Page 1

ISO9001:2000
GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Instruction Manual
Manual P/N: 1601-0237-A1
Manual Order Code: GEK-113190
Copyright © 2005 GE Multilin
GE Multilin
215 Anderson Avenue, Markham, Ontario
Canada L6E 1B3
Tel: (905) 294-6222 Fax: (905) 201-2098
Internet: http://www.GEmultilin.com
T
E
S
I
R
E
G
D
E
R
G
E
GE Multilin's Quality
Management System is
registered to ISO9001:2000
QMI # 005094
UL # A3775
N
I
M
L
I
U
T
L
Page 2

Page 3

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Table of contents
INTRODUCTION Getting started........................................................................................................1–1
Inspecting the package and product.................................................................................................1–1
Contact information...................................................................................................................................1–1
Document conventions..........................................................................................1–2
Description .....................................................................................................................................................1–2
Glossary...........................................................................................................................................................1–2
About the P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter.................................................1–3
Application......................................................................................................................................................1–3
Features....................................................................................................................1–3
General features..........................................................................................................................................1–3
Modbus network..........................................................................................................................................1–3
Fieldbus interface features .....................................................................................................................1–3
Ordering ...................................................................................................................1–4
Order codes....................................................................................................................................................1–4
Specifications ..........................................................................................................1–4
Mechanical .....................................................................................................................................................1–4
Electrical characteristics..........................................................................................................................1–4
Communications .........................................................................................................................................1–4
Environmental...............................................................................................................................................1–4
EMC compliance ..........................................................................................................................................1–4
INSTALLATION Quick install .............................................................................................................2–1
Procedure........................................................................................................................................................2–1
Electrical installation .............................................................................................2–1
Overview..........................................................................................................................................................2–1
Profibus connector .....................................................................................................................................2–2
Configuration cable....................................................................................................................................2–3
Modbus connector......................................................................................................................................2–4
Power connector .........................................................................................................................................2–4
Mechanical installation .........................................................................................2–5
DIN-rail mounting........................................................................................................................................2–5
Indicators and switches ........................................................................................2–5
Status indicators..........................................................................................................................................2–5
Configuration switches.............................................................................................................................2–6
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE i
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Profibus installation procedure ...........................................................................2–7
Profibus configuration tool.....................................................................................................................2–7
Profibus network termination ............................................................................................................... 2–7
Links ..................................................................................................................................................................2–7
Troubleshooting......................................................................................................2–8
dESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................................................. 2–8
DATA EXCHANGE Overview...................................................................................................................3–1
Description.....................................................................................................................................................3–1
Internal memory buffer structure.......................................................................................................3–1
Memory Map............................................................................................................3–2
Memory locations....................................................................................................................................... 3–2
Protocol configuration...........................................................................................3–3
Description.....................................................................................................................................................3–3
Communication mode..............................................................................................................................3–3
Protocol building blocks...........................................................................................................................3–3
SOFTWARE
OVERVIEW
Introduction .............................................................................................................4–1
Description.....................................................................................................................................................4–1
System requirements................................................................................................................................4–1
Installation procedure ...........................................................................................4–1
Description.....................................................................................................................................................4–1
Installing from EnerVista CD ..................................................................................................................4–1
Installing from the GE Multilin website.............................................................................................. 4–1
Using the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software...............................................4–2
Description.....................................................................................................................................................4–2
Configuration wizard................................................................................................................................. 4–2
Select fieldbus type.................................................................................................................................... 4–3
Sub-network properties ...........................................................................................................................4–4
Device types..................................................................................................................................................4–5
Connecting devices....................................................................................................................................4–7
Selecting parameters for each node ................................................................................................. 4–8
Configuration report.................................................................................................................................. 4–8
Configuration main window .................................................................................4–9
Description.....................................................................................................................................................4–9
Navigation window ................................................................................................................................. 4–10
Parameter window.................................................................................................................................. 4–10
Information window ............................................................................................................................... 4–10
Configuration line indicator ................................................................................................................ 4–10
Options window........................................................................................................................................ 4–11
Fieldbus configuration........................................................................................ 4–11
Description.................................................................................................................................................. 4–11
P485/D485 configuration ................................................................................... 4–12
Parameter window.................................................................................................................................. 4–12
Modbus network configuration......................................................................... 4–13
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................... 4–13
Serial interface settings ........................................................................................................................ 4–13
COMMUNICATION
MODEL
ii P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Introduction .............................................................................................................5–1
Description.....................................................................................................................................................5–1
Scan list............................................................................................................................................................ 5–2
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Basic settings ..........................................................................................................5–2
Parameter window .....................................................................................................................................5–2
Communication............................................................................................................................................5–2
Message delimiter.......................................................................................................................................5–2
Nodes ........................................................................................................................5–3
Description .....................................................................................................................................................5–3
Node parameters ........................................................................................................................................5–3
Modbus network menu.............................................................................................................................5–3
Node menu.....................................................................................................................................................5–3
Query parameters ......................................................................................................................................5–4
Response parameters...............................................................................................................................5–5
FRAME AND
COMMAND EDITORS
MODBUS NETWORK
AND NODE
MONITORS
ADVANCED
FUNCTIONS
Frame editor ............................................................................................................6–1
Description .....................................................................................................................................................6–1
Example ...........................................................................................................................................................6–1
Command editor .....................................................................................................6–2
General.............................................................................................................................................................6–2
Specifying a new command ..................................................................................................................6–3
Modbus network monitor......................................................................................7–1
General.............................................................................................................................................................7–1
Operation ........................................................................................................................................................7–2
Node monitor...........................................................................................................7–3
General.............................................................................................................................................................7–3
Operation ........................................................................................................................................................7–3
Control and status registers.................................................................................8–1
Description .....................................................................................................................................................8–1
Control register (Profibus control system to P485)......................................................................8–1
Control codes ................................................................................................................................................8–2
Status register (P485 to fieldbus control system).........................................................................8–2
Status codes ..................................................................................................................................................8–3
Handshaking procedure ..........................................................................................................................8–3
Input/output data during startup .......................................................................8–4
Description .....................................................................................................................................................8–4
Advanced fieldbus configuration.........................................................................8–5
Mailbox command......................................................................................................................................8–5
APPLICATION
EXAMPLE
Introduction.............................................................................................................9–1
Overview..........................................................................................................................................................9–1
Equipment and documents....................................................................................................................9–1
System setup.................................................................................................................................................9–2
Modbus user map setup ........................................................................................9–3
Description .....................................................................................................................................................9–3
PQMII user map............................................................................................................................................9–3
MM2 user map..............................................................................................................................................9–3
System configuration.............................................................................................9–5
Overview..........................................................................................................................................................9–5
Installing the Enervista P485/D485 Setup software ...................................................................9–6
Starting the configuration wizard........................................................................................................9–6
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE iii
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Step 1: Selecting the fieldbus type...................................................................................................... 9–6
Step 2: Selecting the sub-network properties ...............................................................................9–7
Step 3: Include device types ..................................................................................................................9–7
Step 4: Connect devices to the sub-network .................................................................................9–9
Step 5: Select parameters for each node ..................................................................................... 9–10
Step 6: Configuration report ............................................................................................................... 9–11
Saving device data.................................................................................................................................. 9–12
Configuring the queries......................................................................................................................... 9–12
Downloading the configuration file................................................................................................. 9–15
Profibus network setup....................................................................................... 9–16
Description.................................................................................................................................................. 9–16
MISCELLANEOUS Revision history.................................................................................................... 10–1
Release dates............................................................................................................................................. 10–1
Changes to the manual ........................................................................................................................ 10–1
Warranty............................................................................................................... 10–1
GE Multilin warranty statement ........................................................................................................ 10–1
iv P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 7

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 1: Introduction
Introduction
Getting started
INSPECTING THE
PACKAGE AND PRODUCT
CONTACT INFORMATION GE Multilin contact information and call center for product support is shown below:
Examine the shipping container for obvious damage prior to installing this product; notify
the carrier of any damage that you believe occurred during shipment or delivery. Inspect
the contents of this package for any signs of damage and ensure that the items listed
below are included.
Remove the items from the shipping container. Be sure to keep the shipping container
should you need to re-ship the unit at a later date.
In the event there are items missing or damaged, contact the party from whom you
purchased the product. If the unit needs to be returned, please use the original shipping
container, if possible.
GE Multilin
215 Anderson Avenue
Markham, Ontario
Canada L6E 1B3
• Telephone: 905-294-6222 or 1-800-547-8629 (North America),
+34 94 485 88 00 (Europe)
Fax: 905-201-2098 (North America),
+34 94 485 88 45 (Europe)
• E-mail: multilin.tech@ge.com
•Website: http://www.GEmultilin.com
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 1–1
Page 8
INTRODUCTION
Profibus
master
Slave
GE Multilin
P485 Converter
Slave
Modbus
network
Profibus network
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
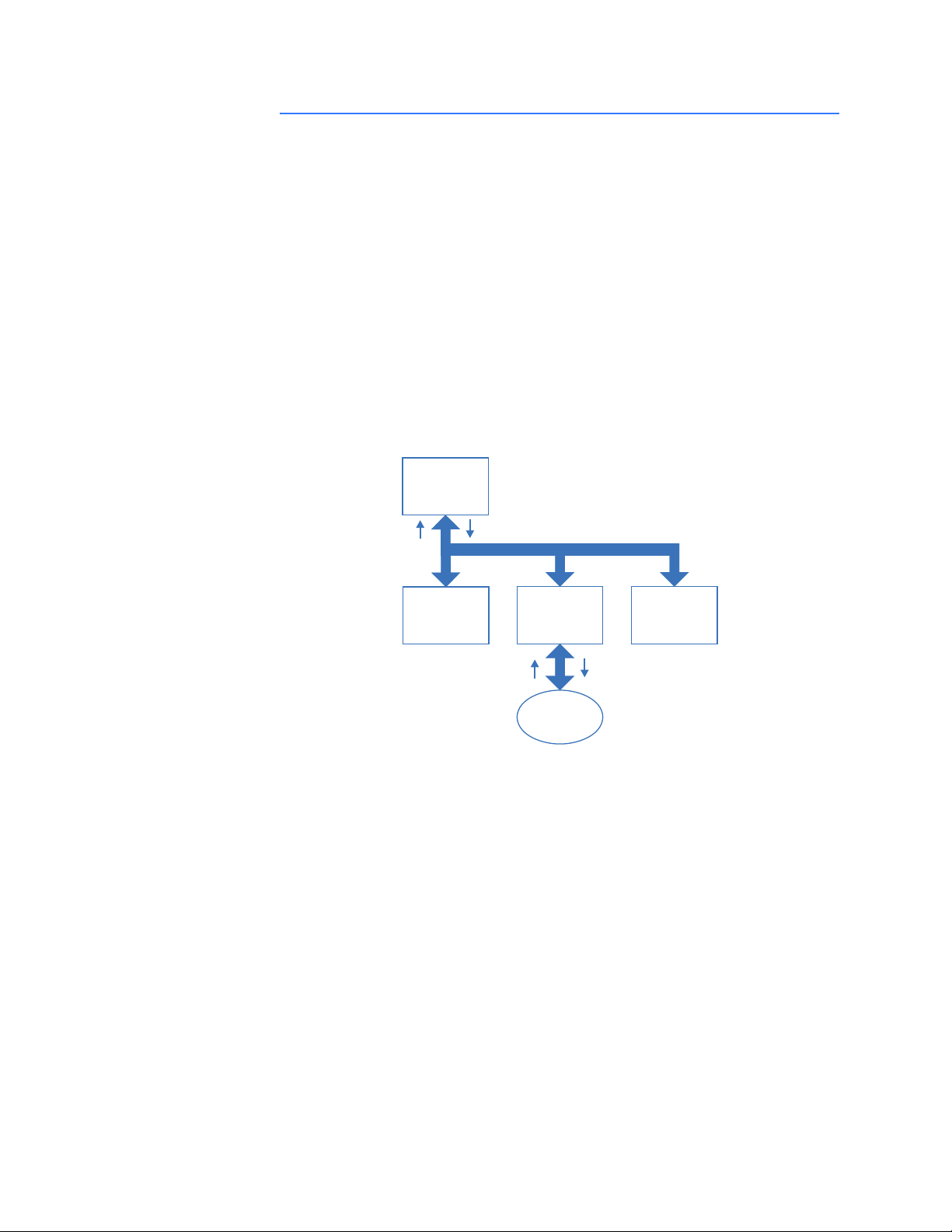
Document conventions
DESCRIPTION The following conventions are used throughout this document:
• Numbered lists provide sequential steps.
• Bulleted lists provide information, not procedural steps.
• The term ‘user’ refers to the person or persons responsible for installing the P485
Modbus to Profibus Converter in a network.
• Hexadecimal values are written in the format 0xNNNN, where NNNN is the
hexadecimal value.
• Decimal values are represented as NNNN, where NNNN is the decimal value.
• As in all communication systems, the terms “input” and “output” can be ambiguous,
since their meaning depends on which end of the link is being referenced. The
convention in this document is that “input” and “output” are always being referenced
to the master/scanner end of the link (see illustration below).
• The term “sub-network” is interchangeably used for “Modbus network”.
Figure 1-1: Input and output definition
GLOSSARY The following terminology is used in the P485 manual:
• Broadcaster: A protocol specific node in the sub-network scan that holds transactions
destined for all nodes.
• Command: A protocol specific transaction.
• Fieldbus: The network to which the converter is connected (Profibus for P485).
• Frame: A higher level series of bytes forming a complete telegram on the sub-network
(Modbus).
• Monitor: A tool for debugging the P485 and network connections.
• Node: A device in the scan list that defines the communication with a slave (GE relay)
on the Modbus sub-network.
• Scan list: List of configured slaves with transactions on the sub-network.
• Sub-network: Modbus network that logically is located on a subsidiary level with
respect to the fieldbus and to which the P485 acts as a gateway.
• Transaction: A generic building block that is used in the sub-network scan list and
1–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
defines the data that is sent out the sub-network.
Page 9

INTRODUCTION
Profibus
master (PLC)
HMI
Profibus
slave
Profibus network
P485
PC for configuration
and monitoring
Multi-drop
Multi-node Modbus network
Single-node Modbus network
RS232 port
PC for configuration
and monitoring
Profibus slave
HMI
Profibus
master (PLC)
Profibus network
P485
About the P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter
APPLICATION The P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter (or P485) acts as a gateway between the Modbus
protocol and a Profibus-DP network. Integration of industrial devices is enabled without
loss of functionality, control, and reliability, both when retrofitting to existing equipment as
well as when setting up new installations.
GENERAL FEATURES • DIN-rail mountable
MODBUS NETWORK • RS232/RS422/RS485 communications
FIELDBUS INTERFACE
FEATURES
Figure 1-2: Typical applications
Features
• Save/load configuration in flash
•CE, UL, and cUL marked
• Multi-drop or single-node configurations
• Modbus RTU Master mode
• Supports up to 50 commands
• Configuration via EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software
• Complete Profibus-DP slave functionality according to IEC 61158
• Node Address range: 1 to 99 using on board switches
• Baud rate range: 9.6 kbps to 12 Mbps. Auto baud rate detection supported.
• Transmission media: Profibus bus line, type A or B specified in IEC 61158
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 1–3
Page 10
INTRODUCTION
ORDER CODES The following table illustrates the order codes for the P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter.
Ordering
Table 1–1: P485 order codes
P485 – *
Base unit P485 | P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter
C With configuration cable
X No configuration cable
Specifications
MECHANICAL HOUSING
Plastic housing with snap-on connection to DIN-rail, protection class IP20
DIMENSIONS
L x W x H: 120 mm × 75 mm × 27 mm
(4.72-in × 2.95-in × 1.06-in)
PROTECTION CLASS
Protection class: IP20
ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
POWER SUPPLY
Power: 24 V ±10% (for use in class 2 circuits)
POWER CONSUMPTION
Maximum power consumption: 280 mA on 24 V
Typically power consumption: approximately 100 mA
COMMUNICATIONS BAUD RATES
Baud rate (Profibus) 9.6, 19.2, 45.45, 93.75, 187.5, and 500 kbps; 1.5, 3, 6, and 12 Mbps
Baud rate (Modbus) 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, and 57600 bps
I/O DATA
I/O input size: 244 bytes
I/O output size: 244 bytes
Total I/O size: 416 bytes
FEATURES AND INTERFACE
Communication profile: Profibus-DP
Supported features: synchronous, freeze, watchdog
Modbus interface: RS232, RS422, RS485
Profibus interface: RS485 (type A or B)
ENVIRONMENTAL RELATIVE HUMIDITY
The product is designed for a relative humidity of 0 to 95% non-condensing
TEMPERATURE
Operating: 0 to 55°C
Non Operating: –5 to 85°C
EMC COMPLIANCE CE-MARK
Certified according to European standards unless otherwise is stated
Emission: according to EN 50081-2:1993
Immunity: according to EN 61000-6-2:1999
UL/C-UL COMPLIANCE
This unit is an open type listed by the Underwriters Laboratories.
The certification has been documented by UL in file E214107.
1–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 11

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 2: Installation
Installation
Quick install
PROCEDURE 1. Snap the P485 on to the DIN-rail (see DIN-rail mounting on page 2–5).
2. Connect the Profibus cable (see Profibus connector on page 2–2).
3. Connect the serial Modbus network cable (see Modbus connector on page 2–4 for
details).
4. Connect a PC using the configuration cable (see Configuration cable on page 2–3).
5. Connect the power cable and apply power to the unit (see Power connector on page
2–4 for details).
6. Start the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software.
7. Normally, the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup detects the correct serial port. If this does
not occur, select the correct port through the Port menu item.
8. Configure the P485 using EnerVista P485/D485 Setup and download the configuration
to the unit.
9. Configure and power-up the Modbus network device for communication.
Electrical installation
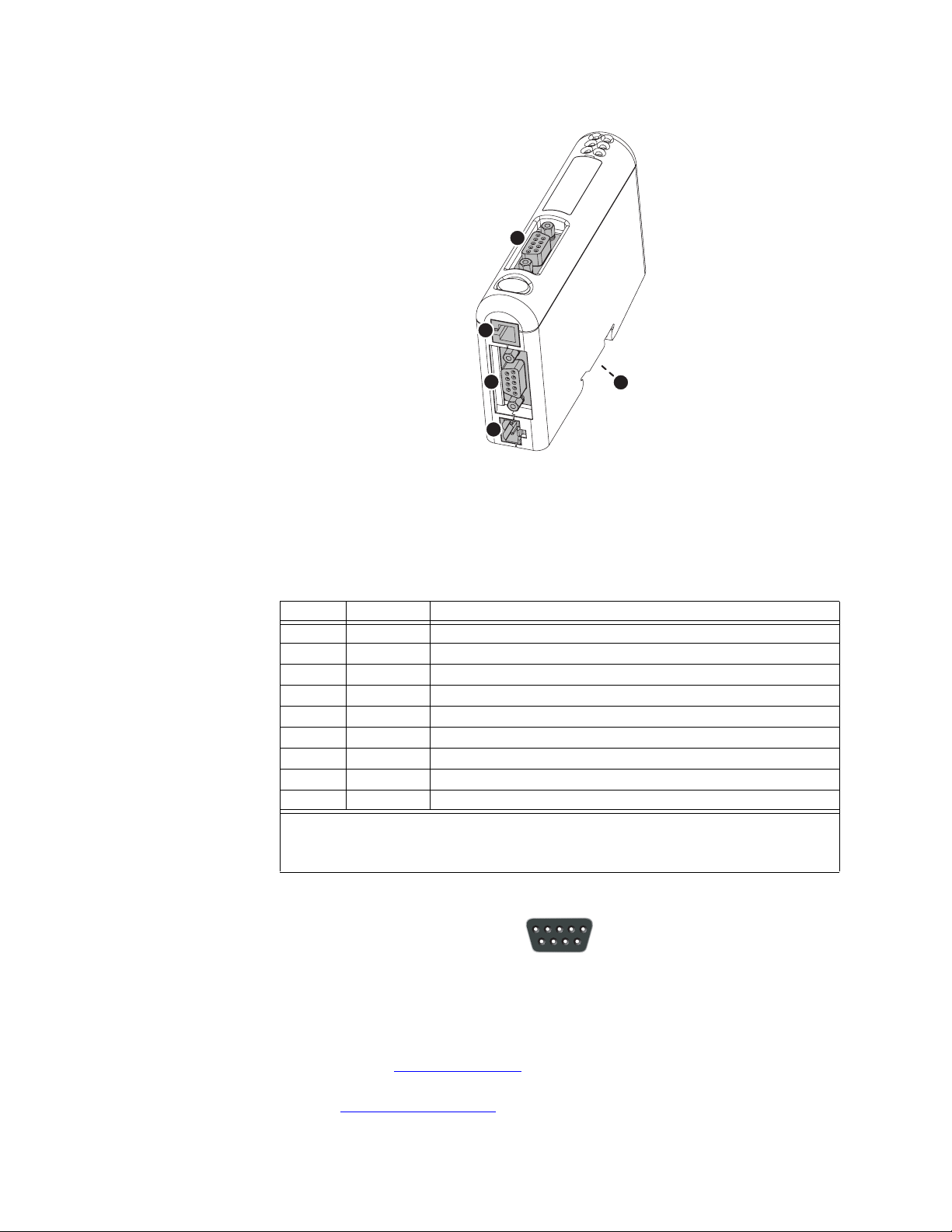
OVERVIEW The location of the various electrical connectors is shown below.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 2–1
Page 12
INSTALLATION
E
A
B
C
D
Figure 2-1: P485 electrical connections
PROFIBUS CONNECTOR The Profibus connector is indicated as A in the figure above. This connector is used to
connect the P485 to the Profibus network.
The pin assignments for the Profibus connector are shown below.
Table 2–1: Profibus connector pin assignments
Pin Signal Description
1- -
2- -
3 B-Line Positive RxD/TxD (RS485)
4 RTS * Request To Send
5 GNDBUS ** Isolated ground from the RS485 side
6 +5 V BUS ** Isolated +5V output from the RS485 side (80 mA maximum)
7- -
8 A-Line Negative RxD/TxD (RS485)
9- -
* Used in some equipment to determine the direction of transmission. However, in normal
applications only A-Line, B-Line and Shield are used.
** Used for bus termination. Some devices such as optical transceivers (RS485 to fibre optics) may
require power from these pins.
51
69
(female)
Figure 2-2: Profibus connector
The following Profibus connectors are recommended:
• Profibus Max standard, part number 134928 and Profibus reversed, part number
104577, from http://www.erni.com
• Fast connect bus connector, part number 6GK1500-0FC00 or 6ES7 972-0BA50-0XA0,
from http://www.siemens.com
2–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 13
INSTALLATION
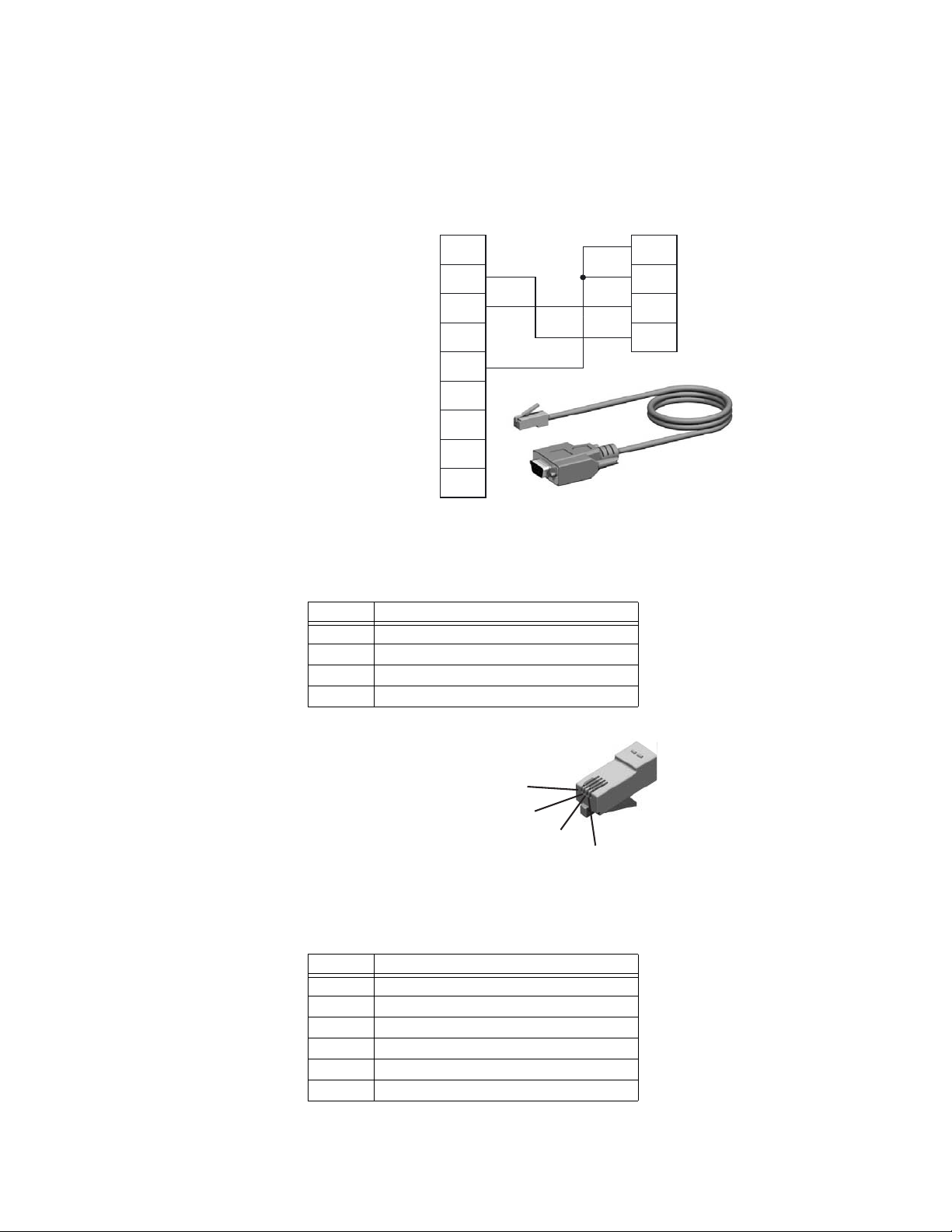
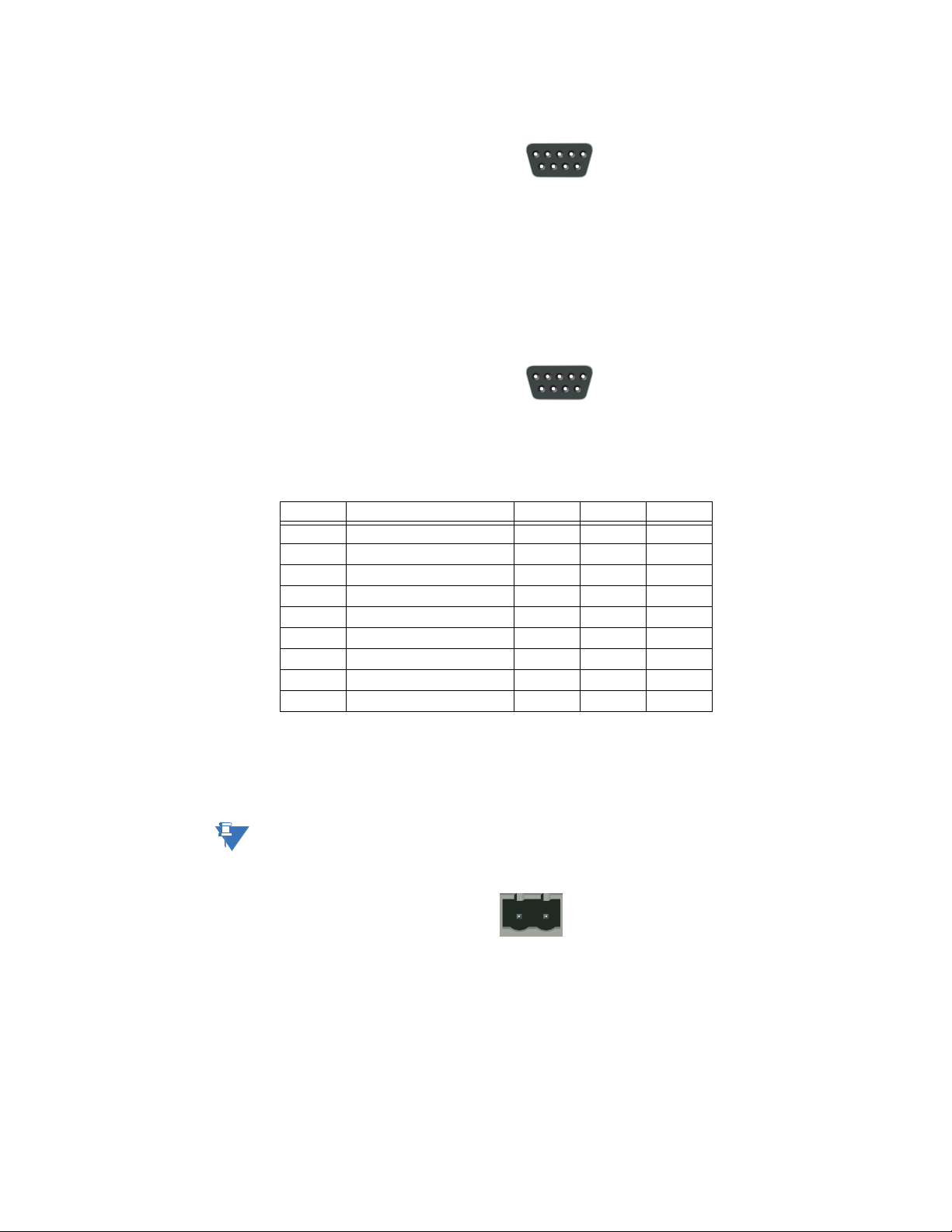
CONFIGURATION CABLE The PC connector is indicated as B in Figure 2-1: P485 electrical connections on page 2–2.
This connector is used to connect the P485 to a PC using the configuration cable for
configuration and monitoring purposes.
A P485/D485 configuration cable can be purchased from GE Multilin. The wiring for the
configuration cable is shown below.
D-sub 9 female (PC) Modular 4/4 RJ11 connector (P485)
RS232 Rx
RS232 Tx
Ground
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Connects to P485
Connects to PC serial port
1
Ground
2
Ground
3
Rx
4
Tx
Figure 2-3: Configuration cable
The pinout for the modular 4/4 RJ11 connector (connects to the P485) is shown below.
Table 2–2: Configuration cable pin assignments (P485 end)
Pin Description
1 Signal ground
2 Signal ground
3 RS232 Rx, data input to P485
4 RS232 Tx, data output from P485
4
3
2
1
Figure 2-4: Configuration cable (P485 end)
The pinout for the DSUB 9-pin serial plug (connects to the PC) is shown below.
Table 2–3: Configuration cable pin assignments (PC end)
Pin Description
1 Not connected
2 RS232 Rx, data input to PC
3 RS232 Tx, data output from PC
4 Not connected
5 Ground
6 to 9 Not connected
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 2–3
Page 14
INSTALLATION
51
69
(female)
Figure 2-5: Configuration cable (PC end)
MODBUS CONNECTOR The Modbus connector is indicated as C in Figure 2-1: P485 electrical connections on page
2–2. This connector is used to connect the P485 to the serial network. Based on the
configuration selected in the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software, the corresponding
signals are activated.
51
69
(female)
Figure 2-6: Modbus connector
Table 2–4: Modbus connector pin assignments
Pin Description RS232 RS422 RS485
1 +5 V output (50 mA max)
2 RS232 Rx 3
3 RS232 Tx 3
4 Not connected
5 Ground 333
6 RS422 Rx + 3
7 RS422 Rx – 3
8 RS485 + / RS422 Tx+ 33
9 RS485 – / RS422 Tx– 33
2–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
POWER CONNECTOR The power connector is indicated as D in Figure 2-1: P485 electrical connections on page
2–2. Use this connector to apply power to the P485.
Pin 1: +24 V DC;
Pin 2: ground
Use 60/75 or 75°C copper (CU) wire only. The terminal tightening torque must be between
5 to 7 lbs-in (0.5 to 0.8 nm).
NOTE
12
Figure 2-7: Power connector
Page 15
Mechanical installation
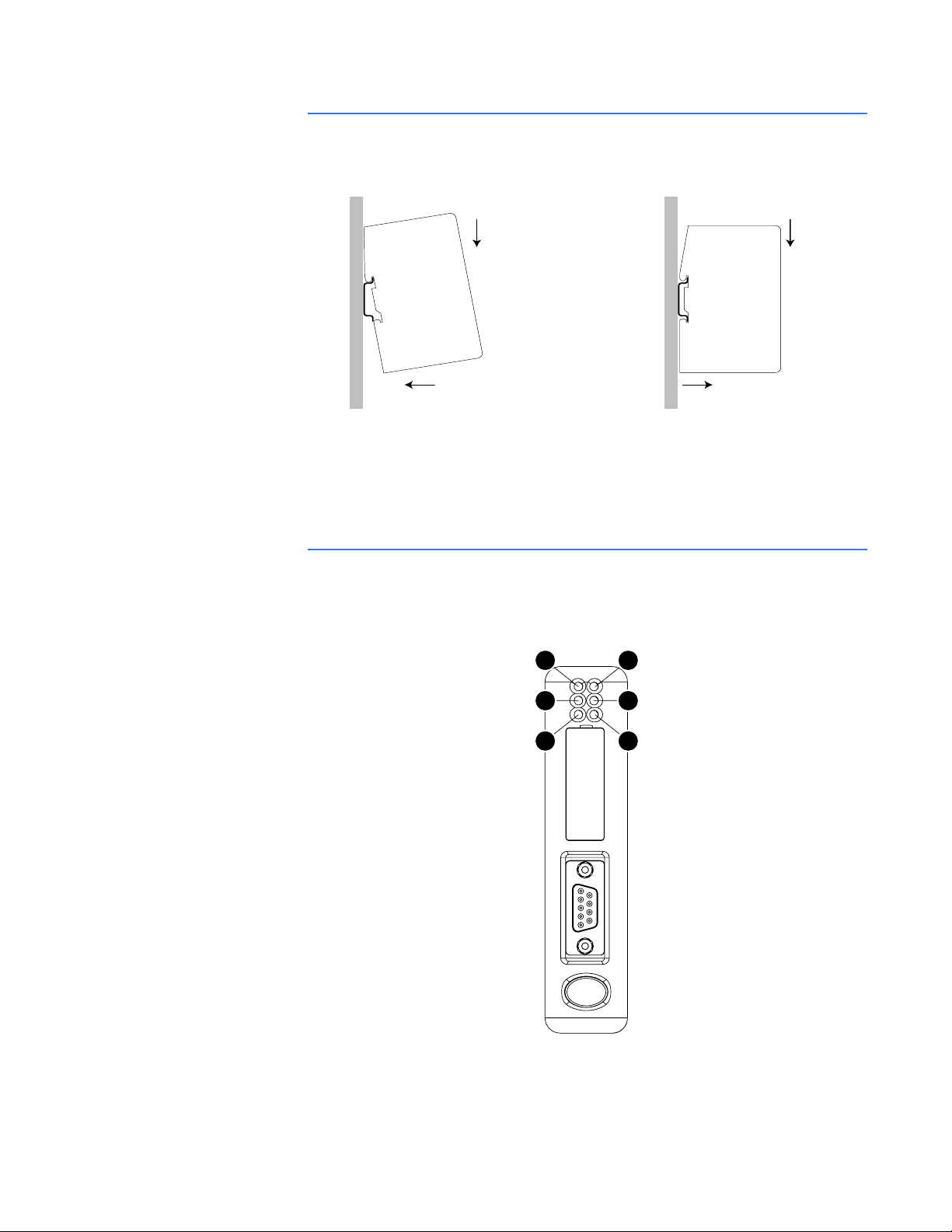
DIN-RAIL MOUNTING The DIN-rail connector is internally connected to the P485.
ON OFF
Figure 2-8: Mounting the P485 to the DIN-rail
To snap the P485 on, first press the P485 downwards (1) to compress the spring on the DINrail connector, then push the P485 against the DIN-rail as to make it snap on (2)
To snap the P485 off, push the P485 downwards (1) and pull it out from the DIN-rail (2), as to
make it snap off from the DIN-rail.
INSTALLATION
11
22
Indicators and switches
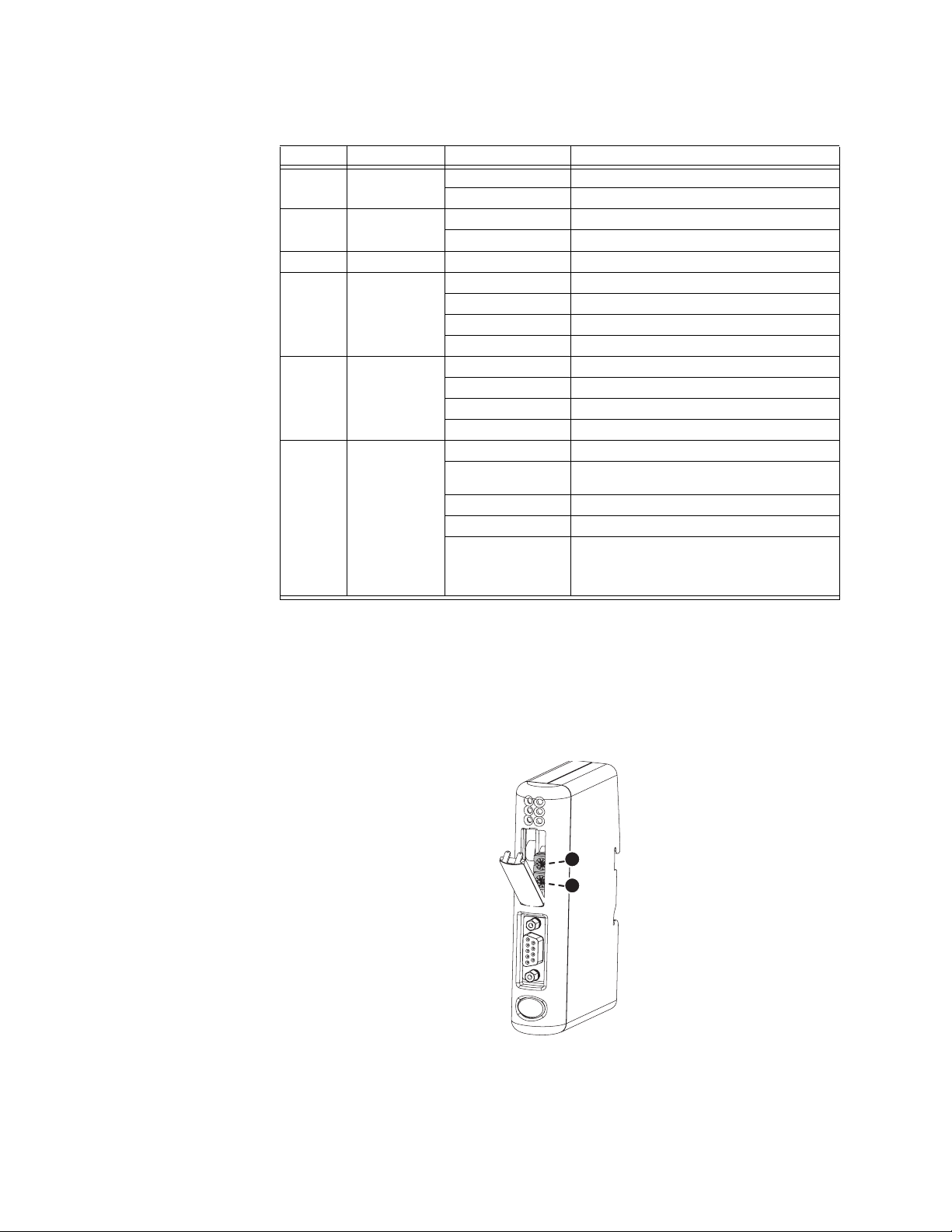
STATUS INDICATORS The status indicators for the P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter are indicated below.
1
3
5
2
4
6
Figure 2-9: P485 status indicators
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 2–5
Page 16
INSTALLATION
Table 2–5: P485 status indicators
Number Description State Status
1 Profibus online Off Not online
Green Online
2 Profibus offline Off Not offline
Red Offline
3Not used- -
4Profibus
diagnostics
5 Subnet status *
(Modbus)
6 Device status Off Power off
* This LED turns green when all transactions have been active at least once. This includes any
transactions using “change of state” or “change of state on trigger”. If a timeout occurs on a
transaction, this LED will turn red.
Off No diagnostics present
Red, flashing 1 Hz Error in configuration
Red, flashing 2 Hz Error in user parameter data
Red, flashing 4 Hz Error in initialisation
Off Power off
Green, flashing Initializing and not running
Green Running
Red Stopped or subnet error, or timeout
Alternating Red/
Green
Green Initializing
Green, flashing Running
Red, flashing If the device status LED is flashing in a
Invalid or missing configuration
sequence starting with one or more red
flashes, note the sequence pattern and
contact GE Multilin
CONFIGURATION
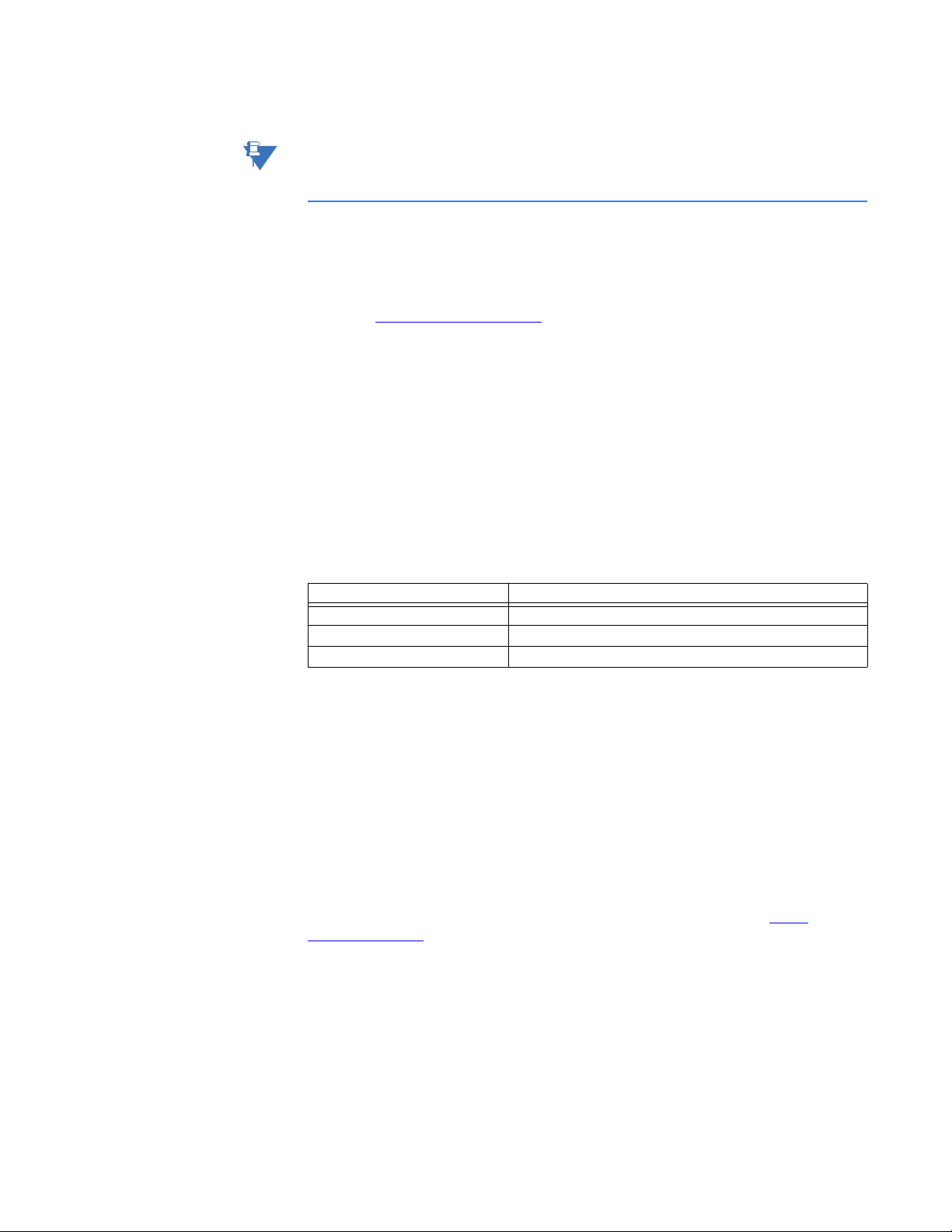
SWITCHES
The configuration switches are used to set the Profibus node address. Normally, these
switches are covered by a plastic hatch. Note that the node address can not be changed
during runtime, i.e. the P485 requires a reset for any changes to have effect. Recycle the
power supply to reset the module
A
B
Figure 2-10: P485 configuration switches
The node address is configured using two rotary switches as follows:
Profibus node address = (Switch B× 10) + (Switch A × 1)
2–6 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 17
NOTE
INSTALLATION
For example, to set the node address to 42, set switch A to “2” and switch B to “4”.
When removing the hatch, avoid touching the circuit boards and components. Exercise
caution when using tools to open the hatch.
Profibus installation procedure
PROFIBUS
CONFIGURATION TOOL
Each device on a Profibus-DP network is associated with a GSD file, which contains all
necessary information about the device. This file is used by the Profibus configuration tool
during configuration of the network. The file is available for download at the GE Multilin
website at http://www.GEmultilin.com
(the GSD file is named ‘P48509E5.GSD’).
It is necessary to import the GSD file in the Profibus configuration tool in order to
incorporate the P485 as a slave in the network. The properties for the P485 must then be
configured from the Profibus configuration tool. This includes setting up the node address,
input/output data areas and offset address.
• Node address: The node address in the Profibus configuration tool should be set to
match the one selected using the on board configuration switches of the P485 (see
Configuration switches on page 2–6).
• Setting up input/output data areas: Input/output data are arranged as logic modules
in the Profibus configuration tool. Which modules to use depends on the application.
The modules are composed together in the “module list” for the P485 device.
It is possible to select modules freely to compose the required input/output sizes, see
example below.
Input/output bytes required Modules
4 inputs and 2 outputs 4 inputs + 2 outputs
7 inputs and 12 outputs 4 inputs + 2 inputs + 1 input + 8 outputs + 4 outputs
68 inputs 64 inputs + 4 inputs
• Offset address: The offset addresses can be chosen freely. However, certain
restrictions may apply depending on what PLC/Profibus master is used.
PROFIBUS NETWORK
TERMINATION
If the P485 is the last node on a Profibus segment, it is necessary to use a Profibus
connector with integrated termination switch.
• The termination switch should be set to ‘ON’ if...
– The P485 is the last physical node on a network segment
– No other termination is used at this end of the network
• The termination switch should be set to ‘OFF’ if...
– There are other nodes on either side of the P485 in the network segment
LINKS Additional information about the Profibus fieldbus system can be found at http://
www.profibus.com.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 2–7
Page 18

INSTALLATION
Troubleshooting
DESCRIPTION Problem during configuration upload/download. The Config Line LED turns red.
• Serial communication failed – try again.
The serial port seems to be available, but it is not possible to connect to the P485.
• The serial port may be in use by another application. Exit EnerVista P485/D485 Setup
and close all other applications including the ones in the system tray and try again.
• Select another serial port and try again.
Poor performance.
• Right click ‘Modbus Network’ in the Navigation window and select ‘Modbus Network
Status’ to see status/diagnostic information about the Modbus network. If the P485
reports very many re-transmissions, check your cabling and / or try a lower baud rate
setting for the sub network (if possible).
• Is the Modbus Network Monitor in EnerVista P485/D485 Setup active? The Modbus
network monitor has a negative influence on the overall performance of the P485, and
should only be used when necessary.
• Is the Node Monitor in EnerVista P485/D485 Setup active? The node monitor has a
negative influence on the overall performance of the P485, and should only be used
when necessary.
2–8 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 19
GE Consumer & Industrial
Internal Memory Buffer
Output data
(up to 244 bytes)
Input data
(up to 244 bytes)
Sub Network
Fieldbus
General data
1024 bytes
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 3: Data exchange
Data exchange
Overview
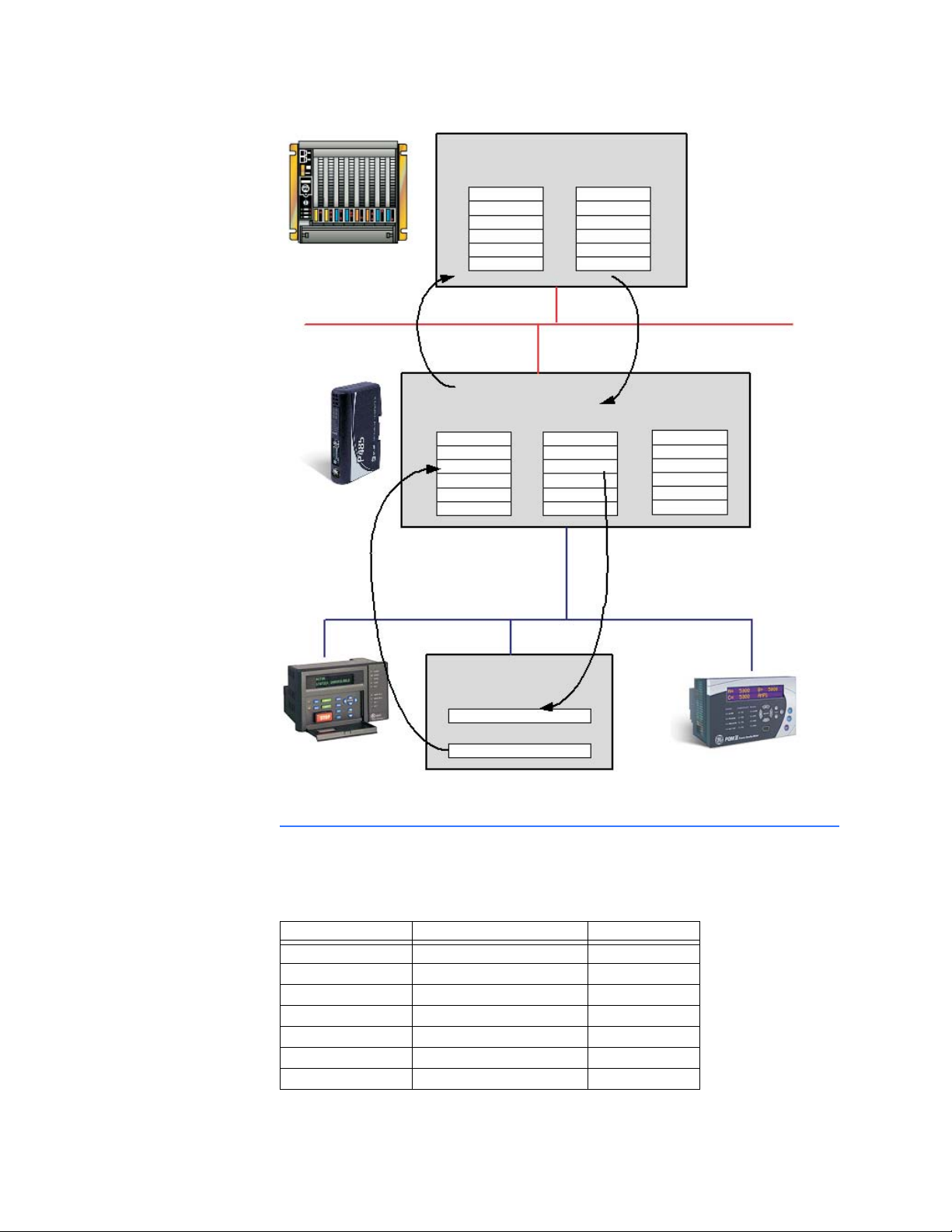
DESCRIPTION Data from the fieldbus (Profibus) and the sub network (Modbus) is stored in an internal
memory buffer. This is a easy method for data exchange where the fieldbus control
system simply reads and writes data to pre-defined memory locations, and the serial sub
network also use the same internal memory buffer to read and write data. Refer to Figure
3-2: Data exchange overview on page 3–2 for details.
INTERNAL MEMORY
BUFFER STRUCTURE
The internal memory buffer can be seen as a memory space with three different types of
data; input data, output data and general data.
• Input data: This is data that should be sent to the fieldbus. The P485 can handle up to
244 bytes of input data. The total input/output data must not exceed 416 bytes.
• Output data: this is data recieved from the fieldbus. The P485 can handle up to 244
bytes of output data.
• General data: This data cannot be accessed from the fieldbus, and is used for
transfers between nodes on the sub-network, or as a general “scratch pad” for data.
The P485 can handle up to 1024 bytes of general data.
Figure 3-1: Internal memory buffer
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 3–1
Page 20
DATA EXCHANGE
PLC memory
The PLC exchanges data
via the Profibus network
between its internal input
area and the input area
of the P485
I/O inputs
Current Ia
Profibus network
Internal memory buffer
of the P485
Input data area Output data area General data area
0x0000 0x0200 0x0400
Current Ia CT PRIMARY
The data in the input area of
the P485 contains data received
from nodes on the Modbus
sub-network (sent in to the P485
from the sub-network)
Modbus sub-network
I/O outputs
CT PRIMARY
The data in the output area of
the P485 contains data received
from Profibus. In this case, it is
the CT PRIMARY setting of the
PQMII meter.
The PLC exchanges data
via the Profibus network
between its internal output
area and the output area
of the P485
Modbus slave (e.g. PQMII)
CT PRIMARY setting
Current Ia actual value
Figure 3-2: Data exchange overview
Memory Map
MEMORY LOCATIONS When configuring the sub-network, use the memory locations shown below:
Address Contents Access
0x0000 to 0x0001 Status register read/write
0x0002 to 0x00F3 Input data area read/write
0x00F4 to 0x01FF Reserved -
0x0200 to 0x0201 Control register read only
0x0202 to 0x02F3 Output data area read only
0x02F4 to 0x03FF Reserved -
0x0400 to 0x7FF General data area read/write
3–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 21
DATA EXCHANGE
Node
Transaction
Transaction
Message frame
Byte
Word Data CRC Byte
Frame objects
Message frame
Byte Word Data CRC Byte
Frame objects
Message frame
Byte
Word Data CRC Byte
Frame objects
• Status register (0x0000 to 0x0001): If enabled, this register occupies the first two
bytes in the input data area. For more information, see Control and status registers on
page 8–1.
• Input data area (0x002 to 0x00F3): This area holds data that should be sent to the
fieldbus (see the status and control registers).
• Control register (0x0200 to 0x0201): If enabled, these register occupies the first two
bytes in the output data area. For more information, see Control and status registers
on page 8–1.
• Output data area (0x200 to 0x2F3): This area holds data received from the fieldbus.
Data cannot be written to this area.
• General data Area (0x0400 to 0x7FF): This data cannot be accessed from the fieldbus,
and should be used for transfers between nodes on the sub-network, or as a general
“scratch pad” for data.
Protocol configuration
DESCRIPTION In order to be able to communicate on the Modbus sub-network, the P485 must be
supplied with a description of the required sub-net protocol. To accomplish this, the
EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software features a flexible protocol-programming system,
allowing the P485 to interpret and exchange data with almost any serial device on the
Modbus sub-network.
COMMUNICATION MODE The P485 supports the Modbus Master communication mode. In this mode, the P485 is
setup to use the Modbus RTU protocol and implements a Modbus master for data
exchange between the fieldbus and one or more devices on the sub-network. Refer to
Chapter 5 for additional details.
PROTOCOL BUILDING
A description of the building blocks used to describe the sub-net protocol is shown below.
BLOCKS
Figure 3-3: Modbus protocol blocks
• Node: In the P485, a node holds all transactions and parameters for a particular
device on the sub network.
• Transaction: Transactions contains messages to be transmitted on the sub-network.
A transaction consists of one or more message frames (see figure above), and has a
few general parameters to specify how and when the transaction should be used on
the sub-network.
• Commands: A command is a pre-defined transaction that has been stored in a list in
the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software. This improves readability as well as
simplifying common operations by allowing transactions to be stored and reused.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 3–3
Page 22

DATA EXCHANGE
• Message frame: The message frame contains a description of what is actually
transmitted on the sub-network and consists of frame objects (see figure above).
• Frame object: Frame objects are used to compose a message frame. Frame objects
include fixed values, dynamic values retrieved from a specified memory location in the
P485, or strings.
3–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 23

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 4: Software overview
Software overvie w
Introduction
DESCRIPTION EnerVista P485/D485 Setup is a PC-based configuration software used to describe the
protocol and communication properties for a serial network. When the configuration is
finished and the functionality is tested, it is possible to send memory allocation information
to a printer using EnerVista P485/D485 Setup.
EnerVista P485/D485 Setup can also be used for troubleshooting and diagnostic of the
P485 and the serial network during runtime.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS The following hardware and software is required to use the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup
software.
• Pentium 133 MHz or higher
• 10 MB of free space on the hard drive
•8 MB RAM
• Windows 95/98/NT/2000/XP
• Internet Explorer 4.01 SP1 or higher
Installation procedure
DESCRIPTION There are two different ways of installing EnerVista P485/D485 Setup; either via the GE
EnerVista CD or from the GE Multilin website at http://www.GEmultilin.com.
INSTALLING FROM
ENERVISTA CD
INSTALLING FROM THE
GE MULTILIN WEBSITE
Run ‘setup.exe’ and follow the on screen instructions
Download the self-extracting EXE file from the GE Multilin website at http://
www.GEmultilin.com.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 4–1
Page 24

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
DESCRIPTION When creating a new sub network configuration, EnerVista P485/D485 Setup provides a
NOTE
Using the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software
choice between starting out with a blank configuration, or using a predefined template
(configuration wizard).
• Configuration Wizard: The wizard option automatically creates a configuration based on information about the sub-network (Modbus) devices; that is, the user simply has to “fill in the blanks”.
• Blank Configuration: This option should be used when creating a new configuration
when the configuration wizard does not fit the application or to modify an existing
configuration for a new application. The following chapters will describe the
configuration process in detail.
It is recommended to use the configuration wizard for its simplicity of use with GE relays
and meters.
The online help system explains each configuration step in detail.
CONFIGURATION
WIZARD
The purpose of the configuration wizard is to help you through the process of creating a
project with a Modbus RTU sub-network. When the wizard is finished, it is possible to
continue editing the project in the configuration tool.
The EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software will open with following screen to select the
configuration.
Select Configuration Wizard and click on OK.
4–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 25

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
Sub-Network (Modbus)
PC for configuration
and Monitoring
Fieldbus Network (P rofibus or DeviceNet)
Fieldbus
Master (PLC)
HMI
Fieldbus
Slave
GE Converter
(P485 or D485)
GE Relays & Meters
SELECT FIELDBUS TYPE The first step in the configuration wizard selects the fieldbus type. The fieldbus is the higher
layer network that communicates with the serial device(s) on the modbus sub-network via
the P485 converter.
Select “Profibus-DP” then click Next to continue. A typical Profibus-DP network
arrangement is shown below.
Figure 4-1: Typical network arrangement
In the event the wizard cannot handle the specific Modbus command(s) required by the
device, use the regular configuration tool or modify the commands produced by the
NOTE
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 4–3
wizard using the regular configuration tool.
Page 26

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
SUB-NETWORK
PROPERTIES
NOTE
The second step in the configuration wizard selects the properties for the Modbus subnetwork. The data flow for the sub-network is shown below.
Fieldbus
Master
Fieldbus
Data Direction
In Out
Modbus
Sub-Network
GE
Converter
Figure 4-2: Sub-network data flow
Refer to the particular sub-network device manual(s) to determine the appropriate settings
and communication options. If multiple devices are being installed on the same subnetwork, they must be configurable for a common set of communication parameters.
All numerical values are entered and shown in decimal unless otherwise specified.
The sub-network properties window is shown below.
• Physical standard: The physical standard can be either RS232, RS485, or RS422.
RS232 is a point-to-point communication standard; that is, it is only possible to have one
sub-network node (Modbus device) connected to the P485 converter when using RS232.
RS232 supports a maximum cable length of 15 meters and is full duplex. It uses two signal
lines (Rx and Tx) and the signal is measured relative to ground.
RS485 is a common multi-drop communication standard. It is used with larger cable
distances with one or several sub-network nodes (Modbus devices) connected. RS485
supports a maximum of 31 nodes, with half duplex and a total cable length up to 1200
meters. It uses two signal lines (A-line and B-line, twisted pair) with the signal being
measured between the two lines.
RS422 is a common multi-drop communication standard. It is used with larger cable
distances with one or several sub-network nodes connected. RS422 supports a maximum
of 31 nodes, with full duplex and a total cable length up to 1200 meters. It uses four signal
lines (receive A1-B1 and transmit A2-B2, twisted pair) with the signals being measured
between the two signal lines A and B.
• Bitrate (bits/s): This parameters refers to the speed of the sub-network. Speeds are
1200 to 57600 bps in predefined steps. The bitrate is also referred to as baud rate.
4–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 27

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
• Parity: The parity can be selected as "Odd", "Even", or "None". This is a simple error
check method capable of detecting single bit communication errors on a serial
network (i.e. the sub-network).
• Data bits: There can be "7" or "8" data bits. Generally, 8 data bits are used. This
parameter determines how many bits per byte of user data that is transmitted on the
sub-network, excluding start, stop and parity bits.
• Stop bits: There can be "1" or "2" stop bits. Determines the number of stop bits at the
end of each byte sent on the sub-network.
DEVICE TYPES The third step in the configuration wizard introduces device types into the project and
configures their parameters. Every device must be unique. Predefined devices can be
loaded from a file, and it is possible to connect devices to the sub-network at a later step in
the wizard. Additional devices can be created by editing previously saved devices.
The device types window is shown below.
The Modbus address range, including bit areas and register areas (words), is shown below.
The Modbus commands are also shown for the corresponding memory areas. Note that
many device manuals ignore the leading digit of the address (i.e. 0, 1, 3 or 4); as such, the
address 40001 is often referred to as 0001. The leading digit can be determined from the
Modbus command specified.
Address Command
0x Output coil (bits) 00001 to 09999 #1 (decimal): Read coil status
1x Inputs status (bits) 10001 to 19999 #2 (decimal): Read input status
3x Input status (word) 30001 to 39999 #4 (decimal): Read input registers
4x Output (word) 40001 to 49999 #3 (decimal): Read holding registers
#15 (decimal): Force multiple cells
#16 (decimal) Preset multiple registers
Users should consult the instruction manuals of the various network devices to determine
the actual Modbus command code(s) implemented or required. This will determine the
implied leading digit of the data address (i.e. 0, 1, 3 or 4).
In most GE Multilin relay and meter documentation, Modbus addresses are indicated in
hexadecimal form. For the Modicon format used for the P485, convert the hex address to
decimal, add 1, then append a prefix of 1, 2, 3, or 4, depending on the type of register. For
example, to convert the input register hexadecimal address 0x0300, we have:
1. 0300h = 0768 decimal
2. 0768 decimal + 1 = 0769 decimal
3. change 0769 → 30769 (prefix “3” for input registers)
Therefore, a Modbus hex address of 0x0300 is 30769 in Modicon format.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 4–5
Page 28

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
NOTE
The wizard can accept memory addresses from 0 to 9999 (0x270F). For higher memory
addresses, please use the protocol building blocks (refer to Protocol building blocks on
page 3–3 for additional details).
The Create Device button creates a new empty device. A new Device tab will be created.
The new device can be named in the Device Name text box. The Remove Device button
removes the selected device.
The Load Device button opens the “open file” dialog box. Select a previously stored device
to include it into the project. Device files (extension D01) for the most commonly used GE
relays and meters are supplied with the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software.
The Save Device button opens the “save device” dialog box. To create similar devices, click
on Save Device to save a particular device parameter list, then click Load Device to
recover a duplicate of the device. The duplicate device should be renamed and then
modified as required. Devices can also be saved for a use at a later stage. All parameters
and address settings are stored in the device file.
The Device tab shows the name of the device and the active node. The tab “in front” of the
other tabs is the active one. The active device's parameters are shown in the parameter list
below the tab list.
The Device Name is typically the technical name or designation of a device found on the
devices name plate. Examples are “MM2”, “469” and “PQMII”. Do not confuse the device
name with the node name, which is entered at a later stage. The node name is typically a
name that is used to identify the device in your application. Examples are “Lube Pump 1”,
“Production feeder” and “Main transformer”.
The Create Parameter button adds a new parameter to the parameter list. The loaded
device from previously saved devices can be modified for a new parameter or change in
the settings of the parameters. The Remove Parameter button removes the selected
parameter from the parameter list. To select a parameter simply click the desired
parameter in the list. Use the scroll bar to move the list up and down. Click the desired
parameter and enter the desired Parameter Name. It is recommended that you enter a
unique name here. Examples are “Phase A Current Ia”, “Voltage Vab”, and “VT ratio”.
The Data Direction column shows if data is read from or written to the device. The P485
converter is the one who reads or writes. It is only possible to read input data; output data
can be both read or written. Refer to Figure 4-2: Sub-network data flow on page 4–4 for
details.
The Register column is where the Modbus register number for the for the parameter in the
device is entered. Only register addresses can be entered here (the register address is the
absolute address +1). Most device manuals contain the register address but some may
provide an absolute address in hexadecimal format. In case absolute addresses are given,
the address must be incremented by 1. If the address range covers multiple coils, inputs, or
registers, only the start address is entered.
The Length column is where the total length of the parameter data is entered. The length is
given in bits for the 0x and 1xxxx areas and in words for the 3xxxx and 4xxxx areas. If the
parameter data for a device on the sub-network are linearly addressable, then
consecutive parameters may be addressed using a single Modbus command from the
P485. For example, five parameters each 2 words long can be addressed using a single
Modbus command (#16 Preset Multiple Registers) with a total length of 10 (5 × 2). Reducing
the number of transactions initiated by the P485 will optimize communications on the
Modbus sub-network.
The Type column shows the type of data that is referenced for the respective parameter.
Possible entries are bit(s) and word(s). This is automatically entered by the wizard based on
the selected address and selected direction.
4–6 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 29

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
The Modbus Command column shows the Modbus command assigned by the wizard. The
Modbus command is automatically selected by the wizard based on the selected address
and direction.
CONNECTING DEVICES The fourth step in the configuration wizard connects one or more devices to the sub-
network. Devices on a sub-network are also known as nodes (Modbus slave devices) and
are the actual nodes that will be physically connected to the Modbus sub-network. It is
possible to connect devices of the same device type more than once. The created nodes
will be listed to the left.
The Node window is shown below:
The Create Node button adds a new node (Modbus slave) to the sub-network. A new row
will be added to the node list to the left. The Remove Node button to remove the selected
node. Select a node in the node list by clicking on the desired node.
When a new node is created, the wizard assigns it a default name. Enter the desired node
name in the Node Name column. The node name is typically a name that identifies the
device in your application. Examples are “Lube pump1”, “Production Feeder” and “Main
transformer “. Do not confuse the node name with the device name assigned at an earlier
stage – the device name is typically the technical name or designation of a device found
on the devices name plate (for example, “MM2”, “SR469” and “PQMII”).
Enter the Modbus slave address of the sub-network node in the Slave Address column. The
wizard automatically assigns a default address which can be changed as needed. The
node address must match the slave address setting of the device you are connecting. If
you only connect one node, this address setting might be irrelevant, depending on the
operation of the device.
The Device Type column is where previously configured devices are connected to the subnetwork. If you click a row in the device column, a list will appear containing all previously
configured device(s). Select the desired device from this list.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 4–7
Page 30

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
SELECTING PARAMETERS
FOR EACH NODE
The fifth step in the configuration wizard selects the parameters that shall be mapped to
the Fieldbus Network. All previously configured parameters will appear at this point,
including parameters saved to a file. All previously configured nodes will appear in the
horizontal Node tab list in the upper left of the configuration wizard. Select the All
Parameters tab to view the complete list of parameters.
The Node tab in the foreground displays the active node. The number within brackets at
the end of the node name is the node Modbus slave address (1 to 255) on the sub-network.
Clicking a specific tab will display the parameters currently mapped to this node address.
For example, for “Lube Pump 1[1]”, the name of the node is “Lube Pump 1” and its slave
address is 1.
The All Parameters tab displays all parameters in the same list. This provides an overview
of data transmitted on the sub-network. It is also possible to add or remove parameters on
configured nodes in this list by using the Add Parameter or Remove Parameter buttons.
The Add Parameter button adds a new parameter to the selected node. The Remove
Parameter button remove the selected parameter from the selected node.
The Parameter Name column displays the user-assigned parameter name. When a new
parameter is inserted, it is named by the software as “Not Configured”. A list of available
parameters will appear when the you click the row. Select the desired parameter by
clicking on it in the list.
CONFIGURATION
REPORT
The sixth and final step in the configuration wizard displays a summary of the
configuration entries. This includes all configured devices, their parameters, and how they
are mapped to the internal memory of the P485. This report can be saved in rich text (RTF)
format or sent to a printer.
4–8 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 31

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
If the Sub-net Overview button is pressed, a new window will appears that graphically
displays how the data is mapped to the internal memory of the P485.
Configuration main window
DESCRIPTION The main window is shown below. It is composed of the navigation window, parameter
window, information window, and configuration line indicator.
A
B
C
D
Figure 4-3: Configurator main window
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 4–9
Page 32

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
NAVIGATION WINDOW The navigation window in EnerVista P485/D485 Setup is the main tool for selecting the
different levels of the configuration. There are three main levels in the navigation window,
namely fieldbus, P485, and Modbus network.
Menu entries preceded by a plus symbol (+) contain more configuration parameters or
sub-menus. To gain access to these parameters, the entry must be expanded by clicking
the ‘+’ symbol.
By right-clicking entries in this window, a popup menu with functions related to this entry
will appear. The options in this popup menu is often also available in the menu bar.
PARAMETER WINDOW The parameters available in this window is different depending on what is selected in the
navigation window. It consists of a grid with parameter names and, on the same row, a
field for editing.
The parameters can be displayed in two modes: alphabetic and categorized. Parameter
values are entered either using selection box or by entering a value. Values can be entered
either in decimal form (for example, 35) or in hexadecimal form (for example, 0x1A).
If a value is entered in decimal format, it will be converted automatically to the equivalent
hexadecimal value.
INFORMATION WINDOW In the right bottom corner of EnerVista P485/D485 Setup, below the parameter window,
lies the information window. It contains descriptions of currently marked parameter
instances.
Figure 4-4: Information window
CONFIGURATION LINE
INDICATOR
In the lower-right corner of the main window, two lights indicate if a connection has been
established between the PC running EnerVista P485/D485 Setup and P485. A green light
indicates that the connection is OK, and a red light indicates no connection.
4–10 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 33

OPTIONS WINDOW In the main window under tools, select options.
Table 4–1: Options window functions
Function Description
Warning on delete When something is to be deleted, a warning window will appear.
Warning on unsaved
data
Show Wizard when
“New” menu is selected
Language next time the
program is launched
Size of log buffer Set the size of the log buffer (0 to 512 bytes).
Firmware download Download the firmware to the
Factory restore Restores the software on the P485 carrier board, to it´s original state.
Block configuration Use with caution. When this button is pressed, the configuration will
Create error log Creates an error log file.
When closing EnerVista P485/D485 Setup with unsaved data, a
warning window will appear.
Each time a new configuration is to be made, the Wizard window will
appear.
Select which language the program should use the next time the
program is launched. Presently, only English is supported.
not be accessible and a new configuration has to be downloaded to
the module.
Fieldbus configuration
SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
P485. Use with caution.
DESCRIPTION During start-up, the fieldbus interface is initialized to fit the configuration created in the
EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software. Since EnerVista P485/D485 Setup supports both the
P485 and D485 converters, the user must verify that the 'Fieldbus' parameter indicates the
correct converter. Additionally, it is possible for advanced users to customize the network
interface inside the converter to meet specific application demands (see Advanced fieldbus
configuration on page 8–5 for details).
Figure 4-5: Fieldbus configuration
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 4–11
Page 34

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
P485/D485 configuration
PARAMETER WINDOW By selecting 'P485/D485 ' in the Navigation window, basic configuration options for the
sub-net will appear in the Parameter window.
Figure 4-6: P485/D485 configuration
• Physical interface: Currently, the P485 supports only a serial interface. The
communication settings for the selected interface are available under 'Modbus
Network (see Serial interface settings on page 4–13 for details).
• Control/status byte: This parameter is used to enable/disable the control/status
registers (see Control and status registers on page 8–1 for details).
– Enable: enable control/status registers. The “Data Valid” parameter (bit 13 in the
control register) must be set by the fieldbus control system to start the sub
network communication.
– Disable: Disables control/status registers.
– Enable but no start up lock: The control/status registers are enabled, but the
fieldbus control system is not required to set the “Data Valid” parameter (bit 13 in
the control register).
• Module Reset: This parameter defines how the module should behave in the event of
a fatal error. If Enabled, the module will reset and restart on a fatal error event, and no
error will be indicated to the user. If Disabled, the module will halt and indicate an error.
• Protocol: The P485 supports Modbus RTU master mode.
• Statistics: If enabled, the receive counter location indicates the number of valid
messages received from the subnet. If enabled, the transmit counter location
indicates the number of messages sent to the sub network. This function is used
primarily for debugging purposes.
4–12 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 35

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
Modbus network configuration
OVERVIEW When controlling a Modbus sub-network with the P485 it is important to understand
functions during starting up. If the P485 starts scanning nodes on the sub-network, before
data is received from the fieldbus control system (fieldbus master), values of ‘00’ may be
transmitted to the nodes before data is updated the first time from the fieldbus.
See Input/output data during startup on page 8–4 for information on how to block
transactions until valid data is received.
SERIAL INTERFACE
SETTINGS
To be able to communicate on the Modbus network, various communication settings
needs to be configured. To gain access to these settings, select ‘Modbus Network’ in the
Navigation window.
Parameter Description Range
Bit rate Selects the bit rate. 1200 to 57600
Data bits Selects the number of data bits. 7, 8
Parity Selects the parity. None, Odd, Even
Physical standard Selects the physical standard. This setting
activates the corresponding signals on the subnet
connector.
Start bits Only one start bit is supported. 1
Stop bits Either one or two stop bits can be selected. 1, 2
RS232, RS422, RS485
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 4–13
Page 36

SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
4–14 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 37

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 5: Communication model
Communicatio n model
Introduction
DESCRIPTION In master mode, the P485 is configured to run as a master on the Modbus sub-network,
using a scan-list for communication with the Modbus slave devices. The scan-list is created
using EnerVista P485/D485 Setup and can consist of multiple nodes with multiple
transactions.
Communications between the P485 and the sub-net nodes (Modbus slaves) is based on
transactions with a query/response architecture. The P485 sends out a query on the
Modbus sub-network, and the addressed node is expected to send a response to this
query. Slave nodes are not allowed to respond without first receiving a query.
An exception to this is broadcaster functionality. Most protocols offer some way of
accessing all network nodes. In the P485, this is called a ‘broadcaster’. The broadcaster can
transmit messages to all nodes on the sub-network without expecting a response.
In Modbus, it is possible to broadcast a message to all nodes by sending a message to
node address 0. The Modbus slaves will receive the message, but not Respond to it.
P485
Query
Response
Broadcast
Fieldbus Master
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 5–1
Fieldbus slave
and
Modbus master
Figure 5-1: Master mode overview
Query
Response
Query
Response
Modbus devicesPLC
Node 1
(Modbus Slave)
Node 2
(Modbus Slave)
Page 38

COMMUNICATION MODEL
SCAN LIST Once the configuration has been downloaded to the P485, the P485 firmware searches the
The P485 uses pre-configured Modbus RTU commands, acting as a Modbus RTU master.
With Modbus RTU, each transaction is substituted with a pre-defined command that can
be selected from a list of available commands.
It is still possible, though, to define custom message frames by creating a transaction
instead of selecting a pre-defined command. A command is actually a transaction that has
been defined in advance and stored in a list.
scan-list, using the defined transactions for communication with the slave-devices.
Each node in the scan-list represents a slave device on the Modbus network. In EnerVista
P485/D485 Setup, each node is given a specific name and assigned an address in standard
Modbus RTU commands. The address must match the internal setting on the slave device.
Figure 5-2: P485 scan list
Basic settings
PARAMETER WINDOW Select ‘Modbus Network’ in the Navigation window to gain access to basic settings in the
Parameter window.
Figure 5-3: Parameter window
COMMUNICATION Refer to Serial interface settings on page 4–13 for details.
MESSAGE DELIMITER The message delimiter value is the minimum time in steps of 10 ms separating the
messages. According to the Modbus specification, the message delimiter has a default
setting of 3.5 characters.If this value is set to “0”, the P485 will use the Modbus standard 3.5
character message delimiter. The time in milliseconds is then dependent on the selected
baud rate, but this is all handled by the P485.
Due to its impact on subnet functionality, use caution when changing this parameter.
NOTE
5–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 39

COMMUNICATION MODEL
Nodes
DESCRIPTION A node in the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software represents a device on the Modbus
sub-network. In it’s simplest form, a Node contains of a single transaction, that consists of
a Query and a Response.
NODE PARAMETERS To gain access to these parameters, select the desired node in the navigation window.
• Slave address: This setting shall be set to match the Modbus address setting of the
destination device.
• Name: Node Name. This name will appear in the navigation window.
MODBUS NETWORK
MENU
NODE MENU Right-click on a node in the Navigation window to gain access to these functions.
Right-click “Modbus Network” in the Navigation window to gain access to these functions.
Figure 5-4: Modbus network menu
• Paste: Paste a node from the clipboard.
• Modbus Network Monitor: Launches the Modbus network monitor. Refer to Modbus
network monitor on page 7–1 for details.
• Add Node: Adds a node to the scanlist.
• Add Broadcaster: Adds a broadcaster node to the scanlist.
• Load Node: Loads a node previously saved using “Save Node” from the Node menu
(see details below).
• Modbus Network Status: Displays status/diagnostic information about the Modbus
network.
Figure 5-5: Node menu
• Cut: Cuts a node to the clipboard.
• Copy: Copies a node to the clipboard.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 5–3
Page 40

COMMUNICATION MODEL
• Insert: Insert a node from the clipboard.
• Delete: Deletes a node and its configuration from the scan list.
• Monitor: Activates the node monitor.
• Add command: Adds a pre-defined protocol specific command to the scan list. The list
of commands are supplied with the P485 and cannot be changed.
• Insert new node: Inserts a new node above the currently selected node.
• Save node: Saves the selected node.
• Insert from file: Inserts a previously saved node above the currently selected node.
QUERY PARAMETERS To gain access to these parameters, select a Query in the Navigation window.
• Minimum time between broadcasts (10 ms): The value entered here is only valid if a
broadcast command is specified in the scan-list and the value specifies how long the
P485 should wait after the broadcast was sent until the next command in the scan-list
will be sent. This time should be selected such that all slave-devices connected to the
P485 have time to finish the handling of the broadcast. The unit is milliseconds (ms)
and the entered value is multiplied by 10, which means that the shortest time is 10 ms.
• Offline options for fieldbus: This parameter defines the behavior of the P485 in case
the Profibus network goes off-line and the selection affects the data that is sent out
the Modbus network
– Clear: All data destined for the slave devices is cleared (set to 0).
– Freeze: All data destined for the slave device is frozen.
– NoScanning: The updating of the Modbus network is stopped.
• Offline options for Modbus network: This parameter defines the behavior of the P485
in case the Modbus network goes offline and the selection affects the data that is
reported to the fieldbus master.
– Clear: All data destined for the fieldbus master is cleared (set to 0).
– Freeze: All data destined to fieldbus is frozen.
Offline options for Modbus networks are configured separately for each command.
NOTE
• Reconnect time (10 ms): This parameter specifies how long the P485 should wait
before trying to re-connect a disconnected node. A node gets disconnected if the max
number of retries is reached. The unit is milliseconds (ms) and the entered value is
multiplied by 10, which means that the shortest time is 10 ms.
• Retries: This parameter specifies how many times a time-out can occur in sequence
before the slave is disconnected.
• Timeout time (10 ms): This parameter specifies the time the P485 waits for a response
from the slave-device. If this time is exceeded the P485 re-sends the command until
the “retries” parameter value is reached.
The unit is milliseconds (ms) and the entered value is multiplied by 10, which means that
the shortest time is 10 ms.
• Trigger byte address: This parameter specifies location in the internal memory buffer
where the trigger byte is located. In P485 a trigger byte is implemented to support
non-cyclic data that means that the
Profibus master has the ability to notify the P485
when it should send a specific command to a slave.
To use this functionality correctly the Profibus master should update the data area
associated with the trigger byte, and then update the trigger byte. The trigger byte should
be incremented by one for activation.
This parameter has no affect unless the “Update mode” parameter is set to “Change of
state on trigger”.
5–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 41

COMMUNICATION MODEL
• Update mode: This parameter is used to specify when the command should be sent
to the slave. The following modes are possible:
– Cyclically: The command is sent to the slave at the time interval specified in the
“Update time” parameter.
– On data change: The command is sent to the slave when the data area connected to
this command changes.
– Single shot: The command is sent to the slave once at start-up.
– Change of state on trigger: The command is sent to the slave when the trigger byte
value is changed.
• Update time (10 ms): This parameter specifies with what frequency this command will
be sent. The unit is milliseconds (ms) and the entered value is multiplied by 10, which
means that the shortest time is 10 ms.
RESPONSE PARAMETERS To gain access to these parameters, select a Response in the Navigation window.
• Trigger byte: This parameter disables and enables the trigger functionality for the
response. If the “trigger byte” is enabled then the P485 will increase the byte at the
“trigger byte address” by one when the P485 receives new data from the Modbus
network. This will notify the Profibus master of updated data.
• Trigger byte address: This parameter is used to specify the address in the internal
memory buffer where the trigger byte is located. Valid settings range from 0x0002 to
0x00F3.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 5–5
Page 42

COMMUNICATION MODEL
5–6 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 43

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 6: Frame and command
editors
Frame and command editors
Frame editor
DESCRIPTION The frame editor makes it easier to add specific custom commands. The same parameters
are available in both the frame editor and the parameter window, but in the frame editor
presents the message frames in a more visual manner than the navigation / parameter
window.
Figure 6-1: Frame editor window
EXAMPLE Consider the following frame. The first byte holds the slave address (0x01) followed by the
function code (0x06). The next word is the register address of the device where data is to be
written (0x1200). This is a query command – the data is to be sent to the slave device and
therefore is to be fetched from the OUT area starting at 0x0202. The next word indicates
the data size (in bytes) to be written (in this case, 0x0002).
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 6–1
Page 44

FRAME AND COMMAND EDITORS
GENERAL The command editor makes it possible to add custom commands to the P485.
This command will allocate two bytes of output data in the OUT area and no swapping will
occur. The data is followed by a two-byte CRC error check field and the CRC calculation
starts with the first byte in the frame (0x0000).
The same steps are required for the response frame. If the response holds data, it should
be allocated in the input area that starts at address 0x002. To apply the changes, select
File > Apply Changes. To exit without saving, select File > Exit.
Command editor
Figure 6-2: Select command window
To open the command editor, right click a node and select ‘Add Command’. A list of
predefined commands will appear.
To add a new command to the command list, select ‘Add Command’ in the ‘Command’
menu. To edit a previously defined command, highlight the command in the command list,
and select ‘Edit Command’ in the ‘Command’ menu.The following window pops up upon
selecting ‘Edit Command’ or ‘Add Command’.
Figure 6-3: Command editor
6–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 45

FRAME AND COMMAND EDITORS
SPECIFYING A NEW
COMMAND
Select ‘Add Command’ as described earlier.
This example is taken from a Modbus RTU implementation, which means that the frame
will always consist of one byte for slave address, one byte for function code and two bytes
for CRC. Furthermore, each command always consists of a query and a response.
The Modbus RTU specific frame objects are already in place and a data object is inserted
between the function code and the CRC. These objects cannot be moved or deleted,
however it is possible to add objects between the function code and the CRC.
Figure 6-4: Specifying a new command
First, enter a name for the command in the Command Name field (A) and an identifier in
the Command ID field (B). If the command is allowed to be broadcast on the sub-network,
check the Allow Broadcasting check box (C).
The Query (D) field has the following characteristics:
Query Column
1: Slave Address. 2: Modbus Function Code 3: See below 4: Error Check field.
DisplayName Slave Address Function Data Checksum
Protocol specific; cannot be altered. (See below)
Object Type Byte Byte Data Checksum
Modbus defines this object as a byte. (See below)
Value [SlaveAddress] ID User User
Linked to the actual ‘Slave
Address’ parameter in the
parameter window.
This value is linked to the
Command ID field.
(See below) Linked to “User”.
Determined by user at
configuration by selecting
the Error Check object in
the parameter window.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 6–3
Page 46

FRAME AND COMMAND EDITORS
It is not possible to alter the contents of columns 1, 2 and 4, as these are pre-defined
commands. However, on column 3 there are two possible actions: Insert Column and
Delete Column. These actions are available in the Columns menu.
Column 3 in the Command Editor is where objects can be added for custom commands.
Supported objects are Byte, Word, DWord, Data and Error Check. In this Modbus example it
makes no sense to add an Error Check object since it is already incorporated in the
standard frame but all other objects could be added in any way.
The “response” field (E) is defined much in the same way as the “query”, with the difference
that a “response” can depend on what is entered in the “query”
Query Column
1: Slave Address. 2: Modbus Function Code 3: See below 4: Error Check field.
DisplayName Slave Address Function Data Checksum
See Query See Query See Query See Query
Object Type Byte Byte Data Checksum
See Query See Query See Query See Query
Value [SlaveAddress] ID User Depend
See Query See Query See Query Object has same setting
as the corresponding
Query object. It also will
appear as non-editable in
the parameter window
(see below)
If ‘Depend’ is selected then this object in the “response” will get the same setting as the
corresponding object in the “query”, furthermore the object will appear as non-editable in
the parameter window (see below).
Figure 6-5: Main window
6–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 47

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 7: Modbus network and
node monitors
Modbus network and node monitors
Modbus network monitor
GENERAL The Modbus network monitor is intended to simplify configuration and troubleshooting of
the Modbus network. It’s main function is to display the data allocated for Modbus network
communication and detect if any area has been allocated twice; that is, if a collision has
occurred.
All configured nodes, together with the commands, are listed in the middle of the screen
(B). Selecting and deselecting commands makes it possible to view any combination of
allocated data.
The Modbus network monitor has a negative influence on the overall performance of the
NOTE
P485. Therefore the monitor functionality should be used with care.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 7–1
Page 48

MODBUS NETWORK AND NODE MONITORS
Start Stop
OPERATION The Modbus network monitor window is shown below.
Figure 7-1: Modbus network monitor
A: Start / Stop sub network scanning
These icons are used to start / stop the scanning of the Modbus network. To stop the
scanning, click on the red light. To start scanning again, simply click on the green light.
B: Nodes / Transactions
To view data blocks linked to a single command, select the command and the data will
appear in the monitor area, see below. (C)
C: Monitor Area: Input / Output / General Data Areas
These areas display the data allocated in the input, output and general data areas. This
information is color coded as follows:
• White: No data allocated.
• Yellow: Data allocated by a response/consume transaction.
• Blue: Data allocated by a query/produce transaction.
• Red: Collision. This area has been allocated more than once.
• Grey: Data allocated by the control/status registers.
7–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 49

MODBUS NETWORK AND NODE MONITORS
Start Stop
Node monitor
GENERAL The node monitor functionality provides an aid when setting up the communication with
the slave-devices on the Modbus network.
It offers an easy way of testing a specific command on a node, and monitor the result. It
also provides an overview of the memory used by the node.
Using the node monitor has a negative influence on the overall performance of the P485.
NOTE
OPERATION The node monitor window is shown below.
Therefore the monitor functionality should be used with care.
NOTE
A: Start / Stop Node Communication
These icons are used to start / stop a node. Stopping is done by clicking the red light and
could be seen as a temporary removal of the node, i.e no data will be sent to the node but
it is still available. To start the node again, simply click on the green light.
This is a powerful feature when there is a problem with a particular node; the other nodes
can be disconnected, helping to isolate the problem.
If the control and status registers are enabled, the subnet cannot be started or stopped
without being activated from the fieldbus.
B: Select/Send Command
Select the command to monitor using the ‘Select’ icon, and click ‘Send’ to send the
command.
Select Send
C: Data Update ON/OFF
These icons are used to turn the monitor functionality ON or OFF (see ‘Monitor Area’ below).
Update OFF Update ON
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 7–3
Page 50

MODBUS NETWORK AND NODE MONITORS
D: Command Area
This area displays the currently selected command.
E: Response Area
This area displays the response of a previously sent command.
F: Monitor Area
This area provides an overview of the data sent/received from the node. Areas in dark grey
are reserved for the status/control registers.
Areas displayed in light grey are data objects used by the node. If data updating is enabled
(see sub-section C above) the contents of these areas are also displayed in hex.
7–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 51

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 8: Advanced functions
Advanced functions
Control and status registers
DESCRIPTION The control/status registers forms an interface for exchanging information between the
fieldbus control system and the P485.
The main purpose of these registers is to report Modbus network related problems to the
fieldbus control system. This interface is also used to ensure that only valid data is going
out on the sub-network and that valid data is reported back to the fieldbus control system.
See 8-4 “Input/output data during startup”.
Using these registers, it is also possible for the fieldbus control system to instruct the P485
to enable / disable specified nodes.
By default, these registers are located in the internal memory buffer at 0x000 - 0x001
(Status Register) and 0x200 - 0x201 (Control Register), however they can be disabled using
EnerVista P485/D485 Setup, see Modbus network configuration on page 4–13. Disabling
these registers will release the 2 reserved bytes in the internal memory buffer, however, the
Status and Control functionality will not be available.
The handshaking procedure described on page 8-3 must be followed for all changes to
these registers
CONTROL REGISTER
(PROFIBUS CONTROL
SYSTEM TO P485)
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 8–1
Bytes 0 and 1 of the control register are shown below.
Byte 0 (Offset 0x200) Byte 1 (Offset 0x201)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - Control Code Data
Page 52

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
CONTROL CODES The following control codes are recognized by the P485 and can be used by the fieldbus
Bits Name Description
15 Handshake Confirmation
Bit (CR_HS_CONFIRM)
14 Handshake Toggle Bit
(CR_HS_SEND)
13 Data Valid (CR_DV) This bit is used to indicate to the P485 if the data in
12 to 8 Control Code (CR_EC) See table below.
7 to 0 Data (CR_ED) See table below.
When the Profibus control system has read the new
information from the status register, it should set this
bit to the same value as bit 15 in the status register
The fieldbus (Profibus) control system should toggle
this bit when new information has been written in the
control register.
the output data area is valid or not. The bit shall be
set by the fieldbus control system when new data
has been written (1 indicates data is valid; 0 indicates
that data is NOT valid)
control system.
Code Name Description
0x10 DISABLE_NODE Slave address of the node to disable. This instructs the P485
0x11 ENABLE_NODE Slave address of the node number to enable. This instructs
0x12 ENABLE_NODES Number of nodes to enable. This instructs the P485 to enable
to disable a specific node from the sub network
communication
the P485 to enable a specific node to be active in the sub
network communication
a number of nodes from a complete configuration
STATUS REGISTER (P485
TO FIELDBUS CONTROL
SYSTEM)
The status codes below are handled by the P485 and reported to the fieldbus control
system using the status code and data bits in the status register. The meaning of these bits
are different depending on the used communication model.
Byte 0 (Offset 0x200) Byte 1 (Offset 0x201)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - Status Code Data
Bits Name Description
15 Handshake Toggle Bit
(SR_HS_SEND)
14 Handshake Confirmation
Bit (SR_HS_CONFIRM)
13 Data Valid (SR_DV) Indicates to the fieldbus control system if the data in
12 to 8 Status Code (SR_EC) Status code, see table below.
7 to 0 Data (SR_ED) Status user data, see table below.
The P485 toggles this bit when new information is
available in the status register.
When the P485 has read the new information from
the control register, it sets this bit to the same value
as bit 14 in the control register
the input data area is valid or not. The bit is set by the
P485 when new data has been written (1 indicates
data is valid; 0 indicates that data is NOT valid).
8–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 53

STATUS CODES The status codes are described in the following table.
Code Error Description
0x00 Re-transmission Number of re-transmissions. Reports the total number of
0x01 Single node missing Slave address of the missing node. Reports if a node is
0x02 Multiple nodes
missing
0x03 Overrun Slave address of the node that sent too much data.
0x04 Other error Slave address. Reports unidentified node
0x1F No error Normal Condition
re-transmissions on the subnetwork
missing
Number of missing nodes. Reports if multiple nodes are
missing
Reports if more data than expected was received from a
node
ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
HANDSHAKING
PROCEDURE
The handshake bits are used to indicate any changes in the status and control registers.
The procedure below must be followed for all changes to these registers with the exception
of the handshake bits themselves (bits 14 and 15).
Status Register Reads Control Register Writes
Start
Compare CR_HS_CONFIRM with
SR_HS_SEND
Yes
Equal?
No
Read Status Register
Compare SR_HS_CONFIRM with
No
Start
CR_HS_SEND
Equal?
Yes
Write to Control Register
Set CR_HS_CONFIRM to
SR_HS_SEND
End
Toggle CR_HS_SEND
End
Figure 8-1: Handshaking flowchart
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 8–3
Page 54

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
Fieldbus control system P485
Updates the output data
area according to the
sub-network configuration
Sets bit 13 (data valid) in
the control register
Complete a full scan
on the sub-network
Sets bit 13 (data valid) in
the status register
Ready
(waiting for bit 13 (data valid)
in the control register to be set...)
DESCRIPTION This section is only relevant when the control/handshake registers are enabled.
Input/output data during startup
Bit 13 in the control register is used to ensure data consistency during start-up and at
fieldbus off-line/on-line transitions. The bit should be treated as follows:
NOTE
Figure 8-2: Input/output data during startup
When the fieldbus changes from off-line to on-line state, the fieldbus control system
should clear (0) the ‘data valid’ bit in the control register. The P485 will then clear the ‘data
valid’ bit in the status register.
During startup, the P485 waits for the fieldbus control system to set the ‘data valid’ bit in
the control register. Before this is done, it will not communicate with the devices on the
Modbus network.
The ‘data valid’ bit in the status register may in some cases be delayed. This latency can be
caused by a missing node or a bad connection to a node with a long timeout value
assigned to it.
Therefore, the fieldbus control system should not wait for this bit to be set before
communicating with the sub-network devices. It should be considered as an aid for the
fieldbus control system to know when all data has been updated.
As with all changes to these registers, the handshaking procedure (refer to Handshaking
procedure on page 8–3) must be followed.
8–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 55

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
Advanced fieldbus configuration
MAILBOX COMMAND This advanced function is specifically designed for DeviceNet converter (D485) and not for
Profibus converter (P485). Right clicking on the Fieldbus submenu items gives option of
inserting a mailbox. Users are advised not to use this option for the P485.
Figure 8-3: Mailbox command
Incorrect usage of mailbox commands may permanently damage the converter. For
CAUTION
additional information, consult the product support team at GE Multilin.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 8–5
Page 56

ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
8–6 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 57

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 9: Application example
Application example
Introduction
OVERVIEW The chapter describes how to configure the P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter to allow
GE Multilin relays and meters to communicate on a Profibus Network. The GE Multilin MM2
Motor Manager 2 and PQMII Power Quality Meter are used as examples.
GE Multilin relays and meters support a very useful feature called the Modbus User
Map in their software. This feature can be used in configuring the P485 to reduce the
number of Modbus transactions and improve communication speed.
It is assumed that the reader is familiar with serial communication, Profibus networks, and
PLC architecture.
EQUIPMENT AND
DOCUMENTS
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–1
The examples in this chapter make use of the following equipment and documentation
• P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter
• RS485 cable to connect P485 to the relays/meters (MM2 and PQMII)
• Enervista P485/D485 Setup software with configuration cable
• GSD file for the P485
• standard Profibus cable with connectors
• 24 V DC power supply for the P485
• PLC with Profibus master card
• PQMII Power Quality meter and instruction manual (publication code GEK-106435D)
• Enervista PQMII Setup software
• MM2 relay and instruction manual (publication code GEK-106294B)
• MM2PC software
Page 58

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
SYSTEM SETUP This chapter describes how to set up the P485 with MM2 relay and PQMII meter to read
and write parameters. It can also be used as a guideline to setup the P485 Modbus to
Profibus Converter for communication with any GE Multilin relays.
The PQMII and MM2 devices are serially connected (daisy-chained) through RS485. The
following data is set up for the PQMII:
• Read phase current Ia, Ib, and Ic actual values from memory locations 0240h to 0242h
• Read average current from memory location 0244h
• Read neutral current from memory location 0245h
• Read average phase voltage from memory location 0286h to 0287h
The following data is set up for the MM2:
• Read motor status from memory location 0023h
• Read switch input status from memory location 0010h
• Read motor load from memory location 0035h
• Read thermal capacity from memory location 0036h
• Read metered voltage from memory location 0040h
• The START A (command code 0x0005) and STOP (command code 0x0004) commands
using Modbus function 10h: Preset multiple registers.
The memory addresses below are taken from the PQMII and MM2 instruction manuals
available at http://www.GEmultilin.com
. For the PQMII, we have:
Type Parameter Address Format Read/write
Actual values Phase current Ia 0x0240 F1 Read only
Actual values Phase current Ib 0x0241 F1 Read only
Actual values Phase current Ic 0x0242 F1 Read only
Actual values Average phase current 0x0244 F1 Read only
Actual values Neutral current 0x0245 F1 Read only
Actual values Average phase voltage (2 words) 0x0286 F3 Read only
For the MM2, we have:
Type Parameter Address Format Read/write
Actual values Motor status 0x0023 F7 Read only
Actual values Switch input status 0x0010 F100 Read only
Actual values Motor Load 0x0035 F1 Read only
Actual values Thermal Capacity 0x0036 F1 Read only
Actual values Voltage 0x0040 F1 Read only
Commands Command function code 0x1160 F1 Read/write
Commands Command operation code 0x1161 F22 Read/write
The write command returns data in the response that should not be visible from the
Fieldbus. Also, the write commands should only be sent if the data from the Profibus
master has changed.
If the P485 detects a timeout while talking to the devices (PQMII and/or MM2), it should try
to re-establish communications before it considers the device in subnet is missing
(Number of retries), and then try again after some time (Reconnect time).
The serial communication parameters are set to 19200 bps, with no parity, 1 stop bit, and
8 data bits. The physical interface is set to RS485.
9–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 59

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
Modbus user map setup
DESCRIPTION GE Multilin Relays and Meters support the Modbus User Map feature in their software. This
feature can be used with the P485 to reduce the number of Modbus transactions and
improve communication speed.
PQMII USER MAP There are six parameters to be read from PQMII as indicated in the previous section.
Normally, six read input register command transactions are required to read these
parameters. However, these parameters can be grouped together with the Modbus User
Map feature and read using only one read input register command transaction.
Set the Modbus User Map for the PQMII as follows.
1. Start the Enervista PQMII Setup software.
2. Establish communication between the device and PC.
3. Select the Setpoint > User Map menu item.
4. Set the user map registers as follows and save to the meter.
User map address Parameter User map data
0000 0x0240 0x0100
0001 0x0241 0x0101
0002 0x0242 0x0102
0003 0x0244 0x0103
0004 0x0245 0x0104
0005 0x0286 0x0105
address
Figure 9-1: PQMII meter user map setting
The six parameters are now mapped to user memory map data at 0x0100 to 0x0106.
These parameters can now be read by one Read input data register command at 0x0100
with register length = 7 words (note that average phase voltage value is in 32-bit).
MM2 USER MAP As indicated earlier, there are five parameters to be read from MM2. Normally, five read
input register command transactions are required to read these five parameters. However,
all the parameters can be grouped together using the Modbus User Map feature and read
using only one read input register command transaction.
Set the Modbus User Map for the MM2 as follows.
1. Start the MM2PC software.
2. Establish communications between the device and PC.
3. Select the Setpoint > User Map menu item.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–3
Page 60

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
4. Set the user map registers as follows and save to the relay.
User map address Parameter User map data
address
1280 0x0023 0x0100
1281 0x0010 0x0101
1282 0x0035 0x0102
1283 0x0036 0x0103
1284 0x0040 0x0104
Figure 9-2: MM2 meter user map setting
The five parameters are now mapped to user memory map data at 0x0100 to 0x0104.
These parameters can now be read by one Read input data register command at 0x0100
with register length = 5 words.
9–4 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 61

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
System configuration
OVERVIEW An overview of the system configuration described in this document is shown below.
Figure 9-3: System configuration
The following procedures describe how to configure for the P485 with the PQMII and MM2.
It is assumed that the reader has some basic knowledge of the Modbus RTU protocol and
Profibus communication protocol.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–5
Page 62

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
INSTALLING THE
ENERVISTA P485/D485
SETUP SOFTWARE
STARTING THE
CONFIGURATION
WIZARD
The following procedure describes how to configure the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup
software.
1. Install the EnerVista P485/D485 Setup software.
2. Connect the configuration port of P485 to the PC via the configuration cable.
3. Connect the devices (PQMII and MM2) to P485 through the DB-9 Modbus network
connector using the proper RS485 connections shown below.
DB9 pin Description
5 Ground
8 RS485 +
9 RS485 –
Start the P485 configuration wizard as follows.
1. Launch the Enervista P485/D485 Setup software.
2. A window for selecting a configuration will be displayed. Select the Configuration
Wizard icon.
Figure 9-4: Select configuration wizard
3. Click OK to proceed to step 1 of the configuration wizard.
STEP 1: SELECTING THE
FIELDBUS TYPE
The first step in the configuration wizard is setting the fieldbus type.
1. Set the Fieldbus type to “Profibus-DP”.
Figure 9-5: Select fieldbus type
2. Click Next to proceed to step 2 of the configuration wizard.
9–6 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 63

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
STEP 2: SELECTING THE
SUB-NETWORK
PROPERTIES
STEP 3: INCLUDE DEVICE
TYPES
The second step in the configuration wizard is to select the sub-network properties.
1. Set the Modbus network properties as follows: baud rate to 19200, with 8 data bits, no
parity, RS485 physical standard, and 1 stop bit.
Figure 9-6: Modbus network properties
2. Click Next to proceed to step 3 of the configuration wizard.
The third step in the configuration wizard is to include device types. The PQMII and MM2
devices are added in this step.
1. The configuration wizard gives the option to create a configuration for a new device or
to load a configuration of saved device.
Figure 9-7: Device types
2. Configuration files for MM2 and PQMII are supplied with the Enervista P485/D485
Setup software. Click the Load Device button to see the available configuration files.
Figure 9-8: Available Modbus devices
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–7
Page 64

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
3. Select the PQMII.D01 file from the list and click on Open.
4. The software will display a list of the most commonly used parameters configured for
the PQMII.
Figure 9-9: Parameters configured for PQMII
5. The Modbus User Map values are already present in the configuration file; as such, it is
not required to create the new parameters. However, it is necessary to save number of
registers to be read. Change the data length to 7 words as required.
6. Similarly, load the configuration file for MM2 by clicking the Load Device button and
selecting the
MM2-MM3.DO1 file.
Figure 9-10: Parameters configured for the MM2
7. The software will display a list of the most commonly used parameters configured for
the MM2. The Modbus User Map values are already present in the configuration file; as
such, it is not required to create the new parameters. However, it is necessary to save
number of registers to be read. Change the data length to 5 words as required.
8. The Motor Start A command and Motor Stop command can be executed using
command function + operation code.
9. Save this device configuration by clicking the Save Device button.
10. Click Next to proceed to step 4 of the configuration wizard.
9–8 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 65

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
STEP 4: CONNECT
DEVICES TO THE SUB-
NETWORK
The fourth step in the configuration wizard is to connect the configured device types to the
sub-network. The PQMII and MM2 devices are connected in this step.
1. Click Next to proceed to create nodes on Modbus network as shown below.
Figure 9-11: Connect devices to sub-network
2. There are two nodes on the Modbus network: the PQMII meter and the MM2 relay. To
insert a node, click the Create Node button.
3. Set the Node Name as “PQMII Meter”, the Slave Address to “20”, and the Device Type
to “PQMII”.
Figure 9-12: Node for PQMII meter
4. Similarly create another node for the MM2. Set the Node Name as “MMII Relay”, the
Slave Address to “4”, and the Device Type as “MM2-MM3”.
Figure 9-13: Node for MM2 relay
5. Click Next to proceed to step 5 of the configuration wizard.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–9
Page 66

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
STEP 5: SELECT
PARAMETERS FOR EACH
NODE
The fifth step in the configuration wizard is to select parameters for each node. The
parameters for the PQMII and MM2 devices are selected in this step.
1. Parameters can now be added to each node. The tabs indicate the node name and
slave address
Figure 9-14: Select parameter window
2. To add parameter for the PQMII meter. select the “User memory map value (F1)” item
from the drop-down list.
Figure 9-15: Choosing parameters for the PQMII meter node
3. Select parameters for MM2 relay by click on the MM2 Relay (4) tab followed by the
Add Parameters button. Choose the following parameters from the drop-down list:
User memory map values (F1)
Command function code + operation code (F22)
Figure 9-16: Choosing parameters for the MM2 relay node
4. The values in the bracket indicate Modbus data format codes – refer to the instruction
manuals for details.
9–10 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 67

5. Click Next to proceed to the final step of the configuration wizard
APPLICATION EXAMPLE
STEP 6: CONFIGURATION
REPORT
The final step in the wizard provides a configuration report for the device.
1. If desired, click on Print to print the configuration report.
Figure 9-17: Configuration report
2. For future reference, saved the file in RTF format by clicking the Save as RTF button
and selecting an appropriate directory.
3. Click the Sub-net Oveview button to view the data mapping.
Figure 9-18: Modbus network monitor
4. Close the Modbus network monitor window.
5. Click on Next to complete the configuration wizard.
Figure 9-19: Wizard finished
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–11
Page 68

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
SAVING DEVICE DATA After the configuration wizard is complete, the software will prompt to save the device
data (if necessary).
Click on Yes to save the device. The data can be saved in the same or different device files.
CONFIGURING THE
QUERIES
Figure 9-20: Save device file
The main screen will appear after the wizard is closed.
9–12 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 69

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
1. Expand the Modbus Network item in the tree. All the configured parameters will
appear as commands.
Figure 9-21: Expanding the tree
2. Expand the User memory map values (F1) command in the PQMII Meter item and
click on Query.
Figure 9-22: Expand query
3. Change the Reconnect time to 5 seconds by changing the value to 500 (500 × 10 ms
= 5 seconds) and the Retries to 5.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–13
Page 70

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
4. Verify that the data Update mode is “Cyclically” with default Update time of
100 × 10 ms = 1000 ms. This can be changed to any value between 10 ms (1 × 10 ms)
to 655350 ms (65535 × 10 ms).
Figure 9-23: Changing configuration parameters for a query
5. Expand the User memory map values (F1) command in the MM2 Meter item and click
on Query. Set the configuration parameters as above.
6. Expand the Command Function code + operation code (F1, F22) command in the
MM2 Meter item and click on Query.
7. Set the following configuration parameters.
Offline option for Fieldbus = Freeze
Offline Options for sub-network = Freeze
Upload mode = On data change
Reconnect time = 500 (5 sec)
Retries = 5
Figure 9-24: Query parameters for the command function
9–14 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 71

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
DOWNLOADING THE
CONFIGURATION FILE
Save the configuration file for future use. The save command is available in File menu. The
following procedure demonstrates how to save the configuration file to the P485.
1. To open the saved configuration file, select the File > Open menu item. The following
window will appear.
Figure 9-25: Opening a saved configuration file
2. To connect to the P485, select the Tools > Port menu item, then select the port
connected to P485.
3. Click on the Connect icon.
4. Verify that the green LED is shown in the right corner of the configuration tool, then
click the download icon in the toolbar. The download in progress bar will appear.
Figure 9-26: Download in progress
5. If the P485 does not respond to the download, ensure all connections are OK and that
the port selection is valid. On some laptop computers, it might be worth trying the
other serial ports. Also ensure that no other software (such as any PLC communication
drivers) are blocking access to the serial ports.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 9–15
Page 72

APPLICATION EXAMPLE
DESCRIPTION Each device on a Profibus-DP network is associated with a GSD file that contains all
NOTE
Profibus network setup
necessary information about the device. This file is used by the Profibus configuration tool
during configuration of the network. The file is available for download at the GE Multilin
website at http://www.GEmultilin.com
It is necessary to import the GSD file in the Profibus configuration tool to incorporate the
P485 as a slave in the network. The properties for the P485 must then be configured from
the Profibus configuration tool. This includes setting up the node address, input/output
data areas and offset address.
• Node address: The node address in the Profibus configuration tool should be set to
match the one selected using the on board configuration switches of the P485.
• Setting up input/output data areas: Input/output data are arranged as logic modules
in the Profibus configuration tool. Which modules to use depends on the application.
The modules are composed together in the module list for the P485 device. It is
possible to select modules freely to compose the required input/output sizes, In the
previous example, where there are 24 bytes of input and 4 bytes of output, the
following modules can be configured.
24 bytes input and 6 bytes output = 16 inputs + 8 inputs + 4 outputs
• Offset address: The offset addresses can be chosen freely. However, certain
restrictions may apply depending on what PLC/Profibus master is used.
If the P485 is the last node on a Profibus segment, it is necessary to use a Profibus
connector with the integrated termination switch. The termination switch should be set to
ON if the P485 is the last physical node on the network and no other termination is used at
this end of the network.
(the GSD file is named P48509E5.GSD).
9–16 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 73

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Chapter 10: Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
Revision history
RELEASE DATES
CHANGES TO THE
MANUAL
GE MULTILIN WARRANTY
STATEMENT
Table 10–1: Release dates
Manual Part No. Revision Release Date
GEK-113190 1601-0237-A1 1.0x December 15, 2005
As this is the first version of the P485 Modbus to Profibus Converter manual, there are no
changes to report.
Warranty
General Electric Multilin (GE Multilin) warrants each device it manufactures to be free from
defects in material and workmanship under normal use and service for a period of 24
months from date of shipment from factory.
In the event of a failure covered by warranty, GE Multilin will undertake to repair or replace
the device providing the warrantor determined that it is defective and it is returned with all
transportation charges prepaid to an authorized service centre or the factory. Repairs or
replacement under warranty will be made without charge.
Warranty shall not apply to any device which has been subject to misuse, negligence,
accident, incorrect installation or use not in accordance with instructions nor any unit that
has been altered outside a GE Multilin authorized factory outlet.
GE Multilin is not liable for special, indirect or consequential damages or for loss of profit or
for expenses sustained as a result of a device malfunction, incorrect application or
adjustment.
For complete text of Warranty (including limitations and disclaimers), refer to GE Multilin
Standard Conditions of Sale.
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE 10–1
Page 74

MISCELLANEOUS
10–2 P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
Page 75

GE Consumer & Industrial
P485 Modbus to Profibus
Converter
Index
A
APPLICATIONS .........................................................................................1–3
B
BAUD RATE .......................................................................1–4, 4–4, 4–13
BROADCASTER ........................................................................................1–2
see entry for SOFTWARE
ENVIRONMENT .......................................................................................1–4
F
FEATURES ..................................................................................................1–3
FIELDBUS TYPE ....................................................................................... 4–3
FRAME EDITOR ........................................................................................ 6–1
C
CHANGES TO THE MANUAL ..........................................................10–1
COMMAND EDITOR ................................................................... 6–2, 6–3
COMPLIANCE ............................................................................................1–4
CONFIGURATION REPORT .................................................................4–8
CONFIGURATION SWITCHES ...........................................................2–6
CONFIGURATION WIZARD ................................................................4–2
CONNECTING NODES ..........................................................................4–7
CONTACT INFORMATION ...................................................................1–1
CONTROL CODES ...................................................................................8–2
CONTROL REGISTERS ..........................................................................8–1
D
DATA BITS ..................................................................................................4–5
DATA DIRECTION ....................................................................................4–6
DATA EXCHANGE ...................................................................................3–2
DATA FLOW ...............................................................................................4–4
DEVICE TYPES ...........................................................................................4–5
DIMENSIONS .............................................................................................1–4
DIN-RAIL CONNECTION ......................................................................2–5
DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS .............................................................1–2
E
ENERVISTA P485/D485 SETUP
G
GLOSSARY .................................................................................................1–2
H
HANDSHAKING PROCEDURE .......................................................... 8–3
HUMIDITY ...................................................................................................1–4
I
INFORMATION WINDOW ................................................................4–10
INPUT/OUTPUT DATA .......................................................................... 8–4
INPUT/OUTPUT DATA AREAS ..........................................................2–7
INSTALLATION ......................................................................................... 2–1
INTERNAL MEMORY BUFFER ...........................................................3–1
L
LEDs ..............................................................................................................2–5
M
MAILBOX COMMAND ..........................................................................8–5
MASTER MODE ........................................................................................5–1
MESSAGE DELIMITER ...........................................................................5–2
P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE i
Page 76

INDEX
MODBUS
address format ...............................................................................4–5
commands
configuration ................................................................................4–13
memory map ..................................................................................3–2
menu
network monitor ............................................................................7–1
protocol
.......................................................................................4–5
...................................................................................................5–3
..............................................................................................3–3
N
NAVIGATION WINDOW ....................................................................4–10
NETWORK TERMINATION ..................................................................2–7
NODE ADDRESS ......................................................................................2–6
NODE MONITOR ......................................................................................7–3
NODE PARAMETERS ..............................................................................4–8
NODES ..........................................................................................................5–3
O
OFFSET ADDRESS ...................................................................................2–7
OPTION WINDOW ...............................................................................4–11
ORDERING ..................................................................................................1–4
P
PARAMETER WINDOW ..........................................................4–10, 5–2
PARITY ............................................................................................4–5, 4–13
POWER SUPPLY
connections .....................................................................................2–4
specifications ..................................................................................1–4
PROFIBUS
configuration ...................................................................................2–7
input/output data areas
node address ..................................................................................2–6
typical network arrangement .................................................4–3
PROTECTION CLASS ..............................................................................1–4
............................................................2–7
communication model
configuration wizard ...................................................................4–2
data exchange ...............................................................................3–1
frame editor
installation .......................................................................................4–1
Modbus network monitor .........................................................7–1
node monitor
overview
SPECIFICATIONS .....................................................................................1–4
STATUS CODES .......................................................................................8–3
STATUS INDICATORS ...........................................................................2–5
STATUS REGISTER ......................................................................8–1, 8–2
STOP BITS ..................................................................................................4–5
SWITCHES ..................................................................................................2–6
....................................................................................6–1
..................................................................................7–3
............................................................................................4–1
...............................................................5–1
T
TECHNICAL SUPPORT .........................................................................1–1
TEMPERATURE ........................................................................................1–4
TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................2–8
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS .....................................................................1–3
U
UNPACKING THE SWITCH .................................................................1–1
W
WARRANTY .................................................................................1–1, 10–1
WEBSITE .....................................................................................................1–1
Q
QUICK INSTALL ........................................................................................2–1
R
REVISION HISTORY .............................................................................10–1
RS232 ...........................................................................................................4–4
RS422 ...........................................................................................................4–4
RS485 ...........................................................................................................4–4
S
SCAN LIST ...................................................................................................5–2
SOFTWARE
advanced functions .....................................................................8–1
command editor
ii P485 MODBUS TO PROFIBUS CONVERTER – USER GUIDE
............................................................................6–2
 Loading...
Loading...