Page 1

PRIMERGY BX Blade Server Systems
RemoteView Management Blade
User Interface Description
Edition November 2007
Page 2

Comments… Suggestions… Corrections…
The User Documentation Department would like to
know your opinion of this manual. Your feedback helps
us optimize our documentation to suit your individual
needs.
Feel free to send us your comments by e-mail to
manuals@fujtsu-siemens.com.
Certified documentation
according to DIN EN ISO 9001:2000
To ensure a consistently high quality standard and
user-friendliness, this documentation was created to
meet the regulations of a quality management system
which complies with the requirements of the standard
DIN EN ISO 9001:2000.
cognitas. Gesellschaft für Technik-Dokumentation mbH
www.cognitas.de
Copyright and Trademarks
Copyright © 2007 Fujitsu Siemens Computers GmbH.
All rights reserved.
Delivery subject to availability; right of technical modifications reserved.
All hardware and software names used are trademarks of their respective manufacturers.
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.1 Notational Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2 Target Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2 PRIMERGY BX Blade Server Systems - Overview . . . . . . . 9
2.1 The Blade Server Concept . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2 Blade Server Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.2.1 Features of the RemoteView Management Blade . . . . . . . . 10
2.2.2 Redundancy of the RemoteView Management Blade . . . . . . 12
2.2.3 Console Redirection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3 Telnet interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.1 Entering the console mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.2 Console main menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.3 Management Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.3.1 Management Agent Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.3.2 Management Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.3.3 System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.3.4 Server Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3.3.4.1 Server Blade Control Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3.3.4.2 Server Blade Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.3.4.3 ServerBlade CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
3.3.4.4 Server Blade Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
3.3.4.5 Server Blade Voltage Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3.3.4.6 Server Blade Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3.3.4.7 Server Blade NIC Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.3.4.8 Server Blade Watch Dog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.3.5 Switch Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.3.6 Username and Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3.3.7 Blue Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3.3.8 Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3.3.8.1 Management Blade Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
RemoteView Management Blade
Page 4

Contents
3.3.8.2 Server Blade Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.3.8.3 Server Blade Power On/Off Event Log Enable . . . . . . . . 40
3.3.8.4 Management Blade Wrap Around Event Log Enable . . . . . 40
3.3.9 Set System Default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3.3.10 Server Blade CMOS Backup/Restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3.3.11 Switch Blade Configuration Backup/Restore . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3.3.12 Deployment Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.3.13 Power Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.3.14 PPP and Modem Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3.4 Emergency Management Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.5 Console Redirection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3.6 TFTP Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
3.7 Logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3.8 Reboot Management Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3.9 System Information Dump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
4 Web user interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4.2 System Property . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
4.2.1 System Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
4.2.1.1 Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
4.2.1.2 Alarm handler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
4.2.2 Environment/Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
4.2.2.1 Firmware Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
4.2.2.2 Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4.2.2.3 UPS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
4.2.2.4 Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
4.2.2.5 Fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
4.2.2.6 Reset Management Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
4.2.3 LAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
4.2.3.1 Internet Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
4.2.3.2 Domain Name Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
4.2.3.3 HTTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
4.2.3.4 Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
4.2.3.5 NTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
4.2.3.6 SSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
4.2.3.7 Duplex Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
RemoteView Management Blade
Page 5

Contents
4.2.4 SNMP Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
4.2.4.1 SNMP Communities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
4.2.4.2 SNMP Trap Destination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
4.2.5 Console Redirection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
4.2.5.1 KVM Switch for Local . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
4.2.5.2 IP Filters for Telnet, HTTP and SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
4.2.6 System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
4.2.7 User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
4.2.8 Deployment Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
4.2.9 PPP and Modem Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
4.3 Management Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
4.4 Switch Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
4.4.1 Switch Blade Info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
4.4.2 Backup/Restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
4.5 Adv. KVM Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
4.5.1 Adv. KVM Blade Info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
4.5.2 Adv. KVM Blade Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
4.5.3 Global Viewer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
4.5.3.1 Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
4.5.3.2 Global Viewer Control Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
4.5.3.3 Global Viewer Operating Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
4.5.4 Adv. KVM Blade Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
4.6 Server Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
4.6.1 Recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4.6.1.1 Automatic Server Restart (ASR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4.6.1.2 Auto Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4.6.1.3 Power Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4.6.1.4 Boot Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4.6.2 Blade Info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4.6.2.1 Blade Info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4.6.2.2 Memory Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
4.6.2.3 Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
4.6.2.4 Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Related publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
RemoteView Management Blade
Page 6

Page 7
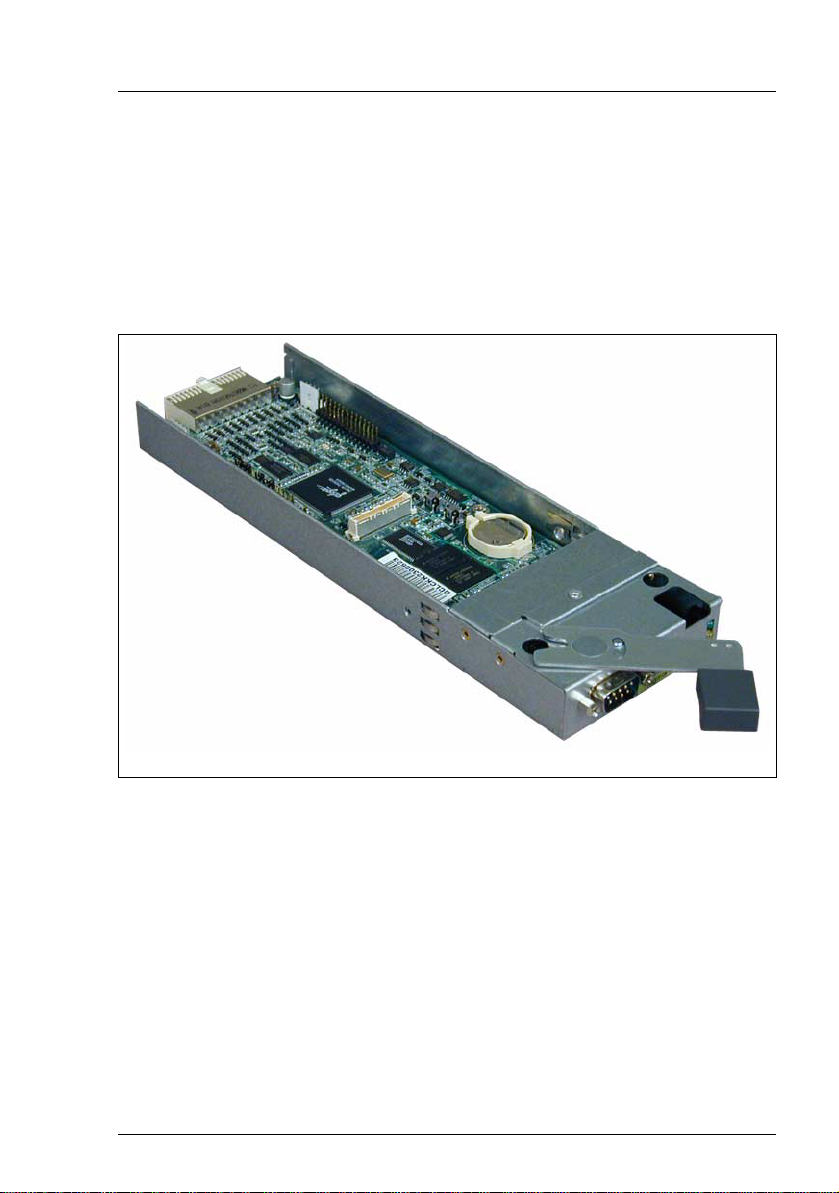
1 Introduction
The PRIMERGY BX Blade Server Systems accommodate two hotswapable,
redundant RemoteView management blades: an integrated management
solution for complete remote administration of the blade server system. For a
complete feature list, see section “Features of the RemoteView Management
Blade” on page 10.
Figure 1: RemoteView management blade
Further information is provided on the PRIMERGY ServerBooks CD:
– PRIMERGY BX300 Blade Server System – Operating Manual
– PRIMERGY BX600 Blade Server System – Operating Manual
– PRIMERGY Server Systems – RemoteDeploy
– PRIMERGY BX Blade Server Systems – LAN Switch Blade
– ServerView User Guide
I For further information on updating BX components please refer to the
Operating Manual of your BX system.
RemoteView Management Blade 7
Page 8

Notational Conventions Introduction
1.1 Notational Conventions
The following notational conventions are used in this manual:
V Caution This symbol points out hazards that can lead to personal
injury, loss of data, or damage to equipment.
I This symbol highlights important information and tips.
Ê This symbol refers to a step that you must carry out in
order to continue with the procedure.
italic Commands, menu items, names of buttons, options, file
names, and path names are written in italic letters in text.
<italic> Marked variables that must be replaced by current values.
fixed font System output is written using a fixed font.
semi-bold
fixed font
[Key symbols] Keys are presented according to their representation on
Commands to be entered through the keyboard are
written in a semi-bold fixed font.
the keyboard. If capital letters are to be entered explicitly,
then the Shift key is shown, e.g. [SHIFT] - [A] for A.
If two keys need to be pressed at the same time, then this
is indicated by placing a hyphen between the two key
symbols.
Table 1: Notational conventions
If there are references to text or sections of text in this manual, then the chapter
or section heading is placed in the reference, and the page stated refers to the
page on which the chapter or section begins.
1.2 Target Group
This manual is intended for system administrators, network administrators, and
service technicians that have a basic knowledge of hardware and software. The
manual informs the reader of the fundamentals of blade server monitoring and
documents the requirements for the use of the RemoteView management
blade.
8 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 9

2 PRIMERGY BX Blade Server
Systems - Overview
In this chapter an overview is given of the blade server system. The concept
underlying this system is explained, and its major features are described.
Furthermore, the system component is described that enables the user to
communicate with the system.
2.1 The Blade Server Concept
A traditional server is a device that includes a multitude of components to do
many different jobs at the same time. Servers like this are distinguished by the
number of CPUs they use, the number of hard disks that can be plugged in, and
the number of PCI cards that can be used to connect them to other devices such
as external storage systems or networks.
Further development has made it necessary to treat the issues of CPU power
and storage capacity separately. Rack optimized servers enable the system
administrator to make adjustments in both fields according to the level that is
needed.
At the next step, the blade server concept is reached, where I/O functions, too,
are separated from the CPU. A blade server system typically consists of a
number CPU boards, known as server blades, together with some switch
blades, which are the I/O modules, and finally a redundantly configured pair of
RemoteView management blades, enabling the user to monitor and control the
system on the whole.
All data traffic moving to and from the system is handled via TCP/IP over a LAN
cable.
The outsourcing of the power supply unit and the use of low-voltage CPUs help
to reduce the size of a server blade. Thus, a high density is achieved for the
system with very little power consumption compared to traditional servers.
RemoteView Management Blade 9
Page 10

Blade Server Management BX Blade Server System Overview
2.2 Blade Server Management
When performing administrative tasks for the blade server system, the user
relies on functions provided by a system component called the RemoteView
management blade. There are two RemoteView management blades in a blade
server system, in order to ensure redundancy.
The user gets access to the functions provided by the RemoteView
management blade, either via a web user interface, or via a console menu using
the Telnet protocol. Both ways of communication are described in more detail in
the next two chapters of this manual (see chapter “Telnet interface” and chapter
“Web user interface”).
2.2.1 Features of the RemoteView Management Blade
Within the blade server system the RemoteView management blade is
equipped with a number of features, which are described in this section.
Controller
The RemoteView management blade is equipped with a Qlogic Zircon V2
controller.
Supported programs
The RemoteView management blade is compliant with IPMI (Internet Protocol
Multicast Iniative) 1.0. It supports schemes like FRU (Field replaceable Units),
SEL (System Event Log), and SDR (Sensor Data Records). It also allows the
configuration of a watchdog timer.
Communication with the server blades
The RemoteView management blade communicates with the server blades via
2
an I
C bus. An IPMB interface is provided to support the user, when performing
hardware monitoring tasks for the server blades.
Communication with the switch blades
To enable communication with the switch blades, a CLI interface is provided. It
allows to configure settings of the switch blades, such as the IP address, the IP
mask, or the IP gateway address.
10 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 11

BX Blade Server System Overview Blade Server Management
Hardware monitoring
The hardware monitoring functions provided by the RemoteView management
blade include:
– Monitoring voltage and temperature of each server blade via the IPMB
interface
– Monitoring the status of the system fans
– Monitoring intrusion into the system fans, i. e. if they have been opened, and
other impacts on air flow conditions
– Setting the the system fans to an optimum speed
– Monitoring the status ot the power supply modules
2
– Monitoring the temperature of the switch blades via the I
C bus
Event repository
To store messages on events that occur in the system environment, the
RemoteView management blade is equipped with an event repository, providing
a 16 KB access EEPROM.
Auto configuration
The management function auto configuration is used to back up system parameters to a ROM, which is located on the management blade. It also provides the
possibility to restore these paramters if required. This reduces the risk if system
configuration data have been corrupted or lost.
SSL (Secure Socket Layer)
The Manager Blade provides SSL for network data privacy for Telnet as well as
for HTTP connections.
RemoteView Management Blade 11
Page 12

Blade Server Management BX Blade Server System Overview
2.2.2 Redundancy of the RemoteView Management Blade
Of the two RemoteView management blades within the blade server system,
one will take over the role of the master, who is in charge of the server
management, while the other one will remain in a standby status as a redundant
component. The two components have the same IP address, but their MAC
adresses differ from each other.
When the system is powered up, it depends on which of the two RemoteView
management blade first outputs a heartbeat. This is then the one that will be the
master.
The master blade and the redundant blade communicate symmetrically with
each other via a TX/RX serial interface. As soon as the master fails to work
properly, for instance, when unplugged by the system administrator, the standby
component will take over control of the server management.
Fail-over scenario
When the redundant RemoteView management blade takes over control from
the master, it will behave according to the following scenario:
– Issue an ICMP broadcast ping to update the ARP table and switch the IP
filtering table, in order to adjust them with regard to the new MAC address
– Define a proprietary protocol in L2, which is used for remote communication
If communication between master and redundant component via the serial
interface has broken down, these components can continue to communicate by
sending IP broadcast packages, using the MAC addresses.
2.2.3 Console Redirection
When using the console redirection feature, the management of the blade
server system may be executed in remote control mode. To support this mode,
the RemoteView management blade acts as the console redirection agent.
The KVM (Keyboard/Video/Mouse) input is captured and sent to the
RemoteView management blade. The RemoteView management blade will in
turn send this input to a server blade, where the appropriate actions will be
executed.
12 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 13

BX Blade Server System Overview Blade Server Management
With the adv. KVM blade, advanced server management functions are
available, such as graphic mode console redirection and remote USB CD-ROM
and floppy disk emulation (PRIMERGY BX600 only).
RemoteView Management Blade 13
Page 14

Page 15

3 Telnet interface
Within the blade server system a console menu is provided for server
management, using the Telnet protocol. A number of configuration activities can
be performed via this menu, e. g. IP address configuration or hardware status
monitoring. The menu is described in this chapter.
3.1 Entering the console mode
To enter the console mode a connection from a PC to the serial port of the blade
server system has to be established first. For this purpose a RS232 cable (null
modem cable) is used. An RX/TX signal will then be exchanged via this cable.
After the connection has been established, the HyperTerminal option is called
up on the PC.
The parameters for this option are to be set as follows:
Baud rate 115200
Parity bits None
Data bits 8
Stop bits 1
Flow control None
Terminal type VT100
The console mode can also be entered via LAN. In this case, the Telnet client
is called up, and the login procedure is performed using the management blade
IP address.
RemoteView Management Blade 15
Page 16
Entering the console mode Telnet interface
The settings are then as follows:
Host IP address 192.168.224.10 (example for a management blade
address)
Telnet port Same as the Telnet port configured for the
management blade (default port: 3172)
Connected protocol TCP/IP (Winsock)
Terminal type VT100
After these parameters have been set, the blade server system is started.
When using the serial port, firstly a number of messages concerning the system
appears on the screen.
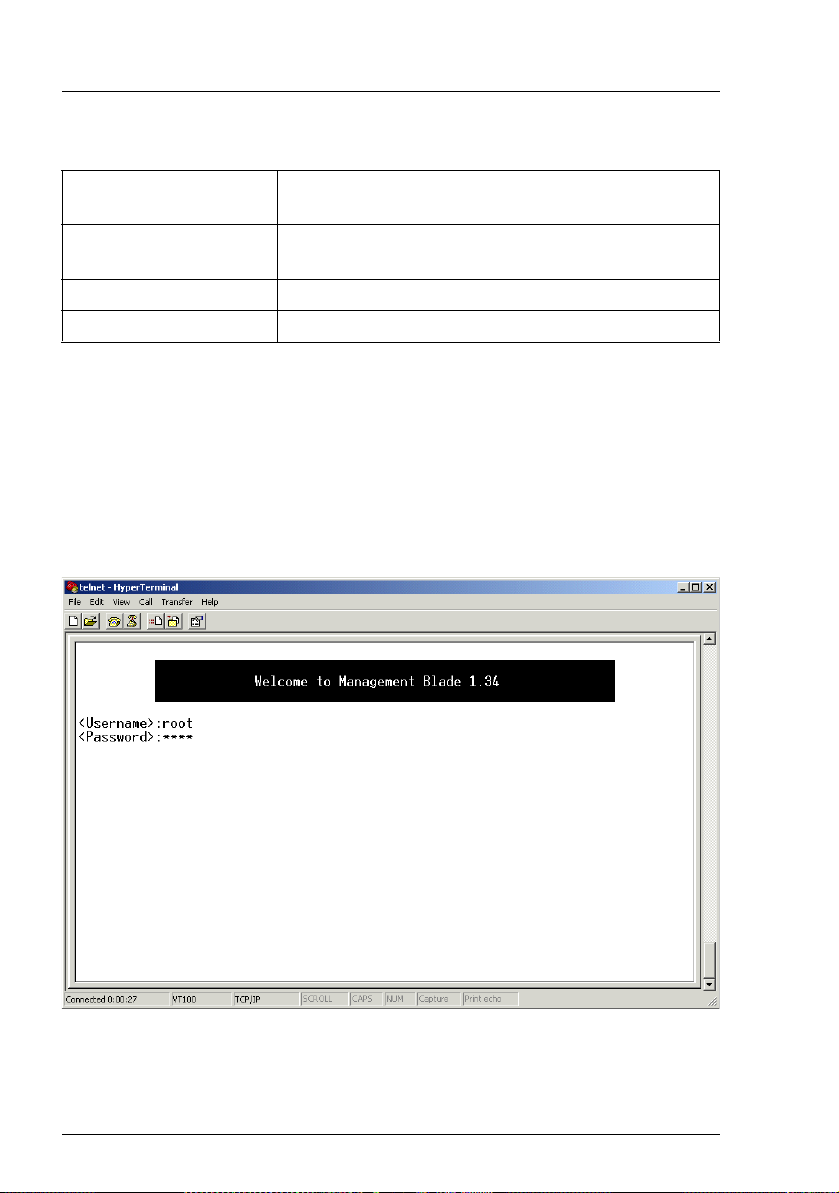
After approximately five seconds a welcome screen is displayed.
The user is requested to enter a user name and eventually a password, to be
admitted to the console main menu:
Figure 2: Welcome screen for access to the console menu
16 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 17
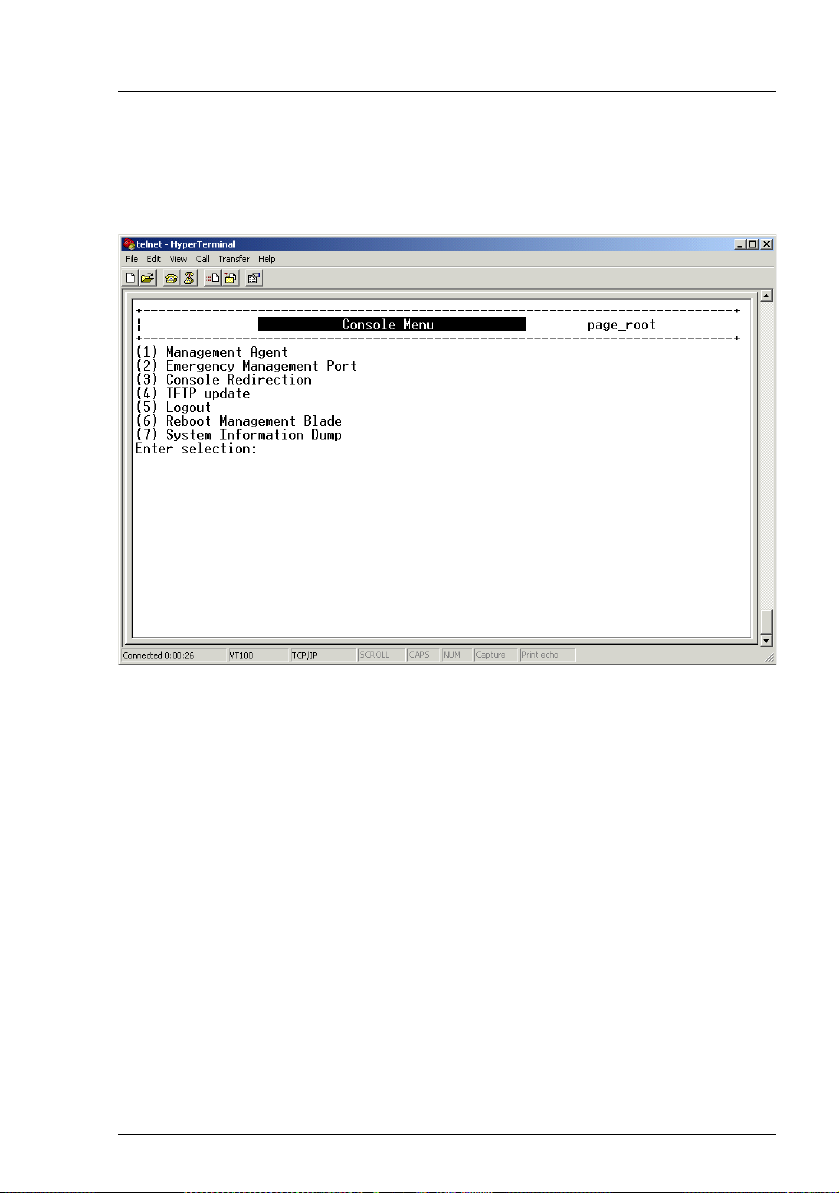
Telnet interface Console main menu
3.2 Console main menu
The console main menu looks like this:
Figure 3: Console main menu
There are seven items in the console main menu:
– Management Agent (see 3.3 on page 19)
This item provides several options for the management of the whole blade
server system, including management blades and switch blades.
– Emergency Management Port (see 3.4 on page 55)
This item provides an interface to send IPMI messages to a management
blade in case of an emergency. It can also be used for debugging purposes.
– Console Redirection (see 3.5 on page 57)
This item is used to configure the console redirection mode. The selected
console redirection target will be active after the next boot.
– TFTP Update (see 3.6 on page 59)
This item is used to update the management blade firmware.
RemoteView Management Blade 17
Page 18

Console main menu Telnet interface
– Logout (see 3.7 on page 61)
This item is used to logout from the system.
– Reboot Management Blade (see 3.8 on page 61)
This item is used to perform a reboot of the system. The reboot is executed
immediately.
– System Information Dump (see 3.9 on page 62)
This item is used to display consecutive lists of information.
The items of the console main menu are described in more detail in the following
sections.
18 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 19

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3 Management Agent
The following items provided in the Management Agent sub-menu for server
management:
– Management Agent Information (see 3.3.1 on page 20)
– Management Blade (see 3.3.2 on page 24)
– System Information (see 3.3.3 on page 26)
– Server Blade (see 3.3.4 on page 28)
– Switch Blade (see 3.3.5 on page 35)
– Username And Password (see 3.3.6 on page 37)
– Blue Screen (see 3.3.7 on page 38)
– Event Log (see 3.3.8 on page 38)
– Set System Default (see 3.3.9 on page 41)
– Server Blade CMOS Backup/Restore (see 3.3.10 on page 43)
– Switch Blade Configuration Backup/Restore (see 3.3.11 on page 45)
– Deployment Parameter (see 3.3.12 on page 46)
– Power Consumption (see 3.3.13 on page 49)
– PPP and Modem Setting (see 3.3.14 on page 51)
RemoteView Management Blade 19
Page 20
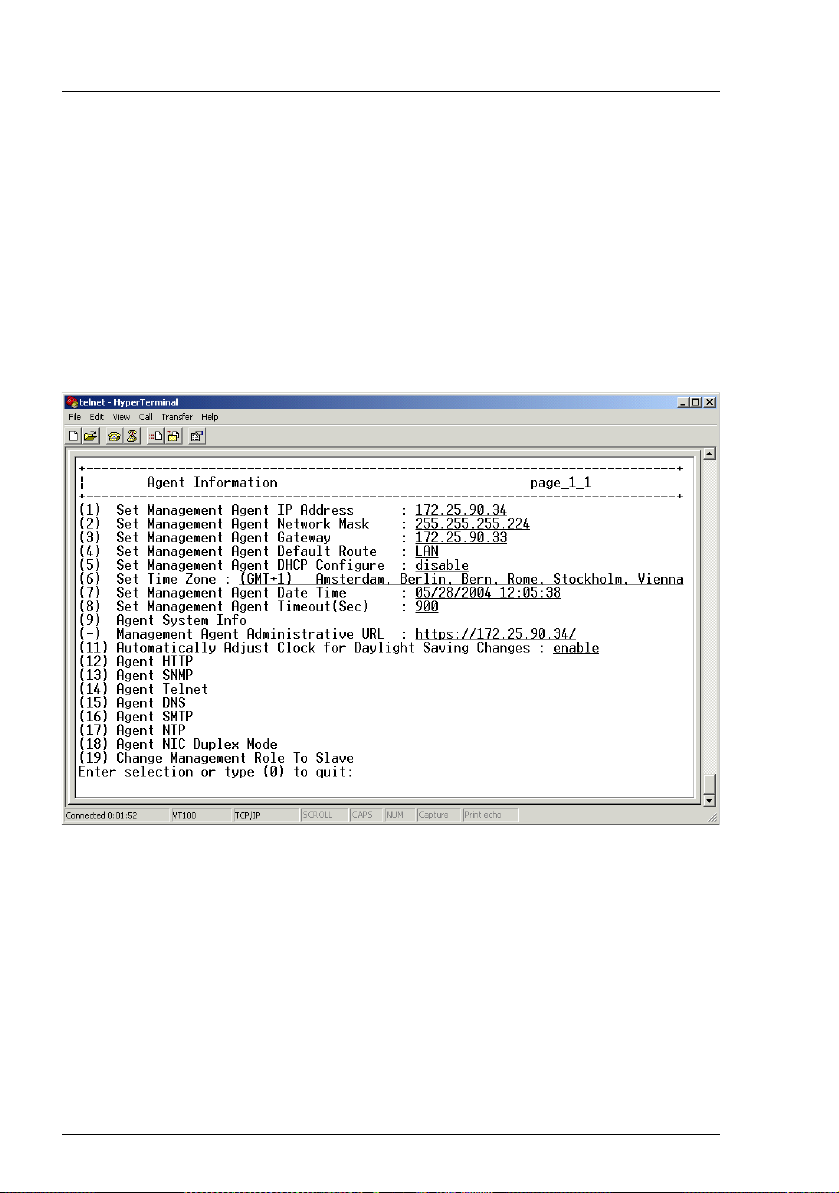
Management Agent Telnet interface
3.3.1 Management Agent Information
This item provides several options to configure and display parameters of the
management agent, such as the network IP address, Telnet and SMTP parameters, or date and time.
There are options that are used to set a single parameter, while others are used
to set more than one. For the former group of parameters their current values
are displayed, too.
Altogether, the menu for these options looks like this:
Figure 4: Agent Information menu
20 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 21
Telnet interface Management Agent
These options are used to perform the following activities:
Option Description
Set Management Agent IP
Address
Set Management Agent Network
Mask
Configuration of the management blade IP
address.
Configuration of the management blade IP
network mask.
Set Management Agent Gateway Configuration of the management blade IP
gateway address.
Set Management Agent Default
Route
Set Management Agent DHCP
Configure
Configuration of the default route:
LAN or PPP.
Configuration of the auto-assigned IP
address mask and enabling of the
gateway via DHCP.
Set Time Zone Configuration of the time zone for the
management blade, which is selected
from a time zone table.
Set Management Agent Date
Time
Configuration of date and time for the
management blade.
Set Management Agent Timeout Configuration of the time-out value for
login to the console menu.
Agent System Info Settings used in SNMP for the
management blade:
– system name
– system location
– system contact
Management Agent Administrative URL
Automatically Adjust Clock for
Daylight Saving Changes
Display of the home page URL for the
management blade.
Configuration of the adjustment for
daylight saving changes (enable/disable,
start date, end date). See also section
“Daylight Saving Time Format Example”
on page 82.
Agent HTTP Configuration of the HTTP settings,
including port number assignment, HTTP
protocol enabling/disabling and HTTP
SSL security control.
RemoteView Management Blade 21
Page 22
Management Agent Telnet interface
Option Description
Agent SNMP Configuration of the SNMP settings,
including SNMP enabling/disabling,
selecting an SMNP community string and
a destination from the SNMP trap table.
Agent Telnet Configuration of the Telnet server settings,
including Telnet port assignment and
Telnet enabling/disabling.
Agent DNS Configuration of the DNS server address
and enabling/disabling DNS support.
Agent SMTP Configuration of the SMTP settings for
mail sending, including SMTP enabling/
disabling, SMTP sender, SMTP relay
server and mail user account.
Agent NTP Configuration of the NTP (network time
protocol) service. You can enable or
disable the NTP service, set the NTP
server’s IP address and choose the Sync
Mode:
– Sync Afterwards
Only if the management blade time is
ahead of NTP server time, the
management blade syncs the time
from NTP server.
– Sync Always
The management blade always syncs
the time from NTP server, no matter
whether the NTP server time is behind
or ahead of management blade.
Agent NIC Duplex Mode Setting of the management blade’s NIC
duplex mode (full duplex or half duplex).
Execution Mode displays the current duplex
mode, Setting Mode allows you to specify
which duplex mode should be active after
the next reset.
22 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 23
Telnet interface Management Agent
Option Description
Change Management Role To
Slave
Change the role of the master
management blade to slave
(only displayed if there are two
management blades installed).
RemoteView Management Blade 23
Page 24
Management Agent Telnet interface
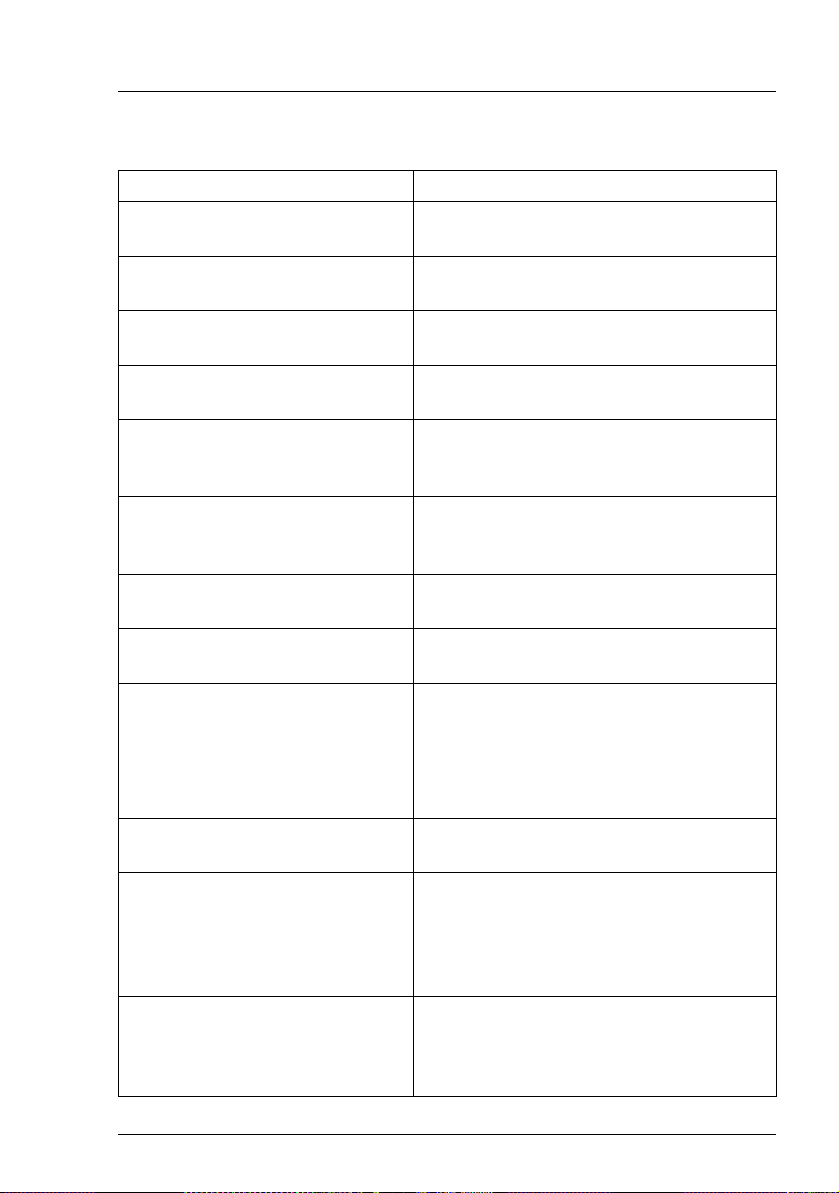
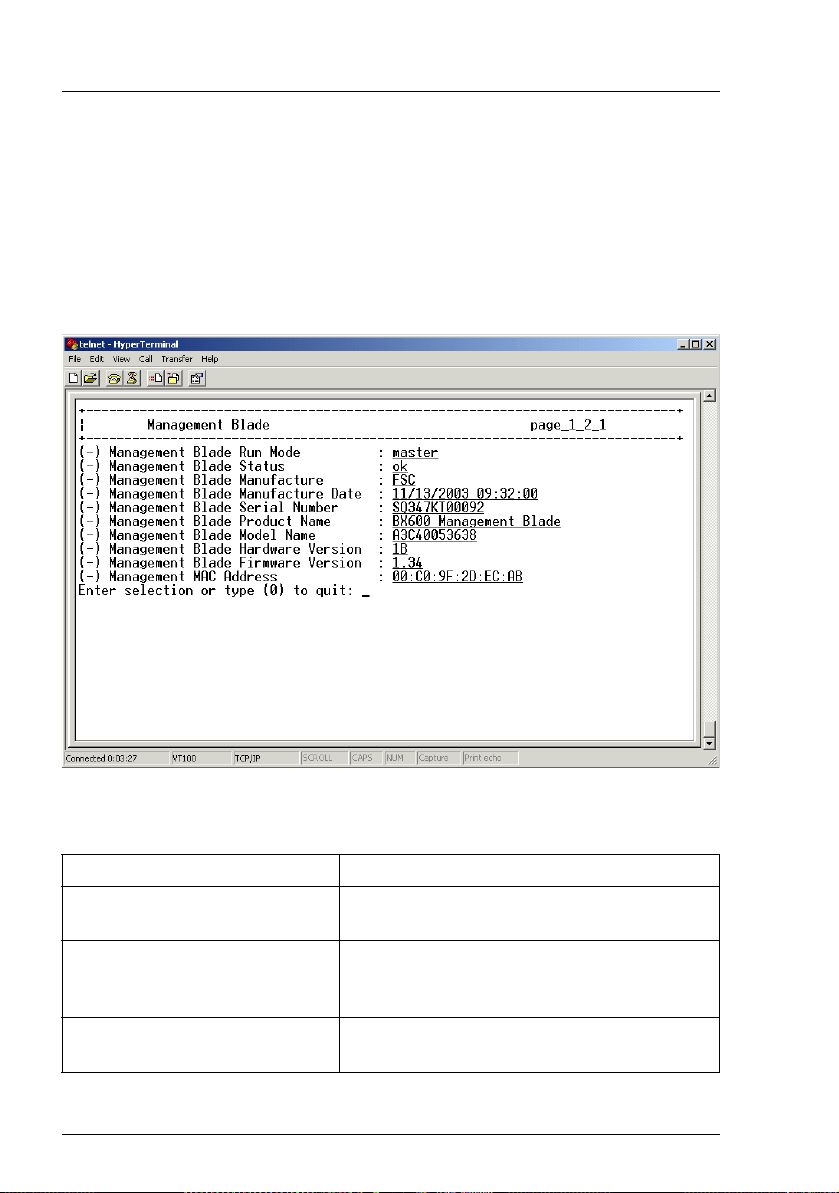
3.3.2 Management Blade
Within the blade server management system there are two management
blades. One of them is active as the master of the server management system.
The other one is in standby mode to ensure the availability of the system.
A number of parameters relating to the management blades is displayed to the
user, showing their current values (see next figure):
Figure 5: Management Blade menu
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Management Blade Run Mode Displays whether the management blade is
run in master mode or slave (standby) mode.
Management Blade Status Displays the health status of the
management blade. A message will be
displayed if this status is disturbed.
Management Blade
Manufacture
24 RemoteView Management Blade
Displays the name of the manufacturer of
the management blade.
Page 25
Telnet interface Management Agent
Parameter Description
Management Blade
Manufacture Date
Management Blade Serial
Number
Management Blade Product
Name
Management Blade Model
Name
Management Blade Hardware
Version
Management Blade Firmware
Version
Displays the date of manufacture for the
management blade.
Displays the serial number of the
management blade.
Displays the product name of the
management blade.
Displays the name of the management blade
model.
Displays the hardware version of the
management blade.
Displays the firmware version of the
management blade.
Management MAC Address Displays the NIC physical address of the
management blade.
RemoteView Management Blade 25
Page 26
Management Agent Telnet interface
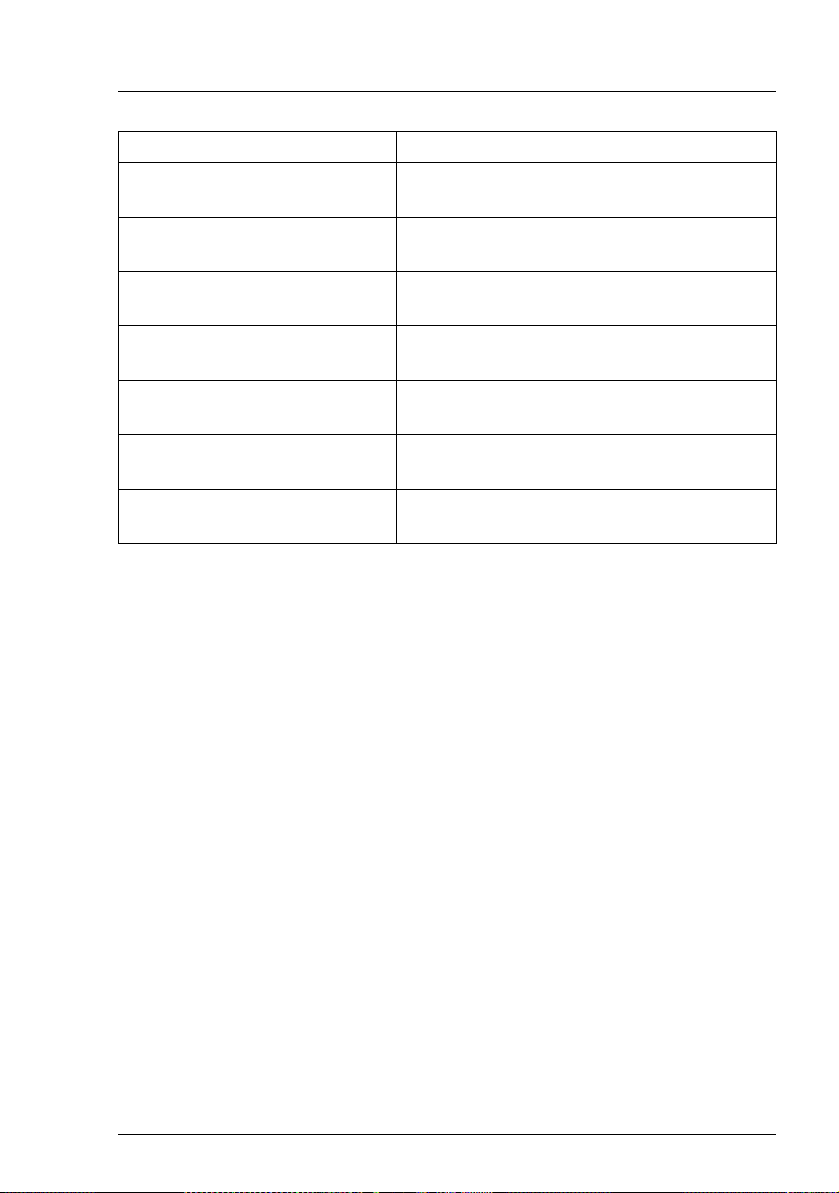
3.3.3 System Information
The System Information option provides information on all components of the
blade server management system, such as power supply, fans, temperature,
KVM (= keyboard/video/mouse).
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 6: System Information menu
The menu offers the following subordinate options to the user:
Parameter Description
System Control Information Displays the number of system fans, power
supply groups and temperature sensors, as well
as the status of all system components,
excepting CPU blades and switch blades.
System Power Supply Displays information on the power supply units.
26 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 27
Telnet interface Management Agent
Parameter Description
System Fan Displays information on the number and status
of the system fans, including parameters like
nominal speed, current speed, speed threshold
and failure reaction. A fan test is also provided,
supporting the fan life time monitor.
System Temperature Displays information on the system temper-
ature, including current value, warning level,
critical level, sensor status and critical temperature reaction.
System Chassis Table Displays information on the system chassis,
including the chassis serial number and if there
has been any intrusion into the inside of the
chassis.
System UPS Displays chassis UPS (uninterruptable power
supply) information, including UPS number,
vendor, type, IP address, connect port, and
SNMP community.
System KVM Specifies, which server blade should get
accessed via KVM.
System LED Control Displays the status of the system control: on,
off, or blinking.
NIC Status Detection Detect whether the network signal of the
management blade‘s NIC is ok or fail.
NIC Status Detection enable
If management blade NIC detection is
fail for the master and ok for the slave, the
master sends out an event log message
and the roles of the management blades
are changed. The role change takes
place after the NIC Detection Timeout
has expired.
NIC Status Deteiction disable
The NIC Status Detection is disabled.
Turn on/off all server blades Turns on or turns off all server blades.
RemoteView Management Blade 27
Page 28
Management Agent Telnet interface
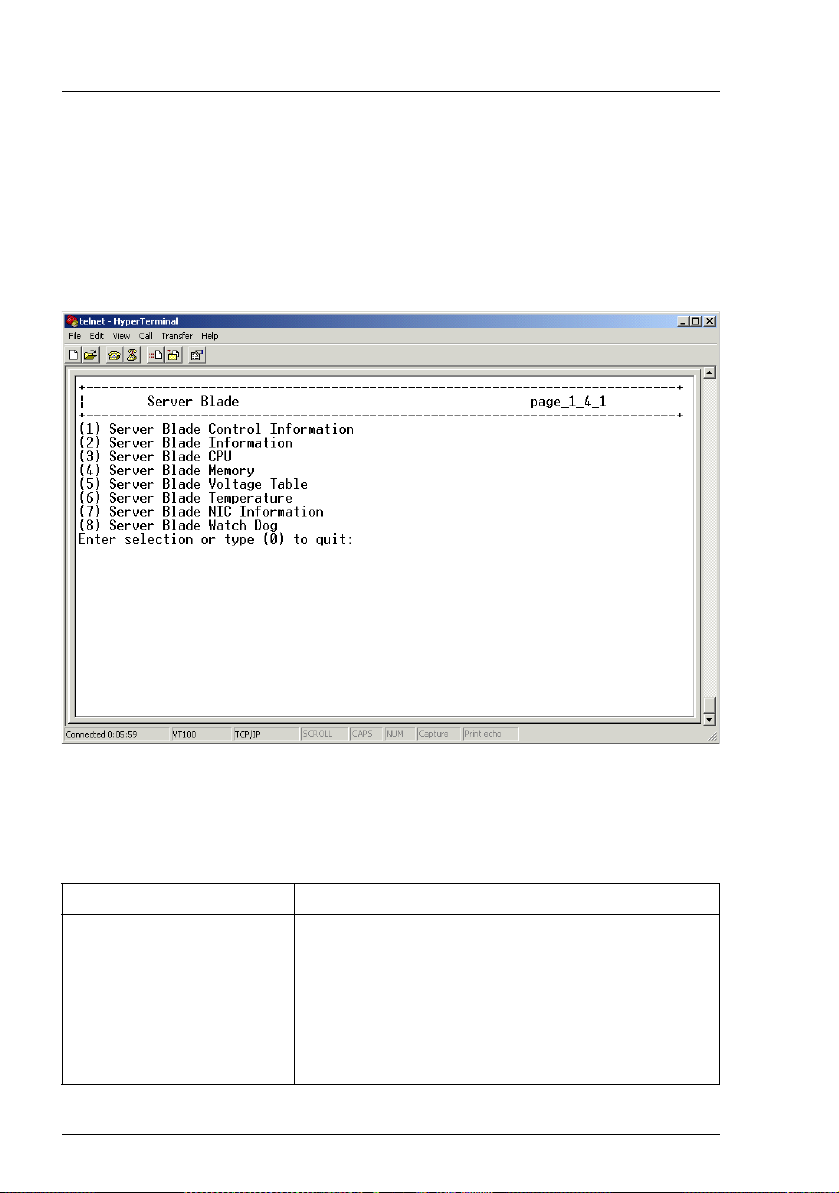
3.3.4 Server Blade
The Server Blade option provides information on the server blades, i. e. information on CPUs, memory modules, voltage, temperature, CMOS configuration
and watchdog timers.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 7: Server Blade menu
3.3.4.1 Server Blade Control Information
This option enables the user to set the following parameters:
Parameter Description
Server Power Set server power:
(1) on
(2) off
(3) power-cycle
(4) reset
(5) NMI
(6) force off
28 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 29
Telnet interface Management Agent
Parameter Description
Set Server Maximum
Restart Retries
Configuration of the maximum number for server
restart retries. If the failure count reaches this
value, the configured reaction will be executed.
Server LED Control Configuration of the LED control at the front of the
blade server: blinking or off.
Server CPU Mode Configuration of the CPU mode: battery or perfor-
mance mode. If the parameter is set to battery
mode, this will save electric power.
Server Administrative URL Configuration of an URL address for the server.
3.3.4.2 Server Blade Information
This option displays some information on the server blade parameters. The
following parameters are included:
Parameter Description
Server Blade Status Displays the server blade health status.
Server Blade Manufacture Displays server blade manufacture vendor infor-
mation.
Server Blade Manufacture
Date
Server Blade Serial
Displays server blade manufacture date information.
Displays server blade serial number information.
Number
Server Blade Product
Displays server blade product name information.
Name
Server Blade Product
Displays server blade product version information.
Version
Server Blade Model Name Displays server blade model name information.
Server Blade Hardware
Version
Server Blade BIOS
Displays server blade hardware version information.
Displays server blade BIOS version information.
Version
Number of CPU Socket Displays how many CPU sockets are available on
the server blade.
RemoteView Management Blade 29
Page 30
Management Agent Telnet interface
Parameter Description
Number of Memory
Socket
ServerBlade OS Type Displays the OS platform currently running on the
ServerBlade OS Version Displays the version of the OS currently running
Server Blade BMC
Firmware Version
Server Blade PCI Add-In
Card
Server Blade FC Daughter
Card
3.3.4.3 ServerBlade CPU
This option displays some information on the server blade CPU parameters.
The following parameters are included:
Displays server blade memory information.
server blade.
on the server blade.
Displays server blade BMC firmware version.
Displays whether a PCI card is installed.
Displays whether a FC (Fibre Channel) daughter
card is installed (only relevant for BX600 Blade
Server Systems).
Parameter Description
CPU Type Displays the CPU type.
CPU Frequency Displays the CPU frequency.
CPU Step Displays the CPU stepping.
30 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 31

Telnet interface Management Agent
Parameter Description
CPU Status Display the CPU status. The values displayed will
be:
OK
NOT_PRESENT
ERROR
CRITICAL
-
MISSING_TERMINATION
CPU Name Displays the CPU name.
CPU Socket Designation Displays the CPU socket designation.
CPU Manufacturer Displays information on the CPU manufacturer.
CPU Clock Displays the CPU clock.
3.3.4.4 Server Blade Memory
This option provides information on the server blade memory. The information
is displayed in two tables:
Table Description
Server Blade Memory
Information Table
Displays information on the total size of the
memory, as well as on the error count, the error
reset record and the error count start time.
Server Blade Memory
Modules Table
RemoteView Management Blade 31
Displays the status of each memory module,
together with memory type and error information.
Page 32

Management Agent Telnet interface
3.3.4.5 Server Blade Voltage Table
This option provides information on the server voltage. The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Server Voltage Designation Displays the voltage designation for the
server blade.
Server Voltage Status Displays the voltage status for the server
blade. The values displayed will be:
- NOT_AVAILABLE
- OK
- TOO_LOW
- TOO_HIGH
Server Voltage Minimum Value Displays the minimum voltage value for the
server blade.
Server Voltage Maximum Value Displays the maximum voltage value for
the server blade.
Server Voltage Current Value Displays the current voltage value for the
server blade.
Server Voltage Nominal Value Displays the nominal voltage value for the
server blade.
3.3.4.6 Server Blade Temperature
This option provides information on the server temperature. Some of the parameters displayed can also be set by the user:
Parameter Description
Server Temperature Sensor
Designation
Server Temperature Sensor
Status
32 RemoteView Management Blade
Displays the designation of the temper-
ature sensor for the server blade.
Displays the status of the temperature
sensor. The values displayed will be:
- SENSOR_DISABLED
- SENSOR_FAIL
- WARNING_TEMP_WARM
- CRITICAL_TEMP_WARM
- NOT-AVAILABLE
Page 33

Telnet interface Management Agent
Parameter Description
Server Temperature Upper
Warning Level
This parameter can be set to configure the
upper warning level of the temperature
sensor for the server blade.
Server Temperature Upper
Critical Level
This parameter can be set to configure the
upper critical level of the temperature
sensor for the server blade.
Server Temperature Lower
Warning Level
This parameter can be set to configure the
lower warning level of the temperature
sensor for the server blade.
Server Temperature Lower
Critical Level
This parameter can be set to configure the
lower critical level of the temperature
sensor for the server blade.
Server Temperature Current
Value
Displays the current temperature value for
the server blade.
RemoteView Management Blade 33
Page 34

Management Agent Telnet interface
3.3.4.7 Server Blade NIC Information
This option displays the NIC1 and NIC2 physical addresses of the server blade.
3.3.4.8 Server Blade Watch Dog
This option is used to configure the watchdog timers for the server blade. There
are two timers that can bet set here:
Timer Description
Server Blade Software Watchdog This timer is used to monitor the operation
system and the software applications. A
watchdog timer agent that resets the timer
must be implemented in the operation
system. When the time-out is reached, a
time-out routine will be started.
Server Blade Boot Watchdog This timer is used to monitor the server
blade POST. It will be reset by the BIOS in
periods configured within the POST code.
When the time-out is reached, a time-out
routine will be started.
34 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 35

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.5 Switch Blade
The Switch Blade option is used to display information on the switch blades that
are part of the blade server system.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 8: Switch Blade menu
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Administrative URL Displays the URL of the switch blade.
Switch Blade Status Displays the status of the switch blade.
This status can be retrieved by the
management blade via a CLI command.
Switch Blade Manufacture Displays information on the manufacturer
of the switch blade.
Switch Blade Manufacture Date Displays the manufacturing date for the
switch blade.
RemoteView Management Blade 35
Page 36

Management Agent Telnet interface
Parameter Description
Switch Blade Serial Number Displays the serial number of the switch
blade.
Switch Blade Product Name Displays the product name of the switch
blade.
Switch Blade Model Name Displays the name of the switch blade
model.
Switch Blade Hardware Version Displays the version of the switch blade
hardware.
Switch Blade Firmware Version Displays the version of the switch blade
firmware.
Switch Blade MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the
management port for the switch blade.
Switch Blade IP Address Displays the current IP address of the
management port for the switch blade.
Switch Blade Subnet Mask Displays the current subnet mask of the
management port for the switch blade.
Switch Blade Gateway Displays the current gateway of the
management port for the switch blade.
Switch Blade IP Address Setting
Value
Switch Blade Subnet Mask
Setting Value
Switch Blade Gateway Setting
Value
Apply Network Setting Activates the specified setting values (IP,
Switch Blade LED Control Sets the LED of the switch blade off or
Reboot Switch Blade Reboots the switch blade.
Specifies a new IP address of the
management port for the switch blade.
Specifies a new Subnet Mask of the
management port for the switch blade.
Specifies a new Gateway of the
management port for the switch blade.
Subnet, Gateway) - either immediately or -
if the UART Port is used by another user -
as soon as this port is available. For
example: If another user runs console
redirection at the moment, the settings will
not be changed until the console
redirection has been completed.
blinking.
36 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 37

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.6 Username and Password
The Username and Password option is used to change and display information
on the access rights of individual users. A user is selected via his or her user ID.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 9: Username and Password menu
The following actions can be performed via this menu:
Parameter Description
Change Username A username may only be changed by the
administrator.
Change Password A password may be changed by the admin-
istrator or by the user that has been
assigned this password.
User Permission User permissions may only be changed by
the administrator.
RemoteView Management Blade 37
Page 38

Management Agent Telnet interface
3.3.7 Blue Screen
The Blue Screen option is available, if the operating system used supports the
blue screen feature, as provided by UART (Windows 2000).
The option will then display which server blades are currently in blue screen
status.
3.3.8 Event Log
The Event Log option is used to display the events that have been logged on the
management blade and the server blades.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 10: Event Log menu
Information is displayed for:
– Events that were logged on the management blade event log
– Events that were logged on a server blade event log
38 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 39

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.8.1 Management Blade Event Log
This sub-option is used to display the events that have been logged on the
management blade event log.
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
All Event All events that have been logged on the
management blade.
Informational Event The informational events that have been
logged on the management blade.
Minor Event The minor events that have been logged on
the management blade.
Major Event The major events that have been logged on
the management blade.
Critical Event The critical events that have been logged
on the management blade.
Clear All Entries This parameter is used to clear all events
from the management blade event log.
3.3.8.2 Server Blade Event Log
This sub-option is used to display the events that have been logged on a server
blade event log.
After a server blade has been selected, the following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
All Event All events that have been logged on the
server blade.
Informational Event The informational events that have been
logged on the server blade.
Minor Event The minor events that have been logged on
the server blade.
Major Event The major events that have been logged on
the server blade.
RemoteView Management Blade 39
Page 40

Management Agent Telnet interface
Parameter Description
Critical Event The critical events that have been logged
on the server blade.
Clear All Entries This parameter is used to clear all events
from a server blade event log.
3.3.8.3 Server Blade Power On/Off Event Log Enable
This option is used to specify, whether power on/off events for the server blades
should be listed in the event log.
3.3.8.4 Management Blade Wrap Around Event Log Enable
This option is used to specify, whether the wrap-around functionality for the
event log should be used or not.
enable
When the event log repository is full, new event log entries replace the
old ones beginning with the first event log entry.
disable
When the event log repository is full, no event log entries are written any
longer.
40 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 41

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.9 Set System Default
The Set System Default option is used to restore the default values.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 11: Set System Default menu
RemoteView Management Blade 41
Page 42

Management Agent Telnet interface
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Set Config Default The configuration of the management
blade is set to the default values.
V Please note that all configured
values are lost and the
management blade has to be
configured newly after using this
option.
Set Username/Password Default All configured user names with the
exception of root are deleted. The
password for the user root is set to the
default (“root“).
Set CMOS Backup Default All switch blade configuration backups and
all server blade BIOS backups are deleted.
Set Deployment Default The deployment parameters (see section
“Deployment Parameter” on page 46) are
set to the default values.
Set Switch Blade Config Default All switch blade configuration backups are
deleted.
42 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 43

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.10 Server Blade CMOS Backup/Restore
This option is used to backup and restore server blade BIOS parameters. The
server blade must be powered on before backup/restore processing. If the
backup is successful, the backup file will be displayed in the CMOS backup file
table.
After selecting the server blade whose BIOS is to be backed up or whose
backup file is to be restored, the Server CMOS Configure option is displayed:
Figure 12: Server CMOS Configure menu
RemoteView Management Blade 43
Page 44

Management Agent Telnet interface
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
CMOS Control Specifies the backup/restore policy:
backup
The BIOS parameters of the selected
server blade are backed up.
smart-restore
After the slot id, BIOS version and
MAC address have been verified, the
backup file of the selected server
blade is restored.
force-restore
The backup file is restored without
verification.
CMOS Configure Restore
Target
Server CMOS ID With BIOS
Versio n
Server CMOS ID With Mac
Address
Backup Date Time Displays date and time of the backup file
Specifies the server blade whose BIOS
parameters are to be restored.
Displays the CMOS ID with BIOS version.
Displays the CMOS ID with MAC address
generation.
44 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 45

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.11 Switch Blade Configuration Backup/Restore
This option is used to backup/restore the configuration values of the
management blade.
Figure 13: Switch Blade Configuration Backup/Restore
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Backup/Restore Control Specifies whether a backup process or a
restore process is to be started.
View Backup Configuration Displays the stored backup configuration
values.
Auto Restore Enable Specifies whether after a hot-swap action
the new management blade is to be
configured automatically according the
stored backup configuration values.
RemoteView Management Blade 45
Page 46

Management Agent Telnet interface
3.3.12 Deployment Parameter
This option is used to display or set the deployment configuration of the server
blades.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 14: Deployment Parameter menu
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Chassis ID Serial number of the blade server chassis.
Slot ID Identification of the server blade slot. If no server
blade is plugged in, no MAC address is available.
The slot id is the only way to assign and store slot
related system information. This is useful for hot
replace functionality.
MAC Address_1 / _2 MAC addresses of the server blade’s two LAN ports.
IP Address_1 / _2 IP addresses of the server blade’s two LAN ports.
Subnet Mask_1 / _2 Subnet masks of the server blade’s two LAN ports.
46 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 47

Telnet interface Management Agent
Parameter Description
Default Gateway_1 / _2 Default gateways of the server blade’s two LAN
ports.
Hostname Hostname for cloning purpose. Allows the clone
agent to patch the right hostname into OS image
during cloning process.
Master Image
Reference
URL in UNC notification (but in ASCII) of the remote
image file (with the extensions of *.img, *.cfg,
*.txt):
\\server-name\subpath\ img-name
Status of Blade Current status of the server blade. Possible values:
!!bitte genau prüfen, die Werte sind in der Spec nicht
explizit beschrieben und an der Oberfläche nicht
testbar!!
power-down
stand by
system boot failure
booting
online
Automatic Recovery Specifies whether after the hot-replacement of a
server blade deployment activities should be started
automatically.
false
After the hot-replacement of a server blade no
automatic deployment activities should be
started.
true
After the hot-replacement of a server blade
RemoteDeploy is triggered to check in the
server list, whether the old MAC address was
assigned to a backup image. If so, the backup
image is used for automatically cloning the
new CPU blade (assumed the same HW is
used). If there is no backup image, another
check is made whether a master image is
assigned to, and if so, this master image is
used for cloning.
RemoteView Management Blade 47
Page 48

Management Agent Telnet interface
Parameter Description
Status of Cloning Specifies the status of the cloning process:
not-cloned
The server blade does not contain a valid
configuration of an OS.
cloning
The cloning process is running. The status
will switch to cloned when the process will
have been completed.
cloned
The assigned image was successfully cloned.
LAN status of slot empty-slot
When a new server blade is plugged in, the IP
settings defined in the deployment parameter
table are NOT used. You have to configure the
IP settings manually. It is recommended to set
the LAN Status of Slot to preset-slot afterwards.
preset-slot
The settings defined in the deployment
parameter table are the reference for the LAN
configuration. If a new or already installed
blade is plugged in, these values are used for
the installation/adaptation.
48 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 49

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.13 Power Consumption
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 15: Power Consumption menu
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Power Budget Control
Threshold
Displays the max. active power of the
redundant power supply.
Base Consumption Power consumption of the base system: The
base system includes four switch blades,
two management blades and all fan moduls.
Total Consumption Current power consumption of the whole
blade server system (including server
blades).
Remaining Difference between Power Budg et Cont rol
Thershold and current Total Consumption.
System Power Unit Status Table Displays the max. active power and the
voltage range of the power supply units.
RemoteView Management Blade 49
Page 50

Management Agent Telnet interface
Parameter Description
Server Blade Power
Consumption Table
Set Power Budget Control dynamic
Displays the current power consumption
value of each server blade.
The power control dynamically takes
into account the current actual power
consumption.
static
The power control statically takes into
account the worst case power
consumption.
50 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 51

Telnet interface Management Agent
3.3.14 PPP and Modem Setting
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 16: PPP and Modem Setting menu
RemoteView Management Blade 51
Page 52

Management Agent Telnet interface
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Fastest COM Port Baud Rate The following COM Port Baud Rates are
supported:
- 19200 bps
- 38400 bps
- 57600 bps
- 115200 bps (default value)
I If you use no modems but a direct
cable connection, only the default
value 115200 bps is supported.
If you choose PPP Enable to be enable
and use modems for connecting, the
maximum baud rate is 57600 bps.
Hardware Flow Control The default value disable is recommended
for connections via LAN. Enable Hardware
Flow Control to avoid buffer overflows for
connections via modem.
Modem Initial String Type The default is standard modem. The
management blades support 56 K standard
modems. In general this default value will
work successfully. If any non-standard
modem is used, you need to specify a User
Define Initial String for initializing the modem.
User Define Initial String Here you can specify any AT command your
modem supports.
PPP Enable The default is disable. If you set enable the
PPP protocol is used with the setting
specified in PPP Connection Type.
52 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 53

Telnet interface Management Agent
Parameter Description
PPP Connection Type Possible values:
direct (default value)
Direct connection via the COM port
(no modem used).
dial-out
If a modem is installed and PPP
Enable is set to enable, the dial-out
phone number is used to establish a
PPP connection.
dial-in
If a modem is installed and PPP
Enable is set to enable, the
management blade waits for an
incoming call.
callback
If a modem is installed and PPP
Enable is set to enable the
management blade checks the
authentication of incoming calls and
uses the dial-out phone number to
call back.
callback extension
In difference to callback, the specified
dial-out phone number isn’t used:
The remote caller is prompted to
specify his modems phone number
after the incoming call has been
authenticated.
PPP Dial-out Phone Mode Possible values:
- touch tone (default value)
- pulse dialing
RemoteView Management Blade 53
Page 54

Management Agent Telnet interface
Parameter Description
PPP Dial-out Phone Number If PPP Connection Type is set to dial-out, the
management blade uses this phone number
to dial out. Max length: 32.
I You can set commas (“,“) between the
digits to cause one second delays
during dialing.
PPP IP Address PPP IP address of the management blade
(default: 192.168.2.1).
PPP Remote IP Address PPP IP address of the remote side
(default: 192.168.2.2).
PPP/Modem States Displays the PPP connection and modem
status:
modem ready
A modem is plugged in the
management blade’s COM port.
null modem cable
A null modem cable is plugged in the
management blade’s COM port.
normal cable
A 9-pin pass through cable or no
connection media is connected to the
management blade’s COM port.
try to dial-out
PPP dial-out process is running.
PPP on-line
PPP connection has been established.
54 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 55

Telnet interface Emergency Management Port
3.4 Emergency Management Port
The Emergency Management Port (EMP) provides a basic range of remote
server management with virtually no additional cost. It operates on top of the
management blade firmware.
Commands for IPMI messages can be sent directly via the EMP agent.
The following facilities are provided:
– Server power up/down
–System reset
– Viewing of critical event logs stored in the non-volatile memory (NVRAM)
– System Event Log (SEL): logging of all critical server events, to be used for
server monitoring and management
– Sensor Data Records (SDR): listing of all sensor fields programmed in the
firmware of the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC), to be used for
server monitoring and management
– Field Replaceable Units (FRU): listing of all replaceable components of the
system by serial number
RemoteView Management Blade 55
Page 56

Emergency Management Port Telnet interface
The starting page for these option looks like this:
Figure 17: Starting page for Emergency Management Port option
56 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 57

Telnet interface Console Redirection
3.5 Console Redirection
There is one console port (serial port interface) within the blade server system.
Console redirection can be configured for server blades or switch blades.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 18: Console Redirection menu
There is a sub-option of console redirection for server blades and one for switch
blades. Furthermore, a return hotkey can be configured:
Sub-option Description
Console Redirection Server
Blade
Console Redirection Switch
Blade
RemoteView Management Blade 57
This option is used to configure a server
blade for console redirection.
This option is used to configure a switch
blade for console redirection.
Page 58

Console Redirection Telnet interface
Sub-option Description
Set Return Hotkey This option is used to configure a return
hotkey.
To do this, a character from A-Z is chosen,
excluding M. The hotkey to exit console
redirection and return to the previous mode
is then Ctrl + the character that has been
set here, e. g. Ctrl + R.
The default character used for the return
hotkey is Q.
58 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 59

Telnet interface TFTP Update
3.6 TFTP Update
The TFTP Update option is used to perform an update of the management
blade firmware.
I For further information on updating BX components please refer to the
Operating Manual of your BX system.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 19: TFTP Update menu
RemoteView Management Blade 59
Page 60

TFTP Update Telnet interface
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Agent Update IP Address Setting of an agent IP address.
I The IP address to be supplied in the
field Agent Update IP Address is
only temporarily used. Enter any IP
address which is not used in the
LAN segment of the server.
TFTP Server IP Address Setting of an IP address for the TFTP
server.
Server Blade BIOS Image File
Name
Server Blade BMC Image File
Name
Management Blade Image File
Name
Management Blade Update
Enable
Setting of a file and path name for the BIOS
image.
Setting of a file and path name for the BMC
image.
Setting of a file and path name for the
management blade image.
Upgrading of the management blade
firmware.
The default value for this parameter is
disable. After setting the parameter to
enable, the TFTP server must be started,
and the management blade must be
rebooted.
The update will then be performed as the
system powers up.
Update Server Blade BIOS Table Upgrading of the Server Blade BIOS. This
option is used to enable/disable the update
and to display the TFTP status.
Update Server Blade BMC Table Upgrading of the Server Blade BMC
firmware. This option is used to
enable/disable the update and to display
the TFTP status.
60 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 61

Telnet interface Logout
3.7 Logout
This option is provided to perform a logout from the Telnet console menu.
3.8 Reboot Management Blade
This option is provided to perform the reboot of a management blade. The
reboot is executed using a Zircon internal reset logic module.
RemoteView Management Blade 61
Page 62

3.9 System Information Dump
This option is used to display the event logs of management blades or server
blades and to display consecutive lists of configuration/status information.
The menu for this option looks like this:
Figure 20: System Information Dump menu
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
System Configuration/Status
SEL for Management Blade Displays the management blade event log.
Server Blade Configu-
ration/Status
SEL for Server Blade Displays the server blade event log.
Displays a consecutive list of system information, e.g. status, IP address, MAC address
and firmware version of the switch blades.
Displays a consecutive list of information about
the server blades, e.g. status, BIOS version,
BMC firmware version, OS type and OS
version.
Page 63

4 Web user interface
On the web server an interactive and user-friendly web user interface, known as
web console, is provided for server management. It does not depend on any
special operating system for a platform. Login to this interface is made via the
web browser.
The options of this interface are explained in this chapter.
4.1 Overview
After login has been made successfully, a home page is displayed to the user,
giving an overview over the system configuration, i.e. the installed components
and their actual states. The navigation frame on the left side of the window
shows options applying to the system properties, by which the system configuration may be modified, as well as options for working with the different kinds of
blades that are embedded into the system.
Altogether, the options of the web user interface have been arranged into the
following main groups:
– System Property (see 4.2 on page 66)
– Management Blade (see 4.3 on page 85)
– Switch Blade (see 4.4 on page 86)
– Adv. KVM Blade
1
(see 4.5 on page 88)
– Server Blade (see 4.6 on page 98)
In the Server Blade and Switch Blade groups there is a sub-directory displayed for
every blade. Thus, the user may see at a glance how many blades there are
currently embedded in the system.
The figure next page shows the home page of the web user interface of the
BX300, giving an overview over its options (the BX600 has some slightly
modified hardware components):
1
PRIMERGY BX600 only
RemoteView Management Blade 63
Page 64

Overview Web user interface
Figure 21: Home page of the web user interface for a BX300 system
64 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 65

Web user interface Overview
Standard icons
There are icons displayed on the pages of the web user interface, so that the
user may perform some standard actions like scrolling, or using the help
function. These icons are also displayed on the other pages of the web user
interface.
The meaning of these icons are as follows:
Display a help page.
Go to the upper part of the page.
Go to the lower part of the page.
Refresh the page.
Go to the home page (if currently on another page).
RemoteView Management Blade 65
Page 66

System Property Web user interface
4.2 System Property
By working with the option System Property the user can apply changes to the
system configuration.
The settings of the system configuration that can be modified by the user have
been grouped into six fields. Corresponding to these are the following options:
– System Events Log (see 4.2.1 on page 66)
– Environment/Maintenance (see 4.2.2 on page 69)
– LAN Interface (see 4.2.3 on page 76)
– SNMP Interface (see 4.2.4 on page 79)
– Console Redirection (see 4.2.5 on page 80)
– System Information (see 4.2.6 on page 82)
– User Accounts (see 4.2.7 on page 82)
– Deployment Table (The parameters are very similar to those of the corre-
sponding Telnet option, thus you can refer to the description in 3.3.12 on
page 46).
– PPP and Modem Setting (The parameters are very similar to those of the
corresponding Telnet option, thus you can refer to the description in 3.3.14
on page 51).
4.2.1 System Event Log
The System Event Log option provides information on events that happened on
the system. Alarms can be configured for events in such a way that an e-mail is
sent whenever an event of a certain kind occurs.
The option comprises two sub-options:
– Event Log
– Alarm Handler
66 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 67

Web user interface System Property
4.2.1.1 Event Log
This option displays all system events to the user. The events displayed can be
filtered according to the blade system that they are related to, or to the error
type.
The events are shown in the following format:
Option Description
Time stamp Month – day – year.
Error type Informational event, minor event, major event,
critical event.
Error code Error code with class.
Content Error message description.
There is a Clear all entries option, which will clear all entries from the event
repository. The user is prompted to confirm this action, before it is executed.
4.2.1.2 Alarm handler
This option is used to configure the e-mails that are sent as alarms after an
event has occurred on the system and to configure the event log.
The following parameters are configured for an e-mail:
Parameter Description
To Mail receiver address.
From Mail sender address.
Host SMTP server address (IP address or host name).
Subject Mail subject (Read only, PRIMMAIL).
Administrator name System administrator name.
Phone number System administrator phone number.
Error Forwarding
Here you select which topics should be considered for error forwarding and
specify the minimum error level to entail forwarding.
RemoteView Management Blade 67
Page 68

System Property Web user interface
Server Blade Power On/Off Event Log Enable
This option is used to specify, whether power on/off events for the server blades
should be listed in the event log.
Management Blade Wrap Around Event Log Enable
This option is used to specify, whether the wrap-around functionality for the
event log should be used.
enable
When the event log repository is full, new event log entries replace the
old ones beginning with the first event log entry.
disable
When the event log repository is full, no event log entries are written any
longer.
68 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 69

Web user interface System Property
4.2.2 Environment/Maintenance
This option is used to adjust the settings of the environment modules. These
modules monitor power supply, chassis and fans of the system. The system
administrator can configure a reaction to be executed when a critical threshold
value is reached for a module.
There are the following sub-options:
– Firmware Update
– Power Supply
–UPS
– Chassis
– Fans
– Reset Management Blade
4.2.2.1 Firmware Update
This option is used to perform firmware updates for the blade server system.
The upgrades are performed via the TFTP service.
There are three different kinds of updates:
– Management blade
– Server blade BMC
– Server blade BIOS
I For further information on updating BX components please refer to the
Operating Manual of your BX system.
RemoteView Management Blade 69
Page 70

System Property Web user interface
Management Blade BMC Update
To perform a management blade BMC update, the following parameters can be
set:
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Address
Agent Update IP
Address
Boot Image File
Name
TFTP Upgrade
Enable
Server Blade BMC Update
To perform a server blade BMC update, the following parameters can be set:
Address of the TFTP server providing the image file for
the management blade firmware.
Setting of an agent IP address.
I The IP address to be supplied in the field Agent
Update IP Address is only temporarily used.
Enter any IP address which is not used in the
LAN segment of the server.
File name for the management blade image file.
This parameter is set to enable the TFTP update for the
management blade system.
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Address
Boot Image File
Name
Select in the list on the right side of the window the server blades you want to
be updated and click on the [ADD>>] button. They are moved into the update
list on the right side. You can remove server blades from the update list by
selecting them and clicking on the [DEL<<] button.
70 RemoteView Management Blade
Address of the TFTP server providing the image file for
the management blade firmware.
Path and file name for the management blade image file.
Page 71

Web user interface System Property
Server Blade BIOS Update
To perform a server blade BIOS update, the following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Address
Boot Image File
Address of the TFTP server providing the image file for
the management blade firmware.
Path and file name for the management blade image file.
Name
Select in the list on the right side of the window the server blades you want to
be updated and click on the [ADD>>] button. They are moved into the update
list on the right side. You can remove server blades from the update list by
selecting them and clicking on the [DEL<<] button.
4.2.2.2 Power Supply
This option contains a number of displays indicating states and faults regarding
the power supply of the system. On delivery, the BX600 is usually set up for
power supply redundancy of 2 + 1. This means that two power supply units
(PSUs) are available for powering the complete blade server system unit. The
third and fourth PSUs serve as redundant PSUs.
In the maximum configuration (maximum configuration per server blade), it may
be necessary to change the power supply redundancy from 2 + 1 to 3 + 1. In
this case, the fourth PSU serves as the redundant one. You can configure this
setting the System Power Supply Redundancy Mode parameter, see below.
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Power Switch Turns on, turn off or shuts down gracefully the blade
server system.
Group status Current status of the power supply modules. If there is
only one module installed, degraded mode will be
indicated.
Power Redundancy Indicates whether redundant power supply is assured.
RemoteView Management Blade 71
Page 72

System Property Web user interface
Parameter Description
System Power Supply
Redundancy Mode
With this parameter the power supply redundancy
mode is set to 2+1 or 3+1. Default is 2+1.
I This function is available as of management
firmware Release >= 2.11 and if four PSUs are
installed.
Fan1 fault Rotational speed status of fan 1. The value displayed
for this parameter will either be ok or fail. If fail is
displayed the rotational speed is below 1500 RPM
(+ – 200).
Fan2 fault Rotational speed status of fan 2. The value displayed
for this parameter will either be ok or fail. If fail is
displayed the rotational speed is below 2700 RPM
(+ – 200).
Fan3 fault Rotational speed status of fan 3. The value displayed
for this parameter will either be ok or fail. If fail is
displayed the rotational speed is below 2700 RPM
(+ – 200).
Thermal High fault Ambient temperature of the system. The value
displayed for this parameter will either be ok or fail. If
fail is displayed the ambient temperature is over
60 °C (+ – 5).
OVP12V fault Over voltage protection in 12V output. The value
displayed for this parameter will either be ok or fail.
UVP12V fault Under voltage protection in 12V output. The value
displayed for this parameter will either be ok or fail.
OCP12V fault Over current protection in 12V output. The value
displayed for this parameter will either be ok or fail.
Current Share fault Current share. The value displayed for this parameter
will either be ok or fail.
PWOK status Power O. K. signal. The value displayed for this
parameter will either be ok or not ok.
EPOW status Early Power Off Warning signal. The value displayed
for this parameter will either be ok or not ok.
AC Range status AC range. The value displayed for this parameter will
either be 180 – 264 V or 90 – 137 V or 200 - 240 V.
72 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 73

Web user interface System Property
Parameter Description
Temperature Ambient temperature for the system.
Life Time Displays the total working time of the battery (hours)
since the latest click on the Reset button.
Life Time Limited
Configures a max value for the battery working time.
Count
OVP 12V fault
reaction
OCP 12V fault
reaction
Server Blade Power
Specifies the reaction to an over voltage fault in 12V
output: continue or shutdown-and-poweroff.
Specifies the reaction to an over current fault in 12V
output: continue or shutdown-and-poweroff.
Powers on/off all server systems sequentially.
Switch
4.2.2.3 UPS
Displays chassis UPS (uninterruptable power supply) information, including
Number of installed UPSs, UPS number, vendor, type, Agent IP Address,
connect port, and SNMP community.
RemoteView Management Blade 73
Page 74

System Property Web user interface
4.2.2.4 Chassis
This option displays information on the chassis status of the blade system,
including front fans panel and rear fans panel. In addition, the environment
temperature is displayed for the system. A reaction can be configured to be
executed whenever this temperature reaches a critical threshold value.
The following parameters are displayed and can be set:
Parameter Description
System LED Controls the System LED: on, off or blinking.
Door Status (BX300)
Rear Fan Door Status (BX600)
Ambient Temperature Ambient temperature as detected by the
Intrusion status of fan panels. The value
displayed will either be closed or open.
sensors of the system. A reaction may be
selected for each sensor to be executed
whenever this temperature reaches a critical
threshold value.
The location of the sensors is as follows:
1: Located at the right of the middle plane
housing
2: Located at the center of the middle plane
housing
3: Located at the left of the middle plane
housing
4: Located at the right of the front fans panel
5 to 8: Located at the switch blades 1 to 4
9 to 10: Located at the PSUs 1 and 2
10 to 11 (only BX600): Located at the PSUs 3
and 4
74 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 75

Web user interface System Property
4.2.2.5 Fans
This option displays all fans that have been integrated into the system.
The fans are numbered, with the fan located at the left most of the modules
being counted as the first one, while looking at the front side of the system.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Fans fail reaction
control
These parameters are used to select a reactions in
case of fan failures (continue or shutdown-and-poweroff).
Fans Test This parameter is used to set the time for the daily
testing of the fan performance.
Fans Life Time
Counter
Displays the total working time of the fan since the
latest click on the Reset button.
Fans Limited Count Configures a max value for the fan working time.
4.2.2.6 Reset Management Blade
This option is used to reboot the management blade. The reboot does not
impact the operation of the blade system.
RemoteView Management Blade 75
Page 76

System Property Web user interface
4.2.3 LAN Interface
Within the management blade system a network service is provided, including
web server, telnet interface, send mail facilities and DNS service. The option
LAN Interface is used to handle the network configuration setting.
For this purpose several sub-options are offered, which are grouped in the
following way:
– Internet Protocol
– Domain Name Server
– HTTP
– Telnet
–NTP
–SSL
– Duplex Mode
4.2.3.1 Internet Protocol
This option is used to configure the IP address for the management blade. The
configuration may be carried out manually, or automatically using the DHCP
service.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Use DHCP This parameter is set to enable or disable the DHCP service.
IP Address IP address for the management blade.
Subnet Mask Subnet mask of the IP address for the management blade.
Gateway IP gateway address.
Default Route Specifies the default route:
LAN or PPP.
76 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 77

Web user interface System Property
4.2.3.2 Domain Name Server
This option is used to configure the Domain Name Server for the management
blade. Actually, there are two server systems provided to perform this service:
DNS Server 1 and DNS Server 2.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
DNS Server 1 IP address of the first server system for the DNS service.
DNS Server 2 IP address of the second server system for the DNS service.
4.2.3.3 HTTP
This option is used to configure a HTTP port. There is one parameter to be set:
Parameter Description
HTTP Port HTTP port number.
4.2.3.4 Telnet
This option is used to configure the Telnet interface.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Port Telnet port number. Default: 3172.
Drop Time Time-out for the Telnet connection. Default: 900 seconds.
After the time-out has elapsed, the user will have to perform
another login.
RemoteView Management Blade 77
Page 78

System Property Web user interface
4.2.3.5 NTP
This option is used to configure the NTP (network time protocol) service. You
can enable or disable the NTP service, set the NTP server’s IP address and
choose the Sync Mode:
– Sync Afterwards
Only if the management blade time is ahead of NTP server time, the
management blade syncs the time from NTP server.
– Sync Always
The management blade always syncs the time from NTP server, no matter
whether the NTP server time is behind or ahead of management blade,
4.2.3.6 SSL
This option is used to enable/disable SSL for HTTP or Telnet connections.
4.2.3.7 Duplex Mode
This option is used to configure the management blade’s NIC duplex mode. It
should be full duplex or half duplex.
Parameter Description
Execution Mode Displays the current execution mode.
Setting Mode Specifies which duplex mode should be active after the next
reset.
78 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 79

Web user interface System Property
4.2.4 SNMP Interface
To configure the SNMP interface two sub-options are used:
– SNMP Communities
– SNMP Trap Destination
4.2.4.1 SNMP Communities
The SNMP Communities option is used to show existing SNMP communities, as
well as to add and delete communities.
After the option has been selected, the SNMP communities table is displayed.
By typing in a community name and clicking the New Community button, a new
community is added to those already existing. The maximum number of
communities in the table is five.
An existing community is deleted from the table by selecting its name, marking
the field Delete and submit with the [Apply] button.
4.2.4.2 SNMP Trap Destination
The SNMP Trap Destination option is used to show existing SNMP trap destinations, as well as to add and delete destinations.
After the option has been selected, the SNMP trap destination table is
displayed. By typing in a destination address and clicking the New Trap Desti-
nation button, a new destination is added to those already existing. The
maximum number of destinations in the table is five.
An existing destination is deleted from the table by selecting its name, marking
the field Delete and submit with the [Apply] button.
RemoteView Management Blade 79
Page 80

System Property Web user interface
4.2.5 Console Redirection
The console redirection option is used to perform KVM
(= Keyboard/Video/Mouse) switching. There are two sub-options:
– KVM Switch for Local
– IP Filters for Telnet, HTTP and SNMP
I For controlling console redirection via adv. KVM blade on PRIMERGY
BX600 see section “Adv. KVM Blade” on page 88.
4.2.5.1 KVM Switch for Local
Within the blade system for server management there are three ways to switch
KVM (Keyboard/Video/Mouse) locally. One is by pressing the switch button at
the front end of the system, the second is switching via a keyboard hotkey
sequence, and the third one is to switch via the web or telnet user interface.
If KVM switching is performed via the web user interface, the following
parameter is to be set:
Parameter Description
Select KVM Used to perform a KVM switch.
4.2.5.2 IP Filters for Telnet, HTTP and SNMP
To perform a remote KVM switch, a new IP address is made known to the
system. An existing IP address can be deleted from the selecting table.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
IP Filter For
Telnet/HTTP/SNMP
New Allowed IP Used to enter a new IP address, which is added to the
Used to select an IP address for Telnet/HTTP/SNMP
connection filtering that is to be deleted.
IP addresses known to the system.
I Note that the number 255 has a function similar to a wildcard character:
80 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 81

Web user interface System Property
If for example the IP filter list contains the IP filter 255.255.255.255, the
system handles all possible IP addresses as known. An IP filter like
192.168.255.255 would handle all IP addresses beginning with
192.168. as known.
RemoteView Management Blade 81
Page 82

System Property Web user interface
4.2.6 System Information
This option contains agent information, daylight saving time, controller time, and
time-zone configuration.
Daylight Saving Time Format Example
● Start Date Example: M03.5.0/02
M03 March (Month 03; range: M01-M12)
5 last week (range: 1-5)
0 Sunday (range: 0-6)
02 2:00 o'clock am (range: 00-23)
Meaning: set the clock ahead one hour at 02:00 am on the Sunday of the
last week of the third month.
● End Date Example: M10.4.1/03
M10 October (Month 10; range: M01-M12)
4 the fourth week (range: 1-5)
1 Monday (range: 0-6)
03 3:00 o'clock am (range: 00-23)
Meaning: set the clock back one hour at 03:00 am on the Monday of the
fourth week of the tenth month.
4.2.7 User Accounts
Within the server management facilities there is a user database provided to
enable user authentication control. New user accounts are added to this
database via the Add New User Account option.
There is a static root user, who has full authorization to perform any activities in
the user database and cannot be deleted. The default password for this root
user is root.
82 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 83

Web user interface System Property
When adding a new user account via the Add New User Account option the
following parameters are to be set:
Parameter Description
Name User name.
Password User password.
Confirm password This field is used to confirm the password entered above.
Permissions The user access rights are set by clicking the options
explained below:
Read Only – The user cannot change any settings except
the password.
Modify values – The user can change any setting, but is
not allowed to add a new user account.
Configure users – The user can change any setting, and is
also allowed to add a new user account.
Reset/Switch off – The user can switch the system on/off.
Access EMP via CLI – The user can access the Emergency
Management Port via CLI.
I The following settings refer to the adv. KVM blade,
which is only supported by the
PRIMERGY BX600.
Adv. KVM User (incl KVM configuration rights)
– The user can configure the adv. KVM blade and
access the server blades marked below.
blade 1 ... blade 10 – The user can access the
marked server blades via Global Viewer.
KVM perm expiration date – Indicates the date when
the adv. KVM blade user permissions expire.
4.2.8 Deployment Table
This option is used to display and to set the deployment configuration for each
server blade. The particular server blade can be selected from a pull-down list.
The parameters are very similar to those of the corresponding Telnet option,
thus you can refer to the description in 3.3.12 on page 46).
RemoteView Management Blade 83
Page 84

System Property Web user interface
4.2.9 PPP and Modem Setting
This option is used to configure the settings for PPP connections and to
configure the modem. The parameters are very similar to those of the corresponding Te ln e t option, thus you can refer to the description in 3.3.14 on
page 51).
84 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 85

Web user interface Management Blade
4.3 Management Blade
The Management Blade option is used to display the number of management
blades that have been embedded into the blade system for server management.
There are up to two management blades in the system. One of these plays the
master role for server management, and the other one is there to ensure redundancy. It is essential that there is at least one management blade installed to
handle server management.
If there are two management blades, one of them will be selected for the master
role in the boot phase. Both management blades will then start to boot up at the
same time. The management blade that is the first to have its heartbeat
detected will be the master.
The following parameters can be displayed or set:
Parameter Description
Play Role Present role of the management blade: Master or
redundant management blade.
Manufacture Information on the manufacturer of the management
blade.
Produce Date Date of management blade production.
Serial Number Serial number of the management blade.
Product Number Product number of the management blade.
Model Name Name of the management blade model.
MAC Address NIC address of the management blade.
Firmware Version Version of the management blade firmware.
Hardware Version Version of the management blade hardware.
Change Management
Blade Role
Used to change the present role of the management
blade from master to slave, i. e. from controlling to
redundant management blade.
RemoteView Management Blade 85
Page 86

Switch Blade Web user interface
4.4 Switch Blade
The Switch Blade option is used to display the number of switch blades that have
been embedded into the blade system for server management.
There are two GB NIC ports for each server blade, which connect to two
separate switch blades. This has been arranged to ensure LAN connection
redundancy.
Up to four switch blades can be installed into the blade system for server
management. In each switch blade there are 10 ports for interconnection to the
server blades and three ports for outbound links.
4.4.1 Switch Blade Info
The following parameters are displayed for information on a switch blade:
Parameter Description
Located LED Switch on/off the located LED.
Manufacture Information on the manufacturer of the switch blade.
Produce Date Date of switch blade production.
Serial Number Serial number of the switch blade.
Product Number Product number of the switch blade.
Model Name Name of the switch blade model.
Board Version Version of the switch blade board.
Firmware Version Version of the switch blade firmware.
Network Setting Information on the network setting for the switch blade,
including the URL address of its web home page.
Mac Address NIC address of the switch blade.
URL URL address of the web home page for the switch blade.
IP Address Setting Value:
Specifies a new IP address for the switch blade.
Current Value:
Displays the current IP address of the switch
blade.
86 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 87

Web user interface Switch Blade
Parameter Description
Subnet Mask Setting Value:
Specifies a new subnet mask for the switch blade.
Current Value:
Displays the current subnet mask of the switch
blade.
Gateway Address Setting Value:
Specifies a new gateway for the switch blade.
Current Value:
Displays the current gateway of the switch blade.
Apply Activates the specified setting values (IP, Subnet,
Gateway) - either immediately or - if the UART Port is
used by another user - as soon as this port is available.
For example: If another user runs console redirection at
the moment, the settings will not be changed until the
console redirection has been completed.
Reload Refreshes the page. After applying the IP setting values
you can use Reload to check whether the new settings
are active already.
4.4.2 Backup/Restore
This option is used to backup/restore the configuration values of the
management blade.
Parameter Description
Backup/Restore Specifies whether a backup process or a
restore process is to be started.
View Backup File Displays the stored backup configuration
values.
Auto Restore Specifies whether after a hot-swap action
the new management blade is to be
configured automatically according the
stored backup configuration values.
RemoteView Management Blade 87
Page 88

Adv. KVM Blade Web user interface
4.5 Adv. KVM Blade
This option is used to administrate the adv. KVM blade. The adv. KVM blade is one
of two types of KVM switch that can be installed in a PRIMERGY BX600 system
unit. Both KVM switches - the standard KVM blade and the adv. KVM blade -
provide VGA and PS2 keyboard and mouse pass-through connection to the
server blades for local administration.
The adv. KVM blade additionally provides the following features:
– Web-based console redirection in graphic mode using the OSX application
Global Viewer, see page 90.
– Remote USB CD-ROM emulation
– Remote USB floppy disk emulation
– Remote boot via emulated USB devices
– Management-blade-controlled user authentication
For information on installing and connecting the adv. KVM blade, please see the
operating manual “PRIMERGY BX600 Basic Unit”.
4.5.1 Adv. KVM Blade Info
The following parameters are displayed to provide information on the adv. KVM
blade:
Parameter Description
Adv. KVM blade Manufacture Information on the manufacturer of the
adv. KVM blade.
Adv. KVM blade Manufacture Date Date of adv. KVM blade production
Adv. KVM blade Serial Number Serial number of the adv. KVM blade
Adv. KVM blade Product Name Product number of the adv. KVM blade
Adv. KVM blade Model Name Name of the adv. KVM blade model
Adv. KVM blade Hardware Version Version of the adv. KVM blade hardware
88 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 89

Web user interface Adv. KVM Blade
4.5.2 Adv. KVM Blade Configuration
This option is used to configure the network settings for the adv. KVM blade and
to launch the redirection of a server blade console. The network configuration
may be carried out manually, or automatically using the DHCP service.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Use DHCP (For KVM IP
Address)
KVM IP Address IP address for the adv. KVM blade.
KVM Gateway IP address of the gateway.
KVM Subnet Mask Subnet mask of the IP address for the adv.
KVM HTTP Port Basic HTTP port of the adv. KVM blade.
KVM Redirection [Launch] – Used to start the redirection of a
This parameter is set to enable or disable the
DHCP service.
KVM blade.
This port and the three subsequent ports
will be occupied by the adv. KVM blade
when launched.
server blade console.
Adv. KVM had been launched by
<user>[<date> <time>] – indicates that the
server blade console redirection has
already been launched by user at date and
time.
RemoteView Management Blade 89
Page 90

Adv. KVM Blade Web user interface
4.5.3 Global Viewer
For the redirection of a server blade VGA screen, the adv. KVM blade provides
the Global Viewer. The Global Viewer is an OSX application that will be
downloaded from the adv. KVM blade when the user selects KVM Redirection –
launch from the KVM Configuration menu. Via a drop-down menu, Global Viewer
provides all the functions needed to select the server blades and emulated
volumes and to configure the video screen redirection.
4.5.3.1 Requirements
Global Viewer requires the Microsoft Windows operating system running on the
client computer. Internet Explorer must be used for the management blade web
user interface session when launching Global Viewer.
Also make sure that ActiveX controls are enabled on the client computer before
launching Global Viewer.
I For safety reasons it is recommended to restrict ActiveX controls to
trusted sites. Proceed as follows to add the adv. KVM blade to the trusted
sites and to enable ActiveX controls for the trusted sites.
Ê Go to the Internet Explorer menu Tools - Internet Options - Security.
Ê Select Trusted sites.
Ê Click Sites to open the Trusted sites menu.
Ê Enter http://address into the field Add this site to the zone, where address is
the IP address of the adv. KVM blade.
Ê Click the Add button to confirm the entry.
Ê Click the Close button to exit the Trusted sites menu.
Ê Select Custom Level.
Ê Enable all the security options for downloading and executing ActiveX
controls.
On the server blade to be redirected, the mouse pointer acceleration must be
disabled. This is necessary for the synchronization of the server blade mouse
and the client computer mouse. The settings for this purpose depend on the
operating system of the redirected server blade.
90 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 91

Web user interface Adv. KVM Blade
If Windows is running on the server blade, select the mouse properties menu
from the control panel.
Win2000:
Ê Go to the Motion menu.
Ê Deactivate the mouse pointer acceleration.
Ê Set the mouse speed to the default of 50%.
Win2003/WinXP:
Ê Enter the Pointer Options menu.
Ê Disable Enhance pointer precision.
If a Linux X Window session is running on the server blade, enter the command
xset m 1.
It is recommended that you insert this command in the /etc/profile of the server
blade to automate this setting. Use the following statement for this setting:
if[$DISPLAY];then
xset m 1
fi
I When installing RedHat or SuSE Linux on a server blade via adv. KVM
blade, you should use a text mode, keyboard-based installation program
instead of a graphical installation program. This is why mouse synchronization is not feasible during that phase.
I You must disable mouse pointer acceleration for each server blade that is
to be redirected via adv. KVM blade.
RemoteView Management Blade 91
Page 92

Adv. KVM Blade Web user interface
4.5.3.2 Global Viewer Control Elements
This section describes the control elements of the Global Viewer user interface.
Drop-down menu
The Global Viewer drop-down menu provides the following functions:
File – Exit
Close the Global Viewer Session
HotKey – (Fullscreen | Ctrl-Enter | Alt-Escape | Alt-F4 | Alt-Space | Alt-SysReq | AltTabCtrl-Escape | Ctrl-Tab | Print Screen | Ctrl-Alt-Backspace | Ctrl-Alt-Delete | CtrlAlt-Escape | Ctrl-Alt-F1 | Ctrl-Alt-F2 | ... | Ctrl-Alt-F10)
Emulate entering reserved key codes by pointing to the appropriate
menu item
Control – KVM Switch – (Blade 1 | Blade 2 | ... | Blade 10)
Select the server blade to be redirected. The selected server blade is
indicated by a check mark. Empty slots are indicated by grayed-out menu
items.
Control – USB Switch – (Blade 1 | Blade 2 | ... | Blade 10)
Select the server blade to be connected with emulated USB devices
(floppy and/or CD-ROM). Grayed-out menu items indicate empty slots.
The selected server blade is indicated by a check mark.
Pointing to a selected server blade again causes the USB devices to be
unplugged
92 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 93

Web user interface Adv. KVM Blade
Control – Image Response Time – (Fast | High | Middle | Low)
Select the video image response time. Higher frame rates require more
LAN bandwidth.
Control – Image Sampling – (4:1:1 | 4:4:4).
Select the color depth. The default value is 4:1:1 and requires lower
bandwidth.
Control – Image Quality – (Best | High | Better | Normal)
Select the image quality (sharpness, etc.). Better quality requires more
LAN bandwidth or results in lower frame rates.
Control – Connection timeout setting
Timeout for reconnecting Global Viewer if the connection would be lost.
The default timeout value is 30 seconds.
Control – Mouse Sync
Synchronize the mouse pointer between client and server blade.
Storage – USB CDROM – CDROM Emulation
Select a CD-ROM drive of the client to be connected to the selected
server blade as an emulated USB device.
Select No Emulation for no CD-ROM emulation.
Storage – USB Floppy – Floppy Emulation
Select a floppy drive of the client or HDD stored floppy image. The
contents of the selected floppy or floppy image will be loaded into the adv.
KVM blade. Then the adv. KVM blade is able to emulate the floppy for the
selected server blade.
Select No Emulation for no floppy emulation.
Storage – USB Floppy – Mount Floppy Drive
Plug in the emulated USB floppy drive. The selected server blade gets
access to the floppy image stored in the adv. KVM blade. The text of the
menu item toggles to Unmount Floppy Drive.
Storage – USB Floppy – Unmount Floppy Drive
Unplug the emulated USB floppy drive. Now the local USB floppy drive
can be accessed by the server blade. The text of the menu item toggles
to Mount Floppy Drive.
Storage – USB Floppy – Save Image To
Save the contents of the emulated floppy. This will cause the floppy
image to be saved from the adv. KVM blade to a selected floppy drive or
as an image file to the specified file on an HDD of the client.
RemoteView Management Blade 93
Page 94

Adv. KVM Blade Web user interface
Video – Brightness
Opens a menu for adjusting the brightness of the Global Viewer window
by means of scale bars for base signal and red, green and blue
separately.
Video – Contrast
Opens a menu for adjusting the contrast of the Global Viewer window by
means of scale bars for base signal and red, green and blue separately.
Video – Auto Adjust
Video settings will be adjusted automatically. This will require ten
seconds, during which Global Viewer will be locked.
Video – Load Default Setting
The factory settings will be loaded.
Video – Save Configuration
The current video settings will be stored permanently.
Help – About
Displays the Global Viewer firmware version.
94 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 95

Web user interface Adv. KVM Blade
Status bar
1
2 34
1 Multi-function region for printing miscellaneous messages.
2 These fields enable the user to enter reserved key code sequences
using a combination of mouse clicking and pressing a key. A left click
on Ctrl, Alt and/or Shift emulates toggling the corresponding key.
Activated keys are highlighted.
3 A left click in this field will synchronize the local and remote mouse
pointers.
4 In this field the video settings of the redirected screen are displayed.
4.5.3.3 Global Viewer Operating Tasks
User authentication
Accessing the KVM redirection via the adv. KVM blade is restricted to the users
defined via the management blade account administration, see section “User
Accounts” on page 82.
To start the KVM redirection proceeed as follows:
Ê Select the menu Adv. KVM blade - KVM Configuration, see page 89.
Ê Click launch.
The Global Viewer Authentication menu appears.
Ê Enter the Username and Password defined via the menu System Property –
Console Redirection – User Accounts.
The Global Viewer window opens with the redirected console of the server blade
selected in the last session.
RemoteView Management Blade 95
Page 96

Adv. KVM Blade Web user interface
Synchronizing the mouse
To operate the redirected console smoothly, you must synchronize the mouse
pointer of server blade ( ) with the mouse pointer of the management client
().
V CAUTION!
Make sure that mouse pointer acceleration is disabled on the server blade
to be redirected, see section “Requirements” on page 90. With mouse
pointer acceleration enabled, mouse synchronization is not feasible.
There are four ways to synchronize the mouse:
– Select Control – Mouse Sync from the Global Viewer drop-down menu.
– Left-click in the Sync. Mouse field of the Global Viewer status bar.
– Double-click the left and right mouse buttons simultaneously.
– Move the mouse pointer over any boundary (menu bar, scroll bar or status
bar) of the activated Global Viewer window.
I You must synchronize the mouse every time you activate the Global
View er window.
How to select a server blade for console redirection
Ê Select the menu Control – KVM Switch.
Ê Select the server blade to be redirected.
How to select a server blade for USB volume emulation
Ê Select the menu Control – USB Switch.
Ê Select the server blade to be connected to a CD-ROM drive or floppy disk
drive of the remote client via USB volume emulation.
How to specify a remote CD-ROM drive to be connected to a server blade
Ê Select the menu Storage – CDROM Emulation.
Ê Select the CD-ROM drive to be emulated as a remote USB volume.
Ê If no CD-ROM drive is to be emulated, select No Emulation.
96 RemoteView Management Blade
Page 97

Web user interface Adv. KVM Blade
How to specify a remote floppy disk drive to be connected to a server
blade
Ê Select the menu Storage – USB Floppy – Floppy Emulation.
Ê Select the floppy disk drive or the floppy disk image to be emulated as a
remote USB volume of a server blade.
The selected floppy disk drive or floppy disk image will be copied into the
memory of the adv. KVM blade to be emulated as a remote USB floppy of a
specified server blade until the end of the Global Viewer session.
To connect the emulated USB floppy drive to a selected server blade you
must execute the function Mount Floppy Drive, see below.
Ê Select Mount Floppy Drive to emulate plugging the remote floppy in the
specified server blade.
Ê Select Unmount Floppy Drive to emulate unplugging the remote floppy from
the specified server blade.
Ê Select Save Image to ... to save the emulated floppy from the adv. KVM blade
to the specified floppy drive or an image file on a hard disk.
4.5.4 Adv. KVM Blade Update
This option is used to perform a firmware update for the adv. KVM blade. The
upgrade is performed via the TFTP service. The current adv. KVM blade firmware
version is printed at the top of the menu.
To perform an adv. KVM blade update, you can set the following parameters:
Parameter Description
Image Name File name of the adv. KVM blade image file.
TFTP Server IP
Address
Update Firmware Used to start the firmware update process.
Firmware Update
Status
RemoteView Management Blade 97
Address of the TFTP server providing the image file for
the adv. KVM blade firmware.
Used to display the progress of the update process in a
new window.
Page 98

Server Blade Web user interface
4.6 Server Blade
The web user interface for server management provides a number of options to
display information on the server blades that have been embedded into the
system. The maximum number of server blades that can be embedded is 20 for
BX300 Systems and 10 for BX600 Systems.
In front of each server blade system that is displayed on the web page there is
an icon showing the power status of the server blade and the
KVM (= Keyboard/Video/Mouse) location.
The following icons are used for this purpose:
Means that the server blade is in power off state.
Means that the server blade is in power on state.
Means that the server blade is in power off state and KVM is located at
this blade.
Means that the server blade is in power on state and KVM is located at
this blade.
There are two parameters that can be set to activate or deactivate the server
blades collectively:
Parameter Description
Turn on all server
blades
Turn off all server
blades
98 RemoteView Management Blade
Power on all server blades sequentially.
Power off all server blades sequentially.
Page 99

Web user interface Server Blade
4.6.1 Recovery
The recovery options provided by the system for server management have been
arranged into four groups:
– Automatic Server Restart (ASR)
– Auto Configuration
– Power Control
– Boot Option
4.6.1.1 Automatic Server Restart (ASR)
Using this option the Boot Watchdog timer can be enabled or disabled and a
time-out can be configured. When the time-out has been reached, the Wat c hd og
Action is executed. The restart is retried until the boot is successful or until the
value Maximum restart retries is reached.
4.6.1.2 Auto Configuration
There is one parameter that can be set to backup the CMOS configuration of
the server blades, and another one to restore it:
Parameter Description
CMOS Backup Used to generate a backup of the BIOS parameters for the
server blade. The server blade must be powered up, before
the backup can be generated. If the backup has been
generated successfully, it will appear in the CMOS file
selecting table.
CMOS
Restore
RemoteView Management Blade 99
Used to restore the server blade parameters. To do this, a
CMOS file is selected and the Restore Policy parameter is set.
If the special option smart Restore is selected, the server blade
parameters will be restored with MAC address and slot ID.
Page 100

Server Blade Web user interface
4.6.1.3 Power Control
Using this option, the power on/off procedure can be configured for the server
blades. It is then performed according to a schedule table, instead of having
power on and off performed manually.
4.6.1.4 Boot Option
Using this option, a boot option can be selected for the server blade. If the PXE
boot option is selected, the server blade will try to boot up from the PXE server.
4.6.2 Blade Info
The Blade Info options have been arranged into four groups: – Blade Info – Memory Module – Voltage – Temperature This option is used to display information on the server blades and their config-
uration.
4.6.2.1 Blade Info
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Blade Status Displays the server blade health status.
Server LED Configuration of the LED control at the front of the blade
server: blinking or off.
OS Type Displays the OS platform currently running on the server
blade.
OS Version Displays the version of the OS currently running on the
server blade.
Model Name of the server blade model.
Serial Number Serial number of the server blade.
BIOS Version Version of the server blade BIOS.
100 RemoteView Management Blade
 Loading...
Loading...