Page 1

EtherNAV™D7600 Series
Installation & Operation Instructions
managed ethernet
switches
GE Security
Page 2

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
PREFACE
This manual describes how to install and use the D7600 series EtherNav”
Manageable 8/9-Port 10/100/1000 Base-TX (100/1000 Base-FX) Ethernet Switch.
This switch integrates full wire speed switching technology with SNMP/RMON webbased management functions. The D7600 series brings
a simple answer to today’s complicated networking environments.
To get the most out of this manual, you should have an understanding of Ethernet
networking concepts.
In this manual, you will find:
• Features on the Switch
• Illustrative LED functions
• Installation Instructions
• Management Configuration
• SNMP…
• Specifications
User’s Manual
Page 3

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
INSTALLATION & OPERATION MANUAL / IFS D7600
PREFACE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Package Contents............................................................................................................................................ 1
Product Features............................................................................................................................ 1
Basic Features................................................................................................................ 1
Management Support ................................................................................................ 2
Front Panel Display....................................................................................................................... 3
Physical Ports................................................................................................................................... 4
Basic Functions............................................................................................................................... 5
Unicast Switching......................................................................................................... 5
Multicast Switching...................................................................................................... 7
VLAN..................................................................................................................................................... 8
Broadcast Containment............................................................................................ 9
Multi-Based Multimedia Applications.................................................................. 9
Enhanced Security....................................................................................................... 9
VLAN Membership........................................................................................................ 9
VLAN Configuration..................................................................................................... 10
Intra-VLAN Communication..................................................................................... 10
Inter-VLAN Communication..................................................................................... 10
GVRP...................................................................................................................................................... 10
IGMP Snooping and IP Multicast Filtering........................................................................... 10
Switch Management..................................................................................................................... 11
INSTALLATION............................................................................................................................................. 12
Selecting A Site For The Switch................................................................................................ 12
Methods for Mounting the D7600............................................................................................. 12-15
Connecting To Power.................................................................................................................... 16
Power-On Self Test (POST)......................................................................................... 16
Connecting To Your Network.................................................................................................... 17
Cable Type & Length................................................................................................... 17
SWITCH MANAGEMENT...................................................................................................................... 18
Management Access Overview............................................................................................... 18-19
Administration Console................................................................................................................ 20
Direct Access................................................................................................................... 20
Web Management......................................................................................................................... 21
Netscape Navigator..................................................................................................... 21
Internet Explorer............................................................................................................ 21
User’s Manual
Page 4

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
INSTALLATION & OPERATION MANUAL / IFS D7600
SWITCH MANAGEMENT CONTINUED….
SNMP-Based Network Management................................................................................... 22
Protocols............................................................................................................................................. 22
Management Architecture........................................................................................................ 22
MENU-DRIVEN CONSOLE MANAGEMENT......................................................................... 23
Logging On To The Switch......................................................................................................... 23
At The Screen Prompt................................................................................................ 23
Switch Management Screen..................................................................................................... 24
Navigating Through The Console Interface...................................................... 25
Performing Basic Management Activities.......................................................................... 25-31
Alarm Configurations................................................................................................................... 32
To Perform Advanced Management Activities................................................ 33-55
Sending and Receiving Files...................................................................................................... 56-57
Logout................................................................................................................................................. 58
Save Settings.................................................................................................................................... 58
Restore Default Settings............................................................................................................. 58
Reboot................................................................................................................................................. 58
WEB-BASED BROWSER MANAGEMENT.............................................................................. 59
Logging On To The Switch......................................................................................................... 59
Understanding The Browser Interface................................................................................ 60
Performing File Activities............................................................................................................ 61
To Perform File Activities........................................................................................... 61
Performing Basic Setup Activities.......................................................................................... 62
To Perform Basic Setup Activities......................................................................... 62-66
Performing Advanced Setup Activities................................................................................. 67
To Perform Advanced Setup Activities................................................................ 67-79
SNMP & RMON MANAGEMENT.................................................................................................... 80
Overview............................................................................................................................................. 80
SNMP Agent and MIB (RFC 1213)............................................................................................ 80
RMON Groups Supported......................................................................................... 81
Bridge Groups Supported......................................................................................... 82
SPECIFICATIONS........................................................................................................................................ 83
APPENDIX A – CONNECTOR PINOUTS.................................................................................. 84
D7600 Front Panel Layouts........................................................................................................... 85-86
User’s Manual
Page 5

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
When you unpack the product package, you shall find the items listed below.
• D7600 EtherNav” Management Switch
• D7600 Quick Start Guide
• External Power Adapter
• CD ROM
Basic Features:
- Provides up to nine (10/100/1000TX and/or 100/1000FX combination) ports
- Multimode fiber using SC connectors up to 2 km; singlemode fiber using
SC connectors up to 15 km for 100FX, 10km for 1000FX
- Auto-negotiation for speed and duplicity on all TX ports
- Store-and-Forward mechanism
- Back-pressure and IEEE 802.3x compliant flow control
- Supports 4K MAC addresses
- Redundant power supply connections
- Optional TX or FX 1000Mbps aggregation port
- Optional contact closure for fiber loss alarm
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
100FX Optical Ports
Console Port
10/100TX Electrical Ports
Front View (D7600-MM-E-CC shown)
10/100/1000TX Port
PACKAGE CONTENTS
PRODUCT FEATURES
User’s Manual 1
Fiber Loss Alarm
Power Ports
Page 6
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
PRODUCT FEATURES CONTINUED...
Management Support:
VLAN
- 802.1Q tagged VLAN (up to 64 VLANs)
- Quality of Service (QoS)
Link Aggregation
- Port-based Aggregation, up to four groups with a maximum
of four ports each group
- Load sharing based on source and destination MAC addresses
Port-Mirroring
- Port-mirroring provided through dedicated port, Port 1
Internet Working Protocols:
Bridging
- 802.1D Spanning Tree
- 802.1P/Q –GARP/GVRP
IP Multicast
- IP Multicast Packet Filtering
Network Management Methods:
- Console port access via RS-232 cable
- Telnet remote access
- SNMP Agent:
• MIB-2 (RFC1213)
• Bridge MIB (RFC1493)
• RMON MIB (RFC1757)-statistics, history, alarm & events
• VLAN MIB (802.1Q/RFC2674)
• Private MIB
- Web browser support based on HTTP server and CGI parser
- TFTP/Web software-upgrade capability
User’s Manual 2
Page 7

User’s Manual 3
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
FRONT PANEL DISPLAY
10/100TX Port Status
(D7600-MM-E-CC Shown)
Optical Status
10/100/1000TX Port Status
Power Indicator
1. Power Indicator
This LED comes on when the switch is properly connected to power.
2. Optical Status LED’s (FX)
The ACT LED’s come on when data is present.
(LED will flash at the rate data is transferred).
The LNK LED’s will be on for 100FX speed transmission.
3. 10/100/1000TX Port Status LED’s
The LED’s are located at each port, displaying status.
Please refer to the Table for more details.
Page 8

User’s Manual 4
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
LED State Indication
GREEN
YELLOW
Steady
A valid network connection established
Flashing
Data transfer
PHYSICAL PORTS
This EtherNav” managed switch provides up to nine (10/100/1000TX and/or 100/1000FX
combinations) ports:
CONNECTIVITY
- RJ-45 connectors
- SC connector on fiber ports
MODE SELECTION
- 10BaseT full-duplex mode
- 10BaseT half-duplex mode
- 100BaseTX full-duplex mode
- 100BaseTX half-duplex mode
- 100BaseFX full-duplex mode
- 100BaseFX half-duplex mode
- 1000BaseTX full-duplex mode
- 1000BaseTX half-duplex mode
- 1000BaseFX full-duplex mode
- 1000BaseFX half-duplex mode
- Auto-sensing mode except 100FX
Page 9
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
BASIC FUNCTIONS
In general, the D7600 is responsible for switching both VLAN tagged and untagged frames
from a receiving port to one or more transmitting ports. The switch performs multiple steps
during the switching process:
VLAN CLASSIFICATION
LEARNING
FILTERING
AGING
Below is additional information about tasks that the switch performs during unicast
and multicast switching.
User’s Manual 5
PLEASE NOTE:
I. Half-duplex mode uses back pressure flow control to prevent the receiving
buffer from being overrun by data from a source node.
II. Full-duplex mode uses 802.3x flow control standard to prevent fast data traffic
from overrunning slow data traffic.
III. Auto-sensing mode is in use after auto-negotiating with the other end of the link.
UNICAST SWITCHING
VLAN CLASSIFICATION
When the switch receives a frame, it classifies the frame in one of two ways:
- If the frame is untagged, the switch classifies the frame to an
associated VLAN.
- If the frame is tagged, the switch uses the tagged VLAN ID to identify the
broadcasting domain of the frame.
Page 10
PLEASE NOTE:
I. Half-duplex mode uses back pressure flow control to prevent the receiving
buffer from being overrun by data from a source node.
II. Full-duplex mode uses 802.3x flow control standard to prevent fast data traffic
from overrunning slow data traffic.
III. Auto-sensing mode is in use after auto-negotiating with the other end of the link.
LEARNING
After VLAN classification, the switch checks the <source MAC address, VLAN> pair in the
switching database (SDB) to see whether the <source MAC address, VLAN> pair is known.
- If it is unknown, the switch inserts the <source MAC address, VLAN> into the SDB
and learns the <source MAC address, VLAN>.
- If it is known, the switch checks the <source MAC address, VLAN> for a mis
matched port ID. If the port ID associated with the <source MAC address, VLAN>
pair in the SDB is different than the receiving port , the switch modifies the port ID in
the SDB and modifies its management database (MDB) accordingly.
FILTERING
After learning the address, the switch checks:
- Whether the source port or destination port is in the forwarding state.
- Whether the source MAC address or destination MAC address is to be filtered.
- Whether the source port ID is the same as destination port ID.
If any of these conditions are met , the switch drops the receiving. Otherwise, it continues with
the forwarding process described below.
FORWARDING
During the forwarding process, the switch checks whether the <destination MAC address,
VLAN> pair is unknown.
- If it is unknown, the switch floods the receiving frame to all ports in the VLAN,
excluding the source port.
- If it is known, the switch forwards the receiving frame to the port associated
with the <destination MAC address, VLAN> pair. At the same time, the switch
ascertains the individual’s ports VLAN tagging and/or un-tagging configuration
and corresponding VLAN ID render the appropriate frame tagging when the frame
is ready to be transmitted.
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 6
Page 11
User’s Manual 7
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
MULTICAST SWITCHING
For multicast switching, the D7600 checks whether the received frame is a BPDU. If a BPDU
is received, the switch forwards the frame to the CPU for processing by the spanning tree
protocol. Otherwise, the D7600 performs the following processes:
VLAN CLASSIFICATION
Same as for unicast switching.
LEARNING
Same as for unicast switching.
FILTERING
After learning the address, the switch checks:
- Whether the source port or destination port is not in the following state.
- Whether the source MAC address or destination MAC address is to be filtered.
If any of these conditions are met , the switch drops the receiving. Otherwise, it
continues with the forwarding process described below.
FORWARDING
The D7600 floods the received multicast frame to all ports that are in the forwarding state
within the VLAN, excluding the source port. At the same time, the switch
ascertains the individual ports VLAN tagging/untagging configuration and
corresponding VLAN to render the appropriate frame tagging when the frame is
ready to be transmitted.
AGING
The switch performs the aging process for the <MAC addresses, VLAN> pair in
the switching database. Once a <MAC address, VLAN> pair is aged out, the SBD
is modified.
SPANNING TREE
The D7600 supports one Spanning Tree per bridged network.
Page 12

User’s Manual 8
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
VLAN
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a network of computers or peripherals that behave as if they are
connected to the same wire, even though they may actually be physically located
in different locations of a LAN. VLANs are similar to a group of end stations, perhaps on
multiple physical LAN segments that are not inhibited by their physical location
and can communicate as if they were on a common LAN.
VLANs are configured through software rather than hardware, which makes the extremely
flexible. One of the biggest advantages of VLANs is that when a peripheral
is physically moved to another location, it can stay on the same VLAN without any
hardware reconfiguration.
Because VLANs are not limited by the hardware constraints that physically connect
traditional LAN segments to a network, they can define a network into various logical configurations. For example, VLANs can define a network by function.
In this setting, a system integrator might create one VLAN for multimedia users
and another for email users. VLANs can also define a network by location or type of service. For example, a location might have one VLAN for its cameras, another for it access
control, and another for its roadside signs.
VLANs can also be set up according to the organization structure within a company. For
example, the company president might have his/her own VLAN, the executive staff might
have a different VLAN, and the remaining employees might have yet another
different VLAN.
As these examples show, VLANs offer matchless flexibility. The following
sections describe how deploying VLANs can benefit system integrators and
reduce design costs.
Page 13
BROADCAST CONTROL
In traditional networks, traffic broadcasts to all network devices, whether they are the intended
recipients or not. However, VLANs can be set up to contain only those devices that need to
communicate with each other. As a result, VLANs considerably reduce
network congestion. In addition, VLANs prevent broadcast storms from causing a
network from crashing due to volumes of traffic.
MULTICAST-BASED MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS
Multimedia applications, such as interactive training, video monitoring, and video/data transmissions, require large amounts of bandwidth. These applications are also extremely sensitive
to variable delays, which are inevitable on a shared Ethernet network. By
defining a VLAN based on the IP multicast address for all defined members on the
VLAN, adequate bandwidth will be available for these applications, providing true
multimedia Ethernet.
IMPROVED SECURITY
Because VLANs are independent, only the devices within the same VLAN can
communicate with each other. If a device in one VLAN wants to communicate with
a device in another VLAN, the traffic must go through a router.
VLAN MEMBERSHIP
VLAN implementation allows:
- Up to 64 VLANs in one switch.
- VLANs across multiple switches by using explicit or implicit tagging and the
GARP/GVRP protocol defined in IEEE802.1p and 802.1Q.
- An end station’s network interface card belongs to multiple VLANs.
-A switch port to be associated with multiple VLANs.
DEFINITIONS OF VLAN MEMBERSHIP
VLAN implementation allows VLAN membership to be defined based on ports.
Physical port numbers organizes port-based VLANs. For example, switch ports
1,2,4 and 6 can be grouped on VLAN, while server ports 3,5,7 and 8 can be on another VLAN.
Broadcasts from servers within each group would only go to the members of its own VLAN.
This ensures that broadcast storms cannot cause a network to crash due to
volumes of traffic.
VLAN MEMBERSHIP LEARNING
Port-based VLAN is defined using a static binding between a VLAN and its associated ports.
The switch’s forwarding decision is based on the destination MAC address and
its associated port ID. Therefore, to make valid forwarding and flooding decisions, the switch
learns the relationship of the MAC address to its related port …and thus to the VLAN…at runtime.
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 9
Page 14

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 10
REMOTE VLAN MEMBERSHIP
Additionally to providing network management tools that allow network administrators to statically add and delete VLAN member ports, the switch also supports GVRP (GARP VLAN
Registration Protocol). GVRP allows for dynamic registration of VLAN port
members within switch and across multiple switches.
Other than supporting dynamic updating of registration entries in a switch, GVRP is
used to communicate VLAN registration information to other VLAN-aware switches,
so that a VLAN member can cover a wide span of switches on a network.
GVRP allows both VLAN-aware workstations and switches to issue and revoke VLAN memberships. VLAN-aware switches register a propagate VLAN membership to all
ports that belong to the active topology of the VLAN.
VLAN CONFIGURATION
The switch provides a Local/Remote Management Console Interface for VLAN
configuration and management. An SNMP-based VLAN MIB is also provided.
INTRA-VLAN COMMUNICATION
The switch supports intra-VLAN communication through hardware as described in
"Basic Functions" section.
INTER-VLAN COMMUNICATION
The switch supports Inter-VLAN communication using CPU-based routing software.
GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol)
IGMP SNOOPING AND IP MULTICAST FILTERING
In addition to network management tools that allow network administrators to statically add
and delete VLAN member ports, the routing switch supports GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
(GVRP). GVRP supports dynamic registration of VLAN port
members within a switch and across multiple switches.
In addition to dynamically updating registration entries with a switch, GVRP is used to communicate VLAN registration information to other VLAN-aware switches, so that
members of a VLAN can cover a wide span of switches on a network.
GVRP allows both VLAN-aware workstations and switches to issue and revoke VLAN memberships. VLAN-aware switches register and propagate VLAN membership to all ports that are
part of the active topology of the VLAN.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) runs between hosts and their immediately
neighboring multicast routers. The protocol’s mechanisms allow a host to inform its local router
that it wants to receive transmissions addressed to a specific multicast group.
Routers periodically query the LAN to determine if known group members are still active.
Page 15
User’s Manual 11
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
IGMP Snooping & IP Multicast Filtering Continued...
If there is more than one router on the LAN performing IP multicasting, one of the routers is
elected ‘querier’ and assumes the reponsibility.
Based on the group membership information learned from the IGMP, a router can determine which (if any) multicast traffic needs to be forwarded to each of its ‘leaf’
sub-networks. Multicast routers use this information, along with a multicast routing
protocol, to support IP multicasting across the Internet.
Routing switches support IP Multicast Filtering by:
• Passively snooping on the IGMP Query and IGMP Report packets transferred
between IP Multicast Routers and IP Multicast host groups to learn about IP
Multicast group members, and
• Actively sending IGMP Query messages to solicit IP Multicast group members.
The purpose of IP multicast filtering is to optimize a switched network’s performance, so
multicast packets will only be forwarded to those ports containing multicast group hosts
members and routers instead of flooding to all ports in the subnet (VLAN).
Routing switches with IP multicast filtering/switching capability not only run passively monitor IGMP Query and Report messages, DVMRP Probe messages, PIM, and MOSPF Hello
messages; they also actively send IGMP Query messages to learn locations of multicast
routers and member hosts in multicast groups within each VLAN.
Note, however, IGMP neither alters nor routes any IP multicast packets. Since IGMP
is not concerned with the delivery of IP multicast packets across sub-networks, an
external IP multicast router is needed if IP multicast packets have to be routed
across different sub-networks.
SWITCH MANAGEMENT
Administration Console Via RS-232 Console Port:
The switch provides an on board serial port, which allows the switch to be configured via a
directly connected terminal or a Telnet session.
Web-Based Browser Interface:
The switch also boasts a point-and-click browser-based interface that lets users access full
switch configuration and functionality from a Netscape or Internet Explorer browser.
External SNMP-Based Network Management:
The switch can also be configured via SNMP.
For more information on switch management, please refer to the "Switch Management" section.
Page 16
User’s Manual
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
INSTALLATION
This section gives step-by-step instructions about how to install
the EtherNav” D7600 switch:
Selecting a Site for the Switch
As with any electric device, you should place the switch where it will not be subjected to
temperatures, humidity, or electromagnetic interference above the rated specifications. The
site you select should meet the following requirements:
• The ambient temperature should be between –40 to 74 degrees Celsius.
• The relative humidity should be less than 95 percent, non-condensing.
• Surrounding electrical devices should not exceed the electromagnetic field
(RFC) standards for EIC 801-3, Level 2 (3V/M) field strength.
• Make sure that the switch receives adequate ventilation. Avoid blocking the
ventilation holes on all sides of the switch.
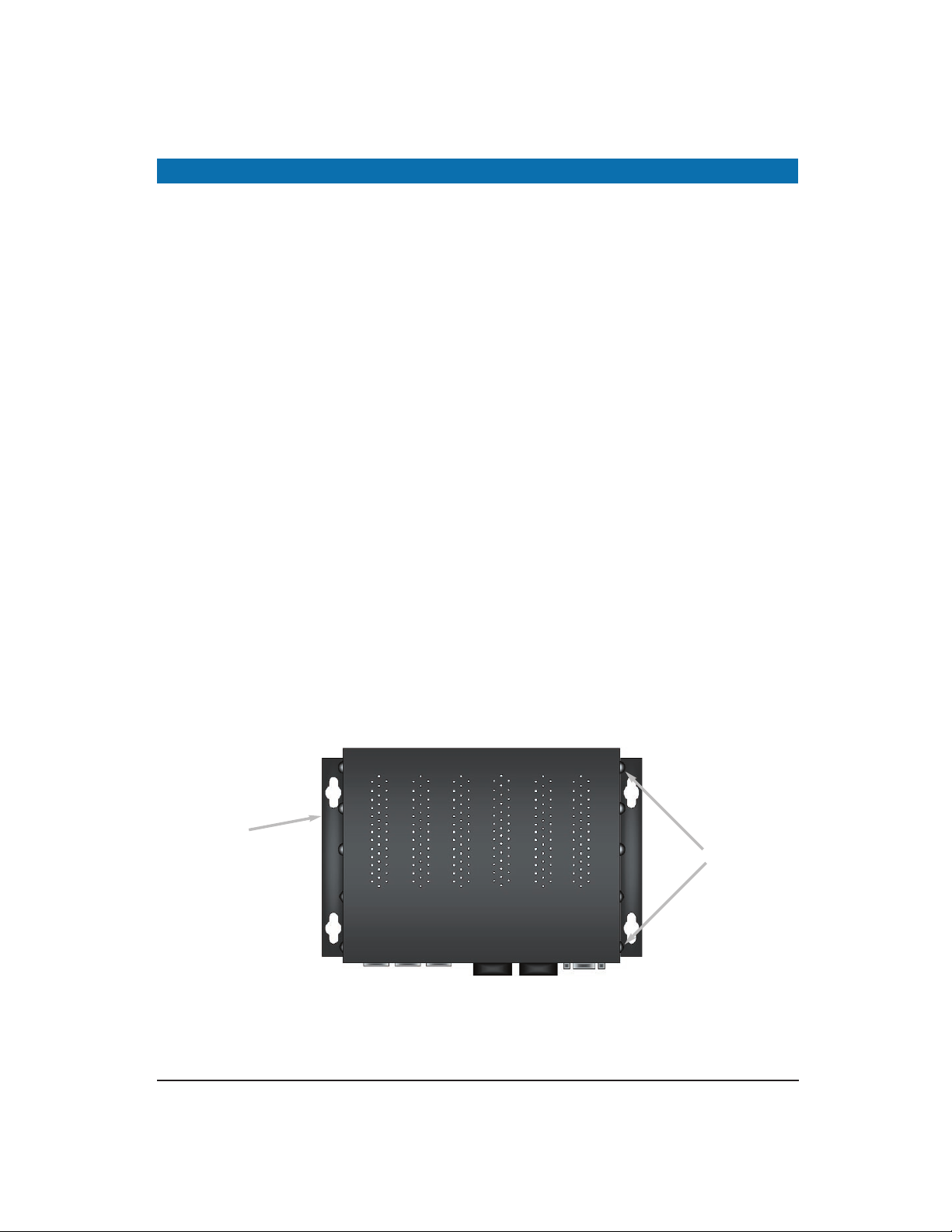
Methods for Mounting the D7600
Several mounting configurations are available for the variety of applications for which this
switch was designed. Each configuration is described as follows:
Wall Mounting (-W Option)
The brackets provided will require the removal and re-installation of the cover screws as
shown below.
Note: Insure that all screw are re-installed for adequate stability in mounting. 12
Bracket
(-W Option)
Cover Screws
Page 17
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 13
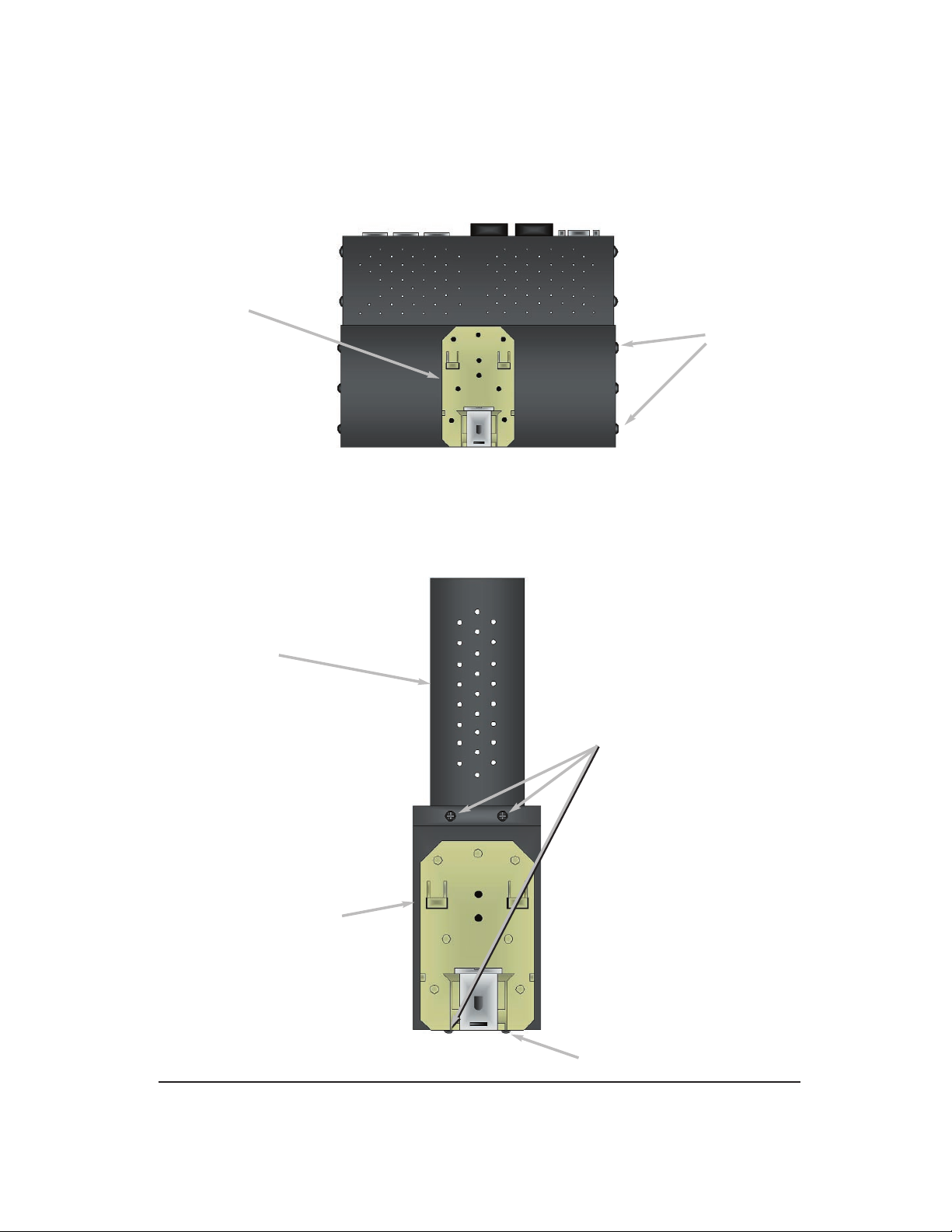
DIN Rail Back Mounting (-DB Option)
The bracket provided will require the removal and re-installation of some cover screws as
shown below.
DIN Rail Side Mounting (-DS Option)
The bracket provided will require the removal and re-installation of one cover screw, the other
screws are provided with the bracket as shown below.
Bracket
(-DB Option)
Cover Screws
Note: Bracket is mounted on the Power
Supply Side (Right Side) of the switch.
Bracket
(-DS Option)
D7600 Unit
(10/100 Port Side)
Cover Screw
Provided Mounting
Screws
Page 18

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 14
Rack Mounting Single Unit (-RS Option)
The brackets provided have screws included for proper mounting as shown below.
Note: All screws must be fastened and secured to insure adequate stability and strength.
Mounting Screws
4 Locations (Provided)
Brackets (-RS Option)
(Top View)
(Front View)
Page 19
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 15
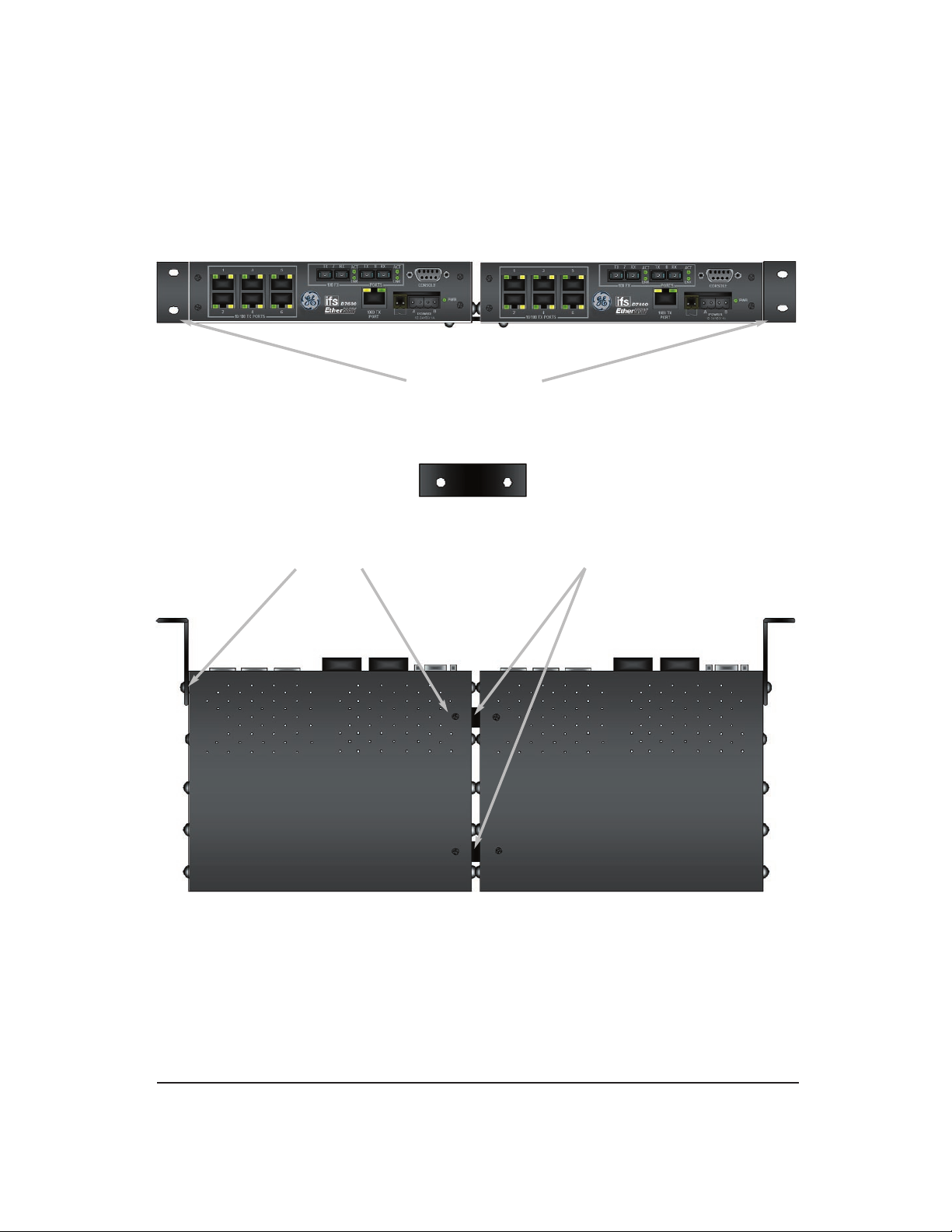
Rack Mounting Dual Units (-RD Option)
The brackets and braces provided have screws included for proper
mounting as shown below.
Brackets (2 Provided)
Mounting
Screws
Brace
Locations
(Front View)
Brace (2 Provided )
(Bottom View)
Page 20
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 16
CONNECTING TO POWER
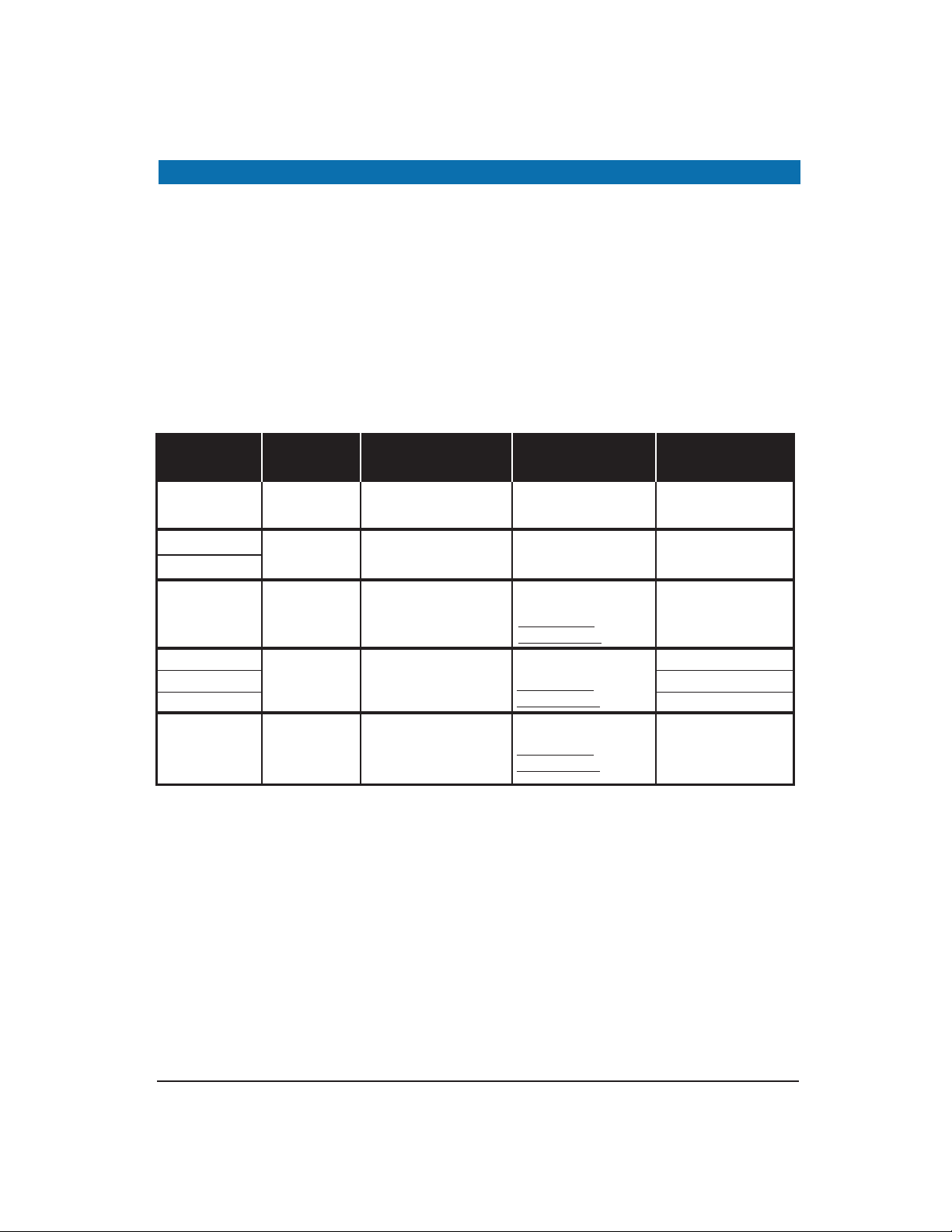
External Power
Step One: Wire the supplied AC power adapter to the “A” receptacle plug
at the front of the switch. — white stripe to pin 1 (+), black to pin 2 (-).
Step Two: Attach the plug into a standard AC outlet with the appropriate AC voltage.
Note: The secondary supply must be equal to or less than the potential of the primary supply.
To Primary Wall Supply
To Secondary Supply
Secondary “B” Power Connector
Primary “A” Power Connector
(D7600-MM-E-CC Shown))
Power On Self Test (POST)
The switch performs its Power-On Self Test (POST) when the power is applied to the switch.
During the POST, the switch CPU will:
• Perform a series of diagnostic procedures to make sure the
basic system is functioning properly
• Decompresses the main switching software runtime image from
the flash ROM into the DRAM area
Page 21
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 17
CONNECTING TO YOUR NETWORK
Cable Type & Length
Wire the supplied AC power adapter to the “A” receptacle plug
at the front of the switch. — white stripe to pin 1 (+), black to pin 2 (-).
Step Two: Attach the plug into a standard AC outlet with the appropriate AC voltage.
It is necessary to follow the cable specifications below when connecting the switch to your
network. Use appropriate cables that meet your speed and cabling requirements.
Table 3: Cable Specifications
Speed Connector Port Speed
Half /Full Duplex
Cable Max. Distance
10BaseT
RJ-45
100 m10/20 Mbps
2-Pair UTP/STP
Cat. 5, 5E, 6
100BaseFX
SC
2 km100/200 Mbps
MMF (50 or 62.5µm)
-25dB R
eturn
Loss Minimum
100BaseFX
100BaseFX-HP
100BaseFX-HP1
SC
37 km
54 km
97 km
100/200 Mbps
SMF (9 or 10µm)
-25dB R
eturn
Loss Minimum
1000BaseFX
SC
28 km500/1000 Mbps
SMF (9 or 10µm)
-25dB R
eturn
Loss Minimum
10BaseTX
1000BaseTX
RJ-45
100 m100/200 Mbps
2-Pair UTP/STP
Cat. 5, 5E, 6
Cabling:
Step 1: First, ensure the power of the switch and end devices are turned off.
NOTE: Always ensure that the power is off before any installation.
Step 2: Prepare cable with corresponding connectors for each type of port in use.
Step 3: Consult Table 3 in previous section for cabling requirements based on
connectors and speed.
Step 4: Connect one end of the cable to the switch and the other end to a
desired device.
Step 5: Once the connections between two end devices are made successfully,
turn on the power and the switch is operational.
Page 22

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 18
SWITCH MANAGEMENT
This section explains the methods that you can use to configure management access to
the switch. It describes the types of management applications and the communication
and management protocols that deliver data between your management device
(workstation or personal computer) and the system. It also contains information about
port connection options.
This section covers the following topics:
• Management Access Overview
• Key Concepts
• Key Guidelines for Implementation
• Administration Console / Telnet Access
• Web Management Access
• SNMP Access
• Standards, Protocols, and Related Reading
MANAGEMENT ACCESS OVERVIEW
The EtherNav” D7600 switch gives you the flexibility to access and manage the switch
using any or all of the following methods.
The administration console and web browser interface support are embedded in the switch
and are available for immediate use.
Page 23
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 19
Administration Console via RS-232 Console Port:
Advantages:
• No IP address or subnet needed
• Text-based
• HyperTerminal built into Windows 95/98/NT/2000
operating systems
Disadvantages:
• Must be near switch
• Inconvenient for remote users
Web-Based Browser Interface:
Advantages:
• Ideal for configuring the switch remotely
• Compatible with all popular browsers
• Can be accessed from any location
• Most visually appealing
Disadvantages:
• Security can be compromised (hackers need only know the IP address
and subnet mask)
• May encounter lag times on poor connections
Telnet Interface:
The connection is the same as Web-Based Browser Interface, but with Console
Port Hyper Terminal type user interface.
External SNMP-Based Network Management Application:
Advantages:
• Communicates with functions at the MIB level
• Based on open standards
Disadvantages:
• Requires SNMP manager software
• Least visually appealing of all three methods
• Some settings require calculations
• Security can be compromised (hackers need only know the community name)
Page 24
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 20
ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE
The administration console is an external, character-oriented, menu-driven user
interface for performing system administration such as displaying statistics or
changing option settings.
Using this method, you can view the administration console from a terminal, personal computer, Apple Macintosh, or workstation connected to the switch’s console port.
There are two ways to use this management method: direct access or modem Telnet
access. The following sections describe these methods:
DIRECT ACCESS
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a terminal or
a PC equipped with a terminal-emulation program (such as Hyper-Terminal) to the switch
console port.
When using the management method, configure the terminal-emulation program to use
the following parameters (you can change these settings after login):
[Default Parameters] 115, 200bps
8 Data Bits
No Parity
1 Stop Bit
This management method is often preferred because you can remain connected and
monitor the system during systems reboots. Also certain error messages are sent to the
Console port regardless of the interface through which the associated action was initiated.
A Macintosh or PC attachment can use any terminal-emulation program for connecting
to the terminal serial port. A workstation attachment under UNIX can use an emulator
such as TIP.
Telnet ACCESS
You can access the switch’s administration console from a PC or Macintosh using DOS
window through network with IP address. The switch management program provides a
CONSOLE PORT screen, accessible from the BASIC MANAGEMENT screen, that lets you
configure parameters for remote access.
Page 25

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 21
WEB MANAGEMENT
The switch provides a browser interface that lets you configure and manage
the switch remotely.
After you set up your IP address for the switch, you can access the switch’s web
interface applications directly in your web browser by entering the IP address of the
switch. You can then use your web browser to list and manage switch configuration
parameters from one central location, just as if you were directly connected to the
switch’s console port .
Web Management requires either Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.01 or later or Netscape
Navigator 4.03 or later.
• Netscape Navigator
If you use Netscape Navigator 4.03 or 4.04, install the Netscape JDK 1.1 Patch.
Download the patch from:
http://help.netscape.com/filelib.html#smartupdate
If you encounter problems accessing Help files when you use Netscape, clear the browser
memory cache and disk cache, and restart the browser.
• Internet Explorer
If you use Internet Explorer, install the latest 4.01 Service Pack 1. This service pack makes
Internet Explorer Year 2000 compliant and fixes other product-support issues. Download
the 4.01 Service Pack 1 from the following location:
http://www.microsoft.com/msdownload/iebuild/ie4sp1_win32/en/ie4sp1_win3
If the above link is unavailable, download the service pack from
the Microsoft home page:
http://www.microsoft.com
Page 26
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 22
SNMP-BASED NETWORK MANAGEMENT
If you enable the SNMP function through the console port , you can use an external SNMPbased application to configure and manage the switch. This management method requires
the SNMP agent on the switch and the SNMP Network Management Station to use the
same community string. This management method, in fact, uses two community strings:
the ‘get’ community string and the ‘set’ community string. If the SNMP Network management station only knows the ‘set’ community string, it can read and write to the MIBs.
However, if it only knows the ‘get’ community string, it can only read MIBs. The default
getting and setting community strings for the switch are public.
PROTOCOLS
The switch support the following protocols:
• Virtual Terminal Protocols, such as Telnet
A virtual terminal protocol is a software program, such as Telnet, that allows
you to establish a management session from a Macintosh, a PC, or a UNIX
workstation. Because Telnet runs over TCP/IP, you must have at least one IP
address configured on the switch before you can establish access to it with a
virtual terminal protocol.
Note: Terminal emulation is different from a virtual terminal protocol in that you must
connect a terminal directly to the console port .
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
SNMP is the standard management protocol for multi-vendor IP networks. SNMP supports
transaction-based queries that allow the protocol to format messages and to transmit
information between reporting devices and data-collection programs. SNMP runs on top of
the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), offering a connectionless-mode service.
Management Architecture
All of the management application modules use the same Messaging Application
Programming Interface (MAPI). By unifying management methods with a single MAPI,
configuration parameters set using one method (e.g. console port) are immediately
displayed as the other management methods (e.g. SNMP agent of web browser).
The management architecture of the switch adheres to the IEEE open standard. This
compliance assures customers that the switch is compatible with, and will interoperate
with other solutions that adhere to the same open standard.
Page 27
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 23
MENU-DRIVEN CONSOLE MANAGEMENT
The switch provides a menu-driven console interface for configuration purposes.
The switch can be configured either locally through its RS-232 port or remotely via
a Telnet session.
This section describes how to configure the switch using its menu-driven console.
Logging On To The Switch
At the screen prompt:
Switch Console Login:
Password:
Login Name
Enter the console interface factory default console name admin.
Password
Enter the factory default password (ethernav, press <Enter> directly).
Or enter a user-defined password if you followed the instructions later and
changed the factory default password.
Factory Default Password: ethernav, press <Enter> directly.
NOTE: Only one console and three Telnet users can log on to the switch
concurrently. However, it is not recommended that multiple users modify
the configuration at the same time.
Page 28

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 24
SWITCH MANAGEMENT SCREEN
Basic Management
Refer to performing basic management activities.
Advanced Management
Refer to performing advanced management activities.
Logout
Highlight this option and press <enter> to log out.
Save Settings
Highlight this option and press <enter> to save the current settings and remain in the con-
figuration program.
Restore Default Settings
Highlight this option and press <enter> to restore the factory default settings.
Reboot
Highlight this option and press <enter> to reboot.
Page 29

NOTE: Remember to release the <Caps Lock> key if you press <K> or <J>
and cannot move the highlight on the screen.
Basic management activities consist of General, LAN Port , and Console Port tasks.
To Perform Basic Management Activities
Step 1: Highlight [Basic Management] from [Switch Management] screen and press
<enter>. The [Basic Management] screens appears:
User’s Manual 25
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Press this key…. To
Up Arrow or “K”
Move the highlight one line up in a menu box
Down Arrow or “J”
Move the highlight one line down in a menu box
Tab
Move the highlight between screens
Enter
Select the highlighted option
Esc
Move to a previous menu
PERFORMING BASIC MANAGEMENT ACTIVITIES
Navigating Through the Console Interface
The console interface consists of a series of menu boxes. Each menu box has several
options, which are listed vertically. Move the highlight to select an option as you wish, press
the <enter> key to activate that option.
Page 30

User’s Manual 26
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2:
Highlight a desired option and press <enter>. Or press <esc> to EXIT.
NOTE: The changes will be effective after you press the <esc>, but will not be saved until
you select the Save Setting function.
GENERAL MANAGEMENT CONFIGURATIONS
Step 1:
Highlight General from [Basic Management] screen and press <enter>.
Page 31

User’s Manual 27
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2: System Name
System Name is highlighted. Press <enter> if you want to change it .
Step 3: Location
Move to highlight Location and press <enter> if you want to change it .
Step 4: admin Password
Move to highlight Admin Password and press <enter> If you want to change it.
Step 5: guest Password
Move to highlight guest Password and press <enter> if you want to change it.
Step 6: Statistics Collection
Move to highlight Statistics Collection and press <enter> If you want to change it,
Disabled or Enabled.
Step 7: Reboot-on-Error
Move to highlight Reboot-On-Error and press <enter> If you want to change it,
Disabled or Enabled.
Step 8: Remote Telnet Login
Move to highlight Remote Telnet Login and press <enter> if you want to change it,
Disabled or Enabled.
Step 9:
Move to highlight Remote Http Login and press <enter> if you want to change it, Disabled
or Enabled.
Step 10:
Press <esc> to return to [Basic Management] screen when complete.
Page 32

User’s Manual 28
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
LAN Port Configurations
Step 1:
Highlight LAN Port from [Basic Management] screen and press <enter>.
Step 2: Speed & Flow Control
Speed & Flow Control is highlighted. Press <enter> if you want to set speed or flow
control on port.
Step 3:
Highlight All Ports and press <enter> to configure at one time. Or move to
highlight each port and press <enter> to configure individually.
Page 33

Step 4:
Port Setting Options screen appears. Highlight Speed & Flow Control
and press <enter>.
Step 5: Line Speed
For Line Speed, move to highlight a desired setting from Speed Options
and press <enter>.
Note: In the Speed Options, HD denotes half-duplex and FD denotes full-duplex.
Step 6:
Press <esc> to previous screen. Highlight Flow Control and press <enter>.
Step 7: Flow Control
For Flow Control, move to highlight a desired setting from Flow Cntl Options
and press <enter>.
User’s Manual 29
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 34

Step 8:
Press <esc> to a previous screen as shown in Step 3.
Step 9: Admin. Control
Highlight All Ports and press <enter> to configure at one time. Or move to
highlight each port and press <enter> to configure individually.
Step 10:
For Admin Control, move to highlight Up or Down from Admin Status Options.
Step 11:
The port is set as Admin Down to stop TX/RX transmission. To allow transmission on the
port, move to highlight Up from the options in Step 10.
User’s Manual 30
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 35

Step 12: Physical Port Address
Press <esc> to a previous screen as shown in Step 1.
Step 13:
Move to highlight Physical Address to view physical port address.
Step 14: Return to Basic Management
Press <esc> to return to [Basic Management] screen when completed.
Console Port Configurations
Step 1:
Move to highlight Console Port from [Basic Management] screen.
Step 2: Baud Rate
Baud Rate is highlighted. Press <enter> if you want to change the current console baud
rate.
Step 3: Flow Control
Press <esc> to return to [Basic Management] screen when completed.
Step 4: Modem Control
Step 5: Modem Setup String
Not Supported.
Step 6: Return to Basic Management
Press <esc> to return to [Basic Management] screen when completed.
User’s Manual 31
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 36

User’s Manual 32
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Alarm Configurations
Page 37

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 33
PERFORMING ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACTIVITIES
Advanced management activities consist of L2 Switching Database/ IP Networking/
Bridging/ Static Filtering/ Spanning Tree/ SNMP/ Other Protocols/ Port Trunking/
Port Mirroring/ File Transfer.
To Perform Advanced Management Activities
Step 1:
Highlight [Advanced Management] from Switch Management screen and press <enter>.
The [Advanced Management] screen appears:
Step 2:
Move to highlight a desired option and press <enter>. Or press <esc> to exit.
Page 38

User’s Manual 34
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
L2 Switching DataBase
View and change VLAN, MAC address, IP multicast group, and port perspectives.
IP Networking
View and change IP settings and ping settings.
Bridging
View and change aging period for MAC address and flood limit for all ports.
Static Filtering
View/add/delete/search all source/destination MAC addresses to be filtered.
Spanning Tree
View and change spanning tree configurations, ports states, path costs, and port priorities.
SNMP
View and change the SNMP configuration.
Other Protocols
View and change GVRP and IGMP settings.
Port Trunking
Assign a range of ports to trunking groups.
Port Mirroring
Mirror one port to Port 1.
File Transfer
Send files using the TFTP or Kermit protocol.
Page 39

User’s Manual 35
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
L2 Switching DataBase
Step 1: VLAN Perspective
Highlight L2 Switching Database from [Advanced Management] screen and press
<enter>.
Step 2:
The VLAN Perspective is highlighted. Press <enter> to view VLAN info of the default VLAN
or if you want to obtain a VLAN perspective instead of the default VLAN.
Note: Default VLAN:
The IEEE802.1Q standard defines VLAN ID #1 as the default VLAN. The default VLAN
includes all the ports as the factory default .
Step 3: Create VLAN
Press <+> on keypad to enter New VLAN Settings. Enter new VLAN ID and
VLAN name.
Note: "Remote" is appended to the VLAN ID automatically if the VLAN is learned from a
remote switch.
Page 40

Step 4:
Press <esc> and appears the following screen. Press <+> to add new switch ports to the
newly created VLAN.
Step 5:
Move to highlight a suitable option from Port Options and press <enter>,
e.g. Untagged Ports.
User’s Manual 36
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 41

Step 6:
From Select Untagged Ports, press <enter> to select All Ports or move to highlight each
port individually and press <enter>. Similar procedure when you select Tagged Ports and
Forbidden Ports in Step 5.
Note: If you added untagged ports and want to now add tagged ports or forbidden
ports, or vice versa, repeat Step 5 and Step 6.
Step 7:
Press <esc> to a previous screen as shown in Step 2.
Step 8: Delete VLAN
Highlight a VLAN ID and press <-> to delete it .
Note: The default VLAN cannot be deleted.
User’s Manual 37
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 42

Step 9:
Press <esc> to a previous screen as shown in Step 2 when completed with deleting a
VLAN.
Step 10: VLAN Info
Highlight an existing VLAN and press <enter> to view VLAN information.
Step 11:
Move to highlight VLAN Activities and press <enter> to view or search
activity information.
User’s Manual 38
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 12:
Return to Step 6. Move to highlight VLAN Settings and press <enter>.
The screen appears as shown in Step 4 for adding or deleting switch ports.
Page 43

User’s Manual 39
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
IP Multicast Group Perspective
Step 1:
Move to highlight IP Multicast Group Perspective from L2 Switching Database screen, and
press <enter>.
Step 2:
Move to highlight an address to view information associated with this IP
multicast group.
MAC Address Perspective
Step 1:
Move to highlight MAC Address Perspective from L2 Switching Database screen, and
press <enter>.
Step 2:
Enter a MAC address to view characteristics information, corresponding VLAN’s, and corresponding ports in the switching database.
Port Perspective
Step 1:
Move to highlight Port Perspective from L2 Switching Database screen, and press
<enter>. You can view VLAN activities and RMON statistics here.
Page 44

Step 2: Per Port VLAN Activities
Per Port VLAN Activities is highlighted. Press <enter>.
Step 3:
Move to highlight a port and press <enter>. Example: select Port 1 to view
corresponding VLAN Activities.
User’s Manual 40
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 4:
View or search by MAC address individually.
Step 5:
Press <esc> to return to a previous screen as shown in Step 1.
Page 45

Step 6: Per Port Statistics
Move to highlight Per Port Statistics and press <enter>.
Step 7:
Move to highlight a port and press <enter>. Example: select Port 1 to view corresponding
VLAN Activities. Press [R] to reset counter for this port.
User’s Manual 41
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 46
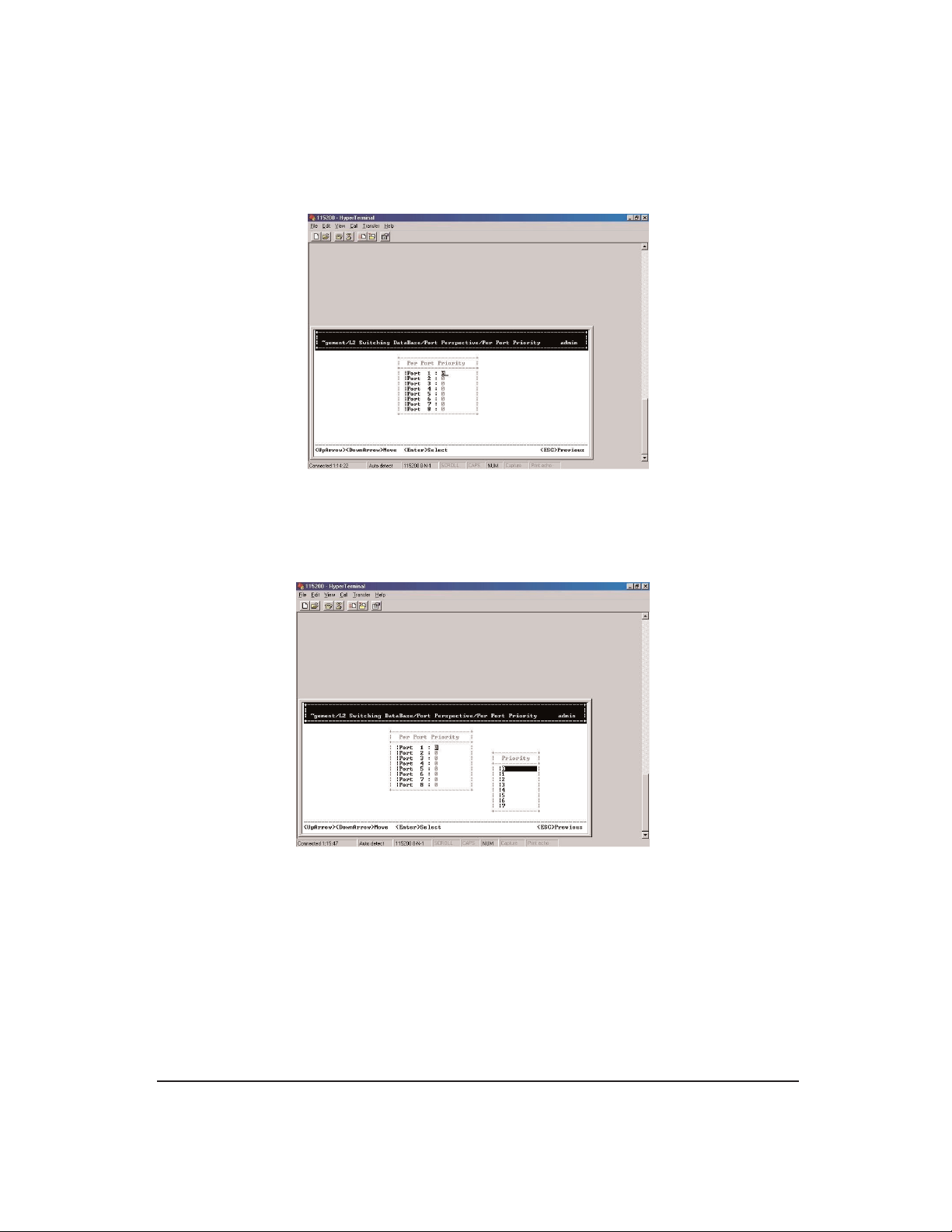
Step 8: Per Port Priority
Move to highlight Per Port Priority and press <enter>.
Step 9:
Move to highlight a port and press <enter>. Example: select Port 1 to view
corresponding priority level.
User’s Manual 42
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 47

User’s Manual 43
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
IP Networking
Step 1:
Move to highlight IP Networking from [Advanced Management]
screen and press <enter>.
Step 2: IP & RIP Settings
Highlight IP & RIP Settings from IP Networking and press <enter>.
Step 3:
The screen shows a list of VLAN IDs, IP addresses, subnet masks, proxy ARPs, and RIPs
currently defined.
Page 48

User’s Manual 44
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 4:
Move to highlight the row that contains the parameters you want to change,
and then press <enter>.
Ping Settings
Step 1:
Move to highlight Ping from IP Networking and press <enter>.
Page 49

User’s Manual 45
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2: Host
Move to highlight Host and press <enter>.
Step 3:
Enter 4 decimal bytes (dot separated) as the IP address to ping.
Step 4: Count
Move to highlight Count and press <enter>.
Step 5:
Specify a packet count number from 1 to 999, or type 0 for an infinite packet count.
Press <enter>.
Step 6: Size (bytes)
Move to highlight Size and press <enter>.
Step 7:
Specify a packet size from 0-1500. Press <enter>.
Step 8: Timeout (sec)
Move to highlight Timeout and press <enter>.
Step 9:
Specify a timeout value from 1-999. Press <enter>.
Step 10:
Press <esc> to start to ping when completed with the ping parameters.
Page 50

User’s Manual 46
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2: Aging Time
Move to highlight Aging Time and press <enter>. Enter a decimal number as bridge aging
period in seconds or, enter 0 for no aging.
Step 3: Flood Limits for all Ports
Move to highlight Flood Limit for All ports and press <enter>. Enter a decimal
number as flood limit in packets per second or, enter 0 for no limit.
Static Filtering
Step 1:
Move to highlight Static Filtering from [Advanced Management] screen,
and press <enter>.
Bridging
Step 1:
Move to highlight Bridging from [Advanced Management] screen and press <enter>.
Page 51

Step 3: Add/Delete/Search
Press [+] on keypad to add a specific MAC address to be filtered. Press [-] to delete a specific MAC
address from being filtered. Press [S] to search through current list of MAC addresses in the static
filtering database. The static filtering database maximum capacity is 64.
Caution:
User’s Manual 47
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2: Source/Destination MAC Address Out-Filters
Move to highlight source MAC addresses or destination MAC addresses for static filtering,
and press <enter>.
* No prec autionary m essa ge app ears before y ou d elet e a speci fic MAC
address from being filtered.
* Be sure you want to delete it bef ore doing so.
Page 52

User’s Manual 48
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Spanning Tree Functions
Step 1:
Move to highlight Spanning Tree from [Advanced Management] screen, and press <enter>.
Step 2: Spanning Tree Configurations
Move to highlight Spanning Tree Configurations if you want to change Spanning Tree Protocol
Configurations.
Step 3: Spanning Tree Protocol
Press <enter> to enter Spanning Tree Options. Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 4: Bridge Priority
Move to highlight Bridge Priority and press <enter>. Type a decimal number for the bridge priority
and press <enter>.
Step 5: Hello Time (sec)
Move to highlight Hello Time and press <enter>. Type a decimal number for the hello time and
press <enter>.
Page 53

User’s Manual 49
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 6: Max Age (sec)
Move to highlight Max Age and press <enter>. Type a decimal number for the max age.
Step 7: Forward Delay (sec)
Move to highlight Forward Delay and press <enter>. Type a decimal number for the
forward delay.
Spanning Tree Port States
Step 1:
Move to highlight Spanning Tree Port States if you want to change per port administration status,
and press <enter>.
Step 2:
Move to highlight a port if you want to change its administration status, and press <enter>.
Disabled (Link Down) denotes Admin Status Up without a link. Forwarding denotes
Admin Status Up with a link. Admin Status Down denotes no TX/RX transmission allowed.
Admin Status Up denotes TX/RX transmission allowed.
Spanning Tree Path Costs
Step 1:
Move to highlight Spanning Tree Path Costs if you want to change the path cost,
and press <enter>.
Page 54

User’s Manual 50
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Spanning Tree Port Priorities
Step 1:
Move to highlight Spanning Tree Port Priorities if you want to change the priority level per port,
and press <enter>.
Step 2:
Move to highlight All Ports or each port individually, and press <enter>. For new priority value,
type a decimal number from 0-255, and press <enter>. A low value gives the port a greater likelihood of becoming a Root port .
SNMP Functions
Step 1:
Move to highlight SNMP from [Advanced Management] screen, and press <enter>.
Step 2: SNMP Options
Move to highlight SNMP and press <enter>. Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Page 55

User’s Manual 51
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 3: Get Community Name
Move to highlight Get Community Name and press <enter>.
Enter text and press <enter>.
Step 4: Set Community Name
Move to highlight Set Community Name and press <enter>. Enter text and press <enter>.
Step 5: Trap Community Name
Move to highlight Trap Community Name 1 and press <enter>. Enter text and press <enter>.
Repeat to specify up to three more trap community names.
Step 6: Trap Host IP Address
Move to highlight Trap Host 1 IP Address and press <enter>. Type an IP address for trap host 1
and press <enter>. Repeat to specify up to two more trap host IP addresses.
Step 7: Cold Start Trap
Move to highlight Cold Start Trap and press <enter>. Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 8: Warm Start Trap
Move to highlight Warm Start Trap and press <enter>. Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 9: Link Down Trap
Move to highlight Link Down Trap and press <enter>. Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 10: Link Up Trap
Move to highlight Link Up Trap and press <enter>. Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 11: Authentication Failure Trap
Move to highlight Authentication Failure Trap and press <enter>.
Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 12: Rising Alarm Trap
Move to highlight Rising Alarm Trap and press <enter>.
Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 13: Falling Alarm Trap
Move to highlight Falling Alarm Trap and press <enter>.
Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Step 14: Topology Change Trap
Move to highlight Topology Change Trap and press <enter>.
Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Page 56

User’s Manual 52
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Other Protocols
Step 1:
Move to highlight Other Protocols from [Advanced Management] screen, and press <enter>.
Step 2: GVRP
Move to highlight GVRP and press <enter>. Decide to have it Disabled or Enabled.
Page 57

Step 3: IGMP
Move to highlight IGMP and press <enter>. Decide to have it Disabled or set in either Passive or
Active mode.
Link Aggregation
See the console screen
Port Mirroring
Step 1:
Move to highlight Port Mirroring from [Advanced Management] screen, and press <enter>. You
can mirror one port to Port 1.
User’s Manual 53
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 58

Step 2:
Press <enter> to enter Port Mirroring Options.
Step 3: Mirror From
Press <enter> to enter Mirror From Options, listing the ports that can be mirrored from.
User’s Manual 54
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 59

Step 4:
Move to highlight the port you want to mirror from and press <enter>.
Step 5: Mirror Mode
Move to select Mirror Mode. From Mode Options, decide whether the port to be mirrored from will
be receiving or transmitting.
Step 6:
Press <esc> when completed.
Quality of Service (QoS)
See Console Screen
Port Access Control
See Console Screen
Radius Server
See Console Screen
User’s Manual 55
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Page 60

User’s Manual 56
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
SENDING AND RECEIVING FILES
The TFTP protocol is used to download upgraded software to the switch.
A VLAN with the proper IP address and routing path to the TFTP server must be configured for the
switch to access the specified TFTP server.
Step 1:
Move to highlight File Transfer from [Advanced Management] screen, and press <enter>.
Step 3:
If the default File Name is not the one you intend to receive, press <enter>. Type the name of the
file you intend to receive and press <enter>.
Step 4:
Move to highlight IP Address and press <enter>. Type the IP address from where the file
will be obtained.
Step 2: Receive File Via TFTP
Move to highlight Receive File Via TFTP and press <enter>.
Page 61

User’s Manual 57
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 5:
Press <esc> when completed.
Step 6:
A dialog box appears to ask if you want to transfer file now. Highlight [Yes] and
press <enter> to start file transfer, or move to highlight [No] and press <enter> to deny it.
Press <esc> to exit .
Step 7: Send File Via TFTP
Move to highlight Send File Via TFTP and press <enter>.
Step 8:
If the default File Type is not the one you intend to send, press <enter>.
Select the file type you intend to send and press <enter>.
Step 9:
Repeat Step 4-6.
Page 62

User’s Manual 58
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Logout
To log out, highlight Logout from [Switch Management] screen and press <enter>.
Please remember to save settings you have changed before you log out.
Save Settings
To save the current settings and remain in the configuration program, highlight Save Settings from
[Switch Management] and press <enter>.
Restore Default Settings
To restore the factory default settings, highlight Restore Default Settings from
[Switch Management] and press <enter>.
The switch will be rebooted after confirming <Yes> as to restore the default settings.
Reboot
To reboot the switch, highlight Reboot from [Switch Management] and press <enter>.
Page 63

User’s Manual 59
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
WEB-BASED BROWSER MANAGEMENT
The EtherNav” D7600 switch provides a web-based browser interface for configuring and managing the switch. This interface allows you to access the switch using a preferred web browser.
This section describes how to configure the switch using its web-based browser interface.
LOGGING ON TO THE SWITCH
Switch IP Address
In your web browser, specify the IP address of the switch.
Login ID
Enter the factory default login ID: admin.
Password
Enter the factory default password (123456, click <Login>).
Page 64

User’s Manual 60
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
UNDERSTANDING THE BROWSER INTERFACE
The web browser interface provides three point-and-click buttons at the upper field of the screen
for configuring and managing the D7600.
The Basic Setup/General parameters appear at the lower field of the screen. These parameters
can also be displayed by clicking Basic Setup button and select General in sub-menu.
File
Save settings configured in the browser interface / download upgraded software via TFTP / reboot
the switch / logout of the browser interface.
Basic Setup
Perform general, LAN port, and console port activities.
Advanced Setup
Perform MAC address management / IP networking / per port statistics / port priority / bridging /
static MAC filters / IP multicast group / VLAN perspective / spanning tree perspective /
SNMP / other protocols / port trunking / port mirroring.
Page 65

User’s Manual 61
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
PERFORMING FILE ACTIVITIES
To Perform File Activities:
Click the [File] button at the upper field of the main display, the menu options appear.
Step 1: Saving Setting
Click Saving Setting to save your configuration settings.
Step 2:
When you click it, a message asks "Are you sure you want to save setting? ", click OK to save it
or Cancel to abort it.
Step 1: Receive File Via TFTP
Click Receive File Via TFTP on the [File] display.
Note: The TFTP protocol is used to download upgraded software to the switch.
A VLAN with the proper IP address and routing path to the TFTP server must be
configured for the switch to access the specified TFTP server.
Step 2:
For File Name, type the name of the file you intend to receive.
Step 3:
For IP Address, type the IP address from where the file will be obtained.
Step 4:
Click Receive Now.
Page 66

User’s Manual 62
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 1: Reboot
Click Reboot on the [File] display.
Step 2:
When you click it, a message asks "Are you sure you want to save setting?", click OK to save it or
Cancel to abort it.
Step 1: Logout
Click Logout on the [File] display.
Step 2:
When you click it, a message asks "Are you sure you want to save setting?", click OK to save it or
Cancel to abort it.
PERFORMING BASIC SETUP ACTIVITIES
To perform Basic Setup Activities:
Click the [Basic Setup] button at the upper field of the main display, the menu options appear.
Step 1: General Management Configuration
Click General and the screen shows’ the Basic Setup/General parameters. The screen here is the
same when you first access the switch browser interface.
Page 67

User’s Manual 63
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2: System Name
Click in System Name text box on the field of Basic Setup/General.
Step 3:
Type a system name if it is blank, or replace the current system name with a new one.
Step 4: Location
Click in Location text box on the field of Basic Setup/General.
Step 5:
Type a location name if it is blank, or replace the current location name with a new one.
Step 6: Statistic Collection
To enable or disable statistics collection at the switch, click the appropriate option from
Statistic Collection drop-down menu.
Step 7: Reboot-On-Error
To allow or prevent the switch from rebooting when a fatal error is detected, click the
appropriate option from Reboot-On-Error drop-down menu.
Step 8: Remote Telnet Login
To enable or disable access to the switch management program via Telnet, click the appropriate option from Remote Telnet Login drop-down menu.
Step 9:
Click Update Setting. A confirmation window appears.
LAN Port Configuration
Step 1:
To access the LAN configuration parameters, click Basic Setup button first and then point
to LAN Port and click a suitable option.
Page 68

User’s Manual 64
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2: Port Status
Click Port Status to view the line speed and flow control for all ports.
Step 4:
In the Port column, click the port you want to configure. E.g. click Port 1.
Note: The information displayed automatically updates every 15 seconds, without requiring
you to refresh the window.
Step 3: Port Setting
Click Port Setting to access the configuration information for all ports.
Page 69

User’s Manual 65
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 5:
Click the drop-down menu under Admin Setting, decide to disable or enable it .
Note:
Disable - places the port in DOWN state.
In this state, packets cannot be switches to and from the port.
Enable: places the port in UP state.
In this state, packets can be switched to and from the port.
Step 6:
Click the drop-down menu under Speed/Duplex Options if you want to change
the line speed and duplex settings.
Note:
Auto: allows the switch to automatically ascertain the line speed and duplex mode. All the other
selections force the port to use a specific line speed and duplex mode. ‘HD’ denotes half-duplex
mode; FD denotes full-duplex mode.
Step 7:
Click the drop-down menu under Flow Control Options if you want to configure the flow
control for this port.
Note:
Auto: allows the switch to automatically decide whether or not to use flow control.
Disable: turns off flow control at all times.
Enable: turns on flow control at all times.
Step 8:
Click Update Setting when completed. A confirmation window appears.
Note:
For your convenience, click the LED’s on the image of the switch and view its
current speed, duplex, and link activity.
Page 70

User’s Manual 66
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Console Port Configuration
Step 1:
To access the console port configuration parameters, click Basic Setup button first and then click
Console Port.
Step 2: Baud Rate
Click an appropriate speed from Baud Rate drop-down menu on the field of
Basic Setup/Console Port Configuration.
Note:
Auto: allows the switch to Auto-baud between 9600bps and 115,200bps
All the other selections force a specific console baud rate.
Step 3: Flow Control
Click a flow control method from Flow Control drop-down menu.
Step 4: Modem Control
Step 5: Modem Setup String Flag
Step 6: Modem Setup String
Step 7:
Click Update Setting when completed. A confirmation window appears.
Page 71

User’s Manual 67
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
PERFORMING ADVANCED SETUP ACTIVITIES
To Perform Advanced Setup Activities:
Click the [Advanced Setup] button at the upper field of the main display, the menu
options appear.
Step 2: Per VLAN View
Click Per VLAN View first and click on the port that you want to view.
Close the VLAN Activities window when finished viewing.
MAC Address Management
Step 1:
From the Advanced Setup menu, point to MAC Address Management to view VLANs and their
associated MAC addresses.
Page 72

User’s Manual 68
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 3: Per Port View
Click Per Port View first and click on the port that you want to view.
Close the Per Port VLAN Activities window when finished viewing.
Step 4: Individual MAC View
From the Advanced Setup menu as shown in Step 1, point to
MAC Address Management. Click Individual MAC View.
Step 5:
Click in the Enter MAC Address text box and type the MAC address that you want to view. Then
click on the Get Information button.
Step 6:
Close the Individual MAC View window when finished viewing.
IP Networking
To access the IP networking parameters, click the Advanced Setup button,
and Point to IP Networking from the selection menu.
Page 73

User’s Manual 69
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 1: IP & RIP Settings
Click IP & RIP Settings to access IP and RIP settings.
A list of VLAN Ids appears, along with their corresponding IP address and subnet mask.
Step 2:
In the VLAN ID column, click a VLAN ID whose settings you want to view and/or change.
Step 3:
To change the IP Address, click in the text box and type a new address.
Alternatively, you can use the Delete IP button to delete the IP address.
Caution:
Step 4:
To change the IP Subnet Mask, click in the text box and type a new address.
Step 5:
To change the Frame Type, click a value from the drop-down list.
Step 6:
To change the BOOTP selection, click a value from the drop-down list.
Step 7:
To change the Proxy ARP selection, click a value from the drop-down list .
Step 8:
To change the RIP Setting, click a value from the drop-down list .
Step 9:
Specify whether you want to broadcast, multicast, or neither from the drop-down list.
Step 10:
Specify whether you want to advertise routes.
Step 11:
Specify whether you want to advertise the default route.
Step 12:
Specify whether you want to accept RIP V1/V2 updates.
Step 13:
Specify whether you want to accept default route updates.
Click to close the confirmation window.
* No precautionary messag e ap p e a rsbefore you delete th e IP
address.
* Be sure you want to deleteit beforedoing so .
* Th e I P ad dress is n ot de let ed until yo u click Update Setting.
Page 74

User’s Manual 70
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 14:
Specify whether split horizon is to be used.
Step 15:
Specify whether poisoned reverse is to be used.
Step 16:
Specify whether the switch is to send triggered responses.
Step 17:
When you finished with these selections, click Update Setting.
A confirmation window appears. Click to close the confirmation window.
Per Port Statistics
Step 1:
To access per port statistics, click the Advanced Setup button, and then click Per Port Statistics from
the selection menu.
Step 2:
Click a port to view statistic data.
Step 3:
Click Update Setting when completed.
Port Priority
Step 1:
To access port priority, click the Advanced Setup button, and then click Port Priority
from the selection menu.
Step 2:
Click a port to change the priority level.
Step 3:
Click the drop-down list for setting a proper priority level.
Step 4:
Click Update Setting when completed.
Bridging
Step 1:
To access bridging parameters, click the Advanced Setup button, and then click Bridging from the
selection menu.
Page 75

User’s Manual 71
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 2: Aging Options
Click the drop-down list for Disabled (No Aging) or Set Aging Time.
Step 3: Aging Time
Click the text box and type a decimal number as bridge aging period in seconds.
Step 4: Flood Limit
Click the drop-down list for No Flooding, Controlled Flooding, Unlimited Flooding.
Step 5: Flood Limit for All Ports
Click the text box and type a decimal number as flood limit in packets per second.
Static MAC Filter
To access the static MAC filter parameters, click the Advanced Setup button, and point to Static
MAC Filter in the selection menu.
Step 1: Source MAC Address Filter
Click Source MAC Address Filters.
Step 2:
Click Add MAC Addr button to add a source MAC address for static filtering.
Page 76

User’s Manual 72
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 3:
The Static Source MAC Filter window appears. Click in the Source MAC Address Filter text box and
type a unique MAC source address you want to add. Then click the Add button.
Step 4:
A confirmation window appears. Close the confirmation window.
Step 5:
If you no longer need a source MAC address, click Delete MAC Addr
button to delete it in Step 2.
Step 6:
The Delete Source MAC Address window appears. Click the Select a MAC Address drop-down list
and select the source MAC address you want to delete. Then click the Delete button.
Step 7:
A confirmation window appears. Close the confirmation window.
Step 1: Destination MAC Address
Click the Advanced Setup button, and point to Static MAC Filter in the selection menu.
Click Destination MAC Address.
Step 2:
Click Add MAC Addr button to add a destination MAC address for static filtering.
Refer to Step 2~4 in Source MAC Address section for similar procedure.
Step 3:
Click Delete MAC Addr button to delete a destination MAC address for static filtering.
Refer to Step 5~7 in Source MAC Address section for similar procedure.
IP Multicast Group
To view the IP multicast group addresses, click the Advanced Setup button, and click IP Multicast
Group in the selection menu. The information is read-only.
VLAN Perspective
To view the VLAN configuration information, click the Advanced Setup button, and point to VLAN
Perspective in the selection menu.
Page 77

User’s Manual 73
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
IP Multicast Group
To view the IP multicast group addresses, click the Advanced Setup button, and click IP Multicast
Group in the selection menu. The information is read-only.
VLAN Perspective
To view the VLAN configuration information, click the Advanced Setup button, and point to VLAN
Perspective in the selection menu.
Step 3:
The VLAN Information window appears. Click to assign switch ports to VLAN ID 1. For each
switch, the port options include Tagged Ports, Untagged Ports, or Forbidden Ports.
Step 4:
Click to close the VLAN Information window.
Step 5: Add a VLAN Entry
Click on the Add VLAN button to create a new VLAN.
Step 1: VLAN Configuration
Click VLAN Configuration.
Step 2:
Click on a VLAN ID whose VLAN configuration you want to change.
Page 78

User’s Manual 74
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
IP Multicast Group
To view the IP multicast group addresses, click the Advanced Setup button, and click IP Multicast
Group in the selection menu. The information is read-only.
VLAN Perspective
To view the VLAN configuration information, click the Advanced Setup button, and point to VLAN
Perspective in the selection menu.
Step 6:
The Add a VLAN Entry window appears.
Step 7:
Click in the VLAN ID text box and specify a new VLAN ID number.
Step 8:
Click in the VLAN Name text box and type a name for this newly created VLAN.
Step 9:
Click to assign switch ports to this VLAN. For each switch, the port options include
Tagged Ports, Untagged Ports, or Forbidden Ports.
Step 10:
Click Add Now button.
Step 11: Delete a VLAN Entry
Click on the Delete VLAN button to delete a VLAN. VLAN ID 1 is the default VLAN and
cannot be deleted.
Step 12:
The Delete a VLAN Entry window appears.
Step 13:
Click the drop-down menu to select a VLAN ID, which you want to delete.
Step 14:
Click the Delete button.
Caution:
* No precautionary message ap p e a rsbefore you delete a
VLAN .
Page 79

User’s Manual 75
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Link Aggregation
To view the spanning tree perspective parameters, click the Advanced Setup button, and point to
Link Aggregation in the selection menu.
Step 1: Aggregation Port Status
To view and/or change the Aggregation configurations, click Port Link Aggregation
from the above screen.
Step 2:
For Link Aggregation, specify whether you want to have it Disabled or Enabled by clicking
the drop-down list.
Step 3:
For Bridge Priority, click in the text box and type a decimal number between 0 and 65535.
Step 4:
For Hello Time, click in the text box and type a decimal number between 0 and 10.
Step 5:
For Max Age, click in the text box and type a decimal number between 6 and 40.
Step 6:
For Forward Delay, click in the text box and type a decimal number between 4 and 30.
Page 80

User’s Manual 76
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 7:
Click Update Setting. A confirmation window appears. Close the confirmation window.
Step 1: Port Setting
To view and/or change the Spanning Tree configurations by port, click the
Advanced Setup button, point to Link Aggregation in the selection menu, and click Aggregation
Port Settings.
Step 3:
For Port Priority, click in the text box and type a decimal number between 0 and 255.
A low value gives the port a greater likelihood of becoming a Root port.
Step 4:
For Path Cost, click in the text box and type a decimal number as a new path cost value.
Step 5:
For Port Status, specify whether the port is up or down by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 6:
Click Update Setting. A confirmation window appears. Close the confirmation window.
Step 2:
In the Port column, click the port whose Aggregation information you want to view.
Page 81

User’s Manual 77
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
SNMP
To view and/or change all SNMP-related information, click the Advanced Setup button, and
click SNMP in the selection menu. The SNMP Configurations window appears.
As shown below, the factory-default SNMP value is enabled and the factory-default Community
Name value is public.
Step 1: SNMP
For SNMP, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 2: Get Community Name
For Get Community Name, click in the text box and type a get community name.
Step 3: Set Community Name
For Set Community Name, click in the text box and type a set community name.
Step 4: Trap Community Name
For each Trap Community Name, click in the text box and type a trap community name.
Step 5: Trap Host IP Address
For each Trap Host IP Address, click in the text box and type a IP address for trap host 1~4.
Step 6: Cold Start Trap
For Cold Start Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 7: Warm Start Trap
For Warm Start Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 8: Link Down Trap
For Link Down Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list.
Page 82

User’s Manual 78
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Step 9: Link Up Trap
For Link Up Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 10: Authentication Failure Trap
For Authentication Failure Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the
drop-down list.
Step 11: Rising Alarm Trap
For Rising Alarm Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 12: Falling Alarm Trap
For Falling Alarm Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 13: Topology Alarm Trap
For Topology Alarm Trap, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list .
Step 14: Update Setting
Click Update Setting when completed. A confirmation window appears.
Close the confirmation window.
Other Protocols
To enable or disable the GVRP and/or IGMP protocols, click the Advanced Setup button,
and click Other Protocols in the selection menu.
Step 1: GVRP
For GVRP, specify whether it is Disabled or Enabled by clicking the drop-down list .
Step 2: IGMP
For IGMP, specify whether it is disabled or Passive or Active by clicking the drop-down list .
Step 3: Update Setting
Click Update Setting when completed. A confirmation window appears.
Close the confirmation window.
Page 83

User’s Manual 79
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Port Mirroring
To use the switch’s mirroring capability to mirror one port to Port 1, click the Advanced Setup
button, and click Port Mirroring in the selection menu. Click Port 1 in the Mirror To column.
Step 1: Mirror From
In the Mirror From column, select a "mirror from" port by clicking the drop-down list.
Data traffic from this port will mirror to Port 1.
Step 2: Mirror Mode
In the Mirror Mode column, specify whether the "mirrored from" port will be receiving
or transmitting data by clicking the drop-down list.
Step 3: Update Setting
Click Update Setting when completed. A confirmation window appears.
Close the confirmation window.
Page 84

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
SNMP & RMON MANAGEMENT
OVERVIEW
SNMP AGENT AND MIB-2 (RFC 1213)
This section describes the switch’s Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and
Remote Monitoring (RMON) capabilities.
The SNMP Agent running on the switch manager CPU is responsible for:
- Retrieving MIB counters from various layers of software modules according to the
SNMP GET/GET NEXT frame messages.
- Setting MIB variables according to the SNMP SET frame message.
- Generating an SNMP TRAP frame message to the Network Management Station if the
threshold of a certain MIB counter is reached or if other trap conditions (such as the following) are met:
RMON is an abbreviation for the Remote Monitoring MIB (Management Information Base).
RMON is a system defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
document RFC 1757, which defines how networks can be monitored remotely.
RMONs typically consist of two components: an RMON probe and a management workstation:
- The RMON probe is an intelligent device or software agent that continually
collects statistics about a LAN segment or VLAN. The RMON probe transfers
the collected data to a management workstation on request or when a
pre-defined threshold is reached.
- The management workstation collects the statistics that the RMON probe
gathers. The workstation can reside on the same network as the probe, or it
can have an in-band or out-of-band connection to the probe.
The switch provides RMON capabilities that allow network administrators to set
parameters and view statistical counters defined in MIB-II, Bridge MIB, and RMON MIB.
RMON activities are performed at a Network Management Station running an SNMP network management application with graphical user interface.
User’s Manual 80
Page 85

User’s Manual 81
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Warm start
Cold start
Link up
Link down
Authentication failure
Rising alarm
Falling alarm
Topology alarm
MIB-2 defines a set of manageable objects in various layers of the TCP/IP protocol suites. MIB-2
covers all manageable objects from layer 1 to layer 4 and, as a result, is the major SNMP MIB supported by all vendors in the networking industry. The switch supports a
complete implementation of SNMP Agent and MIB-2.
The switch provides hardware-based RMON counters in the switch chipset. The switch manager
CPU polls these counters periodically to collect the statistics in a format that complies with the
RMON MIB definition.
RMON Groups Supported
The switch supports the following RMON MIB groups defined in RFC 1757:
- RMON Statistics Group – maintains utilization and error statistics for the
switch port being monitored.
- RMON History Group – gathers and stores periodic statistical samples
from the previous Statistics Group.
- RMON Alarm Group – allows a network administrator to define alarm thresholds for any MIB
variable. An alarm can be associated with Low Threshold, High Threshold, or both. A trigger
can trigger an alarm when the value of a specific MIB variable exceeds
a threshold, falls below a threshold, or exceeds or falls below a threshold.
RMON Event Group – allows a network administrator to define actions based on alarms. SNMP
Traps are generated when RMON Alarms are triggered. The action taken in the Network
Management Station depends on the specific network management application.
RMON MIB (RFC 1757) AND BRIDGE MIB (RFC 1493)
Page 86

User’s Manual 82
Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
Bridge Groups Supported
The switch supports the following four groups of Bridge MIB (RFC 1493):
- The dot1dBase Group – a mandatory group that contains the objects applicable to all types of
bridges.
- The dot1dStp Group – contains objects that denote the bridge’s state with respect to the
Spanning Tree Protocol. If a node does not implement the Spanning Tree Protocol, this group
will not be implemented. This group is applicable to any transparent only, source route, or SRT
bridge that implements the Spanning Tree Protocol.
- The dot1dTp Group – contains objects that describe the entity’s transparent bridging status.
This group is applicable to transparent operation only and SRT bridges.
- The dot1dStatic Group – contains objects that describe the entity’s destination-address filtering status. This group is applicable to any type of bridge which performs destination-address
filtering.
Page 87

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 83
Manageable
8/9-Port Switch
10/100/1000BaseT/TX auto-negotiating ports
with RJ-45 connectors and 100/1000BaseFX
fiber ports combination
Performance
148,80pps for 10Mbps
148,800pps for 100Mbps
1,488,000pps for 1000Mbps
LED Indicators
Per unit – Power status
Per port – LNK (Link) /ACT (Activity)
FDX/COL
Applicable Standards
IEEE 802.3 10BaseT
IEEE 802.3u, ab 100/1000BaseTX/FX
Emissions
FCC part 15 Class A, NEMA TS2, UL,
CE Mark Class A
Switching Method
Store-and-Forward
Dimensions
W 8.5 in _ D 7.5 in _ H 1.75 in
Net Weight
4.5 lbs. Approx.
Power Input
External power adapter 12-24V DC; 1A
Power Consumption
12W max.
Operating Temperature
-40°C to 74° C
Storage Temperature
-40°C to 85° C
Humidity
0%-95% non-condensing
Forwarding Rate
10BaseT:
100BaseTX:
1000BaseTX:
10 / 20Mbps half / full-duplex
100 / 200Mbps half / full-duplex
1000/2000Mbps half/ full-duplex
Cable
110BaseT:
100/1000BaseTX:
100/1000BaseFX:
2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5, 5E, 6
2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5E Both up to 100m (328ft)
MMF (50 or 62.5_m), SMF (9 or10_m)
SPECIFICATIONS
Page 88

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 84
APPENDIX A - CONNECTOR PINOUTS
Pin arrangement of RJ-45 connectors:
1
8
The following table lists the pin out of 10/100/1000BaseT/TX ports.
Pin Regular Ports Uplink Port
1
2
Input Receive Data +
Output Transmit Data +
Input Receive Data -
Output Transmit Data -
3
4
Output Transmit Data +
Input Receive Data +
6
Output Transmit Data -
Input Receive Data -
NC
NC
5
NC
NC
7
NC
NC
8
NC
NC
Page 89

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 85
D7600 SERIES FRONT PANEL LAYOUT
D7600-EE-X-CC
D7600-MM-X-CC, D7600-MS-X-CC, D7600-SS-X-CC
D7600-EE-E-CC
D7600-MM-E-CC, D7600-MS-E-CC, D7600-SS-E-CC
Page 90

Manageable 8/9-Port Switch
User’s Manual 86
D7600 SERIES FRONT PANEL LAYOUT (con’t)
D7600-EE-S-CC
D7600-MM-S-CC, D7600-MS-S-CC, D7600-SS-S-CC
www.GESecurity.com
As a company of innovation, GE Security reserves the right to change product specifications without notice.
For the latest product specifications visit GE Security online at www.GESecurity.com or contact your GE Sales Representative.
Released 04-APRIL-05
Copyright © 2005, GE Security Inc. All rights reserved.
NORTH AMERICA
USA and CANADA
GE Security
IFS Fiber Optic Products
16 Commerce Road
Newtown, CT 06470
Tel: 203-426-1180
Fax: 203-426-3326
ifssales@ge.com
EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST,
and AFRICA
Suite A
1 Abbey Wood Road
West Malling, Kings Hill
Kent ME19 4YT
United Kingdom
Tel: +44 (0) 1732 522 777
Fax: +44 (0) 1732 522 888
sales@ifseurope.com
LATIN AMERICA
MEXICO, CENTRAL
and SOUTH AMERICA
IFS/Crockett International
4407 Bee Caves Road
Suite 422
Austin, TX 78746
Tel: 512-477-8787
Fax: 512-477-8555
sales@crockettint.com
ASIA PACIFIC
IFS/Crockett International
Asia Pacific Pte., Ltd.
3791 Jalan Bukit Merah
#09-12/13/14/15
e-Centre @ Redhill
Singapore 408726
Tel: +65 6235 2661
Fax: +65 6235 2369
ifs@crockettint.com
 Loading...
Loading...