Page 1

FCC ID: EJE-WB0020 (IC: 337J-WB0020) Report No. M050322_Cert_WM3B2200BG_BT
APPENDIX I
USER MANUAL
This document must not be copied or reproduced, except in full without the written permission of
the Manager, EMC Technologies Pty Ltd. The certificate on page 3 may be reproduced in full.
www.emctech.com.au
Page 2
S7010.book Page 91 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Appendix A
Integrated Wireless
LAN* User’s Guide
* Optional device
91
Page 3
S7010.book Page 92 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook
92
Page 4
S Series.book Page 93 Wednesday, April 14, 2004 10:28 AM
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
FCC REGULATORY INFORMATION
Please note the following regulatory information related to the
wireless LAN device.
Regulatory Notes and Statements
Wireless LAN, Health and Authorization for use
Radio frequency electromagnetic energy is emitted from Wireless LAN devices. The energy levels of these emissions, however,
are far much less than the electromagnetic energy emissions
from wireless devices such as mobile phones. Wireless LAN
devices are safe for use by consumers because they operate
within the guidelines found in radio frequency safety standards
and recommendations. The use of Wireless LAN devices may be
restricted in some situations or environments, such as:
On board an airplane, or
In an explosive environment, or
In situations where the interference risk to other devices or
services is perceived or identified as harmful.
In cases in which the policy regarding use of Wireless LAN
devices in specific environments is not clear (e.g., airports,
hospitals, chemical/oil/gas industrial plants, private buildings),
obtain authorization to use these devices prior to operating the
equipment.
Regulatory Information/Disclaimers
Installation and use of this Wireless LAN device must be in
strict accordance with the instructions included in the user
documentation provided with the product. Any changes or
modifications made to this device that are not expressly
approved by the manufacturer may void the user’s authority to
operate the equipment. The manufacturer is not responsible for
any radio or television interference caused by unauthorized
modification of this device, or the substitution or attachment of
connecting cables and equipment other than those specified by
the manufacturer. It is the responsibility of the user to correct
any interference caused by such unauthorized modification,
substitution or attachment. The manufacturer and its authorized resellers or distributors will assume no liability for any
damage or violation of government regulations arising from
failure to comply with these guidelines.
This device must not be co-located or operated in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter.
For Atheros and Intel PRO Set Wireless LAN:
For operation within 5.15~5.25 GHz frequency range, it is
restricted to indoor environments, and the antenna of this
device must be integral.
Federal Communications Commission statement
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This
device may not cause interference, and, (2) This device must
accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of this device.
FCC Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy. If not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, it may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try and correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the distance between the equipment and the
receiver.
3. Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different
from the one the receiver is connected to.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician
for help.
FCC Radio Frequency Exposure statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits
set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment
should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of
20 cms from the WLAN antennas located on the top edge of
the LCD screen. The Bluetooth antenna is located on the left
side of the keyboard and is exempt from minimum distance
criteria due to its low power. The transmitters in this device
must not be co-located or operated in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
Export restrictions
This product or software contains encryption code which may
not be exported or transferred from the US or Canada without
an approved US Department of Commerce export license. This
device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules., as well as ICES 003
B / NMB 003 B. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference,
and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesirable operation.
Modifications not expressly authorized by Fujitsu PC Corporation may invalidate the user's right to operate this equipment.
Canadian Notice
To prevent radio interference to the licensed service, this device
is intended to be operated indoors and away from windows to
provide maximum shielding. Equipment (or its transmit
antenna) that is installed outdoors is subject to licensing.
High power radars are allocated as primary users of 5250 - 5350
MHz and 5650 - 5850 MHz and these radars cause interference
and/or damage to LELAN(license exempt LAN) devices operating
in these bands.
93
Page 5
S Series.book Page 94 Wednesday, April 14, 2004 10:28 AM
LifeBook S Series Notebook - Section Five
Before Using the Wireless LAN
This manual describes the procedures required to properly setup and configure the integrated Wireless LAN
Mini-PCI device (referred to as "WLAN device" in the
rest of the manual). Before using the WLAN device, read
this manual carefully to ensure it's correct operation.
Keep this manual in a safe place for future reference.
Wireless LAN Devices Covered by this Document
This document is applicable to systems containing one
of the following two devices. Most of the procedures are
identical. Sections that differ between the two devices
have been noted in the text:
Intel PROSet Wireless LAN (WM3B2915ABG and
WM3B2200BG)
Atheros Wireless LAN (WLL4070)
If your system is an S7020, your wireless module is the
Intel PROSet wireless LAN; if your system is an S7020D,
your wireless module is the Atheros wireless LAN.
Characteristics of the WLAN Device
The WLAN device is a Mini-PCI card attached to the
mainboard of the mobile computer.
It is a dual-band radio that operates in two license-free
RF bands, therefore eliminating the need to procure an
FCC license to operate. It operates in the 2.4GHz
Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) RF band.
Additionally, the Atheros device operates in the lower
and middle bands of the 5GHz Unlicensed National
Information Infrastructure (UNII) bands.
The Atheros WLAN is capable of three operating
modes, IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11b and IEEE802.11g,
wireless LAN standards governed by the IEEE (Institute of Electronics and Electrical Engineers). The Intel
WLAN is capable of two operating modes,
IEEE802.11b and IEEE802.11g.
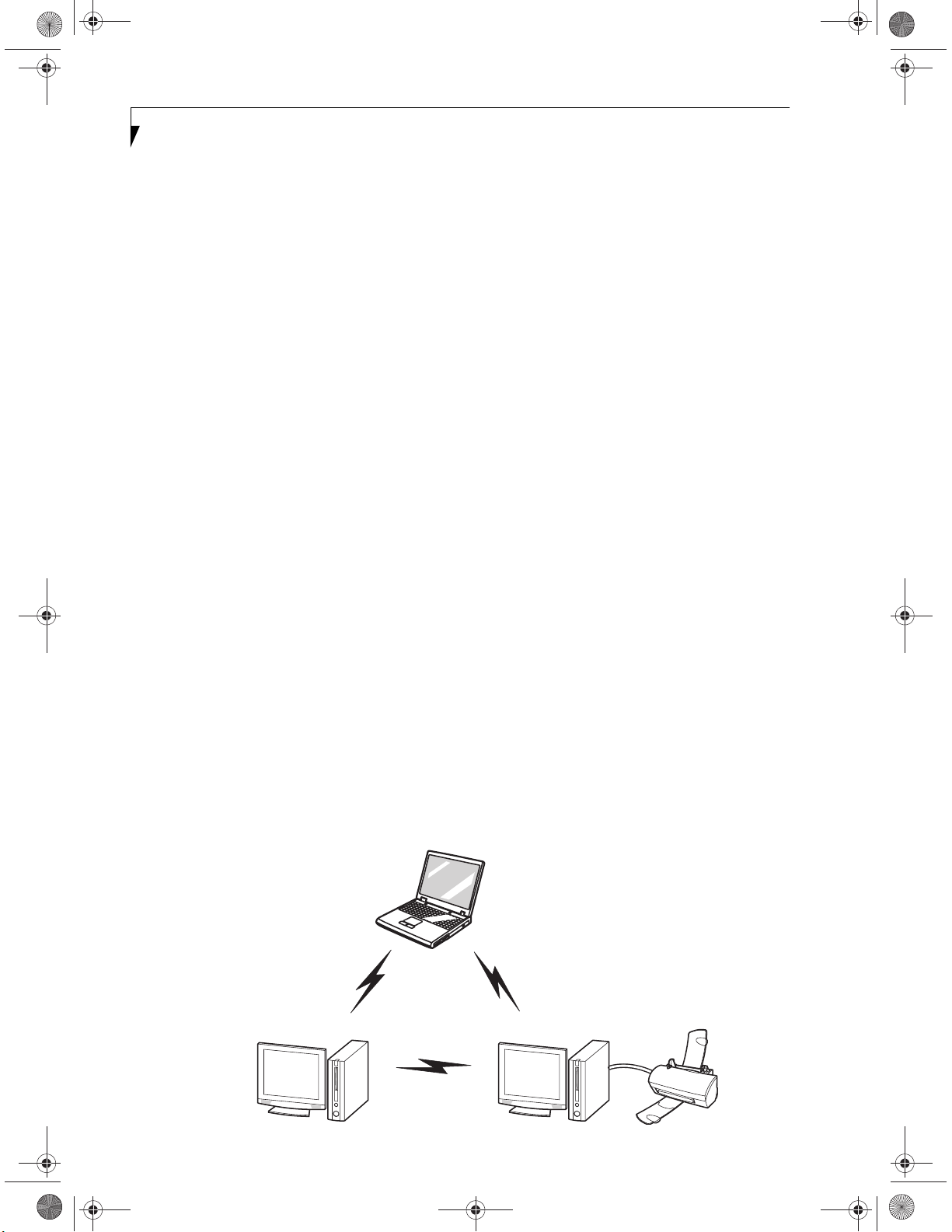
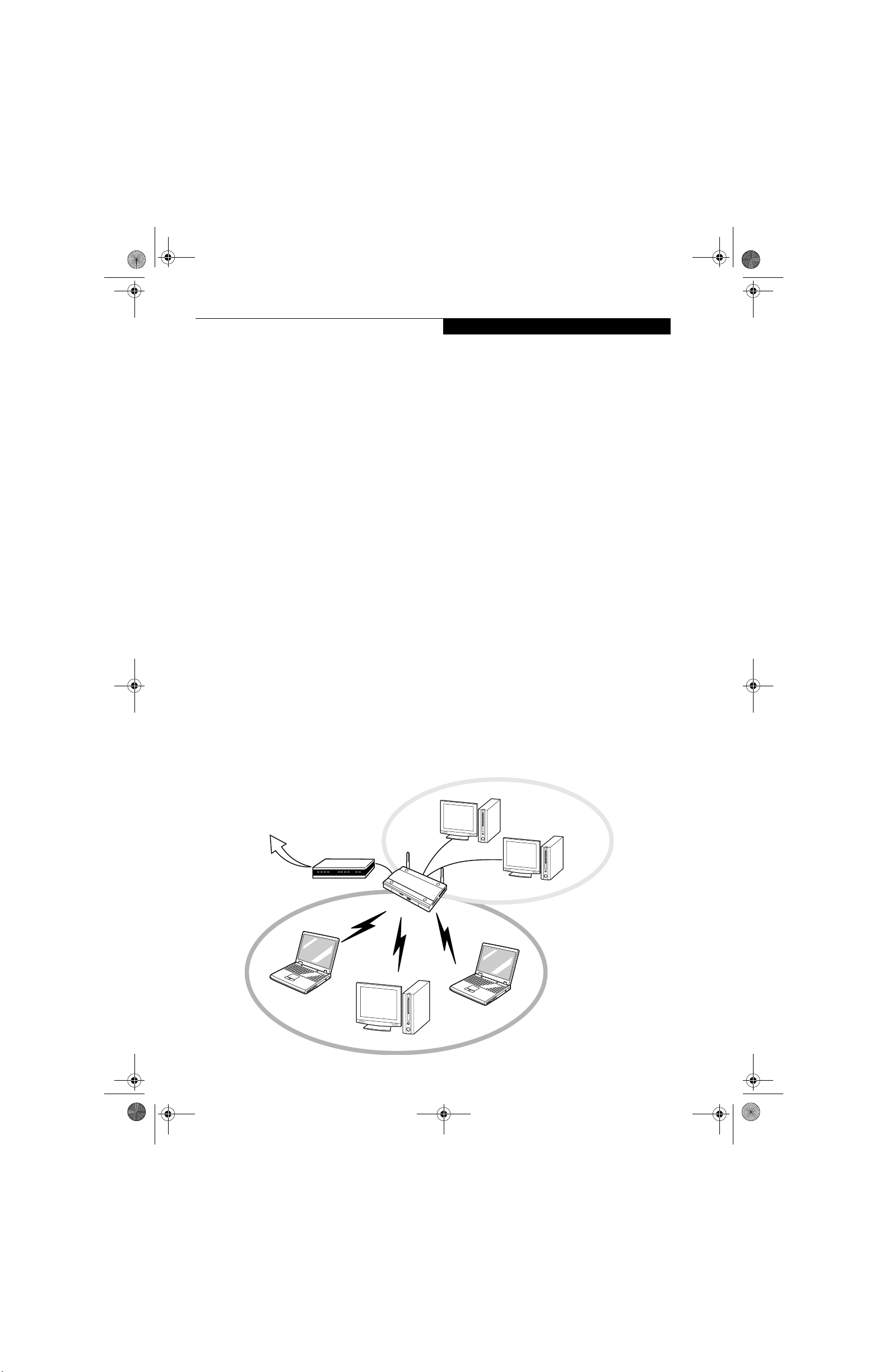
Figure 5-1. Ad Hoc Mode Network
Encoding of data is modulated using Direct Sequence
Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Complementary Code
Keying (CCK) when the WLAN device is operating in
IEEE 802.11b mode and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) when operating in
IEEE802.11a or IEEE802.11g mode.
The WLAN device is Wi-Fi certified and operates at
the maximum data transfer rate of 54 Mbps in
IEEE802.11a or IEEE802.11g mode and 11 Mbps in
IEEE802.11b mode.
The maximum communication range indoors is
approximately 80 feet (25 meters). However, that
range will increase or decrease depending on factors
such as number of walls, reflective material, or interference from external RF sources.
The WLAN device supports the following encryption
methods - WEP, TKIP, and AES encryption.
WIRELESS LAN MODES USING THIS DEVICE
Ad Hoc Mode
(See Figure 5-1)
"Ad Hoc Mode" refers to a wireless network architecture
where wireless network connectivity between multiple
computers is established without a central wireless
network device, typically known as Access Point(s).
Connectivity is accomplished using only client devices in
a peer-to-peer fashion. That is why Ad Hoc networks are
also known as peer-to-peer networks. Ad Hoc networks
are an easy and inexpensive method for establishing
network connectivity between multiple computers.
Ad Hoc mode requires that the SSID, network authentication, and encryption key settings are identically
configured on all computers in the Ad Hoc network.
94
Page 6
S7010.book Page 95 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
Access Point (Infrastructure) Mode
(See Figure A-2)
Infrastructure mode refers to a wireless network architecture in which devices communicate with wireless or
wired network devices by communicating through an
Access Point. In infrastructure mode, wireless devices
can communicate with each other or can communicate
with a wired network. Corporate wireless networks
operate in infrastructure mode because they require
access to the wired LAN in order to access computers,
devices, and services such as file servers, printers, and
databases.
How to Handle This Device
The WLAN device comes pre-installed in your mobile
computer. Under normal circumstances, it should not be
necessary for you to remove or re-install it. The Operating System that your mobile computer comes with has
been pre-configured to support the WLAN device.
WIRELESS NETWORK CONSIDERATIONS
The Intel PRO/Wireless 2200BG WLAN device supports IEEE802.11b and IEEE802.11g. The Intel PRO/
Wireless 2915ABG and Atheros AR5006X WLAN
devices support IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11b and
IEEE802.11g.
The Intel PRO/Wireless 2200BG WLAN device operates in the 2.4GHz ISM band. The Intel PRO/Wireless
2915ABG and Atheros AR5006X WLAN devices operate in the 2.4GHz ISM band and the 5 GHz lower,
middle, and upper UNII bands.
The maximum range of the WLAN device indoors is
typically 80 feet (25 meters). Please note that the maximum range you achieve may be shorter or longer than
80 feet, depending on factors such as access point
transmit power, number and density of obstructions,
or external RF interference.
Microwave ovens will interfere with the operation of
WLAN device as microwave ovens operate in the same
2.4GHz frequency range that IEEE802.11b/g devices
operate in. Interference by microwaves does not occur
with IEEE802.11a radio which operates in the 5 GHz
RF band.
Wireless devices that transmit in the 2.4GHz frequency range may interfere with the operation of
WLAN devices in IEEE802.11b/g modes. Symptoms of
interference include reduced throughput, intermittent
disconnects, and large amounts of frame errors. It is
HIGHLY recommended that these interfering devices
be powered off to ensure the proper operation of the
WLAN device.
DEACTIVATING THE WLAN DEVICE
Deactivation of the WLAN device may be desired in
certain circumstances (to extend battery life) or where
certain environments require it (i.e. hospitals, clinics,
airplanes, etc.). Fujitsu mobile computers employ two
methods with which to deactivate the WLAN device:
Using the Wireless On/Off Switch
In Windows, using the Intel PROSet Software or
Atheros Client Utility software.
Figure A-2. Access Point (Infrastructure) Mode Network
Internet
ADSL modem,
cable modem,
or similar
Wireless LAN
Wired LAN
Access Point*
*An optional hub for a wired
LAN may be required depending
upon the type of access point used.
95
Page 7
S7010.book Page 96 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Series Notebook - Appendix
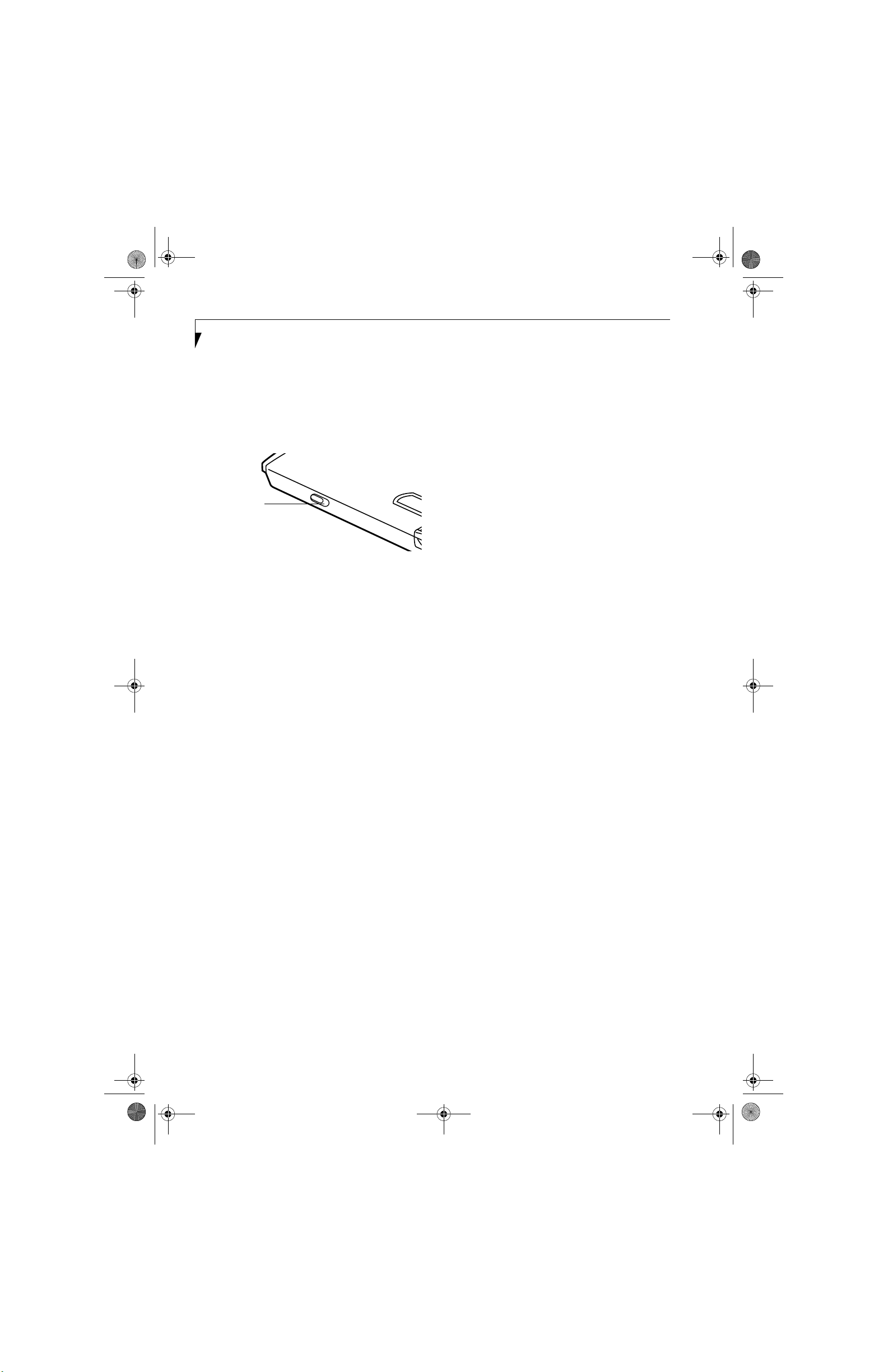
Deactivation using the Wireless On/Off Switch
The WLAN device can be deactivated quickly and efficiently by toggling the Wireless On/Off Switch to the Off
position. (Figure A-3)
The Wireless On/Off switch has no effect on non-Wireless LAN models.
Wireless LAN
On/Off Switch
Figure A-3. Wireless LAN On/Off Switch Location
Deactivation using the Intel PROSet Software
The WLAN device can also be deactivated in Windows
using the Intel PROSet Software. The procedure to
accomplish this:
1. Click [Start]-> [All Programs].
2. Select Intel ProSet Wireless, then click on Intel
ProSet Wireless from the menu that appears. The
Intel ProSet Wireless utility will be displayed.
3. At the bottom left corner of the window, select
Wireless Off from the dropdown list.
Deactivation using Atheros Client Utility software
1. Right-click on Atheros Client Utility icon in the
system tray. Select “Open Atheros Client Utility”
from the menu.
2. Choose Action and click Disable Radio.
ACTIVATING THE WLAN DEVICE
Activation of the WLAN device can be accomplished
using the same methods as the deactivation process
■
Using the Wireless On/Off Switch
■
In Windows using the Intel PROSet Software or
Atheros Software
96
Page 8
S7010.book Page 97 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Configuration of the WLAN Device
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
The WLAN Device can be configured to establish wireless network connectivity using one of the following
tools:
■
Intel PROSet Software - The Intel PROSet Software
allows for multiple profile setup and supports automatic profile switching. Support for most industry
standard security solutions is contained in this software.
■
Atheros Client Utility - The Atheros Client Utility software allows for multiple profile setups and supports
automatic profile switching. Support for most industry standard security solutions is contained in this
software.
FLOW OF OPERATIONS
1. Activate the WLAN Device (See Activating the
WLAN Device on page 96 for more information).
2. Configure the Wireless Network parameters.
■
Enter the network name (SSID)
■
Choose the appropriate WLAN architecture (Ad
Hoc or Infrastructure)
■
Choose Authentication method: Open, Shared,
WPA-Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise, WPAPersonal, or WPA2-Personal
■
If using static WEP keys, enter static WEP key and
choose key index.
3. Configure network settings (See Configure Network Parameters on page 97 for more information)
■
TCP/IP settings
■
Workgroup or Domain settings.
Procedure
1. Activate the WLAN device using either the Wireless
On/Off Switch or the Intel PROSet software.
2. Click the [Start] button first and then [All Programs].
3. Click the icon [Intel PROSet Wireless] to execute
the Intel PROSet Wireless software.
4. Click the [Add] button. The General Settings dialog
displays.
5. Enter a profile name in the Profile Name field.
6. Enter the network SSID, in the Network Name
(SSID) field.
7. Click Infrastructure or Ad Hoc for the operating
mode.
8. Click [Advanced].
9. The Mandatory Access Point option is only used if
Infrastructure mode is selected. Use this option to
connect to a specific access point. Enter the MAC
address for the access point. Click OK to save the
setting and return to the General Settings page.
10. Click [Next].
11. If you are using Cisco CCX, click Cisco Options to
enable Cisco CKIP data encryption on the Security
Settings page. Check the Cisco Compatible Extensions Options. If you have checked the Cisco's
"Mixed-Cell" box in the Advanced Setting, this
option must also be checked.
12. Click [OK].
13. Click Next.
CONFIGURATION USING
INTEL PROSET SOFTWARE
This section explains the procedure to properly
configure the WLAN device using the Intel PROSet Software. Pre-defined parameters will be required for this
procedure. Please consult with your network administrator for these parameters:
Network Name - Also known as the SSID
Network Key (WEP) - Required if using static WEP
keys.
Authent ication Type - Open, Shared, WPA, or WPAPSK
14. Select Open, Shared, WPA-Enterprise, WPA2Enterprise, WPA-Personal, or WPA2-Personal in
the Network Authentication options.
15. Select either None, WEP, CKIP (if Enable Cisco Client eXtentions is enabled, use CKIP or WEP), or
TKIP for the data encryption.
16. If WEP is selected, select either 64 or 128-bit for the
Encryption Level.
17. Select the key index 1, 2, 3 or 4.
18. Enter the WEP key if required. If your network does
not employ a 802.1x/EAP security mechanism,
please skip to step 24.
97
Page 9
S7010.book Page 98 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Series Notebook - Appendix
19. Click the Enable 802.1x checkbox to enable the
802.1x security option. Please contact your network
administrator if configuration of this setting is
required.
20. Select the appropriate Authentication Type. Please
contact your network administrator if configuration of this setting is required.
21. After selecting your authentication type, enter the
user name, domain, and password of the user you
have created on the authentication server. The user
name and password do not have to be the same as
name and password of your current Windows user
login.
22. Click [OK] to save the settings.
23. From the Intel ProSet Wireless page, click the new
profile name shown in the Profile List. Use the up
and down arrows to position the priority of the
new profile in the priority list.
24. Click the Connect button to connect to the network.
25. Click [Close] if you want to close the Intel(R)
PROSet for Wireless window.
CONFIGURATION USING
ATHEROS CLIENT UTILITY SOFTWARE
This section explains the procedure to properly
configure the WLAN device using the Atheros Client
Utility. Pre-defined parameters will be required for this
procedure. Please consult with your network administrator for these parameters:
Network Name - Also known as the SSID
Network Key (WEP) - Required if using static WEP
keys.
Authent icati on Type - Open, Shared, WPA, or WPAPSK
Procedure
1. Activate the WLAN device using either the Wireless
On/Off Switch or the Atheros Client Utility
2. Right-click on the “Atheros Client Utility” icon in
the system tray, and select “Open Atheros Client
Utility” from the menu.
3. From the Current Status page, click the Profile
Management tab.
4. If this is your first time using this utility, highlight
the profile [Default] and Click the [Modify] button,
otherwise Click the [New] button. The General Settings dialog displays.
5. From the General page, enter a profile name in the
Profile Name field.
6. Enter the network SSID, in the SSID1 field. If you
wish to create a profile that can connect to up to 3
different wireless networks, SSID's can be entered
in the SSID2 and SSID3 fields as well.
7. Click the Security tab.
8. The Security tab allows for the configuration of the
Security modes listed in the table below. Please
select the radio button of the desired security
mode. If these settings are not known to you,
please consult with your network administrator for
the correct settings.
Field Name Description
WPA Enables the use of Wi-Fi Protected
Access. Choosing WPA opens the
WPA EAP drop-down menu.
Options include TLS and PEAP. If
these settings are not known to you,
please consult with your network
administrator for the correct settings.
WPA-PSK Enables WPA-Pre-Shared Key. Click
on the Configure button to enter the
WPA Passphrase. If these settings
are not known to you, please consult
with your network administrator for
the correct settings.
802.1x Enables 802.1x security. If these
settings are not known to you,
please consult with your network
administrator for the correct settings.
Choosing this option opens the
802.1x EAP type drop-down menu.
Options include TLS, PEAP, and LEAP
Pre-Shared Key Enables the use of pre-shared keys
that are defined on both the access
point and the station. This is where
static WEP keys are entered. Click
the Configure button to fill in the
Define Pre-Shared Keys window.
None No security
9. Click OK
10. Click the Advanced tab
11. The Advanced tab allows for the configuration of
the options detailed in the table below
98
Page 10
S7010.book Page 99 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
.
Field Name Description
Power Save
Mode
Network Type Options are AP (Infrastructure) or Ad
802.11b
Preamble
Transmit Power
Level
Wireless Mode Specifies 5 GHz 54 Mbps, 5 GHz 108
Wireless Mode
when Starting
Ad Hoc
Network
Options are Maximum, Normal, or
Off
Hoc
Specifies the preamble setting in
802.11b. The default setting is Short
and Long (Access Point mode),
which allows both short and long
headers in the 802.11b frames. Set
to Long Only to override allowing
short frames.
Options are 100%, 50%, 25%,
12.5% or Lowest transmit power
(0mW)
Mbps, 2.4 GHz 11 Mbps, or 2.4 GHz
54 Mbps operation in an access
point network.
Specifies 5GHz 54 Mbps, 5 GHz 108
Mbps, 2.4 GHz 11 Mbps, or 2.4 GHz
54 Mbps to start an Ad Hoc network
if no matching network name is
found after scanning all available
modes.
12. Click OK
13. If the profile you just created does not activate
immediately, click the Profile Management tab,
highlight the desired Profile, and click Activate.
14. Click [Close] if you want to close the Atheros Client
Utility.
CONNECTION TO THE NETWORK
This section explains connection to the network.
If there is an administrator of the network, contact the
network administrator for data settings.
Setting the network
Perform the “Setting TCP/IP” and “Confirming the
computer and work group names” operations required for
network connection.
Setting TCP/IP
To change the setting of the IP address,
you need to be logged in from Windows
as an administrator.
1. Click the [Start] button first and then [Control
Panel].
2. If the Control Panel is in Category view, switch to
Classic view by clicking “Switch to Classic View”
under Control Panel the left frame. (If you are
already in Classic view, “Switch to Category View”
will be displayed.)
3. Double-click [Network Connections]. A list of currently installed networks will be displayed.
4. Right-click [Wireless Network Connection] in the
list, and then click [Properties] in the menu displayed. The [Wireless Network Connection Properties] window will be displayed.
5. Click the [General] tab if it is not already selected.
6. Click [Internet Protocol (TCP/IP] and then click
[Properties]. The [Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties] window will be displayed.
7. Set the IP address as follows:
■
For ad hoc connection: Select [Use the following
IP address:] and then enter data for [IP address]
and [Subnet mask]. See page 106 for IP address
setting.
■
For access point (infrastructure) connection: If
your network uses DHCP, select [Obtain an IP
address automatically] and [Obtain DNS server
address automatically]. If your network uses static
IP addresses, consult with your network administrator for the correct IP address settings.
8. Click the [OK] button. Processing will return to the
[Wireless Network Connection Properties] window.
9. Click the [OK] button.
10. Close the [Network Connection] window.
Following this operation, confirm the names of the
computer and the workgroup as follows.
Confirming the computer and work group names
To modify the computer name and/or the
work group name, you need to be logged
in from Windows as an administrator.
1. Click the [Start] button, then [Control Panel].
2. If the Control Panel is in Category view, switch to
Classic view by clicking “Switch to Classic View”
under Control Panel the left frame. (If you are
already in Classic view, “Switch to Category View”
will be displayed.)
3. Double-click the [System] icon. The [System Properties] window will be displayed.
4. Click the [Computer Name] tab.
99
Page 11

S7010.book Page 100 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Series Notebook - Appendix
5. Confirm the settings of [Full computer name:] and
[Workgroup:].
a. The setting of [Full computer name:] denotes the
name for identifying the computer. Any name
can be assigned for each personal computer.
To change the name, click [Change] and
then proceed in accordance with the
instruction messages displayed on the
screen.
Enter the desired name in less than 15 ASCII
character code format. Identifiability can be
enhanced by entering the model number, the
user name, and other factors.
b. [Workgroup name] is the group name of the
network. Enter the desired name in less than 15
ASCII character code format.
For ad hoc connection: Assign the same network
name to all personal computers existing on the
network.
For access point (infrastructure) connection:
Assign the name of the work group to be
accessed.
3. Double-click [Network Connections]. A list of currently installed networks will be displayed.
4. Right-click [Wireless Network Connection] in the
list, and then click [Properties] in the menu displayed. The [Wireless Network Connection Properties] window will be displayed.
5. If [File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Net-
works] is displayed, proceed to step 6. If [File and
Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks] is not displayed, skip to step 7.
6. Make sure that the [File and Printer Sharing for
Microsoft Networks] check box is checked, and
then click the [OK] button. Skip to “Setting filesharing function”.
7. Click [Install]. The [Select Network Component
Type] window will be displayed.
8. Click [Service], then click the [Add] button. The
[Select Network Service] window will be displayed.
9. Click [File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks] and then click the [OK] button. Processing
will return to the [Wireless Network Connection
Properties] window, and [File and Printer Sharing
for Microsoft Networks] will be added to the list.
6. Click the [OK] button. If a message is displayed
that requests you to restart the personal computer,
click [Yes] to restart the computer.
Setting the sharing function
Set the sharing function to make file and/or printer sharing
with other network-connected personal computers valid.
This operation is not required unless the sharing function is to be used.
The folder and printer for which the sharing function
has been set will be usable from any personal computer
present on the network.
To share a file and/or the connected
printer, you need to be logged in as an
administrator.
Setting the Microsoft network-sharing service
1. Click the [Start] button first and then [Control
Panel].
2. If the Control Panel is in Category view, switch to
Classic view by clicking “Switch to Classic View”
under Control Panel the left frame. (If you are
already in Classic view, “Switch to Category View”
will be displayed.)
10. Click the [Close] button.
Setting the file-sharing function
The procedure for setting the file-sharing function
follows, with the “work” folder in drive C: as an
example.
1. Click the [Start] button first and then [My Computer].
2. Double-click [Local disk (C:)].
3. Right-click the “work” folder (or whichever folder
you want to share), and then click [Sharing and
Security...] in the menu displayed. The [Folder
Name Properties] window will be displayed.
Setting the file-sharing function for the file
which has been used to execute Network
Setup Wizard is suggested on the screen.
For the wireless LAN, however, since
security is guaranteed by entry of the
network name (SSID) and the network
key, the steps to be taken to set the filesharing function easily without using
Network Setup Wizard are given below.
4. Click [Sharing] if it isn’t already selected.
100
Page 12

S7010.book Page 101 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
5. Click the link stating “If you understand the security risks, but want to share files without running
the wizard, click here”.
6. Click “Just enable file sharing” and click [OK].
7. Check the [Share this folder on the network] check
box.
To specify the corresponding folder as a
read-only folder, select the [Read only]
checkbox under the General tab.
8. Click the [OK] button. The folder will be set as a
sharable folder, and the display of the icon for the
“work.” folder will change.
Setting the printer-sharing function
1. Click the [Start] button first and then [Printers and
FAX]. A list of connected printers will be displayed.
2. Right-click the printer for which the sharing function is to be set, and then click [Sharing] in the
menu displayed. The property window correspond-
ing to the selected printer will be displayed.
Setting the printer-sharing function when
Network Setup Wizard has been executed
is suggested on the screen. For the wireless
LAN, however, since security is guaranteed
by entry of the network name (SSID) and
the network key, the steps to be taken to
set the printer-sharing function without
using Network Setup Wizard are laid down
below.
3. Click the [Sharing] tab.
4. Click [Share this printer].
5. Enter the sharing printer name in [Share name].
6. Click the [OK] button.
Confirming connection
After you have finished the network setup operations,
access the folder whose sharing has been set for other
personal computers. Also, confirm the status of the radio
waves in case of trouble such as a network connection
failure.
In the case of access point (infrastructure)
connection, enter the necessary data for
the access point before confirming
connection. Refer to the manual of the
access point for the access point setup
procedure.
Connecting your personal computer to another
personal computer
1. Click [Start] first and then [My Computer]. The
[My Computer] window will be displayed in the left
frame.
2. Click [My Network Places] in the “Other Places”
list. The window [My Network Places] will be displayed.
3. Click [View workgroup computers] under Network
Tasks in the left frame.
4. Double-click the personal computer to which your
personal computer is to be connected. The folder
that was specified in “Setting the file-sharing function” on page 100 will be displayed.
5. Double-click the folder to be accessed.
Confirming the status of the radio
1. Right-click the Intel PRO Wireless icon in the lower
right corner of the screen.
2. Click [Open Intel PROSet for Wireless]. The Intel
PROSet for Wireless window opens.
3. Contained within the General tab and the Details
section (accessed by pressing the [Details] button),
you will find the current operating status of the
radio. (When the radio is turned off or the computer is not yet connected, some of the conditions
will not be displayed.)
■
Profile Name
The current configuration profile is displayed.
■
Network Name (SSID)
Displays the Network Name (SSID) currently
used by the radio.
■
IP Address
The IP address of the current profile.
■
Signal Quality
Displays a message stating the current quality of
the signal.
■
Signal Strength
Displays a graphic representation of the current
signal strength.
Additionally, in the lower section of the display, you
will see a variety of different measurements related
to the WLAN. For additional information about the
items, click on the “Help?” button:
■
Adapter MAC Address
■
Band
■
Supported Data Rates
101
Page 13

S7010.book Page 102 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Series Notebook - Appendix
■
Radio Frequency
■
Channel Number
■
Network Authentication
■
Data Encryption
■
802.1x Authentication Type
■
802.1x Authentication Protocol
■
CCX Version
■
CCX TPC
■
CCX Power Levels
■
Access Point MAC Address
■
Mandatory Access Point
102
Page 14

S7010.book Page 103 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
Troubleshooting the WLAN
TROUBLESHOOTING
Causes and countermeasures for troubles you may encounter while using your wireless LAN are described in the
following table.
Problem Possible Cause Possible Solution
Unavailable
network
connection
Incorrect network
name (SSID) or
network key
Weak received signal
strength and/or link
quality
The WLAN device
has been deactivated
or disabled
The computer to be
connected is turned
off
RF interference from
Access Points or
other wireless
networks
Ad hoc connection: verify that the network names (SSID’s) and network
keys (WEP) of all computers to be connected have been configured
correctly. SSID’s and WEP key values must be identical on each machine.
Access Point (Infrastructure) connection: set the network name (SSID)
and network key to the same values as those of the access point.
Set the Network Authentication value identically to that of the Access
Point. Please consult your network administrator for this value, if
necessary.
Ad hoc connection: Retry connection after shortening the distance to
the destination computer or removing any obstacles for better sight.
Access Point (Infrastructure) connection: Retry connection after shortening the distance to the access point or removing any obstacles for
better sight.
To check the wave condition, refer to the following page:· “Confirming
the status of the radio waves” on page 101.
Check if the wireless switch is turned ON. Also verify “Disable Radio” is
not checked in “Network setting” window. Refer to “Activating the
Wireless LAN” on page 96.
Check if the computer to be connected is turned ON.
The use of identical or overlapping RF channels can cause interference
with the operation of the WLAN device. Change the channel of your
Access Point to a channel that does not overlap with the interfering
device.
Wireless network
authentication has
failed
Incorrectly
configured network
settings
Incorrect IP address
configuration
Re-check your Network Authentication, Encryption, and Security
settings. Incorrectly configured security settings such as an incorrectly
typed WEP key, a mis-configured LEAP username, or an incorrectly
chosen authentication method will cause the LAN device to associate
but not authenticate to the wireless network.
Recheck the configuration of your network settings.
For the method of checking, refer to the following page:·“Connection to
the Network” on page 99.
This only applies to networks using static IP addresses. Please contact
your network administrator for the correct settings.
103
Page 15
S7010.book Page 104 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Series Notebook - Appendix
Wireless LAN Glossary
GLOSSARY
Access point
Wireless network device used to bridge wireless and
wired network traffic.
Ad Hoc Mode
Ad Hoc Mode refers to a wireless network architecture
where wireless network connectivity between multiple
computers is established without a central wireless
network device, typically known as Access Points.
Connectivity is accomplished using only client devices in
a peer-to-peer fashion. For details, refer to “Ad hoc
connection” on page 94.
CCX (Cisco Compatible Extensions)
Implementation that provides improved wireless data
security, ensuring certified compatibility with Cisco
wireless access points.
Channel
Range of narrow-band frequencies used by the WLAN
device to transmit data. IEEE802.11b/g - 11 channels, 22
MHz wide channels.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
A protocol that provides a means to dynamically allocate
IP addresses to computers on a local area network.
DNS (Domain Name System)
A data query service that provides a mechanism with
which to translate host names into Internet addresses.
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol
A protocol implementation that provides a framework
to allow easier user authentication.
IEEE802.11a
Wireless LAN standard that supports a maximum data
rate of 54 Mbps. 802.11a devices operate in the 5 GHz
lower and middle UNII bands.
IEEE802.11b
Wireless LAN standard that supports a maximum data
rate of 11 Mbps. 802.11b devices operate in the 2.4 GHz
ISM band.
IP address
The logical 32-bit host address defined by the Internet
Protocol that uniquely identifies a computer on a
network. The IP address is usually expressed in dotted
decimal notation.
LAN (Local Area Network)
A LAN or Local Area Network is a computer network (or
data communications network) which is confined to a
limited geographical area.
MAC address (Media Access Control Address)
A MAC address (also called an Ethernet address or IEEE
MAC address) is the 48-bit address (typically written as
twelve hexadecimal digits, 0 through 9 and A through F,
or as six hexadecimal numbers separated by periods or
colons, e.g., 0080002012ef, 0:80:0:2:20:ef) which
uniquely identifies a computer that has an Ethernet
interface.
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit)
The maximum size of data which can be transmitted at
one time in networks including the Internet. In an environment whose maximum size of data is too large to
correctly receive data, normal communications can be
restored by setting the size of MTU to a smaller value.
Network key
Data that is used for encrypting data in data communication. The personal computer uses the same network
key both for data encryption and decryption, therefore,
it is necessary to set the same network key as the other
side of communication.
Network name (SSID: Security Set Identifier)
When a wireless LAN network is configured, grouping is
performed to avoid interference or data theft. This
grouping is performed with “Network name (SSID)”. In
order to improve security, the network key is set
allowing no communication unless “Network name
(SSID)” coincides with the network key.
Open system authentication
Null authentication method specified in the 802.11 standard that performs no authentication checks on a wireless client before allowing it to associate.
104
Page 16
S7010.book Page 105 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol)
An improvement over EAP, making authentication
much easier to achieve.
PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet)
A method of allowing the authentication protocol
adopted in telephone line connection (PPP) to be used
over an Ethernet.
Protocol
A procedure or rule of delivering data among
computers. Ordered data communication is allowed by
making all conditions required for communication
including the method of data transmission/reception
and actions upon communication errors into procedures.
Shared key authentication
802.11 network authentication method in which the AP
sends the client device a challenge text packet that the
client must then encrypt with the correct WEP key and
return to the AP. If the client has the wrong key or no
key, authentication will fail and the client will not be
allowed to associate with the AP. Shared key authentication is not considered secure, because a hacker who
detects both the clear-text challenge and the same challenge encrypted with a WEP key can decipher the WEP
key.
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)
Security feature that is a WEP enhancement to defend
against known wireless data security issues.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
Standard wireless security provided by the Wi-Fi standard, used for protecting wireless data.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is a set of standards for wireless local area networks (WLAN) based on the IEEE
802.11 specifications. Certified products can use the
official Wi-Fi logo, which indicates that the product is
interoperable with any other product also showing that
logo.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
Strong replacement for WEP, providing improved data
encryption and user authentication.
Service Set Identifier, a 32-character unique identifier
attached to the header of packets sent over a WLAN that
acts as a password when a mobile device tries to connect
to the BSS. The SSID differentiates one WLAN from
another, so all access points and all devices attempting to
connect to a specific WLAN must use the same SSID. A
device will not be permitted to join the BSS unless it can
provide the unique SSID. Because the SSID is broadcast
in plain text, it does not supply any security to the
network.
Subnet mask
TCP-IP network is controlled by being divided into
multiple smaller networks (subnets). IP address consists
of the subnet address and the address of each computer.
Subnet mask defines how many bits of IP address
comprise the subnet address. The same value shall be set
among computers communicating with each other.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol)
A standard protocol of the Internet.
105
Page 17
S7010.book Page 106 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Series Notebook - Appendix
IP address information
ABOUT IP ADDRESSES
IP addressing is much more complicated
than can be briefly explained in this
document. You are advised to consult with
your network administrator for additional
information.
If IP address is unknown, set IP address as follows:
If you have an access point (DHCP server) on the
network, set the IP address as follows:
[Obtain an IP address automatically]
A DHCP server is a server that
automatically assigns IP addresses to
computers or other devices in the network.
There is no DHCP server for the AdHoc
network.
If the IP address is already assigned to the computer in
the network, ask the network administrator to check the
IP address to be set for the computer.
If no access point is found in the network:
An IP address is expressed with four values in the range
between 1 and 255.
Set the each computer as follows: The value in parentheses is a subnet mask.
<Example>
Computer A: 192.168.100.2 (255.255.255.0)
Computer B: 192.168.100.3 (255.255.255.0)
Computer C: 192.168.100.4 (255.255.255.0)
:
:
Computer X: 192.168.100.254 (255.255.255.0)
106
Page 18
S7010.book Page 107 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
Specifications
Item Specification
Type of network The Atheros AR5006X and the Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG
Network Connections WLAN devices conform to IEEE 802.11a
and 802.11b/g (Wi-Fi based)*. The Intel PRO/Wireless 2200BG
Network Connections WLAN device conforms to 802.11b/g
(Wi-Fi based)
Transfer rate (Automatic switching)
Active frequency 802.11b/g: 2400~2473 MHz
Number of channels 802.11a: 8 independent channels
Security Encryption Types - WEP, TKIP, AES**
Maximum recommended number of computers to
be connected over wireless LAN (during ad hoc
connection)
IEEE 802.11a/g: 54 Mbps maximum data rate
IEEE 802.11b: 11 Mbps maximum data rate
802.11a: 4900 ~ 5850 MHz
802.11b/g: 11 channels, 3 non-overlapping channels
WPA 1.0 compliant
Encryption Keylengths Supported: 64 bits, 128 bits, and 152 bits
(Atheros module using AES encryption only)
802.1x/EAP
10 units or less ***
* “Wi-Fi based” indicates that the interconnectivity test of the organization which guarantees the interconnectivity of
wireless LAN (Wi-Fi Alliance) has been passed.
** Encryption with network key (WEP) is performed using the above number of bits, however, users can set 40 bits/
104 bits after subtracting the fixed length of 24 bits.
*** Depending on practical environments, the allowable number of computers to be connected may be decreased.
107
Page 19

S Series.book Page 108 Wednesday, April 14, 2004 10:28 AM
Using the Bluetooth Device
The Integrated Bluetooth module (UGXZ5-102A) is an
optional device available for Fujitsu mobile computers.
WHAT IS BLUETOOTH
Bluetooth technology is designed as a short-range wireless link between mobile devices, such as laptop
computers, phones, printers, and cameras. Bluetooth
technology is used to create Personal Area Networks
(PANs) between devices in short-range of each other.
WHERE TO FIND INFORMATION
ABOUT BLUETOOTH
The Bluetooth module contains a robust Help user’s
guide to assist you in learning about operation of the
Bluetooth device.
To access the Help file, click [Start] -> All Programs, and
click on Toshiba. Select Bluetooth, then select User’s
Guide.
For additional information about Bluetooth Technology,
visit the Bluetooth Web site at: www.bluetooth.com.
WIreless LAN User’s Guide
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure
limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
The transmitters in this device must not be co-located or
operated in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
Canadian Notice
To prevent radio interference to the licensed service, this
device is intended to be operated indoors and away from
windows to provide maximum shielding. Equipment (or
its transmit antenna) that is installed outdoors is subject
to licensing.
Warranty
Users are not authorized to modify this product. Any
modifications invalidate the warranty.
This equipment may not be modified, altered, or
changed in any way without signed written permission
from Fujitsu. Unauthorized modification will void the
equipment authorization from the FCC and Industry
Canada and the warranty.
108
Page 20
S7010.book Page 109 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Appendix B
Using the
Fingerprint Sensor*
* Optional Device
109
Page 21
S7010.book Page 110 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook – Appendix
110
Page 22

S7010.book Page 111 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Using the Fingerprint Sensor
Fingerprint Sensor Device
INTRODUCING THE OPTIONAL
FINGERPRINT SENSOR DEVICE
Your system may have an optional fingerprint sensor
device in the location at which other models have a
scroll button. (Figure B-1)
Figure B-1 Fingerprint sensor
Although the system may have a
fingerprint sensor in place of a scroll
button, the fingerprint sensor can be used
for scrolling. Simply move your fingerprint
over the sensor the same as you would use
a scroll button.
With a fingerprint sensor, you can avoid having to enter
a username and password every time you want to:
■
Log onto Windows
■
Recover from suspend mode
■
Cancel a password-protected screen saver
■
Log into homepages that require a username and password
After you have “enrolled” - or registered - your fingerprint, you can simply swipe your fingertip over the
sensor for the system recognize you.
The fingerprint sensor uses Softex OmniPass which
provides password management capabilities to
Microsoft Windows operating systems. OmniPass
enables you to use a "master password" for all Windows,
applications, and on-line passwords.
OmniPass requires users to authenticate themselves
using the fingerprint sensor before granting access to the
Windows desktop. This device results in a secure
authentication system for restricting access to your
computer, applications, web sites, and other passwordprotected resources.
OmniPass presents a convenient graphical user interface,
through which you can securely manage passwords,
users, and multiple identities for each user.
GETTING STARTED
This section guides you through the preparation of your
system for the OmniPass fingerprint recognition
application. You will be led through the OmniPass
installation process. You will also be led through the
procedure of enrolling your first user into OmniPass.
INSTALLING OMNIPASS
If OmniPass has already been installed on your system,
skip this section and go directly to “User Enrollment” on
page 112. You can determine whether OmniPass has
already been installed by checking to see if the following
are present:
■
The presence of the gold key-shaped OmniPass icon in
the system tray at the bottom right of the screen.
■
The presence of the Softex program group in the
Programs group of the Start menu
System Requirements
The OmniPass application requires space on your hard
drive; it also requires specific Operating Systems (OS’s).
The minimum requirements are as follows:
■
Windows XP Home Edition or Windows XP Professional operating system
■
At least 35 MB available hard disk space
Installing the OmniPass Application
If OmniPass is already installed on your system, go to
“User Enrollment” on page 112. Otherwise continue
with this section on software installation.
For installation, OmniPass requires that the
user installing OmniPass have
administrative privileges to the system. If
your current user does not have
administrative privileges, log out and then
log in with an administrator user before
proceeding with OmniPass installation.
To install OmniPass on your system you must:
1. Insert the installation media for the OmniPass application into the appropriate drive. If you are
installing from CD-ROM or DVD-ROM, you must
find and launch the OmniPass installation program
(setup.exe) from the media.
2. Follow the directions provided in the OmniPass
installation program. Specify a location to which
you would like OmniPass installed
mended that you NOT install OmniPass in the root
directory (e.g. C:\).
3. Once OmniPass has completed installation you will
be prompted to restart you system. Once your
system has rebooted you will be able to use
OmniPass. If you choose not to restart immediately
after installation, OmniPass will not be available for
use until the next reboot.
. It is recom-
111
Page 23

S7010.book Page 112 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook – Appendix
The installation program automatically places an icon
(Softex OmniPass) in the Windows Control Panel as well
as a golden key shaped icon in the taskbar.
Verifying Information about OmniPass
After you have completed installing OmniPass and
restarted your system, you may wish to check the version
of OmniPass on your system.
To check the version information of OmniPass:
1. From the Windows Desktop, double-click the keyshaped OmniPass icon in the taskbar (usually
located in the lower right corner of the screen),
or,
Click the Start button, select Settings, and click
Control Panel (if you are using Windows XP you
will see the Control Panel directly in the Start menu;
click it, then click Switch to Classic View). Doubleclick Softex OmniPass in the Control Panel, and the
OmniPass Control Center will appear. If it does not
appear, then the program is not properly installed,
or,
Click the Start button, select Programs, and from
the submenu select the Softex program group, from
that submenu click OmniPass Control Center.
2. Select the About tab at the top of the OmniPass
Control Panel. The About tab window appears with
version information about OmniPass.
Uninstalling OmniPass
For uninstallation, OmniPass requires that
the user uninstalling OmniPass have
administrative privileges to the system. If
your current user does not have
administrative privileges, log out and then
log in with an administrator user before
proceeding with OmniPass uninstallation.
To remove the OmniPass application from your system:
1. Click Start on the Windows taskbar. Select Settings,
and then Control Panel.
2. Double-click Add/Remove Programs.
3. Select OmniPass, and then click Change/Remove.
4. Follow the directions to uninstall the OmniPass
application.
5. Once OmniPass has finished uninstalling, reboot
your system when prompted.
USER ENROLLMENT
Before you can use any OmniPass features you must first
enroll a user into OmniPass.
Master Password Concept
Computer resources are often protected with passwords.
Whether you are logging into your computer, accessing
your email, e-banking, paying bills online, or accessing
112
network resources, you often have to supply credentials
to gain access. This can result in dozens of sets of credentials that you have to remember.
During OmniPass user enrollment a "master password”
is created for the enrolled user. This master password
“replaces” all other passwords for sites you register with
OmniPass.
Example: A user, John, installs OmniPass on his system
(his home computer) and enrolls an OmniPass user with
username “John_01” and password “freq14”. He then
goes to his webmail site to log onto his account. He
inputs his webmail credentials as usual (username
“John_02” and password “lifebook”), but instead of
clicking [Submit], he directs OmniPass to Remember
Password. Now whenever he returns to that site,
OmniPass will prompt him to supply access credentials.
John enters his OmniPass user credentials (“John_01”
and “freq14”) in the OmniPass authentication prompt,
and he is allowed into his webmail account. He can do
this with as many web sites or password protected
resources he likes, and he will gain access to all those
sites with his OmniPass user credentials (“John_01” and
“freq14”). This is assuming he is accessing those sites
with the system onto which he enrolled his OmniPass
user. OmniPass does not actually change the credentials
of the password protected resource. If John were to go to
an Internet cafe to access his webmail, he would need to
enter his original webmail credentials (“John_02” and
“lifebook”) to gain access. If he attempts his OmniPass
user credentials on a system other than where he
enrolled that OmniPass user, he will not gain access.
The enrollment procedure assumes you
have no hardware authentication devices
or alternate storage locations that you
wish to integrate with OmniPass. If you
desire such functionality, consult the
appropriate sections of this document.
Basic Enrollment
The Enrollment Wizard will guide you through the
process of enrolling a user. Unless you specified otherwise, after OmniPass installation the Enrollment Wizard
will launch on Windows login. If you do not see the
Enrollment Wizard, you can bring it up by clicking Start
on the Windows taskbar; select Programs; select Softex;
click OmniPass Enrollment Wizard.
1. Click Enroll to proceed to username and password
verification. By default, the OmniPass Enrollment
Wizard enters the credentials of the currently logged
in Windows user.
2. Enter the password you use to log in to Windows.
This will become the “master password” for this
OmniPass user. In most cases, the Domain: value
Page 24

S7010.book Page 113 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Using the Fingerprint Sensor
will be your Windows computer name. In a corporate environment, or when accessing corporate
resources, the Domain: may not be your Windows
computer name. Click [Next] to continue.
3. In this step OmniPass captures your fingerprint.
Refer to “Enrolling a Fingerprint” on page 113 for
additional information.
4. Next, choose how OmniPass notifies you of various
events. We recommend you keep Taskbar Tips on
Beginner mode taskbar tips and Audio Tips on at
least Prompt with system beeps only until you get
accustomed to how OmniPass operates. Click [Next]
to proceed with user enrollment. You will then see a
Congratulations screen indicating your completion
of user enrollment.
5. Click [Done] to exit the OmniPass Enrollment
Wizard. You will be asked if you’d like to log in to
OmniPass with your newly enrolled user; click [Yes].
Enrolling a Fingerprint
Enrolling a fingerprint will increase the security of your
system and streamline the authentication procedure.
You enroll fingerprints in the OmniPass Control Center.
With an OmniPass user logged in, double-click the
system tray OmniPass icon. Select the User Settings tab
and click Enrollment under the User Settings area. Click
Enroll Authentication Device and authenticate at the
authentication prompt to start device enrollment.
1. During initial user enrollment, you will be
prompted to select the finger you wish to enroll.
Fingers that have already been enrolled will be
marked by a green check. The finger you select to
enroll at this time will be marked by a red arrow.
OmniPass will allow you re-enroll a finger. If you
choose a finger that has already been enrolled and
continue enrollment, OmniPass will enroll the
fingerprint, overwriting the old fingerprint. Select a
finger to enroll and click [Next].
2. It is now time for OmniPass to capture your selected
fingerprint. It may take a several capture attempts
before OmniPass acquires your fingerprint. Should
OmniPass fail to acquire your fingerprint, or if the
capture screen times out, click [Back] to restart the
fingerprint enrollment process.
Your system has a “swipe” fingerprint sensor. A
swipe sensor is small and resembles a skinny elongated rectangle. To capture a fingerprint, gently
swipe or pull your fingertip over the sensor (starting
at the second knuckle) towards yourself. Swiping
too fast or too slow will result in a failed capture.
The Choose Finger screen has a [Practice] button;
click it to practice capturing your fingerprint. When
you are comfortable with how your fingerprint is
captured, proceed to enroll a finger.
3. Once OmniPass has successfully acquired the fingerprint, the Ver if y F in ge rp r int screen will automatically appear. To verify your enrolled fingerprint,
place your fingertip on the sensor and hold it there
as if you were having a fingerprint captured.
Successful fingerprint verification will show a green
fingerprint in the capture window and the text Ver i -
fication Successful under the capture window.
USING OMNIPASS
You are now ready to begin using OmniPass. Used regularly, OmniPass will streamline your authentications.
Password Replacement
You will often use the password replacement function.
When you go to a restricted access website (e.g., your
bank, your web-based email, online auction or payment
sites), you are always prompted to enter your login
credentials. OmniPass can detect these prompts and you
can teach OmniPass your login credentials. The next
time you go to that website, you can authenticate with
your fingerprint to gain access.
OmniPass Authentication Toolbar
After installing OmniPass and restarting, you will notice
a dialog you have not seen before at Windows Logon.
This is the OmniPass Authentication Toolbar, and it is
displayed whenever the OmniPass authentication system
is invoked. The OmniPass authentication system may be
invoked frequently: during Windows Logon, during
OmniPass Logon, when unlocking your workstation,
when resuming from standby or hibernate, when
unlocking a password-enabled screensaver, during password replacement for remembered site or application
logins, and more. When you see this toolbar, OmniPass
is prompting you to authenticate.
The Logon Authentication window indicates what
OmniPass-restricted function you are attempting. The
icons in the lower left (fingerprint and key) show what
authentication methods are available to you. Selected
authentication methods are highlighted while unselected
methods are not. When you click the icon for an unselected authentication method, the authentication
prompt associated with that method is displayed.
When prompted to authenticate, you must supply the
appropriate credentials: an enrolled finger for the fingerprint capture window or your master password for the
master password prompt (the key icon).
Remembering a Password
OmniPass can remember any application, GUI, or password protected resource that has a password prompt.
Using the following procedure, you can store a set of
credentials into OmniPass. These credentials will then be
linked to your “master password” or fingerprint.
113
Page 25

S7010.book Page 114 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook – Appendix
Go to a site that requires a login (username and password), but do not log in yet. At the site login prompt,
enter your username and password in the prompted
fields, but do not enter the site (do not hit [Enter],
[Submit], [OK], or Login). Right-click the OmniPass
system tray icon and select Remember Password from
the submenu. The Windows arrow cursor will change to
a golden key OmniPass cursor. Click this OmniPass
cursor in the login prompt area, but do not click the
[Login] or [Submit] button.
Associating a Friendly Name
After clicking the OmniPass key cursor near the login
prompt, OmniPass will prompt you to enter a “friendly
name” for this site. You should enter something that
reminds you of the website, the company, or the service
you are logging into. In its secure database, OmniPass
associates this friendly name with this website.
Additional Settings for Remembering a Site
When OmniPass prompts you to enter a “friendly name”
you also have the opportunity to set how OmniPass
authenticates you to this site. There are three effective
settings for how OmniPass handles a remembered site.
The default setting is Automatically click the “OK” or
“Submit” button for this password protected site once
the user is authenticated. With this setting, each time
you navigate to this site OmniPass will prompt you for
your master password or fingerprint authentication
device. Once you have authenticated with OmniPass,
you will automatically be logged into the site.
Click Finish to complete the remember password procedure. The site location, the credentials to access the site,
and the OmniPass authentication settings for the site are
now stored in the OmniPass secure database. The
OmniPass authentication settings (Settings for this Pass-
word Site) can always be changed in Vault Management.
Logging in to a Remembered Site
Whether or not OmniPass prompts you to authenticate
when you return to a remembered site is determined by
Settings for this Password Site and can be changed in
Vault Management.
The following cases are applicable to using OmniPass to
login to: Windows, remembered web sites, and all other
password protected resources.
With Master Password
Once you return to a site you have remembered with
OmniPass, you may be presented with a master password prompt. Enter your master password and you will
be allowed into the site.
Logging into Windows with a Fingerprint Device
When logging into Windows with a fingerprint device,
the fingerprint capture window will now appear next to
the Windows Login screen. Place your enrolled fingertip
on the sensor to authenticate. You will be simultaneously
logged into Windows and OmniPass. The capture
window will also appear if you have used Ctrl-Alt-Del to
lock a system, and the fingerprint device can be used to
log back in as stated above.
Less secure is the option to Automatically enter this
password protected site when it is activated. Do not
prompt for authentication. Check the upper box to get
this setting, and each time you navigate to this site
OmniPass will log you into the site without prompting
you to authenticate
.
This setting is more convenient in that
whenever you go to a site remembered
with this setting, you will bypass any
authentication procedure and gain instant
access to the site. But should you leave
your system unattended with your
OmniPass user logged in, anyone using
your system can browse to your password
protected sites and gain automatic access.
If you uncheck both boxes in Settings for this Password
Site, OmniPass will prompt you for your master pass-
word or fingerprint authentication device. Once you
have authenticated with OmniPass your credentials will
be filled in to the site login prompt, but you will have to
click the website [OK], [Submit], or [Login] button to
gain access to the site.
114
If a machine is locked and OmniPass
detects a different user logging back in
with a fingerprint, the first user will be
logged out and the second user logged in.
In Windows XP, your login options must be set either for
classic login, or for fast user switching and logon screen
to be enabled to use your fingerprint to log on to
Windows. To change this go to Control Panel, select
User Accounts and then click Change the way users log
on or off. If your Windows screensaver is password
protected, the fingerprint capture window will now
appear next to screensaver password dialog during
resume. You can authenticate to your screensaver password prompt with your enrolled finger.
Password Management
OmniPass provides an interface that lets you manage
your passwords. To access this GUI, double-click the
OmniPass key in the system tray. Click Va ul t M a na ge -
ment; you will be prompted to authenticate. Once you
gain access to Vault Management, click Manage Pass-
words under Vault Settings. You will see the Manage
Passwords interface, with a list of friendly names.
Page 26

S7010.book Page 115 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Using the Fingerprint Sensor
You can view the credentials stored for any remembered
website by highlighting the desired resource under Pass-
word Protected Dialog and clicking Unmask Values.
Should a password be reset, or an account expire, you
can remove stored credentials from OmniPass. Highlight
the desired resource under Password Protected Dialog
and click Delete Page. You will be prompted to confirm
the password deletion.
The two check boxes in Manage Passwords govern
whether OmniPass prompts you to authenticate or
directly logs you into the remembered site.
OmniPass will overwrite an old set of credentials for a
website if you attempt to use Remember Password on an
already remembered site.
The exception to the above rule is the resetting of your
Windows password. If your password is reset in
Windows, then the next time you login to Windows,
OmniPass will detect the password change and prompt
you to “Update” or “Reconfirm” your password with
OmniPass. Enter your new Windows password in the
prompt(s) and click OK and your OmniPass "master
password" will still be your Windows password.
OmniPass User Identities
Identities allow OmniPass users to have multiple
accounts to the same site (e.g., bob@biblomail.com and
boballen@biblomail.com). If OmniPass did not provide
you identities, you would be limited to remembering
one account per site.
To create and manage identities, double-click the
OmniPass key in the system tray. Click Vau lt Ma na ge -
ment; OmniPass will prompt you to authenticate. Once
you gain access to Vault Management, click Manage
Identities under Vault Settings. You can only manage
the identities of the currently logged in OmniPass user
To add a new identity, click New Identity or double-click
Click here to add a new identity. Name the new identity
and click [OK], then click [Apply]. You can now switch
to the new identity and start remembering passwords.
To delete an identity, highlight the identity you want to
delete and click [Delete Identity], then click [Apply]
When you delete an identity, all of its
associated remembered sites and password
protected dialogs are lost.
.
To set the default identity, highlight the identity you
want as default and click [Set as Default]; click [Apply]
to ensure the settings are saved. If you log in to
OmniPass with a fingerprint device, you will automatically be logged in to the default identity for that
OmniPass user. You can choose the identity with which
you are logging in if you login using "master password".
Choosing User Identity during Login
To choose your identity during login, type your username in the User Name: field. Press [Tab] and see that
the Domain: field self-populates. Click the Password:
field to bring the cursor to it, and you will see the pulldown menu in the Identity: field. Select the identity you
wish to login as and then click OK to login.
Switch User Identity
To switch identities at any time, right-click the
OmniPass system tray icon and click Switch User Iden-
tity from the submenu. The Switch Identity dialog will
appear. Select the desired identity and then click OK.
Identities and Password Management
On the Manage Passwords interface of the Va u l t
Management tab of the OmniPass Control Center, there
is a pull-down selection box labeled, Identity. This field
lets you choose which identity you are managing passwords for. When you select an identity here, only those
password protected dialogs that are associated with that
identity are shown. You can perform all the functions
explained in “Password Management” on page 114.
CONFIGURING OMNIPASS
This section gives an overview of both the Export/
Import function and the OmniPass Control Center.
Exporting and Importing Users
Using the OmniPass Control Center, you can export and
import users in and out of OmniPass. The export
process backs up all remembered sites, credentials, and
any enrolled fingerprints for an OmniPass user. All
OmniPass data for a user is backed up to a single
encrypted database file. During the import process, the
Windows login of the exported user is required. If the
proper credentials cannot be supplied, the user profile
will not be imported
.
■
You should periodically export your user
profile and store it in a safe place. If
anything happens to your system, you
can import your OmniPass profile to a
new system and have all your remembered settings and fingerprints instantly.
■
You don't forget the Windows login
credentials when exporting. When you
examine the importation, you are
prompted for authentication. The
credentials that will allow a user profile
to be imported are the Windows login
credentials of the exported user. They
are the credentials that had to be
submitted when the user profile was
exported. You will need User Name,
Password, and Domai
n.
115
Page 27
S7010.book Page 116 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook – Appendix
Exporting an OmniPass User Profile
To export a user, open the OmniPass Control Center,
and click Import/Export User under Manage Users.
Click Exports an OmniPass user profile. OmniPass will
prompt you to authenticate. Upon successfully authentication, you must name the OmniPass user profile and
decide where to save it. An .opi file is generated, and you
should store a copy of it in a safe place.
This .opi file contains all your user specific OmniPass
data, and it is both encrypted and password protected.
This user profile does NOT contain any of your
encrypted data files.
Importing an OmniPass User Profile
You cannot import a user into OmniPass if
there already is a user with the same name
enrolled in OmniPass.
To import an OmniPass user open the OmniPass
Control Center, and click Import/Export User under
Manage Users. Click Imports a new user into OmniPass
and then select OmniPass Import/Export File (*.opi)
and click Next. OmniPass will then prompt you to
browse for the file you had previously exported (.opi
file). When you select the .opi file for importation,
OmniPass will prompt you for authentication. The
credentials that will allow a user profile to be imported
are the Windows login credentials of the exported user.
They are the credentials that had to be submitted when
the user profile was exported. You will need User Name,
Password, and Domain. If you don’t remember the value
for Domain, in a PC or SOHO environment Domain
should be your computer name.
OmniPass will notify you if the user was successfully
imported.
Things to Know Regarding Import/Export
■
Assume you export a local Windows User profile from
OmniPass. You want to import that profile to another
machine that has OmniPass. Before you can import
the profile, a Windows user with the same login credentials must be created on the machine importing the
profile.
Example: I have a Windows user with the username
“Tom” and the password “Sunshine” on my system. I
have enrolled Tom into OmniPass and remembered
passwords. I want to take all my passwords to new system. I export Tom’s OmniPass user profile. I go to my
new system and using the Control Panel I create a user
with the username "Tom" and the password "Sunshine". I can now successfully import the OmniPass
user data to the new system.
■
If you export an OmniPass-only user, you can import
that user to any computer running OmniPass, provided that a user with that name is not already
enrolled in OmniPass.
■
If you attempt to import a user profile who has the
same name as a user already enrolled in OmniPass, the
OmniPass import function will fail.
OMNIPASS CONTROL CENTER
This section will serve to explain functions within the
OmniPass Control Center that weren’t explained earlier.
You can access the OmniPass Control Center any of
three ways:
■
Double-click the golden OmniPass key shaped icon in
the Windows taskbar (typically in the lower-right corner of the desktop)
■
Click the Start button; select the Programs group;
select the Softex program group; and click the
OmniPass Control Center selection.
■
Open the Windows Control Panel (accessible via Start
button --> Settings --> Control Panel) and double-
click the Softex OmniPass icon.
User Management
The User Management tab has two major interfaces:
Add/Remove User and Import/Export User. Import/
Export User functionality is documented in “Exporting
and Importing Users” on page 115. Add/Remove User
functionality is straightforward.
If you click Adds a new user to OmniPass you will start
the OmniPass Enrollment Wizard. The Enrollment
Wizard is documented in “User Enrollment” on
page 112.
If you click Removes a user from OmniPass, OmniPass
will prompt you to authenticate. Authenticate with the
credentials (or enrolled fingerprint) of the user you wish
to remove. OmniPass will prompt you to confirm user
removal. Click OK to complete user removal
Removing a user will automatically destroy
all OmniPass data associated with that
user. All identities and credentials
associated with the user will be lost.
If you are sure about removing the user,
we recommend you export the user
profile.
User Settings
The User Settings tab has four interfaces: Audio Settings,
Tas k ba r T i ps , and Enrollment. User settings allow users
to customize OmniPass to suit their individual preferences. Under User Settings (Audio Settings and Ta s kb a r
Tips) you can set how OmniPass notifies the user of
OmniPass events (e.g., successful login, access denied,
.
116
Page 28

S7010.book Page 117 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Using the Fingerprint Sensor
etc.). The details of each setting under the Audio
Settings and Tas kb ar T ip s interfaces are self-explana-
tory.
The Enrollment interface allows you to enroll fingerprints. For the procedure to enroll and authentication
device refer to Chapter 2.3. To enroll additional fingerprints, click Enroll Authentication Device, and authen-
ticate with OmniPass. Select the fingerprint recognition
device in the Select Authentication Device screen (it
should already be marked by a green check if you have a
finger enrolled) and click Next.
System Settings
The OmniPass Startup Options interface can be found
in the System Settings tab. With these options you can
specify how your OmniPass Logon is tied to your
Windows Logon.
The first option, Automatically log on to OmniPass as
the current user, will do just as it says; during Windows
login, you will be logged on to OmniPass using your
Windows login credentials. If the user logging into
Windows was never enrolled into OmniPass, upon login
no one will be logged on to OmniPass. This setting is
appropriate for an office setting or any setting where
users must enter a username and password to log into a
computer. This is the default setting.
With the second option, Manually log on to OmniPass
at startup, OmniPass will prompt you to login once you
have logged on to Windows.
With the third option, Do not log on to OmniPass at
startup, OmniPass will not prompt for a user to be
logged on.
You can manually log on to OmniPass by right-clicking
the OmniPass taskbar icon and clicking Log in User
from the right-click menu.
TROUBLESHOOTING
You cannot use OmniPass to create Windows users. You
must first create the Windows user, and you will need
administrative privileges to do that. Once the Windows
user is created, you can add that user to OmniPass using
the same username and password
Cannot add Windows users to OmniPass
If you experience difficulties adding a Windows user
to OmniPass, you may need to adjust your local security settings. You can do this by going to Start,
Control Panel, Administrative Tools, and Local
Security Settings. Expand Local Policies, expand
Security Options, and double-click Network Access:
Sharing and Security Model for Local Accounts. The
correct setting should be Classic - Local Users Authenticate as Themselves.
Cannot add a User with a Blank Password to OmniPass
If you experience difficulties adding a user with a
blank password to OmniPass, you may need to adjust
your local security settings. First attempt the procedure explained in the Cannot add Windows user to
OmniPass section. If the difficulties persist, then try
the following procedure.
Click Start, Control Panel, Administrative Tools,
and Local Security Settings. Expand Local Policies,
expand Security Options, and double-click
Accounts: Limit local account use of blank passwords to console login only. This setting should be
set to Disabled.
Dialog appears after OmniPass authentication during
Windows Logon
After installing OmniPass on your system, you can
choose to logon to Windows using OmniPass. You
authenticate with OmniPass (via master password, or
an enrolled security device) and OmniPass logs you
into Windows. You may, during this OmniPass
authentication, see a Login Error dialog box.
This dialog box occurs when OmniPass was unable to
log you into Windows with the credentials supplied
(username and password). This could happen for any
of the following reasons:
■
Your Windows password has changed
■
Your Windows account has been disabled
If you are having difficulties due to the first reason,
you will need to update OmniPass with your changed
Windows account password. Click Update Password
and you will be prompted with a dialog to reconfirm
your password.
Enter the new password to your Windows user
account and click OK. If the error persists, then it is
unlikely the problem is due to your Windows user
account password changing.
117
Page 29

S7010.book Page 118 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook – Appendix
118
Page 30

S7010.book Page 119 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Index
Index
A
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
AC
adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
plug adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
ACPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Active-Matrix Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Anti-theft lock slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Application Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Auto/Airline Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27, 83
Automatically Downloading Driver Updates . . . . . . 67
B
Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
bay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
charging indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
cold-swapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
conserving power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
dead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
faulty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
increasing life . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
level indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
lithium ion battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40, 85
low . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60, 61
recharging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
replacing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
shorted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
suspend mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
BIOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
setup utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29, 83
Built-in Speakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
C
Cache Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
CapsLock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
CardBus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
CD-ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37, 83
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56, 57
Centrino . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Clicking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
CMOS RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Cold-swap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18, 41
COMM Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Configuration Label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10, 77
Controls and Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Conventions Used in the Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
CRT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Cursor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Cursor Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
D
DC Power Jack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Default Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Device Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50, 78
DIMM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45, 84
Disk care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Display Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6, 28
adjusting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
brightness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
closing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
latch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
opening . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
DMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
DMI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Docking Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Dolby Headphone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Double-Clicking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Dragging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Drivers and Application Restore CD . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
DVD drive
access indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
tray release . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
DVD/CD-RW combo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
DVD/CD-RW/CD-ROM
access indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
DVD/CD-RW/CD-ROM drive
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56, 57
DVD-RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
119
Page 31

S7010.book Page 120 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook
E
ECP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Emergency tray release . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Extended Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
External Floppy Disk Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
External Monitor Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7, 52
F
FDU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Fingerprint Sensor Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
enrolling a fingerprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
getting started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
installing OmniPass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
logging into a remembered site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
OmniPass authentication toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
password replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
remembering a password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
uninstalling OmniPass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
user enrollment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
using OmniPass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Flexible Bay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8, 18
cold-swapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
eject lever . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
installing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
removing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Floppy Disk
ejecting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
initializing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
loading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
preparing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
write protect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Fujitsu Contact Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Fujitsu Driver Update utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Fujitsu LifeBook
storing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
traveling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Function Key
F3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
F4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
F6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
F7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
F8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14, 17
F9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14, 17
FN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
H
Hard Disk Drive
access indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Headphone Jack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7, 52
Hibernation Feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
disable/enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
I
IDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
Infrared Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9, 51
Internal LAN Jack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
IrDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51, 85
IRQ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
K
Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6, 13
cursor keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
function keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
numeric keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
windows keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
L
LAN (RJ-45) Jack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
LifeBook Security Application Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
configuring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
deactivating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
deactivating and activating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
launching applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
operating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
uninstalling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
M
Media Player
care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
loading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
removing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37, 38
using . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Memory
capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
compartment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10, 45
installing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
120
Page 32
S7010.book Page 121 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
Index
removing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45, 46
upgrade module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Microphone Jack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7, 52
MIDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Modem Jack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Modem Result Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Modular Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
installing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
removing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Mouse
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
MPU-401 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Multi-Format DVD Writer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
N
NTSC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Numeric Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
NumLk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
O
Optical Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
P
Parallel Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50, 86
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58, 59
PC Card
access indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
installing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
removing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
PCMCIA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Pointing Device
See Touchpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Port Replicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
attaching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
back panel components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
detaching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
POST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Power
AC adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Auto/Airline adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59, 60
indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32, 33
Power On Self Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29, 64
Power/Suspend/Resume Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6, 32
Pre-Installed Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Adobe Acrobat Reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Fujitsu HotKey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
LifeBook Application Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
manuals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Norton AntiVirus 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Quicken New User Edition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
PS/2 Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
R
Registration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30, 31
Restarting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
RJ-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
RJ-45 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
S
ScrLk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
SDRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10, 45
Security Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Security Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51, 87
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58, 59
SMART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Audio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Chipset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Dimensions and Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Environmental Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Microprocessor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Status Indicator Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6, 11
Stereo Line-in Jack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Stereo Speakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
121
Page 33
S7010.book Page 122 Wednesday, October 20, 2004 9:14 AM
LifeBook S7000 Notebook
Suspend . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32, 87
S-Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
T
Touchpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6, 15
buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
U
Universal Serial Bus Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Unpacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
USB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8, 9, 51, 58
problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58, 59
V
Volume control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
W
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
WFM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Windows
Windows XP Home . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Windows XP Professional . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Windows keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Application key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Start keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Wireless LAN
access point (infrastructure) mode . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
activating the WLAN device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
ad hoc mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
before using the wireless LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
deactivating the WLAN device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Devices covered by this document . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
IP address information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
using Atheros Client Utility software . . . . . . . . . . 98
using Intel PROSet software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
wireless LAN glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
wireless network considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
122
 Loading...
Loading...