Ganz ZN-DT2MA User Manual


Contents
1. Product Features.............................................................................................4
2. Accessing the Camera .....................................................................................7
2.1 Access from a Web Browser........................................................................7
2.2 Accessing the Camera from the Internet........................................................7
2.3 Adjusting the Camera Direction ....................................................................8
2.4 Adjusting the Image and Focus ....................................................................8
2.4 Adjusting the Image and Focus (cont’ d)......................................................9
2.5 Live View ................................................................................................10
2.6 Video stream types................................................................................... 10
2.7 How to Stream H.264 ............................................................................... 11
3. Setup ..........................................................................................................12
4. Installation ................................................................................................... 13
4.1 Installation Mode...................................................................................... 13
5. Camera and Image ........................................................................................13
5.1 Video Codec ...........................................................................................13
5.2 Camera .................................................................................................16
5.2.1 Exposure Control................................................................................... 16
5.2.2 Day & Night Control ...............................................................................17
5.2.3 White Balance Control............................................................................ 17
5.2.4 Image Property Control .......................................................................... 17
6. Audio ..........................................................................................................18
7. Live............................................................................................................. 19
8. SD Card....................................................................................................... 20
8.1 Configuration........................................................................................... 20
8.2 Event......................................................................................................21
8.3 Periodical................................................................................................22
9. FTP.............................................................................................................23
9.1 Configuration........................................................................................... 23
9.2 Event......................................................................................................23
9.3 Periodical................................................................................................24
10. Event ......................................................................................................... 25
10.1 Alarm Port .............................................................................................25
10.2 Motion ..................................................................................................26

10.3 Mapping................................................................................................27
11. Network ..................................................................................................... 28
11.1 IP Setup ................................................................................................28
11.2 Service Port ........................................................................................... 30
11.3 RTP ......................................................................................................31
11.4 E-mail ..................................................................................................31
11.5 DDNS ................................................................................................... 32
11.6 UPnP ....................................................................................................33
12. System....................................................................................................... 35
12.1 User .....................................................................................................35
12.2 Date & Time ..........................................................................................35
12.3 Maintenance ..........................................................................................36
12.4 Information ............................................................................................ 38

1. Product Features
The GANZ PixelPro Series HD / Megapixel IP camera (ZN-DTx) is a high performance H.264
network camera, designed for demanding security installations. It delivers crisp, clear images,
disclosing every detail, thanks to its top quality progressive -scan CMOS sensor and advanced
image processing. GANZ PixelPro features a mechanical IR cut filter, which enables color
video in high and low light conditions, as well as IR sensitivity in ‘night’ mode.
Supported by the industry’s largest base of video management software, the GANZ PixelPro
provides the perfect solution for securing bank offices, airports and other fac ilities, and for traffic
surveillance, over IP based networks.
The optimal Power over Ethernet (IEEE 802.3af) supports power to the camera to be delivered
via the network, eliminating the need for a power outlet and reducing installation costs. Reliable
AC power could be guaranteed by using an Uninterruptible Power Sup ply (UPS).
The GANZ PixelPro offers a comprehensive set of network security and manag ement features.
This includes support for port based network control (IEEE802.1X), which allows the camera to be
connected to a network secured with this control and HTTPS encry ption, which provides a secure
channel between camera and application. It also enables authentication of the video source.
GANZ video products are efficiently managed with the powerful GANZ CMS Client Software,
which is provided on the Installation CD which comes with each GANZ PixelPro camera.
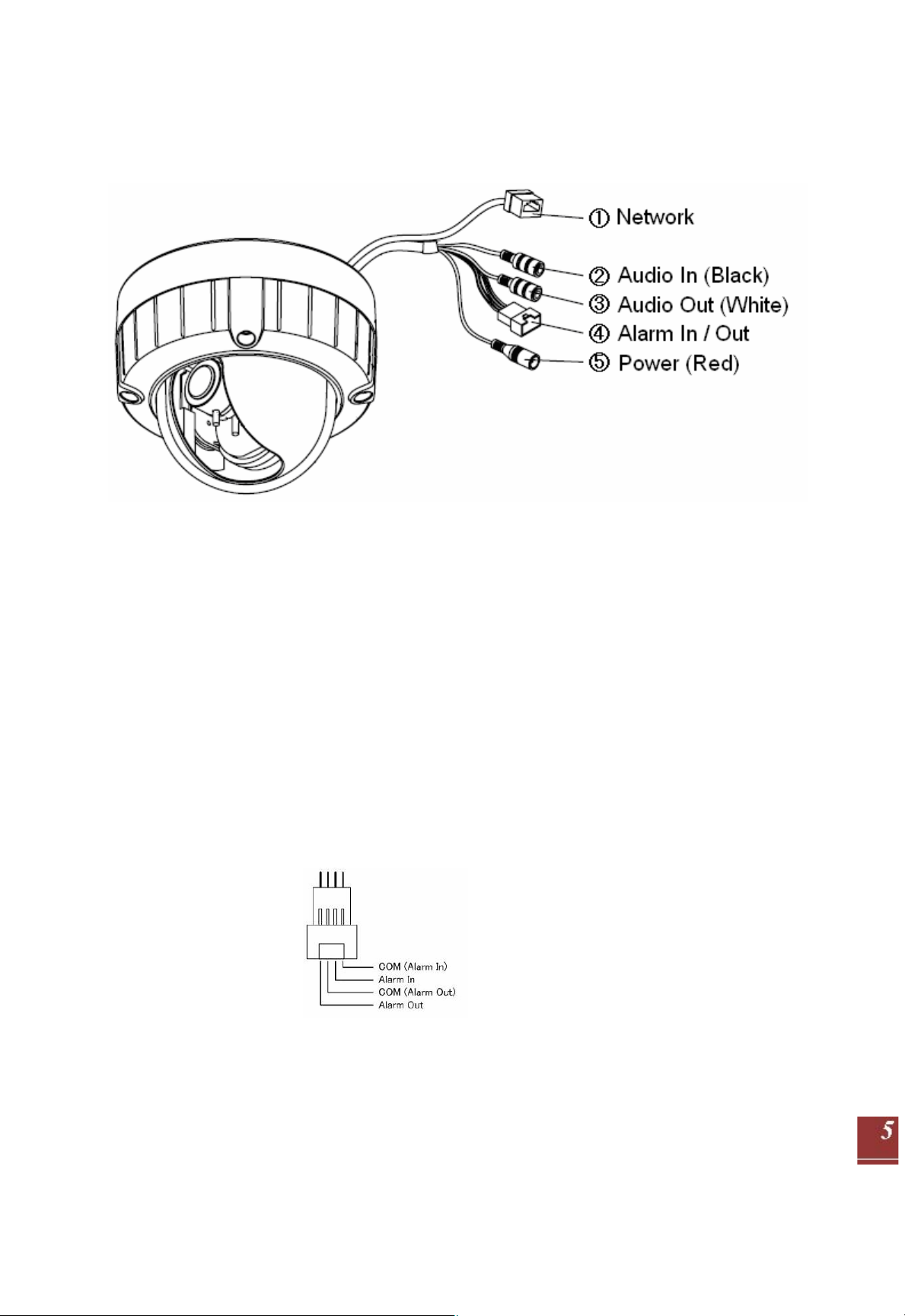
Network connector
1.
The GANZ PixelPro connects to the network via a standard network cable, and automatically
detects the speed of the local network segment (10BaseT/100BaseTX Ethernet). This socket
could also be used to power the GANZ PixelPro via Power over Ethernet (PoE). The cam era
auto-senses the correct power level when using a PoE (Class 2) switch, router or in jector.
2. Audio in
Audio in (line level), for line-in mono signal (only left channel is used from a stereo signal)
3. Audio out
The Audio output (line level), which could be connected to a line output of a microphone system
or an active speaker with a built-in amplifier.
4. Alarm in / Alarm out
One analog (dry contact) alarm input / One relay output (
2A : AC120V / DC60V)
Pin Assignment
5. Power Connector
12VDC or 24VAC power connector
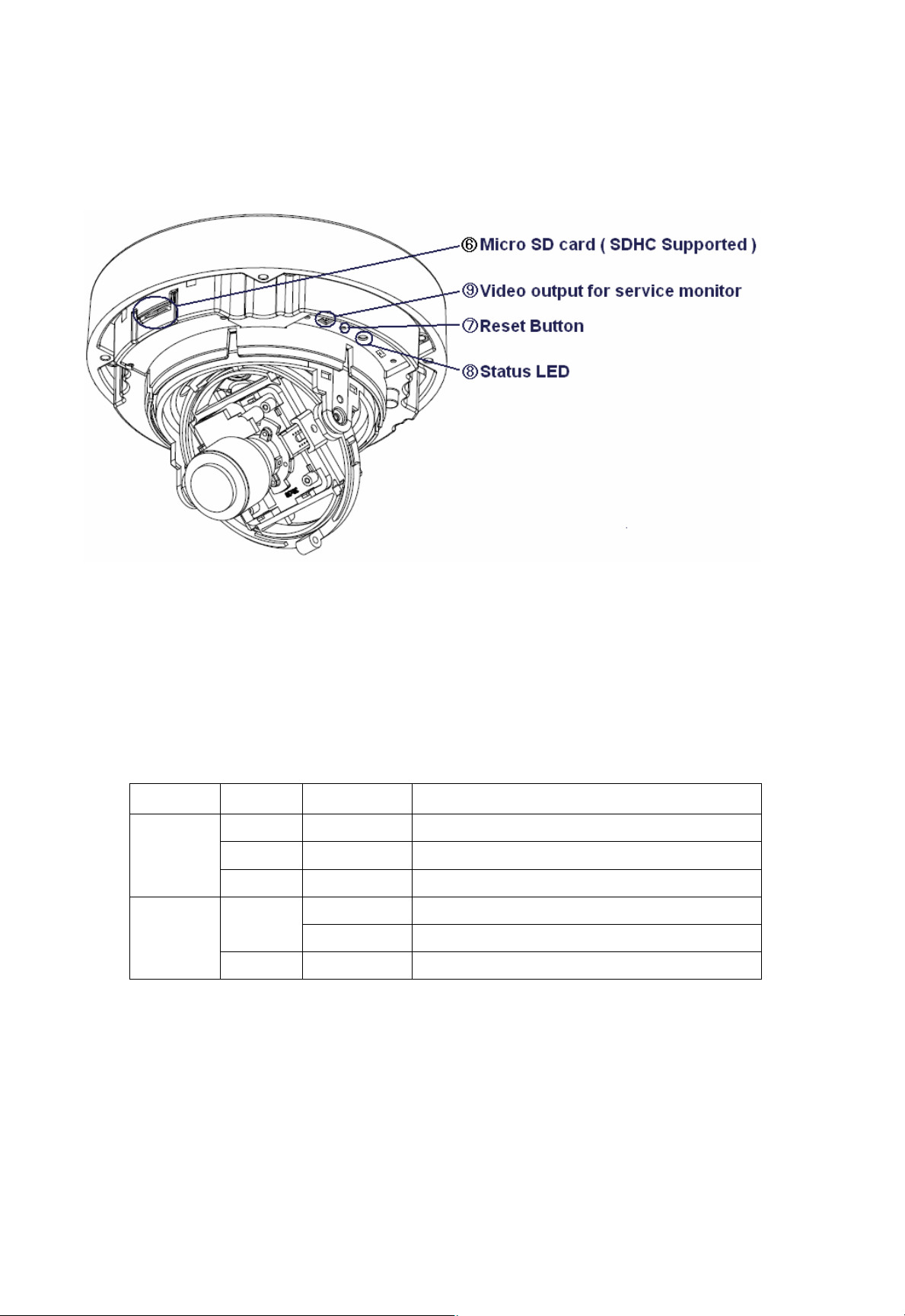
6. Micro SD card
Save snapshot images and video onto a Micro SD card.
7. Reset Button
Press this button to install the camera using the GANZ Dynamic Domain Name Service
(DDNS), or to restore the camera configuration to its factory default settings.
8. Status LED
LED Color Indication System Status
Green On Connection to 10/100Mbps Network / LAN.
Network
Status
9. Video Output for Service monitor
This analog video output is available when installation mode is set to ON. Use access ory cable
to video output.
Amber Flash Indication of network activity.
Unlit - No network connection established.
On Network connection is established.
Green
Flash Camera is booting up.
Red Flash Firmware Upload in progress.
2. Accessing the Camera
Follow the instructions in the GANZ PixelPro Installation Guide to install the camera.
The GANZ PixelPro can be accessed with most standard operating systems and browsers. The
recommended browser is Internet Explorer for Windows.
2.1 Access from a Web Browser
1. Launch a web browser (Internet Explorer or compatible e quivalent)
2. Enter the IP address (or name server address) of the camera into the Address Ba r.
3. Login dialog will appear when the camera is accessed for the first time.
4. The default username is ADMIN and the default password is 1234.
5. The camera’s Live View page is now displayed in your br owser.
NOTE: The layout of the live view page in the camera may have been customized to meet
specific requirements. Consequently, some of the examples and functions featured here may differ
from those displayed on your own Live View page.
2.2 Accessing the Camera from the Internet
Once installed, the camera will be accessible on the Local Area Network (LAN). Then, you must
configure the router/firewall to allow incoming data traffic to access the camera from the Internet.
For security reasons this is usually done on a specific port, using port forwarding. Please refer to
the documentation for router/firewall for further instructions on port forwarding.
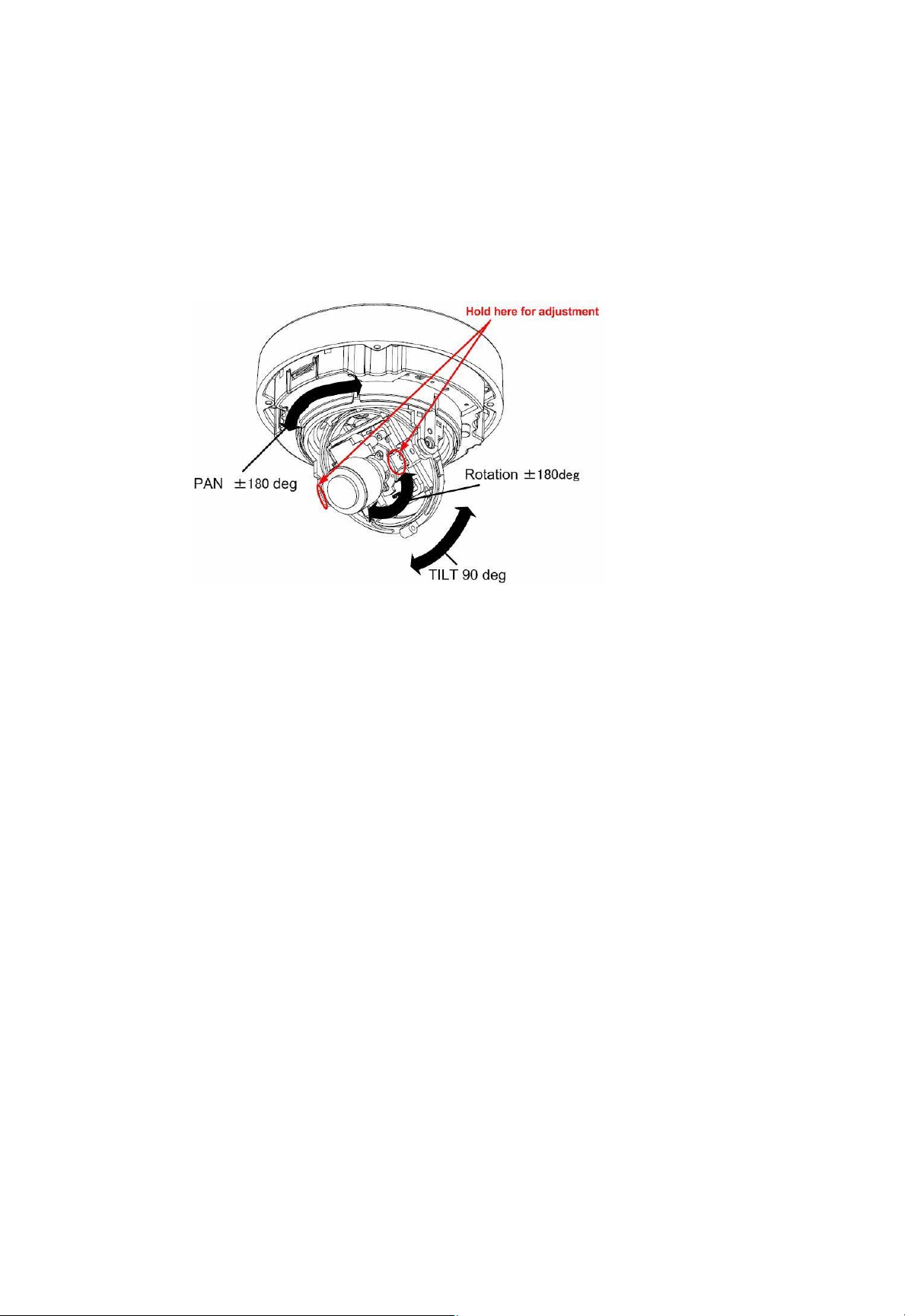
2.3 Adjusting the Camera Direction
The camera body is set in a 3-axis gimbal mount, allowing movement in the pan, tilt and
rotational planes. Adjust the direction of the lens so that it faces the subject.
2.4 Adjusting the Image and Focus
To adjust the position of the lens:
ZN-DT1A (Normal Lens)
1. Open the Live View page in your web browser.
- Select the Setup tab, and open the Installation page.
- Set ‘Installation Mode’ to ‘ON’ and select the ‘Video Format' (NTSC).
2. Connect analog monitor to the VIDEO OUT (BNC) on the cable.
- Unscrew the zoom puller on the lens by turning it counter-clockwise.
- Adjust the zoom setting and re-tighten the zoom puller.
- Unscrew the focus puller on the lens to adjust the focus, and re-tighten the focus puller.
3. Check the image from the Live View page on your web browser.
- Set ‘Installation Mode’ to ‘OFF’ to resume normal camera operation.
NOTE: DC Auto-Iris should always be disabled while focusing the camera. This will set the iris to
the wide open position, which yields the smallest depth of field, and thus the best conditions for
focusing the lens. When the focus has been set by using this method, it will maintain its focus in
any kind of lighting conditions.
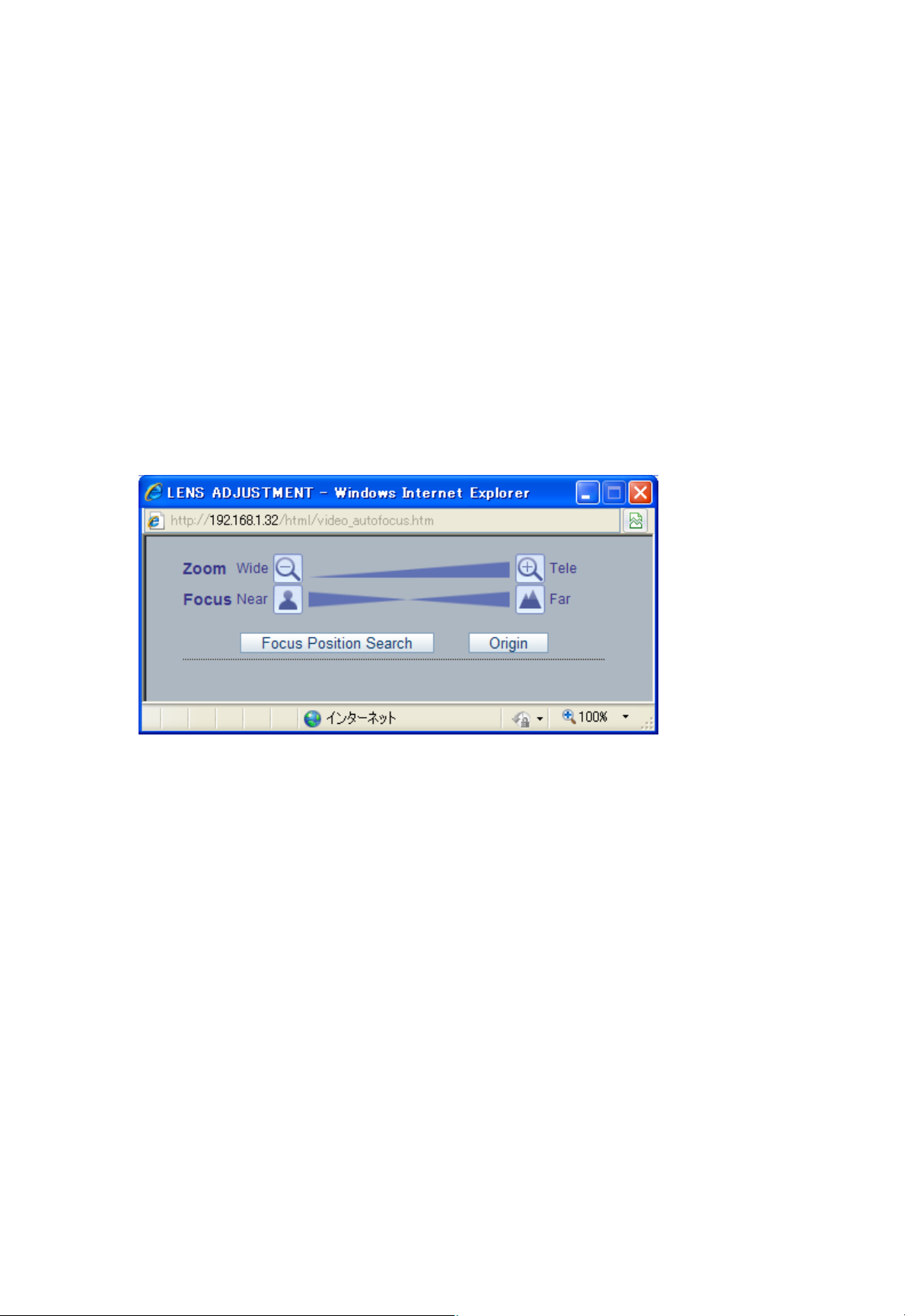
2.4 Adjusting the Image and Focus (cont’d)
ZN-DT1M, ZN-DT2M (MFZ Lens)
1. Open the Live View page in your web browser.
- Select the Setup tab, and open the Video -> Camera page.
- Click ‘Lens Adjustment’.
2. Set the desired Zoom position.
- Wait a few seconds, as the camera unit will attempt to automatically adjust the focus.
3. If the focus has not adjusted properly, click the ‘Focus Position Search’ button.
NOTE: DC Auto-Iris should always be disabled while focusing the camera. This will set the iris to
the wide open position, which yields the smallest depth of field, and thus the best conditions for
focusing the lens. When the focus has been set by using this method, it will maintain its focus in
any kind of lighting conditions.

2.5 Live View
Client PC Speaker (enable / disable)
Client PC Microphone (enable / disable)
Digital Zoom
Snapshot
Full Screen
Video Stream Change (1st Stream <> 2nd Stream)
Play: Start Video Stream
Stop: Stop Streaming
NOTE: It is possible that not all the buttons described below will be visible unless the Live View page
has been customized to display them.
2.6 Video stream types
Motion JPEG
This format uses standard JPEG images in the video stream. These images are then display ed
and updated at a rate sufficient to create a stream that shows constantly updated motion.
The Motion JPEG stream uses considerable amounts of bandwidth, but also prov ides excellent
image quality and access to every individual image contained in the stream.
H.264 Protocols & Communication Methods
- RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) is a protocol that allows programs to man age the real-time
transmission of multimedia data, via unicast or multicast.
- RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol) serves as a control protocol, to negotiate the type of
transport protocol used for the stream. RTSP is used by a viewing client to start a unicast session
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a communications protocol that offers limited service for
exchanging data in a network which uses the Internet Prot ocol (IP). UDP is an alternative to the
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The advantage of UDP is that it is not required to deliver all
data and may drop network packets when there is network congestion. This is suitable for live
video, as there is no point in re-transmitting old information that will not be display ed anyway.

H.264 Protocols & Communication Methods (continued)
Unicasting is communication between a single sender and a single receiv er over a network. This
means that the video stream is transmitted independently to each user, and each user receives
their own video stream. A benefit of unicasting is in case one stream fails, it only affects one user.
Multicasting is bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces bandwidth usage by simultaneously
delivering a single stream of information to multiple network recipients. This technology is used
primarily on delimited networks (intranets), as each user needs an uninterrupted data flow and should
not rely on network routers.
2.7 How to Stream H.264
Deciding on the combination of protocols and methods to use depends on your viewing
requirements and on the properties of your network. Setting the preferred method(s) is done in the
control applet for AMC, which is found in the Windows Control Panel. When this has been set,
AMC will test all the selected methods in the specified order, until the first functioning one is found.
RTP+RTSP This method (actually RTP over UDP and RTSP over TCP) should be your first
consideration for live video, especially when it is important to always have an up-todate video
stream, even if some images are lost due to network problems. This could be configured as
multicast or unicast.
Multicasting provides the most efficient usage of bandwidth, especially when there are large
numbers of clients viewing simultaneously. Note however, that a multicast broadcast cou ld n ot
pass a network router unless the router is configured to allow this. For example, it is not possible
to multicast over the Internet.
Unicasting should be used for video-on-demand broadcasting, so that there is no video traffic
on the network until a client connects and requests the stream. However, as more and more
unicast clients get connected, the traffic on the network will increase and may cause
congestion. Although there is a maximum of 20 unicast viewers, note that all multicast users
combined count as 1 unicast viewer.
RTP/RTSP This unicast method is RTP tunneled over RTSP. This could be us ed to exploit the
fact that it is relatively simple to configure firewalls to allow RTSP traffic.
RTP/RTSP/HTTP or RTP/RTSP/HTTPS These two methods could also be used to traverse
firewalls. Firewalls are commonly configured to allow the HTTP protocol, allowing RTP to be
tunneled.
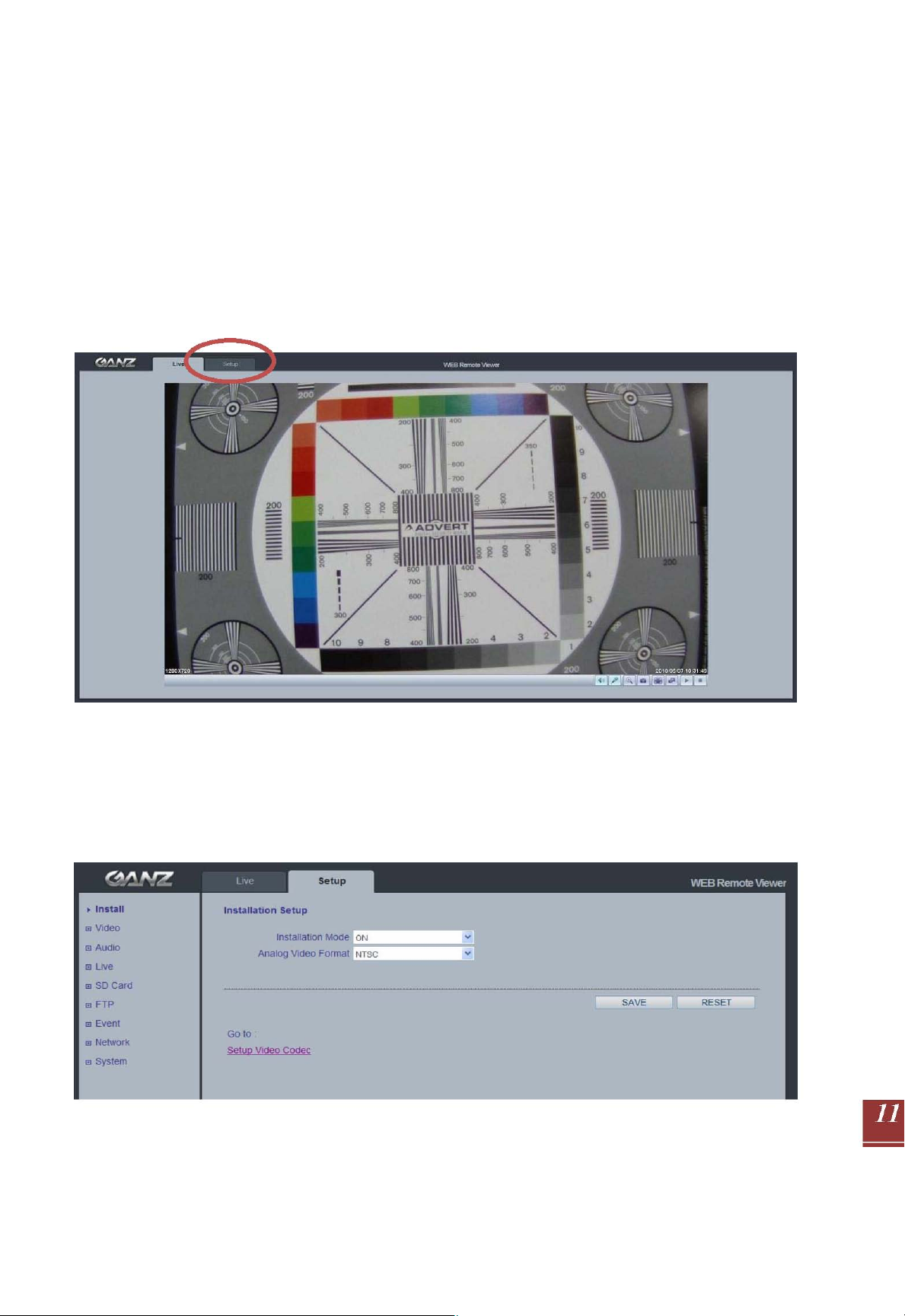
3. Setup
The GANZ PixelPro is configured from the Setup tab, which is available on the upper-left hand
side in the web interface. This configuration could be performed by:
- Administrators, who have unrestricted access to all settings under the Setup tab.
- Users, who have access to the Video & Image, Live View, and Event Configu ration sections.
Accessing the Setup link from a browser:
1. Start your web browser and enter the IP address or name server address of the camera into the
address bar.
2. The Live View page is now displayed. Click on the Setup tab.

4. Installation
The following descriptions show examples of some of the features available with GANZ PixelPro.
4.1 Installation Mode
Installation Mode allows use of the analog BNC output from the camera to connect the camera
to a service monitor, in order to adjust the positioning of the camera and focus the len s.
ON : Analog Output is enabled; both IP video streams are set to VGA (640 x 480) resolution.
OFF : Analog Output will be disabled.
NOTE: You must turn Installation Mode OFF to utilize the Megapixel features of the camera.
5. Camera and Image
The following descriptions show examples of some of the features available with GANZ PixelPro.
5.1 Video Codec
This section allows you to choose the compression codec for each of the video streams.
Motion JPEG
This format uses standard JPEG still images in the video stream. These images then are displayed
and updated at a rate sufficient to create a stream that shows constantly updated motion.
The Motion JPEG stream uses considerable amounts of bandwidth, but also provides excellent
image quality and access to every individual image contained in the stream.
Multiple clients accessing Motion JPEG streams could use different image settings.
H.264
This is a video compression standard that makes good use of bandwidth and could provide
high-quality video streams at less than 1 Mbit/s.
The H.264 standard provides the scope for a large range of different coding tools for use by
various applications in different situations, and the GANZ PixelPro provides certain subsets of
these tools.
Using H.264, it is also possible to control the bit rate, which in turn allows the amount of bandwidth
usage to be controlled. CBR (Constant Bit Rate) is used to achieve a specific bit rate by varying the
quality of the H.264 stream. While using VBR (Variable Bit Rate), the quality of the video stream is
kept as constant as possible, at the cost of a varying bit rate.
 Loading...
Loading...