
OPERATOR'S MANUAL
MULTI BEAM SONAR
Model
DFF-3D
www.furuno.com

9-52 Ashihara-cho,
A:DEC
2016
.
G:JUN.05, 2024
Pub. No.
(
)
Nishinomiya, 662-8580, JAPAN
・FURUNO Authorized Distributor/Dealer
All rights reserved.
REFU
DFF-3D
Printed in Japan
OME-13520-G
0 0 0 1 9 1 4 2 9 1 6

IMPORTANT NOTICES
Cd
Ni-Cd Pb
General
• This manual has been authored with simplified grammar, to meet the needs of international users.
• The operator of this equipment must read and follow the instructions in this manual.
Wrong operation or maintenance can void the warranty or cause injury.
• Do not copy any part of this manual without written permission from FURUNO.
• If this manual is lost or worn, contact your dealer about replacement.
• The contents of this manual and the equipment specifications can change without notice.
• The example screens (or illustrations) shown in this manual can be different from the screens you
see on your display. The screens you see depend on your system configuration and equipment
settings.
• Save this manual for future reference.
• Any modification of the equipment (including software) by persons not authorized by FURUNO will
void the warranty.
• The following concern acts as our importer in Europe, as defined in DECISION No 768/2008/EC.
- Name: FURUNO EUROPE B.V.
- Address: Siriusstraat 86, 5015 BT, Tilburg, The Netherlands
• The following concern acts as our importer in UK, as defined in SI 2016/1025 as amended SI 2019/
470.
- Name: FURUNO (UK) LTD.
- Address: West Building Penner Road Havant Hampshire PO9 1QY, U.K.
• All brand, product names, trademarks, registered trademarks, and service marks belong to their
respective holders.
How to discard this product
Discard this product according to local regulations for the disposal of industrial waste. For disposal in
the USA, see the homepage of the Electronics Industries Alliance (http://www.eiae.org/) for the
correct method of disposal.
How to discard a used battery
Some FURUNO products have a battery(ies). To see if your product has a battery, see the chapter
on Maintenance. If a battery is used, tape the + and - terminals of the battery before disposal to prevent fire, heat generation caused by short circuit.
In the European Union
The crossed-out trash can symbol indicates that all types of batteries must
not be discarded in standard trash, or at a trash site. Take the used batteries to a battery collection site according to your national legislation and the
Batteries Directive 2006/66/EU.
In the USA
The Mobius loop symbol (three chasing arrows) indicates that
Ni-Cd and lead-acid rechargeable batteries must be recycled.
Take the used batteries to a battery collection site according to
local laws.
In the other countries
There are no international standards for the battery recycle symbol. The number of symbols can increase when the other countries make their own recycle symbols in the future.
i

SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Do not operate the equipment with
wet hands.
Electrical shock can result.
Do not place liquid-filled containers
on the top of the equipment.
Electrical shock can result.
Use the proper fuse.
Use of a wrong fuse can damage the
equipment and may cause fire.
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
may result in minor or moderate injury.
Warning, Caution
Mandatory Action
Prohibitive Action
The installer and user must read the applicable safety instructions before attempting to install
or operate the equipment.
WARNING
WARNING
Do not open the equipment.
Only qualified personnel can work inside
the equipment.
Do not disassemble or modify the
equipment.
Fire, electrical shock or serious injury can
result.
Turn off the power immediately if the
equipment is emitting smoke or fire.
Fire or electrical shock can result if the
power is left on.
Turn off the power immediately if water
leaks into the equipment or an object is
dropped inside the equipment.
Continued use can cause fire or electrical
shock.
Turn off the power immediately if you
feel the equipment is acting abnormally.
If the equipment is hot to the touch or is
emitting strange noises, turn off the power
immediately and contact your dealer for
advice.
WARNING
Safety instructions for the operator
ii

SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
CAUTIONCAUTION
The transducer cable must be handled
carefully, following the guidelines
below.
• Keep fuels and oils away from the
cable.
• Locate the cable away from chemicals.
• Locate the cable away from locations
where it might be damaged.
Do not disconnect the motion sensor
while the sonar is powered.
The sensor may be damaged.
Do not apply the power with the
transducer exposed to air.
The transducer may be damaged.
A magnetic compass may receive interference if it is placed too close to this
unit. Observe the compass safe
distances shown below to prevent
interference to a magnetic compass.
Standard compass: 1.25 m
Steering compass: 0.80 m
WARNING
WARNING
Do not work inside the equipment
unless qualified to do so.
Electrical shock can occur.
Turn off the power before beginning
the installation.
Fire or electrical shock can result if the
power is on.
Be sure no water leaks at the mounting
location for the transducer.
Water leakage can sink the vessel. Also,
confirm that the transducer will not loosen
by vibration. The installer is solely
responsible for the installation.
Confirm that the power supply voltage
is within the rating of this equipment.
Incorrect voltage will damage the equipment and may cause fire.
Safety instructions for the installer
iii

TABLE OF CONTENTS
FOREWORD ...................................................................................................................vi
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION .........................................................................................vii
1. INSTALLATION .....................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Equipment Lists..........................................................................................................1-1
1.2 How to Install the Sonar ............................................................................................. 1-2
1.3 Transducer ................................................................................................................. 1-3
2. WIRING ..................................................................................................................2-1
2.1 Ground .......................................................................................................................2-1
2.2 Transducer Cable.......................................................................................................2-2
2.3 External KP Cable......................................................................................................2-5
2.4 LAN Cable..................................................................................................................2-9
3. INITIAL SETTINGS ................................................................................................3-1
3.1 DIP Switch Setting .....................................................................................................3-1
3.2 Operation Check ........................................................................................................3-3
3.3 Multi Function Display Initial Settings.........................................................................3-4
4. OPERATION ..........................................................................................................4-1
4.1 Menu Operations........................................................................................................4-1
4.1.1 How to start/stop transmission.......................................................................4-1
4.1.2 How set the background color........................................................................4-1
4.1.3 How to adjust the bottom range shift.............................................................. 4-2
4.1.4 How to change the transmission rate (PRR).................................................. 4-2
4.2 Display Screens Overview .........................................................................................4-3
4.3 Multi-Sounder Display Operations ............................................................................. 4-6
4.3.1 How to switch between TX and STBY ...........................................................4-6
4.3.2 How to switch between single beam and triple beam presentations.............. 4-6
4.3.3 How to set the TX beam angle....................................................................... 4-6
4.3.4 How to set the TX beam width ....................................................................... 4-6
4.3.5 How to change the picture advance speed....................................................4-6
4.3.6 How to show or hide the scale box ................................................................4-7
4.3.7 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point ............4-7
4.4 Side Scan Display Operations ...................................................................................4-8
4.4.1 How to switch between TX and STBY ...........................................................4-8
4.4.2 How to change echo color.............................................................................. 4-8
4.4.3 How to show or hide the scale box ................................................................4-8
4.4.4 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point ............4-9
4.5 Cross Section Display Operations ........................................................................... 4-10
4.5.1 How to switch between TX and STBY .........................................................4-10
4.5.2 How to show or hide the grid........................................................................ 4-10
4.5.3 Zoom display................................................................................................ 4-10
4.5.4 How to smooth echoes (distance)................................................................ 4-10
4.5.5 How to smooth echoes (time) ......................................................................4-11
4.5.6 How to apply correction to the speed of sound ............................................ 4-11
4.5.7 How to show or hide the scale box ..............................................................4-11
4.5.8 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point ..........4-12
4.6 3D Sounder History Display Operations .................................................................. 4-13
4.6.1 How to switch between TX and STBY .........................................................4-13
4.6.2 How to move, zoom in, zoom out the viewpoint position .............................4-13
4.6.3 How to mark school of fish...........................................................................4-13
iv

TABLE OF CONTENTS
4.6.4 How to pause advancement of the display...................................................4-14
4.6.5 How to adjust the echo detection level.........................................................4-14
4.6.6 How to calibrate the seabed echo................................................................4-14
4.6.7 How to use the noise filter............................................................................4-14
4.6.8 How to use terrain shading...........................................................................4-15
4.6.9 How to change the picture advance speed ..................................................4-15
4.6.10 Depth/Color Shading display ........................................................................4-15
4.6.11 How to show or hide the scale box...............................................................4-19
4.6.12 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point...........4-19
4.7 Personal Bethymetric Generator (PBG) ...................................................................4-20
4.7.1 Setting up for PBG .......................................................................................4-21
4.7.2 How to map the seabed ...............................................................................4-21
4.7.3 How to select the depth shading method .....................................................4-22
4.7.4 How to change/remove coloration (depth shading)......................................4-23
4.7.5 How to delete seabed maps.........................................................................4-24
4.7.6 How to share seabed maps between units ..................................................4-25
5. MAINTENANCE,
TROUBLESHOOTING...........................................................................................5-1
5.1 Maintenance...............................................................................................................5-1
5.2 How to Replace the Fuse ...........................................................................................5-2
5.3 How to Restore Default Settings ................................................................................5-2
APPX. 1 MENU TREE ..............................................................................................AP-1
APPX. 2 JIS CABLE GUIDE ....................................................................................AP-3
APPX. 3 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER B54, SS54 ......................................AP-4
APPX. 4 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER TM54 ............................................AP-10
SPECIFICATIONS .....................................................................................................SP-1
PACKING LISTS ......................................................................................................... A-1
OUTLINE DRAWING................................................................................................... D-1
INTERCONNECTION DIAGRAM ................................................................................ S-1
INDEX ......................................................................................................................... IN-1
v

FOREWORD
A Word to the Owner of the DFF-3D
Congratulations on your choice of the FURUNO DFF-3D Multi Beam Sonar. We are confident you
will see why the FURUNO name has become synonymous with quality and reliability.
Since 1948, FURUNO Electric Company has enjoyed an enviable reputation for quality marine
electronics equipment. This dedication to excellence is furthered by our extensive global network
of agents and dealers.
This equipment is designed and constructed to meet the rigorous demands of the marine environment. However, no machine can perform its intended function unless installed, operated and
maintained properly. Please carefully read and follow the recommended procedures for installation, operation and maintenance.
Thank you for considering and purchasing FURUNO.
Features
The DFF-3D Multi Beam Sonar provides high definition images of underwater conditions and the
seabed. Connected to the NavNet TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2 Multi Function Display, the DFF-3D
distributes images of the undersea throughout the NavNet network, via LAN.
The main features of the DFF-3D are as follows.
• TX beam detects undersea conditions 120° in port and starboard directions.
• The motion sensor, provided standard, stabilizes the display to give clear and stable images
even under rough sea conditions.
CE/UKCA declaration
With regards to CE/UKCA declarations, please refer to our website (www.furuno.com) for further
information about RoHS conformity declarations.
Disclosure of Information about China RoHS
With regards to China RoHS information for our products, please refer to our website
(www.furuno.com).
vi

SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
MULTI BEAM SONAR
DFF-3D
NavNet TZtouch
TZT9/TZT14/TZTBB
NavNet TZtouch2
TZTL12F/TZTL15F/TZT2BB
NavNet TZtouch3
TZT12F/TZT16F/TZT19F
12-24 VDC
Rectifier
PR-62
100/110/220/230 VAC
1ø, 50/60 Hz
External
KP
Transducer
B54, SS54, or TM54
: Optional or local supply
: Standard supply
vii

SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This page is intentionally left blank.
viii

1. INSTALLATION
1.1 Equipment Lists
Standard supply
Name Type Code No. Qty Remarks
Multi Beam
Sonar
Transducer B54 - 1 Select one.
Spare Parts SP02-05601 001-033-740 1 set Fuses
Installation
Materials
DFF-3D - 1
SS54 -
TM54 -
CP02-09400 000-029-992 1 set • Power cable assy. (3.5 m)
B54: Thru-hull mount (bronze)
SS54: Thru-hull mount (stainless steel)
TM54: Transom mount
• LAN cable assy. (5 m)
• Self-tapping screws
• Conductive tape
Optional supply
Name Type Code No. Remarks
Connector Kit for TX Sync OP02-86 001-205-780
Cable Assembly MOD-Z072-020+ 001-167-880-10 2 m, for HUB-101
Cable Assembly MOD-Z072-100+ 001-167-900-10 10 m, for HUB-101
Rectifier PR-62 000-013-484 100 VAC
000-013-485 110 VAC
000-013-486 220 VAC
000-013-487 230 VAC
AC/DC Power Supply Unit PR-241 -
Ferrite Core OP86-11 001-594-450 For use with PR-241,
1-1

1. INSTALLATION
1.2 How to Install the Sonar
This sonar can be installed on a deck or on a bulkhead. When selecting a mounting
location, keep the following points in mind:
• Install the unit indoors.
• The operating temperature range of this unit is -15°C to 55°C (5°F to 131°F). Be
sure the mounting location satisfies this requirement.
• Locate the unit away from exhaust pipes and vents.
• The mounting location should be well ventilated.
• Mount the unit where shock and vibration are minimal.
• Keep the unit away from electromagnetic field-generating equipment such as motors and generators.
• Observe the minimum recommended maintenance space shown in the outline
drawing at the back of this manual. Also, leave slack in cables for maintenance and
servicing ease.
• A magnetic compass may receive interference if it is placed too close to this unit.
Observe the compass safe distances noted in the safety instructions to prevent interference to the magnetic compass.
• For mounting on a bulkhead, the connectors must face downward.
Fasten the unit to the mounting location with four self-tapping screws (5×20, supplied),
referring to the outline drawing at the back of this manual for mounting dimensions.
1-2

1.3 Transducer
Thru-hull mount
The installation position of the transducer directly affects the performance of the transducer. For best performance, keep the following points in mind when selecting the
mounting location.
• Select a location where the influence of water flow and air bubbles is minimal.
• Select a place least influenced by engine noise.
• Do not install the transducer inboard.
• For FRP vessel, do not cover the transducer with fiberglass, to prevent damage to
the transducer if the temperature rises.
• Bottom slope angle less than 24°
The illustration below is the transducer with fairing, and was created by the Airmar
Technology Corporation. The BOW mark (arrow) on the fairing and the triangular recess should be facing the bow.
1. INSTALLATION
®
Unit of measurement
Top: millimeter
Bottom: inch
BOW
BOW
BOW
Triangular recess
BOW mark
1-3

1. INSTALLATION
Unit of measurement
Top: millimeter
Bottom: inch
1-4

1. INSTALLATION
Unit of measurement
Top: millimeter
Bottom: inch
Transom mount
For a vessel with an inboard engine, the transducer cannot be installed aft of the propeller screw because of the turbulence created by the propeller ahead of the transducer. Determine the mounting location considering the guidelines shown below and the
instructions on page AP-8.
• Select a location as far as possible from the propeller screw.
• Select a location where the propeller screw is not within 120° of the beam range of
the transducer.
Be sure to select the location considering these guidelines, to prevent echo noise on
the display.
The illustration below was created by the Airmar
®
Technology Corporation.
1-5

1. INSTALLATION
This page is intentionally left blank.
1-6

2. WIRING
Ground wire
(IV-2 sq)
MOD-Z072-050+, 5 m
(option: 2/10 m)
TZT9/TZT14/TZTBB
TZTL12F/TZTL15F/TZT2BB
TZT12F/TZT16F/TZT19F
GROUND
MJ-A3SPF0013-035C
(3.5 m)
External
KP
Transducer
B54, SS54, or TM54
Power supply
(12-24 VDC)
1.4-0.7A
Connect the power cable and transducer cable as shown below. See the next page
for how to fabricate the transducer cable.
2.1 Ground
Connect a ground wire (IV-2 sq, local supply) between the ground terminal and ship’s
ground to prevent interference to the sounder picture. Make the length of the wire as
short as possible. For FRP vessels, install a ground plate (approx. 20 cm by 30 cm)
on the outside of the hull bottom and connect the ground wire there.
2-1

2. WIRING
x9
Shield
2.2 Transducer Cable
Separate the transducer cable as far as possible from power cables to prevent interference to the sonar. Keep the transducer cable away from televisions and monitors
to prevent noise in the cable.
Fabricate the cable as shown in the procedure below, then connect it inside the unit
with a WAGO connector.
1. Fabricate the cable as shown below.
Note: Keep the recommended lengths to prevent noise in the cable.
Sheath
110
80
Sheath
The cable has one or three shield cores. Wrap the shield(s)
around the sheath.
Wrap shield with conductive tape.
Unit: mm
6
x9
Shield
Wrap with vinyl tape (width: 30 mm).
2. Remove the outer cover.
3. Unfasten four screws to remove the inner chassis cover.
2-2

4. Detach three WAGO connectors, TB1, TB2, TB3.
WAGO connector
opener
WAGO connector
TB1TB2TB3
Super gland
Sealing nut
Unfasten these screws to
remove the clamping plate.
5. Unfasten the sealing nut from the super gland for the transducer cable.
2. WIRING
6. Unfasten two screws to remove the clamping plate for the transducer cable.
7. Pass the transducer cable through the sealing nut (unfastened at step 5), then
pass the cable through the super gland and into the unit.
2-3

2. WIRING
How to connect cable to WAGO connector
Push down
Opener
WAGO
connector
Wire
Twist
<Procedure>
1. Twist core.
2. Insert opener in hole and
push down.
3. Insert core into hole.
4. Release opener.
5. Tug on wire to confirm tight
connection.
2 mm
8. Referring to the interconnection diagram (at the back of this manual) and the illustration below, connect the transducer cable to WAGO connectors. (The WAGO
connector opener is provided inside the unit. See the figure at step 4 for the location.)
9. Reattach the WAGO connectors.
10. Set the cable where the clamping plate was removed (at step 6). As shown in the
figure below, lay the cable such that its conductive tape lies beneath the clamping
plate. Hold the clamping plate in place with your fingers then fasten the plate.
Conductive
tape
Clamping plate
11. Fasten the sealing nut into the super gland. The gap between the sealing nut end
and the super gland should be 2 mm. The fastening torque is 1.8 - 2.0 N•m.
12. Reattach the inner and outer covers.
2-4

2. WIRING
(b)
Approx. 10 mm
(a)
Approx. 100 mm
(c)
Fold back core.
A
2.3 External KP Cable
The Connector Kit for TX Sync (see the table below) and the cable MPYC(SLA)-4 are
required to connect external KP.
Contents of Connector kit for TX sync
Name Type Code No. Qty Remarks
Upset UI Screw-B M4×20 000-163-756-10 2
Super Gland MGB20M-12B 000-177-248-10 1
PH Connector Assembly 02-1097 (4P) 001-206-000 1
Cable Clamping Plate 02-167-1528 100-379-090-10 1
Rainproof Panel 02-167-1529 100-379-100-10 1 No use. May be
discarded.
EMI Core GRFC-10 000-177-010-10 1
Crimp-on Lug NCW-1.25 000-157-213-10 4
Note: FURUNO recommends use of the JIS cable MPYC(SLA)-4 (or equivalent, see
Appendix 1). However, if the wiring environment is such that the cable may contact
seawater, use a cable whose armor is covered with a vinyl sheath to prevent corrosion.
1. Fabricate the cable for the external KP as shown below.
a) Make the length of the wires of the PH connector assembly (supplied) 100 mm.
b) Remove the sheath from the cores 10 mm.
c) Fold back the cores in half. Attach crimp-on lug NCW-1.25 (supplied) to each
core.
d) Remove the armor 300 mm and cut off the vinyl sheath 130 mm
MPYC(SLA)-4
rmor
Vinyl sheath
300 mm
80 mm
Shield
130 mm
2-5

2. WIRING
Approx. 5 mm
This part is fixed with
the sealing nut.
Lay this part in
the cable clamp.
Armor
Vinyl sheath
NCW-1.25
Wrap with
vinyl tape.
Wrap with
vinyl tape.
Crimp-on lug
FV1.25-4(LF) RED
Protective sheet
e) Remove 5 mm of the vinyl sheath from the cores then connect a crimp-on lug
to each core as shown below.
f) Attach supplied crimp-on lug (FV1.25-4(LF) RED)) to the shield.
g) Referring to the illustration below, wrap the armor with vinyl tape at the loca-
tions shown. Pass the cable through its cable gland. Fix the cable with the cable clamp and sealing nut.
2. Remove the outer cover.
3. Loosen four screws to remove the inner chassis cover.
4. Detach the protective sheet from the location for the external KP cable.
2-6

2. WIRING
Lock nut
Super gland
Cable for external KP
(MPYC(SLA)-4)
Sealing nut
4 mm
Secure cable with cable clamping plate.
5. Unfasten the sealing nut and lock nut from the supplied super gland. As shown
below, pass the cable through the sealing nut, super gland, hole in the unit and
the lock nut.
6. Fasten the lock nut to fix the super gland to the unit.
7. Fasten the sealing nut into the super gland. The gap between the sealing nut end
and the super gland should be 4 mm. The fastening torque is 1.8 - 2.0 N m.
8. Position the cable so its vinyl sheath lies in the cable clamp. Use the supplied cable clamping plate to secure the cable.
2-7

2. WIRING
J9
Clamp
Lay vinyl sheath in the cable clamp and
secure the cable with the cable clamp.
Make sure cable does
not contact TB3.
Shield
EMI coreEMI core
10 mm10 mm
Super glandSuper gland
9. Connect the KP cable. Pass the PH connector through the clamp shown below,
then connect it to J9 on th DIGI board. Make sure the cable does not contact the
WAGO connector (TB3). Also, secure the shield of the external KP cable to the
plate where the transducer cable is fixed.
Note 1: As shown in the figure below, pass the cable through the cable saddle.
Make sure the crimp connectors are not clamped by the cable saddle.
Note 2: Confirm that the direction of the clamping plate is as shown below.
Cable saddle
Crimp connectors
Clamping
plate
10. Attach the supplied EMI core (GRFC-10) to the cable for the external KP, approx.
10 mm from the super gland.
11. Reattach the inner and outer covers.
2-8

2.4 LAN Cable
How to detach clamping claw
Hold the clamping
claw/seal assy. as shown
left, with the teeth of
the clamping claw toward
you.
Push in the sealing insert
with your thumbs.
Sealing nut
Seal assy.Seal assy.
Clamping
claw
Sealing
insert
Super
gland
Sealing nut
LAN cable
Sealing insert
(Push cable into slit.)
Clamping claw
Do as follows to connect the supplied LAN cable (MOD-Z072-050+) or the optional
LAN cable (MOD-Z072-020+, MOD-Z072-100+).
1. Unfasten the sealing nut from the LAN connector then remove the sealing insert
and clamping claw.
2. Detach the sealing insert from the clamping claw as shown below.
2. WIRING
3. Pass the sealing nut, clamping claw and sealing insert onto the LAN cable in the
order shown in the figure below. Connect the cable to the LAN connector. (Note
the orientation of the sealing insert when passing it onto the cable. Push the cable
into the slit in the sealing insert.)
4. Set the sealing insert and clamping claw into the sealing nut then tighten the nut.
2-9

2. WIRING
Screw (2 pcs.)
Gland
5. Fasten the sealing nut to fasten the LAN cable. The clearance between the sealing nut and the super gland shall be 3 mm. The fastening torque for the sealing
nut is 1.8 - 2.0 Nm.
3 mm
How to disconnect the LAN cable
Loosen the two screws on the gland to access the cable’s connector. A lock washer
is fitted to the gland, so the screws cannot be unfastened completely.
2-10

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
S2S3
WARNING
Do not open the equipment unless totally
familiar with electrical circuits.
Only qualified personnel are permitted to
work inside the equipment.
3.1 DIP Switch Setting
The DIP switches S2 and S3 should be left in the default position (OFF).
DIP switch S2
12345678
OFF
DIP switch S3
1234
OFF
3-1

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
DIP switch S2 setting options (reference only)
Switch
No.
1 Automatic IP address assignment OFF: Fixed (static) IP address. Set the IP address
2 IP address no. Effective when #1 segment is OFF. (See the table
3 Restore default settings (other than
LAN)
4 Restore ALL default settings See section 5.3.
5 - 6 Keep these switches in the OFF position.
7 No use.
8 No use.
#2 Host name IP address
OFF ES092021 172.031.092.021
ON ES092022 172.031.092.022
Function Setting
with switch #2.
ON: IP address assigned automatically.
below for IP address. Currently, this function has no
use.)
See section 5.3.
After setting up the DFF-3D transducer, initial settings must also be done on your
NavNet device (NavNet TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3). See respective Installation Manual for the procedure.
3-2

3.2 Operation Check
After connecting the NavNet TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3, power the
unit on/off from the ship’s switchboard. The LED on the cover of the DFF-3D lights or
flashes according to equipment state, as described in the table below.
LED state Meaning
Lit continuously Standby state. (If no signal is received via LAN for more
Blinking every two seconds Normal operation
㻸㻱㻰
3. INITIAL SETTINGS
LED state and meaning
than 10 minutes, the equipment automatically goes into
standby to lessen power consumption.)
3-3

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
3.3 Multi Function Display Initial Settings
How to open the menu
NavNet TZtouch:
1. Push the Home button (or tap the home icon) to display the menu icon bar.
2. Select [Menu], [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Enter initial settings referring to the table below.
NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3:
1. Tap the Home icon to go to the home screen.
2. Select [Settings], [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Enter initial settings referring to the tables that follow.
Multibeam Sonar menu
Menu item Description Options (setting range)
[Transducer Draft] Set the distance between the transducer
and the draft line to show the distance
from the sea surface.
[Salt Water] Select [ON] to use this equipment in salt
water.
[Transducer Setup] See "Transducer Setup menu" on page 3-6.
[Transmission Power Au-
to]
[Transmission Power] Set the TX power level manually. Inter-
[External KP] Select [ON] to synchronize with external
[Bottom Level] The default bottom level setting (0) de-
[Auto Gain Offset (Multi
Sounder)],
[Auto Gain Offset (Side
Scan)],
[Auto Gain Offset (Cross
Section)]
Turn on to automatically adjust trans-
mission power to display the seabed
echo properly.
ference may appear on your display
when a sonar of the same frequency as
yours is being operated on a vessel
nearby. When this occurs, lower the
transmission power and request the
nearby vessel to lower its sonar’s TX
power to reduce the interference. The
setting range is 0 to 10 and 10 is maxi-
mum power.
sounder’s keying pulse.
termines that two strong echoes re-
ceived in sequence are seabed echoes.
If the depth indication is not stable in the
default setting, adjust the bottom level
here. If you can not discriminate the fish
near the seabed from the seabed echo,
increase the bottom level.
In the auto mode, lower or raise the gain
as necessary.
[0.0m] to [99.9m]
[OFF], [ON]
[OFF], [ON]
[0] to [10]
[ON], [OFF]
[-40] to [40]
[-5] to [5]
3-4

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
Menu item Description Options (setting range)
[STC (Side Scan)],
[STC (Multi Sounder)]
[TX Pulse] The pulse length is automatically set ac-
[DFF-3D Monitoring] Display pitch and roll (measured by internal sensor) and B voltage.
[Set Hardware to Factory
Default]
[Restore Default Settings] Restore all menu settings to default. [OK], [Cancel]
STC reduces surface layer noise, to discriminate surface fish from surface layer
noise. [0] is OFF and [10] reduces noise
approx. 5 m from the transducer. Too
high a setting may erase wanted fish
echoes.
cording to range. Use a short pulse for
better resolution and a long pulse when
detection range is important. To improve
resolution on the side scan display, etc.,
use [Short 1] or [Short 2].
• [Short 1] improves the detection resolution, but the detection range is
shorter than with [Std] (pulse length is
1/4 of [Std]).
• [Short 2] raises the detection resolution, however detection range is
shorter (pulse length is about 1/2 of
([Std]) than [Std].
• [Std] is the standard pulse length, and
is suitable for general use.
• [Long] increases the detection range
but lowers the resolution (about 1/2
compared to the [Std] pulse length)
Reset the external fish finder to its factory default settings.
[0] to [10]
[Short1], [Short2],
[Standard], [Long]
[OK], [Cancel]
3-5

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
Transducer Setup menu
For the oscillation center see "Motion Sensor menu" on page 3-7.
Port dir.: "+"
Top view
GCTD
Stern dir.: “+”
Up dir.: "+"
GC
TD
GC: Gravity Center, TD: Transducer
Starboard view
If the center of gravity is not known, see the drawing below.
W/2
GC
GC
Top view
L
Starboard view
H/2
Engine
W
L/3
H
Engine
GC: Gravity Center
Note: The location of the center of gravity may be different than as shown in the figures above, depending on hull shape, engine position and the installation status of
other equipment. However, the method of estimating the center of gravity location remains the same; approximately one-third of the ship length from stern (L/3), one half
of ship width (W/2) and one half of ship height from keel to roof (H/2).
Menu item Description
[Transducer Mis-
Set to [ON] if the transducer is installed facing the stern. [ON], [OFF]
mount Correction]
[Transducer Position
Bow/Stern]
Set the distance from the transducer to the ship’s center
of gravity in the bow/stern direction. For stern location,
set a positive value.
[Transducer Position
Up/Down]
Set the distance from the transducer to the ship’s center
of gravity in the up/down (vertical) direction. For upward
location, set a positive value.
[Transducer Position
Port/Starboard]
Set the distance from the transducer to the ship’s center
of gravity in the port/starboard direction. For port location,
set a positive value.
Options
(setting range)
-100.0 to 100.0
(m)
-100.0 to 100.0
(m)
-100.0 to 100.0
(m)
3-6

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
GC
GC
W
W/2
Top view
Starboard view
Engine
H
H/2
L/3
L
GC: Gravity Center
GC: Gravity Center, TD: Transducer
Engine
Motion Sensor menu
Select [Transducer Setup] on the [Multibeam Sonar] menu to show the [Motion Sensor] menu (below the [Transducer Setup] menu).
Port dir.: "+"
SC
GCTD
Stern dir.: "+"
SC
Up dir.: "+"
GC
TD
GC: Gravity Center, TD: Transducer,
Top view
Starboard view
SC: Satellite Compass
If the center of gravity is not known, see the drawing below.
Note: The location of the center of gravity may be different than as shown in the figures above, depending on hull shape, engine position and the installation status of
other equipment. However, the method of estimating the center of gravity location remains the same; approximately one-third of the ship length from stern (L/3), one half
of ship width (W/2) and one half of ship height from keel to roof (H/2).
Menu item Description
[Motion Sensor
Source]
[Motion Sensor
Pos. Bow/Stern]
Select the sensor connected to your NavNet TZtouch/TZtouch2/TZtouch3 unit.
Set the distance from the transducer to the motion sensor
in the bow-stern direction. For the stern side, set a positive
value.
Note: This menu appears if the motion sensor source is
selected to [SC].
Options
(setting range)
[SC], [Internal],
[OFF]
-100 to 100.0 (m)
3-7

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
Heading sensor time lag: 20 msec
DFF-3D
SC-30
-----------------Ethernet
CAN bus
------------
Motion sensor time lag: 20 msec
Position sensor time lag: 20 msec
Multi Function
Display
Menu item Description
[Motion Sensor
Pos. Up/Down]
[Motion Sensor
Pos. Port/Starboard]
[GPS Sensor
Pos. Bow/Stern]
[GPS Sensor
Pos. Up/Down]
[GPS Sensor
Pos. Port/Starboard]
[Roll Sensor Offset]
[Pitch Sensor
Offset]
[Motion Sensor
Time Lag (in ms)]
Set the distance from the transducer to the motion sensor
in the up/down (vertical) direction. Use a "+" value for upward direction.
Note: This menu appears if the motion sensor source is
selected to [SC].
Set the distance from the transducer to the motion sensor
in the port-starboard direction. For port location, set a positive value.
Note: This menu appears if the motion sensor source is
selected to [SC].
Set the distance from the transducer to the GPS sensor in
the bow-stern direction. For stern location, set a positive
value.
Set the distance from the transducer to the GPS sensor in
the up/down (vertical) direction. Use a "+" value for upward
direction.
Set the distance from the transducer to the GPS sensor in
the port-starboard direction. For port location, set a positive value.
Set the roll offset to use with the motion sensor. -45.0 to 45.0
Set the pitch offset to use with the motion sensor. -45.0 to 45.0
Set the time lag to use with the external motion sensor.
Note: This menu appears if the motion sensor source is
selected to [SC].
Options
(setting range)
-100 to 100.0 (m)
-100 to 100.0 (m)
-100 to 100.0 (m)
-100 to 100.0 (m)
-100 to 100.0 (m)
0 to 400
[Heading Sensor
Time Lag (in ms)]
[Position Sensor
Time Lag (in ms)]
Note: All length-related settings items, such as GPS sensor position, are internally
processed in metric units (m), regardless of the user-selected measurement unit.
Sync (time lag) setting
• If the equipment is connected as shown below, no adjustment to the time lag settings is necessary.
Set the time lag for the data received from the position sensor.
Set the time lag for the data received from the position sensor.
0 to 3500
0 to 3500
3-8

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
Heading sensor time lag: 65 msec
DFF-3D
PG-700 (Motion data and heading data)
-----------------Ethernet CAN bus
------------------
Motion sensor time lag: 65 msec
Position sensor time lag: 65 msec
-----------
㻂
㻂
GP-330B (Position data)
Multi Function
Display
• If the equipment is connected as shown in the figure below, change the time lag settings as indicated.
• If the connection is different from those mentioned here, calculate the time lag for
each sensor and enter them accordingly, using the following formula.
Time lag = Transmission delay + Propagation delay
Transmission delay: Delay required for calculation and output by the motion sensor, heading sensor, and position sensor.
SC-30: Use 5 msec for the calculation.
PG-700: Use 50 msec for the calculation.
GP-330B: Use 50 msec for the calculation.
Propagation delay: Time required for the data to reach the DFF-3D, via repeater
and data route. For the multi function display connected by CAN bus, use 15 msec
for the calculation. If NMEA data is fed to the DFF-3D via the NMEA Data Converter
(IF-NMEA2K2), set the calculation figure according to the baud rate between the
sensor and the IF-NMEA2K2 as shown below.
38400 bps: Use 40 msec for the calculation.
4800 bps: Use 145 msec for the calculation.
For example, the sensor feeding data to the multi function display via the IFNMEA2K2 has a transmission delay of 30 msec and a baud rate of 38400 bps.
Then, the time lag would be as shown in the calculation below.
Time lag 70 msec = Transmission delay 30 msec + Propagation delay 40 msec
3-9

3. INITIAL SETTINGS
This page is intentionally left blank.
3-10

4. OPERATION
This chapter describes the display and operations for the Multi Beam Sonar. For basic
operations with the NavNet TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3 multi function display, such as touch operations and power on/off, see the Operator’s Manual
for your NavNet TZtouch unit.
The DFF-3D has four display screens (modes), multi sounder, side scan, cross section, and 3D sounder history.
4.1 Menu Operations
This section covers the top layer of the [Multi-beam Sonar] menu. For details regarding menu operations with each of the displays, see the respective section.
Display Section no.
Multi-Sounder section 4.3
Side Scan section 4.4
Cross Section section 4.5
3D Sounder section 4.6
Note: This section is authored with the understanding that the user has already accessed the [Multi Beam Sonar] menu from their NavNet TZtouch unit. For the procedure for each TZtouch model, see the table below.
TZtouch model(s) Menu access procedure
TZT9, TZT14 Press the Menu key, then select [Multi Beam Sonar]
TZTBB Tap the [Menu] icon, then select [Multi Beam Sonar]
TZTL12F, TZTL15F,
TZT2BB; TZT12F, TZT16F,
TZT19F
Tap [Home] → [Settings], then select [Multi Beam Sonar]
4.1.1 How to start/stop transmission
You can start/stop transmissions from the Multi Beam Sonar by using the menu.
In the [Multi Beam Sonar] menu, tap the [Multi Beam Sonar Transmit] item to toggle
between [OFF] and [ON].
4.1.2 How set the background color
You can set the background color for Day mode and Night mode to suit your preferences.
1. From the [Multi Beam Sonar] menu, select [Day Background Color] or [Night
Background Color] as required.
2. Select the desired color.
3. Close the menu.
4-1

4. OPERATION
5050
Seabed
3030
Seabed
7070
Seabed
4.1.3 How to adjust the bottom range shift
The bottom range shift feature changes the location at which the seabed appears on
the screen. This is particularly useful when the seabed is “off-screen”.
Note: This feature requires [Auto Range] to be active. See your respective Operator’s
Manual for details.
Slide the slide bar at [Bottom Range Shift Area] (in the [Multi Beam Sonar] menu) to
adjust the value as required. The following figure shows some examples of how the
settings affect the on-screen display.
A lower value places the seabed at a higher location on-screen. A higher value places
the seabed at a lower location on-screen.
4.1.4 How to change the transmission rate (PRR)
You can adjust the rate at which the sonar beam is transmitted (PRR, Pulse Repetition
Rate) using one of the three available settings. Each setting has distinct characteristics allowing for a broad range of applications.
Setting Characteristics
[Manual] Affected by the selected range. A shorter range has a
faster transmission rate; a longer range has a slower rate.
[Auto] Affected by vessel speed. Slow speeds have a slower
transmission rate; high speeds have a faster rate.
Note: Speeds of 20 kn or higher are fixed at a transmission rate of 20.
[Maximum] Affected by detected depth. Shallows have a faster trans-
mission rate; deeper waters have a slower rate.
Note: Where the selected range exceeds the detected
depth, the transmission rate may exceed 20.
1. From the [Multi Beam Sonar] menu, select [Transmit Rate Mode].
2. Select [Manual], [Auto] or [Maximum] as required.
3. If you selected [Manual], adjust the rate at [Transmit Rate Manual Value], using
the slide-bar or the software keyboard. For [Auto] or [Maximum], go to step 4.
4. Close the menu.
Note: Adjustments made to the transmission rate also affect how the on-screen display appears for the Multi-Sounder and 3D Sounder History features. The following
figures show examples of the same object and how the echo display is affected.
4-2

4. OPERATION
A-scope
Frequency
Depth scaleDepth scale
19.5
Below transducerBelow transducer
Seabed
echo
Max. display depthMax. display depth
Depth
Display Screen
Multi Sounder
3D History
Rate = 0
Rate = 10 Rate = 20
4.2 Display Screens Overview
Multi-sounder display
Tap the multi-sounder display icon on the home screen to show the multi-sounder display.
The multi-sounder display operates similar to the conventional fish finder, providing information about the seabed and underwater conditions. The video display scrolls from
the right to left with the passing of time.
The echoes appearing at the right edge of the display are the latest echoes. Echoes
from individual fish, schools of fish and the seabed are shown. With the gain set properly, the distance to the seabed appears on the screen.
The gain, clutter suppressor and TVG are adjusted according to the mode selected,
auto fishing or auto cruising. Manual adjustment of those controls is also possible.
The single beam presentation displays the information detected by the downwardlooking beam. The triple beam presentation displays the information detected by the
port beam, starboard beam, and downward-looking beam.
Single beam display
4-3

4. OPERATION
19.5
Depth
scale
Depth
scale
Seabed
echo
Frequency
Depth
PortPort StarboardStarboardDownwardDownward
Max. display depthMax. display depth
Depth
Port direction echoes Starboard direction echoes
Fish bedFish bed
Fish bedFish bed
Depth scale
FrequencyFrequency
Max. display depthMax. display depth
Underwater
Underwater
Underwater
Underwater
SeabedSeabed
SeabedSeabed
Side scan display
Tap the side scan display icon on the home screen to show the side scan display.
Triple beam display
The side scan display shows the echoes received from the port and starboard directions.
The side scan display starts from the center of the vessel, and traces in the port and
starboard directions. The most recent echoes are at the top of the screen and the oldest are at the bottom of the screen.
The side scan display is different from the other modes employed by this equipment it clearly displays the shape of echoes (fish bed, etc.).
Cross section display
Tap the cross section display icon
on the home screen to show the
cross section display.
4-4
The cross section display, shows
seabed and underwater conditions.
㻻㼣㼚㻿㼔㼕㼜㻻㼣㼚㻿㼔㼕㼜
Seabed
STBDPORT
School of
fish

4. OPERATION
Horizontal range scaleHorizontal range scale
SeabedSeabed
FrequencyFrequency
GridGrid
Depth
Depth
scale
Depth
scale
Max. display depthMax. display depth
Transducer
position
Transducer
position
UnderwaterUnderwater
DownwardDownwardPortPort StarboardStarboard
Horizontal range scaleHorizontal range scale
FrequencyFrequency
Depth
Own shipOwn ship
Depth/Color Shading
color scale
Max. display depthMax. display depth
Depth scaleDepth scale
School of fishSchool of fish
SeabedSeabed
This multi beam sonar uses a 120° beam (downward to port 60°; downward to starboard 60°), providing highly accurate underwater images.
3D sounder history display
Tap the 3D sounder history display icon on the home screen to show the 3D sounder
history display.
The 3D sounder history provides a 3D graphic of the past seabed and underwater
echoes detected by your vessel. The display can be used to detect schools of fish.
4-5

4. OPERATION
4.3 Multi-Sounder Display Operations
This section covers the functions available with the multi-sounder display. For the
menu items shared with the conventional fish finder, see the applicable Operator’s
Manual.
4.3.1 How to switch between TX and STBY
Tap the multi-sounder display to show the pop-up menu. Select [TX] to start transmitting. [ST-BY] appears at the center of the screen when transmission is stopped.
4.3.2 How to switch between single beam and triple beam presentations
1. Tap the multi-sounder display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Mode].
3. Select [Single Beam] or [Triple Beam] as required.
4. Select [Close] to close the pop-up menu.
4.3.3 How to set the TX beam angle
You can set the TX beam angle for the port, starboard and downward beams.
1. Tap the multi-sounder display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Beam Angle].
3. Set the beam angle as required.
4.3.4 How to set the TX beam width
You can set the TX beam width for the port, starboard and downward beams.
1. Tap the multi-sounder display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Beam Width].
3. Set the beam width as required.
4.3.5 How to change the picture advance speed
The Picture Advance setting sets how quickly vertical scan lines move across the display. When viewing a seabed with sharp rises and falls, such as a reef-bed or submerged wreck, a fast advance speed helps to “smooth” out the seabed for easier
viewing. On the other hand, when viewing a smooth seabed with little to no undulations, a slow advance speed helps to identify rises and falls.
4-6
1. From the [Multi Beam Sonar] menu, select [Multi-Sounder].
2. Select [Picture Advance].
3. Select an advance speed to suit your requirements.
The default speed is [1/1] (normal speed), the fastest speed is [4/1] (four times
normal speed) and the slowest speed is [1/16] (sixteen times slower than normal
speed).
Select [Stop] to stop the picture advance for closer examination and screenshots/
photos.

4. OPERATION
4.3.6 How to show or hide the scale box
The scale box, shown at the bottom left corner on the display, shows depth, current
range, and TX frequency. You can show the box as follows.
1. Tap the multi-sounder display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Scale Box] to show the scale box.
4.3.7 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point
For how to register points and event marks, see Operator’s Manual for your NavNet
TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3.
The table below shows function availability according to latitude/longitude, heading
data presence or absence. If there is no latitude/longitude data, none of the functions
below are available.
For NavNet TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3, input PGN data. The PGN
data available is as shown below.
Latitude/longitude data
• 129025 Position, Rapid Update
• 129029 GNNS Position Data
Heading data
• 127237 Heading/Track Control
• 127250 Vessel Heading
• 130577 Direction Data
Latitude/Longitude / Heading data: YES
Item Starboard Downward Port
Point registration Yes Yes Yes
Go to point Yes Yes Yes
Event mark registration Yes Yes Yes
Latitude/Longitude: YES, Heading data: NO
Item Starboard Downward Port
Point registration No Yes No
Go to point No Yes No
Event mark registration Yes Yes Yes
4-7

4. OPERATION
Port
Starboard
Downward
Port
Downward
Starboard
4.4 Side Scan Display Operations
This section covers the functions available with the side scan display. For the menu
items shared with the conventional fish finder, see the applicable Operator’s Manual.
4.4.1 How to switch between TX and STBY
Tap the side scan display to show the pop-up menu. Select [TX] to start transmitting.
[ST-BY] appears at the center of the screen when transmission is stopped.
4.4.2 How to change echo color
1. Select [Menu] from the menu icon bar to show the menu.
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Select [Echo Color].
4. Select [White], [Blue] or [Brown] as required.
5. Select [Close] to close the pop-up menu.
4.4.3 How to show or hide the scale box
The scale box, shown at the bottom left corner on the display, shows depth, current
range, and TX frequency. You can show the box as follows.
1. Tap the side scan display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Scale Box] to show the scale box.
4-8

4. OPERATION
4.4.4 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point
For how to register points and event marks, see the manual for your NavNet TZtouch/
NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3.
The table below shows function availability according to latitude/longitude, heading
data presence or absence. If there is no latitude/longitude data, none of the functions
below are available.
For NNavNet TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3, input PGN data. The
PGN data available is as shown below.
Latitude/longitude data
• 129025 Position, Rapid Update
• 129029 GNNS Position Data
Heading data
• 127237 Heading/Track Control
• 127250 Vessel Heading
• 130577 Direction Data
Latitude/Longitude / Heading data: YES
Item Starboard Port
Point registration Yes Yes
Go to point Yes Yes
Event mark registration Yes Yes
Latitude/Longitude: YES, Heading data: NO
Item Starboard Port
Point registration No No
Go to point No No
Event mark registration Yes Yes
4-9

4. OPERATION
Zoomed display
Normal display
4.5 Cross Section Display Operations
This section covers the functions available with the cross section display. For the
menu items shared with the conventional fish finder, see the applicable Operator’s
Manual.
4.5.1 How to switch between TX and STBY
Tap the cross section display to show the pop-up menu. Select [TX] to start transmitting. [ST-BY] appears at the center of the screen when transmission is stopped.
4.5.2 How to show or hide the grid
The grid, which is useful for measuring the distance to a target, can be shown or hidden as follows.
1. Tap the cross section display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Grid] to show the grid.
4.5.3 Zoom display
The seabed echo can be zoomed.
1. Tap the cross section display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Zoom] to zoom the seabed echo. Select [Zoom] again to restore the normal display.
4.5.4 How to smooth echoes (distance)
If echoes are "disconnected" because of an undulating seabed, change the setting to
[Low], [Medium] or [High] as necessary. Smoothing is done in the range direction to
smooth the echo presentation.
4-10
1. Select [Menu] from the menu icon bar to show the menu.
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Select [Echo Smoothing (Distance)].
4. Select [Low], [Medium] or [High] as required. The default setting is [Medium]. Select [OFF] to stop smoothing.
5. Select [Close] to close the pop-up menu.

4.5.5 How to smooth echoes (time)
If echoes are difficult to see because they appear "speckled," use the echo smoothing
feature to suppress the speckling by time.
1. Select [Menu] from the menu icon bar to show the menu.
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Select [Echo Smoothing (Time)].
4. Select [Low], [Medium] or [High] as required. The default setting is [Medium]. Select [OFF] to stop smoothing.
5. Select [Close] to close the pop-up menu.
4.5.6 How to apply correction to the speed of sound
Even though the sea bottom is flat, the left or right edge, up or down may be distorted.
To compensate for this problem, adjust the speed of sound. The procedure differs
slightly, depending on your equipment and defines the TZT9/14/BB as “TZtouch1”;
TZTL12F/15F/TZT2BB as “TZtouch2”; TZT9F/12F/16F/19F as “TZtouch3”.
4. OPERATION
Manual correction
1. For TZtouch1 users, select [Menu] from the menu icon to show the menu.
For TZtouch2 and 3 users
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar] → [Cross Section].
3. Select [Sound Speed Correction], then enter a correction. The setting range is
-200 to +200.
For reference, if a flat seabed appears to have a “mound”, enter a negative value
for correction. If a flat seabed appears to have a “valley”, enter a positive value.
4. Select [Close] to close the menu.
, select [Settings] on the home screen.
Automatic correction
1. For TZtouch1 users, select [Menu] from the menu icon to show the menu.
For TZtouch2 and 3 users
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar] → [Cross Section].
3. For TZtouch1 users
For TZtouch2 and 3 users
[ON].
Select [OFF] to remove the correction.
4. Select [Close] to close the menu.
, select [Temp.-Based Correction], then select [ON].
, select [Settings] on the home screen.
, select [Temperature Based Correction], then select
4.5.7 How to show or hide the scale box
The scale box, shown at the bottom-left corner on the display, shows depth, current
range, and TX frequency. You can show the box as follows.
1. Tap the cross section display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Scale Box] to show the scale box.
4-11

4. OPERATION
4.5.8 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point
For how to register points and event marks, see the manual for your NavNet TZtouch/
NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3.
The table below shows function availability according to latitude/longitude, heading
data presence or absence. If there is no latitude/longitude data, none of the functions
below are available.
For NavNet TZtouch/NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3, input PGN data. The PGN
data available is as shown below.
Latitude/longitude data
• 129025 Position, Rapid Update
• 129029 GNNS Position Data
Heading data
• 127237 Heading/Track Control
• 127250 Vessel Heading
• 130577 Direction Data
Latitude/Longitude / Heading data: YES
Point registration Yes
Go to point No
Event mark registration Yes
Latitude/Longitude: YES, Heading data: NO
Point registration No
Go to point No
Event mark registration Yes
Item Cross section
Item Starboard
4-12

4. OPERATION
4.6 3D Sounder History Display Operations
This section covers the functions available with the 3D sounder history display. For the
menu items shared with the conventional fish finder, see the applicable Operator’s
Manual.
4.6.1 How to switch between TX and STBY
Tap the 3D sounder history display to show the pop-up menu. Select [TX] to start
transmitting. [ST-BY] appears at the center of the screen when transmission is
stopped.
4.6.2 How to move, zoom in, zoom out the viewpoint position
How to move the viewpoint
The viewpoint can be moved by dragging.
How to zoom in, zoom out
Zoom in Zoom out
How to restore default view
If you get lost in viewpoint or zoom, you can restore the default view as follows.
1. Tap the 3D sounder history display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Default View] to show the depth/frequency box.
4.6.3 How to mark school of fish
A detected school of fish can be marked with a "dot" mark for
easy identification.
1. Tap the 3D sounder history display to show the pop-up
menu.
2. Select [Fish School Icon] to mark the detected school of fish with the dot mark.
4-13

4. OPERATION
4.6.4 How to pause advancement of the display
You can pause advancement of the history display to observe the distribution of sea
floor topography and school of fish.
1. Tap the 3D sounder history display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Pause] to pause the display.
4.6.5 How to adjust the echo detection level
Adjust the echo detection level if schools of fish are detected unstably.
1. Select [Menu] from the menu icon to show the menu.
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Select [Fish Detection Level].
4. Select [Low], [Medium] or [High] as required. The default setting is [Medium]. If too
many schools of fish are being detected, select [Low]. If too few schools are detected, select [High].
5. Select [Close] to close the menu.
4.6.6 How to calibrate the seabed echo
If schools of fish or a fish reef are detected and displayed as the seabed echo, adjust
the strength of the seabed echo as shown below to correctly identify the seabed echo.
1. Select [Menu] from the menu icon to show the menu.
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Select [Seabed Echo Calibration]. Drag the slider bar to adjust.
The setting range is -15 to +15. A large figure helps distinguish bottom fish from
the seabed echo; however, it is difficult to distinguish a fish bed. Use a small figure
to distinguish a fish bed; however, it is difficult to distinguish bottom fish from the
seabed echo.
4. Select [Close] to close the menu.
4.6.7 How to use the noise filter
If the seabed echo is displayed with undulations, use the noise filter to smooth the seabed echo.
1. Select [Menu] from the menu icon to show the menu.
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar].
4-14
3. Select [Noise Filter].
4. Select [Low], [Medium] or [High] as required. The default setting is [Medium].
5. Select [Close] to close the menu.

4.6.8 How to use terrain shading
Setting: 0 Setting: 50
Setting: 100
The thickness of the shading for the seabed terrain can be adjusted.
1. Select [Menu] from the menu icon to show the menu.
2. Select [Multibeam Sonar].
3. Select [Terrain Shading]. Drag the slider bar to adjust.
The default setting is 50. See the figure below for setting and resulting terrain
shading
4. Select [Close] to close the menu.
4. OPERATION
4.6.9 How to change the picture advance speed
The [Picture Advance] setting sets how quickly vertical scan lines move across the display. When viewing a seabed with sharp rises and falls, such as a reef-bed or submerged wreck, a fast advance speed helps to “smooth” out the seabed for easier
viewing. On the other hand, when viewing a smooth seabed with little to no undulations, a slow advance speed helps to identify rises and falls.
1. From the [Multi Beam Sonar] menu, select [3D Sounder History].
2. Select [Picture Advance].
3. Select an advance speed to suit your requirements.
The default speed is [1/1] (normal speed), the fastest speed is [4/1] (four times
normal speed) and the slowest speed is [1/8] (eight times slower than normal
speed). The following figure shows examples of the same object at [4/1], [1/1] and
[1/4] speeds.
[
1/4
]
] [
1/1
4/1
][
Select [Stop] to stop the picture advance for closer examination and screenshots/
photos.
4.6.10 Depth/Color Shading display
The seabed echo and schools of fish can be shown in shades of colors according to
depth, to help you see the differences in depths more easily.
Color shading display
Color shading can be applied to the seabed echo or schools of fish. For the seabed
display, the seabed color can be multi tone or single tone, and schools of fish can be
4-15

4. OPERATION
Minimum Value
Maximum Value
Auto Seabed Shading
Minimum Value
Maximum Value
Auto Fish Shading
Seabed Color
Fish Monochrome Color
0 m
50 m
0 m
50 m
Classic Hue
Gray Hue
Minimum Value
Maximum Value
Auto Seabed Shading
Minimum Value
Maximum Value
Auto Fish Shading
Fish Color
Seabed Monochrome Color
0 m
50 m
0 m
50 m
Classic Hue
Gray Hue
[Color Mode] selected to [Seabed] [Color Mode] selected to [Fish]
shown in single tone or single color. For the schools of fish display, schools can be
shown in multi tone or single tone and the bottom color is in a single tone.
Note: Objects that are detected outside of the selected color range are shown onscreen in white color.
[Color Mode] selected to [Seabed]
Depth/Color
Shading display
Color Scale
1. Tap the 3D sounder history display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Color Mode].
3. Select [Seabed] or [Fish] as required.
How to set color shading
Open the menu, select Multi Beam to show the menu for setting color shading.
Depth/Color Shading
Depth/Color Shading
display
display
[Color Mode] selected to [Fish]
Depth/Color
Shading display
Color Scale
Depth/Color Shading
Depth/Color Shading
display
display
[Seabed Color] For setting multi tone or single tone. [Classic Hue]
4-16
Menu item Description Setting options
[Color Mode] selected to [Seabed]
[Inverted Classic Hue]
[Red Hue]
[Blue Hue]
[Green Hue]
[Yellow Hue]

4. OPERATION
[Minimum Value]
Shallowest depth value
0.0 m
50.0 m
AUTO
[Maximum Value]
Shallowest depth value
0.0 m
50.0 m
AUTO
Menu item Description Setting options
[Fish Monochrome Color] For setting single tone or single color. [Gray Hue]
[Brown Hue]
[Red]
[Green]
[Blue]
[Cyan]
[Magenta]
[Black Or White]
[Pink]
[Light Green]
[Yellow]
[Auto Seabed Shading] Use automatic or manual seabed shading.
Tap here to turn the automatic
seabed shading scale [ON] or [OFF].
[ON], [OFF]
0.0 m
0.0 m
AUTO
ON
AUTO
OFF
(AUTO is greyed out)
50.0 m
50.0 m
Note: Objects that are detected outside of
the selected color range are shown onscreen in white color.
[Minimum Value] Use the software keyboard to set the shal-
lowest depth to use. [Auto Seabed Shading]
must be OFF to enter depth.
Alternatively, tap the minimum value indication on the color bar scale to show the slider
bar. Drag the slider bar to set.
0 to 1200 (m)
[Maximum Value] Use the software keyboard to set the deepest
0 to 1200 (m)
depth to use. [Auto Seabed Shading] must be
OFF to enter depth.
Alternatively, tap the maximum value indication on the color bar scale to show the slider
bar. Drag the slider bar to set.
4-17

4. OPERATION
[Minimum Value]
Shallowest depth value
0.0 m
50.0 m
AUTO
[Color Mode] selected to [Fish]
Menu item Description Setting options
[Fish Color] For setting multi tone or single tone. [Classic Hue]
[Inverted Classic Hue]
[Red Hue]
[Blue Hue]
[Green Hue]
[Yellow Hue]
[Fish Monochrome Color] For setting single tone or single color. [Gray Hue]
[Brown Hue]
[Auto Fish Shading] Use automatic or manual fish shading.
Tap here to turn the automatic fish
shading scale [ON] or [OFF].
[ON], [OFF]
0.0 m
0.0 m
AUTO
ON
AUTO
OFF
(AUTO is greyed out)
50.0 m
50.0 m
Note: Objects that are detected outside of
the selected color range are shown onscreen in white color.
[Minimum Value] Use the software keyboard to set the shal-
lowest depth to use. [Auto Fish Shading]
must be OFF to enter depth.
Alternatively, tap the minimum value indication on the color bar scale to show the slider
bar. Drag the slider bar to set.
0 to 1200 (m)
[Maximum Value] Use the software keyboard to set the deepest
4-18
depth to use. [Auto Fish Shading] must be
OFF to enter depth.
Alternatively, tap the maximum value indication on the color bar scale to show the slider
bar. Drag the slider bar to set.
0.0 m
AUTO
[Maximum Value]
Shallowest depth value
0 to 1200 (m)
50.0 m

4. OPERATION
4.6.11 How to show or hide the scale box
The scale box, shown at the bottom left corner on the display, shows depth, current
range, and TX frequency. You can show the box as follows.
1. Tap the 3D sounder history display to show the pop-up menu.
2. Select [Scale Box] to show the scale box.
4.6.12 Availability of points and event marks registration, and go to a point
For how to register points and event marks, see the multi function display operator’s
manual.
The table below shows function availability according to latitude/longitude, heading
data presence or absence. If there is no latitude/longitude data, none of the functions
below are available.
For the multi function display, input PGN data. The PGN data available is as shown
below.
Latitude/longitude data
• 129025 Position, Rapid Update
• 129029 GNNS Position Data
Heading data
• 127237 Heading/Track Control
• 127250 Vessel Heading
• 130577 Direction Data
Latitude/Longitude / Heading data: YES
Item Fish Seabed
Point registration Yes Yes No
Go to point Yes Yes No
Event mark registration No No Yes
Latitude/Longitude: YES, Heading data: NO
Item Fish Seabed
Point registration No No No
Go to point No No No
Event mark registration No No Yes
Other than Fish
or Seabed
Other than Fish
or Seabed
4-19

4. OPERATION
Depth and coloration bar. Minimum
detected depth is shown on the left,
maximum on the right.
Coloration mode indicator
Own vessel icon
Map width indicator
PBG map
4.7 Personal Bethymetric Generator (PBG)
Note: This feature is available only for the NavNet TZtouch3 series (TZT9F, TZT12F,
TZT16F and TZT19F). Seabed maps recorded on a networked unit are not shared
across the network. Use the file transfer functions of the TZT3, or record using each
of the desired units.
The PBG feature creates a map of the seabed, colored according to recorded depth
readings. An area of roughly twice the size of the depth is mapped, with the transducer
as the center point. For example, a map of a 20 m deep seabed will be approximately
20 m wide to both port and starboard. Unlike 3D Sounder History, the color-mapped
seabed appears on the plotter display.
Note: Tide data received from tidal stations is applied as an offset to show a depth
which as close as possible to the actual depth.
Requirements
This feature is supported on all software versions of the DFF-3D provided the following
requirements are met:
• Connection to a NavNet TZtouch3 using software version 2.01 or later.
• A micro SD card with sufficient blank space, inserted into the TZtouch3 unit.
Note 1: Chart cards may be used, provided sufficient free space is available.
Note 2: The data space required varies, depending on several factors, such as sea-
bed complexity, own ship speed and length of time spent mapping.
The following cases, both based on a 24 hours period of recording, are intended as
a reference for space required:
A highly complex seabed, at depth of 200 m, traversed at a speed of 10 knots, with
no overlaps in mapping area, uses approximately 13 MB.
A shallow and relatively plain and flat seabed, traversed at a slow speed and with
overlaps in the mapping area uses approximately 2 MB.
4-20
• Heading and positioning PGN data input to the NavNet TZtouch3.*
Heading: 127237 (Heading/Track Control) or 127250 (Vessel Heading) or 130577
(Direction Data).
Positioning: 129025 (Position, Rapid Update) or 129029 (GNSS Position Data).
*: FURUNO’s SC-33 or SCX-20, both boasting high quality positioning and relatively
easy setup/synchronization, are recommended as a positioning/heading data source.

4.7.1 Setting up for PBG
To use the PBG feature, following settings must be completed in advance:
• Transducer initial settings, Motion Sensor initial settings, EPFs device (GPS antenna, etc.) initial settings. The procedure for these items are covered in the “HOW TO
SET UP YOUR EQUIPMENT” chapter of your TZTouch3 Installation Manual.
• DFF-3D initial settings. See "Multi Function Display Initial Settings" on page 3-4.
• Sound speed adjustments. See "How to apply correction to the speed of
sound" on page 4-11.
4.7.2 How to map the seabed
To start mapping, open the plotter screen, swipe the right edge of the screen inwards
to show the slide menu, then tap [PBG Recording]. The menu item changes to a yellow color, indicating that the feature is active. The coloration mode indicator also appears with a white background.
A thin blue line appears to the stern of the own ship icon. This line indicates the section
of seabed being mapped. The length of the line changes according to depth; short for
shallow waters, long for deep waters.
4. OPERATION
Note 1: Traveling over the same area more than once overwrites the previous seabed
map with the latest scanned map. For this reason, avoid recording when the weather
is inclement, or there is excessive roll/pitch, to avoid over-writing a clear map with a
lower quality map.
Note 2: Depth is calculated and recorded with applicable adjustments made for tide
height. Tide height is calculated based on the latest information received from Tide
Stations.
To stop mapping, swipe the right edge of the screen inwards to show the slide menu,
then tap [PBG Recording]. The menu item changes to a white color, indicating that the
feature is inactive.
4-21

4. OPERATION
Configuring the speed filter to save data space
You can set a speed limit at which map recording is paused, preventing the mapping
of unnecessary areas. When the own ship speed drops below this setting, mapping is
resumed. The default speed setting is 15 knots.
To change the speed setting, do the following:
1. From the Home menu, tap [Settings] → [Chart Plotter].
2. Scroll the menu to show the [PBG FILTER] settings.
3. Tap [Use Speed Filter] to enable ([ON]) or disable ([OFF])the filter.
4. Tap [Maximum Speed] to show the software keyboard.
5. Set the desired speed at which to pause mapping, then tap the check icon ()at
the bottom-right of the screen.
6. Close the menu.
4.7.3 How to select the depth shading method
Depth shading colors the on-screen seabed based on the depth and/or contour lines.
To show/hide the depth shading, do the following:
1. On the chart plotter screen, swipe the bottom-edge of the screen upwards to show
the layers menu.
2. At [Depth Shading], tap the appropriate menu item, referring to the descriptions
below.
Menu item Description
OFF Disables all overlays and shows only the plotter display.
Note: This hides the seabed map, but does not disable the
PBG feature. To disable PBG, use the slide menu (swipe the
right-hand edge of the screen leftwards, then tap [PBG Recording].).
3D Chart Shows a rough seabed overlay based on contour lines from
the currently used chart’s data.
HR 3D Chart Not used.
DFF3D Shows the seabed map as recorded by the DFF-3D.
3. Close the menu.
4-22

4.7.4 How to change/remove coloration (depth shading)
Classic Hue
Inverted Classic Hue
Yellow HueGreen HueBlue HueRed Hue
The map generated by the PBG feature can be colored with several hues, varying
shades of a single hue, or without color. Contour lines can also be shown or hidden.
How to select a depth shading scheme
1. From the Home menu, tap [Settings] → [Chart Plotter].
2. Scroll the menu to show the [DEPTH SHADING VALUES] settings.
3. Tap [Depth Color Shade] to show the list of shading schemes.
4. Referring to the below examples, select the desired shading scheme.
4. OPERATION
5. Close the menu.
How to remove coloration (show contour lines only)
You can remove the coloration, regardless of which depth shading scheme is selected, by doing the following:
1. Tap the minimum or maximum depth indication on the depth and coloration bar to
show the slide bar at the right-side of the screen.
2. Set the minimum and maximum depths to [0.0], then tap [Done] at the top-right of
the screen.
Coloration mode indicator
Minimum depth indication
Maximum depth indication
3. Coloration is removed and only the contour lines are displayed. The coloration
mode indicator also changes as shown in the above figure.
How to adjust inclination shading
You can adjust the shading which indicates the steepness of the seabed.
1. From the Home menu, tap [Settings] → [Chart Plotter].
2. Scroll the menu to show the [DEPTH SHADING VALUES] settings.
3. Tap [PBG Terrain Shading] to show the options.
4. Tap the desired inclination shading.
• [Off]: No shading applied to the seabed map.
• [Light]: Shadows are applied lightly to the inclines.
• [Medium]: A moderate amount of shading is applied to the inclines.
• [Strong]: Inclines appear with heavy shading.
5. Close the menu.
4-23

4. OPERATION
Area selection pinArea selection pin
How to show/hide the contour lines
On the chart plotter screen, swipe the bottom-edge of the screen upwards to show the
layers menu, then tap the button at Contour Lines to show [ON] or [OFF] as desired.
4.7.5 How to delete seabed maps
You can delete seabed maps by selecting a section to delete, or delete the entire seabed map.
Deleting a section of the seabed map
1. Tap anywhere on the seabed map to show the pop-up menu.
2. Scroll the menu, then tap [Delete PBG Area]. An area selection pin appears onscreen.
3. Tap at least two more locations to show the selection pins.
Note: The delete area function requires a minimum of three points in total.
4. Drag the selection pins to cover the area of the seabed map you want to delete.
5. Tap the [Delete] button at the top-right of the screen. The selected area is deleted.
Deleting the entire seabed map
1. Remove the micro SD card from the TZT3 unit.
2. Insert the card into a PC.
3. Use the File Explorer and navigate to the micro SD card directory.
4-24
4. Delete the [PBG] folder.

4.7.6 How to share seabed maps between units
You can import/export the seabed maps, allowing the same maps to be used on multiple TZT3 units.
Note: Seabed maps are updated by each unit individually, not across the network.
Exporting seabed maps
1. Connect a blank USB flash memory to the USB connector of the unit whose seabed maps you want to export.
2. Open the Home screen, then tap [Settings]→[Files]→[Export PBG].
3. Tap the data you want to export. A confirmation message appears.
4. Tap [OK] to begin the export.
Note: Depending on the size of the data, this may take several minutes.
5. When the export is complete, the message "EXPORT SUCCEEDED" appears.
6. Remove the USB flash memory.
Importing seabed maps
4. OPERATION
1. Connect the USB flash memory (containing the exported map data) to the USB
connector of the unit to which you want to import the seabed maps.
2. Open the Home screen, then tap [Settings]→[Files]→[Import PBG].
3. Tap the data you want to import. A confirmation message appears.
4. Tap [OK] to begin the import.
Note: Depending on the size of the data, this may take several minutes.
5. When the import is complete, the message "IMPORT SUCCEEDED" appears.
6. Remove the USB flash memory.
4-25

4. OPERATION
This page is intentionally left blank.
4-26

5. MAINTENANCE,
WARNING
NOTICE
Do not apply paint, anti-corrosive sealant or
contact spray to coating or plastic parts of
the equipment.
Those items contain organic solvents that can
damage coating and plastic parts, especially
plastic connectors.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Do not open the equipment.
Only qualified personnel are
permitted to work inside the
equipment.
TROUBLESHOOTING
5.1 Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for good performance. Check the items listed in the
table below at the suggested interval to help keep your equipment in good shape for
years to come.
Item Check point, action Check interval
Cable condition Check that cables are not damaged. Replace if
damaged.
Cable connector Check that the connector of each cable is tightly
fastened and not damaged. Refasten if necessary. Replace if damaged.
Ground terminal, ground
wire
Power supply voltage Check voltage. If out of rating correct problem. Once a month
Cabinet cleanliness Dust or dirt on the cabinet may be removed with a
Transducer Marine life on the transducer face will result in a
Check for corrosion. Clean if necessary. Replace
ground wire if damaged.
dry cloth. Do not use chemical-based cleaners to
clean the cabinet; they can remove markings and
damage the cabinet.
gradual decrease in sensitivity. Check the transducer face for cleanliness each time the boat is
removed from the water. Carefully remove any
marine life with a piece of wood or fine-grade
sandpaper.
Once a month
Once a month
Once a month
Once a month
When the vessel is
removed from the
water.
5-1

5. MAINTENANCE, TROUBLESHOOTING
WARNING
5.2 How to Replace the Fuse
The 5 A fuse (Type: FGBO-A 125V 5A PBF, Code No. 000-155-853-10) in the snapin fuse holder on the power cable protects the equipment from equipment fault and
reverse polarity of the power supply. If the equipment cannot be powered, the fuse
may have blown. Find out the cause for the blown fuse before replacing the fuse. If the
fuse blows again after replacement, contact a FURUNO agent or dealer for instructions.
Use the proper fuse.
Use of a wrong fuse can damage the equipment and cause fire.
5.3 How to Restore Default Settings
This procedure restores all default multibeam sonar settings on your NavNet TZtouch/
NavNet TZtouch2/NavNet TZtouch3 device. You can restore all default settings or restore those other than LAN. This procedure should only be performed by a suitably
qualified FURUNO technician.
1. Disconnect the power and LAN cables from the DFF-3D.
2. Open the outer cover and shield cover. Turn on the #3 or #4 switch of DIP Switch
S2 as applicable.
#3: Restore default settings (IP address, etc.) except LAN related.
#4: Restore all default settings. Use this when changing transducers.
3. Connect the power cable to the DFF-3D, then turn on the power at the ship’s
switchboard.
If #4 of DIP Switch S2 is set to ON, the LED blinks every 0.4 seconds.
4. Set up the transducer at the NavNet equipment, referring to chapter 3.
5-2

APPX. 1 MENU TREE
Day Background Color (White, Light Blue, Black, Blue)
Night Background Color (Black, Dark Blue)
Show Range Slider (OFF, ON)*
5
Bottom Range Shift Area (15~85(%); 50)
Transmit Rate Mode (Auto, Manual, Maximum*
6
)
Transmit Rate Manual Value (0~20)
Multi-beam Sonar Transmit*
7
(OFF, ON)
Multi-Sounder
Side Scan
Cross Section
3D Sounder History
MENU
Multibeam
Sonar
Default settings in bold italic.
*1: Settable when Color Mode is set to
Seabed.
*2: Settable when Color Mode is set to Fish.
*3: Settable when Auto Seabed Shading is
set to ON.
*4: Settable when Auto Fish Shading is set
to ON.
Fish Detection Level (Low, Medium, High)
Seabed Echo Calibration (-15~15; 0)
Temp.-Based Correction (OFF; ON)*
8
Noise Filter (Off, Low, Medium, High)*
9
Terrain Shading (0~100(%); 50)
Picture Advance (4/1, 2/1, 1/1, 1/2,1/4, 1/8, Stop)
Color Mode (Seabed, Fish)
Seabed Color*
1
(Classic Hue, Inverted Classic Hue, Red Hue, Blue Hue,
Green Hue, Yellow Hue)
Fish Monochrome Color*
1
(Gray Hue, Brown Hue, Red, Green, Blue,
Cyan,
Magenta, Black or White, Pink, Light Green, Yellow)
Auto Seabed Shading (OFF, ON)
Minimum Value*
3
(0~1200; 0m)
Maximum Value*
3
(0~1200; 50m)
Auto Fish Shading (OFF, ON)
Minimum Value*
4
(0~1200; 0m)
Maximum Value*
4
(0~1200; 50m)
A-Scope Peak Hold (OFF, ON)
High Resolution (OFF, ON)
Picture Advance (4/1, 2/1, 1/1, 1/2,1/4, 1/8, 1/16, Stop)
Clutter (0~100(%); 25)
TVG (0~9; 5)
TVG Distance (10~1000; 400m)
Echo Color (White, Blue, Brown)
Picture Advance (4/1, 2/1, 1/1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, Stop)
Clutter (0~100(%); 60)
TVG (0~9; 5)
Clutter (0~100(%); 0)
TVG (0~9; 5)
Echo Smoothing (Distance) (OFF, Low, Medium, High)
Echo Smoothing (Time) (OFF, Low, Medium, High)
Sound Speed Correction (-15~15; 0)
Temperature Based Correction (ON, OFF)*
5
*5: Not shown for TZT9/14.
*6: Appears as “Max” for TZT9/14.
*7: Appears as “Sounder Transmit”
for TZT9/14.
*8: Not shown for TZtouch2 or
TZtouch3 series units.
*9: Appears as “Bathymetry
Smoothing Level” for TZtouch2
and TZtouch3 series units.
AP-1

APPX. 1 MENU TREE
Fish Finder Alarms
Initial Setup
Fish Alarm (OFF, Single Beam, Triple Beam)
Range Minimum Value (0~1200; 0m)*
Range Maximum Value (0~1200; 10m)*
Fish Alarm Level (Low, Medium, High)*
Transducer Draft (0~99.9; 0)
Salt Water (OFF, ON)
Transducer Setup (Show the menu for setting up the transducer)
Transmission Power Auto (OFF, ON)
Transmission Power (0~10; 10)
External KP (OFF, ON)
Bottom Level (-40~40; 0)
Auto Gain Offset (Multi-Sounder) (-5~5; 0)
Auto Gain Offset (Side Scan) (-5~5; 0)
Auto Gain Offset (Cross Section) (-5~5; 0)
STC (Side Scan) (0~10; 5)
STC (Multi-Sounder) (0~10; 5)
TX Pulse (Short1, Short2, Standard, Long)
DFF-3D Monitoring
Set Hardware to Factory Default
Reset Default Settings
*: Settings have no effect when
Fish Alarm is set to OFF.
AP-2

APPX. 2 JIS CABLE GUIDE
Core
Type Area Diameter
The following reference table lists gives the measurements of JIS cables commonly used with Furuno products:
TTYCSLA-4
MPYC-4
TPYCY
DPYCY
Cable
Diameter
DPYC-1.5 1.5mm2 1.56mm 11.7mm
DPYC-2.5 2.5mm
2
2.01mm 12.8mm
DPYC-4 4.0mm
2
2.55mm 13.9mm
DPYC-6 6.0mm
2
3.12mm 15.2mm
DPYC-10 10.0mm
2
4.05mm 17.1mm
DPYCY-1.5 1.5mm
2
1.56mm 13.7mm
DPYCY-2.5 2.5mm
2
2.01mm 14.8mm
DPYCY-4 4.0mm
2
2.55mm 15.9mm
MPYC-2 1.0mm
2
1.29mm 10.0mm
MPYC-4 1.0mm
2
1.29mm 11.2mm
MPYC-7 1.0mm
2
1.29mm 13.2mm
MPYC-12 1.0mm
2
1.29mm 16.8mm
TPYC-1.5 1.5mm
2
1.56mm 12.5mm
TPYC-2.5 2.5mm
2
2.01mm 13.5mm
TPYC-4 4.0mm
2
2.55mm 14.7mm
TPYCY-1.5 1.5mm
2
1.56mm 14.5mm
TPYCY-2.5 2.5mm
2
2.01mm 15.5mm
TPYCY-4 4.0mm
2
2.55mm 16.9mm
TTYCSLA-1 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 9.4mm
TTYCSLA-1T 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 10.1mm
TTYCSLA-1Q 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 10.8mm
TTYCSLA-4 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 15.7mm
TTYCY-1 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 11.0mm
TTYCY-1T 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 11.7mm
TTYCY-1Q 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 12.6mm
TTYCY-4 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 17.7mm
TTYCY-4SLA 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 19.5mm
TTYCYSLA-1 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 11.2mm
TTYCYSLA-4 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 17.9mm
TTPYCSLA-1 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 9.2mm
TTPYCSLA-1T 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 9.8mm
TTPYCSLA-1Q 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 10.5mm
TTPYCSLA-4 0.75mm
2
1.11mm 15.3mm
EX: TTYCYSLA - 4 MPYC - 4
Designation type
# of twisted pairs
Designation type
# of cores
1 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4
Cables listed in the manual are usually shown as Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS). Use the following guide to locate
an equivalent cable locally.
JIS cable names may have up to 6 alphabetical characters, followed by a dash and a numerical value (example:
DPYC-2.5).
For core types D and T, the numerical designation indicates the cross-sectional Area (mm
2
) of the core wire(s) in the
cable.
For core types M and TT, the numerical designation indicates the number of core wires in the cable.
1. Core Type
D:
Double core power line
T:
Triple core power line
M:
Multi core
TT:
Twisted pair communications
(1Q=quad cable)
2. Insulation Type
P:
Ethylene Propylene Rubber
3. Sheath Type
Y:
PVC (Vinyl)
4. Armor Type
C:
Steel
5. Sheath Type
Y:
Anticorrosive vinyl
sheath
6. Shielding Type
SLA:
All cores in one shield, plastic
tape w/aluminum tape
-SLA:
I
ndividually shielded cores,
plastic tape w/aluminum tape
Core
Type Area Diameter
Cable
Diameter
AP-3

APPX. 3 INSTALLATION OF TRANS-
17-621-01-rev. 03 09/05/17
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
WARNING
Installation of the anti-rotation bolt is mandatory!
Depth Transducer
with Temperature Sensor &
High-Performance Fairing
Models: B54_SS54
Applications
• Bronze transducer recommended for fiberglass or wood hull.
• Stainless steel transducer compatible with all hull materials.
Recommended for aluminum hulls to prevent electrolytic corrosion
provided the stainless steel transducer is isolated from the metal hull.
• Maximum deadrise angle of 24°.
Follow the precautions below for optimal product
performance and to reduce the risk of property damage,
personal injury, and/or death.
WARNING: The transducer must be installed with a HighPerformance Fairing.
WARNING: When installing the High-Performance Fairing
carefully follow these installation instructions.
WARNING: Always wear safety glasses, a dust mask, and
ear protection when installing.
WARNING: The fairing must be installed parallel to the keel
to ensure proper boat handling.
WARNING: Do not install a fairing that has been mis-cut.
Replace it.
• Cutting the fairing at an angle greater than the maximum
allowed will cut into the transducer and/or bolt pocket,
thus weakening the fairing.
• Do not allow any gap between the fairing and the hull that is
greater than 3mm (1/8"). When the boat is underway,
water will enter any gaps and push against the fairing with
considerable force, possibly rotating it.
WARNING: Immediately check for leaks when the boat is
placed in the water. Do not leave the boat unchecked for
more than three hours. Even a small leak may allow
considerable water to accumulate.
CAUTION: Bronze transducer —Never mount a bronze
transducer in a metal hull, because electrolytic corrosion will
occur.
CAUTION: Bronze transducer —Never install a bronze
transducer on a vessel with a positive ground system.
CAUTION: Stainless steel transducer in a metal hull—
Use sleeving to isolate the stainless steel transducer and
anti-rotation bolt from the metal hull. Failure to do so will
cause electrolytic corrosion.
CAUTION: Never pull, carry, or hold the transducer by the
cable as this may sever internal connections.
CAUTION: Never strike the transducer.
CAUTION: Do not over-tighten the hull nut and the nut on
the anti-rotation bolt, crushing the fairing and/ or hull.
CAUTION: The transducer and the yellow triangular plug
must be flush with the fairing for smooth water flow under the
transducer.
CAUTION: Never use solvents. Cleaner, fuel, sealant, paint,
and other products may contain solvents that can damage
plastic parts, especially the transducer’s face.
IMPORTANT: Read the instructions completely before
proceeding with the installation. These instructions
supersede any other instructions in your instrument manual
if they differ.
The anti-rotation bolt holds the fairing firmly in place. Failure to install the antirotation bolt may result in the fairing rotating while the boat is underway. The
effect may be violent movement and loss of steering. This could result in serious
injury or death to passengers and/or damage to the boat or other property.
DUCER B54, SS54
This appendix provides a copy of the installation instructions and Installation supplement for the
®
AIRMAR
tions, see the materials provided with the transducer.
Technology Corporation Transducer B54, SS54. For the latest version of these instruc-
AP-4

APPX. 3 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER B54, SS54
2
Identify Your Model
The model name is printed on the cable tag.
Tools & Materials
Safety glasses
Dust mask
Ear protection
Electric drill
Drill bits and hole saws
Pilot hole 3mm or 1/8"
Angle finder
Band saw (sharp blade)
Rasp or power tool
Sandpaper
Mild household detergent or weak solvent (such as alcohol)
File (installation in a metal hull)
Marine sealant (suitable for below waterline)
Slip-joint pliers
Mallet
Grommets (some installations)
Cable ties
Water-based anti-fouling paint (mandatory in salt water )
Installation in a cored fiberglass hull (see page 5)
Cylinders, wax, tape, and casting epoxy.
Model
(Housing)
Hull Material
Transducer
Hole-Saw Size
Anti-rotation Bolt Hole
Drill Bit Size
B54
SS54
solid fiberglass
wood
51mm or 2" 11 mm or 7/16"
SS54 metal 57mm or 2-1/4" 13 mm or 1/2"
Model
(Housing)
Hole Saw for
Transducer
(outer skin)
Minimum Size
Hole Saw for
Transducer
(inner cored hull)
Drill Bit for
Anti-rotation Bolt
(outer skin)
Mininimum Size
Drill Bit for
Anti-rotation Bolt
(inner cored hull)
B54
SS54
51mm or 2" 65mm or 2-5/8" 11 mm or 7/16" 25 mm or 1"
Mounting Location
CAUTION: Do not mount in line with or near water intake or
discharge openings or behind strakes, struts, fittings, or hull
irregularities that will disturb the water flow.
• The water flowing under the hull must be smooth with a
minimum of bubbles and turbulence (especially at high speeds).
• The transducer’s face must be continuously immersed in water.
• The transducer beam must be unobstructed by the keel or
propeller shaft(s).
• Choose a location away from interference caused by power and
radiation sources such as: the propeller(s) and shaft(s), other
machinery, other echosounders, and other cables. The lower
the noise level, the higher the echosounder gain setting that
can be used.
• Choose a location with a minimum deadrise angle.
• Choose an accessible spot inside the vessel with adequate
space for the height of the stem and tightening the nut.
Boat Types
(Figure 1)
• Displacement hull powerboat—Locate 1/3 of the way back
along the LWL and 150– 300 mm (6–12") off the centerline. The
starboard side of the hull where the propeller blades are moving
downward is preferred.
• Planing hull powerboat—Mount well aft near the centerline and
well inboard of the first set of lifting strakes to insure that it is in
contact with the water at high speeds. The starboard side of the
hull where the propeller blades are moving downward is preferred.
Outboard and I/O—Mount just forward and to the side of the
engine(s).
Inboard—Mount well ahead of the propeller(s) and shaft(s).
Stepped hull —Mount just ahead of the first step.
Boat capable of speeds above 25kn (29MPH)—Review
transducer location and operating results of similar boats before
proceeding.
Figure 1.
pressure waves
1/3 aft
displacement hull
(6-12")
150- 300mm
LWL
Best location for the transducer
(Load Waterline Length)
stepped hull
outboard and I/O
planing hulls
Copyright © 2005 Airmar Technology Corp.
inboard
deadrise
angle
slope of hull
parallel to
water surface
Figure 2. Deadrise angle and fairing thickness
backing block
min. fairing
thickness
45mm (1-3/4")
aft view
fairing
hull
Copyright © 2016 Airmar Technology Cor p.
NOTE: fairing must
be flush with housing
stem
transducer face
hull nut
transducer
AP-5

APPX. 3 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER B54, SS54
3
Installation
Cored Fiberglass Hull —Follow separate instructions on page 5.
Hole Drilling: Transducer
1. Drill a 3mm or 1/8" pilot hole perpendicular to the waterline from
inside the hull (Figure 2). If there is a rib, strut or other hull irregularity
near the selected mounting location, drill from the outside.
2. Using the appropriate size drill bit or hole saw, cut a hole from
outside the hull. Be sure to hold the drill plumb, so the hole will
be perpendicular to the water surface.
Cutting the High-Performance Fairing
CAUTION: The end of the fairing with the arrows/ triangular
recess always points forward toward the bow when installed. Be
sure to orient the fairing on the band saw, so the angle cut
matches the intended side of the hull and not the mirror image.
1. Measure the deadrise angle of the hull at the selected mounting
location using an angle finder (Figure 2). Check to be sure the
angle does not exceed 24°.
2. Tilt the band saw table to the measured angle and secure the
cutting fence (Figure 3). Do not exceed 24°.
3. Place the fairing on the table, so the cutting guide rests against
the fence (Figure 4). The end with the arrows and triangular
recess will be pointing toward you for installation on the
starboard side of the boat or away from you for installation on
the port side.
4. Adjust the cutting fence, so the fairing will be cut in about two equal
parts (Figure 3). The section that will become the fairing must be a
minimum of 45mm (1-3/4") at its thinest dimension (Figure 2).
5. Recheck steps 1 through 4. Then cut the fairing.
6. When the boat is underway, especially at high speeds, water
will enter any gaps and push against the fairing with
considerable force, possibly rotating it. Shape the fairing to the
hull as precisely as possible with a rasp or power tool. If there is
a gap of more than 3mm (1/8"), replace the fairing.
7. Check to be sure the transducer is flush with the fairing. If it is
recessed more than 0.5mm (1/64") inside the fairing, you may
shim the transducer or carefully file/ sand the fairing.
8. The remaining section of the fairing with the cutting guide will
be used as the backing block inside the hull. It will provide a
level surface for tightening the nuts.
Hole Drilling: Anti-rotation Bolt
To locate and drill the hole for the anti-rotation bolt, use the fairing
as a guide. This will ensure that the hole is perpendicular to the
waterline and not drilled at the angle of the hull.
Figure 5. Bedding and installing in a solid fiberglass or wood hull
Copyright © 2016 Airmar Technology Corp.
BOW
►
anti-rotation
bolt
nut &
washer
triangular plug
backing
block
High-
surface facing
outward
hull
hull nut
stem
Performance
Fairing
NOTE: Be sure
the arrow on the
transducer
points forward
toward the bow.
marine sealant on following (shown in red):
- transducer, extending above hull nut 1/4" (NOT surface that will touch water)
- backing block that contacts hull
- hull nut that contacts backing block
- anti-rotation washer that contacts backing block
- yellow triangular plug: fill hollow half way (NOT curved surface that will touch water)
- anti-rotation bolt including bolt head, extending above nut 1/4"
- fairing that contacts hull
with curved
B54
Figure 3. Cutting the High-Performance Fairing
deadrise
angle
cutting
guide
band saw
table
triangular recess
for installation
on starboard side
fence
Copyright © 2005 - 2010 Airmar Technology Co rp.
of the hull
end with arrows and
Figure 4. High-Performance Fairing
Copyright © 2005 - 2017Airmar Technology Corp.
triangular
cutting
recess for
anti-rotation bolt
guide
AP-6

4
1. Dry fit the transducer in the fairing. Thread the cable through the
large hole in the fairing and through the mounting hole in the hull.
Seat the transducer firmly within the recess in the fairing
(Figure 5 or 6). Be sure the arrow on the transducer points
toward the triangular recess in the fairing.
2. Slide the transducer with the fairing in place into the mounting
hole. Using the bolt hole in the fairing as your guide, drill a 3mm
(1/8”) pilot hole through the hull for the anti-rotation bolt.
3. Using the appropriate size drill bit, hold the fairing in place and
drill a hole for the anti-rotation bolt.
4. Remove the assembly and cable from the mounting hole.
5. Sand and clean the area around both holes, inside and outside,
to ensure that the sealant will adhere properly to the hull. If
there is any petroleum residue inside the hull, remove it with
either mild household detergent or a weak solvent such as
alcohol before sanding.
Metal hull—Remove all burrs with a file and sandpaper.
Bedding the Transducer
CAUTION: Be sure the surfaces to be bedded are clean and dry.
1. Remove the transducer from the fairing.
2. Apply a 2mm (1/16") thick layer of marine sealant to the surface
of the transducer that will contact the fairing and up the stem
(Figure 5 or 6, areas in red). The sealant must extend 6mm
(1/4") higher than the combined thickness of the fairing, hull,
backing block, and hull nut. This will ensure there is marine
sealant in the threads to seal the hull and hold the hull nut
securely in place.
Stainless steel transducer in a metal hull —To prevent
electrolytic corrosion, the stainless steel housing must be
isolated from the metal hull. Slide the isolation sleeve over the
bedded transducer stem as far down as possible (Figure 6).
Apply a 2mm (1/16") thick layer of the marine sealant to the
outside of the sleeve.
3. Apply a 2 mm (1/16") thick layer of marine sealant to the
following surfaces:
• Fairing that will contact the hull
• Backing block that will contact the inside of the hull
• Hull nut that will contact the backing block
4. Thread the transducer cable through the fairing and seat the
transducer firmly within the recess. Be sure the arrow on the
transducer points toward the triangular recess in the fairing.
Installing the Transducer
1. From outside the hull, thread the transducer cable through the
mounting hole. Push the stem of the transducer (with the fairing
in place) into the mounting hole using a twisting motion to
squeeze out excess sealant (Figure 5 or 6). Be sure the arrow
on the transducer points forward toward the bow.
NOTE: The transducer must be FLUSH with the fairing. If it is
recessed more than 0.5mm (1/64") inside the fairing, you may
shim the transducer or carefully file/ sand the fairing.
Stainless steel transducer in a metal hull —Be sure the
isolation sleeve is between the transducer stem and the hull
(Figure 6). However, the isolation sleeve must be below the
washer and hull nut to prevent the sleeve from interfering with
tightening the hull nut.
2. From inside the hull, slide the backing block onto the transducer
cable and stem, seating the backing block firmly against the
hull. Screw the hull nut in place, but do not tighten it at this time.
Bedding & Installing the Anti-rotation Bolt
CAUTION: Be sure the surfaces to be bedded are clean and dry.
1. Apply a 2 mm (1/16") thick layer of marine sealant to the antirotation bolt including the flange (Figure 5 or 6). The sealant
must be 6mm (1/4") higher than the combined thickness of the
fairing, hull, backing block, washer, and nut. This will ensure that
there is marine sealant on the threads to seal the hull and hold
the nut securely in place.
Figure 6. Bedding and installing the SS54 in a metal hull
Copyright © 2017 Airmar Technology Cor p.
BOW
►
anti-rotation
bolt
nut &
washer
triangular plug
backing
block
High-Performance
surface facing
outward
hull
hull nut
stem
Fairing
NOTE: Be sure
the arrow on the
transducer
points forward
toward the bow.
with curved
SS54
marine sealant on following (shown in red):
- transducer, extending above hull nut 1/4" (NOT surface that will touch water)
- backing block that contacts hull
- hull nut that contacts backing block
- anti-rotation washer that contacts backing block
- yellow triangular plug: fill hollow half way (NOT curved surface that will touch water)
- anti-rotation bolt including bolt head, extending above nut 1/4"
- fairing that contacts hull
- isolation sleeve on stem
isolation
isolation sleeve
- isolation sleeve on anti-rotation bolt
sleeve
APPX. 3 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER B54, SS54
AP-7

APPX. 3 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER B54, SS54
Stainless steel transducer in a metal hull—To prevent
electrolytic corrosion, the stainless steel anti-rotation bolt must
be isolated from the metal hull. Slide the isolation sleeve over the
bedded anti-rotation bolt as far down as possible (Figure 6).
Apply a 2mm (1/16") thick layer of the marine sealant to the
outside of the sleeve.
2. Apply a 2 mm (1/16") thick layer of marine sealant to the side of
the washer that will contact the backing block.
3. Push the anti-rotation bolt through the fairing and the hull.
4. From inside the hull, screw the washer (sealant side down) and
the nut onto the anti-rotation bolt.
Stainless steel transducer in a metal hull—Be sure the
isolation sleeve is between the anti-rotation bolt and the hull
(Figure 6). However, the isolation sleeve must be below the
washer and nut to prevent the sleeve from interfering with
tightening the nut.
5. Use slip-joint pliers to tighten the hull nut. Then tighten the nut
on the anti-rotation bolt. Do not over-tighten, crushing the
fairing or hull.
Cored fiberglass hull—Do not over tighten, crushing the hull.
Wood hull—Allow for the wood to swell before tightening the nut.
6. Use marine sealant to half-fill the hollow in the yellow triangular
plug. Apply a 2mm (1/16") thick layer of marine sealant to the
three sides of the plug that form the triangle. The sealant will
hold the plug firmly within the fairing and fill any gap between
the anti-rotation bolt and the plug.
7. The yellow triangular plug fits one way only. Push the yellow
plug into the recess in the fairing until it is FLUSH with the
outside of the fairing. This will squeeze out excess sealant. If
necessary, tap it into place with a mallet.
NOTE: If the triangular plug is slightly recessed within the
fairing, use sealant to fill the gap. The plug must be FLUSH with
the fairing for good performance.
8. When the boat is underway, especially at high speeds, water
will enter any gaps and push against the fairing with
considerable force, possibly rotating it. Fill any gaps between
the fairing and the hull with marine sealant. If there is any gap
greater than 3mm (1/8"), replace the fairing. Remove the
excess sealant on the outside of the fairing and hull to ensure
smooth water flow under the transducer.
Cable Routing & Connecting
CAUTION: If the sensor came with a connector, do not remove it
to ease cable routing. If the cable must be cut and spliced, use
Airmar’s splash-proof Junction Box No. 33-035 and follow the
instructions supplied. Removing the waterproof connector or
cutting the cable, except when using a water-tight junction box,
will void the sensor warranty.
1. Route the cable to the instrument being careful not to tear the
cable jacket when passing it through the bulkhead(s) and other
parts of the boat. Use grommet(s) to prevent chafing. To reduce
electrical interference, separate the transducer cable from other
electrical wiring and the engine. Coil any excess cable and
secure it in place with cable ties to prevent damage.
2. Refer to the instrument owner’s manual to connect the
transducer to the instrument.
Checking for Leaks
When the boat is placed in the water, immediately check around the
transducer for leaks. Note that very small leaks may not be readily
observed. Do not leave the boat in the water for more than 3 hours
before checking it again. If there is a small leak, there may be
considerable bilge water accumulation after 24 hours. If a leak is
observed, repeat “Bedding” and “Installing” immediately (see page 4).
Installation in a Cored Fiberglass Hull
The core (wood or foam) must be cut and sealed carefully. The
core must be protected from water seepage, and the hull must be
reinforced to prevent it from crushing under the hull nut allowing
the transducer to become loose.
CAUTION: Completely seal the hull to prevent water seeping into
the core.
1. Drill a 3mm or 1/8" pilot hole perpendicular to the waterline from
inside the hull (Figure 7). If there is a rib, strut, or other hull
irregularity near the selected mounting location, drill from the
outside. If the hole is drilled in the wrong location, drill a second
hole in a better location. Apply masking tape to the outside of the
hull over the incorrect hole and fill it with epoxy.
2. Using the appropriate size drill bit or hole saw, cut a hole from
outside the hull through the outer skin only. Be sure to hold the
drill plumb, so the hole will be perpendicular to the water surface.
3. The optimal interior hole diameter is affected by the hull’s
thickness and deadrise angle. It must be large enough in
diameter to allow the core to be completely sealed.
Using the appropriate size drill bit or hole saw, cut through the
inner skin and most of the core from inside the hull keeping the
drill perpendicular to the hull. The core material can be very soft.
Apply only light pressure to the hole saw after cutting through the
inner skin to avoid accidentally cutting the outer skin.
4. Remove the plug of core material, so the inside of the outer skin
and the inner core of the hull is fully exposed. Sand and clean
the inner skin, core, and the outer skin around the hole.
5. Coat a hollow or solid cylinder of the correct diameter with wax
and tape it in place. Fill the gap between the cylinder and hull
with casting epoxy. After the epoxy has set, remove the cylinder.
6. Sand and clean the area around the hole, inside and outside, to
ensure that the sealant will adhere properly to the hull. If there
is any petroleum residue inside the hull, remove it with either
mild household detergent or a weak solvent, such as alcohol,
before sanding.
7. Follow the same procedure to prepare the hull for the antirotation bolt. Repeat steps 1 through 6.
8. Proceed with the installation beginning with "Cutting the
Fairing" on page 3. Note that all holes are already drilled.
Anti-fouling Paint
Surfaces exposed to salt water must be coated with anti-fouling
paint. Use water-based anti-fouling paint only. Never use ketonebased paint since ketones can attack many plastics possibly
damaging the transducer. Reapply anti-fouling paint every 6
months or at the beginning of each boating season.
hull’s outer skin to
hull
outer skin
solid or hollow
cylinder
pour in
casting
epoxy
core
inner skin
Figure 7. Preparing a cored fiberglass hull
Dimension equal to
the thickness of the
ensure adequate
clearance
Copyright © 2005 Airmar Technology Corp.
5
AP-8

Maintenance, Parts & Replacement
Cleaning
Aquatic growth can accumulate rapidly on the transducer’s face
reducing its performance within weeks. Clean the surface with a
Scotch-Brite® scour pad and mild household detergent taking
care to avoid making scratches. If the fouling is severe, lightly wet
sand with fine grade wet/dry paper.
Replacement Transducer & Parts
The information needed to order a replacement transducer is
printed on the cable tag. Do not remove this tag. When ordering,
specify the part number, date, and frequency in kHz. For
convenient reference, record this information below.
Part No.________________Date___________Frequency_________kHz
Lost, broken, and worn parts should be replaced immediately.
Hull nut, bronze 02-030
Hull nut, stainless steel 02-530-02
Fairing 04-883-01
Please contact your Furuno dealer to obtain parts.
6
APPX. 3 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER B54, SS54
AP-9

APPX. 4 INSTALLATION OF TRANS-
D-17-299-04-rev.3 17-299-04 rev.3 04/05/19
Transom Mount:
1kW with Release Bracket
Depth Transducer
with Temperature Sensor
Model TM54
Tools & Materials
Safety goggles
Dust mask
Ear protection
Angle finder
Masking tape (some installations)
Pencil
Electric drill
Drill bits and hole saws:
Bracket holes 5mm, #4, or 7/32"
Transom hole (optional) 21mm or 13/16"
Cable clamp holes 3mm or 1/8"
Marine sealant (suitable for below waterline)
Socket wrench
Straight edge
Small screwdriver
Grommet(s) (some installations)
Cable ties
Water-based anti-fouling paint (mandatory in salt water)
Applications
• Recommended for outboard and inboard /outboard sport fishing
powerboats 10m (32') and up
• Not recommended for boats with inboard engine(s)
• Not recommended for stepped hull
• Adjusts to transom angles from 3
–21
• Vertically orients sound beam on hull with deadrise angle up to 28
• Good operation up to 30kn (35 MPH)
Mounting Location
Guidelines
CAUTION: Do not mount the transducer in line with or near water
intake or discharge openings or behind strakes, fittings, or hull
irregularities that may disturb the water flow.
CAUTION: Do not mount the transducer in a location where the
boat may be supported during trailering, launching, hauling, or
storage.
• For best performance, the transducer’s face must be in contact
with smooth water. To identify an area of “clean” water, observe
the flow off the transom while the boat is underway.
• Allow vertical space above the bracket for it to release and
rotate the transducer upward.
• Mounting the transducer on the side of the transom where the
propeller blades are moving downward is preferred (Figure 1).
• Mount the transducer as far away from the propeller as possible
while ensuring the transducer’s face remains in the water when
the boat is turning.
Record the information found on the cable tag for future reference.
Part No.________________ Date___________ Frequency________ kHz
Follow the precautions below for optimal
product performance and to reduce the risk of
property damage, personal injury, and/or death.
WARNING: Always wear safety glasses, a dust mask,
and ear protection when installing.
WARNING: When the boat is placed in the water,
immediately check for leaks around the screws and
any other holes drilled in the hull.
CAUTION: Never pull, carry, or hold the transducer by
the cables as this may sever internal connections.
CAUTION: Never strike the transducer to release it.
When mounted on the bracket, remove the transducer
by removing the locking pin and hinge pin.
CAUTION: The bracket protects the transducer from
frontal impact only.
CAUTION: Never use solvents. Cleaner, fuel, sealant,
paint and other products may contain solvents that can
damage plastic parts, especially the transducer’s face.
IMPORTANT: Please read the instructions completely
before proceeding with the installation. These
instructions supersede any other instructions in your
instrument manual if they differ.
TM54
bracket with shims
(operational position shown)
Figure 1. Mounting location on single drive boat
NOTES:
-To avoid noise interference, it is recommended that the propeller is
located outside the transducer beam coverage of 120°.
-The side of the transom where the propeller blades are moving
downward is preferred.
hull projection
0–3mm (0–1/8")
parallel to
waterline
120°
OWNER’ S GUIDE & INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
DUCER TM54
This appendix provides a copy of the installation instructions and Installation supplement for the
AIRMAR
see the materials provided with the transducer.
®
Technology Corporation Transducer TM54. For the latest version of these instructions,
AP-10

Boat Types
• Single drive—Mount a minimum of 15 cm (6") beyond the
swing radius of the propeller (Figure 1).
• Twin drive—Mount between the drives a minimum of 15 cm
(6") beyond the swing radius of the propeller.
• Trim tabs—Mount inside the trim tab, space permitting.
• Stepped transom—Mount the transducer on the lowest step
being sure there is enough vertical space above the bracket for
it to release and rotate the transducer upward (Figure 2).
Installation
Assembling the Transducer & Bracket
1. There are two cables. Thread each cable through the
corresponding hole in the transducer support (Figure 3).
2. Fasten the support to the transducer using the three sockethead-cap screws and washers supplied. Tighten the screws
with the 3/16" Allen wrench supplied.
3. Attach a safety ring to one end of each pin (Figure 4).
4. While holding the transducer assembly against the bracket, insert
a pin through the upper hole in the bracket and the support.
Slide the spacer onto the pin and push it through the remaining
hole in the support and the bracket. Attach a second safety ring.
This pin will function as a hinge when the transducer is released.
5. Slide a washer onto the remaining pin. Push it through the
lower hole in the bracket, slide it along the channel in the
support, and through the second hole in the bracket. Slide the
second washer onto the free end of the pin and attach the
second safety ring. This will function as the locking pin to hold
the transducer in the operational position when underway.
Compensating for Transom Angle: Shims
For the best performance, the transducer beam must be aimed
straight at the bottom. Since the transom of most boats is angled,
the bracket must compensate for it. Measure the transom angle of
the boat with an angle finder.
• Standard transom (12
transom angle)—The bracket is
designed for a standard 12
transom angle. No shim is needed
for this installation. If your boat is capable of speeds above
20kn (28 MPH), install the bracket with one 3
shim, taper
down. This will ensure that the transducer is in contact with the
water at high speeds.
• Using shims—The bracket is supplied with three shims; each
one has a 3
angle. Up to three shims can be combined for a
maximum of 9
. The shims are designed to mate together. Two
bosses on the face fit into recesses in the back of another shim or
the holes in the bracket.
- Transom angles greater than 12
—Add the appropriate
number of shims with the taper up to the 12
bracket angle.
- Transom angles less than 12
—To reduce the bracket’s
12° angle, group the appropriate number of shims with the
taper down.
• If you are unsure about using the shim(s), experiment with
them by following the instructions “Mounting & Adjusting the
Bracket.”
Hole Drilling
CAUTION: To prevent drilling too deeply, wrap masking tape
around the bit 22mm (7/8") from the point.
NOTE: Fiberglass hull—Minimize surface cracking by running
the drill in reverse until the gelcoat is penetrated.
1. At the selected mounting location, position the assembly so the
transducer projects 3mm (1/8") below the bottom edge of the
transom (Figure 1). Be sure any shim(s) is in place. (You may
want to tape the shim(s) to the bracket temporarily.) With the
transducer in the operational position and the bracket parallel to
the waterline, mark the bottom corners of the bracket.
2. Remove the transducer assembly from the bracket by removing
the locking pin and the hinge pin (Figure 4). Hold the bracket
with any shim(s) in place against the transom at the marked
location. Draw an “X” at 12mm (1/2") from the top and the
bottom of each slot (Figure 6).
3. Using a 5 mm, #4, or 7/32" drill bit, drill four holes 22mm (7/8")
deep at the marked locations.
Figure 3. Assembling the transducer
bracket
support
transducer
hinge
locking
spacer
safety
Figure 4. Attaching the transducer to the bracket
screw (3)
washer (3)
support
transducer
cable
washer (2)
pin
pin
ring (4)
detail
channel
Figure 2. Stepped transom: vertical space required
TM54: 244mm (9-3/4")
vertical space
APPX. 4 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER TM54
AP-11
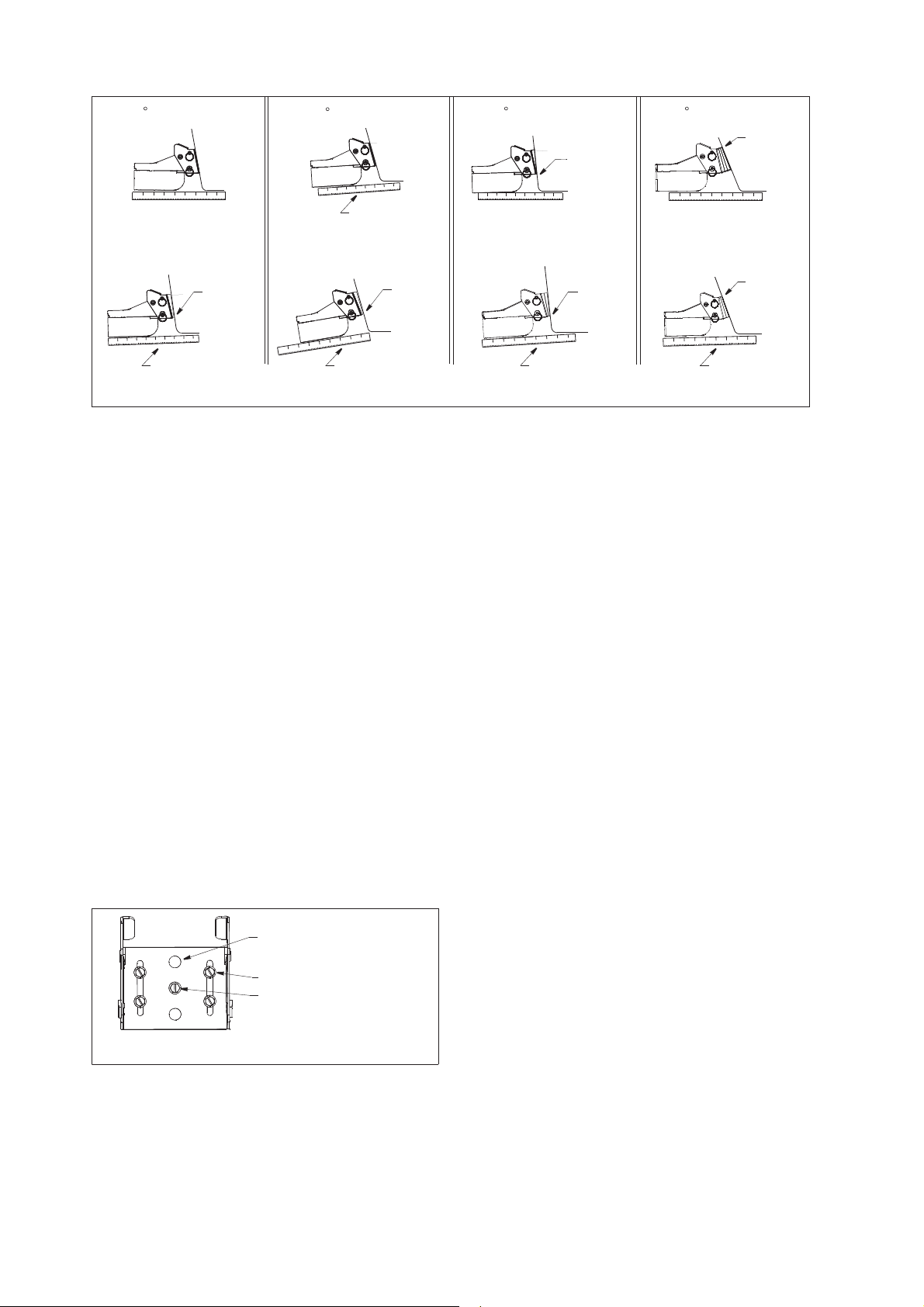
APPX. 4 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER TM54
Mounting & Adjusting the Bracket
CAUTION: Do not position the leading edge of the transducer
lower than the trailing edge because aeration will occur.
CAUTION: Do not position the transducer deeper in the water
than necessary to avoid increasing drag, spray, and water noise
and reducing boat speed.
CAUTION: The stainless steel bracket must be isolated from a
metal hull to prevent electrolytic corrosion. If no shim is being
used, place non-metal insulating washers between the bracket
and the metal hull.
1. Apply marine sealant to the threads of four of the hex-washerhead screws to prevent water seepage into the transom. Being
sure any shim(s) is in place, screw the bracket to the hull using a
socket wrench (Figure 4). Do not tighten the screws at this time.
2. Reinstall the transducer. While holding the transducer assembly
against the bracket, insert the hinge pin through the upper hole
in the bracket and the support. Slide the spacer onto the pin
and push it through the remaining hole in the support and the
bracket. Reattach the safety ring.
3. Slide a washer onto the locking pin. Push it through the lower
hole in the bracket, slide it along the channel in the support, and
through the second hole in the bracket. Slide the second
washer onto the free end of the pin and reattach the safety ring.
4. With the transducer in the operational position, use a straight edge
to sight the underside of the transducer relative to the underside of
the hull (Figure 5). The trailing edge of the transducer should be
1– 6mm (1/16–1/4") below the leading edge.
5. Using the vertical adjustment space in the bracket slots, slide the
assembly up or down until the bottom inside corner of the
transducer projections 0– 3mm (0–1/8") below the bottom of the
hull (Figure 1). When you are satisfied with the position of the
transducer, tighten the four bracket screws. For clear access to
the screws, remove the transducer assembly from the bracket
(Figure 4). When reattaching, be sure to include the spacer.
Testing on the Water
1. Test the transducer at 165 kHz with the engine off.
2. Become familiar with your echosounder’s performance at a
speed of 4kn (5 MPH).
3. Gradually increase the boat speed and observe the gradual
decline of performance due to turbulent water flowing under the
transducer’s face.
NOTE: As the speed increases the performance at 50kHz will
deteriorate more rapidly because more acoustic noise is
generated at low frequencies.
4. If the decline in performance is sudden (not gradual), identify
the boat speed at which the onset occurred. Return the boat to
this speed, then gradually increase speed while making
moderate turns in both directions.
5. If the performance improves while turning to the side on which the
transducer is installed, its position probably needs adjustment. The
transducer is probably in turbulent or aerated water.
To improve performance, try the following, one at a time,
in the order given, in small increments.
a. Increase the transducer’s angle in the water. Review
“Compensating for Transom Angle: Shims” and Figure 5.
b. Move the transducer deeper into the water in increments of
3mm (1/8") (Figure 1).
c. Move the transducer closer to the centerline of the boat.
Fill unused screw holes with marine sealant.
6. Calibration—To match the speed shown on the display to the
actual speed of the boat, you may need to calibrate the
instrument. Refer to your instrument owner’s manual.
Stabilizing the Bracket
1. Prevent the bracket from moving out of position using the
remaining hex-washer-head screw. Drill the hole for the
stabilizing screw through the center hole of the bracket, any
shim(s), and the hull (Figure 6).
3
12 transom angle
13
transom angle
Figure 5. Adjusting the transducer angle
21
transom angle9 transom angle
parallel
slight angle
one
shim
three shims
taper down
slight angle
parallel
one shim
taper down
parallel
May improve operation
above 20kn (23MPH)
May improve operation
above 20kn (23 MPH)
slight angle
two shims
taper down
slight angle
May improve operation
above 20kn (23 MPH)
May improve operation
above 20kn (23 MPH)
one
shim
taper down
more angle
Figure 6. Screw locations on bracket
screw (4)
stabilizing screw
NOTE: Draw an “X”
at 12mm (1/2") from
the top and bottom
of both slots.
taper up
two shims
taper up
hole (2) mate
with bosses
on shim
AP-12

2. Apply marine sealant to the threads of the remaining screw to
prevent water seeping into the transom.
3. Fasten the stabilizing screw into place with a socket wrench.
For clear access to the screw, remove the transducer assembly
from the bracket (Figure 4). When reattaching the transducer,
be sure to include the spacer.
Cable Routing & Connecting
CAUTION: Do not remove the connectors to ease cable routing. If
the cables must be cut and spliced, use Airmar’s splash-proof
Junction Box No. 33-035 and follow the instructions provided.
Removing the waterproof connectors or cutting the cables, except
when using a water-tight junction box, will void the sensor warranty.
Route the cables over the transom for a detachable installation.
For permanent mounting, route the cables through a drain hole or
through new holes drilled in the transom above the waterline.
1. If holes must be drilled through the transom,
choose a location
well above the waterline (Figure 7). Check for obstructions
such as trim tabs, pumps, or wiring inside the hull. Mark the
locations with a pencil. Drill each hole using a 21mm or 13/16"
bit to
accommodate the connector.
2. Route the cables over or through the transom.
3. On the outside of the hull, secure each cable against the
transom using the cable clamps supplied. For the first cable,
position one cable clamp 30cm (12") above the bracket. Mark
the mounting hole with a pencil.
4. Position the second cable clamp halfway between the first
clamp and the cable hole. Mark this mounting hole.
5. If a hole has been drilled through the transom, open the large
slot in each transom cable cover. Position a cover over the
cable where it enters the hull. Mark the two mounting holes.
6. For the second cable, repeat steps 3, 4, and 5.
7. At each of the marked locations, use a 3 mm or 1/8" bit to drill a
hole 10mm (3/8") deep.
8. Apply marine sealant to the threads of the #6 x 1/2" self-tapping
screws to prevent water from seeping into the transom. If you
have drilled holes through the transom, apply marine sealant to
the space around the cables where they pass through the
transom.
9. Position the four cable clamps and fasten them in place. If
used, push a cable cover over each cable and screw them in
place.
10.Route the cables to the instrument being careful not to tear the
cable jackets when passing it through the bulkhead(s) and
other parts of the boat. Use grommet(s) to prevent chafing. To
reduce electrical interference, separate the transducer cables
from other electrical wiring and the engine(s). Coil any excess
cable and secure it in place with cable ties to prevent damage.
11.Refer to your echosounder owner’s manual to connect the
transducer to the instrument.
Checking for Leaks
When the boat is placed in the water, immediately check for
leaks around the screws and any other holes drilled in the hull.
Note that very small leaks may not be readily observed. Do not
leave the boat in the water unchecked for more than three hours.
Maintenance
Anti-fouling Paint
Aquatic growth can accumulate rapidly on the transducer’s face
reducing performance within weeks. Surfaces exposed to salt
water that do not interlock must be coated with anti-fouling paint.
Use water-based anti-fouling paint only. Never use ketone-based
paint, since ketones can attack many types of plastic possibly
damaging the transducer. Repaint every 6 months or at the
beginning of each boating season.
Cleaning
CAUTION: Do not use a lubricant on the bracket; grit will stick to
it, increasing friction and wear.
Clean the sensor with a Scotch-Brite
®
scour pad and mild
household detergent, taking care to avoid making scratches on
the transducer’s face. If the fouling is severe, lightly wet sand with
fine grade wet/ dry paper.
Transducer Replacement & Parts
The information needed to order a replacement transducer is printed
on the cable tag. Do not remove this tag. When ordering, specify the
part number, date, and frequency in kHz. For convenient reference,
record this information on the top of page one.
Lost, broken, and worn parts should be replaced immediately.
Please contact your Furuno dealer to obtain parts.
Figure 7. Cable routing
30cm (12")
cable cover (2)
cable clamp (4)
APPX. 4 INSTALLATION OF TRANSDUCER TM54
AP-13

FURUNO
SPECIFICATIONS OF MULTI BEAM SONAR
DFF-3D
1 GENERAL
1.1 TX frequency 165 kHz
1.2 Output power 800 W nominal
1.3 Amplifier type Straight amplifier (H/L gain sampling simultaneously)
1.4 Minimum range 3 m
1.5 Display mode Multi-sounder, Side scan, Section, 3D history
1.6 Depth range and Pulse repetition rate (PRR) (TX rate: 20, Pulse length: standard)
Range (m) PRR (times/min, max.)
5 600
10 600
40 484
100 200
200 100
500 40
1200 37
DFF-3D
2 INTERFACE
2.1 Number of port
LAN 1 port, Ethernet 10/100Base-TX
External KP 1 port (optional external KP kit required)
3 POWER SUPPLY
3.1 Multi beam sonar 12-24 VDC: 1.4-0.7 A
3.2 Rectifier (PR-62, option) 100/110/220/230 VAC, 1 phase, 50/60Hz
4 ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS
4.1 Ambient temperature
Main unit -15°C to +55°C
Transducer -5°C to +35°C
4.2 Relative humidity 93% or less at +40°C
4.3 Degree of protection IP55
4.4 Vibration IEC 60945 Ed.4
5 UNIT COLOR
N2.5 (fixed)
SP - 1 E1352S01C
161124

㹎㸿㹁㹉㹇㹌㹅ࠉ㹊㹇㹑㹒
*5;
'))'
1$0(
287/,1(
'(6&5,37,21&2'(θ
47<
ࣘࢽࢵࢺ
81,7
㺭㺷㺟㺩㺼㺎㺯㺝㺣㺎
08/7,%($0621$5
'))'
ணഛရ
63$5(3$576
63
㺩㺋㺎㺛㺼
*/$6678%()86(
)*%$9$3%)
ᕤᮦᩱ
,167$//$7,210$7(5,$/6
㺗㺎㺪㺼㺷⤌ရ/$1
/$1&$%/($66(0%/<
02'=
㺗㺎㺪㺼㺷⤌ရ0-
&$%/($66(0%/<
0-$63)&$
ᕤᮦᩱ
,167$//$7,210$7(5,$/6
&3
ᅗ᭩
'2&80(17
ྲྀᢅㄝ᭩
23(5$72560$18$/
20
䡶㻙䢀䢚␒ྕᮎᑿ䛾㼇㻖㻖㼉䛿䚸㑅ᢥရ䛾௦⾲䡶䡬䢀䢚䜢⾲䛧䜎䛩䚹
㻯㻻㻰㻱㻌㻺㼁㻹㻮㻱㻾㻌㻱㻺㻰㻵㻺㻳㻌㼃㻵㼀㻴㻌 㻎㻖㻖㻎㻌㻵㻺㻰㻵㻯㻭㼀㻱㻿㻌㼀㻴㻱㻌㻯㻻㻰㻱㻌㻺㼁㻹㻮㻱㻾㻌 㻻㻲㻌㻾㻱㻼㻾㻱㻿㻱㻺㼀㻭㼀㻵㼂㻱㻌㻹㻭㼀㻱㻾㻵㻭㻸㻚
䠄␎ᅗ䛾ᑍἲ䛿䚸ཧ⪃್䛷䛩䚹㻌㻌㻰㻵㻹㻱㻺㻿㻵㻻㻺㻿㻌㻵㻺㻌㻰㻾㻭㼃㻵㻺㻳㻌㻲㻻㻾㻌㻾㻱㻲㻱㻾㻱㻺㻯㻱㻌㻻㻺㻸㼅㻚䠅
.5
&=$
A-1
&2'(12
7<3(
&3
␎ࠉࠉᅗ
287/,1(
ྡࠉࠉ⛠
1$0(
ᩘ㔞
47<
⏝㏵㸭ഛ⪃
5(0$5.6
␒ྕ
12
ᆺྡ㸭つ᱁
'(6&5,37,216
,167$//$7,210$7(5,$/6
ᕤᮦᩱ⾲
*5;
㺢㺵㺛㺞㺍㺩㺽㺻㺦㺚㺼ࠉ㺚㺋
6(/)7$33,1*6&5(:
;686
&2'(
12
ᅽ╔➃Ꮚ
&5,0321/8*
)9/)5('
&2'(
12
ᑟ㟁ᛶ㺡㺎㺪㺽
&21'8&7,9(7$3(
12;<00
&2'(
12
㸦␎ᅗࡢᑍἲࡣࠊཧ⪃್࡛ࡍࠋࠉ',0(16,216,1'5$:,1*)255()(5(1&(21/<㸧
㹄㹓㹐㹓㹌㹍ࠉ㹃㹊㹃㹁㹒㹐㹇㹁ࠉ㹁㹍ࠉ㸬㸪㹊㹒㹂
ဳᑼ㩄㨺㩎㩨⇟ภ߇㧞Ბߩ႐วޔ ᲑࠃࠅᲑߦઍࠊࠆㆊ ᦼຠߢࠅޔߤߜࠄ߆ ߇ߞߡ߹ߔޕޓߥ߅ ޔຠ⾰ߪᄌࠊࠅ߹ߖࠎޕ
6916;2'5#0&%1&'5/#;$'.+56'&(14#0+6'/6*'.19'4241&7%6/#;$'5*+22'&+02.#%'1(6*'722'4241&7%6
37#.+6;+56*'5#/'
A
-2
&0&
)9/)5('.
ဳ

D-1
20/Sep/2016 H.MAKI
20/Sep/2016 H.MAKI

'))'
S-1
࣐ࣝࢳࣅ࣮࣒ࢯࢼ࣮
┦⤖⥺ᅗ
08/7,%($0621$5
,17(5&211(&7,21',$*5$0
࣮ࢧࢿࢵࢺࣁࣈ
(7+(51(7+8%
+8%
ࡲࡓࡣ 25
08/7,)81&7,21',63/$<
࣐ࣝࢳࣇࣥࢡࢩࣙࣥࢹࢫࣉࣞ
7=77=77=7%%
7=7/)7=7/)7=7%%
7=7)7=7)7=7)
እ㒊ᶵჾ
(;7(51$/(48,30(17
.3287
.3,1
7,7/(
1$0(
ྡ⛠
02'=P
P
03<&6/$
5- 5-
-
1(7:25.
࣐ࣝࢳࣅ࣮࣒ࢯࢼ࣮
08/7,%($0621$5
'))'
9'&
0-$63)
%/.
:+7ࢩࣟ
ࢡࣟ
$
*51
㺮㺢㺼㺶
7%
7'
75$16'8&(5
ࢳࣕ %51
7'
࢜ %/8
1&
7'B&20021
%/.
ࢡࣟ
,9VT
7%
7'
ࢩࣟ :+7
7'
㺮㺢㺼㺶 *51
7%
1&
7'
7'1&7'
ࢲ 25*
࢟ <(/
6+,(/'
-
ࣁ *5<
7'
㺯㺵㺙㺕 33/
3%
Pȭ
027,216(1625
-
0-$63)
03<&6/$
3
(;7.3
-3+3
Pȭ
%51
5('
25*
ࢳࣕ࢝ࢲ
75,*B,1B3
75,*B,1B1
75,*B287B3
%
75$16'8&(5
㏦ཷἼჾ
<(/
࢟
75,*B287B1
3%
70
66
,9VT
'5$:1
7<$0$6$.,
+0$.,
-XQ
-XQ
&+(&.('
22/Jun/2020 H.MAKI
$33529('
6&$/( 0$66
5()1R
NJ
&&+
':*1R
35
ᩚὶჾ
$
'3<&
5(&7,),(5
9$&
ȭ+]
127(
6+,3<$5'6833/<
ὀグ
㸨㸯㸧㐀⯪ᡤᡭ㓄ࠋ
㸨㸰㸧࢜ࣉࢩࣙࣥࠋ
㸨㸱㸧.3࢟ࢵࢺ㸦23㸧ࡀᚲせࠋ
%
&
237,21
.3.,7235(48,5('
0-$63)&P
9'&
*1'

INDEX
Numerics
3D sounder history display
echo detection level ...............................4-14
example....................................................4-5
function availability.................................4-19
marking school of fish ............................4-13
noise filter...............................................4-14
picture advancement..............................4-14
scale box................................................4-19
terrain shading .......................................4-15
TX and ST-BY ........................................4-13
viewpoint position...................................4-13
B
Beam angle (multi-sounder display)...........4-6
Beam type selection (multi-sounder display)4-6
Beam width (multi-sounder display) ...........4-6
Bottom echo calibration ...........................4-14
C
Cross section display
example....................................................4-4
function availability.................................4-12
grid .........................................................4-10
scale box................................................4-11
speed of sound correction......................4-11
TX and ST-BY ........................................4-10
D
Default settings ..........................................5-2
Depth/color shading .................................4-15
DIP switch settings.....................................3-1
E
Echo color (side scan display) ...................4-8
Echo detection level.................................4-14
Echo smoothing
distance..................................................4-10
time ........................................................4-11
External KP cable installation ....................2-5
F
Function availability
3D sounder history display.....................4-19
cross section display..............................4-12
multi-sounder display ...............................4-7
side scan display......................................4-9
Fuse replacement ......................................5-2
G
Grid (cross section display)......................4-10
I
Installation..................................................1-2
DIP switch settings...................................3-1
external KP cable.....................................2-5
ground......................................................2-1
LAN cable.................................................2-9
multi beam sonar......................................1-2
multi function display settings ..................3-4
operation check........................................3-3
transducer ......................... 1-3
transducer cable.......................................2-2
wiring........................................................2-1
, AP-4, AP-10
J
JIS cable guide .......................................AP-3
L
LAN cable installation.................................2-9
M
Maintenance ..............................................5-1
Menu tree................................................AP-1
Multi-sounder display
beam angle ..............................................4-6
beam type selection .................................4-6
beam width...............................................4-6
example....................................................4-3
function availability...................................4-7
scale box..................................................4-7
TX and ST-BY ..........................................4-6
N
Noise filter ................................................4-14
P
PBG .........................................................4-20
Personal Bathymetric Generator..............4-20
S
Scale box
3D sounder history display.....................4-19
cross section display..............................4-11
multi-sounder display ...............................4-7
side scan display......................................4-8
Seabed mapping
change/remove coloration......................4-23
deleting a section ...................................4-24
deleting whole maps ..............................4-24
export .....................................................4-25
how to use..............................................4-21
import .....................................................4-25
requirements ..........................................4-20
setup ......................................................4-21
shading method......................................4-22
sharing maps..........................................4-25
speed filter..............................................4-22
Side scan display
echo color.................................................4-8
example....................................................4-4
function availability...................................4-9
scale box..................................................4-8
TX and ST-BY ..........................................4-8
IN-1

T
Terrain shading ....................................... 4-15
Transducer cable installation .................... 2-2
Transducer installation ........ 1-3
TX and ST-BY
3D sounder history display.................... 4-13
cross section display ............................. 4-10
multi-sounder display .............................. 4-6
side scan display..................................... 4-8
, AP-4, AP-10
V
Viewpoint position (3D sounder history display)
4-13
Z
Zoom display........................................... 4-10
INDEX
IN-2


 Loading...
Loading...