ADSL MODEM ROUTER
Installation Guide
Single / 4 Port
&
Plus Wireless
F300000013

FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions:(1) this device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
NOTE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiated radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
-Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
-Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
-Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
-Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user‘s authority to operate the equipment.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. In order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the
FCC radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity to the antenna shall
not be less than 20cm (8 inches) during normal operation. Proposed RF
exposure safety information to include in User’s Manual.

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 check and prepare
1.1 Package checklist…………………………..…………………………. 1
1.2 Hardware Requirement. ………………….…………………………….1
1.3 Data Requirement………………………………………………………..1
1.3.1 For Static IP Address User..………………..……………………… .1
1.3.2 For Dynamic IP Address (PPPoE / PPPoA) User..…………… …1
Chapter 2 Introduction
2.1 Wireless ADSL Router
2.1.1 Features………………………………………………………………...2
2.1.2 ADSL Compliance…………………………………………………….3
2.1.3 ATM Protocols and Encapsulations………………………………..3
2.1.4 Bridge/Router Protocols………………………………………………3
2.1.5 Management……………………………………………………………4
2.2 ADSL Modem Route
2.2.1 Features………………………………………………………………...5
2.2.2 ADSL Compliance……………………………………………………..6
2.2.3 ATM Protocols and Encapsulations………………………………..6
2.2.4 Bridge/Router Protocols………………………………………………6
2.2.5 Management…………………………………………………………...7
2.3 LED Indicators………………………………………………………..7
2.3.1 ADSL Modem Router / Wireless…………………………….…. ………8
2.3.2 4-port ADSL Modem Router / Wireless……………………..…..……….8
Chapter 3 Installation
3.1 Hardware Connection…………………………………………………9
3.1.1 4-PORT Wireless ADSL Modem Router / Switch HUB……….…9
3.1.2 Wireless ADSL Modem Router / Switch HUB……..…………..10
3.1.3 4-PORT ADSL Modem Router / Switch HUB………..………...11
3.1.4 ADSL Modem Router / Switch HUB……………………………..12
3.2 USB Installation………………………………………………………12
Chapter 4 Configuration Setting
4.1 LAN Card Setting…………………………………………..……….…13
4.2 ADSL Modem Router Parameter Setting……...………..…………13
4.2.1 Router mode for static IP with DHCP function………………..15
4.2.2 Bridge mode with DHCP function …………………………….…..16
4.2.3 Wireless Introduction function ………………………………. 19
4.3 Wireless Setup …………………. ………………………………..…. 20

Chapter 1 Check and Prepare
1.1 Package Checklist
One Ethernet ADSL Router
One Power Adapter
One RJ45 Cable
One USB Cable
One RJ11 phone cable
One CD driver for USB interface
One 2.4G Antenna ( Wireless only )
One Installation Guide
1.2 Hardware Requirement
ADSL Line from your telephone company
LAN Card inside your PC or Uplink port on Switch HUB
IEEE 802.11b compliant PCMA Wireless LAN card ( Wireless
only )
1.3 Data Requirement
Please get the following data information from your ISP
or phone company before setting up this ADSL Modem
Router.
1.3.1 For Static IP address user:
IP address
Gateway Address
Subnet mask
DNS
VPI / VCI value
Encapsulation mode (example: RFC 1483,1577…etc.)
1.3.2 For Dynamic IP address (PPPoE/PPPoA) user:
VIP value
VCI value
Encapsulation mode (example: RFC 2516, 2364…etc.)
User name &Password
1

Chapter 2 Introduction
2.1.1 Features
The ADSL Router providing fast and reliable Internet access
over the existing copper wires is an ideal solution for SOHO
users. Using the existing phone lines to deliver data at rates up
to 8Mbps-140 times faster than traditional analogue modem.
Meanwhile, you can share a single IP account within your
entire network to enjoy internet convenience at the same time.
In order to bring the most convenience to users, this Wireless
ADSL Modem router builds in three kind of interfaces: IEEE
802.11b wireless, USB and Ethernet . Taking advantage of
wireless, you can setup an ADSL connection to Internet easily.
Meanwhile, user-friendly web-based configuration and
management tool via Ethernet allows easy configuration.
Support RJ-45 Ethernet interface & USB interface
Support IEEE802.11b for Wireless LAN
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2, ITU G..DMT(G.992.1),ITU-T
G..Lite(G..992.2)
DHCP server & client
NAT (Network Address Translation) function for Net Meeting,
ICQ or CUseeMe…etc. Internet application programs
PPPoE / PPPoA function
Wireless data encryption 64/128 bit for security
Support IP, PPP, Transparent bridging ..etc. multi-protocols
Configuration ,management & firmware update via Web
browser
Two-level password protection for management
Flash memory included for future firmware upgrade
2

2.1.2 ADSL Compliance
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
ITU G..992.1 (G.. DMT)
ITU G..992.2 (G.. Lite)
ITU G..994.1 (G.. hs)
2.1.3 ATM Protocols and Encapsulations
PPP over ATM VCMUX ( RFC 2364)
PPP over ATM LLCSNAP ( RFC 2364)
Bridged IP over ATM LLCSNAP ( RFC 1483)
Routed IP over ATM LLCSNAP ( RFC 1483)
Bridged IP over ATM VCMUX ( RFC 1483)
Routed IP over ATM VCMUX ( RFC 1483)
Classical IP over ATM ( RFC 1577)
PPP over Ethernet VCMUX ( RFC 2516)
PPP over Ethernet LLCSNAP ( RFC 2516)
8 PVCs (simultaneous and encapsulation independent)
VPI/VCI range 0-255, 0-65536
Encapsulation hunting of up to 8 pre-defined VPI/VCI &
encapsulation sets
AAL5 UBR & CBR
OAM F4/F5
2.1.4 Bridge/Router protocols
IEEE 802.1D(self learning transparent bridge)
128 MAC Address support
Static IP routing (configurable route table)
RIPv2 (backward compatible with RIPv1)
DHCP server ( configurable and supports up to
32 addresses)
DHCP relay agent
DHCP client
PPP auto reconnect and configurable timeouts
PPP auto reconnect on WAN access
3

PAP/CHAP
128 character support for PPPx username/passwords
DNS proxy
Port forwarding
NAT
NAPT
ALG support (MSN Messenger 4.x, H.323 ( Microsoft
NetMeeting) , AOL Instant Messenger…ect.)
Wild Card DMZ
Virtual server
VPN pass through ( IPSec-ESP Tunnel mode, L2TP, PPTP)
Bridge filtering
ICMP
IGMP
MAC Address Spoofing
PPP Half Bridge
2.1.5 Management
HTTP client and server
Password protection (2 levels)
Configurable Web pages
FTP server / client
Telnet
Local firmware upgrade via FTP or Web
Remote firmware upgrade via FTP client
Configuration of LAN, WAN, and ADSL
Restore to Factory defaults via Web or Hardware
7 layer diagnostics with links to help pages
System logging
4

2.2.1 Features
Using existing twisted-pair telephone lines, ADSL technology
provides data rates more than 100 times as fast as traditional
dial-up modem delivers, without an interruption in telephone
service. With data transfer rates of up to 8 Mbps downstream
and 1Mbps upstream, ADSL is the ideal solution for
high-bandwidth application such as access to a corporate
network, Internet access and video delivery.
This ADSL Modem Router using industry-standard discrete
multimode (DMT) line-code technology supports the full range
of ADSL standards. This solution is not limited by host pc
processor speed, operation system or memory configuration
and is fully compliant with the full-rate ADSL (T1.413 Issue 2
and G.dmt) and the splitter less G.lite ( G.992.2)standard.
Support dual interface-RJ-45 & USB interface
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2, ITU G..DMT(G.992.1),ITU-T
G..Lite(G..992.2)
DHCP server & client: Automatically assign IP address to
network users & automatically get IP address from DHCP
server
IP Sharing : sharing a single IP account within your entire
network via NAT routing function
NAT (Network Address Translation) function for Net Meeting,
ICQ or CUseeMe…etc. Internet application programs
PPPoE / PPPoA function
Full ATM protovol support
Support IP, PPP, Transparent bridging ..etc. multi-protocols
Configuration ,management & firmware update via Web
browser
Two-level password protection for management
5

2.2.2 ADSL Compliance
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
ITU G..992.1 (G.. DMT)
ITU G..992.2 (G.. Lite)
ITU G..994.1 (G.. hs)
2.2.3 ATM Protocols and Encapsulations
PPP over ATM VCMUX ( RFC 2364)
PPP over ATM LLCSNAP ( RFC 2364)
Bridged IP over ATM LLCSNAP ( RFC 1483)
Routed IP over ATM LLCSNAP ( RFC 1483)
Bridged IP over ATM VCMUX ( RFC 1483)
Routed IP over ATM VCMUX ( RFC 1483)
Classical IP over ATM ( RFC 1577)
8 PVCs (simultaneous and encapsulation independent)
VPI/VCI range 0-255, 0-65536
Support AAL5 and service class UBR & CBR
OAM F4/F5 loop back
2.2.4 Bridge/Router protocols
IEEE 802.1D(self learning transparent bridge)
128 MAC Address support
Static IP routing (configurable route table)
RIPv2 (backward compatible with RIPv1)
DHCP server / client / relay agent
PAP / CHAP
128 character support for PPPx username / password
NAT / NAPT / DynamicNAPT
ALG support ( MSN Messenger 4.x, h.323(Microsoft
NetMeeting),
AOL Instant Messenger, Windows Media
Player…etc.),CuSeeMe 5.00
Virtual server and DMZ
VPN pass through (IPSec-ESP Tunnel mode, L2TP,PPTP)
ICMP / IGMP
MAC address Spoofing
PPP Half Bridge
6

2.2.5 Management
HTTP client and server
Password protection (2 levels)
Configurable Web pages
FTP server / client
Telnet
Local firmware upgrade via FTP or Web
Remote firmware upgrade via FTP client
Restore to Factory defaults via Web or Hardware
System logging and diagnostics
7

2.6 LED Indicators
2.6.1 ADSL Modem Router / Wireless
LED NAME Description
PWR On: ADSL modem is power on
RDY Blink: ADSL modem is ready
Off : ADSL modem is not ready or has
malfunctioned.
ADSL Blink: ADSL modem is ready to connect
or the link is down.
ON: the ADSL modem links to DSLAM
successfully.
DATA Blink: when data is sent or received..
LAN_LINK ON: ADSL modem has a successful
Ethernet connection.
2.6.2 4-port ADSL Modem Router / Wireless
LED NAME Description
READY Blink: ADSL modem is ready.
Off: ADSL modem is not ready or has
malfunctioned.
Always On: Please send back for repair.
ADSL Blink: ADSL modem is ready to connect
or the link is down.
On : ADSL modem links to DSLAM
successfully.
LAN 1-4 On : ADSL modem has a successful
Ethernet connection
8

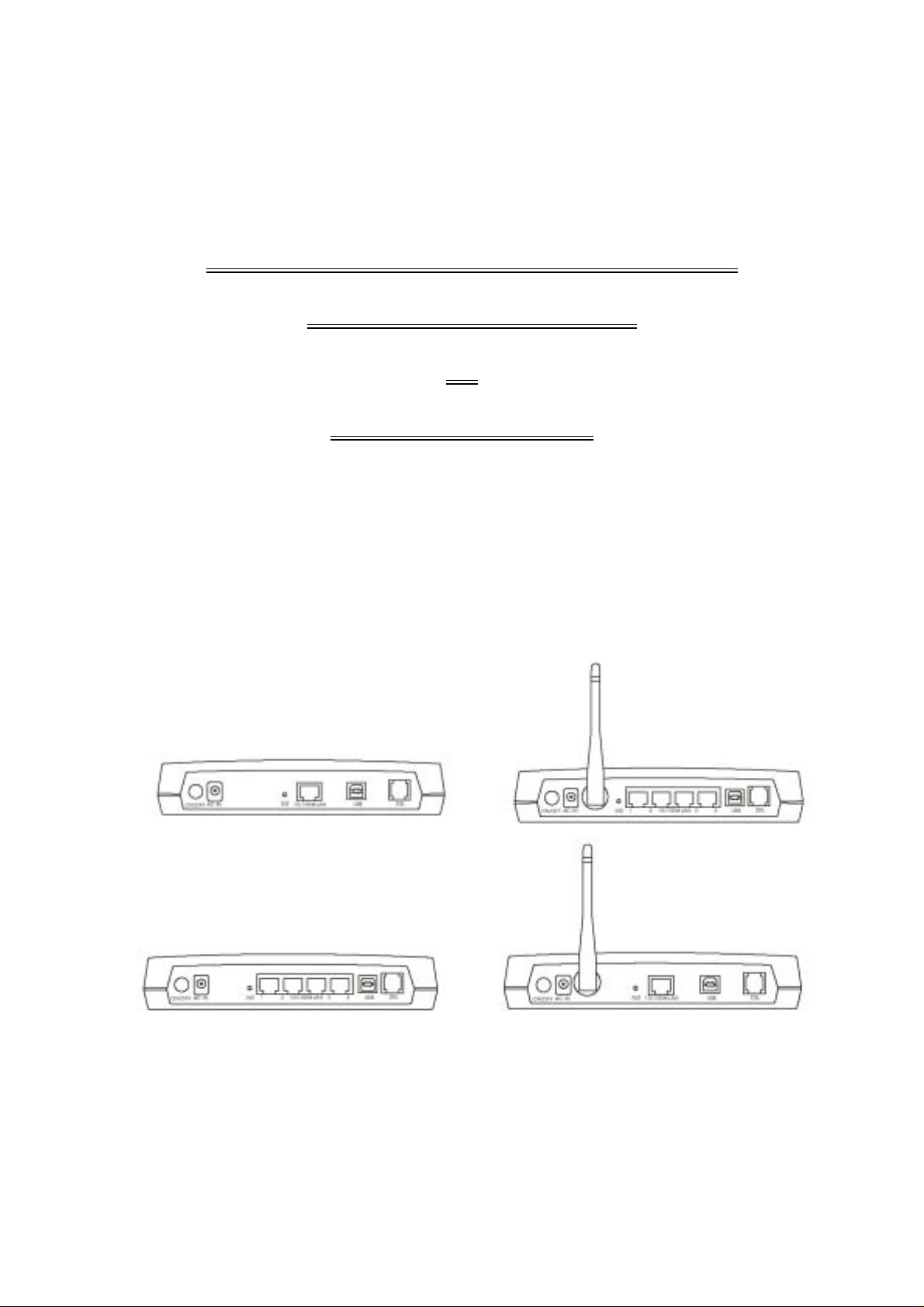
Chapter 3 Installation
3.1 Hardware Connection
Note: When plug-in in power cord, router starts working after
around 15 seconds.
Note: If you push the “Reset” button, all the parameter setting
will revert back to factory default
Make sure the antenna is securely screwed onto
the antenna connectors
3.1.1 4-Port Wireless ADSL Modem Router / Switch HUB
9

3.1.2 Wireless ADSL Modem Router / Switch HUB
Make sure the antenna is securely screwed
onto the antenna connectors
10

3.1.1 4-Port Wireless ADSL Modem Router without Switch HUB
11

3.1.2 Wireless ADSL Modem Router without Switch HUB
3.2 USB Installation
The ADSL Modem Router supports extra USB port for PC use
and this USB port works together with Ethernet port at the same
time.
If you don’t intend to use USB port , please ignore this section,
1. Turn on your PC.
2. Insert the rectangular end of a USB cable into the USB port of
your PC. Then, insert the square end of the USB cable into the
USB port of the Modem Router.
3. PC will automatically detect this router as “USB Net Card”.
4. Insert bundled USB driver CD into the proper drive and follow
installation to install this router
After successful installation, the router will be installed as
“USB Network Adaptor” at Device Manager of Windows OS
12

Chapter 4 Configuration Setting
4.1 LAN Card Setting
When PC is on. Move cursor to “Network Neighborhood”
1. Push the right button of mouse, click “Properties”
2. Select the TCP/IP of your LAN card
3. Click “Properties”
4. Under IP address, select Obtain IP address automatically.
5. Under “DNS Configuration”, select “Disable DNS”
6. Under “Gateway”, please remove all installed gateway
7. Click “OK”, system will ask you to reboot your PC.
8. Restart your PC
4.2 ADSL Modem Router Parameter Setting
1. Launch the Web browser.
2. Enter the LAN port default IP address http://10.0.0.2 to
access
this ADSL Modem
3. Enter of the username and password will be prompted.
Enter the default login User Name and Password.
( see Figure 1 )
The default login User Name of the administrator is
admin , and the de fault login Password is epicrouter.
The default login User Name of the non-administrator
is user, and the default login Password is Password.
Note: The Non-administrator and Administrator password
can be changed at the Password Configuration page,
If you forget the changed password, please reset your
ADSL Modem Router by pushing reset button and all the
parameter settings will revert back to factory default.
13

Figure 1
4. After entering the user name and password, you will
see the Homepage shown as below (SEE figure 2 ) .
Please select the Configuration section to start setting up
your ADSL Modem Router.
Note: Please refer Annex A (page 15) for ADSL Modem Router
configuration.
Figure 2
14

5. Following is two example of setting for your reference.
For further configuration, Please refer to the User Guide.
pdf inside the driver CD.
6.
4.2.1 PPPoE/PPPoA mode with DHCP
function
1. Following is example of “PPPoE/PPPoA mode with
DHCP function” ( see figure 3)
Go to the Configuration section, click WAN
VPI, VCI, User name, Password and ENCAPSULATION.
Note: ( please get this data information form your ISP or
phone company
BRIDGE: select Disable, keep the other values unchanged and select
“SUBMIT”, then clink Save configuration
Figure 3.
).
. Enter
15
4.2.2 Router mode for Static IP with DHCP

1. Following is example of Router mode for Static IP with
Go to the Configuration section, click WAN .Enter
Default Gateway, VPI, VCI, Static IP address, Subnet
Figure 4
function
DHCP function (see figure 4.)
Mask
value (Note: please get this data information from
your ISP or phone company ).
ENCAPSULATION: refer to the data from your ISP or the
phone company; BRIDGE: select Disabled, keep the
other setups unchanged and then select “Submit”.
16

2.Please select DNS. Select” Auto Discovery + User Configured”
and enter the Preferred DNS Server, Alternate DNS Server,
then Click “Submit”.
Figure 5
3. Click Save Settings , “Submit”. This ADSL Modem Router will
save
these parameter settings and restart automatically.
It takes about 15 seconds.
Figure 6
17

4. Finished
Note: The default IP address of this Router is 10.0.0.2.
If you forget the modified IP address, you can’t
access this device anymore and the only solution is
to reset it by pushing reset button.
4.2.3 Bridge mode with DHCP function
1. Following is example of “Bridge mode with DHCP
function”
(see Figure 7).
Go to the Configuration section, click WAN. Enter
VPI, VCI value(Note: please get this data information
from your ISP or phone company).
ENCAPSULATION: refer to the data from your ISP
or the phone company; BRIDGE: select Enable, keep
the other setups unchanged and select
“Submit ”, then click Save configuration.
Figure 7
2. Finished
18
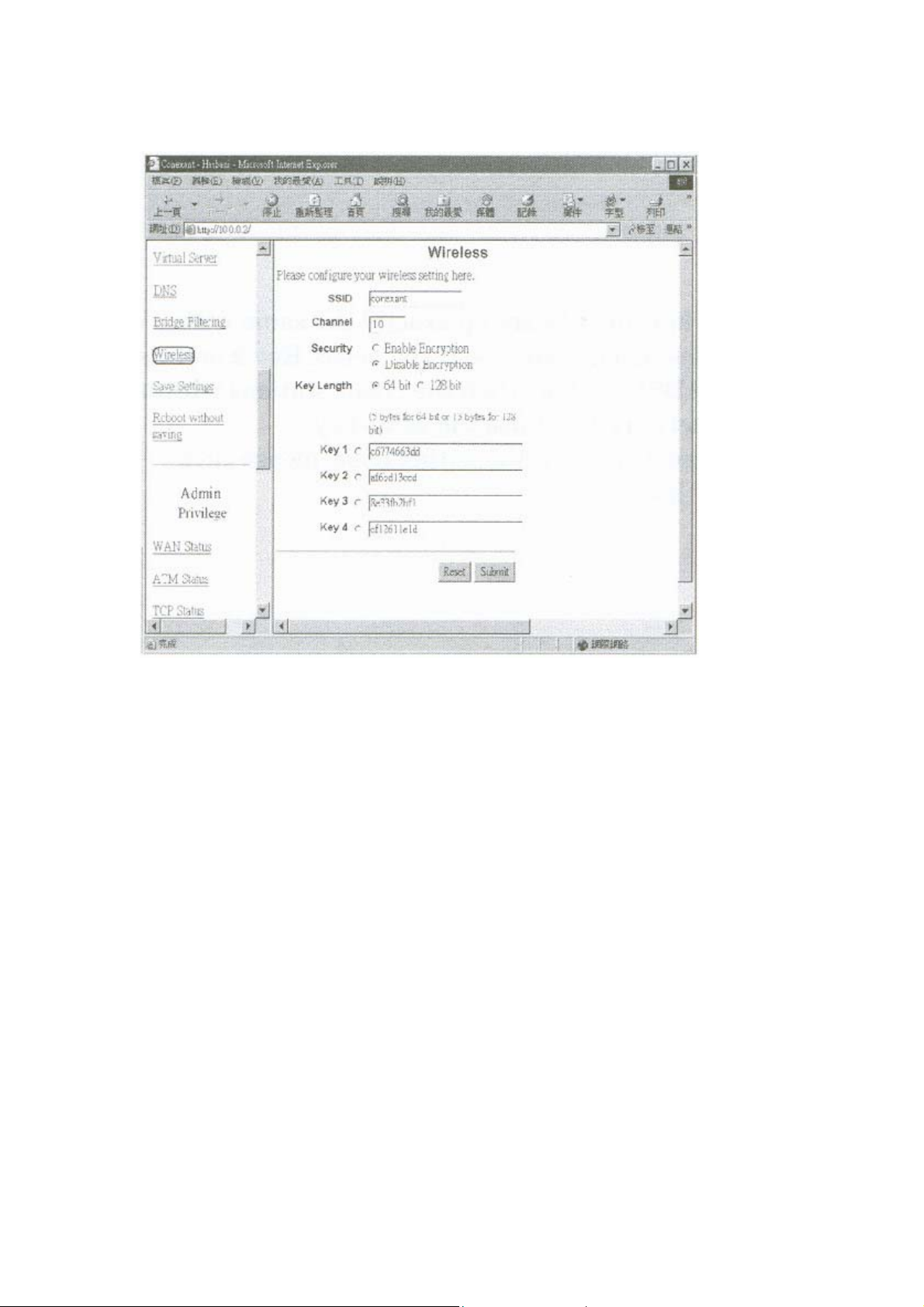
4.3 wireless setup
SSID: The SSID is an unique ID given to this Wireless ADSL Modem.
Whole wireless clients associating to this wireless LAN must
have the same SSID. (e.g. default value is conexant)
Channel: Please select any of available channels as an operation
channel. 1~11
Security: To select “enable encryption”, it allows you to create 4 data
encryption keys to secure your data transfer from
eavesdropping by unauthorized wireless users. You can also
enter WEP keys in Key 2, Key 3 and Key 4. WEP will use the
key that you select.
19

When 64 bit is selected, type 5 bytes(alphanumeric
characters) in the range of “a-z”, “A-Z” and “0-9”(e.g.
Honey).
When 128 bit is selected, type 13 bytes(alphanumeric
characters) in the range of “a-z”, “A-Z” and “0-9”(e.g.
Mypassword123).
NOTE:
1) The WEP key must be set up exactly the same within
entire this Wireless client stations. If you select Key 2 on
this Wireless ADSL modem, then the client stations
within this wireless network must use the same key.
2) After you modify any value of this page, please click
“Submit” button.
20
 Loading...
Loading...