Page 1

C141-E166-02EN
MAP3147NC/NP
MAP3735NC/NP
MAP3367NC/NP
DISK DRIVES
PRODUCT/MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Page 2

FOR SAFE OPERATION
Handling of This manual
This manual contains important information for using this product. Read thoroughly before using the
product. Use this product only after thoroughly reading and understanding especially the section “Important
Alert Items” in this manual. Keep this manual handy, and keep it carefully.
FUJITSU makes every effort to prevent users and bystanders from being injured or from suffering damage
to their property. Use the product according to this manual.
IMPORTANT NOTE TO USERS
READ THE ENTIRE MANUAL CAREFULLY BEFORE USING THIS PRODUCT.
INCORRECT USE OF THE PRODUCT MAY RESULT IN INJURY OR DAMAGE
TO USERS, BYSTANDERS OR PROPERTY.
While FUJITSU has sought to ensure the accuracy of all information in this manual, FUJITSU assumes no
liability to any party for any damage caused by any error or omission contained in this manual, its updates
or supplements, whether such errors or omissions result from negligence, accident, or any other cause. In
addition, FUJITSU assumes no liability with respect to the application or use of any porduct or system in
accordance with the descriptions or instructions contained herein; including any liability for incidental or
consequential damages arising therefrom.
FUJTSU DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES REGARDING THE INFORMATION CONTAINED
HEREIN, WHETHER EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY.
FUJITSU reserves the right to make changes to any products described herein without further notice and
without obligation.
This product is designed and manufactured for use in standard applications such as office work, personal
devices and household appliances. This product is not intended for special uses (atomic controls,
aeronautic or space systems, mass transport vehicle operating controls, medical devices for life support, or
weapons firing controls) where particularly high reliability requirements exist, where the pertinent levels of
safety are not guaranteed, or where a failure or operational error could threaten a life or cause a physical
injury (hereafter referred to as "mission-critical" use). Customers considering the use of these products for
mission-critical applications must have safety-assurance measures in place beforehand. Moreover, they are
requested to consult our sales representative before embarking on such specialized use.
The contents of this manual may be revised without prior notice.
The contents of this manual shall not be disclosed in any way or reproduced in any media without the
express written permission of Fujitsu Limited.
All Right Reserved, Copyright © FUJITSU LIMITED 2002
C141-E166
Page 3
REVISION RECORD
Edition Date published Revised contents
01 May, 2002
02 July, 2002
• Table 2.1 is partly modified.
• Specifications of Table 2.2 and 2.3 are partly modified.
• Specifications in Figure 3.1 and subsection 3.1.1(1) are partly modified.
• Specification of mounting screw in subsection 4.1.1 is added.
• Procedures of spindle motor startup in section 4.2(4) is modified.
• Section 4.3 is revised.
• Section 5.3 is revised.
• Length of mounting screw in subsection 5.4.2 is modified.
• Troubleshooting in Table 6.2 is added.
• APPENDIX A and B are revised.
Specification No.: C141-E166-**EN
C141-E166 i
Page 4
Related Standards
Product specifications and functions described in this manual comply with the following ANSI
(*1) standards.
Document number Title
T10/1236D Rev.20
[NCITS.351:2001]
T10/996D Rev.8c
[NCITS.306:1998]
T10/1157D Rev.20 SCSI Architecture Model-2 (SAM-2)
T10/1365D Rev.7 SCSI Parallel Interface-4 (SPI-4)
*1 ANSI = American National Standard Institute
In case of conflict between this manual and any referenced document, this manual takes
precedence.
SCSI Primary Commands-2 (SPC-2)
SCSI-3 Block Commands (SBC)
ii C141-E166
Page 5

PREFACE
This manual describes the MAP3147NC/NP, MAP3735NC/NP and MAP3367NC/NP (hereafter, MAP
series), 3.5 type fixed disk drives with an embedded SCSI controller.
This manual details the specifications and functions of the above disk drive, and gives the requirements and
procedures for installing it into a host computer system.
This manual is written for users who have a basic understanding of fixed disk drives and their use in
computer systems. The MANUAL ORGANIZATION section describes organization and scope of this
manual. The need arises, use the other manuals.
OVERVIEW OF MANUAL
This manual consists of the following eight chapters:
CHAPTER 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
This chapter introduces the MAP series disk drives and discusses their standard features, hardware, and
system configuration.
CHAPTER 2 SPECIFICATIONS
This chapter gives detailed specifications of the MAP series disk drives and their installation environment.
CHAPTER 3 DATA FORMAT
This chapter describes the data structure of the disk, the address method, and what to do about media
defects.
CHAPTER 4 INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
This chapter describes the basic physical and electrical requirements for installing MAP series disk drives.
CHAPTER 5 INSTALLATION
This chapter explains how to install MAP series disk drives. It includes the notice and procedures for
setting device number and operation modes, mounting the disk drive, connecting the cables, and confirming
drive operation.
CHAPTER 6 DIAGNOSIS AND MAINTENANCE
This chapter describes the automatic diagnosis, and maintenance of MAP series disk drive. This chapter
also describes diagnostic methods for operation check and the basics of troubleshooting the disk drives.
CHAPTER 7 ERROR ANALYSIS
This chapter describes in details how collect the information for error analysis and how analyze collected
error information.
APPENDIX A TO B
The appendixes give supplementary information, including a list of setting items and the signal assignments
of interface connector.
C141-E166 iii
Page 6
CONVENTIONS FOR ALERT MESSAGES
This manual uses the following conventions for alerts to prevent physical or property damages to users or
by standards.
CAUTION
NOTICE
IMPORTANT
CONVENTIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL
The MAP3147NC/NP, MAP3735NC/NP and MAP3367NC/NP disk drives are described as "the intelligent
disk drive (IDD)", "the drive" or "the device" in this manual.
Decimal number is represented normally.
Hexadecimal number is represented as X'17B9', 17B9h or 17B9H.
Binary number is represented as "010".
This indicates that either minor or moderate
personal injury may occur if the user does not
perform the procedure correctly.
This indicates that inconvenience to the user
such as damages to the product, equipment, data,
and/or other property may occur if the user does
not pay attention or perform the procedure
correctly.
This indicates information that the helps the user
use the product more effectively.
ATTENTION
Please forward any comments you may have regarding this manual.
To make this manual easier for users to understand, opinions from readers are needed. Please write your
opinions or requests on the Comment at the back of this manual and forward it to the address described in
the sheet.
iv C141-E166
Page 7
Important Alert Items
Important Alert Messages
The important alert messages in this manual are as follows:
A hazardous situation could result in minor or moderate personal injury if the
user does not perform the procedure correctly. This alert signal also indicates
that damages to the product or other property may occur if the user does not
perform the procedure correctly.
Task Alert message Page
Mounting Installation
Data loss
For MAP series, Reed Solomon codes are applied for their ECC.
The sector-data is divided into 6 interleaving sectors, and ECC is
performed in each sector where the maximum number of errors
(up to 5 byte) can be corrected. [Total maximum byte: 5 byte
( interleave) = 30 byte]
If the error of read sector keeps allowable error byte number,
correction is performed.
However, if error byte exceeds its allowable number, correction
may not be performed properly.
Hot temperature
To prevent injury, do not handle the drive until after the device has
cooled sufficiently after turning off the power. The DE and LSI
become hot during operation and remain hot immediately after
turning off the power.
Data loss
1. The user must not change the setting of terminals not described
in this section. Do not change setting status set at factory
shipment.
2. Do not change the setting of terminals except following setting
pins during the power is turned on.
• Write protect: CN2 9-10 (NP model only)
3. To short the setting terminal, use the short plug attached when
the device is shipped from the factory.
Damage
1. Make sure that system power is off before connecting or
disconnecting cables.
2. Do not connect or disconnect cables when power is on.(except
NC model)
×
6
2-5
5-1
5-5
5-11
C141-E166 v
Page 8

Task Alert message Page
Mounting Installation
Damage
1. Be careful of the insertion orientation of the SCSI connectors.
With the system in which terminating resistor power is supplied
via the SCSI cable, if the power is turned on, the overcurrent
protection fuse of the terminating resistor power supplier may
be blown or the cable may be burnt if overcurrent protection is
not provided.
When the recommended parts listed in Table 4.2 are used,
inserting the cables in the wrong direction can be prevented.
2. To connect SCSI devices, be careful of the connection position
of the cable. Check that the SCSI device with the terminating
resistor is the last device connected to the cable.
Data loss
When the SEND DIAGNOSTIC command terminates with the
CHECK CONDITION status, the INIT must collect the error
information using the REQUEST SENSE command. The RECEIVE
DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS command cannot read out the error
information detected in the self-diagnostics.
Caution
1. To avoid shocks, turn off the power before connecting or
disconnecting a cable, connector, or plug.
2. To avoid injury, do not touch the mechanical assembly during
disk drive operation.
3. Do not use solvents to clean the disk drive.
Caution
1. Always ground yourself with a wrist strap connected to ground
before handling. ESD (Electrostatics Discharge) may cause
the damage to the device.
2. To prevent electrical damage to the disk drive, turn the power
off before connecting or disconnecting a cable, connector, or
plug.
3. Do not remove a PCA. This operation is required to prevent
unexpected or unpredictable operation.
4. Do not use a conductive cleaner to clean a disk drive assembly.
5. Ribbon cables are marked with a colored line. Connect the
ribbon cable to a cable connector with the colored wire
connected to pin 1.
Damage
Never open the disk enclosure in the field. Opening the disk
enclosure may cause an irreparable fault.
Data loss
Save data stored on the disk drive before requesting repair. Fujitsu
does not assume responsibility if data is destroyed during servicing
or repair.
5-11
6-4
6-5
6-6
6-6
6-15
6-7
vi C141-E166
Page 9
MANUAL ORGANIZATION
PRODUCT/
MAINTENANCE
MANUAL
(This manual)
SCSI Physical
Interface
Specifications
SCSI Logical
Interface
Specifications
1. General Description
2. Specifications
3. Data Format
4. Installation Requirements
5. Installation
6. Diagnostics and Maintenance
7. Error Analysis
1. SCSI Bus
2. SCSI Message
3. SCSI Bus Error Recovery Processing
1. Command Processing
2. Data Buffer Management
3. Command Specification
4. Sense Data and error Recovery Procedure
5. Disk Medium Management
C141-E166 vii
Page 10

This page is intentionally left blank.
Page 11

CONTENTS
page
CHAPTER 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................1-1
1.1 Standard Features ..............................................................................................................1-2
1.2 Hardware Structure............................................................................................................1-6
1.3 System Configuration........................................................................................................1-9
CHAPTER 2 SPECIFICATIONS...........................................................................................2-1
2.1 Hardware Specifications....................................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 Model name and order number..........................................................................................2-1
2.1.2 Function specifications......................................................................................................2-2
2.1.3 Environmental specifications ............................................................................................2-4
2.1.4 Error rate ...........................................................................................................................2-5
2.1.5 Reliability..........................................................................................................................2-5
2.2 SCSI Function Specifications............................................................................................2-7
CHAPTER 3 DATA FORMAT...............................................................................................3-1
3.1 Data Space.........................................................................................................................3-1
3.1.1 Cylinder configuration.......................................................................................................3-1
3.1.2 Alternate spare area...........................................................................................................3-4
3.1.3 Track format......................................................................................................................3-5
3.1.4 Sector format.....................................................................................................................3-7
3.1.5 Format capacity.................................................................................................................3-9
3.2 Logical Data Block Addressing.........................................................................................3-9
3.3 Defect Management...........................................................................................................3-11
3.3.1 Defect list ..........................................................................................................................3-11
3.3.2 Alternate block allocation .................................................................................................3-11
CHAPTER 4 INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS .............................................................4-1
4.1 Mounting Requirements ....................................................................................................4-1
4.1.1 External dimensions ..........................................................................................................4-1
4.1.2 Mounting...........................................................................................................................4-4
4.1.3 Notes on mounting ............................................................................................................4-4
4.2 Power Supply Requirements .............................................................................................4-8
4.3 Connection Requirements..................................................................................................4-11
4.3.1 SCA2 connector type 16-bit SCSI model (NC model)......................................................4-11
C141-E166 ix
Page 12

4.3.2 68 pin connector type 16-bit SCSI model (NP model)......................................................4-13
4.3.3 Cable connector requirements ...........................................................................................4-20
4.3.4 External operator panel (on NP model drives only) ..........................................................4-21
CHAPTER 5 INSTALLATION...............................................................................................5-1
5.1 Notes on Handling Drives.................................................................................................5-1
5.2 Connections.......................................................................................................................5-3
5.3 Setting Terminals ..............................................................................................................5-5
5.3.1 SCSI ID setting..................................................................................................................5-6
5.3.2 Each mode setting .............................................................................................................5-8
5.3.3 Mode settings ....................................................................................................................5-10
5.4 Mounting Drives................................................................................................................5-11
5.4.1 Check before mounting .....................................................................................................5-11
5.4.2 Mounting procedures.........................................................................................................5-11
5.5 Connecting Cables.............................................................................................................5-12
5.6 Confirming Operations after Installation and Preparation for use.....................................5-13
5.6.1 Confirming initial operations.............................................................................................5-13
5.6.2 Checking SCSI connection................................................................................................5-14
5.6.3 Formatting .........................................................................................................................5-17
5.6.4 Setting parameters .............................................................................................................5-19
5.7 Dismounting Drives...........................................................................................................5-23
5.8 Spare Disk Drive ...............................................................................................................5-23
CHAPTER 6 DIAGNOSTICS AND MAINTENANCE ........................................................6-1
6.1 Diagnostics........................................................................................................................6-1
6.1.1 Self-diagnostics .................................................................................................................6-1
6.1.2 Test programs....................................................................................................................6-4
6.2 Maintenance Information ..................................................................................................6-5
6.2.1 Precautions........................................................................................................................6-5
6.2.2 Maintenance requirements.................................................................................................6-6
6.2.3 Maintenance levels............................................................................................................6-8
6.2.4 Revision numbers..............................................................................................................6-9
6.2.5 Tools and test equipment...................................................................................................6-10
6.2.6 Tests ..................................................................................................................................6-10
6.3 Operation Check................................................................................................................6-12
6.3.1 Initial seek operation check...............................................................................................6-12
6.3.2 Operation test ....................................................................................................................6-12
x C141-E166
Page 13

6.3.3 Diagnostic test ...................................................................................................................6-12
6.4 Troubleshooting Procedures..............................................................................................6-13
6.4.1 Outline of troubleshooting procedures ..............................................................................6-13
6.4.2 Troubleshooting with disk drive replacement in the field .................................................6-13
6.4.3 Troubleshooting at the repair site......................................................................................6-15
6.4.4 Troubleshooting with parts replacement in the factory .....................................................6-16
6.4.5 Finding possibly faulty parts .............................................................................................6-16
CHAPTER 7 ERROR ANALYSIS .........................................................................................7-1
7.1 Error Analysis Information Collection ..............................................................................7-1
7.1.1 Sense data..........................................................................................................................7-1
7.1.2 Sense key, sense code, and subsense code ........................................................................7-1
7.2 Sense Data Analysis ..........................................................................................................7-3
7.2.1 Error information indicated with sense data ......................................................................7-3
7.2.2 Sense data (3-0C-03), (4-40-xx), (4-44-xx), and (4-C4-xx) ..............................................7-4
7.2.3 Sense data (1-1x-xx), (3-1x-xx) and (E-1D-00): Disk read error ....................................7-4
7.2.4 Sense data (5-2x-xx), (5-3D-00), (5-90-00), (B-47-xx), (B-49-00),
(B-4D-xx) and (B-4E-00): SCSI interface error...............................................................7-4
APPENDIX A SETTING TERMINALS..................................................................................A-1
A.1 Setting Terminals (on NP model only)..............................................................................A-2
APPENDIX B CONNECTOR SIGNAL ALLOCATION.......................................................B-1
B.1 SCSI Connector Signal Allocation: SCA2 type LVD 16-bit SCSI...................................B-2
B.2 SCSI Connector Signal Allocation: 68 pin type LVD 16-bit SCSI ..................................B-3
INDEX ........................................................................................................................................IN-1
C141-E166 xi
Page 14

FIGURES
page
Figure 1.1 NC model drives outer view .................................................................................................1-6
Figure 1.2 NP model drives outer view .................................................................................................1-6
Figure 1.3 Disk/head configuration........................................................................................................1-7
Figure 1.4 System configuration ............................................................................................................1-9
Figure 3.1 Cylinder configuration..........................................................................................................3-2
Figure 3.2 Spare area in cell ..................................................................................................................3-5
Figure 3.3 Alternate cylinder .................................................................................................................3-5
Figure 3.4 Track format.........................................................................................................................3-6
Figure 3.5 Track skew/head skew..........................................................................................................3-7
Figure 3.6 Sector format ........................................................................................................................3-7
Figure 3.7 Alternate block allocation by FORMAT UNIT command .................................................3-13
Figure 3.8 Alternate block allocation by REASSIGN BLOCKS command ........................................3-14
Figure 4.1 NC external dimensions........................................................................................................4-2
Figure 4.2 NP external dimensions........................................................................................................4-3
Figure 4.3 IDD orientations ...................................................................................................................4-4
Figure 4.4 Mounting frame structure .....................................................................................................4-5
Figure 4.5 Limitation of side-mounting .................................................................................................4-5
Figure 4.6 Surface temperature measurement points .............................................................................4-6
Figure 4.7 Service clearance area ..........................................................................................................4-7
Figure 4.8 Spin-up current waveform (+12 VDC).................................................................................4-8
Figure 4.9 Power on/off sequence (1)....................................................................................................4-8
Figure 4.10 Power on/off sequence (2)....................................................................................................4-9
Figure 4.11 Power on/off sequence (3)....................................................................................................4-9
Figure 4.12 AC noise filter (recommended) ..........................................................................................4-11
Figure 4.13 NC connectors location ......................................................................................................4-11
Figure 4.14 SCA2 type 16-bit SCSI connector......................................................................................4-12
Figure 4.15 NP connectors and terminals location ................................................................................4-13
Figure 4.16 68 pin type 16-bit SCSI interface connector.......................................................................4-14
Figure 4.17 Power supply connector (68 pin type 16-bit SCSI) ............................................................4-14
Figure 4.18 External operator panel connector (CN1)...........................................................................4-15
Figure 4.19 External operator panel connector (CN2)...........................................................................4-15
xii C141-E166
Page 15

Figure 4.20 16-bit SCSI ID external input.............................................................................................4-16
Figure 4.21 Output signal for external LED ..........................................................................................4-18
Figure 4.22 SCSI cables connection ......................................................................................................4-19
Figure 4.23 External operator panel circuit example .............................................................................4-21
Figure 5.1 SCSI bus connections ..........................................................................................................5-4
Figure 5.2 Setting terminals location (on NP models only) ...................................................................5-5
Figure 5.3 CN2 setting terminal (on NP models only)...........................................................................5-6
Figure 5.4 Checking the SCSI connection (A).....................................................................................5-15
Figure 5.5 Checking the SCSI connection (B).....................................................................................5-16
Figure 6.1 Revision label.......................................................................................................................6-9
Figure 6.2 Indicating revision numbers................................................................................................6-10
Figure 6.3 Test flowchart.....................................................................................................................6-11
Figure 7.1 Format of extended sense data..............................................................................................7-2
C141-E166 xiii
Page 16

TABLES
page
Table 2.1 Model names and order numbers..............................................................................................2-1
Table 2.2 Function specifications.............................................................................................................2-2
Table 2.3 Environmental/power requirements..........................................................................................2-4
Table 2.4 SCSI function specifications.....................................................................................................2-7
Table 3.1 Zone layout and track capacity.................................................................................................3-3
Table 3.4 Format capacity ........................................................................................................................3-9
Table 4.1 Surface temperature check point...............................................................................................4-6
Table 4.2 Recommended components for connection............................................................................4-20
Table 5.1 SCSI ID setting.........................................................................................................................5-7
Table 5.2 Setting SCSI terminator power supply (NP model)..................................................................5-8
Table 5.3 Motor start mode setting...........................................................................................................5-8
Table 5.4 Write protect setting (NP model)..............................................................................................5-9
Table 5.5 Setting of the SCSI interface operation mode (NP model).......................................................5-9
Table 5.6 Setting the bus width of the SCSI interface (NP model)..........................................................5-9
Table 5.7 Default mode settings (by CHANGE DEFINITION command) ............................................5-10
Table 5.8 Setting check list (NP model only) .........................................................................................5-11
Table 6.1 Self-diagnostic functions ..........................................................................................................6-1
Table 6.2 System-level field troubleshooting .........................................................................................6-14
Table 6.3 Disk drive troubleshooting .....................................................................................................6-15
Table 7.1 Definition of sense data............................................................................................................7-3
Table A.1 CN2 setting terminal (on NP model drives only).................................................................A-2
Table B.1 SCSI connector (SCA2 type LVD 16-bit SCSI): CN1 ...........................................................B-2
Table B.2 SCSI connector (68 pin type LVD 16-bit SCSI): CN1........................................................... B-3
xiv C141-E166
Page 17

CHAPTER 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
1.1 Standard Features
1.2 Hardware Structure
1.3 System Configuration
This chapter describes the feature and configuration of the MAP series intelligent disk drives (IDD).
IDDs are high performance large capacity 3.5 type fixed disk drives with an embedded SCSI controller.
The MAP series disk drives support the Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) as described in the ANSI
SCSI SPI-4 [T10/1365D Rev.7] to the extent described in this manual.
The flexibility and expandability of the SCSI, as well as the powerful command set of the IDD, allow the
user to construct a high-performance reliable disk subsystem with large storage capacity.
The data format can be changed from the format at factory shipment by reinitializing with the user's system.
Refer to SCSI Logical Interface Specifications for details.
C141-E166 1-1
Page 18

1.1 Standard Features
(1) Compactness
Since the SCSI controller circuit is embedded in the standard 3.5 type fixed disk drive form factor,
the IDD is extremely compact. The IDD can be connected directly to the SCSI bus of the host
system.
(2) SCSI standard
The IDD provides not only SCSI basic functions but also the following features:
• Arbitration
• Disconnection/Reconnection
• Data bus parity
The SCSI commands can manipulate data through logical block addressing regardless of the
physical characteristics of the disk drive. This allows software to accommodate future expansion
of system functions.
(3) 8-bit SCSI/16-bit SCSI
The IDD has 16-bit data bus width (16-bit SCSI), which have the wide transfer function suitable
for SCSI-2. 8-bit data bus is available only with NP model.
See subsection 5.3.2 for details of the bus width setting.
For the ultra SCSI model, number of connectable SCSI devices on the same SCSI bus is varied as
follows.
• 8-bit SCSI: 8 drives max. (option for NP model)
• 16-bit SCSI: 16 drives max.
(4) High speed data transfer
Such a high data transfer rate on the SCSI bus can be useful with the large capacity buffer in the
IDD.
• 8-bit SCSI: The data transfer rate on the SCSI bus is 40 MB/s maximum at the
synchronous mode.
• 16-bit SCSI: The data transfer rate on the SCSI bus is 320 MB/s maximum at the paced
transfer synchronous mode.
1-2 C141-E166
Page 19

Note:
The maximum data transfer rate in asynchronous mode may be limited by the response time of
initiator and the length of SCSI bus length. The maximum data transfer rate in synchronous
mode may be limited by the cable length, transmission characteristics of the SCSI bus and the
connected SCSI device number.
(5) Continuous block processing
The addressing method of data blocks is logical block address. The initiator can access data by
specifying block number in a logically continuous data space without concerning the physical
structure of the track or cylinder boundaries.
The continuous processing up to [64K-1] blocks in a command can be achieved, and IDD can perform
continuous read/write operation when processing data blocks on several tracks or cylinder.
(6) Programmable multi-segment data buffer
The data buffer is 8M bytes. Data is transferred between SCSI bus and disk media through this
data buffer. This feature provides the suitable usage environment for users.
Since the initiator can control the disconnect/reconnect timing on the SCSI bus by specifying the
condition of stored data to the data buffer or empty condition of the data buffer, the initiator can
perform the effective input/output operations with utilizing high data transfer capability of the
SCSI bus regardless of actual data transfer rate of the disk drive.
(7) Cache feature
After executing the READ command, the IDD reads automatically and stores (prefetches) the
subsequent data blocks into the data buffer (Read-ahead caching).
The high speed sequential data access can be achieved by transferring the data from the data buffer
without reaccessing the disk in case the subsequent command requests the prefetched data blocks.
You should ensure that the cashed data is surely flushed to the disc
media before you turn off the drive's power.
To ensure it, you should issue either the SYNCHRONIZE CASHE
command or the STOP UNIT command and then confirm that the
command is surely terminated with the GOOD STATUS.
(8) Command queuing feature
The IDD can queue maximum 128 commands, and optimizes the issuing order of queued
commands by the reordering function. This feature realizes the high speed processing.
IMPORTANT
C141-E166 1-3
Page 20

(9) Reserve and release functions
The IDD can be accessed exclusively in the multi-host or multi-initiator environment by using the
reserve and release functions.
(10) Error recovery
The IDD can try to recover from errors in SCSI bus or the disk drive using its powerful retry
processing. If a recoverable data check occurs, error-free data can be transferred to the initiator
after being corrected in the data buffer. The initiator software is released from the complicated
error recover processing by these error recovery functions of the IDD.
(11) Automatic alternate block reassignment
If a defective data block is detected during read or write the IDD can automatically reassign its
alternate data block.
(12) Programmable data block length
Data can be accessed in fixed-block length units. The data block length is programmable, and can
be specified at initializing with a multiple of four within the range of 512 to 528 bytes.
Error rate increase
1. The drive format at factory shipment is generally 512 byte.
2. The Recoverable Error of the drive might increase when the
format would be modified from 512 bytes to the following values:
516 bytes, 520 bytes, 524 bytes, 528 bytes.
3. The Recoverable Error referred to here is sense data (1-13-xx).
(13) Defective block slipping
A logical data block can be reallocated in a physical sequence by slipping the defective data block
at formatting. This results in high speed contiguous data block processing without a revolution
delay due to defective data block.
(14) High speed positioning
A rotary voice coil motor achieves fast positioning.
IMPORTANT
1-4 C141-E166
Page 21

(15) Large capacity
A large capacity can be obtained from 3.5 inch disk drives by dividing all cylinders into several
partitions and changing the recording density on each partition (constant density recording). The
disk subsystem with large capacity can be constructed in the good space efficiency.
(16) Start/Stop of spindle motor
Using the SCSI command, the host system can start and stop the spindle motor.
(17) Diagnosis
The IDD has a diagnostic capability which checks internal controller functions and drive
operations to facilitate testing and repair.
(18) Low power consumption
By using highly integrated LSI components, the power consumption of the IDD is very low, and
this enables the unit to be used in wide range of environmental conditions.
(19) Low noise and low vibration
The noise level is low; approx. 3.4 Bels Ready for MAP series. This makes it ideal for office use.
(20) Microcode downloading
The IDD implements the microcode download feature. This feature achieves easy maintainability
of the IDD and function enhancing.
C141-E166 1-5
Page 22
1.2 Hardware Structure
An outer view of the IDD is given in Figures 1.1 and 1.2. The IDD is composed of the disk, head,
spindle motor, mounted disk enclosure (DE) with actuator and air circulation filter, as well as
read/write pre-amp with the printed circuit assembly (PCA) of the controller.
Figure 1.1 NC model drives outer view
Figure 1.2 NP model drives outer view
1-6 C141-E166
Page 23
(1) Disks
The disks have an outer diameter of 84 mm (3.3 inch) and an inner diameter of 25 mm (0.98 inch)
for MAP series. The disks are good for at least 20,000 contact starts and stops. Each model
contains following number of disks.
(2) Heads
The MR (Magnet - Resistive) of the CSS (contact start/stop) type heads are in contact with the
disks when the disks are not rotating, and automatically float when the rotation is started. Figure
1.3 shows the configuration of disks and heads
MAP3147NC/NP: 4
MAP3735NC/NP: 2
MAP3367NC/NP: 1
Base
Cover
(3) Spindle motor
The disks are rotated by a direct-drive hall-less DC motor. The motor speed is controlled by a
feedback circuit using the counter electromotive current to precisely maintain of the specified
speed.
MAP3147NC/NP
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Figure 1.3 Disk/head configuration
MAP3735NC/NP
0
1
2
3
MAP3367NC/NP
0
1
(4) Actuator
The actuator, which uses a rotary voice coil motor (VCM), consumes little power and generates
little heat. The heads at the end of the actuator arm is controlled and positioned via feedback of
servo information in the data.
The heads are positioned on the CCS zone over the disks when the power is off or the spindle
motor is stopped.
C141-E166 1-7
Page 24

(5) Air circulation (recirculation filter, breather filter)
The disk enclosure (DE) configures a clean room to keep out particle and other contaminants. The
DE has a closed-loop air recirculation system. Using the movement of the rotating disks, air is
continuously cycled through a filter. This filter will trap any particle floating inside the enclosure
and keep the air inside the DE contaminant free. To prevent negative pressure in the vicinity of the
spindle when the disks begin rotating, a breather filter is attached. The breather filter also
equalizes the internal air pressure with the atmospheric pressure due to surrounding temperature
changes.
(6) Read/write circuit
The read/write circuit utilizes a read channel mounted with a head IC that supports high-speed
transmission and an MEEPR4ML (Modified Enhanced Extended Partial Response Class 4
Maximum Likelihood) modulation/demodulation circuit in order to prevent errors being triggered
by external noise and to improve data reliability.
(7) Controller circuit
The controller circuit uses LSIs to increase the reliability and uses a high speed microprocessing
unit (MPU) to increase the performance of the SCSI controller.
1-8 C141-E166
Page 25
1.3 System Configuration
Figure 1.4 shows the system configuration. The IDDs are connected to the SCSI bus of host
systems and are always operated as target. The IDDs perform input/output operation as specified
by SCSI devices which operate as initiator.
SCSI bus
Figure 1.4 System configuration
C141-E166 1-9
Page 26

(1) SCSI bus configuration
Up to eight SCSI devices operating as an initiator or a target can be connected to the SCSI bus for
the 8-bit SCSI and up to 16 SCSI devices operating as an initiator or a target can be connected to
the SCSI bus for the 16-bit SCSI in any combination.
For example, the system can be configured as multi-host system on which multiple host computers
that operate as initiator or connected through the SCSI bus.
Using disconnect/reconnect function, concurrent input/output processing is possible on multi-SCSI
devices.
(2) Addressing of peripheral device
Each SCSI device on the bus has its own unique address (SCSI ID:#n in Figure 1.4). For
input/output operation, a peripheral device attached to the SCSI bus that operates as target is
addressed in unit called as logical unit. A unique address (LUN: logical unit number) is assigned
for each logical unit.
The initiator selects one SCSI device by specifying that SCSI ID, then specifies the LUN to select
the peripheral device for input/output operation.
The IDD is constructed so that the whole volume of disk drive is a single logical unit, the
selectable number of SCSI ID and LUN are as follows:
• SCSI ID: 8-bit SCSI:Selectable from 0 to 7 (option for NP model, switch selectable)
16-bit SCSI:Selectable from 0 to 15 (switch selectable)
• LUN: 0 (fixed)
1-10 C141-E166
Page 27
CHAPTER 2 SPECIFICATIONS
2.1 Hardware Specifications
2.2 SCSI Function Specifications
This chapter describes specifications of the IDD and the functional specifications of the SCSI.
2.1 Hardware Specifications
2.1.1 Model name and order number
Each model has a different recording capacities and interface connector type when shipped. Table
2.1 lists the model name and order number.
The data format can be changed by reinitializing with the user's system.
Table 2.1 Model names and order numbers
Model name Order number SCSI type Capacity
(user area)
MAP3147NC CA06200-B400 SCA2, LVD
147.01 GB 4 8
MAP3147NP CA06200-B460 68-pin, LVD
MAP3735NC CA06200-B200 SCA2, LVD
73.50 GB 2 4
MAP3735NP CA06200-B260 68-pin, LVD
MAP3367NC CA06200-B100 SCA2, LVD
36.74 GB 1 2
MAP3367NP CA06200-B160 68-pin, LVD
Number of
disks
Number
of heads
C141-E166 2-1
Page 28
2.1.2 Function specifications
Table 2.2 shows the function specifications of the IDD.
Table 2.2 Function specifications
Item
MAP3147NC/NP MAP3735NC/NP MAP3367NC/NP
Specification
Formatted capacity/device (*1) 147.01 GB 73.50 GB 36.74 GB
Number of disks 4 2 1
Number of heads 8 4 2
Number of cylinders (*2) 47,926 47,996 48,122
Formatted capacity/track (B) 272,896 to 479,232
Number of rotations min-1 (rpm) 10,025±0.2%
Average latency time 2.99 msec
Seek time (*3)
(Read/Write)
Start/stop time
(*4)
Track to Track
Average
Full stroke
Start time
Stop time
0.3 ms/0.5 ms
4.5 ms/5.0 ms
10.0 ms/11.0 ms
30 s typ. (60 s max.)
30 s typ.
Recording mode 32/34 MEEPRML
External
dimensions
Height:
Width:
Depth:
25.4 mm
101.6 mm
146.0 mm
Weight (max) 0.75 kg
Power consumption (*5) 9.5 W 6.6 W 5.8 W
Fast 5 SCSI Cable length: 6 m max
SingleEnded
Interface
LVD
Data
transfer
rate (*10)
Fast 10 SCSI Cable length: 3 m max
Fast 20 SCSI
U160
Disk drive
Synchronous
SCSI
mode
Cable length: 3 m max (*6)
Cable length: 1.5 m max (*7)
Cable length: 25 m max (*8)
Cable length: 12 m max (*9)
64.1 to 107.86 MB/s
320 MB/s max.
Logical data block length (*11) 512 to 528 byte (Fixed length)
SCSI command specification
SPI-4 (T10/1365D Rev.7), SAM-2 (T10/1157D Rev.20),
SPC-2 (T10/1236D Rev.20), SBC (T10/996D Rev.8c)
Data buffer 8 MB FIFO ring buffer
Acostic noise (Ready) 3.4 Bels
2-2 C141-E166
Page 29
(*1)
[
]
The formatted capacity can be changed by changing the logical block length and using spare sector
space. See Chapter 3 for the further information. The formatted capacity listed in the table is an
estimate for 512 bytes per sector.
(*2)
(*3)
The number of user cylinders indicates the max., and includes the alternate cylinder. The number
of user cylinders and alternate cylinders can be specified at format of the IDD.
The positioning time is as follows:
ms
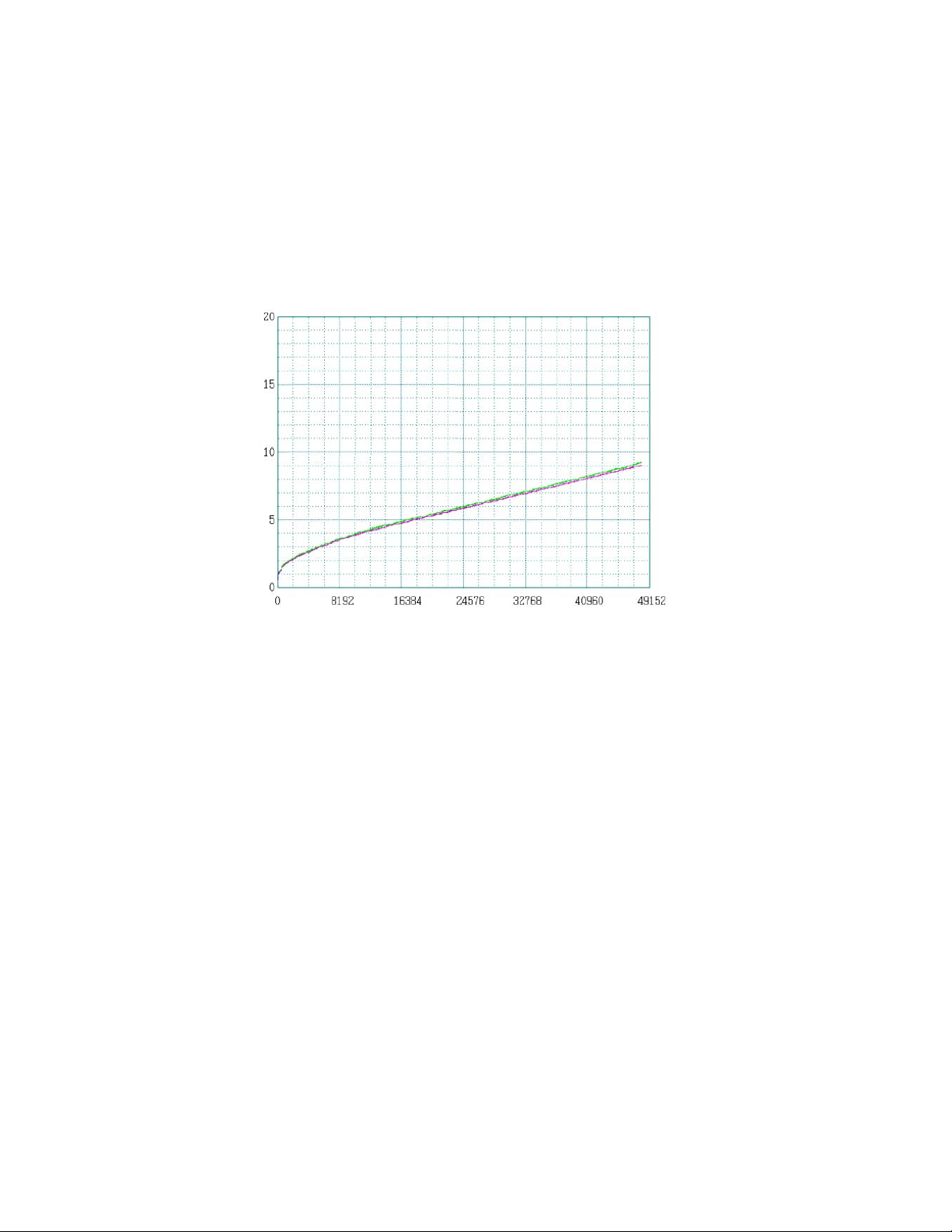
Seek time
Seek Difference [2048 Cyl/div]
(*4)
The start time is the time from power on or start command to when the IDD is ready, and the stop
time is the time for disks to completely stop from power off or stop command.
(*5)
(*6)
(*7)
(*8)
(*9)
(*10)
This value indicates at ready mode.
Up to 4 SCSI devices having capacitance of 25pF or less can use cable length of up to 3.0 m.
5 to 8 SCSI devices having capacitance of 25pF or less can use cable length of up to 1.5 m.
1 on 1 connection case.
1 host, 15 devices case.
The maximum data transfer rate may be restricted to the response speed of initiator and by
transmission characteristics.
(*11)
The terminator power pin (SCSI connector) which supplies power to other terminators is not used.
C141-E166 2-3
Page 30
2.1.3 Environmental specifications
Table 2.3 lists environmental and power requirements.
Table 2.3 Environmental/power requirements
Temperature
(*1)
Relative
humidity
Vibration
(*2)
Shock (*2)
(above sea
level)
Power
requirements
Input power
(*5)
Item
MAP3147NC/NP MAP3735NC/NP MAP3367NC/NP
Specification
Operating 5 to 55°C
Non-operating –40 to 70°C
Transport
(within a week)
DE surface temperature
at operating
–40 to 70°C
5 to 60°C
Gradient 15°C/h or less
Operating 5 to 95%RH
Non operating 5 to 95%RH
Transport
(within a week)
Maximum wet bulb
temperature
5 to 95%RH
29°C (no condensation)
Operating (*3) 0.3 mm (5 to 20Hz)/9.8 m/s2 (1G) (20 to 300 Hz) or less
Non-operating (*4) 3.1 mm (5 to 20Hz)/49m/s2 (5G) (20 to 300Hz) or less
Transport (packaged) 3.1 mm (5 to 20Hz)/49m/s
2
(5G) (20 to 300Hz) or less
Operating 637.4m/s2 (65G) (2 ms)
Non-operating 1961.3m/s2 (200G) (2 ms)
Transport (packaged) 1961.3m/s
2
(200G) (2 ms)
Operating –300 m to 3,000 mAltitute
Non-operating –300 m to 12,000 m
Ready
(Average)
0.65 A 0.42 A 0.33 A
Peak within
+12 VDC
±5%
100 µs at
spin-up
Random
W/R
(about 80
0.90 A 0.65 A 0.55 A
3.0 A
IOPS)
Ready 0.38 A
+5 VDC
±5% (*6)
Random
W/R
(about 80
0.70 A
IOPS)
Ripple (*7) +5 V/+12 V 250 mVp-p
(*1)
(*2)
For detail condition, see Section 4.1.
Vibration applied to the drive is measured at near the mounting screw hole on the frame as much
as possible.
(*3)
At random seek write/read and default on retry setting with log sweep vibration.
2-4 C141-E166
Page 31

(*4)
At power-off state after installation
Vibration displacement should be less than 2.5 mm.
(*5)
(*6)
Input voltages are specified at the drive connector side, during drive ready state.
The terminator power pin (SCSI connector) which supplies power to other terminators is not used
(See Section 4.3).
(*7)
High frequency noise (over 20 MHz) is less than 100 mVp-p.
2.1.4 Error rate
Errors detected during initialization and replaced by alternate block assignments are not included
in the error rate. Data blocks to be accessed should be distributed over the disk medium equally.
(1) Unrecoverable error rate
Errors which cannot be recovered within 63 retries and ECC correction should not exceed 1 per
15
10
bits.
Data loss
For MAP series, Reed Solomon codes are applied for their ECC.
The sector-data is divided into 6 interleaving sectors, and ECC is
performed in each sector where the maximum number of errors (up
to 5 byte) can be corrected. [Total maximum byte: 5 byte
interleave) = 30 byte]
If the error of read sector keeps allowable error byte number,
correction is performed. However, if error byte exceeds its
allowable number, correction may not be performed properly.
CAUTION
×
6 (
(2) Positioning error rate
Positioning errors which can be recovered by one retry should be 10 or less per 10
8
seeks.
2.1.5 Reliability
(1) Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
MTBF of the IDD during its life time is 1,2000,000 hours (operating: 24 hours/day, 7 days/week
average DE surface temperature: 50°C or less).
Note:
The MTBF is defined as:
Operating time (hours) at all field sites
MTBF=
The number of equipment failures from all field sites
C141-E166 2-5
Page 32

Failure of the equipment means failure that requires repair, adjustments, or replacement.
Mishandling by the operator, failures due to bad environmental conditions, power trouble, host
system trouble, cable failures, or other failures not caused by the equipment are not considered.
(2) Mean Time to Repair (MTTR)
MTTR is the average time taken by a well-trained service mechanic to diagnose and repair a drive
malfunction. The drive is designed for a MTTR of 30 minutes or less.
(3) Service life
The service life under suitable conditions and treatment is as follows.
The service life is depending on the environment temperature. Therefore, the user must design the
system cabinet so that the average DE surface temperature is as possible as low.
• DE surface temperature: 40°C or less 5 years
• DE surface temperature: 41°C to 45°C 4.5 years
• DE surface temperature: 46°C to 50°C 4 years
• DE surface temperature: 51°C to 55°C 3.5 years
• DE surface temperature: 56°C to 60°C 3 years
• DE surface temperature: 61°C and more Strengthen cooling power so that DE surface
Even if the IDD is used intermittently, the longest service life is 5 years.
temperature is 60°C or less.
Note:
The "average DE surface temperature" means the average temperature at the DE surface
throughout the year when the IDD is operating.
(4) Data security at power failure
Integrity of the data on the disk is guaranteed against all forms of DC power failure except on
blocks where a write operation is being performed. The above does not applied to formatting
disks or assigning alternate blocks.
2-6 C141-E166
Page 33

2.2 SCSI Function Specifications
Table 2.4 shows the SCSI functions provided with the IDD.
Table 2.4 SCSI function specifications
Item Specification
Single-ended type
HVD type (High Voltage Differential)
Electrical
requirements
(*1)
LVD type (Low Voltage Differential)
Single-ended type
Differential type
TERMPWR signal send function
68 pin P cable connector
Connector
80 pin SCA2 connector
Data bus parity (Data bus CRC)
Bus arbitration function
Disconnection/reconnection function
SCSI ID 16-bit SCSI
Addressing
LUN (logical unit number) #0 fixed
8-bit SCSI (Single-ended type)
Data transfer
(Synchronous
mode)
(LVD type)
16-bit SCSI (Single-ended type)
(LVD type)
(U160 LVD type)
(U320 LVD type)
Position where the terminating
resistor is mounted on the PCA
Position where the terminating
resistor is mounted on the PCA
Ο
×
Ο
×
×
Ο
Ο (NP model)
Ο (NC model)
Ο
Ο
Ο
#0 to #15
(Jumper selection)
Ο 20 MB/s max.
Ο 40 MB/s max.
Ο 40 MB/s max.
Ο 80 MB/s max.
Ο 160 MB/s max.
Ο 320 MB/s max.
Data buffer 8 MB
Data block length (Logical data length=Physical data length) (*2)
512 to 528 bytes
(Fixed length)
Ο : Provided × : Not provided
(*1)
The driver mode (Single-ended or LVD) changes automatically by Diffsence signal level.
(*2)
Refer to (12) of Section 1.1.
C141-E166 2-7
Page 34

This page is intentionally left blank.
Page 35

CHAPTER 3 DATA FORMAT
3.1 Data Space
3.2 Logical Data Block Addressing
3.3 Defect Management
This chapter explains data space definition, logical data block addressing, and defect management on the
IDD.
3.1 Data Space
The IDD manages the entire data storage area divided into the following three data spaces.
• User space: Storage area for user data
• Internal test space: Reserved area for diagnostic purposes
• System space: Area for exclusive use of IDD itself
The user space allows a user access by specifying data. These space can be accessed with the
logical data block addressing method described in Section 3.2. The internal test space is used by
Read/write test of self-diagnostics test, but user can’t use direct access. The system space is
accessed inside the IDD at power-on or during the execution of a specific command, but the user
cannot directly access the system space.
3.1.1 Cylinder configuration
The IDD allocates cylinders to the user space, Internal test space, and system space. Figure 3.1 is
the cylinder configuration.
Spare areas (alternate areas) for defective sectors are provided in the user space. Several sectors in
the last track of one cylinder and several cylinders (alternate cylinders) in the user space are
allocated as alternate areas according to the user's assignment (MODE SELECT command). See
Subsection 3.1.2 for details.
C141-E166 3-1
Page 36

Cylinder –85
to
Cylinder –78
Internal test cylinder
Internal test space
~~
~~
Cylinder –73
to
Cylinder –4
Zone Cell Cylinder
0
0
1
.
P1
1
1
.
13
14
15
.
270
m-13
.
m
(1)
SAS69
•
SA0
User Space for Cell 0-0
Spare Sectors per Cell 0
User Space for Cell 1-0
Spare Sectors per Cell 1
User Space for Cell P1-0
Spare Sectors per Cell P1
Alternate Cylinder
User Space for Cell xx-1
System space
~~
~~
User space
(Primary
Cylinder
0 - (n - 1))
.
.
17
n =47,925 (MAP3147NC/NP)
47,995 (MAP3735NC/NP)
48,121 (MAP3367NC/NP)
Apart from the above logical configuration, the IDD intends to increase the storage capacity by
dividing all cylinders into several zones and changing a recording density of each zone. Tables 3.1
to 3.3 show the zone layout and the track capacity.
n
Note: Spare sectors on the last track in each cylinder are not necessarily placed at the end of the track
because of a track skew or a cylinder skew. (Details are explained in Subsection 3.1.3.)
User Space for Cell yy-17
Figure 3.1 Cylinder configuration
3-2 C141-E166
Page 37

Table 3.1 Zone layout and track capacity
Cylinder
Zone
MAP3147NC/NP MAP3735NC/NP MAP3367NC/NP
0 0 - 1,120 479,232 936
1 1,121 - 4,117 465,920 910
2 4,118 - 6,078 459,264 897
3 6,079 - 9,075 452,608 884
4 9,076 - 12,884 439,296 858
5 12,885 - 16,077 425,984 832
6 16,078 - 19,270 412,672 806
7 19,271 - 21,637 402,432 786
8 21,638 - 24,354 399,360 780
9 24,355 - 27,561 379,392 741
10 27,562 - 29,256 372,736 728
Byte/track Sector/track
11 29,257 - 32,351 359,424 702
12 32,352 - 34,942 346,112 676
13 34,943 - 37,855 330,240 645
14 37,856 - 41,062 319,488 624
15 41,063 - 43,961 299,520 585
16 43,962 - 46,342 284,672 556
17 46,343 - 47,925 46,343 - 47,995 46,343 - 48,121 272,896 533
Note: When the logical data block length is 512 bytes, the sector/track capacity indicates above amount
(1) User space
The user space is a storage area for user data. The data format on the user space (the length of data
block and the number of data blocks) can be specified with the MODE SELECT or MODE
SELECT EXTENDED command.
The default value of cylinders in the user space is MAP3174NC/NP = 47,926, MAP3735NC/NP =
47,996, MAP3367NC/NP = 48,122. These also equal the maximum cylinders number for each
series. The user can also specify the number of logical data blocks to be placed in the user space
with the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT EXTENDED command. When the number of
logical data blocks is specified, as many cylinders as required to place the specified data blocks are
allocated in the user space.
C141-E166 3-3
Page 38

A number starting with 0 is assigned to each cylinder required in the user space in ascending order.
If the number of cylinders do not reach the maximum, the rest of the cylinders will not be used.
Always one cylinder that is located at the end of each zone in the user space can be established as
an alternate cylinder. Alternate cylinders will be used for alternate blocks when primary cylinders
in the user space are used up. See Subsections 3.1.2 and 3.3.2 for details.
(2) Internal test space
The Internal test space is an area for diagnostic purposes only and its data block length is always
512KByte. The Internal test space consists of 8 cylinders and outer-host cylinder is always
assigned. The user cannot change the number of cylinders in the Internal test space or their
positions.
(3) System space
The system space is an area for exclusive use of the IDD itself and the following information are
recorded.
• Defect list (P list and G list)
• MODE SELECT parameter (saved value)
• Statistical information (log data)
• Controller control information
The above information is duplicated in several different locations for safety.
Note:
The system space is also called SA space.
3.1.2 Alternate spare area
The alternate spare area consists of the last track of each cell in the user space and an alternate
cylinder allocated to the last cylinder of each zone.
The spare area in each cylinder is placed at the end of the last track as shown in Figure 3.2. These
spare sectors are located in the end of the track logically, not necessarily located at the end
physically because of track skew or cylinder skew. (Details are explained on Subsection 3.1.3.)
Size can be specified by the MODE SELECT command.
The number of spare sectors per cell can be specified exceeding 32. The default for the spare
sectors number is 84.
3-4 C141-E166
Page 39

Cell
Note: This drive manages alternate spare areas for each cell, which is a set of cylinders. One
cell consists of 14 cylinders.
Figure 3.2 Spare area in cell
An alternate cylinder is used when spare sectors in a cell are used up or 0 is specified as the
number of spare sectors in a cell. 1 cylinder at the end of each zone of the user space is allocated
as alternate cylinders as shown in Figure 3.3.
The user space and the system space share the alternate cylinders.
Zone
Note: The number of alternate cylinders can not be changed.
3.1.3 Track format
(1) Physical sector allocation
Figure 3.4 shows the allocation of the physical sectors in a track. The length in bytes of each
physical sector and the number of sectors per track vary depending on the logical data block
length. The unused area (G4) exists at the end of the track in formats with most logical data block
lengths.
The interval of the sector pulse (length of the physical sector) is decided by multiple of 40MHz
free running frequency. This clock is not equal to the interval of the byte clock for each zone.
Therefore, the physical sector length cannot be described with a byte length.
Figure 3.3 Alternate cylinder
C141-E166 3-5
Page 40

(2) Track skew and head skew
To avoid waiting for one turn involved in head and cylinder switching, the first logical data block
in each track is shifted by the number of sectors (track skew and head skew) corresponding to the
switching time. Figure 3.5 shows how the data block is allocated in each track.
5.99 msec
Servo frame
n = 241 (zone 0) ~ 408 (zone 17)
Figure 3.4 Track format
At the head switching location in a cylinder, the first logical data block in track t + 1 is allocated at
the sector position which locates the track skew behind the sector position of the last logical data
block sector in track t.
At the cylinder switching location, like the head switching location, the first logical data block in a
cylinder is allocated at the sector position which locates the head skew behind the last logical
sector position in the preceding cylinder. The last logical sector in the cylinder is allocated when
formatting, and is an unused spare sector.
3-6 C141-E166
Page 41

Cylinder skew
Head
Cylinder skew
Track skew
Head
Leading logical
sector in head p+1
Figure 3.5 Track skew/head skew
The number of physical sectors (track skew factor and head skew factor) corresponding to the
skew time varies depending on the logical data block length because the track skew and the head
skew are managed for individual sectors. The IDD automatically determines appropriate values
for the track skew factor and the head skew factor according to the specified logical data block
length. The value can be read out by the MODE SENSE or MODE SENSE EXTENDED
command after the track has been formatted.
3.1.4 Sector format
Each sector on the track consists of an ID field, a data field, and a gap field which separates them.
Figure 3.6 gives sector format examples.
SCT
SCT
G1
PLO
SyncG1
PLO
Sync
SM1
SM1
DATA1
DATA1
SM2 BCRCDATA2 ECC
Servo
SM2 DATA3
PAD
G2
PAD
G2
PLO
SyncG1
SCT
SM1
DATA1 SM2 DATA4
BCRC ECC
PAD
Figure 3.6 Sector format
Each sector on the track consists of the following fields:
C141-E166 3-7
SCT
G3
Page 42

(1) Gaps (G1, G2, G3)
No pattern is written on the gap field.
(2) PLO Sync
In this field, pattern X'00' in the specified length in bytes is written.
(3) Sync Mark (SM1, SM2)
In this field, special pattern in the specified length in bytes is written. This special pattern indicates
the beginning of the data field.
(4) Data field (DATA1-DATA4)
User data is stored in the data field of the sector. The length of the data field is equal to that of the
logical data block which is specified with a parameter in the MODE SELECT command. Any
multiple of 4 between 512 and 528 bytes can be specified as the length.
(5) BCRC
It is a 4-byte error detection code. Errors in the ID field. Single burst errors with lengths of up to
32 bits for each logical block can be detected.
(6) ECC
This is the 60-byte code that allows detection and correction of errors in the data field, which is
capable of correcting the single burst error up to 240 bits max. on the fly.
(7) PAD
In this field, pattern X'00' in the specified length in bytes is written. This field includes the
variation by rotation and circuit delay till reading/writing.
3-8 C141-E166
Page 43

3.1.5 Format capacity
The size of the usable area for storing user data on the IDD (format capacity) varies according to
the logical data block or the size of the spare sector area. Table 3.4 lists examples of the format
capacity when the typical logical data block length and the default spare area are used. The
following is the general formula to calculate the format capacity.
[Number of sectors of each zone] = [number of sectors per track × number of tracks per cell –
number of alternate spare sectors per cell] × [number of cells in the zone]
[Formatted capacity] = [total of sectors of all zones] ÷ [number of physical sectors in logical
block] × [logical data block length]
The following formula must be used when the number of logical data blocks are specified with the
parameter in the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT EXTENDED command.
[Format capacity] = [logical data block length] × [number of logical data blocks]
The logical data block length, the maximum logical block address, and the number of the logical
data blocks can be read out by a READ CAPACITY, MODE SENSE, or MODE SENSE
EXTENDED command after initializing the disk medium.
Table 3.4 Format capacity
Model Data heads Data block length User blocks Format capacity (GB)
MAP3147NC/NP 8 287,132,440 147.01
MAP3735NC/NP 4 143,571,316 73.50
MAP3367NC/NP 2
Note:
Total number of spare sectors is calculated by adding the number of spare sectors in each
primary cylinder and the number of sectors in the alternate cylinders.
3.2 Logical Data Block Addressing
Independently of the physical structure of the disk drive, the IDD adopts the logical data block
addressing as a data access method on the disk medium. The IDD relates a logical data block
address to each physical sector at formatting. Data on the disk medium is accessed in logical data
block units. The INIT specifies the data to be accessed using the logical data block address of that
data.
The logical data block addressing is a function whereby individual data blocks are given addresses
of serial binaries in each drive.
512
71,775,284 36.74
C141-E166 3-9
Page 44

(1) Block address of user space
The logical data block address number is consecutively assigned to all of the data blocks in the
user space starting with 0 to the first data block.
The IDD treats sector 0, track 0, cylinder 0 as the first logical data block. The data block is
allocated in ascending order of addresses in the following sequence (refer to Figure 3.5):
1) Logical data blocks are assigned in ascending order of sector number in the same track.
2) Subsequent logical data blocks are assigned to sectors in every track except the last track in
ascending order of track number in the same track (head). Within the same track, logical data
blocks are assigned in the same way as step 1).
3) Subsequent logical data blocks are assigned to sectors in every track except the last track in
ascending order of track number in the same cell. Within the same track, logical data blocks
are assigned in the same way as step 1).
4) For the last track in the same cell, subsequent logical data blocks are assigned to sectors other
than spare sectors in ascending order of sector number.
5) After blocks have been assigned in the same cell according to steps 1) to 4), subsequent logical
data blocks are assigned in ascending order of cell number in the same way as in steps 1) to 4).
Logical data blocks are assigned starting from track 0 in the next cell until the last cylinder
(immediately preceding the alternate cylinder n-1 shown in Figure 3.1) of the zone except
alternate cylinders in cells in the user space.
When the logical data block is allocated, some sectors (track skew and head skew) shown in Figure
3.5 are provided to avoid waiting for one turn involving head and cylinder switching at the location
where the track or the head is physically switched.
See Subsection 3.3.2 for defective/alternate block treatment and the logical data block allocation
method in case of defective sectors exist on the disk.
(2) Alternate area
Alternate areas in the user space (spare sectors in the cell and alternate cylinders) are not included
in the above logical data block addresses. Access to sectors which are allocated as an alternate
block in the alternate area is made automatically by means of IDD sector slip treatment or alternate
block treatment (explained in Subsection 3.3.2), so the user does not have to worry about accessing
the alternate area. The user cannot access with specifying the data block on the alternate area
explicitly.
3-10 C141-E166
Page 45

3.3 Defect Management
3.3.1 Defect list
Information of the defect location on the disk is managed by the defect list. The following are
defect lists which the IDD manages.
• P list (Primary defect list): This list consists of defect location information available at the
disk drive shipment and is recorded in a system space. The defects in this list are permanent,
so the INIT must execute the alternate block allocation using this list when initializing the disk.
• D list (Data defect list): This list consists of defect location information specified in a
FORMAT UNIT command by the INIT at the initialization of the disk. This information is
recorded in the system space of the disk drive as the G list. To execute the alternate block
allocation, the FORMAT UNIT command must be specified.
• G list (Growth defect list): This list consists of defective logical data block location
information specified in a REASSIGN BLOCKS command by the INIT, information on
defective logical data blocks assigned alternate blocks by means of IDD automatic alternate
block allocation, information specified as the D list, and information generated as the C list.
They are recorded in the system space on the disk drive.
The INIT can read out the contents of the P and G lists by the READ DEFECT DATA command.
3.3.2 Alternate block allocation
The alternate data block is allocated to a defective data block (= sectors) in defective sector units
by means of the defect management method inside the IDD.
The INIT can access all logical data blocks in the user space, as long as there is no error.
Spare sectors to which alternate blocks are allocated can be provided in either "spare sectors in a
cell" or "alternate cylinders". See Subsection 3.1.2 for details.
The INIT can specify the size and area for spare sectors by the MODE SELECT command at the
time of the initialization of the disk.
Both of the following are applicable to the alternate block allocation.
• Sector slip treatment: Defective sectors are skipped and the logical data block corresponding
to those sectors is allocated to the next physical sectors. This treatment is made on the same
cell as the defective sector's and is effective until all spare sectors in that cell are used up.
• Alternate sector treatment: The logical data block corresponding to defective sectors is
allocated to unused spare sectors in the same cell or unused spare sectors in the alternate
cylinder.
C141-E166 3-11
Page 46

The alternate block allocation is executed by the FORMAT UNIT command, the REASSIGN
BLOCKS command, or the automatic alternate block allocation. Refer to OEM Manual–SCSI
Logical Specifications–for details of specifications on these commands. The logical data block is
allocated to the next physically continued sectors after the above sector slip treatment is made. On
the other hand, the logical data block is allocated to spare sectors which are not physically
consecutive to the adjacent logical data blocks. If a command which processes several logical data
blocks is specified, the IDD processes those blocks in ascending order of logical data block.
(1) Alternate block allocation during FORMAT UNIT command execution
When the FORMAT UNIT command is specified, the allocation of the alternate block to those
defective sectors included in the specified lists (P, G, or D) is continued until all spare sectors in
the same cell are used up. When they are used up, unused spare sectors in the alternate cylinder
are allocated to the subsequent sectors in the cylinder by means of alternate sector treatment.
Figure 3.7 is examples of the alternate block allocation during the FORMAT UNIT command
execution.
3-12 C141-E166
Page 47

: n represents a logical data block number
: Defective sector
: Unused spare sector
Figure 3.7 Alternate block allocation by FORMAT UNIT command
If the data block verifying operation (certification) is not permitted (DCRT flag = 0) in the
FORMAT UNIT command, the IDD checks all initialized logical data blocks by reading them out
after the above alternate block allocation is made to initialize (format) the disk. If a defective data
block is detected during the check, the IDD allocates the alternate block to the defective data
block. This alternate block allocation is made by means of alternate sector treatment only like
processing by the REASSIGN BLOCKS command even if unused spare sectors exists in the same
cell.
C141-E166 3-13
Page 48

(2) Alternate block allocation by REASSIGN BLOCKS command
When the REASSIGN BLOCKS command is specified, the alternate block is allocated to the
defective logical data block specified by the initiator by means of alternate sector treatment. If
there are unused spare sectors in the same cell as the specified defective logical data block, the
alternate block is allocated to these unused spare sectors. However, the alternate block is allocated
to unused spare sectors in the alternate cylinder when all spare sectors in the cell are used up.
Figure 3.8 is examples of the alternate block allocation by the REASSIGN BLOCKS command.
Alternate sectors
The same cell
: n represents a logical data block number
: Defective sector
: Unused spare sector
Figure 3.8 Alternate block allocation by REASSIGN BLOCKS command
(3) Automatic alternate block allocation
• Automatic alternate block allocation at read operation
If the ARRE flag in the MODE SELECT parameter permits the automatic alternate block
allocation, the IDD automatically executes the alternate block allocation and data duplication on
the defective data block detected during the READ or READ EXTENDED command. This
allocation method is the same as with the REASSIGN BLOCKS command (alternate sector
treatment).
3-14 C141-E166
Page 49

• Automatic alternate block allocation at write operation
If AWRE flag in the MODE SELECT parameter permits the automatic alternate block allocation,
the IDD executes the automatic alternate processing during WRITE command processing as
described below:
1) Commands to be applied
-WRITE
- WRITE EXTEND
- WRITE at executing WRITE AND VERIFY
2) Application requirements
When any of the above commands is issued to LBA registered in the uncorrectable error log of
the READ command (LBA log of uncorrectable error while the READ command is executed),
the AWRE processing is applied.
3) AWRE processing
The following processings are performed when the LBA matches the one in the uncorrectable
error log:
a) Primary media check
- Creates an uncorrectable error pattern (invalid LBA pattern) in the position of the
error LBA, repeats the primary media check up to three times. If the error still occurs
after the check repeated three times, it is judged to be defective. Then, it performs the
alternate processing.
b) Alternate processing
- Alternate media check
Writes the data that causes an unrecoverable error into the alternate block, and
performs the media check.
(If the alternate block is a defective sector, the block is registered to the G list, another
alternate block is allocated.)
c) SA and defect map update processing (on alternate side)
When an error occurs in the alternate processing, this WRITE command terminates with error.
When the alternate processing normally terminates, the WRITE command is executed.
Depending on the alternate processing result, one of the following sense codes is returned:
Alternate processing is succeeded: 01-OC-01
Alternate medium is defective: 03-OC-01
Fatal error (SA write retry out): 03-OC-02
C141-E166 3-15
Page 50

IMPORTANT
Automatic alternate block allocation is made only once during the
execution of one command. If second defective block is detected, the
alternate block assignment processing for the first defective block is
executed but the alternate block assignment processing for the
second one is not executed and the command being executed
terminates. However, the initiator can recover the twice error by
issuing the same command again.
When an error is detected in a data block in the data area, recovery
data is rewritten and verified in automatic alternate block allocation
during the execution of the READ or READ EXTENDED command.
Alternate block allocation will not be made for the data block if
recovery is successful.
Example: Even if the data error which is recoverable by the WRITE
LONG command is simulated, automatic alternate block
allocation will not be made for the data block.
3-16 C141-E166
Page 51

CHAPTER 4 INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
4.1 Mounting Requirements
4.2 Power Supply Requirements
4.3 Connection Requirements
This chapter describes the environmental, mounting, power supply, and connection requirements.
4.1 Mounting Requirements
4.1.1 External dimensions
Figures 4.1 and 4.2 show the external dimensions of the IDD and the locations of the holes for the
IDD mounting screws.
Dimensions are in mm.
Note:
Mounting screw: #6-32UNC
C141-E166 4-1
Page 52

The value marked with (*) indicates the dimension between mounting holes on the bottom
face.
Figure 4.1 NC external dimensions
4-2 C141-E166
Page 53

The value marked with (*) indicates the dimension between mounting holes on the bottom
face.
Figure 4.2 NP external dimensions
C141-E166 4-3
Page 54

4.1.2 Mounting
The permissible orientations of the IDD are shown in Figure 4.3, and the tolerance of the angle is
±5° from the horizontal plane.
(a) Horizontal –1 (b) Horizontal –2
(d) Vertical –2 (e) Upright mounting –1 (f) Upright mounting –2
4.1.3 Notes on mounting
(1) Mounting frame structure
Special attention must be given to mount the IDD disk enclosure (DE) as follows.
(c) Vertical –1
Direction of
gravity
Figure 4.3 IDD orientations
a) Use the frame with an embossed structure, or the like. Mount the IDD with making a gap
of 2.5 mm or more between the IDD and the frame of the system.
b) As shown in Figure 4.4, the inward projection of the screw from the IDD frame wall at the
corner must be 5.0 mm or less.
c) Tightening torque of screw must be secured with 0.59N·m (6kgf·cm) ±12%.
d) Impact caused by the electric driver must be within the device specifications.
e) Must be handled on an anti-static mat.
4-4 C141-E166
Page 55

Figure 4.4 Mounting frame structure
(2) Limitation of side-mounting
Mount the IDD using the 4 screw holes at the both ends on the both sides as shown in Figure 4.5.
Do not use the center hole by itself.
In case of using the center hole, it must be used in combination with 2 holes on both ends.
(Total 6 screws for 6 holes enclosed)
5.0 or less
5.0 or less
Holes for
4
mounting screw.
3
2
Do not use these holes
Holes for mounting screw.
1
Use four holes (No.1-4) to mount.
Figure 4.5 Limitation of side-mounting
(3) Limitation of bottom-mounting
Use all 4 mounting holes on the bottom face.
C141-E166 4-5
Page 56

(4) Environmental temperature
Temperature condition at installed in a cabinet is indicated with ambient temperature measured
30 mm from the disk drive. At designing the system cabinet, consider following points.
• Make a suitable air flow so that the DE surface temperature does not exceed 60°C.
• Cool the PCA side especially with air circulation inside the cabinet. Confirm the cooling effect
by measuring temperature of specific ICs and the DE. These measurement results should be
within a criteria listed in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 Surface temperature check point
No. Measurement point Criteria
1 Center of DE cover 60°C
2 Read channel LSI 88°C
3 VCM/SPM Driver 92°C
4 HDC 91°C
5 MPU 91°C
3
1
Figure 4.6 Surface temperature measurement points
(5) Service clearance area
The service clearance area, or the sides which must allow access to the IDD for installation or
maintenance, is shown in Figure 4.7.
4
5
2
4-6 C141-E166
Page 57

[Surface P]
• Cable connection
(6) External magnetic field
The drive should not be installed near the ferromagnetic body like a speaker to avoid the influence
of the external magnetic field.
[Surface P’]
• Setting terminal (on NP model only)
• External operator panel connector
[Surface R]
• Hole for mounting screw
[Surface Q]
• Hole for mounting screw
Figure 4.7 Service clearance area
(7) Leak magnetic flux
The IDD uses a high performance magnet to achieve a high speed seek. Therefore, a leak
magnetic flux at surface of the IDD is large. Mount the IDD so that the leak magnetic flux does
not affect to near equipment.
(8) Others
Seals on the DE prevent the DE inside from the particle. Do not damage or peel off labels.
C141-E166 4-7
Page 58

4.2 Power Supply Requirements
(1) Allowable input voltage and current
The power supply input voltage measured at the power supply connector pin of the IDD (receiving
end) must satisfy the requirement given in Subsection 2.1.3. (For other requirements, see Items (4)
and (5) below.)
(2) Current waveform (reference)
Figure 4.8 shows the spin-up current waveform of +12 VDC.
MAP3147NC/NP
Current(500mA/div)
Time(2 sec/div)
Figure 4.8 Spin-up current waveform (+12 VDC)
(3) Power on/off sequence
a) The order of the power on/off sequence of +5 VDC and +12 VDC, supplied to the IDD, does
not matter.
b) In a system which uses the terminating resistor power supply signal (TERMPWR) on the SCSI
bus, the requirements for +5 VDC given in Figure 4.9 must be satisfied between the IDD and
at least one of the SCSI devices supplying power to that signal.
MAP3735NC/NP
Current(500mA/div)
Time(2 sec/div)
MAP3367NC/NP
Current(500mA/div)
Time(2 sec/div)
Figure 4.9 Power on/off sequence (1)
4-8 C141-E166
Page 59

c) In a system which does not use the terminating resistor power supply signal (TERMPWR) on
the SCSI bus, the requirements for +5 VDC given in Figure 4.10 must be satisfied between the
IDD and the SCSI device with the terminating resistor circuit.
SCSI devices with
the terminating
resistor
Figure 4.10 Power on/off sequence (2)
d) Between the IDD and other SCSI devices on the SCSI bus, the +5 VDC power on/off sequence
is as follows:
• In a system with its all SCSI devices designed to prevent noise from leaking to the SCSI
bus when power is turned on or off, the power sequence does not matter if the
requirement in b) or c) is satisfied.
• In a system containing an SCSI device which is not designed to prevent noise from
leaking to the SCSI bus, the requirement given in Figure 4.11 must be satisfied between
that SCSI device and the IDD.
SCSI devices
without noise
leaking designed
Figure 4.11 Power on/off sequence (3)
C141-E166 4-9
Page 60

(4) Sequential starting of spindle motors
After power is turned on to the IDD, a large amount of current flows in the +12 VDC line when the
spindle motor rotation starts. Therefore, if more than one IDD is used, the spindle motors should
be started by the following procedures to prevent overload of the power supply unit. Regarding
how to set a spindle motor start control mode, see Subsection 5.3.2.
For the NP model drives, the spindle motors should be started sequentially using of the following
procedures.
a) Issue START/STOP commands at more than 12-second intervals to start the spindle motors.
For details of this command specification, refer to SCSI Logical Interface Specifications.
b) Turn on the +12 VDC power in the power supply unit at more than 12-second intervals to start
the spindle motors sequentially.
For the NC model drives, the spindle motors should be started after a delay of 12 seconds times
[SCSI ID] by setting CN1-38 pin to open and CN1-78 pin to short.
SCSI ID Delay time of spindle motor starting
0
1
2
.
.
.
15
0
12 s
24 s
.
.
.
180 s
(5) Power supply to SCSI terminating resistor
If power for the terminating resistor is supplied from the IDD to other SCSI devices through the
SCSI bus, the current-carrying capacity of the +5 VDC power supply line to the IDD must be
designed with considering of an increase of up to 200 mA.
A method of power supply to the terminating resistor is selected with a setting terminal on the IDD
(NP model only). See Subsection 5.3.2 for this selection.
For the electrical condition of supplying power to the terminating resistor, refer to Subsection 1.4.2
in SCSI Physical Interface Specifications.
(6) Noise filter
To eliminate AC line noise, a noise filter should be installed at the AC input terminal on the IDD
power supply unit. The specification of this noise filter is as follows:
• Attenuation: 40 dB or more at 10 MHz
• Circuit construction: T-configuration as shown in Figure 4.12 is recommended.
4-10 C141-E166
Page 61

Figure 4.12 AC noise filter (recommended)
4.3 Connection Requirements
4.3.1 SCA2 connector type 16-bit SCSI model (NC model)
(1) Connectors
Figure 4.13 shows the locations of connectors on the SCA2 connector type 16-bit SCSI model (NC
model).
SCSI connector (CN1)
(including power supply)
Figure 4.13 NC connectors location
C141-E166 4-11
Page 62

(2) SCSI connector and power supply connector
The connector for the SCSI bus is an unshielded SCA-2 connector conforming to SCSI-3 type
which has two 40-pin rows spaced 1.27 mm (0.05 inch) apart. The power connector is included in
the SCSI connector.
Figure 4.14 shows the SCSI connector. See Section B.1 in Appendix B for signal assignments on
the connector.
For details on the physical/electrical requirements of the interface signals, refer to Sections 1.3 and
1.4 in SCSI Physical Interface Specifications.
Figure 4.14 SCA2 type 16-bit SCSI connector
(3) Connector for external operator panel
This connector is not available for NC model drives.
4-12 C141-E166
Page 63

4.3.2 68 pin connector type 16-bit SCSI model (NP model)
(1) Connectors
Figures 4.15 show the locations of connectors and terminals on the 68 pin connector type 16-bit
SCSI model (NP model).
• Power supply connector
• SCSI connector
• External operator panel connector
External operator panel
connector (CN2)
Power supply
connector
(CN1)
(2) SCSI connector and power supply connector
External operator
panel connector
(CN1)
a. 16-bit SCSI
The connector for the SCSI bus is an unshielded P connector conforming to SCSI-3 type which
has two 34-pin rows spaced 1.27 mm (0.05 inch) apart. Figure 4.16 shows the SCSI
connector. See Section B.2 in Appendix B for the signal assignments on the SCSI connector.
For details on the physical/electrical requirements of the interface signals, refer to Sections 1.3
and 1.4 in the SCSI Physical Interface Specifications.
SCSI connector
(CN1)
Figure 4.15 NP connectors and terminals location
C141-E166 4-13
Page 64

Pin 34
Pin 1
2.00mm
Pin A1
Pin 1
2.54mm
Pin 68
Figure 4.16 68 pin type 16-bit SCSI interface connector
b. Power supply connector
Figure 4.17 shows the shape and the terminal arrangement of the output connector of DC
power supply.
1.27mm
0.40mm
0.635mm
Pin 35
0.40mm
1.00mm
2.00m
Pin A2
5.08mm
1.30mm
5.08mm
Figure 4.17 Power supply connector (68 pin type 16-bit SCSI)
(3) SG terminal
The IDD is not provided with an SG terminal (fasten tab) for DC grounding. Therefore, when
connecting SG and FG in the system, use the +5 VDC RETURN (ground) inside the power supply
connector as the SG on the power supply side.
(4) Connector for external operator panel
• Connector for 16-bit SCSI external operator panel
CN1 provides connector for the external operator panel other than the SCSI bus as shown in
Figure 4.18. Also, a connector for the external operator panel are provided on the IDD as
shown in Figure 4.19. This allows connection of an external LED on the front panel, and an
SCSI ID setting switch. For the recommended circuit of the external operator panel, see
Subsection 4.3.4.
4-14 C141-E166
Page 65

Pin Signal
A1 –ID0
A2 Fault LED
A3 –ID1
A4 ESID
A5 –ID2
A6 (Reserved)
A7 –ID3
A8 –LED
A9 OPEN
A10 GND
A11 +5 V
A12 –WTP
Figure 4.18 External operator panel connector (CN1)
Pin 2
Pin 1
C141-E166 4-15
2.0mm
2.0mm
Figure 4.19 External operator panel connector (CN2)
Pin 24
Pin 23
Page 66

(5) External operator panel connector Signals
a. 16-bit SCSI –ID3, –ID2, –ID1, –ID0: Input signals (CN1-A1, A3, A5, A7 pin and CN2-02,
04, 06, 08 pin)
These signals are used for providing switches to set the SCSI ID of the IDD externally. Figure
4.20 shows the electrical requirements. For the recommended circuit examples, see Subsection
4.3.4.
Figure 4.20 16-bit SCSI ID external input
4-16 C141-E166
Page 67

b. Fault LED: Output signal (CN1-A2 pin)
The IDD indicates that the write-protect status is in effect (CN1-A12 is connected to the GND, or the
CN2-9 and CN2-10 are short-circuited.) A signal for driving the LED is output.
(IDD)
74LS06 or equivalent
This signal is temporarily driven at the GND level when the micro
program reads the SCSI ID immediately after the power supply to
the IDD has been switched on (it is possible to set up the SCSI ID by
short circuiting CN1-A1 and CN1-A2.)
c. CN1-A6 (reserved)
This pin is temporarily driven at the GND level when the micro program reads the SCSI ID
immediately after the power supply to the IDD has been switched on (it is possible to set up the SCSI
ID by short circuiting CN1-A3 and CN1-A4, and CN1-A5 and CN1-A6.)
This pin gets high impedance status except above.
150
Ω
IMPORTANT
CN1-A2
d. –LED and LED (+5V): Output signals (CN1-A8 pin and CN2-21, 22 pin)
These signals drive the external LED as same as LED on the front of the disk drive. The
electrical requirements are given in Figure 4.21.
IMPORTANT
1. The external LED is identical in indication to the LED on the front of the
IDD.
2. Any load other than the external LED (see Subsection 4.3.5) should not
be connected to the CN2-21, 22 pin (LED [V] and –LED terminals).
3. This signal is temporarily driven at the GND level when the micro
program reads the SCSI ID immediately after the power supply to the
IDD has been switched on (it is possible to set up the SCSI ID by short
circuiting CN1-A7 and CN1-A8.)
C141-E166 4-17
Page 68

Figure 4.21 Output signal for external LED
e. –WTP: Input signal (CN1-A12 and CN2-9, 10 pin)
By connecting the CN1-A12 and CN2-10 pins to the GND, writing operations into the IDD
disc media are set to disable.
4-18 C141-E166
Page 69

(6) Cable connection requirements
The requirements for cable connection between the IDD, host system, and power supply unit are
given in Figure 4.22. Recommended components for connection are listed in Table 4.2.
External operator panel
(example)
Figure 4.22 SCSI cables connection
C141-E166 4-19
Page 70

4.3.3 Cable connector requirements
Table 4.2 lists the recommended components cable connection.
Table 4.2 Recommended components for connection
Applicable
model
NC
NP
(*1) See Figure 4.22.
SCSI connector
(CN1)
SCSI cable (CN1)
Power supply
cable (CN1)
External operator
panel (CN1)
External operator
panel (CN2)
Name
Connector
Cable socket
(closed-end type)
Signal cable
Cable socket housing 1-480424-0
Contact 170148-1
Cable (AWG18 to 24)
Cable socket housing A3B-12D-2C
Contact A3B-2630SCC
Cable (AWG26 to 36)
Cable socket housing FCN-723J024/2M
Contact FCN-723J-G/AM
Cable (AWG28)
Par number
(Size)
787311-1
87689-0001 Molex
DHJ-PAC68-2AN DDK
UL20528-FRX-68P0.635
Manufacturer
Tyco Electronics
AMP
Fujikura
Tyco Electronics
AMP
Tyco Electronics
AMP
HIROSE
ELECTRIC
HIROSE
ELECTRIC
FUJITSU
TAKAMIZAWA
FUJITSU
TAKAMIZAWA
Reference
(*1)
S1
S2
S3
S4
(1) SCSI cable
See Section 1.3, “Physical Requirements”, and Section 1.4, “Electrical Requirements”, in SCSI
Physical Interface Specifications.
(2) Power cable
IDDs must be star-connected to the DC power supply (one to one connection) to reduce the
influence of load variations.
(3) DC ground
The DC ground cable must always be connected to the IDD because no fasten tab dedicated to SG
is provided with the IDD. Therefore, when SG and FG are connected in the system, it is necessary
to connect SG and FG at the power supply or to connect SG of the power supply to FG of the
system.
4-20 C141-E166
Page 71

(4) External operator panel (NP model only)
The external operator panel is installed only when required for the system. When connection is not
required, leave open the following pins in the external operator panel connector of the IDD : Pins
21, 22 and pins 01 through 08 in CN2 and pins A1 through A12 in CN1.
4.3.4 External operator panel (on NP model drives only)
A recommended circuit of the external operator panel is shown in Figure 4.23. Since the external
operator panel is not provided as an option, this panel must be fabricated at the user site referring
to the recommendation if necessary.
(IDD)
S3
(*1)
A1
C
N
1
C
N
2
A3
A5
A7
A10
S3
A8
A11
S4
21
22
-ID0
-ID1
-ID2
-ID3
GND
-LED
+5V
LED (+5V)
-LED
Approx. 300
ID0
ID1
ID2
ID3
(LED)
R
Ω
(LED)
(for 16-bit SCSI)
(*1) For connecting the external LED to CN2.
Figure 4.23 External operator panel circuit example
C141-E166 4-21
Page 72

IMPORTANT
Do not connect the external LED to both CN1 and CN2. Connect it
to either of them.
4-22 C141-E166
Page 73

CHAPTER 5 INSTALLATION
5.1 Notes on Handling Drives
5.2 Connections
5.3 Setting Terminals
5.4 Mounting Drives
5.5 Connecting Cables
5.6 Confirming Operations after Installation and Preparation
for Use
5.7 Dismounting Drives
5.8 Spare Disk Drive
This chapter describes the notes on handling drives, connections, setting switches and plugs, mounting
drives, connecting cables, confirming drive operations after installation and preparation for use, and
dismounting drives.
5.1 Notes on Handling Drives
The items listed in the specifications in Table 2.1 must be strictly observed.
(1) General notes
a) Do not give the drive shocks or vibrations exceeding the value defined in the standard because
it may cause critical damage to the drive. Especially be careful when unpacking.
b) Do not leave the drive in a dirty or contaminated environment.
c) Since static discharge may destroy the CMOS semiconductors in the drive, note the following
after unpacking:
• Use an ESD strap and body grounding when handling the drive.
• Do not touch any components on the PCAs except setting terminal (CN1 and CN2).
Hot temperature
To prevent injury, do not handle the drive until after the device has cooled
sufficiently after turning off the power. The DE and LSI become hot during
operation and remain hot immediately after turning off the power.
CAUTION
C141-E166 5-1
Page 74

(2) Unpackaging
a) Use a flat work area. Check that the "This Side Up" sign side is up. Handle the package on
soft material such as a rubber mat, not on hard material such as a wooden desk.
b) Be careful not to give excess pressure to the internal unit when removing cushions.
c) Be careful not to give excess pressure to the PCAs and interface connector when removing the
drive from the antistatic bag.
d) Do not remove the sealing label or cover of the DE and screws.
(3) Installation/removal/replacement
a) Do not attempt to connect or disconnect connections when power is on. The only pin settings
that may be altered are pins 9, 10 (Write Protect) in CN2. (NP model)
b) Do not move the drive when power is turned on or until the drive completely stops (for 30
seconds) after power is turned off.
c) Place and keep removed screws and other parts where they will not get lost or damaged.
d) Keep a record of all maintenance work for replacing.
(4) Packaging
a) Store the drive in an antistatic bag.
b) It is recommended to use the same cushions and packages as those at delivery. If those at
delivery cannot be used, use a package with shock absorption so that the drive is free from
direct shocks. In this case, fully protect the PCAs and interface connector so that they are not
damaged.
c) Indicate "This Side Up" and "Handle With Care" on the outside of the package so that it is not
turned over.
(5) Delivery
a) When delivering the drive, provide packaging and do not turn it over.
b) Minimize the delivery distance after unpacking and avoid shocks and vibrations with cushions.
For the carrying direction at delivery, use one of the mount allowable directions in Subsection
4.2.2 (vertical direction is recommended).
(6) Storage
a) Provide moistureproof packaging for storage.
b) The storage environment must satisfy the requirements specified in Subsection 2.1.3 when the
drive is not operating.
c) To prevent condensation, avoid sudden changes in temperature.
5-2 C141-E166
Page 75

5.2 Connections
Figure 5.1 shows examples of connection modes between the host system and the IDD. For the 16bit SCSI, up to 16 devices including the host adapter, IDD, and other SCSI devices can be
connected to the SCSI bus in arbitrary combinations. Install a terminating resistor on the SCSI
device connected to both ends of the SCSI cable.
See Section 4.4 for the cable connection requirements and power cable connections.
(1) Connecting one IDD
C141-E166 5-3
Page 76

(2) Connecting more than one IDD (single host)
Figure 5.1 SCSI bus connections (1 of 2)
(3) Connecting more than one IDD (multi-host)
: SCSI terminator
Figure 5.1 SCSI bus connections (2 of 2)
5-4 C141-E166
Page 77

5.3 Setting Terminals
A user sets up the following terminals and SCSI terminating resistor before installing the IDD in
the system as required.
• Setting terminal: CN1 (NC model), CN2 (NP model)
Figure 5.2 shows the location of setting terminal (NP model only. For NC model, see Figure 4.13
because the setting terminal is included in SCSI connector CN1.). Figure 5.3 shows the allocation
and default settings (NP model only. For allocation of NC model, see Table B.).
Data loss
1. The user must not change the setting of terminals not described in this
section. Do not change setting status set at factory shipment.
2. Do not change the setting of terminals except following setting pins
during the power is turned on.
• Write protect: CN2 9-10 (NP model only)
3. To short the setting terminal, use the short plug attached when the device
is shipped from the factory.
CAUTION
Pin 24
Pin 23
CN2
Pin 2
Pin 1
Figure 5.2 Setting terminals location (on NP models only)
C141-E166 5-5
Page 78

5.3.1 SCSI ID setting
24222018161412108642
2321191715131197531
Terminator power supply: Supply
(LED signal)
(IDD Reset signal)
N.C.
Force Single Ended: LVD mode
Force Narrow: 16-bit SCSI
Motor start mode
Write protect: enabled
SCSI ID #15
Figure 5.3 CN2 setting terminal (on NP models only)
Table 5.1 shows the SCSI ID setting. For the terminal location and allocation of NC model, see
Figure 4.13 and Table B.1. For NP model, see Figure 5.2 and 5.3.
IMPORTANT
When the SCSI ID is set using the external operator panel connector
CN1 of NP model, all pins listed in Table 5.1 should be open. If any
of pins are shorted, unexpected SCSI ID is set.
5-6 C141-E166
Page 79

Table 5.1 SCSI ID setting
SCSI
ID
0 Open Open Open Open Open Open Open Open
1 Short Open Open Open Short Open Open Open
2 Open Short Open Open Open Short Open Open
3 Short Short Open Open Short Short Open Open
4 Open Open Short Open Open Open Short Open
5 Short Open Short Open Short Open Short Open
6 Open Short Short Open Open Short Short Open
7 Short Short Short Open Short Short Short Open
8 Open Open Open Short Open Open Open Short
9 Short Open Open Short Short Open Open Short
10 Open Short Open Short Open Short Open Short
11 Short Short Open Short Short Short Open Short
12 Open Open Short Short Open Open Short Short
39 79 40 80 1-2 3-4 5-6 7-8
NC model (CN1) NP model (CN2)
13 Short Open Short Short Short Open Short Short
14 Open Short Short Short Open Short Short Short
15 (*1) Short Short Short Short Short Short Short Short
*1 Set at factory shipment.
IMPORTANT
1. To set the setting terminals on NC models to short, apply voltage ranging
between -0.3 V and 0.8 V to the setting terminals externally. To set the
setting terminals on NC models to open, apply voltage ranging between
2.0 V and 5.5 V to the setting terminals from an external source.
2. Set the SCSI ID so that there are no duplicates between SCSI devices on
the same SCSI bus.
3. The priority of SCSI bus use in ARBITRATION phase is determined by
SCSI ID as follows:
7 > 6 > 5 > 4 > 3 > 2 > 1 > 0 > 15 > 14 > 13 > 12 > 11 > 10 > 9 > 8
C141-E166 5-7
Page 80

5.3.2 Each mode setting
(1) Setting terminator power supply
Refer to Table 5.2 for controlling the supply of power from the drive to the SCSI terminator power
source (TERMPOW).
For information on NP model, refer to Figures 5.2 and 5.3.
Table 5.2 Setting SCSI terminator power supply (NP model)
Supply on/off of SCSI terminator power from
*1. Set at factory shipment.
For NC model, the function of the terminator power supply setting is not supported.
(2) Motor start mode
Set how to control the starting of the IDD spindle motor according to Table 5.3. This setting only
determines the operation mode when the power supply is turned on or the microcode is
downloaded. In both modes, stopping or restarting the spindle motor can be controlled by
specifying the START/STOP UNIT command.
Start timing of the spindle motor
Starting of the motor is controlled with the
START/STOP UNIT command.
CN2 23-24
IDD
Supply off Open
Supply on Short (*1)
Table 5.3 Motor start mode setting
NC model (*3) NP model
CN1 38 CN1 78 CN2 11-12
Short Open or Short Open
The motor is started immediately after the
power supply is turned on or after the
microcode is downloaded.
The motor is started after the elapse of a delay
time that is based on the SCSI ID. The delay
time is provided immediately after the power
supply is turned on or after the microprogram is
downloaded.
*1. Set at factory shipment.
*2. For NP model, delay starting of spindle motor is supported by the CHANGE DEFINITION
command only.
*3. To set the setting terminals on NC models to short, apply voltage ranging between-0.3 V and
0.8 V to the setting terminals externally. To set the setting terminals on NC models to open,
apply voltage ranging between 2.0 V and 5.5 V to the setting terminals from an external source.
Refer to Chapter 3 of the SCSI Logical Interface Specifications for details of the START/STOP
UNIT command.
5-8 C141-E166
Open Open Short (*1)
Open Short (*2)
Page 81

(3) Write protect
When the write protect function is enabled on NP model, writing to the disk medium is disabled.
Table 5.4 Write protect setting (NP model)
Write protect CN2 9-10
Write operation is enabled. Open (*1)
Write operation is disable. Short
*1. Set at factory shipment.
For NC model, the function of the write protect setting is not supported.
(4) Setting of the SCSI interface operation mode
By establishing a short-circuit between CN2-15 amd CN2-16 on NP model, the SCSI interface
operation mode is forcibly set to the single-ended mode. When this setup terminal is open, the IDD
automatically identifies the DIFFSNS signal level on the SCSI bus and the IDD SCSI interface
operation mode is set to the operation mode.
Table 5.5 Setting of the SCSI interface operation mode (NP model)
Operation mode CN2 15-16
Follows the DIFFSNS signal level on the SCSI bus Open (*1)
Single-Ended mode Short
*1. Set at factory shipment.
For NC model, the function of the SCSI interface operation mode is not supported, so the SCSI
interface operation mode follows the level of the DIFFSNS signal on the SCSI bus.
(5) Setting the bus width of the SCSI interface
By establishing a short-circuit between CN2-13 and CN2-14 on NP model, the bus width for the
SCSI interface is forcibly set to the 8-bit bus mode. This setup terminal must be set in order to
guarantee the physical level of the SCSI interface’s upper bus (DB8-15, P1) inside the IDD only
when the top-level bus (DB8-15, P1) for the IDD SCSI interface is not connected to the external
part of the IDD.
Table 5.6 Setting the bus width of the SCSI interface (NP model)
Bus width CN2 13-14
16 bit bus Open (*1)
8 bit bus Short
*1. Set at factory shipment.
For NC model, the function of the bus width setting for the SCSI interface is not supported.
C141-E166 5-9
Page 82

5.3.3 Mode settings
In addition to the previously described settings using setting terminals, the IDD is provided with several
mode settings. The mode settings are enabled by specifying the CHANGE DEFINITION command.
Table 5.7 lists the mode settings and their settings at factory shipment.
Refer to Section 3.1.4 of the SCSI Logical Interface Specifications for details of the command.
Table 5.7 Default mode settings (by CHANGE DEFINITION command)
SCSI level SCSI-2
Mode setting Contents
SYNCHRONOUS DATA TRANSFER REQUEST message
sending
UNIT ATTENTION report mode Reported
Reselection retry count Not restricted
WIDE DATA TRANSFER REQUEST message sending Not sent from IDD
Reselection time-out delay 250 ms
Spindle motor start delay time
Not sent from IDD
0 sec (NP)
12 sec × SCSI ID (NC)
5-10 C141-E166
Page 83

5.4 Mounting Drives
5.4.1 Check before mounting
Reconfirm if the setting terminals are set correctly according to Table 5.8 before mounting the NP
model drives in the system cabinet. For setting terminals location, see Section 5.3.
The NC model drives do not require the following check.
Table 5.8 Setting check list (NP model only)
Setting
terminal
CN2
5.4.2 Mounting procedures
No.
1 SCSI ID CN2 1 - 2
2 Write protect CN2 9 - 10 ¤ Short ¤ Open
3 Motor start mode CN2 11 - 12 ¤ Short ¤ Open
4 Force Narrow CN2 13 - 14 ¤ Short ¤ Open
5 Force single ended CN2 15 - 16 ¤ Short ¤ Open
6
Since mounting the drive depends on the system cabinet structure, determine the work procedures
considering the requirements specific to each system. The general mounting method and items to
be checked are shown below.
See Subsection 4.1 for the details of requirements for installing the IDD.
Setting contents
(Check item)
Terminator power
supply
Setting
position
3 - 4
5 - 6
7 - 8
CN2 23 - 24 ¤ Short ¤ Open
Check Remarks
¤ (SCSI ID = __) Upper bus
(DB 8 to 15 PI)
not connected
1) With a system to which an external operator panel is mounted, if it is difficult to access the
connector after the drive is mounted on the system cabinet, connect the external operator panel
cable before mounting the drive.
2) Fix the drive in the system cabinet with four mounting screws as follows:
• The drive has 10 mounting holes (both sides: 3 × 2, bottom: 4). Fix the drive by using
four mounting holes of both sides or the bottom. (See Figure 4.5)
• Use mounting screws whose lengths inside the drive mounting frame are 5.0 mm or less
when the screws are tightened (see Figure 4.4).
• When mounting the drive, be careful not to damage parts on the PCAs.
3) Check to ensure that the DE is not touching the frame on the system side after tightening the
screws. At least 2.5mm of clearance is required between the DE and the frame. (Indicated in
Figure 4.4)
4) When an electric driver is in use, less than device specifications must be used.
C141-E166 5-11
Page 84

5.5 Connecting Cables
Connect the IDD and system with the following cables. See Section 4.3 for further details of the
requirements for IDD connector positions and connecting cables.
• Power cable
• SCSI cable
• External operator panel cable (if required for NP model)
The general procedures and notes on connecting cables are described below. Especially, pay
attention to the inserting orientation of each cable connector.
Damage
1. Make sure that system power is off before connecting or disconnecting
cables.
2. Do not connect or disconnect cables when power is on. (except NC
model)
a) Connect power cable.
CAUTION
b) Connect the external operator panel (if required for NP model).
c) Connect the SCSI cable.
d) Fix the cables so that they do not touch the DE and PCAs, or so that the smooth flow of the
cooling air in the system cabinet is assured.
CAUTION
Damage
1. Be careful of the insertion orientations of the SCSI connectors. With the
system in which terminating resistor power is supplied via the SCSI
cable, if the power is turned on, the overcurrent protection fuse of the
terminating resistor power supplier may be blown or the cable may be
burnt if overcurrent protection is not provided.
When the recommended parts listed in Table 4.2 are used, inserting the
cables in the wrong orientation can be prevented.
2. To connect SCSI devices, be careful of the connection position of the
cable. Check that the SCSI device with the terminating resistor is the last
device connected to the cable.
5-12 C141-E166
Page 85

5.6 Confirming Operations after Installation and Preparation for use
5.6.1 Confirming initial operations
This section describes the operation check procedures after power is turned on. Since the initial
operation of the IDD depends on the setting of the motor start mode, check the initial operation by
either of the following procedures.
(1) Initial operation in the case of setting so that motor starts at powering-on
a) When power is turned on, the LED blinks an instant and the IDD executes initial self-
diagnosis.
b) If an error is detected in the initial self-diagnosis, the LED blinks periodically.
Remark:
The spindle motor may or may not start rotating in this stage.
c) When the IDD status is idle, the LED remains off (when the initiator accesses the IDD via the
SCSI bus, the LED lights).
(2) Initial operation in the case of setting so that motor starts with START/STOP command
a) When power is turned on, the LED blinks an instant and the IDD executes initial self-
diagnosis.
b) If an error is detected in the initial self-diagnosis, the LED blinks.
c) The spindle motor does not start rotating until the START/STOP UNIT command for the start
is issued. The INIT needs to issue the START/STOP UNIT command to start the spindle
motor by the procedure in Subsection 5.6.2.
d) The disk drive enters the READY status in 60 seconds after the START/STOP UNIT
command is issued. At this time, the IDD reads "system information" from the system space
on the disk.
e) The LED blinks during command execution.
(3) Check items at illegal operation
a) Check that cables are mounted correctly.
b) Check that power and voltages are supplied correctly (measure them with the IDD power
connection position).
c) Check the setting of each setting terminal. Note that the initial operation depends on the
setting of the motor start mode and LED display requirements.
C141-E166 5-13
Page 86

d) If an error is detected in initial self-diagnosis the LED blinks. In this case, it is recommended
to issue the REQUEST SENSE command from the initiator (host system) to obtain information
(sense data) for error analysis.
The LED lights during the IDD is executing a command. However,
in same commands, the lighting time is only an instant. Therefore, it
seems that the LED blinks or the LED remains off.
5.6.2 Checking SCSI connection
When the initial operation is checked normally after power is turned on, check that the IDD is
connected to the SCSI bus from the host system. Although checking the connection depends on
the structure of the host system, this section describes the general procedures.
(1) Checking procedure
Issuing the commands and determining the end status depends on the start mode of the spindle
motor and UNIT ATTENTION report mode (specified with setting terminal). Figure 5.4 shows
the recommended checking procedure for the mode that the motor starts when power is turned on.
Figure 5.5 shows for the mode that the motor starts by the START/STOP command. In these
recommended checking procedures, following items are checked.
IMPORTANT
Note:
Following steps a) to e) correspond to a) to e) in Figures 5.4 and 5.5.
a) Issue the TEST UNIT READY command and check that the IDD is connected correctly
to the SCSI bus and the initial operation after power is turned on ended normally. The
command issue period of the TEST UNIT READY command shall be more than 20 ms.
b) To control starting of the spindle motor from the host system, issue the START/STOP
UNIT command to start the spindle motor.
c) Check the SCSI bus operations with the WRITE BUFFER and READ BUFFER
commands. Use data whose data bus bits change to 0 or 1 at least once. (Example: Data
with an increment pattern of X'00' to X'FF')
d) Start the IDD self-diagnostic test with the SEND DIAGNOSTIC command and check the
basic operations of the controller and disk drive.
5-14 C141-E166
Page 87

Motor starts when power is turned on
(60
Self test = 1
Unit Of =1
No parameter
Figure 5.4 Checking the SCSI connection (A)
C141-E166 5-15
Page 88

Motor starts by START/STOP command
* Executing time: about 60 seconds
Figure 5.5 Checking the SCSI connection (B)
5-16 C141-E166
Page 89

(2) Checking at abnormal end
a) When sense data can be obtained with the REQUEST SENSE command, analyze the sense
data and retry recovery for a recoverable error. Refer to Chapter 5 of SCSI Logical Interface
Specifications for further details.
b) Check the following items for the SCSI cable connection:
• All connectors including other SCSI devices are connected correctly.
• The terminating resistor is mounted on both ends of the cable.
• Power is connected to the terminating resistor.
c) Check the setting of the terminals. Note that the checking procedure of SCSI connection
differs depending on the setting of the motor start mode and UNIT ATTENTION report mode.
5.6.3 Formatting
Since the disk drive is formatted with a specific (default) data format for each model (part number)
when shipped from the factory, the disk need not be formatted (initialized) when it is installed in
the system.
However, when the system needs data attributes different from the default format, all recording
surface of the disk must be formatted (initialized) according to the procedures below.
The user can change the following data attributes at initialization:
• Logical data block length
• Number of logical data blocks or number of cylinders in the user space
• Alternate spare area size
This section outlines the formatting at installation. Refer to Chapters 3 and 6 of SCSI Logical
Interface Specifications for further details.
(1) MODE SELECT/MODE SELECT EXTENDED command
Specify the format attributes on the disk with the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT
EXTENDED command. The parameters are as follows.
a. Block descriptor
Specify the size (byte length) of the logical data block in the "data block length" field. To
explicitly specify the number of logical data blocks, specify the number in the "number of data
blocks" field. Otherwise, specify 0 in "number of data blocks" field. In this case, the number
of logical data blocks after initialization is determined by the value specified in the format
parameter (page code = 3) and drive parameter (page code = 4).
C141-E166 5-17
Page 90

b. Format parameter (page code = 3)
Specify the number of spare sectors for each cell in the "alternate sectors/zone" field and
specify the number of tracks for alternate cylinders (= number of alternate cylinders × number
of disk drive heads) in the "alternate tracks/zone" field. It is recommended not to specify
values smaller than the IDD default value in this field.
(2) FORMAT UNIT command
Initialize all recording surface of the disk with the FORMAT UNIT command. The FORMAT
UNIT command initializes all surface of the disk using the P lists, verifies data blocks after
initialization, and allocates an alternate block for a defect block detected with verification. With
initialization, the value "00" is written into all bytes of all logical data blocks. Only the position
information of defect blocks detected with verification is registered in the G list. The
specifications are as follows:
a. Specifying CDB
Specify 0 for the "FmtData" bit and the "CmpLst" bit on CDB, 000 for the "Defect List
Format" field, and data pattern written into the data block at initialization for the "initializing
data pattern" field.
b. Format parameter
When the values in step a. are specified with CDB, the format parameter is not needed.
5-18 C141-E166
Page 91

5.6.4 Setting parameters
The user can specify the optimal operation mode for the user system environments by setting the
following parameters with the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT EXTENDED command:
• Error recovery parameter
• Disconnection/reconnection parameter
• Caching parameter
• Control mode parameter
With the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT EXTENDED command, specify 1 for the "SP" bit
on CDB to save the specified parameter value on the disk. This enables the IDD to operate by
using the parameter value set by the user when power is turned on again. When the system has
more than one INIT, different parameter value can be set for each INIT.
When the parameters are not set or saved with the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT
EXTENDED command, the IDD sets the default values for parameters and operates when power is
turned on or after reset. Although the IDD operations are assured with the default values, the
operations are not always optimal for the system. To obtain the best performance, set the
parameters in consideration of the system requirements specific to the user.
This section outlines the parameter setting procedures. Refer to Chapter 3 of SCSI Logical
Interface Specifications for further details of the MODE SELECT and MODE SELECT
EXTENDED commands and specifying the parameters.
IMPORTANT
1. At factory shipment of the IDD, the saving operation for the MODE
SELECT parameter is not executed. So, if the user does not set
parameters, the IDD operates according to the default value of each
parameter
2. The model select parameter is not saved for each SCSI ID of but as the
common parameter for all IDs. In the multi-INIT System, parameter
setting cannot be changed for each INIT.
3. Once parameters are saved, the saved value is effective as long as next
saving operation is executed from the INIT. For example, even if the
initialization of the disk is performed by the FORMAT UNIT command,
the saved value of parameters described in this section is not affected.
4. When the IDD, to which the saving operation has been executed on a
system, is connected to another system, the user must pay attention to
that the IDD operates according to the saved parameter value if the
saving operation is not executed at installation.
C141-E166 5-19
Page 92

5. The saved value of the MODE SELECT parameter is assumed as the
initial value of each parameter after the power-on, the RESET condition,
or the BUS DEVICE RESET message. The INIT can change the
parameter value temporary (actively) at any timing by issuing the MODE
SELECT or MODE SELECT EXTENDED command with specifying "0"
to the SP bit in the CDB.
(1) Error recovery parameter
The following parameters are used to control operations such as IDD internal error recovery:
a. Read/write error recovery parameters (page code = 1)
• AWRE:
• ARRE:
• TB:
• EER:
• PER:
• DCR:
• Retry count at read operation
• Retry count at write operation
• Recovery time limit
Automatic alternate block allocation at Write
operation
Automatic alternate block allocation at read
operation
Uncorrectable data transfer to the INIT
Immediate correction of correctable error
Report of recovered error
Suppression of ECC error correction
Parameter Default value
1 (enabled)
1 (enabled)
1 (enabled)
1 (enabled)
0 (disabled)
0 (Correction is
enabled.)
63
63
30 sec
b. Verify error recovery parameters (page code = 7)
Parameter Default value
• ERR:
• PER:
• DTE:
• DCR:
• Retry count at verification 63
c. Additional error recovery parameters (page code = 21)
• Retry count at seek error 15
Immediate correction of recoverable error
Report of recovered error
Stop of command processing at successful
error recovery
Suppression of ECC error correction
Parameter Default value
1 (enabled)
0 (disabled)
0 (Processing is
continued.)
0 (Correction is
enabled.)
5-20 C141-E166
Page 93

Notes:
1. The user can arbitrarily specify the following parameters according to the system
requirements:
• ARRE
• AWRE
• TB
• PER
2. The user also can arbitrarily specify parameters other than the above. However, it is
recommended to use the default setting in normal operations.
(2) Disconnection/reconnection parameters (page code = 2)
The following parameters are used to optimize the start timing of reconnection processing to
transfer data on the SCSI bus at a read (READ or READ EXTENDED command) or write
operation (WRITE, WRITE EXTENDED, or WRITE AND VERIFY command) of the disk.
Refer to Chapter 2 of SCSI Logical Interface Specifications for further details.
Parameter Default value
• Buffer full ratio 00 (HEX)
• Buffer empty ratio 00 (HEX)
Notes:
1. In a system without the disconnection function, these parameters need not be specified.
2. Determine the parameter values in consideration of the following performance factors of
the system:
• Time required for reconnection processing
• Average data transfer rate of the SCSI bus
• Average amount of processing data specified with a command
Refer to Chapter 2 of SCSI Logical Interface Specifications for how to obtain the rough
calculation values for the parameter values to be set. It is recommended to evaluate the
validity of the specified values by measuring performance in an operation status under the
average system load requirements.
C141-E166 5-21
Page 94

(3) Caching parameters
The following parameters are used to optimize IDD Read-Ahead caching operations under the
system environments. Refer to Chapter 2 of SCSI Logical Interface Specifications for further
details.
• IC: Initiator control 0 (Drive-specific
• RCD: Disabling Read-Ahead caching operations 0 (enabled)
• WCE: Write Cache Enable 1 (enabled)
• MS: Specifying the multipliers of "minimum
• DISC: Prefetch operation after track switching during
• Number of blocks for which prefetch is suppressed X'FFFF'
• Minimum prefetch X'0000'
• Maximum prefetch X' XXXX'
• Number of blocks with maximum prefetch restrictions X'FFFF'
• Number of segments X'08'
Parameter Default value
prefetch" and "maximum prefetch" parameters
prefetching
control (page
cache))
0 (Specifying
absolute value)
1 (enable)
(1 cache segment)
Notes:
1. When Read-Ahead caching operations are disabled by the caching parameter, these
parameter settings have no meaning except write cache feature.
2. Determine the parameters in consideration of how the system accesses the disk. When the
access form is not determined uniquely because of the processing method, the parameters
can be re-set actively.
3. For sequential access, the effective access rate can be increased by enabling Read-Ahead
caching operations and Write Cache feature.
(4) Control mode parameters
The following parameters are used to control the tagged queuing and error logging.
5-22 C141-E166
Page 95

a. Control mode parameters
• Queue algorithm modifier 0 (Execution
• QErr: Resume or abort remaining suspended
• DQue: Disabling tagged command queuing 0 (enabled)
5.7 Dismounting Drives
Since dismounting the drive to check the setting terminals, change the setting, or change the drive
depends on the structure of the system cabinet, the work procedures must be determined in
consideration of the requirements specific to the system. This section describes the general
procedures and notes on dismounting the drive.
It is recommended before dismounting the drive to make sure the spindle motor completely stops
after power was turned off.
a) Remove the power cable.
Parameter Default value
commands after sense pending state
sequence of
read/write
commands is
optimized.)
0 (command is
resumed)
b) Remove the SCSI cable.
NC Model uses a single cable for power supply and the SCSI interface.
c) When the external operator panel is mounted, remove the cable. If it is difficult to access the
connector position, the cable may be removed after step e).
d) Remove the DC ground cable.
e) Remove the four mounting screws securing the drive, then remove the drive from the system
cabinet.
f) To store or transport the drive, keep it in an antistatic bag and provide packing (see Section
5.1).
5.8 Spare Disk Drive
See 2.1.1, “Model name and order number,” to order a disk drive for replacement or as a spare.
C141-E166 5-23
Page 96

This page is intentionally left blank.
Page 97

CHAPTER 6 DIAGNOSTICS AND MAINTENANCE
6.1 Diagnostics
6.2 Maintenance Information
6.3 Operation Check
6.4 Troubleshooting Procedures
This chapter describes diagnostics and maintenance information.
6.1 Diagnostics
6.1.1 Self-diagnostics
The IDD has the following self-diagnostic function. This function checks the basic operations of
the IDD.
• Initial self-diagnostics
• Online self-diagnostics (SEND DIAGNOSTIC command)
Table 6.1 lists the contents of the tests performed with the self-diagnostics. For a general check of
the IDD including the operations of the host system and interface, use a test program that runs on
the host system (see Subsection 6.1.2).
Table 6.1 Self-diagnostic functions
C141-E166 6-1
Page 98

Brief test contents of self-diagnostics are as follows.
a. Hardware function test
This test checks the basic operation of the controller section, and contains following test.
• RAM (microcode is stored)
• Peripheral circuits of microprocessor (MPU)
• Memory (RAM)
• Data buffer
b. Seek test
This test checks the positioning operation of the disk drive using several seek modes (2 points
seek, 1 position sequential seek, etc.). The positioning operation is checked with confirming
the physical address information by reading the ID field (LBA) from the data block on track 0
after completion of the seek operation to the target cylinder.
c. Write/read test
This test checks the write/read function by using the Internal test space of the disk drive.
(1) Initial self-diagnostics
When power is turned on, the IDD starts initial self-diagnostics. The initial self-diagnostics checks
the basic operations of the hardware functions.
If an error is detected in the initial self-diagnostics, the LED on the drive front panel blinks. In this
status, the IDD posts the CHECK CONDITION status to all I/O operation requests other than the
REQUEST SENSE command. When the CHECK CONDITION status is posted, the INIT should
issue the REQUEST SENSE command. The sense data obtained with the REQUEST SENSE
command details the error information detected with the initial self-diagnostics.
Even if CHECK CONDITION status and sense data are posted, the LED continues blinking. Only
when the power is turned off or re-turned on, this status can be cleared. When this status is
cleared, the IDD executes the initial self-diagnosis again.
6-2 C141-E166
Page 99

The IDD does not reply to the SCSI bus for up to 2 seconds after the initial self-diagnostics is
started. After that, the IDD can accept the I/O operation request correctly, but the received
command, except the executable commands under the not ready state (such as INQUIRY,
START/STOP UNIT), is terminated with the CHECK CONDITION status (NOT READY
[=2]/logical unit is in process of becoming ready [=04-01] or logical unit not ready, initializing
command required [=04-02]) during the interval from the spindle motor becomes stable to the IDD
becomes ready. The executable command under the not ready state is executed in parallel with the
initial self-diagnostics, or is queued by the command queuing feature and is executed after
completion of the initial self-diagnostics. When the command that comes under the exception
condition of the command queuing is issued at that time, the IDD posts the BUSY status for the
command. When the error is detected during the initial self-diagnostics, the CHECK
CONDITION status is posted for all commands that were stacked during the initial selfdiagnostics. For the command execution condition, refer to Section 1.4 and Subsection 1.7.4 in
SCSI Logical Interface Specifications.
(2) Online self-diagnostics (SEND DIAGNOSTIC command)
The INIT can make the IDD execute self-diagnostics by issuing the SEND DIAGNOSTIC
command.
The INIT specifies the execution of self-diagnostics by setting 1 for the SelfTest bit on the CDB in the
SEND DIAGNOSTIC command and specifies the test contents with the UnitOfl bit.
When the UnitOfl bit on the CDB is set to 0, the IDD executes the hardware function test only
once. When UnitOfl bit is set to 1, the IDD executes the hardware function test, seek (positioning)
test, and data write/read test for the Internal test space only once.
a. Error recovery during self-diagnostics
During the self-diagnostics specified by the SEND DIAGNOSTIC command, when the
recoverable error is detected during the seek or the write/read test, the IDD performs the error
recovery according to the MODE SELECT parameter value (read/write error recovery
parameter, additional error recovery parameter) which the INIT specifies at the time of issuing
the SEND DIAGNOSTIC command.
PER Operation of self-diagnostics
0 The self-diagnostics continues when the error is recovered. The self-
diagnostics terminates normally so far as the unrecoverable error is not
detected.
1 The self-diagnostics continues when the error is recovered. If the
unrecoverable error is not detected, the consecutive tests are executed till last
test but the self-diagnostics terminates with error. The error information
indicates that of the last recovered error.
b. Reporting result of self-diagnostics and error indication
When all specified self-diagnostics terminate normally, the IDD posts the GOOD status for the
SEND DIAGNOSTIC command.
C141-E166 6-3
Page 100

When an error is detected in the self-diagnostics, the IDD terminates the SEND DIAGNOSTIC
command with the CHECK CONDITION status.
The INIT should issue the REQUEST SENSE command when the CHECK CONDITION
status is posted. The sense data collected by the REQUEST SENSE command indicates the
detail information of the error detected in the self-diagnostics.
The IDD status after the CHECK CONDITION status is posted differs according to the type of
the detected error.
a) When an error is detected in the seek or write/read test, the subsequent command can be
accepted correctly. When the command other than the REQUEST SENSE and NO
OPERATION is issued from the same INIT, the error information (sense data) is cleared.
b) When an error is detected in the hardware function test, the IDD posts the CHECK
CONDITION status for all I/O operation request except the REQUEST SENSE
command. The error status is not cleared even if the error information (sense data) is
read. Only when the power is turned off or re-turned on, the status can be cleared. When
this status is cleared, the IDD executes the initial self-diagnostics again (see item (1)).
Refer to Chapter 3 of SCSI Logical Interface Specifications for further details of the command
specifications.
CAUTION
6.1.2 Test programs
The basic operations of the IDD itself can be checked with the self-diagnostic function. However,
to check general operations such as the host system and interface operations in a status similar to
the normal operation status, a test program that runs on the host system must be used.
The structure and functions of the test program depend on the user system requirements.
Generally, it is recommended to provide a general input/output test program that includes SCSI
devices connected to the SCSI bus and input/output devices on other I/O ports.
Including the following test items in the test program is recommended to test the IDD functions
generally.
Data loss
When the SEND DIAGNOSTIC command terminates with the
CHECK CONDITION status, the INIT must collect the error
information using the REQUEST SENSE command. The RECEIVE
DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS command cannot read out the error
information detected in the self-diagnostics.
6-4 C141-E166
 Loading...
Loading...