Fuli Deep Cycle series, DC series Technical Manual

Web:http://www.fulibattery.net Page 1 of 7
Technical Manual For DC Series Batteries
TTEECCHHNNIICCAALL FFEEAATTUURREESS
Deep Cycle series batteries are designed to have a large amount of stored current discharged between charging sessions, with very heavy non-porous battery plates to withstand repeated
major discharging and charging cycle(deep cycle). The Deep-cycle batteries uses a different chemistry for the plates active paste material, and a slightly stronger electrolyte than normal
battery electrolyte, which allows for a much longer life in deep cycle applications.
The batteries in solar application are always over discharged, or operated under partial state of charge (PSOC). The working conditions of batteries in solar application are worse than those
in situations where technical support is readily available. FUli DC series batteries have an advanced grid structure, superior leady paste, and are manufactured using improved plate
formation methods to meet the requirements of frequently cyclic & deeply discharge.DCbatteries are also suitable to low & high temperature conditions.
Sealed Construction
FULI’s unique construction and sealing technique guarantees that no electrolyte leakage can occur from the terminals or case of any FULI battery. This feature insures safe and efficient
operation of FULI batteries in any position. FULI batteries are classified as "Non-Spillable" and will meet all requirements of the International Air Transport Association. (I.A.T.A Dangerous
Goods Regulation).
Long Service Life, Float or Cyclic
The FULI VRLA battery has a long life in float or cyclic service. Depending on the average depth of discharge, over 500 cycles (50-70%D.O.D) can be expected from FULI VRLA batteries..
Design float life should reached 10 years.
Maintenance-Free Operation
During the life of FL batteries, there is no need to check the specific gravity of the electrolyte, or add water. In fact, there is no provisions for such maintenance functions to be carried out.
Low Self Discharge
Because of the use of Lead Calcium grids alloy, FULI VRLA battery can be stored for long periods of time without recharge.
High Recovery Capability
FULI battery has excellent recharging capability, even after very deep discharge.
Heavy Duty Grids
The heavy-duty lead calcium-alloy grids in FULI batteries provide an extra margin of performance and service life in both float and cyclic applications, even in conditions of deep discharge.
Operating Temperature Range
FULI batteries can be used over a broad range of ambient temperatures, allowing considerable flexibility in system design and location.

Web:http://www.fulibattery.net Page 2 of 7
AAPPPPLLIICCAATTIIOONN FFIIEELLDDSS
Alarm&Security System
Cable Television
Solar and Wind Power System
Emergency Lighting
Medical Equipment
UPS Generator Starting
Communication Equipment
Power tools &Control Equipment/ Toys
BBAATTTTEERRYY CCHHAARRGGIINNGG
Correct battery charging ensures the maximum possible working life for the battery. There
are four major methods of charging:
Constant Voltage Charging.
Constant Current Charging.
Two Stage Constant Voltage Charging.
Taper Current Charging.
Constant Voltage Charging:
This is the recommended method of charging for VRLA batteries. It is necessary to closely
control the actual voltage to ensure that it is within the limits advised.
Float Service: 2.25-2.30 Vpc at 25℃ .
Cycle Service: 2.4-2.45 Vpc at 25℃
FULI suggests that the initial current be set within 0.2 C Amps. Figure 1 shows one
example of a constant voltage charging.
Constant Current Charging
This method of charging is generally not recommended for VRLA batteries, but is an effective method for charging a number of series connected batteries at the same time. It is necessary to
understand that if the batteries are not removed from the charger after reaching a state of full charge, considerable damage will occur to the batteries due to overcharging. Figure 2 shows
the characteristics of a FULI battery under constant current charging conditions.
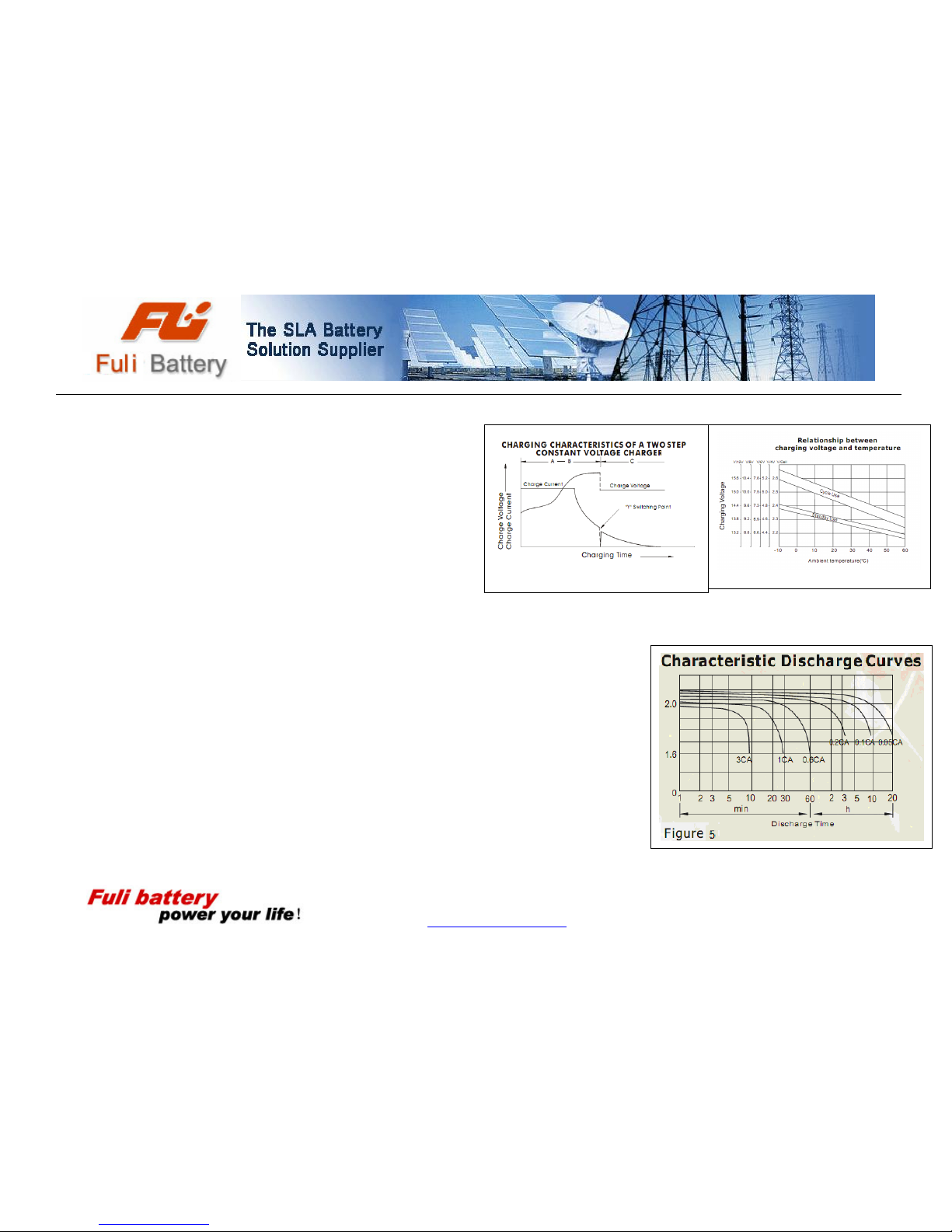
Two Stage Constant Voltage Charging
Figure 1
Figure 2
Web:http://www.fulibattery.net Page 3 of 7
Figure 4
Two stage of constant voltage charging is a recommended method for charging valve regulated lead acid battery in a short period of time and then maintain them in a fully charged float or
standby condition. Figure 3 illustrates the characteristics of a two stages constant voltage charging.
Taper Current Charging
This method is not recommended for VRLA batteries for it has somewhat harsh on battery
performance. However, because of the simplicity of the charger circuit and its low cost, taper
current charging is often used to charge a number of series connected batteries that are
subject to cyclic use. If this method is to be used, it is suggested that the FULI technical
department should be contacted.
Effect of Temperature on Charging Voltage
As temperature rises, electrochemical activity in a battery increases. Similarly, as
temperature falls, electrochemical activity decreases. Therefore, conversely, as temperature
rises, charging voltage should be reduced to prevent overcharge and increased as
temperature falls to avoid undercharge. In general, to assure optimum service life, use of a temperature compensated charger is recommended. The recommended compensation factor for
DC batteries is -3mV/℃/Cell (standby use) and-5mV/℃/Cell (cyclic use). The standard center point for temperature compensation is 20℃. Figure 4 shows the relationship between
temperatures and charging voltages in both cyclic and standby applications.
Effect of Voltage on Battery Gassing
Although the batteries are of the recombination type and the amount of gassing at normal operating voltages and temperature are
negligible, if the charging voltage is increased, gassing will occur despite the recombination design of the product. Gassing does
not normally occur while the battery is operating under float conditions and normal constant voltage recharge of 2.27-2.30 Vpc at
20℃. Very little gassing occurs when the battery is recharged under normal cycling recharge procedures. However, it can be seen
on the accompanying graph the higher voltages that this especially under conditions of constant current charging will substantially
increase the volume of gas.
DDIISSCCHHAARRGGEE CCHHAARRAACCTTEERRIISSTTIICC
The discharge capacity of a lead acid battery varies and is dependant on the discharge current. FULI VRLA battery capacity is
measured at the 20-hour rate. The standard industry practice to determine the nominal capacity of a valve regulated lead acid
battery is to discharge the battery under test at its 20-Hour rate to a final voltage of 1.75 volts per cell. The curves in Figure 5 show
the different currents that can be drawn at various discharge capacity rates at an ambient temperature of 20 ℃.The rated nominal
capacity of a battery is reduced when it is discharged at a value of current that exceeds its 20-Hour discharge rate. This should be taken into consideration when a battery is being selected
Figure 3
 Loading...
Loading...