Page 1

GE Oil & Gas
Masoneilan*
41005
Cage Guided, Balanced Globe Valve
Instruction Manual
Series
GE Data Classification : Public
Page 2

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
THESE INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDE THE CUSTOMER/OPERATOR WITH IMPORTANT PROJECT-SPECIFIC REFERENCE INFORMATION
IN ADDITION TO THE CUSTOMER/OPERATOR’S NORMAL OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES. SINCE OPERATION AND
MAINTENANCE PHILOSOPHIES VARY, GE (GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY AND ITS SUBSIDIARIES AND AFFILIATES) DOES NOT ATTEMPT
TO DICTATE SPECIFIC PROCEDURES, BUT TO PROVIDE BASIC LIMITATIONS AND REQUIREMENTS CREATED BY THE TYPE OF EQUIPMENT
PROVIDED.
THESE INSTRUCTIONS ASSUME THAT OPERATORS ALREADY HAVE A GENERAL UNDERSTANDING OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR SAFE
OPERATION OF MECHANICAL AND ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT IN POTENTIALLY HAZARDOUS ENVIRONMENTS. THEREFORE, THESE
INSTRUCTIONS SHOULD BE INTERPRETED AND APPLIED IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE SAFETY RULES AND REGULATIONS APPLICABLE AT
THE SITE AND THE PARTICULAR REQUIREMENTS FOR OPERATION OF OTHER EQUIPMENT AT THE SITE.
THESE INSTRUCTIONS DO NOT PURPORT TO COVER ALL DETAILS OR VARIATIONS IN EQUIPMENT NOR TO PROVIDE FOR EVERY POSSIBLE
CONTINGENCY TO BE MET IN CONNECTION WITH INSTALLATION, OPERATION OR MAINTENANCE. SHOULD FURTHER INFORMATION
BE DESIRED OR SHOULD PARTICULAR PROBLEMS ARISE WHICH ARE NOT COVERED SUFFICIENTLY FOR THE CUSTOMER/OPERATOR'S
PURPOSES THE MATTER SHOULD BE REFERRED TO GE.
THE RIGHTS, OBLIGATIONS AND LIABILITIES OF GE AND THE CUSTOMER/OPERATOR ARE STRICTLY LIMITED TO THOSE EXPRESSLY
PROVIDED IN THE CONTRACT RELATING TO THE SUPPLY OF THE EQUIPMENT. NO ADDITIONAL REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES BY
GE REGARDING THE EQUIPMENT OR ITS USE ARE GIVEN OR IMPLIED BY THE ISSUE OF THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
THESE INSTRUCTIONS CONTAIN PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OF GE, AND ARE FURNISHED TO THE CUSTOMER/OPERATOR SOLELY TO
ASSIST IN THE INSTALLATION, TESTING, OPERATION, AND/OR MAINTENANCE OF THE EQUIPMENT DESCRIBED. THIS DOCUMENT SHALL
NOT BE REPRODUCED IN WHOLE OR IN PART NOR SHALL ITS CONTENTS BE DISCLOSED TO ANY THIRD PARTY WITHOUT THE WRITTEN
APPROVAL OF GE.
2 | GE Oil & Gas
Page 3

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
Contents
1. General .............................................................................4
1.2 Serial Plate ...............................................................................................4
1.3 After Sales Service .......................................................................................4
1.4 Spare Parts ..............................................................................................4
1.5 Actuator and Other Accessories ..........................................................................4
2. Numbering System ...................................................................5
3. Installation ..........................................................................6
3.1 Cleanness of Piping ......................................................................................6
3.2 Isolating By-Pass Valve ...................................................................................6
3.3 Heat Insulation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.4 Hydraulic Test and Cleaning of Lines ......................................................................6
3.5 Flow Direction ...........................................................................................6
4. Disassembly .........................................................................7
4.1 Removal of Actuator .....................................................................................7
4.2 Opening of the Pressurized Chamber .....................................................................7
4.3 Disassembly of Valve Plug Stem ..........................................................................8
4.4 Disassembly of the Auxiliary Pilot Plug ....................................................................8
5. Maintenance – Repair ................................................................9
5.1 Packing Box ..............................................................................................9
5.2 Repair of Parts ...........................................................................................9
6. Valve Reassembly ...................................................................11
6.1 Pinning the Valve Plug Stem .............................................................................11
6.2 Assembly of Ring or Spring-Energized Seal Ring ..........................................................12
6.3 41405 Valve Plug and Cage Assembly ....................................................................13
6.4 Assembly of the Parts Inside the Valve Body .............................................................13
6.5 Assembly of Bonnet .....................................................................................13
6.6 Tightening of Body Stud Nuts ............................................................................14
6.7 Assembly of Packing Box ................................................................................15
7. Actuator ...........................................................................16
7.1 Coupling of Actuator Type 88 No. 6 ......................................................................16
7.2 Coupling of Actuator Type 87 No. 6 ......................................................................16
7.3 Coupling of Actuator Type 87 No. 10, 16 and 23 ..........................................................16
7.4 Coupling of Actuator Type 88 No. 10, 16 and 23 ..........................................................17
7.5 Coupling of Air-to-Extend Actuator (Type 37) .............................................................18
7.6 Coupling of Air-to-Retract Actuator (Type 38) .............................................................18
7.7 Other Types of Pneumatic Actuators .....................................................................18
Body Sub Assembly .....................................................................21
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 3
Page 4

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
1. General
Important
This document contains all the instructions required for the installation, operation and maintenance of the
equipment.
Regular maintenance, strict observance of these instructions and the use of manufacturer’s replacement parts will
guarantee optimum operation and reduce maintenance costs.
1.1 Scope
The following instructions are designed to guide the user
through the installation and maintenance of the 41005
series valves for all sizes and all pressure classes.
1.2 Serial Plate
The serial plate is usually fixed to the side of the actuator
yoke. It indicates, amongst other things, the type of valve,
the pressure class, the material used for the pressurized
chamber and the air supply pressure of the actuator.
1.3 After Sales Service
GE offers it clientele an After Sales Service comprising
highly qualified technicians, for the operation,
maintenance and repair of its equipment. To benefit from
this service, contact our local representative or the After
Sales Service of the factory whose address is given at the
end of the document.
1.4 Spare Parts
When carrying out maintenance operations, only
manufacturer’s replacement parts must be used,
obtained through our local representatives or our
Spare Parts Service.
When ordering spare parts, the model and serial
numbers indicated on the manufacturer’s serial plate
must be given.
The recommended spare parts are indicated in the parts
list included in this instruction manual on page 20.
1.5 Actuator and Other Accessories
The valve is equipped with an actuator; like all the other
valve accessories, actuators are the subject of special
instructions which provide information on the electric
and pneumatic connections. The instruction manuals to
be used for standard actuators are GEA31171 for types
37/38, GEA19530A for types 87/88.
4 | GE Oil & Gas
Page 5
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
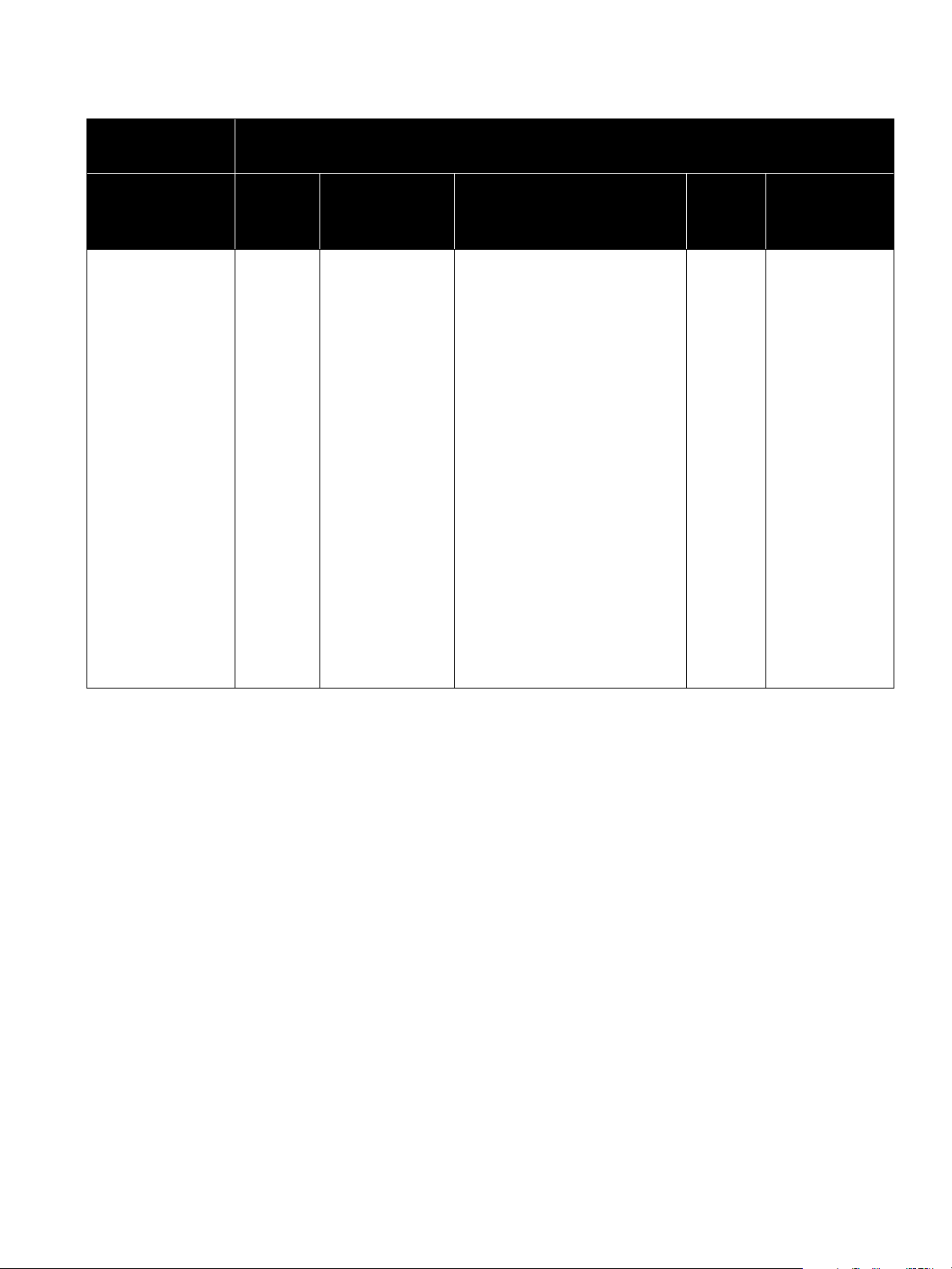
2. Numbering System
Actuator
(2 Digits)
Actuator Type
and Action on Air
Failure
Conventional
37 – Open
38 – Close
Cylinder
51– Double Acting
52 – Open
53 - Close
Multispring
87 – Open
88 – Close
Body
Series
41
Cage
guided
globe
Balanced Plug
Seal Type
0. Undefined
3. Pressure
energized
PTFE seal ring
4. With pilot
5. With seal ring
6. With PTFE
seal
9. Graphite seal
ring
Body S/A (5 Digits)
Trim Type/Characteristic
0. Undefined
1. Standard cage/Linear
2. Standard cage/Equal
percentage
3. Lo-dB
4. Lo-dB* single stage with
5. Lo-dB* double stage/Linear
6. VRT (stack) TYPE S/Linear
7. VRT (stack partial)/Type S/
*
/ anticavitation single
stage/Linear
diffuser/Linear
modified percentage
Design
Series
5 A. Angle Body
Optional Config.
EB. Extension
bonnet
C. Cryogenic
extension
bonnet
8. VRT (cage) TYPE C/Linear
9. Anticavitation
double stage/Linear (1)
Note: This instruction manual describes all the standard options in the 41005 valve series. To satisfy the particular
conditions of your application, GE may have had to develop a special option which is the subject of an additional
clause to this instruction manual. In this case, the instructions given in the additional clause always take precedence
over the general instructions.
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 5
Page 6

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
3. Installation
3.1 Cleanness of Piping
Before installing the valve in the line, clean piping and
valve of all foreign material such as welding chips, scale,
oil, grease or dirt. Gasket surfaces must be thoroughly
cleaned to insure leak-free joints.
3.4 Hydraulic Test and Cleaning of Lines
During this operation, the control valve must not be used
as an isolating valve.
This means that the valve must always be opened before
carrying out pressure tests in the process line, cleaning of
pipes, etc., otherwise equipment damages or destroying
of seal rings could result.
3.2 Isolating By-Pass Valve
To allow for in-line inspection, maintenance and
removal of the valve without service interruption,
provide a manually operated stop valve on each side
of the control valve and a manually operated throttling
valve in the by-pass line.
3.3 Heat Insulation
In case of heat insulated installation, do not insulate the
valve bonnet and take protection measures related to
personal safety.
3.5 Flow Direction
The valve must be installed so that the controlled
substance will flow through the valve in the direction
indicated by the flow arrow located on the body.
6 | GE Oil & Gas
Page 7
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
4. Disassembly
4.1 Removal of Actuator
(Figures 15 and 16)
A. Remove the packing flange nuts (3) then remove
the packing flange (4) and the packing follower (23).
B. Check that the exposed part of the valve plug
stem (1) is clean enough for the bonnet (7) to be
removed easily.
Access to the internal components of the body should be
accomplished with the actuator removed. To carry out
this operation, follow the instructions below and refer
to the specific actuator instructions, reference
GEA19530A for a type 87/88 actuator and GEA31171 for
the type 37/38 actuator.
4.1.1 Disconnection of instruments
Disconnect all mechanical couplings between the
positioner and the other instruments on the one hand
and the valve stem/actuator stem coupling on the
other hand.
4.1.2 Plug stems screwed into the actuator stem
In the case of air-to-retract actuators, apply sufficient air
pressure on the diaphragm to retract the stem completely.
Loosen the counter-nut, unscrew the stem.
Caution: During this operation, make sure that the
plug does not turn when it is seated. If the plug travel
is very small and there is a large amount of plug stem
inside the actuator, it may be necessary to remove
the yoke nut and lift the actuator so that the plug is
not touching the seat.
C. Remove the body stud nuts (8).
D. By means of a pad eye secured instead of the
actuator, lift the bonnet (7) up and separate it from
the valve body (18). During this operation, the valve
plug stem (1) must be pushed downwards so that
the valve plug remains in the valve body (18).
E. Remove the spring washer (17) and the body
gasket (10).
F. In the case of type 41305, 41375, 41505, 41605 and
41905 valves, remove the valve plug stem (1) and
valve plug (15) assembly from the cage by pulling the
valve plug stem upward, then remove the cage (16)
and “stack” (37) assembly for 41375 type valve.
Caution: Because of the cage gasket (31), the cage
can sometimes be lifted along with the valve plug. If
this should happen, press down on the cage so that it
remains in the body. If the cage is lifted along with the
valve plug, it could slip during handling and fall
In the case of a 41905 series valve [equipped with
a graphite ring (45)], make sure that the ring is not
damaged during the operation.
4.1.3 Stems attached with a stem connector
In the case of air-to-retract actuators, apply sufficient
air pressure on the diaphragm to retract the stem
completely.
Loosen the screws and remove the stem connector.
4.1.4 Removal of actuator
Disconnect all the ingoing and outgoing air and electrical
connections from the actuator. Loosen the yoke nut or
attachment screws and lift the actuator, making sure
that the concentricity and/or the thread of the bonnet is
not damaged.
4.2 Opening of the Pressurized Chamber
(Figures 17, 18 and 19)
Danger: Prior to disassembly, vent the process
pressure and isolate the valve if necessary.
Note: The valve must always be reassembled with new
packing rings and gaskets; before disassembly, make
sure that the appropriate parts are available.
G. In the case of a 41405 valve, remove the valve
plug and body cage assembly by pulling the valve
plug stem upward; in this case, the valve plug has
a shoulder which prevents the cage from falling.
Remove the valve plug from the cage by pulling on
the end of the valve plug stem.
H. Remove the seat ring (13) and the seat ring gasket
(14) from the valve body (18).
I. Remove the packing (6), the packing spacer (5) and
the guide bushing (22) from the bonnet (7).
Note: A packing spacer (5) is only mounted when the
bonnet has a side connection.
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 7
Page 8
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
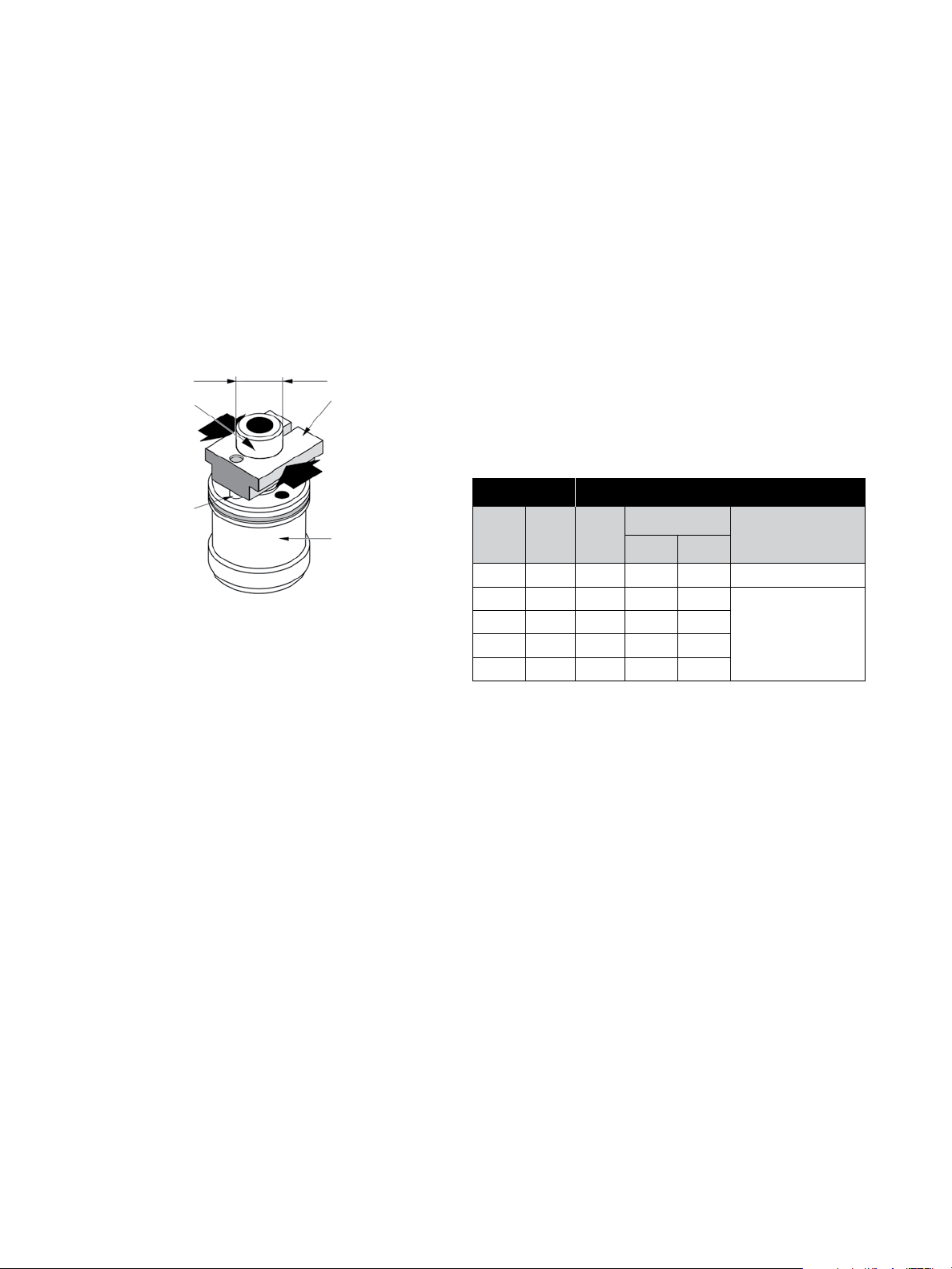
4.3 Disassembly of Valve Plug Stem
The valve plug stem is screwed and pinned into the
valve plug (15).
To dismount the stem, the valve plug must be held as
indicated below, taking care not to damage the guiding
surfaces; the plug stem pin (9) is then removed. By means
of flats or using a nut and counter-nut on the end of the
stem, unscrew the stem taking care not to apply
a bending moment which could deform it.
Cylindrical machining diameter of the jaw =
plug shank diameter: Dia. A
Tight only on
this no guiding
surface
Soft metal
vise draw
4.4 Disassembly of the Auxiliary Pilot Plug
When the valve is of the 41405 type.
In the case of 50, 80 or 100 mm (2”, 3” or 4”) valves
(Figure 17).
Exert a sufficient force on the auxiliary pilot plug (20) to
compress the spring washers (12). The retaining ring (19)
can then be removed, releasing the auxiliary pilot plug
and spring washers.
In the case of 150 to 400 mm (6” to 16”) valves (Figure 17).
To carry out this operation safely, screws of the diameter
and length indicated in the table in Figure 2 must be used.
Thread the socket head cap screws through the holes
in the auxiliary pilot plug (20). Tighten until the retainer
ring (19) can be removed. Loosen the screws gradually.
Remove the auxiliary pilot plug and the spring (12).
Stop pin
integrated in
vise jaw and
inserted into a
plug hole
Figure 1
Do not tight
on the plug
skirt
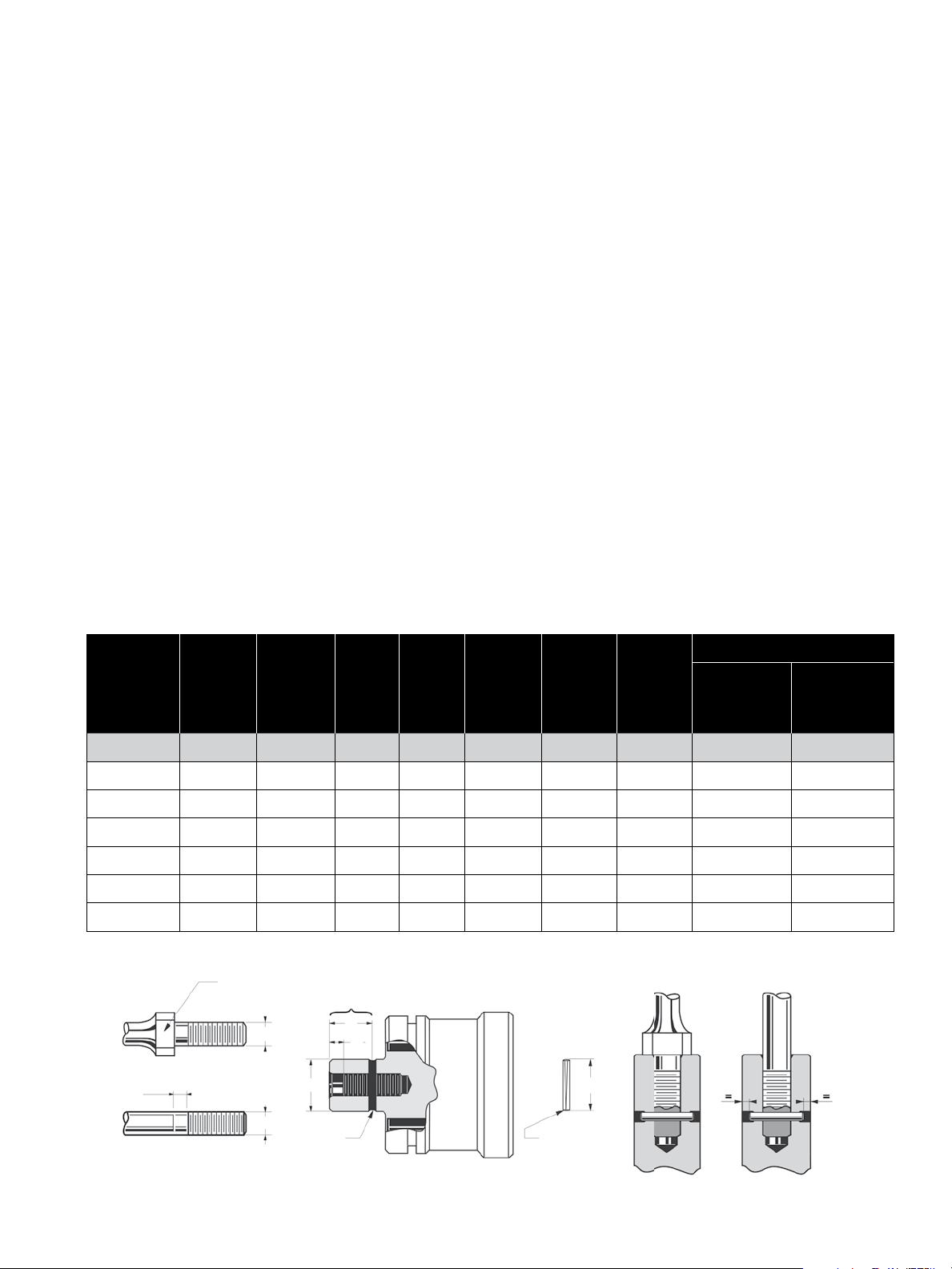
Valve size Pilot Dismounting Screws Size
Length
mm in. Qty.
Dia.
mm in.
150 6 2 57 2.25 1/4” – 20 UNC 2A
200 8 2 70 2.75
250 10 2 63.5 2.5
300 12 3 101.5 4
3/8” – 16 UNC 2A
400 16 3 63.5 2.5
Figure 2
8 | GE Oil & Gas
Page 9

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
5. Maintenance – Repair
5.1 Packing Box
Tightness of the packing box is obtained by compression
of the packing (6). Compression must be achieved by
evenly tightening the packing flange nuts (3) on the
packing flange (4). Periodical retightening of the packing
flange nuts is required to maintain tightness.
Make sure that the packing is not over tightened as this
could prevent smooth operation of the valve. If a leak
persists after the packing has been compressed to a
maximum, the packing needs to be changed.
A packing spacer (5) is only mounted when the bonnet
has a side connection.
5.1.1 Carbon/PTFE and pure PTFE packing rings
Carbon/PTFE and pure PTFE packing rings are cut in
such a way that they can be replaced without having to
separate the valve plug stem from the actuator stem.
A. Unscrew and remove the packing flange nuts (3).
B. Lift the packing flange (4) and packing follower (23)
up along the valve stem.
C. By means of a puller, remove the packing (6) and
packing spacer (5), taking care not to damage the
sealing surface of the packing box lantern or the
valve plug stem.
D. Replace the packing rings, with the cut in each ring
placed about 120° from the next, pressing them
down one at a time and respecting the table below:
G. Put the valve back into service and check for
tightness. Tighten packing flange nuts (3) as required.
5.1.2 Graphite packing ring
To carry out this operation, the valve plug stem must be
removed. See chapter on actuator disassembly.
A. Loosen and remove packing flange nuts (3).
B. Remove packing flange (4), and packing follower (23)
from the plug stem.
C. By means of a puller, remove packing rings (6),
insuring not to damage the sealing surface of
packing box or plug stem.
D. Replace new packing set (6); first one back-up ring
(Carbon/Graphite braided ring), then expanded
graphite rings (smooth rings), at last, one other
braided back-up ring; it is important to press the
rings down one at a time in the packing box.
Number of
packing set
N.D. mm (in.) Braided Graphite Braided
50 (2”) 1 4 1
80 – 100
(3” – 4”)
150 to 600
(6” to 24”)
Number of rings
1 6 1
1 5 1
Figure 4
Carbon/PTFE and pure PTFE packing box
Number of rings
N.D. mm (in.)
50
(2”)
80 – 100
(3” – 4”)
150 to 600
(6” to 24”)
E. Put the follower (23) and the packing flange (4)
back on.
F. Screw and tighten the packing flange nuts (3) without
cramming the packing rings.
without side
connection
6 2 4
8 3 5
7 2 5
Figure 3
with side connection
on top of
packing
spacer
under
packing
spacer
E. Put the follower (23) and packing flange (4) back on.
F. Screw and moderately tighten the packing flange
nuts (3).
G. Reassemble the valve plug stem (see chapter on
actuator re-assembly).
H. Open and close the valve several times then tighten
the packing.
I. Put the valve back into service and check for
tightness. Tighten packing flange nuts (3) as required.
5.2 Repair of Parts
Before re-assembly, the parts must be carefully
examined in order to eliminate any scratched, worn or
damaged parts.
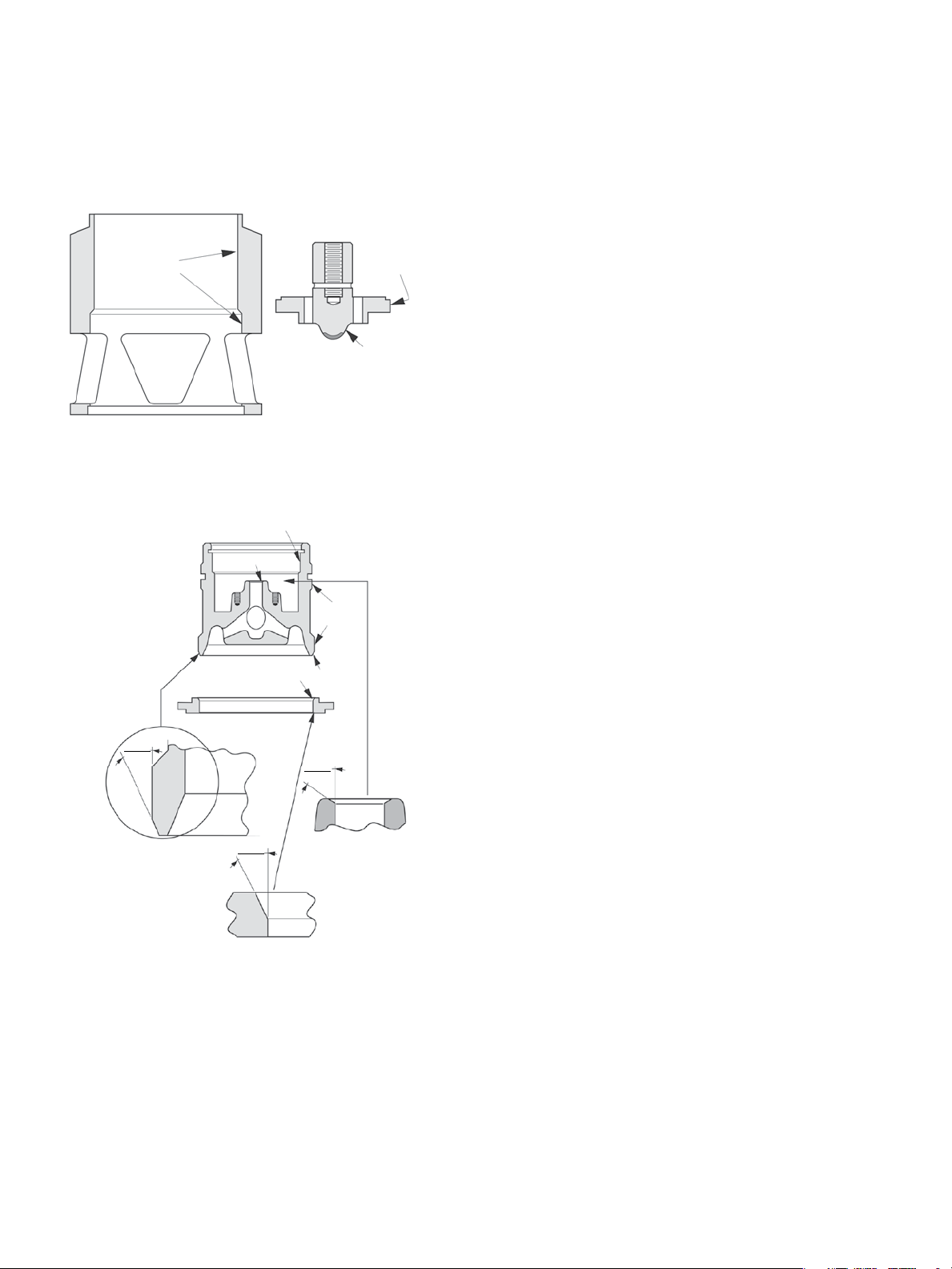
5.2.1 Guiding surfaces
The guiding surfaces of the cage and valve plug, the
guide bushing, and the guiding surfaces of the plug stem
and auxiliary pilot plug must be checked in particular. If
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 9
Page 10
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
there is only slight damage, a light abrasive can be used.
Otherwise the part must be replaced as soon as possible
(see paragraph “Spare parts”).
However, not more than 0.25 mm (0.010”) of metal must
be removed in the case of a 50, 80 or 100 mm (2”, 3” or 4”)
valve or more than 0.4 mm (0.015”) in the case of a 150 to
400 mm (6” to 16”) valve. Make sure that the seating angle
indicated in Figure 6 is respected.
Guiding
surface
Cage
Figure 5
5.2.2 Sealing surfaces (Figure 6)
Guiding surface
Seating surface
31°30'
32°30'
Valve Plug
Seat Ring
Seating surface
Pilot
62°30'
57°30'
Guiding
surface
Guiding
surface
Seating
surface
If a slight defect exists on any of the above seating
surfaces, lapping can be envisaged, in which case the
following must be respected:
• Spreadafinelayerofhighqualitysealingcompound
on the seating surface.
• Puttheseatring(13)inthebody,notingtheangle.
• Inthecaseof41305,41505,41605and41905valves,
put the cage (16) on the seat ring.
• Incaseof41375valves,putthestack(48)ontheseat
ring and the cage (16) on the stack.
• Inthecaseof41405valves,assemblethevalveplug,
cage and stem (15)-(16)-(1).
• Incaseof41305,41505,41605,41375and41905,
assemble the valve plug (15) and stem (1).
• Assemblethebonnet(7)anditsguidebushing(22).
• Placeanappropriatetoolonthevalveplugstem(1)to
turn it.
• Lapbyslightlyrotatingthevalveplugortheauxiliary
pilot plug in alternative directions. After several
rotations, lift the valve plug, turn it 90°, and start again.
• Lappingcanberepeated,butmustbelimitedasmuch
as possible so that the seat remains sufficiently narrow
to guarantee tightness.
Plug seating
surface
29°30'
30°30'
Seat ring seating surface
Figure 6
If the surface of the auxiliary pilot plug (20) is damaged,
the auxiliary pilot plug must be replaced (see paragraph
“Spare parts”).
The seat ring (13), plug and auxiliary pilot plug (20)
seating surfaces must be completely free of dents,
wear and scratches.
If the auxiliary pilot plug seat in the valve plug (15) and/or
other valve plug or seat ring seating surfaces show signs
of slight deterioration, they can be touched up on a lathe.
10 | GE Oil & Gas
Pilot seating
surface
(41405 only)
• Disassembletheparts,cleanthemandputthemback,
respecting the initial angle.
5.2.3 Gasket seating surfaces
Gasket seating surface must be free of dents, scratches
and corrosion; otherwise, they will need to be repaired.
5.2.4 Seal rings and gaskets
Spiral-wound gaskets (10), (14) and (36) must always be
changed after disassembly. Seal rings (11A), (11C) or (11E)
can be reused if they are free of scratches, erosion and
corrosion.
5.2.5 Valve plug, valve plug stem
If the valve plug has to be changed, then the stem must
also be completely changed to guarantee correct pinning
of the assembly. If only the valve plug stem has to be
changed, then the valve plug can be reused.
Page 11
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
6. Valve Reassembly
Two flats of wrench size “E”
6.1 Pinning the Valve Plug Stem
The valve plug (15) and stem (1) assembly consists of a
rod threaded into the valve plug and pinned in place.
If the valve plug (15) [or the auxiliary pilot plug (20)
in the case of a 41405 valve] needs to be replaced,
it is recommended using a new stem. The hole of the
original pin in an old stem often prevents satisfactory
results being obtained and can seriously impair the
mechanical strength of the stem-valve assembly.
Assembly is carried out as follows:
6.1.1 Reference marking on the
valve plug stem
Make a reference mark on the valve plug stem at a
distance “X” (Figures 7 and 8), equivalent to the stem
recess in the valve plug.
Note: For shouldered plug stems with two flats, the
above marking is unnecessary.
6.1.2 Tightening of the plug stem
To carry out this operation, the valve plug must be
prevented from moving by holding the plug shank with an
appropriate tool.
Screw two nuts on to the end of the new plug stem and
lock them together. Screw the valve plug stem solidly into
the plug, checking that the reference mark is level with
the end of the plug shank.
If the stem has flats, apply a torque “T” using a wrench of
dimension “E” (see Figure 7).
6.1.3 Drilling the pin hole (Figures 7 and 8)
Note: For this operation, it is recommended clamping
the valve plug-stem assembly by the plug shank to avoid
damaging the guiding surfaces; particular care must be
taken so that the pin hole goes through the valve plug axis.
If the valve plug is new, drill a hole of diameter “C” at a
distance “D” from the end of the valve plug; choose the
diameter “C” from the table according to the type of pin
used (metric or Anglo Saxon pin).
If the hole is already drilled in the valve plug, use the hole
as a guide to drill through the valve plug stem.
Non-
stem
Torque T
Shouldered
stem
Standard
stem
Valve
plug stem
diameter B
mm (in.) mm (in.) mm In. mm (in.) mm (in.) mm (in.) mm (in.) N.m (Ft.lbs) N.m (Ft.lbs)
12.7 (1/2) 20 (.79) 3.5 0.14 18 (.70) 18.5 (.73) 6 (.24) 17 (11/16) 50 (37) 60 (44)
15.87 (5/8) 25.5 (.98) 5.0 0.2 24 (.95) 28 (1.1) 8 (.30) 22 (7/8) 50 (37) 160 (118)
19.05 (3/4) 35 (1.38) 5.0 0.2 30 (1.2) 45 (1.77) 19 (.75) 27 (11/16) 160 (118) 160 (118)
25.4 (1.0) 44.5 (1.66) 8.0 5/16 40 (1.58) 47.5 (1.88) 25 (.98) 30 (11/4) 160 (118) 250 (184)
31.75 (1 1/4) 58 (2.28) 8.0 5/16 55 (2.20) 70 (2.76) 31.5 (1.24) 40 (1 5/8) - 800 (590)
38.1 (1 1/2) 70 (2.76) 10.0 - 65 (2.56) 90 (3.54) 33 (1.30) 50 (2) - 1 500 (1100)
Diameter
A
Metric
pin,
diameter
C
B
Anglo-
Saxon
pin dia.
C
Plug shank
D
F D
Figure 7
Distance
X
Shouldered
stem
E
Shouldered
X
Shouldered stem
X
A
F
Standard stem
B
Dia. CStem pin
Figure 8
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 11
Page 12

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
6.1.4 Pinning
Pushing
Direction
FTOFTC
Pushing
Direction
By means of a hammer, introduce the pin into the hole.
Complete the pinning operation, taking care to ensure that
the pin is recessed by the same amount at both sides.
Using a ball tooling and hammer, caulk the pin hole edge
of the plug.
Place the assembly in the soft jaw chuck of a lathe to check
alignment of the two parts; correct any alignment defects.
6.2 Assembly of Ring or
Spring-Energized Seal Ring
6.2.1 41305 valve
(Figures 9, 18 and 19)
These valves have a spring-energized seal rings
composed of a PTFE-based jacket maintained expanding
by a spring.
To insert the ring into the plug groove:
• Lubricatetheentrychamber.
• Placetheringovertheconicaltopoftheplugsothat
the lips of the ring face to the pressure (see Figure 9).
Caution to the assembly direction of the radial ring
(11F) on the plug (see Figure 9).
Flow Tends to Open: the open side is in the top.
Flow Tends to Close: the open side is in the lower part.
• Sliptotheringintothegroove(withoutspinningit)as
shown in Figure 9. This operation can be facilitated by
heating the ring. The temperature of the ring should
not exceed 150°C.
6.2.2 41405 and 41505 valves
(Figures 17 and 19)
These valves are equipped with metal rings; the inner ring
has a straight cut while the outer ring has a staggered cut.
To insert the rings into the cage groove, open the rings
slightly by hand and slide them, one after the other, along
the plug making sure that the parts are not damage.
Note: The cuts in the outer and inner rings are to be
placed at about 180° from each other.
6.2.3 41605 valve
(Figure 19)
These valves are equipped with an inner elastomeric ring
and a PTFE gasket.
Insert the elastomeric ring (11D) in the groove.
Place the PTFE gasket (11C) at a temperature of 100°C
(boiling water) to 160°C for a few minutes to facilitate
insertion, then slide along the plug until it slips into the
groove.
For optimum insertion of the ring, a Serflex type ring
compressor can be used to compress the ring in the
groove for several minutes.
6.2.4 41905 valve
(Figure 19)
These valves are equipped with rings; the inner metal ring
has a straight cut and the outer ring is made of graphite.
The new graphite seal ring (11A) is supplied in the form of
a closed ring in which a notch must be cut before being
inserted.
• Keeptheringretaineduntilitreturnstoroom
temperature and goes back in place within the groove.
Clamping with a collar (SERFLEX type) will help to
properly position the ring.
Figure 9
12 | GE Oil & Gas
Caution: Graphite seal rings are fragile and the
following operations must be carried out very carefully.
Using a sharp blade, carry out two V notches on the two
opposite faces. Hold the ring on either side of the notch
between the thumb and index and bend until it breaks.
Using a very fine file, adjust each end of the ring so that
its external circumference corresponds to the internal
circumference of the inside diameter of the cage (16).
To adjust the length of the ring correctly, insert the new
graphite ring into the cage, with the ring against the
inner wall of the hole in the cage, allowing minimum play
between the two ends of the ring.
To insert the inner ring, then the graphite ring into the
cage groove, slightly open the rings by hand and slide
them one after the other along the plug, taking care not
to damage the parts.
Page 13

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
Note: The cuts on each ring are to be placed at about
180° from each other.
6.2.5 41375 high temperature valve
(232°C to 316°C)
(Figure 19)
These valves are equipped with a seal ring composed of a
jacket and a metallic spring and two backup rings (11G).
Assemble the different parts as shown in Figure 19,
starting by the backup rings.
Caution: put these parts as shown in Figure 19,
the angle of 90° of the backup ring in front of the
extrusion gap between cage and plug.
Caution: for the double-cage assembly, carry out the
following operations:
• Puttheinnercage(16)upsidedown,
• Encasetheoutercage(75)ontheinnercage,maintain
them together with the two pins (76).
• Inthecaseofvalvesotherthan41405valves,insert
the valve plug/stem/ring assembly into the cage taking
particular care as it goes past the ring or springenergized seal ring.
• InthecaseofvalveswithaN.D.lessthan150(6”),place
the body/cage gasket in the valve body, making sure
that it is centered as well as possible.
6.3 41405 Valve Plug and
Cage Assembly
(Figure 17)
6.3.1 Assembly of valve plug and auxiliary pilot plug
Assemble, as appropriate, the flat spring or the coil
springs then the valve plug/plug stem assembly.
Using the same tools as those used for disassembly
(see chapter “Disassembly”), compress the springs so
that the retaining ring can be inserted in the groove of
the main plug.
6.3.2 Assembly of cage
Place the cage over the valve plug assembly via the top
of the plug stem. When doing so, take particular care to
position the ring correctly.
6.4 Assembly of the Parts Inside
the Valve Body
(Figures 17, 18 and 19)
Proceed as follows:
• Aftercheckingthatthesurfacesareperfectlyclean,
place the seat gasket (14) in the valve body, making
sure that it is centered as well as possible.
• Forvalvesizes150to400mm(6to16”),inserteither
the cage gasket (24) or the flat spring washer (17).
• Forvalvesizes450,600and750mm(18,20and24”),
insert either the first cage gasket, the cage washer and
the second cage gasket or the flat spring depending
on the type of valve, then place the body gasket (10) in
the valve body making sure that it is centered as well
as possible.
Caution to the direction of assembly of spring washer:
• ND150(6”)to450(18”)valves,theconcavefaceis
upwards,
• ND500(20”),and600(24”),theconcavefaceis
downwards and the tapped holes are visible.
6.5 Assembly of Bonnet
Check that the packing ring (6), the spacer (5) and the
guide bushing (22) have been removed from the bonnet.
Position the bonnet (7) above the valve, so that the
packing flange studs (2) are perpendicular to the flow
direction of the valve.
Thread the bonnet (7) onto the valve stem (1) and push it
down carefully until it goes into the valve body studs (21)
and takes up its correct position.
• Mounttheseatringorthediffuserseat(13).
• Mount:
– The cage (16) for 41305, 41605 and 41905 valves,
– The cage/plug/stem assembly for 41405 valves,
– TheSTACKassembly(makingsurethatthefacewith
the smallest number of holes is in contact with the
seat ring), and cage (16) for 41375 valves.
Grease the threads of the valve body studs (21) and the
bearing surfaces of the body stud nuts (8).
Screw on the body stud nuts by hand. Tighten the nuts
lightly and evenly so that the internal parts are held in
place. The face of the bonnet should be parallel to the
upper face of the body.
Slide the guide bushing (22) onto the valve plug stem and
let it drop to the bottom of the packing box housing.
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 13
Page 14

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
6.6 Tightening of Body Stud Nuts
Alignment of internal parts
In order to achieve perfect alignment of the seat ring and
the valve plug, a force must be applied to the plug stem
during tightening of the bonnet which results in correct
relative positioning of the two parts.
The force can be applied with the pneumatic actuator
as follows:
Place the actuator on the valve bonnet (7) by means of
the yoke nut (33) or attachment screws and connect the
valve plug stem to the actuator stem. See chapter on
actuators for installation instructions.
Caution: During this operation, make sure that the
plug does not turn when it is seated. If the plug travel
is very small and there is a large amount of plug stem
inside the actuator, it may be necessary to remove
the yoke nut and lift the actuator so that the plug is
not touching the seat.
Align the internal parts as follows:
In the case of air-to-extend actuators, supply air to the
actuator at the maximum pressure indicated on the
serial plate and in the case of spring-to-extend actuators,
do not supply air to the actuator, so that the optimum
positioning of the valve plug and seat can be obtained.
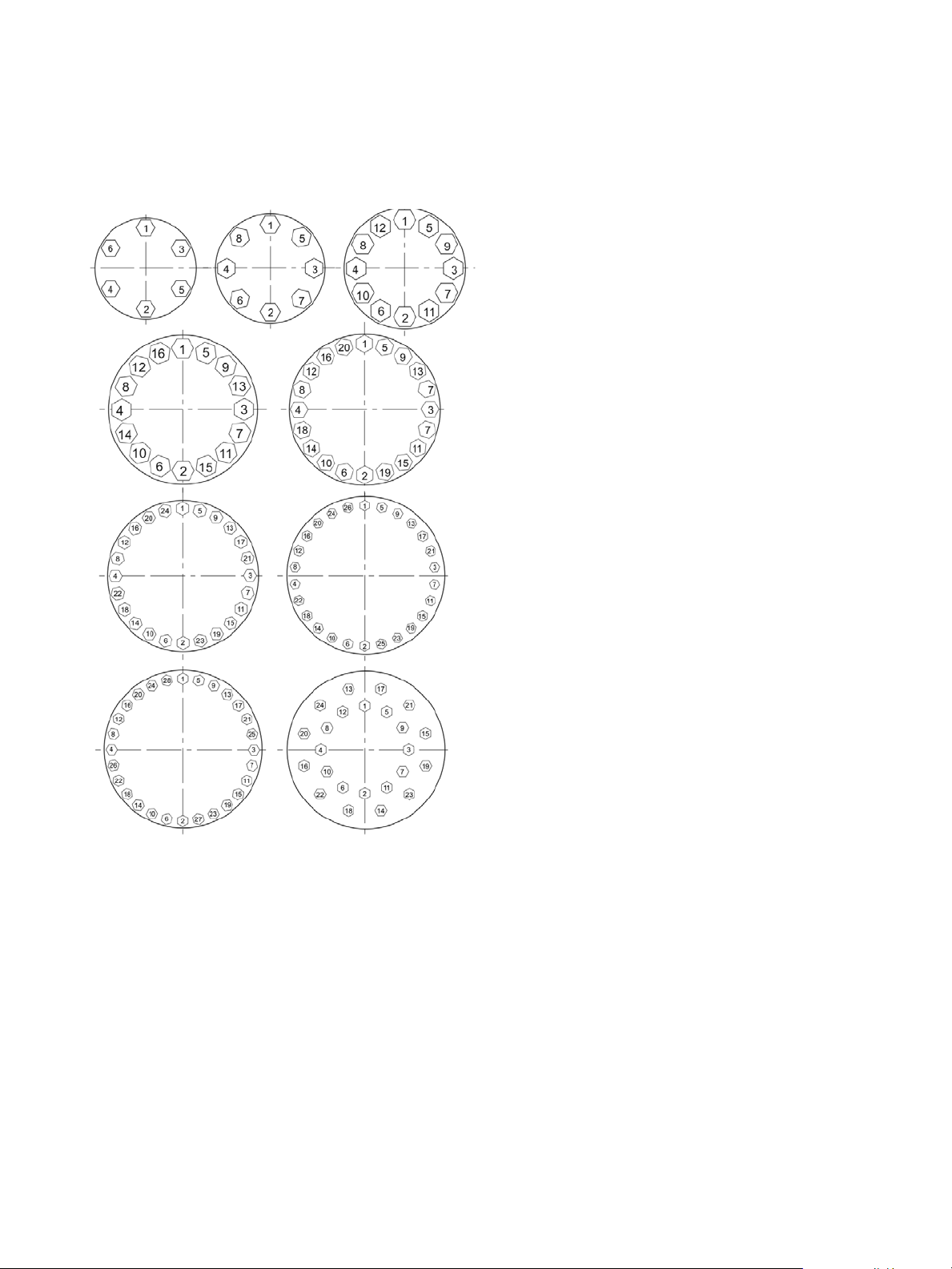
Single bolting circle:
Evenly tighten the nuts (8) by applying the torque
indicated in table in Figure 10 and the tightening
sequence in Figure 11.
Double bolting circle:
Beginning by the internal nuts, manually screw all the
bolts. Screw the internal nuts in order indicated by the
Figure 2 and screw them by successive, uniform and
progressive levels. During the tightening, make sure
that the bonnet face stays parallel at that of the body.
When the torque values given in the following table are
reached, the bonnet face must be in contact with that
of the body. Screw the external nuts in order indicated
by the Figure 2 and screw them by successive, uniform
and progressive levels until the torque values given in the
following table.
Torque Valve body stud/Bonnet
Body Nuts (21) Torque
Nominal
size (in)
2
3 x 2
4 x 2
2
3 x 2
4 x 2
3
4 x 3
6 x 2
3 2500 1 1/2 – 8 6 1050 775
4
6 x 4
8 x 4
4 2500 1 5/8 – 8 8 1250 930
6
8 x 6
10 x 6
6 2500 1 7/8 – 8 8 1900 1400
8
10 x 8
12 x 8
8 2500 1 3/4 – 8 12 1650 1220
10
12
16 x 12
12 2500 1 7/8 – 8 20 2200 1630
16
20
24
30 300 1 3/4 – 8 28 2000 1500
ASME
Pressure
classe
300/600 3/4 – 10 6 150 110
900/1500 7/8 – 9 8 250 180
2500 1 1/4 – 8 6 550 410
900/1500 1 – 8 8 400 300
300/600 3/4 – 10 8 150 110
900 /
1500
900/1500
300/600 7/8 – 9 8 250 180
900 1 1/2 – 8 6 1200 900
1500 1 1/2 – 8 6 1400 1000
300 1 – 8 8 400 300
600 1 – 8 12 350 250
900/1500 1 3/4 – 8 8 1800 1300
300/600 1 1/4 – 8 8 700 500
900 1 3/4 – 8 8 1900 1400
1500 1 3/4 – 8 8 2300 1700
300 1 1/2 – 8 8 1200 900
600 1 1/2 – 8 12 1200 900
900 1 3/4 – 8 12 1800 1300
1500 1 3/4 – 8 12 2000 1500
2500 2 – 8 12 2800 2070
300 1 1/2 – 8 8 1300 950
600 1 1/2 – 8 12 1200 900
900 1 1/2 – 8 16 1200 900
1500 1 3/4 – 8 16 2000 1500
300 1 1/2 – 8 12 1300 950
600 1 1/2 – 8 16 1300 950
900 1 1/2 – 8 20 1400 1000
1500 1 3/4 – 8 20 2300 1700
2500 2 – 8 24 2650 1960
300 1 3/8 – 8 24 900 650
600 1 3/4 – 8 24 2000 1500
900 1 7/8 – 8 24 2700 2000
300 1 3/4 – 8 20 1900 1400
600 1 3/4 – 8 26 2200 1600
Size (in) No. m.N ft.lb
1 1/4 – 8 6 800 600
14 | GE Oil & Gas
Figure 10
Page 15
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
6.7 Assembly of Packing Box
To assemble the packing box, proceed as indicated in the
“maintenance” chapter, paragraph 5.1.1 or 5.1.2.
Figure 11. Tightening sequence of nuts (8)
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 15
Page 16

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
7. Actuator
Caution: for coupling operations of actuators on
valves, it is necessary as a preliminary:
• topositiontheplug(15)onitsseatring(13).(Inno
case, one should not turn the plug on its seat, to
avoid any deterioration of tightness seat).
• connectatemporaryairsupplylinetotheactuator.
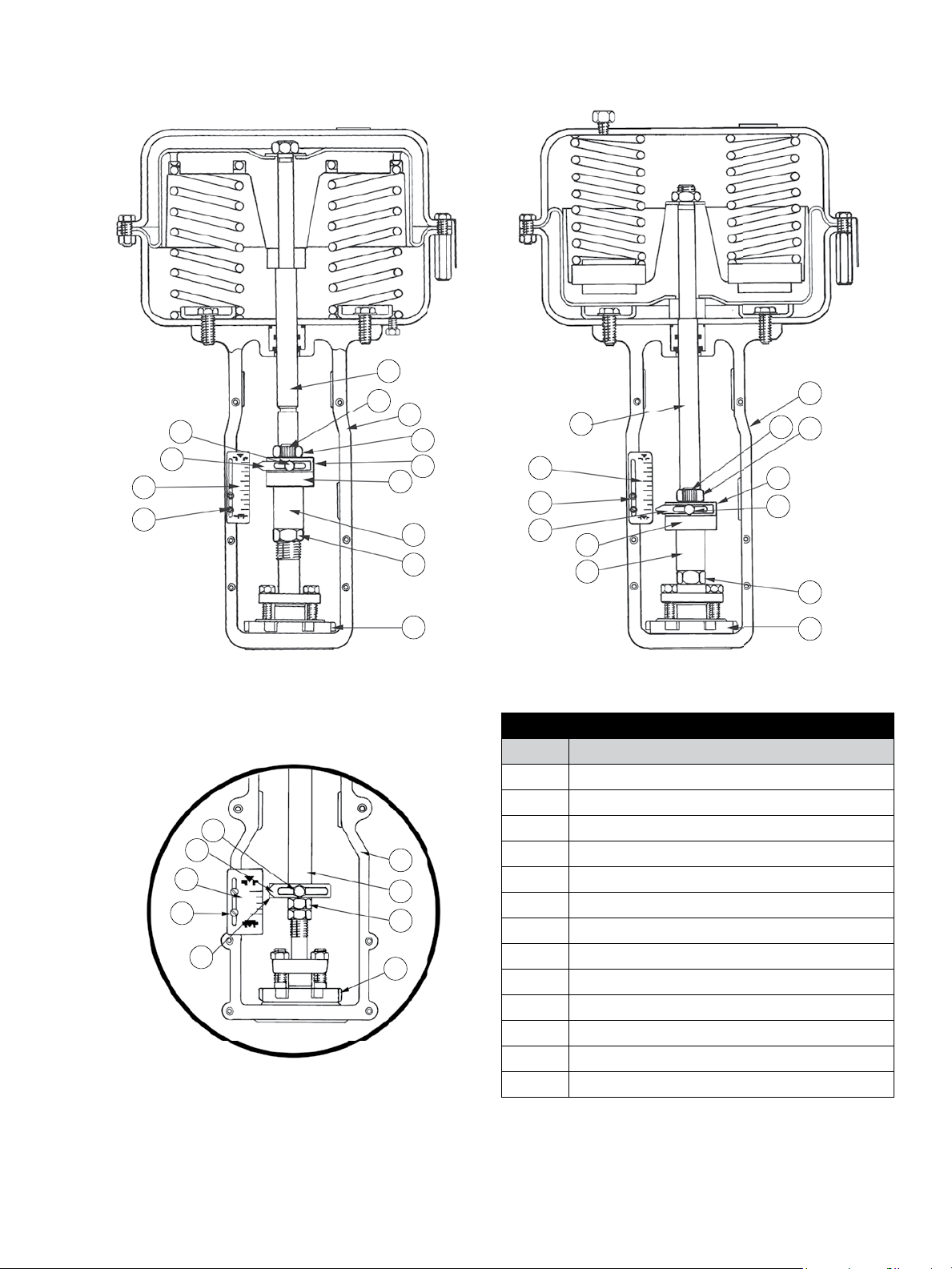
7.1 Coupling of Actuator Type 88 No. 6
(Figure 15)
A. Tightly screw the two hex nuts (1) onto the plug stem.
B. Push down the actuator and, at the same time, screw
on the yoke nut (33), then the bottom stem connector
(2). As soon as it becomes possible, insert the valve
stem into the actuator stem. The stem must be
inserted far enough so that when there is no air in
the actuator, the valve plug does not touch the seat.
C. Tighten the yoke nut.
D. Unscrew the valve plug stem until the valve plug
comes into contact with the seat. Do not turn the
valve plug on the seat as this could damage the
sealing surfaces.
E. Supply air to the actuator until the stem has travelled
at least 10 mm.
F. Unscrew the plug stem the number of turns N1
specified in Figure 13.
D. Supply air to the actuator at the initial pressure of
spring range.
E. Use the pointer (7) to set the travel scale (9) to the
open valve position.
F. Supply the actuator with air at a high enough
pressure to obtain a travel equal to the nominal
travel of the valve.
Caution: in the case of the 41405 valves, reduce the
travel by value A indicated in Figure 14.
G. Unscrew the plug stem until the valve plug is in
contact with the seat. Do not turn the valve plug on
the seat as this could damage the sealing surfaces.
H. Screw the 2 nuts (1) as far as they will go and check
that operation is correct.
7.3 Coupling of Actuator Type 87
No. 10, 16 and 23
(Figure 15)
A. Tightly screw hex nut (1) onto the plug stem.
B. Screw the top stem connector assembly tightly onto
the actuator stem.
C. Push down the actuator and, at the same time, screw
on the yoke nut (33), then the bottom stem connector
assembly by screwing until they come into contact
with the hex nut (1).
Caution: in the case of 41405 valves, use the N2 valve
so ensure tightness of the pilot plug.
G. Screw the 2 nuts (1) as far as they will go and check
that operation is correct.
H. Use the pointer (7) to set the travel scale (9) to the
closed valve position.
7.2 Coupling of Actuator Type 87 No. 6
(Figure 15)
A. Tightly screw the two hex nuts (1) onto the plug stem.
B. Push down the actuator and, at the same time, screw
on the yoke nut (33), then the bottom stem connector
(2). As soon as it becomes possible, insert the valve
stem into the actuator stem. The stem must be
inserted far enough so that, when there is air in the
actuator, the valve plug does not touch the seat.
C. Tighten the yoke nut.
16 | GE Oil & Gas
D. Push down the actuator and tighten the yoke nut.
E. Supply the actuator with air at the initial pressure
indicated on the spring scale.
F. Position the stem connector assembly at distance “X”
indicated in Figure 12.
G. Use the pointer (7) to set the travel scale (9) to the
open valve position.
H. Supply the actuator with air at a high enough
pressure to obtain a travel equal to the nominal
travel of the valve
Caution: in the case of the 41405 valves, reduce the
travel by value A indicated in Figure 14.
I. With the plug correctly positioned on the seat,
unscrew the bottom stem connector assembly until
it comes into contact with the top stem connector.
Tighten the socket head cap screws (5), nuts (1) and
(32) and check that operation is correct.
Page 17

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
Actuator
No
10 20 0.8 130 5.12
10 38 1.5 138.2 5.44
16 20 0.8 203.2 8.00
16 38 1.5 228.6 8.50
16 51 2.0 235.7 9.28
16 63.5 2.5 241.3 9.50
23 20 0.8 209.5 8.25
23 38 1.5 218.9 8.62
23 51 2.0 231.6 9.12
23 63.5 2.5 243.6 9.59
Figure 12. Position of top stem connector
Travel
mm inches mm inches mm inches
“X”
Actuator 87
“X”
Actuator 88
117.3 4.62
178.3 7. 02
J. Shut off the supply pressure in the actuator and use
the pointer (7) to set the travel scale (9) to the closed
valve position and check that operation is correct.
Valve
size
(in)
2
2 900 to 2500 3.25
3 and 4 150 to 1500
4 and 6 2500
6 150 to 1500
8 2500
8 150 to 1500
10 2500
ASME
class
150, 300 or
600
Plug stem
diameters
mm (in)
12.7
(1/2”)
15.87
(5/8”)
19.05
(3/4”)
N2
N1
41405
(turn)
(turn)
3.5
1.5
1.5 3.5
1.25 4.25
4.5
a
mm
(in)
1.9
(0.075)3 2500
2.0
0.08)
2.0
(0.08)
7.4 Coupling of Actuator Type 88
No. 10, 16 and 23
(Figure 15)
A. Tightly screw hex nut (1) onto the plug stem.
B. Tightly screw the top stem connector assembly onto
the actuator stem.
C. Push down the actuator and, at the same time, screw
on the yoke nut (33), then the bottom stem connector
assembly by screwing until they come into contact
with the hex nut (1).
D. Push down the actuator and tighten the yoke nut.
E. Unscrew the top stem connector to respect
dimension “X” in Figure 12.
F. With the plug correctly positioned on the seat,
unscrew the bottom stem connector assembly to
bring it into contact with the top stem connector.
G. Supply air to the actuator until the stem has travelled
at least 15 mm.
H. Unscrew the bottom stem connector the number of
turns N1 specified in Figure 13 then lock manually
with hex nut (1).
Caution: for 41405 valves, use the N2 valve so ensure
tightness of the pilot plug.
I. Release the pressure in actuator so that the two
parts of connector come into contact and tighten the
socket head cap screws and nuts (1) and (32).
10, 12
and 16
12 and 16 2500
18 150 to 1500
20 150 to 900
24 150 to 600
Figure 13. Reverse actuators – seating values for
Valve size
3 and 4 150 to 1500
4 and 6 2500
10, 12 and 16 150 to 1500
150 to 1500
25.4
(1”)
41305 – 41505 – 41605 – 41905 valves
ASME
(in)
2 150, 300 or 600
3 2500
2 900 or 2500 2 (0.08) 3.9 (0.15)
6 150 to 1500
8 2500
8 150 to 1500
10 2500
18 150 to 1500
Figure 14. Seating value for 41405 valves
class
A = Pilot plug travel
1.25
Value A
mm (in)
2.5 (0.1) 4.4 (0.17)
3 (0.12) 5 (0.2)
5 (0.2) 7 (0.27)
6 (0.24) 8.3 (0.33)
7 (0.275) 9.3 (0.37)12 and 16 2500
5
—
Value a1
mm (in)
2.3
(0.09)
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 17
Page 18

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
7.5 Coupling of Air-to-Extend Actuator
(Type 37)
(Figure 16)
7.6 Coupling of Air-to-Retract Actuator
(Type 38)
(Figure 16)
A. Push down on the plug stem (1) until the plug rests
is seated.
B. Attach the actuator to the valve bonnet with the
yoke nut (33) or attachment screws. Apply a sufficient
pressure to the diaphragm to extend the actuator
stem by the normal valve travel for valves 41305,
41505, 41605 and 41905 and the travel minus the
value of A in Figure 14 for 41405 valves.
C. Assemble the two parts of the stem connector (51)
and the point (58). The number of threads inside the
stem connection must be approximately equal for
each stem. Tighten screw(s) (52).
D. Check that the travel of the actuator stem
corresponds to the normal travel of the valve and
that the closed position is obtained for the maximum
spring range indicated on the serial plate.
E. Shut off the air pressure. Use the pointer (58) to set
the travel scale (56). The pointer (58) must indicate
“open” when the air pressure is off.
A. Connect a temporary air supply line to the actuator.
Apply sufficient pressure to the diaphragm to
retract the actuator stem completely. Attach the
actuator to the valve bonnet with the yoke nut (33)
or attachment screws.
B. Shut off the air pressure completely. Increase the air
pressure to retract the actuator stem by the value of
a in Figure 13.
Caution: For 41405 valves, use value a1 of Figure 14.
C. Assemble the two stem connectors (51) and the
pointer (58). The number of threads inside the stem
connection must be approximately equal for each
stem. Tighten screw(s) (52).
D. Check that the travel of the actuator stem
corresponds to the effective travel of the valve and
that the closed position is obtained for the minimum
spring range indicated on the serial plate.
E. Shut off the air pressure then use the pointer (58)
to set the travel scale (56). The pointer (58) must
indicate “closed” when the air pressure is nil.
7.7 Other Types of Pneumatic Actuators
For other type of actuators which the coupling valve
actuator is realized by coupling parts (see Figure 16)
follow the procedure:
• §7.5.foractuatoropensbyairfailure.
• §7.6.foractuatorclosesbyairfailure.
18 | GE Oil & Gas
Page 19
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
10
5
31
3
7
9
32
4
2
10
9
8
8
6
1
7
2
6
31
5
32
4
3
1
Model 87
No. 10-16-23
3
7
9
8
2
Detail of 87/88 Model
No. 6
33
31
10
33
33
Model 88
No. 10-16-23
Parts Reference
Ref. Designation
1 Hex nut
2 Bottom stem connector
3 Pointer screw
H
4 Top stem connector
H
5 Cap screw, soc, head
H
6 Connector Insert
1
7 Pointer
8 Screw, Pan head (travel scale)
9 Travel scale
10 Actuator stem
31 Yoke
H
32 Lock nut
33 Drive nut
H
Not provided for size 6 actuator
Figure 15. Spring diaphragm actuators – types 87/88 multispring
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 19
Page 20

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
36
56
33
1/4” NPT
26
Plug stem coupling
part the size
(see detail)
56
33
72
36
1/4” NPT
26
Parts Reference
Ref. Designation
1 Valve Plug Stem
26 Actuator stem
27 Stem nut
33 Drive nut
36 Spring adjustor
51 Coupling
52 Coupling screw
53 Coupling nut
55 Frein de tige
56 Travel indicator scale
57 Machine screw
58 Travel indicator
72 Spring barrel cap
Typ e 37
Air-to-extend actuator
53
26
51
58
1
52
57
Coupling parts
(No 18 and 18L actuators)
Typ e 38
Air-to-retract actuator
58
1
57
Coupling parts
(No 24 actuator)
26
51
52
1
Detail of coupling types of plug stem
Figure 16. Spring diaphragm actuator 37/38 types
20 | GE Oil & Gas
Page 21

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
Body Sub Assembly
19
20
16
15
13 13
41405 TRIM : 2" to 4" 41405 TRIM : 6" to 18"
41405 TRIM: 2” to 4” 41405 TRIM: 6” to 18”
12
14 15
19
20
16
12
14
Diffuser Option
diffuser option
Figure 17. Internal parts of pilot plug valve – 41405 type
31
16
15
37
14
13
Figure 18. Internal parts of VRT anticavitation valves – 41375 type
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 21
Page 22

22 | GE Oil & Gas
© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
22 | GE Oil & Gas
Page 23

© 2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
1
2" to 4" ≤ 1500 lb
10
Without spring washer
6" to 16" ≤ 1500 lb
and 8" to 16" 2500 lb
10
With spring washer
6" to 18" ≤ 1500 lb
and 8" to 16" 2500 lb
Packing with lateral
2" to 6" 2500 lb
10
18", 20" and 24"
10
24
20" and 24"
connection
2
3
5
24
24
25
16
Double cage
4
23
6
22
7
8
21
10
24
9
16
15
13
14
18
75
76
ac
11G28 29
11A
17 17
Valve working in
Flow to closeFlow to open
11B11B11C11D 11E11F 11F
41095
4160541405 & 4150541305
High
temperature
4130541375
Parts Reference
Ref. Designation Ref. Designation Ref. Designation
1 Valve plug stem
2 Packing flange stud
3 Packing flange nut
4 Packing flange
5 Packing spacer
●
6 Packing 13 Seat/diffuser seat
7 Bonnet
H ●
■ ●
▲ ●
❍
❖
11D Elastomer seal ring 21 Valve body stud
11E Metallic seal ring 22 Guide bushing
11F Tec seal 23 Packing follower
11G Seal ring and backup ring 24 Cage gasket
12 Spring (or spring washers set) 25 Cage washer
●
14 Seat ring gasket
❍
❍
28 Retaining ring
29 Retainer ring
8 Valve body nut 15 Valve plug 37 Stack
●
●
o ●
o ●
H ●
On 41405 series valves only
❖
On 6” to 24” valves sizes only (150 to 600 mm)
♦
On 41605 series valves only
H
9 Plug stem pin 16 Cage 50 Washer (body nuts)
10 Body gasket
♦
17 Spring washer 75 Double cage
11A Graphite seal ring 18 Valve body 76 Pin
11B Metallic ring
11C U PTFE seal ring
❖
❖
●
o
■
19 Retaining ring
20 Auxiliary pilot plug
Recommended spare part
On 41905 series valves only
On 41405/505 Series valves only
On 41305 series valves only
▲
On 41375 high temperature valves only
❍
Masoneilan 41005 Series Globe Valve | 23
Page 24

DIRECT SALES OFFICE LOCATIONS
AUSTRALIA
Brisbane
Phone: +61-7-3001-4319
Fax: +61-7-3001-4399
Perth
Phone: +61-8-6595-7018
Fax: +61-8-6595-7299
Melbourne
Phone: +61-3-8807-6002
Fax: +61-3-8807-6577
BELGIUM
Phone: +32-2-344-0970
Fax: +32-2-344-1123
BRAZIL
Phone: +55-11-2146-3600
Fax: +55-11-2146-3610
CHINA
Phone: +86-10-5689-3600
Fax: +86-10-5689-3800
FRANCE
Courbevoie
Phone: +33-1-4904-9000
Fax: +33-1-4904-9010
GERMANY
Ratingen
Phone: +49-2102-108-0
Fax: +49-2102-108-111
INDIA
Mumbai
Phone: +91-22-8354790
Fax: +91-22-8354791
New Delhi
Phone: +91-11-2-6164175
Fax: +91-11-5-1659635
ITALY
Phone: +39-081-7892-111
Fax: +39-081-7892-208
JAPAN
Chiba
Phone: +81-43-297-9222
Fax: +81-43-299-1115
KOREA
Phone: +82-2-2274-0748
Fax: +82-2-2274-0794
MALAYSIA
Phone: +60-3-2161-0322
Fax: +60-3-2163-6312
MEXICO
Phone: +52-55-3640-5060
Fax:
THE NETHERLANDS
Phone: +0031-15-3808666
Fax: +0031-18-1641438
RUSSIA
Veliky Novgorod
Phone: +7-8162-55-7898
Fax: +7-8162-55-7921
Moscow
Phone: +7 495-585-1276
Fax: +7 495-585-1279
SAUDI ARABIA
Phone: +966-3-341-0278
Fax: +966-3-341-7624
SINGAPORE
Phone: +65-6861-6100
Fax: +65-6861-7172
SOUTH AFRICA
Phone: +27-11-452-1550
Fax: +27-11-452-6542
SOUTH & CENTRAL
AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN
Phone: +55-12-2134-1201
Fax: +55-12-2134-1238
SPAIN
Phone: +34-93-652-6430
Fax: +34-93-652-6444
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
Phone: +971-4-8991-777
Fax: +971-4-8991-778
UNITEDKINGDOM
Wooburn Green
Phone: +44-1628-536300
Fax: +44-1628-536319
UNITED STATES
Massachusetts
Phone: +1-508-586-4600
Fax: +1-508-427-8971
Corpus Christi, Texas
Phone: +1-361-881-8182
Fax: +1-361-881-8246
Deer Park, Texas
Phone: +1-281-884-1000
Fax: +1-281-884-1010
Houston, Texas
Phone: +1-281-671-1640
Fax: +1-281-671-1735
* Masoneilan and Lo-dB are registered trademarks of the General Electric Company.
Other company names and product names used in this document are the registered trademarks
or trademarks of their respective owners.
© 2014 General Elec tric Compa ny. All rights res erved.
GEA19369B 06/2014
 Loading...
Loading...