Page 1
MANUAL
GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S)
Gravimetric Blender
Serial No. ...................
ISO 08.01.02.064.GB
986731
Rev. May 2001
Page 2

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 1
Gravimetric Blender
1.0 INTRODUCTION
2.0 CONTROLS
2.1 Blender startup
2.2 Blender status
2.3 Machine-mode
2.4 Production-modes
2.5 Mixer-mode
2.6 Dispense modes
2.7 Batch handling
2.7.1 Production control
2.7.2 Recipe to weight calculation
2.7.2.1 Method Standard
2.7.2.2 Method Percentage
2.7.3 Adding extra materials
2.7.4 Additive to regrind
2.7.5 Regrind control
2.7.5.1 Empty regrind Control
2.7.5.2 Stock Silo Control
2.7.6 Dispensing
2.7.7 Calculations
2.8 Datalogging
2.9 Certifi cates
3.0 USER INTERFACE
3.1 Operator-interface
3.1.1 Keyboard
3.1.2 User control
3.2 Recipes
3.2.1 Change components
3.2.2 Add/change recipes
3.2.3 Change current recipe
3.3 Timely information
3.3.1 Production screen
3.3.2 Material usage screen
3.3.3 Input & Output monitor
3.4 Adjustment of the gravimetric blender
3.4.1 Calibration of the weighbin
3.4.2 Tare of the weighbin
3.4.3 Hardware-reactiontime
3.5 Overview of parameters
3.5.1 Public parameters
3.5.2 Protected parameters
3.6 Reports and overviews
Page 3

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 2
Gravimetric Blender
3.7 Settings of the user-interface
3.7.1 Change the rights of an operator
3.7.2 Change entrycode
3.7.3 Change date and time
3.7.4 Revision code of the system
3.8 Menu hierarchy
4.0 INSTALLATION
4.1 Demanded connections
4.2 Attaching
5.0 ALARMS
5.1 Alarm reports and solutions
6.0 MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
6.1 Maintenance
6.2 Replacement of parts
6.2.1 Replacement of printed circuit
6.3 Cleaning the machine
6.4 Transportation of the GraviMaster
7.0 TECHNICAL INFORMATION
7.1 General machine specifi cations
7.1.1 Safety measures
7.2 User-interface specifi cations
7.3 Valves specifi cations
7.4 Air pressure cylinders specifi cations
7.5 Electrical diagrams
Page 4

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 3
Gravimetric Blender
1.0 INTRODUCTION
GRAVIMETRIC FEEDING
An effi cient materials blending system is an essential feature of the modern plastics
processing industry. Dosing each component on the basis of weight shows distinct
advanta ges over traditional volumetric systems. The quantity of material delivered is
precise and unaffected by variations in bulk density, fl ow characteristics and particle size.
Ferlin Plastics Automation now have a range of more than twenty blenders that deliver
the benefi ts of gravimetric blending at a price that makes other gravimetric ... and most
volumetric systems ... look distinctly expensive.
FGB SERIES GRAVIMETRIC BLENDERS
“GraviMaster” blending systems are available in more than twenty diffe rent models with a
throughput capacity range from 10 to 750 kg/hr for the standard units. The number of
components on the standard unit is two to six. But purpose-built units may designed for
additional feeds up to a maximum of ten and a throughput capacity up to 1500 kg/hr.
The blending units may either fl ow-control-valve design or have a combination with
auger-feeders. The proven “GraviMaster” blending systems are being used successfully in
Injection-moulding, Blow-moulding, Sheet-extrusion and Film-extrusi on.
ACCURATE WEIGH SYSTEM
Each component is dispensed into a weigh-pan using one set of load cells. When all the
components are correctly weighed, the blend is discharged into a mixing chamber. A high
effi ciency horizontal mixer is programmed to give a uniform blend which discharges to a
storage bin with suction device, or directly into the processing machine hopper.
The system is capable of extremely accurate measurements of additive, even at very small
percentages or ratios. Load cells of the highest accuracy are used, weighing to within
0.01 gm. The accuracy of the process is enhanced by the software system which is
designed to compensate in a subsequent batch for any errors arising in a prece ding batch.
Overall accuracy of 0.1% can be achieved.
COMPACT AND MODULAR CONSTRUCTION
The units are designed and built as a modular construction using standard components
where possible, so that all components are readily obtainable. All components which
are in contact with the raw material are made in stainless steel. This includes hoppers,
valves, augers, weigh pan, mixer and mixing chamber. When auger feeders are instal led,
these can be quickly accessed for easy cleaning. The mixing chamber and weigh pan can
be removed easily for cleaning and access. The construction is in accordance with the
essential require ments under the CE regulations.
Page 5

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 4
Gravimetric Blender
RELIABLE PROCESS CONTROL
The FGB control system incorporates the latest in computer and micro processor
technology for total automation of recipe entry and stora ge, inventory control and process
monitoring. The control panel (user-interface) is provi ded with a micro-controller and
industrial PC with LCD-display, functional keyboard, fi ber optic communication cable (or
RS-422) and parallel printer port.
Features are:
• data storage of all plant raw materials.
• easy call up of materials for the formulation of recipes.
• fast identifi cation of recipes and call up for machine operation.
• automatic regrind control within chosen limits, so that regrind generation is matched
with usage.
• automatic additive to regrind control.
• a fi xed weight of blended material can be produced according to any of the stored
formulations.
• screen display of all process operation.
• reports of material used and batch histories can be printed on an optional printer
regularly.
• storage facility for components and recipes.
• functions are menu driven and take the operator through the required sequence of
actions with simple instructions.
• the software is pre-programmed with many options for the future, these are blenders
you won’t outgrow.
Options are:
• automatic stock silo control.
• extra level control of the blender hoppers.
• extra level control of the machine hopper.
• control and data for materials management systems.
• different language on the display.
• automatic loading of the hoppers can be provided separately with Ferlin loaders or
others of your choice.
• several blenders may be linked to a central user-interface to give integrated inventory
control over the whole process.
Page 6

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 5
Gravimetric Blender
2.0 CONTROLS
When all components are available the dispense of a batch starts. The cycle begins with
closing the weigh-pan. Then each of the requested components is dispensed and weighed in
the weigh-pan. When all the components of the recipe are correctly weighed, the blend is
dischar ged into the mixing-chamber. A horizontal mixer mixes the compo nents to a
uniform blend which discharges to a storage bin, or direct ly into the machine hopper.
2.1 Blender start-up
In this section is a short description of the normal start-up action of the blending system.
More details of the controls are described in the following sections. An emergency stop
can be made to shut-down the machine by pushing the button as indicated in drawing
1 in § 7.7.1.
Steps to follow for the start-up of the blending system:
[1] Plug the communication cable into the user-interface and control box on the blender.
[2] Connect air pressure to the blender and turn it on, 6 bar is recommended.
[3] Turn on the power. On the user-interface and control-box.
[4] Select the right language. The selected language is indicated.
Select a different language through key <↑> or <↓> and press <ENTER>.
[5] If necessary adjust date and time.
[6] Select the blender to be started.
[7] Select on the interface the desired recipe from the menu (F1)
‘controller / select recipe’
[8] Be sure there is no alarm active.
[9] Start the blender, press <START>.
The blender will now operate automatically on the select recipe.
2.2 Blender status
The control of the blender is based on a number of status. Each status gives an exact
description in which situation the controller is. The controller knows the following status:
Inactive
At the start-up of the blender several internal tests will be done automatically if the controller
can’t fi nd a recipe. In this status the blender will not start until a recipe is edited.
Standby
The blender is complete in rest but can be started any moment by giving the start-command.
In this status recipes, parameters and debug-commands can be sent to the controller.
Operating
The blender will now produce a blend for the selected recipe.
Page 7

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 6
Gravimetric Blender
Pause
When the pause-command is given for a temporary stop the blender will stop after the
cycle is complete.
Stop requested
The blender is operating but has received a stop-command. The stop-command will be
executed at the end of a batch-cycle. This status will be replaced automatically with ‘standby’
if nothing is done. If a start-command is given during the status ‘stop requested’ the status
will be ‘operate’ again.
Error
The controller has detected an error and therefore the system will stop. In a sub-menu at
the operator-interface the error will be displayed. The error situation can be recovered using
the <ENTER> command. The error must be solved then.
2.3 Machine-mode
The controller can be in two modes: Automatic and Manual. The operator can change the
mode using the menu item ‘controller’. This changing of mode is only possible while the
blender has status ‘standby’.
If a controller is in Automatic-mode, the recipe will be executed without the need of
an operator. This mode is used for production purposes and is only dependent on the
settings ‘production-mode’.
In automatic mode the keys mentioned below mean:
F5 Start-command (start-key)
F6 Stop-command (stop-key)
F7 Pause-command
F8 Continue-command (clear pause)
After a start-command in Manual-mode one batch will be executed. After this the machine status will be ‘standby’ again. The weighbin and mixbin-valve can be controlled manually.
In manual mode the keys mentioned below meaning:
F5 Step-command (One component of a batch)
F6 Reset-command (Back to the fi rst component of a batch)
F7 Empty weighbin
F8 Empty mixbin
Page 8

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 7
Gravimetric Blender
2.4 Production-modes
The production-mode of the blender indicates how the production will stop in automatic mode. This parameter can be changed using the menu (F1) ‘controller / public parameters’.
The production-mode has three options:
Continue
The blender will not stop automatically after the start-command. The blender will continue
the production, unless the blender runs out of material or an error occurs.
Weight->Alarm
If ‘Weight->Alarm’ has been chosen, a requested weight has to be given. After a start the
requested weight will be compared with ‘produced-weight’. If both are the same or the
‘produced-weight’ higher, the controller will send an alarm to the operator-interface. The
production will continue.
The alarm can be recovered setting the ‘production-weight’ to zero (0). This command is part
of the option-menu (F2) of the status screen.
Weight->Error
When using the option ‘Weight->Error’ a weight has to be given. After a start the requested
weight will be compared with ‘production-weight’. If both are the same or the
‘production-weight’ higher, the controller will send an error to the operator-interface. The
production will not continue in this case.
2.5 Mixer-mode
When all components are dispensed, the contents of the weighbin will be emptied. The
mixer in the mixing chamber, which contains the dispensed components, can be put in
different modes. Choose the menu (F1) ‘controller/public parameters’.
Normal
The mixer is off during production. If the components are dumped from the weighbin into the
mixer chamber the mixer will be on for a predefi ned number of seconds, defi ned by
‘mixerOnTime’. This parameter can only be changed if this option is chosen.
Pulsing
The mixer will pulse during production. Both on- and off-time ca be defi ned using the
parameters mixerPulseOnTime (time on) and mixerPulseOffTime (time off). These
parameters can only be changed if this option is chosen.
Off
The mixer is always off.
On
The mixer is always on, when the machine status is active.
Page 9

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 8
Gravimetric Blender
2.6 Dispense modes
The blender has two ways of dispensing: gravimetric and volumetric. One mode can be
selected or a combination of both. This can be defi ned choosing menu (F1) ‘controller /
public parameters’.
Gravimetric
All component of the batch are dispensed and measured separately. Gravimetric is more
accurate than volumetric, but takes more production time, ie., lower output.
Volumetric
All components of the batch are dispensed at the same time using the dispense time of each
component (calculated by the system). The components are dumped directly in the mixer
chamber. No measurement is done in this mode. Therefore this method is less accurate, but
the production time is faster, ie., maximum output
Combination
When combination is defi ned, one gravimetric will be followed by a defi ned number of
volumetric dispenses. This is defi ned by the parameter combinationRatio. This parameter can
only be defi ned if ‘combination’ is chosen. This mode has the best of gravimetric and
volumetric.
Use: normally the defi ned combination will be done (ex. 1:3). However, if the mixer chamber
is full, the process will automatically do a gravimetric dispense instead of a (possible)
volumetric one.
2.7 Batch handling
2.7.1 Production control
If a start command is given the controller will check if the blender actually can start. If a
hopper has a low-indication (optional) the controller will alarm.
Also the parameters are checked. These can be in confl ict with the recipe to be executed.
The following items will be checked (if applicable):
* Empty Regrind control
- The controlled hopper must contain regrind (according to recipe)
* Stock silo control (optional)
- Controlled hopper must contain regrind (according to recipe)
* Additive to regrind
- Controlled hopper must contain additive (according to recipe)
The blender will not start unless all conditions are met. A message will be sent to the user interface.
Page 10

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 9
Gravimetric Blender
2.7.2 Recipe to weight calculation
After a start-command the controller will calculate the requested weights of all components
of the selected recipe.
A recipe can be defi ned in two ways: ‘Standard’ and ‘Percentage’. These methods can
be defi ned in the recipe choosing menu (F1) ‘recipes / edit recipes’. The methods
‘Standard’ end ‘Percentage’ defi ne the relation of the components (Regrind, Natural and
Additive) in a recipe.
2.7.2.1 Method Standard
The different components are defi ned as follows:
Regrind : Percentage of the batch weight
Natural : Relation between other naturals
Additive : Percentage of the totals of all naturals
Example
Batchweight 2000.0 gr.
Regrind 20.0%
Natural 1 4
Natural 2 1
Additive 5.0%
Regrind : 20.0% of 2000.0 gr. 400.0
Naturals : naturals + additive = 80.0%
naturals + (0,05 * naturals) = 80.0%
naturals = 80.0/1.05 = 76.2%
natural 1 = 4/5 * 76.2 = 61.0% 1220.0
natural 2 = 1/5 * 76.2 = 15.2% 304.0
Additive : 80.0 - 61.0 - 15.2 = 3,8% 76.0
TOTAL 2000.0
Page 11

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 10
Gravimetric Blender
2.7.2.2 Method Percentage
The different component are defi ned as follows:
Regrind : Percentage of the batch weight
Natural : Percentage of the batch weight
Additive : Percentage of the batch weight
Total sum must be 100%.
Example
Batchweight 2000 gr.
Regrind 20.0%
Natural 1 60.0%
Natural 2 15.0%
Additive 5.0%
Regrind : 20.0% of 2000.0 400.0
Natural 1 : 60.0% of 2000.0 1200.0
Natural 2 : 15.0% of 2000.0 300.0
Additive : 5.0% of 2000.0 100.0
TOTAL 2000.0
2.7.3 Adding extra materials
The defi ned amount of the component defi ned in the recipes can be changed external
using some special parameters. The controller has two methods: ‘Additive to regrind’ and
‘Regrind Control’.
IMPORTANT
Addition of extra material using ‘Additive to regrind’ and ‘Regrind Control’ is only
possible when a ‘standard’ recipe is used.
Page 12

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 11
Gravimetric Blender
2.7.4 Additive to regrind
It is possible to dispense more additive in relation to the amount of regrind. Choose for
this defi nition menu (F1) ‘controller / public parameters’. A maximum of two hoppers
(additive) can be defi ned (additiveToRegrindHopper). The defi nition must be completed
defi ning the requested percentage (additiveToRegrindPerc).
ADDITIVE TO REGRIND
Not activated Activated with 2.0%
Component Recipe Weight (g) Recipe Weight (g)
Regrind 20.0% 400.0 20.0% 400.0
Natural 1 4 1219.0 4 1213.0
Natural 2 1 304.8 1 303.2
Additive 5.0% 76.2 5.0% + 2.0% 83.8
2.7.5 Regrind control
The fl ow of ‘regrind’ is very often not continuous due to the process. There are two
methods to adjust the amount of regrind to the actual process: ‘Empty Regrind’ or ‘Stock
Silo’.
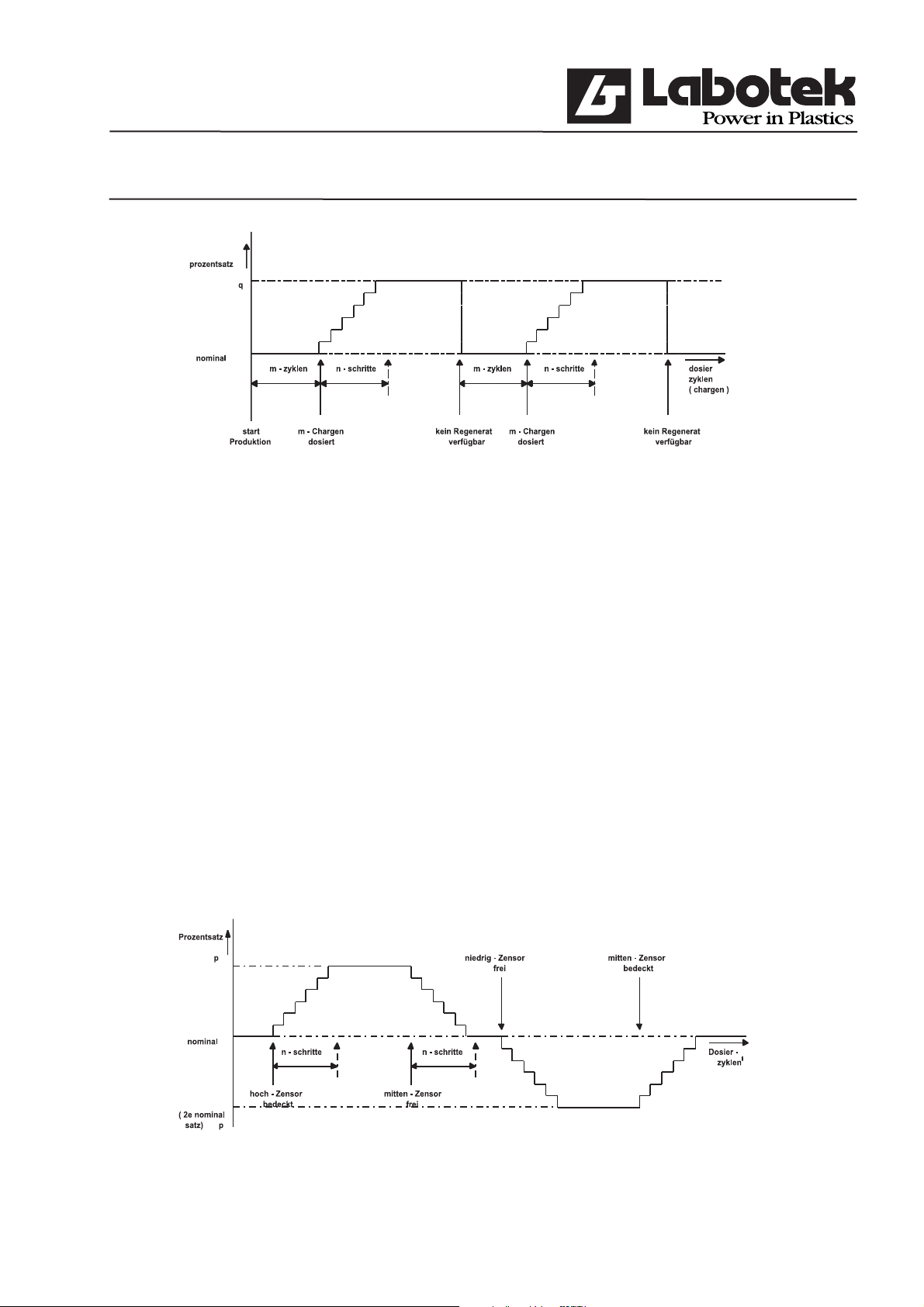
2.7.5.1 Empty regrind Control
Empty regrind control means: keep the regrind-hopper empty. The material must be
dispensed, because otherwise another parts of the process can be destroyed (regrind return
mechanism).
Through menu (F1) ‘controller / protected parameters’ the process can be activated. After
the process is started a defi ned amount of batches (Empty regrind wait count) must be
awaited before the percentage will be increased. The percentage will be increased in
the defi ned number of steps (Dispensevariation cycl.) until the requested percentage is
reached (Dispense increase).
If not enough material can be dispensed from the regrind hopper, then regrind will be reset
to the original setting (recipe).
Page 13
Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 12
Gravimetric Blender
2.7.5.2 Stock Silo Control
A regrind silo can have (optional) three sensors to detect high- low- and middle. If the
controller has these sensors, ‘Stock-Silo’ regrind control can be activated, choosing menu
(F1) ‘controller / protected parameters’.
If the high-sensor is true, the silo is almost full. Therefore more regrind will be dispensed.
This is the same as described in ‘empty regrind control’. This will be done until the middle
sensor is not true anymore. In a defi ned number of steps the process will dispense the
original setting of the recipe.
If the low-sensor is true, the silo is almost empty. Therefore less regrind will be dispensed.
This is the inverse as described in ‘empty regrind control’. This will be done until the
middle sensor will become true. In a defi ned number of steps the process will dispense
the original setting of the recipe.
Page 14

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 13
Gravimetric Blender
2.7.6 Dispensing
Dispensing of the different components will start after the calculation of the related weights.
The components are dispensed in the order as defi ned in the recipe (gravimetric only). In
volumetric mode all components are dispensed at the same time.
Every mechanical valve has a reaction time. The controller uses the ‘Hardware Reaction
Time’ to calculate the time which the dispense valve must be activated. The ‘Hardware
Reaction Time’ is the maximum active time of the valve when no material is dispensed. The
controller uses a pulse of 5ms in the following algorithm:
OpenTime = Weight [g] / dipenseSpeed [g/s]
OpenPulses = (OpenTime [s] / 0.005 [s]) + HardwareReactionTime [Puls]
After every dispense cycle the weight is measured. The weight bin must be stable before
the weight can be measured, therefore a time delay is inserted between dispense and
measuring. When the controller starts measuring the signal must be stable for at least 1 sec.
(signal within the ‘Weighbin-variationband’)
After measuring the weight of the fi rst dispense some calculations can be done, and with
the results parameters can be changed. Result is a more accurate next dispense. After the
fi rst dispense of a material one of the following situation occurs:
Dispense is correct
The difference between calculated- and measured weight is less then the dispense accuracy.
In this case extra dispense tries of this material are not necessary.
Dispense not correct (too little)
The difference between calculated- and measured weight is more than the dispense
accuracy but there is less dispensed (measured) than calculated. In this case the controller
reacts according to the chosen ‘alarm-type’. The following ‘alarm-types’ are possible:
IGNORE No extra dispense-tries. Relations within the recipe will corrected by
re-calculations.
WARNING The controller tries to reach the dispense-accuracy by extra dispenses. The
extra dispenses are limited by the parameter ‘dispenseTry’. When after a
maximum number of dispense tries, the accuracy is not reached the controller
sends a warning only to the user (= The controller continues with the next
material).
ERROR The reaction of the controller is equal to ‘WARNING’ only an error is sent
to the user when the accuracy is not reached. Now the controller waits for a
confi rmation (enter) to initiate new dispense tries of the same material. This
process goes on until the dispense accuracy is reached.
Page 15

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 14
Gravimetric Blender
Dispense not correct (too much)
To much material has been dispensed so there is nothing the controller can do. Of course
the relations within the recipe will corrected by re-calculations.
After the fi rst dispense try in all of the above mentioned cases a new dispense rate will
be calculated. If the measured dispenserate (measured weight / dispense time) differs from
the used dispenserate a correction can be made. A correction is only made if the difference
between the measured- and used dipenserate is less then the boundary
(dispenseRateVarBand). This method prevents the controller calculating incorrect values
e.g. if a hopper runs out of material. The new dispenserate is calculated by the next
algorithm:
dispenseRate = ((4 * dispenseRate) + (measuredWeight/dispenseTime))/5
When all components of a recipe are dispensed the contents of the weighbin is dumped
in to the mixer chamber. The weighbin dumps the material by opening a valve for a given
time. This time (weighbinDumpTime) is a parameter which can be changed. It is also
possible to start the mixer at this time (see mixer-mode). There are two conditions for
opening the weighbin valve:
Condition 1. The mixbin-vale may not be open (if present)
Dispensed material must be mixed fi rst before it can be used. Therefore the mixbin-valve
and weighbin-valve may not be open at the same time.
Condition 2. The mixerchamber may not be full
If the input-device indicates a full mixerchamber no material may be dumped into it (it
is full)
2.7.7 Calculations
In order to be able to dispense with high accuracy, the actual measured weights will be
used to recalculate the requested weight of the next component. The dispense will be
optimised if possible in order to guarantee a good batch (good relation).
IMPORTANT
Best dispense order is:
Regrind, Natural, Additive
Page 16

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 15
Gravimetric Blender
2.8 Datalogging
Some production data is stored. This is shown at the user interface and can also be printed.
* Batch data
- measured weight (each component)
- dispenserate of each component
- recalculation to recipe
* Total data
- Sum of batch data
* Material usage
- dispensed amount of each hopper
- percentages
The controller saves all data in battery-backup memory.
Page 17

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 16
Gravimetric Blender
2.9 EQ-Net Certifi cate
Page 18

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 17
Gravimetric Blender
2.10 ISO Certifi cat
Page 19

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 18
Gravimetric Blender
3.0 USER INTERFACE
3.1 Operator-interface
3.1.1 Keyboard
Description:
F1 Open main menu. All other sub-menu’s can be selected
F2 Open option menu. The contents is dependent of the actual screen.
F3 Will be used during calculation
F4 Choose node number
The function keys F5 up to F8 is dependent of the machine mode (automatic, manual).
FUNCTION KEY IN MACHINE-MODE
Function key Automatic Manual
F5 Start production Dispense one component
F6 Stop production Mixer
F7 Pause Dump weightbin
F8 Start after pause Dump mixer chamber
Page 20

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 19
Gravimetric Blender
Besides the function key there are some special keys:
DIRECT MACHINE-CONTROL KEYS
Key Description
# or F4 Select FGB
START Start command, the same as F5
STOP Stop command, the same as F6
DATA ENTRY KEYS
Key Description
0-9 Entry of numbers
+/- Increase and decrease function (value of fi eld can be changed by step)
ENTER Select function. (choise is made and entered values are saved)
. Decimal point
ESC Escape, Leave menu without choice
(Home) (Arrow up with line) Jump to fi rst element of row
(End) (Arrow down with line) Jump to last element of row
INS Insert function to add recipes and components
DELL Delete function to delete recipes and components
← Backspace (above DELL-key) delete the character left of the cursor
← ↑ → ↓
Cursor-keys, move cursor and menu-items
Page 21

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 20
Gravimetric Blender
3.1.2 User control
The user-interface consists of several screens which can be selected by a menu. A screen
consists of objects only one object in a screen is active (selected). By using the ↓ en ↑
arrow keys the actual selected object can be changed. Pressing <ENTER> activates the
selected object.
Button
After activating the button a command (or set of commands) is (are) executed. The name of
the button represents the functionality of the button.
Number input fi eld
When a number input fi eld is selected it can be activated by either the <ENTER> key or
just typing the numbers. The activated input fi eld shows a cursor at the position where
the next number will be placed. To deactivate (leave) the input fi eld use one of the the
following keys <ENTER>, <ESC>, ↓ or ↑
Text input fi eld
The text input fi eld is equal to a number input fi eld but it also accepts characters. Because
the keyboard doesn’t have character-keys a special method is implemented to enter
characters.
To enter a character in a text inputield fi rst activate the object with the <ENTER> key.
When the input fi eld is activated a cursor is shown at the fi rst position. At this moment it
possible to select a character with the <+> and <-> keys. After a character is chosen the
next position can be selected with the → arrow key.
Option fi eld
Option fi elds are objects with a toggle function (yes/no) or (true/false). When the button
according to the option fi eld is activated the value is toggled. The actual value of the option
fi eld is displayed by a cross. When the cross is visible the object has the value ‘yes’ or
‘true’ otherwise the value is ‘no’ or ‘false’.
Optionlist
Optionlist fi elds are fi elds that can contain a limited set of values. The optional values
become visible as the object is activated. Now the required value can be selected by using
the ↑ and ↓ key and select it with <ENTER>.
3.2 Recipes
Recipes constitute the core of the controller. They contain all information about the
material to be produced. By the menu (F1) ‘recipes / edit recipes’ it is possible to add
recipes to the controller. One recipe consists of one or more (max 12) components which
can be changed independently.
Page 22

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 21
Gravimetric Blender
3.2.1 Change components
There is a components list available in the controller. The list can be used by the operator
to defi ne recipes. The components list stores the name and type of a component and is
maximised to 100 components. The operator is free to chose a name for a component.
There are only three options namely:
Regrind Scrap-material
Natural Basic-material
Additive Additive-material (e.g. masterbatch)
One component of every type is already present in the list. These components have the
name ‘no name’ and can not be deleted from the list.
To add or modify components chose the menu (F1) ‘recipes / edit components’. The next
screen will be displayed:
[0]OPERATING AUTO[ ] [ ] [ ]
STATN:[0] FGB#00: (No name) STATUS OPERATING
MODE: AUTOMATIC
------------------------ [Edit components]
Name Type
SCR GARDEN CHAIR REGRIND
ADEG-2RN NATURAL
ADEG-4RN NATURAL
ANTISTATIC ALU ADDITIVE
<ENTER> = edit component
<INSERT> = insert component
<DELETE> = delete component
F1Menu F2Option F3 F4Clear F5Start F6Stop F7Pauze
F8Cont.
Page 23

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 22
Gravimetric Blender
In the screen it is possible to select a component with the arrow keys. After a component has
been activated by <ENTER> the name and type can be changed. If the fi eld type has been
activated an option list will appear. One of the options (Regrind, Natural or Additive) must be
chosen.
By pressing the <INS> insert-button a new component will be added to the list. The controller
places a standard name and type into the fi elds. The operator now can change these fi elds to
the correct name and type.
Deleting a component from the list can be done by pressing the <DEL> delete-key. The
component pointed to by the highlighted line will be deleted from the list.
The option-key (F2) contains two functions in the screen ‘edit components’: print components
and search components, activate one of them by selecting and push <ENTER>.
Example: Add a new component
Goal: Component with he name “WHITE” and type “ADDITIVE”
Actions:
Step: Menu (F1) ‘recipes’ <ENTER>
Step: ‘edit components’ <ENTER> (By using the arrow-keys)
Name Type
Step: Press <INS> key (INS = insert)
Name Type
< > [NATURAL]
Step: Search for the character W by using the + or - key:
<+> Starts with special characters and numbers then the alphabet
<-> Starts at the end of the alphabet
When the + or - key is hold down the character will change fast.
Page 24

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 23
Gravimetric Blender
If the character W has been found the ? key is pressed.
Name Type
<W> ? [NATURAL]
Step: Repeat the same procedure for the character H, I, T and E. When the whole name is
given press <ENTER>. Now the name ‘WHITE” is stored.
Name Type
?WHITE? [NATURAL]
Step: Press the ? key again to select the type-fi eld.
Name Type
[WHITE] NATURAL ?
Step: Press <ENTER> to activate the fi eld.
Name Type
[WHITE] [NATURAL ]
REGRIND
NATURAL
ADDITIVE
Step: Select ADDITIVE by using the arrow keys and confi rm by pressing <ENTER>.
Name Type
[WHITE] ?ADDITIVE ?
Step: To confi rm the new component press the arrow key ? or use the <ESC> key.
Now the “ADDITIVE” component “WHITE” is added to the list. The maximum number of
components is 100.
Page 25

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 24
Gravimetric Blender
3.2.2 Add/change recipes
The terminal has the capacity for 340 recipes. This space is divided into 4 spices so every
connected FGB can contain 85 recipes. If the menu item (F1) ‘recipes / edit recipes’ is
chosen a list with recipes will be displayed.
Now recipes can be added, changed or deleted. The <DEL>-key deletes the current recipe of
course there will be a conformation for the operator. By adding <INS>-key or changing
<ENTER> the current recipe the same screen is used.
[0]OPERATING AUTO[ ] [ ] [ ]
STATN:[0] FGB#00: (No name) STATUS OPERATING MODE: AUTOMATIC
+--------------------------EDIT RECIPE
Number : [ 10]
Name : CRATE
Colour : [YELLOW ]
Batch : [ 2]Kg.
Interpretation : [STANDARD ]
H# Component Quant Alarm Rate (g/s)
1 noname (r) 50.0 IGNORE 957.2
2 noname (n) 2.0 IGNORE 891.4
3 noname (n) 2.0 IGNORE 875.5
5 noname (a) 4.0 IGNORE 8.3
4 <ENTER> = edit line
5 <INSERT> = insert line
6 <DELETE> = delete line
7 <HOME> = sort up
8 <END> = sort down
9
10
11
12
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------
F1Menu F2Option F3 F4Clear F5Start F6Stop F7Pauze
F8Cont.
All fi elds of the recipe are visible in the screen. By selecting the objects with the arrow-keys
and activate them with the <ENTER>-key it is possible the change the them. Below a list is
given with every fi eld of the recipe giving some extra information about the fi eld.
Page 26

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 25
Gravimetric Blender
FIELD OF A RECIPE
Fields Description
Number Unique recipe number
Name Recipe name
Colour Characterfi eld for the colour-name
Batch Total batchweight
Interpretation Recipe calculation
Component Link hopper to component
The screen can be left by pressing the <ESC>-key. Now the terminal checks the recipe and if
it is correct it will be stored. If the recipe is not correct the operator can chose either changing
the recipe or discard all changes.
The option-key (F2) contains other functions in the screen ‘edit recipes’. The next functions
are available:
OPTION MENU IN EDIT-RECIPE
Option Description
Copy recipe Copies the recipe to the same or other terminal.
Find number Searches for the recipe with the given number.
Find colour Searches for the recipe with the given colour.
Find name Searches for the recipe with the given name.
Print recipe Sends the current recipe to the printer.
Print all recipes Prints all recipes of the actual controller.
Example: Add a new recipe
Goal: Add a 2 kg standard recipe .
Remark: The required component names should have been added.
Page 27

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 26
Gravimetric Blender
Actions:
Step: Menu (F1) ‘recipes’ <ENTER>
Step: ‘edit recipes’ <ENTER>
Name Nr. Colour
Step: Press the <INS> key (INS = insert)
Number: [1]
Name: ? ?
Colour: [ ]
Batch: [ 2.0] kg
Interpretation: [ STANDARD ]
H# Component Quantity. Alarm Speed (g/s) 1 2 : : 10 11 12
The name and colour of the recipe is entered in the same way as the components name
(§ 3.2.1).
Step: Press the arrow key <↓> to select the batch.
Batch: < 2.0> kg
When the batchweight must be changed it can be done by the use of the numeric-keys
IMPORTANT Never enter a batchweight higher then the standard value.
Page 28

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 27
Gravimetric Blender
Step: Press the arrow-key <↓> once
Interpretation: < STANDARD>
Step: When the interpretation must be changed into PERCENTAGE press the <ENTER>
key. Now select PERCENTAGE with the arrow keys and confi rm with <ENTER>.
Interpretation: STANDARD
PERCENTAGE
Step: Press the arrow key <↓> once.
H# Component QTY Alarm Speed (g/s)
1
2
:
12
Step: Select the hopper you want to edit with the arrow-keys and press <ENTER> to
activate.
H# Component Quantity Alarm Speed (g/s)
1
2
:
12
Step: Press <ENTER>.
Name Type
Noname REGRIND
Noname NATURAL
Noname ADDITIVE
WHITE ADDITIVE
Page 29

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 28
Gravimetric Blender
Step: Use the arrow-keys <↓> to select a component and press <ENTER>.
Use the arrow-key <?> to select Quantity. Enter the quantity and press <ENTER>.
Use the arrow-key <→> to select Alarmtype and press <ENTER>.
Alarm
Ignore
Ignore
Warning
Error
Step: Select an alarm type by using the arrow-keys and press <ENTER>.
It is not necessary to enter a speed (g/s) because the terminal already has entered
standard values and the GraviMaster calculates new speeds and updates the recipe.
Step: Press the arrow-key <ο> to select the next hopper number.
Depending on the model, it is possible to use upto 12 hoppers.
The terminal has a keyboard but the keyboard doesn’t contain characters. Therefore it is
possible to connect a standard AT keyboard to the terminal. This keyboard must connect to
a connector which is placed on the PCB in the terminal. When using a AT keyboard, than:
• Switch power off the terminal
• Disconnect the internal keypath from the PC board
• Connect the AT keyboard on the PC board
• Switch on the terminal
Now you can use the AT-keyboard. When you are ready, than connect the terminal-keyboard
again. This has to be done when the terminal is switched off.
3.2.3 Change current recipe
When an operator wishes to produce a new product a change of the current recipe must be
done. To change the current recipe select menu (F1) ‘controller / select recipe’. The terminal
now shows a list with all recipes. The recipe which is marked with an <↓> is the actual
recipe, this recipe is also loaded in the controller.
IMPORTANT
When a new recipe is selected be sure that all hoppers are fi lled with material. The controller
calculates new dispense-rates by a fast algorithm in the fi rst 5 batches.
Page 30

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 29
Gravimetric Blender
3.3 Timely information
It is possible to get an over view of one of the connected controllers. Therefore three screens
are available on the terminal: production-screen, material usage-screen and input/output screen.
3.3.1 Production screen
The production-screen can be reached by selecting menu (F1) ‘production / production
status’. The production-screen displays information about the current controller. The
information on the screen is updated every 0.3 sec.
Page 31

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 30
Gravimetric Blender
OPERATING AUTO[ ] [ ] [ ]
STATUS:[0] FGB#00: (No name) STATUS OPERATING MODE: AUTOMATIC
PRODUCTION STATUS]
Production mode :
CONTINUE Dispense mode: GRAVIMETRIC
Name: PIR-HOUSING Mix mode : PULSE
Recipe CRATES YELLOW
[current] [previous] [total]
H# Type Recipe Requested Dispensed Recipe Dispensed Recipe Dispensed
1 REG [ 20.0] 400.0 20.0 400.0 20.0 1600
2 NAT [ 1.0] 1523.8 1.0 1523.8 1.0 6095
3 ADD [ 5.0] 76.2 5.0 76.2 5.0 305
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
totals
[ACCEPT] [UNDO CHANGES] 0.1 2000.0 8000
Produced weight: 82000
F1Menu F2Option F3 F4Node F5Start F6Stop F7Pauze
F8Cont.
During production it is possible to change the recipe without a change of the current recipe.
The recipe can be changed in the production-screen by selecting a fi eld (arrow-keys). Next
enter a new value and press <ENTER> to confi rm. Now the recipe is changed but the
controller uses the new values at the start of a new batch.
3.3.2 Material usage screen
The material usage screen menu (F1) ‘production / material usage’ displays the total
quantity of material witch is used ordered by hopper number. The quantities which are stored
doesn’t depend on the current recipe. The material usage screen is erased from memory by
one of the following actions:
* Command given by the operator
* After a operator prints the screen.
This is possible by using option-key (F2) and selecting the option you require and pressing
<ENTER>.
Other values witch are stored in the material usage screen are: date of the last erase-action,
number of batch-cycles and production speed (kg/hour).
Page 32

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 31
Gravimetric Blender
3.3.3 Input & Output monitor
The input & Output screen menu (F1) ‘controller / digital I/O monitor’ displays all digital
input and output lines. Every object in the screen can be selected by using the arrow-keys.
When a output line is selected and <ENTER> is given the digital output will toggle. The
operator has control of the digital outputs when the controller is in ‘manual mode’.
3.4 Adjustment of the gravimetric blender
The controller has some system-parameters. These parameters must be entered during the
installation of the GraviMaster. The controller uses these parameters to read the weigh bin
signal correctly, to open the weigh bin-valve, control the dispense-valves or motors etc.
3.4.1 Calibration of the weigh bin
The controller uses two known (entered) calibration-points to calculate a weighline. The
controller uses this line to fi nd a weight by every input-signal. The two calibration-points
must be entered by the operator by the menu (F1) ‘controller / calibration / loadcell’.
The calibration-procedure of the loadcell has two steps. Extra information is given to the
operator by every step. This information is displayed at the top of the screen. First be sure
that the weighbin is empty and press (F3). The weight of the empty weighbin is measured
and stored by the controller. Next step is to fi ll the weighbin with a reference-weight and be
sure that the input fi eld on the terminal has the same value. Now press (F3) again and the
second calibration-point is measured and stored. The calibration-procedure is now ready.
IMPORTANT
The second calibration-point must be greater then the fi rst one.
3.4.2 Tare of the weighbin
Due to temperature, age, overload etc. it is possible that the weighline of the controller
‘moves’. When the line has moved a zero-weight will be displayed that isn’t zero. To move
the weightline back it is possible to start a new calibration procedure. But the calibration procedure takes a lot of time and the weightline is correct (it only moved). The tare-function
moves the line back to its zero-point. To start the tare function enter menu (F1) ‘controller
/ calibration / loadcell-tarration’.
Page 33

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 32
Gravimetric Blender
3.4.3 Hardware-reactiontime
The adjustment of the number of pulses is very important for the autopulse system of the
FGB-M05. When dosing less than 8 gram of material, the GraviMaster will switch over to the
autopulse system. In the hardware-reactiontime the opening time can be adjusted by increasing
the clockpulses. One clockpulse is 5 ms (0,005 s).
The autopulse system does not caculate the rate in g/s but in g/puls. It calculates how many
pulses he needs for an amount of material. This is why it is very important that the opening time
of the pulse is not too long, because it cannot dose accurate anymore.
Standard adjustment:
Hopper
Clockpulses
Time (s)
1 3 0,015
2 4 0,020
3 4 0,020
4 3 0,015
3.5 Overview of parameters
The controller has a great number of parameters. The parameters are necessary to control
the machine with all its features. The parameters are broken down into two groups; public parameters and protected-parameters. Free parameters may be changed by an operator,
protected parameters may only be changed if the password is given.
3.5.1 Public parameters
Below a list is given of all parameters which are attainable by the menu (F1) ‘controller /
public parameters’.
Page 34

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 33
Gravimetric Blender
PUBLIC PARAMETERS
Parameter Description Init
AlarmReport Indicates if alarm-reports must be printed. No
ProductionReport Indicates if production-reports must be printed. No
*)
*)
If so the parameter interval-time must be given also.
Interval
BatchReport Indicates if batch-reports must be printed. No
Pauze (time) before printing the next production-report.
01:00.00
*)
ProductionMode Actual production-mode. There are three possible CONTINUE
modes; CONTINUE, WEIGHT and ALARM_
WEIGHT. If the mode WEIGHT os ALARM_
WEIGHT has been selected the parameter production
Weight must also be given.
ProductionWeight The FGB stops his production when the production 100 [Kg]
Weight is reached. (productionMode must be
WEIGHT or ALARM_WEIGHT).
DispenseMode Actual dispense-mode. There are three possible GRAVIMETRIC
modes; GRAVIMETRIC, VOLUMETRIC and
COMBINATION. If the mode COMBINATION is
chosen the parameter combinationRatio must be given.
CombinationRatio Relation between the volumetric and gravimetric 3
dispenses. (one gravimetric dispense and x
volumetric dispenses).
MixMode Actual mixermode. There are four possible modes; PULSE
ON, OFF, NORMAL and PULSE. In normal-mode
the parameter mixerOnTime must be given. In the
mode pulse the parameters mixerPulseOnTime and
mixerPulseOffTime must be given.
MixerOnTime Time the mixer is activated after the material is 10 [s]
dumped out of the weighbin.
MixerPulseOnTime Time the mixer is activated in pulse-mode. 5 [s]
MixerPulseOffTime Time the mixer is not activated in pulse-mode. 15 [s]
AdditiveToRegrind Percentage additive to regrind which must be added. 0 [%]
Percentage 1/2
AdditiveToRegrind Hoppernumber in which the additive is. Hopper 5
Hopper 1/2
WeighbinDumpTime Time the weighbinvalve is activated (dumping of 4 [s] 0,5 kg unit
material into the mixerchamber). 6 [s] 1,2,5 and
25 kg unit
LevelControlWaitTime Time between the full signal of the mixerchamber 8 [s]
sensor and opening the mixerchamber-valve.
LevelControlDumpTime Time between the free signal of the mixerchamber
sensor and closing the mixerchamber-valve. 1 [s]
*) No = [ ], Yes = [X]
Page 35

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 34
Gravimetric Blender
For example if the alarm report must be activated. First select the option fi eld by using the
up- and down-keys. Now press <ENTER> to activate the option fi eld. If the option fi eld
displays a [X] the alarm report is activated. The parameters must be updated into the
controller, so select the OK button and activate it by pressing <ENTER>. Updating the
parameters into the controller must be done for every parameter.
3.5.2 Protected parameters
Below a list is given of all parameters with are attainable by the menu (F1) ‘controller /
protected parameters’.
Page 36

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 35
Gravimetric Blender
PROTECTED PARAMETERS
Parameter Description Init
BatchWeight Total weight of one batch. This value is copied into 0,5 [kg]
every recipe when it is created.
DispenseTry Maximum number of tries per component to reach 4
maximum accuracy
DispenseAccuracy Minimum accuracy for each component. 25 [%]
DispenseRate Maximum deviation when a re-calculation of the 30 [%]
CorrectionBand dispense-speed is done
SiloPresent Indicates the ‘Stock-Silo’ regrind control process No
is activated.
MaximumTare Maximum absolute deviation from the zeropoint 40 [g]
Variation of the weighbin.
SiloHighCount Number of batches with the highness activated 100
before the controller initiates an alarm.
SiloLowCount Number of batches with the lowsensor not activated 100
before the controller initiates an alarm.
EmptyRegrind Indicates the ‘Empty Regrind’ regrind control No
process is activated.
EmptyRegrindHopper Indicates the hopper which is used in the empty Hopper 1
regrind process
EmptyRegrindCycles Number of batches empty regrind waits before 1
increasing regrind (startprocess)
Dispense inc/dec Maximum percentage for the regrind control 10 [%]
processes
Dispense Number of steps in whitch the maximum must 10
VariationCycles be reached.
LoadcellGain Amplifi cation-factor for the loadcell signal 16
LoadcellOverload Maximum weight in the weighbin. The controller 800 [g]
initiates an error on this point.
LoadcellSettleTime Time between the dispense of the last component 1 [s]
and reading the weigbin-signal.
(to eliminate vibrations).
LoadcellWeight To read a correct weight 8 samples must fi t to this 10 [g]
BandWidth absolute band.
FGB-Name/Nr. Name of the controller; This name is used in the
user-interface of the terminal.
Page 37

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 36
Gravimetric Blender
3.6 Reports and overviews
There is the possibility of printing several reports and overviews. Underneath a list is made
with the reports and overviews with behind them the section and page where instructions for
printing are given.
* batch report § 3.5.1
* production report § 3.5.1
* material usage report § 3.3.2
* error report § 3.5.1
* recipe overview § 3.2.2
* component overview § 3.2.1
* alarm overview § 5.1
3.7 Settings of the user-interface
3.7.1 Change the rights of an operator
The terminal has some area’s which are protected by a password; protected-parameters, debug monitor etc. Before an operator can use, modify or see these area’s he has to perform a login
procedure. This procedure starts by choosing menu (F1) ‘system / login’ the controllers asks
now for an ID (see below). When the ID is correct the menu item login changes to logout.
To lock the system select menu (F1) ‘system / logout’ the menu item changes to login again.
3.7.2 Change entrycode
To change ID chose menu (F1) ‘system / change ID’.
IMPORTANT
Standard the ID is set to 1234. After it is changed the ID 1234 can’t be used.
There is no way to display the current ID so store the actual ID in a safe place.
When you lost the new code, please contact your dealer.
Page 38

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 37
Gravimetric Blender
3.7.3 Change date and time
Date and time of the terminal can be changed by entering menu (F1) ‘system / time and date’.
3.7.4 Revision code of the system
The terminal has the possibility to display the revision and those of the connected controllers.
This information can be important for system-errors when you inform the dealer. To display
this information chose menu (F1) ‘system / revision’
3.8 Menu hierarchy
PRODUCTION CONTROLLER RECIPES SYSTEM
Production status Select recipe Edit recipes Login/logout
Change ID
Material usage Public parameters Edit components
Protected parameters Time and date
Revision
Alarm history
Cablibration >>>
Hardware reaction time
Digital I/O Loadcell
monitor Loadcell tarration
Select automatic
mode
Select manual mode
Page 39

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 38
Gravimetric Blender
Reference to section:
Production
Production status § 3.3.1
Material usage § 3.3.2
Controller
Select recipe § 2.1
Public parameters § 3.5.1
Protected parameters § 3.5.2
Alarm history § 5.1
Calibration
Hardware reaction time § 3.4.3
Load cell § 3.4.1
Load cell tarration § 3.4.2
Digital I/O monitor § 3.3.3
Select automatic mode § 2.3
Select manual mode § 2.3
Recipes
Edit recipes § 3.2.2
Edit components § 3.2.1
System
Login/logout § 3.7.1
Change ID § 3.7.2
Time and date § 3.7.3
Revision § 3.7.4
Page 40

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 39
Gravimetric Blender
4.0 INSTALLATION
4.1 Services
For installation 1ph or 3ph supply is required dependent on type of unit and a 1/4” air supply
with a minimum 6bar.
4.2 Mounting
There are several ways where to place the GraviMaster, namely
- on a frame
- on a mezzanine
- on the machine
Before mounting the unit fi rst open the front panel and take out the mixing chamber.
Make sure nothing is connected yet.
The front panel can be opened by opening the fasteners.
You can take out the mixer chamber and the weigh bin when the frontdoor is open.
s
4.2. Mountingplate
Page 41

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 40
Gravimetric Blender
The foot plate of the GraviMaster should be attached on a steel attachment plate on the frame
or mezzanine or fl ange pertinent to the machine.
The mounting holes are 9 mm and are positioned as shown in drawing 4.2
The unit should be mounted as stably as possible, in connection with the accuracy of the
loadcell.
Now mixer chamber, the weighbin and the front panel can be replaced.
Connect the air pressure to the regulator (max. 12 bar). Put the plugs of the GraviMaster and
the user interface in the sockets (220 V), these should be “clean”, without fl uctuations and it
must not be drawn off a 400 V wire. Then the communication cable should be plugged into
the user-interface and the control-box.
The raw material supply should be connected to the hoppers. For startup refer to section 1
of chapter 2.
Page 42

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 41
Gravimetric Blender
5.0 Alarms
5.1 Alarm reports and solutions
The operating system sends a message to the terminal when a failure is detected. The
message will be displayed and stored with date and time in the alarm history. Underneath is
a list of all possible messages, with the solutions.
Page 43

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 42
Gravimetric Blender
ALARMS
Alarm-message Description Action to cancel alarm
Press enter Alarm already cancelled Press enter
Operator must confi rm
No control voltage No 24V control voltage present Turn on the main-switch
or check fuses
Covers open Security cover not present or mixerchamber Place security-cover /
removed mixer-chamber
Production weight producedWeight equals produktionweight Reset the
reached producedWeight
No weighbin or Zero weight of the weighbin is greater then Loadcell must be
calibrate ‘maximumTareVariation’ calibrated or a tare
procedure must be done.
Parameters corrupted The controller can’t read his parameters Check the parameters
*)
correctly. All parameters will be fi lled with
standard values.
Data corrupted The controller can’t read the productiondata Confi rm
*)
(production-screen). The data will be cleared.
Hopper low The hoppersensor (optional) indicates that a Fill hopper with material
hopper runs out of material.
Hopper empty No material is dispensed so the controller
indicates that a hopper must be empty.
Fill hopper with material and
press the start-button.
***)
Loadcell not calibrated The controller can’t read the loadcell Calibrate the weighbin
parameters correctly.
Loadcell overload Weight of the weighbin is greater than the Remove material out of
loadcellOverload parameter. the weigbin.
Check in recipe the
Loadcell not stable Weightsignal from the loadcell doesn’t fi t Press enter
*) **)
the band.
Loadcell need Controller needs more samples to generate a Press enter
*)
more samples stable weight.
Loadcell boundary error
To much weight-samples doesn’t fi t the band. Press enter
*)
Silo high Silo supply hopper is full for several batches. Counter will
(High sensor is activated) automaticaly cleared.
Regrind process par Given hoppernumbers doesn’t contain regrind Check the regrind
confl ict or percentage control parameters
Additive regrind par Given hoppernumber doesn’t contain additive Check the
confl ict AdditiveToRegind
parameters
Page 44

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 43
Gravimetric Blender
*) If this error occurs frequently contact your dealer
**) Other problems which initiate this error are:
- The weighbinDumpTime too short
- Weighbin valve touches the material when mixerchamber is full
When the second problem occurs the position of the mixerchamber-sensor must be set
lower. This actions affects the total production capacity of your system.
***) Through a too short dispense valve opening time, the machine could think that there is
no material in the hopper. There are three possible reasons for this.
-1 dispense accuracy is too narrow
-2 dispense speed is too high
-3 number of dispense attempts is too low solutions:
-1 increase dispense accuracy (§ 3.5.2)
-2 adjust speed in recipe (§ 3.2.2)
-3 increase number of attempts (§ 3.5.2)
An error message on the terminal must be confi rmed by pressing the <ENTER>-key. The
terminal stores all error messages these can be displayed by the menu (F1) ‘controller / alarm
history’. This screen shows the last 256 errors and the number of times the error occurred. The
error-list can de cleared by pressing (F2) option button and choose clear, with this button it is
also possible to print a report of alarms, select ‘print alarm history’ and push <ENTER>.
Page 45

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 44
Gravimetric Blender
[0]OPERATING AUTO[ ] [ ] [ ]
STATUS:[0] FGB#00: (No name) STATUS OPERATING
----------------------------[ALARM HISTORY]
No control voltage 1 Loadcell overload 0
Covers are open 1 Loadcell not stable 0
Production weight reached 0 Loadcell needs more samples 0
No Weighbin / Need calibration 0 Loadcell boundary error 0
Parameters are corrupted 0 Silo full error 0
Production data corrupted 0 Silo empty error 0
Hopper number (n) is empty 0 Confl ict with regrind parameter 0
Loadcell is not calibrated 0 Confl ict with addi.-regr.param 0
1 Date: 06-04-94 Time: 13:14:00 No control voltage
0 Date: 06-04-94 Time: 13:14:00 Covers are open
<Home>top of list
<↑> scroll up
<↓> scroll down
F1Menu F2Option F3 F4Clear F5Start F6Stop
F7Pauze F8Cont.
If your problems can not be solved by these directives, please contact your dealer.
Page 46

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 45
Gravimetric Blender
6.0 MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
Make sure ,when maintenance or repair is carried out, the power is shut off (by pulling the
plugs out) and the air pressure (by disconnecting the air pressure).
6.1 Maintenance
Everything is set right and tested in the factory, adjustments should only be carried out if a
part of the machine is not working correctly
Air pressure: Set air pressure to about 6 bar for best accuracy. However, lower
pressure will work. If your plant air fl uctuates, set the regulator to the
low end so that the dispense valves always see a consistent pressu re.
Level sensor: The sensor should protrude into the mixer chamber about 1 cm past
the inside surface of the stainless mounting plate. If it protrudes too
far, it will sense the mixer blades. If it does not protrude far enough, it
will sense the mounting plate itself.
Adjusting sensor sensitivity:
At the end of the sensor is a small screw, with this the sensitivity is adjustable.
step1: fi ll the mixer chamber until the sensor is covered.
step2: turn screw counter-clockwise until the led goes on (if the led already
is on, then turn clockwise until led goes off and proceed with step 4).
step3: turn screw clockwise until led goes off.
step4: turn screw another 3/4 turn clockwise.
step5: Empty the mixer chamber and check to be sure the sensor does not
react on the mixer blades.
Weighbin dump valve:
The weighbin dump valve should open and close smoothly. Two
airfl ow regula tors are attached on the cylinder. This can be adjusted
by the screw that is on top of it.
Page 47

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 46
Gravimetric Blender
6.2 Replacement of parts
6.2.1 Replacement of printed circuit
For the replacement of the printed circuit of the control-box, the cover should be removed
by unscrewing the bolts. unplug the connectors which are attached to the printed circuit.
Now unscrew all M3 bolts and remove the circuit. It is important to fi rst disconnect the
connectors and then unscrew the bolts. attach the new printed circuit in the same way,
but in reverse.
It is wise to use a wrist band with ground cord which is connected with earth (PE). This
because of the of static electricity.
6.3 Cleaning the machine
The frequency of cleaning will depend on the number of times the raw material is changed.
For cleaning the machine the front panel, the mixer chamber, the weighbin and the mixer
should be removed (as described in section 4.2). Disconnect the electrical power and
air supply.
Clean the machine by using air pressure. Use safety-goggles when cleaning. After it has
been cleaned, put it back together in the reverse way of stripping it.
6.4 Transportation of the GraviMaster
The weigh bin should be removed, before moving the GraviMaster, this can be done as
described in the previous section. The weigh bin should be removed to prevent damaging
the loadcell. The machine can now be transported on a fi rm pallet.
Page 48

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 47
Gravimetric Blender
7.0 TECHNICAL INFORMATION
7.1 General machine specifi cations
Connecting voltage : 1-phase 240 V
Communication cable : Fiber optic cable (or RS–422)
Air pressure : max. connecting pressure: 12 bar (+/- 170 psi)
working pressure: 4-6 bar (+/- 57-86 psi)
Sound level : < 70 dB (A)
Surroundings temperature : -18°C to +50°C
Batch weight : 0,5 kg
Machine weight : 25 kg
Machine dimensions : 450 x 450 x 640 mm
7.1.1 Safety measures
The GraviMaster is secured by 1 safety switch, which is positioned on the frontdoor. When
the frontdoor is opened, the machine will stop.
7.2 User-interface specifi cations
Connecting voltage : 240 V
Printer connection : Parallel port
7.3 Valves specifi cations
The machine is supplied with valves from the brand MAC, type 45A-SC1-DDAJ-1KJ. The
number of valves is similar to the number of hoppers + 1 for the weighbin + 1 for the
mixer chamber valve (optional).
The connection: (drawing 7 and 7.1) The valve of the weighbin is sealed at W1, so
connection on W2 is the only possibility. Connecting dispenser valves
H1 and H2 is as follows;
* H1-1 onto C1, as H2-1 onto C1 etc.
* H1-2 onto C2, as H2-2 onto C2 etc.
H1-1 and H1-2 should be connected to the cylinder under hopper 1,
H2-1 and H2-2 to the one under hopper 2 etc.
If there is a mixer chamber valve, it should be connected to B-1 and
B-2, one of the lines is numbered, like one side of the cylinder.
Connect the concordant ones.
Page 49

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 48
Gravimetric Blender
Drawing 7.1 Cylinder
Maschine
1
2
W H 1 H 2 B
W= Wiegeschalenanschluss
H1= Dosierschieber 1
H2= Dosierschieber 2
B= Mischkammerschieber
Option
(
Drawing 7.2 Topview valves
)
7.4 Air pressure cylinders specifi cations
See specifi cations on cylinder.
Ein
Page 50

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 49
Gravimetric Blender
7.5 Electrical diagrams
Page 51

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 50
Gravimetric Blender
Page 52

Rev. May 2001 GraviMaster-FGB-M05 (S) Page 51
Gravimetric Blender
 Loading...
Loading...