
查询MB90455供应商
FUJITSU SEMICONDUCTOR
DATA SHEET
16-bit Proprietary Microcontroller
CMOS
F2MC-16LX MB90455 Series
MB90F455 (S) /F456 (S) /F457 (S)
MB90455 (S) /456 (S) /457 (S) /V495G
DESCRIPTION
■
MB90455 series devices are general-purpose high-performance 16-bit micro controllers designed for process
control of consumer products, which require high-speed real-time processing.
The system, inheriting the architecture of F
guages, expanded addressing mode , enhanced multiply-divide instructions, and enriched bit-processing instructions. Furthermore, employment of 32-bit accumulator achieves processing of long-word data (32 bits).
The peripheral resources of MB90455 series include the following:
8/10-bit A/D converter, UART 1, 8/16-bit PPG timer , 16-bit input-output timer (16-bit free-run timer, input capture
0, 1, 2, 3 (ICU)).
2
MC”, an abbreviation for FUJITSU Flexible Microcontroller, is a registered trademark of FUJITSU Ltd.
*: “F
2
MC* family, employs additional instruction ready for high-level lan-
DS07-13728-3E
FEATURES
■
••••
Clock
• Built-in PLL clock frequency multiplication circuit
• Selection of machine clocks (PLL clocks) is allowed among frequency division by two on oscillation clock, and
multiplication of 1 to 4 times of oscillation clock (for 4-MHz oscillation clock, 4 MHz to 16 MHz).
• Operation by sub-clock (8.192 kHz) is allowed.
• Minimum execution time of instruction: 62.5 ns (when operating with 4-MHz oscillation cloc k, and 4-time m ultiplied PLL clock).
(Continued)
PACKAGE
■
48-pin plastic-LQFP
(FPT-48P-M26)

MB90455 Series
••••
16 Mbyte CPU memory space
• 24-bit internal addressing
••••
Instruction system best suited to controller
• Wide choice of data types (bit, byte, word, and long word)
• Wide choice of addressing modes (23 types)
• Enhanced multiply-divide instructions and RETI instructions
• Enhanced high-precision computing with 32-bit accumulator
••••
Instruction system compatible with high-level language (C language) and multitask
• Employing system stack pointer
• Enhanced various pointer indirect instructions
• Barrel shift instructions
••••
Increased processing speed
• 4-byte instruction queue
••••
Powerful interrupt function with 8 levels and 34 factors
••••
Automatic data transfer function independent of CPU
• Expanded intelligent I/O service function (EI
••••
Low power consumption (standby) mode
• Sleep mode (a mode that halts CPU operating clock)
• Time-base timer mode (a mode that operates oscillation clock, sub clock, time-base timer and cloc k timer only)
• Clock mode (a mode that operates sub clock and clock timer only)
• Stop mode (a mode that stops oscillation clock and sub clock)
• CPU blocking operation mode
2
OS): Maximum of 16 channels
••••
Process
•CMOS technology
••••
I/O port
• General-purpose input/output port (CMOS output): 34 por ts(MB90F455/F456/F457, MB90455/456/457) (including 4 high-current output ports) (When sub clock is not used, 36 ports(MB90F455S/F456S/F457S,
MB90455S/456S/457S))
••••
Timer
• Time-base timer, clock timer, watchdog timer: 1 channel
• 8/16-bit PPG timer: 8-bit x 4 channels, or 16-bit x 2 channels
• 16-bit reload timer: 2 channels
• 16-bit input/output timer
- 16-bit free run timer: 1 channel
- 16-bit input capture: (ICU): 4 channels
Interrupt request is issued upon latching a count value of 16-bit free run timer by detection of an edge on pin
input.
••••
UART 1: 1 channel
• Equipped with full-duplex double buffer
• Clock-asynchronous or clock-synchronous serial transmission is available
(Continued)
2

(Continued)
••••
DTP/External interrupt: 4 channels
• Module for activation of expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
••••
Delay interrupt generator module
• Generates interrupt request for task switching.
••••
8/10-bit A/D converter: 8 channels
• Resolution is selectable between 8-bit and 10-bit.
• Activation by external trigger input is allowed.
• Conversion time: 6.125 µs (at 16-MHz machine clock, including sampling time)
••••
Program patch function
• Address matching detection for 2 address pointers.
2
OS), and generation of external interrupt.
MB90455 Series
3

MB90455 Series
PRODUCT LINEUP
■
Part Number
Parameter
Classification Flash ROM Mask ROM Evaluation product
ROM capacity
RAM capacity 2 Kbytes 6 Kbytes
Clock
Process CMOS
Package LQFP-48 (0.50 mm width) PGA256
Operating power supply voltage 3.5 V to 5.5 V
Special power supply for
emulator*
CPU functions
Low power consumption
(standby) mode
I/O port
Time-base timer
Watchdog timer
16-bit input/
output timer
16-bit reload timer
Clock timer
1
16-bit free-run
timer
Input capture
MB90F455 (S) /
F456 (S) /F457 (S)
MB90F455 (S) : 24 Kbytes
MB90F456 (S) : 32 Kbytes
MB90F457 (S) : 64 Kbytes
MB90F455/F456/F457 :
2 systems
MB90F455S/F456S/F457S :
1 system
None
Number of basic instructions
Instruction bit length
Instruction length
Data bit length
Minimum instruction execution time : 62.5 ns (at 16-MHz machine clock)
Interrupt processing time : 1.5 µs at minimum (at 16-MHz machine clock)
Sleep mode/Clock mode/Time-base timer mode/
Stop mode/CPU intermittent
General-purpose input/output ports (CMOS output) : 34 ports (36 ports*
including 4 high-current output ports (P14 to P17)
18-bit free-run counter
Interrupt cycle : 1.024 ms, 4.096 ms, 16.834 ms, 131.072 ms
(with oscillation clock frequency at 4 MHz)
Reset generation cycle: 3.58 ms, 14.33 ms, 57.23 ms, 458.75 ms
(with oscillation clock frequency at 4 MHz)
Number of channels: 1
Interrupt upon occurrence of overflow
Number of channels: 4
Retaining free-run timer value set by pin input (rising edge, falling edge, and
both edges)
Number of channels: 2
16-bit reload timer operation
Count clock cycle: 0.25 µs, 0.5 µs, 2.0 µs
(at 16-MHz machine clock frequency)
External event count is allowed.
15-bit free-run counter
Interrupt cycle: 31.25 ms, 62.5 ms, 12 ms, 250 ms, 500 ms, 1.0 s, 2.0 s
(with 8.192 kHz sub clock)
MB90455 (S) /
456 (S) /457 (S)
MB90455 (S) : 24 Kbytes
MB90456 (S) : 32 Kbytes
MB90457 (S) : 64 Kbytes
MB90455/456/457 :
2 systems
MB90455S/456S/457S :
1 system
: 351 instructions
: 8 bits and 16 bits
: 1 byte to 7 bytes
: 1 bit, 8 bits, 16 bits
MB90V495G
2 systems
4.5 V
to 5.5 V
2
)
(Continued)
4

(Continued)
Parameter
8/16-bit PPG timer
Part Number
MB90455 Series
MB90F455 (S) /
F456 (S) /F457 (S)
Number of channels: 2 (four 8-bit channels are available also)
PPG operation is allowed with four 8-bit channels or one 16-bit channel.
Outputting pulse wave of arbitrary cycle or arbitrary duty is allowed.
Count clock: 62.5 ns to 1 µs
(with 16 MHz machine clock)
MB90455 (S) /
456 (S) /457 (S)
MB90V495G
Delay interrupt generator
module
DTP/External interrupt
8/10-bit A/D converter
UART 1
*1 : Settings of DIP switch S2 f or using emulation pod MB2145-507. For details, See MB2145-507 Hardw are Manual
(2.7 Power Pin solely for Emulator).
*2 : MB90F455S/F456S/F457S, MB90455S/456S/457S
Interrupt generator module for task switching. Used for Real-time OS.
Number of inputs: 4
Activated by rising edge, falling edge, “H” level or “L” level input.
External interrupt or expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
Number of channels: 8
Resolution: Selectable 10-bit or 8-bit.
Conversion time: 6.125 µs (at 16-MHz machine clock, including sampling time)
Sequential conversion of two or more successive channels is allowed. (Setting
a maximum of 8 channels is allowed.)
Single conversion mode : Selected channel is converted only once.
Sequential conversion mode: Selected channel is converted repetitively.
Halt conversion mode : Conversion of selected channel is stopped and
activated alternately.
Number of channels: 1
Clock-synchronous transfer: 62.5 Kbps to 2 Mbps
Clock-asynchronous transfer: 9,615 bps to 500 Kbps
Communication is allowed by bi-directional serial communication function and
master/slave type connection.
2
OS) is available.
5

MB90455 Series
PACKAGES AND PRODUCT MODELS
■■■■
Packa ge MB90F455 (S) /F456 (S) /F457 (S) MB90455 (S) /456 (S) /457 (S)
FPT-48P-M26
: Yes × : No
Note : Refer to “ PACKAGE DIMENSION” for details of the package.
PRODUCT COMPARISON
■■■■
Memory space
When testing with test product for evaluation, check the differences between the product and a product to be
used actually. Pay attention to the following points:
• The MB90V495G has no built-in ROM. However, a special-purpose development tool allows the operations
as those of one with built-in ROM. ROM capacity depends on settings on a development tool.
• On MB90V495G, an image from FF4000
FF3FFFH is viewed only on FE bank and FF bank. (Modified on settings of a development tool.)
• On MB90F455 (S) /F456 (S) /F457 (S) , MB90455 (S) /456 (S) /457 (S) , an image from FF4000
is viewed on 00 bank and an image of FE0000H to FF3FFFH is viewed only on FF bank.
H to FFFFFFH is viewed on 00 bank and an image of FE0000H to
H to FFFFFFH
6

PIN ASIGNMENT
■■■■
(TOP VIEW)
X1A/P36*
X0A/P35*
P33
AVSS
P32
P31
P30
P44
P43
P42/SOT1
P41/SCK1
P40/SIN1
MB90455 Series
AVCC
AVR
P50/AN0
P51/AN1
P52/AN2
P53/AN3
P54/AN4
P55/AN5
P56/AN6
P57/AN7
P37/ADTG
P20/TIN0
4847464544434241403938
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1314151617181920212223
P22/TIN1
P24/INT4
P25/INT5
P21/TOT0
P26/INT6
P23/TOT1
MD2
P27/INT7
MD1
MD0
37
24
RST
CC
V
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
(FPT-48P-M26)
* : MB90F455/F456/F457, MB90455/456/457 : X1A, X0A
MB90F455S/F456S/F457S, MB90455S/456S/457S : P36, P35
P17/PPG3
P16/PPG2
P15/PPG1
P14/PPG0
P13/IN3
P12/IN2
P11/IN1
P10/IN0
X1
X0
C
V
SS
7

MB90455 Series
PIN DESCRIPTION
■
Pin No. Pin name
1AVcc Vcc power input pin for A/D converter
2 AVR Power (Vref+) input pin for A/D converter. Use as input for Vcc or lower.
Circuit
format
Description
P50 to P57
3 to 10
AN0 to AN7
P37
11
ADTG
P20
12
TIN0
P21
13
TOT0
P22
14
TIN1
P23
15
TOT1
P24 to P27
16 to 19
INT4 to INT7
20 MD2 F Input pin for specifying operation mode. Connect directly to Vss.
E
D
D
D
D
D
D
General-purpose input/output ports.
Functions as an analog input pin for A/D converter. Valid when analog
input setting is “enabled.”
General-purpose input/output port.
Function as an external trigger input pin for A/D converter. Use the pin by
setting as input port.
General-purpose input/output port.
Function as an event input pin for reload timer 0. Use the pin by setting as
input port.
General-purpose input/output port.
Function as an event output pin for reload timer 0. Valid only when output
setting is “enabled.”
General-purpose input/output port.
Function as an event input pin for reload timer 1. Use the pin by setting as
input port.
General-purpose input/output port.
Function as an event output pin for reload timer 1. Valid only when output
setting is “enabled.”
General-purpose input/output ports.
Functions as an external interrupt input pin. Use the pin by setting as input
port.
21 MD1 C Input pin for specifying operation mode. Connect directly to Vcc.
22 MD0 C Input pin for specifying operation mode. Connect directly to Vcc.
23 RST B External reset input pin.
24 Vcc Power source (5 V) input pin.
25 Vss Power source (0 V) input pin.
26 C
27 X0 A Pin for high-rate oscillation.
28 X1 A Pin for high-rate oscillation.
P10 to P13
29 to 32
IN0 to IN3
8
D
Capacitor pin for stabilizing power source. Connect a ceramic capacitor of
approximately 0.1 µF.
General-purpose input/output ports.
Functions as trigger input pins of input capture channels 0 to 3. Use the
pins by setting as input ports.
(Continued)

(Continued)
Pin No. Pin name
Circuit
format
MB90455 Series
Description
P14 to P17
33 to 36
PPG0 to PPG3
P40
37
SIN1 Serial data input pin for UART. Use the pin by setting as input port.
P41
38
SCK1
P42
39
SOT1
40 P43 D General-purpose input/output port.
41 P44 D General-purpose input/output port.
42 to 45 P30 to P33 D General-purpose input/output ports.
X0A*
46
P35* General-purpose input/output port.
X1A*
47
P36* General-purpose input/output port.
G
D
D
D
A
A
General-purpose input/output ports. High-current output ports.
Functions as output pins of PPG timers 01 and 23. Valid when output
setting is “enabled.”
General-purpose input/output port.
General-purpose input/output port.
Serial clock input pin for UART. Valid only when serial clock input/output
setting on UART is “enabled.”
General-purpose input/output port.
Serial data input pin for UART. Valid only when serial data input/output
setting on UART is “enabled.”
Pin for low-rate oscillation.
Pin for low-rate oscillation.
48 AVss Vss power source input pin for A/D converter.
* : MB90F455/F456/F457, MB90455/456/457 : X1A, X0A
MB90F455S/F456S/F457S, MB90455S/456S/457S : P36, P35
9

MB90455 Series
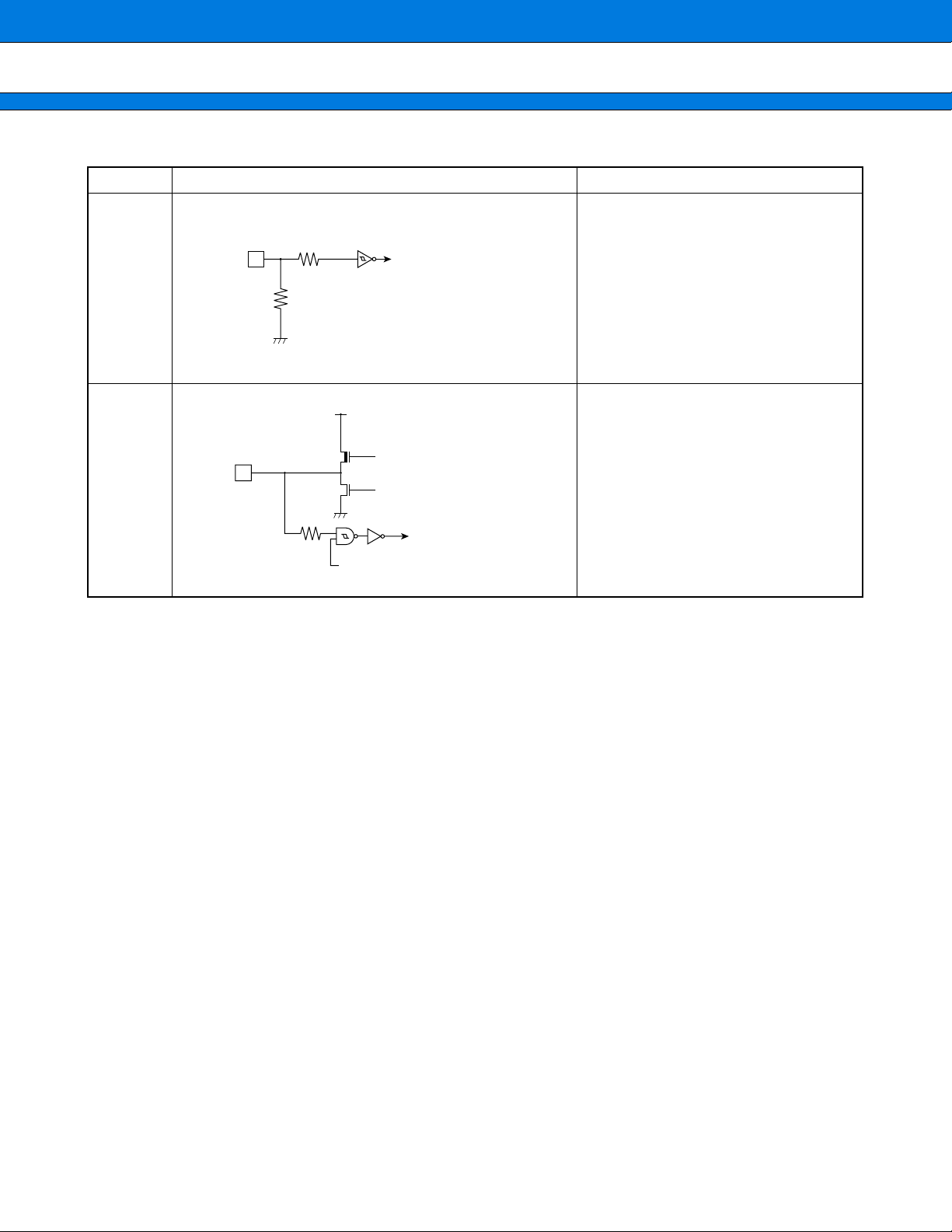
I/O CIRCUIT TYPE
■
Type Circuit Remarks
• High-rate oscillation feedback
X1
Clock input
X1A
A
X0
resistor, approx.1 MΩ
• Low-rate oscillation feedback
resistor, approx.10 MΩ
X0A
Standby control signal
• Hysteresis input with pull-up
Vcc
resistor.
• Pull-up resistor, approx.50 kΩ
B
R
R
Hysteresis input
• Hysteresis input
C
R
Hysteresis input
• CMOS hysteresis input
Vcc
• CMOS level output
• Standby control provided
Pch
Digital output
D
R
Digital output
Nch
Vss
Hysteresis input
10
Standby control
• CMOS hysteresis input
Vcc
• CMOS level output
• Shared for analog input pin
Pch
Digital output
E
R
Digital output
Nch
Vss
• Standby control provided
Hysteresis input
Standby control
Analog input
(Continued)
MB90455 Series
(Continued)
Type Circuit Remarks
• Hysteresis input with pull-down
resistor
R
Hysteresis input
F
R
Vss
Vcc
Pch
High-current output
• Pull-down resistor, approx. 50 kΩ
• FLASH product is not provided with
pull-down resistor.
• CMOS hysteresis input
• CMOS level output (high-current
output)
• Standby control provided
G
R
High-current output
Nch
Vss
Hysteresis input
Standby control
11

MB90455 Series
HANDLING DEVICES
■■■■
••••
Do not exceed maximum rating (preventing “latch up”)
• On a CMOS IC, latch-up may occur when applying a voltage higher than Vcc or a voltage lower than Vss to
input or output pin, which has no middle or high withstand voltage. Latch-up may also occur when a voltage
exceeding maximum rating is applied across Vcc and Vss.
• Latch-up causes drastic increase of power current, which ma y lead to destruction of elements by heat. Extreme
caution must be taken not to exceed maximum rating.
• When turning on and off analog power source, take extra care not to apply an analog power voltages (AVcc
and AVR) and analog input voltage that are higher than digital power voltage (Vcc).
••••
Handling unused pins
• Leaving unused input pins open may cause permanent destruction by malfunction or latch-up. Apply pull-up
or pull-down process to the unused pins using resistors of 2 kΩ or higher . Leav e unused input pins open under
output status, or process as input pins if they are under input status.
••••
Using external clock
• When using an external clock, drive only X0 pin and leav e X1 pin open. An e xample of using an e xternal clock
is shown below.
Using external clock
X0
Open
••••
Notes when using no sub clock
• If an oscillator is not connected to X0A and X1A pin, apply pull-down resistor to X0A pin and leav e X1A pin open.
••••
About power supply pins
• If two ore more Vcc and Vss exist, the pins that should be at the same potential are connected to each other
inside the device. For reducing unwanted emissions and preventing malfunction of strobe signals caused by
increase of ground lev el, howev er , be sure to connect the Vcc and Vss pins to the power source and the ground
externally .
• Pay attention to connect a power supply to Vcc and Vss of MB90455 series device in a lowest-possible
impedance.
• Near pins of MB90455 series device, connecting a bypass capacitor is recommended at 0.1 µF across Vcc
and Vss.
••••
Crystal oscillator circuit
• Noises around X0 and X1 pins cause malfunctions on a MB90455 series device. Design a print circuit so that
X0 and X1 pins, an crystal oscillator (or a ceramic oscillator), and bypass capacitor to the ground become as
close as possible to each other. Furthermore, avoid wires to X0 and X1 pins crossing each other as much as
possible.
• Print circuit designing that surrounds X0 and X1 pins with grounding wires, which ensures stable operation,
is strongly recommended.
X1
MB90455 series
12

MB90455 Series
••••
Caution on Operations during PLL Clock Mode
• If the PLL clock mode is selected, the microcontroller attempt to be working with the self-oscillating circuit ev en
when there is no external oscillator or external clock input is stopped. P erf ormance of this operation, howe v er ,
cannot be guaranteed.
••••
Sequence of turning on power of A/D converter and applying analog input
• Be sure to turn on digital power (Vcc) before applying signals to the A/D converter and applying analog input
signals (AN0 to AN7 pins).
• Be sure to turn off the power of A/D converter and analog input before turning off the digital power source.
• Be sure not to apply AVR exceeding AVcc when turning on and off. (No problems occur if analog and digital
power is turned on and off simultaneously.)
••••
Handling pins when A/D converter is not used
• If the A/D converter is not used, connect the pins under the following conditions: “AVcc=AVR=Vcc,” and
“Avss=Vss”
••••
Note on turning on power
• For preventing malfunctions on built-in step-down circuit, maintain a minimum of 50 µs of voltage rising time
(between 0.2 V and 2.7 V) when turning on the power.
••••
Stabilization of supply voltage
• A sudden change in the supply voltage may cause the device to malfunction even within the specified Vcc
supply voltage operating range. Therefore, the Vcc supply voltage should be stabilized.
For reference, the supply voltage should be controlled so that Vcc ripple variations (peak-to-peak values) at
commercial frequencies (50 Hz to 60 Hz) fall below 10% of the standard V
of fluctuation does not exceed 0.1 V/ms at instantaneous power switching.
CC supply voltage and the coefficient
13

MB90455 Series
BLOCK DIAGRAM
■
X0,X1
RST
X0A,X1A
SOT1
SCK1
SIN1
AVcc
AVss
AN0 ~ AN7
AVR
ADTG
Clock
control circuit
Clock timer
Time-base timer
RAM
ROM/FLASH
Prescaler
UART1
8/10-bit A/D
converter (8ch)
CPU
2
F
MC-16LX core
Internal data bus
16-bit
free-run timer
Input
capture
(4ch)
16-bit
PPG timer
(2ch)
DTP/External
interrupt
16-bit
reload timer
(2ch)
IN0 ~ IN3
PPG0 ~ PPG3
INT4 ~ INT7
TIN0,TIN1
TOT0,TOT1
14

MB90455 Series
MEMORY MAP
■■■■
MB90455 series allows specifying a memory access mode “single chip mode.”
1. Memory allocation of MB90455
MB90455 series model has 24-bit wide internal address bus and up to 24-bit bus of external address bus.
A maximum of 16 Mbyte memory space of external access memory is accessible.
2. Memory map
000000H
0000C0H
000100H
Address #1*
003800H
004000H
010000H
FE0000H
FF0000H
Address #2*
FFFFFFH
(with ROM mirroring
function available)
Peripheral
RAM area
1
Register
Extension IO
area
(with ROM mirroring
function not available)
Peripheral
RAM area
Register
Extension IO
area
ROM area
(FF bank image)
ROM area*
1
ROM area
2
Product
ROM area*
ROM area
Address #1*
2
1
Address #2*
MB90F455 (S) /455 (S) 000900H FFA000H
MB90F456 (S) /456 (S) 000900H FF8000H
1
MB90F457 (S) /457 (S) 000900H FF0000H
MB90V495G 001900H
: Internal access memory
: Access disallowed
*1 : Addresses #1 and #3 are product-specific.
*2 : On MB90F455 (S) /F456 (S) /F457 (S) , 455 (S) /456 (S) /457 (S) , to read “FE0000
“FEFFFF
H” is to read out “FF0000H” to “FFFFFFH”.
H” to
Note : When internal ROM is operating, F2MC-16LX allows viewing ROM data image on FF bank at upper-level of
00 bank. This function is called “mirroring ROM,” which allows effective use of C compiler small model.
2
F
MC-16LX assigns the same low order 16-bit address to FF bank and 00 bank, which allows referencing
table in ROM without specifying “far” using pointer.
For e xample, when accessing to “00C000
H”, ROM data at “FFC000H” is accessed actually . Howe ver , because
ROM area of FF bank exceeds 48 Kb ytes, viewing all areas is not possible on 00 bank image . Because ROM
data of “FF4000
“FF4000
H” to “FFFFFFH.”
H” to “FFFFFFH” is viewed on “004000H” to “00FFFFH” image, store a R OM data table in area
15

MB90455 Series
I/O MAP
■■■■
Address
000000
Register
abbreviation
H (Reserved area) *
Register name Reset value
Peripheral
function name
Read/
Write
000001H PDR1 Port 1 data register XXXXXXXXB Port 1 R/W
000002
H PDR2 Port 2 data register XXXXXXXXB Port 2 R/W
000003H PDR3 Port 3 data register XXXXXXXXB Port 3 R/W
000004H PDR4 Port 4 data register XXXXXXXXB Port 4 R/W
000005
H PDR5 Port 5 data register XXXXXXXXB Port 5 R/W
000006H
to
000010
000011
000012
H
H DDR1 Port 1 direction data register 00000000B Port 1 R/W
H DDR2 Port 2 direction data register 00000000B Port 2 R/W
(Reserved area) *
000013H DDR3 Port 3 direction data register 000X0000B Port 3 R/W
000014H DDR4 Port 4 direction data register XXX00000B Port 4 R/W
000015
H DDR5 Port 5 direction data register 00000000B Port 5 R/W
000016H
to
00001A
00001B
00001C
to
000025
000026
H
H ADER Analog input permission register 11111111B
H
H
H SMR1 Serial mode register 1 00000000B
(Reserved area) *
(Reserved area) *
8/10-bit
A/D converter
R/W
R/W
000027H SCR1 Serial control register 1 00000100B R/W, W
000028
000029
00002A
00002B
00002C
to
00002F
000030
000031
000032
000033
SIDR1/
H
SODR1
H SSR1 Serial status data register 1 00001000B R, R/W
H (Reserved area) *
H CDCR1
H
Serial input data register 1/ Serial
output data register 1
Communication prescaler control
register 1
XXXXXXXXB R, W
0XXX0000B UART1 R/W
(Reserved area) *
H
H ENIR
H EIRR
H (Reserved area) *
H ELVR Detection level setting register 00000000B
DTP/External interrupt permission
register
DTP/External interrupt permission
register
00000000B
XXXXXXXXB R/W
UART1
DTP/External
interrupt
DTP/External
interrupt
R/W
R/W
16
(Continued)

MB90455 Series
Address
000034
Register
abbreviation
H
Register name Reset value
00000000
Peripheral
function name
B
Read/
Write
R/W
ADCS A/D control status register
000035
000036
H 00000000B R/W, W
H
XXXXXXXX
8/10-bit
A/D converter
B W, R
ADCR A/D data register
000037H 00101XXXB R
000038
00003F
000040
000041H PPGC1
000042
000043
000044H PPGC2
000045H PPGC3
H
to
H
H PPGC0
PPG0 operation mode control
register
(Reserved area) *
PPG1 operation mode control
register
H PPG01
H (Reserved area) *
PPG0/1 count clock selection
register
PPG2 operation mode control
register
PPG3 operation mode control
register
0X000XX1B
0X000001B R/W, W
8/16-bit
PPG timer 0/1
R/W, W
000000XXB R/W
0X000XX1B
0X000001B R/W, W
8/16-bit
PPG timer 2/3
R/W, W
000046
000047
H PPG23
H
to
00004F
H
000050H
IPCP0 Input capture data register 0
000051
H XXXXXXXXB
000052H
IPCP1 Input capture data register 1
000053
H XXXXXXXXB
000054H ICS01
000055
H ICS23 00000000B
000056H
TCDT Timer counter data register
000057
H 00000000B
PPG2/3 count clock selection
register
(Reserved area) *
Input capture control status register
000000XXB R/W
XXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXX
00000000B
00000000
B
B
16-bit input/output
timer
B
R/W
R/W
R
R
000058H TCCS Timer counter control status register 00000000B R/W
000059H (Reserved area) *
00005A
00005B
00005CH
00005D
H
XXXXXXXX
IPCP2 Input capture data register 2
H XXXXXXXXB
XXXXXXXX
IPCP3 Input capture data register 3
H XXXXXXXXB
B
16-bit input/output
timer
B
R
R
(Continued)
17

MB90455 Series
Address
00005E
to
000065
000066
000067
000068
000069
00006AH
to
00006E
00006F
000070
to
00007F
000080H
to
00008F
Register
abbreviation
H
Register name Reset value
Peripheral
function name
Read/
Write
(Reserved area) *
H
H
TMCSR0
H XXXX0000B R/W
00000000
B
16-bit reload timer 0
R/W
Timer control status register
H
00000000
TMCSR1
H XXXX0000B R/W
B
16-bit reload timer 1
R/W
(Reserved area) *
H
ROM mirroring
function selection
module
W
H ROMM
H
ROM mirroring function selection
register
XXXXXXX1B
(Reserved area) *
H
(Reserved area) *
H
000090
00009D
00009E
00009F
0000A0
0000A1
0000A2
0000A7
H
to
H
H PACSR Address detection control register 00000000B
H DIRR
H LPMCR
H CKSCR Clock selection register 11111100B Clock R,R/W
H
Delay interrupt request generation/
release register
Lowe power consumption mode
control register
to
H
(Reserved area) *
XXXXXXX0B
00011000B
(Reserved area) *
Address matching
detection function
Delay interrupt
generation module
Lowe power
consumption mode
R/W
R/W
W,R/W
0000A8H WDTC Watchdog timer control register XXXXX111B Watchdog timer R,W
0000A9
0000AA
H TBTC Time-base timer control register 1XX00100B Time-base timer R/W,W
H WTC Clock timer control register 1X001000B Clock timer R,R/W
0000ABH
to
0000AD
H
(Reserved area) *
(Continued)
18

MB90455 Series
Address
0000AE
0000AF
Register
abbreviation
H FMCS
H (Reserved area) *
Flash memory control status
register
Register name Reset value
000X0000B
0000B0H ICR00 Interrupt control register 00 00000111B
0000B1
H ICR01 Interrupt control register 01 00000111B
0000B2H ICR02 Interrupt control register 02 00000111B
0000B3H ICR03 Interrupt control register 03 00000111B
0000B4H ICR04 Interrupt control register 04 00000111B
0000B5H ICR05 Interrupt control register 05 00000111B
0000B6H ICR06 Interrupt control register 06 00000111B
0000B7H ICR07 Interrupt control register 07 00000111B
0000B8H ICR08 Interrupt control register 08 00000111B
0000B9H ICR09 Interrupt control register 09 00000111B
0000BAH ICR10 Interrupt control register 10 00000111B
0000BBH ICR11 Interrupt control register 11 00000111B
0000BCH ICR12 Interrupt control register 12 00000111B
Peripheral
function name
512 k-bit flash
memory
Read/
Write
R,W,R/W
Interrupt controller R/W
0000BDH ICR13 Interrupt control register 13 00000111B
0000BEH ICR14 Interrupt control register 14 00000111B
0000BFH ICR15 Interrupt control register 15 00000111B
0000C0H
to
0000FF
001FF0
001FF2H
001FF3H
001FF5H
003900H
003901
H
H
H
PADR0
Detection address setting register 0
(low-order)
Detection address setting register 0
(middle-order)
Detection address setting register 0
(high-order)
Detection address setting register 1
(low-order)
PADR1
Detection address setting register 1
(middle-order)
Detection address setting register 1
(high-order)
TMR0/
TMRLR0
H XXXXXXXXB
16-bit timer register 0/16-bit reload
register
(Reserved area) *
XXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXB
XXXXXXXXB
XXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXB
XXXXXXXXB
XXXXXXXX
B
Address matching
detection function
B
B
16-bit reload
timer 0
R/W001FF1
R/W001FF4H
R,W
(Continued)
19

MB90455 Series
(Continued)
Address
003902
003903
Register
abbreviation
H
TMR1/
TMRLR1
H XXXXXXXXB
16-bit timer register 1/16-bit reload
register
Register name Reset value
XXXXXXXX
B
Peripheral
function name
16-bit reload timer 1 R,W
003904H
to
00390F
003910
003911
H
H PRLL0 PPG0 reload register L XXXXXXXXB
H PRLH0 PPG0 reload register H XXXXXXXXB R/W
(Reserved area) *
003912H PRLL1 PPG1 reload register L XXXXXXXXB R/W
003913
H PRLH1 PPG1 reload register H XXXXXXXXB R/W
8/16-bit PPG timer
003914H PRLL2 PPG2 reload register L XXXXXXXXB R/W
003915H PRLH2 PPG2 reload register H XXXXXXXXB R/W
003916
H PRLL3 PPG3 reload register L XXXXXXXXB R/W
003917H PRLH3 PPG3 reload register H XXXXXXXXB R/W
003918H
to
003BFF
003C00
to
003C0F
003C10
to
003FFF
H
H
H
H
H
(Reserved area) *
RAM (General purpose RAM)
(Reserved area) *
Read/
Write
R/W
Reset values :
0 : Reset value of this bit is “0.”
1 : Reset value of this bit is “1.”
X : Reset value of this bit is undefined.
* : “Reserved area” should not be written anything. Result of reading from “Reserved area” is undefined.
20

MB90455 Series
■■■■
INTERRUPT SOURCES, INTERRUPT VECTORS, AND INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTERS
2
EI
Interrupt source
Reset #08 08
INT 9 instruction #09 09
Exceptional treatment #10 0A
OS
readiness
×
×
×
Interrupt vector Interrupt control register
Number Address ICR Address
H FFFFDCH High
H FFFFD8H ↑
H FFFFD4H
Reserved × #11 0BH FFFFD0H
Reserved × #12 0CH FFFFCCH
Reserved #13 0DH FFFFC8H
Reserved #14 0EH FFFFC4H
Reserved #15 0FH FFFFC0H
Time-base timer #16 10H FFFFBCH
×
×
×
×
16-bit reload timer 0 ∆ #17 11H FFFFB8H
8/10-bit A/D converter ∆ #18 12H FFFFB4H
16-bit free-run timer overflow ∆ #19 13H FFFFB0H
Reserved #20 14H FFFFACH
Reserved #21 15H FFFFA8H
×
×
PPG timer ch0, ch1 underflow × #22 16H FFFFA4H
Input capture 0-input ∆ #23 17H FFFFA0H
External interrupt (INT4/INT5) ∆ #24 18H FFFF9CH
ICR00 0000B0H
ICR01 0000B1H
ICR02 0000B2H
ICR03 0000B3H*
ICR04 0000B4H
ICR05 0000B5H
ICR06 0000B6H*
1
1
Priority*
3
Input capture 1-input ∆ #25 19H FFFF98H
ICR07 0000B7H*
2
PPG timer ch2, ch3 underflow × #26 1AH FFFF94H
External interrupt (INT6/INT7) ∆ #27 1BH FFFF90H
ICR08 0000B8H*
1
Clock timer ∆ #28 1CH FFFF8CH
Reserved #29 1DH FFFF88H
Input capture 2-input
Input capture 3-input
Reserved #31 1FH FFFF80H
Reserved #32 20H FFFF7CH
Reserved #33 21H FFFF78H
Reserved #34 22H FFFF74H
Reserved #35 23H FFFF70H
×
× #30 1EH FFFF84H
×
×
×
×
×
ICR09 0000B9H
ICR10 0000BAH
ICR11 0000BBH
↓
ICR12 0000BCH
16-bit reload timer 1 #36 24H FFFF6CH Low
(Continued)
21

MB90455 Series
(Continued)
2
OS
Cause of interrupt
EI
readiness
UART1 reception completed #37 25
UART1 transmission completed ∆ #38 26
Reserved #39 27
Reserved #40 28H FFFF5CH
Flash memory #41 29H FFFF58H
Delay interrupt generation
module
×
×
×
×
: Available
×
: Unavailable
: Available El
2
OS function is provided.
∆ : Available when a cause of interrupt sharing a same ICR is not used.
*1: • Peripheral functions sharing an ICR register have the same interrupt level.
• If peripheral functions share an ICR register, only one function is available when using expanded intelligent
I/O service (EI
2
OS) .
• If peripheral functions share an ICR register, a function using expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
not allow interrupt by another function.
*2: Input capture 1 is ready only for EI
2
EI
OS with Input capture 1.
2
OS, and PPG is not ready for EI2OS. Disable PPG interrupt when using
*3: Priority when two or more interrupts of a same level occur simultaneously.
Interrupt vector Interrupt control register
Number Address ICR Address
H FFFF68H
ICR13 0000BDH*
H FFFF64H ↑
H FFFF60H
ICR14 0000BEH
ICR15 0000BFH
#42 2AH FFFF54H
1
2
Priority*
High
↓
Low
OS) does
3
22

MB90455 Series
PERIPHERAL RESOURCES
■■■■
1. I/O Ports
The I/O ports are used as general-pur pose input/output ports (parallel I/O ports). The MB90455 series model
is provided with 5 ports (34 inputs). The ports function as input/output pins for peripheral functions also.
••••
I/O port functions
An I/O port, using port data resister (PDR), outputs the output data to I/O pin and input a signal input to I/O port.
The port direction register (DDR) specifies direction of input/output of I/O pins on a bit-by-bit basis.
The following summarizes functions of the ports and sharing peripheral functions :
• Port 1 : General-purpose input/output port, used also for PPG timer output and input capture inputs.
• Port 2 : General-purpose input/output port, used also for reload timer input/output and external interrupt input.
• Port 3 : General-purpose input/output port, used also for A/D converter activation trigger pin.
• Port 4 : General-purpose input/output port, used also for UART input/output.
• Port 5 : General-purpose input/output port, used also analog input pin.
••••
Port 1 pins block diagram (single-chip mode)
Peripheral
function input
Port data register (PDR)
Internal data bus
Standby control : Control among Stop mode (SPL=1), Time-base timer mode (SPL=1), and clock mode
••••
Port 1 registers (single-chip mode)
• Port 1 registers include port 1 data register (PDR1) and port 1 direction register (DDR1).
• The bits configuring the register correspond to port 1 pins on a one-to-one basis.
PDR read
Output latch
PDR write
Port direction register (DDR)
Direction
latch
DDR write
DDR read
(SPL=1).
Peripheral
function output
Peripheral function
output permission
Pch
Pin
Nch
Standby control (SPL=1)
Relation between port 1 registers and pins
Port name Bits of register and corresponding pins
PDR1, DDR1 bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Port 1
Corresponding pins P17 P 16 P15 P14 P13 P12 P11 P10
23

MB90455 Series
••••
Port 2 pins block diagram (general-purpose input/output port)
Peripheral
function input
Port data register (PDR)
Internal data bus
Standby control : Control among Stop mode (SPL=1), Time-base timer mode (SPL=1), and clock mode
••••
Port 2 registers
• Port 2 registers include port 2 data register (PDR2) and port 2 direction register (DDR2).
• The bits configuring the register correspond to port 2 pins on a one-to-one basis.
PDR read
Output latch
PDR write
Port direction register (DDR)
Direction
latch
DDR write
DDR read
(SPL=1).
Peripheral
function output
Peripheral function
output permission
Pch
Pin
Nch
Standby control (SPL=1)
Relation between port 2 registers and pins
Port name Bits of register and corresponding pins
Port 2
PDR2,DDR2 bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Corresponding pins P27 P26 P25 P24 P23 P22 P21 P20
24

••••
Port 3 pins block diagram (general-purpose input/output port)
MB90455 Series
Peripheral
function input
Port data register (PDR)
Internal data bus
Standby control : Control among Stop mode (SPL=1), Time-base timer mode (SPL=1), and clock mode
••••
Port 3 registers
• Port 3 registers include port 3 data register (PDR3) and port 3 direction register (DDR3).
• The bits configuring the register correspond to port 3 pins on a one-to-one basis.
PDR read
Output latch
PDR write
Port direction register (DDR)
Direction
latch
DDR write
DDR read
(SPL=1).
Peripheral
function output
Peripheral function
output permission
Pch
Pin
Nch
Standby control (SPL=1)
Relation between port 3 registers and pins
Port name Bits of register and corresponding pins
Port 3
* : P35 and P36 do not exist on MB90F455/F456/F457, and MB90455/456/457.
PDR3, DDR3 bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Corresponding pins P37 P36* P35* P33 P32 P31 P30
25

MB90455 Series
••••
Port 4 pins block diagram
Peripheral
function input
Port data register (PDR)
Internal data bus
Standby control : Control among Stop mode (SPL=1), Time-base timer mode (SPL=1), and clock mode
••••
Port 4 registers
• Port 4 registers include port 4 data register (PDR4) and port 4 direction register (DDR4).
• The bits configuring the register correspond to port 4 pins on a one-to-one basis.
PDR read
Output latch
PDR write
Port direction register (DDR)
Direction
latch
DDR write
DDR read
(SPL=1).
Peripheral
function output
Peripheral function
output permission
Pch
Pin
Nch
Standby control (SPL=1)
Relation between port 4 registers and pins
Port name Bits of register and corresponding pins
Port 4
26
PDR4, DDR4 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Corresponding pins P44 P43 P42 P41 P40

••••
Port 5 pins block diagram
MB90455 Series
ADER
Port data register (PDR)
Internal data bus
Standby control: Control among Stop mode (SPL=1), Time-base timer mode (SPL=1), and clock mode
••••
Port 5 registers
• Port 5 registers include port 5 data register (PDR5), port 5 direction register (DDR5), and analog input
permission register (ADER).
• Analog input permission register (ADER) allows or disallows input of analog signal to the analog input pin.
• The bits configuring the register correspond to port 5 pins on a one-to-one basis.
PDR read
Output latch
PDR write
Port direction register (DDR)
Direction
latch
DDR write
DDR read
(SPL=1).
Analog input
Pch
Pin
Nch
Standby control (SPL=1)
Relation between port 5 registers and pins
Port name Bits of register and corresponding pins
PDR5, DDR5 bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Port 5
ADER ADE7 ADE6 ADE5 ADE4 ADE3 ADE2 ADE1 ADE0
Corresponding pins P57 P56 P55 P54 P53 P52 P51 P50
27

MB90455 Series
2. Time-Base Timer
The time-base time is a 18-bit free-run counter (time-base timer counter) that counts up in synchronization with
the main clock (dividing main oscillation clock by 2).
• Four choices of interval time are selectable , and generation of interrupt request is allowed for each interval time.
• Provides operation clock signal to oscillation stabilizing wait timer and peripheral functions.
••••
Interval timer function
• When the counter of time-base timer reaches an interval time specified by interval time selection bit
(TBTC:TBC1, TBC0), an overflow (carrying-ov er) occurs (TBTC: TBOF=1) and interrupt request is generated.
• If an interrupt by overflo w is permitted (TBTC: TBIE=1), an interrupt is generated when overflow occurs (TBTC:
TBOF=1).
• The following four interval time settings are selectable :
Interval time of time-base timer
Count clock Interval time
12
2
/HCLK (Approx. 1.0 ms)
14
2
2/HCLK (0.5 µs)
/HCLK (Approx. 4.1 ms)
16
/HCLK (Approx. 16.4 ms)
2
19
2
/HCLK (Approx. 131.1 ms)
HCLK: Oscillation clock
Values in parentheses “( )” are those under operation of 4-MHz oscillation clock.
28

••••
Time-base timer block diagram
Time-base timer counter
To PPG timer
MB90455 Series
To watchdog
timer
21/HCLK
212
2
3
2
· · ·
· · ·
9
8
2
2
Power-on reset
Stop mode
CKSCR : MCS = 1 0
CKSCR : SCS = 0 1
1
2
Counter-
clear circuit
TBOF clear
Time-base timer control register
(TBTC)
Re-
served
Time-base timer interrupt signal
OF : Overflow
HCLK : Oscillation clock
*1 : Switch machine clock from main clock to PLL clock.
10
2112122132142152162172
2
OF
OF
OF
Interval timer
selector
TBOF set
TBIE TBOF TBC1 TBC0TBR
18
OF
To clock controller
oscillation stabilizing
wait time selector
*2 : Switch machine clock from sub clock to main clock.
Actual interrupt request number of time-base timer is as follows:
Interrupt request number: #16 (10
H)
29

MB90455 Series
3. Watchdog Timer
The watchdog timer is a 2-bit counter that uses time-base timer or clock timer as count clock. If the counter is
not cleared within an interval time, CPU is reset.
••••
Watchdog timer functions
• The watchdog timer is a timer counter that prev ents runaway of a prog ram. Once a watchdog timer is activated,
the counter of watchdog timer must always be cleared within a specified time of interval. If specified interval
time elapses without clearing the counter of a watchdog timer, CPU resetting occurs . This is the function of a
watchdog timer.
• The interval time of a watchdog timer is determined by a clock cycle, which is input as a count cloc k. Watchdog
resetting occurs between a minimum time and a maximum time specified.
• The output target of a clock source is specified by the w atchdog clock selection bit (WTC: WDCS) in the cloc k
timer control register.
• Interval time of a watchdog timer is specified by the time-base timer output selection bit/clock timer output
selection bit (WDTC: WT1, WT0) in the watchdog timer control register.
Interval timer of watchdog timer
Min Max Clock cycle Min Max Clock cycle
14
Approx. 3.58 ms Approx. 4.61 ms
Approx. 14.33 ms Approx. 18.3 ms
Approx. 57.23 ms Approx. 73.73 ms
Approx.
458.75 ms
Approx.
589.82 ms
2
± 2
/HCLK
16
2
± 2
/HCLK
18
2
± 2
/HCLK
21
± 2
2
/HCLK
11
Approx. 0.457 s Approx. 0.576 s
13
Approx. 3.584 s Approx. 4.608 s
15
Approx. 7.168 s Approx. 9.216 s
18
Approx.
14.336 s
Approx.
18.432 s
12
± 2
2
/SCLK
15
± 2
2
/SCLK
16
± 2
2
/SCLK
17
± 2
2
/SCLK
9
12
13
14
HCLK: Oscillation clock ( 4 MHz) , CSCLK: Sub clock (8.192 kHz)
Notes: • If the time-base timer is cleared when watchdog timer count clock is used as time base timer output
(carry-over signal), watchdog reset time may become longer.
• When using the sub clock as machine clock, be sure to specify watchdog timer clock source selection bit
(WDCS) in clock timer control register (WTC) at “0,” selecting output of clock timer.
30

••••
Watchdog timer block diagram
MB90455 Series
Reset occurs
Shift to sleep mode
Shift to time-base
timer mode
Shift to clock mode
Shift to stop mode
Main clock
(dividing HCLK by 2)
Sub clock
SCLK
Watchdog timer control register(WDTC)
PONR
Watchdog timer
WRST
2
SRST
WTE
WT1
ERST
Counter
clear control
circuit
Count clock
selector
Clear
4
Time-base timer counter
212
2
2
8
2
10
9
2112122132142152162172
2
Clock counter
212
2
2
5
2
7
6
28 292102112122132142
2
WT0
Activate
2-bit
counter
Clock timer control register (WTC)
WDCS
Watchdog
reset
generation
circuit
Internal reset
generation
circuit
4
18
15
HCLK: Oscillation clock
SCLK: Sub clock
31

MB90455 Series
4. 16-bit Input/Output Timer
The 16-bit input/output timer is a compound module composed of 16-bit free-run timer, (1 unit) and input capture
(2 units, 4 input pins). The timer , using the 16-bit free-run timer as a basis, enables measurement of cloc k cycle
of an input signal and its pulse width.
••••
Configuration of 16-bit input/output timer
The 16-bit input/output timer is composed of the following modules:
• 16-bit free-run timer (1 unit)
• Input capture (2 units, 2 input pins per unit)
••••
Functions of 16-bit input/output timer
(1) Functions of 16-bit free-run timer
The 16-bit free-run timer is composed of 16-bit up counter, timer counter control status register, and prescaler.
The 16-bit up counter increments in synchronization with dividing ratio of machine clock.
• Count clock is set among four types of machine clock dividing rates.
• Generation of interrupt is allowed by counter value overflow.
• Activation of expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
• Counter value of 16-bit free-run timer is cleared to “0000
count clear bit (TCCS: CLR).
• Counter value of 16-bit free-run timer is output to input capture, which is available as base time for capture
operation.
2
OS) is allowed by interrupt generation.
H” by either resetting or software-clearing with timer
(2) Functions of input capture
The input capture, upon detecting an edge of a signal input to the input pin from external device , stores a counter
value of 16-bit free-run timer at the time of detection into the input capture data register. The function includes
the input capture data registers corresponding to four input pins, input capture control status register, and edge
detection circuit.
• Rising edge, falling edge, and both edge are selectable for detection.
• Generating interrupt on CPU is allowed by detecting an edge of input signal.
• Expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
• The four input capture input pins and input capture data registers allows monitoring of a maximum of f our events.
2
OS) is activated by interrupt generation.
32

••••
16-bit input/output timer block diagram
MB90455 Series
Internal data bus
••••
16-bit free-run timer
Input capture
Special-
purpose bus
16-bit free-run
timer
Counter value of 16-bit free-run timer is used as reference time (base time) of input capture.
••••
Input capture
Input capture detects rising edge, falling edge or both edges and retains a counter value of 16-bit free-run timer .
Detection of edge on input signal is allowed to generate interrupt.
••••
16-bit free-run timer block diagram
Timer counter data register
(TCDT)
Output counter value
to input capture
16-bit free-run timer
Prescaler
2
Timer counter
control status register
(TCCS)
IVF IVFE CLK2 CLK1 CLK0STOP CLR
φ : Machine clock
OF : Overflow
OF
CLK
STOP
Re-
served
CLR
Internal data bus
Free-run timer
interrupt request
33

MB90455 Series
••••
Detailed pin assignment on block diagram
The 16-bit input/output timer includes a 16-bit free-run timer. Interrupt request number of the 16-bit free-run
timer is as follows:
Interrupt request number: 19 (13
••••
Prescaler
The prescaler divides a machine clock and provides a counter clock to the 16-bit up counter. Dividing ratio of
the machine clock is specified by timer counter control status register (TCCS) among four values.
••••
Timer counter data register (TCDT)
The timer counter data register is a 16-bit up counter. A current counter v alue of the 16-bit free-run timer is read.
Writing a value during halt of the counter allows setting an arbitrary counter value.
H)
34

••••
Input capture block diagram
MB90455 Series
Edge detection
circuit
IN3
Pin
IN2
Pin
Input capture control
status register
(ICS23)
Input capture control
status register
(ICS01)
16-bit free-run timer
Input capture data register 3 (IPCP3)
Input capture data register 2 (IPCP2)
2
2
EG00EG01EG10EG11ICE0ICE1ICP0ICP1
EG00EG01EG10EG11ICE0ICE1ICP0ICP1
Input capture
interrupt request
EG00EG01EG10EG11ICE0ICE1ICP0ICP1
2
Internal data bus
IN1
Pin
IN0
Pin
Edge detection
2
Input capture data register 1 (IPCP1)
Input capture data register 0 (IPCP0)
circuit
35

MB90455 Series
5. 16-bit Reload Timer
The 16-bit reload timer has the following functions:
• Count clock is selectable among 3 internal clocks and external event clock.
• Activation trigger is selectable between software trigger and external trigger.
• Generation of CPU interrupt is allowed upon occurrence of underflow on 16-bit timer register. Available as an
interval timer using the interrupt function.
• When underflow of 16-bit timer register (TMR) occurs, one of two reload modes is selectable between oneshot mode that halts counting operation of TMR, and reload mode that reloads 16-bit reload register value to
TMR, continuing TMR counting operation.
• The 16-bit reload timer is ready for expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
• MB90455 series device has 2 channels of built-in 16-bit reload timer.
••••
Operation mode of 16-bit reload timer
Count clock Activation trigger Operation upon underflow
Internal clock mode Software trigger, external trigger One-shot mode, reload mode
Event count mode Software trigger One-shot mode, reload mode
2
OS).
••••
Internal clock mode
• The 16-bit reload timer is set to internal clock mode, by setting count cloc k selection bit (TMCSR: CSL1, CSL0)
to “00
B”, “01B”, “10B”.
• In the internal clock mode, the counter decrements in synchronization with the internal clock.
• Three types of count clock cycles are selectable by count clock selection bit (TMCSR: CSL1, CSL0) in timer
control status register.
• Edge detection of software trigger or external trigger is specified as an activation trigger.
36

••••
16-bit reload timer block diagram
TMRLR
TMR
16-bit timer register UF
Internal data bus
16-bit reload register
Reload signal
MB90455 Series
Reload
control
circu
it
Count clock generation
CLK
circuit
Machine
clock
φ
Pin
TIN
Prescaler
Clear
Input
control
circuit
3
Gate
input
3
Internal
clock
External clock
2
Select function
CSL1 CSL0
MOD2 MOD1 OUTLOUTE
Timer control status register (TMCSR)
Valid
clock
decision
circuit
CLK
Clock
selector
Select
signal
MOD0
Wait signal
Output control
circuit
Output signal
generation
circuit
RELD INTEUFCNTE TRG
Output to internal
peripheral
functions
Pin
EN
Operation control
circuit generation
circuit
TOT
Interrupt request
output
37

MB90455 Series
6. Clock Timer Outline
The clock timer is a 15-bit free-run counter that increments in synchronization with sub clock.
• Interval time is selectable among 7 choices, and generation of interrupt request is allowed for each interval.
• Provides operation clock to the subclock oscillation stabilizing wait timer and watchdog timer.
• Always uses subclock as a count clock regardless of settings of clock selection register (CKSCR).
••••
Interval timer function
• In the clock timer, a bit corresponding to the interval time o verflows (carry-over) when an interval time, which
is specified by interval time selection bit, is reached. Then overflow flag bit is set (WTC: WTOF=1).
• If an interrupt by overflow is per mitted (WTC: WTIE=1), an interrupt request is generated upon setting an
overflow flag bit.
• Interval time of clock timer is selectable among the following seven choices :
••••
Interval time of clock timer
Sub clock cycle Interval time
8
2
/SCLK (31.25 ms)
9
2
/SCLK (62.5 ms)
10
/SCLK (125 ms)
2
SCLK (122 µs)
11
2
/SCLK (250 ms)
12
2
/SCLK (500 ms)
13
/SCLK (1.0 s)
2
14
2
/SCLK (2.0 s)
SCLK: Sub clock frequency
Values in parentheses “( )” are calculation when operating with 8.192 kHz clock.
38

••••
Clock timer block diagram
Clock timer counter
MB90455 Series
To watchdog
timer
SCLK
1
2
3
2
2
2
Power-on reset
Shift to hardware standby
Shift to stop mode
2
4
5
2
Counter
clear
circuit
6
2
2
292102112122132142
2
OFOF
8
7
Interval timer
selector
Clock time interrupt
OF : Overflow
SCLK : Sub clock
Clock timer control register (WTC)
WDCS
SCE
WTIE
Actual interrupt request number of clock timer is as follows :
Interrupt request number : #28 (1C
H)
OF
WTOF
OF
OF
WTR
15
OF
OF
OF
To sub clock oscillation
stabilizing wait time
WTC1 WTC0WTC2
••••
Clock timer counter
A 15-bit up counter that uses sub clock (SCLK) as a count clock.
••••
Counter clear circuit
A circuit that clears the clock timer counter.
39

MB90455 Series
7. 8/16-bit PPG Timer Outline
The 8/16-bit PPG timer is a 2-channel reload timer module (PPG0 and PPG1) that allows outputting pulses of
arbitrary cycle and duty cycle. Combination of the two channels allows selection among the follo wing operations:
• 8-bit PPG output 2-channel independent operation mode
• 16-bit PPG output operation mode
• 8-bit and 8-bit PPG output operation mode
MB90455 series device has two 8/16-bit built-in PPG timers. This section describes functions of PPG0/1.
PPG2/3 have the same functions as those of PPG0/1.
••••
Functions of 8/-16-bit PPG timer
The 8/-16-bit PPG timer is composed of four 8-bit reload register (PRLH0/PRLL0, PRLH1/PRLL1) and two PPG
down counters (PCNT0, PCNT1).
• Widths of “H” and “L” in output pulse are specifiable independently. Cycle and duty factor of output pulse is
specifiable arbitrarily.
• Count clock is selectable among 6 internal clocks.
• The timer is usable as an interval timer, by generating interrupt requests for each interval.
• The time is usable as a D/A converter, with an external circuit.
40

••••
8/16-bit PPG timer0 block diagram
PPG0 reload
register
PPLH0
(“H” level side)
PPLL0
(“L” level side)
PEN0
PE0
MB90455 Series
“H” level side data bus
“L” level side data bus
PPG0 operation mode control
register (PPGC0)
PIE0 PUF0
Re-
served
PPG0 temporary
buffer 0(PRLBH0)
Reload register
L/H selector
Count start
value
PPG0 down counter
(PCNT0)
CLK
Time-base timer output
Peripheral clock (1/φ)
Peripheral clock (2/φ)
Peripheral clock (4/φ)
Peripheral clock (8/φ)
Peripheral clock (16/φ)
Select
signal
Reload
Underflow
(512/HCLK)
Clear
PPG0
output latch
Re-
versed
Count clock
selector
3
Select signal
R
SQ
2
Operation mode
control signal
PPG1 underflow
PPG0 underflow
Pulse selector
(To PPG1)
Pin
PPG0
PPG output control circuit
Interrupt
request output*
PCS2 PCS0 PCM2 PCM1 PCM0PCS1
PPG0/1 count clock selection register (PPG01)
− : Undefined
Reserved : Reserved bit
HCLK : Oscillation clock frequency
φ : Machine clock frequency
* : Interrupt output of 8/16-bit PPG timer 0 is incorporated into one by the OR circuit against
interrupt output of 8/16-bit PPG timer 1.
41

MB90455 Series
••••
8/16-bit PPG timer 1 block diagram
PPG1 reload
register
Operation
mode
control
signal
buffer 0(PRLBH1)
PRLH1
(“H” level side)
PPG1 temporary
PRLL1
(“L” level side)
PEN1
“H” level side data bus
“L” level side data bus
PPG1 operation mode control
register (PPGC1)
PE1
PIE1 PUF1
2
MD1 MD0
Re-
served
Interrupt
R
SQ
request output*
Count start
value
counter (PCNT1)
PPG1 underflow
(To PPG0)
PPG0 underflow
(from PPG0)
Peripheral clock (16/φ)
Reload selector
L/H selector
Reload
Under-
PPG1 down
CLK
flow
Time-base timer output
(512/HCLK)
Peripheral clock (1/φ)
Peripheral clock (2/φ)
Peripheral clock (4/φ)
Peripheral clock (8/φ)
Count clock
selector
Select signal
Clear
PPG1
Re-
versed
output latch
Pin
PPG1
PPG output control circuit
MD0
3
Select signal
PCS2 PCS0 PCM2 PCM1 PCM0PCS1
PPG0/1 count clock selection register (PPG01)
42
− : Undefined
Reserved : Reserved bit
HCLK : Oscillation clock frequency
φ : Machine clock frequency
* : Interrupt output of 8/16-bit PPG timer 1 is incorporated into one by the OR circuit against
interrupt output of 8/16-bit PPG timer 0.

MB90455 Series
8. Delay Interrupt Generation Module Outline
The delay interrupt generation module is a module that generates interrupts for switching tasks. Generation of
a hardware interrupt request is performed by software.
••••
Delay interrupt generation module outline
Using the delay interrupt generation module, hardwa re interrupt request is generated and released by software .
Delay interrupt generation module outline
Function and control
Set “1” in R0 bit of delay interrupt request generation/release register (DIRR: R0=1),
Cause of interrupt
generating an interrupt request.
Set “0” in R0 bit of delay interrupt request generation/release register (DIRR: R0=0),
releasing an interrupt request.
Interrupt number #42 (2A
H)
Interrupt control No setting of permission register is provided.
Interrupt flag Retained in DIRR: R0 bit
2
EI
OS Not ready for expanded intelligent I/O service.
••••
Delay interrupt generation module block diagram
Internal data bus
R0
Delay interrupt request generation/release
S Interrupt request
R Latch
Interrupt
request signal
register (DIRR)
− : Not defined
••••
Interrupt request latch
A latch that retains settings on delay interrupt request generation/release register (generation or release of dela y
interrupt request).
••••
Delay interrupt request generation/release register (DIRR)
Generates or releases delay interrupt request.
••••
Interrupt number.
An interrupt number used in delay interrupt generation module is as follows:
Interrupt number: #42 (2A
H)
43

MB90455 Series
9. DTP/External Interrupt Outline
DTP/external interrupt transfers an interrupt request generated by an e xternal peripheral device or a data transmission request to CPU, generating external interrupt request and activating expanded intelligent I/O service.
••••
DTP/external interrupt function
An interrupt request input from external peripheral device to external input pins (INT7 to INT4), just as interrupt
request of peripheral device, generates an interrupt request. The interrupt request generates an e xternal interrupt
and activates expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
2
OS).
If the expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
2
OS) has been disabled by interrupt control register (ICR: ISE=0),
external interrupt function is enabled and branches to interrupt processing.
If the EI
performed by EI
2
OS has been enabled, (ICR: ISE=1), DTP function is enabled and automatic data transmission is
2
OS. After performing specified number of data transmission processes , the process branches
to interrupt processing.
DTP/external interrupt
External interrupt DTP function
Input pin 4 pins (INT4 to INT7)
Specify for each pin with detection level setting register (ELVR).
Interrupt cause
Interrupt number #24 (18
Interrupt control
Input of “H” level/“L” level/rising edge/falling
edge.
H) , #27 (1BH)
Input of “H” level/ “L” level
Enabling or disabling output of interrupt request, using DTP/external interrupt permission
register (ENIR).
Interrupt flag Retaining interrupt cause with DTP/external interrupt cause register (EIRR).
Process selection Disable EI
2
OS (ICR: ISE=0) Enable EI2OS (ICR: ISE=1)
After automatic data transmission by EI
Process Branch to external interrupt process
specified number of times, branch to interrupt
process.
2
OS for
44

••••
DTP/External interrupt block diagram
Detection level setting register (ELVR)
MB90455 Series
LA4LB4LA5LB5LA6LB6LA7LB7
Pin
INT7
Pin
INT6
Internal data bus
Pin
INT5
Pin
INT4
DTP/external interrupt input
detection circuit
Level/edge
selector
Level/edge
selector
Level/edge
selector
Level/edge
selector
ER4ER5ER6ER7
DTP/external interrupt
cause register (EIRR)
Interrupt
request signal
Re-
EN4EN5EN6EN7
served
Re-
served
Re-
served
DTP/external interrupt
Re-
served
permission register (ENIR)
45

MB90455 Series
10. 8/10-bit A/D Converter
The 8/10-bit A/D converter converts an analog input voltage into 8-bit or 10/bit digital value, using the RC-type
successive approximation conversion method.
• Input signal is selected among 8 channels of analog input pins.
• Activation trigger is selected among software trigger, internal timer output, and external trigger.
••••
Functions of 8/10-bit A/D converter
The 8/10-bit A/D converter converts an analog voltage (input voltage) input to analog input pin into an 8-bit or
10-bit digital value (A/D conversion).
The 8/10-bit A/D converter has the following functions:
• A/D conversion takes a minimum of 6.12 µs*1 for one channel, including sampling time. (A/D conversion)
• Sampling of one channel takes a minimum of 2.0 µs*.
• RC-type successive approximation conversion method, with sample & hold circuit is used for conversion.
• Resolution of either 8 bits or 10 bits is specifiable.
• A maximum of 8 channels of analog input pins are allowed for use.
• Generation of interrupt request is allowed, by storing A/D conversion result in A/D data register.
• Activation of EI
even if A/D conversion is performed successively.
• An activation trigger is selectable among software trigger , internal timer output, and external trigger (fall edge).
2
OS is allowed upon occurrence of an interrupt request. With use of EI2OS, data loss is av oided
*: When operating with 16-MHz machine clock
••••
8/10-bit A/D converter conversion mode
Conversion mode Description
Singular conversion
mode
Sequential conversion
mode
Pausing conversion
mode
The A/D conversion is performed form a start channel to an end channel sequentially.
Upon completion of A/D conversion on an end channel, A/D conversion function stops.
The A/D conversion is performed form a start channel to an end channel sequentially.
Upon completion of A/D conversion on an end channel, A/D conversion function
resumes from the start channel.
The A/D conversion is performed by pausing at each channel. Upon completion of A/D
conversion on an end channel, A/D conversion and pause functions resume from the
start channel.
46

••••
8/10-bit A/D converter block diagram
MB90455 Series
A/D control
status register
(ADCS)
INT
ADTG
TO
AN7
AN6
AN5
AN4
AN3
AN2
AN1
AN0
Interrupt request output
INTE
PAUS STS1 STS0 STRTBUSY ANS2
2
Re-
served
MD1
Activation
selector
Sample&
hold circuit
Analog
channel
selector
AVR
AVcc
AVss
MD0
2
Comparator
ANS1 ANS0 ANE2 ANE1 ANE0
D/A converter
6
Decoder
Internal data bus
Control circuit
A/D data
register
(ADCR)
ST0ST1 CT1 CT0 D9 D8S10 D5D6 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0D7
TO : Internal timer output
− : Not defined
Reserved : Be sure to set to “0”
φ : Machine clock
2
2
47

MB90455 Series
11. UART Outline
UART is a general-purpose serial data communication interface for synchronous and asynchronous communication using external devices.
• Provided with bi-directional communication function for both clock-synchronous and clock-asynchronous
modes.
• Provided with master/slave communication function (multi-processor mode). (Only master side is available.)
• Interrupt request is generated upon completion of reception, completion of transmission and detection of
reception error.
• Ready for expanded intelligent service, EI
UART functions
Data buffer Full-duplex double buffer
2
OS.
Description
Transmission mode
Clock synchronous (No start/stop bit, no parity bit)
Clock asynchronous (start-stop synchronous)
Built-in special-purpose baud-rate generator. Setting is selectable
Baud rate
among 8 values.
Input of external values is allowed.
Use of clock from external timer (16-bit reload timer 0) is allowed.
Data length
7 bits (only asynchronous normal mode)
8 bits
Signaling system Non Return to Zero (NRZ) system
Framing error
Reception error detection
Overrun error
Parity error (not detectable in operation mode 1 (multi-processor
mode))
Receive interrupt (reception completed, reception error detected)
Interrupt request
Transmission interrupt (transmission completed)
2
Ready for expanded intelligent I/O service (EI
OS) in both transmis-
sion and reception
Master/slave communication function
(asynchronous, multi-processor mode)
Communication between 1 (master) and n (slaves) are available
(usable as master only).
Note : Start/stop bit is not added upon clock-synchronous transmission. Data only is transmitted.
UART operation modes
Data length
Operation mode
Synchronization Stop bit length
With parity Without parity
Asynchronous mode
0
(normal mode)
1 Multi processor mode 8+1
7-bit or 8-bit Asynchronous
*1
Asynchronous
2 Synchronous mode 8 Synchronous No
: Disallowed
*1 : “+1” is an address/data selection bit used for communication control (bit 11 of SCR1 register: A/D)
*2 : Only 1 bit is detected as a stop bit on data reception.
48
1- bit or 2-bit *
2

••••
UART block diagram
Special-purpose
baud-rate
generator
16-bit reload
timer
Pin
SCK1
Clock
selector
Reception
clock
Start bit
detection circuit
Control bus
Reception
control
circuit
Transmission
clock
Transmission
start circuit
MB90455 Series
Reception interrupt
request output
Transmission interrupt
request output
Transmission
control
circuit
Pin
SIN1
Reception status
decision circuit
Communication
prescaler
control
register
MD
DIV2
DIV1
DIV0
Reception bit
counter
Reception
parity counter
Shift register for
reception
Serial input data
register 1
Internal data bus
MD1
Serial
mode
register
1
MD0
CS2
CS1
CS0
RST
SCKE
SOE
Recep-
tion
com-
pleted
Transmission
bit counter
Transmission
parity counter
Shift register for
transmission
Serial output data
register 1
PEN
Serial
control
register
1
P
SBL
CL
A/D
REC
RXE
TXE
Pin
SOT1
Start
transmission
Reception error
occurrence
signal for EI
(to CPU)
Serial
status
register
1
2
OS
PE
ORE
FRE
RDRF
TDRE
BDS
RIE
TIE
49

MB90455 Series
12. Address Matching Detection Function Outline
The address matching detection function checks if an address of an instruction to be processed next to a currentlyprocessed instruction is identical with an address specified in the detection address register. If the addresses
match with each other, an instruction to be processed ne xt in progr am is f orcib ly replaced with INT9 instruction,
and process branches to the interrupt process program. Using INT9 interrupt, this function is available for
correcting program by batch processing.
••••
Address matching detection function outline
• An address of an instruction to be processed next to a currently-processed instruction of the program is alwa ys
retained in an address latch via internal data bus. By the address matching detection function, the address
value retained in the address latch is alwa ys compared with an address specified in detection address setting
register. If the compared address values match with each other, an instruction to be processed next by CPU
is forcibly replaced with INT9 instruction, and an interrupt process program is executed.
• Two detection address setting registers are provided (PADR0 and PADR1), and each register is provided with
interrupt permission bit. Generation of interrupt, which is caused by address matching between the address
retained in address latch and the address specified in address setting register, is permitted and prohibited on
a register-by-register basis.
••••
Address matching detection function block diagram
Address latch
Internal data bus
Detection address setting register 0
Detection address setting register 1
PACSR
Reserved ReservedReservedReservedReservedReserved
Address detection control register (PACSR)
Reserved: Be sure to set to “0.”
• Address latch
Retains address value output to internal data bus.
• Address detection control register (PACSR)
Specifies if interrupt is permitted or prohibited when addresses match with each other.
• Detection address setting (PADR0, PADR1)
Specifies addresses to be compared with values in address latch.
PADR0 24bit
PADR1 24bit
AD1E AD0E
Comparator
INT9 instruction
(generate INT9 interrupt)
50

MB90455 Series
13. ROM Mirror Function Selection Module Outline
The ROM mirror function selection module sets the data in ROM assigned to FF bank so that the data is read
by access to 00 bank.
••••
ROM mirror function selection module block diagram
ROM mirror function selection register
(ROMM)
Address
Internal data bus
Reserved
Address area
FF bank
Data
••••
FF bank access by ROM mirror function
004000H
00FFFFH
Reserved Reserved
ROM
00 bank
00 bank
ROM mirror area
ReservedReservedReserved
Reserved
MI
FBFFFF
FC0000H
FEFFFFH
FF0000H
FF4000H
FFFFFFH
FF bank (ROM
mirror applicable
area)
51

MB90455 Series
14. 192 K/256 K/512 Kbit Flash Memory Outline
The following three methods are provided for data writing and deleting on flash memory:
1. Parallel writer
2. Serial special-purpose writer
3. Writing/deleting by program execution
••••
192 K/256 K/512 Kbit flash memory outline
The 192 K/256 K/512K-bit flash memory is allocated on FF
H bank of CPU memory map. Using the function of
flash memory interface circuit, the memory allows read access and program access from CPU.
Writing/deleting on flash memory is performed by instruction from CPU via flash memor y interface. Because
rewriting is allowed on mounted memory, modifying program and data is performed efficiently.
••••
Features of 192 K/256 K/512 Kbit flash memory
• Dividing into many sectors
• Automatic program algorithm (Embedded Algorithm
TM
: Similar to MBM29LV200.)
• Built-in deletion pause/deletion resume function
• Detection of completed writing/deleting by data polling and toggle bits.
• Detection of completed writing/deleting by CPU interrupt.
• Deletion is allowed on a sector-by-sector basis (sectors are combined freely).
• Number of writing/deleting operations (minimum): 10,000 times
• Sector protection
• Extended sector protection
• Temporary sector unprotection
Embedded Algorithm
TM
is a registered trademark of Advanced Micro Device.
Note : A function of reading manufacture code and device code is not provided. These codes are not accessible
by command either.
••••
Flash memory writing/deleting
• Writing and reading data is not allowed simultaneously on the flash memory.
• Data writing and deleting on the flash memory is performed by the processes as follows: Make a copy of
program on flash memory onto RAM. Then, execute the program copied on the RAM.
••••
List of registers and reset values in flash memory
Flash memory control status register (FMCS)
76bit 543210
00000X00
× : Undefined
52

••••
Sector configuration of 192 K/256 K/512 Kbit flash memory
• Sector configuration of 192 Kbit to flash memory (MB90F455 (S) )
MB90455 Series
Flash memory CPU address
FFA000H
Writer address*
SA0 (8 Kbytes)
FFBFFFH
FFC000H
SA1 (16 Kbytes)
FFFFFFH
• Sector configuration of 256 Kbit to flash memory (MB90F456 (S) )
Flash memory CPU address
FF8000H
SA0 (8 Kbytes)
FF9FFFH
FFA000H
SA1 (8 Kbytes)
FFBFFFH
FFC000H
SA2 (16 Kbytes)
FFFFFFH
Writer address*
• Sector configuration of 512 Kbit to flash memory (MB90F457 (S) )
Flash memory CPU address
FF0000H
SA0 (32 Kbytes)
Writer address*
7A000H
7BFFFH
7C000H
7FFFFH
78000H
79FFFH
7A000H
7BFFFH
7C000H
7FFFFH
70000H
FF7FFFH
FF8000H
77FFFH
78000H
SA1 (8 Kbytes)
FF9FFFH
FFA000H
79FFFH
7A000H
SA2 (8 Kbytes)
FFBFFFH
FFC000H
7BFFFH
7C000H
SA3 (16 Kbytes)
FFFFFFH
7FFFFH
* : “Writer address” is an address equivalent to CPU address, which is used
when data is written on flash memory, using par allel writer. When writing/
deleting data with general-purpose writer, the writer address is used for
writing and deleting.
53

MB90455 Series
ELECTRIC CHARACTERISTICS
■■■■
1. Absolute Maximum Rating
Parameter Symbol
V
CC VSS − 0.3 VSS + 6.0 V
Power supply voltage
AV
CC VSS − 0.3 VSS + 6.0 V VCC = AVCC*
AVR VSS − 0.3 VSS + 6.0 V AVCC ≥ AVR*
Input voltage VI VSS − 0.3 VSS + 6.0 V *2
Rating
Unit Remarks
Min Max
(VSS = AVSS = 0.0 V)
1
1
Output voltage V
O VSS − 0.3 VSS + 6.0 V *2
Maximum clamp current ICLAMP − 2.0 + 2.0 mA *6
Total maximum clamp current ∑ | I
CLAMP | 20 mA *6
OL1 15 mA Normal output*
I
“L” level maximum output current
IOL2 40 mA High-current output*
OLAV1 4 mA Normal output*
I
“L” level average output current
IOLAV2 30 mA High-current output*
OL1 125 mA Normal output
∑I
“L” level maximum total output current
∑I
OL2 160 mA High-current output
OLAV1 40 mA Normal output*
∑I
“L” level average total output current
∑IOLAV2 40 mA High-current output*
I
OH1 −15 mA Normal output*
“H” level maximum output current
IOH2 −40 mA High-current output*
OHAV1 −4 mA Normal output*
I
“H” level average output current
IOHAV2 −30 mA High-current output*
OH1 −125 mA Normal output
∑I
“H” level maximum total output current
∑I
OH2 −160 mA High-current output
OHAV1 −40 mA Normal output*
∑I
“H” level average total output current
∑IOHAV2 −40 mA High-current output*
3
3
4
4
5
5
3
3
4
4
5
5
Power consumption PD 245 mW
Operating temperature TA −40 +105 °C
Storage temperature Tstg −55 +150 °C
*1 : AVcc and AVR should not exceed Vcc. Also AVR should not exceed AVcc.
*2 : V
I, VO, should not exceed Vcc + 0.3V.
*3 : A peak value of an applicable one pin is specified as a maximum output current.
*4 : An average current value of an applicable one pin within 100 ms is specified as an average output current.
(Average value is found by multiplying operating current by operating rate.)
*5 : An average current value of all pins within 100 ms is specified as an average total output current. (Average
value is found by multiplying operating current by operating rate.)
(Continued)
54

MB90455 Series
(Continued)
*6 : •Applicable to pins: P10 to P17, P20 to P27, P30 to P33, P35*, P36*, P37, P40 to P44, P50 to P57
Note : P35 and P36 are applicable only for products of MB90F455S/F456S/F457S , MB90455S/456S/457S.
• Use within recommended operating conditions.
• Use at DC voltage (current) .
• The +B signal should always be applied a limiting resistance placed between the +B signal and the
microcontroller.
• The v alue of the limiting resistance should be set so that when the +B signal is applied the input current to the
microcontroller pin does not exceed rated values, either instantaneously or for prolonged periods.
• Note that when the microcontroller drive current is low, such as in the power saving modes, the +B input
potential may pass through the protective diode and increase the potential at the V
other devices.
• Note that if a +B signal is input when the microcontroller power supply is off (not fixed at 0 V) , the power supply is
provided from the pins, so that incomplete operation may result.
• Note that if the +B input is applied during power-on, the power supply is provided from the pins and the
resulting supply voltage may not be sufficient to operate the power-on reset.
• Care must be taken not to leave the +B input pin open.
• Note that analog system input/output pins other than the A/D input pins (LCD drive pins, comparator input
pins, etc.) cannot accept +B signal input.
• Sample recommended circuits:
CC pin, and this may affect
• Input/Output Equivalent circuits
Limiting
resistance
+B input (0 V to 16 V)
Protective diode
VCC
P-ch
N-ch
R
WARNING: Semiconductor devices can be permanently damaged by application of stress (voltage, current,
temperature, etc.) in excess of absolute maximum ratings. Do not exceed these ratings.
55

MB90455 Series
2. Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol
Power supply voltage
CC
V
AV
CC 4.0 5.5 V *2
Min Typ Max
3.5 5.0 5.5 V Under normal operation
3.0 5.5 V
(VSS = AVSS = 0.0V)
Value
Unit Remarks
Retain status of stop
operation
Smoothing capacitor C
S 0.1 1.0 µF*1
Operating temperature TA −40 +105 °C
*1 : Use a ceramic capacitor, or a capacitor of similar frequency characteristics. On the Vcc pin, use a bypass
capacitor that has a larger capacity than that of Cs.
Refer to the following figure for connection of smoothing capacitor Cs.
*2 : AVcc is a voltage at which accuracy is guaranteed. AVcc should not exceed Vcc.
• C pin connection diagram
C
C
S
WARNING: The recommended operating conditions are required in order to ensure the normal operation of the
semiconductor device. All of the device’s electrical characteristics are warranted when the device is
operated within these ranges.
Always use semiconductor devices within their recommended operating condition ranges. Operation
outside these ranges may adversely affect reliability and could result in device failure.
No warranty is made with respect to uses, operating conditions, or combinations not represented on
the data sheet. Users considering application outside the listed conditions are advised to contact their
FUJITSU representatives beforehand.
56

3. DC Characteristics
Parame-
ter
Sym-
bol
Pin name Conditions
MB90455 Series
(VCC = 5.0 V±10%, VSS = AVSS = 0.0 V, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
Value
Unit
Min Typ Max
Remarks
“H” level
input
voltage
“L” level
input
voltage
“H” level
output
voltage
“L” level
output
voltage
Input
leak
current
CMOS
V
hysteresis input
IHS
— 0.8 V
CC —VCC + 0.3 V
pin
VIHM MD input pin — VCC − 0.3 — VCC + 0.3 V
CMOS
V
hysteresis input
ILS
—V
SS − 0.3 — 0.2 VCC V
pin
V
ILM MD input pin — VSS − 0.3 — VSS + 0.3 V
Pins other than
VOH1
P14 to P17
V
OH2 P14 to P17
Pins other than
V
OL1
P14 to P17
VOL2 P14 to P17
I
IL All input pins
VCC = 4.5 V,
I
OH = −4.0 mA
VCC = 4.5 V,
I
OH = −14.0 mA
VCC = 4.5 V,
I
OL = 4.0 mA
VCC = 4.5 V,
I
OL = 20.0 mA
VCC = 5.5 V,
V
SS < VI < VCC
VCC – 0.5 — — V
VCC – 0.5 — — V
——0.4V
——0.4V
–5 — +5 µA
VCC = 5.0 V,
Internally operating at
—2530mA
16 MHz, normal operation.
Power
supply
current*
I
I
I
CC
CCS
CTS
VCC
V
CC = 5.0 V,
Internally operating at
16 MHz, writing on flash
memory.
V
CC = 5.0 V,
Internally operating at
16 MHz, deleting on flash
memory.
VCC = 5.0 V,
Internally operating at
16 MHz, sleeping.
VCC = 5.0 V,
Internally operating at
2 MHz, transition from
main clock mode,
in time-base timer mode.
—4550mA
—4550mA
Flash ROM
product
Flash ROM
product
—812mA
0.75 1.0 mA
Flash ROM
product
—
0.2 0.35 mA
Mask ROM
product
(Continued)
57

MB90455 Series
(Continued)
Parame-
ter
Sym-
bol
Pin name Conditions
(VCC = 5.0 V±10%, VSS = AVSS = 0.0 V, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
Rating
Unit Remarks
Min Typ Max
Power
supply
current*
Input
capacity
Pull-up
resistor
I
CCL
VCC = 5.0 V,
Internally operating at
8 kHz, subclock
operation,
T
A = + 25°C
—0.31.2mA
— 40 100 µA
VCC = 5.0 V,
Internally operating at
CCLS
I
VCC
8 kHz, subclock,
sleep mode,
T
A = + 25°C
—1030µA
VCC = 5.0 V,
I
CCT
ICCH
Internally operating at
8 kHz, clock mode,
T
A = + 25°C
Stopping,
T
A = + 25°C
—825µA
—520µA
Other than
AV
C
IN
R
UP RST 25 50 100 kΩ
CC, AVSS,
AVR, C, V
V
SS
CC,
— 5 15 pF
Flash ROM
product
Mask ROM
product
Pull-down
resistor
R
DOWN MD2 25 50 100 kΩ
* : Test conditions of power supply current are based on a device using external clock.
Flash ROM
product is not
provided with
pull-down resistor.
58

4. AC Characteristics
(1) Clock timing
Parameter Symbol Pin name
Clock frequency
Clock cycle time
MB90455 Series
(V
CC = 5.0 V±10%, VSS = AVSS = 0.0 V, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
Value
Min Typ Max
3—8MHz
f
C X0, X1
3 — 16 MHz External clock *
fCL X0A, X1A — 32.768 — kHz
tHCYL X0, X1 125 — 333 ns
t
LCYL X0A, X1A — 30.5 — µs
Unit Remarks
When crystal or ceramic
resonator is used*
2
1, *2
Set duty factor at 30% to
70% as a guideline.
Input clock pulse width
WH, PWL X0 10 — — ns
P
PWLH,PWLL X0A — 15.2 — µs
Input clock rise time and fall
time
Internal operation clock
frequency
Internal operation clock cycle
time
t
CR, tCF X0 — — 5 ns
f
CP — 1.5 — 16 MHz When main clock is used
fLCP — — 8.192 — kHz When sub clock is used
t
CP — 62.5 — 666 ns When main clock is used
t
LCP — — 122.1 — µs When sub clock is used
When external clock is
used
*1 : Internal operation clock frequency should not exceed 16 MHz.
*2 : When selecting the PLL clock, the range of clock frequency is limitted. Use this product within range as mentioned
in “Relation among external clock frequency and internal clock frequency”.
• Clock timing
HCYL
t
X0
PWH
PWL
tCF tCR
0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC
X0A
PWLH
LCYL
t
tCF
0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC
PWLL
tCR
59

MB90455 Series
• PLL operation guarantee range
5.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
Power voltage VCC (V)
Relation between internal operation clock
frequency and power supply voltage
Operation guarantee range of MB90F455 (S) /F456 (S) /F457 (S)
and MB90455 (S) /456 (S) /457 (S)
A/D converter
accuracy
guarantee range
PLL operation guarantee range
34 8 16
121.5
Internal clock fCP (MHz)
Relation among external clock frequency and internal clock frequency
Multiply
by 4
16
12
9
8
4
Multiply
by 3
Multiply
by 2
Internal clock fCP (MHz)
34 8
External clock fC (MHz)*
* : fc is 8 MHz at maximum when crystal or ceramic resonator is used.
Multiply by 1
x1/2
(no multiplication)
16
Rating values of alternating current is defined by the measurement reference voltage values shown below:
• Input signal waveform
Hysteresis input pin
0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC
• Output signal waveform
Output pin
2.4 V
0.8 V
60

(2) Reset input timing
Parameter
Reset input time t
Sym-
bol
RSTL RST
Pin
name
Condi-
tions
Value
Min Max
3
CP*
16 t
Oscillation time of oscillator*
+ 100 µs + 16 tCP*
3
MB90455 Series
Unit Remarks
ns Normal operation
1
In sub clock*
2
sleep*
, watch*2
and stop mode
2
, sub
100 µs
In time base timer
mode
*1 : Oscillation time of oscillator is time until oscillation reaches 90% of amplitude. It takes se veral milliseconds to
sever al dozens of milliseconds on a crystal oscillator, se veral hundreds of microseconds to sev eral milliseconds
on a FAR/ceramic oscillator, and 0 milliseconds on an external clock.
*2 : Except for MB90F455S/F456S/F457S, MB90455S/456S/457S.
*3 : Refer to "(1) Clock timing" ratings for t
CP (internal operation clock cycle time).
• In sub clock, sub sleep, watch and stop mode
tRSTL
RST
0.2 VCC 0.2 VCC
90% of
amplitude
X0
Internal operation
clock
100 s
+ 16 t
CP
Oscillation
time of
oscillator
Wait time for stabilizing
oscillation Execute instruction
Internal reset
61

MB90455 Series
(3) Power-on reset
Parameter Symbol Pin name Conditions
(V
CC = 5.0 V ± 10%, VSS = AVSS = 0.0 V, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
Value
Unit Remarks
Min Max
Power supply rise time t
Power supply shutdown
time
VCC
Sudden change of power supply voltage may activate the power-on reset function. When
changing power supply voltages during operation, raise the power smoothly by suppressing
variation of voltages as shown below. When raising the power, do not use PLL clock. However, if voltage drop is 1V/s or less, use of PLL clock is allowed during operation.
VCC
3.0 V
VSS
R VCC
0.05 30 ms
t
OFF VCC 1 ms Repeated operation
tR
2.7 V
0.2 V 0.2 V0.2 V
tOFF
Limiting the slope of rising within
50 mV/ms is recommended.
RAM data hold period
62

(4) UART timing
Parameter Symbol Pin name Conditions
MB90455 Series
(V
CC = 4.5 V to 5.5 V, VSS = 0.0 V, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
Value
Min Max
Unit Remarks
Serial clock cycle time t
SCK ↓ → SOT delay time t
Valid SIN → SCK ↑ t
SCK ↑ → valid SIN hold time t
Serial clock “H” pulse width t
Serial clock “L” pulse width t
SCYC SCK1
SLOV
IVSH
SHIX
SHSL SCK1
SLSH SCK1 4 tCP * ns
SCK ↓ → SOT delay time tSLOV
Valid SIN → SCK ↑ t
SCK ↑ →valid SIN hold time t
* : Refer to "(1) Clock timing" ra tings for t
IVSH
SHIX
CP (internal operation clock cycle time).
Notes: • AC rating in CLK synchronous mode.
• C
L is a load capacitance value on pins for testing.
SCK1,
SOT1
SCK1,
SIN1
SCK1,
SIN1
SCK1,
SOT1
SCK1,
SIN1
SCK1,
SIN1
Internal shift clock
mode output pin is :
CL = 80 pF+1TTL.
External shift clock
mode output pin is :
CL = 80 pF+1TTL.
8 tCP * ns
−80 +80 ns
100 ns
60 ns
4 tCP * ns
150 ns
60 ns
60 ns
63

MB90455 Series
• Internal shift clock mode
SCK
SOT
SIN
• External shift clock mode
SCK
SOT
tSCYC
2.4 V
0.8 V 0.8 V
tSLOV
2.4 V
0.8 V
tIVSH tSHIX
0.8 V
CC
0.2 VCC
tSLSH tSHSL
0.8 VCC 0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC 0.2 VCC
tSLOV
2.4 V
0.8 V
0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC
SIN
tIVSH tSHIX
0.8 V
CC
0.2 VCC
0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC
64

(5) Timer input timing
Parameter Symbol Pin name Conditions
t
TIWH TIN0, TIN1
Input pulse width
t
TIWL IN0 to IN3
MB90455 Series
(V
CC = 4.5 V to 5.5 V, VSS = 0.0 V, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
4 t
Value
Min Max
CP * ns
Unit Remarks
* : Refer to "(1) Clock timing" ratings for t
• Timer input timing
TIN0, TIN1,
IN0 ~ IN3
0.8 VCC
(6) Trigger input timing
Parameter Symbol Pin name Conditions
TRGH
Input pulse width
t
tTRGL
* : Refer to "(1) Clock timing" ratings for t
• Trigger input timing
CP (internal operation clock cycle time).
0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC
tTIWH tTIWL
CC = 4.5 V to 5.5 V, VSS = 0.0 V, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
(V
0.2 VCC
Min Max
INT4 to INT7,
ADTG
CP (internal operation clock cycle time).
5 tCP * ns
Value
Unit Remarks
INT4 ~ INT7,
ADTG
0.8 VCC 0.8 VCC
0.2 VCC 0.2 VCC
tTRGH tTRGL
65

MB90455 Series
5. A/D converter
(VCC = AVCC = 5.0 V ± 10%, VSS = AVSS = 0.0 V, 3.0 V ≤ AVR − AVSS, TA = −40 °C to +105 °C)
Parameter Symbol
Pin
name
Conditions
Resolution 10 bit
Total error ± 3.0 LSB
Nonlinear error ± 2.5 LSB
Differential linear error ± 1.9 LSB
Zero transition voltage V
Full-scale transition
voltage
V
OT
FST
AN0 to
AN7
AN0 to
AN7
AVSS − 1.5
LSB
AVR − 3.5
LSB
AVSS + 0.5
AVR − 1.5
Value
Min Max
AVSS + 2.5
LSB
LSB
AVR + 0.5
LSB
LSB
Unit Remarks
V
1 LSB = AVR/1024
V
Compare time
Sampling time
128 t
Analog port input
current
Analog input voltage V
I
AIN
AIN
AN0 to
AN7
AN0 to
AN7
Reference voltage AVR AV
A AVCC 3.5 7.5 mA
I
Power supply current
IAH AVCC 5 µA*2
I
Reference voltage
supplying current
Variation among
channels
R AVR 165 250 µA
I
RH AVR 5 µA*2
AN0 to
AN7
CP *
CP *
CP *
1
1
1
1
ns
ns
ns
ns
66 t
88 tCP *
32 t
10 µA
AVSS AVR V
SS + 2.7 AVCC V
4LSB
With 16 MHz
machine clock
5.5 V ≥ AV
CC ≥ 4.5 V
With 16 MHz
machine clock
4.5 V > AV
CC ≥ 4.0 V
With 16 MHz
machine clock
5.5 V ≥ AV
CC ≥ 4.5 V
With 16 MHz
machine clock
4.5 V > AV
CC ≥ 4.0 V
*1 : Refer to "(1) Clock timing" ratings for t
CP (internal operation clock cycle time).
*2 : If A/D converter is not operating, a current when CPU is stopped is applicable (Vcc=AVcc=AVR=5.0 V).
66

MB90455 Series
6. Definition of A/D Converter Terms
Resolution : Analog variation that is recognized by an A/D converter.
Linear error : Deviation between a line across zero-transition line (“00 0000 00 0 0” ←→“00 0000 0001”)
and full-scale transition line (“11 1111 11 1 0” ←→ “11 1111 1111”) and actual conversion
characteristics.
Differential linear
error
Total error : Difference between an actual value and an ideal value. A total error includes zero transition
: Deviation of input voltage, that is required for changing output code by 1 LSB, from an ideal
value.
error, full-scale transition error, and linear error.
Total error
3FF
Actual conversion
3FE
characteristics
3FD
{1 LSB × (N − 1) + 0.5 LSB}
1.5 LSB
004
Digital output
003
002
Actual conversion
characteristics
Ideal characteristics
001
0.5 LSB
AVss AVR
Analog input
Total error of digital output “N” =
1 LSB = (Ideal value)
VNT − {1 LSB × (N − 1) + 0.5 LSB}
1 LSB
AVR − AVSS
1024
[V]
VOT (Ideal value) = AVSS + 0.5 LSB [V]
V
FST (Ideal value) = AVR − 1.5 LSB [V]
V
NT : A voltage at which digital output transits from (N-1) to N.
V
NT
(Actually-measured value)
[LSB]
(Continued)
67

MB90455 Series
(Continued)
Linear error
3FF
Actual conversion
3FE
3FD
004
Digital output
003
002
001
Differential linear error of digital output N =
characteristics
{1 LSB × (N − 1)
OT }
+ V
measurement value)
Actual conversion
characteristics
Ideal characteristics
V
OT (actual measurement value)
AVss AVR AVss AVR
Analog input
FST (actual
V
measurement
value)
VNT (actual
N + 1
N
Digital output
N − 1
N − 2
VNT − {1 LSB × (N − 1) + VOT}
Linear error of digital output N =
V (N + 1) T − VNT
1 LSB
1 LSB
−1LSB [LSB]
Differential linear error
Ideal characteristics
Actual conversion
characteristics
VNT
(actual measurement value)
Actual conversion
characteristics
Analog input
[LSB]
V
(N + 1) T
(actual measurement
value)
1 LSB =
OT : Voltage at which digital output transits from “000H” to “001H.”
V
V
FST : Voltage at which digital output transits from “3FEH” to “3FFH.”
1022
VFST − VOT
[V]
68

MB90455 Series
7. Notes on A/D Converter Section
Use the device with external circuits of the following output impedance for analog inputs:
Recommended output impedance of external circuits are: Approx. 3.9 kΩ or lower (4.5 V ≤ AVc c ≤ 5.5 V)
(sampling period=2.00 µs at 16-MHz machine clock), Approx. 11 kΩ or low er (4.0 V ≤ AVcc < 4.5 V) (sampling
period=8.0 µs at 16-MHz machine clock).
If an external capacitor is used, in consideration of the effect by tap capacitance caused by external capacitors
and on-chip capacitors, capacitance of the external one is recommended to be several thousand times as high
as internal capacitor.
If output impedance of an external circuit is too high, a sampling period for an analog voltage ma y be insufficient.
• Analog input circuit model
Analog input
Note : Use the values in the figure only as a guideline.
••••
About errors
As [AVR-AVss] become smaller, values of relative errors grow larger.
R
Comparator
C
MB90F455 (S) /F456 (S) /F457 (S) and MB90455 (S) /456 (S) /457 (S)
4.5 V
≤ AVCC ≤ 5.5 V R := 2.35 kΩ, C := 36.4 pF
4.0 V
≤ AVCC < 4.5 V R := 16.4 kΩ, C := 36.4 pF
8. Flash Memory Program/Erase Characteristics
Parameter Conditions
Sector eraset time
T
Chip erase time 4 s
A = + 25 °C
V
CC = 5.0 V
Min Typ Max
115s
Value
Unit Remarks
Excludes 00
prior to erasure
Excludes 00H programming
prior to erasure
H programming
Word (16 bit width)
programming time
Program/Erase cycle 10,000 cycle
16 3,600 µs
Except for the over head
time of the system
69

MB90455 Series
EXAMPLE CHARACTERISTICS
■■■■
•MB90F457
30
ICC − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
25
20
15
ICC (mA)
10
10
8
6
4
ICCS (mA)
2
0
5
0
2.5
2.5
f = 16 MHz
f = 10 MHz
f = 8 MHz
f = 4 MHz
f = 2 MHz
3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5
VCC (V)
ICCS − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
f = 16 MHz
f = 10 MHz
f = 8 MHz
f = 4 MHz
f = 2 MHz
3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5
VCC (V)
70
ICCL − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
350
300
250
A)
200
m
150
ICCL (
100
50
0
3
4567
VCC (V)
f = 8 kHz
(Continued)

MB90455 Series
ICCLS − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
15
14
13
12
11
10
A)
9
m
8
7
6
ICCLS (
5
4
3
2
1
0
3
4567
VCC (V)
ICCT − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
10
9
8
7
6
A)
m
5
4
ICCT (
3
2
1
0
3
4567
VCC (V)
f = 8 kHz
f = 8 kHz
ICCH ( A)
30
25
20
15
10
ICCH − VCC
Stopping, TA = +25 °C
5
0
2
3
4567
VCC (V)
(Continued)
71

MB90455 Series
(Continued)
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
LCC-VOH (mV)
300
200
100
0
0
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
VOL (mV)
300
200
100
0
0
(VCC − VOH) − IOH
2
46810
IOH (mA)
VOL − IOL
2
46810
IOL (mA)
TA = +25 °C, VCC = 4.5 V
TA = +25 °C, VCC = 4.5 V
72
VIN (V)
5
4
3
2
1
0
2.5
“H” level input voltage/ “L” level input voltage
VIN − VCC
TA = +25 °C
3 5 5.5
3.5 4 4.5 6
VCC (V)
VIH
VIL

• MB90457
MB90455 Series
ICC − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
25
20
15
10
ICC (mA)
ICCS (mA)
f = 16 MHz
f = 10 MHz
f = 8 MHz
5
0
2.5
3.5 4 4.5 6
3 5 5.5 6.5 7
VCC (V)
f = 4 MHz
f = 2 MHz
ICCS − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
2.5
3.5 4.5
5.5 6.5
VCC (V)
f = 16 MHz
f = 10 MHz
f = 8 MHz
f = 4 MHz
f = 2 MHz
ICCL − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
100
90
80
70
60
A)
m
50
40
ICCL (
30
20
10
0
3
45
VCC (V)
f = 8 kHz
67
(Continued)
73

MB90455 Series
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
ICCLS ( A)
3
2
1
0
3
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
ICCT ( A)
3
2
1
0
3
ICCLS − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
45
VCC (V)
67
ICCT − VCC
TA = +25 °C, external clock operation
f = Internal operation frequency
4
56
VCC (V)
f = 8 kHz
f = 8 kHz
7
74
ICCH ( A)
30
25
20
15
10
ICCH − VCC
Stopping, TA = +25 °C
5
0
2
3
4567
VCC (V)
(Continued)

(Continued)
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
VCC - VOH (mV)
300
200
100
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
VOL (mV)
300
200
100
MB90455 Series
(VCC − VOH) − IOH
TA = +25 °C, VCC = 4.5 V
0
0
0
0
2
13579
46
IOH (mA)
810
VOL − IOL
TA = +25 °C, VCC = 4.5 V
2
15379
46
IOL (mA)
810
VIN (V)
“H” level input voltage/ “L” level input voltage
VIN − VCC
5
4
3
2
1
0
2.5
3
3.5 5
4 4.5
VCC (V)
TA = +25 °C
VIH
VIL
5.5 6
75

MB90455 Series
ORDERING INFORMATION
■■■■
Part number Package Remarks
MB90F455PMT
MB90F456PMT
MB90F457PMT
MB90455PMT
MB90456PMT
MB90457PMT
MB90F455SPMT
MB90F456SPMT
MB90F457SPMT
MB90455SPMT
MB90456SPMT
MB90457SPMT
48-pin plastic LQFP
(FPT-48P-M26)
76

PACKAGE DIMENTION
■■■■
MB90455 Series
48-pin plastic LQFP
(FPT-48P-M26)
9.00±0.20(.354±.008)SQ
7.00±0.10(.276±.004)SQ
36 25
37
48
LEAD No.
0.50(.020)
1
INDEX
12
0.20±0.05
(.008±.002)
Note : Pins width and pins thickness include plating tackiness.
0.145±0.055
(.006±.002)
24
Details of "A" part
1.50
.059 –.004
0˚~8˚
0.50±0.20
(.020±.008)
0.60±0.15
(.024±.006)
+0.20
–0.10
+.008
(Mounting height)
0.25(.010)
13
0.08(.003)
0.08(.003)
"A"
M
0.10±0.10
(.004±.004)
(Stand off)
C
2001 FUJITSU LIMITED F48040S-c-1-1
Dimensions in mm (inches)
77

MB90455 Series
FUJITSU LIMITED
All Rights Reserved.
The contents of this document are subject to change without notice.
Customers are advised to consult with FUJITSU sales
representatives before ordering.
The information and circuit diagrams in this document are
presented as examples of semiconductor device applications, and
are not intended to be incorporated in devices for actual use. Also,
FUJITSU is unable to assume responsibility for infringement of
any patent rights or other rights of third parties arising from the use
of this information or circuit diagrams.
The products described in this document are designed, developed
and manufactured as contemplated for general use, including
without limitation, ordinary industrial use, general office use,
personal use, and household use, but are not designed, developed
and manufactured as contemplated (1) for use accompanying fatal
risks or dangers that, unless extremely high safety is secured, could
have a serious effect to the public, and could lead directly to death,
personal injury, severe physical damage or other loss (i.e., nuclear
reaction control in nuclear facility, aircraft flight control, air traffic
control, mass transport control, medical life support system, missile
launch control in weapon system), or (2) for use requiring
extremely high reliability (i.e., submersible repeater and artificial
satellite).
Please note that Fujitsu will not be liable against you and/or any
third party for any claims or damages arising in connection with
above-mentioned uses of the products.
Any semiconductor devices have an inherent chance of failure. You
must protect against injury, damage or loss from such failures by
incorporating safety design measures into your facility and
equipment such as redundancy, fire protection, and prevention of
over-current levels and other abnormal operating conditions.
If any products described in this document represent goods or
technologies subject to certain restrictions on export under the
Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Law of Japan, the prior
authorization by Japanese government will be required for export
of those products from Japan.
F0208
FUJITSU LIMITED Printed in Japan
 Loading...
Loading...