Page 1

GE
Automation & Controls
Programmable Control Products
RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
PACSystems*
RX3i PROFINET
IO-Scanner
User Manual
GFK-2737F
December 2016
Page 2

Legal Information
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes as Used in this Publication GFL-002
Warning
Warning notices are used in this publication to emphasize that hazardous voltages,
currents, temperatures, or other conditions that could cause personal injury exist in this
equipment or may be associated with its use.
In situations where inattention could cause either personal injury or damage to
equipment, a Warning notice is used.
Caution
Caution notices are used where equipment might be damaged if care is not taken.
Note: Notes merely call attention to information that is especially significant to understanding and
operating the equipment.
These instructions do not purport to cover all details or variations in equipment, nor to provide for every
possible contingency to be met during installation, operation, and maintenance. The information is supplied
for informational purposes only, and GE makes no warranty as to the accuracy of the information included
herein. Changes, modifications, and/or improvements to equipment and specifications are made
periodically and these changes may or may not be reflected herein. It is understood that GE may make
changes, modifications, or improvements to the equipment referenced herein or to the document itself at
any time. This document is intended for trained personnel familiar with the GE products referenced herein.
GE may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter in this document. The
furnishing of this document does not provide any license whatsoever to any of these patents.
GE provides the following document and the information included therein as-is and without warranty of
any kind, expressed or implied, including but not limited to any implied statutory warranty of
merchantability or fitness for particular purpose.
* indicates a trademark of General Electric Company and/or its subsidiaries.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
©Copyright 2013-2016 General Electric Company.
All Rights Reserved
If you purchased this product through an Authorized Channel Partner, please contact the seller directly.
Page 3

Contact Information
General Contact Information
Online technical support and GlobalCare
www.geautomation.com/support
Additional information
www.geautomation.com
Solution Provider
solutionprovider.ip@ge.com
Technical Support
If you have technical problems that cannot be resolved with the information in this manual, please
contact us by telephone or email, or on the web at www.geautomation.com
Americas
Phone
1-800-433-2682
International Americas Direct Dial
1-780-420-2010 (if toll free 800 option is unavailable)
Customer Care Email
customercare.ip@ge.com
Primary language of support
English
Europe, the Middle East, and Africa
Phone
+800-1-433-2682
EMEA Direct Dial
+420 239015850 (if toll free 800 option is unavailable or
if dialing from a mobile telephone)
Customer Care Email
customercare.emea.ip@ge.com
Primary languages of support
English, French, German, Italian, Czech, Spanish
Asia Pacific
Phone
+86-400-820-8208
+86-21-3877-7006 (India, Indonesia, and Pakistan)
Customer Care Email
customercare.apo.ip@ge.com
customercare.cn.ip@ge.com (China)
Page 4

GFK-2737F December 2016 i
Table of Contents
RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
Table of Contents ............................................................................................................................................... i
Table of Figures ................................................................................................................................................ iv
Chapter 1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Revisions in this Manual .............................................................................................................. 3
1.2 RX3i PROFINET Scanner Specifications ..................................................................................... 4
1.3 RX3i PROFINET Scanner Controls and Indicators ................................................................... 5
1.3.1 LEDs on the PROFINET Scanner Module ..................................................................................................................... 6
1.3.2 SD Card Slot ............................................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.3.3 Pushbutton ................................................................................................................................................................................. 6
1.3.4 USB Port ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.3.5 Ethernet Port Connections ................................................................................................................................................. 6
1.4 PROFINET Communications ........................................................................................................ 7
1.4.1 Notes on Available PROFINET Controllers .................................................................................................................. 7
1.4.2 Operations of the PROFINET Scanner .......................................................................................................................... 8
1.5 PROFINET Redundant Media ....................................................................................................... 9
1.6 System Limits .............................................................................................................................. 10
1.7 Supported Modules, Power Supplies and Backplanes ......................................................... 11
1.8 Glossary ........................................................................................................................................ 16
1.9 Documentation ........................................................................................................................... 18
Chapter 2 LED Operation and Connector Details ............................................................................. 19
2.1 Normal Operation of Individual LEDs ..................................................................................... 20
2.1.1 OK LED........................................................................................................................................................................................ 20
2.1.2 LAN LED ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
2.1.3 Status LED ................................................................................................................................................................................ 20
2.1.4 CONN LED................................................................................................................................................................................. 20
2.1.5 Port LEDs ................................................................................................................................................................................... 21
2.1.6 Active LED ................................................................................................................................................................................. 21
2.1.7 USB LED ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 21
2.1.8 Special LED Blink Patterns ............................................................................................................................................... 21
Page 5

Contents
ii PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
2.2 Ethernet Network Ports ............................................................................................................. 24
2.3 SD Card Slot ................................................................................................................................. 25
2.4 USB Port ........................................................................................................................................ 26
Chapter 3 Installation ............................................................................................................................ 27
3.1 Pre-Installation Check ............................................................................................................... 28
3.2 Installation in Hazardous Areas............................................................................................... 29
3.2.1 ATEX Marking .......................................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.3 Module Installation ..................................................................................................................... 30
3.3.1 Power Requiremnents ....................................................................................................................................................... 30
3.3.2 Hot Insertion and Removal ............................................................................................................................................. 30
3.3.3 Removing the Backplane Knockout ........................................................................................................................... 30
3.3.4 Module Installation .............................................................................................................................................................. 31
3.3.5 Module Removal ................................................................................................................................................................... 31
3.4 Replacing a PROFINET Scanner ................................................................................................ 32
3.4.1 Method 1 – Using the SD Card ...................................................................................................................................... 32
3.4.2 Method 2 – Using the DCP Tool .................................................................................................................................... 32
3.5 SFP Modules for Ethernet Ports................................................................................................ 33
3.6 External Switch VLAN Priority Settings ................................................................................... 33
3.7 Installing the USB Port Driver ................................................................................................... 33
3.8 Firmware Updates ...................................................................................................................... 33
Chapter 4 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 35
4.1 Configuration Overview ............................................................................................................ 36
4.1.1 Basic Configuration Steps ............................................................................................................................................... 36
4.1.2 Configuration Tool ............................................................................................................................................................... 36
4.2 Adding an IO-Device to a PROFINET LAN ............................................................................... 37
4.2.1 Adding an RX3i PROFINET Scanner to the PROFINET LAN .............................................................................. 37
4.2.2 Configuring an RX3i PROFINET Scanner .................................................................................................................. 38
4.2.3 Adding RX3i Modules .......................................................................................................................................................... 40
4.2.4 Support for Analog Modules with HART Features............................................................................................... 44
4.2.5 Configuring Module Parameters .................................................................................................................................. 44
4.3 Assigning Device Names ........................................................................................................... 48
4.3.1 Transferring the Device Name with an SD Card .................................................................................................. 48
Page 6

Contents
GFK-2737F December 2016 iii
4.4 After the Configuration is Stored to the PROFINET Controller........................................... 49
Chapter 5 Operations ............................................................................................................................. 51
5.1 Power-up ...................................................................................................................................... 52
5.2 I/O Scanning ................................................................................................................................ 53
5.2.1 PROFINET Scanner Status and Control Data ......................................................................................................... 53
5.2.2 Data Coherency .................................................................................................................................................................... 54
5.2.3 Sampling Rate ........................................................................................................................................................................ 54
5.2.4 Differences from Main (CPU) Rack ............................................................................................................................... 54
5.2.5 Output Control ....................................................................................................................................................................... 55
5.3 Hot Swap of I/O Modules ........................................................................................................... 56
Chapter 6 Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................... 57
6.1 Configuration Faults .................................................................................................................. 58
6.2 Version Information ................................................................................................................... 59
6.3 Fatal Error Handling ................................................................................................................... 60
6.4 Connection Troubleshooting .................................................................................................... 61
Appendix A PROFINET Specifications .......................................................................................................... 63
A-1 PROFINET Protocol Support ................................................................................................................... 63
A-2 Technical Data .......................................................................................................................................... 63
A-3 Limitations ................................................................................................................................................ 64
A-3.1 PACSystems Features ........................................................................................................................................................ 64
A-3.2 PROFINET Features .............................................................................................................................................................. 64
Page 7

Contents
iv PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
Table of Figures
Figure 1: Front View IC695PNS001 ___________________________________________________________________ 5
Figure 2: Ethernet Port Connectors on IC695PNS001 _____________________________________________________ 6
Figure 3: IC695PNS001 LEDs _______________________________________________________________________ 23
Figure 4: Underside of IC695PNS001 Showing Ethernet Ports _____________________________________________ 24
Figure 5: RX3i Backplane showing Removable Plastic Knockout ___________________________________________ 30
Figure 6: Install Module into RX3i Backplane __________________________________________________________ 31
Figure 7: Remove Module from RX3i Backplane ________________________________________________________ 31
Figure 8: Select System Redundancy Parameters in PME _________________________________________________ 39
Figure 9: Change Submodule List produces list of Eligible SFP Modules _____________________________________ 40
Figure 10: Analog Module with Configurable Parameters ________________________________________________ 42
Figure 11: Analog Module with Multiple Possible Option Settings __________________________________________ 43
Page 8

GFK-2737F December 2016 1
Chapter 1 Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Scanner (PNS) module and its
operation. The last two pages of this chapter are a glossary that summarizes many terms used in the
manual.
Chapter 2, LED Operation and Connector Details, provides detailed description of the module’s indicators
and ports
Chapter 3, Installation, gives instructions for PNS module installation and replacing a PNS module.
Provides information for selecting SFP modules and network cabling and connectors.
Chapter 4, Configuration, describes how to configure the RX3i PROFINET Scanner and its associated IOdevices.
Chapter 5, Operations, describes powering up and restarting the RX3i PROFINET Scanner, the input status
data, replacing I/O modules while scanning, and how to update the firmware.
Chapter 6, Diagnostics, describes configuration faults, how to check the RX3i PROFINET Scanner version
information, fatal error handling, and some common troubleshooting suggestions.
Appendix A, PROFINET Specifications, summarizes the features specified for PROFINET v2.3 Class A IODevices that are supported by the RX3i PROFINET Scanner module
Page 9

Chapter 1. Introduction
2 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
The PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Scanner (PNS) module, IC695PNS001, connects a remote universal RX3i
I/O rack of Series 90-30 or RX3i modules to a PROFINET I/O Controller. The PROFINET Scanner scans the
modules in its rack, retrieving input data and providing output data, and exchanges that data on the
PROFINET I/O LAN at the configured production rate.
The PNS manages PROFINET communication and module configuration between an I/O Controller and
modules in the remote rack. If network communications are lost, the PNS manages I/O states according
to the individual module configurations.
The PNS supports 10/100/1000 Mbps Copper, 100/1000 Mbps Multi-mode Fiber, and 100/1000 Mbps
Single-mode Fiber. PROFINET communications on the network require 100 or 1000 Mbps link speed.
Although 10 Mbps cannot be used for PROFINET communications, 10 Mbps can be used for other types of
Ethernet traffic such as PING. Features of the RX3i PNS include:
Full programming and configuration services for all supported Series 90-30 and RX3i I/O Modules
using Proficy* Machine Edition. For a list of currently supported I/O modules, refer to the Important
Product Information (IPI) document provided with the firmware version on your PNS module.
Support for daisy-chain/line, star, or ring (redundant media) topologies.
Four switched Ethernet ports - two 8-conductor RJ45 shielded twisted pair 10/100/1000 Mbps copper
interfaces and two Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) cages for user-supplied SFP devices.
The network can include media interfaces of more than one type.
Support for transfer of IO-Device Name to another PNS module using an SD card. This eliminates the
need to connect a configuration tool, such as Proficy Machine Edition when replacing a module.
A USB port for field updates of firmware using WinLoader.
Note: The USB port is for firmware upgrades only. It is not intended for permanent connection.
Page 10

Chapter 1. Introduction
GFK-2737F December 2016 3
1.1 Revisions in this Manual
Rev
Date
Description
F
Dec2016
• Updates for CPE400 (new related product).
• Updated list of supported I/O Modules in Section 1.7 per GFK-2738L
• Added footnotes tracking PNS firmware support for various I/O modules.
• Added footnotes tracking PNS firmware support for various features, such as HART Pass
Through.
• Added note on support for Remote Get HART Device Information COMMREQ.
E
Apr2015
In Section 1.7, corrected data for IC695SPF010 in table
D
May2014
In Section 4.2.5, Configuring Module Parameters, added Universal Analog Input Module and
Power Sync and Measurement Module and related rules to the table,
In Section 4.2.5.1, RX3i PROFINET Scanner Configuration Validation, added IC695ALG600 to the
table.
Page 11

Chapter 1. Introduction
4 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
1.2 RX3i PROFINET Scanner Specifications
PROFINET Support
PROFINET Version 2.3 Class A IO-Device
Redundantly controlled operation conforms to PROFINET V2.3 Type S-2 System
Redundancy.
Controller CPU Version
Required
RX3i CPU315/CPU320 with firmware version 7.10 or later RX3i CPE305/CPE310 with
firmware version 7.10 or later RXi Controller with firmware version 7.80 or later
Proficy Machine Edition
Version Required
Version 8.0 or later
Power Requirements
3.3 Vdc:
1.2 A with no SFP devices installed
1.9 A maximum (two SFP devices installed, 0.35 A per SFP)
5 Vdc:
1.1 A maximum
Operating Temperature
Range
0 to 60°C De-rated to 57°C:
• If 100 Mbps Fiber SFPs installed, or
• If Copper SFPs operating at 1 Gbps
Number of Port
Connectors
Two RJ45 and Two SFP Cages
(SFP devices not included, available separately.)
USB Connector (for
firmware upgrades)
One Micro-B connector. USB 2.0 compliant running at Full-speed
(12 MHz)
SD Card
Supports SD and SDHC cards.
PNS Status and
Control Bits
32 input status bits and 32 output control bits
PROFINET I/O
production rate (ms)
(I/O Update Rate)
Configurable selections: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 or 512 ms
Number of IP Addresses
Five. One per external port and one internal.
I/O Station Maximum
Limits
Number of
I/O Modules
per station
Number of backplane slots in the host RX3i rack
less one for PNS001 module itself
less the number of slots occupied by the RX3i power supply
I/O data
per station
2880 bytes total
1440 bytes of input data
1440 bytes of output data
Configuration
V2.3 GSDML file.
The file is included with Proficy Machine Edition; available for import into 3rd-Party tools.
Note: Configuration software that supports GSDML V2.3 MenuList elements (such as
Proficy Machine Edition 8.0 or later) is required to display the configuration
parameters of most IC695xxx I/O modules.
For product standards, general operating specifications, and installation requirements, refer to the
PACSystems RX3i System Manual, GFK-2314
Page 12

Chapter 1. Introduction
GFK-2737F December 2016 5
1.3 RX3i PROFINET Scanner Controls and Indicators
Figure 1: Front View IC695PNS001
Page 13

Chapter 1. Introduction
6 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
1.3.1 LEDs on the PROFINET Scanner Module
LEDs provide an immediate visual indication of the operational state of the PNS and port link status. The
LEDs and their operation are described in Chapter 2 LED Operation and Connector Details.
1.3.2 SD Card Slot
The SD Card Slot supports an SD or SDHC card. It can be used to transfer the IO-Device Name to another
PROFINET Scanner Module unit without a configuration tool such as Proficy Machine Edition.
1.3.3 Pushbutton
The pushbutton adjacent to the USB port is reserved for future use.
1.3.4 USB Port
The USB Port is used for installing new firmware using the WinLoader tool.
1.3.5 Ethernet Port Connections
Each port on an RX3i PNS operates independently, so devices that operate at different speeds and/or
duplex modes may be attached to the ports. By default, all ports, including empty, unconfigured SFP
cages, are set for Automatic, which enables auto negotiation for the widest range of options supported by
the port.
Figure 2: Ethernet Port Connectors on IC695PNS001
Connections to the PROFINET Scanner can be made using standard Cat 5e/6 Ethernet cables. Different
devices on the same network can be connected using the multiple ports on the RX3i PNS (Figure 2).
For other options, refer to Chapter 4, the section Adding and Configuring an Ethernet Port.
Page 14

Chapter 1. Introduction
GFK-2737F December 2016 7
1.4 PROFINET Communications
For a full discussion of PROFINET Communications and interactions with the controlling RX3i CPU, refer to
Chapter 4 of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual, GFK-2571. The following topics are
covered:
PROFINET Operation Overview
PROFINET Communications
Application Relationships
Types of PROFINET Communications
Operations of the PROFINET Controller in the RX3i System
Duplicate PROFINET Device IP Address
Duplicate PROFINET Controller IP Address
Resolving Duplicate IP Addresses
I/O Scanning
Data Coherency
Performance Factors
PROFINET IO Update Rate Configuration
RX3i CPU Operations for PROFINET
Reference ID Variables for the RX3i Application
PNIO_DEV_COMM Function Block
Reset Smart Module for the PROFINET Controller
DO I/O for Remote IO Modules
Scan Set I/O for Remote I/O Modules
RX3i CPU Defaults - Inputs
RX3i CPU Defaults – Outputs
1.4.1 Notes on Available PROFINET Controllers
Each PROFINET I/O Network is controlled by one or more PROFINET I/O Controllers. PROFINET I/O
Controllers may be GE products or third-party products.
GE Automation and Control offers the following RX3i PROFINET Controllers:
IC695PNC001: this is a rack-based intelligent module located in a slot of the host RX3i CPU rack.
The host CPU may be equipped with a maximum of four IC695PNC001 modules.
The IC695CPE330 provides an optional embedded PROFINET Controller. To utilize this feature,
LAN2 must be configured as a PROFINET Controller. In addition, the IC695CPE330 may host a
maximum of four IC695PNC001 modules in its CPU rack.
The IC695CPE400 also provides an optional embedded PROFINET Controller. To utilize this feature,
LAN2 must be configured as a PROFINET Controller. Since the IC695CPE400 is a Rackless CPU, it
cannot host any IC695PNC001 modules.
Each of the RX3i PROFINET Controllers mentioned above is capable of controlling a PROFINET I/O Network
containing PROFINET Scanners supplied by GE or by third-party vendors. Many vendors also supply I/O
devices that connect directly to the PROFINET network.
For PROFINET Controller product details, refer to the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual,
GFK-2571.
Page 15

Chapter 1. Introduction
8 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
1.4.2 Operations of the PROFINET Scanner
The RX3i PROFINET Scanner (PNS) is the head-end unit responsible for monitoring and controlling I/O
modules installed in its RX3i I/O rack. All PROFINET communications are passed between the PROFINET I/O
Controller and the PNS. The PNS is one type of IO-Device the PROFINET I/O Controller expects to
encounter. Other third-party IO-Devices may also be present on the PROFINET network.
A PNS will normally be present on a PROFINET network controlled by an RX3i PROFINET Controller (PNC).
However, it is possible to use a PNS in conjunction with any qualified PROFINET I/O Controller.
The RX3i PNS performs the following operations:
Consumes PROFINET IO-Device configuration from the PROFINET IO-Controller over the PROFINET
network and applies it to its modules.
Scans input data from each module it manages and produces that data to the PROFINET
IO-Controller.
Consumes the output data that it receives from the PROFINET IO-Controller and applies it to each
module it manages.
GE Automation and Control offers the following types of PROFINET Scanners:
IC695PNS001: the RX3i PROFINET Scanner. It may control a sub-set of RX3i I/O modules located in
the same RX3i I/O rack. This product is discussed in detail in this manual.
IC695CEP001: a PROFINET Scanner which may control a sub-set of RX3i I/O modules in a remote
I/O drop. For product details, refer to the PACSystems RX3i CEP PROFINET Scanner User Manual,
GFK-2883.
Page 16

Chapter 1. Introduction
GFK-2737F December 2016 9
1.5 PROFINET Redundant Media
For a full discussion of PROFINET Redundant Media and interactions with the controlling RX3i CPU, refer to
Chapter 6 of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual, GFK-2571. The following topics are
covered:
PROFINET Media Redundancy Protocol
MRP Failover Performance
Bumpless Operation with MRP
MRP Operation for I/O Update Rates of 16ms or Greater
MRP Operation at I/O Update Rates Less Than 16ms
Minimum I/O Rate When Configured in an MRP Ring
Minimum I/O Update Rates for Bumpless Operation in a Ring Topology
Third-party MRP Manager Use with PNC as MRP Client
Ring Topology with One Controller
Ring Topology with Multiple Controllers
Setting Up Media Redundancy Protocol
Media Redundancy Setup for a PROFINET I/O Controller
Sequence for Enabling Media Redundancy
Sequence for Replacing a Media Redundancy Manager
Procedure for Disabling Media Redundancy
Page 17

Chapter 1. Introduction
10 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
1.6 System Limits
I/O Controllers will have limitations on the system they support. One of these limits is the number of
PROFINET submodules supported. In the RX3i PNS rack, each power supply or I/O module is represented
by one PROFINET submodule. The RX3i PNS uses four to six submodules:
• two submodules for basic operation of the PNS module
• two built-in port submodules that are always configured
• up to two additional port submodules, one for each optional Ethernet port configured
Other limitations, such as the configuration and I/O sizes, are specific to the configuration options chosen.
Note that not every combination of options is supported in every system.
If the configuration uses all slots in every device with a large device count, the memory of the I/O
Controller system will be a limiting resource.
Page 18
Chapter 1. Introduction
GFK-2737F December 2016 11
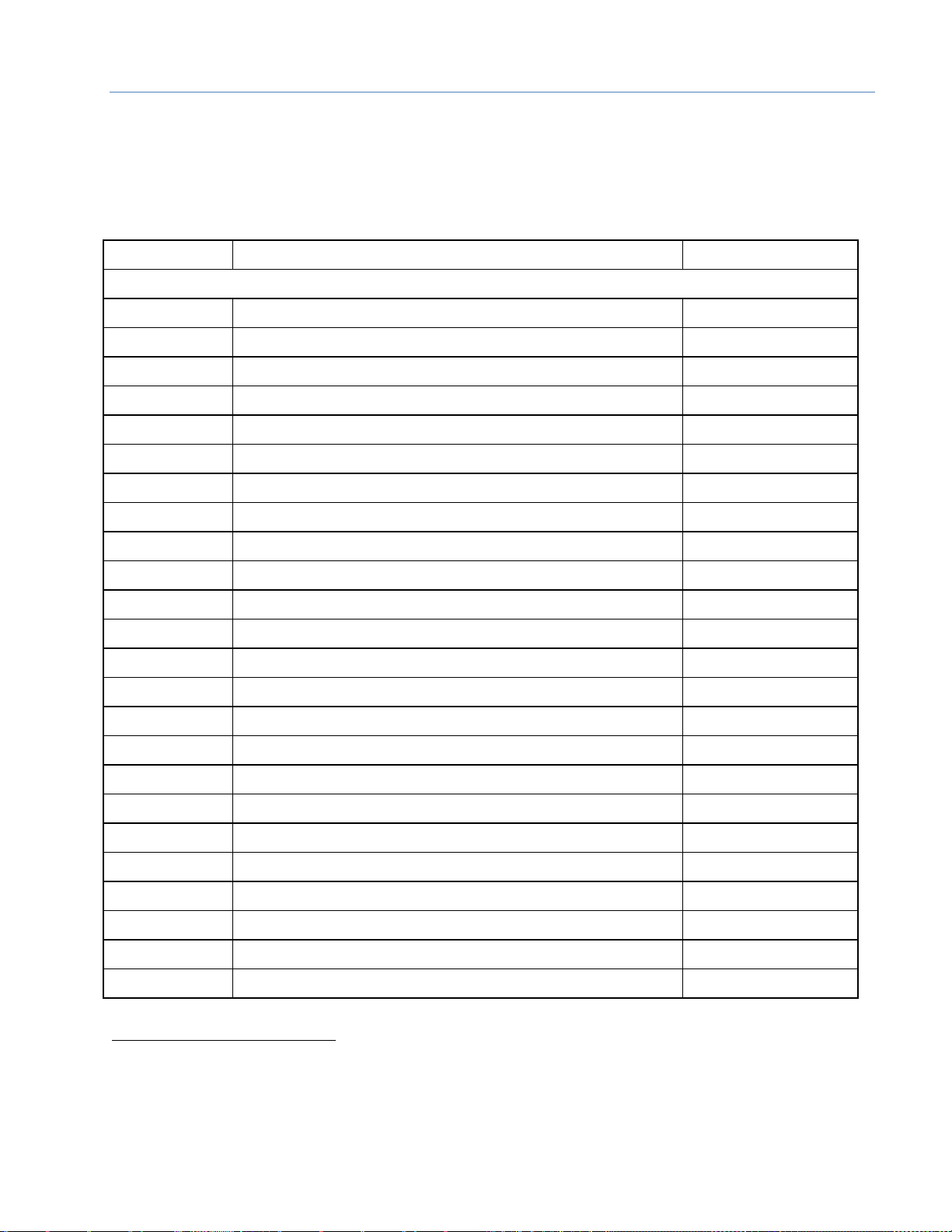
1.7 Supported Modules, Power Supplies and Backplanes
For an updated list of modules, power supplies and backplanes that can be used with an RX3i PROFINET
Scanner, refer to the most recent version of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Scanner Important Product
Information, GFK-2738. The list below was published in GFK-2738L (June 2016).
Catalog Number
Module Description
Distinguishing Classes1
Discrete Input Modules
IC693ACC300
Input Simulator Module (8-pt & 16-pt operation)
8 in, 16 in
IC693MDL230
8-Circuit Input 120 Vac Isolated
8 in
IC693MDL231
8-Circuit Input 240 Vac Isolated
8 in
IC693MDL240
16-Circuit Input 120 Vac
16 in
IC693MDL241
16-Circuit Input 24 Vac / Vdc
16 in
IC693MDL250
16-Circuit Isolated Input 120 Vac, Input Filtering Off
16 in
IC693MDL250
16-Circuit Isolated Input 120 Vac, Input Filtering On
none
IC693MDL260
32-Circuit Input 120 Vac, Input Filtering Off
32 in
IC693MDL260
32-Circuit Input 120 Vac, Input Filtering On
32 in/out
IC693MDL632
8-Circuit Input 125 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
8 in
IC693MDL634
8-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
8 in
IC693MDL635
16-Circuit Input 125 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
16 in
IC693MDL645
16-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
16 in
IC693MDL646
16-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic Fast
16 in
IC693MDL648
16-Circuit Input 48 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic Fast
16 in
IC693MDL654
32-Circuit Input 5/12 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
32 in
IC693MDL655
32-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic Fast
32 in
IC693MDL660
32-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic, Input Filtering Off
32 in
IC693MDL660
32-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic, Input Filtering On
32 in/out
IC694ACC300
Input Simulator Module (8-pt & 16-pt Mode)
8 in, 16 in
IC694MDL230
8-Circuit Input 120 Vac Isolated
8 in
IC694MDL231
8-Circuit Input 240 Vac Isolated
8 in
IC694MDL240
16-Circuit Input 120 Vac
16 in
IC694MDL241
16-Circuit Input 24 Vac / Vdc
16 in
1
The PNS001 cannot distinguish between modules within the same Distinguishing Class type. This means that any module
physically present that is within the same class as the one configured will not alert the user with a System Configuration
Mismatch fault on the Controller Fault Table. Refer to the section entitled CPU operation during System Configuration Mismatch
Faults in PACSystems RX7i and RX3i CPU Reference Manual, GFK-2222.
Page 19

Chapter 1. Introduction
12 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
Catalog Number
Module Description
Distinguishing Classes1
IC694MDL250
16-Circuit Input 120 Vac Isolated
none
IC694MDL260
32-Circuit Input 120 Vac
none
IC694MDL632
8-Circuit Input 125 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
8 in
IC694MDL634
8-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
8 in
IC694MDL635
16-Circuit Input 125 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
16 in
IC694MDL645
16-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
16 in
IC694MDL646
16-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic Fast
16 in
IC694MDL654
32-Circuit Input 5/12 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
32 in
IC694MDL655
32-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic Fast
32 in
IC694MDL658
32-Circuit Input 48 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic Fast
32 in
IC694MDL660
32-Circuit Input 24 Vdc Positive / Negative Logic
none
IC695MDL664
16-Circuit Smart Input 24 Vdc Positive Logic2
none
Discrete Output Modules
IC693MDL310
12-Circuit Output 120 Vac 0.5A
16 out
IC693MDL330
8-Circuit Output 120/240 Vac 2A
8 out
IC693MDL340
16-Circuit Output 120 Vac 0.5A
16 out
IC693MDL350
16-Circuit Output 120/240 Vac Isolated
16 out
IC693MDL390
5-Circuit Output 120/240 Vac 2A Isolated
8 out
IC693MDL730
8-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 2A Positive
8 out
IC693MDL731
8-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 2A Negative
8 out
IC693MDL732
8-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Positive
8 out
IC693MDL733
8-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Negative
8 out
IC693MDL734
6-Circuit Output 125 Vdc 1A Positive/Negative
8 out
IC693MDL740
16-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Positive
16 out
IC693MDL741
16-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Negative
16 out
IC693MDL742
16-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 1A Positive
16 out
IC693MDL748
8-Circuit Output 48 Vdc 0.5A Positive
8 out
IC693MDL752
32-Circuit Output 5/24 Vdc 0.5A Negative
32 out
IC693MDL753
32-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Positive
32 out
IC693MDL754
32-Circuit Output 24 Vdc 0.75A Positive with ESCP, Diagnostics Off
32 out
IC693MDL754
32-Circuit Output 24 Vdc 0.75A Positive with ESCP, Diagnostics On
32 in/out
2
The PNS001 currently does not support Fault Reporting from this module.
Page 20
Chapter 1. Introduction
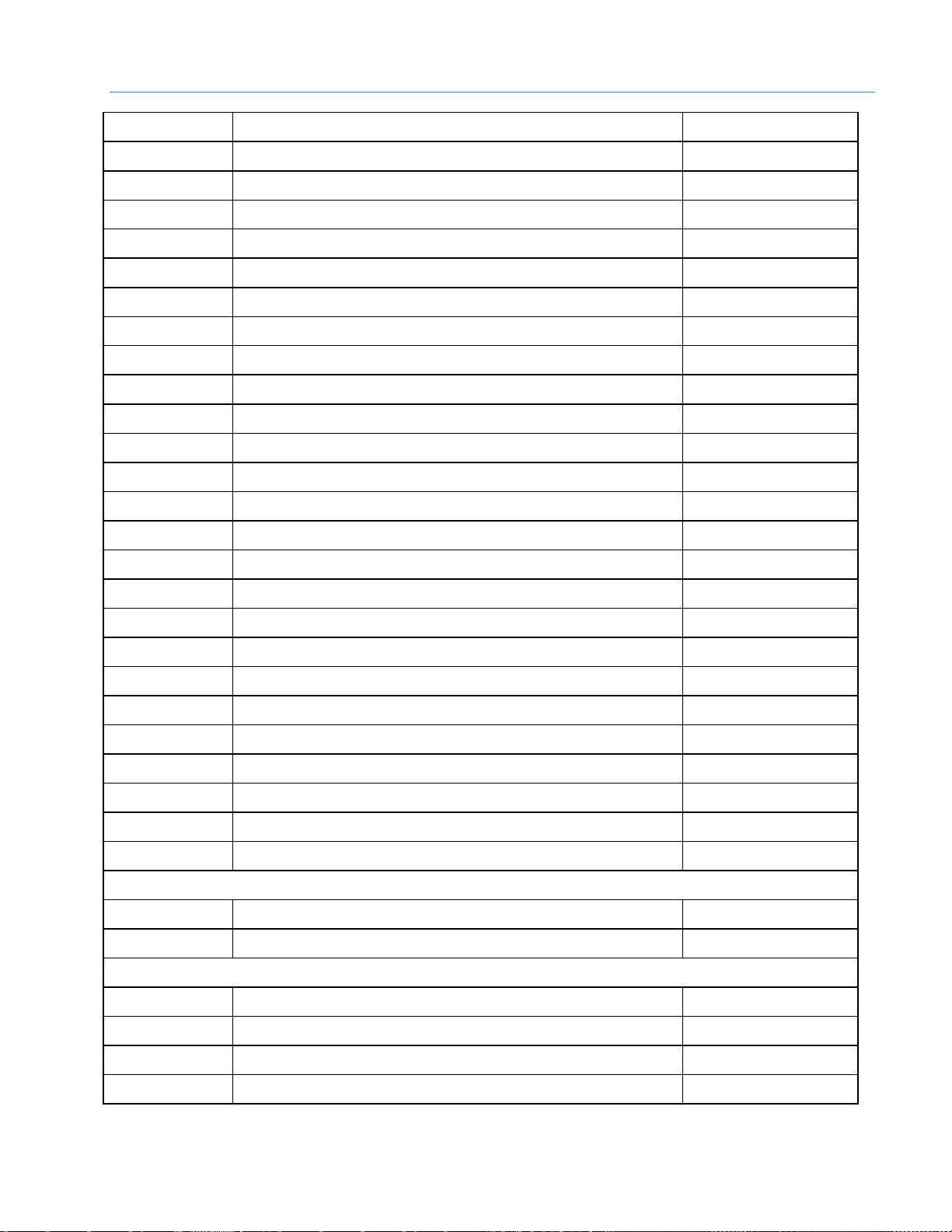
GFK-2737F December 2016 13
Catalog Number
Module Description
Distinguishing Classes1
IC693MDL758
32-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Positive with ESCP
2,3
32 out
IC693MDL760
Solenoid Valve Output Module
16 out
IC693MDL916
16-Circuit Output 4A Relay
16 out
IC693MDL930
8-Circuit Output 4A Relay Isolated
8 out
IC693MDL931
8-Circuit Output Relay Form BC Isolated
8 out
IC693MDL940
16-Circuit Output 2A Relay
16 out
IC694MDL310
12-Circuit Output 120 Vac 0.5A
16 out
IC694MDL330
8-Circuit Output 120/240 Vac 2A
8 out
IC694MDL340
16-Circuit Output 120 Vac 0.5A
16 out
IC694MDL350
16-Circuit Output 120/240 Vac Isolated
none
IC694MDL390
5-Circuit Output 120/240 Vac 2A Isolated
8 out
IC694MDL732
8-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 2A Positive
8 out
IC694MDL734
6-Circuit Output 125 Vdc 1A Positive/Negative
8 out
IC694MDL740
16-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Positive
16 out
IC694MDL741
16-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 1A Negative
16 out
IC694MDL742
16-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 1A Positive
16 out
IC694MDL752
32-Circuit Output 5/24 Vdc 0.5A Negative
32 out
IC694MDL753
32-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Positive
32 out
IC694MDL754
32-Circuit Output with ESCP
none
IC694MDL758
32-Circuit Output 12/24 Vdc 0.5A Positive with ESCP2
none
IC694MDL916
16-Circuit Output 4A Relay
none
IC694MDL930
8-Circuit Output 4A Relay Isolated
8 out
IC694MDL931
8-Circuit Output Relay Form BC Isolated
8 out
IC694MDL940
16-Circuit Output 2A Relay
16 out
IC695MDL765
16-Circuit Smart Output 24/125 Vdc 2A Positive Logic2
None
Discrete Mixed Modules
IC693MAR590
8-Circuit Mixed 120 Vac Input / Relay Output
8 in/out
IC693MDR390
8-Circuit Mixed 24 Vdc Input / Relay Output
8 in/out
Analog Input Modules
IC693ALG220
4-Point Analog Voltage Input
ALG IN 4
IC693ALG221
4-Point Analog Current Input
ALG IN 4
IC693ALG222
16-Point Analog Voltage Input
ALG IN 16
IC693ALG223
16-Point Analog Current Input
ALG IN 16
Page 21

Chapter 1. Introduction
14 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
Catalog Number
Module Description
Distinguishing Classes1
IC694ALG220
4-Point Analog Voltage Input
ALG IN 4
IC694ALG221
4-Point Analog Current Input
ALG IN 4
IC694ALG222
16-Point Analog Voltage Input
ALG IN 16
IC694ALG223
16-Point Analog Current Input
ALG IN 16
IC695ALG106
6-Point Isolated Analog Input Current/Voltage
3,4
none
IC695ALG112
12-Point Isolated Analog Current/Voltage Input4
none
IC695ALG600
8-Point Universal Analog Input Module4
none
IC695ALG608
8-Point Analog Input Current / Voltage Input
3, 4
none
IC695ALG616
16-Point Analog Current / Voltage Input4
none
IC695ALG626
16-Point Analog Current / Voltage Input4 (HART5 Support)
none
IC695ALG628
8-Point Analog Current / Voltage Input
3, 4
(HART5 Support)
none
Analog Output Modules
IC693ALG390
2-Point Analog Voltage Output
ALG OUT 2
IC693ALG391
2-Point Analog Current Output
ALG OUT 2
IC693ALG392
8-Point Analog Current / Voltage Output
ALG OUT 8
IC694ALG390
2-Point Analog Voltage Output
ALG OUT 2
IC694ALG391
2-Point Analog Current Output
ALG OUT 2
IC694ALG392
8-Point Analog Current / Voltage Output
ALG OUT 8
IC695ALG704
4-Point Analog Current / Voltage Output
3, 4
none
IC695ALG708
8-Point Analog Current / Voltage Output4
none
IC695ALG728
8-Point Analog Current / Voltage Output4 (HART5 Support)
none
IC695ALG808
8-Point Isolated Analog Current / Voltage Output4
none
Analog Mixed Modules
IC693ALG442
4-Input / 2-Output, Current / Voltage
ALG IN 4, ALG OUT 2
IC694ALG442
4-Input / 2-Output, Current / Voltage
ALG IN 4, ALG OUT 2
RTD Input Modules
IC695ALG508
8-Channel Isolated RTD Input4
none
Thermocouple Input Modules
IC695ALG312
12-Point Isolated Thermocouple Input
3, 4
none
IC695ALG412
12-Point Isolated High Speed Thermocouple Input
3, 4
none
3
PNS001 firmware version 2.40 required for this product.
4
PNS001 currently does not support Fault Reporting or Interrupts from this module.
5
PNS001 firmware version 2.30 supports the HART Pass Through capabilities of this module. HART-compatible PNC001 and CPU
versions are also required.
Page 22

Chapter 1. Introduction
GFK-2737F December 2016 15
Catalog Number
Module Description
Distinguishing Classes1
High-Speed Counter Modules
IC695HSC308
High-Speed Counter Module - 8 Counters4
None
Specialty Modules
IC694PSM001
Power Sync and Measurement Module
none
Power Supply Modules
IC695PSA040
Universal 120/240 Vac, 125Vdc 40W Power Supply
none
IC695PSA140
Multifunctional 120/240 Vac, 125Vdc 40W Power Supply
none
IC695PSD040
24Vdc 40W Power Supply
none
IC695PSD140
Multifunctional 24Vdc 40W Power Supply
none
Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Modules
IC695SPC100
10/100/1000Base-T Copper SFP
none
IC695SPF002
100Base-FX (fiber 2km) SFP
none
IC695SPF010
1000Base-LX (fiber 10km) SFP
none
IC695SPF550
1000Base-SX (fiber 550m) SFP
none
Page 23

Chapter 1. Introduction
16 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
1.8 Glossary
AR
Application Relationship. PROFINET term for a relationship that is established between an IO-Controller/
IO-Supervisor and IO-Device. For any data to be exchanged between an IO-Controller/IO-Supervisor and a
given IO-Device, an Application Relationship must be established. Within the Application Relationship,
various Communication Relationships (CRs) are then established for the different types of data to be
exchanged.
Broadcast
In Ethernet, the transmission of a network message to all hosts on the network.
CPU Node
In a PACSystems RX3i PROFINET network, a CPU Node is a node in which a PACSystems RX3i CPU is
connected to the PROFINET network.
CR
Communication Relationship. PROFINET term for a channel that is established within an Application
Relationship (AR) to transfer specific data between an IO-Controller/IO-Supervisor and a given IO-Device.
Multiple CRs are established within an AR to transfer data.
DAP
Device Access Point. This access point is used to address an IO-Device as an entity.
Gratuitous ARPs
An Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) request sent by the host to resolve its own IP Address.
GSDML
General Station Description Markup Language - definition of PROFINET Device Characteristics.
IOC
PROFINET IO-Controller
IOD
PROFINET IO-Device
IOCR
Input Output Communication Relationship – describes the type (input/output) and amount of I/O data to be
transferred, the sequence of the transfers and the transfer cycle between a PROFINET IO-Controller (or
IO-Supervisor) and a PROFINET IO-Device.
IOCS
PROFINET Input/Output Consumer Status is transmitted on the PROFINET network to provide feedback on
Input Data for an IO-controller and Output Data for an IO-device.
IOPS
PROFINET Input/Output Provider Status is transmitted on the PROFINET network to provide feedback on
Output Data for an IO-controller and the Input Data for an IO-device.
IOxS
PROFINET abbreviation for the IOCS and/or IOPS (see above).
LLDP
Link Layer Discovery Protocol. IEEE standardized protocol used by network devices to advertise their
identity and capabilities.
LLDPDU
Link Layer Discovery Protocol Data Unit.
MAC
Media Access Control address (MAC address)
MAU
Medium Attachment Unit
MIB
Management Information Basis
MRC
Media Redundancy Client. Within Media Redundancy Protocol, an MRC is responsible for helping the MRM
detect breaks/no breaks in the ring.
MRM
Media Redundancy Manager. Within Media Redundancy Protocol, an MRM is responsible for ensuring that
the ring does not have a closed loop, while simultaneously ensuring maximal connectivity between nodes
on the ring.
MRP
Media Redundancy Protocol. An Ethernet protocol that provides redundant paths for PROFINET-IO cyclic
traffic by supporting a ring topology.
Multicast
In Ethernet, the transmission of a network message to all hosts within a host group.
NOS
Name of Station
OID
Object Identifier
Phase
If the IOCR Update Period is greater than the Send Clock time, the Update Period is divided into multiple
phases where each phase is equal to one Send Clock.
Page 24

Chapter 1. Introduction
GFK-2737F December 2016 17
Glossary, continued
PNC
PROFINET Controller. This could be a separate module, e.g. IC695PNC001 for the RX3i family, or a functional
component of a product such as the PROFINET controller embedded in the ICRXICTL000, IC695CPE330, or
IC695CPE400. Refer to Section 1.4.1.
PNS
PROFINET Scanner. Refer to Section 1.4.2.
RDO
Record Data Object. Services used to read and write structured data stored in a PROFINET IO-Device.
Reduction Ratio
Along with Send Clock determines the Update Period for a PROFINET cyclic data transfer between two
devices (see IOCR). The Update Period equals the Reduction Ratio multiplied by the Send Clock time. For
example, if the Reduction Ratio is 4 and the Send Clock is 1ms, the Update Period is 4ms.
Remote Node
For an RX3i PROFINET network, a Remote Node is any PROFINET IO-Device, such as a rack of I/O modules
with a Remote Scanner or a third party PROFINET IO-Device.
RTA
Real-Time Acyclic. A PROFINET-IO Mechanism used to exchange non-periodic data such as alarms.
RTC
Real-Time Cyclic. A PROFINET-IO Mechanism used to exchange input and output data.
Send Clock
Value between 1 and 128 inclusive in units of 31.25 µs (equivalent to a range of 31.25 µs to 4 ms) used to
calculate the Update Period for a PROFINET cyclic data transfer between two devices (see IOCR). The Send
Clock is the basis for all other scheduling parameters.
Send Offset
The time to delay a scheduled PROFINET cyclic data transfer frame.
Measured in nanoseconds from 0 to 3,999,999. Must be less than the Send Clock time.
SFP
Small Form-factor Pluggable. Pluggable, hot-swappable transceivers.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol. UDP-based network protocol that facilitates the exchange of
management information between network devices.
Submodule
PROFINET-IO representation of the smallest configurable entity of a PROFINET Module.
SVC_REQ
Service Request Function Block. A control system service initiated by the RX3i CPU.
TLV
Type-Length-Value
Unicast
In Ethernet, the transmission of a network message to an individual host.
Update Period
The time between PROFINET cyclic data transfers between an IO-Controller and an IO-Device.
WinLoader
A software utility used to download and install firmware upgrades.
Page 25

Chapter 1. Introduction
18 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
1.9 Documentation
PACSystems Manuals
PACSystems RX7i and RX3i CPU Reference Manual
GFK-2222
PACSystems RX7i and RX3i CPU Programmer’s Reference Manual
GFK-2950
PACSystems Hot Standby CPU Redundancy User Manual
GFK-2308
PACSystems Battery and Energy Pack Manual
GFK-2741
Proficy Machine Edition Logic Developer Getting Started
GFK-1918
Proficy Process Systems Getting Started Guide
GFK-2487
PACSystems RXi, RX3i, and RX7i Controller Secure Deployment Guide
GFK-2830
RX3i Manuals
PACSystems RX3i System Manual
GFK-2314
PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller Command Line Interface Manual
GFK-2572
PACSystems RX3i Max-On Hot Standby Redundancy User’s Manual
GFK-2409
PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual
GFK-2571
PACSystems RX3i CEP PROFINET Scanner User Manual
GFK-2883
PACSystems HART Pass Through User Manual
GFK-2929
PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Scanner Important Product Information
GFK-2574
VersaMax Manuals
VersaMax PROFINET Scanner Manual
GFK-2721
In addition to these manuals, datasheets and product update documents describe individual modules
and product revisions. The most recent PACSystems documentation is available on the GE Automation
and Controls support website www.geautomation.com.
Page 26

GFK-2737F December 2016 19
Chapter 2 LED Operation and Connector Details
This chapter describes:
LEDs
Ethernet Network Ports
SD Card Slot
USB Port
Page 27

Chapter 2. LED Operation and Connector Details
20 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
2.1 Normal Operation of Individual LEDs
2.1.1 OK LED
LED
LED Status
Green On
PNS OK
Off
PNS Not OK
2.1.2 LAN LED
The LAN LED indicates access to and activity on the Ethernet network. The LAN LED indicates network
packets are being processed by the network interface (not just passing through the embedded switch).
LED
LED Status
Green Blinking
The corresponding network interface is active.
Off
The corresponding network interface is not active.
2.1.3 Status LED
The STATUS LED stays green during normal operation.
LED
LED Status
Green On
Normal operation
Red Blinking
A MAC address read from non-volatile memory is invalid. Ports with invalid MAC
addresses remain disconnected from the Ethernet network
2.1.4 CONN LED
The CONN LED indicates the status of PROFINET connections.
LED
LED Status
Green On
At least one PROFINET connection (AR) exists with an I/O Controller
Amber Blinking
No Device Name configured.
Off
No PROFINET connection (AR) exists.
Page 28

Chapter 2. LED Operation and Connector Details
GFK-2737F December 2016 21
2.1.5 Port LEDs
The PROFINET I/O Scanner has four Port LEDs, PORT1, PORT2, PORT3, and PORT4 that indicate link speed,
link connection and link activity corresponding to the four possible external Ethernet ports.
LED
LED Status
Blue On
Link connected, 1000 Mbps
Blue Blinking
Port active, 1000 Mbps
Green On
Link connected, 100 Mbps
Green Blinking
Port active, 100 Mbps
Purple On
Link connected, 10 Mbps
Purple Blinking
Port active, 10 Mbps
Off
The associated Ethernet port is not connected to an active link (can be disabled by
configuration)
Red On
Port 3 and port 4 only. Incompatible SFP plugged into port.
2.1.6 Active LED
The Active LED indicates the Scanner is connected to a PROFINET IO-Controller that is controlling the I/O
data for the I/O modules located in the same rack as the PNS001.
LED
LED Status
Green On
PNS is connected to a PROFINET I/O Controller that is controlling IO Module IO
data
Off
PNS is not connected to a PROFINET I/O Controller or no established connection to
an Active I/O Controller
2.1.7 USB LED
LED
LED Status
Green On
A USB cable is connected.
Green Blinking
The corresponding network interface is active.
Off
No USB port activity.
2.1.8 Special LED Blink Patterns
The PNS’s LEDs can operate in tandem to indicate fatal error, module location/identification,
microprocessor over temperature, and update conditions, as described below. There is also a startup
sequence that tracks the startup processing of the module with the LEDs.
Page 29

Chapter 2. LED Operation and Connector Details
22 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
2.1.8.1 Fatal Error Codes
When the PNS encounters a fatal error, it will blink an error code pattern on the OK LED with an Amber
color or on the STATUS LED with a Green color. In this mode all LEDs flash Green once to indicate the start
of the error code. Next the OK or STATUS LED blinks a 4-digit decimal error code. The LED first blinks to
indicate the most significant error digit, then after a brief pause blinks again to indicate the next
significant error digit and so forth. After another brief pause, all LEDs flash Green again and the error code
pattern repeats. Repetitions continue indefinitely until the module is power-cycled.
2.1.8.2 Module Identification
The LEDs on a PNS module can be commanded to repeatedly turn ON and OFF in a special sequence, to
help locate or identify the module:
First the green LEDs are turned on in the following circular order: OK, LAN, STATUS, CONN, PORT 4,
PORT 3, PORT 2, PORT 1. There is a short delay between turning on each LED.
The LEDs are then turned off in the same order. There is a short time delay between turning off each
LED.
The Module Identification LED Pattern is initiated by the PROFINET DCP Identify Device command. Module
Identification can be initiated using the Proficy Machine Edition Discovery Tool by refreshing the device
list, double clicking on the RX3i PNS module, and clicking the Identify Device button on the PNS properties
pop-up window.
2.1.8.3 Microprocessor Over Temperature
If the maximum threshold temperature for the PNS’s microprocessor is crossed, the PNS goes into power-
saving mode. While the PNS is in an over-temperature condition, the following blink patterns are
alternated:
• PORT 1, PORT 2, and STATUS LEDs turn on RED for 0.5 seconds (all other LEDs off)
• Then PORT 3 and PORT 4 LEDs turn on RED for 0.5 seconds (all other LEDs off)
The PNS stays in power-saving mode until the temperature drops to a safer level. Once a safe
temperature is reached, the PNS module restarts.
Note: Under certain ambient operating temperatures, the PNS may momentarily display the over
temperature pattern during power-up while it is calibrating its thermal protection functions. This
indication can be ignored.
2.1.8.4 Firmware Update
While the PNS is in firmware update mode, the OK, LAN, and STATUS LEDs blink Green for 0.5 seconds and
then off for 0.5 seconds in unison. During firmware update operation, the ports are disabled, so all of the
PORT LEDs are off and the CONN LED is off. The USB LED operates normally displaying the condition of the
USB port.
2.1.8.5 Internal Update
Some changes from a firmware update are applied to the system on the next power up. During this
internal update process, the STATUS and LAN LEDs blink Green for 0.5 seconds and then off for 0.5
seconds in unison. At the completion of the internal update process, the PNS restarts and should power
up normally.
Page 30

Chapter 2. LED Operation and Connector Details
GFK-2737F December 2016 23
2.1.8.6 Power-up LED Patterns
At power-up, the LEDs show the patterns described below. The LEDs also blink diagnostic patterns for
certain operating errors and for module identification. See the section on Special LED Blink Patterns above
for a description of the special blink patterns.
Step
LED/Blink Pattern
Description
Figure 3: IC695PNS001 LEDs
1
All LEDs off
Initial state
2
STATUS LED solid green
Normal operation
OK LED blinks amber with
special blink code
Fatal initialization or diagnostics
Failure; Hardware Module Identity
Information not available.
STATUS LED blinks green
with special blink code
Fatal initialization failure.
OK, LAN, and STATUS LEDs
blink green in unison (1 Hz)
Invalid firmware detected or
firmware update initiated. Module is
waiting for firmware update. Blink
pattern continues during firmware
update. After the automatic update
completes, the LAN and STATUS
LEDs blink Amber and the module
resets, which restarts the power-up
process.
STATUS and LAN LEDs blink
green in unison (1 Hz)
Internal update in process following
a firmware update. Unit should
complete update and restart
automatically.
3
LAN and STATUS LED solid
green
Normal operation
4
OK LED solid green
Normal operation. Power-up
completed.
Note: Under certain ambient operating temperatures, the PROFINET Scanner may momentarily display
the over temperature pattern during power up, while it is calibrating its thermal protection
functions. This indication can be ignored. For details, refer to the section Microprocessor Over
Temperature above.
Page 31

Chapter 2. LED Operation and Connector Details
24 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
2.2 Ethernet Network Ports
The four external Ethernet ports (two RJ45 and two SFP Cages) are on the bottom of the module. Figure 4
shows the underside view of the RX3i PNS. Ports 1 and 2 are standard RJ45 connectors. Ports 3 and 4 are
Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) ports.
Figure 4: Underside of IC695PNS001 Showing Ethernet Ports
The two RJ45 ports provide 10/100/1000 Mbps copper interfaces. The two SFP cages accommodate usersupplied SFP devices, which can support a number of different media types. Refer to SFP Modules for
Ethernet Ports in the Installation chapter for additional information about SFPs.
The two RJ45 ports support CAT5e/6 cabling of up to 100m. Each Ethernet port automatically senses the
type of network and adjusts speed and connection parameters.
The PROFINET protocol can be sent and received over any or all of the four external ports.
Devices connected to the PROFINET Scanner ports should have Ethernet Autonegotiation enabled. The
Ethernet ports can be disabled to support requirements such as IT policies for unused ports. Disabled
ports do not establish a link on their Ethernet network. RX3i PNS modules and other participating modules
can be connected in a daisy chain/line, or star topology. The ports can also be configured to limit their
advertised Autonegotiation setting. This can be used to force a copper interface to establish a link at
100 Mbps rather than 1 Gbps to have quicker link change detection during MRP operation.
Caution
Multiple ports on the Ethernet Interface must not be connected, directly or indirectly, to
the same device so as to form a circular network.
Caution
Port disable settings are non-volatile. If an SFP port is configured as the only enabled
port and that SFP is removed, the RX3i Scanner will not be accessible until an SFP is
returned to that port.
Page 32

Chapter 2. LED Operation and Connector Details
GFK-2737F December 2016 25
2.3 SD Card Slot
The SD Card Slot, located on the front of the PROFINET Scanner, can be used to transfer the Device Name
from a different PROFINET Scanner without the need for a configuration tool such as PME to commission
the new hardware. A card is not required to be present. Refer to Section 4.3.1, Transferring the Device
Name with an SD Card for more details.
Note that when installing an SD Card, the label should face to the left with the write-protect (Lock) switch
to the bottom. The card should enter easily and click when fully inserted. The spring action will return the
card back slightly from its fully depressed position. Do not force the card into the slot as that can damage
the unit. To release the card, press the card in again until it clicks, and the spring action will eject the card
out enough to easily grab hold of it.
SD and SDHC capacity cards are supported. An SD Card can be formatted as either FAT12 or FAT16 per
the SD Card standard and an SDHC card should be formatted using FAT32 per the SD Card standard.
Page 33

Chapter 2. LED Operation and Connector Details
26 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
2.4 USB Port
The USB port, located on the front of the PROFINET Scanner, can be used to connect a computer for
firmware updates for the PROFINET Scanner. The USB port accepts a standard USB cable (USB Micro B
Male to USB Type A Male, not included). The port must be set up before using it, as described in
Section 3.7, Installing the USB Port Driver.
Note: The USB port is for firmware upgrades only. It is not intended as a permanent connection.
Page 34

GFK-2737F December 2016 27
Chapter 3 Installation
This chapter provides instructions for installing PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller modules.
Pre-Installation check
Power Requirements
Hot insertion and removal
Removing the backplane knockout
Module installation and removal
Port connections
Installing SFP devices
Installing the USB Port Driver
Firmware updates
For additional information about system installation, also refer to the PACSystems RX3i Systems Manual,
GFK-2314.
Page 35

Chapter 3. Installation
28 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
3.1 Pre-Installation Check
Upon receiving your RX3i equipment, carefully inspect all shipping containers for damage. If any part of
the system is damaged, notify the carrier immediately. The damaged shipping container should be saved
as evidence for inspection by the carrier.
As the consignee, it is your responsibility to register a claim with the carrier for damage incurred during
shipment. However, GE Automation and Controls will fully cooperate with you, should such action be
necessary.
After unpacking the RX3i equipment, record all serial numbers. Serial numbers are required if you should
need to contact Customer Care during the warranty period. All shipping containers and all packing
material should be saved should it be necessary to transport or ship any part of the system.
Verify that all components of the system have been received and that they agree with your order. If the
system received does not agree with your order, contact Customer Care.
If you need technical help, contact Technical Support. For phone numbers and email addresses, see the
General Contact Information page in the front of this manual.
Page 36

Chapter 3. Installation
GFK-2737F December 2016 29
3.2 Installation in Hazardous Areas
EQUIPMENT LABELED WITH REFERENCE TO CLASS I, GROUPS A, B, C & D, DIV. 2 HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS IS
SUITABLE FOR USE IN CLASS I, DIVISION 2, GROUPS A, B, C, D OR NON-HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS ONLY.
Warning
EXPLOSION HAZARD - SUBSTITUTION OF COMPONENTS MAY IMPAIR SUITABILITY FOR
CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Warning
EXPLOSION HAZARD - WHEN IN HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS, TURN OFF POWER BEFORE
REPLACING OR WIRING MODULES.
Warning
EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT CONNECT OR DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT UNLESS POWER
HAS BEEN SWITCHED OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
Warning
EXPLOSION HAZARD - USB PORT IS ONLY FOR USE IN NON-HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS, DO
NOT USE UNLESS AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
3.2.1 ATEX Marking
II 3 G Ex nA IIC T5 X Ta: 0 - 60C
Page 37

Chapter 3. Installation
30 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
3.3 Module Installation
3.3.1 Power Requiremnents
More than one power supply may be required to support some configurations. To determine the loading
within the PNS rack, refer to the Module Load Requirement section in the PACSystems RX3i System Manual,
GFK-2314. Calculate the 3.3 Vdc and 5 Vdc needs of the modules within the rack, and select power
supplies accordingly.
3.3.2 Hot Insertion and Removal
The PNS Module does not support hot insertion or removal. Turn power off at the rack before removing or
inserting a PNS.
Certain I/O Modules within the rack may be removed and/or inserted while the rack is powered up. Refer
to Section 5.3, Hot Swap of I/O Modules.
For a full discussion of this topic, refer to the Hot Insertion and Removal section in the PACSystems RX3i
System Manual, GFK-2314.
3.3.3 Removing the Backplane Knockout
The PNS can be installed in slot 1 or slot 2 of a 7-, 12-, or 16-slot RX3i Universal Backplane (IC695CHS007,
CHS012 or CHS016), or in slot 6 of a 7-slot RX3i Universal Backplane. It may not be located in the same
rack as an RX3i CPU module. For details, refer to the PACSystems RX3i System Manual, GFK-2314.
The rear of the PNS module has an exposed heat sink and backplane connector. Before inserting the
module into the backplane, remove the plastic knockout in the slot into which the module will be placed.
The installation slot must match the slot selected for the module in the Proficy Machine Edition (PME)
hardware configuration.
Figure 5: RX3i Backplane showing Removable Plastic Knockout
Page 38

Chapter 3. Installation
GFK-2737F December 2016 31
3.3.4 Module Installation
RX3i rack power must be turned off. The
PNS does not support insertion/removal
while power is applied to the rack.
Figure 6: Install Module into RX3i Backplane
Holding the module firmly, align the module
with the correct slot and connector.
Engage the module’s rear pivot hook in the
notch on the top of the backplane (1).
Swing the module down (2) until the
module’s connector engages the
backplane’s backplane connector.
Visually inspect the module to be sure it is
properly seated.
Secure the bottom of the module to the
backplane using the machine screws
provided with the module (3).
Tighten the heat sink screw on the front of
the module in the threaded hole in the back
plate to 6 in-lbs (0.68 Nm), using a flat-tip
screwdriver.
3.3.5 Module Removal
RX3i rack power must be turned off.
Figure 7: Remove Module from RX3i Backplane
Loosen the heat sink screw on the front of
the module to release the heat sink from
the backplane’s aluminum back plate.
Loosen the screws at the bottom of the
module (1).
Pivot the module upward until its connector
is out of the backplane (2).
Lift the module up and away from the
backplane to disengage the pivot hook (3).
Page 39

Chapter 3. Installation
32 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
3.4 Replacing a PROFINET Scanner
If a PNS module needs to be replaced for any reason, follow these steps to commission a replacement
module.
Note: If the replacement PNS module has no assigned Device Name (the CONN LED is blinking Amber
slowly), the network cabling can be plugged back in and the name assigned over the PROFINET
network.
However, if the replacement PNS module already has an assigned Device Name, there will be a
risk of a duplicate Device Name on the network. This condition cannot be tolerated by the
PROFINET Controller. This situation can be avoided by transferring the Device Name from the
installed PNS to the replacement PNS via the SD Card prior to connecting the replacement unit to
the PROFINET network.
If there is a possibility of duplicate Device Names or duplicate IP Addresses existing on the
network, these should be assigned before inserting the replacement PNS into a working PROFINET
network. The Device Name and IP Address settings can be updated offline (for example, in an
office setting).
Use the Proficy Machine Edition DCP Tool to store the Device Name to the RX3i SD Card installed in
the PNS SD slot. Avoid hand-editing Device Name files contained on the SD Card. Storing an illegal
name to the RX3i PNS will prevent it from connecting to its PROFINET Controller until a valid Device
Name is stored.
3.4.1 Method 1 – Using the SD Card
1) Remove power from the PNS module. This should be done before network cabling is removed,
especially in the case of fiber connections.
2) Remove network cabling from the module.
3) Remove the SD Card from the module.
4) Remove the module.
5) Install the replacement PNS module.
6) Insert the SD Card from Step 3) in the replacement PNS module.
7) Connect network cabling to the replacement PNS module.
8) Apply power to the replacement PNS module hardware. The PROFINET IO-Controller will update
any IP Address settings automatically when it connects.
3.4.2 Method 2 – Using the DCP Tool
Refer to Section 4.3, Assigning Device Names.
1) Remove power from the PNS module. This should be done before network cabling is removed,
especially in the case of fiber connections.
2) Remove network cabling from the module
3) Remove the module.
4) Install the replacement PNS module.
5) Connect network cabling to the replacement PNS module.
6) Apply power to the replacement PNS module hardware.
7) Using the utility PROFINET DCP click on the Refresh Device List command button.
8) Highlight the row representing the newly installed PNS.
9) Click on the Edit Device command button and type in the Device Name.
10) Click on the Set Device Name command button.
Page 40

Chapter 3. Installation
GFK-2737F December 2016 33
3.5 SFP Modules for Ethernet Ports
Refer to Chapter 2 of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual, GFK-2571.
3.6 External Switch VLAN Priority Settings
Refer to Chapter 4 of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual, GFK-2571.
3.7 Installing the USB Port Driver
The USB port is only used for firmware updates. USB driver files are provided as part of upgrade packages
compatible with the PNS.
With the provided installation files accessible on either a local or network drive, connect the computer’s
USB port to the USB port on the PNS module to be upgraded. When requested, direct the installation to
the proper location of the installation files.
The serial port name is COM followed by the next available number from 1 to 256. After the computer
assigns the USB port a COM port number, that computer uses the same COM port number each time it
connects to that PNS module.
Note: When connecting the USB cable to the PNS, you may receive a warning for installing a driver that
has not passed Windows Logo testing. This warning should be ignored. Because each PNS has a
different serial number, the operating system recognizes each driver installation as different.
3.8 Firmware Updates
Note: The RX3i PNS does not prevent initiation of firmware update when it is actively connected to an
I/O Controller. When the PNS enters firmware update mode, the PNS and its modules go to their
I/O default modes. During the update, the PNS does not drive module outputs or send inputs to
the I/O Controller. When the firmware update is completed and the PNS is rebooted, its previous
connections are re-established and control resumes. Refer to section 2.1.8.6 Power-up LED
Patterns.
The PNS enters firmware update mode when commanded to do so from the WinLoader update utility, or
if a firmware component is corrupted or invalid. In firmware update mode, the PNS module blinks its LEDs
in a special pattern as described previously, and its Ethernet ports are not operational.
If the PNS has experienced a fatal error, the module goes to an LED blink-code error condition and does
not communicate with WinLoader, causing WinLoader to return a timeout failure indication. The module
must be power-cycled before reattempting the update.
Page 41

Page 42

GFK-2737F December 2016 35
Chapter 4 Configuration
This chapter explains how to configure a PROFINET IO-Device consisting of an RX3i PROFINET Scanner
and the I/O modules located in its rack into a PACSystems RX3i system controlled by an RX3i CPU.
Additional information about RX3i configuration is available in other PACSystems documentation (refer to
Section 1.9, PACSystems Manuals) and in the Logic Developer online help.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
Configuration Overview
o Basic Configuration Steps
o Configuration Tools
Adding an RX3i PROFINET Scanner to a LAN
- Configuring RX3i PROFINET Scanner
- Adding RX3i Modules to a Remote Node
o Adding a Power Supply
o Adding and Configuring an Ethernet Port
o Configuring Module Parameters
o Configuring Analog Modules that have DIP Switches
o Configuring Analog Modules that have Jumpers
• Assigning Device Names
- Transferring the IO-Device Name with an SD Card
After the Configuration is Stored to the PROFINET Controller
Page 43

Chapter 4. Configuration
36 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
4.1 Configuration Overview
The RX3i PNS receives its configuration from a connected PROFINET Controller (PNC), which has been
configured by a PROFINET configuration tool. The GSDML files required for configuring the PROFINET
Scanner (PNS) are provided with Proficy Machine Edition. For other PROFINET configuration tools, the PNS
GSDML must be imported. The GSDML file for the RX3i PNS can be obtained at www.geautomation.com.
PNS001 GSDML files are also included in all RX3i firmware upgrade kits.
Note: For details on using the Proficy Machine Edition PLC Logic Developer programmer to create and
download the configuration for an RX3i PROFINET network and its IO-Devices, refer to the
PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller Manual, GFK 2571.
4.1.1 Basic Configuration Steps
The basic configuration steps are:
Configure a PROFINET I/O Controller and its PROFINET LAN using the I/O Controller manufacturer’s
recommended PROFINET I/O configuration tool.
Configure the parameters of the PROFINET I/O Controller.
Add IO-Devices to the LAN.
PROFINET Scanners and other types of IO-Devices use GSDML files to describe their capabilities. The
PROFINET I/O configuration tool imports these GSDML files and incorporates the devices into the
configuration.
Configure the parameters of the RX3i PROFINET Scanner.
Configure the communications properties of the PROFINET I/O Controller and RX3i
PROFINET Scanner.
Add RX3i/Series 90-30 modules to the RX3i PROFINET Scanner.
Configure the parameters of the modules.
When the configuration is ready, use a DCP tool to assign a Device Name to the RX3i PROFINET
Scanner so the PROFINET IO-Controller can connect to it and deliver the configuration.
Store the configuration data from the configuration tool to the PROFINET I/O Controller.
4.1.2 Configuration Tool
The configuration tool used to configure the PROFINET LAN containing the PNS module must support
IO-Devices configured with GSDML V2.3 files.
The Proficy Machine Edition PLC Logic Developer programmer is used to create and download the
configuration for an RX3i PROFINET network and its devices.
Page 44

Chapter 4. Configuration
GFK-2737F December 2016 37
4.2 Adding an IO-Device to a PROFINET LAN
Use the PROFINET I/O configuration tool to add an IO-Device to the LAN:
In the case of an IO-Device consisting of a rack of RX3i I/O modules, that rack must contain an
RX3i Scanner PNS001 as its head-end.
In the case of an IO-Device consisting of a remote drop of RX3i I/O modules, but no RX3i I/O rack,
the CEP001 acts as the head-end unit. For product details, refer to the PACSystems RX3i CEP
PROFINET Scanner User Manual, GFK-2883.
In the case of an IO-Device consisting of a rack of VersaMax I/O modules, that rack must contain
a VersaMax Scanner IC200PNS001 or IC200PNS002 as its head-end. For product details, refer to
the VersaMax PROFINET Scanner Manual, GFK-2721.
4.2.1 Adding an RX3i PROFINET Scanner to the PROFINET LAN
Begin this process by importing the GSDML file corresponding to the PNS001 module and its associated
RX3i I/O Rack. Seven versions of this GSDML file are available, based
1) on the size of the host RX3i I/O Rack backplane and
2) upon which slot in that rack the PNS will occupy.
Apart from these two aspects, the GSDML files are otherwise identical. Select and import the version that
corresponds to your application.
Once the IO-Device is created, the slot occupied by the PNS is fixed and cannot be altered. If the
application requires that the PNS be moved to a different slot, a new IO-Device must be created (using the
process described in this section) and the original IO-Device must be removed from the configuration.
Page 45

Chapter 4. Configuration
38 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
4.2.2 Configuring an RX3i PROFINET Scanner
The PROFINET I/O Scanner is automatically assigned 32 bits of Status data and 32 bits of Control data.
These should be mapped to the I/O Controller’s memory. For definitions of these bits, refer to Section 5.2.1,
PROFINET Scanner Status and Control Data.
The PROFINET Controller (PNC) to which the PNS is connected determines the state of the inputs whenever
the PNS is unable to provide them. This could happen when the PNS is not powered on, not connected to
the network, or there is a network or configuration issue such that the PNC cannot communicate with the
PNS. PNCs available from GE’s Automation and Controls support defaulting inputs to Force Off or Hold
Last State values until PROFINET communications are restored.
Configure the network parameters of a PNS (IP Address, subnet mask, and gateway) so that each device
on the PROFINET network has a unique IP Address. The PNC will configure the network parameters for the
PNS during the Connect sequence.
When the network parameters are set with the DCP tool, they will be maintained over a power-cycle while
no PNC is connected. If a PNC is connected and the network parameters configured for the PNS do not
match the currently retentive parameters stored on the device (those set using a DCP Tool), then the PNC
will assign the configured network parameters to the PNS for immediate use during the connection
process. This will have the effect of overwriting the retentive values that were set by DCP with the factory
default values for IP, subnet, and gateway, (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0). Note that if the PNS is subsequently
power-cycled without a PNC connected, the PNS will power up with the default network settings because
network settings configured by the PNC are not retentive. In order to maintain settings over a power-cycle
without a PNC connected, the network settings assigned by the PNC must match the network settings
configured with the DCP Tool.
The rate of data exchange on the PNS is usually configured in PME configuration tools. The PNS supports
update rates from 1 ms to 512 ms. The correct setting for each device can depend on the dynamics of the
equipment being controlled, the network loading on the PROFINET-I/O LAN, and the loading of the PNC.
Refer to the section on PNC Loading in the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual, GFK-2571.
It is possible to have better performance at 2 ms, 4 ms or greater periods than at 1 ms depending on the
overall system requirements, design, and loading. The duration of data indicating very brief states or
conditions should be taken into consideration in choosing the correct setting.
4.2.2.1 Media Redundancy Parameters
For a full discussion of PROFINET Redundant Media and interactions with the controlling RX3i CPU, refer to
Chapter 6 of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual, GFK-2571.
By default, the PROFINET Scanner is not set up for Media Redundancy. If the PROFINET Scanner will be a
Media Redundancy Client (MRC), use Proficy Machine Edition to configure the related parameters, as
follows. For the PNS module itself, select the module ports that will be used for Ring Port 1, Ring Port 2 and
the MRP Domain. The MRP Domain name is used to assign MRP Clients to the Media Redundancy
Manager (MRM) for the network ring. The Domain Name is defined in the Media Redundancy tab of the
associated PROFINET Controller.
Page 46

Chapter 4. Configuration
GFK-2737F December 2016 39
4.2.2.2 System Redundancy Parameters
The Redundancy tab selects whether or not the PNS is to be redundantly controlled.
Figure 8: Select System Redundancy Parameters in PME
When the PNS supports PROFINET System Redundancy and is configured in an HSB CPU Redundancy
system, the Programmer defaults the Redundancy Mode parameter to HSB CPU Redundancy. Refer to the
PACSystems Hot Standby CPU Redundancy User’s Manual, GFK-2308G or later, for detailed information on
setting up a Hot Standby Redundancy system.
When the PNS does not support PROFINET System Redundancy or is not configured in an HSB CPU
Redundancy system, the PNS Programmer defaults the Redundancy Mode parameter to None. This
selects simplex operation.
To configure a redundancy-capable PNS for simplex operation within an HSB CPU Redundancy system,
change the Redundancy Mode parameter from HSB CPU Redundancy to None.
Transfer List
All redundantly controlled I/O must be included in the CPU’s I/O transfer list. Note that once the HSB CPU
Redundancy Mode is set, Proficy Machine Edition automatically expands the Primary CPU’s input transfer
list to include all redundantly controlled PROFINET inputs as reference addresses are being assigned.
Proficy Machine Edition also automatically expands the Primary CPU’s output transfer list to include all
redundantly controlled PROFINET outputs.
The configuration should be stored to both the Primary and Secondary racks before attempting to control
any I/O in the RX3i PNS.
Changing a Redundant PNS Configuration
Changes to the device’s configuration on either the Primary while the Secondary is running or the
Secondary while the Primary is running will cause a Loss of Device I/O fault on the controller that is being
updated. The controller with the changed configuration will be prevented from re-connecting as long as a
non-matching connection exists with the device from any controller.
To make changes to the PNS configuration once the system is running, refer to the PACSystems Hot
Standby CPU Redundancy User’s Manual, GFK-2308, and follow the procedure Download a Modified
Configuration to a Redundancy System – Stopping the Process.
Page 47

Chapter 4. Configuration
40 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
4.2.3 Adding RX3i Modules
For a list of modules, power supplies and backplanes that can be used with an RX3i PROFINET Scanner I/O
Device, refer to Section 1.7. Select the slot in the rack into which a particular module will be placed, then
select the catalog number for that module from the drop-down list provided.
4.2.3.1 Adding a Power Supply
Some power supplies occupy two slots in the backplane. When adding a two-slot power supply to an RX3i
Scanner configuration, it should be configured in the left-most slot occupied by the module, and nothing
configured for the other slot. For example, when installing an IC695PSA140 power supply in slots 0 and 1
in the backplane, it is configured in slot 0 and nothing is configured in slot 1. Because both slots of a twoslot power supply must fit within the rack, a 2- slot power supply cannot be placed in the last nonexpansion slot of a rack.
Adding power supplies to the configuration sets up power supply alarms. Loss of Module alarms will be
triggered if the power supply is configured but not working, or configured in the wrong subslot. These
power supplies have no configurable parameters, but their power supply and GSDML details can be
viewed by double-clicking on a power supply icon or right-clicking and selecting Configure.
4.2.3.2 Adding and Configuring an Ethernet Port
SFP modules may be added to the RX3i PNS by selecting the desired SFP module type from the available
SFP module list and assigning it to Port 3 or Port 4. Refer to Section 3.5, SFP Modules for Ethernet Ports for
more details.
To add an SFP module to a PNS: using Proficy Machine Edition, right-click the slot containing the PNS and
select Change Submodule List (Figure 9) to display a dialog box that will present a list of supported SFP
modules.
Figure 9: Change Submodule List produces list of Eligible SFP Modules
The RX3i PNS001 supports setting a port to
Automatic (Auto-negotiation enabled),
a designated fixed speed, or
Disabled.
Page 48

Chapter 4. Configuration
GFK-2737F December 2016 41
Automatic enables auto-negotiation for the widest range of options supported by the port.
Designated speed options limit the auto-negotiation to that one setting such as limiting a 1 Gbps
connection to 100 Mbps.
The Disabled setting powers down the port so that it does not establish any link.
All ports, including empty, unconfigured SFP cages, are set to Automatic by default.
Once an SFP port is populated with an SFP device, the PNS001 will treat that port as present. RJ45 ports
are always treated as present.
The PNS001 rejects configurations that disable all present ports. This rejection causes the Scanner to fail
to establish a connection. For example, if no SFP modules are present and a configuration is attempted
which disables the two built-in RJ45 ports, that configuration does not connect. A configuration which
disables the two built-in RJ45 ports, but has an SFP module configured which is not present also does not
connect. In this last example, once an SFP module is installed in the specified port, the port will become
present, the configuration becomes valid and a connection can be established.
Caution
The port delivering the configuration can be disabled by a new configuration and
that setting stored to non-volatile storage. Be sure to understand the network
topology before disabling Ethernet ports.
Caution
Port disable settings are non-volatile. If an SFP port is configured as the only
enabled port and that SFP is removed, the RX3i Scanner will not be accessible until
an SFP is reinserted into that port.
Page 49

Chapter 4. Configuration
42 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
4.2.3.3 Configuring Modules with Submodules
Certain PACSystems RX3i I/O Modules (such as the Analog Module in Figure 10) have configurable
parameters that must be selected prior to operation. Proficy Machine Edition indicates an error on the
module until its submodule-level configuration has been completed, as described below.
Figure 10: Analog Module with Configurable Parameters
To complete this level of configuration, right-click the slot containing the I/O Module and select Change
Submodule List. This opens a dialog box that presents a list of submodule options. For example, an analog
module which employs jumpers to determine its functional voltage or current range would require an
equivalent submodule-level setting to be selected in PME.
Page 50

Chapter 4. Configuration
GFK-2737F December 2016 43
4.2.3.4 Configuring Modules with Multiple Modes of Operation
Some PACSystems RX3i modules have multiple modes of operation that change the appropriate limits for
their configuration parameters. For example, an IC695ALG616 analog input module supports a different
set of A/D Scaling Units when in 4 to 20 mA operation than when it is in -10 Vdc to +10 Vdc operation.
These different configuration options are implemented as groups of controls which are activated by a
choice made outside of the group and marked with +/- expander controls. Typically, this choice is directly
preceding the first group.
Figure 11: Analog Module with Multiple Possible Option Settings
Whenever multiple options are available, only those parameters associated with the active choice are
used. The other settings are maintained, but are ignored by the module. To prevent confusion, it is
recommended that only the active choice be expanded.
The state of the expander control does not affect the choice of active parameters. If the active setting is
collapsed and not visible, it is still active and its values are used for the module configuration.
Page 51

Chapter 4. Configuration
44 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
4.2.3.5 Configuring Discrete Modules that Have DIP Switches
Some PACSystems RX3i discrete output modules have a physical DIP switch that controls the operation of
their output circuits whenever connection to an IO-Controller is lost. A switch selects between Force Off
and Hold Last State. This setting applies to all outputs on the module.
The documentation for each such module lists any additional requirements for Hold Last State to operate
correctly. For some modules, field power must be maintained on the PACSystems backplane in order for
Hold Last State to operate correctly.
If a discrete output or discrete mixed module does not have a switch or an additional configuration option
specifying the default behavior of its outputs, the hardware default is to turn outputs off.
4.2.3.6 Configuring Modules that have Jumpers
Certain PACSystems RX3i analog modules have jumpers on their terminal strips that control the operation
of their I/O. For example, the IC69xALG220 can operate as a +10 Vdc to -10 Vdc analog input or a
4-20 mA analog input depending on a jumper setting. The IC69xALG390 is another example: it uses a
jumper rather than a DIP switch to determine whether to Force Off or Hold Last State.
Jumper settings are latched when the module is powered up, so the jumper setting cannot be altered
during operation. The module itself must experience a power cycle for an altered jumper setting to have
effect.
4.2.4 Support for Analog Modules with HART Features
PNS001 firmware version 2.30 and later supports the HART Pass Through feature of a number of modules,
as listed in Section 1.7. HART-compatible PNC001 and compatible RX3i CPU versions are also required.
Refer to the PACSystems HART Pass Through User Manual, GFK-2929.
PNS001 firmware version 2.41 added support for the Remote Get HART Device Information COMMREQ.
Using this COMMREQ, information from a HART device connected to an RX3i Analog Module located in a
rack controlled by an RX3i PROFINET Scanner may be read into the user application. Refer to the
PACSystems RX3i System Manual, GFK-2314M or later, for details concerning this COMMREQ.
PNS001 does not support HART variables at time of publication.
4.2.5 Configuring Module Parameters
After adding PACSystems RX3i modules to the remote IO-Device, their parameters must be configured.
For all PACSystems RX3i modules, this includes configuring a set of basic parameters such as reference
address. Configuration details for those basic parameters are given on the following pages. If the module
has no module-specific parameters, a blank grouping of Module Parameters may be displayed in the
Configuration Tool.
The RX3i modules listed in the following table require additional configuration beyond the basic
parameters described in this chapter. Refer to the PACSystems RX3i System Manual, GFK-2314, or to the
individual module datasheet for detailed parameter information.
Page 52

Chapter 4. Configuration
GFK-2737F December 2016 45
Catalog #
Module Description
Datasheet
IC693ALG222
Analog Voltage Input Module – 16-Channel
GFK-2654
IC693ALG223
Analog Current Input Module – 16-Channel
GFK-2655
IC693ALG392
Analog Current/Voltage Output Module – 8-Channel
GFK-2557
IC693ALG442
Analog Module, 4 Inputs / 2 Outputs Current/Voltage
GFK-2687
IC694ALG222
Analog Voltage Input Module – 16-Channel
GFK-2654
IC694ALG223
Analog Current Input Module – 16-Channel
GFK-2655
IC694ALG392
Analog Current/Voltage Output Module – 8-Channel
GFK-2557
IC694ALG442
Analog Module, 4 Inputs / 2 Outputs Current/Voltage
GFK-2687
IC694PSM001
Power Sync and Measurement Module
GFK-2748
IC695ALG106
Isolated Analog Current/Voltage Input Module – 6-Channel
GFK-2482
IC695ALG112
Isolated Analog Current/Voltage Input Module – 12-Channel
GFK-2482
IC695ALG312
Isolated Thermocouple Input Module – 12-Channel
GFK-2500
IC695ALG412
Isolated High Speed Thermocouple Input Module – 12-Channel
GFK-2578
IC695ALG508
Analog Isolated RTD Input Module – 8-Channel
GFK-2501
IC695ALG600
Universal Analog Input Module – 8-Channel
GFK-2348
IC695ALG608
Analog Current/Voltage Input Module – 8-Channel
GFK-2372
IC695ALG616
Analog Current/Voltage Input Module – 16-Channel
GFK-2372
IC695ALG626
Analog Current/Voltage Input Module – 16-Channel with HART
GFK-2372
IC695ALG628
Analog Current/Voltage Input Module – 8-Channel with HART
GFK-2372
IC695MDL664
Digital Input Module with Diagnostics – 16-Channel
GFK-2590
IC695MDL765
Digital Output Module with Diagnostics – 16-Channel
GFK-2591
IC695ALG704
Analog Current/Voltage Output Module – 4-Channel
GFK-2373
IC695ALG708
Analog Current/Voltage Output Module – 8-Channel
GFK-2373
IC695ALG728
Analog Current/Voltage Output Module – 8-Channel with HART
GFK-2373
IC695ALG808
Isolated Analog Current/Voltage Output Module – 8-Channel
GFK-2481
IC695HSC308
High-Speed Counter Module - 8 Counters
GFK-2441
Page 53

Chapter 4. Configuration
46 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
4.2.5.1 RX3i PROFINET Scanner Configuration Validation
Certain elements of configuration data are validated by the RX3i PROFINET Scanner upon receipt. The
following table indicates the configuration validations performed by the PNS on behalf of the indicated I/O
modules. If the scanner detects an invalid configuration for a given module, the module transitions to
module default operation. At the PLC CPU, this will result in the corresponding point faults being
energized.
If any module listed below receives an invalid configuration, it rejects the configuration, energizes point
faults and blinks its OK LED. The module does not transition to an operational state, as indicated by the
OK LED being On-Solid, until a valid configuration has been stored.
Catalog #
Rules
IC695MDL664
1. Pulse test diagnostic reporting must be disabled when pulse testing is disabled.
2. Open wire and short circuit diagnostic reporting must be disabled when the channel is
configured for dual-state input type.
3. Short circuit diagnostic reporting must be disabled when the channel is configured for tri-state
input type.
IC695MDL765
1. Pulse test diagnostic reporting must be disabled when pulse testing is disabled.
2. Auto Pulse Normal State and Auto Pulse Default State must not be equal to each other if pulse
testing is enabled.
IC695ALG508
IC695ALG600
1. – 5. Same as C695ALG112
6. The Lead Resistance Compensation must be set to disabled for RTD 2-wire operation.
IC695ALG112
IC695ALG616
IC695ALG626
1. The High Scale Value Engineering Units cannot be equal to the Low Scale Value Engineering
Units.
2. The High Scale Value A/D Units must be greater than the Low Scale Value A/D Units.
3. The Alarm Limits must be in order, with the High High Alarm greater than or equal to the High
Alarm, which is greater than the Low Alarm, which is greater than or equal to the Low Low
Alarm.
4. The Alarm Limits must be within the configured Engineering Units plus User Offset range, for
example if the High and Low Engineering Unit Scale values are 10,000 and -10,000 and User
Offset is 1000, the alarm limit range is +11,000 to -9,000
5. The Alarm Deadbands must be set such that the Alarm can be cleared. For example, if the
Engineering Units Scale Range is -5 to 5 and the High Alarm is 4, the High Deadband must be
less than 9 or else it is not possible to reach a value that is low enough to clear the High Alarm.
Note that the User Offset modifies the range of Alarms and Alarm Deadbands. The User Offset
is added to the High and Low Engineering Unit Scale Values to set the alarm range limits.
Page 54

Chapter 4. Configuration
GFK-2737F December 2016 47
Catalog #
Rules
IC695ALG708
IC695ALG728
1. The High Scale Value Engineering Units cannot be equal to the Low Scale Value Engineering
Units.
2. The High Scale Value A/D Units must be greater than the Low Scale Value A/D Units.
3. The High Alarm must be greater than the Low Alarm.
4. The Alarm Limits must be within the configured Engineering Units minus User Offset range.
For example, if the High and Low Engineering Unit Scale values are 10,000 and -10,000 and
User Offset is 1000, the alarm limit range is +9,000 to -11,000.
5. The valid range of Clamp Limits (if enabled) and Default Value is extended slightly beyond the
alarm limits minus User Offset, depending on the configured Range.
6. Integer Current: ±400 Eng Units (0-20mA +400 Eng Units only)
Floating Point Current: ±0.4 Eng Units (0-20mA +0.4 Eng Units only)
Integer Voltage: ±500 Eng Units
Floating Point Voltage: ±0.5 Eng Units.
7. The minimum (slowest) ramp rate is the higher Engineering Unit Scale Value minus the lower
Engineering Unit Scale Value divided by 60,000. Put another way, the minimum ramp rate must
be no slower than the full Engineering Units range traversed in 60 seconds.
IC695ALG808
1. -7, Same as IC695ALG708
8. Open Wire Enable Diagnostic reporting is only valid when the module’s Range Type is
Voltage/Current and the Range is set to a Current Range.
9. Short Circuit Enable Diagnostic reporting is only valid when the module’s Range Type is
Voltage/Current and the Range is set to a Voltage Range.
IC695HSC308
1. The counter High Range value must be greater than the Low Range Value.
2. If a counter is configured as Continuous within high/low range or One-shot within high/low
range, the PreLoad Value must also be within the range.
3. If 1ms is selected as the Timebase Units, the Timebase range is 1 to 429496.
If units are 1 µS, the range is 1 to 429496729.
If units are 100 nS, the range is 1 to 2147483647.
4. To be used as a counter Setpoint Output an External Output must be configured as Setpoint(s)
on the Outputs Tab.
4.2.5.2 Basic Module Parameters
The module parameters define how the PNC scans and stores the module’s data. The number of address
ranges varies by module and submodule. For discrete data, there is a starting address and a length for
input data and another starting address and length for output data. Analog data can be listed with each
analog value as a separate address and a length of one or as a group with the starting address listed and
an overall length value. What is available can depend on the Configuration Tool.
Input Data /
Output Data
The address in the I/O Controller’s reference memory for the module’s data.
For PACSystems CPUs: Discrete Data can be added to %G, %I, %Q, %T, and %M memory areas.
Non-Discrete Data can be added to %AI, %AQ, %R, %W, %G, %T, and %M memory areas.
Length
For discrete modules, the length of the input /output data is fixed and cannot be edited.
Other Data
Some modules have other data areas such as Module Status, ESCP Point Status, or Digital Filter
settings. Refer to PACSystems RX3i System Manual, GFK-2314, or the appropriate User’s Manual for
more details about the data of each I/O Module.
Page 55

Chapter 4. Configuration
48 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
4.3 Assigning Device Names
After the PROFINET Scanner and other IO-Devices on the LAN have been entered into the configuration,
the Discovery and Configuration Protocol (DCP) tool must be used to assign a Device Name to each
IO-Device. The name of each device on the LAN must match the hardware configuration resident in the
PROFINET IO-Controller. This step is required before downloading the configuration from the PROFINET IOController; otherwise the PROFINET IO-Controller will be unable to connect to the devices on its network
and will be unable to deliver configuration data to those IO-Devices.
The DCP tool must be connected directly to the PROFINET IO-LAN. The DCP tool allows you to display an
identification pattern on an IO-Device. This can be helpful to distinguish devices apart when all are at
factory default settings.
The DCP tool supports issuing a reset command to an IO-Device. A reset clears the Device Name and sets
other non-volatile settings such as IP Address, subnet mask, and gateway mask to the factory defaults. A
Reset to Factory DCP command also clears all Ethernet port settings such as port disabling. This defaults
all ports to Enabled with Auto-negotiation on.
4.3.1 Transferring the Device Name with an SD Card
To allow replacement hardware to be commissioned without requiring a DCP Tool, the PROFINET Device
Name can be written to an SD Card and then transferred to replacement hardware via the SD Card.
To write the Device Name to an SD Card, the SD Card must be inserted into the PNS when the DCP Tool
assigns a Device Name to the PNS. An assignment of a Device Name using a DCP Tool writes that name to
both the SD Card and the non-volatile storage in the PNS. If the card is subsequently removed, the PNS
maintains its Device Name from its internal non-volatile storage memory.
If a PNS is powered up with an SD Card inserted that is programmed with a valid, non-blank Device Name,
that PNS will read the Device Name on the SD Card and update its non-volatile storage with that Device
Name.
An SD Card without a Device Name (such as a new, un-programmed SD Card) will not affect the PNS at
power-up. The PNS will power up and use the Device Name settings present in its internal non-volatile
storage.
If an SD Card is present on a PNS when a DCP Reset to Factory command is issued from the DCP Tool, the
Device Name on the SD Card will be erased. The DCP Reset to Factory command is a method to remove a
Device Name from an SD Card.
Page 56

Chapter 4. Configuration
GFK-2737F December 2016 49
4.4 After the Configuration is Stored to the PROFINET Controller
For complete instructions, refer to the documentation for the I/O Controller and the PROFINET I/O
configuration tool.
After successfully processing and applying its configuration data, the PROFINET Controller transfers the
configuration for remote IO-Devices over the PROFINET network.
A PROFINET Controller delivers configuration data to an IO-Device whenever it establishes (or
re-establishes connection) with that IO-Device. In the case of the IO-Device being a PNS:
If all connections are lost, the PNS retains the most recent configuration received since it was last
powered up.
If a PNS has not been configured since being powered up, it remains in its hardware default condition.
Whenever the PROFINET connection is re-established and a configuration is sent to the PNS, the PNS
cross-checks the configuration data; if the configuration has changed, the PNS applies the new
configuration.
If there are differences between the expected, configured modules and the modules physically present in
the PNS rack when a connection is established, the PNS transmits appropriate Alarm messages to the
PROFINET Controller. Refer to Chapter 6, Diagnostics for more detail.
Page 57

Page 58

GFK-2737F December 2016 51
Chapter 5 Operations
This chapter describes:
Power-up
I/O Scanning
Hot Swap of I/O Modules
Firmware Updates
Page 59

Chapter 5. Operations
52 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
5.1 Power-up
When power is applied to the PNS module, it loads a firmware image. During the power-up process, the
module runs diagnostics and initializes its hardware components.
After completing power-up sequence, the OK LED changes from being off to solid on green. If a fatal error
occurs during power-up, the amber OK LED blinks a unique pattern indicating the nature of the failure.
If the module encounters a hardware failure, invalid firmware image, or the power-up diagnostics fail, the
module will not become operational or may enter firmware update mode. Cycling power to the module
may restore operation. Refer to Section 6.3, Fatal Error Handling for more details.
Non-volatile settings such as the PROFINET Device Name, Ethernet network configuration, and Ethernet
Port disable settings are activated before a PROFINET connection is allowed.
Page 60

Chapter 5. Operations
GFK-2737F December 2016 53
5.2 I/O Scanning
5.2.1 PROFINET Scanner Status and Control Data
The RX3i PNS001 provides 32 bits of input status data and receives 32 bits of output control data.
The application program in the control system in which the PROFINET Controller is resident should contain
code that will monitor the input status bits from the PNS module.
5.2.1.1 Output Control Bits
The 32 bits of control output assigned to the PNS module are reserved for future use.
5.2.1.2 Input Status Bits
The 32 bits of input status assigned to the PNS module provide information about the scanner. All status
bits are active high. Bit 1 is the least significant bit.
Bit #
Name
Description
1
Module OK
Indicates the health of the module. A value of 0 indicates the module is powering up or
has failed. A value of 1 indicates the module is functioning properly.
2
Reserved
Set to 0
3
Port1 Link Up
1 = port is connected to another device and is communicating.
0 = port is not connected to another device, or the port has some sort of error
preventing communications.
4
Port2 Link Up
5
Port3 Link Up
6
Port4 Link Up
7–10
Reserved
Set to 0
11
MRP Enabled
Indicates whether MRP has been enabled or not. A value of 0 indicates that MRP
is not enabled. A value of 1 indicates that MRP is enabled.
12
MRP Role
Indicates the MRP role the PNS is operating as when MRP is enabled.
A value of 0 indicates that the PNS is currently an MRP Client.
A value of 1 indicates that the PNS is currently an MRP Manager, however the PNS does not
currently support MRP Manager configuration. If MRP is not enabled, then this bit will be set
to zero.
13–32
Reserved
Set to 0
Page 61

Chapter 5. Operations
54 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
5.2.2 Data Coherency
The RX3i PNS provides coherency at a submodule basis only. This means that output data from a single
I/O Controller for multiple modules in the PNS rack might not be applied by the PNS during the same
output scan. Likewise, input data from all modules read in a single PNS input scan may not be produced
by the PNS during the same PROFINET I/O cycle.
5.2.3 Sampling Rate
The PROFINET Device Update Rate should be taken into consideration with regard to I/O devices in a
Scanner rack. I/O data that changes quickly, such as status bits that represent an event in a module and
are only set for one scan of the module, may be missed if the update period spans multiple scans of the
module. In some cases, other functionality may be utilized to capture momentary events. For example,
High-Speed Counter Over Range, Under Range, Overflow, and Underflow status conditions can be latched
by configuring an unused counter to mirror the operating counter and assigning the event condition as a
strobe source. The corresponding strobe status and acknowledge bits may be used to monitor and
acknowledge the condition.
5.2.4 Differences from Main (CPU) Rack
The following CPU operations are not supported or exhibit different behavior than when used with I/O
modules in a CPU rack.
5.2.4.1 Interrupts
Interrupts are not supported for I/O modules in a PNS rack. Service Requests that disable, enable,
suspend, or resume interrupts have no effect. Interrupt driven Logic blocks cannot be used with I/O
modules in a PNS rack, and interrupt status bits should be ignored.
5.2.4.2 Do I/O and Suspend I/O
Do I/O and Suspend I/O operations are limited to updating or suspending the data between the CPU and
PNC. The PROFINET I/O scan is not altered (that is, DO_IO data is not exchanged with the PNS any faster
than the PROFINET update rate allows).
Page 62

Chapter 5. Operations
GFK-2737F December 2016 55
5.2.5 Output Control
If an output module has not been configured since being powered up, it remains in its hardware default
condition. If an output module has been configured, the configuration will specify the output action when
communication with the I/O Controller is lost. This is typically one of the following:
transition to the zero state
default to a specified state or value, or
hold the last given state or value.
5.2.5.1 Simplex Connections
For simplex PROFINET connections (one I/O Controller connection to the RX3i PNS), communications with
the I/O Controller are lost when no message has been received from the I/O Controller in a number of I/O
Update periods (typically three).
5.2.5.2 Redundancy Connections
For PROFINET system redundancy connections, the configured output action is applied immediately by
the PNS whenever the controlling Primary connection is lost and no matching Backup connection is
established. A Primary connection is lost if no message is received from the Primary IO-Controller within a
defined number of I/O Update periods.
If the Primary connection is lost in PROFINET system redundancy but a matching Backup connection
exists, outputs are held at their last given value for a period of time to allow the Backup connection to be
switched into the Primary role. The period allowed is calculated by the configuration tool. (Proficy Machine
Edition uses the CPU sweep rate, I/O Update Rate, network loading, and values from the GSDML to
generate this value). If the Backup connection does not switch to Primary within this period, the RX3i PNS
terminates the connection and follows the rules for when no connections exist. If the Backup connection
is lost during this period, outputs immediately follow the rules for when no connections exist.
For a full discussion of PROFINET Redundancy and interactions with the controlling RX3i CPU, refer to
Chapter 6 of the PACSystems RX3i PROFINET Controller User Manual, GFK-2571.
Page 63

Chapter 5. Operations
56 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
5.3 Hot Swap of I/O Modules
If an I/O module is removed while power is applied to the I/O rack (hot extracted), the resident PNS detects
the removal and generates a PROFINET Pull Alarm. When the PNS is connected to a PACSystems PNC, the
Pull Alarm is reported as a Loss of I/O Module fault. At the RX3i Controller, all point faults corresponding to
the missing module will have the Fault Contact asserted.
When an I/O module is hot inserted into its rack, the PNS detects the insertion and determines whether
the configuration expects the module to be present or not.
• If the module is not present in the configuration, no alarm or fault is generated. The module remains
idle at its default state.
• If a module is inserted while the PNS has an established PROFINET connection and the module does
not match the configured module, including any hardware setting such as a DIP Switch position, a
PROFINET Plug Wrong Submodule alarm is generated. This appears as a System Configuration
Mismatch PLC Fault in RX3i systems. Fault Contacts corresponding to the mismatched module remain
in the Fault (on) state.
• If a module is inserted while the PNS has an established PROFINET connection and the module
matches the configured module, a PROFINET Plug Alarm is generated. This appears as an Addition of
I/O Module I/O Fault in RX3i systems. The module is configured using the established PROFINET
connection and once the I/O module is ready, I/O will start scanning and point fault contacts will
transition to reflect any change in the state of the I/O.
Operation must comply with the conditions outlined in the Hot Insertion and Removal section in the
PACSystems RX3i System Manual, GFK-2314.
Note: The PNS module should not be installed or removed while power is applied to the system. System
power must be removed before installing or removing the module.
Page 64

Chapter 6. Diagnostics
GFK-2737F December 2016 57
Chapter 6 Diagnostics
This chapter describes:
• Configuration Faults
• Version Information
• Fatal Error Handling
• Connection Troubleshooting
Page 65

Chapter 6. Diagnostics
58 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
6.1 Configuration Faults
If there are differences between the expected, configured modules and the I/O modules physically
present in the PNS rack, and/or differences between the expected and detected slot locations, the
PROFINET Scanner indicates those differences back to the PROFINET Controller once a connection is
established.
• If an I/O module is configured, but is not present or operational in the rack, the PNS indicates the
difference to the PROFINET Controller, and the Controller generates an alarm to the CPU. When used
with a PACSystems CPU, a Loss of Module fault is reported and all point faults corresponding to the
missing module will have the Fault Contact on.
• If an I/O module is configured but does not match the module present in the designated slot, the PNS
indicates the mismatch as part of the configuration sequence and the PNC generates an alarm to the
CPU. When used with a PACSystems CPU, a System Configuration Mismatch fault is reported and all
point faults corresponding to the module will have the Fault Contact on.
• If the I/O module configured matches the module installed in the assigned slot, but the module itself
has submodule options that relate to DIP Switch or jumper settings on the hardware and the physical
settings do not match the configuration, the PNS indicates a mismatch at the submodule level to the
PNC which generates an alarm to the CPU. When used with a PACSystems CPU, a System
Configuration Mismatch fault is reported and all point faults corresponding to the affected module will
have the Fault Contact on.
• If the physical module matches the configured module, but the configuration for the module is
unacceptable, the module itself rejects the configuration and energizes point faults until the
configuration is corrected. Many modules blink their OK LED in the event they reject the configuration.
Refer to Section 4.2.5.1, RX3i PROFINET Scanner Configuration Validation which specifies the rules
different modules use to validate their configuration.
• If an SFP module is configured but a different SFP is present (and that SFP is a supported SFP), the PNS
will allow the installed SFP to become operational. The PNS identifies the difference to the PNC in the
connection messaging sequence, and the PNC generates an alarm to the CPU. The SFP module
operates fully as if no difference had been detected. When used with a PACSystems CPU, a Valid
Module Substitution fault is reported.
• If an I/O module is installed but not included in the PNS configuration, no problem is reported. The
module is ignored by the PNS and defaults itself.
• If an SFP is installed but not included in the PNS configuration, default operation is enabled and active.
Page 66

Chapter 6. Diagnostics
GFK-2737F December 2016 59
6.2 Version Information
The RX3i PROFINET Scanner supports the standard PROFINET Identification and Maintenance (I&M)
functions. I&M0 Revision information is returned for the PNS slot with the information for the PROFINET
Scanner.
Please consult the documentation for your IO-Controller and configuration tool for how to access I&M
data. For PACSystems PROFINET I/O Controllers, this is available under the Explore PROFINET Networks
option in Proficy Machine Edition (for details, refer to this topic in the applicable PROFINET Controller
User’s Manual).
Page 67

Chapter 6. Diagnostics
60 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
6.3 Fatal Error Handling
Any failures that occur during power-up or firmware update mode are considered fatal errors. This
includes faults detected on non-critical devices such as the USB port. After successful power-up of the
PROFINET Scanner, only catastrophic errors are treated as fatal. When a fatal error occurs, the PROFINET
scanner blinks an error code on its LEDs (refer to Section 2.1.8.1, Fatal Error Codes).
Certain conditions can prevent the module from powering up and becoming operational or entering
firmware update mode:
Problem
Indication
Action
Hardware failure
• All LEDs off and the module is
unresponsive, or
• The STATUS LED is solid Green
and is the only LED that is on.
Return the module to GE
Automation and Controls.
Invalid firmware
Power-up diagnostics/hardware
initializations failures that are considered
fatal
LED Fatal Error blink code
Note the blink code and
contact Customer Service
Catastrophic error during operation
LED Fatal Error blink code
Note the blink code and
contact Customer Service
Page 68

Chapter 6. Diagnostics
GFK-2737F December 2016 61
6.4 Connection Troubleshooting
A PROFINET IO-Device can be challenging to troubleshoot if a connection to the PROFINET IO-Controller
will not establish. Below are some suggestions of possible things to consider:
• Verify the network cabling. Scan the network using both the DCP and Explore PROFINET Networks
tools in Proficy Machine Edition. The PROFINET IO-Controller and PROFINET IO-Devices should appear
in both tools.
• Verify the spelling of a Device Name in the DCP return value from the IO-Device versus the
corresponding Device Name in the PROFINET Controller configuration. Verify the PROFINET
IO-Controller configuration matches the configuration actually active in the IO-Controller.
• Simplify the configuration. Extra, unconfigured modules are generally not an error in PROFINET, so a
simpler configuration might connect.
• Invalid configurations will be rejected. For example, disabling all Ethernet ports would lead to
significant problems, so the connection with such a configuration is rejected outright. Simplifying the
configuration back to defaults can help isolate problem areas and settings.
• PROFINET configuration occurs using the Ethernet IP settings. If an IO-Device cannot be PINGed from
the PROFINET IO-Controller’s network location, the problems are more likely to exist in the network or
in the DCP settings for the IO-Device (i.e. the IO-Device has an incorrect Device Name or no IP Address)
than in the IO-Device configuration.
• Verify the MRP Ring ports selected. If MRP is configured to use Ethernet ports that are not available,
then the connection will fail. This may be an MRP Ring port configured for a removable port (SFP) that
is not present, or an MRP Ring port configured for a removable port (SFP) that is malfunctioning.
Disabling MRP Client during debugging may help identify SFP problems.
Page 69

Page 70

GFK-2737F December 2016 63
Appendix A PROFINET Specifications
Release 2.00 of the RX3i PROFINET I/O Scanner supports PROFINET v2.3 Class A I/O Device with the
clarifications listed below. For version-specific updates, refer to the Important Product Information
document provided with your module
A-1 PROFINET Protocol Support
RTC
Real time Cyclic Protocol: RT_CLASS_1
DCP
Discovery and Configuration Protocol
CL-RPC
Connectionless Remote Procedure Call
LLDP
Link Layer Discovery Protocol – transmission only
MRP
Media Redundancy Protocol – Client only
A-2 Technical Data
API
Single API (0) used.
Number of Application Relations (ARs)
supported
2
(1 backup and 1 primary forming a redundant-AR set or 1 simplex)
Maximum length of cyclic input data
1440 bytes
Maximum length of output data
1440 bytes
Alarm Types
Pull, Plug, PlugWrong
DCP
Get/Set/Identify supported.
Only All and Name of Station filters supported.
Identification & Maintenance
I&M Data (I&M0 only)
Context Management
by CL-RPC
Minimum cycle time
1 ms
Ethernet rate
100/1000 Mbps full duplex with auto-negotiation
Page 71

Appendix A. PROFINET Specifications
64 PACSystems* RX3i PROFINET IO-Scanner User Manual GFK-2737F
A-3 Limitations
The following features are not supported in release 2.41.
A-3.1 PACSystems Features
Alarms
Command Feedback data
COMMREQ commands targeted at I/O Modules in the RX3i rack under the control of the PNS001.
Exception: Release 2.41 adds support for the Remote Get HART Device Information COMMREQ.
Alarms on Hot Swap of SFP modules
Firmware update of I/O Modules
Interrupts from I/O Modules
A-3.2 PROFINET Features
Autoconfiguration
Configure In Run
DCP Hello service
DHCP
Diagnostic Alarms
DNS (Domain Name Service protocol)
FastStartUp
IRT (Isochronous Real Time Protocol)
Multicast communication
PROFIenergy Profile
PROFIsafe Profile
PROFINET CBA
PTCP (Precision Transparent Clock Protocol)
RT over UDP
Shared I/O device
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
Substitute Data
Supervisor-AR
Only one Input-CR and one Output-CR are supported per AR.
1. Remote Get HART Device Information COMMREQ operation is described in the PACSystems RX3i
System Manual, GFK-2314M.
2. A UDFB that automates the COMMREQ control logic is available for download from the GE support
website. (Article ID: 000017816) https://ge-ip.force.com/communities/en_US/Download/Remote-Get-
HART-Device-Information-COMMREQ-UDFB
Page 72

Page 73

GE Automation & Controls
Information Centers
Headquarters:
1-800-433-2682 or 1-434-978-5100
Global regional phone numbers
are available on our web site
www.geautomation.com
Additional Resources
For more information, please
visit GE’s Automation &
Controls web site:
www.geautomation.com
Copyright ©2013-2016 General Electric
Company. All Rights Reserved
*Trademark of General Electric Company.
All other brands or names are property of their
respective holders.
GFK-2737F
 Loading...
Loading...