Future Technology Devices International Ltd
DB9-USB-RS232 Module
Male & Female
Datasheet
Document Reference No.: FT_000204
Version 1.1
Issue Date: 2010-02-19
Future Technology Devices International Ltd (FTDI)
Unit 1, 2 Seaward Place, Centurion Business Park, Glasgow, G41 1HH, United Kingdom
Tel.: +44 (0) 141 429 2777 Fax: + 44 (0) 141 429 2758
E-Mail (Support): support1@ftdichip.com Web: http://www.ftdichip.com
Neither the whole nor any part of the information contained in, or the product described in this manual, may be adapted or reproduced
in any material or electronic form without the prior written consent of the copyright holde r. This product and its documentation are
supplied on an as-is basis and no warranty as to their suitability for any particular purpose is either made or implied. Future Technology
Devices International Ltd will not accept any claim for damages howsoever a rising as a result of use or failure of this product. Your
statutory rights are not affected. This product or any variant of it is not intended for use in any medical appliance, device or system in
which the failure of the product might reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. This document provides preliminary
information that may be subject to change without notice. No freedom to use patents or other intellectual property rights is implied by
the publication of this document. Future Technology Devices International Ltd, Unit1, 2 Seaward Place, Centurion Business Park,
Glasgow, G41 1HH, United Kingdom. Scotland Registered Number: SC136640
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
1 Introduction
1.1 Functional Description
The DB9-USB-RS232 modules are designed to directly replace an existing DB9, the industry accepted
name for a DE9 connector, (male or female) RS232 connection with a drop-in USB replacement
connection. The modules will replace (pin-for-pin) a male or female DB9 RS232 connector with a USB
mini-B connector. The application PCB containing the existing DB9 RS232 connector does not require any
modification, only the replacement of the D-type connector with the appropriate DB9-USB-RS232
module. A male DB9 should be replaced by a male DB9-USB-RS232-M and a female DB9 should be
replaced by a female DB9-USB-RS232-F. The modules contain all necessary electronics to convert
between USB and RS232.
The purposes of the modules is to provide a simple method of adapting legacy serial devices with RS232
interfaces to modern USB ports by replacing the DB9 connector with this miniaturised module which
closely resembles a DB9 connector. This is accomplished by incorporating the industry standard FTDI
FT232R USB-Serial Bridge IC plus the required level shifters inside the module.
Figure 1.1 – DB9-USB-RS232
The module uses a standard USB-MINI-B connector for connection to an upstream host or hub port.
RS232-level signals, including modem handshake signals, can transmit data at rates up to 1 Mega Baud.
The DB9-USB-RS232 module requires USB device drivers, available free from www.ftdichip.com, which
are used to make the DB9-USB-RS232 appear as a Virtual COM Port (VCP). This allows existing serial
communications software, such as HyperTerminal, to exchange data through the DB9-USB-RS232 to a
legacy RS232 peripheral device.
Note: The connector is referred as a DB9 connector since DE9 is often referred to by this name.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 1
Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
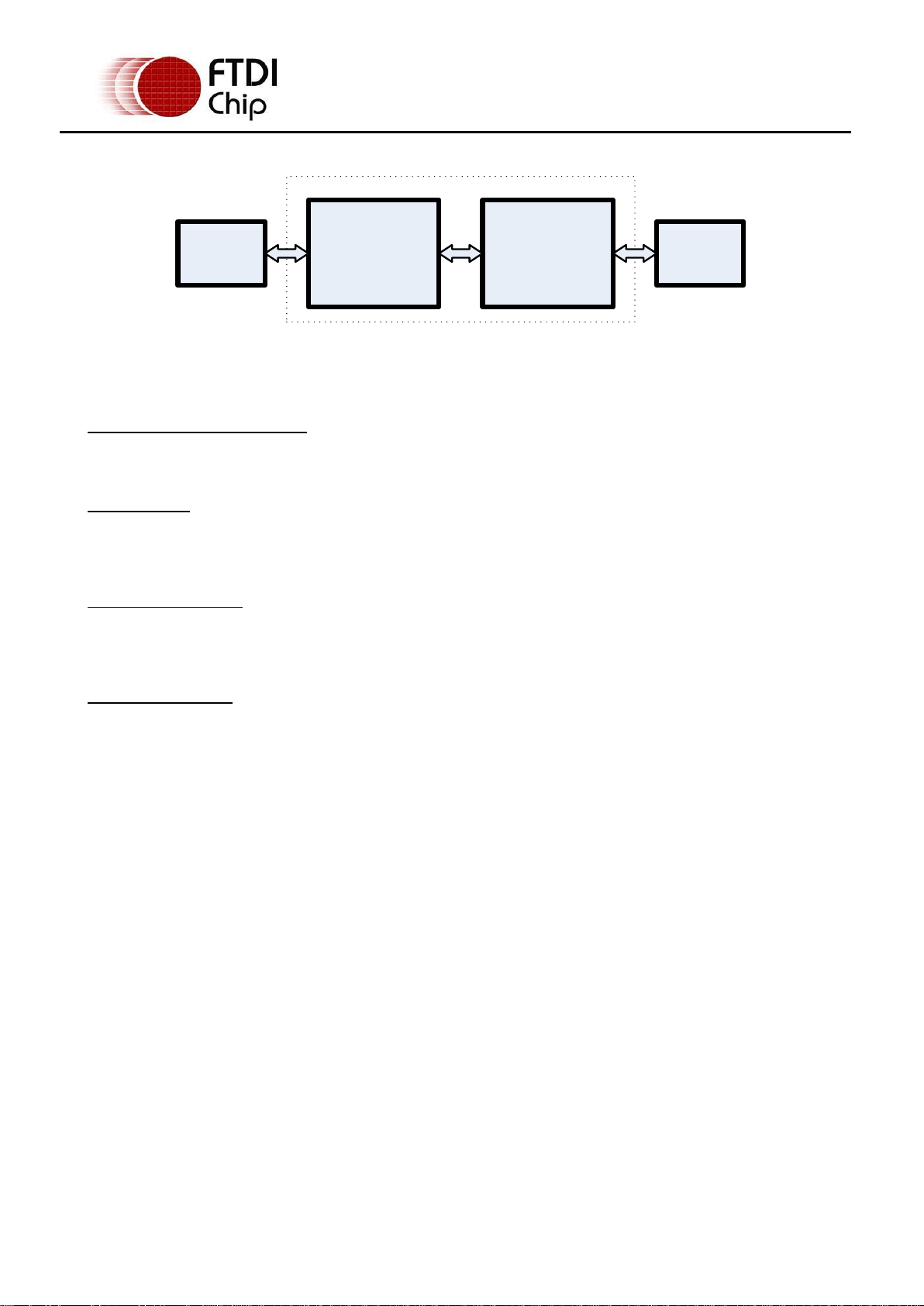
1.2 Block Diagram
FTDI FT232R
USB Serial Bridge
RS232
Level Shifter
USB Mini B
Client
Connector
DB9 PCB
Decal
DB9 Module
DB9 Module
Figure 1.2 – DB9-USB-RS232 Block Diagram
1.2.1 Block description
USB Mini B Client Connector
This connector provides the interface for connection to a USB Host or Hub port.
FTDI FT232R
The FTDI FT232R provides the USB-to-Serial conversion. Operating system device drivers are required in
order to operate with the FT232R to provide the Virtual COM Port serial functionality.
RS232 Level Shifter
The RS232 level shifter converts the signals provided by the FT232R into the voltage levels required by
application RS232 interface.
DB9 PCB Footprint
The DB9 pin-out configured in an industry standard (TIA/EIA-574) pin-out to provide connection to
RS232 peripherals through a standard DB9 footprint . See section 2.1.2
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 2
Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
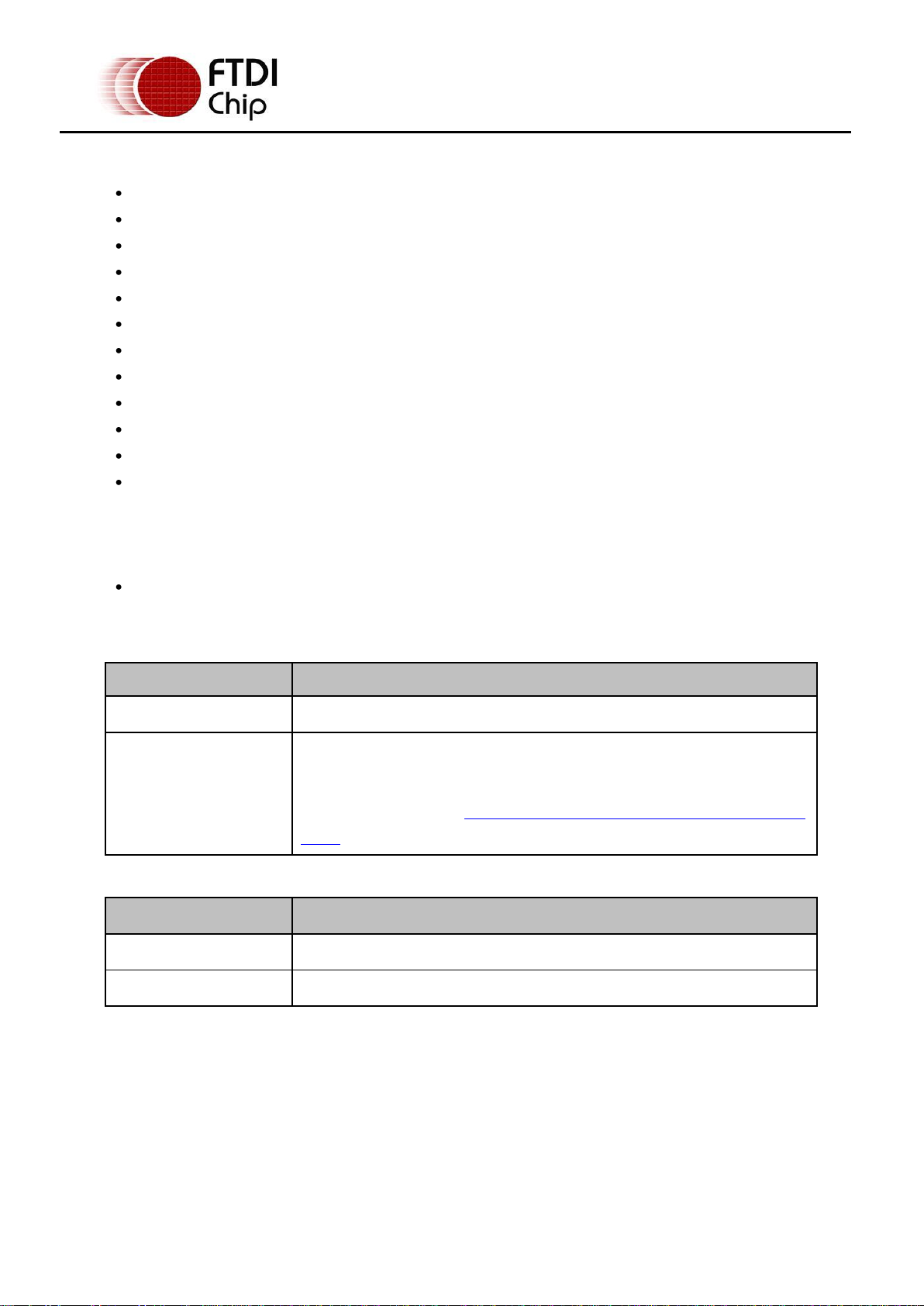
Parameter
Performance
USB Interface
12Mbps USB 2.0 Full-Speed
RS232 Interface
Standard Windows baud rates (300bps to 921.6Kbps)
Custom baud rates (300bps to 1Mbps) through baud rate aliasing. See
FTDI Application Note: Configuring FT232R, FT2232 and FT232BM Baud
Rates
Part Number
Description
DB9-USB-M
Full Speed USB to 1-Port RS232 module to replace RS232 DB9 male connector
DB9-USB-F
Full Speed USB to 1-Port RS232 module to replace RS232 DB9 female connector
1.3 Features
Adds one USB serial port by connecting to the RS232 DB9 footprint of a device
Easy placement for an standard Male and Female RS232 DB9 footprint of a device
Works with USB 1.1 & 2.0 Host and Hub ports
Industry Standard FTDI chip set & device drivers for maximum compatibility
Microsoft Windows
Installs as a standard Windows COM port
Supports Windows Server 2008, 2003, Vista, XP 2000, Linux, Mac OS X
128 byte transmit buffer, 256 byte receive buffer
RS-232 data signals: TxD, RxD, RTS, CTS, DSR, DTR, DCD, RI, GND
Powered by USB port. No external power adapter required.
Serial port speed up to 1Mbps
Serial Communication Parameters
o Parity: None, Even, Odd
o Data bits: 7, 8
o Flow control: RTS/CTS , DSR/DTR, X-ON/X-OFF, None
Operating temperature of -40°C to +85°C
®
WHQL-certified, Mac OS X, Linux and Windows CE device drivers
1.4 Performance Figures
Table 1.1 – Performance Specifications
Table 1.2 – Ordering Information
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 3

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
1 Introduction ................................................................................... 1
1.1 Functional Description .................................................................................. 1
1.2 Block Diagram ............................................................................................... 2
1.2.1 Block description ....................................................................................... 2
1.3 Features ........................................................................................................ 3
1.4 Performance Figures ..................................................................................... 3
2 Connections .................................................................................... 5
2.1 External Connections .................................................................................... 5
2.1.1 USB ......................................................................................................... 5
2.1.2 Replacing an RS232 DB9 MALE (DTE defined) Connector ................................ 6
2.1.3 Replacing an RS232 DB9 FEMALE (DCE defined) Connector ............................ 7
3 Installation ..................................................................................... 8
3.1 Device Driver Installation ............................................................................. 8
3.1.1 Microsoft Windows Installation .................................................................... 8
3.1.2 Mac OS X, Linux, Windows CE ................................................................... 12
4 Electrical details ........................................................................... 13
4.1 USB ............................................................................................................. 13
4.2 RS232 ......................................................................................................... 13
5 Mechanical Details ........................................................................ 14
6 Physical Environment Details ....................................................... 15
6.1 Storage ....................................................................................................... 15
6.2 Operating .................................................................................................... 15
7 Environmental Approvals & Declarations ...................................... 16
7.1 EMI Compatibility ........................................................................................ 16
7.2 Safety.......................................................................................................... 16
7.3 Environmental ............................................................................................. 16
7.4 Reliability .................................................................................................... 16
7.4.1 MTTF ..................................................................................................... 16
7.5 Import / Export Information ....................................................................... 17
8 Troubleshooting ........................................................................... 18
9 Contact Information ..................................................................... 19
Appendix A – List of Figures and tables ............................................. 21
Appendix B – DCE and DTE Wire Configurations ................................. 22
B.1 Wire Configuration for the Male and Female Modules ..................................... 22
B.1.1 RS232 Wiring ............................................................................................... 22
Appendix C – Revision History ........................................................... 24
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 4
Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
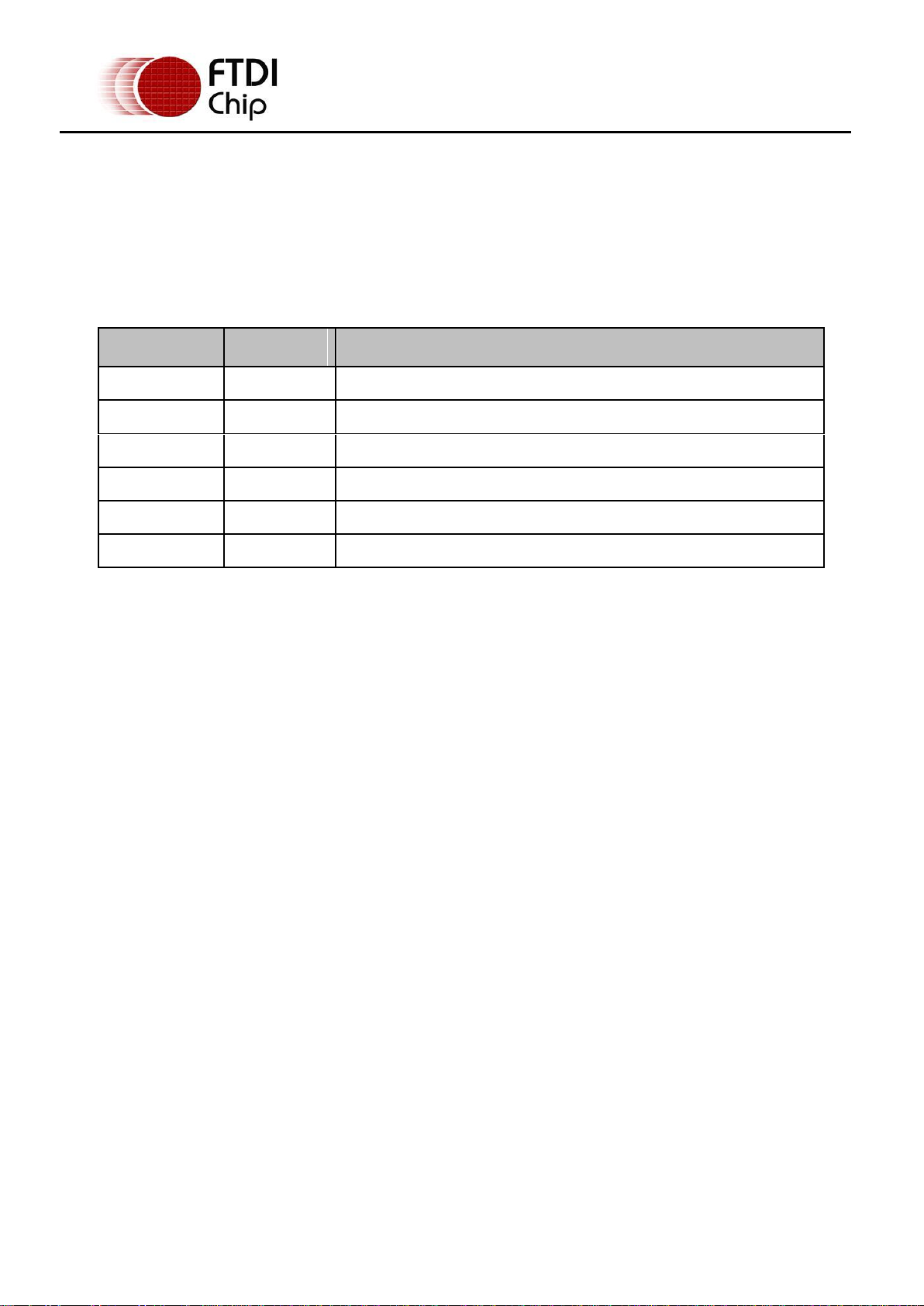
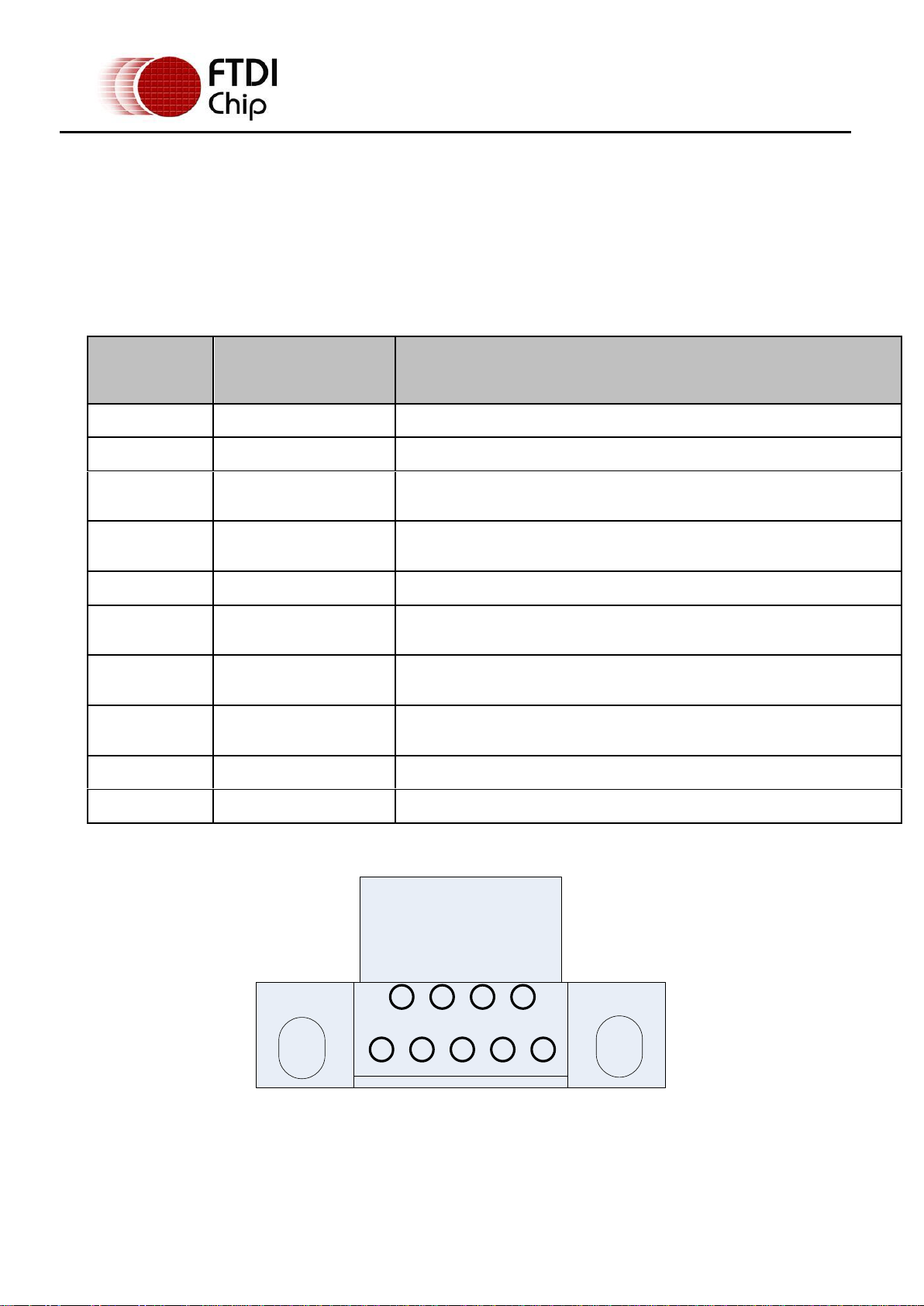
Pin Number
Pin Type
Description
1
Power
VBUS – USB Power provided from upstream USB Host or Hub
2
Bidirectional
D– = USB data signal, negative polarity
3
Bidirectional
D+ = USB data signal, positive polarity
4
ID
Not Connected
5
Ground
GND = USB signal ground
Shield
Case Ground
Drain = typically connected to the host PC case
2 Connections
2.1 External Connections
2.1.1 USB
The DB9-USB-RS232 module is a downstream USB 2.0 Device. A “USB mini B” receptacle is mounted
inside the module to facilitate connection to an upstream USB Host or Hub.
Table 2.1 – USB “mini-B” Receptacle Pin-Out
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 5
Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
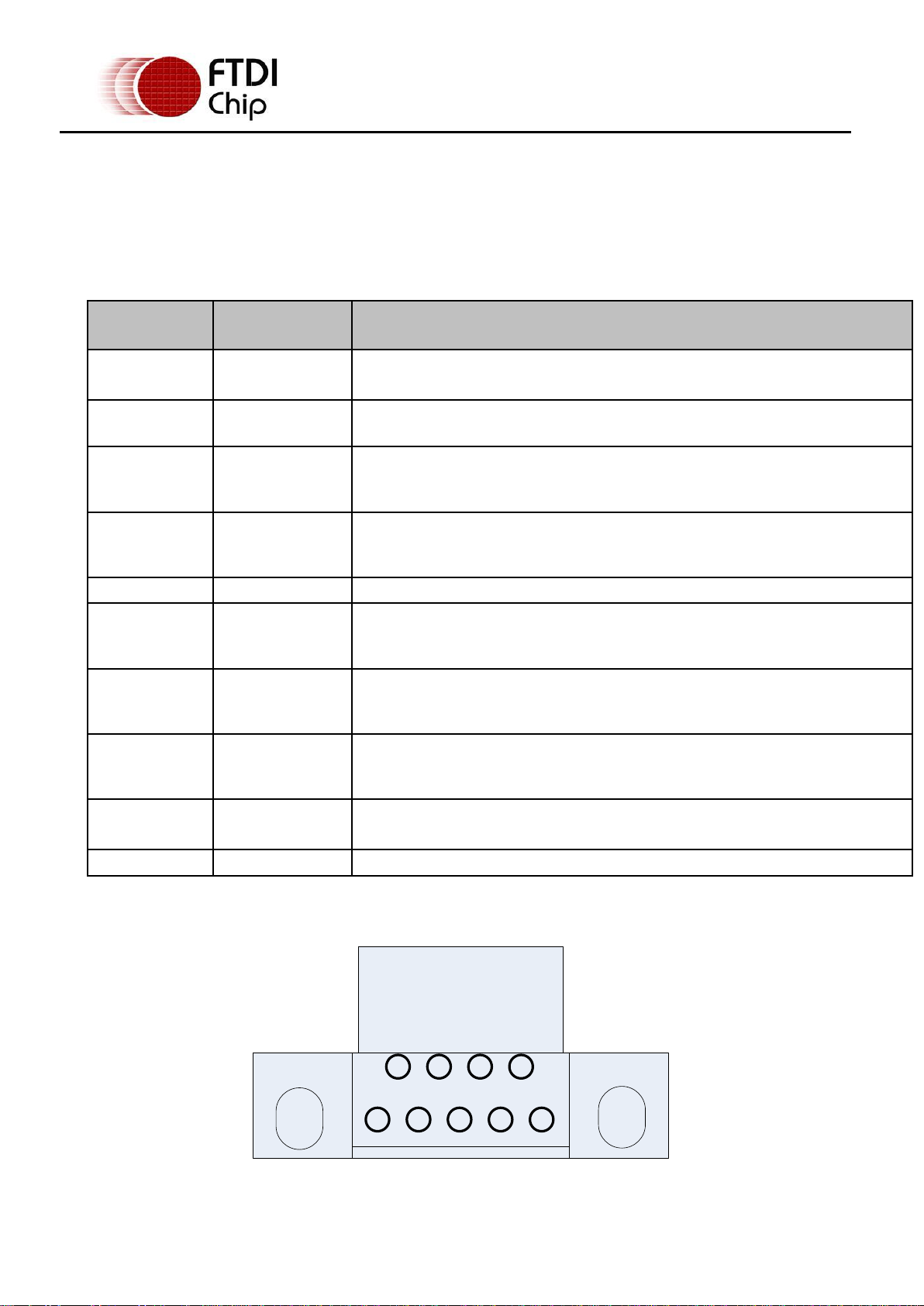
Pin Number
Pin Type of
application
Description
1
Input
DCD = Data Carrier Detect
2
Input
RXD = Receive Data
(this is an output from the DB9-USB-RS232-M to the application Rx input)
3
Output
TXD = Transmit Data
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-M from the application Tx output)
4
Output
DTR = Data Terminal Ready
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-M from the application DTR output)
5
Ground
GND = RS232 signal ground
6
Input
DSR = Data Set Ready
(this is an output from the DB9-USB-RS232-M to the application DSR input)
7
Output
RTS = Request To Send
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-M from the application RTS output)
8
Input
CTS = Clear To Send
(this is an output from the DB9-USB-RS232-M to the application CTS input)
9
Input
RI = Ring Indicator
Shield
Case Ground
Drain = typically connected to the host PC case
GND
DTR TXD RXD
DCD
RI CTS RTS DSR
12345
9 8 7 6
2.1.2 Replacing an RS232 DB9 MALE (DTE defined) Connector
The DB9-USB-RS232-M can be used to replace a male DB9 connector used for transmitting RS232
protocol. With the DB9-USB-RS232-M in place instead of the standard USB connector a USB bridge is
created, this allow the application to communicate with other devices via USB. Installing the DB9-USBRS232-M is simple. Simply replace the male DB9 connector with the DB9-USB-RS232-M connector (same
PCB footprint), install drivers and the device is ready to use.
Table 2.2 gives the pin out description of each pad of an RS232 footprint. Figure 2.2 gives a description
of the connections between the DB9-USB-RS232-M and the footprint of a male DB9 module.
Table 2.2 – A Male RS232 DB9 footprint Pin-Out
Figure 2.2 illustrates these connections from a PCB footprint point of view.
Figure 2.1 – DB9-USB-RS232-M Pin-Out from a Top View through the module
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 6
Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Pin Number
Pin Type at
application
Description
1
Output
DCD = Data Carrier Detect
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application DCD output)
2
Output
RXD = Receive Data
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application Tx output, normally
labelled RXD in DCE convention)
3
Input
TXD = Transmit Data
(this is an output to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application Rx input, normally
labelled TXD in DCE convention)
4
Input
DTR = Data Terminal Ready
(this is an output to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application DSR input, normally
labelled DTR in DCE convention)
5
Ground
GND = RS232 signal ground
6
Output
DSR = Data Set Ready
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application DTR output, normally
labelled DSR in DCE convention)
7
Input
RTS = Request To Send
(this is an output to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application CTS input, normally
labelled RTS in DCE convention)
8
Output
CTS = Clear To Send
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application RTS output, normally
labelled CTS in DCE convention)
9
Output
RI = Ring Indicator
(this is an input to the DB9-USB-RS232-F from the application RI output)
Shield
Case Ground
Drain = typically connected to the host PC case
GNDDTR
TXD
RXDDCD
RICTSRTSDSR
1 2
3
4 5
6
7
8
9
2.1.3 Replacing an RS232 DB9 FEMALE (DCE defined) Connector
The DB9-USB-RS232-F can be used to replace a female DB9 connector used for transmitting RS232
protocol. With the DB9-USB-RS232-F in place instead of the standard USB connector a USB bridge is
created, this allow the application to communicate with other devices via USB. Installing the DB9-USBRS232-F is simple. Simply replace the female DB9 connector with the DB9-USB-RS232-F connector
(same PCB footprint), install drivers and the device is ready to use.
Table 2.3 gives the pin out description of each pad of an RS232 footprint. Figure 2.3 gives a description
of the connections between the DB9-USB-RS232-F and the footprint of a female DB9 module.
Table 2.3 – A Female RS232 DB9 footprint Pin-Out
Figure 2.2 – DB9-USB-RS232-F Pin-Out from a Top View through the module
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 7

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
3 Installation
3.1 Device Driver Installation
The drivers for the DB9-USB-RS232 modules are available for download from:
www.ftdichip.com
The following section illustrates an example installation on the Windows OS.
3.1.1 Microsoft Windows Installation
With the device drivers being Windows Hardware Quality Labs (WHQL) certified, they are also available
through download directly from the Microsoft® Windows® Update service. Additional installation options
are noted below:
Installation Executable shown on Windows XP
1) Login to the system as Administrator, or a user with Administrator rights.
2) Prior to connecting the DB9-USB-RS232 module to the USB Host or Hub port, download the latest
device driver version from the FTDIChip web site.
3) Run this executable to install the device drivers.
4) Connect the DB9-USB-RS232 module to your computer. A notification will appear near the task
bar indicating that new hardware has been installed and is ready for use. It is normal if this
notice appears twice.
Figure 3.1 – Hardware Ready
Windows Update shown on Windows XP
You must have an active Internet connection and the Windows Update Service enabled.
1) Connect the DB9-USB-RS232 module to your USB Host or Hub.
2) The “Found New Hardware” Wizard will appear. The first dialog should ask whether it is
acceptable to use the Windows Update Service to find the device driver.
Figure 3.2 – Found New Hardware Wizard
3) Select one of the “Yes” choices and click “Next”.
4) The following screen appears:
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 8

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Figure 3.3 – Automatic Install
5) Wait while the driver is found, downloaded, and installed. This step may take a couple minutes
depending on the Internet speed.
6) After the files are found and installed, click “Finish” to complete the installation.
Figure 3.4 – Complete Hardware Installation
7) Steps 2 through 6 will repeat. The first time installs the basic USB Serial Converter in the USB
device tree. The second time installs the Virtual COM Port layer in the Ports tree and assigns the
COM port number.
8) When both portions of the device driver have been installed successfully, the following message
will appear, indicating that the device is ready.
Figure 3.5 – Hardware Ready
COM Port Assignment
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 9

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Next, to determine which COM port has been assigned, open the Windows Device Manager from the
System Control Panel.
Figure 3.6 – Device Manager
Click on the Plus “+” sign next to the Ports tree to list the available COM port. You will see “USB Serial
Port”, followed by a COMn assignment. In the figure below, the DB9-USB-RS232 module is assigned to
COM3.
Figure 3.7 – COM Port Assignment
Use this COM port number with your application software in order to access the DB9-USB-RS232 module.
If an application requires use of a different COM port number, the assignment may be changed through
the Advanced Driver Options settings.
From the Device Manager listing above, right-click on the USB Serial Port and select Properties.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 10

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Figure 3.8 – Access COM Port Properties
Next, click on the “Port Settings” tab.
Figure 3.9 – Settings Tab
Then click on the “Advanced…” button.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 11

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Figure 3.10 – Advanced Options
This will display the various advanced settings. Note the COM port assignment in the upper left. Clicking
on the drop-down list will display the available port numbers. Select one that is not in use and click OK
on each dialog box to activate the selection. Windows will remember this COM port number.
3.1.2 Mac OS X, Linux, Windows CE
Device drivers and FTDI installation guides for Mac OS X, Linux and Windows CE are available for
download on the FTDIChip web sites. Follow the respective FTDI installation guides for the chosen
operating system.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 12
Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
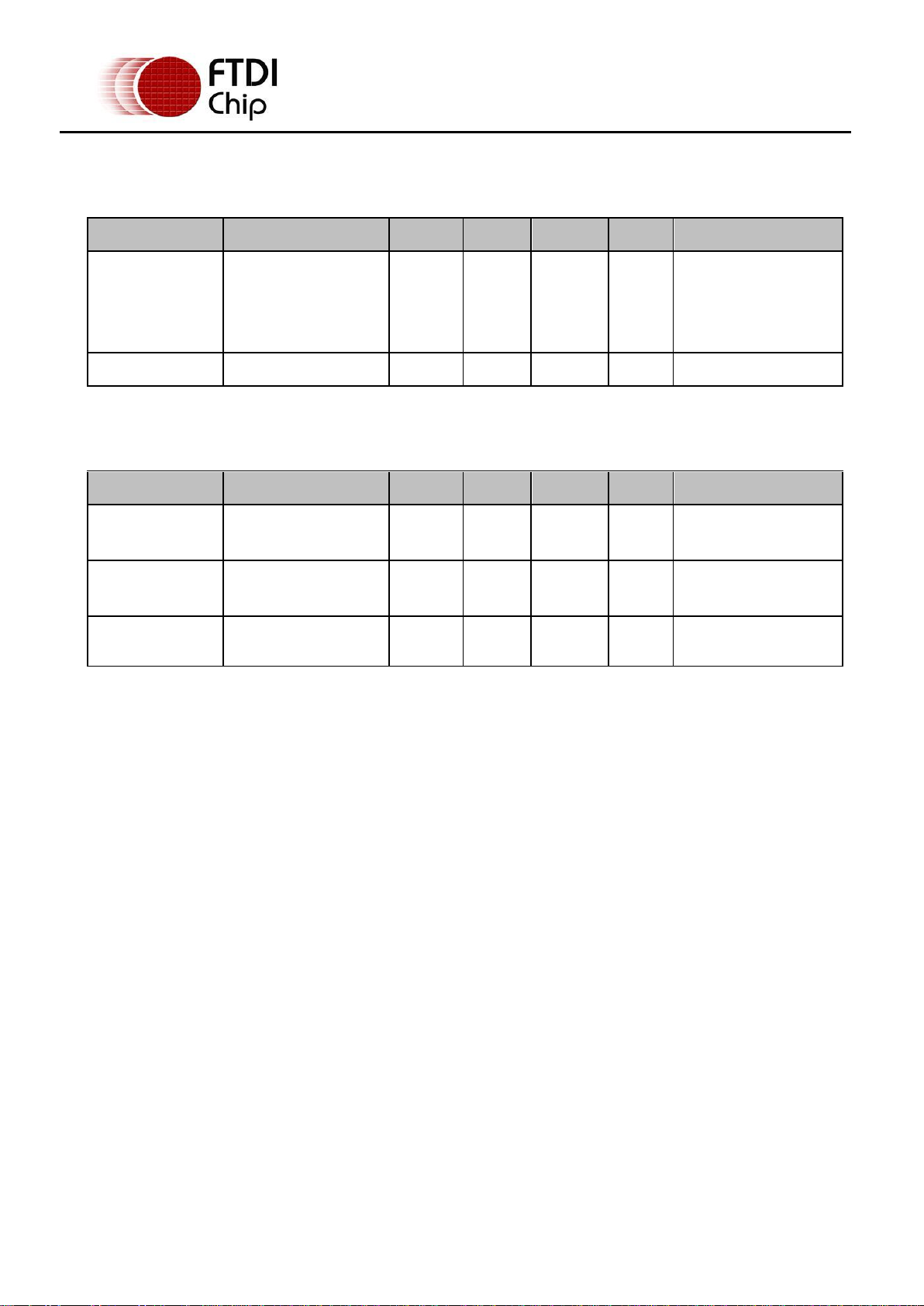
Parameter
Description
Minimum
Typical
Maximum
Units
Conditions
USB_VCC
Input Power Voltage*
4.25
5.0*
5.25
V
*Present when USB
cable is attached and
USB Host or Hub
powered.
Icc
USB current
30
50
mA
Parameter
Description
Minimum
Typical
Maximum
Units
Conditions
V
trans
Transmitter output
voltage swing
± 5
V
RL = 3KΩ
V
rec
Receiver input voltage
range
±2.4 ±25
V
Input resistance = 3KΩ
to 7KΩ
ESD HBM
±15
KV
RS-232 Inputs and
Outputs
4 Electrical details
4.1 USB
4.2 RS232
Table 4.1 – USB Electrical Details
Table 4.2 – RS232 Electrical Details
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 13

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
5 Mechanical Details
Figure 5.1 – DB9-USB-RS232-M/F module Dimensions
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 14

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Parameter
Description
Minimum
Typical
Maximum
Units
Conditions
T
Storage Temperature
Range
TBD TBD oC
Parameter
Description
Minimum
Typical
Maximum
Units
Conditions
T
Operating Temperature
Range
–40 +85 oC
5% to 95% RH,
non condensing
6 Physical Environment Details
6.1 Storage
Table 6.1 – Storage Temperature
6.2 Operating
Table 6.2 – Operating Temperature
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 15

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
7 Environmental Approvals & Declarations
7.1 EMI Compatibility
FCC and CE
At the time of launch, the DB9-USB-RS232 is undergoing testing to be compliant with both FCC Part 15
Subpart B and European EMC Directive.
NOTE: This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference,
in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
NOTE: This equipment is currently undergoing testing to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
7.2 Safety
The DB9-USB-RS232 is defined as Limited Power Supply (LPS) device, with operating voltages under
60VDC.
7.3 Environmental
The DB9-USB-RS232 is a lead-free device that complies with the following environmental directives:
RoHS, WEEE, REACH, PFOS and DecaBDE.
7.4 Reliability
The DB9-USB-RS232 is designed as a robust USB-Serial module for use in many environments. There
are no user-serviceable parts. Any failure will require a replacement of the unit.
7.4.1 MTTF
The Mean Time To Failure is calculated at TBD hours.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 16

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Import / Export Information
Country of Origin
China
Harmonized Code
7.5.1.1 8471.80.4000
Product Description
USB to RS232 Connector Adapter, Single Port
USA ECCN
EAR99 – No License Required
7.5 Import / Export Information
Table 7.1 – Import / Export Information
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 17

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
8 Troubleshooting
Ensure the latest device driver is in use. See www.ftdichip.com
If USB devices other than FTDI chips are installed in the system, then check with all manufacturers of
these devices for the latest device drivers.
Section 3 details driver installation. If the user continues to have driver installation isues, then please
refer to the FTDI installation guides http://ftdichip.com/Documents/InstallGuides.htm for additional
details.
Common Windows Device Driver Troubles:
DEVICE TIMES OUT: The default settings of the device driver assume typical data transfers of
hundreds to thousands or more bytes at a given time. Some applications, such as a GPS device,
only send data in short packets, often only a few bytes. If this is the case, it may be necessary
to adjust the driver buffer size and/or latency timer to smaller values. These values can be
adjusted through the Advanced driver options. The buffer size can be reduced to 64 bytes. The
latency timer can be set as low as 2ms. A setting of 1ms will cause unnecessary USB traffic and
could adversely affect data transmission. Advanced driver options are described in
http://www.ftdichip.com/Documents/AppNotes/AN_107_AdvancedDriverOptions_AN_000073.pdf
ERRATIC MOUSE POINTER: The device driver defaults to query an attached device to find out
whether it is a mouse or modem, consistent with native COM port operation. Some RS232
peripherals constantly send short packets of data, causing the host system to “think” a mouse or
modem has been attached. These short packets will interfere with normal mouse operation
causing the pointer to jump around the screen. If this happens, disconnect the RS232 device and
uncheck the Serial Enumerator option, also found on the Advanced driver options.
COM PORT IN USE: Windows keeps track of all COM port assignments. If multiple FTDIChip
products have been connected to a single system, the COM port number will increase, even if the
other devices are not attached. If the higher COM port assignments are not acceptable for the
application, known unused COM port numbers should be uninstalled according to the FTDI
installation guide: http://ftdichip.com/Documents/InstallGuides.htm.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 18

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
9 Contact Information
Head Office – Glasgow, UK
Future Technology Devices International Limited
Unit 1, 2 Seaward Place
Centurion Business Park
Glasgow, G41 1HH
United Kingdom
Tel: +44 (0) 141 429 2777
Fax: +44 (0) 141 429 2758
E-mail (Sales) sales1@ftdichip.com
E-mail (Support) support1@ftdichip.com
E-mail (General Enquiries) admin1@ftdichip.com
Web Site URL http://www.ftdichip.com
Web Shop URL http://www.ftdichip.com
Branch Office – Shanghai, China
Future Technology Devices International Limited (China)
Room 408, 317 Xianxia Road,
ChangNing District,
ShangHai, China
Tel: +86 (21) 62351596
Fax: +86(21) 62351595
E-Mail (Sales): cn.sales@ftdichip.com
E-Mail (Support): cn.support@ftdichip.com
E-Mail (General Enquiries): cn.admin1@ftdichip.com
Web Site URL: http://www.ftdichip.com
Branch Office – Taipei, Taiwan
Future Technology Devices International Limited (Taiwan)
2F, No 516, Sec. 1 NeiHu Road
Taipei 114
Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: +886 (0) 2 8791 3570
Fax: +886 (0) 2 8791 3576
E-mail (Sales) tw.sales1@ftdichip.com
E-mail (Support) tw.support1@ftdichip.com
E-mail (General Enquiries) tw.admin1@ftdichip.com
Web Site URL http://www.ftdichip.com
Branch Office – Hillsboro, Oregon, USA
Future Technology Devices International Limited (USA)
7235 NW Evergreen Parkway, Suite 600
Hillsboro, OR 97123-5803
USA
Tel: +1 (503) 547 0988
Fax: +1 (503) 547 0987
E-Mail (Sales) us.sales@ftdichip.com
E-Mail (Support) us.support@ftdichip.com
E-mail (General Enquiries) us.admin@ftdichip.com
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 19

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Distributor and Sales Representatives
Please visit the Sales Network page of the FTDI Web site for the contact details of our distributor(s) and
sales representative(s) in your country.
Vinculum is part of Future Technology Devices International Ltd. Neither the whole nor any part of the information contained in, or the product described in
this manual, may be adapted or reproduced in any material or electronic form without the prior written consent of the copyright holder. This product and its
documentation are supplied on an as-is basis and no warranty as to their suitability for any particular purpose is either made or implied. Future Technology
Devices International Ltd will not accept any claim for damages howsoever arising as a result of use or failure of this product. Your statutory rights are not
affected. This product or any variant of it is not intended for use in any medical appliance, device or system in which the failure of the product might
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. This document provides preliminary information that may be subject to change without notice. No
freedom to use patents or other intellectual property rights is implied by the publication of this document. Future Technology Devices International Ltd, Unit
1, 2 Seaward Place, Centurion Business Park, Glasgow G41 1HH United Kingdom. Scotland Registered Number: SC136640
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 20

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Appendix A – List of Figures and tables
List of Figures:
Figure 1.1 – DB9-USB-RS232 ......................................................................................................................... 1
Figure 1.2 – DB9-USB-RS232 Block Diagram ............................................................................................... 2
Figure 2.1 – DB9-USB-RS232-M Pin-Out from a Top View through the module ....................................... 6
Figure 2.2 – DB9-USB-RS232-F Pin-Out from a Top View through the module ........................................ 7
Figure 3.1 – Hardware Ready ......................................................................................................................... 8
Figure 3.2 – Found New Hardware Wizard .................................................................................................... 8
Figure 3.3 – Automatic Install ......................................................................................................................... 9
Figure 3.4 – Complete Hardware Installation ................................................................................................ 9
Figure 3.5 – Hardware Ready ......................................................................................................................... 9
Figure 3.6 – Device Manager ........................................................................................................................ 10
Figure 3.7 – COM Port Assignment ............................................................................................................. 10
Figure 3.8 – Access COM Port Properties................................................................................................... 11
Figure 3.9 – Settings Tab .............................................................................................................................. 11
Figure 3.10 – Advanced Options .................................................................................................................. 12
Figure 5.1 – DB9-USB-RS232-M/F module Dimensions ............................................................................. 14
List of tables:
Table 1.1 – Performance Specifications ........................................................................................................ 3
Table 1.2 – Ordering Information ................................................................................................................... 3
Table 2.1 – USB “mini-B” Receptacle Pin-Out .............................................................................................. 5
Table 2.2 – A Male RS232 DB9 footprint Pin-Out ......................................................................................... 6
Table 2.3 – A Female RS232 DB9 footprint Pin-Out ..................................................................................... 7
Table 4.1 – USB Electrical Details ................................................................................................................ 13
Table 4.2 – RS232 Electrical Details ............................................................................................................ 13
Table 6.1 – Storage Temperature ................................................................................................................. 15
Table 6.2 – Operating Temperature ............................................................................................................. 15
Table 7.1 – Import / Export Information ....................................................................................................... 17
Table B.1 – RS232 DTE to DCE connection with straight-through wiring ............................................... 22
Table B.2 – RS232 DTE to DTE connection with null-modem wiring ....................................................... 23
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 21

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
DTE Pin Number
Signal Name
DCE Pin Number
1
DCD = Data Carrier Detect
1
2
RXD = Receive Data
2
3
TXD = Transmit Data
3
4
DTR = Data Terminal Ready
4
5
GND = RS232 signal ground
5
6
DSR = Data Set Ready
6
7
RTS = Request To Send
7
8
CTS = Clear To Send
8
9
RI = Ring Indicator
9
Appendix B – DCE and DTE Wire Configurations
This section is included for reference when designing a PCB for a DB9-USB-RS232 module; here some of
the subtle details of DTE and DCE wire configurations will be outlined.
B.1 Wire Configuration for the Male and Female Modules
When designing a PCB for the DB9-USB-RS232 module consideration should be given to Data Terminal
Equipment (DTE) and Data Communication Equipment (DCE) connection standards. The DB9-USB-RS232
modules are designed as a DTE device. When a DTE devices is being connected to the DB9-USB-RS232 a
“null-modem” wiring is used, when the DB9-USB-RS232 is connected to a DCE a “straight through” wiring
is used. The expressions “null-modem” and “straight through” are explained in the next subsection.
The male DB9-USB-RS232-M module is designed to replace a male DB9 connector of a DTE device
(according to TIA standards Male DB9 connectors are to be used only with wiring DTE to UART). The
female DB9-USB-RS232-F module is designed to replace a female DB9 connector of a DCE device
(according to TIA standards Female DB9 connectors are to be used only with wiring DCE to UART).
B.1.1 RS232 Wiring
RS232 cables have followed a standard 9-pin configuration on a D-sub connector since the mid 1980s.
The DB9-USB-RS232-M modules are DTE devices. To connect a DB9-USB-RS232 module to a DCE device,
a “straight-through” wiring scheme, as described in Table B.1, needs to be used.
Table B.1 – RS232 DTE to DCE connection with straight-through wiring
To connect a DB9-USB-RS232 module to a DCE device, a “null-modem” wiring scheme, as described in
Table B.2 needs to be used.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 22

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
DTE Pin Number
Signal Name
DTE Pin Number
2
RXD = Receive Data
3
3
TXD = Transmit Data
2
4
DTR = Data Terminal Ready
6
5
GND = RS232 signal ground
5
6
DSR = Data Set Ready
4
7
RTS = Request To Send
8
8
CTS = Clear To Send
7
Table B.2 – RS232 DTE to DTE connection with null-modem wiring
Note that the DB9-USB-RS232-M is not a DB9-USB-RS232-F with its pins latterly inverted; there is a
“null-modem” wiring configuration present in the DB9-USB-RS232-M module. This means that a DB9-
USB-RS232-M is not pin compatible with a female footprint when placed on the underneath side of the
board.
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 23

Document Reference No.: FT_000204
DB9-USB-RS232 Datasheet
Version 1.1
Clearance No.: FTDI# 130
Appendix C – Revision History
Version Draft First Draft October 2009
Version 1.0 First release 18th November 2009
Version 1.1 Updated part numbers 19th February 2010
Copyright © 2010 Future Technology Devices International Limited 24
 Loading...
Loading...