original out-of-the-box state.
All Non-Network Settings: erases all settings except the Network and User
Accounts.
4.2.9 Firmware Update
Use the Firmware Update page to load firmware updates into the unit. Firmware
updates, when available, can be found on the Geist website: http://geistglobal.com/
support/monitor/firmware
You can also subscribe to a mailing list, to be notified of when firmware updates
become available.
Firmware updates will typically come in a .ZIP archive file containing several files
including the firmware package itself, a copy of the SNMP MIB, a "readme" text file
explaining how to install the firmware, and various other support files as needed. Be
sure to un-ZIP the archive and follow the included instructions.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

4.3 Help
4.3.1 Info
The Info Page displays the unit's current configuration information, including the device
name and ID, the type of IMD installed, the unit's current firmware versions, and
network information. Manufacturer support information is also here.
Web Interface 41
4.3.2 Support Site
Technical support and documentation can be found at http://www.geistglobal.com/
support/power
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Upgradeable PDU Instruction Manual42
5 Technical Support
5.1 Resetting PDU
Should the PDU lose communication, the processor may be manually rebooted without
affecting power to the outlets. Pressing the reboot button on the face of the IMD will
cause the processor to reboot. The web interface will remain off-line during boot up.
For more information, see the Interchangeable Monitoring Device section of this
manual.
5.2 Service and Maintance
No service or maintenance is required. Do not attempt to open the PDU or you may
void the warranty. There are no serviceable parts inside the PDU other than the field
replaceable Interchangeable Monitoring Device (IMD). It is recommended that power
be removed from the unit before installing or removing any equipment.
The Interchangeable Monitoring Device is designed to be field replaceable by
qualified service personnel only. The IMD is designed to be replaced while the
PDU is still connected to AC Mains power. Please refer to the IMD section of this
document for removal and installation instructions.
5.3 More Technical Support
http://geistglobal.com
1 (800) 432-3219
1 (402) 474-3400
Email: support@geistglobal.com
or contact your distributor
5.4 Using Microsoft Exchange as an SMTP server
If your facility uses a Microsoft Exchange e-mail server, it can be used by the IMD
PDU to send Alarm and Warning notification e-mails if desired. However, the
Exchange server may need to be configured to allow SMTP connections from the unit
first, as later version of Exchange often have SMTP services or basic authentication
disabled by default. If you encounter difficulties in getting your IMD PDU to send emails through your Exchange server, the following notes may be helpful in resolving the
problem.
Note that these suggestions only apply if you are using your own, physical Exchange
server! Microsoft’s hosted “Office365” service is not compatible with the IMD PDU at
this time, as Office365 requires a Start-TLS connection rather than a fully-encrypted
connection, and the IMD PDU does not currently support Start-TLS connections.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist

Technical Support 43
First, since the IMD PDU cannot use IMAP or Microsoft’s proprietary MAPI/RPC
Exchange/Outlook protocols to send messages, you will need to enable SMTP by
setting up an “SMTP Send Connector” in the Exchange server. More information on
setting up an SMTP Send Connector in Exchange can be found at this Microsoft
TechNet article: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa997285.aspx
Next: Your Exchange server may also need to be configured to allow messages to be
“relayed” from the monitoring unit. Typically, this will involve turning on the “Reroute
incoming SMTP mail” option in the Exchange server’s Routing properties, then
adding the IMD PDU’s IP address as a domain which is permitted to relay mail
through the Exchange server. More information about enabling and configuring SMTP
relaying in Exchange can be found at this Microsoft TechNet article: http://
technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd277329.aspx
The SMTP “AUTH PLAIN” and “AUTH LOGIN” authentication methods (also known as
“Basic Authentication) for logging in to the server are often no longer enabled by
default in Exchange; only Microsoft’s proprietary NTLM authentication method is
enabled. The AUTH LOGIN method which the IMD PDU requires can be re-enabled
as follows:
1. In the Exchange console under server configuration, select hub transport.
2. Right-click the client server, and select properties.
3. Select the authentication tab.
4. Check the Basic Authentication checkbox.
5. Uncheck the Offer Basic only after TLS checkbox
6. Apply or save these changes, and exit. Note that you may need to restart the
Exchange service after making these changes.
Finally, once you have enabled SMTP, relaying, and the AUTH LOGIN Basic
Authentication method, you may also need to create a user account specifically for the
IMD PDU to log into. If you have already created an account prior to enabling the
SMTP Send Connector, or you are trying to use an already-existing account created
for another user, and the IMD PDU still cannot seem to connect to the Exchange
server, the account probably did not properly inherit the new permissions when you
enabled them as above. (This tends to happen more often on Exchange servers that
have been upgraded since the account(s) you are trying to use were first created, but
can sometimes happen with accounts when new connectors and plug-ins are added
regardless of the Exchange version.) Delete the user account, then create a new one
for the monitoring unit to use, and the new account should inherit the SMTP
authentication and mail-relaying permissions correctly.
If none of the above suggestions succeed in allowing your Geist IMD PDU to send
mail through your Exchange server, then you may need to contact Microsoft’s
technical support for further assistance in configuring your Exchange server to allow
SMTP e-mails to be sent from a 3rd-party, non-Windows device through your
network.
GM1157 - GU PDU Instruction Manual
© 2015 Geist
 Loading...
Loading...