GE Profile FQROMF Instruction Manual And Performance Data Sheet
Instruction Manual and Performance Data Sheet
Manual de Instrucciones y Ficha Técnica del Funcionamiento
FQROMF
Reverse Osmosis Replacement Cartridge/
Cartucho de Osmosis Inversa
Your new GE Appliances reverse osmosis replacement cartridge provides you with filteredwater. Cartridge should be changed
when the measured Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) rejection is less than 75%.
Su nuevo cartucho de reemplazo osmosis inversa GE Appliances le suministra de agua filtrada. El cartucho deberá cambiarse
cuando la medición de rechazo de sólidos totales disueltos sea inferior a 75%.
WARNING
To reduce the risk associated with the
ingestion of contaminants, do not use with water that is
microbiologically unsafe or of unknown quality without
adequate disinfection before or after the system.
Small parts remaining after the installation could be a
choke hazard. Discard safely.
ADVERTENCIA
ingestión de contaminantes, no use con agua que no sea
segura a nivel microbacteriológico o de calidad desconocida,
sin una desinfección adecuada, antes o después, del sistema.
Las pequeñas piezas que sobran después de la instalación
pueden constituir un riesgo de asfixia. Deséchelas
adecuadamente.
A fin de reducir el riesgo asociado con la
SPECIFICATIONS ESPECIFICACIONES
• This System has been tested according to NSF/ANSI
58 for the reduction of the substances listed below. The
concentration of the indicated substances in water entering
the system was reduced to a concentration less than or
equal to the permissible limit for water leaving the system,
as specified in NSF/ANSI 58.
• The NSF/ANSI 58 testing were performed under standard
testing conditions. Actual performance may vary with local
water conditions.
• Systems certified for cyst reduction may be used on
disinfected waters that may contain filterable cysts.
Tested and certified by NSF International
against NSF/ANSI Standard 58 in models
PXRQ15FBL, PXRQ15RBL, PNRQ15FBL,
Replacement
Element
PNRQ15RBL, PNRQ20FBL, PNRQ20FWW,
PNRQ20FBB, PNRQ20FCC, PNRQ21LBN,
PNRQ21LRB, PNRQ20RBL, PNRQ21RBN, and
PNRQ21RRB for the reduction of the claims
specified on the Performance Data Sheet.
Probado y certificado por NSF International contra
los Estándares NSF/ANSI 58 en los modelos
PXRQ15FBL, PXRQ15RBL, PNRQ15FBL,
Elemento de
reemplazo
• Este sistema ha sido probado de acuerdo con NSF/ANSI 58 para
la reducción de las sustancias mencionadas más adelante. La
concentración de las sustancias indicadas contenidas en el agua
que entra al sistema fue reducida a una concentración menor o
igual al límite permitido para el agua que sale del sistema, según
las normas establecidas por NSF/ANSI 58.
• Las pruebas NSF/ANSI 58 se realizaron en condiciones normales
para pruebas. El desempeño real puede variar según las
condiciones locales del agua.
• Los sistemas certificados para la reducción de quistes se podrán
usar en aguas desinfectadas que puedan contener quistes
filtrables. EPA Est, nº10350-MN-005.
PNRQ15RBL, PNRQ20FBL, PNRQ20FWW,
PNRQ20FBB, PNRQ20FCC, PNRQ21LBN,
PNRQ21LRB, PNRQ20RBL, PNRQ21RBN, and
PNRQ21RRB para la reducción de los reclamos
especificados en la Hoja de Datos de Desarrollo.
Replacement Cartridges/Estimated Replacement
Costs
FQROMF- Replacement cartridge $70–$80
For replacement parts, call toll free 877.959.8688.
Cartuchos de Reemplazo/Costos Estimados de Reposic
Wión
FQROMF - Reposición del recipiente $70–$80
Para partes de reemplazo, llame gratis al
34-8719-4114-1 49-50320 07-16 GEA
877.959.8688.
1
Performance Data Sheet Profile™ Reverse Osmosis System Models: PXRQ15FBL, PXRQ15RBL, PNRQ15FBL, PNRQ15RBL, PNRQ20FBL, PNRQ20FWW, PNRQ20FBB, PNRQ20FCC, PNRQ21LBN, PNRQ21LRB, PNRQ20RBL, PNRQ21RBN, and PNRQ21RRB.
Ficha Técnica del Funcionamiento de Profile™ en Modelos con Sistema de Ósmosis Inversa : PXRQ15FBL, PXRQ15RBL, PNRQ15FBL, PNRQ15RBL, PNRQ20FBL, PNRQ20FWW, PNRQ20FBB, PNRQ20FCC, PNRQ21LBN, PNRQ21LRB, PNRQ20RBL, PNRQ21RBN, y
PNRQ21RRB.
System tested and certified by NSF International against NSF/ANSI Standard 42
and against NSF/ANSI Standard 58 for the
reduction of substances as listed below according to Standard 42 and 58
Sistema controlado y certificado por NSF International contra el Estándar 42 y contra el
Estándar 58 de NSF/ANSI para la reducción
de las sustancias que figuran a continuación,
de acuerdo con los Estándares 42 y 58.
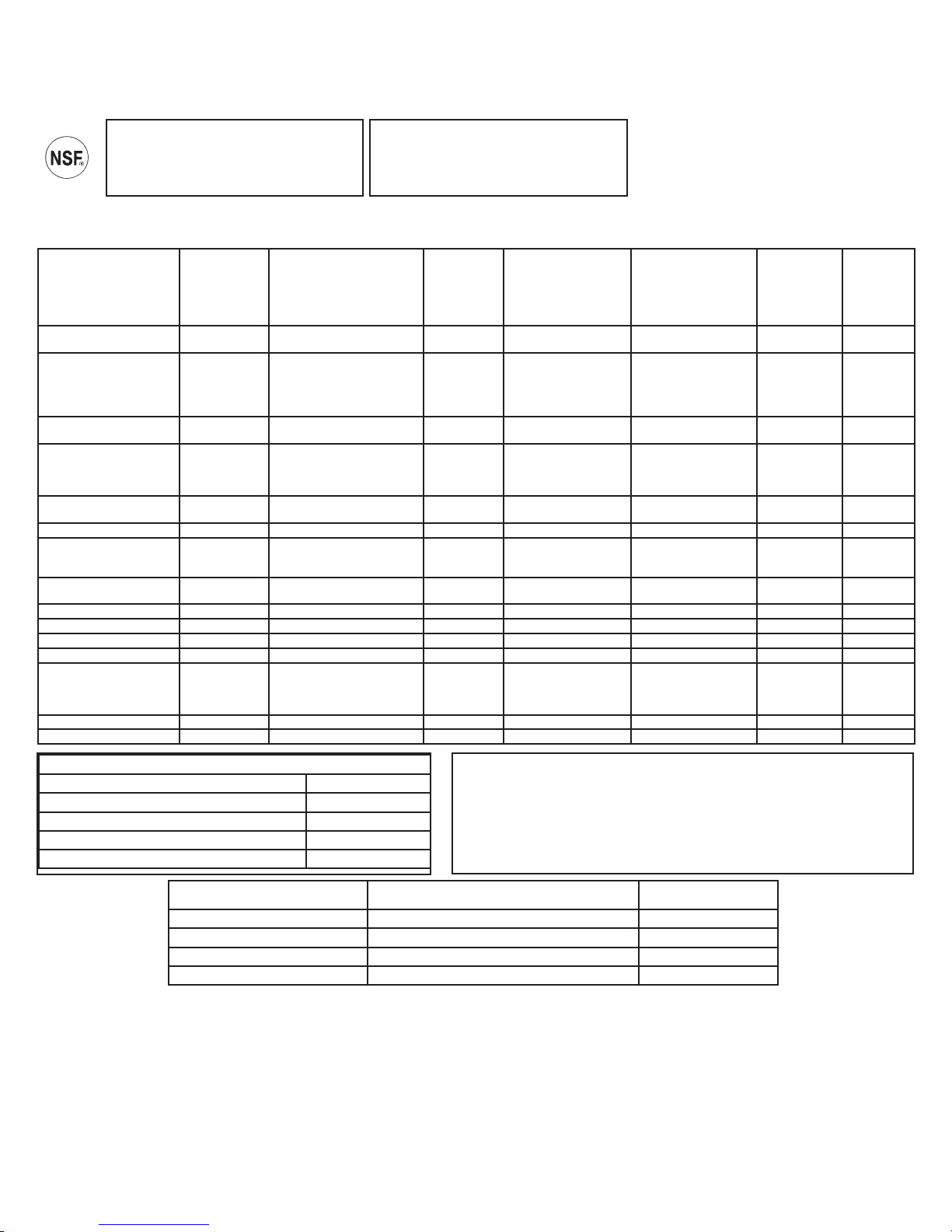
Contaminant Reduction Determined by
NSF testing.
Reducción de Contaminantes
Determinada por la evaluación de NSF.
Capacity 11.15 gpd (gallons per day) 42.2 lpd (liters per day). Contaminant Reduction Determined by NSF testing.
Capacidad: 11,15 galones por dia (42,2 Litros por dia) Reducción de la Contaminación Deteminada por la evaluación del NSF
Substance Reduction/
Reducción de
contaminantes
Chlorine Taste and Odor/
Cloro sabor y olor
Nominal Particulate
&ODVV,,,WR
μm / Partículas Nominales
&ODVH,,,D
micras
Arsenic (pentavlent)/
Arsénico (pentavalente)
Asbestos/ Amianto 136 fibers/L 10
Barium/ Bario 9.6 mg/L 10 mg/L
Cadmium/ Cadmio 0.028 mg/L 0.03 mg/L ± 10% 98.9% 0.0003 mg/L 0.005 mg/L N/A J-00122059
Chromium/ Chromo
(Hex.)
Chromium/ Chromo
(Tri.)
Copper/ Cobre 2.9 mg/L 3.0 mg/L + 10% 99.1% 0.027 mg/L 1.3 mg/L N/A J-00122061
Cyst/ Quistes 140,000 cysts/L Minimum 50,000 cysts/L 99.99% 3 cyst/L N/A J-00122065
Lead / Plomo 0.14 mg/L 0.15 mg/L + 10% 99.1% 0.001 mg/L 0.010 mg/L N/A J-00122059
Radium/ Radio 226/228 25 pCi/L 25 pCi/L ± 10% 80.0% 5 pCi/L 5 pCi/L N/A J-00122055
Selenium/ Selenio 0.1 mg/L 0.10 mg/L ± 10% (added as ½
TDS 760 mg/L 750 mg/L + 40 mg/L 94.5% 42 mg/L 187 mg/L N/A J-00122067
Turbidity/ Turbiedad 11 NTU 11 ± 1 NTU 99.1% 0.1 NTU 0.5 NTU N/A J-00122064
Average
Influent/
Promedio
influyente
2.0 mg/L 2.0 mg/L ± 10% 97.5% 0.05 mg/L N/A J-00137933
70,333 pts/mL At least 10,000 particles/
0.032 mg/L 0.050 mg/L ± 10% 98.1% 0.006 mg/L 0.010 mg/L N/A J-00122054
0.28 mg/L 0.3 mg/L ± 10% (added as
0.32 mg/L 0.3 mg/L ± 10% (added as
NSF specified Challenge
Concentration/
Concentración Máxima
Especificada por NSF
mL/ Por lo menos10,000
partículas/mL
7
to 108 fibers/L; fibers
greater than 10μm / 10
fibras/L; fibras superiores a
ȝPGHORQJLWXG
± 10%
hexavalent)/
(agregado como trivalente)
triavalent)
selenite and ½ selenate)
(agregado como ½ selentio et
½ selenato)
7
a 108
Avg %
Reduction/
% Promedio
de Reducción
99.9% 23 pts/mL N/A J-00147439
99.9% ILEHU/ NA 99% J-00122066
96.8% 0.310 mg/L 2.00 mg/L N/A J-00122055
97.2% 0.008 mg/l 0.1 mg/L N/A J-00122054
96.7% 0.01 mg/l 0.1 mg/L N/A J-00122055
97.6% 0.002 mg/L 0.05 mg/L N/A J-00122057
Average Product
Water Concentration/
Promedio de
Concentración del
Agua Procesada
Max Permissible
Product Water
Concentration/
Concentración Máxima
Autorizada Aceptable
de Agua Procesada
NSF Reduction
Requirements/
Requisitos de
Reducción de
NSF
NSF Test
Report/
Informe de
Evaluación
de NSF
Operating Specifications/Especificaciones de Funcionamiento
Inlet Pressure/ Presión de Entrada 40-120 psig (2.8-7.0 kg/cm2)
Inlet Temperature/ Temperatura de Entrada 40-100 F° (5-38° C)
Maximum TDS Level/ Nivel Máximo de TDS 2000 mg/L
Maximum Hardness @ 6.9pH/ Dureza Máxima de 6.9pH 10 grains per gal. (171 mg/L)
Maximum Chlorine/ Nivel Máximo de Cloro 2.0 mg/L
Models: PNRQ20FBL, PNRQ20FWW, PNRQ20FBB, PNRQ20FCC, PN-
RQ21LBN, PNRQ21LRB, PNRQ20RBL, PNRQ21RBN, and PNRQ21RRB.
pH Range/ Rango de pH 4 – 10 4-10
Daily Production Rate/ Índice de Producción Diaria 13.16 GPD (49.8 L/day) 8.46 GPD (32.0L/day)
Efficiency Rating(3)/ Promedios de Eficiencia (3) 12.75% 9.05%
Recovery Rating(4)/ Promedios de Recuperación (4) 23.14% 19.84%
Notes:
(1)Tested by NSF International per NSF/ANSI Standard 58 or NSF/ANSI
Standard 42.
(2)NTU is Nephelometric Turbidity Units
(3)Efficiency rating means the percentage of the influent water to the system
that is available to the user as reverse osmosis treated water under operat-
ing conditions that approximate typical daily usage.
(4)Recovery rating means the percentage of influent water to the membrane
portion of the system that is available to the user as reverse osmosis
treated water when the system is operated without a storage tank or when
the storage tank is bypassed.
The concentration of the indicated substances in water entering the system was
reduced to a concentration less than or equal to the permissible limit for water
leaving the system as specified in NSF/ANSI Standard 58.
La concentración de las sustancias indicadas en el agua que ingresa al sistema
fue reducida a una concentración inferior o igual al límite tolerable de agua que
puede dejar el sistema, de acuerdo con lo especificado en el Estándar 58 de
NSF/ANSI.
Models: PXRQ15FBL, PXRQ15RBL,
PNRQ15FBL, and PNRQ15RBL.
Notas:
(1)Evaluado por NSF Internacional de acuerdo con el Estándar 58 de NSF/
ANSI o el Estándar 42 de NSF/ANSI..
(2)NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Units) significa Unidades de Turbidez Ne-
felométrica.
(3Promedio de eficiencia se refiere al porcentaje del agua entrante al sistema
que está disponible para el usuario como agua tratada por ósmosis inversa, de acuerdo con condiciones de funcionamiento típicamente adecuadas
en el uso diario.
(4)Promedio de recuperación se refiere al porcentaje de agua entrante a
la parte de la membrana del sistema que está disponible para el usuario
como agua tratada por ósmosis inversa, cuando el sistema es operado sin
un tanque de almacenamiento o cuando se aplica al tanque de acumulación una circulación alternativa.
2

ARSENIC FACT SHEET
PÁGINA DE DATOS DEL ARSÉNICO
Background
Arsenic (abbreviated “As”) can occur naturally in well
water. There are two forms of arsenic: pentavalent
arsenic (also called As(V), As(+5), and arsenate), and
trivalent arsenic (also called As(III), AS(+3), and arsenite).
Although both forms are potentially harmful to human
health, trivalent arsenic is considered more harmful
than pentavalent arsenic. In well water, arsenic may be
pentavalent, trivalent, or a combination of both. Additional
information about arsenic in water can be found on the
Internet at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
(USEPA) website at: www.epa.gov/safewater/arsenic.html.
Testing Your Water
Arsenic in water has no color, taste or odor. It must be
measured by a lab test. Public water utilities must have
their water tested for arsenic. You can get the results from
your water utility. If you have your own well, you can have
the water tested. The local health department or the state
environmental health agency can provide a list of certified
labs. The cost is typically $15 to $30.
Pentavalent v. Trivalent Arsenic Removal
This system is very effective at reduction of pentavalent
arsenic from drinking water. This model was tested in
a lab and proven to reduce 300 parts per billion (ppb)
pentavalent arsenic to below 10 ppb, the USEPA standard
for safe drinking water. RO systems are not as effective at
reducing trivalent arsenic from water. This model will not
convert trivalent arsenic to pentavalent arsenic. If you have
free chlorine residual in your water supply, any trivalent
arsenic will be converted to pentavalent arsenic and
reduced by this Reverse Osmosis system.
Other water treatment chemicals, such as ozone and
potassium permanganate will also change trivalent arsenic
to pentavalent arsenic. A combined chlorine residual (also
called chloramine) may not convert all of the trivalent
arsenic to pentavalent arsenic. Water systems using an
in-line chlorinator should provide a one-minute chlorine
contact time before the Reverse Osmosis system. If you
get your water from a public water utility, contact the utility
to find out if free chlorine or combined chlorine is used in
the water system.
Maintenance
It is strongly recommended that you follow the
maintenance instructions in your Owner’s Manual and
have your water tested periodically to make sure the
system is performing properly. See replacement element
information for recommendations on maintaining your
Reverse Osmosis drinking water treatment system.
Información de fondo
El arsénico (abreviado como) puede ocurrir naturalmente en
un pozo de agua. Existen dos formas de arsénico: arsénico
pentavalente (también llamado As(V), As(+5), y arsenato), y el
arsénico trivalente (también llamado As(III), AS(3), y arsenita).
Aunque ambas formas son potencialmente dañinas para la salud
humana, el arsénico trivalente es considerado más dañino que
el arsénico pentavalente. En el agua de pozo, el arsénico podría
ser pentavalente, trivalente, o una combinación de ambos. Usted
puede encontrar información adicional acerca del arsénico en el
agua en la Internet en la página Web de la U.S Environmental
Protection Agency (USEPA): www.epa.gov/safewater/arsenic.
html.
Cómo probar su agua
El arsénico en el agua no tiene color, sabor u olor. El arsénico
debe medirse en pruebas de laboratorio. Las compañías de
suministro de agua deben probar su agua en busca de arsénico.
Usted puede obtener los resultados de sus compañías de
utilidades. Si usted tiene su propio pozo, usted puede hacer
los arreglos para que un laboratorio le pruebe su agua. El
departamento de salud local o la agencia de salud ambiental
estatal le pueden proporcionar una lista de los laboratorios que
son certificados. El coste oscila entre
15 y 30 dólares.
Cómo remover el arsénico pentavalente y trivalente
Este sistema es muy efectivo para la reducción de arsénico
pentavalente en el agua potable. Este modelo fue evaluado en
un laboratorio y se probó que reduce 300 partes por millar de
millones (ppb) de arsénico pentavalente a menos 10 ppb, el
estándar de USEPA para un agua potable segura. Los sistemas
RO no son tan efectivos para reducir el arsénico trivalente
del agua. Este modelo no convertirá el arsénico trivalente en
arsénico pentavalente. Si posee residuos de cloro puro en el
suministro de agua, cualquier arsénico trivalente será convertido
en arsénico pentavalente o reducido por este sistema de
Ósmosis Inversa.
Otros químicos de tratamiento de agua, tales como el ozono y el
pergamanato de potasio también cambiarán a arsénico trivalente
o a arsénico pentavalente. Un cloruro residual combinado
(también llamado cloramina) podría no convertir todo el arsénico
trivalente en arsénico pentavalente. Los sistemas de agua que
usan un clorinador en línea deberían proporcionar un tiempo de
contacto de un minuto antes del Sistema de Osmosis Reversa.
Si usted recibe su agua del suministro de su compañía local de
utilidades, póngase en contacto con ellos para enterarse si su
suministro está libre de clorina o clorina combinada.
El mantenimiento
Se recomienda enfáticamente que se sigan las instrucciones
de mantenimiento que figuran en el Manual del Usuario y que
se realice un control periódico del agua para asegurar que el
sistema esté funcionando de forma correcta. Para acceder
a recomendaciones sobre cómo mantener su sistema de
tratamiento de agua potable de Ósmosis Inversa, consulte la
información de elementos de reemplazo.
3
 Loading...
Loading...