Interference Current Stimulation Devices
STEREODYNATOR 928
User Manual
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

2
STEREODYNATOR
928
Das vorliegende Handbuch wurde von der gbo Medizintechnik AG erstellt und auf seine Richtigkeit
überprüft. Es erhebt jedoch keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit. Alle Angaben und Daten können ohne
vorherige Ankündigung geändert werden.
Ohne ausdrückliche schriftliche Genehmigung der gbo Medizintechnik AG darf kein Teil dieses Handbuch
für irgendwelche Zwecke vervielfältigt oder übertragen werden, unabhängig davon, auf welche Art und
Weise oder mit welchen Mitteln, elektronisch oder mechanisch, dies geschieht.
The gbo Medizintechnik AG has taken care in preparation of this manual, but makes no expressed or
implied warranty of any kind and assume no responsibility for errors or omissions.
All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced, in any form or by any means (electronic,
mechanical, or otherwise) without the prior written permission of the gbo Medizintechnik AG.
© gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004
gbo Medizintechnik AG
Kleiststraße 6
D-64668 Rimbach
Telephone:+49 / 6 25 3 / 808-0
Telefax: +49 / 6 25 3 / 808-300
E-Mail: info@gbo-med.de
Internet: http://www.gbo-med.de
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19

STEREODYNATOR
928
Comments According to the Medical Device Directive
The STEREODYNATOR 928 is a mains operated current stimulation device of protection class I.
The device is in accordance with the EC Medical Device Directive (93/42/EEC) and therefore carries the
CE-sign with the number of the ”notified body for medical devices”. The according graphical symbol is
placed on the type plate.
According to the Medical Device Directive, STEREODYNATOR 928 is a device of class IIb.
The manufacturer is only responsible for the security, operational reliability and functionality of the device
if:
• the device is used in accordance with the user manual;
• the electrical installation of the location where the device will be used corresponds to the
respective current requirements of electrical safety;
• the device is not used in hazardous environments and humid locations;
• the mountings, add ons, internal adjustments, modifications or repairs are realized only by
personnel authorized for that by the manufacturer;
• the operator regulation of this EC-directive is observed within the scope of the Medical Device
Directive.
3
You may obtain technical support by the manufacturer or the dealers or service authorized by the
manufacturer. The manufacturer provides a life time of at least 10 years for this product.
STEREODYNATOR 928 is a
electronic device. Disposing has to be done according to regulations
for electronic devices. Consumables have to be disposed as garbage.
On request, the manufacturer will provide you with further technical descriptions for all serviceable parts of
the device, such as circuit diagrams, spare part lists, and adjustment instructions as far as these are of use for
the qualified technical staff of the user.
Comments on electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Medical, electrical devices are subject to special precautions concerning the EMC. They must be installed
and operated according to the EMC-advice given in the accompanying documents. In particular medical,
electrical devices may be influenced by portable and mobile RF-communication devices.
The manufacturer guarantees the conformity of the unit with the EMC-requirements only when using
accessories which are listed in the EC declaration of conformity. The usage of other accessories my cause an
increased emission of electromagnetic disturbances or may lead to a reduced electromagnetic immunity.
The unit must not be arranged physically close to other devices or stacked with them. If such an order is
necessary nevertheless, the unit must be observed in order to check it for the intentional operation.
You find more EMC-comments in the chapter “Warnings and Safety Precautions” of this manual as well as
in the Technical Information on the next two pages.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
4
STEREODYNATOR
928
In accordance with the EMC-regulations for medical products we are obliged by law to
provide the following information.
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic emissions
The equipment is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or
the user of the equipment should assure that it is used in such an environment.
Emissions test Compliance Electromagnetic environment – guidance
RF emissions,
CISPR 11
RF emissions,
CISPR 11
Harmonic emissions,
IEC 61000-3-2 (*)
Voltage fluctuation/flicker
emissions, IEC 61000-3-3 (*)
(*) Note: For devices with a power consumption between 75 W and 1000 W only.
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic immunity
The equipment is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or
the user of the equipment should assure that it is used in such an environment.
Immunity test IEC 60601- test level Compliance level Electromagnetic environment –
Electrostatic discharge (ESD),
IEC61000-4-2
Electrical fast transient/burst,
IEC 61000-4-4
Surge,
IEC 61000-4-5
Voltage dips, short
interruptions and voltage
variations on power supply
input lines,
IEC 61000-4-11
Group 1 The equipment uses RF energy only for its internal function.
Therefore, its RF emissions are very low and are not likely to cause
any interference in nearby electronic equipment.
Class B
Class A
Complies
The equipment is suitable for use in all establishments, including
domestic establishments and those directly connected to the public
low-voltage power supply network that supplies buildings used for
domestic purposes.
guidance
±6 kV contact
±8 kV air
±2 kV for power supply
lines
±1 kV for input/output
lines
±1 kV differential mode
±2 kV common mode
<5% U
τ
for ½ cycle
(>95% dip)
40% U
τ
for 5 cycles
60% dip)
70% U
τ
for 25 cycles
30% dip)
±6 kV contact
±8 kV air
±2 kV for power supply
lines
±1 kV for input/output
lines
±1 kV differential mode
±2 kV common mode
<5% U
τ
for ½ cycle
(>95% dip)
40% U
τ
for 5 cycles
60% dip)
70% U
τ
for 25 cycles
30% dip)
Floors should be wood, concrete or
ceramic tile. If floors are covered with
synthetic material, the relative humidity
should be at least 30 %.
Mains power quality should be that of a
typical commercial or hospital
environment.
Mains power quality should be that of a
typical commercial or hospital
environment.
Mains power quality should be that of a
typical commercial or hospital
environment.
If the user of the equipment requires
continued operation during power mains
interruptions, it is recommended that the
equipment be powered from an
uninterruptible power supply or a
battery.
<95% U
for 5 s
(>5% dip)
Power frequency (50/60 Hz)
magnetic field,
IEC 61000-4-8
Note: Uτ is the a.c. mains voltage prior to application of the test level.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19
3 A/m 3 A/m Power frequency magnetic fields should
τ
<95% U
for 5 s
(>5% dip)
τ
be at levels characteristic of a typical
location in a typical commercial or
hospital environment.
STEREODYNATOR
928
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration — electromagnetic immunity
The equipment is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or
the user of the equipment should assure that it is used in such an environment.
Immunity test IEC 60601- test level Compliance level Electromagnetic environment –
guidance
Portable and mobile RF communications
equipment should be used no closer to any
part of the equipment, including cables,
than the recommended separation distance
calculated from the equation applicable to
the frequency of the transmitter.
Recommended separation distance:
Conducted RF,
IEC 61000-4-6
Radiated RF,
IEC 61000-4-3
3 V
rms
150 kHz to 80 MHz
3 V/m
80 MHz to 2,5 GHz
3 V
3V/m
eff
d=1,2√P
d=1,2√P
for 80 MHz to 800 MHz
d=2,3√P
for 800 MHz to 2,5 GHz
Where P is the maximum output power
rating of the transmitter in watts according
to the transmitter manufacturer and d is the
recommended separation distance in
meters (m).
5
Interference may occur in the vicinity of
equipment marked with the following
symbol:
Recommended separation distances to portable and mobile RF communication equipment
The equipment is intended to be operated in an electromagnetic environment, where radiated RF
interference is controlled. The user can help in avoiding interferences by means of meeting minimum
separation distances between portable and mobile RF communication equipment (transmitters) according
to the maximum output power of the communication equipment.
Separation distance according to the tranmission frequency (m)Rated power of the
transmitter (W)
0,01 0,12 0,12 0,23
0,1 0,38 0,38 0,73
1 1,2 1,2 2,3
10 3,8 3,8 7,3
100 12 12 23
150 kHz to 80 MHz
d=1,2√√√√P
80 MHz to 800 MHz
d=1,2√√√√P
800 MHz to 2,5 GHz
d=2,3√√√√P
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
6
STEREODYNATOR
928
EC - DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Name of manufacturer : gbo Medizintechnik AG
Address : Kleiststrasse 6
D - 64668 Rimbach
Germany
We hereby declare under our sole responsibility that the product described below conforms in design and
make as well as in the versions delivered to the corresponding safety and protection requirements defined in
the applicable EC regulations.
Harmonized standards have been used for all conformity checks, national standards have not been applied.
Any change to the product design that is not validated by us will render this declaration invalid.
Type of product : Stimulation Current Unit
Label :
STEREODYNATOR 928 Part-No. 014-0-928
Options : Ultrasound therapy module Part-No. 014-0-928-U
Suction application module Part-No. 014-0-928-V
Accessories :
Description Part-No.
Bow electrode 011-0-0024
Handle with finger-tip 45-38-401EH725
Rubber electrode 3 x 4 cm
Rubber electrode 6 x 8 cm
Rubber electrode 8 x 12 cm
Tin plate electrode 9 x 12 cm
Patient cable 45-38-435EH725
Suction electrode 34 mm 45-38-518EH722
Suction electrode 70 mm 45-38-526EH722
Suction electrode 50 mm 45-38-500EH722
Ultrasound probe 2,5 cm
Ultrasound probe 5 cm
Vaginal electrode 014-0-0006
Rectal electrode 014-0-0007
Star electrode small 45-38-708EH725
Star electrode standard 45-38-716EH725
Star electrode large 45-38-724EH725
Stereo suction electrode 45-38-856EH722
2
2
2
2
2
2
45-38-880EH725
45-38-898EH725
45-38-492EH725
45-38-468EH725
023-0-0140
023-0-0141
Corresponding EC regulations : EC medical devices directive (93/42/EEC)
Conformity assessment
procedure : Annex II of the directive 93/42/EEC
Classification : IIb (according to MDD, appendix IX)
Name und registration no.
of the notified body : TÜV Product Service in Munich/Germany with the
registration no. 0123
Additional information : none
Date :
January-1, 2006
Name of persons responsible : Dr. Eberhard Keck
Title/Function : CEO
Signature :
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19

STEREODYNATOR
928
Notations
Times New Roman in type size 11 - descriptions and explanations
7
Arial in type size 10
Lucida in type size 11 - text appears on the display of the current stimulation device
[[[[Descriptions]]]]
- functions and keys of the current stimulation device
- text appears on the display next to the soft key
Pictographs
Attention
Warnings which have to be observed by all means !
Attention !
Observe the instructions for use !
!! Note Information that will facilitate your work.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

8
STEREODYNATOR
928
Table of Contents
OVERVIEW 11
1 INTRODUCTION 12
1.1 Intended Use 12
1.2 Operating Concept 14
1.3 Short Instructions 15
1.4 Modes of Action of the Therapeutic Current Types 17
2 START OF OPERATION 18
2.1 Transport and Assembly 18
2.2 Connection and Switch-On 18
2.3 Settings 19
2.3.1 Device Settings 19
2.3.2 Basic Settings of the Current Types 20
3 DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTION 21
3.1 Operating Notes 21
3.1.1 Optical and Acoustical User Support 21
3.1.2 Intensity Regulator 22
3.1.3 Current and Polarity 22
3.1.4 Surge Parameters 24
3.1.5 Galvanic Base 24
3.1.6 Frequency Lock 24
3.1.7 Pulse Parameter 25
3.1.8 Therapy Time 25
3.1.9 Stimulation shifting 26
3.1.10 Menu 27
3.1.11 Menu Programs 28
3.2 Integrated Suction Application Aid 29
3.3 Ultrasound Therapy Module 30
4 THERAPY 32
4.1 Therapy with interference currents 32
4.1.1 Sedat 32
4.1.2 Myomot 33
4.1.3 Vegetative Stimulation I 33
4.1.4 Vegetative Stimulation II 33
4.1.5 Vegetative Stimulation III 33
4.1.6 Universal 33
4.1.7 Sedation Modulation 33
4.1.8 Automated programs 34
4.2 Menu Application With Electrotherapy 35
4.3 Menu ‘Applications with ultrasound’ 36
4.4 ”One - Touch” - Operation 36
4.4.1 Diadynamic Currents 36
4.4.2 Strong Muscle Stimulation (SMS) According to Eichhorn 37
4.4.3 Middle Frequency Currents 37
4.4.4 Ultrastimulation Current 38
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19

STEREODYNATOR
4.4.5 High-Voltage Currents 38
4.4.6 Galvanic Current and Iontophoresis 39
4.4.7 Faradic Current 40
4.4.8 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation 40
4.4.9 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation With Impulse Groups 41
4.4.10 Micro-Stimulus Current 42
4.4.11 Universal Therapy 42
4.5 Special types of current Menu 42
4.5.1 Impulse Galvanization 43
4.5.2 Frequency Modulation 43
4.5.3 Diadynamic Currents MF Monophasé Fixe and LP Longues Périodes 43
4.5.4 Rectangular Current for Incontinence 43
4.6 GYM 44
4.6.1 GYM current 44
4.6.2 GYM Training 45
4.6.3 Burning mode 45
928
5 GALVANOPALPATION 46
6 ELECTROKINETIC THERAPY 47
6.1 Detection of Trigger Points With the Electrode Handpiece 47
9
6.2 Stimulation Massage 47
7 ELECTRODES 48
7.1 Electrode Positioning 48
7.1.1 Monophase Electrode Techniques 49
7.1.2 Biphase Electrode Techniques 49
7.2 Single-Pole Electrodes 49
7.3 Three-pole electrodes 51
7.4 Suction Electrodes 51
7.4 Suction Electrodes 52
7.5 Electrode Handpiece 52
8 TROUBLESHOOTING 53
9 MAINTENANCE 54
9.1 Safety Controls 54
9.2 Cleaning, Disinfection and Care 54
9.2.1 Current Stimulation Device 54
9.2.2 Electrode Fleece, Electrode Pockets or Felts 54
10 WARNINGS AND SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 55
11 EXPLANATION OF THE SIGNS USED 57
12 TECHNICAL DATA 58
13 ACCESSORIES 61
INDEX 57
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

10
STEREODYNATOR
928
APPENDIX: STORING OF THERAPEUTIC CURRENT TYPES 59
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19

STEREODYNATOR
928
11
Overview
Chapter 1 describes the basic characteristics of the current stimulation device.
Chapter 2 explains the start of operation of the current stimulation device. It describes its setting
possibilities.
Chapter 3 describes all functions of the device and their operation.
Chapter 4 explains the realization of therapies.
Chapter 5 explains the realization of galvanopalpation.
Chapter 6 explains the realization of electrokinesis.
Chapter 7 refers to the arrangement and the use of the electrodes.
Chapter 8 explains the error messages and gives some hints in the case of faults.
Chapter 9 refers to safety controls in accordance with the MDD and to routine maintenance.
Chapter 10 shows the possible threats when using the current stimulation device. Furthermore, it
indicates how to avoid possible threats.
Chapter 11 explains the signs used.
Chapter 12 speifies all relevant technical data of the current stimulation device.
Chapter 13 shows the scope of supply of the device and informs about further accessories indicating
their order number.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

12
STEREODYNATOR
928
1 Introduction
1.1 Intended Use
The devices with interference current are microprocessor controlled electrical stimulus devices for Electro
Therapy. Their wide range of usage predestinates these medical devices for use in physiotherapeutic
departments of clinics as well as in modern well-equipped private practices.
The devices with interference current represent a continued development, based on the 8
All accessories of the 8
th
series can also be used with the 9th generation in the same manner. A suction
th
series equipment.
application aid for vacuum therapy as well as a module for ultrasound therapy with continuous and impulse
ultrasound waves are optionally available. The control elements for suction application aid and ultrasound
have already been integrated on the keyboard.
A stereodynamic interference current is generated through the superposition of three middle-frequency
currents flowing in different directions. The stimulating lower frequencies are already generated through
interference of two phase shifted circuits in the area being stipulated. The additional third circuit generates,
as opposed to classical interference methods, on one side a slow change in intensity and on the other side a
rhythmic shifting of the interference field. These dynamics of the stimulation location and the intensity
dynamics decrease the habituation effect and therefore improve the therapeutic effect. The
STEREODYNATOR 928 uses the three-dimensional interference method. The special characteristics are
as follows:
• Local stimulation effect.
• Multi-site stimulation effect.
• Intensity dynamics.
• Dynamic behavior of stimulation site coupled with endogenous/exogenous stimulation shifting.
Automated programs improve the handling: The STEREODYNATOR 928 is equipped with several
programs which automatically adjust the treatment frequency and the treatment time. Treatment frequencies,
particularly for sedation, myokinetics and vegetative stimulation, are available.
The stimulating effect can alternatively be administrated endogenously or exogenously. During endogenous
application, the interference is generated through superposition of the electrical circuits in the body. This
allows an intense effect. During exogenous application, the interference is created in the medical device.
The stimulating effect takes place directly underneath the electrodes on the body surface.
In addition to the three-circuit interference current, STEREODYNATOR 928 offers a complete selection of
single circuit currents for all known therapeutic procedures.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19

STEREODYNATOR
928
13
The STEREODYNATOR 928 is particularly suitable for:
• Pain therapy with three-dimensional interference current.
• Muscle toning and muscle detoning.
• Galvanization and iontophoresis.
• Pelvic floor stimulation.
• Treatment of urinary and fecal incontinence.
• Neurodiagnostic examination with galvano-palpations.
• Treatment of paralyses with complete or partial muscular degeneration.
• Treatment of atrophies due to inactivity or weakened muscles after longer periods of inactivity.
• Electrical stimulation therapy without electrolytic side effects and only slight muscle fatigue.
• Treatment of pain, muscle spasms, functional diseases of the locomotor system, such as sports injuries,
peripheral circulatory disturbances, influencing of the vegetative system with diadynamic currents,
ultrastimulation current, microstimulation current, TENS- and TENS Burst currents, high-voltage
currents and middle-frequency currents.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

14
STEREODYNATOR
928
1.2 Operating Concept
”One-Touch”-Philosophy
Immediately after pushing the key for the desired current type, the therapy or diagnosis can be started.
Ergonomic Control Panel
Function keys are colored black and modification keys are white. Keys for identical functions on different
models are located in the same position on all devices. They are easy to recognize – which is particularly
important for the visually handicapped - and also have a pressure point. The parameter settings can be
carried out with keys or the modification knob.
The
modification knob has an upper and lower limit stop by software. So the values can only be modified
in a defined range of values even by overturning the knob. The according limit stop can be equipped with a
signal tone with the device setting, see chapter 2.3.1 .
In case of key operating there is no limit stop; after the last setting possibility it will restart with the first
one. Here it is also possible to have a key click by the appropriate device setting, see chapter 2.3.1.
After the expiration of the therapy time, the current to the patient automatically is switched off and the
intensity
is set to ”0.0”.
Display
All devices are equipped with a high-resolution graphic display. The selected stimulation current type is
shown graphically. The parameters are also shown. They are modified using the white modification keys
located around the display or by the modification knob.
LED keys
Optical user support is furnished in the form of LED lights incorporated into the keys:
∗ flashing -
∗ constantly lit -
∗ not lit -
key was selected and remains active
key is active and operational
key is not active and not operational
Menu
In addition to the ”One-Touch” operation, a user-guided method for selection can also be chosen by way of
the menu. By selecting the desired effect (analgesia, hyperemia, muscle toning, muscle detoning) and the
site of action (head and neck, spinal column and trunk, upper extremities, lower extremities), the
appropriate current type is automatically selected and a recommendation for the electrode application is
provided. The menu also allows the use of special types of current.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19
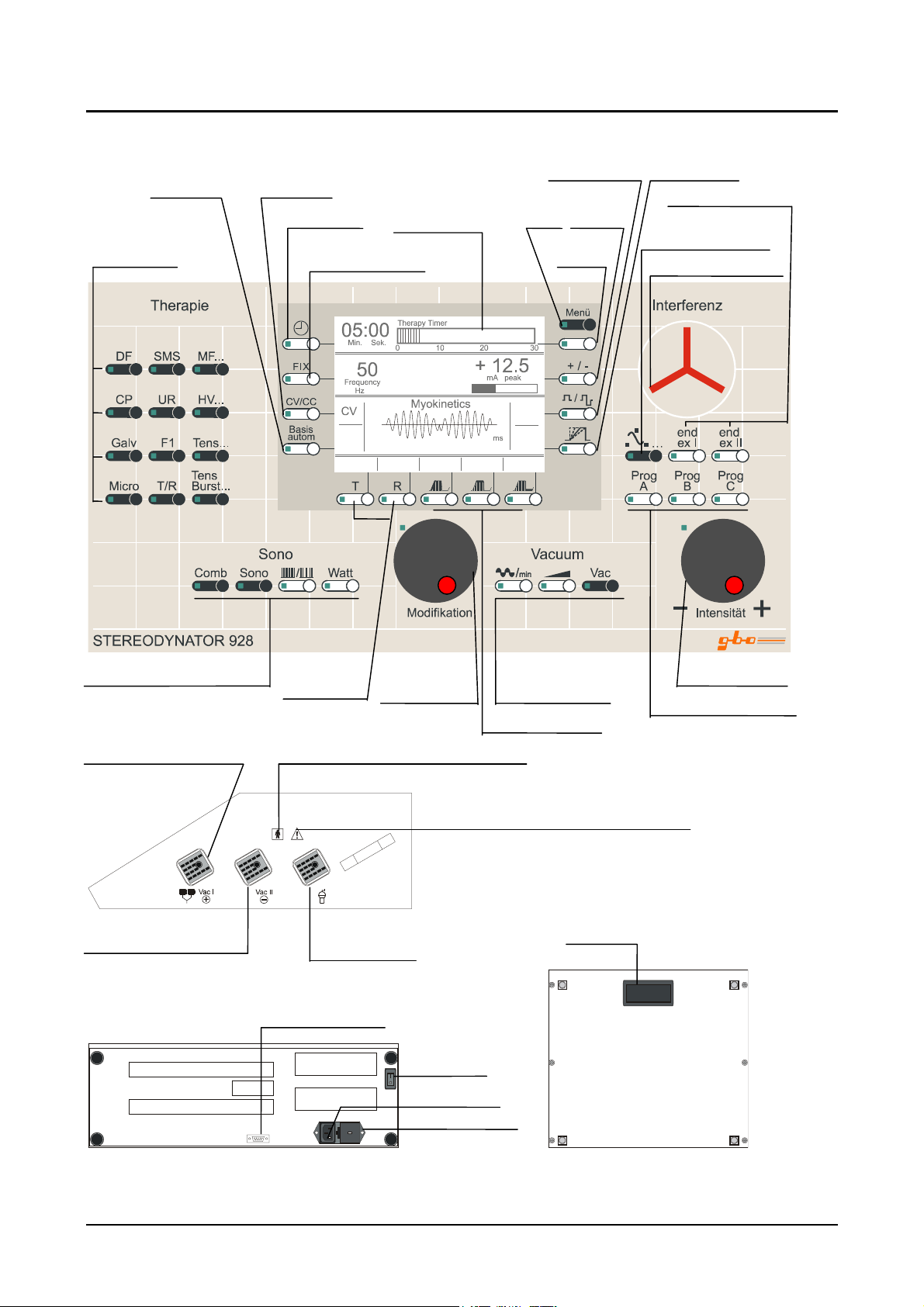
STEREODYNATOR
A
)
928
1.3 Short Instructions
Galv. base Operation mode
Therapy time Graphic display Menu Polarity
Types of therapy
stimulation currents
Frequency lock Soft key
15
mono-/biphase pulse rise
End./ex. change
Stereodynamic
interference currents
Stim. frequency
Ultrasound therapy unit* Pulse-/Pause Modification- Suction aid for- Intensity knob
Patient cable connection
and/or vacuum cable I
= socket (1)
Vacuum cable II
= socket (2)
*)
depending on unit configuration
Application part ungrounded, protection BF
Service interface
duration knob vacuum therapy*
Surge parameter
ttention! Observe the instructions for use !
Carrying
Connection for
ultrasound probe
= socket (3
Power inlet
Fuses and voltage
selector
*
Mains
switch
handle
Automatic programs
Figure 1: STEREODYNATOR 928
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

16
STEREODYNATOR
928
1. Switch on with the mains switch at the back of the device. The device carries out an automatic test of all
its functions. The faultless selftest ends with the acoustic signal.
2. Connect the accessories with the according socket on the right side of the device.
3. Optical user support is furnished in the form of LED lights incorporated into the keys:
∗ flashing -
∗ constantly lit -
∗ not lit -
key was selected and remains active
key is active and operational
key is not active and not operational
4. The three-ray star display serves as stimulation frequency display and electrode contact display. The
green luminous bars are lit in the three circuit mode and show the frequencies effective in the body. The
red LEDs indicate:
∗ Red LEDs lit - there is current flowing
∗ Red LED not lit - there is no current flowing
5. Furthermore, an acoustic user support is furnished
∗ Confirmation beep 1 x - admissible pressing of a
key
∗ Information sound 1 x - inadmissible pressing of a key
- disconnection of the patient plug during operation
∗ Alarm ca. 2 s - insufficient electrode contact, dropping electrodes during the
- therapy (
- in case of unintended current increase during therapy
CC)
∗ Triad-gong 1 x - at the beginning of the automatic check to control the gong
3 x - at the end of therapy
- the key of the electrode handpiece has not been pressed for
2 min
- in operating mode CV no current has flown for 2 min
6. Put the electrodes on to the patient (exception: in case of using the suction application aid the
key
and the Types of stimulation current key have to be pressed first).
Vacuum
7. Select the current type by pressing the corresponding current key or select it from the Menu.
8. The default setting of the current type is activated automatically.
9. Select additional modifications:
• By pressing the desired
• By turning the
Modification knob or repeatedly pressing of the Modification key until the desired
Modification key.
value has been set.
10. Increase the current slowly with the
Intensity regulator until the desired stimulation effect occurs.
11. At the end of the therapy the triad gong will sound three times. The current to the patient will be faded
out within 10 s.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 19
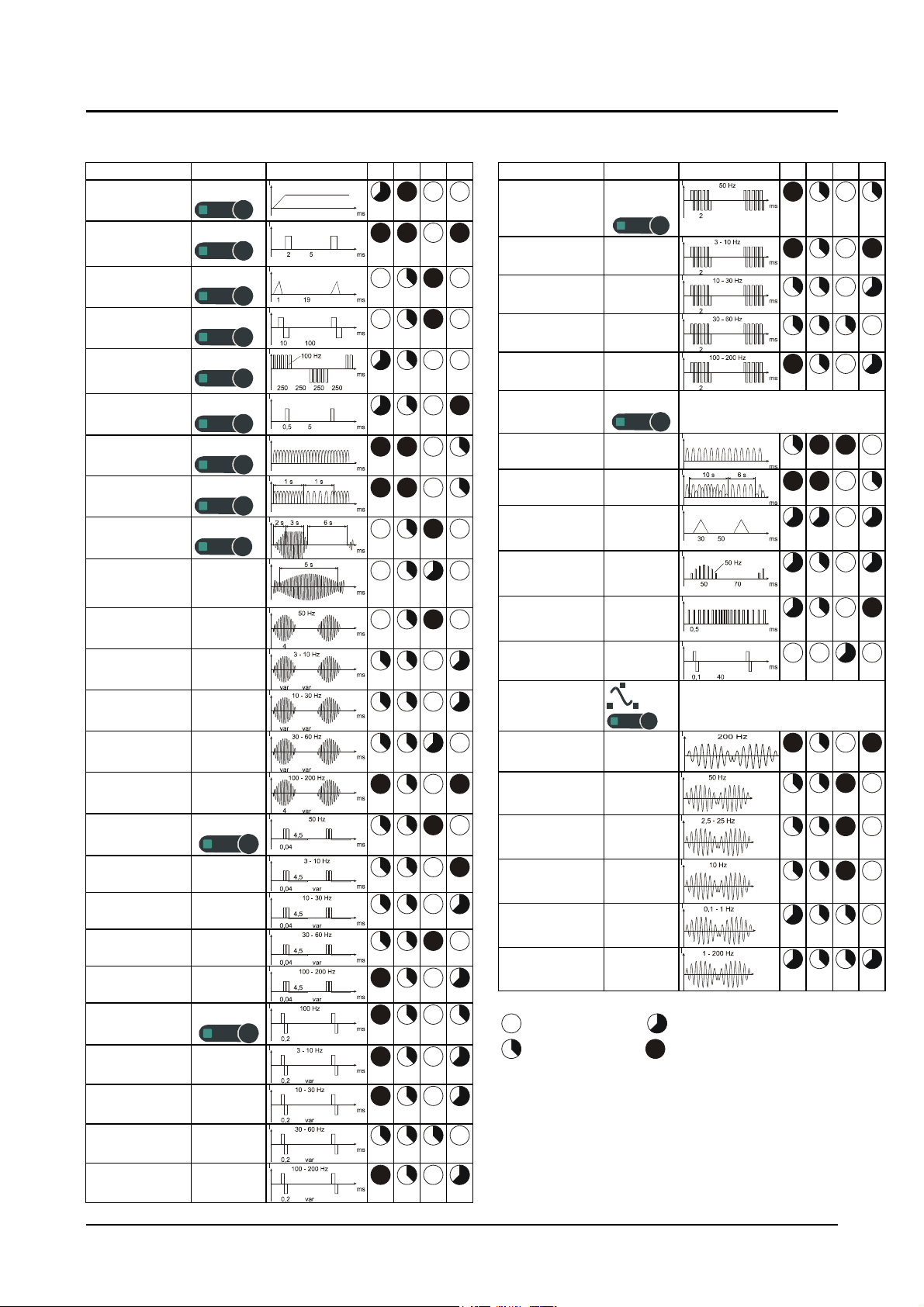
STEREODYNATOR
R
928
1.4 Modes of Action of the Therapeutic Current Types
Current
Galvanic current
Ultrastimulation
current
Faradic current
Strong muscle
stimulation
Micro-stimulus
current
Universal therapy
Diphasé fixe
Courtes périodes
MF I / surged
MF II / sinus surged
MF III / 50 Hz
Key Grafics I II III IV
Galv
UR
F1
SMS
Micro
T/
DF
CP
MF...
Current
Tens Burst I /
50 Hz
Tens Burst II /
3 - 10 Hz
Tens Burst III /
10 - 30 Hz
Tens Burst IV /
30 - 60 Hz
Tens Burst V /
100 - 200 Hz
Special currents
Monophasé fixe
MF
Longues périodes
LP
Impulse
galvanization
IG 30
Impulse
galvanization
IG 50 / surged
Frequency
modulation
FM / 7 - 14 Hz
Key Grafics I II III IV
Te ns
Burst...
Menu
17
MF IV / 3 - 10 Hz
MF V / 10 - 30 Hz
MF VI /
30 - 60 Hz
MF VII /
100 - 200 Hz
HV I / 50 Hz
HV II / 3 -10 Hz
HV III /
10 - 30 Hz
HV IV /
30 - 60 Hz
HV V /
100 - 200 Hz
Tens I / 100 Hz
Tens II /
3 - 10 Hz
Tens III /
10 - 30 Hz
Tens IV /
30 - 60 Hz
Tens V /
100 - 200 Hz
HV...
Ten s. ..
Incontinence
Stereodynamic
Interference
currents
Sedat
200 Hz
Myomot
50 Hz
Vegetat. Stim I
2.5 - 25 Hz
Vegetat. Stim II
10 Hz
Vegetat. Stim III
0.1 - 1 Hz
Universal
1 - 200 Hz
…
With depth effect
No effect Good effect
Slight effect Very good effect
I Analgesia III Muscle toning
II Hyperämia IV Muscle detoning
Table 1:Modes of action of the therapeutic current types
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

18
STEREODYNATOR
928
2 Start of Operation
2.1 Transport and Assembly
The current stimulation device is a portable unit. There is a carrying handle in the form of a recessed grip in
the base plate. To place the unit, each flat surface is appropriate. A wall distance of at least 20 cm has to be
provided. The device should not be placed in front of radiators.
The current stimulation device corresponds to the regulations DIN/VDE 0750, EN 60601. It is a device of
protection class I. Within the scope of the Medical Device Directive (MDD) the current stimulation device
belongs to class IIb (see also chapter 10 Warnings and Safety Precautions).
Attention
The unit is not designed to be operated in places with the inherent risk of explosions. If it is
used in dangerous areas of anesthesia departments, the possibility of an explosion cannot be
excluded.
If the patient and/or the patient cable is directly exposed to a radiator of a medical device for
high frequency heat therapy, the damage of the device or a danger to the patient cannot be
excluded. As a rule, a distance of 3 m is sufficient.
2.2 Connection and Switch-On
The current stimulation device has been adjusted for the connection to a supply voltage of 230 V. If needed,
the device can be switched over to the following supply voltages:
• 240 V
• 230 V
• 120 V
• 100 V.
Irrespective of the adjusted supply voltage, the device is appropriate for mains frequencies of 48 to 62 Hz.
Voltage Selection and Fuses:
1. Unplug the mains plug.
2. The device is protected by 2 fuses on the mains side that are located in a pluggable box at the back of the
device next to the power inlet (see Figure 1).
3. The adjusted supply can be seen through the small window of the box.
4. With a screw driver the box can be pulled out of the line filter unit by the small slot.
5. Remove the voltage selector out of the holder and set the usual supply voltage.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
STEREODYNATOR
g
g p
y
y
y
928
19
Attention
The mains socket has been sealed with a scotch tape. This is to remember to check
prior to switch-on, whether the adjusted voltage corresponds to the supply voltage of
the treatment room.
The scotch tape over the mains socket is easy to remove. Connect the current stimulation device with the
mains cable to a (grounded) safety power outlet.
The current stimulation device is switched on by the mains switch at the back of the device. By this
arrangement erroneous, unintended disconnection of the device during normal operations shall be avoided.
After switching on the device, an automatic selftest of all device functions will be performed (see chapter
1.3 Short Instructions).
2.3 Settings
2.3.1 Device Settings
Once the unit has been switched on and is ready, you can start immediately with the standard settings.
Device settin
Signal for adjustment knob
Signal for keys yes / no yes
Max. value of therapy time 20 min / 40 min 20 min
Ultrasound power emission W / W/cm
Automatic pump switch off yes / no Yes
Signal volume bargraph 0 - 15 7
Language German
Contrast of display 0 - 15 7
Inverse representation yes / no No
Display mode of action yes / no yes
Therapy time adjustment 1 min – max. value standard
Vacuum default intensity 0 % - 100 % 0 %
sSettin
es / no
English
Italian
Portuguese
Spanish
Czech
French
ossibilities Deliver
es
2
W/cm
German
2
Table 2: Device settings
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

20
If you would like to change them, please proceed as follows:
1) Press the black
2) You are in the Main menu.
3) Move the scroll bar with the
4) Confirm by pressing the white
5) You are in the Device settings menu.
6) Move the scroll bar with the
7) Confirm by pressing the white
8) Move the cursor with the
9) Confirm by pressing the white
10) Exit the Device settings menu by pressing the black
11) On the display the Main menu appears again.
Menu key.
Modification knob to Device settings.
Soft key.
Modification knob to the device setting to be changed.
Soft key.
Modification knob to the desired value.
Soft key.
Menu key.
STEREODYNATOR
!! Note
On Vacuum default intensity setting the pump is switched off, if no suction electrodes are connected.
If suction electrodes are connected the pump will run corresponding to the set value.
928
2.3.2 Basic Settings of the Current Types
Upon pressing the desired current type key, the default settings for this current type are set. Altered
parameters are canceled by pressing the current type key again, i.e. the default settings are available again.
Modifications will not be stored.
!! Note
If the default settings for the therapy time have been modified by therapy time adjustment, the new
settings are permanently stored and recalled each time after pressing the current type key.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
21
3 Description of Function
3.1 Operating Notes
Each current type can be modified specifically. Certain modifications can be set only when the intensity
control
optical user support.
3.1.1 Optical and Acoustical User Support
Optical user support is furnished in the form of LEDs incorporated into the keys:
LED Condition of the key
Flashing key was selected and remains active
Constantly lit key is active and operational
not lit key is not active and not operational
is ”0.0”. Other modifications can be set also during therapy. Please observe the acoustical and
Table 3: Optical user support
Furthermore, optical user support is furnished on the display:
• A modification which is just being changed is shown inversely.
• If in case of a current type Pulse duration T and/or Pause duration R are modifiable, only the letter T
and/or R will be shown under the current type diagram. The numerical values are shown next to the
Pulse duration key and/or Pause duration key, see Figure 12 and Figure 13.
• If in case of a current type Pulse duration T and/or Pause duration R are not modifiable, the numerical
values are shown under the current type diagram.
Star display:
Interferenz
Figure 2: Three-ray star display
The three-ray star display has multiple functions and serves as stimulation frequency display and electrode
contact display. In case of single-circuit mode, the star display is switched off.
The green luminous bars indicate the stimulation frequencies. In case of the three-circuit mode, all three bars
are lit. If stereodynamic interference current is applied, they show the beat frequencies effective in the body.
The vertical bar shows the interference between circuit 1 and circuit 2, the left bar between circuit 2 and
circuit 3, and the right bar between circuit 1 and circuit 3.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

22
The red LEDs in the center of the star are lit, when current is flowing. Without current flowing, all red LEDs
are turned off.
The following table explains the acoustic signals and their meaning:
Type of signal Cause
Confirmation ”beep”
Information sound
Alarm
Triad gong
1 ×
1 ×
approx. 2 s
1 ×
3 ×
• in case of an admissible key operation
• in case of an inadmissible key operation
• in case of disconnecting the patient plug during
operation
• in case of insufficient electrode contact and dropping
electrodes during therapy (CC)
• in case of unintended current increase during therapy
(CV)
• at the beginning of the automatic check to control the
gong
• at the end of therapy
• if in manual operation the key has not been pressed
for 2 min
• if in ”CV” there was no current flows for 2 min
STEREODYNATOR
928
Table 4: Acoustical user support
3.1.2 Intensity Regulator
The Intensity regulator serves for setting the current intensity. It is furnished in the form of a incremental
encoder. The current increases by turning right (in
direction). The numerical value is shown on the display.
The current value can be set in the following steps:
• Galvanic Current, Micro-Stimulus Current → 0.1 mA
• all the rest of therapy current types → 0.5 mA.
+ direction) and it is reduced by turning left (in -
!! Notes
• The Intensity regulator automatically reverts to ”0.0” after the expiration of the therapy time.
• When changing over from one current type to another, the
”0.0”. Control the current indication on the display.
3.1.3 Current and Polarity
On the display, both the peak value of the stimulation current in mA peak as well as the polarity + and/or –
are shown. The polarity sign always refers to the red plug of the accessories. The polarity change over is not
active in case of biphase currents. When selecting biphase currents the polarity sign disappears.
Intensity regulator has to be set to
+ 12.5
mA peak
Figure 3: Current indication on the display with the Polarity key
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
+ / -

STEREODYNATOR
928
Automatic pole changing:
By pressing the Polarity key polarity changes as follows:
23
1. Press → automatic pole changing, at first the polarity is positive (”
(”
-” flashes) after half of the therapy time.
2. Press → polarity changes from positive to negative.
3. Press → polarity is positive again.
When the polarity changes, the current will be faded out and restored again within 10 s. In case of
combination of the current types
DF and CP, polarity will be changed after half of the therapy time.
+” flashes) and reverts to negative
!! Notes
• The automatic pole changing can only be set before starting the therapy.
• During therapy however, the polarity can be changed by pressing the
current will also be faded out and restored again within 10 s.
Monophase current:
/
Figure 4: Monophase current
The current flows only in one direction.
Polarity key. By this, the
Biphase current:
/
Figure 5: Biphase current
Each pulse consists of two parts with different polarities.
Current display in CC-Mode:
CV/CC
CC
Figure 6: Operating mode key as displayed on the screen
The current set with the
display shows the peak value that is also constantly shown during puls pauses.
A dynamic current limiter reduces the released current and/or the voltage to such a minimal deviation from
the set value, that this will not lead to any comfort losses for the patient even in irregular application modes.
Therefore, the operating mode CC can be used without any comfort limitations. There are no voltage
sensations even in case of insufficient electrode contact or dropping electrodes.
Intensity regulator remains constant even when the patient resistance changes. The
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

24
Display in CV-Mode:
CV/CC
CV
Figure 7: Operating mode key as displayed on the screen
STEREODYNATOR
928
Constant voltage is set with the
patient resistance. The value of the Voltage is shown in V peak.
Intensity regulator. The value of the current to the patient depends on the
!! Note In CV-Mode the intensity will be shown in V peak not in mA peak.
3.1.4 Surge Parameters
Some current types can be surged individually by a surge cycle. The three surge parameters
rise time
duration time
pause time
determine a surge cycle. Each surge parameter can be changed within 0 to 60 s in steps of 0.5 s. The descent
time in each surge cycle is always set to 1 s constantly.
s s
2
3
s
6
Figure 8: Surge parameter key with the according displays
3.1.5 Galvanic Base
Basis
autom
Figure 9:
The current types DF, CP, MF and LP can be underlayed by a d.c. current whose amplitude corresponds to
20 % and/or 50 % of the peak current. By repeatedly pressing the key it can be changed between 0 %, 20 %
and 50 % of the d.c. current underlaying. This is shown on the display.
0 %
Galvanic Base key with its display
3.1.6 Frequency Lock
FIX
310
5
Frequency
Figure 10: FIX key with the display of the fixed therapy frequency
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
r
In case of frequency modulated current types, the frequency can be locked and released with this key during
the treatment. The first key pressure locks, another actuation releases the frequency.
928
25
!! Note
If you want to modify the frequency, please press the white Soft key [
can be modified step by step with the
the
modification knob. Herewith also changes the pulse and/or pause duration. The according times
change in the current type display and will not be shown by the
modification knob. The frequency can be modified by turning
3.1.7 Pulse Parameter
Pulse rise:
Figure 11: Pulse rise key as displayed on the screen
[frequency]]]]. The frequency now
[[
T and/or R display.
The stimulation impulses can be modified in 5 steps to a rectangular, trapecoidal or triangular shape.
Setting possibilities for the pulse duration and pause duration:
4.0
ms
T
Figure 12: Pulse duration key as displayed
on the display
Pulse duration T and pause duration R can be modified before and during the treatment:
• If in case of a current type Pulse duration T and Pause duration R are modifiable, only
shown under the current type diagram. The numerical values are shown above the
and/or the Pause duration key.
• If in case of a current type Pulse duration T and Pause duration R are not modifiable, the letters
R will be shown with the according numerical values under the current type diagram.
• The pulse and/or pause duration can be modified via the frequency by pressing the
according times change in the diagram and are not shown above the
• If for pulse duration T or pause duration R there have been set higher values than 9000 ms, the unit will
change from
ms to s.
16
ms
R
Figure 13: Pause duration key as displayed on the
display
T and R will be
Pulse duration key
FIX key. The
T and/or R keys.
T and
3.1.8 Therapy Time
Therapy Time
05:00
Min Sec
Figure 14: Therapy time key as displayed on the display
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

26
You can set the therapy time as follows:
1. Depending on the current type an appropriate therapy time will be suggested.
2. If you want to change the therapy time, press the
1 minute. The maximum therapy time to select is 40 min (see chapter 2.3.1 Device Settings).
3. Set the desired therapy time:
• By repeatedly pressing the
• By using the
!! Notes
• The selected or given therapy time passes only if the Intensity regulator is turned out of its ”0.0”
position.
• The therapy time can be modified during the treatment.
• At the end of the therapy time the stimulation current to the patient will be faded out automatically
within 10 s:
∗ The Intensity automatically reverts to ”0.0” after cutting off the stimulation current to the
∗ The selected current type and possible modifications will be kept.
∗ The therapy time setting remains on 0 min.
∗ The triad gong sounds 3 times (see also Table 4: Acoustical user support).
∗ The therapy can be continued by setting a new therapy time and turning on the intensity.
∗ Pressing again the same current type key leads to the basic setting of this current type.
Modification knob.
patient.
Therapy time key or
Therapy time key. The time can be modified in steps of
STEREODYNATOR
928
3.1.9 Stimulation shifting
end
ex I
Figure 15: stimulation shifting keys
In the basic setting, the stereodynamic interference currents are endogenous, that means they have an intense
effect.
The stimulation effect can be shifted towards electrode I (or II) by pressing the
). By that, the stereodynamic interference currents are exogenous, that means that the stimulating effect
key
takes place on the body surface. As the following figure shows, the actual status of stimulation shifting is
indicated below the current type.
end
ex II
end ex I key (or end ex II
!! Notice The stimulation shifting can not be switched over during therapy.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
27
Figure 16: Stimulation shifting switched off
3.1.10 Menu
Menü
Menu key - The black Menu key serves for calling the menus.
Soft key – Within the menu, the white Soft key serves as a confirmation key.
Figure 17:
A soft key is a key with a context-sensitive meaning. The according meaning of the key is shown on the
display right next to the key.
The main menu puts the following menus at your disposal:
• Special current types, see chapter 4.5
• Programs, see chapter 3.1.11
• Application with Electro Therapy, see chapter 4.2
• Application with ultrasound, see chapter 4.3
• Device settings, see chapter 2.3.1
Menu key and Soft key
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

28
STEREODYNATOR
928
3.1.11 Menu Programs
Besides the current types, which are already stored in the device, there is a possibility to create your own
programs of current types and to store and select them.
Program and store a current type:
1. Select the desired current type.
2. Select all desired modifications.
3. Press the
4. Move the cursor by means of the
5. Select by pressing the
6. The cursor points to store program.
7. Select by pressing the
8. Move the cursor by means of the modification knob to the wanted storage location Program NN.
9. Select by pressing the
10. The device exits the menu and returns to the current type.
Select a stored current type program:
Menu-key.
modification knob to Programs.
Soft key [select].
Soft key [store].
Soft key [store].
1. Press the Menu-key.
2. Move the cursor by means of the
3. Select by pressing the
Soft key [select].
modification knob to Programs.
4. The cursor points to store program.
5. Move the cursor by means of the
6. Select by pressing the
Soft key [select].
modification knob to the wanted storage location Program NN.
7. The device exits the menu and returns to the current type.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
29
3.2 Integrated Suction Application Aid
The suction application aid is optionally available. The operating elements for the suction application aid are
integrated on all membrane keyboards.
!! Note The suction application aid cannot be used during diagnostic programs.
Vac
Figure 18: Vacuum key Figure 19: Vacuum-Intensity key Figure 20: Suction massage key
1. Press the Vacuum key, the pump will be switched on. The basic pressure is immediately available.
2. Press the
repeated pressure of the key, so that the suction electrodes can be comfortably applied to the patient.
The vacuum intensity is shown on the display in the form of a cylinder diagram.
Vacuum-Intensity key and set the vacuum intensity with the Modification knob or by
!! Notes
• The operating mode CC can be used without any comfort limitations; there are no voltage
sensations even in case of dropping electrodes.
• In case of the galvanic mode the maximum admissible output current will be limited to 20 mA
when suction electrodes are used to prevent cauterization.
• In case of the galvanic mode the current density must not exceed 0.2 mA/cm
5).
2
(see also Table
3. Press the
• By repeatedly pressing the
• By turning the
Vacuum massage key and set the suction massage frequency:
Vacuum massage key or
Modification knob.
!! Note
The vacuum frequency can be modified in steps of 5 pulses/minute within the range of 0 to 60
pulses/minute.
4. If upon switching on the vacuum application no current is applied for 2 min or if the therapy time has
expired since 2 min, the pump automatically switches off, provided that this has been activated in the
Device settings menu, see chapter 2.3.1.
For the different suction electrodes, the following current values must not be exceeded when galvanic
current is applied:
Suction electrode Size Current value
Electrode plate small 6 cm
Electrode plate standard 12 cm
Electrode plate large 28 cm
Table 5: Current values of the suction electrodes in case of galvanic mode
2
2
2
1.2 mA
2.4 mA
6 mA
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

30
STEREODYNATOR
928
3.3 Ultrasound Therapy Module
Depending on the device configuration, the ultrasound therapy module is either optional or standard. The
operating elements have already been integrated on the membrane keyboard.
Comb
Sono
Figure 21: Comb key (1/3 MHz) Figure 22: Sono key (1/3 MHz)
Watt
Figure 23: Continous/Pulsed key Figure 24: Ultrasound power key
!! Notes
• The ultrasound frequency can be changed to 1 or 3 MHz.
• The frequency for pulsed mode 100 Hz.
• The pulse parameters are 1:5, 1:10 or 1:20.
• The coupling status of the probe is shown by an LED on the probe housing. The LED will be off in
case of insufficient coupling. The LED will be flashing in case of good contact.
• As a standard setting the ultrasound power is shown in W/cm
(see chapter 2.3.1) you can select between the formats W and W/cm
• If you want to exit the ultrasound operation prematurely, i.e. before expiration of the therapy time,
press the
Sono- and/or Comb key again.
2
on the display. In the device settings
2
.
Attention
• Do not forget the contact gel!
• Be careful with the ultrasound probe, because rough external influences such as a
mechanical shock or impact can alter its characteristics. We recommend to carry out a
visual examination at least once a year to check for fissures that allow liquids to enter, as
well as regarding the integrity of the cables and connectors.
Power for
5 cm2 ultrasound probe 2,5 cm2 ultrasound probe
1 MHz Continuous wave
1 MHz impulse wave
3 MHz Continuous wave
3 MHz impulse wave
0.5 to 15 W 0.1 to 3 W/cm
0.5 to 15 W 0.1 to 3 W/cm
0.1 to 7,5 W 0.1 to 1.5 W/cm
0.1 to 7,5 W 0.1 to 1.5 W/cm
2
2
0.1 to 7,5 W 0.1 to 3 W/cm
0.1 to 7,5 W 0.1 to 3 W/cm
2
0.1 to 2.5 W 0.1 to 1.5 W/cm
2
0.1 to 2.5 W 0.1 to 1.5 W/cm
Table 6: Setting possibilities of the ultrasound power, increments are shown in bold.
For combined operation we recommend the following procedure:
1. Select the current type.
2. Set the desired modification.
3. Select the operation mode „Combined Operation“ by pressing the
Comb key.
2
2
2
2
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
31
4. By pressing the Comb key once you reach the ultrasound frequency 1 MHz. By pressing the Comb key
twice you reach the ultrasound frequency 3 MHz.
5. Set the desired modification.
6. In case of this operation mode the blue plug of the patient cable is currentless. In the basic setting the
red plug has positive polarity, whereas the backplate electrode – the metallic ultrasound probe surface –
is negative.
7. Connect the red plug of the patient cable with the neutral electrode.
8. Apply the neutral electrode.
9. By pressing the
Continous/Pulsed key select the pulse wave 1:5, 1:10, 1:20 or continuous wave. The
current impulse type is shown on the display.
10. Press the
• By repeatedly pressing the
• By turning the
Ultrasound power key and set the ultrasound power:
Ultrasound power key or
Modification knob.
11. Put the ultrasound probe on the patient’s treatment area (important: contact gel !!) and move it slowly.
12. Set the current intensity by turning the
Intensity regulator. If the patient experiences a pain, reduce the
stimulation intensity.
!! Notes
• By combined operation the therapy time will pass if the Intensity regulator is turned and / or the
ultrasound probe has been coupled to the patient.
• Combined operation is only possible in CV-Mode, since the ultrasound probe can be moved and/or
removed during the therapy.
• Due to the acidification of the contact gel, the ultrasound therapy cannot be operated with the
Galvanic current type.
• In combined operation it is not possible to apply the electrode handpiece.
• The current density should not exceed 2 mA/cm
2
.
For pure ultrasound operation we recommend the following procedure:
1. Select the operation mode by pressing the Sono key.
2. By pressing the Sono key once you reach the ultrasound frequency 1 MHz. By pressing the Sono key
twice you reach the ultrasound frequency 3 MHz.
3. The therapy time will be set to 10 minutes.
4. If needed, modify the therapy time.
5. By pressing the
Continous/Pulsed key select the pulse wave 1:5, 1:10, 1:20 or continuous wave. The
current impulse type is shown on the display.
6. Press the
• By repeatedly pressing the
• By turning the
Ultrasound power key and set the ultrasound power:
Ultrasound power key or
Modification knob.
7. Put the ultrasound probe on the patient’s treatment area (important: contact gel !!) and move it slowly;
now the therapy time passes.
!! Note
If the ultrasound probe has not been coupled to the patient, no therapy time will pass. When the probe
has been coupled again, the therapy time will continue to pass. Hence, the ultrasound probe can be
removed in between.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

32
STEREODYNATOR
928
4 Therapy
4.1 Therapy with interference currents
Upon switching on the electrical stimulus device and its automatic check, the interference current Sedat will
always appear with its basic setting, if multipolar electrodes are connected. In addition, the Menu for
interference currents is available.
If there are no or single circuit electrodes connected, the single circuit therapy current DF appears and the
Menu for single circuit therapy currents is available.
!! Notice
• Interference currents can only be applied with constant voltage (mode CV).
• The frequency ranges are passed in a minute’s rhythm.
• During therapy, you can switch over between interference currents, but not between the automatic
programs.
• For visually handicapped, interference current Sedat can be dubbed with a signal
Generally, there is the following procedure for therapy with interference current:
1. Connection through the mains switch at the back of the device.
2. The device executes an automatic check of all functions.
3. The faultless automatic check ends with the acoustic signal.
4. Connect the accessories for interferential currents with the according socket on the right side of the
device.
5. Interference current Sedat is available with its basic settings.
6. Apply the electrodes on the patient.
7. Select the required interference current by repeatedly pressing the
required automatic program by pressing the respective
Programs
8. Set the required modification.
9. Turn the
muscular contracture.
• The luminous bars of the stimulation frequency display move in the rhythm of the stimulation
• Three red lights must be lit in the center of the stimulation frequency. This is a control display for
10. At the end of the therapy the triad gong will sound three times and intensity automatically reverts to
„0.0“.
.
Intensity regulator slowly, until the current is clearly perceptible, but do not generate any
frequencies.
the correct electrode contact: one red light has been assigned for each current circuit which
extinguishes in case of faulty electrode contact in its current circuit.
Program key or selecting from Menu →→→→
Interference current key or the
4.1.1 Sedat
The interference current Sedat (200 Hz) has an analgesic effect and at the same time a sedative effect on the
Nervus sympathicus; by this, it indirectly stimulates the blood flow in case of hypertonia of the vascular
walls. Almost all therapies of painful functional disturbances can be initiated with this frequency. The first
interference current that appears is Sedat.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
33
4.1.2 Myomot
Interference current Myomot (50 Hz) stimulates the skeletal muscles. The dynamics of the area being
stimulated and of the intensity generate a special physiological kind of muscle contraction. As opposed to
the classical method, the individual muscle fibers are activated alternately. By this, a fatigue effect through
continuous contractions is avoided. Proceed as indicated in chapter 4.1. You must press the
current key
twice !
Interference
4.1.3 Vegetative Stimulation I
Interference current Vegetat. Stim. I (2.5 Hz bis 25 Hz) leads to normal tonus of the vegetative nerve system,
accompanied by vibrations. This frequency range is also indicated in case of peripheral venous circulatory
disturbances and blockings. The rhythmical muscle contractions press out the contents of veins. In addition,
with low frequencies there is a stimulation of the sympathic nervous system (Lullies). Proceed as indicated
in chapter Kapitel 4.1. You must press the
Interference current key three times !
4.1.4 Vegetative Stimulation II
Interference current Vegetat. Stim. II (10 Hz) leads to a normal tonus of the vegetative nerve system,
accompanied by a „shaking“. Ankyloses and muscular contractions can be mobilized. Proceed as indicated
in chapter 4.1. You must press the
Interference current key four times !
4.1.5 Vegetative Stimulation III
Interference current Vegetat. Stim. III (0.1 bis 1 Hz) leads to a normal tonus of the vegetative nerve system
and it is often combined with Sedat. Individual muscle contractions can be generated. Proceed as indicated
in chapter 4.1. You must press the
Interference current key five times !
4.1.6 Universal
Interference current Universal contains the therapy frequencies from 1 to 200 Hz. Proceed as indicated in
chapter 4.1. You must press the
Interference current key six times !
4.1.7 Sedation Modulation
Interference current Sedation Modulation contains the therapy frequencies from 100 to 200 Hz. Proceed as
indicated in chapter 4.1. You must press the
Interference current key seven times !
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

34
STEREODYNATOR
928
4.1.8 Automated programs
The electrical stimulus device is equipped with five automated programs to facilitate the adjustment of
therapy frequencies and times. If you press the respective
the
Menu the menu entry Programs (programs D and E), the programs indicated in the table below will
automatically run. If you wish to select the programs D and E, proceed as indicated in chapter Menu special
types of current.
Program key (programs A,B and C) or select in
ProgAProg
B
Figure 25: Program keys
Automated
Program
A
B
C
D
E
200 Hz (Sedat) 50 Hz
200 Hz (Sedat) 2.5 - 25 Hz
200 Hz (Sedat) 10 Hz
200 Hz (Sedat) 0.1 - 1 Hz
200 Hz (Sedat) 1 Hz
Prog
C
3 min 10 min 2 min
Therapy time Effects
200 Hz (Sedat) analgesia,
(Myomot)
200 Hz (Sedat) analgesia,
(Vegetat. Stim. I)
200 Hz (Sedat) analgesia, hyperemia,
(Vegetat. Stim. II)
200 Hz (Sedat) analgesia,
(Vegetat. Stim. III)
200 Hz (Sedat) analgesia,
(Vegetat. Stim. IV)
hyperemia,
muscle stimulation
venous relaxation,
hyperemia
mobilization of ankyloses and
muscular contractions
hyperemia,
vegetative stimulation
hyperemia,
vegetative stimulation
Table 7: Automated programs
Proceed as indicated in chapter 4.1.
!! Notices
• The therapy time of an automated program always takes 15 minutes and cannot be modified.
• During therapy it is not possible to switch over between the automated programs.
• The three types of interference currents are shown on the current type window of the display. The
actual type of current is clearly displayed:
Sedat - Vegetat.Stim. III - Sedat.
• In case of the automated programs, frequency cannot be stopped.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
35
4.2 Menu Application With Electrotherapy
This menu driven additional program facilitates stimulation therapy by selecting area of application and
mode of action.
1) Press the
2) Move the scroll bar/cursor with the
3) Confirm by pressing the white
4) Move the scroll bar/cursor with the
Menu key.
Modification knob to Application with electrotherapy .
Soft key.
Modification knob to the desired application area:
• Head & Neck
• Vertebral column & Trunk
• Upper extremities
• Lower extremities
5) Confirm by pressing the white Soft key.
6) A list of the modes of action appears on the display:
• Analgesia
• Hyperemia
• Muscle toning
• Muscle detoning
7) Move the scroll bar/cursor with the Modification knob to the desired mode of action.
8) Confirm by pressing the white
Soft key.
9) The notes of application referring to the application area and the mode of action are shown on the
display.
10) Apply the electrodes in accordance to the suggestion given, as long as there are not any contra-
indications.
11) Confirm by pressing the white
Soft key.
12) If necessary, modify the therapy time.
13) Turn on the
Intensity regulator and therapy starts.
!! Notes
• Only the therapy time can be modified!
• If there are suction electrodes connected, the vacuum pump will be automatically switched on, that
means that it is not necessary to press the
Attention
The current type DF for Hyperemia has a d.c. portion. Therefore a certain current
density of 0.31 mA/cm
be exceeded. Depending on the electrode size there are the following current values:
Rubber electrode small 3 x 4 cm
Rubber electrode standard 6 x 8 cm
Rubber electrode large 8 x 12 cm
Suction electrode small (6 cm
Suction electrode standard (12 cm
Suction electrode large (28 cm
2
(corresponds to 64 % d.c. portion of the peak value) should not
Vacuum key to switch on.
2
2
) 1.9 mA
2
)8mA
3.7 mA
2
15 mA
2
29 mA
2
) 3.6 mA
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

36
STEREODYNATOR
928
4.3 Menu ‘Applications with ultrasound’
Tthe additional program Menu includes the Application with ultrasound for the single circuit therapy. The
procedure is described correspondingly in the previous chapter. The only difference is by point 6 there
appears a list of indications not a list of modes of action.
4.4 ”One - Touch” - Operation
The following therapy current types are assigned to keys on the membrane keyboard:
DF
CP
SMS
MF I to VII
UR
HV I to V
Galv
F1
TENS I to V
TENS Burst I to V
Micro
T/R
Diadynamic current (diphasé fixe)
Diadynamic current (modulé en courtes périodes)
Strong muscle stimulation according to Eichhorn
Middle frequency I to VII
Ultrastimulation current
High voltage I to V
Galvanic current
Faradic current
Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation I to V
Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation in impulse groups
I to V
Micro-stimulus current
Universal - Therapy
Chapter 4.1 is also valid correspondingly for the therapy with single circuit currents. The procedure for the
single circuit therapy is as follows, as far as it has not been described otherwise:
1) Put the electrodes on to the patient (see chapter 7.1 Electrode ).
2) Connect the accessories with the according socket on the right side of the device.
3) Select the current therapy type by pressing the according Current type key or by selecting the Special
current types menu or by selecting the Application menu.
4) Set the required modifications.
5) Turn on the
otherwise).
6) The intensity of current is shown on the display.
7) At the end of therapy time the triad gong will sound three times.
Intensity regulator up to the sensitive tolerance limit (as far as it has not been described
!! Notes
• Before switching over from one current type to another you have to set the Intensity regulator to
„0.0“.
• At the beginning, the polarity of mono-polar current types is always positive.
• For the visually handicapped the multiple allocation keys can be dubbed with a signal for the first
current type (
• In the case of multiple allocation of the current type keys, the LED flashes during the selection of
the according currents. This shows that the key remains active.
MF key, HV key, Tens key and Tens-Burst key) (see chapter 2.3.1).
4.4.1 Diadynamic Currents
The current type DF serves for the treatment of sympathicotonic states, e.g. spastic circulatory
disturbances. It produces a local analgesia in the area to be treated. With it e.g. the symptoms hardening →
pain → hardening can be eliminated for a while.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
The current type CP is suited very well for the treatment of functional disturbances of the locomotion
system, circulatory disturbances, neuralgia and radiculopathies. It is mostly applied after the
but it is also possible the other way round.
Therapy with the combination of the current types DF and CP:
1. Press the DF key.
2. Set the desired modifications for DF.
3. On the display there appears [combination with CP] next to the
4. Select the combination mode by pressing the
5. Set the desired modifications for CP.
6. Turn the
7. On the display the selected current type and the total therapy time are shown.
Intensity regulator to the sensitive tolerance limit.
928
DF program,
Soft key.
Soft key.
37
!! Notes
• When changing from one current type to another, the first current will be faded out within 10 s and
then the second one will rise within 40 s to 80 % and within further 20 s to 100 % of ist intensity.
• A maximum of two current types can be combined in sequence.
4.4.2 Strong Muscle Stimulation (SMS) According to Eichhorn
In case of long-lasting, chronic muscle detriments the muscular apparatus can be built up again with SMS.
Visible and palpable continuous muscular contractions will be caused, whereas the patients tolerate higher
intensities of current due to biphase stimulation impulses.
The current type SMS consists of a biphase rectangular pulse with a pulse duration of 10 ms and a pause
duration of 100 ms.
4.4.3 Middle Frequency Currents
The middle frequency currents are applied in case of diseases and injury sequels of the locomotion and
supporting system, especially also in the wide rheumatic area.
There are seven middle frequency currents available. By repeatedly pressing the
from MF 1 to MF VII.
Surged middle frequency MF I:
The surged middle frequency current MF I has a rise time of 2.0 s, a duration time of 3.0 s and a pause time
of 6.0 s in the basic setting.
MF key you can switch
Sinus surged middle frequency MF II:
The current type MF II is a sinus surged middle frequency current.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

38
STEREODYNATOR
928
Middle frequency with fix therapy frequencies MF III:
As a basic setting of the current type MF III a middle frequency current of 50 Hz is offered. In this, the
current has a rise time of 2.0 s, a duration time of 3.0 s and a pause time of 6.0 s for the surge.
!! Notes
• The pause duration R can be modified with the Pause duration key and/or the modification
knob
. Hence an adjustable frequency range of 0.1 - 200 Hz is possible.
• The frequency adjusted with the pause duration is shown on the display.
• By turning the
Frequency modulated middle frequencies MF IV - MF VII:
In case of the frequency modulated middle frequency currents, the therapy always starts with the lower
frequencies, whereas the frequency ranges will be passed twice within 15 s. In case of MF IV to MF VI
pulse and pause duration vary. In case of the middle frequency current MF VII only the pause duration R
varies. Pulse duration T will remain constant.
Intensity regulator the adjusted fix frequency will be taken over.
1. Press the
2. The frequency range will be shown on the display.
3. Set the desired modifications.
4. The therapy is started by turning the
5. The intensity of the current will be shown on the display.
6. The frequency traverse can be stopped by pressing the
7. The fixed frequency will be shown on the display.
8. The therapy time continues to pass.
9. Press the white
10. The frequency can be readjusted by turning the
11. Press the
12. The frequency traverse will be released again.
13. The triad gong will sound three times after the expiration of the therapy.
MF key in accordance to the desired middle frequency.
Intensity regulator.
FIX key.
Soft key [frequency].
Modification knob.
FIX key again.
4.4.4 Ultrastimulation Current
The ultrastimulation current UR is applied in case of pain and muscle spasms, peripheral circulatory
disturbances and for producing isometric muscle contractions.
!! Notes
• In case of patients with high current sensitivity apply the biphase mode.
• Do not cause any continuous muscular contractions!
4.4.5 High-Voltage Currents
The high-voltage therapy includes diseases of the muscular, ligament and skeleton systems, peripheral
nerves, circulatory disturbances and the detection of ”trigger-points”.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
As the stimulation impulses are biphase, there do not exist any electrolytic side effects under the
stimulation electrodes. Negative and positive impulses have the same energy; therefore, a treatment in the
area of metallic implants is possible.
There are five high-voltage currents available. You can change from HV I to HV V by repeatedly pressing
the
HV key.
928
39
High voltage with fix therapy frequencies HV I:
In the basic setting, the high-voltage current type HV I has a rise time of 2.0 s, a duration period of 3.0 s and
a pause time of 6.0 s with a frequency of 50 Hz.
!! Notes
• The pause time R can be modified with the Pause duration key and/or the Modification knob.
Hence an adjustable frequency range of 0.1 - 200 Hz is possible.
• The fix frequency adjusted with the pause duration will be shown on the display.
• The adjusted frequency will be taken over by turning the
Intensity regulator.
Frequency modulated high-voltage current HV II - HV V:
In case of the frequency modulated high-voltage currents, the therapy always starts with the low frequencies,
whereas the frequency ranges will be passed twice within 15 s.
1. Press the
2. The frequency range will be shown on the display.
3. Set the desired modifications.
4. The therapy is started by turning the
5. The intensity of the current will be shown on the display.
6. The frequency traverse can be stopped by pressing the
7. The fixed frequency will be shown on the display.
8. The therapy time continues to pass.
9. Press the white
10. The frequency can be readjusted by turning the
11. Press the
12. The frequency traverse will be released again.
13. The triad gong will sound three times after the therapy time expires.
HV key in accordance with the desired high-voltage current types.
Intensity regulator up to the sensitive tolerance limit.
FIX key.
Soft key [frequency].
Modification knob.
FIX key again.
4.4.6 Galvanic Current and Iontophoresis
The galvanic current is used to stimulate the circulation in the area to be treated. It has alleviating
characteristics and can be recommended as a preparing measure for electrogymnastics (see chapter 4.4.7).
Furthermore, with iontophoresis it serves for percutaneous penetration of drugs. Here the procedure is the
same as in case of galvanization. The quantity of the penetrated drug depends on the purity of its solution,
the size of the electrodes, the intensity of current, the polarity and the penetration time. The knowledge of
the loading of the drug is especially important for a successful treatment. Acids are always transported to the
anode, bases to the cathode.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

40
STEREODYNATOR
!! Notes
• Turn the Intensity regulator only until the patient notices a slightly increasing current.
• Apply the intermediate layers dripping wet.
• In case of anode-effective drugs the layer of the anode will be saturated with the solution of the
drug, and in case of cathode-effective drugs the same is made with the layer of the cathode.
• The electrode layers have to be washed out thoroughly after the expiration of ionthophoresis.
There should not remain any residuals (see chapter 9.2.2).
Attention
• In case of iontophoresis do not exceed the intensity of current of 0.1 mA/cm
(active) electrode surface.
• In case of galvanization do not exceed the intensity of current of 0.2 mA/cm
(active) electrode surface.
• The patient must not feel a burning .
928
2
2
4.4.7 Faradic Current
Neofardic currents are applied for electrogymnastics of the faradising or restimulating muscles. This applies
especially for atrophies due to inactivity after longer periods of inactivity and for post operation
electrogymnastics to avoid thromboses.
!! Note Turn the Intensity regulator until the stimulation effect becomes obvious.
4.4.8 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
The TENS current types are applied in case of chronic and also acute pain syndromes such as the post
operative pain, birth pain and acute post traumatic and rheumatic pain. This includes neurological, internal,
surgical, traumatological, orthopedic, sports medicine and gynecological areas.
There are five current types available. You can change from TENS I to TENS V by repeatedly pressing the
Tens key.
TENS with fixed therapy frequency TENS I:
The current type TENS I has a frequency of 100 Hz and a pause duration R of 10 ms in its basic setting.
!! Notes
• Pause duration R can be modified with the Pause duration key and/or the Modification knob.
Hence an adjustable frequency range of 0.1 - 1400 Hz is possible.
• The fixed frequency adjusted with pause duration will be shown on the display.
• The fixed frequency will be taken over by turning the
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
Intensity regulator.

STEREODYNATOR
928
41
Frequency modulated TENS II - TENS V:
In case of the current types TENS II - TENS V the pause duration R will alter within certain areas and the
pulse duration will remain constant at 0.2 ms. The therapy always starts with the low frequencies, whereas
the frequency ranges will be passed twice within 15 s.
1. Press the
Tens key in accordance to the desired current type.
2. The frequency range will be shown on the display.
3. Set the desired modifications.
4. The therapy is started by turning the
Intensity regulator.
5. The intensity of the current will be shown on the display.
6. The frequency traverse can be stopped by pressing the
FIX key.
7. The fixed frequency will be shown on the display.
8. The therapy time continues to pass.
9. Press the white
10. The frequency can be readjusted by turning the
11. Press the
Soft key [frequency].
Modification knob.
FIX key again.
12. The frequency traverse will be released again.
13. The triad gong will sound three times after the expiration of the therapy time.
4.4.9 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation With Impulse Groups
The application area of TENS Burst currents is very similar to that of TENS currents, but with a less
analgesic but more detoning effect.
There are five current types available. You can go from TENS Burst I to TENS Burst V by repeatedly
pressing the
Tens-Burst key.
TENS Burst with fix therapy frequencies TENS Burst I:
The current type TENS Burst I has a frequency of 50 Hz and a pause duration R of 18 ms in its basic setting.
!! Notes
• Pause duration R can be modified with the Pause duration key and/or the Modification knob.
Hence an adjustable frequency range of 0.1 - 400 Hz is possible.
• The fixed frequency adjusted with the pause duration will be shown on the display.
• The fixed frequency will be taken over by turning the
Frequency modulated TENS Burst II - TENS Burst V:
In case of the current types TENS Burst II - TENS Burst V the pause duration R will alter within certain
ranges and the pulse duration T remains constant at 2 ms. The therapy always starts with the low
frequencies, whereas the frequency ranges will be passed twice within 15 s.
1. Press the
2. The frequency range will be shown on the display.
3. Set the desired modifications.
4. The therapy will be started by turning the
5. The intensity of current will be shown on the display.
6. The frequency traverse can be stopped by pressing the
Tens-Burst key in accordance to the selected current type.
Intensity regulator.
Intensity regulator.
FIX key.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

42
7. The fixed frequency will be shown on the display.
8. The therapy time continues to pass.
9. Press the white
10. The frequency can be readjusted by turning the
11. Press the
12. The frequency traverse will be released again.
13. The triad gong will sound three times after the expiration of the therapy time.
Soft key [frequency].
Modification knob.
FIX key again.
STEREODYNATOR
928
4.4.10 Micro-Stimulus Current
Micro-stimulus current is applied in kinds and stages of diseases, as well as in injury consequences, for
which depth warming seems to be a successful therapy. It includes surgical, traumatological, orthopedic,
sports medicine and gynecological areas.
The impulse sequences of the micro-stimulus current have an extremely low intensity, which amounts to 5
mA maximum.
!! Note
The pulse duration and pause duration can be adjusted only within a limited range. The maximum
period duration is 50 ms.
4.4.11 Universal Therapy
The basic setting of the Universal therapy T/R is especially suited for the application in case of severe
paralyses. Pulse duration and pause duration are adjustable within wide limits for middle and mild paralyses.
4.5 Special types of current Menu
Some current types cannot be selected by key but within the menu. The user support is driven by dialog on
the display.
The following therapy current types are filed in the Special types of current menu:
IG 30
IG 50
FM
MF
LP
Incontinence
1. Press the
2. Move the scroll bar/cursor with the
3. Confirm by pressing the white
4. The content of the display will be shown inversely, to indicate that you are in the Special types of
current menu.
5. Move the scroll bar/cursor with the
6. Confirm by pressing the white
Menu key.
Impulse galvanization with 30 ms single-pulse duration
Impulse galvanization with 50 ms group-pulse duration
Frequency modulation
Diadynamic current (monophasé fixe)
Diadynamic current (longues périodes)
Rectangular current for incontinence
Modification knob to Special types of current.
Soft key.
Modification knob to the desired special current type.
Soft key.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
7. The selected current type will be shown on the display.
8. Set the desired modifications.
9. Turn on the
928
Intensity regulator and therapy will be started.
43
4.5.1 Impulse Galvanization
The impulse galvanization currents are so-called shaking frequency currents. Hyperemia, analgesia and
detoning are the main fields of application.
The current type IG 30 consists of triangular impulses with a pulse duration T of 30 ms and a pause duration
R of 50 ms.
The current type IG 50 consists of rectangular impulses with a pulse duration of 1 ms and a pause duration
of 19 ms (50 Hz). The rectangular impulses are released in groups with a pulse duration T of 50 ms and a
pause duration R of 70 ms.
4.5.2 Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulation is suited for electrostimulation of the muscles. The frequency modulation FM
consists of rectangular impulses. The frequency range will be passed twice within 6 s.
4.5.3 Diadynamic Currents MF Monophasé Fixe and LP Longues Périodes
The diadynamic currents monophasé fixe (MF) and longues périodes (LP) are used in pain therapy, for
stimulating blood circulation, stimulating absorption (post Trauma) and for neuromuscular
electrostimulation.
Attention
Do not mistake the current type monophasé fixe (MF) for the middle frequency
currents MF I - MF VII.
4.5.4 Rectangular Current for Incontinence
The current type Incontinence current is applied in case of incontinence caused by neurological damages,
transverse lesion of the cord with paraplegia, paralyses after dislocation of the disk, stress incontinence etc.
The current type is a biphase rectangular current (d.c.-free) with a pulse duration T of 0.1 ms and a pause
duration R of 40 ms (25 Hz). In addition, a surge cycle with a rise time of 2 s, a duration time of 4 s and a
pause time of 8 s are preset.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

44
STEREODYNATOR
928
4.6 GYM
In the STEREODYNATOR 3 different types of Gymnastic currents are included.
This current types cannot be selected by key but within the menu. The user support is driven by dialog on
the display.
GYM current
GYM Training
Burning mode
1. Press the
Menu key.
2. Move the scroll bar/cursor with the
3. Confirm by pressing the white
Surged medium frequency
Modulated medium frequency
Modulated medium frequency
Modification knob to the desired GYM current type.
Soft key.
4. The selected current type will be shown on the display.
5. Set the desired modifications. (Only GYM current slow/med/fast)
6. Turn on the
Intensity regulator and therapy will be started.
4.6.1 GYM current
GYM current is a surged medium frequency current. The carrier frequency is 8000 Hz.
It is possible to use this current in single-channel mode and three-channel mode.
The parameters of the GYM current are described below.
I
200 ms 200 ms400 ms break
Figure 26 GYM current
The surge parameters are:
Rise time: 200 ms
Hold time 400 ms
Fall time 200 ms.
break variable (depends on the rythm slow, med, fast)
There are 3 different rythms for the GYM current:
Slow = 15 rythms per minute
Med = 20 rythms per minute
Fast = 30 rythms per minute
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
z
s
0
0
0
4.6.2 GYM Training
The GYM Training current is a modulated medium frequency current in surged mode.
The carrier frequency is 8000 Hz.
It is possible to use this current in single-channel mode and three-channel mode.
The parameters of the GYM Training current are described below.
15 15 1555
Figure 27 GYM Training current
928
50 H
ms
45
The surge parameters are:
Rise time: 3 s
Hold time 3 s
Break time 3 s
4.6.3 Burning mode
The Burning mode current is a modulated medium frequency current
The carrier frequency is 8000 Hz.
It is possible to use this current in single-channel mode and three-channel mode.
The parameters of the GYM Training current are described below.
3 Hz
m
30
Figure 28 Burning mode current
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
33
30
30
30

46
STEREODYNATOR
928
5 Galvanopalpation
The sensitive and vasomotor cutaneous nerves in certain body segments are examined to get indirect
conclusions on diseases of inner organs.
1. Connect the electrode handpiece to the socket (1).
2. Connect the electrolytically inactive electrode to the red cable.
3. The electrolytically inactive electrode will be applied far from the examination place as a cathode
(switch-over of polarity, s.b.).
4. Press the
5. Set the operation mode to CV by pressing the
6. Set the polarity to ”-” by pressing the
7. Now the active electrode handpiece is the anode. It serves for palpation.
8. Set the intensity (by turning the
examination area.
9. Turn the
10. Now the electrode handpiece can be moved over the skin and herewith also removed. With the
movement the stimulating current will alter depending on the patient resistance and the electrode
pressure.
11. After the expiration of treatment set the
automatically run down) to ”0.0”. If the device remains unused for more than 2 minutes with the
intensity adjusted, the patient will be disconnected from the circuit.
Galv key.
Operation mode key.
Polarity key.
Intensity regulator) and place the electrode handpiece firmly on the
Intensity regulator slowly until the stimulus is just noticeable.
Intensity regulator and Therapy time (as far as it has not
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
47
6 Electrokinetic Therapy
Electrokinetic therapy is the application of stimulation current with moving electrodes. The application is
only carried out in operation mode CV (= constant voltage).
Attention
Moisten the electrode intermediate layers (dripping wet)!
6.1 Detection of Trigger Points With the Electrode Handpiece
Sometimes it is advisable to detect the appropriate muscular trigger point by moving the electrode handpiece
on the skin.
1. Connect the electrode handpiece to the socket (1).
2. Connect the electrolytically inactive electrode to the red cable.
3. The electrolytically inactive electrode will be placed as a cathode (switch over of polarity, s.b.) away
from the area to be examined.
4. Press the desired current type key.
5. Set the operation mode on CV by pressing the
6. Set the polarity to ”-” by pressing the
7. The active electrode handpiece is anode now.
8. Set the intensity (by turning the
to be examined.
9. Turn the
10. Now you can move the electrode handpiece over the skin and you can also remove it. The stimulating
current alters according to the patient resistance and the electrode pressure.
11. Set the
expiration of examination. If you do not work with the device for more than 2 minute with the intensity
adjusted, the patient will be interrupted from the circuit.
Intensity regulator slowly until stimulation is slightly noticeable.
Intensity regulator and Therapy time (as long as it has not yet expired itself) to ”0.0” after the
Polarity key.
Intensity regulator) and put the electrode handpiece firmly on the area
operation mode key.
6.2 Stimulation Massage
The stimulation massage will be realized with a moving plate electrode under current conduction.
1. Use two plate electrodes in well moistened electrode pockets.
2. One electrode will be fixed firmly on the skin.
3. The second (active, mobile) electrode will be moved over the skin.
4. It is advisable to put on rubber gloves in order not to get electrified yourself when you touch the active
electrode.
5. Press the desired current type key.
6. Set the operation mode to CV by pressing the
7. Put the mobile electrode firmly on the skin.
8. Turn the
9. Move the mobile electrode over the skin. There is no adverse effect if you take off the electrode.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
Intensity regulator slowly until the desired stimulation has been achieved.
Operation mode key.

48
STEREODYNATOR
928
7 Electrodes
Basically all usual electrodes are connectable in electrotherapy. Plate electrodes and rubber electrodes are
appropriate for large-area treatments.
The electrode handpiece with fingertip switch and connecting cable has proved effective for diagnostics.
Current can flow only when the key is pressed. Additionally you need an electrode set (see chapter 13
Accessories).
The therapy can be realized without any problem with suction electrodes or plate electrodes.
7.1 Electrode Positioning
The positioning of the patient and/or muscle to be treated is very important. The therapy shall always be
carried out in a comfortable and relaxed position. The joints shall be located in an angular position, so that
they are placed in a mid-position, from which both the flexor as well as the extensor muscles can be
stimulated.
In general the preparation and application of the electrodes is carried out as follows:
1. Always put a wet electrode intermediate layer or electrode pocket between the electrode and the skin in
order to avoid current sensations on the skin. The layer must always be about 1 cm larger than the
electrode itself.
2. Put the electrode completely into the electrode pocket, so that the pocket protrudes on the open side
with about 1 cm.
3. After multiple use the electrode intermediate layer or electrode pocket can slightly shrink. If the
distance of about 1 cm is no longer given, the intermediate layer or pocket must be replaced.
4. Prior to the initial use, the macroporous intermediate layers and pockets made of viscose sponge must
be thoroughly washed out under running water to remove manufacturing residues.
5. To moisten the intermediate layer or pocket put them into normal tap water, or better into 1% salt
solution. The intermediate layers or pockets should be soaked; remove them and let them drop; do not
wring them out.
6. If necessary, flatten deformed electrodes, insert them into the pocket and/or put them on the
intermediate layer. Put them on the area to be treated and fit them to the given body surface. Use only
thick and well moistened sponges.
7. Apply the holding strap in a way that the electrode fits completely.
8. The sponge pockets or intermediate layers have to be cleaned after the expiration of treatment, see
chapter 9.2.2.
!! Note The above mentioned applies for the application of suction electrodes accordingly.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
49
Attention
• Do not apply the electrodes on skin injuries. Even minor abrasions can cause a
burning to the patient. Herewith the intensity of current by the patient can be
erroneously judged. If this cannot be avoided, apply zinc ointment to cover.
• It is recommended not to exceed the current density of 2 mA/cm
surfaces. In case of galvanization the limiting value is 0.2 mA/cm
iontophoresis it is 0.1 mA/cm
2
.
• Do not use one way (self adhesive) electrodes in case of currents with galvanic
portion, there is the danger of acid burns!!
7.1.1 Monophase Electrode Techniques
In case of monophase techniques, direct and indirect stimulation are distinguished. Generally the cathode is
used as a stimulating electrode. In case of direct stimulation it is applied on the nervous stimulant point (all
muscles react) and in case of indirect stimulation on the muscle stimulant point (only the stimulated muscle
reacts). Apply the electrolytically inactive electrode (mostly a large anode) distally.
2
in all electrode
2
and in case of
For differentiated therapeutic treatments and easy electro-diagnostics it is recommended to use the electrode
handpiece as a electrolytically active electrode.
7.1.2 Biphase Electrode Techniques
A characteristic of this method is that both (mostly equally large) electrodes are applied on the muscle to be
stimulated or on the functionally related muscle group. The cathode is to be placed distally.
7.2 Single-Pole Electrodes
Single-pole electrodes are applicable for all therapy currents. For large-area treatment we recommend to use
plate electrodes, for all other applications self-cut electrodes. The last-mentioned need an electrode
connector for current supply. Both electrode types have to be connected to the device with a patient cable.
The electrode positioning is realized as described in chapter 7.1 Electrode positioning.
The electrode size depends on the area that should be passed by the current. Under small electrodes the
current flow will be more concentrated and more localized than when applying large electrodes. The
application area depends on the clinical picture.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

50
Attention
STEREODYNATOR
928
For current types for which there exists the threat of cauterization (currents with
galvanic portion), the maximum recommended current density is 0.5 mA/cm
electrode surface. In case of galvanization the limit value is 0.2 mA/cm
of iontophoresis 0.1 mA/cm
2
.
2
and in case
Electrode Surface Max. Current / Galv / Iontophoresis
Conductive rubber electrode 3 cm x 4 cm 12 cm
Conductive rubber electrode 6 cm x 8 cm 48 cm
Conductive rubber electrode 8 cm x 12 cm 96 cm
Plate electrode 9 cm x 12 cm 108 cm
2
2
2
2
24 mA / 2.4 mA / 1.2 mA
96 mA / 9.6 mA / 4.8 mA
192 mA / 19.2 mA / 9.6 mA
216 mA / 21.6 mA / 10.8 mA
Table 1: Maximum Current of conductive rubber electrodes and plate electrode
2
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
7.3 Three-pole electrodes
The triple-pole electrodes can be used for
stereodynamic interference currents.
The conductive rubber electrodes of the three
circuits are placed in two flexible three-pole
star electrode sets (I and II) and attached to a
common patient cable. There are three sizes
available (small, standard and large). Electrode
pockets are necessary for the application and
fixing material for the bandage (see
accessories).
Each stereodynamic electrode set is placed into
a well wetted pocket so that the black
conductive rubber electrodes face the humidity
carrier. The reverse side of the pocket consists
of transparent synthetic material in order to be
able to check the correct positioning of the
electrode.
51
A)
B)
Electrode position:
A) If the electrodes are placed opposite to each
other (transverse current flow,
transregional) the cable connections must
point in opposite directions.
B) If the electrodes are placed on one side
(longitudinal current flow), their cables
must point in the same direction.
Only in the case of these electrode positions the
flow paths of current of the three circuits can
transpose and optimal stereodynamic
stimulation currents are generated.
In special cases (e.g. depending on the
application in the case of shoulder-hand
syndrome) it is possible to deviate from this
general rule.
You can also use triple-pole suction electrodes,
if your device is equipped with a suction
application aid. The above mentioned also
7.4 Suction Electrodes
applies to the application with suction
electrodes.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

52
STEREODYNATOR
928
7.4 Suction Electrodes
Instead of the above-mentioned electrodes, suction electrodes can be used for faster application. The device
technics necessary for this is described in chapter 3.2 Integrated Suction Application Aid .
Achtung
• For current types for which there exists the threat of cauterization (currents with
galvanic portion), the maximum recommended current density is 0.5 mA/cm
electrode surface. In case of galvanization the limit value is 0.2 mA/cm
• In case of iontophoresis don’t use suction electrodes.
Suction electrode Surface Max. current value / Galv
Electrode plate small 6 cm
Electrode plate standard 12 cm
Electrode plate large 28 cm
Table 2: Maximum current of the suction electrodes
2
2
2
12 mA / 1.2 mA
24 mA / 2.4 mA
56 mA / 6 mA
2
.
2
7.5 Electrode Handpiece
The electrode handpiece is applicable for small, local treatments and simple electro-diagnostics (see also
chapter 7.1.1 Monophase Electrode Tcs). The electrode handpiece (electrolytically active electrode) is
firmly connected to the patient cable. With a second wire the plate electrode is connected (electrolytically
inactive electrode). In addition an electrode set is necessary, which consists of metal shaft, electrode pockets
and rubber rings (see chapter 13 Accessories).
The following procedure is advisable:
1. Connect the electrode handpiece.
2. The electrode handpiece will be recognized by the device.
!! Note
The fingertip is without any function in the therapy mode. The selected current is issued
independently from the switch position!
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
53
8 Troubleshooting
The following exceptions are signaled by the current stimulation device optically via the display and
acoustically. Most of the exceptions can be cleared by following the displayed instructions.
In general an exception is characterized by the following sequence of events:
1. The device does not react on a command, given by a key or by turning a regulator.
1. A warning signal is sounded.
2. An error message is displayed.
3. If the user does not react according to the displayed messages, the most recent faultless device condition
is restored after a time-out.
Global Error Conditions
Error messages:
♦ Error in the 386 EX-module !
♦ Error: DSP is not responding !
♦ Error while booting the DSP
♦ Error while writing to the DSP !
♦ Task Timeout !
♦ Overheating !
♦ Defect of the power amplifier !
♦ Turn off unit and call service !
Suggestions:
Turn off and turn on unit. A full selftest of all device functions is performed and the unit is reinitialized. If
the unit does not come up in normal state please call your local service.
Application Errors
Error message:
♦ Wrong electrode !
Suggestion:
You have connected an unsuitable electrode. Please use a suitable electrode for the current type of your
choice (see chapter 7 Electrodes).
Error Messages:
♦ Check placement of electrodes !
♦ Patient cables are shortcircuited !
Suggestion:
The current loop to the patient is cut off. Please check electrodes, cables and connectors.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

54
STEREODYNATOR
928
9 Maintenance
Functionality, reliability, and safety characteristics of the current stimulation device are only guaranteed in
case of proper use in accordance with the operating instructions. Safety control, maintenance work, repair
work, and modifications shall be carried out only by the manufacturer or by service agents authorized by
him. In case of a failure, parts which influence the safety of the device shall be only replaced by original
spare parts of the manufacturer. The electric installation must correspond to the requirements in accordance
with VDE/IEC. The device does not contain any parts which need maintenance work done by the user.
9.1 Safety Controls
The device is subject to the provisions of the Medical Device Directive. The safety controls have to be
carried out on the basis of this directive. Thereby, the operator regulation has to be especially observed.
Irrespective of the legal rules or beyond the scope of the Medical Device Directive, it is recommended to
have the device checked by the manufacturer or by a service agency authorized by him at 12- months
intervals.
The check shall consist of at least the following criteria:
• Electrical safety check in accordance with the test plan of the manufacturer,
• Check of the device in respect of external integrity,
• Check of all display and operating elements in respect of damages,
• Check of all inscriptions in respect of legibility.
9.2 Cleaning, Disinfection and Care
9.2.1 Current Stimulation Device
For cleaning and disinfection of the current stimulation device and its accessories (except electrode fleece,
electrode pockets or felts, see chapter 9.2.2) there should not be used any agents containing higher portions
of phenol derivatives, alcohol, compounds of chlorine or peracetic acid. It is recommended to use
disinfectants on aldehyde basis.
The device is not suited for heat sterilization or for sterilization with gases.
Attention
Before cleaning or disinfection unplug the mains plug out of the socket!
The current stimulation device is suited for wiping disinfection. It has to be observed that no liquids enter
the device. In no case shall the plug or socket get wet. For cleaning or disinfection the device may not be
drizzled.
9.2.2 Electrode Fleece, Electrode Pockets or Felts
1. Put the material into neutral soap-suds and rub it slightly. If necessary, disinfect with disinfectant
solution, but do not put it into it.
2. Leave the parts over the night in the neutral soap-suds or tap water.
3. Take them out, and wash them several times thoroughly out under cold or warm running water.
4. Let them drop, but do not wring them out.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
10 Warnings and Safety Precautions
Attention !
• In case of patients with implanted electronic device carry out electrical stimulation
treatment only after having checked whether there is any risk.
• Pieces of jewellery and glasses have to be taken off during the treatment.
• Turn off cellular phones and radiophone or place them in a distance of 3 m from the
device.
• Cardiac pacemakers can extremely be disturbed. In these cases the therapy should be
only carried out under continuous pulse and ECG control.
• If the patient and/or the patient cable is in direct range of a high-frequency, short-
wave or micro-wave therapeutic device, a damage to the device or an injury of the
patient cannot be excluded. Please keep a distance of 3 m.
• A simultaneous connection of the patient to a high-frequency surgery device can
lead to burns under the electrical stimulus electrodes.
• It is recommended not to exceed the current density of 2 mA/cm2 on all electrode
surfaces.
• For current types for which there exists the threat of cauterization (currents with
galvanic portion), the maximum recommended current density is 0.5 mA/cm
electrode surface. In case of galvanization the limit value is 0.2 mA/cm
of iontophoresis 0.1 mA/cm
• Do not use one way (self adhesive) electrodes with currents with galvanic portion,
there is the threat of cauterization!!
• The unit is not designed to be operated in places with the inherent risk of
explosions. If it is used in dangerous areas of anesthesia departments, the possibility
of an explosion cannot be excluded.
• In case of all visible failures contact immediately gbo Medizintechnik AG or one of
the service agencies authorized by gbo Medizintechnik AG .
2
.
2
and in case
55
2
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

56
Contraindications for use of ultrasound
Ultrasonic therapy must not be used in the following instances:
• Patients with a fever
• Infectious diseases, dermatological conditions
• Blood coagulation problems
• Pregnancy
• Tuberculosis, stomach ulcers
• Peripheral vascular disease
• Tumors, circulatory instability and coronary diseases
• Acute rheumatoid arthritis
• Diabetes mellitus
• Septic inflammation
• Following recent thorium-X treatment or x-ray depth treatment
The following organs must not be treated directly:
• Eyes
• Medulla
• Laminectomy-related spinal incisions
• Heart, lungs
• Anesthetized areas
STEREODYNATOR
928
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
11 Explanation of the Signs Used
57
0123
CE – conformity sign
Attention !
Observe the instructions for use !
Application part ungrounded, protection degree Type BF
Ultrasound probe connection
Patient cable connection
Suction electrode I connection
Suction electrode II connection
This product complies with WEEE Directive 2002/96/EG
(waste electrical and electronic equipment). Separate
collection for electrical and electronic equipment.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

58
t
n
t
t
t
py
n
t
n
n
t
t
STEREODYNATOR
12 Technical Data
Mains voltage and frequency: 100, 120, 230, 240 V, 48-62 Hz
Current consumption*: 120 V: max. 3.3 A 230 V: max. 1.65 A
Mains fuse*: 120 V: T3.2 A 230 V: T1.6 A
Output current: max. 200 mA
Output voltage: max. 200 V
MDD device class IIb
Protection against ingress of liquids IP X1
Protection class: I in accordance to IEC 601 / VDE 0750
Protection degree: BF in accordance to IEC 601
Dimensions*: max. 15 cm x 41 cm x 48 cm (H x D x W)
Weight*: max. 17 kg without accessories
Color: white RAL 9002
Display: LCD backlighted, 320 X 240 dots full graphic
Battery: CR 2032
environmental conditions: operation of the
device:
transport and
storage:
Current types: Galv - Galvanic curren
SMS - Strong muscle stimulation according to Eichhor
DF/CP - Diadynamic currents
UR - Ultra stimulation curren
Micro - micro-stimulus curren
F1 - Faradic curren
HV - high voltage
T/R - Universal-Thera
TENS - Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulatio
TENS Burs
MF I – VII - Middle-frequency currents
IG 30/50 - Impulse galvanizatio
FM - Frequency modulatio
LP/MF - Diadynamic currents
Incontinence - Rectangular current incontinence
Seda
Myomo
Vegetat. Stim. I - Interference current 2.5 - 25 Hz
Vegetat. Stim. - Interference current 10 Hz
Vegetat. Stim. - Interference current 0.1 - 1 Hz
Universal - Interference current 1 - 200 Hz
Sedat.Mod. - Interference current 100 - 200 Hz
GYM currentsurged MF current in single and three channel mode
GYM Trainingmodulated MF current in single and three channel mode
Burning mode modulated MF current in single and three channel mode
Therap.ultrasound module:
Ultrasound frequency: 1/3 MHz
Ultrasound power: max. 3 W per 1 cm2 radiating surface at 1 MHz
Ultrasound probe: 2,5 cm2 and 5 cm2 radiating surface
Suction application module:
Suction: At least 150 mbar in maximum position
Suction massage frequency: 0 - 60 pulses per minute
*) dependent on the device type and/or whether the device is equipped with therapeutic ultrasound modules and
suction application modules.
Continuous and pulse mode 1:5, 1:10, 1:20
max. 1,5 W per 1 cm
temperature range +10 °C ... +40 °C
relative humidity of air 30 ... 75 %
temperature range +5 °C ... +50 °C
relative humidity of air < 90 %, non condensing
- Trans. electr. nerve stimulation in impulse groups
- Interference current 200 Hz
- Interference current 50 Hz
2
radiating surface at 3 MHz
928
gbo Medizintechnik AG reserves the right to modify the design and specification without prior notice.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928
59
Current
Galvanic current
Ultrastimulation
current
Faradic current
Strong muscle
stimulation
Micro-stimulus
current
Universal therapy
Diphasé fixe
Courtes périodes
Middle frequency
current 8 kHz
MF I / surged
MF II / sinus surged
Grafics Pulse
duration T in
ms
1.0 - 3.0 17.0 - 19.0 2.6 50 70 70
0.02 - 2000 0.5 ms - 10s0 0.1 - 2000 70 70
0.02 - 40 0.5 ms - 10s0 20 - 2000 5 5
0.02 - 2000 0.5 ms - 10
Pause
duration
R in ms
D.C.
portion
in %
Frequency
in Hz
Maximum output
voltage by CV in
V
peak
Max. output
current by CC in
mA
peak
- - 100 0 70 70
2.0 5.0 28.6 143 70 70
0.1 - 2000 70 70
s
- - 63 100 70 70
- - 47.25 50 / 100 70 70
- - 0 - 140 140
- - 0 - 140 140
1)
MF III / 50 Hz
MF IV / 3 - 10 Hz
MF V / 10 - 30 Hz
MF VI /
30 - 60 Hz
MF VII /
100 - 200 Hz
High voltage
currents
HV I / 50 Hz
HV II / 3 -10 Hz
HV III /
10 - 30 Hz
HV IV /
30 - 60 Hz
HV V /
100 - 200 Hz
Tens currents
Tens I / 100 Hz
Tens II /
3 - 10 Hz
4.0 0.5 ms - 10s0 0.1 –
140 140
222.2
50 - 167 50 - 167 0 3.0 - 10 140 140
16.5 – 50.0 16.5 – 50. 0 0 10 - 30 140 140
8.3 – 16. 0 8.3 – 16.0 0 30 - 60 140 140
4.0 1.0 – 6.0 0 100 - 200 140 140
4.5 0.5 ms - 10s0 0.1 - 200 200 200
4.5 95.5 –
0 3.0 - 10 200 200
325.5
4.5 28.5 – 95.5 0 10 - 30 200 200
4.5 12.5 – 28.5 0 30 - 60 200 200
4.5 0.5 – 5.5 0 100 - 200 200 200
0.2 0.5 ms – 10s0 0.1 -
100 100
1428.6
0.2 100.0 -
0 3.0 - 10 100 100
330.0
1)
In case of using the suction electrodes the maximum current is reduced to 20 mA.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

60
STEREODYNATOR
928
Current
Tens III /
10 - 30 Hz
Tens IV /
30 - 60 Hz
Tens V /
100 - 200 Hz
Tens Burst
currents
Tens Burst I /
50 Hz
Tens Burst II /
3 - 10 Hz
Tens Burst III /
10 - 30 Hz
Tens Burst IV /
30 - 60 Hz
Tens Burst V /
100 - 200 Hz
Special currents
Monophasé fixe MF
Grafics Pulse
duration T in
ms
Pause
duration
R in ms
D.C.
portion
in %
Frequency
in Hz
Maximum output
voltage by CV in
V
peak
Max. output
current by CC in
mA
peak
0.2 33.0 - 100.0 0 10 - 30 100 100
0.2 17.0 - 33.0 0 30 - 60 100 100
0.2 5.0 - 10.0 0 100 - 200 100 100
2.0 0.5 ms – 10s0 0.1 - 400 100 100
2.0 98.0 - 328.0 0 3.0 - 10 100 100
2.0 31.0 – 98.0 0 10 - 30 100 100
2.0 15.0 – 31.0 0 30 - 60 100 100
2.0 3.0 – 8.0 0 100 - 200 100 100
10 10 31.5 50 70 70
Longues périodes LP
Impulse
galvanization
IG 30
Impulse
galvanization
IG 50 / surged
Frequency
modulation
FM / 7 - 14 Hz
Incontinence
Interference
currents2)
Sedat
200 Hz
Myomot
50 Hz
Vegetat. Stim I
2.5 - 25 Hz
Vegetat. Stim II
10 Hz
Vegetat. Stim III
0.1 - 1 Hz
- - 46 50 / 100 70 70
30.0 50.0 18 12.5 70 70
50.0 70.0 0.3 8.3 70 70
0.5 70.9 –
0.4 7 - 14 70 70
142.4
0.02 - 100 0.5 - 100 0 10 - 90 70 70
- - 0 200 140 -
- - 0 50 140 -
- - 0 2.5 - 25 140 -
- - 0 10 140 -
- - 0 0.1 - 1 140 -
Universal
1 - 200 Hz
Sedat.Modulation
100 - 200 Hz
2)
The output current is reduced to 100 mA.
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
- - 0 1 - 200 140 -
- - 0 100 - 200 140 -

STEREODYNATOR
928
13 Accessories
Article Article number
STEREODYNATOR® 928
STEREODYNATOR® 928
inclusive ultrasonic therapy module, inclusive 1 ultrasonic transducer 5 cm
inclusive 1 contact gel 250 ml
STEREODYNATOR® 928 inclusive suction application aid
STEREODYNATOR® 928
inclusive ultrasonic therapy module, inclusive 1 ultrasonic transducer 5 cm
inclusive 1 contact gel 250 ml and inclusive suction application aid
Adapter connector, drill hole and pin diameter 4 mm, in case of use with older
accessories with new cable to the patient 45-38-245EH725
Bow electrode 011-0-0024
Conductive rubber electrode with cable 3 cm x 4 cm (fleece pockets small) 45-38-880EH725
Conductive rubber electrode with cable 6 cm x 8 cm (fleece pockets medium) 45-38-898EH725
Conductive rubber electrode with cable 8 cm x 12 cm (fleece pockets 45-38-
203EH725 or viscose sponge pockets 22-73-621Q1408) 45-38-492EH725
Contact gel Lectro-Sonic, 250 ml 45-39-128EH725
Device cart UNICAR® 900 014-0-0008
Diagnostic set (patient cable, sheet tins with cutting template, intermediate fleece
layers, electrode connector, connecting terminals, rubber straps, fixing buttons)
Diagnosis sheet, I/T curves (100 pieces) 71-21-635E2200
Diagnosis sheet, trigger points trunk (100 pieces) 71-21-643E2200
Diagnosis sheet, upper extremities (100 pieces) 71-21-650E2200
Diagnosis sheet, lower extremities (100 pieces) 71-21-668E2200
Elastic tape with closure (velcro), 70 cm long , 7.5 cm wide (2 pieces) 45-38-997EH725
Electrode handpiece with finger tip switch 45-38-401EH725
Electrode set for electrode handpiece 45-38-450EH725
Electrode pockets, small, (10 pcs.) for star electrode small 49-07-317E3020
Electrode pockets, standard, (10 pcs.) for star electrode standard 49-07-309E3020
Electrode pockets, large, (10 pcs.) for star electrode large 49-07-325E3020
Electrode intermediate layers small, diameter 36 mm (12 pieces) for suction
electrodes, small 45-38-518EH722 45-38-922EH722
Electrode intermediate layers standard, diameter 52 mm (12 pieces) for suction
electrode set, standard 45-38-500EH722 45-38-930EH722
Electrode intermediate layers large, diameter 72 mm (12 pieces) for suction
electrodes, large 45-38-526EH722 45-38-948EH722
Sponge pockets, large (10 pieces) for plate electrodes 45-38-468EH725 and
conductive rubber electrodes 45-38-492EH725 45-38-203EH725
Sponge pockets, large (10 pieces) for plate electrodes 45-38-468EH725 and
conductive rubber electrodes 45-38-492EH725 45-38-203EH725
Sponge pockets, small (10 pieces) for conductive rubber electrodes small 45-39-102EH725
Sponge pockets, medium (10 pieces) for conductive rubber electrodes medium 45-39-110EH725
Electrode pockets, large, (10 pcs.) for star electrode large 49-07-325E3020
014-0-928
014-0-928-U
2
,
014-0-928-V
014-0-928-UV
2
,
45-39-177EH725
61
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

62
STEREODYNATOR
Article Article number
Intermediate layer made of viscose sponge, 30 cm x 20 cm x 1 cm (5 pieces) 45-38-476EH725
Intermediate layer made of fleece, 32 cm x 22 cm (5 pieces) 45-38-211EH725
Paper sheets for suction electrodes 45-38-856EH722 and 45-38-864EH722 71-21-841EH060
Patient cable, double-wire, 2.5 m long 45-38-435EH725
Plate electrode with cable, 9 cm x 12 cm 45-38-468EH725
Rectal electrode 014-0-0007
Sheet tin, 18 cm x 28 cm (3 pieces) for making plate electrodes (use it with electrode
connector 45-38-237EH725 and connecting terminal 45-02-076EH023) 45-38-229EH725
Sheet tin plate electrode 9 cm x 12 cm with fix cable and socket 4 mm 45-38-468EH725
Suction electrode I with cable 45-38-534EH722
Suction electrode II with cable 45-38-542EH722
Suction electrode, single-pole, small, diameter 34 mm 45-38-518EH722
Suction electrode, single-pole, large, diameter 70 mm 45-38-526EH722
Suction electrode set, single-pole, standard, diameter 50 mm 45-38-500EH722
Suction cub small, diameter 34 mm 45-38-567EH722
Suction cub standard, diameter 50 mm 45-38-575EH722
Suction cub large, diameter 70 mm 45-38-583EH722
Stereo suction electrode set (Stereo suction electrode pair, paper sheets) 45-38-856EH722
Star electrode pair, small (diameter 80 mm) 45-38-708EH725
Star electrode pair, standard (diameter 130 mm) 45-38-716EH725
Star electrode pair, large (diameter 180 mm) 45-38-724EH725
Stern electrode set Standard (star electrodes 3-pole, electrode pockets, rubber tapes) 45-38-260EH719
Therapy set 1 (patient cable, sheet tin electrodes, intermediate fleece layers, rubber
45-39-151EH725
tapes, fixing buttons)
Therapy set 2 (cable to the patient, conductive rubber electrodes, fleece pockets,
45-39-169EH725
elastic tapes with closure (velcro)
3-channel therapy-set (complete) 014-0-0011
Ultrasound probe with cable and plug, ultrasound surface 5 cm
Ultrasound probe with cable and plug, ultrasound surface 2,5 cm
2
2
023-0-0141
023-0-0140
Vaginal electrode 014-0-0006
Viscose sponge pockets (10 pieces) 22-73-621Q1408
928
UNICAR® 1000 device cart (basic rack) and
device porter (large)
UNICAR® 1000E device cart (basic rack with electric distribution and switch) and
device porter (large)
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
014-0-1000 and
014-0-1020
014-0-1000E and
014-0-1020

STEREODYNATOR
Index
928
63
A
acoustic user support 13
alarm beep 19
Application errors 51
assembly 15
attention 15, 27, 32, 47, 48, 52, 53
Automatic programs 31
B
biphase current 20
biphase electrode technics 47
C
care 52
CC mode 20
connection 15
current value 19
D
diadynamic currents 33, 40
disinfection 52
display 18
duration time 21
E
electrode handpiece 50
elektrode fleece 52
elektrode positioning 46
error messages 51
exceptions 51
L
LED 13, 18
longitudinal current flow 49
M
maintenance 52
menu 24
menu application with electrotherapy 32
Menu Programs 31
menu special current types 39
MF 40
micro-stimulus current 39
middle frequency currents 34
Monophase current 20
monophase electrode technics 47
monophasé Fixe 40
Myomot 30
O
operation mode 20, 45
optical user support 13
P
pause duration 18, 22
pause time 21
polarity 19
pole change 20
pulse duration 18, 22
pulse rise 22
R
F
faradic current 37
FM 40
frequency lock 21
frequency modulation 40
G
galvanic base 21
galvanic current 19, 36
H
high-voltage currents 35
rise time 21
S
safety controls 52
Sedat 29
Sedation Modulation 30
settings 16
short instruction 12
single-pole electrodes 47
soft key 24
Star display 18
strong muscle stimulation 34
suction application unit 26
suction electrodes 26, 50
surge parameters 21
switching on 16
I
impuls galvanization 40
incontinence 40
intensity regulator 19
inverse representation 18
iontophoresis 36
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
TENS 37
TENS Burst 38
therapy time 22
Three pole electrodes 49
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation 37
T

64
STEREODYNATOR
928
transport 15
transverse current flow 49
troubleshooting 51
U
ultrasound module 27
ultrasound/current-combination 27
ultrastimulation current 35
Universal 30
universal-therapy 39
unsuitable electrode 51
V
Vegetat. Stim. I 30
Vegetat. Stim. II 30
Vegetat. Stim. III 30
Voltage Selection 15
W
warning signal 19, 51
warnings 15, 53
wrong electrode 51
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2003, Medical Devices Division Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928 65
Number Current type
CV/CC
Basis
autom
T
R
/
+ / -
Remarks
Storing of Therapeutic Current Types
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9

STEREODYNATOR
928 66
Correction sheet
gbo Medizintechnik AG
- Dokumentation Kleiststraße 6
64668 Rimbach
Please work on the faults and/or suggestions to the present documentation:
Page Line faulty text right text
(If needed, please attach an additional sheet)
Address:
Part-No. 014-7-0019
gbo Medizintechnik AG 2004 Version 1.9
 Loading...
Loading...