Page 1

How to Monitor Effectively - Using the Hot Spot and Hot Spot V.C.
Without stage monitors, today's live music would probably not sound as good as it does. If you are a
musician or vocalist, you know how important it is to hear yourself clearly; you need to keep in tune and in
sync with the other instruments in the band. The high sound pressure levels of the amplifiers used today
often make this difficult. But monitors can also cause more than their share of problems. After reading this
section, you will understand why this is so, and what can be done about it.
Gain vs. Power
Feedback, the dreaded "Soundman's Curse", that awful squealing and screeching sound, is caused by a
regeneration of sound leaving the speaker and entering the microphone. A never-ending cycle is created
and the volume must be decreased to stop it. In a sound system, the amount of gain, or volume before
feedback, is not merely determined by the size of the power amplifier. The relationship between the
microphones and speakers and the room they are in will affect the gain of the system as well. Let's look at
two extreme cases:
Figure 1-2
In figure 1-2 we see the worst possible case of gain limiting. The microphone is pointed directly at the n the
speaker. We can't turn volume up at all without going into feedback immediately. We may be using only
1/1000th of the power available to us. With a 100-watt amp, that's only 1/10 of a watt!
In figure 1-3, we have increased the distance between the microphone and the speaker to 500'. We can get
100% gain and use all 100 watts of power without going into feedback.
Figure 1-3
Setting up your P.A. System and Monitors.
Obviously, in most cases we can't locate the microphones 500' away from the speakers. Therefore, we
have to place the speakers to adequately cover the listening area and, at the same time, place the
microphones so that we maximize the gain. Figure 1-4 shows a typical example:
In most cases, the speakers should be placed on stands, slightly above the heads of the audience, and in
front of and to each side of the stage. They should be turned slightly inward, but be careful! The more they
are turned in, the less gain you will have, as the sound begins to be directed at the microphones. Remember,
a few degrees of rotation can make a big difference!
Page 2
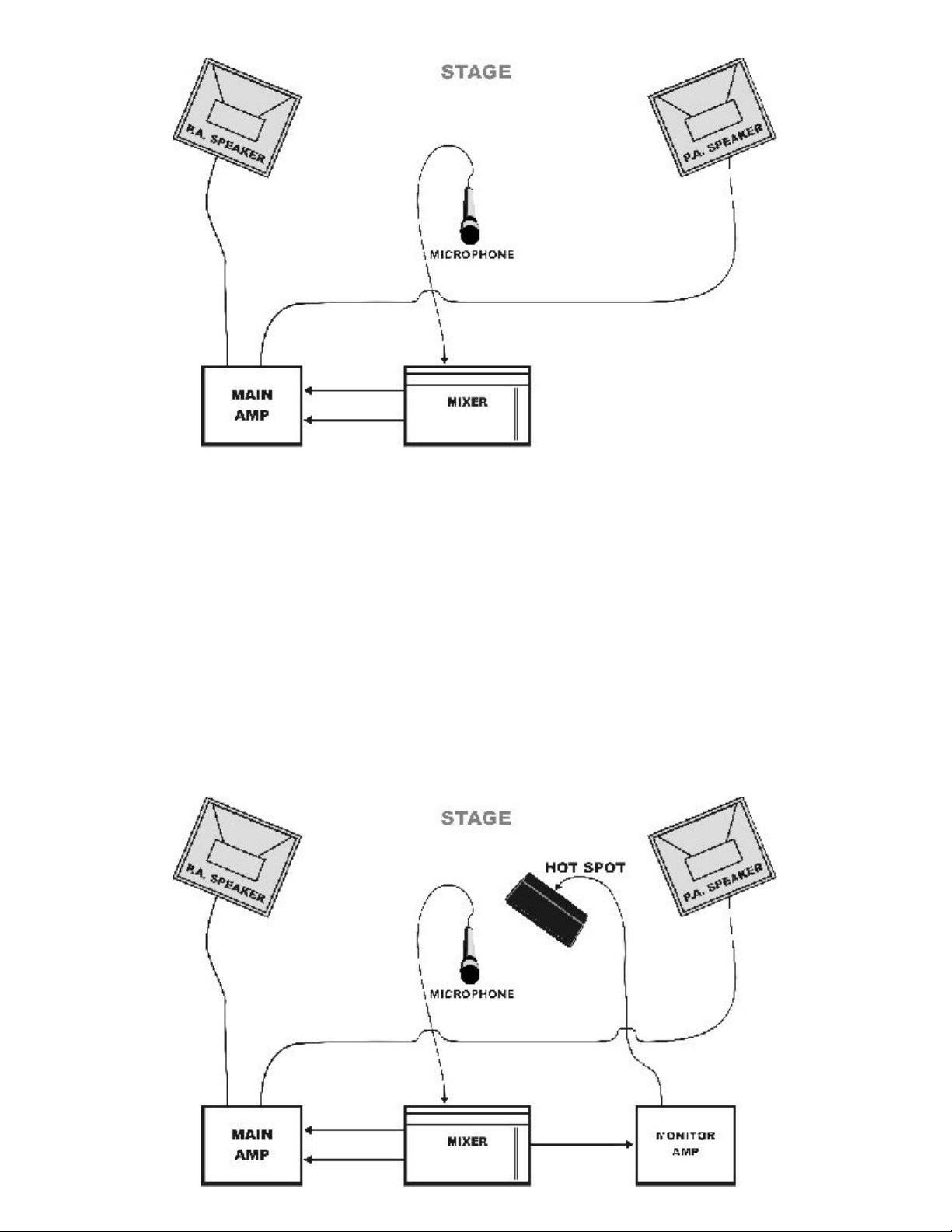
FIGURE 1-4
Figure 1-5 shows a monitor speaker on stage, in very close proximity to the microphone. If we were to
power this monitor speaker with the same amplifier used to power the main speakers, we would experience
major feedback problems. Given our knowledge of speaker/microphone relationships and their effect on
gain, what do you suppose would happen if the volume were turned up? The monitor speakers, being closer
to the microphone than the main speakers, and pointed towards the microphone, will go into feedback first,
causing the main speakers to feedback, and so limiting the gain of our entire system to that of the stage
monitors.
In order to eliminate this problem, the monitor speaker should have its own volume control, or, ideally, it
should be connected to a separate amplifier. With this setup, we can adjust the volume of one speaker
system without affecting the other. Thus, the gain of the monitors does not affect that of the main system.
Today's mixers give great flexibility in controlling separate monitor and main levels. Because you put only
what each musician needs to hear into his respective monitor mix, the monitors are clearer and easier to
listen to.
FIGURE 1-5
Page 3

Suggestions for Better Monitoring.
A. Proper Placement - The most important factor.
1. Each performer that needs to hear needs his own Hot Spot.
2. The Hot Spot should be placed close enough to touch. The closer the Hot Spot is to you, the louder it is.
One of the primary advantages of to the Hot Spot is its ability to be placed close to the performer, so take
full advantage of this.
3. The Hot Spot should be placed behind the mic.
4. If one Hot Spot is substantially closer to a vocal mic, its volume may need to be reduced so that it will not
reduce the gain of the entire monitor system.
B. Use a unidirectional microphone. There are many good brands on the market, with a wide variance in the
amounts of rejection, so experiment with several, if possible.
C.Equalizing your system.
1. With all the mics at their working volume in the P.A., increase the volume of the monitors gradually until
they reach the point immediately before feedback - they should just ring. Cut the frequency level that is
ringing by 2 to 3 d13. Periodically talk through the system while repeating this process, until you either get
several notes ringing at once, or you start to have a reduction in quality from over equalization.
2. In high volume applications, reduce all frequencies below 150 Hz in the monitor mix. Since low notes are
non directional, they are not really needed in the monitors, as they can be heard equally well anywhere on
stage.
D. Distortion problems - If your Hot Spots are distorting, it is probably because your amp is running out of
power. Either use a larger amp, or reduce the bass frequencies in the monitor mix.
E. Do Not plug or unplug your Hot Spot while it is operating, as this may place a temporary short on your
amplifier, which could be damaging.
 Loading...
Loading...