Page 1

Technical Manual
900 MHz and 2400 MHz
Extended Range IP Networking Transceivers
Firmware Code 3.0
MDS entraNET
™
900
MDS entraNET
™
2400
Remote
Access Point
05-4055A01, Rev. E
JANUARY 2011
Page 2
COM1
ETH
PWR
LINK
LAN
PORT
PC RUNNING PING UTILITY
ACCESS POINT
ETHERNET REMOTE
ETH
PORT
ETHERNET ENDPOINT
(Device Being Pinged)
STRAIGHT THROUGH
CABLE
CROSS-OVER
CABLE
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
Quick Start Instructions
Listed below are the basic steps for installing GE MDS entraNET transceivers. Refer to the
appropriate sections in the manual for detailed information.
1. Initial Checkout
• Set the equipment up in a tabletop arrangement as described in 2 TABLETOP SETUP AND
EVALUATION, (
beginning on Page 15).
• Follow all steps to ensure proper cable connection
s and unit configuration. As a minimum, Access
Points must have the following programmed: IP A ddress, IP Network identifie r , and Radio Networ k
Address. (RF output power and Password should also be reviewed and set if necessary.) Remote
radios normally require only a Radio Network Address to be set. (Note: The Remote Radio Network Address must matc
• Connect data equipment to the transceivers
h that of the AP.)
. Use LAN/ETH ports for Ethernet systems, or COM2
ports for Serial data systems.
• Verify proper exchange of data communications by vie
wing the LEDs. The following indications
should be seen on the LED panel within 30 seconds of startup:
PWR—Lit co
LINK—
ETH—L
COM2—Blinking
ntinuously
Lit continuously
it continuously (unless Sleep is activated)
to indicate exchange of data communications
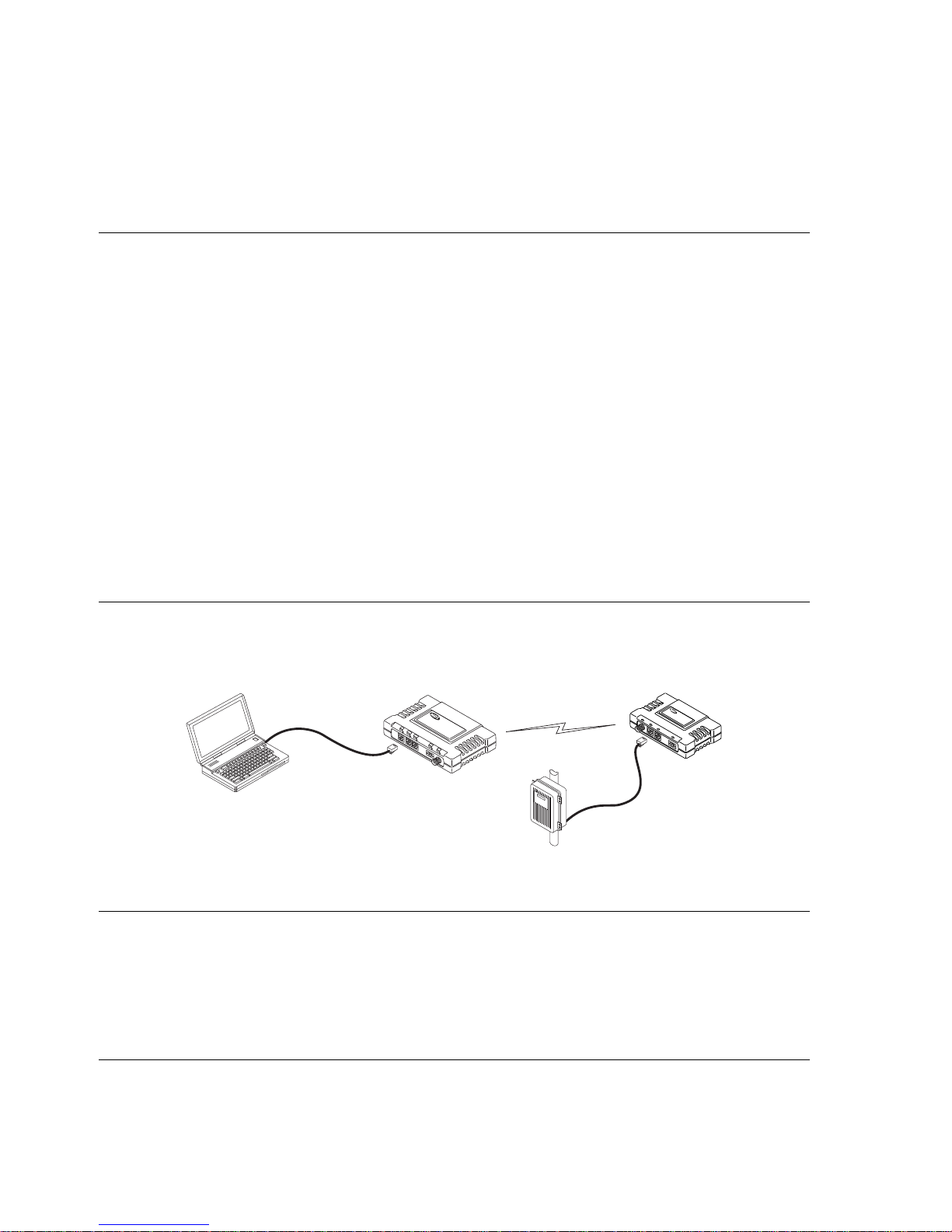
2. Endpoint Connectivity (PING) Test—for Ethernet Systems Only
• For Ethernet systems, verify the link integrity between the Access Point and endpoint devices connected to Remotes by issuing a PI
NG command from the AP. Below is a basic setup diagram for
the PING test. (NOTE: Endpoint devices must have a compatible IP address for this test to work.)
3. Set Configuration of AP and Remote Radios
• Refer to 3 AP MANAGEMENT beginning on Page 29 for details on connecting to the AP and
using the built-in menu system. Refer to 4 REMOTE RADIO MANAGEMENT be
Page 99 for details on programming Remotes.
• If you have a large number of radios to configure, a co
process. See USING CONFIGURATION SCRIPTS b
4. Install the Equipment in the Field
• Refer to 6 INST ALLATION beginning on Page 147 for details on site selection, mounting, cabling,
and antenna/feedline recommendations.
• After basic installation, optimize the performance of the radio network following the recommendations beginning on Page 160.
Invisible place holder
ginning on
nfiguration script may be used to speed the
eginning on Page 181 for details.
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCING THE
MDS entraNET SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL ........................................................................................................3
1.1.1 Supplemental Information Online ...............................................................................................3
1.2 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION................................................................................................... 3
1.2.1 Model Offerings ..........................................................................................................................6
1.3 APPLICATIONS....................................................................................................................6
1.3.1 Long-Range Wireless LAN .........................................................................................................6
Antenna Placement..........................................................................................................................6
Communication Rules......................................................................................................................6
1.3.2 Combining Serial and Ethernet Devices .....................................................................................7
1.3.3 DNP3 Protocol-Aware Networks ................................................................................................8
1.3.4 Upgrading an Older Wireless Network with
Serial Interfaces ....................................................................................................................................9
Replacing Legacy Wireless Products ..............................................................................................9
Supplementing a Legacy Wireless Network with IP Services..........................................................9
1.3.5 P22 Protected Network (Redundant) Configuration ...................................................................9
1.4 GE MDS SECURITY SUITE...............................................................................................10
1.4.1 Intrusion Detection via SNMP Traps ........................................................................................11
1.5 ACCESSORIES..................................................................................................................12
2 TABLETOP SETUP AND
EVALUATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.1 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................17
2.2 CONNECTOR OVERVIEW ................................................................................................17
2.3 TEST SETUP......................................................................................................................18
STEP 1—CONNECT THE ANTENNA PORTS ................... ... .... ...................................................19
STEP 2—MEASURE AND CONNECT DC POWER.....................................................................19
STEP 3—CONFIGURE THE AP ...................................................................................................22
Log-in and Configuration...................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..........................................................22
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual i
Page 4
Set Key AP Parameters.................................................................................................................23
STEP 4—CONFIGURE THE REMOTE RADIO ............................................................................24
Log-in and Configuration...................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............................................24
Set or Verify Network Address.......................................................................................................25
STEP 5—CONNECT TERMINAL EQUIPMENT............................................................................26
Ethernet Device Connection to Remote..................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............................26
Serial Device Connection to Remote.............................................................................................26
STEP 6—CHECK FOR NORMAL OPERATION ...........................................................................26
2.3.1 Verify Connectivity (PING command) .......................................................................................27
Serial Connections............................................................ ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .......................................27
3 AP MANAGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.1 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................31
3.1.1 PC-Based Configuration Software ............................................................................................31
3.1.2 Menu Structure .........................................................................................................................32
3.1.3 Differences in the User Interfaces ............................................................................................35
3.2 ACCESSING THE MENU SYSTEM................................................................................... 36
3.2.1 Methods of Control ...................................................................................................................36
3.2.2 PC Connection and Log-In Procedures ................................................................................... .37
3.2.3 Navigating the Menus ......................................................................................... ... ... ................42
Navigating via Terminal or Telnet Sessions
Recommended for first-time users.................................................................................................42
Navigating via a Web Browser.......................................................................................................42
3.3 BASIC DEVICE INFORMATION......................................................................................... 43
3.3.1 Starting Information Screen ......................................................................................................43
3.3.2 Main Menu ................................................................................................................................44
3.4 CONFIGURING NETWORK PARAMETERS ..................................................................... 45
3.4.1 Network Configuration Menu ....................................................... ... ... .... ...................................45
3.4.2 IP Configuration Menu ..............................................................................................................46
3.4.3 Wireless MAC Configuration Menu ..........................................................................................48
3.4.4 Mobility Configuration Menu .....................................................................................................49
3.4.5 SNMP Agent Configuration Menu ............................................................................................50
3.4.6 Bridge Configuration Menu ............................. ............................. ............................. ................51
3.5 CONFIGURING RADIO PARAMETERS ............................................................................ 52
3.5.1 Radio Configuration Menu ........................................................................................................52
Skip Zones Menu...........................................................................................................................53
3.6 CONFIGURING THE SERIAL INTERFACES..................................................................... 54
3.6.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................54
Serial-to-Serial Services ................................................................................................................55
ii MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 5
IP-to-Serial Services......................................................................................................................55
Configuration..................................................................................................................................56
Serial Configuration Wizard................................................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ................56
3.6.2 Local Serial Configuration Menu ..............................................................................................57
View Current Settings Screen—Serial-to-Serial Example .............................................................59
View Current Settings Screen—Unicast UDP Mode Example.......... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...61
3.6.3 Remote Serial Gateway Configuration (IP-to-Remote Serial) ..................................................62
3.7 SECURITY CONFIGURATION........................................................................................... 64
3.7.1 Security Configuration Menu ............................. ... ....................................................................65
3.8 WIRELESS NETWORK MENU ..........................................................................................69
3.8.1 Remote Management Submenu ..............................................................................................70
Manage Selected Remote Submenu
.......................................................................................................................................................71
Broadcast Remote Reprogramming Menu
.......................................................................................................................................................72
Remote Database Menu................................................................................................................74
Group Database Menu................................................................................................... ... ... ..........75
Endpoint Database Menu ..............................................................................................................75
Access Point Database Menu.............................................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ......76
3.9 STATISTICS AND EVENT LOG ......................................................................................... 77
3.9.1 COM1 and COM2 Data Statistics Menus ................................................................................78
3.9.2 Remote Serial Gateway Statistics ............................................................................................79
3.9.3 Ethernet and Wireless Packet Statistics ...................................................................................80
Ethernet Packet Statistics....................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................................................80
Wireless Packet Statistics..............................................................................................................80
3.9.4 Radio Packet Statistics .............................................................................................................81
3.9.5 Event Log Menu .......................................................................................................................82
Time and Date Stamping................................................................................................................82
3.10 DEVICE INFORMATION MENU.......................................................................................84
Device Names Menu......................................................................................................................85
3.11 MAINTENANCE AND TOOLS.......................................................................................... 85
3.11.1 Reprogramming Menu .............................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ..........................................86
3.11.2 Configuration Scripts Menu ...................................................................................................87
A Brief Description of Configuration Files ......................................................................................87
3.11.3 RSG Configuration Script Menu ............................................................................................89
3.11.4 Authorization Codes Menu ....................................................................................................91
3.11.5 Transmitter Test Menu ....................................... .... ................................................................92
3.12 REDUNDANCY MENU.....................................................................................................93
Packet Rx Errors Exceeded Threshold Menu................................................................................96
3.13 DNP3 ROUTING MENU................................................................................................... 97
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual iii
Page 6

4 REMOTE RADIO MANAGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4.1 INTRODUCTION ..............................................................................................................101
4.2 Programming Methods......................................................................................................101
4.2.1 Terminal Interface Mode .........................................................................................................101
4.2.2 Remote Management via the AP ...........................................................................................101
4.3 Log-in Procedure ..............................................................................................................101
4.4 Commands........................................................................................................................ 102
4.4.1 Entering Remote Commands .................................................................................................102
4.5 Minimum Configuration for Remotes................................................................................102
4.5.1 Detailed Command Descriptions ............................................................................................103
4.6 UPGRADING REMOTE FIRMWARE................................................................................117
5 SAMPLE CONFIGURATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
5.1 INTRODUCTION ..............................................................................................................121
5.2 IP-to-Local Serial Application Example.............................................................................121
Establishing a Connection ................................ ...........................................................................121
5.3 IP-to-Remote Serial Application Example......................................................................... 122
5.3.1 Endpoint Device Connected to the AP ...................................................................................123
5.4 Point-to-Point, Serial-to-Serial Application Example......................................................... 123
5.4.1 Step-by-step Instructions for Configuring a Point-to-Point Serial Connection ........................124
5.5 Point-to-Multipoint, Serial-to-Serial Application Example..................................................132
5.5.1 Step-by-Step Instructions for Configuring a Point-to-Multipoint Serial Connection ................133
5.6 Mixed-Mode Application Example.....................................................................................140
5.6.1 Operation and Data Flow ........................................................................................................140
5.7 Group Broadcast Session Example..................................................................................142
iv MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 7
6 INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
6.1 INSTALLATION.................................................................................................................149
6.1.1 General Requirements ...........................................................................................................149
6.1.2 Site Selection .........................................................................................................................149
6.1.3 Conducting a Site Survey .......................................................................................................150
Terrain and Signal Strength..........................................................................................................150
A Word About Radio Interference................................................................................................150
Mounting Dimensions for Radios.................................................................................................152
6.1.4 Antenna and Feedline Selection ............................................................................................153
Antennas......................................................................................................................................153
Feedlines .....................................................................................................................................154
6.2 HOW MUCH OUTPUT POWER CAN BE USED?
(U.S.A. and Canada, 900 MHz systems)..................................................................................156
6.2.1 Calculating System Gain ........................................................................................................156
6.3 HOW MUCH OUTPUT POWER CAN BE USED?
(U.S.A. and Canada, 2400 MHz systems)................................................................................157
6.3.1 Calculating System Gain ........................................................................................................157
6.4 HOW MUCH OUTPUT POWER CAN BE USED? (ETSI 2400 MHz systems)................. 158
6.4.1 Calculating System Gain ........................................................................................................159
6.5 OPTIMIZING PERFORMANCE........................................................................................160
6.5.1 Principles of Wireless Network Operation ..............................................................................160
6.5.2 Aiming Directive Antennas for Maximum RSSI ...................................................................... 162
Procedure ....................................................................................................................................162
6.5.3 Tips for Improving Data Throughput .......................................................................................163
To Maximize Throughput of Data and Reduce Latency Time......................................................163
To Maximize Overall Data Performance ......................................................................................164
7 TROUBLESHOOTING AND RADIO TESTS . . . . . 165
7.1 TROUBLESHOOTING......................................................................................................167
7.1.1 Interpreting the Front Panel LEDs ..........................................................................................167
7.1.2 Troubleshooting Using the Embedded Management System ................................................168
Serial Port and Remote Serial Statistics Menu............................................................................171
Diagnostic Tools...........................................................................................................................171
7.1.3 Using Logged Operation Events .................................................. ... ... .....................................172
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual v
Page 8

8 TECHNICAL REFERENCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
8.1 UPGRADING AP FIRMWARE..........................................................................................179
8.2 USING CONFIGURATION SCRIPTS...............................................................................181
Sample of an Exported Configuration File ...................................................................................182
Editing Configuration Files...........................................................................................................186
8.3 DATA INTERFACE CONNECTORS................................................................................. 187
8.3.1 LAN/ETH Port .........................................................................................................................187
8.3.2 COM1 Port .............................................................................................................................188
8.3.3 COM2 Port .............................................................................................................................189
8.4 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS.......................................................................................189
8.5 dBm-WATTS-VOLTS CONVERSION CHART.................................................................. 193
9 TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Copyright Notice
This publication is protected by U.S.A. copyright law. Copyright 2011, GE MDS. All rights reserved.
ISO 9001 Registration
GE MDS adheres to the internationally-accepted ISO 9001 quality system standard.
Related Materials on the Internet
Data sheets, frequently asked questions, application notes, information on firmware upgrades, and other valuable
information can be found on the GE MDS Web site at
www.gemds.com.
About GE MDS
Over two decades ago, GE MDS began building radios for business-critical applications. Since then, we’ve installed
more than 500,000 radios in over 110 countries. To succeed, we overcame impassable terrain, brutal operating condi
tions and disparate, complex network configurations. We also became experts in wireless communication standards
and system applications worldwide. The result of our efforts is that today, thousands of utilities around the world rely
on GE MDS-based wireless networks to manage their most critical assets.
The majority of GE MDS radios deployed since 1985 are still installed and performing within our customers' wireless
networks. That’s because we design and manufacture our products in-house, according to ISO 9001 which allows us
to control and meet stringent global quality standards.
Thanks to our durable products and comprehensive solutions, GE MDS is the wireless leader in industrial automation—including oil and gas production and transportation, water/wastewater treatment, supp ly and transportation,
electric transmission and distribution and many other utility applications. GE MDS is also at the forefront of wireless
communications for private and public infrastructure and online transaction processing. Now is an exciting time for
GE MDS and our customers as we look forward to further demonstrating ou r abilities in new and emerging markets.
As your wireless needs change you can continue to expect more from GE MDS. We'll always put the performance of
your network above all. Visit us at
www.gemds.com for more information.
-
vi MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 9

OPERATIONAL & SAFETY NOTICES
RF Exposure
U.S. Installations: Professional installation required. The radio equipment
described in this guide emits radio frequency energy. Although the power level is
low, the concentrated energy from a directional antenna may pose a health hazard.
For 900 MHz units, do not allow people to come closer than 23 cm (9 inches) to
the antenna. For 2.4 GHz units, do not allow people to come closer than 5 cm (2
inches) to the antenna. These distances apply whether the transmitter is operated
in indoor or outdoor environments. More information on RF exposure i s available
on the Internet at www.fcc.gov/oet/info/documents/bulletins.
ETSI Installations: In regions where the Europea
dards Institute (ETSI) standards apply, 2.4
GHz units with a maximum output
n Telecommunications Stan-
power of 100 mW EIRP are supplied. Do not allow people to come closer than 2.2
cm (1 inch) to the antenna.
CSA/US Notice
The transceiver has been recognized for use
in hazardous locations by the Canadian Standards Association
(CSA), which also issues the U.S. mark of approval. The CSA Certification is in accordance with CSA STD
C22.2 No. 213-M1987.
FCC Part 15 Notice
The transceiver complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. This device is specificall
the FCC Rules and Regulations. Any unauthorized modification or changes to this device without the express approval
of GE MDS may void the user’s authority to operate this device. Furthermore, this device is intended to be used onl y
when installed in accordance with the instructions outlined in this manual. Failure to comply with these instructions
may also void the user’s authority to operate this device.
y designed to be used under Section 15.247 of
Manual Revision and Accuracy
While every reasonable effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of this manual, product improvements may result
in minor differences between the manual and the product shipped to you. If you have additional questions or need an
exact specification for a product, please contact our Customer Service Team using the information at the back of this
guide. In addition, manual updates can often be found on the GE MDS Web site at www.gemds.com.
Environmental Information
The manufacture of this equipment has required the extraction and use of natural resources. Improper disposal may
contaminate the environment and present a health risk due to hazardous substances contained within. To avoid dissemination of these substances into our environment, and to li
use the appropriate recycling systems for disposal. These systems will reuse or recycle most of the materials found in
this equipment in a sound way. Please contact GE MDS or your supplier for more information on the proper disposal
of this equipment.
Battery Disposal–This product may contain a battery. Batteries must be disposed of properly, and may not be disposed
of as unsorted municipal waste in the European Union. See the product documentation for specific battery information.
Batteries are marked with a symbol, which may include lettering to indicate cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), or mercury (Hg).
For proper recycling return the battery to your supplier or to a designated collection point. For more information see:
www.weeerohsinfo.com.
mit the demand on natural resources, we encourage you to
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual vii
Page 10

LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
viii MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 11

INTRODUCING THE
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
1
1 Chapter Coun ter Reset Paragraph
1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL 3
1.2 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3
1.3 APPLICATIONS 6
MDS entraNET SYSTEM
1.1.1 Supplemental Information Online ..................................................3
1.2.1 Model Offerings .............................................................................6
1.3.1 Long-Range Wireless LAN ............................................................6
Antenna Placement ............................................................................6
Communication Rules ........................................................................6
1.3.2 Combining Serial and Ethernet Devices .......................................7
1.3.3 DNP3 Protocol-Aware Networks ...................................................8
1.3.4 Upgrading an Older Wireless Network with
Serial Interfaces .......... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...................9
Replacing Legacy Wireless Products.................................................9
Supplementing a Legacy Wireless Network with IP Services ............9
1.3.5 P22 Protected Network (Redundant) Configuration ......................9
1.4 GE MDS SECURITY SUITE 10
1.4.1 Intrusion Detection via SNMP Traps ...........................................11
1.5 ACCESSORIES 12
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 1
Page 12

2 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
Page 13

1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This guide provides installation and operating instructions for the MDS
entraNET 900TM and MDS entraNET 2400TM series radio system. The
guide is intended for use by those who install, configure, and operate the
entraNET wireless network.
Quick Start instructions are provided on the inside front cover of this
guide. They provide the basic steps for installing and operating the
transceivers, but do not cover all of the configurable parameters. The
main section of this guide contains complete information on menu
functions, as well as detailed installation, operation, and troubleshooting
information. This guide is arranged into the following eight chapters:
• Chapter 1—Introducing the MDS entraNET System (Page 1)
• Chapter 2—Tabletop Setup and Evaluation (Page 15)
• Chapter 3—Access Point (AP) Management (Page 29)
• Chapter 4—Remote Radio Management (Page 99)
• Chapter 5—Sample Configurations (Page 119)
• Chapter 6—Installation (Page 147)
• Chapter 7—Troubleshooting and Radio Tests (Page 165)
• Chapter 8—Technical Reference (Page 177)
• Chapter 9—Terms and Abbreviations (Page 195). Terms
defined in Chapter 9 are italicized on first appearance.
1.1.1 Suppl emental In fo rm ation Online
Release notes, manual updates, and other supplemental materials are
available online for many GE MDS products. For more information,
visit us at online at www.gemds.com.
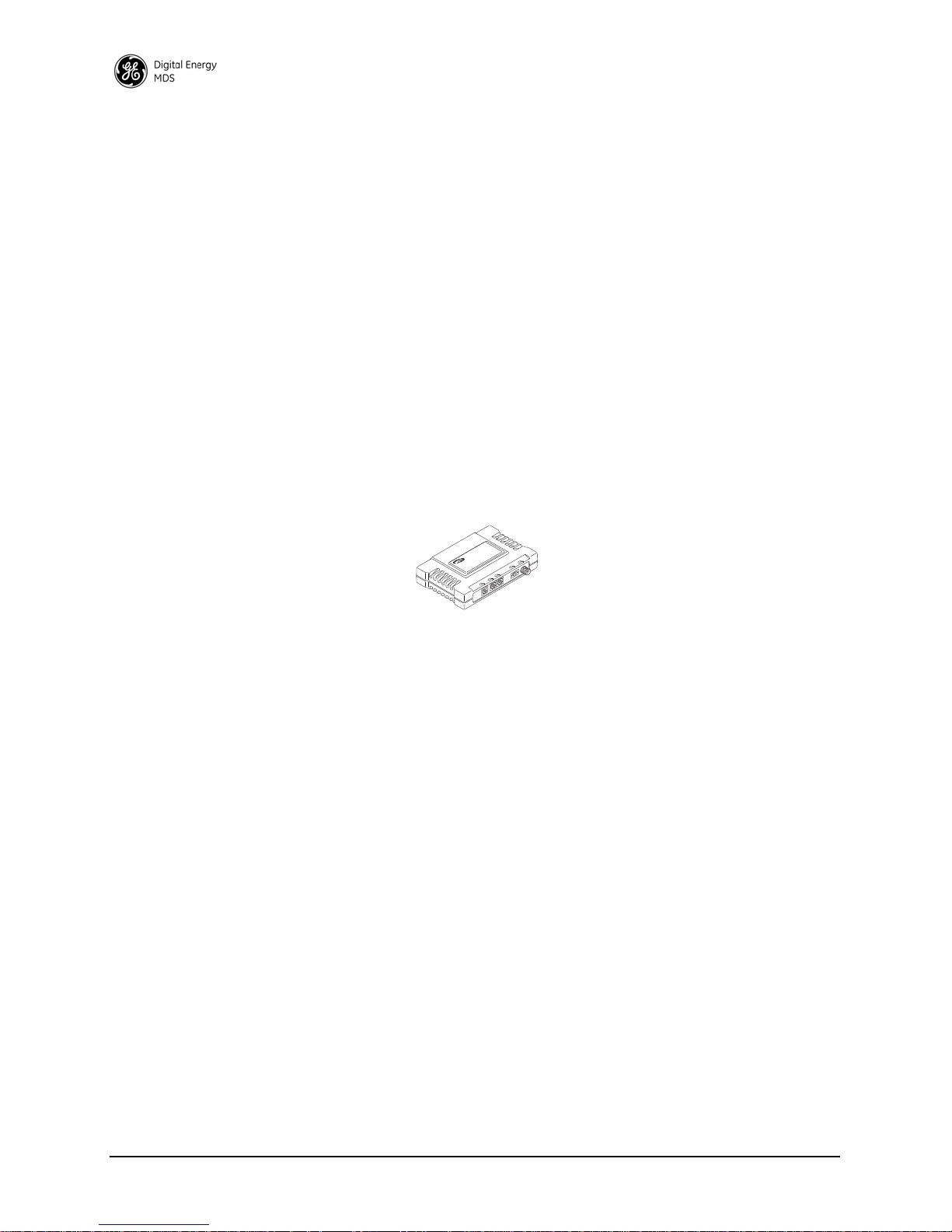
1.2 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The entraNET system is an easy-to-install wireless solution supporting
long-range serial and Ethernet data transmission at speeds up to
106 kbps. The system includes an Access Point (AP) transceiver and a
Remote transceiver capable of serial and Ethernet communication.
These radios serve a variety of network configurations. Figure 1-1
shows the two radios.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 3
Page 14

Invisible place holder
Access Point
Remote
Figure 1-1. MDS entraNET Transceiver Models
Robust Radio
Operation
MDS entraNET transceivers use an advanced Media Access Controller
(MAC) to ensure network access for stations with data to send. The
MAC permits data to be sent from endpoint devices on an on-demand
basis, preventing over-the-air data collisions and ensuring that data gets
through as intended. MAC functionality eliminates the need for active
polling of Remotes, an important requirement in Report-by-Exception
(RBE) applications.
Rugged Packaging MDS entraNET radios are housed in compact and rugged die-cast cases
that need only be protected from direct exposure to the weather. The
transceivers are supplied with flat surface-mounting brackets or optional
35 mm DIN rail brackets, depending on customer requirements.
Simple Installation Basic installation typically employs an omni-directional antenna at the
AP site and a directional antenna at each associated Remote site. The
antenna is a vital link in the system and must be chosen and installed
correctly. INSTALLATION PL ANNING on Page 149 provides guidance
on choosing proper antennas and installation sites.
T o establish basic service, connect an antenna, connect an Ethernet LAN
(Local Area Network) to the AP, connect a serial or Ethernet device to
the Remotes, apply power, set a few operating parameters using a
personal computer, and you are done. No license is required for
operation in the U.S.A., Canada, and many other countries. Check the
regulations in your country before placing the radios on the air.
GE MDS Security
Suite
Network security is a vital issue in today’s wireless world. The
MDS entraNET system provides multiple tools to help you build a
network that minimizes the risk of eavesdropping or unauthorized
access. Some security features are inherent to radio operation, such as
the use of spread-spectrum transmission. Other techniques are built into
4 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 15

the radio firmware, including data encryption, enabling or disabling
remote access channels, and password protection.
Security is not a one-step process that can be simply turned on and
forgotten. It must be practiced and enforced at multiple levels, every
day. Section 1.4 contains additional information about entraNET
security features.
License-Free
Operation
The transceivers are designed for frequency-hopping spread-spectrum
operation in the license-free 900 MHz or 2400 MHz band. They can
provide reliable long distance communications over line-of-sight signal
paths.
Multiple Services Networks can include a mixture of equipment requiring Ethernet and
serial data interfaces on the same cell or AP. This flexibility allows the
transceiver to provide services in data networks that are on a migration
path from legacy serial or EIA-232-based hardware to faster and more
easily interfaced Ethernet systems.
Flexible
Management
Configuration, troubleshooting and other management activities are
performed using a connected PC, locally or remotely. Modes of access
include a local RS-232 console, local or remote IP access through
Ethernet, Telnet, or a Web browser, and Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP).
Feature Summary The MDS entraNET design makes installation and configuration an
easy task, while allowing for configuration changes in the future.
• Long-ra nge transmission over favorable, unobstructed terrain, with
sufficient antenna heights
• Low power consumption—Sleep and Shutdown modes to enable
solar-powered operation
• Repeater configurations—A repeater scheme can be established to
extend the transmission range or to work around obstructions in a
network. This is accomplished by connecting two radios back to
back at a single site.
• Industrial-grade product—Extended temperature range for
trouble-free operation in extreme environments
• Robust radio communications—Designed to perform in
high-interference environments
• GE MDS Security Suite—Blocks common attack schemes and
prevents “rogue” hardware from gaining access to or control of a
network. Common attack events are logged and reported using
alarms.
• Fast, 106 kbps data speed—Ten times faster than 9.6 kbps radios
• Simple setup—Ethernet bridge configuration option requires
minimal setup
• Serial ports—Gateway for serial interface equipment to IP or
Ethernet networks with an embedded terminal server
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 5
Page 16

1.2.1 Model Offe rings
The MDS entraNET system includes two primary radio types— APs
and Remotes. Table 1-1 summarizes the interface capabilities for each
entraNET radio type.
NOTE: A Remote can serve multiple endpoint MAC addresses if the
Remote is provided an authorization code.
Table 1-1. MDS entraNET Models and Data Interface Services
Model LAN/ETH
AP LAN Yes Yes
Remote ETH Yes Yes
NOTES
*This connector provides access to the radio menu system.
COM1
*
COM2
1.3 APPLICATIONS
The following sections describe typical entraNET installations. All
installations should be reviewed by a network manager to ensure proper
integration with existing equipment.
1.3.1 Long-Range Wireless LAN
The wireless LAN is a common application of the entraNET system. It
consists of a central control station (AP) and one or more associated
Remote radios, as shown in Figure 1-2 on Page 7. A LAN provides
communications between a central LAN/WAN and remote Ethernet
endpoints. Remote radios can support multiple Ethernet endpoints if the
Remote is provided an authorization code.
The operation of the radio system is transparent to the computer
equipment connected to it. As such, the system behaves just as it would
in a hardwired arrangement, with respect to data format and integrity.
Over-the-air messages are exchanged at the Ethernet level, including all
types of IP traffic.
Antenna Placement
The AP antenna is positioned at a location from which it can reliably
communicate with all of the Remote radios in the system. Commonly,
this is a relatively high location on top of a building, communications
tower or other elevated point.
Communication Rules
• A Remote transceiver can only talk over-the-air to an AP.
• Peer-to-peer communications between Remotes can take place
6 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
indirectly through the AP.
Page 17
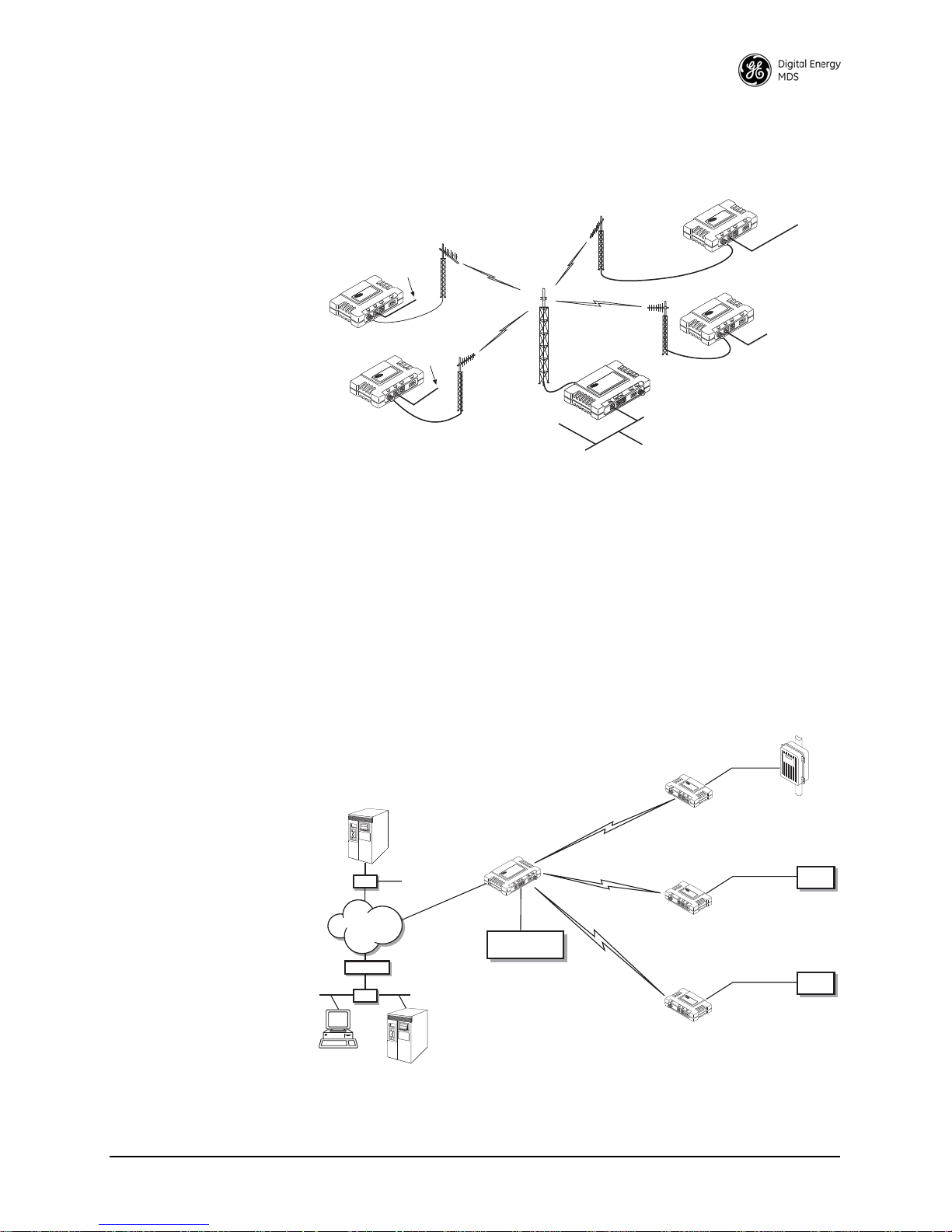
• An AP can only talk over-the-air to Remote radios; however, two
Remote
Remote
Access Point
Remote
Remote
WAN/LAN
Ethernet
Device
Ethernet
Device
LINK
ETH
COM1
PWR
LINK
ETH
COM1
PWR
Ethernet
Device
LINK
ETH
COM1
PWR
LINK
ETH
COM1
PWR
Ethernet
Device
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
PC Running
NetView
SCADA Host
Total Flow
Access Point
Remote
SCADA Host
Modbus/IP
Serial Polling
Converter
Remote
Remote
RTU
EIA-232
EIA-232
TCP/IP
C
O
M
2
P
W
R
L
I
N
K
C
O
M
1
C
O
M
2
P
W
R
L
I
N
K
C
O
M
1
C
O
M
2
P
W
R
L
I
N
K
C
O
M
1
HUB
Serial
Device
HUB
HUB
WAN
Ethernet
Device
ROUTER
HUB
L
A
N
C
O
M
1
C
O
M
2
P
W
R
L
IN
K
APs can communicate with each other through their Ethernet
connectors when a wired LAN/WAN is utilized.
Invisible place holder
Figure 1-2. Typical Wireless LAN System
1.3.2 Combining Serial and Ethernet Devices
Prior to the introduction of the entraNET series, multiple networks were
often needed to service different types of communication protocols. An
entraNET system provides this functionality through a single AP radio.
Each of the Remote radios in a system can be connected via IP to
different SCADA or telemetry hosts, transporting different (or the same)
protocols. Both data streams are completely independent, and the
transceiver provides seamless, simultaneous operation, as shown in
Figure 1-3.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 7
Invisible place holder
Figure 1-3. Multiple Protocol Network
Page 18

By using a single AP , the cost of infrastructure deployment is cut in half,
with only one antenna, one feedline, and one lightning protector
required. Other cost reductions come from the system as a whole,
including reduced management requirements when using GE
MDS NETview Management System (MS) software. In addition,
entraNET offers nearly unlimited potential for future applications that
run over IP and Ethernet services.
In an IP-to-serial scenario, every Remote is sent information received by
the AP Ethernet port. Likewise, information received at the Remote
serial port is transmitted to the AP, and the AP delivers this information
through its Ethernet port in the form of an IP packet.
Additionally, the AP serial port can be used as a virtual Remote. This
means that encapsulated serial information received by the AP is sent
out the serial port of all Remotes as well as the AP serial port. The
reverse is also true, meaning that data received by the serial port of any
Remote or the AP serial port is encapsulated and sent out the AP
Ethernet port.
This arrangement can be used to connect an endpoint device at a
Repeater site without the need for an additional Remote radio.
1.3.3 DNP3 Protocol-Aware Networks
The GE MDS implementation of Distributed Network Protocol 3
(DNP3) allows the transfer and routing of DNP3 messages between
serial devices, while also supporting the conversion to an IP Ethernet
network. As DNP3 messages are routed through the system, the APs
“learn” the locations of all end devices, regardless of whether they are
configured for serial or Ethernet communication, eliminating the need
to configure their individual locations.
DNP3 devices with an Ethernet or IP interface can be connected to a
transceiver in one of two ways:
• To the Ethernet port of an AP radio
• To the Ethernet port of a Remote radio
DNP3 devices with a serial RS-232 interface can be connected to a
transceiver in one of two ways:
• To the serial port of an AP radio
• To the serial port of a Remote radio
The capability for DNP3 message routing is optional for the transceiver .
An Authorization Key is required to enable this functionality, and is
available for purchase from GE MDS.
8 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 19

NOTE: Detailed information on the DNP3 protocol is available on the
DNP Users’ Group Web site at www.dnp.org.
1.3.4 Upgrading an Older Wireless Network with
Serial Interfaces
Millions of wireless data products have been sold in the last two decades
for licensed and license-free operation, many of them manufactured by
GE MDS. There are several ways that these systems can benefit from
employing MDS entraNET wireless equipment, including flexible serial
and Ethernet interfaces, higher data throughput, and ease of installation.
MDS entraNET radios are well suited to replace leased lines, dial-up
lines, or existing data radios by taking advantage of the built-in serial
and Ethernet interfaces on the transceiver. The sections below discuss
two common scenarios.
Replacing Legacy Wireless Products
In most cases, legacy radio transceivers supporting serial interface
equipment can be replace d wit h M DS en traN ET r adios with l ittl e or no
special configuration. This equipment can be connected to MDS
entraNET radios through the COM1 or COM2 port with a DB-25 to RJ-45
cable wired for EIA-232 signaling. The COM2 port supports standard
EIA-232 signaling and acts as a data communications equipment (DCE)
device.
NOTE: Several previous GE MDS-brand products contained signal
lines on their interface connectors that are not used or required
on entraNET radios. Consult the equipment manual(s) for
interface pinout information, and connect only the required
pins.
Supplementing a Legacy Wireless Network with IP Services
MDS entraNET Remotes support most polled protocols. The serial
interfaces encapsulate serial data in two different modes: connectionless
(User Datagram Protocol, or UDP) and connection-oriented
(Transmission Control Protocol, or TCP).
For complete details on serial gateway interface modes, see
“CONFIGURING THE SERIAL INTERFACES” on Page 54.
1.3.5 P22 Protected Network (Redundant)
Configuration
For mission-critical applications, GE MDS offers the Prote cted Network
Station. This radio incorporates two entraNET AP transceivers, two
power supplies, and a switchover logic board that automatically selects
between Transceiver A and Transceiver B as the active radio. Figure 1-4
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 9
Page 20

shows a view of the protected chassis. For system-level information on
this product, see GE MDS publication 05-4161A01.
Invisible place holder
Figure 1-4. GE MDS P22 Protected Network Station
(incorporates two MDS entraNET APs)
1.4 GE MDS SECURITY SUITE
Today, the operation and management of an enterprise is becoming
increasingly dependent on electronic information flow. An
accompanying concern becomes the security of the communication
infrastructure and the security of the data itself.
The MDS entraNET is capable of dealing with many common security
issues. Table 1-2 profiles security risks and how the MDS entraNET
provides a solution for minimizing vulnerability.
Table 1-2. Security Risk Management
Security Risk The MDS entraNET Solution
Unauthorized access to the backbone
network through a foreign remote radio
“Rogue” AP, where a foreign AP takes
control of some or all Remote radios and
thus remote devices
“Dictionary attacks”, where an intruder
runs a program that sequentially tries to
break a password
Approved Remotes List
Only radios on the Approved
Remotes list connect
Approved AP List
A Remote connects onl y to APs on
its Approved AP List
Failed log-in lockdown
After three tries, a transceiver
ignores log-in requests for 5 min.
Critical event reports (traps) are
generated as well.
10 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 21

Table 1-2. Security Risk Management
Security Risk The MDS entraNET Solution
Denial of service, where Remote radios
could be reconfigured with bad
parameters, bringing the network down
Remote log-in
Local console log-in
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer
Protocol) and Telnet disabled,
enabling only local management
services
Airsnort and other war-drivin g intruders in
parking lots, near buildings, and so on
Frequency-hopping spread
spectrum (FHSS) does not talk
over the air with stan dard 802 .11 b
cards
The transceiver cannot be put in a
“promiscuous” mode
Proprietary data framing
Eavesdropping, intercepting messages
Key cracking
Replaying messages
Unprotected access to configuration using
SNMP
128-bit encryption
Automatic Key Rotation algorithm.
In addition, a Force Key Rotation
command is available to
immediately rotate the keys of the
AP and synchronize all Remotes
with it.
128-bit encryption with rotating
keys
Non-secure SNMP ve rsions can be
enabled or disabled at will.
SNMPv3 password protection
Potential, ongoing attacks
Provides early warning using
SNMP through critical event
reports of unauthorized log-in
attempts and suspicious activities
1.4.1 Intrusion Detection using SNMP Traps
In addition to the operative tools and techniques, the entraNET system
provides an SNMP-based network management system with traps
(alarms) that report suspicious activities or events. These include:
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 11
• Log-in attempt limit exceeded (accessed using HTTP)
• Successful log-in or logout (accessed using HTTP)
Page 22

1.5 ACCESSORIES
MDS entraNET transceivers may be used with the accessories listed in
Table 1-3. Contact GE MDS for ordering details.
Table 1-3. Accessories
Accessory Description GE MDS Part
AC Power
Adapter Kit
OmniDirectional
Antennas
Yagi Antenna
(Directional)
TNC Male-to-N
Female Adapter
TNC Male-to-N
Female Adapter
Cable
2-Pin Power
Plug
Ethernet RJ-45
Straight-thru
Cable (CAT5)
Ethernet RJ-45
Crossover
Cable (CAT5)
RJ-12 to DB-9
Female Adapter
RJ-45 to DB-9
Female Adapter
EIA-232
Shielded Data
Cable
Fuse Small, board-mounted fuse used to protect
A small power supply module designed for
continuous service. UL approved. Input:
120/220; Output: 13.8 Vdc at 2.5 A
Rugged antennas well suited for use at AP
installations. Ask your GE MDS Sales
Representative for details.
Rugged antennas well suited fo r use at Remote
installations. Ask your GE MDS Sales
Representative for details.
One-piece RF adaptor plug. 97-1677A161
Short length of coaxial cable used to connec t
the TNC antenna connector to a Type N
connector commonly used on large-diameter
coaxial cables.
Mates with power connector on t he transceiver.
Screw terminals are provid ed for wires; locking
screws are threaded to prevent accidental
disconnection.
Cable assembly normally used to connect an
Ethernet device o r LAN to the transcei ver. Both
ends of the cable are wired identically.
(Cable length 3 ft/1 m)
Cable assembly used to connect an AP to an
Ethernet endpoint. (Cable leng th 3 ft/1 m)
Allows access to Data Serial port COM1 on
Remotes or APs.
Allows access to Data Serial port COM2 on
Remotes or APs.
Shielded cable terminated with a DB-9 male
connector on one end, and a DB-9 female on
the other end. (Cable length 6 ft/1.8 m)
against overcurrent conditions.
No.
01-3682A02
Contact GE
MDS
Contact GE
MDS
97-1677A159
(3 ft./1m)
97-1677A160
(6 ft./1.8m)
73-1194A39
97-1870A20
97-1870A21
73-2434A02
73-2434A12
97-1971A03
29-1784A03
12 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 23

Table 1-3. Accessories
Accessory Description GE MDS Part
Flat-Surface
Mounting
Brackets and
Screws
DIN Rail
Mounting
Bracket
Ethernet Surge
Protector
Brackets: 2 in. x 3 in. plates designed to be
screwed onto the bottom of the radio for
surface-mounting the radio.
Screws: 6-32, 1/4 in. with locking adhesive.
(Industry Standard MS 51957-26)
Bracket used to attach the transceiver to
standard 35 mm DIN rails commonly found in
equipment cabinets and panels.
Protects against voltage spikes or surges on
Ethernet lines. These conditions may be
caused by nearby lightning strikes or transient
conditions.
No.
82-1753-A01
70-2620-A01
03-4124A01
(Remote)
03-4125A02
(AP)
29-4018A01
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 13
Page 24
14 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
Page 25

TABLETOP SETUP AND
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
2
2 Chapter Coun ter Reset Paragraph
2.1 INTRODUCTION 17
2.2 CONNECTOR OVERVIEW 17
2.3 TEST SETUP 18
EVALUATION
STEP 1—CONNECT THE ANTENNA PORTS................................19
STEP 2—MEASURE AND CONNECT DC POWER........................19
STEP 3—CONFIGURE THE AP ......................................................22
Log-in and Configuration ..................................................................22
Set Key AP Parameters....................................................................23
STEP 4—CONFIGURE THE REMOTE RADIO...............................24
Log-in and Configuration ..................................................................24
Set or Verify Network Address..........................................................25
STEP 5—CONNECT TERMINAL EQUIPMENT..............................26
Ethernet Device Connection to Remote...........................................26
Serial Device Connection to Remote................................................26
STEP 6—CHECK FOR NORMAL OPERATION..............................26
2.3.1 Verify Connectivity (PING command) ..........................................27
Serial Connections ...........................................................................27
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 15
Page 26

16 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
Page 27

2.1 INTRODUCTION
Prior to installation in the field, you should set up the radio system in an
office or lab and become familiar with its operation and features. This
also allows tests of various network designs and configurations prior to
arrival at a field site. A tabletop test can be performed with any number
of radios.
This section describes the hardware setup and software configuration
needed for testing an Ethernet connection. To simul ate data traffic flow
over the radio network, a PC or LAN is connected to the LAN port of the
AP and used to PING (Packet INternet Groper) a device connected to
the Remote transceiver.
NOTE: It is important to use a radio system network address and
device IP address that are different from any radios currently
in use in your region or network. This greatly reduces the
possibility of disruption to traffic on existing systems during
testing.
A recommended technique for minimizing the chance of radio
network address conflicts is to use the last four digits of the AP
serial number.
2.2 CONNECTOR OVERVIEW
The following illustrations show all of the interface connectors present
on entraNET transceivers. Review these items when making the
connections described in this section.
Figure 2-1 on Page 18 shows the interface connectors for the AP
transceiver.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 17
Page 28
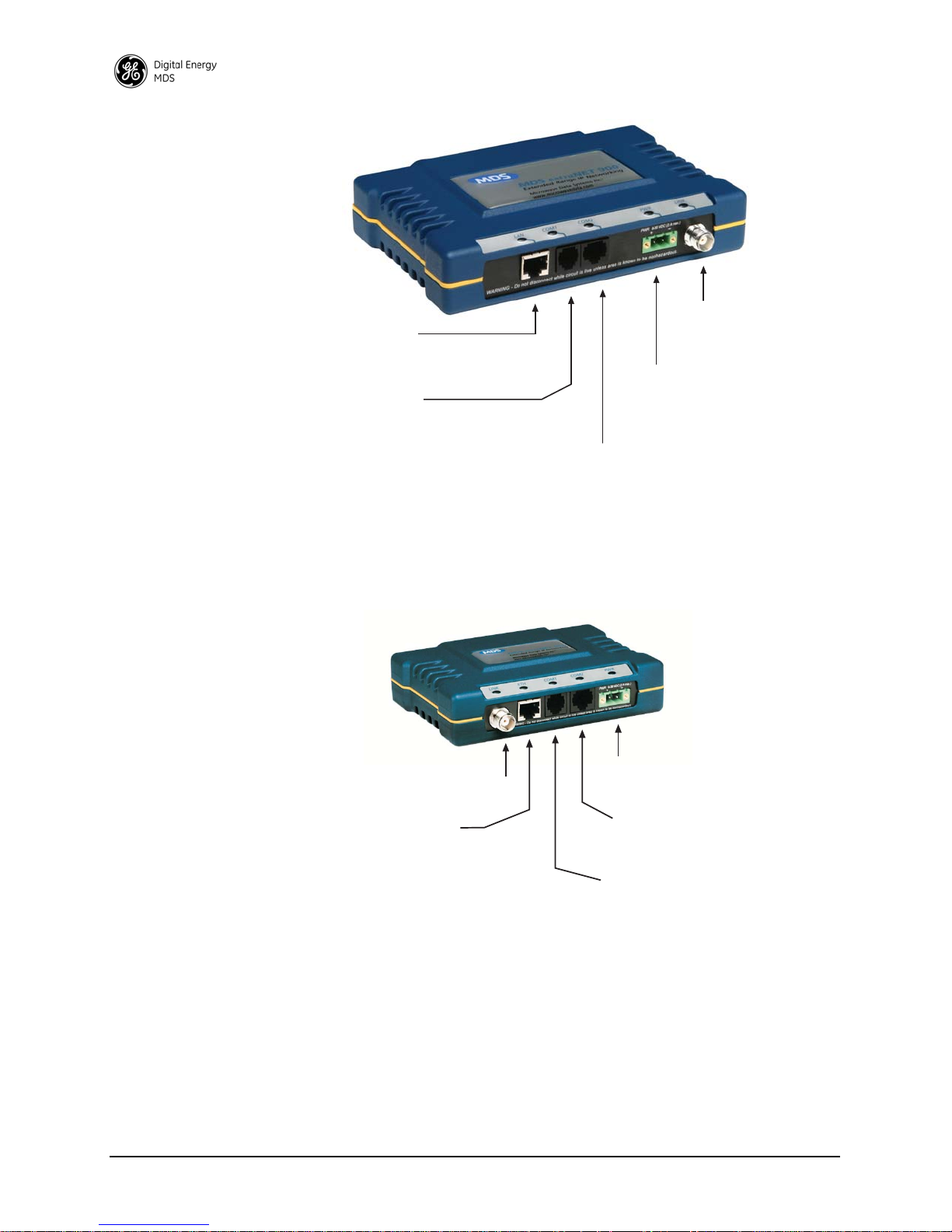
Invisible place holder
COM1
◆DCE (Console/Terminal only)
◆ 19,200 bps/8N1
◆No Handshaking
◆ RS/EIA-232
COM2
◆ DCE (Connects to serial data equip.)
◆ 9,600 bps/8N1
◆ Full Handshaking
◆ RS/EIA-232
PRIMARY POWER
◆ 6–30 Vdc
(800 ma @ 13.8 Vdc)
◆ Negative Ground
ANTENNA
◆ 50Ω TNC
◆ +30 dBm/1W Out (Max.)
◆ –30 dBm Input (Max.)
LAN
◆10-Base-T
◆ IP/Ethernet Port
◆IP Address: 192.168.0.1
COM1
◆DCE (Console/Terminal only)
◆ 19,200 bps/8N1
◆No Handshaking
◆ RS/EIA-232
PRIMARY POWER
◆ 6–30 Vdc
(600 ma @ 13.8 Vdc)
◆ Negative Ground
ANTENNA
◆ 50Ω TNC
◆ +30 dBm/1W Out (Max.)
◆ –30 dBm Input (Max.)
LAN
◆10-Base-T
◆ IP/Ethernet Port
◆No IP Address–Endpoint
Bridge Only
COM2
◆DCE (Connects to serial data equip.)
◆ 115,200 bps/8N1
◆Full Handshaking
◆ RS/EIA-232
Figure 2-1. AP Interface Connectors
Figure 2-2 shows the interface connectors for the Remote transceiver.
Invisible place holder
Figure 2-2. Remote Interface Connectors
Invisible place holder
2.3 TEST SETUP
18 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
The following steps explain how to make connections to the transceiver
system, power it up, and set basic configuration. After these steps are
complete, the system is ready for field installation.
Page 29
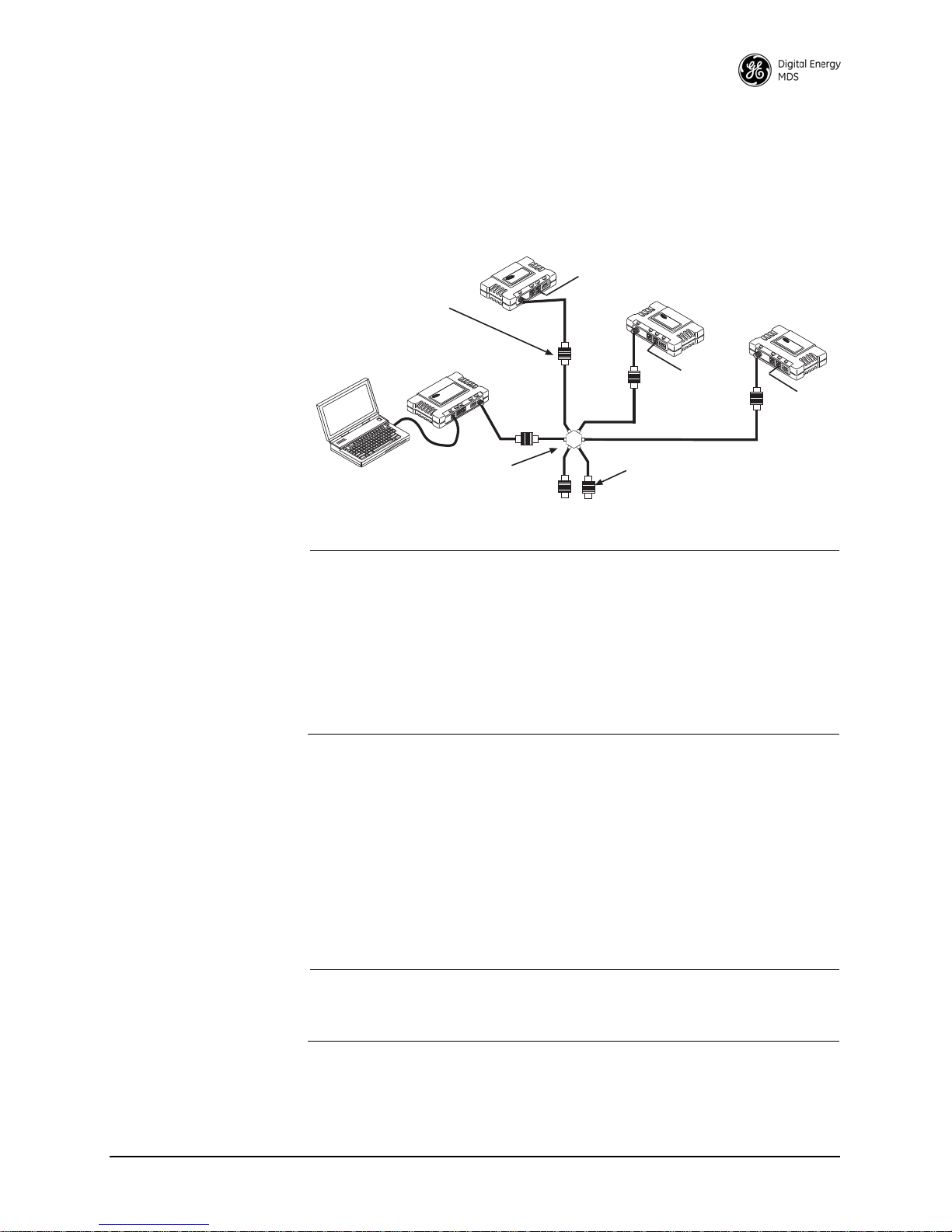
STEP 1—CONNECT THE ANTENNA PORTS
POWER ATTENUATORS
Fixed or adjustable
1W Minimum Rating
POWER DIVIDER
NON-RADIATING ATTENUATORS
Install on unused divider ports (if any)
1W Minimum Rating
COMPUTER
COM
2
PW
R
L
IN
K
C
OM1
C
O
M2
PWR
L
IN
K
COM1
L
IN
K
C
O
M
2
C
O
M1
P
W
R
Remote
Remote
Access Point
Remote
L
A
N
C
O
M
1
C
O
M
2
P
W
R
L
IN
K
Figure 2-3 is a drawi ng of a tabletop arrangement. Connect the antenna
ports of each transceiver as shown through attenuators and an RF power
divider. This provides for stable communications between each radio,
while preventing interference to nearby electronic equipment.
Invisible place holder
Figure 2-3. Typical Setup for Tabletop Radio Testing
NOTE: It is very important to use attenuation between radios in the test
setup. The amount of attenuation required depends on the
number of radios being tested and the desired signal strength
(Received Signal Strength Indicator, or RSSI) at each
transceiver during the test. In no case should a signal greater
than –30 dBm be applied to any transceiver in the test setup. A
transmit RF power output level of +20 dBm (100 mW) is
recommended. This can be set via the radio menu (Main Menu >
Radio Configuration > RF Output Power Setpoint).
STEP 2—MEASURE AND CONNECT DC POWER
The power applied to transceivers (AP and Remotes) must be within
6–30 Vdc and be capable of continuously providing a minimum of 11 W
(typical power consumption is 800 mA at 13.8 Vdc for the AP and
600 mA at 13.8 Vdc for Remotes).
A power connector with screw terminals is provided with each radio.
Strip the wire leads to 6 mm (0.25 in.). Observe proper polarity, as
shown in Figure 2-4 on Page 20, with the positive lead (+) on the left.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 19
NOTE: It takes about 30 sec for the AP transceiver to power up and be
ready for operation. The Remote requires approximately 5 sec
to power up.
Page 30

Invisible place holder
Wire Ports
Lead
Screws (2)
Binding
POSSIBLE
EQUIPMENT
DAMAGE
CAUTION
POSSIBLE
EQUIPMENT
DAMAGE
Figure 2-4. Power Connector
(polarity: left +, right –)
The transceiver must be used only with negative-ground systems. Make sure the polarity of the
power source is correct. The radio is protected from
reverse polarity by an inte rnal diode an d an on-boar d
fuse.
Power Supply
Connections at
28 Vdc
Common 28 Vdc supplies are often high-current power supplies
designed primarily to charge battery banks. The radio can be operated
from these supplies, providing there are no transients on the leads as
power is applied to the radio. Transients can be created that rise above
30 Vdc to a voltage that exceeds the primary voltage rating of the radio
and can destroy its voltage regulators and other components. It is
important to keep this potential hazard in mind when designing 28 Vdc
power supply connections for the radio.
• Use a two-conductor cable to power to the radio. Then the
currents in the positive and negative wires are equal and
opposite, causing their magnetic fields to cancel. The result is
no net inductance in the connection to cause voltage overshoot.
• Do not connect a radio to a power supply that is already
powered up, unless necessary (that is, when connecting a radio
to a battery bank and charger). When power is applied by
switching on a power supply, the rise time of the supply is too
slow to cause overshoot.
• Typically, there are multiple return paths for the negative side
of the power supply, through the coaxial cable shield and the
chassis, for example. Any imbalance in the currents in the
power cable results in voltage overshoot, so this should be
minimized during initial power-up if the supply cannot be
turned off.
• Add a 1 to 2 , 2 W resistor in series with the positive lead. This
greatly limits voltage overshoot. Since these radios draw very
little current in receive mode , and transmit only briefly, there i s
little loss in power efficiency. In transmit, the voltage drop is
minimal and has no effect.
20 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 31

• Minimize the length of the power cabling, within reason.
• When power is applied from a power source having a relatively
high (1 or 2 ) source impedance, or from a power source
without a large amount of output capacitance, no overshoot
occurs. Therefore, use a power supply that is rated appropriately
for the radio if possible—avoid using power supplies that far
exceed the radio’s current requirements.
Direct any questions you may have about interfacing to GE MDS radios
to GE MDS Technical Services at gemds.techsupport@ge.com, or
telephone +1-585-241-5510.
STEP 3—CONFIGURE THE AP
The instructions below summarize essential AP settings for tabletop
testing. For detailed AP log-in and menu navigation instructions, see
ACCESSING THE MENU SYSTEM on Page 36.
Log-in and Configuration
The AP must be configured first, as Remote transceivers depend on the
AP beacon signal to achieve a connected (linked) state. Figure 2-5
shows the basic setup for configuring an AP with a personal computer.
Invisible place holder
Console Terminal
Connection
(recommended for
first-time log-in)
To configure the AP using a console terminal:
1. Connect a PC to the COM1 port on the radio.
2. Establish a terminal session (using HyperTerminal, for example)
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 21
Figure 2-5. AP Configuration Setup
using the following data parameters:
• 19200 bps
•8 bits
• no parity
• one stop bit (8N1)
• hardware flow control disabled
• VT100 emulation
Page 32

NOTE: The exact parameters given above must be used for console
ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
terminal communication. Improper settings are a common
cause of difficulty.
Telnet Connection
Using the AP LAN
Port (a valid IP
address must be set)
To configure the AP using its LAN port:
1. Connect a PC Ethernet port to the AP with an Ethernet crossover
cable.
NOTE: The radio must first have a valid IP address programmed—the
default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
2. Log in to the AP as follows:
a. Press the key to receive the login prompt. The COM1/LAN
LED flashes to indicate data communications.
a. At the login prompt, enter the username (admin is the default
username). Press .
b. At the Password prompt, enter the password (admin is the default
password). Press . Upon successful log-in, the Starting
Information Screen appears.
3. Review the current menu settings and make any necessary changes.
Refer to Set Key AP Parameters on Page 22 for configuration guidance.
4. Repeat Steps 1 through 3 for any other AP radios in your system.
NOTE: You can save time by using configuration scripts to uniformly
configure multiple transceivers. This technique is discussed in
the Configuration Scripts Menu on Page 87.
Set Key AP Parameters
Table 2-1 provides a listing of key AP operating parameters, their
default settings, and their values or range. Typically, these are the only
settings that need to be set or reviewed for a basic check of the radio
system. A complete list of AP commands appears in CHAPTER 3 AP
MANAGEMENT, beginning on Page 29.
22 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 33

Table 2-1. Key AP Parameters and Defaults
Menu Item Management System Loca-
IP Address Main Menu >> Network
IP Address
Mode
IP Netmask Main Menu >>
Net Address Main Menu >>
RF Output
Power
(non-ETSI)
RF Output
Power (ETSI)
Password
Changes
* We recommend setting Net Address to the last four digits of the AP serial number to reduce the chance of conflict
with other nearby entraNET systems.
tion
Configuration > IP
Configuration
Main Menu >> Network
Configuration > IP
Configuration
Network Conf iguration > IP
Configuration
Network Conf iguration >
Wireless MAC Configuration
Main Menu >>
Radio Configuration >
Main Menu >>
Radio Configuration > 2.4 GHz: 20 dBm 2.4 GHz: 10-20 dBm
Main Menu >>
Security Configuration >
User Passwords
Default Values or Range
192.168.1.1 Contact your Network
Static Static | Dynamic
255.255.0.0 Settable per customer
9999 1-15 alphanumeric characters*
900 MHz: 30 dBm
2.4 GHz: 27 dBm
Administrator Password:
admin (lower case)
Guest Password:
guest (lower case)
Administrator.
If IP Addr ess Mode (bel ow) is s et
to Dynamic, IP Address is
configured automatically.
requirements
900 MHz: 20–30 dBm
2.4 GHz: 17-27 dBm
•1–8 alphanumeric characters
•Passwords are case sensitive;
can be mixed case
STEP 4—CONFIGURE THE REMOTE RADIO
The instructions below summarize essential Remote settings for
tabletop testing. For detailed log-in and menu navigation instructions,
see CHAPTER 4 REMOTE RADIO MANAGEMENT, beginning on
Page 99.
Log-in and Configuration
Prepare the Remote for configuration as follows:
1. Connect a PC to the
COM1 port on the radio.
2. Establish a terminal session (using HyperTerminal, for example)
using the following data parameters:
• 19200 bps
• 8 bits
• no parity
• one stop bit (8N1)
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 23
Page 34

• hardware flow control disabled
ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
• VT100 emulation
NOTE: The exact parameters given above must be used for console
terminal communication. Improper settings are a common
cause of difficulty.
Invisible place holder
Invisible place holder
Invisible place holder
Invisible place holder
Invisible place holder
Figure 2-6. Remote Configuration Setup
3. Press several times to receive the entranet> prompt (the
COM1/ETH LED blinks to indicate data communication).
4. At the entranet> prompt, enter login. Press .
5. At the next prompt, enter the username (the default username is
admin). Press .
6. At the next prompt, enter the password (the default password is
admin). Press . The radio is now ready to accept commands.
Set or Verify Network Address
The only setting normally required for initial checkout of a Remote
radio is the network address. All radios in a given network must be
programmed with the same network address as the AP, or
communication is impossible. Follow the steps below to check the
address, and program a new one if necessary.
1. Enter the RADIO NETADDR= command. This displays the currently
programmed network address.
2. If changes are required, enter the
RADIO NETADDR=<net a ddr> com-
mand, where <netaddr> is 1 to 15 alphanumeric characters (the network address of the Remote radio must match that of the AP).
3. Verify that the
24 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
LINK LED lights to indicate successful connection
with the AP (it might take several seconds for the LED to light).
Page 35

4. Repeat S teps 1 through 3 for each Remote radio to be installed in the
network.
This concludes the basic setup of a Remote radio. A full listing of
Remote programming commands is given in CHAPTER 4 REMOTE
RADIO MANAGEMENT, beginning on Page 99.
With all radios connected, you are ready to connect data devices to the
transceivers so that their operation can be tested over the wireless
network. This is discussed in the next step.
STEP 5—CONNECT TERMINAL EQUIPMENT
This step describes connection of external data equipment to the Remote
radio. V erify that your transceiver is capable of supporting your devices.
See Table 1-1 on Page 6 for a summary of model capabilities.
Be sure not to overload the radio network with high-bandwidth LAN
traffic during this test. Refer to the Bridge Configuration Menu on
Page 51 for more information.
Ethernet Device Connection to Remote
NOTE: Verify that the Remote ETH port is enabled (on) using the ETH
command. If it is not, use the ETH=ON command to enable the
port.
Connect an Ethernet endpoint to the Remote ETH port. The ETH port
supports any Ethernet-compatible device. This includes a device that
uses Internet Protocol (IP).
Serial Device Connection to Remote
Connect a serial device to the Remote
COM2 port and verify that the port
settings are compatible with the connected device (baud rate, data
format, and so on).
STEP 6—CHECK FOR NORMAL OPERATION
With data equipment connected, you are ready to check the transceivers
for normal operation.
Observe the transceiver LEDs on the top cover for the proper
indications. In a normally operating system, the following LED
indications should be seen within 30 sec of start-up:
• PWR—Lit continuously
• LINK—Lit continuously (unless Sleep is enabled)
• ETH—On, or blinks intermittently
• COM1/COM2—Blinks to indicate data communications
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 25
Page 36

Table 2-2 provides details on the LED functions for Remotes and AP
radios.
Table 2-2. Transceiver LED Functions
LED Label Activity Indication
LAN/ETH ON LAN or endpoint detected
Blinking Data TX or RX
OFF LAN or endpoint not detected
COM1
(MGT System)
COM2 Blinking Data TX or RX
PWR ON Primary power (DC) present
LINK (AP) ON Lights when radio has finished
LINK (Remote) ON Connected to an AP
Blinking Data TX or RX
OFF No data activity
OFF No data activity
Blinking Radio in “Alarmed” state
OFF Primary power (DC) absent
its startup cycle. Remains lit.
OFF Not connected to an AP
2.3.1 Verify Connectivity (PING command)
If the radio LEDs indicate that the radio network is operating properly,
you can use the PING command from the AP to verify the link integrity
between the AP and an endpoint device connected to the Remote radio.
Figure 2-7 shows the typical arrangement for this test.
NOTE: To conduct a PING test, an Ethernet-enabled device must be
connected to the Remote, and it must have a compatible IP
address. Remote radios do not have an IP address and cannot
be verified directly using this method.
26 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Figure 2-7. PING Test Setup
(to test connectivity between an AP and an Ethernet endpoint )
Page 37

Serial Connections
To check a serial connection, refer to Local Serial Configuration Menu
on Page 57. This section contains details on establishing an IP-to-serial
or serial-to-serial connection.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 27
Page 38

28 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
Page 39

AP MANAGEMENT
LAN
COM1
COM2
PWR
LINK
3
3 Chapter Coun ter Reset Paragraph
3.1 INTRODUCTION 31
3.1.1 PC-Based Configuration Software ..............................................31
3.1.2 Menu Structure ............................................................................32
3.1.3 Differences in the User Interfaces ...............................................35
3.2 ACCESSING THE MENU SYSTEM 36
3.2.1 Methods of Control ......................................................................36
3.2.2 PC Connection and Log-In Procedures ......................................37
3.2.3 Navigating the Menus .................................................................42
Navigating via Terminal or Telnet Sessions
Recommended for first-time users ...................................................42
Navigating via a Web Browser..........................................................42
3.3 BASIC DEVICE INFORMATION 43
3.3.1 Starting Information Screen .........................................................43
3.3.2 Main Menu ..................................................................................44
3.4 CONFIGURING NETWORK PARAMETERS 45
3.4.1 Network Configuration Menu .......................................................45
3.4.2 IP Configuration Menu ................................................................46
3.4.3 Wireless MAC Configuration Menu .............................................48
3.4.4 Mobility Configuration Menu ........................................................49
3.4.5 SNMP Agent Configuration Menu ...............................................50
3.4.6 Bridge Configuration Menu .........................................................51
3.5 CONFIGURING RADIO PARAMETERS 52
3.5.1 Radio Configuration Menu ..........................................................52
Skip Zones Menu..............................................................................53
3.6 CONFIGURING THE SERIAL INTERFACES 54
3.6.1 Overview .....................................................................................54
Serial-to-Serial Services ......................................................... ...... ....55
IP-to-Serial Services.........................................................................55
Configuration ....................................................................................56
Serial Configuration Wizard..............................................................56
3.6.2 Local Serial Configuration Menu .................................................57
View Current Settings Screen—Serial-to-Serial Example................59
View Current Settings Screen—Unicast UDP Mode Example .........61
3.6.3 Remote Serial Gateway Configuration (IP-to-Remote Serial) .....62
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 29
Page 40

3.7 SECURITY CONFIGURATION 64
3.7.1 Security Configuration Menu .......................................................65
3.8 WIRELESS NETWORK MENU 69
3.8.1 Remote Management Submenu .................................................70
Manage Selected Remote Submenu
..........................................................................................................71
Broadcast Remote Reprogramming Menu
..........................................................................................................72
Remote Database Menu...................................................................74
Group Database Menu .....................................................................75
Endpoint Database Menu .................................................................75
Access Point Database Menu ..........................................................76
3.9 ST ATISTICS AND EVENT LOG 77
3.9.1 COM1 and COM2 Data Statistics Menus ...................................78
3.9.2 Remote Serial Gateway Statistics ...............................................79
3.9.3 Ethernet and Wireless Packet Statistics ......................................80
Ethernet Packet Statistics.................................................................80
Wireless Packet Statistics.................................................................80
3.9.4 Radio Packet Statistics ................................................................81
3.9.5 Event Log Menu ..........................................................................82
Time and Date Stamping..................................................................82
3.10 DEVICE INFORMATI ON MENU 84
Device Names Menu ........................................................................85
3.11 MAINTENANCE AND TOOLS 85
3.11.1 Reprogramming Menu ..............................................................86
3.11.2 Configuration Scripts Menu ......................................................87
A Brief Description of Configuration Files.........................................87
3.11.3 RSG Configuration Script Menu ...............................................89
3.11.4 Authorization Codes Menu .......................................................91
3.11.5 Transmitter Test Menu ..............................................................92
3.12 REDUNDANCY MENU 93
Packet Rx Errors Exceeded Threshold Menu ..................................96
3.13 DNP3 ROUTING MENU 97
30 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 41

3.1 INTRODUCTION
The GE MDS entraNET AP embedded Management System (MS) is
accessible through various data interfaces. These include the COM1
(
serial) port, LAN (Ethernet) port, and SNMP. Essentially the same
capabilities are available through any of these paths.
For SNMP management, the transceiver is compatible with GE MDS
NETview MS™ software. Refer to GE MDS publication 05-2973A01
for more information on this product. For support of other SNMP
software, a set of MIB files is available for download from the GE MDS
Web site at www.gemds.com.
The entraNET MS has the following functions:
• 3.4 CONFIGURING NETWORK PARAMETERS (beginning
on page 45)
• 3.5 CONFIGURING RADIO PARAMETERS (beginning on
page 52)
• 3.6 CONFIGURING THE SERIAL INTERFACES (beginning
on page 54)
• 3.7 SECURITY CONFIGURATION (beginning on page 64)
• 3.8 WIRELESS NETWORK MENU (beginning on page 69)
• 3.9 STATISTICS AND EVENT LOG (beginning on page 77)
• 3.10 DEVICE INFORMATION MENU (beginning on page 84)
• 3.11 MAINTENANCE AND TOOLS (beginning on page 85)
• 3.12 REDUNDANCY MENU (beginning on page 93)
• 3.13 DNP3 ROUTING MENU (beginning on page 97)
Each of these sections has a focus that is reflected in its heading. The
section you are now reading provides you with information on
connecting to the AP, how to navigate through its menus, and how to
perform some top-level configuration tasks.
3.1.1 PC-Based Configuration Software
The GE MDS Remote Access Manager Application (Part Number
06-4490A01) makes it possible to authenticate all Access Points and
associated Remotes from a PC, without having to update individual
radios. The software maintains a Master Approved Remotes List, and al l
participating access points are synchronized with this list. Contact GE
MDS for more information.
NOTE: If a PC is connected to a Remote radio while the Remote is
asleep, the PC does not enable its Ethernet adapter, as it
believes the port is disconnected. Also, if a PC is connected to
a Remote and the radio goes to sleep, the PC goes into a “port
disconnected” state. The PC must be properly configured to
avoid these scenarios.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 31
Page 42

The commands for Remote radios are presented separately in
CHAPTER 4 REMOTE RADIO MANAGEMENT, beginning on Page
99.
NOTE: Any parameter options, ranges, or default values are displayed
at the end of the field description between square brackets. The
default value is always shown last in a series of items. For
example:
[Range, Options or Description; Default]
3.1.2 Menu Structure
The following illustrations (Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2) show an overall
view of the entraNET MS. Detailed information for screens and menu
items is provided on the pages that follow.
32 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 43

Figure 3-1. entraNET MS Menu Flowchart
(diagram 1 of 2)
• Spacebar used to make some menu selections
MAIN MENU—Diagram 1 of 2
Starting Information Screen (read-only items)
Radio
Configuration
RF Output
Power
Dwell Time
Contention Window
(Min.)
Contention Window
(Max.)
Repeat Count
Retry Count
Skip Zone Options
Zones 1-8
IP Address
Ethernet Address
Network
Configuration
Bridge Configuration
SNMP Configuration
Mobility Configuration
IP Configuration
Wireless MAC Config.
IP Netmask
IP Gateway
Security
Configuration
Approved Remotes
Approved Remotes List
Delete Remote
Add Remote
Add Associated
Remotes
Delete A l l
HTTP Security Mode
Encryption Enable
Encryption Phrase
HTTP Access
Forced Key Rotation
Telnet Access
User Passwords
Net Address
X Address
FEC
Remote Serial
Gateway
RSG Talkback Enable
RSG Talkback Timeout
Remote Serial Wizard
Local Serial
Configuration
Mode
Port Status
COM1/2
Serial Data Config.
Com 1/2 Serial
Data Wizard
BSP Routing Enable
IAPP Enable
Unit Update Enable
Ethernet Bridging
Bridge Priority
Bridge Hello Time
Bridge Forward Delay
Read Community
Write Community
Trap Community
v3 Auth Password
v3 Priv Password
SNMP Mode
Trap Version
Auth Trap Enable
v3 Password Mode
Trap Managers
IAPP Multicast Address
IAPP Multicast Port
IAPP Multicast TTL
IAPP Unicast Port
RSG Entries
SNMP Mode
Auto Key Rotation
Max Remotes
NOTES
• Chart shows top-level view only. The pages that follow
provide detailed screen-by-screen explanations.
• Not all items are-user configurable
• Some menu items depend on Device Mode
Various submenus/parameters,
depending on mode selected
Serial
Network
DNP3
RSG Routing (COM2 Only)
Various submenus/parameters,
depending on mode selected
Invisible place holder
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 33
Page 44

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-2. entraNET MS Menu Flowchart
(diagram 2 of 2)
• Spacebar used to make some menu selections
MAIN MENU—Chart 2 of 2
Starting Information Screen (read-only items)
COM 1/2 Data Stats
Remote Management
Wireless Network
Reprogramming
Configuration/RSG Scripts
Ping Utility
Authorization Codes
Statistics/Even t Log
Maintenance/Tools
Bytes in Port
Bytes out Port
Bytes in Socket
Bytes out Socket
Clear Statistics
Remote Serial Gateway Statistics
Device
Information
Serial Number
Uptime
Date
Date Format
Time
Model Number
Console Baud Rate
Device Names Menu
Device Name
Contact
Location
Description
UnitID
Com Port
Local IP Port
Client IP Address
State (transport, status,
client address)
Packets In
Bytes In
Bytes Out
Packets Out
Event Log
Current Alarms
View Event Log
Send Event Log
TFTP Host Address
TFTP Host Filename
TFTP Timeout
Syslog Server
Ethernet Packet Statistics/
Radio Packet Statistics
Packets Received
Lost Carrier Detected
Receive Errors
Packets Dropped
Bytes Sent
Bytes Receive d
Packets Sent
TFTP Host Address
Filename
TFTP Timeout
Retrieve File
Image Verify
Image Copy
Reboot Device
Current Firmware
Host Address
Filename
TFTP Timeout
Retrieve File
Send File
IP Address
Count
Packet Size
Execute Ping
Authorization Key
Authorized Features
DNP3 Routing
DNP Multicast Address
DNP Multic ast Port
DNP Unicast Port
DNP Routing Enable
DNP Routing Database
Redundancy
Network Event Triggers
Hardware Event Triggers
Redundancy Config. Options
Redundancy Configuration
Force Switchover
Database Tim eou t
Max Remotes
Remote Database
Remote to Manage
Manage Selected Remote
Bdcst. Rem. Reprogramming
Endpoint Database
Access Point Database
Endpoint Logging
NOTES
• Chart shows top-level view only. The pages that follow
provide detail ed sc reen-by-screen explanations.
• Not all items are-user configurable
• Some menu items depend on Device Mode
(Ethernet Only)
Transmitter Test
Frequency
Duration
Tx Key
Group Database
34 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 45

3.1.3 Differences in the User Interfaces
There are slight differences in navigation between Telnet, terminal, and
Web interfaces. Generally, the screen content is the same. There are
minor differences in capabilities from limita tions of the access channel.
Below are samples of the S tarting Information Scr een as seen through a
terminal session and a Web browser.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-3. View of entraNET MS Using a Terminal Session
(a Telnet session is similar)
Invisible place holder
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 35
Figure 3-4. View of the entraNET MS from a Web Browser
Page 46

3.2 ACCESSING THE MENU SYSTEM
The radio has no external controls. All configuration, diagnostics and
control is performed electronically using a connected PC. This section
explains how to connect a PC, log in to the radio, and access the built-in
menu screens.
3.2.1 Methods of Control
The radio configuration menus may be accessed in several ways:
• Local Console—This is the primary method used for the
examples in this manual. Connect a PC directly to the COM 1
port on the radio using a serial communications cable and
launch a terminal communications program such as
HyperTerminal. This method provides text-based access to the
radio menu. Console control is a hardware-based technique, and
is intended for local use only.
• Telnet*—Connect a PC to the
directly or over a network, and launch a Telnet session. This
method provides text-based access to the radio menu, similar to
a Local Console session. Telnet sessions may be run locally or
remotely through an IP connection.
• Web Browser*—Connect a PC to the
either directly or over a network, and open a Web browser
(Internet Explorer, Netscape, and so on). This method provides
a graphical representation of each screen, just as you see when
viewing an Internet Web site. The menu screens look a little
different from other methods of control, but the content and
organization of screen items is similar. Web browser sessions
may be run locally or remotely over the Internet.
LAN port on the radio, either
LAN port on the radio,
* Telnet and Web browser sessions require the use of a straight-through or Ethernet crossover
36 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
cable, depending on the whether the PC-to-radio connection is made directly or through an
Ethernet switch or hub. For direct connection, a crossover cable is required; for connection
via a switch or hub, a straight-through cable is needed.
To identify the cable type, hold the two cable ends side by side and in the same plug
orientation (that is, both locking tabs are up or down). Now look at the individual wire colors
on each plug. If the wires on both plugs are ordered in the same sequence from left to right,
the cable is a straight-through type. If they are not in the same order, it may be a crossover
cable, or it may be wired for some other application. Refer to DATA INTERFACE
CONNECTORS on Page 187 for detailed pinout information.
Page 47

3.2.2 PC Connection and Log-In Procedures
Configuration PC
To COM1 or LAN Port
(See T e xt)
Serial or Ethernet
Crossover Cable
(See T e xt)
The following steps describe how to access the radio menu. These steps
require a PC to be connected to the COM 1 or LAN port on the radio, as
shown in Figure 3-5.
USB
LAN
COM1
COM2
COM3
PWR
Figure 3-5. PC Configuration Setup
Starting a Local
Console Session
(recommended for
first-time users)
1. Connect a serial communications cable between the PC and the
COM 1 port on the radio. If necessary, a cable may be constructed for
this purpose, as shown in Figure 3-6.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-6. Serial Communications Cable (RJ-12 to DB-9)
(maximum recommended cable length is 50 ft/15m)
2. Launch a terminal emulation program such as HyperTerminal.
TIP: The HyperTerminal program can be accessed on most PCs by
selecting Start > Programs > Accessories > Communications
> HyperTerminal.
3. Configure the connection with the following settings:
• 19200 bps
• 8 bits
• no parity
• one stop bit (8N1)
• hardware flow control disabled
• VT100 emulation
The exact parameters given above must be used for console terminal communication. Improper settings are a common cause
of difficulty.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 37
Page 48

NOTE: If the radio is powered up or restarted while connected to a
ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
terminal, a series of pages of text relating to the startup of the
internal microcomputer is displayed. Wait fo r the log-in screen
before proceeding.
4. Press to receive the
login prompt.
5. Enter the username (the default username is admin). Press .
6. Enter your password (the default password is admin). For security,
your password keystrokes do not appear on the screen. Press .
NOTE: Passwords are case sensitive. Do not use punctuation marks.
You may use up to eight alphanumeric characters.
The Starting Information Screen is displayed (Figure 3-7). From
here, you can review basic information about the radio, or press G to
proceed to the Main Menu.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-7. Starting Information Screen—Local Console Session
Starting a Telnet
Session
NOTE: This method requires that you know the IP address of the radio
1. Connect a PC to the
38 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
beforehand. If you do not know the address, use the Local
Console method (above) and access the Starting Information
Screen. The address is displayed on this screen.
LAN port on the radio, either directly or over a
network. If connecting directly, use an Ethernet crossover cable; if
connecting over a network, use a straight-through cable. The
LAN
LED lights to indicate an active connection.
Page 49

NOTE: When using a Local Area Network (LAN) to access the radio,
ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
it may be necessary to change the computer IP access to the
LAN in order to be compatible with the entraNET radio
(compatible subnets). You can identify or verify the radio IP
address by using a Local Console session to communicate with
the entraNET radio through its COM 1 port and viewing the
Starting Information Screen.
2. Start the Telnet program on your computer, targeting the IP address
of the radio to which you are connected, and press .
TIP: A Telnet session can be started on most PCs by selecting
grams > Accessories > Command Prompt
. At the command prompt
Start > Pro-
window, enter the word telnet, followed by the radio IP address (for
example,
telnet 10.1.1.168). Press to display the Telnet log-in
screen.
NOTE: Never connect multiple radios to a network with the same IP
address. Address conflicts will result in improper operation.
3. Enter the username (the username default is admin). Press .
Next, the Password prompt appears. Enter your password (the default
password is admin). For security, your password keystrokes do not
appear on the screen. Press .
The Starting Information Screen is displayed (Figure 3-8). From
here, you can review basic information about the radio, or press G to
proceed to the Main Menu.
NOTE: Passwords are case sensitive. Do not use punctuation marks.
You may use up to eight alphanumeric characters.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 39
Page 50

Invisible place holder
ENTER
Figure 3-8. Starting Information Screen—Telnet Example
Starting a Web
Browser Session
NOTE: This method requires that you know the IP address of the radio
to which you are connecting. If you do not know the address,
start a Local Console session (see Starting a Local Console
Session (recommended for first-time users) on Page 37) and
access the Starting Information Screen. The IP address is
displayed on this screen.
1. Connect a PC to the
LAN port on the radio, either directly or over a
network. If connecting directly, use an Ethernet crossover cable; if
connecting over a network, use a straight-through cable. The LAN
LED lights to indicate an active connection.
2. Open a Web browser on your computer (for example, Internet
Explorer or Netscape Navigator).
3. Enter the radio IP address and press .
4. A log-in page i s displayed (Figure 3-1) where you enter a user name
and password to access the radio menu. The default entries are made
in lower case (default username:
admin; default password: admin).
40 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 51

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-9. Log-in Page when using a Web Browser
NOTE: Passwords are case sensitive. Do not use punctuation marks.
You may use up to eight alphanumeric characters.
5. Click OK. The radio responds with a startup menu (Figure 3-10).
From here, you can review basic information about the radio, or
click one of the menu items on the left side of the page.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-10. Starting Information Page—Web Browser Example
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 41
Page 52

3.2.3 Navigating the Menus
ESCAPE
SPACE
ENTER
SPACE
ESCAPE
Navigating Using Terminal or Telnet Sessions
Recommended for first-time users
Local console and Telnet sessions use multi-layered text menu systems
that are nearly identical.
• To select a menu item, press the letter shown at the beginning of
that item. This takes you to an associated screen where you can
view or change settings.
• To return to the previous menu (in most cases), press .
In general, the top portion of menu screens show read-only information
(with no menu selection letter). The bottom portion of the screen
contains parameters that can be selected for further information,
alteration of values, or to navigate to other submenus.
When you arrive at a screen with user-definable parameter fields:
• Press the letter shown at the beginning of the user-definable
parameter.
If there is a user-definable value, the field clears to the right of
the menu item, and you can enter the value you wish to use.
Log Out Using
Terminal Emulator
or Telnet
In some cases, when you select a parameter, you see a prompt
at the bottom of the screen that says Choose an Option. Press
to step through the available selections.
• Press to accept the displayed parameter (the one you
entered, or the one you chose by pressing ). In some
cases, several parameters may be changed and then saved with
a single keystroke.
• To cancel the parameter change, simply press to restore
the previous value.
From the Main Menu Screen, press Q to quit and terminate the session.
Navigating Using a Web Browser
Navigating with a Web browser is straightforward, with a scrollable,
clickable “page” instead of a command-line interface. The primary
navigation menu is permanently located on the left side of this page.
Click a desired menu item to display it.
NOTE: To maintain security, it is best to log out of the menu system
entirely when you are done working with it. If you do not log
out, the session automatically ends after 10 min of inactivity.
42 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 53

Log Out Using a
Web Browser
Click Logout in the left-hand frame of the browser window. The
right-hand frame changes to a log-out page. Follow the remaining
instructions on this screen.
This completes the instructions for connecting to the entraNET radio for
PC configuration and control. The next section contains detailed menu
screens and settings you can use to specify the behavior of the radio.
3.3 BASIC DEVICE INFO RMATION
3.3.1 Starting Info rm ation Scr een
Upon successful log-in to the menu system, the Starting Information
Screen appears. This screen provides a read-only overview of the
current operating conditions on the transceiver (Figure 3-11), although
some items can be changed using the Device Information Screen
described on Page 84.
Invisible place holder
NOTE: If an alarm is present when this screen is displayed, an “A”
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 43
Figure 3-11. Starting Information Screen
• Device Name—This is a user-defined name for the radio that
appears on every screen (40 characters maximum).
• IP Address—Shows the radio Internet Protocol (IP) address.
• Device Status —Shows the transceiver condition:
• Operational—The radio is operating normally
• Alarmed—An alarm event has been logged and not cleared.
appears to the left of the Device Status field. (The PWR LED
also flashes.) Typing “A” on your keyboard takes you directly
to the Current Alarms Screen.
Page 54

• Associated Remotes— Shows current number of Remote radios
associated with the AP.
• Location—User-definable string that you can use to identify the
radio location (40 characters maximum).
• Serial Number—Unique identifier for this device. It must be
provided to GE MDS when purchasing Authorization Keys to
upgrade radio capabilities. See “ Authorization Codes Menu”
on Page 91.
• Uptime—Elapsed time since the transceiver was powered up.
• Current Firmware—Version of firmware that is c urrently active in
the radio.
• Current User—Privilege level of the currently logged in user.
3.3.2 Main Menu
The Main M enu (Figure 3-12) is the entryway to all customer-definable
features. The radio
screens as a reminder of the radio that is being interrogated.
Device Name appears at the top of this and all other
Invisible place holder
44 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Figure 3-12. Main Menu
Invisible place holder
• Starting Inform ation Scre en—Select this item to return to the
Starting Information Screen. See “Starting Information
Screen” on Page 43.
• Network Configuration—Tools to configure the transceiver data
network settings. See “Network Configuration Menu” on
Page 45.
• Radio Configuration—Tools to configure the transceiver wireless
(radio) functions. See “Radio Configuration Menu” on
Page 52.
•
Local Serial Configuration—Tools to configure the AP COM1 and
COM2 serial ports. See “Local Serial Configuration Menu” on
Page 57.
Page 55

• Remote Serial Gateway—Tools to configure the data connections
to the Remote transceiver serial ports. See “Remote Serial
Gateway Configuration (IP-to-Remote Serial)” on Page 62.
• Security Configuration—Tools to configure the transceiver
security services. See “SECURITY CONFIGURATION” on
Page 64.
• Wireless Network—Tools to manage Remote and AP databases,
and manage Remote radios. See “WIRELESS NETWORK
MENU” on Page 69.
• Statistics/Event Log—Tools to measure the radio and data layer
network performance. See “STATISTICS AND EVENT LOG”
on Page 77.
• Device Information—Top-level customer-specific and definable
parameters, such as the date, time, console baud rate, and device
name information. See “DEVICE INFORMATION MENU” on
Page 84.
• Maintenance/Tools—Tools for upgrading and selecting firmware
images and configuration files, and applying Authorization
Keys to change radio capabilities. See “MAINTENANCE AND
TOOLS” on Page 85.
• Redundancy—Places the radio in a “1+1”
redundancy-compatible mode. This mode is specifically for use
with GE MDS P22 packaged model chassis. Check with your
GE MDS sales representative for available configurations.
See “REDUNDANCY MENU” on Page 93.
• DNP3 Routing—This selection provides access to a submenu
where you can manage DNP3 routing attributes. See “DNP3
ROUTING MENU” on Page 97.
3.4 CONFIGURING NETWORK
PARAMETERS
3.4.1 Network Configuration Menu
The Network Configuration Menu (Figure 3-13) is the home of all IPand Ethernet-level parameters.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 45
Page 56

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-13. Network Configuration Menu
(From Access Point)
This menu is subdivided into the following sections:
• IP Configuration—The transceiver IP address, netmask, and
gateway addresses.
• Wireless MAC Configuration—Parameters for the Media Access
Control (MAC) wireless protocol.
• Mobility Configuration—Parameters that control handoffs.
• SNMP Configuration—Details that control the operation of the
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). SNMP is used
in conjunction with GE MDS NETview MS software.
See publication 05-2973A01 for details.
• Bridge Configuration—Specialized parameters for the operation
of Ethernet bridging, including priority and forward delay
settings.
3.4.2 IP Configuration Menu
The radios use a local IP address to support remote management and
serial device services. Y ou can set the IP address of a radio as a static IP
address or as a dynamic IP address using the IP Configuration Menu
(Figure 3-14).
46 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 57

Figure 3-14. IP Configuration Menu
When static IP addressing is used, the user must manually configure the
IP address and other parameters. When dynamic addressing is used, the
radio uses a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Client
process to obtain an IP address from a DHCP Server, along with other
parameters such as a net mask and a default gateway.
CAUTION:Changing any of the following parameters while
communicating over the network (LAN or over-the-air) might
cause a loss of communication with the unit being configured.
You will need to reestablish communication using the new IP
address.
• IP Address Mode—Defines how the IP address of this device is
obtained: either statically configured, or dynamically assigned
from a DHCP server. [Static, Dynamic; Static]
• Static IP Address—(We recommend that you review this setting.)
Essential for connectivity to the tra nsceiver MS using the LAN
port, and to encapsulate serial data over an IP . Enter any valid IP
address that is unique within the network. [
192.168.1.1]
This field is unnecessary if you enable DHCP.
• Static IP Netmask—The IPv4 local subnet mask. This field is
unnecessary if DHCP is enabled. [
255.255.0.0]
• Static IP Gateway—The IPv4 address of the network gateway
device, typically a router. This field is unnecessary if DHCP is
enabled, or if all devices are on the same subnet. [
0.0.0.0]
• Current IP Address—(We recommend that you review this
setting.) Displays the IP address.
•
Current IP Netmask—Displays the IPv4 local subnet mask.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 47
Page 58

• Current IP Gateway—Displays the IPv4 address of the default
gateway device, typically a router.
NOTE: The radio is not a router, so all IP parameters access local
management only and have no effect on the routing of system
data.
3.4.3 Wireless MAC Configur ation Menu
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-15. Wireless Mac Configuration Menu
Invisible place holder
• Net(work) Address—(You must review this setting.) ID of the
network to which this radio belongs (1-15 alphanumeric
characters). An address is essential for connection of Remotes
to the AP in the entraNET network. The radio network address
is not programmed at the factory. [
9999]
• X Address—Extended Address, used for installations with
multiple APs supporting mobility. This address must be a
unique value for each AP. This parameter has no effect in single
AP networks. [0]
• FEC—Forward Error Correction status (enabled or disabled).
The FEC setting has a significant effect on the throughput or
speed of the radio network. For a discussion of this and other
issues affecting throughput, see “OPTIMIZING
PERFORMANCE” on Page 160. In particular, Table 6-7 on
Page 163 of this section shows the FEC settings and how they
relate to hop times and the bytes-per-packet rate. [Enabled,
Disabled; Disabled]
48 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 59

3.4.4 Mobili ty Configurati on Menu
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-16. Mobility Configuration Menu
Invisible place holder
• BSP Routing Enable—This parameter controls intra-cell
transmission and routing of Basic Serial Protocol
packets.[Enabled, Disabled; Disabled]
• IAPP Enable—This parameter enables the Inter-Access Point
Protocol (IAPP), which allows APs to pass payload data over
the Ethernet LAN. [Enabled, Disabled; Disabled]
• Unit Update Enable—This parameter allows the AP to
immediately send out an IAPP update when a Remote connects
or disconnects. [Enabled, Disabled; Disabled]
• IAPP Multicast Address—An address that allows multicast
messaging to reach all radios in a subnetwork (all radios with a
common network address). [
• IAPP Multicast Port—An assigned software port that allows
multicast messaging to reach all radios in a subnetwork (all
radios with a common network address). [39990]
• IAPP Multicast TTL—Multicast “time to live” number. This is the
number of hops that a message is allowed to make before it is
no longer transportable. This feature prevents “infinite life”
packets that degrade system performance. [1-15; 1]
• IAPP Unicast Port—An address that allows messaging to travel to
a specific radio when that message has originated from another
subnetwork. [39990]
224.254.1.1]
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 49
Page 60

3.4.5 SNMP Agent Configuration Menu
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-17. SNMP Agent Configuration Menu
Invisible place holder
This menu provides configuration and control of SNMP functionality.
• SNMP V3 Agent ID—The alphanumeric string that appears in the
upper right-hand corner of the screen. The entry of this string is
required in non-GE MDS SNMP manager programs (for
example, SNMPc). Refer to program documentation for details.
• SNMP Read Community—Community name with SNMP
read-level access. Any eight-character alphanumeric string.
• SNMP Write Community—Community name with SNMP
write-level access. Any eight-character alphanumeric string.
• Snmp Trap Community—Communit y name with SNMP access to
receive traps. Any eight-character alphanumeric string.
Snmp v3 Auth Password—The password used in an MD5
•
(Message-Digest algorithm 5) hash along with the message data
to create a message digest. The digest is used by the SNMP
entities to validate the source of the packet. The password can
be any alphanumeric string between eight and 30 characters in
length.
• Snmp v3 Priv Password—The privacy password stored in the
transceiver flash memory. The password is used in DES (Data
Encryption Standar d) encryption , and can be any alphanumeric
string between eight and 30 characters in length. It is used when
the SNMP Agent is managing passwords locally (or initially for
all cases on restart).
• SNMP Mode—Set or display current state of the SNMP agent.
[
Disabled, v1 only, v2 only, v3 only, v1-v2, v1-v2-v3; v1-v2-v3]
• Trap Version—Set the SNMP version for traps. [v1 Tra ps, v2 T r aps,
v3 Traps; v1 Traps]
50 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 61

• Auth Trap Enable—Current state of the authentication traps.
[Disabled/Enabled; Disabled]
• SNMP v3 Password Mode—Determines whether v3 passwords are
managed locally or using an SNMP Manager. The different
behaviors of the Agent, depending on the mode selected, are
described in SNMP Mode above. [Manager, Local; Manager]
• Trap Manager (#1–#4)— Table of up to four locations to which
traps are sent. [Any valid IP address]
3.4.6 Bridge Config uratio n Menu
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-18. Bridge Configuration Menu
Invisible place holder
• Ethernet Bridging—Select the type of Ethernet frames sent over
the air to Remote radios. [All, Disabled, No Broadcast/Multicast,
IP/ARP Only; All]
Bridge Priority—This value is used along with the MAC address
•
to define the bridge ID. The Bridge ID is used by the Spanning
Tree protocol to determine the root bridge in the network. This
value is useful for forcing a certain bridge to always be the root.
• Bridge Hello Time—Defines how often Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) are sent out by the AP.
Each bridge in the network should have the same hello time.
[Number of seconds; 2]
• Bridge Forward Delay—This value decides how long a bridge is in
the “learning” and “listening” states. Traffic begins forwarding
through the bridge after twice the Forward Delay time. [ Number
of seconds; 5
]
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 51
Page 62

3.5 CONFIGURING RADIO
PARAMETERS
There are two primary data layers in the MDS entraNET
network—radio (RF) and data. The data layer is dependent on the radio
layer to work properly. The Radio Configuration Menu is the primary
menu used to set radio parameters. This screen includes the Skip Zone
Options Submenu.
3.5.1 Radio Configuration Menu
Figure 3-19. Radio Configuration Menu
From Access Point
• RF Output Power—(We recommend that you review this setting.)
Use this selection to set the RF output level of the transceiver.
Settings are displayed in dBm, and must comply with regulatory
limitations for your area. See Table 2-1 for default settings and
range. [
20-30; 30]
• Dwell Time—Duration of one hop on a particular frequency in the
hopping pattern. This field is only changeable on an AP;
Remotes get their value from the AP upon association. Dwell
time is the same as hop time. [7, 14, 28 msec; 14 msec]
• Contention Window Min—Sets the number of random contention
slots to use on first attempt. [0-15; 2]
• Contention Window Max—Sets the maximum number of random
contention slots to use. [0-15; 10]
•
Broadcast Repeat Count—Because broadcast messages are not
acknowledged, noisy environments can prevent some Remotes
from receiving a broadcast. This parameter sets the number of
times that point-to-multipoint messages are transmitted by the
AP. Higher values increase the reliability of communications,
but also increase over-the-air congestion. [
0-14; 3]
52 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 63

• Unicast Retry Count—Sets the maximum number of attempts
SPACE
made to deliver point-to-point messages. Higher values are
more reliable, but increase over-the-air congestion. [0-14; 10]
• Skip Zones (editable at AP only)—Displays the current use of
frequency zones. Each zone consists of 16 RF channels.
See “Skip Zones Menu” on Page 53 for details.
Skip Zones Menu
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-20. Skip Zones Menu
(“Commit changes” displayed only on AP, after a change is made)
Invisible place holder
This screen displays the current use of eight frequency operating
zones in the network. You can toggle zones between Active and
Skipped at APs by first typing the letter of the zone to be changed,
and then pressing to toggle between the two options for each
zone. The screen is read-only at Remote radios, and Remotes must
be synchronized to the AP to display valid status.
Skipping zones is one way of dealing with constant interference on
one or more frequencies. See “A Word About Radio Interference”
on Page 150 for more interference-combatting techniques.
When you have made the desired changes to the Skip Zones Menu,
select
Commit Changes to implement the new settings. These
changes are forwarded to all radios in the network through the AP
beacon signal.
NOTE: In the USA, up to four zones may be skipped for 900 MHz
systems, and a maximum of three skipped for 2.4 GHz
systems, per FCC regulations. The skip function may be
disabled in some radios, due to regulatory requirements in
some countries.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 53
Page 64

Table 3-1 shows the frequency range covered by each zone for
900 MHz radios. Table 3-2 shows the same information for
2400 MHz radios.
Table 3-1. Frequency Zones
(900 MHz systems)
ZONE 1 ZONE 2 ZONE 3 ZONE 4 ZONE 5 ZONE 6 ZONE 7 ZONE 8
902.200
to
905.200
905.400
to
908.400
908.600
to
911.600
911.800
to
914.800
915.000
to
918.000
918.200
to
921.200
921.400
to
924.400
924.600
to
927.600
Table 3-2. Frequency Zones
(2400 MHz systems)
ZONE 1 ZONE 2 ZONE 3 ZONE 4 ZONE 5 ZONE 6 ZONE 7 ZONE 8
2401.6
to
2404.6
2404.8
to
2407.8
2408.0
to
2411.0
2411.2
to
2414.2
2414.4
to
2417.4
2417.6
to
2420.6
2420.8
to
2423.8
2424.0
to
2427.0
NOTE: Use caution when changing the operating band of 2.4 GHz
radios. If a Remote and AP are set to different bands, and
communication is lost with the AP, you might have to visit the
Remote site to restore operation.
3.6 CONFIGURING THE SERIAL
INTERFACES
3.6.1 Overview
T o understand the operation of the radio system, it is helpful to visuali ze
the AP and the Remotes as being in a single box, with the AP ports on
one side and all of the Remotes on the other side (see Figure 3-21). In
practice, the radios are typically separated by considerable distances, but
thinking of them grouped in the same box is helpful for this discussion.
Most data routing is done at the AP, so you must also perform the
majority of system configuration at the AP. The AP requires
configuration of its local interfaces (Ethernet or Serial) and knowledge
of its remote interfaces, which are physically located at the Remote
radios. There are also a few parameters that you can configure at the
individual Remote radios.
54 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 65

Invisible place holder
ACCESS POINT
(AP)
Ethernet
IP-TO-LOCAL SERIAL EXAMPLE
Serial
(showing port steering)
ACCESS POINT
(AP)
REMOTE 1
REMOTE 2
REMOTE 3
REMOTE 4
Serial Data
Serial Data
Serial Data
Serial Data
Serial Data
SERIAL-TO-SERIAL EXAMPLE
(Showing Remote port routing)
Figure 3-21. Conceptual Views of Radio System Usage
The AP includes an embedded terminal server that provides access to
Remote serial ports using an IP or serial connection at the AP. In this
capacity , it acts as a gateway between IP and remote serial devices (thus
the name “serial gateway” ), or a transpa rent over -the-a ir serial-t o-serial
connection.
Serial-to-Serial Services
When the AP transceiver has remote serial units and is primarily passing
RS-232 (serial-based) traffic, it might be necessary to implement
serial-to-serial interface transfers, as shown in the lower part of
Figure 3-21. Additional information for serial-to-serial wireless
networks is provided on Pages 123 and 132 of this manual.
IP-to-Serial Services
When the AP transceiver is used as an IP-to-serial gateway , two types of
IP terminal services are available—TCP and UDP. TCP provides a
connection-oriented link, with end-to-end acknowledgment of data.
This requires some added overhead, but provides confirmation that data
has been successfully conveyed, which may be needed for
mission-critical applications.
UDP, on the other hand, provides a best-effort delivery service with less
overhead than TCP. It broadcasts data, transmitting information packets
without an expected acknowledgment. This method minimizes
overhead requirements and is acceptable for repetitive exchanges of
information, where an occasional missed packet would not affect
performance.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 55
Most polled protocols are best served by UDP services, as the protocol
itself has built-in recovery mechanisms (error correction). UDP
Page 66

provides the needed multidrop operation by means of multicast
addressing, where multiple remote devices receive and process the same
poll message.
On the other hand, TCP services are best suited for applications that do
not have a recovery mechanism and must have the guaranteed delivery
that TCP provides despite its extra overhead. The IP-to-Serial example
shows how to do this. See “IP-to-Local Serial Application Example” on
Page 121.
T o configure either of these services, use the Serial Configuration Menu
(Figure 3-22 on Page 57).
To configure IP-to-remote serial services, use the Remote Serial
Gateway Menu (Figure 3-28 on Page 64).
Configuration
There are several configuration parameters for the remote s erial gateway
found under the Serial Configuration Menu. Note that some of the
parameters are not applicable to IP-to-serial mode. After making
changes to the configuration, you must use the Commit Changes option to
force the transceiver to implement the requested changes.
If you are connecting EIA-232 serial devices to the transceiver, review
these parameters carefully.
Serial Configuration Wizard
The Serial Configuration Wizard, available through the Local Serial
Configuration Menu, is recommended for configuration of serial ports.
The Wizard uses a step-by-step process that eliminates conflicting
settings and streamlines complex configurations.
56 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 67

3.6.2 Local Serial Configuration Menu
SHIFT
ENTER
Figure 3-22. COM1/2—Local Serial Configuration Menu
• Port Status (COM1, COM2)—Defines whether the specified
port is enabled or disabled to pass payload data.
typically disabled to allow it to be used for console terminal
control.
COM1 is
NOTE: If COM1 is inadvertently ena bled, it will be come imposs ible to
log in using a console terminal connected to the
COM1
connector. This problem can be remedied by typing the Hayes
modem-compatible escape sequence of + + + followed
by . This restores COM1 to console terminal mode. You
must log in again.
Serial Configuration Wizard—This is a tool for configuration of
•
the serial ports using a step-by-step process. When the
Wizard is started, you can choose between beginning the
step-by-step process, or simply viewing the current settings
(see Figure 3-23 on Page 58).
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 57
Page 68

Figure 3-23. Serial Configuration Wizard (Initial Screen)
To start the Serial Configuration Wizard, choose Begin Wizard. The
Wizard presents an opening screen (Figure 3-24) where you select the
method the host computer uses to connect to the radio.
Invisible place holder
Next, a series of screens are presented where you set all of the
parameters needed for proper operation of the serial port(s). The screens
provide text that assist you in making your selections.
At the end of the configuration process, the View Current Settings
Screen is displayed, where you can review or change any of the settings.
Once you are satisfied with the settings, you can commit the changes
and exit the Serial Configuration Wizard by choosing the last selection
on the View Current Settings Screen.
58 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Figure 3-24. Serial Configuration Wizard Menu
(Host Connection screen)
Page 69

View Current Settings Screen—Serial-to-Serial Example
SHIFT
ENTER
If you choose View Current Settings from the Serial Configurat ion W izar d
Menu, you see a summary screen (Figure 3-25) showing the serial
configuration settings. This is the same screen that is also shown at the
end of the configuration process. Here, you can choose the letter of an
item to change, or exit the Serial Configuration Wizard completely.
NOTE: Selecting any item other than Commit Changes and Exit Wizard
returns you to the configuration process. After making the
necessary change(s), you can use the Continue Wizard selection
repeatedly to reach the end of the configuration process, and
then exit.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-25. Serial Configuration Current Setti ngs Sc reen
(Serial-to-Serial example)
The following text explains the key settings for the Serial Configuration
Menu (serial-to-serial example).
• Port Status—This selection is used to enable or disable the
serial data port for payload data operation. Normally, COM1
is set to Disabled to permit console terminal operation.
NOTE: When COM1 is enabled for data, management of the radio
through COM1 is disabled. This problem can be remedied by
typing the escape sequence + + + followed by .
This restores COM1 to console terminal mode. You must log in
again.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 59
Page 70

• Mode—Set the method the host uses to connect to the radio.
[Serial, Network; Network]
• Remote UnitID—Specify the Remote(s) to which
transmissions are directed. Enter “broadcast” to send
transmissions to all Remotes, or enter the Unit ID num ber of
a particular Remote for unicast (directed) data. The Unit ID
defaults to the last four digits of the radio serial number, but
can be set to any 32-bit integer.
[Remote ID, Broadcast; Broadcast]
• Remote COM Port—Choose which serial port on the Remote
radios through which all data are sent (COM1 or COM2).
[COM1, COM2; COM2]
• Baud Rate—Set the data rate (payload) for the COM port in
bits per second. [1200–115200; 19200]
• Byte Format—Set the interface signaling parameters: baud
rate (see
parity, and stop bits. [
Baud Rate above for allowable range), data bits,
7N1, 7E1, 7O1, 8N1, 8E1, 8O1; 8N1]
• Buffer Size—Select the appropriate value for the buffer size
for each serial message. The maximum AP buffer size for
incoming serial data is 256 bytes. Incoming serial packets
(from the RTU) larger than 256 bytes are split by the AP into
256-byte packets before being transmitted over the air. The
associated remote(s), on receiving these packets, transmit
them out the serial port as separate packets. This parameter
does not affect serial data/packets received by the AP (from
remotes) over the air and transmitted out of the local AP
serial port. [32, 64, 128, 256 bytes; 64]
• Inter-Packet Delay—Set the number of characters that signify
the end of a message (inter-character time-out). A transceiver
receiving data through the serial port sends an
end-of-message signal to the remote end. MODBUS®
defines a “3.5-character” parameter. [
0–65535; 4]
• Commit Changes and Exit Wizard—Implements the settings
shown on the screen and closes the Serial Configuration
Wizard.
60 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 71

View Current Settings Screen—Unicast UDP Mode Example
SHIFT
ENTER
Figure 3-26 shows a sample View Current Settings Screen for a system
configured for Unicast UDP mode. The selections shown are similar to
the serial-to-serial example above, but some items are UDP specific.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-26. Serial Configuration Current Setti ngs Sc reen
The following text explains the key settings for the Serial Configuration
Menu (Unicast UDP example).
• Port Status—This selection is used to enable or disable the
serial data port for payload data operation. Normally, COM1
is disabled to permit Console Terminal operation.
NOTE: When COM1 is enabled for data, management of the radio
through COM1 is disabled. This problem can be remedied by
typing the escape sequence + + + followed by .
This restores COM1 to console terminal mode. You must log in
again.
Mode—Used to set the method the host uses to connect to the
•
radio. [Serial, Network; Network]
• RX IP Port—This selection is used to specify which local IP
port address should be used to receive data from the host, as
well as the IP address and port number of the host to send
data to at the remote end.
• TX IP Addre ss—This selection is used to specify the local IP
address that will receive data f rom the host, as well as the IP
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 61
Page 72

address and port number of the host to send data to (at the
remote end).
• TX IP Port—A dynamically assigned software port used by
external applications such as HMI interfaces, host polling
programs, and so on.
• Talkback Enable—Used to enable or disable Talkback mode.
[Enabled, Disabled; Disabled]
• Baud Rate—This menu item is used to set the data rate
(payload) for the COM port in bi ts per second. [ 1,200–115,200;
19200]
• Byte Format—This item allows you to set the interface
signaling parameters: baud rate (see Baud Rate above for the
allowable range), data bits, parity, and stop bits. [7N1, 7E1,
7O1, 8N1, 8E1, 8O1; 8N1
•
Buffer Size—This selection selects the size of the buffer
]
available for passing serial traffic. The maximum AP buffer
size for incoming serial data is 256 bytes. Incoming serial
packets (from the RTU) larger than 256 bytes are split by the
AP into 256 byte packets before being transmitted over the
air. The associated remote(s), on receiving these packets,
transmits them from the seri al port a s se para te pac ke ts. This
parameter does not affect serial data/packets received by the
AP (from remotes) over the air and tr ansmitted from the local
AP serial port. [16, 32, 64, 128, 256; 64 Bytes]
• Inter-Packet Delay— Specifies the number of characters that
signify the end of a message (inter-character time-out). A
transceiver receiving data through the serial port sends an
end-of-message signal to the remote end. MODBUS defines
a “3.5-character” parameter. [0–65535; 4]
• Commit Changes and Exit Wizard—Implements the settings
shown on the screen and closes the Serial Configuration
Wizard.
3.6.3 Remote Serial Gateway Configuration
The Remote Serial Gateway (RSG) Menu (Figure 3-27) controls the IP
encapsulation behavior of all Remote radios. The gateway function is
essentially a table with one entry for each Remote radio passing serial
data. No further configuration is required at Remote radios.
The AP can be configured to accept IP traffic to be exchanged with
devices connected to the serial ports of one or more Remotes.
Figure 3-27 shows the starting point for configuring the remote serial
gateway settings.
62 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
(IP-to-Remote Serial)
Page 73

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-27. Remote Serial Gateway Menu—Initial Sc reen
• RSG Talkback Enable (UDP IP-to-Serial)—When Talkback is
enabled and the RSG is set up for UDP mode, a message
from a Remote radio (usually a reply to a poll) is sent to the
last IP address or port from which a message was received.
[Enabled, Disabled; Enabled]
• RSG Talkback Timeout—Use this selection to set a time limit
after which, if no data has been received from the IP host, the
RSG talkback feature expires. When this happens, the RSG
reverts to its configured IP address and port for upstream data
destined for an IP host. [Time in seconds; 30]
• RSG Entries—This selection allows entry of key RSG
parameters including Unit ID, COM port se tting, Mode, and
Local IP Port. This screen is shown in Figure 3-28 on
Page 64.
Remote Serial Wizard—This tool assists you in adding or
•
changing a configuration to your remote serial gateway
entries. These are the same settings contained in RSG Entries
Screen, but the Remote Serial Wizard presents a step-by-step
series of screens with explanatory text to assist you in making
your selections.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 63
Page 74

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-28. Remote Serial Gateway (RSG) Entries Menu
(TCP configuration; UDP is similar)
• Unit ID—Enter Broadcast, or enter the Unit ID of the Remote
for unicast (directed) data. The Unit ID defaults to the last
four digits of the radio serial number, but can be set to any
32-bit integer. If set to Broadcast, then all remotes are
targeted.
• Group Id—Identifies a group used for serial multicast traffic.
When set to a non-zero value, the Unit Id and COM Port
parameters are not available because the entry identifies a
Group, and a Group does not use these parameters. Unit Id and
COM Port parameters are available when this value is set to
zero. [0-15; 0]
• COM Port—The remote serial port associated with this IP
connection.
• Mode—The type of IP port, or socket, used by the AP for
encapsulation of serial traffic.
[TCP Server; UDP]
• Local IP Port—The IP port number at the AP to which the
application must connect when exchanging data with the
corresponding remote radio(s).
• TCP Keepalive—This value sets the number of seconds that a
TCP connection can be inactive before it is disconnected. If
the value is set to zero, the port is off. [0-600; 5]
NOTE: Although a Group is defined at the AP, the members of the
3.7 SECURITY CONFIGURATION
The entraNET system contains built-in security features for your
transceivers and the network. These options start with controlling
64 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
group are defined at each remote radio. See “Group Database
Menu” on Page 75 for more information.
Page 75

remote access to the network using Telnet, Web browser, and SNMP.
Other areas include multiple levels of encryption and MD5-level
security for HTTP connections. The Security Configuration Menu
(Figure 3-29) contains all of the settings related to these functions.
NOTE: Security enhancements in entraNET 2.3.0 firmware
necessitate that encryption must be turned OFF prior to
upgrading entraNET Remote radios with the new firmware.
Failure to turn encryption off results in loss of communication
between an AP and entraNET Remote radios. Once the
firmware upgrade is complete, you can re-enable encryption.
Additionally, any changes to encryption settings should be
made first at all Remote radios, then at the AP. This pr events a
loss of communication between the AP and Remote radios due
to security mismatches. Communication loss requires a
personal visit to each affected remote site, where restoration
can be performed at the Remote itself (see CHAPTER 4
REMOTE RADIO MANAGEMENT, beginning on Page 99).
3.7.1 Security Configuration Menu
The Security Configuration Menu (Figure 3-29) allows settings of
several parameters related to network access, user credentials, and
encryption. A review of each item on the menu is important to
safeguarding your network from unauthorized access. Review these
settings occasionally to make sure they are applicable to the current state
of your network.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 65
Figure 3-29. Security Configuration Menu
Page 76

• Approve Remotes—Enables authentication of Remote radios
before granting access to the network. Enabling forces the
entraNET radio to check the Approved Remotes List (described
below) before continuing the authorization process. Before
enabling this option, at least one entry must already exist in the
Approved Remotes List. [Enabled, Disabled; Disabled]
• Encryption Enable— Enable encryption of over-the-air data
packets. Enabling forces the transceiver to use 128-bit
encryption on all over-the-air messages. This option requires
that you have already configured the Encryption Phrase (see
below). [Enabled, Disabled; Enabled]
• HTTP Access—Prevents remote access through HTTP (a Web
browser) on Port 80. [Enabled, Disabled; Enabled]
• Telnet Access—Prevents remote access through Telnet sessions
on Port 23. [Enabled, D isabled; Enabled]
• SNMP Mode— Prevents remote access through SNMP
commands on Port 161. [Disabled, v1 only; v2 only, v3 only, v1-v2,
v1-v2-v3; v1-v2-v3
]
• Approved Remotes List (Menu)—Presents a menu where the
creation and management of Remote radios allowed to
communicate with the AP is performed. For more information,
refer to Approved Remotes List Menu below.
•
Remote Access Manager—Allows management of the Approved
Remotes List using optional GE MDS Remote Access Manager
software (Part Number 06-4490A01). Set the Remote multicast
address to use with the Remote Access IP setting (listed below).
[Enabled, Disabled; Disabled]
• Encryption Phrase—An alphanumeric phrase added to the
encryption algorithm. You must enter a minimum of eight
characters for this string. [Any 8-41 character alphanumeric string;
Blank
]
NOTE: When changing the Encryption Phrase, it is recommended that
66 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
you change the most distant Remotes first, followed by the
APs, so that proper association occurs.
• HTTP Security Mode—Select the security mode or level of log-in
using an HTTP browser. Disabling HTTP Access pre vents access
through HTTP. HTTP Security Mode is functional if HTTP Ac cess is
enabled. [Basic Auth, MD5 Digest; Basic Auth]
Basic mode requires a password, but the actual password text is
transmitted unencrypted.
MD5 Digest is more secure because it encrypts the password.
•
Auto Key Rotation—Used to select whether or not the encryption
key is automatically rotated (changed) periodically. [
Disabled; Enabled
]
Enabled,
Page 77

• Force Key Rotation—Thi s selection invokes an immediate change
in the encryption key. For this function to work, encryption
must be enabled, a valid Encrypt ion Phrase must be set, and key
rotation must be enabled. Note that there is no feedback on the
screen—the change takes place as soon as the menu selection is
made.
• Max Remotes—Maximum number of Remotes permitted to be
connected to (served by) this AP. [Default=50]
• User Passwords—Administrative and Guest password for this
radio. Used at log-in using the COM1 Port, Telnet session, or a
Web browser session.
To reset the admin password to the factory default (“admin”)
(Figure 3-30):
1.At the login prompt, type authcode.
2.At the password prompt, type authcode.
3.At the authorization prompt, enter the authorization code.
Up to eight case-sensitive, non-blank, alphanumeric characters;
[
admin
]
TIP: For enhanced security, consider using a misspelled word. This
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 67
Figure 3-30. Reset Password to Factory Default
helps protect against sophisticated hackers who use a database of
common words (as in a dictionary attack) to determine a password.
An even better approach is to use a password that includes some
numbers. Making the password as long as possible (up to the full
eight characters) also improves its security.
• Remote Access IP—Remote multicast address to use when
running optional GE MDS Remote Access Manager software
(see
Remote Access Manager above). [Default=239.254.1.10]
Page 78

Approved Remotes List Menu
Figure 3-31. Approved Remotes List Menu
The AP restricts communication to only those Remotes included in the
Approved Remotes List. Messages received from Remotes that are not
in this list are discarded.
• Add Approved Remote—Enter the Remote serial number. This
entry must consist of seven or more characters.
[Serial number of Remote–at least seven characters]
• Delete Approved Remote—Enter the Remote serial number.
NOTE: For security, delete a decommissioned or stolen radio
immediately.
• Previous Page—Returns you to the last page viewed within the
Approved Remotes Menu.
Add Associated Remotes—Adds all curr ently associated Remote s
•
(1-1024) to the approved Remote list. Alternatively, you can
enter each Remote serial number manually.
• Delete All—Completely purges all Remotes from the current list.
• Next Page—Moves you to the next page within the Approved
Remotes List Menu.
• Number of Remotes—Shows the number of Remotes that are
currently connected to the AP.
•
Approved Remotes List—Simple listing of the serial numbers of
Remotes that are authorized to communicate with this AP. If a
Remote is not on this list, it cannot associate with this AP.
68 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 79

3.8 WIRELESS NETWORK MENU
The Wireless Network Menu (Figure 3-32) monitors the operation of
Remote radios in the network, regardless of the type of data they are
passing (Ethernet or serial) from the perspective of the AP. This
information is stored in a local database at the AP, and is not sent to the
Remotes.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-32. Wireless Network Menu
• Database Timeout—Number of minutes until a database entry
expires. Remotes must be refreshed through a handshake
process to stay in the database. This allows decommissioned or
faulty radios to fall out of the database. [1-720; 10]
• Max Remotes—Maximum number of Remotes allowed to
associate with the AP. [1-1024;100]
• Remote Management—Presents a menu for management of a
particular Remote. See “Remote Management Menu” on
Page 70 for more information.
Remote Database—Lists all Remotes connected to this AP.
•
See “Remote Database Menu” on Page 74 for more
information.
• Group Database —Lists all Remotes connected to this AP that
belong to a specific Group. See “Group Database Menu” on
Page 75 for more information.
• Endpoint Database—Lists the IP or MAC addresses of Ethernet
endpoints connected to Remote radios. See “Endpoint
Database Menu” on Page 75 for more information.
• Access Point Database—Lists the APs in the wireless network.
Inter-Access Point Protocol must be enabled (see “Mobility
Configuration Menu” on Page 49) for this function to work).
IAPP traffic can be passed using these transceivers.
See “Access Point Database Menu” on Page 76 for more
information.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 69
Page 80

• EndPoint Logging—This selection is used to specify whether
endpoint logging is enabled or disabled. [Enabled, Disabled;
Enabled
]
3.8.1 Remote Management Menu
The Remote Management Menu (Figure 3-33) allows selection of a
particular Remote to manage, based on the radio Unit ID number
(generally the last four digits of its serial number).
Figure 3-33. Remote Management Menu
• Remote to Manage—Radio address of the Remote to be managed
(typically a four-digit code).
• Manage Selected Remote—Displays the screen shown in
Figure 3-34 on Page 71, which contains several parameters used
to set the characteristics of Remote radios in the network.
Broadcast Remote Programming—Selecting this item brings up a
•
submenu (Figure 3-36) where you can initiate the broadcast of
new firmware images and Remote restart commands.
NOTE: Before programming a Remote radio over the air, be sure to set
ETHERNET BRIDGING (see “Bridge Configuration Menu” on
Page 51) from ALL (default) to either DISABLED or NO
BROADCAST/MULTICAST
.
Otherwise, you might experience sync errors, or programming
might not complete. Excessive broadcast/multicast traffic
from a connected LAN can also cause problems.
70 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 81

Manage Selected Remote Menu
Figure 3-34. Manage Selected Remote Menu
• Device Information—Selecting this item brings up a submenu
(Figure 3-36) where you can change a Remote radio Owner,
Name, and Location. Hardware and software version information,
including the bootloader version, is also displayed.
• Network—Tool for control of the Ethernet port (enable or
disable).
• Radio—Tool for setting the transmit power level (in dBm).
• Serial Configuration—Tool for configuring COM1 and COM2
parameters, including port mode, baud rate, byte format,
inter-packet delay, and buffer size.
• Statistics—Presents packet throughput and retry data for the
selected Remote.
Remote Reprogramming—Opens a submenu (Figure 3-35 on
•
Page 72) for sendi ng new firmware images to specific Remotes,
and for specifying the image that will be active when the radio
is restarted.
• Authorization—Opens a submenu showing the authorized
capabilities of the Remote entere d in the Unit ID fie ld (enabled
or disabled): Ethernet capabilities, network management, serial
capabilities, and multiple endpoints.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 71
Page 82

Figure 3-35. Remote Reprogramming Menu (Single Remote)
Invisible place holder
• Remote to Manage—This field shows the Unit ID of the Remote
to be managed.
• Package (Image) to Transmit—There are two available firmware
images in the AP. This allows selection of either image to be
transmitted to the remote.
• Send Images—Begins transmitting the selected firmware image
to the Remote.
• Remote Reboot—Restarts the Remote radio with one of the two
firmware images.
Broadcast Remote Reprogramming Menu
72 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Figure 3-36. Broadcast Remote Reprogramming Menu
Page 83

Broadcast
reprogramming with
different firmware
versions on a
network
Broadcast reprogramming is used to upgrade the firmware of all radios
in a network. If your network contains a mix of radios with 2.x and 3.x
version firmware, it is normal to see the status message “Some R emotes
Failed Programming”.
For example, if you select 2.x firmware to reprogram, only the older
remotes will accept the image; if you select 3.x firmware, only new
remotes will accept the firmware. Release 3.x firmware can only be
installed on radios equipped with 2 MB expanded flash memory.
Release 2.x is compatible only with older radios having 1 MB flash
memory.
Use the Manage Selected Remote Menu on Page 71 to determine whi ch
radios were not upgraded.
The Broadcasting Remote Reprogramming menu items are:
• Package to Transmit—Identifies which of the two available
firmware images (1 or 2) will be sent to the associa ted Remotes.
• Broadcast Images—Starts transmission of the selected firmware
package to all associated Remotes.
• Status—Shows either Not Started, or the progress (in percent) of
a firmware image transmission. At the end of a transmission, the
word Complete is shown.
• Broadcast Remote Reboot—Causes a reboot of all associated
Remotes to the new (offline) firmware image. This image then
becomes the active firmware file.
The bottom of this screen shows the software versions of the OIB and
TOR boards inside the entraNET radio. The OIB is the interface board
section of the transceiver; th e TOR is the radio section of the transceiver .
Both sections use different portions of the firmware package, which
explains the difference in version numbers.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 73
Page 84

Remote Database Menu
The Remote Database Menu (Figure 3-37) shows several parameters
related to the associated Remotes. It is updated about once every 8 sec.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-37. Remote Database Menu
• UnitID—The unit ID of the associated remote.
• State—Shows whether or not the Remote is connected to the AP.
• AgeOut—Number of minutes until the entry expires and is removed
from the table. Each AP maintains a table with the addresses of the
devices it communicates with. The AgeOut countdown restarts to the
Database T imeout value every time a message to or from that device is
detected. If no traffic with that device occurs, and it does not
respond to a final handshake request, it then “ages out” of the table.
An expired Remote must reconnect before it is again included in the
table. See
Database Timeou t on the Wireless Network Menu,
Figure 3-32 on Page 69.
• TX Pkts—Number of packets sent to this Remote.
• RX Pkts—Number of packets received from this Remote.
• Num EPs—Number of endpoints connected to this Remote.
74 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 85

Group Database Menu
The Gr oup Database Menu (Figure 3-38) shows the remotes associated
with this AP that belong to the specified Group ID.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-38. Group Database Menu
• Group ID—Allows the selection of a particular group and displays the
remote radios defined for the group. [0-15; 0]
• UnitID—The unit ID of the associated remote.
• GroupID—The ID number of the group.
• Com Port—The COM port that the remote uses to pass the serial
multicast traffic associated with this Group ID.
Endpoint Database Menu
The Endpoint Database Menu (Figure 3-39 on Page 76) shows all
non-entraNET Ethernet devices that are known to the transceiver; this is
similar to the AP table of IP devices. The list shows endpoint MAC and
IP addresses, as well as packet exchange data.
NOTE: A Remote does not have an IP address; rather, it acts as a
transparent bridge for IP traffic to the connected Ethernet
endpoint.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 75
Page 86

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-39. Endpoint Database Menu
(Lists all equipment attached to Remote transceivers in the network)
• MAC Address—Ethernet address of the endpoint device.
• AgeOut—Number of minutes until the device (address) is removed
from the table.
Each transceiver maintains a table with the addresses of the devices
it communicates with. The age time countdown restarts to its default
setting every time a message to or from that device is detected. If no
traffic with that device happens, it then “ages out” of the table.
When traffic is detected, it is included again in the table.
• Via Remote—Unit ID of the transceiver connected to this device.
• IP Address—IP Address of endpoint device (not the Remote radio
itself).
TxPkt—Number of packets received from the endpoint device and
•
passed over the air.
• RxPkts—Over-the-air data packets received by the transceiver and
passed on to the endpoint device.
Access Point Data base Menu
The Access Point Database Menu (Figure 3-40) lists all APs contained
in the wireless network, and includes details about each radio.
76 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 87

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-40. Access Point Database
• Serial Number—Factory-assigned serial number for the AP.
• IP Address—IP Address of the AP.
• Number of Remotes—Current number of Remotes connected to
the AP.
• List of Remotes—Lists all Remotes (by Unit I D number) that are
currently connected to the AP.
3.9 STATISTICS AND EVENT LOG
The S tatistics/ Event Log Menu (Figure 3-41) contains a variety of items
related to the health and performance of the wireless network. Data
throughput statistics, as well as past and present events and alarms, are
all presented and stored in this menu area.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 77
Figure 3-41. Statistics/Event Log Menu (Main Screen)
Page 88

• COM1/COM2 Data Statistics—These screens show in and out bytes
for the COM1 and COM2 ports.
• Remote Serial Gateway Statistics—Shows Unit ID, status, and
throughput data for associated Remotes.
• Ethernet Packet Sta tistics—Shows vital data on packets, in and out
bytes, errors detected, and lost Ethernet carriers.
• Radio Packet Statistics—Summarizes data packets sent and
received by the radio, including overflows, good or failed data,
retries, and timeouts.
• Event Log—Database of past and present events and alarms for
the wireless network. A listing of event log codes appears in
Table 7-5 on Page 172.
3.9.1 COM1 and COM2 Data Statistics Menus
Invisible place holder
78 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Figure 3-42. Com1/2 Data Statistics Menu
Invisible place holder
• Bytes in on port—Number of bytes received by the transceiver
through the serial interface.
• Bytes out on port—Number of bytes transmitted by the
transceiver through the serial interface.
• Bytes in on socket—Number of bytes received by the transceiver
through the IP socket.
• Bytes out on socket—Number of bytes transmitted by the
transceiver through the IP socket.
Page 89

3.9.2 Remote Serial Gateway Statistics Menu
The Remote Serial Gateway Statistics menu (Figure 3-43) summarizes
port activity for Remote Serial Gateway entr ies that have been set up for
IP-to-Remote serial data. These values are reset to zero when a radio is
restarted.
Figure 3-43. Serial Data Statistics Menu
(Both COM1 and COM2 are shown, if applicable)
• Index—Sequential number assigned to the associated Remote.
• UnitID—The unit ID of the associated Remote. Group IDs are
displayed, when defined, to show statistics. A Group ID is
identified as Grp x.
• Com—Communication port being monitored (COM1 or COM2).
• IP Port—IP port associated with the listed device.
• State—State of the AP server for this Remote.
Listening; Connected]
[
• Remote:P,B—Displays the incoming port byte count.
• Socket:P,B—Displays the outgoing port byte count.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 79
Page 90

3.9.3 Ethernet and Wireless Packet Statistics Menu
The Ethernet/W i r eless Packet S tatistics menu (Figure 3-44) shows vital
data on packets and bytes sent or received, and errors detected. The
screen is updated approximately every 3 sec.
Figure 3-44. Sample Packet Statistics Menu
Ethernet Packet Statistics
• Packets recei ved—Packets received through the Ethernet port of
the transceiver.
• Packets sent—Packets sent through the Ethernet port of the
transceiver.
• Bytes received—Data bytes received by this radio.
• Bytes sent—Data bytes sent by this radio.
• Packets dropped—Received packets dropped from a lack of
buffers.
• Receive errors—Packets discarded after more than five retries.
Lost carrier detected—Number of times the carrier signal on the
•
Ethernet port has been missing. This count increases
significantly when the Ethernet cable is inserted or removed.
• Clear Statistics—Resets the statistics counter.
Wireless Packet Statistics
• Packets received—Over-the-air data packets received by this
radio.
•
Packets sent—Over-the-air data packets sent by this radio.
• Bytes received—Over-the-air data bytes received by this radio.
• Bytes sent—Over-the-air data bytes sent by this radio.
• Packets dropped—Received packets dropped from a lack of
buffers.
80 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 91

• Receive errors—Packets that do not pass a Cyclic Redundancy
Check (CRC). This may be due to transmissions corrupted by
RF interference.
• Clear Statistics—Resets the statistics counter.
3.9.4 Radio Packet Statistics Menu
The previous screen dealt with Ethernet-related information. The Radio
Packet Statistics screen (Figure 3-45) contains statistics that relate
directly to over-the-air transmission of data. It provides valuable insight
into the quality of the RF link between entraNET radios with respect to
the handling of data packets.
Figure 3-45. Radio Packet Statistics Menu
• Overflow—TX packets with “LCP buffer overflow data”
responses.
No Ack—Number of packets that were sent but not
•
acknowledged.
• Lost Data—TX packets lost; over-the-air retries exceeded.
• Timeout—TX data packets lost; contention timeout.
• Good Data—Data packets with CRC “good” responses.
• Failed—TX packets failed; data integrity failed.
• Over the Air Data—Data packets successfully delivered over the
air.
• Frags—Total fragments of data received.
• Retries—Total number of times packets were re-transmitted.
• Diags—TX packets with “Remote not synchronized” data
responses.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 81
Page 92

3.9.5 Event Log Menu
The microprocessor within the transceiver monitors many operational
parameters and logs them. Events are classified into four levels of
importance, which are described in Table 3-3. Some of these events
result from a condition that prevents the normal operation of the radio;
these are “critical” events. These cause the radio to enter an “alarmed”
state, and the POWER LED to blink, until the condition is corrected. All
events are stored in the Events Log, which holds approximately 5,000
entries.
Table 3-3. Event Classifications
Level Description or Impact
Informational Normal operating activitie s
Minor Does not affect radio operation
Major Degraded radio performance, but stil l
Critical The radio cannot operate
Time and Date Stamping
The events stored in the Event Log ar e time stamped using the time and
date. You must manually enter the date and time at the AP.
See “DEVICE INFORMATION MENU” on Page 84. The manually set
time and date clock is backed up by an internal battery.
capable of operation
82 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Figure 3-46. Event Log Menu
• Current Alarms (Telnet or Terminal only)—Lists events that have
placed the radio in the alarmed state.
• View Event Log (see Figure 3-47)—Lists events stored in the
current log. Some of these events are stored in volatile memory,
and are lost if power is removed.
Page 93

Invisible place holder
Figure 3-47. View Event Log Screen
Invisible place holder
•
Clear Event Log—Purges the log of all stored events.
TIP: Save your Event Log before clearing it to retain poten-
tially valuable troubleshooting information. See USING
CONFIGURATION SCRIPTS on Page 181 for an over-
view of how to transfer files from the transceiver to a computer on the network using TFTP (Trivial File Transfer
Protocol).
• Send Event Log (Telnet or Terminal only)—Initiates TFTP
transfer of the Event Log in a plain te xt (ASC II ) f ile to a TF TP
server on the connected LAN.
• Event Log Host Address (Telnet or Terminal only)—IP address of
the computer on which the TFTP server resides.
Any valid IP address; 127.0.0.1]
[
• Event Log Host Filename (Telnet or Terminal only)—Name to be
given to the Event Log file sent to the TFTP server for
archiving.
[Any 40-char alphanumeric string; eventlog.txt]
NOTE: You might want to change the Event Log file name to reflect
the type of log you intend to archive, or its date.
• TFTP Timeout (Telnet or Terminal only)—Number of seconds
the TFTP server waits for a packet ACK (acknowledgment)
from the transceiver before suspending the file transfer.
[
10 to 120 sec; 30]
• Syslog Server Address—The radio can also pass log messages to
a syslog server as they occur. Use this field to enter the IP
address of this server. [
Valid server IP address]
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 83
Page 94

3.10 DEVICE INFORMATION MENU
The Device Information menu (Figure 3-48) displays basic
administrative data on the radio to which you are connected. It also
provides a date and time display, Console Baud Rate setting, and
customer-specific parameters under the Device Names selection.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-48. Device Information Menu
• Model (display only)—Model type of the connected radio.
• Serial Number (display only)—Serial number of the connected
radio.
• Uptime (display only)—Elapsed time since powering up the radio.
• Date—Current date being used for the transceiver logs
(customer settable).
• Time—Current time of day (customer settable). Setting:
HH:MM
Date Format—Select a presentation format:
•
• Generic = dd Mmm yyyy
• European = dd-mm-yyyy
• U.S.A. = mm-dd-yyyy
NOTE: The date and time are maintained by an internal battery
module, which is not customer serviceable.
• Console Baud Rate—Allows setting the console baud rate to
match the connected terminal.
• Device Names Me nu (Figure 3-49)—The Device Name is used by
the transceiver as the network realm name and as the
entraNET MS screen heading. The contact, location, and
description fields for each radio can be used to record whatever
radio-specific information is useful to your organization. The
information appears on this screen only.
84 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 95

Device Names Menu
Figure 3-49. Device Names Menu
• Device Name—Device Name, used by the transceiver as the
realm name for network security and menu headings.
• Contact—Customer defined; appears on this screen only.
• Location—Customer defined; appears on this screen only.
• Description—Customer defined; appears on this screen only.
3.11 MAINTENANCE AND TOOLS
As part of operating your network, you might want to take advantage of
product improvements, and to read and archive the configuration of your
individual transceivers. The Maintenance Menu provides several tools
to make this possible. This section provides detailed information on how
to use these services.
Key maintenance tasks are:
• Reprogramming— Managing and selecting the radio operating
system firmware resources. See “ Reprogramming Menu” on
Page 86
• Configuration Scripts—Saving and importing data files
containing radio operating parameters or settings.
See “ Configuration Scripts Menu” on Page 87.
• RSG Configuration Scripts—Scripts for configuring the
Remote Serial Gateway. See “Remote Serial Gateway
Configuration (IP-to-Remote Serial)” on Page 62.
•
PING Utility—Diagnostic tool to test network connectivity.
See “ PING Utility Menu” on Page 90.
.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 85
Page 96

• Authorization Codes (Keys)—Alter the radio capabilities by
enabling the built-in resources using purchased keys.
See “ Authorization Codes Menu” on Page 91.
• Transmitter Test—Diagnostic commands for RF transmitter.
See “ Transmitter Test Menu” on Page 92.
Figure 3-50. Maintenance/Tools Menu
3.11.1 Reprogramming Menu
The AP transceiver has two copies of the firmware (microprocessor
code) used for the operating system and applications. One copy is active
and the second copy is standing by, ready to be used. Using the
Reprogramming Menu (Figure 3-51), you can upload a new firmware
release into the inactive position and place it in service whenever you
desire.
NOTE: See “UPGRADING AP FIRMWARE” on Page 179 for
complete details on downloading new firmware code into the
transceiver using TFTP.
86 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 97

Figure 3-51. Reprogramming Menu
• TFTP Host Address—IP address of the host computer from which
to get the file. [Any valid IP address]
• Firmware Filename—Name of file to be received from the TFTP
server. Verify that this string corresponds to the TFTP directory
location. May require a sub-directory (for
example: entranet/bkrfto-1_0_0.gpk).
[Any 40-character alphanumeric string]
• TFTP Timeout—Time in seconds the TFTP server waits for a
packet ACK (acknowledgment) from the transceiver before
suspending the file transfer. [10 to 120 sec; 30]
• Retrieve File—Initiate the file transfer from the TFTP server.
Placed into inactive firmware position in the transceiver’s
non-volatile memory. [Y, N]
Image V erify—Verify the integrity of the firmwar e file held in the
•
radio.
• Image Copy—Initiate the copying of the active firmware into the
inactive image.
• Reboot Device—Initiate restarting the transceiver. This interrupts
data traffic through this radio and the network, if performed on
an AP. Use this command to toggle between firmware images.
• Current Firmware—Shows the current firmware revision level.
3.11.2 Configuration Scripts Menu
A Brief Description of Configuration Files
If you plan to have more than a few transceivers in your network, you
might want to use the Configuration Scripts Menu (Figure 3-52 on
Page 88) to configure similar radios from a common set of parameters.
Over 50 customer settings that optimize the network are saved in a
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 87
Page 98

configuration file (data file). However, only a few essential parameters
need to be reviewed and altered to use the file with another transceiver.
A configuration file makes it easy to apply your unique settings to any
transceiver(s) you wish. Configuration files also provide you with a tool
to restore parameters to a known working set, in the event that a
parameter is improperly set and performance is affected. See “USING
CONFIGURATION SCRIPTS” on Page 181 for detailed instructions
and a sample configuration file.
Figure 3-52. Configuration Files Menu
• TFTP Host Address—IP address of the computer on which the
TFTP server resides. [Any valid IP address]
• Config Filename—Name of the file containing the configuration
profile to be transferred to the TFTP server. The configuration
information is in ASCII format. May require a sub-directory
(for example:
[
Any 40-character alphanumeric string]
config\entranet-config.txt).
NOTE: The filename field is used in identifying the desired incoming
file and as the name of file being exported to the TFTP server.
Before exporting the configuration profile, you might want to
name it something that ref lects radio service s or identific ation.
• TFTP Timeout—Time in seconds the TFTP server waits for a
packet ACK (acknowledgment) from the transceiver before
suspending the file transfer. [10 to 120 sec; 30]
• Retrieve File—Initiate the file transfer of the configuration file
from the TFTP server into the transceiver.
•
Send File—Initiate the file transfer from the current
configuration file to the TFTP server.
88 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
Page 99

3.11.3 RSG Configuration Scripts Menu
The RSG Configuration Scripts Menu (Figure 3-53) is used to manage
the download of configuration script files for the transceiver.
Invisible place holder
Figure 3-53. RSG Configuration Script Menu
• RSG Config Host Address—This is the IP address of the host
computer. This computer also runs a TFTP server to transmit or
receive configuration files.
•
RSG Config Filename—The name of the file that has been created
or uploaded from an existing AP. This file contains all of the
programmable parameters of the transceiver.
• TFTP Timeout—This field shows the amount of time that the
radio receiving information waits before reporting a fault
condition.
• Send File—Sends the onboard configuration file to a remote host
device.
Retrieve File—This command initiates the download of the
•
configuration file from the TFTP server PC.
05-4055A01, Rev. E MDS entraNET Technical Manual 89
Page 100

PING Utility Menu
CTRL
Use the PING Utility Menu (Figure 3-54) to verify IP connectivity with
LAN nodes or Ethernet endpoints.
Figure 3-54. PING Utility Menu
• Address to Ping—Address to send a PING. [Any valid IP address]
• Count—Number of PING packets to be sent.
• Packet Size—Size in bytes of each PING data packet.
• Ping—Start sending PING packets to the address shown on the
screen. The process can be stopped at any time by pressing
C on the PC keyboard.
The screen then displays a detailed report of PING activity. Press
any key after viewing the results to return to this menu.
90 MDS entraNET Technical Manual 05-4055A01, Rev. E
 Loading...
Loading...