Page 1

DIRECTORY OF INSTRUMENTS IN
GARRITAN WORLD INSTRUMENTS
66
Page 2

THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Africa
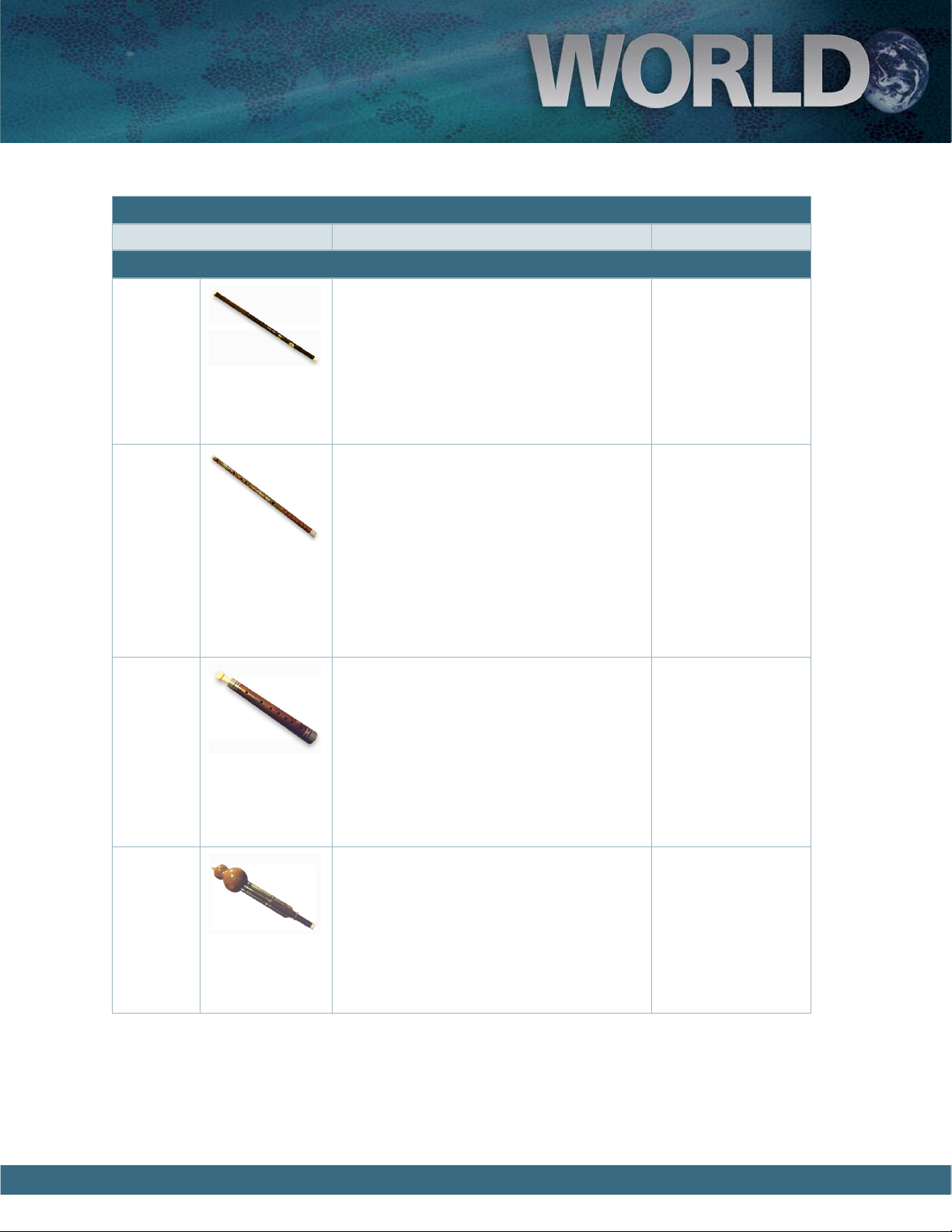
Arghul e Arghul is a reed woodwind instrument that
consists of two asymmetrical pipes. One pipe,
a chanter with between five and seven finger
holes, is dedicated to the melody. e second
pipe, longer than the first, produces a drone.
Arghuls come in different sizes and are played in
Egypt and surrounding regions.
Range: C3- C6
•
Mijwiz 1
Mijwiz 2
e Mijwiz is a traditional instrument of Egypt
and is one of the oldest wind instruments. Its
name means “dual” as it consists of two short
bamboo reed pipes tied together. Instead of having a separate reed attached to a mouthpiece,
the reed in the Mijwiz is a vibrating tongue
made from a slit cut into the wall of the instrument itself.
Range: C3 - C6
•
Another Mijwiz instrument with a different
range and character.
Range: C4 - C6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 3
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
China
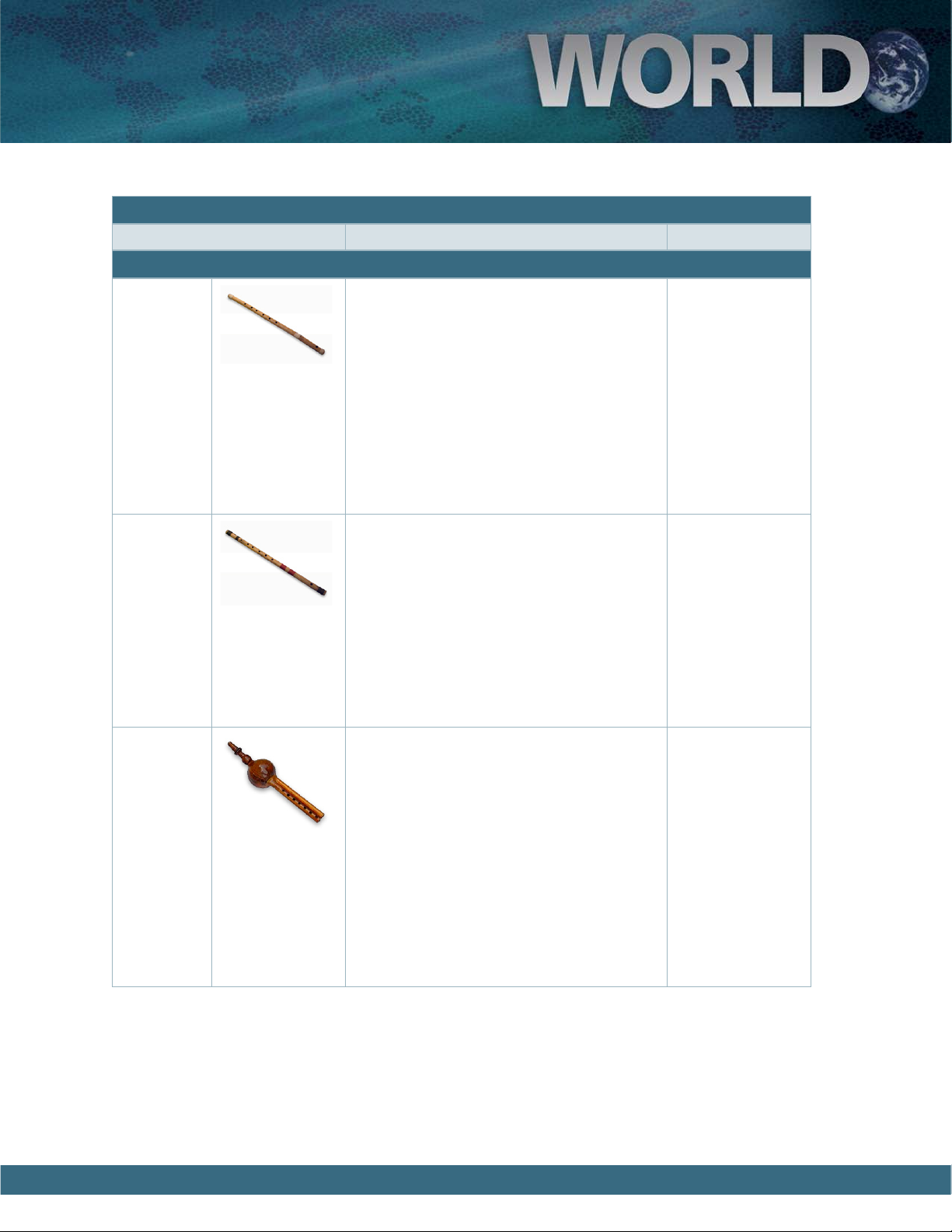
Bawu e Bawu is a side-blown wind instrument
found throughout China. Although it resembles a flute, it is actually a reed instrument.
It is often played as a solo instrument, and is
featured in films and in popular music. It is
also referred to as a Bawoo.
Range: G3- C6
•
Di-Zi
Guanzi
Hulusi
e Di-Zi, or Chinese bamboo flute, is the
most common flute of China. e Di-Zi is
a side-blown bamboo flute having six finger
holes, and is characterized by an additional
hole covered by a piece of thin fiber (Muo
kong) that buzzes when played and creates a
distinctive tone. e Di-Zi is also known as
the Ti-tzu or Hengdi.
Range: C4- C7
•
e Guanzi is a Chinese double-reed wind
instrument. Its name literally means “tube,”
which describes its cylindrical shape. It is usually made from rosewood and has seven finger
holes with one or two thumb holes. e ends
of the instrument are decorated with metal.
Also called Guan or Bili.
Range: G3- C6
•
e Hulusi is a popular Chinese reed instrument. e instrument has a gourd wind
chamber, a main melody pipe with seven
finger holes, and one or two auxiliary drone
pipes. Hulusi means “gourd silk,” referring to
the instrument’s soft silky tone.
Range: G3- C6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato,
BndSpd, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato,
BndSpd, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato,
BndSpd, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato,
BndSpd, Keyswitches
Page 4

THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
China
Sheng e Sheng, or Chinese Mouth Organ, is a
multiple free-reed instrument consisting of a
bundle of 13-17 vertical pipes fastened together. Sound is produced by blowing air into a
mouthpiece at the base and covering the holes
on the various pipes. e Sheng can produce
interesting chords as well as single notes, and is
used as both a solo and accompanying instrument. Also called Shung.
Range: C4- C7
•
Suona
Xiao
e Suona is a double-reed wind instrument
with a flaring metal bell at its end. It has a
distinctively loud tone and is used in Chinese
traditional music ensembles and outdoor performances. e Suona is also known as a Laba.
Range: C4 - G6
•
e Xiao is a Chinese end-blown flute that has
been used in Chinese music for over two millenenia. e instrument has six finger holes and
is played vertically—similarly to the Shakuhachi. It is usually made of dark brown bamboo.
e Xiao has a soft and low tone. e Xiao is
also known as the the Di Xiao or Dong Xiao.
Range: C3- C7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato,
BndSpd, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato,
BndSpd, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato,
BndSpd, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 5
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
India
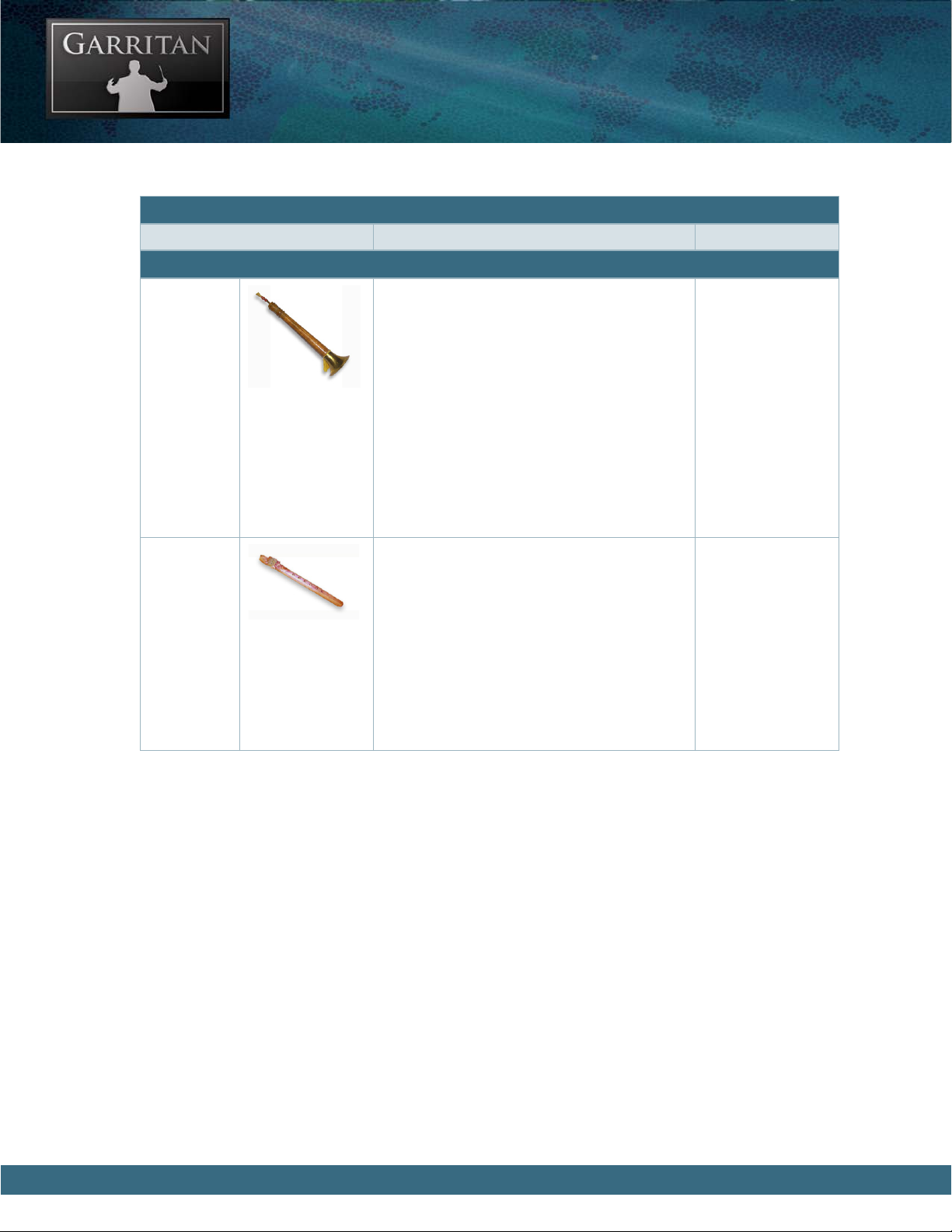
Bansuri 1 e Bansuri is a large side-blown alto flute of
Northern India and surrounding regions. It
is made of a single length of bamboo with six
or seven finger holes. Bansuris range in length
from about 12 inches up to about 40 inches,
with 20-inch bansuris being the most common. is instrument is associated with the
god Krishna who was often depicted playing a
Bansuri.
Range: C3- C8
•
Bansuri 2
(Venu)
Pungi Snake
Charmer
Another Bansuri instrument with a different
timbre and character. Venu is a variant of the
Bansuri used in Southern Indian Carnatic
music.
Range: C3- C8
•
e Pungi Snake Charmer’s pipe is a North
Indian reed instrument used by snake charmers. It consists of two pipes, a melody chanter
and a drone, that are attached to a gourd. To
produce sound, the player blows into a mouthpiece attached to the top and plays the chanter
with his fingers. e reeds are placed inside
a protective gourd, so the player’s lips never
touch them. e instrument is also known as
the Bean.
Range: C3- C6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 6
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
India
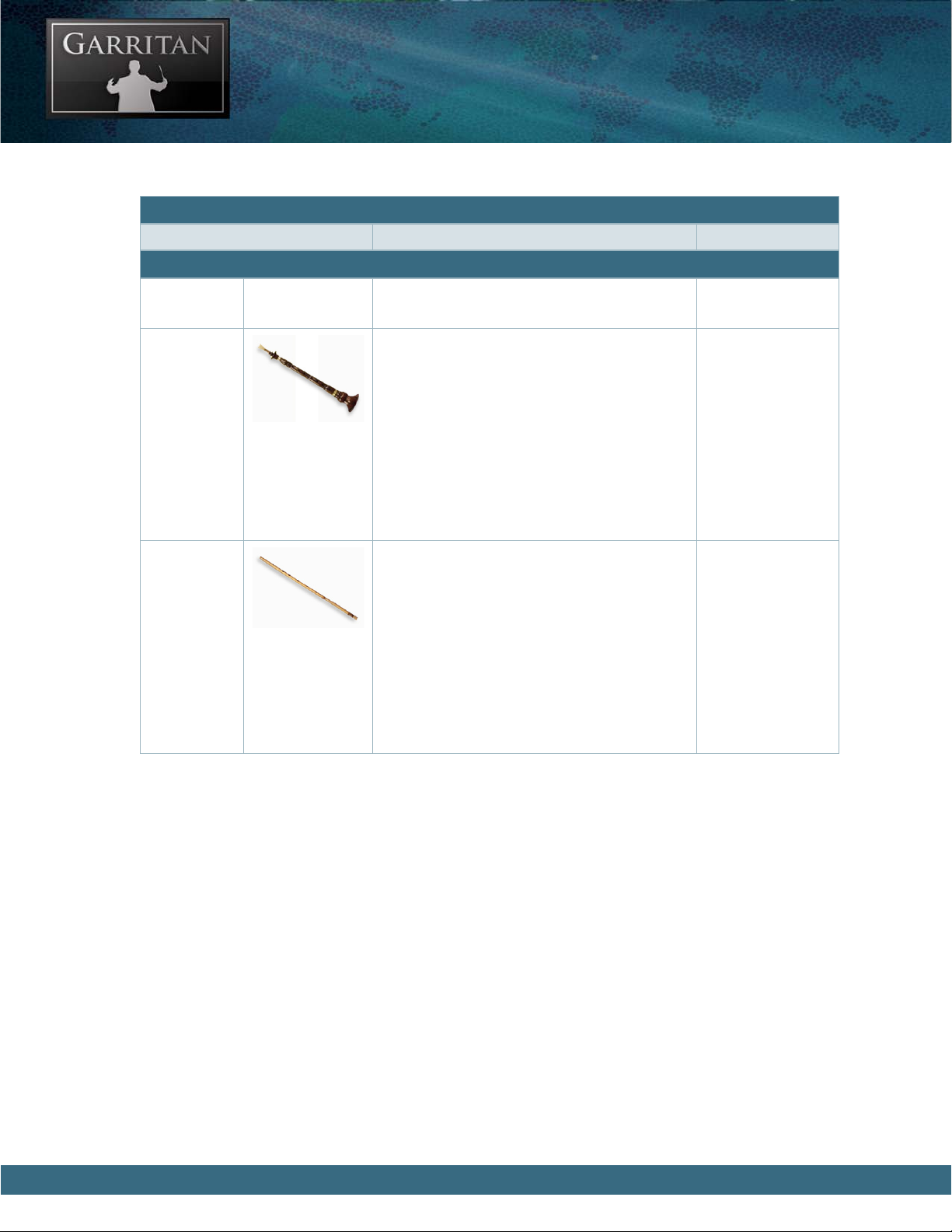
Shenai e Shenai is an Indian reed instrument with
a wooden body and a brass bell. It is mainly
a Northern Indian instrument although there
are Carnatic variants in Southern India. e
instrument commonly has seven to nine finger
holes and is played like an oboe. It is actually
a quadruple-reed instrument that has two upper reeds and two lower reeds. e Shenai is
thought to bring good luck and is often played
at Indian weddings and festivals.
Range: C3- C7
•
Shiva
Whistle
e Shiva Whistle is a small wooden wind
instrument. It has a picture of the Hindu diety
Shiva on it. It differs from the Bansuri in that it
is an end blown instrument and not a sideblown flute.
Range: C5- C8
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 7

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Japan
Hichiriki e Hichiriki is a cylindrical double-reed wind
instrument used in the Gagaku (court) music
of Japan. It is characterized by its nasal timbre.
e instrument has a narrow range but with its
large reed there is great flexibility of pitch and
embellishment techniques.
Range: C4- G6
•
Knotweed
Flute
Shakuhachi
is Knotweed Flute is a small six-holed endblown flute made from the bamboo-like stalks
of the Knotweed.
Range: C4- C8
•
e Shakuhachi is a traditional notched flute
from Japan. e end-blown flute has five
finger holes and a thumb hole. e instrument
is made from the root of the bamboo and is
crafted with precision. Although tuned to a
pentatonic (five note) scale, by using various
fingerings (partial holings) and by controlling
the embouchure, the player can produce great
flexibility in tone and pitch.
Range: C3- C7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 8
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Other Asian Regions
Bamboo
Flute
Jogi Baja
Piri
See Europe: Bamboo Flute
e Jogi Baja is a double-reed instrument from
Nepal played in various ceremonies and rituals.
Players of the instrument often use the technique of circular breathing, which allows the
player to play extended passages.
Range: C3- C7
•
e Piri is a Korean double reed instrument
used in both the folk and court music of Korea.
It is made of bamboo and has seven finger
holes. Its large reed and cylindrical bore give
it a sound mellower than that of many other
types of oboe.
Range: C3- C6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 9

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
End Blown Flutes:
Double Flute e Double Flute originates from Albania.
is flute is distinctive in that it combines
two flute bores, combining a familiar six-hole
shepherd pipe and an overtone flute.
Range: C4- C7
•
Dvojnice
Double Flute
Dvojnice
Double Flute
Drone
Kaval
e Dvojnice (double shepherd pipe) is a
carved wooden double-tube flute from the
Balkans. is traditional instrument has seven
finger holes, three on one pipe and four on
the other, allowing the player to play a harmony at the same time as the melody.
Range: C4- C8
•
is instrument is the second pipe for the
Double Flute above. e player begins a tune
by playing one pipe to state the melody and
the harmony on the drone side is then added.
Range: C4- C8
•
e Kaval is a long end-blown flute from
Bulgaria and the Balkans and is used in folk
music in the region. e Kaval is fully open
at both ends and sound is made by blowing
across the sharpened edge of the mouthpiece.
e instrument has eight playing holes (seven
in front and one in the back) and four extra
holes near the bottom of the instrument.
Range: C4- C7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 10

THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Overtone Flutes:
Bass
Overtone
Flute
Koncovka
Alto Flute
Tenor
Overtone
Flute
Whistles:
Clarke
Pennywhistle
is Overtone Bass Flute, or Bass Fujara, is a
large instrument in the key of G. is contrabass Slovakian instrument can be as large as
five and a half feet long and produces a wide
range of harmonics and overtones.
Range: C3- C6
•
e Koncovka is a Slovakian overtone alto
flute that is traditionally played by shepherds.
is instrument is in the key of D and plays
melodies with no finger holes. Melodies are
created on the Koncovka flute by blocking
(fully or partially) the bottom hole of the flute
with the index finger to create various pitches.
Range: G4- C8
•
e Fujara is a folk shepherd’s flute originating from the Slovakian mountain region. is
Tenor Overtone Flute is often played while
standing. Although it has no finger holes, a
range of a few octaves can be achieved with
the right combination of breath and blocking.
Range: C4 - C7
•
Clarke has been the leading maker of Irish
Pennywhistles for over 150 years. Clarke Pennywhistles are known for their clear distinctive tone quality. Penywhistles come in a
variety of sizes and keys. A skilled player can
make a Pennywhistle sing with ornaments,
trills, flutter tonguing, and effects.
Range: C4 – C8
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 11
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Handmade
Pennywhistle
Low Irish
Whistle
Pennywhistle
in Bb
Pennywhistle
in D
is handmade Pennywhistle is a fine handcrafted six-holed instrument. In recent years,
with the popularity of Titanic and Riverdance,
a number of instrument craftsmen in different countries have started lines of high-end
Pennywhistles made of exotic woods and fine
materials.
Range: C4 – C8
•
e Low Irish Whistle has one of the most
distinctive sounds in Irish music. Its unique
sound has been used in films such as the
haunting Titanic soundtrack and in River-
dance. e Low Whistle is the Low D that is
pitched one octave below the traditional D
whistle.
Range: C3 – C7
•
Pennywhistles originated in Ireland centuries
ago. is pennywhistle is an end-blown flute
tuned in the key of Bb, which is the lowest
note it is capable of playing. e Bb Pennywhistle is one of the most standard Pennywhistle instruments.
Range: F4 - F7
•
e D Pennywhistle is the most popular key
because so much Irish and Celtic music is in
the key of D. Although a diatonic instrument, it is also possible to play chromatically
by half-holing or cross-fingering.
Range: A4 - A7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 12
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Pennywhistle
in G
Sopilka
Whistle
Susato
Pennywhistle
Tin Whistle
in Bb
e G Pennywhistle is rare and not as common as the other keys.
Range: D5 - C8
•
e Sopilka Whistle is a Ukrainian highpitched folk whistle. e instrument is similar
in range to the common piccolo flute. e
sound of the Sopilka depends on the strength
of the player’s blowing into the instrument.
Range: C5 – C8
•
e Susato Pennywhistle is made of sturdy
plastic. Some prefer these whistles not only
for their tone, but also because they are less
affected by changes in temperature or atmosphere than metal-based whistles.
Range: C4 – C8
•
Another version of the Bb Pennywhistle.
Range: F4 - F7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 13
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Recorders:
Alto
Recorder
e Recorder (also known as “flûte à bec” in
France, “blockflöte” in Germany, and “flauto
dolce” in Italy) has a long history in Europe
dating from Medieval times. Recorders are
generally end-blown flutes with seven finger
holes and a range of about two octaves. e
alto instrument is pitched in the key of F and
is also known as the Treble Recorder.
Range: C4- G7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Bass
Recorder
Piccolo
Recorder
e Bass Recorder is the largest and deepest-voiced instrument of the recorder family.
is instrument has a bocal or bent-neck
design to direct the player’s breath to the
main body of the instrument. e instrument
is pitched in the key of F.
Range: C3- C6
•
e Piccolo Recorder, or Garklein, is the
smallest of all the recorders, approximately
six inches in length. ough not used as
frequently as other recorders it often serves to
fill out chords in ensembles. is instrument
is pitched in the key of C.
Range: C5- C8
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 14

THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Sopranino
Recorder
Soprano
Recorder
Tenor
Recorder
Reeds:
Diplica e Alto Natural clarinet, or Diplica, is an
e Sopranino Recorder is the highest voiced
recorder used in a typical recorder family. It is
pitched in the key of F.
Range: F5 – C8
•
e Soprano Recorder is the most common
among learners and is often used in classroom
setting. It is about twelve inches in length
and pitched in the key of C.
Range: G4- G7
•
e Tenor Recorder is known for its soft, melodious sound. It is pitched in the key of C.
Range: G3- G6
•
ancient, clarinet-like instrument from the
Czech Republic, Hungary, and parts of Croatia. is single-reed instrument consists of a
single wood pipe with seven finger holes.
Range: G2 – C5
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 15
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Folk Shawm e Folk Shawm, also known as a Mey, is
an ancient folk instrument that has changed
little over the centuries. is double-reed
instrument is made from cherry wood and
has seven finger holes.
Range: C3 – C5
•
Chanters & Bagpipes:
Bagpipes have a long history throughout Europe and are part of the musical traditions of many countries.
e instrument consists of a single- or double-reed instrument that uses a bag (traditionally made from
animal skin) to retain and blow air to vibrate reeds. e bag is pressed with the arm to send air to a reed
pipe with finger holes called the chanter, which produces the melody notes. Some bagpipes can also
produce a drone that accompanies the melody, but unlike the familiar Scottish bagpipes, many European
bagpies are droneless.
Catalan
Bagpipes
Duda
Bagpipes
e Catalan bagpipes have a different character and the widest range, approximately three
octaves. ere are several names for the Catalan
bagpipes: coixinera, caterineta, borrega, manxa
borrega, mossa verda, ploranera, Sac de les
Aspres, and Sac de Gemecs (which means “bag
of moans”).
Drone Range: C2- B2
•
Melodic Range: C3- C6
•
e Duda is popular throughout Eastern
Europe. e chanter of the Duda has a
double reed similar to an oboe, and a conical
bore with seven finger-holes. is chanter is
relatively high pitched and has a range of approximately two octaves.
•
Drone Range: C2- B2
•
Melodic Range: C4- C6
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 16

THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Gaita
Bagpipes
Koza
Bagpipes
Scottish
Highland
Bagpipes
Uilleann
Pipes
e Gaita, which means “bagpipe,” is a traditional bagpipe used in Spain and Portugal.
e Gaita has become popular in recent years
in pipe bands. e Gaita chanter has a range
of approximately three octaves.
•
Drone Range: C2- B2
•
Melodic Range: C4- C7
e Koza is a Polish bagpipe that consists of
a large goatskin bag and a single reed chanter.
e chanter has a range of approximately two
octaves.
•
Drone Range: C2- B2
•
Melodic Range: C3- C5
Scottish Highland Bagpipes, or the Great
Highland Bagpipes, are the most recognized of
the bagpipes and represent the national instrument of Scotland. Scottish Bagpipes are commonly used in formal ceremonies throughout
the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth
Nations.
Drone Range: C2- B2
•
Melodic Range: C3- E5
•
e Uilleann Pipes are the national bagpipe
of Ireland. ey are distinguished from other
bagpipes as air is not blown with the mouth
but rather air is pumped into the bag by
means of a bellows attached to the player’s
elbow. e instrument is known for its sweet
tone and wide range of expression. e instrument has been more recently popularized
years in Riverdance.
Melodic Range: G3-G6 (drone C2-B2)•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 17
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Side Blown Flutes:
Bamboo
Flute
Bone Flute 1
Bone Flute 2
Irish Flute
is small instrument is a simple Bamboo
Flute with six holes and is in the key of F.
ere are a variety of small bamboo flutes
from many cultures.
Range: C4 - C8
•
A Bone Flute unearthed in Slovenia is reported to be the oldest handcrafted musical
instrument. is six-hole Bone Flute is also
from Slovenia and is carved from the thighbone of a turkey.
Range: C5 - C7
•
Another Bone Flute from Slovenia. is
instrument has seven finger holes.
Range: C5 – C8
•
e Irish Flute is a popular side-blown flute
used in traditional Irish music. e basic
instrument is a simple wooden flute with
six open holes and tuned in the key of D, a
widely used key for Irish music.
Range: C3 - C7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 18
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Europe
Shepherds
Folk Pipe 1
Shepherds
Folk Pipe 2
e Shepherds Folk Pipe, or Soprano Folk
Pipe, is a six-hole end-blown flute in the key
of D. e Shepherd’s Pipe is played by Slovak
shepherds to accompany them while herding
their sheep.
Range: G4 - G7
•
A tenor version of the Soprano Shepherd’s
Folk Pipe. is flute is a six-hole end-blown
folk flute and plays an octave lower than the
Shepherds Folk Pipe 1
Range: G3 – G6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 19
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Latin America
Andean
Panpipes
Ocarina 1
Ocarina 2
e Andean Panpipes (or panflutes) is a popular folk instrument in the Andes mountains
region of South America. e instrument consists of two rows of bamboo pipes of gradually
increasing length, joined together in a bundle
and giving the alternate notes of the scale. Each
pipe is tuned to a certain note depending on
its length. Panpipes produce their distinctive
breathy sound when the player blows horizontally across the open end of the pipes. Panpipes
are also known as Zampoñas.
Range: C4 – C7
•
e Ocarina is a simple wind instrument having a hollow oval body with finger holes. Sound
is produced by covering various holes with the
fingers and by blowing through the sound hole.
e tone can also be varied by how hard the
player blows into the instrument. e Ocarina
is believed to have originated from Mesoamerica with the Mayan and the Aztecs.
Range: G4 – C7x
Another Ocarina instrument with a different
timbre and character.
Range: G4 – C7
x
Vel (attack),
MW (vol/eq),
Porta, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, Keyswitches
Vel (attack),
MW (vol/eq),
Porta, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack),
MW (vol/eq),
Porta, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 20
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Latin America
Peruvian
Panpipes
Quena
Ta r ka
Panpipes have long been a part of the culture of
Peru and other Andean regions. is Panpipe
instrument has a different range and character
than the traditional Andean panpipes. It is
played by Peruvian folk musicians of the Andes
mountains. Also known as Siku.
Range: C5- C8
•
e Quena is an end-blown Shepherd’s flute
originating in the Andean region of South
America prior to the Spanish conquest. e
instrument is made from carved bamboo cane
with a U-shaped mouthpiece and has six finger
holes in front and one in the back. It is also
known as a Kena.
Range: C4 - C7
•
e Tarka is a unique rectangular flute that
originates from the Andes Mountain highlands.
It is made from wood, carved with traditional
designs, and hand painted in rich colors. e
instrument has six finger holes and a whistletype mouthpiece.
Range: C4 - G6
•
Vel (attack),
MW (vol/eq),
Porta, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, Keyswitches
Vel (attack),
MW (vol/eq),
Porta, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack),
MW (vol/eq),
Porta, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 21
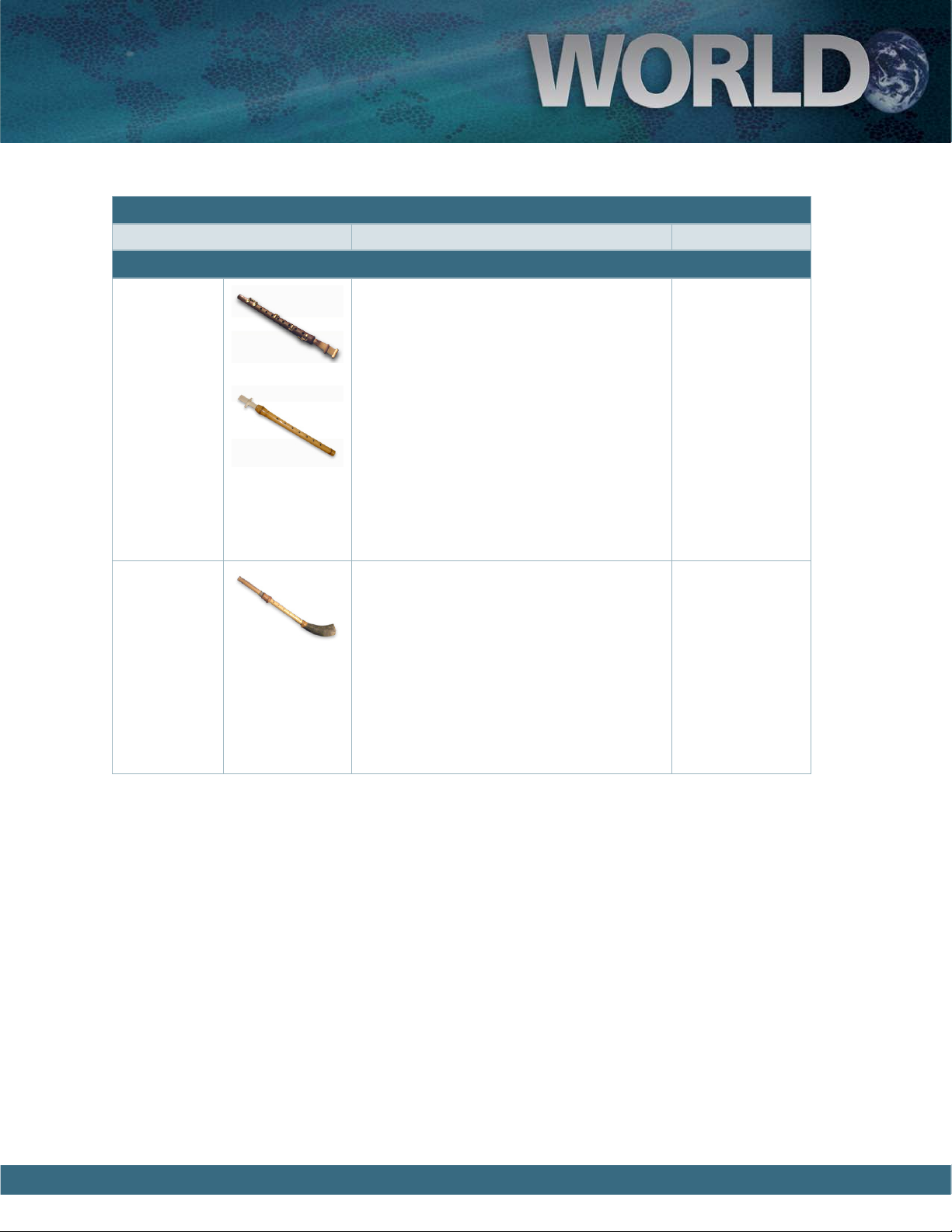
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Middle East
Duduk e Duduk is known for its hauntingly beauti-
ful and expressive tone. is instrument has
a small body with a large double reed and is
capable of sustaining drone notes for long
periods of time. Originally from Armenia,
the Duduk can be found throughout Turkey,
Persia, and surrounding areas. e instrument
has not changed through the centuries and has
become popular in recent years. It is featured
in such films as Gladiator and e Lion, the
Witch and the Wardrobe.
Range: G2 - G5
•
Maqrunah
e Maqrunah is a reed instrument from Tunisia and Libya and often played by shepherds.
A unique characteristic is its horn bell at one
end. Although the Maqrunah has a limited
melodic range, it produces a distinctly ornate
and breathy tone.
Range: C4 – C6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 22
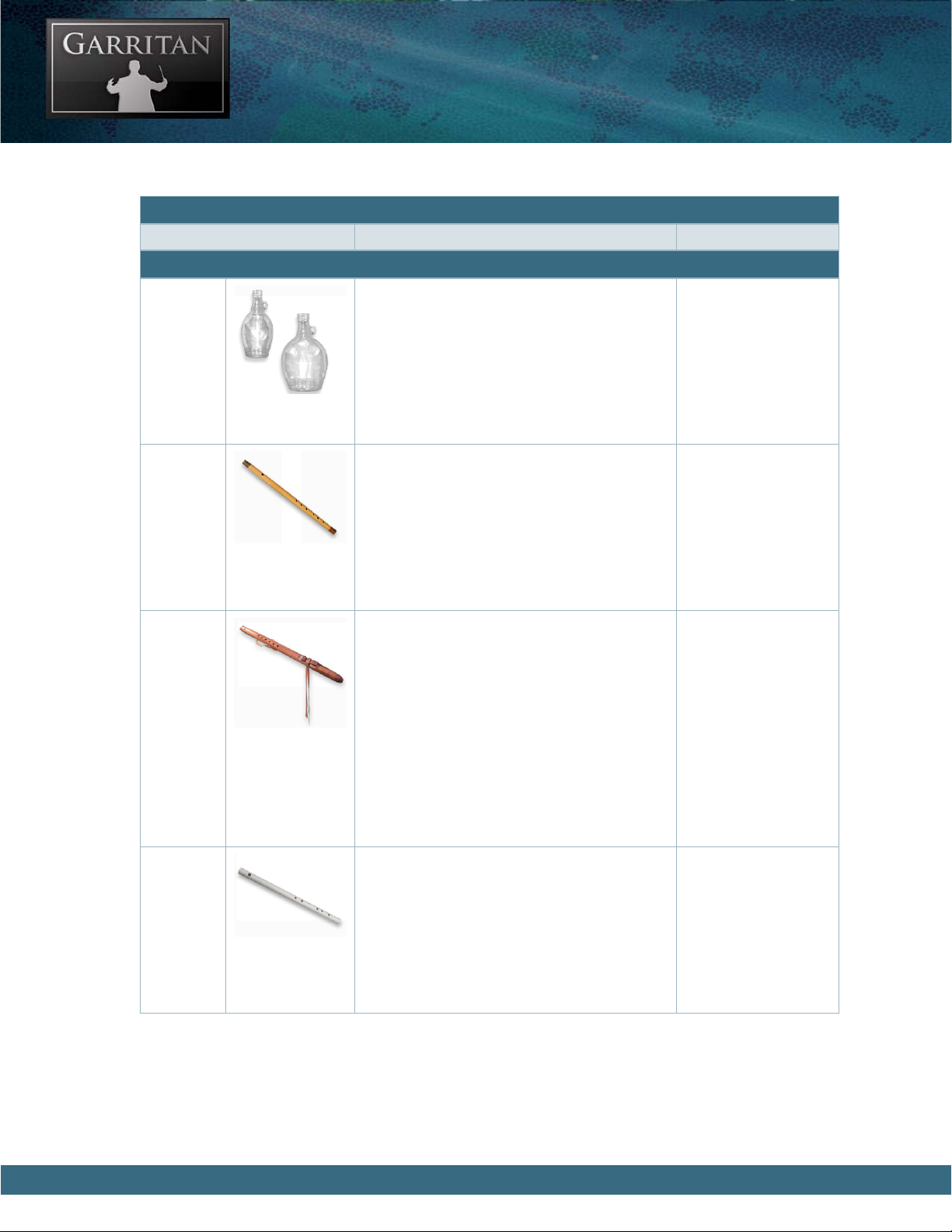
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
North America
Bottle
Blows
Fife
Native
American
Flute
PVC
Flute
e Bottle Blows consist of different size
bottles and jugs of different materials. Sound
is produced by the player holding the mouth
of the bottle or jug near his or her mouth and
blowing across the top. ese instruments are
common in jug bands.
Range: C2 - G4
•
e Fife is a small, high-pitched, transverse
flute used in Appalachian folk music. It is a
simple instrument usually consisting of a tube
with six finger holes and diatonic tuning. e
Fife is similar to a piccolo, but can be louder
and shriller due to its narrower bore.
Range: C4 – C8
•
e design of the Native American Flute is
significantly different than the construction
of flutes from anywhere else in the world. It
has five or six finger holes on the bottom and
is typically made with two air chambers. e
Native American flute has achieved some
measure of fame for its distinctive sound, and
is used in a variety of films, documentaries, and
world music recordings.
Range: C3 – C7
•
e Plumber’s Pipe is a simple flute made from
inexpensive plastic PVC plumbing pipe. Plastic
plumbing pipe is considered ideal for simple
flutes since it is easy to work with, waterproof,
nearly unbreakable, and sounds remarkably
good.
Range: C4 – G6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, Fluttr,
Auto-Legato, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, Fluttr,
Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, Fluttr,
Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, Fluttr,
Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 23
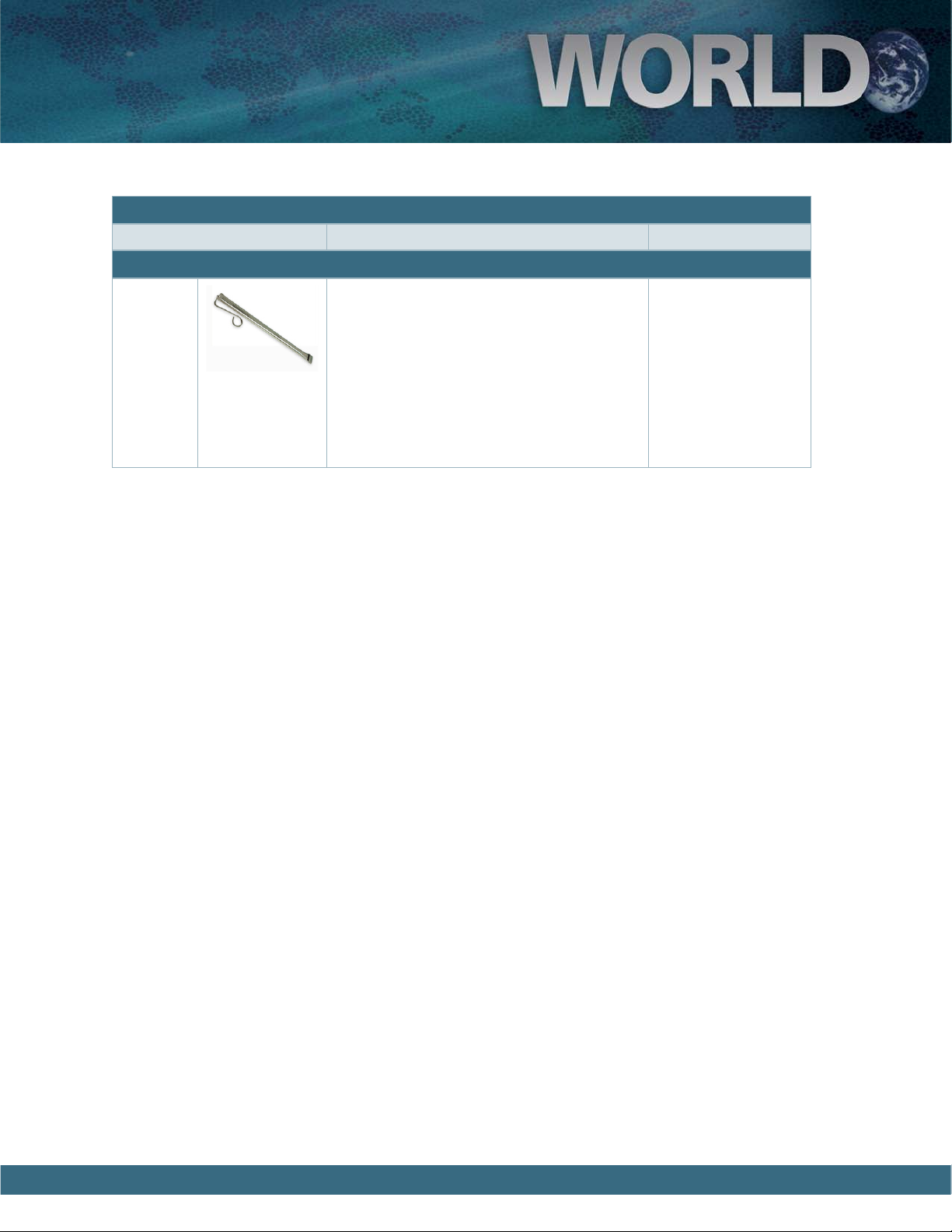
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
North America
Slide
Whistle
e Slide Whistle, also known as a Swanee
Whistle, is a wind instrument consisting of a
tube with a slide piston in it. Moving the slide
varies the pitch. e slide whistle is commonly
used as a sound effect (in animated cartoons or
in comedy soundtracks). It is possible to play
serious melodies on the slide whistle.
Range: G3 – G7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, Vib
Amt, AirNs, Fluttr,
Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 24
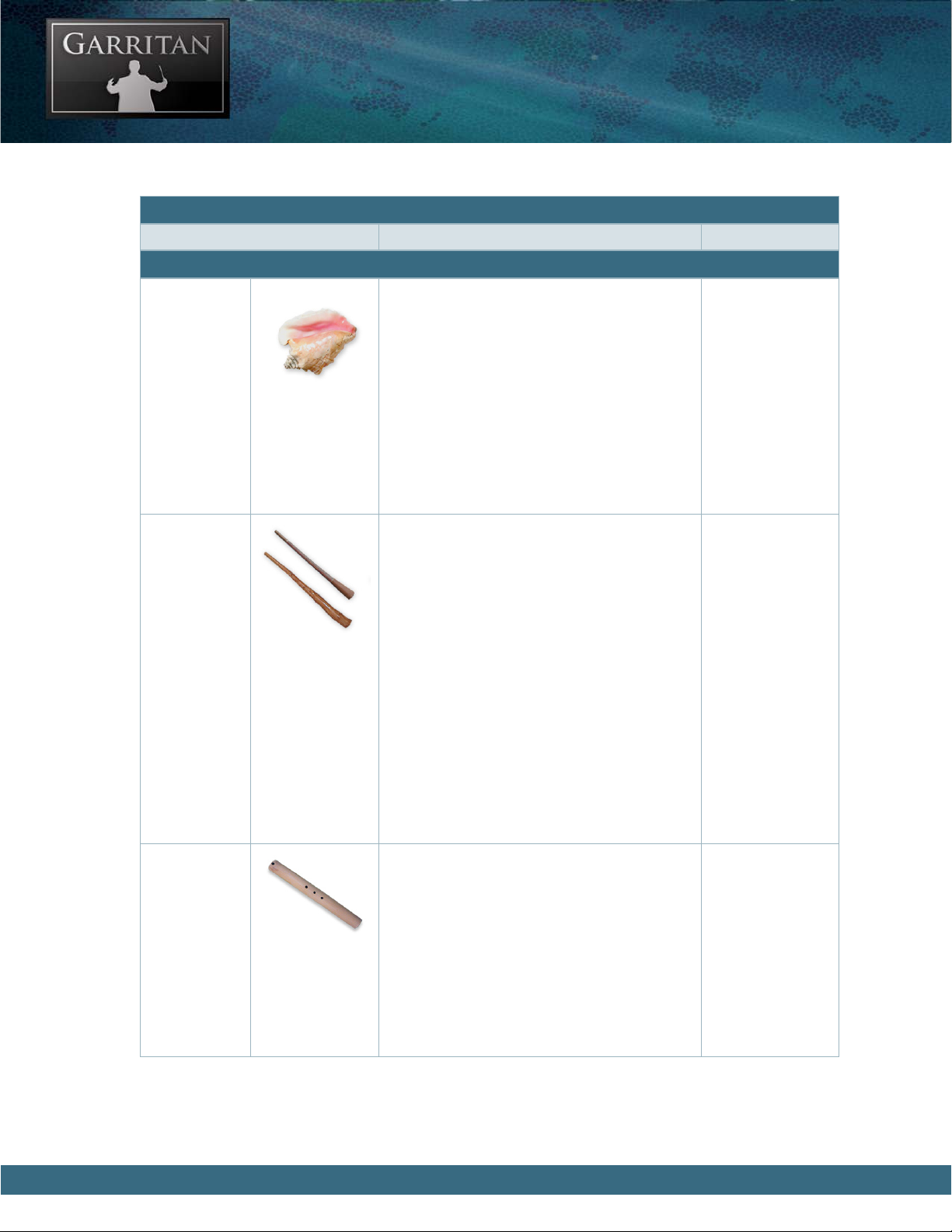
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Oceania
Conch Shell e Conch Shell, or shell trumpet, is a wind
instrument made from a seashell. A hole is
carved in the end of the shell and the player
blows into the instrument like a trumpet. Polynesian Conch Shell trumpets were historically
used throughout the South Pacific. In some
Polynesian islands it is known as the Putatara
to the Maori. is instrument was featured in
the score for the film Alien.
Range: C3 - E4
•
Didgeridoo
Hawaiian
Nose Flute
e Didgeridoo is a wind instrument developed by indigenous Australians and is now
popular throughout the world. e didgeridoo
is traditionally made from hollowing out a
eucalyptus tree, but modern instruments are
made from a variety of woods, PVC, and other
materials. It is played by holding the end to
the mouth and vibrating the lips to produce
a drone sound while using a special circular
breathing technique. e sound can be varied
by imparting vocalizations. e Didgeridoo
is used by indigenous Australians to bring the
listener into a dream state.
Range: C3 – C6
•
e Hawaiian Nose Flute, or Ohe Hano Ihu,
is a bamboo flute that is played with the breath
from the nose rather than the mouth. Although capable of only one octave, it produces
a beautiful tone. Like other nose flutes in various cultures, it was traditionally used between
lovers.
Range: G4 – C7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 25

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE WIND INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description: Controls:
Oceania
Suling 1 e Suling is a four-holed bamboo flute used
in Balinese Gamelan orchestras. A notch is cut
into the side of the top end and encircled with
a thin band made of rattan, leaving a small slit
into which the player will blow. e Suling
provides one of the most expressive sounds in
the Gamelan ensemble.
Range: G3 – C7
•
Suling 2
Suling 3
A different Suling instrument with a different
range and character.
Range: C4 – C7
•
Another Suling instrument of a different size
and type.
Range: C4 – C8
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, Auto-Legato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 26

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Adodo e Adodo is a cluster of small bells shaped
like a dumbbell with three bells on either end.
It is played by holding the center handle while
striking the bells with a stick. is instrument
originates from Ghana and is also known as a
Flower Bell.
C2-F2 – single hits
•
African Log
Drum
Apentima
Ashiko
Balafon
e Log Drum is common throughout Africa.
It is made by hollowing out a log and carving
out slit openings for the sound to resonate. e
Log Drums are usually played with wood sticks.
e instrument is known by many names and is
found in a variety of sizes.
C2-F2 – single hits
•
F#2-G2 – rolls
•
e Apentima is a single-headed carved drum
made from Tenebrous wood, a hard wood believed to have spiritual powers. e Apentima is
played by the Ashanti people of Ghana.
C2-A2 – various hits
•
e Ashiko is a large conical drum designed to
be played with bare hands. It is found throughout sub-Saharan Africa and West Africa. Some
tribes consider the Ashiko to be male and the
Djembe female.
C2-B3 – various hand hits
•
e Balafon (or Balaphon) is a mallet instrument of West Africa consisting of wooden bars
laid out like a xylophone. e player strikes the
bars using mallets.
Range is C3 – C7
•
Controller Assignments:
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 27

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Basic African
Percussion
Bougarabou e Bougarabou is a single-headed drum cov-
Dawuro
e Basic African Percussion set includes a select
combination of African percussion instruments.
C2-C#2 – African Log
•
Drum
D2-D#2 – Apentima
•
E2-F#2 – Ashiko
•
G2-A2 – Bourarabou
•
A#2-C3 – Djembe
•
C#3-D#3 – Dondo
•
E3-F3 – Doun Doun
•
Ba
F#3-G3 – Kagan
•
G#3-A3 – Kpanlogo 1
•
A#3-B3 – Kpanlogo 2
•
C4-C#4 – Kpanlogo 3
•
D4-D#4 –
•
Fontomfrom
E4-F#4 – Ibo
•
ered with cow skin over an elongated gobletshaped drum. It is often placed on a single
stand or played in sets of three or four. e
drum is also known as Boucarabou and originates in Senegal.
C2-A4 – various hits
•
e Dawuro is a banana-shaped metal bell with
a slit along its upper surface. It is played by musicians in Ghana and surrounding regions. e
Ewe name is Toke.
C2-G2 – various hits
•
G4-A4 – Kenkeni
•
A#4-C5 – Krin Slit
•
Drum
C#5-D#5 – Morocco
•
Drum
E5-F#5 – Sakara
•
G5-A5 – Sangban
•
A#5-C6 – Tama
•
C#6-G6 – Sistrum
•
G#6-B6 – Televi
•
B6-D7 – Tonetang
•
Stir Drum
D#7-F7 – Adodo
•
F#7-G#7 – Dawuro
•
A7-A#7 – Atoke
•
B7-C8 – Axatse
•
Controller Assignments:
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 28

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Controller Assignments:
Djembe e Djembe is a popular hand drum from West
Africa and literally means “everyone gather
together”. e instrument is shaped like a large
goblet with skin covering the large end. It is
played with bare hands. ere are three main
notes in the Djembe: bass tone (the lowest),
medium tone (a round, full sound), and slap (a
high, sharp sound).
C2-G2 – various hits with flat hand,
•
palm, edge, slap and mute.
Dondo
Doun Doun
Ba
A Dondo is a double-headed wooden “talking”
drum with lacings connecting the two heads.
e player hits the heads while squeezing the
lacings, thus creating variations in pitch in
which the drum seems to “talk”.
C2-D7 – various hits and pitch variations
•
e Doun Doun Ba is the largest of the doun
doun set of West Africa bass drums. e other
drums in the dun dun set are Kenkeni and
Sangban. e instrument consists of a doubleheaded cylindrical drum with cowskin heads
on each end. It is known by various names
throughout West Africa such as Dun-Dun,
Dunun, and Junjun.
C2-D3 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 29

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Controller Assignments:
Africa
Ewe Drums
Ewe drums refer to a collection of percussion instruments played by the Ewe people of Ghana, Benin, and
Togo. Ewe drum ensembles typically consist of drums, bells, and rattles. e drums in a Ewe ensemble
come in several different sizes and typically have wooden conical bodies and are covered with animal skin.
e Ewe peoples use these instruments for drum dialoging to mimic the tone of spoken language.
Atoke e Atoke is a small banana-shaped metal bell from Ghana.
It is made from forged iron and produces a bell-like tone
when struck with its iron rod beater. It is held in the palm of a
player’s hand while being hit with the rod in the other hand.
C2 – D3 – various hits
•
Axatse
Gankokwe
Kagan
Kpanlogo 1 Large
e Axatse, from Ghana, is a gourd shaker covered with a net
of small hard objects such as beads or seeds. e dry rattling
sound of the Axatse is produced by striking it lightly on the
thigh and the palm. It is also called Chekere.
C2 – C3 – various rattles and shakes
•
e Gankokwe is a hand-forged iron bell-like instrument
played with a wooden stick. Some Ewe ensembles include two
Gankokwe, one larger than the other. Two different Gankokwe are included in this patch.
C2 – E3 and A3-B3– various hits on the various bells, open and
•
clasped.
e Kagan is part of a traditional Ewe drum ensemble. It is
constructed of a solid carved piece of wood and is approximately twenty inches tall with a head five to six inches in
diameter.
C2 – G2 – various hits and slaps
•
e Kpanlogo is a deep-sounding conga-shaped drum from
Ghana. It is headed with antelope skin and tuned by hammering in pegs. e Kpanlogo is used in rituals and to summon
the town.
i C2 – F2 – various hits and slaps
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
BDFund, Keyswitches
Page 30

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Controller Assignments:
Kpanlogo 2
Medium
Kpanlogo 3
Combo
Sogo
Fontomfrom
Gome
A different Kpanlogo instrument that is smaller in size.
C2 – F2 – various hits and slaps
•
Another Kpanlogo instrument combining different drums.
C2 – C4 – various hits on a different Kpanlogo.
•
e Sogo is part of the Ewe drum ensemble and represents
one of the master drums played by the leader of the group.
e Sogo can be played either with two wooden sticks, one
hand and one stick, or both hands.
C2 – C3 – various hits
•
e Fontomfrom is a tribal drum from the
Ashanti regions of Ghana. e drums are carved
from a tree trunk and skins are stretched over
the tops and fastened with long pegs.
C2-A2 – various hits
•
e Gome is a box-like drum from Ghana
made with goatskin stretched over a wooden
box frame. e drummer sits atop the box and
plays this drum with both his hands. e heels
of the feet also press against the skin to change
the pitch.
C2-C3 – various hits and pitch bends
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 31

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Controller Assignments:
Gyil e Gyil is a pentatonic mallet instrument
from Ghana. It is made of 14 hardwood keys,
called liga, mounted on a wooden frame. Below
it are hanging gourds and spider web silk that
produce a resonating sound.
Range: G3–C7
•
Ibo
Kalimbas
Kenkeni
Kpoko
Kpoko
Krin Slit
Drum
e Ibo is a “pot drum” from the Ibo and
Hausa tribes of Nigeria. Ibo is the Nigerian
name for pottery.
C2-C3 – various hits
•
e Kalimba, also called a thumb piano, is an
ancient instrument from Africa. Kalimbas are
made of small springy metal strips attached to
a sounding box made of either gourd or wood.
Kalimbas come in many shapes and sizes.
Range: C2–C6
•
e Kenkeni is a mid-sized West African drum
with double animal skin heads. It the smallest
drum in the Doun Doun set of bass drums.
C2-D3 – various hits
•
e Kpoko Kpoko is a double-ended rattle
instrument from the Ibo tribe of Nigeria. It
produces a unique wood rattling sound.
C2-A2 – various rattles
•
e Krin is a slit drum made from a piece
of hollowed tree trunk with slots of different
lengths and is played with a stick. e instrument is originally from the forest regions of
Guinea and is used to transmit messages between villages. Also known as Kolokolos.
C2-G4 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 32

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Controller Assignments:
Likembe e Likembe is a kalimba-like instrument from
Uganda, the Congo, and Zaire. Also known as
a Kisani, this instrument is common throughout the African continent.
C2-A2 – various plucks
•
Mbira
Morocco
Drum
Nigerian Log
Drum
Sakara
e Mbira is a thumb piano from Zimbabwe
that is similar to the kalimba and likembe. It
is considered a sacred instrument in various
African cultures and is used to communicate
with ancestors, ward off harmful spirits, and
cure illness.
Range is C2–C8
•
e Morocco drums are a pair of ceramic drums
with heads consisting of cow hide. ey are similar to a bongo drum except that they are closed
on the bottom.
C2-E3 – various hits•
Nigerian Log Drums, also known as Obrom,
are hand-carved from a solid log. ey are
made from cutting slits in the side of the log
and hollowing it out through the slit. Log
Drums are used to communicate between villages. Under the right conditions, the sound can
be heard miles away.
C2-F3 – various hits
•
e Sakara, originating from the Yoruba region
of Nigeria, is a frame drum instrument whose
circular body is made of baked clay covered
with goatskin. Pegs around the body of the
instrument are used for tuning.
C2-G2 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 33

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Controller Assignments:
Sangban e Sangban is a mid-sized drum in a Doun
Doun set of West African bass drums. e
drum is carved out of a single piece of wood
and both ends are covered with cowskin heads.
C2-E3 – various hits
•
Sanza
Sistrum
Tama
(Talking
Drum)
e Sanza is a thumb piano from Zaire with
resonators (rattles of various kinds). It is played
by depressing and releasing the tongues with the
thumbs and fingers.
C2-C5 – various hits with rattles
•
e Sistrum is a small wooden instrument from
Egypt and other regions of Africa. It consists of
a U-shaped metal frame which, when shaken,
produces a jingling sound.
C2-A5 – various shakes and jingles.
•
e Tama, or Talking Drum, is an hourglassshaped double-headed drum from Nigeria.
C2-C3 – various hits and rolls.
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Televi
Tonetang
(Stir Drum)
e Televi is a small rattle from Ghana consisting of two small gourds filled with seeds and
attached to either end of a string. Also known as
an Asalato.
C2-A3 - various hits and rattles
•
e Tonetang Stir Drum is a small octagonal
wooden bowl-like instrument played with a
wooden beater.
C2-B2 - various hits and stirs
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 34

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Africa
Controller Assignments:
Udu Drums Udu means “vessel” and the instrument con-
sists of a jug made of clay. It is played with the
fingers and the holes are cupped alternately,
making sound by compressing and releasing the
air inside it, producing a unique and unusual
sound. e Udu drum originates from the Ibo
and Hausa peoples of Nigeria.
C2 – Hole Pop
•
C#2 – Hole Pop Release
•
D2 – Hole Pop Rel Mute
•
D#2 – Low Fast Release
•
E2 – Low Hole Pop
•
F2 – Low Hole Pop-Rel
•
F#2 – Low Open
•
G2 – Low Slow Release
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 35

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
China
Controller Assignments:
Basic
Chinese
Percussion
Bianzhong
Bo
Chinese
Cymbals
e Basic Chinese Percussion set includes a set
of Chinese percussion instruments.
C2-G#2 – Datangu Lion Drum
•
A2-G3 – Temple Blocks
•
G#3-C#4 – Bianzhong
•
D4-E4 – Bo
•
F4-A#4 – Chinese Cymbals
•
B4-F#5 – Temple Bells
•
G5-C6 – Chinese Gongs
•
e Bianzhong is an ancient Chinese instrument
consisting of a large rack of bronze bells, played
melodically using poles.
Range is C2–B2
•
Bo are Chinese cymbal instruments often used
in Sichuan Opera to accent the movement of the
actors. Bo are made of bronze and are played by
striking the cymbals together.
C2 – D2 – different hits
•
e Chinese cymbals in this collection consist
of an assortment of cymbals played with various
mallets and sticks.
C2 – B3 – different hits in different cymbals
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Chinese
Gongs
Datangu
Lion Drum
Gongs belong to the oldest and most important
musical instruments of China and much of Asia.
e Chinese gongs in this collection consist
of an assortment of traditional Chinese gongs
played with various mallets and sticks.
C2 – D4 – different hits in different gongs
•
e Datangu is a large bass drum used to accompany traditional Chinese Lion Dancing. e
Datangu is played with two sticks in a low stance
with the knees bent.
C2 – G#2 – different hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Page 36

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
China
Controller Assignments:
Pan
Clappers
Temple
Bells
Temple
Blocks
Pan Clappers are a Chinese rhythm instrument
played by striking both clappers together. e
instrument is also known as Pi Pan Clappers or
Shooing Pan Clappers.
C2 – E2 – different hits
•
Temple Bells are often a symbol of peace and
good luck in Chinese traditions. e Temple
Bells in this collection consist of an assortment
of bells played with various beaters.
C2 – C3 – different hits on different bells
•
with varying ringing.
Temple blocks are hollow carved wooden instruments played using rubber or wooden mallets.
ey are common throughout China and are
used for religious ceremonies.
C2 – F5 – different hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 37

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
India
Basic Indian
Percussion
Chenda e Chenda is a hollow cylindrical Indian
Chimta
Chippli
is Basic Indian Percussion set includes a set
of Indian percussion instruments.
C2-D2 – Chenda
•
D#2-C3 – Damroo
•
C#3-D3 – Dhol
•
D#3-C#4 – Dholak
•
D4-G4 – Kanjeera
•
G#4-A#4 – Naal
•
B4-C5 – Nagara
•
C#5-E5 – Tabla
•
F5-G5 – Tamte
•
drum with ends covered with cow hide. It is
played upright and struck with two slender
sticks. e Chendra is often used as accompaniment in Hindu dance.
C2 – A3 – different hits
•
e Chimta (literally tongs) consists of a long
folded steel strip with small metal jingles. ere
are several Chimtas presented in this collection.
is instrument is a traditional percussion
instrument used in popular Punjabi music.
C2 – C7 – hits and shakes from different
•
Chimtas
e Chippli consist of a pair of small handheld wood instruments each with a jingle. e
instrument is also known as a Kattai.
C2 – F#2 – different hits and jingles
•
Controller Assignments:
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Dafli
e Dafli is an Indian tambourine consisting
of a circular wooden or metal ring with a skin
drum head. It is often used in weddings and
other celebrations and is also known as Dufli
or Daf.
C2 – F2 – different hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 38

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
India
Controller Assignments:
Damroo
Dhol
Dholak
Ghatam
Ghungroo
e Damroo, or Damru, is a two-sided drum
with an hour-glass shape. e instrument is also
known as the “monkey talking drum.” ere are
two different Damroos in this collection.
C2 – D#4 – Damroo 1—different hits,
•
flams and rolls
C5 – G#5 – Damroo 2—different hits
•
and boings
e Dhol is a large double barrel-shaped drum
played with sticks. It is a loud instrument and
often used in weddings in the Indian subcontinent and is now used in Indian pop music. It is
also known as a Dohol.
C2 – D4 – different hits and slaps
•
e Dholak is popular folk drum played in
North India, Pakistan, and Nepal. e instrument is made of hollowed out wood and has
two tunable heads.
C2 – G4 – different hits and slaps on
•
different parts of the head and drum
e Ghatam is a clay goblet drum used in
South Indian classical music. It is played with
the fingers and sometimes with metal rings on
the fingers. Similar to the African Udu drum
and also known as a Matka.
C2 – B3 – different hits and pops
•
e Ghungroo, or Indian Ankle Bells, consists
of a cluster of small bells worn around the
ankles of classical dancers to accent rhythmic
movements. e pitch of the sounds produced
depends on the size and composition of the
bells.
C2 – E3 – different hits
•
C4 – F#4 – sustained shakes
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 39

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
India
Controller Assignments:
Gong
(Singing
Gong)
Hatheli
Kanjeera
Khartal
Khol
is small Gong from India, also known as a
Singing Gong, is common in Hindu religious
ceremonies. e instrument is played by hitting
with a stick or stirring the surface with a stick.
C2 – F#2 – different hits and stirs
•
Hatheli are wooden hand-held jingles. ey
produce sound by shaking the instrument.
C2 – A#4 – Hatheli set 1 - different hits,
•
jingles, and rattles
e Kanjeera is a small tambourine-like instrument with copper or bronze discs in its frame.
It is held with one hand and struck with fingers
and palm of the other hand.
C2 – D#4 – various hits
•
e Khartal is a small percussion instrument of
India consisting of a block of hard wood with
jingles. Khartals are shaken to produce their
sound. ey can also be clapped together to
make rhythmic beats.
C2 – A2 – Khartal set 1 -various hits &
•
jingles
C3 – G3 – Khartal set 2 -various hits &
•
jingles
e Khol is a double-sided drum covered with
goatskin leather and laced together with leather
straps around the circumference of the drum.
C2 – A3 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 40

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
India
Controller Assignments:
Manjeera Manjeera are small unpitched cymbals used
in folk and devotional music. ey are usually made of bronze, brass, or copper and are
held and played with the hands. ey are also
known as Manjira or Jhanji.
C2 – C3 –Manjeera 1 - various hits
•
C4 – A4 – Manjeera 2 -various hits
•
Murchang
Mridangam
Naal
Nagara
e Murchang is a mouth instrument that is
very similar to a Jaw harp. It is used in the
Carnatic music of South India and Pakistan
and is also known as the Morsing.”
C2 – G#5 – various hit
•
e Mridangam is a double-sided oblong
drum. Its body is made of hollowed jackfruit
wood and both ends of the drum are covered
by animal skin laced with leather straps. e
Mridangam is often used in South Indian
dance.
C2 – G5 – various hits
•
e Naal is an Indian folk drum with a highpitched head on one side and a lower-pitched
head on the other side. e instrument is also
known as a Dholki.
C2 – C4 – various hits and slaps
•
e Nagara is a kettle drum played in traditional Indian ensembles. ese drums are
about one to two feet in diameter and played
with sticks.
C2 – C3 – various head hits and rim hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 41

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
India
Controller Assignments:
Pakhawaj
Stir Drum
Tablas
e Pakhawaj is a double-sided barrel drum
used in traditional classical music of North
India. e instrument is played horizontally set
on a cushion in front of a crossed-leg player.
e larger bass skin is played with the one hand
and the smaller treble skin by the other hand.
It is similar to the Mridangam of South India.
C2 – C3 – various hits and slaps•
e Stir Drum is a small percussion instrument
consisting of graduated tongues of wood. It is
played by using a beater in a circular motion
around the inner sides of the instrument.
C2 – D3 – various hits
•
Tablas are the most popular percussion instrument of India. e set includes two drums.
e tabla dayan (right hand drum) is made of
wood and the bayan (left hand drum) is a medium-low pitched kettledrum made of metal.
Both drums have heads made of goatskin.
C2 - Tabla na C#2 - Tabla thin
D2 - Tabla ti D#2 - Tabla ra
E2 - Tabla ta F2 - Tabla tun
F#2 - Tabla traka G2 - Tabla traka
G#2 - Tabla ga A2 - Tabla ka
A#2 - Tabla dha B2 - Tabla Dhin
C3 - Tabla ka C#3 - Tabla hits dha
D3 - Tabla hits dhin D#3 - Tabla hits ta
E3 - Tabla hits tin F3 - Tabla misc ti
F#3 - Tabla misc ra G3 - Tabla misc ka
G#3 - Tabla misc ta A3 - Tabla misc ga
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Tamte e Tamte is a flat circular drum with a skin
pulled over it and played with a stick. e
Tamte is also called Tammatai and is played
throughout North India.
C2 – F3 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 42

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
India
Controller Assignments:
Tasha e Tasha is a small kettle drum that is played
with the hand or with bamboo beaters. e
Tasha is used in ceremonial occasions in India.
C2 – G3 – various hits
•
Tavil
Udaku
e Tavil is a round-bodied drum with two
skins wrapped around two large hemp hoops
on both sides. One side is usually played with
a stick while the other side is played with the
hands or with metal thimbles on the fingers
is instrument is played often in South Indian
festivals.
C2 – F4 – various hits with stick and hand
•
e Udaku is a small drum with heads held in
position by interlacing cotton threads that can
be pulled to change the pitch. e instrument
is also known as the Udukke.
C2 – D4 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 43

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Japan
Japanese percussion is generally known as Taiko which means “big drum.” Taiko includes
a variety of percussion instruments. Taiko drums come in different sizes and some can be
as large as six feet (two meters) long.
Chanchiki
Chu-daiko
Daibyoshi
Hira-daiko
Hyoushigi
e Chanchiki is a saucer-shaped bell, suspended by a cord like a gong, and played with
a mallet. e instrument is also known as the
Atarigane.
C2-B2 – various hits
•
e Chu-daiko is a medium-sized drum that is
popular in the Taiko ensemble. e Chu-daiko
comes in various sizes. In this collection there
are several Chu-daiko (18”, 21”, and 22”).
C2 – E2 – various combo hits
•
C3 – A4 – various hits
•
C5 – D#6 – various rim hits
•
C7 – F7 – various hits
•
e Daibyoshi is a short-bodied tunable drum
made with stave construction. e Daibyoshi
is relatively high-pitched and is often used in
Kabuki eater.
C2 – A2 – Various hits
•
e Hira-daiko, meaning “stout drum,” is a type
of drum that is wider than it is deep. e instrument is carved from a single piece of wood with
drumheads tacked to its rims. e Hira-daiko
come in a variety of sizes and some are quite large.
C2 – F#2 – Various hits•
e Hyoushigi is a simple Japanese musical instrument consisting of two wooden blocks used
as clappers, similar to a clave. e Hyoushigi are
used in Taiko ensembles.
C2-A3 – various hits and strikes
•
Controller Assignments:
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 44

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Japan
Controller Assignments:
Ko-daiko e Ko-daiko represents the smaller members of
the Nagado-daiko family of drums. e Kodaiko in this collection is a 14” drum.
G3 – 14” Kodaiko 1 drum hit
•
G#3 – 14” Kodaiko 1 rim hit
•
A3 – 14” Kodaiko 2 drum hit
•
A#3 – 14” Kodaiko 2 rim hit
•
Nagado-daiko
O-daiko
Okawa
e Nagado-daiko, meaning “elongated drum,”
is one of the most popular taiko drums used in
modern groups. It is known for its distinctively
deep and resonant tone. e Nagado-daiko is
carved from a single piece of wood and comes in
a wide range of sizes. e instrument is played a
number of ways on a variety of stands.
C2 – E3 – various hits
•
e O-daiko, meaning “big fat drum,” are large
barrel-shaped drums. O-daiko are nearly three feet
in diameter and typically placed on a stand and
played horizontally, often by two people at once.
C2 – F#4 – various hits
•
C5 – G5 – various hits
•
e Okawa, also called the Otsuzumi,”is a small
hand drum used in Kabuki theater. e drum
consists of two heads stretched over steel rings,
placed over an hourglass shaped body and laced
together with rope.
C2 – A#2 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 45

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Japan
Controller Assignments:
Okedo-daiko e Okedo-daiko is a large double headed drum
used in Kodo playing. is instrument can be
set on a stand or strapped to the player’s body.
Kodo playing is known for its speedy stick
work and cross-over arm movements. In Kodo
playing, other instruments are also used (such as
small cymbals, rattles, or jingles) to add contrast.
C2-B3 – various hits, upper notes with
•
jingles
Shime-daiko
Tebyoshi
e Shime-daiko is a small rope-tensioned drum
with animal skin drumheads on both sides. e
shime-daiko is played with sticks called “bachi.”
e Shime-daiko is often used in Japanese folk
music.
C2 – E3 – various hits
•
e Tebyoshi is a small ashtray-shaped brass
cymbal that produces a unique metallic sound.
It is held in one hand by a cord and played by
striking or scraping it with a beater. e instrument is also called the Chappa.
C2-B2 – various hits, open and clas
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Tsuzumi
Uchiwa-daiko
e Tsuzumi is a small hourglass-shaped drum
with two taut drum heads with cords that can
be squeezed to change pitch. e Tsuzumi is
used in Taiko ensembles and is one of the few
Japanese drums played with hands or fingers.
C2-B3 – various hits and strikes
•
e Uchiwa-daiko is a natural-skin drum with
a round ring and no body. is hand-held
drum can be played individually or set up in a
rack and played as a set. Uchiwa literally means
“wind fan.”
C2-E2 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 46

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Other Asian Regions
Controller Assignments:
Chabara e Chabara are circular brass cymbals from
Korea used in Buddhist rituals and processionals. ey are held by cloth handles and played
by striking each other. e Chabara produce a
clanging sound. e instrument is also known
as Jabara.
C2-F2 – various hits
•
Ching
Geduk
Jang Gu
e Ching are small bowl-shaped finger cymbals used in Cambodia and ailand. ey are
made of a mixture of iron, copper, and gold.
ey measure about two inches in diameter and
are played by striking the two cymbals together.
C2-B2 – various hits and clasps
•
e Geduk is a short barrel-shaped doubleheaded drum used in Malaysian folk music.
C2-F2 – various hits
•
e Jang Gu is an hourglass drum that is played
in Korea. e instrument is also known as the
Changgo.
C2-D#3 – various hits on both heads
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Kesi
Kkwenggwari
e Kesi consists of a pair of cymbals, one of
which is affixed to a rack, while the other is tied
by rope. Sound is made by clashing one cymbal
against another. is instrument is used in the
traditional Paluan ensemble of Malaysia.
C2-A2 – various hits
•
e Kkwenggwari is a small brass gong from
Korea played with a wooden mallet. e instrument is also known as the Koeagkari.
C2-C3 – various hits
•
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 47

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Other Asian Regions
Controller Assignments:
Kompang e Kompang is a shallow wooden frame drum
with a goat or cow hide skin. It is played in
kompang ensembles throughout Malaysia for
processions and to accompany choral singing
C2-C3 – various hits
•
Luo Gong
Madal
Tangku
ai Gong
Tibetan
Cymbals
e Luo Gong, or Kai Luo Gong, is a type of
bronze gong from Malaysia and is played with a
wooden mallet.
C2-D#3 – various hits and bongs
•
e Madal is a Nepalese hand drum made of
wood or clay. Both heads of the drum are played
with the hands, holding the drum horizontally.
C2-C3 – various hits
•
e Tangku is a tomtom-like drum used in
ceremonies throughout Taiwan and other Asian
regions. e drum is sometimes suspended in a
wooden frame and produces a deep sound.
C2-F#2 – various hits
•
e ai Gong is a heavy iron gong and is
crafted to produce a clear tone. It has a hump
in its centre and is also known as Hump Gong
or Nipple Gong. ai Gongs are often played
with other instruments throughout ailand
and Myanmar.
C2-B2 – various hits
•
Tibetan Cymbals are made of different metals.
ey are played by holding one in each hand
and rubbing or lightly tapping them together.
Tibetan Cymbals are used in religious processions and ceremonies.
C2-C8 – various hits, clangs and clasps
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 48

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Other Asian Regions
Controller Assignments:
Tibetan Singing Bowl
Tibetan Bells
Tingsha
e Tibetan Singing Bowl produces a characteristic sustaining ringing sound. It is made of
metal and played by rubbing or stirring a mallet
clockwise around the outside edge or inside surface of the bowl. Singing bowls are often used in
Buddhist meditation and prayer. ese instruments are also known as Himalayan bowls.
C2-C5 – various hits and stirs
•
C6-A6 – more bowls, various hits
•
Tibetan Temple Bells are ritual instruments used
by Tibetan Buddhist practitioners. Sound is
produced by striking the bell with a Puja stick.
C2-C3 – Bell1 - various hits
•
C4-D#4 – Bell 2 hits & stir
•
C5-D#5 – Bell 3 hits
•
e Tingsha are small hand cymbals used in
Tibetan Buddhist rituals. Sound is produced by
striking the two small cymbals together at right
angles. ey make clear and beautiful ringing
tones and overtones. Typical sizes range from
two to four inches in diameter. e Tingsha is
sounded at the beginning and end of meditation and teaching sessions.
C2-C3 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 49

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Europe
Controller Assignments:
Bodhrán e Bodhrán is a traditional and popular
Celtic drum. is single-headed drum consists
of a round wooden frame with an animal skin
stretched over it. Although common in Irish
music, the bodhrán has more recently gained
popularity throughout the world.
C2-F4 – various hits and slaps
•
Hang Drum
Jaw Harps
Rattle Cog
e Hang Drum, or Hang, is a contemporary
instrument made in Switzerland. It consists
of a harmonically tuned steel shell similar to a
steelpan. It differs from a steelpan in that it is
played with hands and fingers while resting on
the player’s lap. e sound of the Hang Drum
sound is considered softer and warmer than
the traditional steelpan.
C3-C5 – various hits
•
e Jaw Harp is known by many names,
including Jew’s harp, Khomuz, and Marranzano. It consists of an oblong metal frame with
a single key or tongue down the middle that is
plucked with the finger. It produces a buzzing
tone and the sounds can be varied by changing the size and shape of the mouth. In this
collection, there are three different Jaw harps
in various keys:
C2-C3 – Jaw Harp in D
•
C4-D#5 – Jaw Harp in F#
•
C6-G7 – Jaw Harp in G
•
e Rattle Cog consists of a cog wheel set in
a frame that, when spun, causes a flat piece of
wood to move across the cog wheel to produce
a clacking sound.
C2-E2– various rattle rolls
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 50

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Latin America
Controller Assignments:
Afoxê e Afoxê consists of a gourd shaker (cabaça)
wrapped with cords that are strung with
beads. e instrument is shaken to produce its
sound.
C2-D3 – various shakes
•
Agogo Bell
Agogo
Block
Atabaque
Berimbau
Agogo Bells consist of two cone-shaped bells,
one larger and one smaller. e instrument is
played by striking them with a wooden stick.
C2-C6 – various hits
•
e Agogo Block is an instrument used in
Brazilian and Latin music. It is made of wood
blocks of different sizes, resulting in different pitches. e instrument is played with a
wooden beater.
C2-G2 – various hits
•
e Atabaque is a tall, wooden Brazilian
drum. e conical shell is traditionally made
of Jacaranda wood and has a single head made
from calfskin.
C2-G4 – various hits and slaps
•
e Berimbau is a single-string percussion
instrument from Brazil. It consists of a single
metal string strung across a four to five foot
long wooden bow. To produce sound, the
string is struck with a wooden stick called a
baqueta. A hollowed-out gourd acts as a resonator. e player changes the tone by pressing against the steel string. e instrument
originated from the mbelz, or musical bow, of
Africa.
C3 open hit, D3 close hit, E3 clasped,
•
F3 buzz
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 51

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Latin America
Controller Assignments:
Bombo e Bombo is an Argentinian drum made of a
hollowed tree trunk covered with animal skin.
e Bombo is played while hanging to the
side of the player and is struck with a mallet or
stick. e Bombo sometimes serves as a bass
instrument and has a deep and dark tone.
C2-C3 – various hits
•
Cuica
e Cuica is a Brazilian friction drum. e
drum has a bamboo stick running inside the
body of the drum which, when rubbed with
a wet cloth, produces a high-pitched squeaky
sound with variable pitches.
C2-F2 – various rubs and squeaks
•
Latin Percussion 1
C2 Batá (iyá /low)
C#2 Batá (iyá /low muffled)
D2 Batá (iyá /low slap)
D#2 Batá (Itótele /mid open)
E2 Batá (Itótele /mid muffled)
F2 Batá (Itótele /mid slap)
F#2 Batá (okónkolo/high open)
G2 Batá (okónkolo/high muffled)
G#2 Batá (okónkolo/high slap)
A2 Bongo (low open)
A#2 Bongo (low muffled)
B2 Bongo (low slap)
C3 Bongo High (open)
C#3 Bongo (high muffled)
D3 Bongo High slap)
D#3 Cajón (low)
E3 Cajón (slap)
F3 Cajón (stick hit)
F#3 Conga (low)
G3 Conga (open)
G#3 Conga (muffled)
A3 Conga (slap)
A#3 Cuica (low)
B3 Cuica (mid)
C4 Cuica (high)
C#4 Djembe (open)
D4 Djembe (muffled)
D#4 Djembe (slap)
E4 Pandeiro (open)
F4 Pandeiro (muffled)
F#4 Pandeiro (slap)
G4 Quinto (open)
G#4 Quinto (muffled)
A4 Quinto (slap)
A#4 Super Tumba (low)
B4 Super Tumba (open)
C5 Super Tumba (muffled)
C#5 Super Tumba (slap)
D5 Surdu (open)
D#5 Surdu (muffled)
E5 e Box (low)
F5 e Box (mid)
F#5 e Box (high)
G5 Timbales (low)
G#5 Timbales (high)
A5 Timbales (edge)
A#5 Tumba (low)
B5 Tumba (open)
C6 Tumba (muffled)
C#6 Tumba (slap)
D6 Udu (long)
D#6 Udu (short)
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BDFund,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq),
Var 1, Var
2, Lgth,
FiltLv,
FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 52

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Latin America
Latin Percussion 2
C2 Cabasa (short)
C#2 Cabasa (shake)
D2 Cabasa (slap)
D#2 Guiro (medium - short)
F2 Guiro (medium - long)
F# Guiro (medium - short)
G#2 Guiro (medium - long)
A2 Guiro (high - short)
B2 Guiro (high - long)
C3 Maracas (short)
C#3 Maracas (long)
D3 Maracas 2 (short)
D#3 Maracas 2 (long)
E3 Egg Shaker (short)
F3 Egg Shaker 2 (short)
F#3 Egg Shaker 3 (short)
G3 Egg Shaker (medium)
G#3 Egg Shaker 2 (medium)
A3 Shekere (low)
A#3 Shekere (high)
B3 Shekere (short)
C4 Shekere 2 (short)
C#4 Claves (high)
D4 Jam block (medium)
D#4 Jam block (high)
E4 Woodblock (high)
F4 Agogo Bell (medium)
F#4 Agogo Bell (closed)
G4 Agogo Bell (high)
G#4 Agogo Bell (high mute)
Rain Stick
e Rain Stick is a long, hollow tube filled
with small beads which, when turned,
simulate the sound of rain. Rain Sticks can
be found in Chile and other regions of South
America. e Chilean name for the Rain stick
is “Palo de Lluvia.”
C2 - A2 – various pouring rain sounds
•
Controller Assignments:
A4 Bongo Bell (low open)
A#4 Bongo Bell (low mute)
B4 Bongo Bell (high open)
C5 Bongo Bell (high mute)
C#5 Cha Cha Bell (open)
D5 Cha Cha Bell (mute)
D#5 Timbale Bell (open)
E5 Timbale Bell (mute)
F5 Castanets
F#5 Hand Claps
G5 Finger snaps
G#5 Jawbone
A5 Rainstick 1
A#5 Rainstick 2
B5 Tambourine (short stroke)
C6 Tambourine (roll)
C#6 Tambourine (hit)
D6 Triangle 1 (open)
D#6 Triangle 1 (mute)
E6 Triangle 2 (open)
F6 Triangle 2 (mute)
F#6 Whistle 1 (short)
G6 Whistle 2 (long)
G#6 Whistle 1 (short)
A6 Whistle 2 (long)
A#6 Whistle 3 (short flutter)
B6 Whistle 3 (medium
flutter)
C7 Whistle 3 (long flutter)
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq),
Var 1, Var
2, Lgth,
FiltLv,
FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 53

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Latin America
Controller Assignments:
Teponaxtli e Teponaxtli is a wooden slit drum from
central Mexico originally played by the
Aztecs and surrounding cultures. It is made
from a section of a hollowed hardwood tree
trunk and has three slits on its top, cut into
the shape of an “H.” e instrument is also
known as the Teponaztli.
C2 - C3 – various hits
•
Tinaja
e Tinaja is an earthenware jug used for
percussion in Flamenco music.
C2 - G#2 – various hits and pops
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 54

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Middle East
Arabian
Frame Drum
Basic
Middle East
Percussion
Bendir e Bendir is a frame drum from Morocco,
Daff
Darabuka
Arabian Frame Drums come in many sizes
and variety. ey consist of a round wooden
frame drum whose diameter is much bigger than its depth. Animal skin traditionally
is stretched over the frame. Arabian Frame
Drums are known by various names throughout the region.
C2 - E2 – various hits and a roll (E2)
•
e Basic Middle East Percussion set includes
a select combination of percussion instruments from the Middle East region.
C2-D#2 – Bendir
•
E2-G#2 – Daff
•
A2-E3 – Darbuka
•
F3-A#3 – Doira
•
B3-G#4 – Duff
•
with two strings stretched across the underside, producing a distinctive buzzing sound,
not unlike a snare.
C2 - D3 – various hits
•
e Daff is a small-framed tambourine with
metal discs commonly used throughout the
Middle East. e instrument is also known as
the Def.
C2 - D#7 – various hits and shakes
•
e Darabuka is a goblet-shaped drum used
throughout the Middle East and surrounding
regions. e instrument is also known by as a
Darbuka.
C2 - E5 – various hits
•
Controller Assignments:
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 55

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Middle East
Controller Assignments:
Doira e Doira is a medium-sized frame drum
with jingles, used in classical music of Iran.
e instrument is also known as a Ghaval.
C2 - F#3 – various hits
•
Duff
Dumbek
Kashiklar
Kudum
Naqqāra
e Duff is a frame drum that has a goatskin
head stretched over the frame.
C2 - F#3 – various hits
•
e Dumbek is a very popular drum in the
Middle East. It is goblet-shaped with a head
stretched over the bowl that can produce a variety of sounds by being played by the hands
and fingers.
C2 - E3 – various hits, taps and rolls
•
e Kashiklar is a percussive wooden spoon
instrument used in dance in various countries
in the Middle East.
C2 - D#3 – various single and multiple
•
hits
e Kudum consists of a pair of small, hemispherical drums from Turkey that are used in
dervish mystical music. e instrument is also
known as the Ghodum.
C2 - A3 – various hits
•
e Naqqāra is a small drum with a rounded
back and a hide head. e Naqqāra can be
found in different sizes in different regions of
Iran and there are some other Middle Eastern
varieties of the instrument.
C2 - G2 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 56

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Middle East
Controller Assignments:
Riqq e Riqq is a type of tambourine used in Ara-
bic music. It has a round wooden frame that
is covered with thin animal or fish skin and
equipped with double rows of metal jingles.
In various regions the instrument is similar to
the Daff.
C2 - F5 – various hits and shakes
•
Ta r
Tumbak
Zarb
Zills
e Tar is a large single-headed frame drum
from Egypt and the Middle East. e Tar is
usually held with one hand and played with
the other. Depictions of Tar drums date back
thousands of years.
C2 - E4 – various hits
•
e Tumbak is a small single-headed drum
played throughout Persia and the Middle
East. It is shaped like a goblet with the upper
half being wider than the lower, similar to the
Darbuka.
C2 - F3 – various hits
•
e Zarb is an Iranian goblet-shaped drum,
made of wood and covered with a goatskin.
e Zarb is often used in classical Persian
music as a main rhythm instrument.
C2 - F4 – various hits
•
Zills are small brass finger-cymbals used by
belly dancers in the Middle East. ey are
worn on the thumb and middle finger by
dancers. e instrument is also known as the
Sagat in some countries.
C2 - F4 – various rings, clangs and
•
clasps.
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 57

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
North America
Controller Assignments:
Buffalo Drum e Buffalo Drum is a large Native American
frame drum used for ceremonies and religious
rituals. In the Native American tradition, music is a means of communicating with nature
and the supernatural.
C2-F2 – various hits
•
Powwow
Drums
e Powwow Drum comes in various sizes.
e largest Powwow drum is often played by
multiple drummers together in unison sitting
in a circle around the drum. e Powwow
drum has a large base covered with hide (buffalo, deer, or cow) and produces a deep sound.
C2-F2 – various hits
•
Native Log
Drum
e Native American log drum is a small
drum made from animal skin stretched over a
hollowed log.
C2-A2 – various hits
•
Pueblo Drum
(Taos)
e Taos drum is a traditional Pueblo Indian
drum made from a hollow log frame with its
walls thinned down.
C2-A3 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1, Var
2, Lgth, FiltLv, FiltFq,
BDFund, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Spoons See Kashiklar in Middle East percussion.
Washboard
e Washboard is used as a percussion instrument in bluegrass, dixieland, and other American folk music traditions. Sound is produced
by scraping the corrugated metal surface of the
washboard with comon metal finger thimbles.
C2-F3 – various hits and scrape rolls
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 58

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Oceania
Gamelan Balinese
Gamelan means orchestra in Balinese and represents the traditional music ensemble of
Indonesia. Java and Bali have distinctive Gamelan ensembles and this collection includes
both. e instruments in a Gamelan ensemble include a variety of instruments such as
metallophones, xylophones, drums, gongs, and chimes. e distinctive ethereal sound
of the gamelan can be attributed to the differences in tuning between instruments while
playing interweaving patterns.
Angklung
Ceng Ceng
Gendér
Giying
(Ugal)
e Angklung consists of pitched bamboo
tubes hung from a wooden frame. In addition
to being part of the Balinese Gamelan, there
are also ensembles of angklung called Gamelan
Angklung.
C2-A#2 – various hits of the various
•
bamboo tubes.
e Ceng Ceng is a set of small cymbals used
in the Balinese gamelan for rhythm and color.
Each cymbal differs in diameter and thickness
and creates a different pitch.
C2-F#2 – various hits
•
e Gendér is a metallophone used in both
Balinese and Javanese gamelan ensembles. It
consists of 10 to 14 tuned metal bars suspended over tuned resonators. e Gendér instruments usually play the elaboration part to
support the melody. Gendér Barung is pitched
an octave lower than Gendér Panerus.
C2 – D#4 – various hits
•
e Giying, or Ugal, has ten keys and is the
largest and deepest of the gangsa metallophones. It is played with wooden mallets while
sitting on a chair or bench. e Giying plays
an improvised version of the core melody,
C2 – C3 – various hits
•
Controller Assignments:
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 59

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Oceania
Controller Assignments:
Kantil e Kantil has ten metal keys and is played
with wooden mallets. It is the highest-pitched
and one of the smallest gangsa instruments.
e Kantil often plays the main melody and
also interlocking parts.
C2 – D#4 – various hits
•
Kemong See Kenong in Gamelan Java
Kendhang
Pemade
Penyacah
Reyong
e Kendhang drums often provide the
underlying beat for the Balinese gamelan
orchestra. e Kendhang Ageng is the largest
of the Kendhang drums and has a rich deep
tone. e Kendhang Ciblon is a mediumsized drum that plays more complex rhythms.
is instrument is similar to the Gendang in
Malaysia and Ghi Nang in Vietnam.
C2 – G3 – Various strikes
•
•
C4–A4 – Ageng; C5-G#5 - Ciblon
e Pemade has ten metal bars that rest in
a carved wooden frame and is played with
wooden mallets. It is pitched one octave
lower than the Kantil and also plays the main
melody and interlocking parts.
C2 – C3– various hits
•
e Penyacah is a metallophone instrument
with seven metal keys in a decorated wooden
frame. It is played with wooden mallets with
rubber tips. e Penyacah often plays the
main melody.
C2 - G#2 – various hits
•
e Reyong consists of a long row of metal
gong-chimes (resembling upside-down kettle
pots) suspended on cords in a wood frame.
Each pot has a different pitch and is played
with padded sticks.
C2 – A3 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 60

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Oceania
Gamelan Javanese
Bonang e Bonang is a series of gong-chimes (some-
times called kettles or pots) resting on cords
in a wooden cradle and arranged in two rows.
Each gong has a different pitch and is played
with sticks that are lightly padded with coiled
string. Bonang Panerus sounds one octave
higher then Bonang Barung. e Bonang are
similar to the Balinese Reyong.
C2 – E7 – various hits
•
Gong &
Gong Ageng
e Gong Ageng is usually hung at the back
of the gamelan. It has a flat surface with a
protruding knob at the center of the sphere. It
can vary in size but is usually the largest hanging gong in the Javanese gamelan. e Gong
Ageng is believed to embody the spirit of the
gamelan and is therefore the most respected
instrument in a gamelan.
C2 - A2 - Gong Ageng – various hits
•
Controller Assignments:
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1, Var
2, Lgth, FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Kempul
Kempyang
e Kempul is a set of hanging pitched gongs
used in Javanese gamelan. Each gong has a
flat surface with a protruding knob at the
center. e number of Kempul can vary from
gamelan to gamelan and the different sizes
produce different pitches.
C2 – G#2 – various hits
•
e Kempyang consists of two kettle-gongs
made of bronze and mounted in a wooden
cradle. e two kettles are pitched about a
semitone apart, producing a dissonant sound
when played together. Together with the
Ketuk, they keep the beat in the colotomic
structure of the gamelan.
C2 – A#2 - various sustains & choke
•
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 61

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Oceania
Controller Assignments:
Kenong
(Kemong)
Ketuk
Pelog Panerus
Saron Barung
e Kenong is a series of cradled kettle-gongs
made of bronze and mounted in wooden
cases. e Kenong comes in different sizes
and various sets are often situated around
the player. e numbers of Kenong vary in
different gamelan ensembles and it is not
uncommon for there to be about ten Kenongs
in a gamelan. Also called Kemong in Balinese
Gamelan.
C2 – C3 – various hits
•
A4 – G6 – various hits
•
e Ketuk consists of a single cradled kettlegong of definite pitch. In a Javanese gamelan
ensemble, there usually is only one Ketuk,
which serves as a punctuating instrument. It
is often situated next to the Kempyang and
pitched lower than the Kempyang.
C2 – A#2 - various sustains & choke
•
e Pelog Panerus is a metallophone instrument with seven bronze bars placed over a
wooden frame—each bar tuned to a different
pitch. Javanese music uses two scales: a sevennote scale called pelog, and a five-note scale
called slendro.
C2 – A2 – various hits
•
e Saron typically consists of seven bronze
bars placed on top of a resonating frame. e
Saron Barung is pitched one octave lower
than the Saron Panerus and one octave higher
than the Saron Demung. It is played with a
wooden mallet.
C2 – A3 - various sustaining hits•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 62

THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Oceania
Controller Assignments:
Saron
Demong
Saron Panerus
(Peking)
Slendro
Panerus
Slentem
Hawaiian Percussion
Basic
Hawaiian
Percussion
e Saron Demung posseses the largest metal
bars and produces the lowest sound among
the sarons. Its pitches are an octave lower than
the Saron Barung.
C2 – G#3 – various sustaining hits
•
Also known as Peking, the Saron Panerus is
the smallest Saron in the Saron family. e
Saron Panerus sounds an octave higher than
the Saron Barung.
C2 – G#2 – various sustaining hits
•
e Slendro Panerus is similar to the Saron
Panerus, but tuned to a different tuning
system. Slendro Panerus has seven metal bars
placed on a resonating frame.
C2 – G#2 – various hits
•
e Slentem consists of bronze bars suspended
over tube resonators. It has a range of about
an octave. Slentem usually have seven bars
that are tuned to either the Pelog system or the
Slendro system. is instrument usually plays
the main melody in a Gemelan ensemble.
C2 – C4 – various dampened hits
•
B4 – C6 – various sustaining hits
•
e Basic Hawaiian Percussion set includes
a select combination of Hawaiian percussion
instruments.
C2-E2 – Kaekeeke
•
F2-D#3 – Ipu
•
E3-G3 – Kaekeeke
•
G#3-D4 – Pahu Hula
•
D#4-C#7 – Lava Stones & Rattles
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 63

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Program Description:
Oceania
Controller Assignments:
Ipu e Ipu is a percussion instrument made from
a gourd and used for Hawaiian hula dancing.
C2-D#3, C4 – A#4 – various hits and
•
slaps
Kaekeeke
Kala’au
Lava Stones
& Rattles
(Ili’ili &
‘Uli’uli)
Pahu Hula
Toere
e Kaekeeke are long bamboo sticks played
by striking the instrument on the floor.
C2-A#2, E3 – G3, C4 – E4 – various
•
hits and strikes on the floor
e Kala`au are rhythm sticks shaped from a
resonant hardwood and played in pairs, often
in association with Hawaiian hula dances.
C2-B3 – various hits of the sticks
•
Lava Stones, or ili’ili, are played by hula dancers. Lava stones are personal to the player as
their size is chosen to fit the player’s hands.
Prior to the introduction of the ukulele into
Hawaiian music over a century ago, most Hawaiian instruments were percussive. us, the
main function of the ‘ili‘ili and other Hawaiian instruments is to help maintain the beat.
Included in this instrument patch are Hawaiian ili’ili and ‘uli’uli rattle.
iE4 – G5 – various hitsx
e Hawaiian term “Pahu” literally means
“drum.” Pahu drums are made of hollowed
out coconut trunks and covered by either
sharkskin or calfskin.e drum was seen as a
vehicle for the spirit of the gods and is important for performing the hula.
G#4 – D5 – various hits
•
e Toere is a hollow log drum with a slit
along the side. It is made from Hawaiian hardwoods and varies in size. Toere drum sticks are
made from ironwood.
A5 – C7 – various hits
•
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var
1, Var 2, Lgth,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Page 64

THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Africa
Controls:
Begena e Begena is an Ethiopian stringed instrument
that resembles a large lyre. e Begena has ten
strings and leather thongs that give a buzzing
sound.
Range: F1 – G3
•
Bolon
Domu
Kora
Ngoni
e Bolon, also known as the Nbolon, is a bass
instrument with four strings. It is made of a
gourd body with a bent ngoni-wood neck and
twisted rawhide strings. is instrument is played
in Guinea and surrounding regions and is used to
accompany other instruments. e sound can be
described as mellow and full.
Range: C2 - G2
•
e Domu (or Mangbetu) is a small arched bow
harp from the Congo. e resonator is tightly
covered with animal hide and fur, and it has two
sound holes and an arched wood neck.
Range: G3 – G6
•
e Kora is a 21-stringed harp made out of a large
calabash gourd covered with stretched skin, and it
has a protruding stick to which strings are attached.
e strings, made of fishing line, are plucked using
the thumb and index finger of both hands. e
sound of a kora is similar to that of a delicate harp.
e instrument is played throughout West Africa
and most popular in Gambia and Senegal.
Range: C2 – C6•
e Ngoni is a banjo-like instrument found
throughout West Africa. Its body is a hollowed-out
piece of wood with dried animal skin stretched
over it like a drum. e neck is a fretless dowel
protruding from the body. e Ngoni’s strings
are made of fishing line. e American banjo is
believed to be a descendant of the Ngoni.
Range: C2 – C5
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
(includes mutes)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 65

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
China
Controls:
Choazhou
Guzheng
Erhu
Guzheng
Pipa
e Choazhou Guzheng is popular in the southern coastal Chinese provinces, Taiwan, and other
areas of Southeast Asia. is 17 metal-stringed
Guzheng is a smaller version of the common 21to 26-string silk-stringed Guzheng. It has thin
gauged strings and moveable bridges to adjust
the pitch of each string.
Range: G2 – G5
•
e Erhu is a stringed instrument played with
a bow and is one of the most popular Chinese
instruments. e Erhu has two strings, a small
body, and a long neck. e sound is similar to a
violin, but thinner sounding due to the Erhu’s
smaller resonating chamber.
Range: G3 – G6
•
e Guzheng is a long, zither-like instrument
with 21 to 26 silk strings and movable bridges.
e instrument has a long, rounded, wooden
base over which the strings are stretched. Players play the strings with picks attached to their
fingers while touching or bending the strings
with their other hand. It is also known as the
Gu-Zheng, the Zheng, or Cheng. It is one of the
most ancient Chinese musical instruments and
still one of the most popular.
Range: C2 – C6
•
e Pipa is a four-stringed, pear-shaped, plucked
instrument that is often used in Chinese music.
e history of the Pipa dates back over 2,000
years. is instrument has a wide dynamic range
and many playing techniques have developed.
Range: C2 – C7
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BowNs,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches (include
pizzicato)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(includes mutes)
Page 66

THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
China
Controls:
Yueqin
e Yueqin is also known as the Chinese moon
lute and dates back over 2,000 years. “Yue”
means “the moon” in Chinese. It is a fretted
string instrument with a circular body, short neck
and four metal strings played with a plectrum.
Range: C3 – G6•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(includes mutes)
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 67

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
India
Controls:
Electric
Sitar
Sarangi
Sarangi
Drone
Sitar
e Electric Sitar is an electric instrument
designed to mimic the sound of the traditional
Indian sitar. e instrument has six playing
strings and additional sympathetic strings that
are amplified with electric pickups.
Range: C2 – C7 (Drone: C2-B2)
•
e Sarangi is a bowed, boxy, short-necked
fiddle from the Indian subcontinent. e
instrument is roughly rectangular in shape and
is about two feet long. It has three or four main
playing strings that are played with a bow, and
a number of metal strings (several dozen) that
resonate sympathetically. e instrument has no
frets or fingerboard and notes are determined
by sliding the fingernail against the string rather
than pressing it against a fingerboard.
Range: C2 – C6 – Single notes plus the
•
resonating sympathetic string.
e sympathetic resonating string for the Sarangi.
Range: C2 – C6•
e Sitar is the most popular Indian stringed
instrument. e instrument has a long neck with
raised frets and a gourd base. Sitars have six or
seven melody strings and about thirteen sympathetic strings that act as a drone. e drone
notes resonates with the melody notes, giving the
Sitar its distinctive sustaining sound. e Sitar is
used for playing extended improvised melodies
known as ragas.
Range: C2 – C6
•
C2-C3 cand be used as drone
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
Page 68

THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
India
Controls:
Tambura e Tambura (or Tanpura) is an accompaniment
stringed instrument that provides a drone in
classical Indian music. e instrument has a long
neck and four to six sustaining strings that produce a long sustaining and buzzing drone sound.
Although resembling a Sitar, Tamburas have
fewer strings, no sympathetic strings, no frets,
and a moveable bridge used to adjust the pitch.
Range: E1 – C5
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 69

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Japan
Controls:
Koto e Koto is a Japanese zither. It is the largest of
the Asian zithers at around six feet in length. e
instrument usually has 13 silk strings set upon
movable bridges. e Koto is played horizontally and the player plucks the strings using
picks attached to his or her fingers. A common
technique is “tsuki,” where the player plucks the
string while pressing the string on the other side
of the bridge with the other hand, causing the
note to bend. Another technique is to pluck the
string rapidly in alternating directions to produce
a tremolo effect.
Range: C3 – C6
•
Sanshin
Shamisen
e Sanshin is a three-string instrument that is
very important in traditional Okinawan music. It
is a precursor of the Japanese Shamisen and consists of a roughly square sound box covered with
snakeskin, a long neck, and three strings. It is
played with a plectrum worn on the index finger.
Range: C2- C6•
e Shamisen is a long-necked, fretless, threestringed instrument (Shamisen literally means
“three flavor strings”). e instrument is similar
in sound and size to a banjo with a box-like
skin-covered body. It has soap-soaked strings thar
are plucked with a heavy ivory plectrum called a
“bachi.”
Range: C2 – F6•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches
(incudles mutes)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches
(incudles mutes)
Page 70

THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Other Asian Regions
Controls:
Dan Tranh
Dan Ty Ba
Gopichand
e Dan Tranh is a zither-like instrument that is
popular in Vietnam. It is similar to a small Chinese Zheng with 17 thin-gauged steel strings and a
moveable bridge for each string. e Dan Tranh’s
body is made from the Vietnamese wootung tree
and has a distinctive bright and clear tone.
Range: C3 – G6•
e Ti-Ba, or Dan Ty Ba, is a pear-shaped and
lute-like stringed instrument from Vietnam. is
instrument has four strings of braided silk and
four wooden tuning pegs on the neck. It is made
from wood of the wootung tree and used in royal
court ensembles is instrument is played with a
plectrum.
Range: C2 – G6
•
e Gopichand is a popular folk instrument
of Bengal. e two bamboo legs are squeezed
together by the left hand while the right hand
plucks the string, producing a distinctive bending sound. e Gopichand is used mainly as a
rhythmic instrument.
Range: G3 – C6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq) Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq) Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd,VibAmt,
Keyswitches (incudles mutes)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq) Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd,VibAmt,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 71

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Europe
Controls:
Balalaika e Balalaika is one of the most popular and
best known instruments in Russia and Eastern
Europe. is stringed instrument has a unique
triangular body, a fretted neck, and three
strings (sometimes four or six), and is played
by plucking or strumming.
Range: G3 – C7
•
Bulgarska
Tambura
Celtic
Harp
Fiddle
Hurdy
Gurdy
e Bulgarian Tambura is a mandolin-like instrument popular in folk music in the Balkans.
e long neck is fretted and the eight strings
(four pairs in unison) are played with a pick.
Range: C3 – E6
•
e Celtic harp is the national instrument of
Ireland and its history extends over 1000 years.
e Celtic harp often has 36 strings but that
can vary. It uses sharping levers, rather than
pedals, to play in different keys. e instrument is played with both hands. Its sound is
brighter than that of an orchestral harp.
Range: C2 – C7
•
e fiddle usually refers to a folk violin used
for playing a wide variety of ethnic or traditional folk music. e fiddle is very popular
in Irish, Gypsy, and other folk traditions
throughout the world.
Range: G3 – G7
•
e Hurdy Gurdy, also known as a wheel
fiddle, is a stringed instrument in which the
strings are rubbed with a rosined rotating
wheel. is wheel is turned with a crank,
functioning much like a violin bow, and the
left hand plays the melody on the keys of the
keybox.
Range: C3 – G4
•
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches (includes
mutes)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt, Keyswitches (incudles mutes)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches (includes
Bisbigliando)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd, BowNs,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(includesPizzicato)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Page 72

THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Europe
Controls:
Mandolin e Mandolin is a lute-like instrument with a
teardrop-shaped (or oval) body with a soundhole and a straight fretted neck. e modern
versions usually have eight metal strings in
four pairs, tuned in unisons or octaves, and
are either plucked or strummed in a tremolo.
is instrument has become popular in Italy
and throughout Europe.
Range: G3 – C7
•
Octave
Mandolin
Wire
Strung
Harp
(Clarsach)
Zitter
A pear-shaped Italian instrument with a fretted neck and from four to six pairs of strings,
tuned an octave lower than a typical mandolin.
Range: C2 – C6•
e Wire Strung Harp, or Clarsach, is a
traditional instrument of Ireland and serves as
its national symbol. e technique of playing a wire-strung harp is different from a gut
or nylon strung harp. While certain fingers
play, other fingers dampen the strings. e
wire-string harp produces a beautiful, bell-like,
haunting tone.
Range: F2 – C7
•
is Zitter is a ten string dulcimer-like instrument from Slovenia, with fretted bottom
strings and the others playing open. e
Zitter comes in many sizes and types throughout Europe and is believed to be the ancestor
of the Mountain Dulcimer. It is known by
various names—Epinette (France), Langspil
(Iceland), and Scheitholz (Germany).
Range: C2 – C7
•
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches (includes
mutes)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches (includes
mutes)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches (includes
bisbigliando)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 73

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Latin America
South
American
Harp
(Arpa)
Veracruz
Harp
Guitarron e Guitarron is a large, deep-bodied Mexican
e South American Harp (or arpa) is common
throughout South America and is the national
instrument of Paraguay. is instrument is
triangular in shape and is very light for its size.
It typically has 36 nylon strings that are played
with the fingernails. e South American Harp
produces a distinctly bright, clear sound.
Range: C2 – C7
•
e Veracruz Harp is popular in the Veracruz region of Mexico and is played in Mariachi bands.
It is similar to the South American Harp in appearance and playing technique but usually has a
wider body, a deeper tone, and is played standing
up rather than sitting.
Range: C2 – C7
•
bass guitar with six strings and a fretless neck.
e strings are thick and often played in octaves,
with a strong, pronounced plucking action.
Range: G1 – G4
•
Controls:
Vel (attack), MW (vol/eq),
Sus, Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq, Keyswitches
(includes bisbigliando)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/eq),
Sus, Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq, Keyswitches
(includes Bisbigliando)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(includes mutes)
Page 74

THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Middle East
Controls:
Oud e Oud is a pear-shaped Middle Eastern
lute with a short neck and eleven strings. e
player uses a pick (originally made from a bird’s
feather) to pluck the strings. e Oud is one
of the most important instruments in Arabic
classical music. e instrument is also known as
the Ud.
Range: C3 – G5
•
Santoor
e Santoor is a dulcimer-like stringed instrument originating in Iran and is popular
throughout the Middle East. Its wooden body
is trapezoidal, with narrow sides and a wide
soundboard. e instrument’s 72 strings are
grouped into 2 to 3 strings per note. e instrument is played with two wooden hammers. One
common technique is a bounce stroke where
the mallet is bounced across the strings, producing quick repetitions. It is also known as the
Santour, Santur, and Sanduri.
Range: G3 – G7
•
Vel (attack), MW (vol/
eq), Sus, Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches (includes.
Mutes)
Vel (attack), MW (vol/eq),
Sus, Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq, Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 75

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
North America
Controls:
Banjo e Banjo is a popular instrument in American
folk music. It consists of a circular drum body
covered with a parchement drum head. Attached to the drum body is a long neck, similar
to that of a guitar, with five or six strings. It is
a descendant of African stringed instruments
originating with African slaves.
Range: G2 – G6
•
Banjolele
Dulcimer
Fiddle See Europe: Strings
Fretless
Zither
Hammered
Dulcimer
e Banjolele (or banjo ukulele) is a fourstringed musical instrument with a small banjotype body and a fretted ukulele neck.
Range: G3 – C7
•
e Dulcimer is a stringed instrument that
originates from the Appalachian Mountains of
America. e Appalachian Dulcimer is shaped
like an hourglass, played on the lap, and has a
narrow fingerboard attached to a larger soundbox underneath.
Range: G2 – C6
•
e Fretless Zither consists of a simple shallow
box with many open metal strings stretched
over the top. e melody strings on the right are
tuned either diatonically (or sometimes chromatically). To the left are several chords made
up of several strings that are grouped together.
is instrument is also known as an American
Zither.
Range: G3 – C7
•
See Middle East: Strings: Santoor
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(includes. mutes)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(includes. mutes)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 76

THE STRING INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
North America
Controls:
Washtub
Bass
e Washtub Bass, or “gutbucket,” is a singlestringed bass instrument that uses a metal
washtub as a resonator.
Range: C2 – C4
•
Oceania
Rebab e Rebab is a two-stringed bowed instrument
used as a melodic voice in the Balinese gamelan.
e Rebab’s heart-shaped body is made from
wood or coconut shell and is covered with
animal gut. e instrument is played with the
player sitting cross-legged and holding it in a
vertical position. e bow is made from wood
and horse hair, similar to a violin bow.
Range: B4 – G5
•
Tenor
Ukulele
Ukulele
e Tenor Ukulele is a larger version of the
standard Ukulele. is instrument has eight
strings: two strings are doubled and the third
and fourth are paired with octaves.
Range: C3 – C6
•
e Ukulele is small guitar-shaped instrument
of Hawaiian origin and the most popular instrument of the islands. e instrument has four
nylon strings tuned to G-C-E-A. Ukuleles come
in many different sizes.
Range: C3 – G6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq) Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, BowNs,
VibSpd,VibAmt,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(including mutes)
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
VibAmt, Keyswitches
(including mutes)
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 77

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
OTHER INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Asia
Controls:
Bullroarer e Bullroarer consists of a piece of wood con-
nected to a long cord. It is played by swinging
it lasso-style, over the head, which causes it to
spin and make a humming sound. is type of
instrument has been used in Hawaii, Polynesia,
Native America, and other cultures throughout
the world.
C3 – F3 – various whirs
•
Harmonium
Khaen
Mouth
Organ
e harmonium is a free-standing keyboard
instrument. Sound is produced by air supplied
by foot- or hand-operated bellows being blown
through sets of free reeds. Notes are selected by
playing the white and black keys on the front of
the instrument. Some models feature a stop that
creates a form of vibrato. A popular example of
the use of a harmonium can be found in Beatles
songs such as “We Can Work It Out.”
Range: C2 – C6
•
e Khaen, or ai Mouth Organ, is a small
free-reed mouth organ from ailand. e instrument consists of a group of pipes connected
with a small, hollowed-out hardwood reservoir
into which air is blown. e Khaen is tuned to
a pentatonic scale. It is also called a Pi Joom in
Northern ailand.
Range: C5 – C7
•
Vel (vol/eq),
Lgth, Var 1, Var
2, FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, VibAmt,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Sus, Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq, AirNs,
Bellows, Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Page 78

OTHER INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Europe
Controls:
Alphorn e Alphorn, used by dwellers in the Swiss Alp
Mountains and Alpine regions, is a long hollow tube with a wooden mouthpiece. It is also
known as the alpenhorn or alpine horn.
Range: C2 – C6
•
Concertina
Concert
Accordion
French
Accordion
e Concertina is a type of small accordion with
a unique shape. It typically has buttons on both
sides. Each button produces one note, unlike the
accordion, which produces chords with a single
button. e Concertina was reportedly developed in England and Germany. Its compact size
makes it very mobile and visually entertaining.
Range: C3 – F6
•
e Accordion, also known as a squeezebox,
originated in Austria in the nineteenth century
and is now a common folk instrument throughout the world. e instrument consists of a
bellows that the player expands and contracts,
forcing air across a set of metal reeds to produce
sound. Notes on a keyboard trigger the various
reeds. In this library the Accordion uses the
bassoon switch (one reed in the chamber) for a
round warm sound.
Range: C2 – G6
•
French Accordion using a switch with three
reeds.
Range: C2 – C6
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
AirNs, Fluttr, AutoLegato
Vel (attack), Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
Bellows, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
Bellows, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
Bellows, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
Page 79

A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
OTHER INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
Europe
Controls:
Italian
Mussette
Accordion
e Italian Mussette Accordion is played
throughout Italy. It uses a switch with three reeds
(two mids and one high).
Range: C2 – C6
•
Latin America
Bandoneón e Bandoneón is a square-built button ac-
cordion, commonly used in Argentinean tango.
Unlike the typical keyboard accordion, the Bandoneón has buttons on both sides rather than a
keyboard. e switch used is a combined middle
and low reed.
Range: C3 – C7
•
Steel
Drums
Steel Drums are a set of pitched percussion
instruments, each drum tuned chromatically.
Each drum is skillfully hammered from 55-gallon steel oil drums and fine tuned by beating
the head into separate tuned areas. e instrument originates from Trinidad and is also known
as steelpan or pans. ere are several pans in a
steelpan band consisting of Tenor (lead), second,
mid-range, and bass pans.
Range: G1 – G6
•
Vel (attack), Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
Bellows, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), Lgth,
VAR1, VAR2,
FiltLv, FiltFq,
VibSpd, Vib Amt,
Bellows, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (vol/eq), Var 1,
Var 2, Lgth, FiltLv,
FiltFq, Keyswitches
Page 80

OTHER INSTRUMENTS
ARIA name: Description:
North America
Controls:
Melodica e melodica is a mouth-blown free-reed instru-
ment consisting of a tube attached to a keyboard.
e player blows into the tube while playing the
keys of the keyboard. It can be played with articulation and expression like a wind instrument.
Range: C3 – C7
•
Harmonica
Bass
Harmonic
e Harmonica is a free-reed wind instrument
that is played by blowing or sucking air through
holes (reed chambers). Each tone is determined
by the size of reed. Longer reeds make deep, low
sounds and short reeds make higher-pitched
sounds. Pitches can alse be changed (bending a
note) by redirecting air flow into the chamber.
ere are many types of Harmonicas, including
diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, orchestral, and bass
versions.
Range: C5 – G7
•
e Bass Harmonica has double sets of reeds
tuned in octaves, with the bottom reeds play ing
lower than the upper reeds.
Range: C2 – G3
•
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
Vel (attack), MW
(vol/eq), Porta,
Lgth, VAR1,
VAR2, FiltLv,
FiltFq, VibSpd,
Vib Amt, AirNs,
Fluttr, AutoLegato, BndSpd,
Keyswitches
A User’s Guide to Garritan World Instruments
 Loading...
Loading...