Page 1

Page 2

Product name: Indoor IP Dome Camera (ZN-D2024)
Release Date:
Manual Revision: 1.0
Web site: www.ganz.jp
Email: zn-tech@cbc.co.jp
2007/12/03
zn-sales@cbc.co.jp
Made in Taiwan. ©Copyright 2007. All rights reserved
- 1 -
Page 3

Before You Use This Product
The use of surveillance devices may be prohibited by law in your country. The IP
Camera is not only a high-performance web-ready camera but also can be part of a
flexible surveillance system. It is the user’s responsibility to ensure that the
operation of such devices is legal before installing this unit for its intended use.
It is important to first v erify that all c ontents received are complete according to the
list in the "Package Contents" chapter. Take notice of the warnings in “Quick
installation guide” before the IP Camera is installed, then ca refully read and follow
the instructions in the “Installation” chapter to avoid damages due to faulty assembly
and installation. This also ensures the product is used properly as intended.
The IP Camera is a network device and its use should be straightforward for those
who have basic network knowledge. The “T roubleshooting” chapter in the Appendix
provides remedies to the most common errors in set up and configuration. You
should consult this chapter f irst if you run into a system error.
The IP Camera is designed for various applications including video sharing, general
security/surveillance, etc. The “How to Use” chapter suggests ways to best utilize
the IP Camera and ensure proper operations. For the creative and professional
developers, the "URL Commands of The IP Camera" chapter serves to be a helpful
reference to customize existing homepages or integrating with the current web
server.
For paragraphs preceded by the reader should use caution to understand
completely the warnings. Ignoring the warnings may result in serious hazards or
injuries.
- 2 -
Page 4

Table of Contents
Before Yo u Use This Product......................................................................2
Package Content .....................................................................................5
Installation.............................................................................................6
Hardware installation..........................................................................6
Software installation...........................................................................7
Initial Access to the IP Camera ............................................................8
Check Network Settings ................................................................8
Add Password to prevent Unauthorized Access..................................8
How to Use .......................................................................................9
Authentication..............................................................................9
Installing plug-in.............................................................................. 10
Primary user’s capability ...................................................................11
Main Screen with Camera View.....................................................11
Digital Zoom.............................................................................. 14
MP4 Recording ........................................................................... 15
Snapshot...................................................................................15
Client settings............................................................................16
Digital output.............................................................................18
Audio communication.................................................................. 19
Administrator’s capability.................................................................. 20
Fine-tuning for Best Performance..................................................20
Opening accounts for new users ................................................... 23
Build a security application ..........................................................24
Software revision upgrade ........................................................... 25
Definitions in Configuration.....................................................................26
System parameters.......................................................................... 27
Security settings.............................................................................. 28
Network settings.............................................................................. 30
Network type.............................................................................30
HTTP ........................................................................................31
FTP ..........................................................................................31
RTSP Streaming .........................................................................31
- 3 -
Page 5

DDNS.............................................................................................34
Access List......................................................................................35
Audio and Video............................................................................... 36
Video Settings............................................................................36
Audio settings............................................................................37
Image Settings ..........................................................................39
Privacy Mask..............................................................................40
Motion detection.............................................................................. 41
Application...................................................................................... 43
Event........................................................................................ 44
Server ......................................................................................45
Media .......................................................................................47
Recording .......................................................................................49
System log......................................................................................50
Maintenance.................................................................................... 52
Appendix.............................................................................................. 54
A. Troubleshooting ........................................................................... 54
Status LED ................................................................................ 54
Reset and restore....................................................................... 54
B. Technical specifications .................................................................55
C. Technology License Notice............................................................. 57
D. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) ..............................................58
- 4 -
Page 6

Package Content
- 5 -
Page 7

Installation
In this manual, "User" refers to whoever has access to the IP Camera, and
"Administrator" refers to the person who can configure the IP Camera and grant user
access to the camera.
Hardware installation
Please verify that your product package contains all the accessories listed in the
foregoing Package Contents. Depending on the user’s application, an Ethernet cable
may be needed. The Ethernet cable should meet the specs of UTP Category 5 and not
exceed 100 meters in length.
Connect the power adapter jack to the IP Camera before plugging in to the
power socket. This will reduce the risk of accidental electric shock.
Upon powering up, the status LED will become lighted first and then the device will go
through booting process. The status LED will be steady orange for getting IP address.
After getting IP Address, the LED will blink orange and red as heartbeat to indicate
alive.
- 6 -
Page 8

To install in Ethernet
Make sure the Ethernet is firmly connected to a switch hub. After attaching the
Ethernet cable plug in the power adapter. If the LED turns out to blink orange-color, go
to next paragraph “Software installation”.
This IP Camera provides a general I/O terminal block with one digital input and one
digital output device control. The pin definition is as below.
1: Power
2: Digital output
3: Digital input
4: Ground
Ext./Int.
Switch “Internal” or “Microphone” to set up the source of audio input
Software installation
At the end of the hardware installation, users can use Installation Wizard program
included in the product CDROM to find the location of the IP Camera. There may be
many IP Cameras in the local network. Users can differentiate the IP Cameras with the
serial number. The serial number is printed on the labels on the carton and the
bottom of the IP Camera body. Please refer to the Quick installation guide of
Installation Wizard for details.
Once installation is complete, the Administrator should proceed to the next
section "Initial Access to the IP Camera" for necessary checks and
configurations.
- 7 -
Page 9

Initial Access to the IP Camera
Check Network Settings
The IP Camera can be connected either before or immediately after software
installation onto the Local Area Network. The Administrator should complete the
network settings on the configuration page, including the correct subnet mask and IP
address of gateway and DNS. Ask your network administrator or Internet service
provider for the detail information. By default the IP Camera requires the Administrator
to run installation every time it reboots. If the network settings are to remain
unchanged, disable the Install option. Refer to “Network settings” on the System
Configuration page for details. If any setting is entered incorrectly and cannot proceed
to setting up the IP Camera, restore the factory settings following the steps in the
“Troubleshooting” chapter of the Appendix.
Add Password to prevent Unauthorized Access
The default Administrator’s password is blank and the IP Camera initially will not ask for
any password. The Administrator should immediately implement a new
password as a matter of prudent security practice. Once the Administrator’s
password is saved, the IP Camera will ask for the user’s name and password before
each access. The Administrator can set up a maximum of twenty ( 20) u ser a ccounts.
Each user can access the IP Camera except to perform system configuration. Some
critical functions are exclusive for the Administrator , such as system configur ation, user
administration, and software upgrades. The user name for the Administrator is
permanently assigned as “root”. Once the password is changed, the browser will
display an authentication window to ask for the new password. Once the password is
set, there is no provision to recover the Administrator’s password. The only
option is to restore to the original factory default settings.
- 8 -
Page 10
How to Use
A PC with Windows operating system can use the Internet Explorer to connect to the IP
Camera. A plug-in will be installed into the IE when it is connected for the first time. A
PC with Linux operating system can connect to the camera using a browser like Firefox.
It needs to install QuickTime first to view streaming.
Authentication
After opening the Web browser and typing in the URL of the IP Camera, a dialogue
window pops up to request a username and password. Upon successful authentication,
the following figure is displayed.
The foreground is the login window and the background shows the message if
authentication fails. The user may check the option box to save the password for future
convenience. This option is not available to the Administrator for obvious reason.
- 9 -
Page 11

Installing plug-in
For the initial access to the IP Camera in Windows, the web browser may prompt for
permission to install a new plug-in for the IP Camera on the Internet Explorer.
Permission request depends on the Internet security settings of the user’s PC or
notebook. If the highest security level is set, the computer may prohibit any installation
and execution attempt. This plug-in has been registered for certificate and is used to
display the video in the browser. Users may click on
to proceed. If the w eb
browser does not allow the user to continue to install, check the Internet security
option and lower the security levels or contact your IT or networking su pervisor for
help.
- 10 -
Page 12
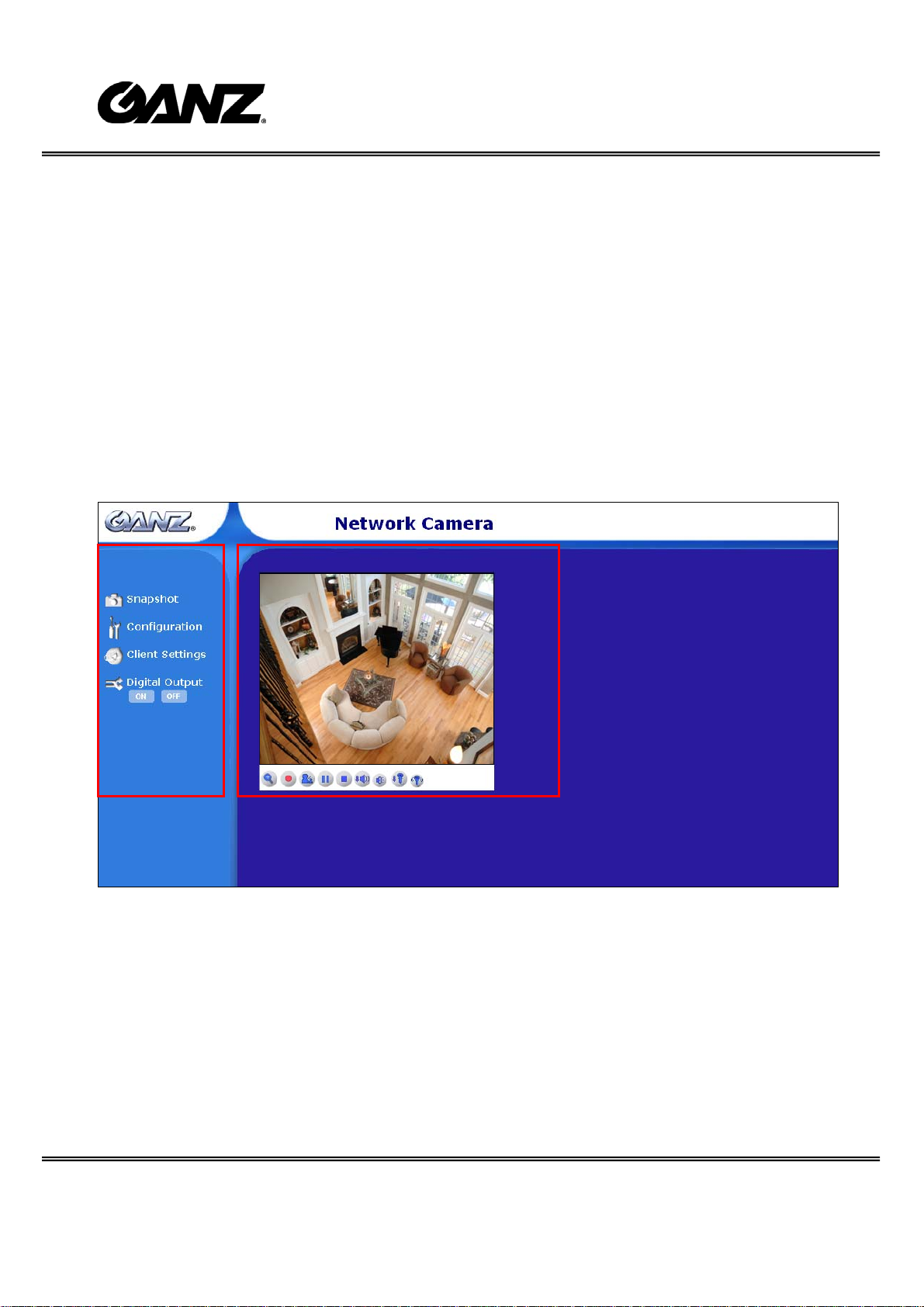
Primary user’s capability
Main Screen with Camera View
The main page layout has two parts:
Configuration functions: The camera can be configured using these user interfaces.
Camera View: What the camera sees.
Click on the configuration link to the left of the image window to enter the configuration
page.
Here is the layout in IE when it is MPEG-4 streaming.
- 11 -
Page 13
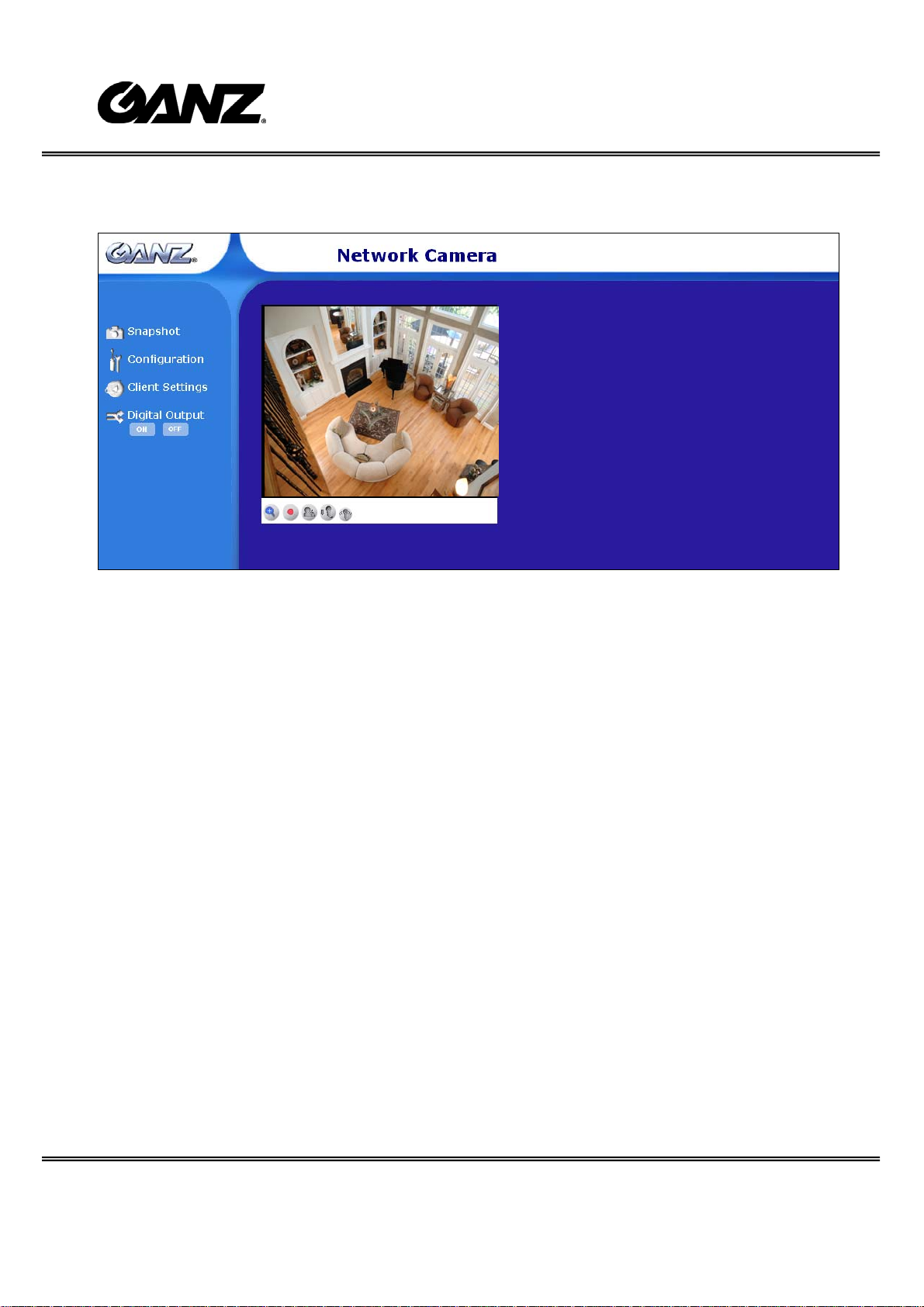
The function in JPEG will be a little different when it is JPEG streaming. Only d igital
zoom and record button are supported.
- 12 -
Page 14

Here is the layout in Firefox when it is MPEG-4 streaming. It uses QuickTime to
streaming.
Here is the layout in Firefox when it is JPEG streaming.
- 13 -
Page 15
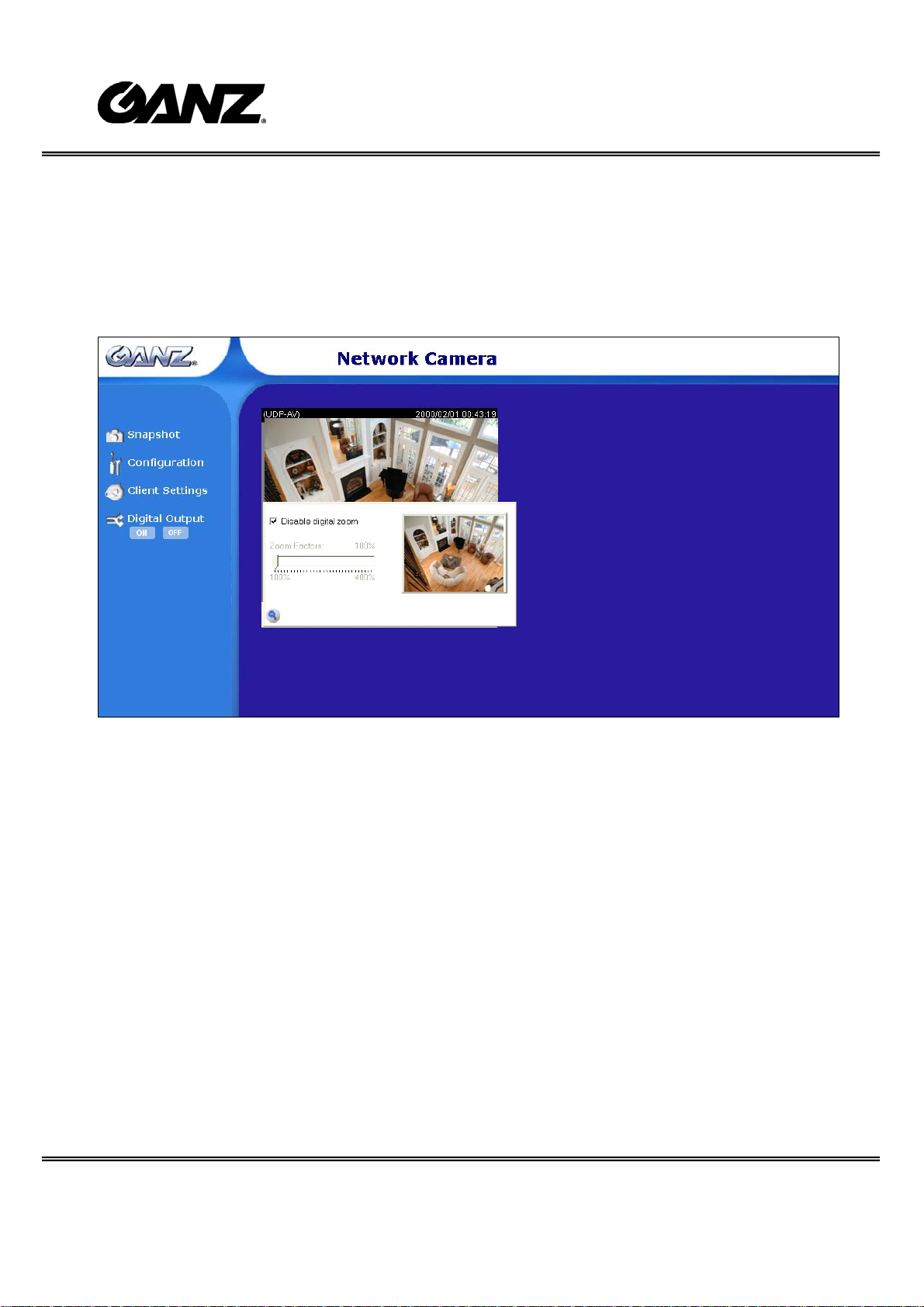
Digital Zoom
Click on the magnifier icon under the camera view then the digital zoom control panel
will be shown. Uncheck “Disable digital zoom” and use the slider control to change the
zoom factors.
- 14 -
Page 16
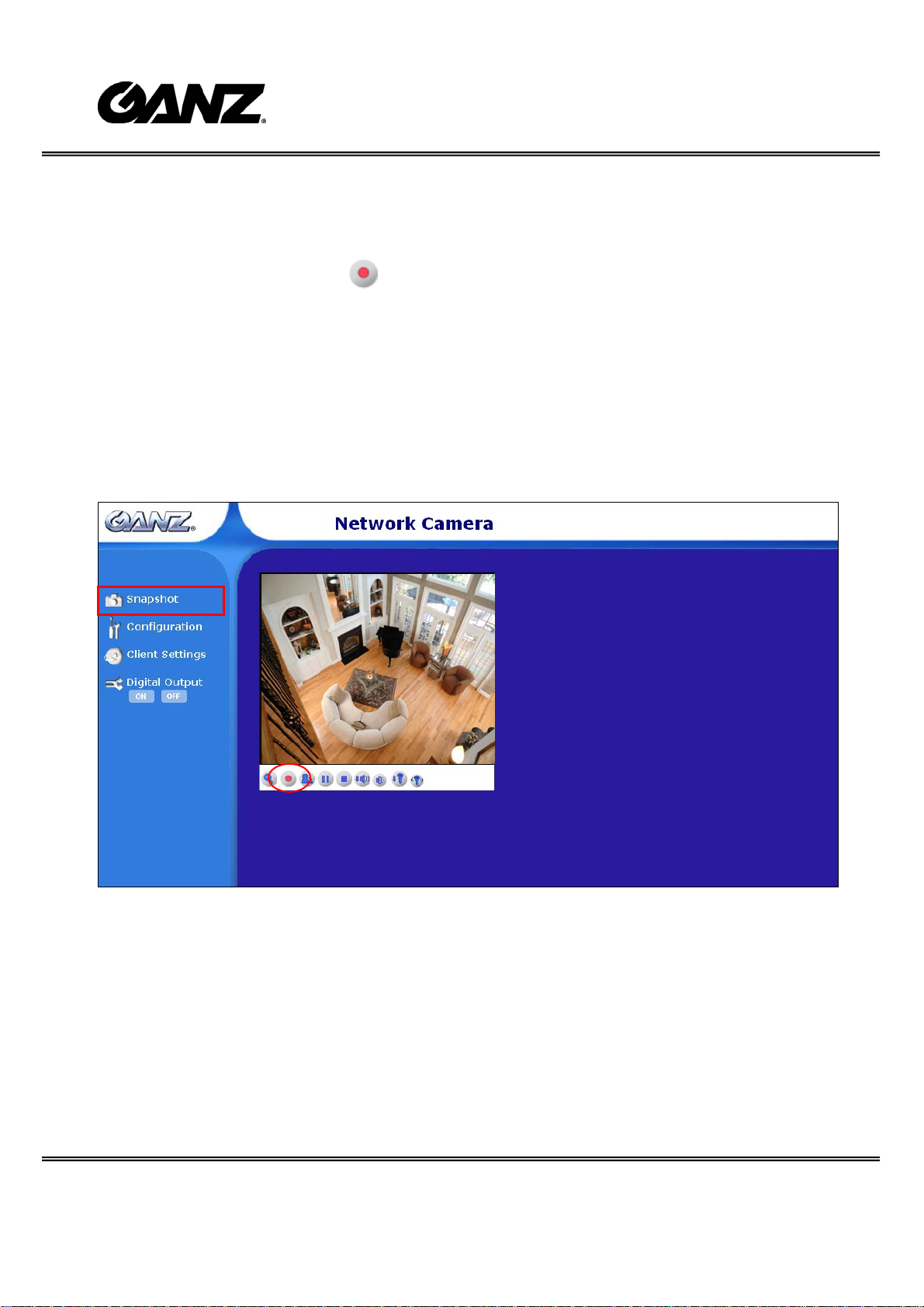
MP4 Recording
Click on the red circle button on the plugin to start MP4 recording. Y ou can set the
related options in client setting page.
Snapshot
Click on “Snapshot”, web browser will pop up a new window to show the snapshot.
Users can point at the snapshot and click the right button of mouse to save it.
- 15 -
Page 17
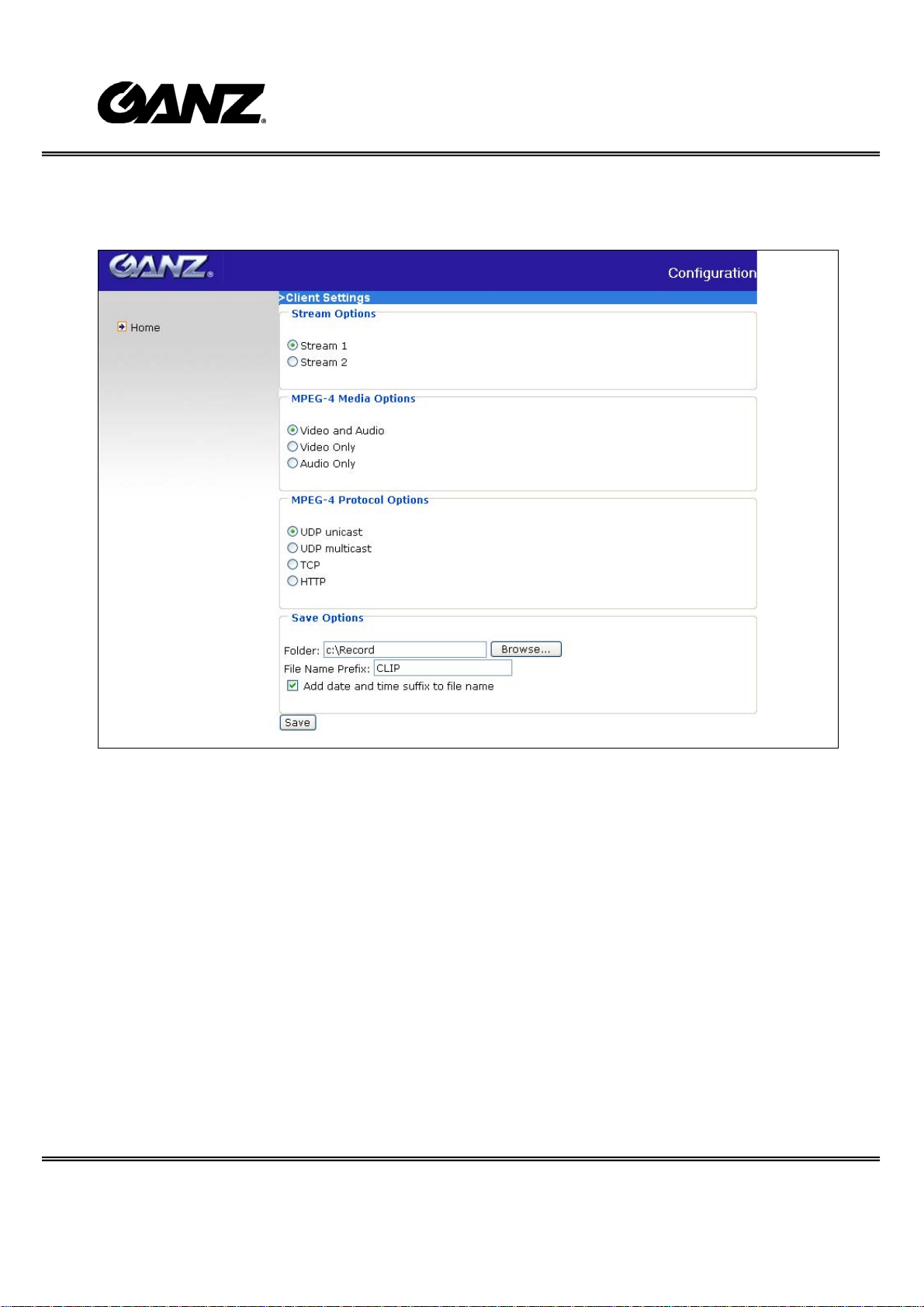
Client settings
1.
2.
3.
4.
There are four settings for the client side in IE.
1. The first one is “Stream Options” for users to determine which stream to be
streaming. This product supports dual-stream. Therefore, there are two streams to
choose.
2. The second one is “MPEG-4 Media Options” for users to determine which media to
be streaming under MPEG-4 mode.
3. The third one is “MPEG-4 Protocol Options” which allows choices on connection
protocol between client and server. There are four protocols choices to optimize
your usage – UDP unicast, UDP multicast, TCP and HTTP.
z The UDP unicast protocol allows for more real-time audio and video streams.
However, some packets may be lost due to network bu rst traffic and images
- 16 -
Page 18

may be obscured.
z The UDP multicast protocol allows to save the ba ndwidth of server while
serving multiple clients at the same time.
z The TCP protocol allows for less packet loss and produces a more accurate
video display. The downside with this protocol is that the real-time effect is
worse than that with the UDP protocol.
z The HTTP protocol allows the same quality as TCP protocol and the user don’t
need to open specific port to streaming under some network environment.
If no special need is required, UDP unicast protocol is recommended. Generally
speaking, the client’s choice will be in the order of UDP multicast → UDP unicast →
TCP → HTTP. After the IP Camera is connected successfully, “Protocol Option” will
indicate the selected protocol. The selected protoco l will be recorded in the user' s PC
and will be used for the next connection. If the network environment is changed, or the
user wants to let the web browser to detect again, manually select the UDP protocol,
save, and return HOME to re-connect.
4. The fourth one is “Save Options” . User can specify the recording folder, file name
prefix and suffix here.
- 17 -
Page 19

There is only one setting “Stream Options” for the client side in Firefox. User can
choose to view stream1 and stream2.
<url> http://<IP Camera>/clientset.html <IP Camera> is the domain name or the
original IP address of the IP Camera.
Digital output
Click on “ON” , the digital output of the IP Camera will be triggered. Or , clicking on “OFF”
can let the digital output turn into normal state.
- 18 -
Page 20

Audio communication
The camera supports two-way audio communication so that operators can transmit
and receive audio simultaneously. By using the camera’s built-in microphone and an
external speaker , you can communicate and give instructions to people at the camera’s
location.
Please note that as JPEG only transmits a series of JPEG images to the client, to make
- 19 -
Page 21

use of this function, make sure the video mode is set to “MPEG-4” and the media option
is set to “Video and Audio”.
Click
to enable audio transmission to the camera; click to adjust the volume
of microphone; click
to turn off the audio. To stop talking, click again.
Audio is being transmitted
to the camera.
Administrator’s capability
Fine-tuning for Best Performance
Best performance generally equates to the fastest image refresh rate with the best
video quality, and at the lowest network bandwidth as possible. The three factors,
“Maximum frame rate”, “Constant bit rate”, and “Fixed quality” for MPEG-4 mode and
“Maximum frame rate” and “Fixed quality” for JPEG mode on the Audio and Video
Configuration page, are correlative to allow for achieving the best performance
possible.
- 20 -
Page 22

For Best Real-time Video Images
T o achiev e good real-time visual eff ect, the network bandwidth should be large enough
to allow a transmission rate of greater than 20 image frames per second. If the
broadband network is over 1 Mbps, set the “Constant bit rate” to 1000Kbps or
1200Kbps, or set “Fixed quality” at the highest quality . The maximum frame rate is 30.
If your network bandwidth is more than 512Kbps, you can adjust the bit rate according
to your bandwidth and set the maximum frame rate to 30 fps. If the images vary
dramatically in your environment, you may want to slow the maximum frame rate
down to 20 fps in order to lower the rate of data transmission. This allows for better
video quality and the human eyes cannot readily detect the differences between those
- 21 -
Page 23

of 20, 25, or 30 frames per second. If yo ur network bandwidth is below 512 Kbps, set
the “Constant bit rate” according to your bandwidth and try to get the best
performance by fine-tuning with the “Maximum frame rate” . In a slow network, greater
frame rate results in blur images. Video quality performance will vary somewhat due to
the number of users viewing on the network; even when the parameters have initially
been finely tuned. Performance will also suffer due to poor connectivity because of the
network’s burst constraint.
Only Quality Images Will Do
To have the best video quality, you should set “Fixed quality” at “Detailed” or
“Excellent” and adjust the “Maximum frame rate” to match your network’s bandwidth.
If your network is slow and you receive “broken” pictures, go to the TCP or HTTP
protocol in “MPEG-4 Protocol Options” and choose a more appropriate mode of
transmission. The images may suffer a time delay due to a slower connection. The
delay will also increase with added number of users.
Somewhere Between Real-time and Clear Images
If you have a broadband network, set “Fixed quality” at “Good” or better, rather than
setting “Constant bit rate”. You can also fix the bandwidth according to your actual
network speed and adjust the frame rate. Start from 30 fps down for best results but
not below 15 fps. If the image qualities are not improved, select a lower bandwidth
setting.
- 22 -
Page 24

Opening accounts for new users
1
2
3
Protect IP Camera by passwords
The IP Camera is shipped without any password by default. That means everyone can
access the IP Camera including the configuration as long as the IP address is known. It
is necessary to assign a password if the IP Camera is intended not to be a ccessed by
others. Type a new word twice in ○
1
to en able protection. This password is used to
identify the administrator. Then add an account with user name, password and
2
authentication for your friends in ○
. You can edit or delete users from ○3.
- 23 -
Page 25

Build a security application
The Administrator can use the built-in motion detection to monitor any movement to
perform many useful security applications. T o upload the snapshots, users can choose
either email, FTP, HTTP or Network storage according to user’s needs. All servers
setting are in Server section on Application page. Refer to the definiti on section for
detail configuration.
1. Click on “Configuration” on homepage,
2. Click on “Motion detection” at the left column,
3. Check “Enable motion detection” ,
4. Click on new to have a new window to monitor video,
5. Type in a name to identify the new window,
6. Use the mouse to click, hold, and drag the window corner to resize or the title bar to
move
7. Fine-tune using the “Sensitivity” and “Percentage” fields to best suit the camera’s
environment. Higher “Sensitivity” detects the slighter motion. Higher “Percentage”
discriminates smaller objects,
8. Clicking on “Save” enables the activity display. Green means the motion in the
window is under the watermark set by Administrator and red means it is over the
watermark,
9. Click on “Application” at the left column,
10.Add a server in server section,
11.Add a media with snapshot type in media section. And Set the number of pre-event
and post-event images to be uploaded
12.Add a event in event section
z Enter one event name and enable this event.
z Check the weekdays as you need and give the time interval to monitor the
motion detection ev ery day,
z Select the T rigger on Motion detection and Check the window name set in step
5
z Set the appropriate delay time to avoid continuous false alarms following the
original event
- 24 -
Page 26

z Check the server name set in Step 10 and select the media name set in Step
11.
13. Click on save to validate.
Software revision upgrade
Customers can obtain the up-to-date software from the web site of GANZ. An
easy-to-use Upgrade Wizard is provided to upgrade the IP Camera with just a few clicks.
The upgrade function is opened to the Administrator only. To upgrade the system,
follow the procedures below.
1. Download the firmware file named “xxx.pkg” from the appropriate product folder.
2. Run the Installation Wizard 2 and proceed following the prompts. Refer to the
instructions of the Installation Wizard 2 on CD-ROM for details.
3. Or upgrade firmware from HTTP web page directly.
4. The whole process will finish in a few minutes and it will automatically restart t he
system.
If power fails during the writing process of Flash memory, the program in the
memory of the IP Camera may be destroyed permanently. If the IP Camera cannot
restart properly, ask your dealer for technical service.
- 25 -
Page 27

Definitions in Configuration
Only the Administrator can access system configuration. Each category in the left
column will be explained in the following pages. The bold texts are the specific phrases
on the Option pages. The Administrator may type the URL below the figure to directly
enter the frame page of configuration. If the Administrator also wants to set certain
options through the URL, read the reference appendix for details.
<url> http://<IP Camera>/setup/system.html
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 26 -
Page 28

System parameters
"Host name" The text displays the title at the top of the main page.
“Turn off the LED indicator” Check this option to shut off the LED on the rear . It can
prevent the camera’s operation being noticed.
"Time zone" Adjust the time with that of the time-servers for local settings.
"Keep current date and time" Click on this to reserve the current date and time of
the IP Camera. An internal real-time clock maintains the date and time even when the
power of the system is turned off.
"Sync with computer time" Synchronize the date and time of the IP Camera with the
local computer. The read-only date and time of the PC is displayed as updated.
“Manual” Adjust the date and time according to what is entered by the Administrator .
Notice the format in the related fields while doing the entry.
IP Camera starts up. It will fail if the assigned time-server cannot be reached.
“NTP server” Assign the IP address or domain name of the time-server. Leaving the
text box blank connects the IP Camera to the default time-servers.
“Update interval” Select hourly , daily , weekly , or monthly update with the time on the
NTP server.
“Digital input” Select High or Low to define normal status of the digital input. The
current status is shown, too.
“Digital output” Select Grounded or Open to define normal status of the digital output.
The current status is shown, too.
Remember to click on
to immediately validate the changes. Otherwise, the
correct time will not be synchronized.
- 27 -
Page 29

Security settings
“Root password” Change the Administrator’s password by typing in the new
password identically in b oth text boxes. The typed ent ries will be displayed as aster isks
for security purposes. After press ing
, the web browser will ask the Adminis trator
for the new password for access.
“Add user” T ype the new user's name and password and press
to insert the new
entry. The new user will be displayed in the user name list. There is a m aximum of
twenty user accounts. There are three kinds of authentication: Administrator , Operator
and Viewer. Administrator can fully control the camera operation. Operator’s access
right can modify most of camera’s parameters except some privilege and network
options. Viewer can view, listen to camera; control DIDO of camera. IP Camera can
provide twenty accounts for your valuable customers or friends.
“Manage user” Pull down the user list to find the user’s name and press
to
delete the selected user. Or edit the password or authentication of the selected user
and press
to take effect.
- 28 -
Page 30

<url> http://<IP Camera>/setup/security.html
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 29 -
Page 31

Network settings
Any changes made on the Network type section wi ll restart the system in order to
validate the changes. Make sure every field is entered correctly before clicking on
.
Network type
“LAN” & “PPPoE”
The default type is LAN. Select PPPoE if using ADSL
"Get IP address automatically" & “Use fixed IP address”
The default status is “Get IP address automatically”. This can be tedious having to
perform software installation whenever the IP Camera starts. Therefore, once the
network settings, especially the IP address, have been entered correctly, select “Use
fixed IP address” then the IP Camera will skip installation at the next boot. The I P
Camera can automatically restart and operate normally after a power outage. Users
can run IP installer to check the IP address assigned to the IP Camera if the IP address
is forgotten or using the UPnP function provided by the IP Camera (MS Windows XP
provides UPnP function at My Network Place). “IP address” This is necessary for
network identification.
“Subnet mask” This is used to determine if the destination is in the same subnet. The
default value is “255.255.255.0”.
“Default router” This is the gateway used to forward frames to destinations in a
different subnet. Invalid router setting will fail the transmission to destinations in
different subnet.
“Primary DNS” The primary domain name server that translates hostnames into IP
addresses.
“Secondary DNS” Secondary domain name server that backups the Primary DNS.
“Primary WINS server” The primary WINS server that maintains the database o f
computer name and IP address.
“Secondary WINS server” The secondary WINS server that maintains the database
of computer name and IP address.
“PPPoE” If using the PPPoE interface, fill the following settings from ISP
“User name” The login name of PPPoE account
- 30 -
Page 32

“Password” The password of PPPoE account
“Confirm password” Input password again for confirmation
HTTP
“Authentication” It supports basic and digest modes.
“HTTP port” This can be other than the default Port 80. Once the port is changed, the
users must be notified the change for the connection to be successfu l. For instance,
when the Administrator changes the HTTP port of the IP Camera whose IP address is
192.168.0.100 from 80 to 8888, the users must type in the web browser
“http://192.168.0.100:8888” instead of “http://192.168.0.100”.
“Secondary HTTP port” It support alternate port to access HTTP server.
“Access name for stream 1” This is the access URL of stream 1 for making
connection from client software when its codec type is JPEG.
“Access name for stream 2” This is the access URL of stream 2 for making
connection from client software when its codec type is JPEG.
Using http://<ip address>:<http port>/<access name> to make connection.
FTP
“FTP port” This can be other than the default port 21. The user can change this value
from 1025 to 65535. After the changed, the external FTP client program must change
the server port of connection accordingly.
RTSP Streaming
“Authentication” It supports disable, basic and digest modes.
“Access name for stream 1” This is the access URL of stream 1 for making
connection from client software when the codec type is MPEG-4.
“Access name for stream 2” This is the access URL of stream 2 for making
connection from client software when the codec type is MPEG-4.
Using rtsp://<ip address>/<access name> to make connection
“RTSP port” This can be other than the default Port 554
“RTP port for video” The video channel port for RTP. It must be an even number.
- 31 -
Page 33

“RTCP port for video” The video channel port for RTCP. It must be the port number
of video RTP plus 1.
“RTP port for audio” The audio channel port for RTP. It must be an even number.
“RTCP port for audio” The audio channel port for RTCP. It must be the port number
of audio RTP plus 1.
User can modify Multicast setting for stream1 and stream2.
“Always multicast” Select it to enable multicast always.
“Multicast group address” It is used by sources and the receivers to send and
receive content.
“Multicast video port” The video channel port for multicast. It must be an even
number.
“Multicast RTCP video port” The video channel port for multicast RTCP. It must be
the port number of multicast video port plus 1.
“Multicast audio port” The audio channel port for multicast. It must be an e ven
number.
“Multicast RTCP audio port” The audio channel port for multicast RTCP. It must be
the port number of multicast audio port plus 1.
“Multicast TTL” It specifies the number of routers (hops) that multicast traffic is
permitted to pass through before expiring on the network.
- 32 -
Page 34

<url>
http://<IP Camera>/setup/network.html
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 33 -
Page 35

DDNS
“Enable DDNS” This option turns on the DDNS function.
“Provider” The provider list contains seven hosts that provide DDNS services. Please
connect to the service provider’s website to make sure the service charges.
“Host Name” If the User wants to use DDNS service, this field must be filled. Please
input the hostname that is registered in the DDNS server.
“Username/E-mail” The Username or E-mail field is necessary for logging in the
DDNS server or notify the User of the new IP address. Note: when this field is input as
“Username” the following field must be input as “Password”.
“Password/Key” Please input the password or key to get the DDNS service.
“Save” Click on this button to save current settings for the DDNS service and UPnP
function.
<url> http://<IP Camera>/setup/ddns.html
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 34 -
Page 36

Access List
The access list is to control the access permission of clients by checking the client IP
address.
There are two lists for permission control: Allow List and Deny List. Only those
clients whose IP address is in the Allow List and not in the Deny List can connect to
the Video Server or IP Camera for receiving the audio/video streaming.
Both Allow List and Deny List consist of a list of IP ranges. If you want to add a new
IP address range, type the Start IP Address and End IP Address in the text boxes
and click on the Add button. If you want to remove an existing IP address range, just
select from the pull-down menu and click on the Delete button.
Both the Allow List and Deny List can have 10 entries.
<url> http://<IP Camera>/setup/accesslist.html
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 35 -
Page 37

Audio and Video
This product supports dual-stream. It provides two setting for video streams, but only
one setting for audio.
Video Settings
“Video title” The text string can be displayed on video
“Color” Select either for color or monochrome video display.
“Power line frequency” The fluorescent light will flash according to th e power line
frequency that depends on local utility. Change the frequency setting to eliminate
uncomfortable flash image when the light source is only fluorescent light.
“Video orientation”
z Flip: Vertically rotate the video.
z Mirror: Horizontally rotate the video. Check options both if the IP Camera is
installed upside down.
“White balance” Adjust the value for best color temperature.
“Maximum Exposure Time” Adjust the maximum exposure time in different
environment.
z Overlay title and time stamp on video: Check it the title is shown on video.
There are different video quality settings for stream1 and stream2.
z Mode: It can be MPEG-4 or JPEG. If MPEG-4 is selected, it is streamed in RTSP
protocol. If JPEG is selected, it is streamed in server push mode.
z Frame size: If the mode is MPEG-4, there are three options, “176x144”,
“320x240” and “640x480”. If the mode is JPEG, there are three options,
“176x144”, “320x240” and “640x480”.
There are three dependent parameters provided in MPEG-4 mode for video
performance adjustment.
“Intra frame period” The interval of intra frame.
“Maximum frame rate” This limits the maximal refresh frame rate, which can be
combined with the “Video quality” to optimize bandwidth utilization and video quality .
- 36 -
Page 38

Choose “Constant bit rate” If the user wants to fix the bandwidth utilization
regardless of the video quality, choose “Fixed quality” and select the desired
bandwidth. The video quality may be poor due to the sending of maximal frame rate
within the limited bandwidth when images are moving rapidly . Consequently , to ensure
detailed video quality (quantization rate) regardless of the network, it will utilize more
bandwidth to send the maximal frames when images change drastically.
In JPEG mode, user can set “Maximum frame rate” and “Video quality” to adjust
the video performance.
Audio settings
“Mute” Turn off audio.
“Internal microphone input gain” Modify the gain of the internal audio input.
“External microphone input” There are two gain options, 0db and 20db.
“Audio type” Select audio codec “AAC” or “GSM-AMR” and the bit rate.
- 37 -
Page 39

<url>
http://<IP Camera>/setup/audiovideo.htm
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 38 -
Page 40

Image Settings
Click on this button to pop up another window to tune “Brightness”,
“Contrast”, “Hue” and “Saturation” for video compensation. Each field has elev en
levels ranging from -5 to +5. In “Brightness” and “Contrast” fields the value 0
indicates auto tuning. The user may press
image is O.K., press
to set the image settings. Click on to recall the
to fine-tune the image. When the
original settings without incorporating the changes.
- 39 -
Page 41

Privacy Mask
Click on the button to pop up another window to set privacy mask window. All users can
not view the block under privacy mask window.
“Enable privacy mask” Check this option to turn on privacy mask.
Click on this button to add a new window. At most five windows can exist
simultaneously. Use the mouse to click, hold, and drag the window fr ame to resize or
the title bar to move. Clicking on the ‘x’ at the upper right-hand corner of the window
deletes the window. Remember to click save in order to validate the changes. The base
of window axis is eight. You can see the X, Y, width and height of the window.
Click on this button to save the related window settings.
"Window Name" The text will show at the top of the window.
- 40 -
Page 42

The following figure shows the screen when is clicked and the privacy mask is
enabled.
Motion detection
“Enable motion detection” Check this option to turn on motion detection.
Click on this button to add a new window. At most three windows can exist
simultaneously. Use the mouse to click, hold, and drag the window fr ame to resize or
the title bar to move. Clicking on the ‘x’ at the upper right-hand corner of the window
deletes the window. Remember to save in order to validate the changes.
Click on this button to save the related window settings. A graphic bar will rise or
fall depending on the image variation. A green bar means the image variation is under
monitoring level and a red bar means the image variation is over monitoring level.
- 41 -
Page 43

When the bar goes red, the detected window will also be outlined in red. Going back to
the homepage, the monitored window is hidden but the red frame shows when motion
is detected.
"Window Name" The text will show at the top of the window.
“Sensitivity” This sets the endurable difference between two sequential images.
“Percentage” This sets the space ratio of moving objects in the monitoring window.
Higher sensitivity and small percentage will allow easier motion detection.
The following figure shows the screen when
is clicked.
<url>
http://<IP Camera>/setup/motion.htm
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 42 -
Page 44

Application
There are three sections in application page. They are event, server and media. Click
to pop a window to add a new item of event, server or media. Click to
delete the selected item from event, server or media. Click on the item name to pop a
window to edit it.
There can be at most three events. There can be at most five server and five media
configurations.
User can know the event name, status, weekly and time schedule and trigger type in
event section. The server name, type and address/location are shown in server section.
The current media free space, media name and type are shown in media section. After
adding a new media, the value of free space will be updated. User cannot add media
which size is larger than media free space.
It is suggested to set server and media first before setting event. The servers and
media selected in event list are not modified or deleted. Please remove them first from
the event if you want to delete or modify them. Recommend that using different media
in different event to make use all media be produced and received correctly. If using
the same media in different events and the events trigger almost simultaneously , the
servers in the second triggered event will not receive any media; there would be only
notifications.
- 43 -
Page 45

<url>
http://<IP Camera>/setup/application.htm
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
Event
“Event name” The unique name for event
“Enable this event” Check it to enable this event.
“Priority” The event with higher priority will be executed first.
“Delay second(s) before detecting next event” The delay to check next event. It
is used in motion detection and digital input trigger type.
There are four kinds of trigger supported.
“Video motion detection” Select the windows which need to be monitored.
“Periodic” The event is triggered in speci fied inte rvals. The unit of trigger interval is
minute.
“Digital input” To monitor digital input
“System boot” The event is triggered when the system boots up.
- 44 -
Page 46

The weekly and time schedules are provided.
“Sun” ~ “Sat” Select the days of the week to perf orm the event.
“Time” show “Always” or input the time interval.
The default action is triggering DO. If there are servers configured, the user can select
them from “Server name”, too.
“Trigger DO” Check it to trigger digital output for specific seconds when event is
triggered.
“Server name” Check it to sending the selected media when event is triggered.
Server
“Server name” The unique name for server
There are four kinds of servers supported. They are email server, FTP server, HTTP
- 45 -
Page 47

server and network storage.
Here is setting for email server.
“Sender email address” The email address of the sender
“Recipient email address” The email address of the recipient
“Server address” The domain name or IP address of the external email server.
“User name” This granted user name on the external email server.
“Password” This granted password on the external email server.
Here is setting for FTP server.
“Server address” The domain name or IP address of the external FTP server.
“Server port” This can be other than the default port 21. The user can change this
value from 1025 to 65535.
“User name” This granted user name on the external FTP server.
“Password” This granted password on the external FTP server.
“Remote folder name” Granted folder on the external FTP server. The strin g must
conform to that of the external FTP server. Some FTP servers cannot accept preceding
slash symbol before the path without virtual path mapping. Refer to the instructions for
the external FTP server for details. The folder privilege must be open for upload.
“Passive Mode” Check it to enable passive mode in transmission.
Here is setting for HTTP server.
“URL” The URL to upload the media.
“User name” This granted user name on the external HTTP server.
“Password” This granted password on the external HTTP server.
Here is setting for network storage. Only one network storage is supported.
“Network storage location” The path to upload the media
“Workgroup” The workgroup for network storage.
“User name” This granted user name on the network storage.
“Password” This granted password on the network storage.
After input the setting of server, user can click on
to test whether the setting is
correct. The testing result will be shown in a pop-up window.
- 46 -
Page 48

Media
“Media name” The unique name for media
There are three kinds of media. They are snapshot, video clip and system log.
Here is setting for snapshot.
“Source” The source of stream, stream1 or stream2.
“Send pre-event images” The number of pre-event images
“Send post-event images” The number of post-event images
“File Name Prefix” The prefix name will be added on the file name of the snapshot
images.
- 47 -
Page 49

“Add date and time suffix to file name” Check it to add timing information as file
name suffix.
Here is setting for video clip
“Source” The source of stream, stream1 or stream2.
“Pre-event recording” The interval of pre-event recording in seconds
There are two limitations for video clip file.
“Maximum duration” The maximal recording file duration in seconds
“Maximum file size” The maximal file size would be generated.
“File name prefix” The prefix name will be added on the file name of the video clip.
- 48 -
Page 50

Recording
The IP Camera supports recording on network storage. The operation of editing
recording item is the same as the one in application page. User can know the recording
name, status, weekly and time schedule, stream source and destination of recording.
There can be at most two recording entries. T o do recording on network storage, please
add network storage server in application page first.
<url>
http://<IP Camera>/setup/recording.htm
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
“Recording entry name” The unique name for recording entry
“Enable this recording” Check it to enable this event.
“Priority” The recording with higher priority will be executed first.
“Source” The source of stream, stream1 or stream2.
The weekly and time schedules are provided.
- 49 -
Page 51

“Sun” ~ “Sat” Select the days of the week to perf orm the event.
“Time” shows “Always” or input the time interval.
“Destination” Network storage server user added.
“Total cycle recording size” The total size for cycle recording in Kbytes
“Size of each file for recording” The single file size in Kbytes
“File Name Prefix” The prefix name will be added on the file name of the recording.
System log
The IP Camera support log the system messages on remote server. The protocol is
compliant to RFC 3164. If you have external Linux server with syslogd service, use “-r”
option to turn on the facility for receiving log from remote m achine. Or you can use
- 50 -
Page 52

some software on Windows which is compliant to RFC 3164.
Check “Enable remote log” and input the “IP address” and “port” number of the
log server to enable the remote log facility.
In the “Current log”, it displays the current system log file. The content of the log
provides useful information about configuration and connection after system boot- up.
<url>
http://<IP Camera>/setup/syslog.htm
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 51 -
Page 53

Maintenance
Five actions can be selected.
“Reboot system” Click the reboot button to restart system.
“Restore” Click it to restore all setting to factory de fault except setting in “Network
type” in network page.
“Factory default” Click on Factory default button on the configuration page to restore
the factory default settings. Any changes made so far will be lost and the system will be
reset to the initial factory settings. The system will restart and require the installer
program to set up the network again.
“Upgrade firmware” Select the firmware file and click upgrade button.
- 52 -
Page 54

<url> http://<IP Camera>/setup/maintain.htm
<IP Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the IP Camera.
- 53 -
Page 55

Appendix
A. Troubleshooting
Status LED
The following table lists the LED patterns in general.
Condition LED color
Loading system after power on Blink green and orange (twice)
During booting procedure Non light
Detecting and setting network Steady orange till IP address is confirmed
After network is setup (system up) Blink orange and red
During the upgrade firmware process Rapidly blink orange till firmware is
upgraded
Reset and restore
There is a button in the back of the IP Camera. It is used to reset the system or restore
the factory default settings. Sometimes resetting the system sets the system back to
normal state. If the system problems remain after reset, restore the factory settin gs
and install again.
RESET: Click on the button.
RESTORE:
1. Press on the reset button continuously until the status LED
rapidly blinks orange. It takes about 30 seconds.
2. Upon successful restore, the status LED will blink orange and
red.
Restoring the factory defaults will erase any previous settings. Reset or
restore the system after power on.
- 54 -
Page 56

B. Technical specifications
System
z CPU: CBC-1000 SoC
z Flash: 8MB
z RAM: 64MB
z Embedded OS: Linux 2.4
Lens
Vari-focal board lens, f=2mm~4mm, F1.4~1.8,
Focus range: 50 cm to infinity
Angle of View
53.2 ° ~ 105.1 ° (horizontal)
Shutter Time
1/5 sec. to 1/15000 sec.
Image Sensor
MICRON 1/4” CMOS sensor with VGA resolution
Minimum Illumination
1.5 Lux / F1.4
Video
z Compression: MJPEG & MPEG-4 video
z Streaming:
Simultaneous dual-stream
MPEG-4 streaming over UDP, TCP, or HTTP
MPEG-4 multicast streaming
MJPEG streaming over HTTP
z Supports 3GPP mobile surveillance
z Frame rates: 640x480 up to 30fps
Image settings
z Adjustable image size, quality, and bit rate
z Time stamp and text caption overlay
z Flip & mirror
z Configurable brightness, contrast,
saturation, sharpness and white balance
z AGC, AWB, AES
z Supports privacy masks
Audio
z Compression:
GSM-AMR speech encoding, bit rate: 4.75
kbps to 12.2 kbps
MPEG-4 AAC audio encoding, bit rate: 16
Kbps to 128 Kbps
z Interface:
Built-in microphone
External microphone input
Audio output
z Supports two-way audio by SIP protocol (*)
z Supports audio mute
Networking
z 10/100 Mbps Ethernet, RJ-45
z Protocols: IPv4, TCP/IP, HTTP, UPnP,
RTSP/RTP/RTCP, IGMP, SMTP, FTP, DHCP,
NTP, DNS, DDNS, and PPPoE
Alarm and Event Management
z Triple-window video motion detection
z One D/I and one D/O for external sensor
and alarm
z Event notification using HTTP, SMTP, or FTP
Security
z Triple-level user access with password
protection
z IP address filtering
Users
Camera live viewing for up to 10 clients
Dimension
143mm (D) x 106mm (H)
Weight
Net: 566g
Viewing System Requirements
z OS: Microsoft Windows 2000/XP/Vista
z Browser: Internet Explorer 6.x or above
- 55 -
Page 57

LED Indicator
z System power and status indicator
z System activity and network link indicator
Power
z 12V DC
z Consumption: Max 3.6W
z 802.3af compliant Power over Ethernet
Approvals
CE, FCC
Operating Environments
z Temperature: 0 ° ~ 55 ° C
z Humidity: 20 % ~ 80 % RH
z Real Player 10.5 or above
z Quick Time 6.5 or above
Installation, Management, and Maintenance
z 3-axis mechanism for flexible ceiling and
wall mount installation
z Installation Wizard 2
z 16-ch recording software
z Supports firmware upgrade
Applications
SDK available for application development and
system integration
- 56 -
Page 58

C. Technology License Notice
MPEG-4 AAC Technology
THIS PRODUCT IS LICENSED UNDER THE MPEG-4 AAC AUDIO PATENT LICENSE. THIS
PRODUCT MAY NOT BE DECOMPILED, REVERSE-ENGINEERED OR COPIED, EXCEPT
REGARD TO PC SOFTWARE, YOU MAY MAKE SINGLE COPIES FOR ARCHIVAL PURPOSES.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, PLEASE REFER TO HTTP://WWW.VIALICENSING.COM
MPEG-4 Visual Technology
THIS PRODUCT IS LICENSED UNDER THE MPEG-4 VISUAL PATENT PORTFOLIO
LICENSE FOR THE PERSONAL AND NON-COMMERCIAL USE OF A CONSUMER FOR (i)
ENCODING VIDEO IN COMPLIANCE WITH THE MPEG-4 VISUAL STANDARD ("MPEG- 4
VIDEO") AND/OR (ii) DECODING MPEG-4 VIDEO THAT WAS ENCODED BY A CONSUMER
ENGAGED IN A PERSONAL AND NON-COMMERCIAL ACTIVITY AND/OR WAS OBTAINED
FROM A VIDEO PROVIDER LICENSED BY MPEG LA TO PROVIDE MPEG-4 VIDEO. NO
LICENSE IS GRANTED OR SHALL BE IMPLIED FOR ANY OTHER USE. ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION INCLUDING THAT RELATING TO PROMOTIONAL, INTERNAL AND
COMMERCIAL USES AND LICENSING MAY BE OBTAINED FROM MPEG LA, LLC. SEE
HTTP://WWW.MPEGLA.COM
.
AMR-NB Standard
THIS PRODUCT IS LICENSED UNDER THE AMR-NB STANDARD PATENT LICENSE
AGREEMENT. WITH RESPECT TO THE USE OF THIS PRODUCT, THE FOLLOWING
LICENSORS’ PATENTS MAY APPLY:
TELEFONAKIEBOLAGET ERICSSON AB: US PAT. 6192335; 6275798; 6029125; 6424938;
6058359. NOKIA CORPORATION: US PAT. 5946651; 6199035. VOICEAGE CORPORATION:
AT PAT. 0516621; BE PAT. 0516621; CA PAT. 2010830; CH PAT. 0516621; DE PAT. 0516621;
DK PAT. 0516621; ES PAT. 0516621; FR PAT. 0516621; GB PAT. 0516621; GR PAT. 0516621; IT
PAT. 0516621; LI PAT. 0516621; LU PAT. 0516621; NL PAT. 0516621; SE PAT 051 6621; US PAT
5444816; AT PAT. 819303/AT E 198805T1; AU PAT. 697256; BE PAT. 819303; BR PAT.
9604838-7; CA PAT. 2216315; CH PAT. 819303; CN PAT. ZL96193827.7; DE PAT.
819303/DE69611607T2; DK PAT. 819303; ES PAT. 819303; EP PAT. 819303; FR PAT. 819303;
GB PAT. 819303; IT PAT. 819303; JP PAT. APP. 8-529817; NL PAT. 819303; SE PAT. 819303; U S
PAT. 5664053. THE LIST MAY BE UPDATED FROM TIME TO TIME BY LICENSORS AND A
CURRENT VERSION OF WHICH IS AVAILABLE ON LICENSOR’S WEBSITE AT
HTTP://WWW.VOICEAGE.COM.
.
- 57 -
Page 59

D. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
This device compiles with FCC Rules Part 15. Operation is subject to the following two conditions.
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
USA - This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limi ts for a Class B di gital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residentia l installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequenc y energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a partial installa tion. If this equipmen t does cau se
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determin ed by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures:
-- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
-- Increase the seperation between the equipment and receiver.
-- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
-- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission lim its.
Europe
limit B of EN55022/1998, and the requirement for immunity according to EN50082-1/1992.
Liability
GANZ Inc. cannot be held responsible for any technical or typographical errors and reserves the
right to make changes to the product and manuals without prior notice. GANZ Inc. makes no
warranty of any kind with regard to the materi al contained withi n this document, incl uding, but
not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for any particular purpose.
- This digital equipment fulfills th e requirement for radiated emission accordin g to
 Loading...
Loading...